question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
[Python 3] Explanation with pictures, DFS
|
python-3-explanation-with-pictures-dfs-b-cdvm
|
Each node has a depth and height. The longest path passing it has a length equals depth + height.\n\n\n\nWhen a node (Let\'s say D) is removed, all of its child
|
Bakerston
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:01:08.851821+00:00
|
2022-11-07T15:42:34.841023+00:00
| 16,156 | false |
Each node has a **depth** and **height**. The longest path passing it has a length equals `depth + height`.\n\n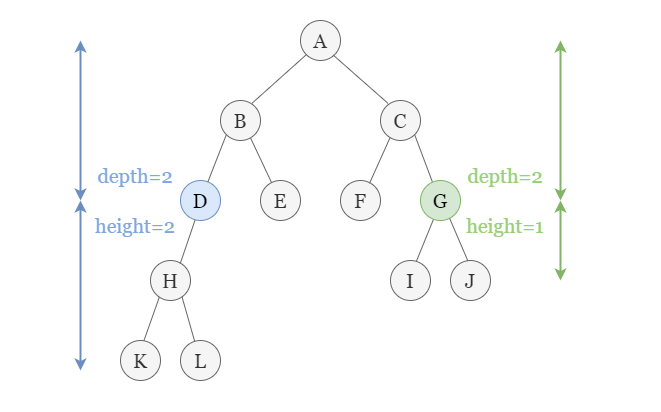\n\nWhen a node (Let\'s say **D**) is removed, all of its children are removed as well. So every path that goes through **D** stops by here. However, if **D** has some cousions, then the paths through these cousins will certainly be longer. We should look for the longest path among these paths through the cousins of **D**, which is equivalent to finding the cousin with the largest **height**.\n\n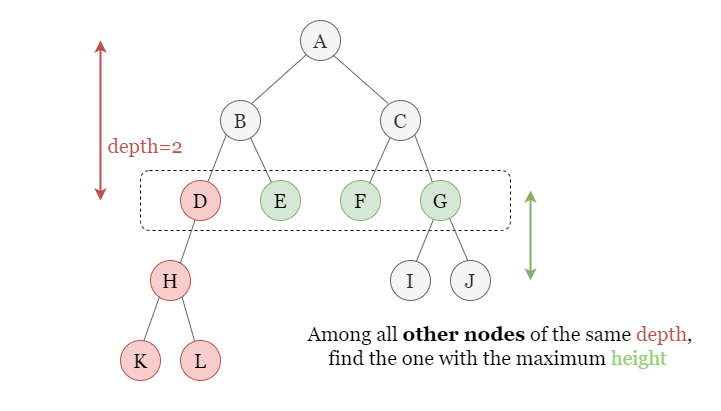\n\nTherefore, we store the nodes according to **depth**. For nodes having the same depth, we sort them by their heights and only keep the top 2 of them that having the maximum depth.\n\n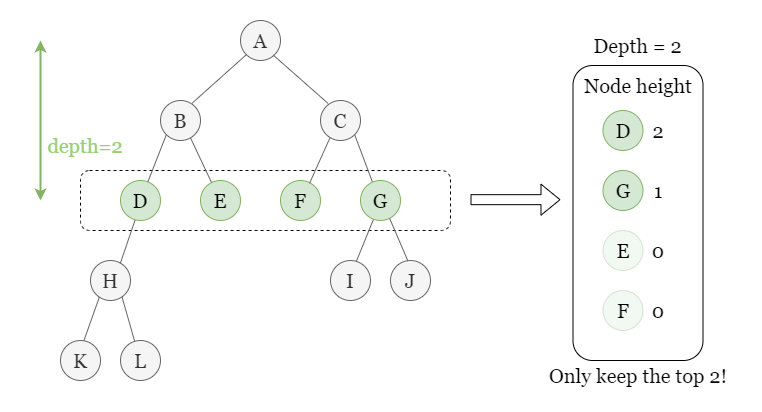\n\n\nOnce we \'remove\' a node from `queries`, we locate all of its cousins, find the one with the maximum height and the job is done.\n\n- If the size of `cousins[depth]` is 1, which means that the `removed` node has no cousin, so the longest resting path equals `depth - 1`. \n- Otherwise, at least one of them is the cousin, we get its depth.\n\n\nTCSC:\n- Time O(N)\n- Space O(N)\n\n<br>\n<br>\n\n\n\n```python\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, R: Optional[TreeNode], Q: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n Depth, Height = collections.defaultdict(int), collections.defaultdict(int)\n\n def dfs(node, depth):\n if not node:\n return -1\n Depth[node.val] = depth\n cur = max(dfs(node.left, depth + 1), dfs(node.right, depth + 1)) + 1\n Height[node.val] = cur\n return cur\n dfs(R, 0)\n\n cousins = collections.defaultdict(list) # Group nodes according to their depth. Keep the top 2 heights.\n for val, depth in Depth.items():\n cousins[depth].append((-Height[val], val))\n cousins[depth].sort()\n if len(cousins[depth]) > 2:\n cousins[depth].pop()\n\n ans = []\n for q in Q:\n depth = Depth[q]\n if len(cousins[depth]) == 1: # No cousin, path length equals depth - 1.\n ans.append(depth - 1)\n elif cousins[depth][0][1] == q: # The removed node has the largest height, look for the node with 2nd largest height.\n ans.append(-cousins[depth][1][0] + depth)\n\t\t\telse: # Look for the node with the largest height.\n ans.append(-cousins[depth][0][0] + depth)\n return ans\n```
| 448 | 1 |
[]
| 56 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Level + Depth
|
level-depth-by-votrubac-bk95
|
I initially solved this problem as O(m * h), but I got TLE when the trie is a vine (so the complexity is O(m * n)). The level-based approach below is O(n + m) f
|
votrubac
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:01:35.773448+00:00
|
2022-10-31T00:37:37.237895+00:00
| 11,130 | false |
I initially solved this problem as O(m * h), but I got TLE when the trie is a vine (so the complexity is O(m * n)). The level-based approach below is O(n + m) for any tree shape.\n\nFor each node, we store its `level` and `depth` of its subtree.\n\nAlso, for each level, we store largest (`d1`) and second largest (`d2`) depth from all nodes on that level.\n\nNow, when we process a query, we can figure out the level and depth of the node.\n\nThe result is the level plus a) the largets depth of that level, or b) second largest if the queried node depth is the largest.\n\n**C++**\n```cpp\nint level[100001] = {}, depth[100001] = {};\nint d1[100001] = {}, d2[100001] = {};\nint traverse(TreeNode* n, int l = 0) {\n if (n == nullptr)\n return 0;\n level[n->val] = l;\n depth[n->val] = 1 + max(traverse(n->left, l + 1), traverse(n->right, l + 1)); \n if (d1[l] < depth[n->val]) {\n d2[l] = d1[l];\n d1[l] = depth[n->val];\n } \n else if (d2[l] < depth[n->val])\n d2[l] = depth[n->val];\n return depth[n->val];\n};\nvector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n traverse(root, 0);\n transform(begin(queries), end(queries), begin(queries), [&](int q){\n int l = level[q];\n return l + (d1[l] == depth[q] ? d2[l] : d1[l]) - 1;\n });\n return queries;\n}\n```
| 102 | 1 |
['C']
| 19 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
[C++/Python] Preoder and Postorder DFS
|
cpython-preoder-and-postorder-dfs-by-lee-d0bf
|
Explanation\nPre-order dfs the tree (node, left, right),\nupdate res[i] to the max height before node i in preorder,\ncan cover all nodes on the left of node i
|
lee215
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T09:29:04.096499+00:00
|
2022-10-30T09:29:15.967409+00:00
| 7,352 | false |
# **Explanation**\nPre-order dfs the tree (node, left, right),\nupdate `res[i]` to the max height before node `i` in preorder,\ncan cover all nodes on the left of node `i` in the tree.\n\nPost-order dfs the tree (node, right, left),\nupdate `res[i]` to the max height before node `i` in postorder,\ncan cover all nodes on the right of node `i` in the tree.\n<br>\n\n# **Complexity**\nTime `O(n)`\nSpace `O(n)`\n<br>\n\n**C++**\n```cpp\n int preh[100001], posth[100001], maxh;\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n maxh = 0; pre(root, 0);\n maxh = 0; post(root, 0);\n vector<int> res;\n for (int q : queries)\n res.push_back(max(preh[q], posth[q]));\n return res;\n }\n\n void pre(TreeNode* root, int h) {\n if (!root) return;\n preh[root->val] = maxh;\n maxh = max(maxh, h);\n pre(root->left, h + 1);\n pre(root->right, h + 1);\n }\n\n void post(TreeNode* root, int h) {\n if (!root) return;\n posth[root->val] = maxh;\n maxh = max(maxh, h);\n post(root->right, h + 1);\n post(root->left, h + 1);\n }\n```\n**Shorter C++**\n```cpp\n int seen[100001], maxh;\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n maxh = 0; dfs(root, 0);\n maxh = 0; dfs(root, 0);\n vector<int> res;\n for (int q : queries)\n res.push_back(seen[q]);\n return res;\n }\n\n void dfs(TreeNode* root, int h) {\n if (!root) return;\n seen[root->val] = max(seen[root->val], maxh);\n maxh = max(maxh, h);\n dfs(root->left, h + 1);\n dfs(root->right, h + 1);\n swap(root->right, root->left);\n }\n```\n\n**Python**\n```py\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n res = defaultdict(int)\n\n def dfs(root, h, maxh):\n if not root: return maxh\n res[root.val] = max(res[root.val], maxh)\n root.left, root.right = root.right, root.left\n return dfs(root.right, h + 1, dfs(root.left, h + 1, max(maxh, h)))\n\n dfs(root, 0, 0)\n dfs(root, 0, 0)\n return [res[q] for q in queries]\n```\n
| 94 | 5 |
[]
| 13 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
✅ Explained step by step | Beats 100% | ✅ Working 26.10.2024
|
explained-step-by-step-beats-100-working-gzl4
|
python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n # Initialize arrays to store heights
|
Piotr_Maminski
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T00:26:44.133567+00:00
|
2024-10-26T01:48:41.315180+00:00
| 18,360 | false |
```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n # Initialize arrays to store heights and node information\n heights = [0] * 50000 # Heights of leaf nodes\n d = [0] * 100001 # Depth of each node\n l = [0] * 100001 # Left index for each node\n r = [0] * 100001 # Right index for each node\n len_leaves = 0 # Counter for leaf nodes\n \n def search(p: TreeNode, h: int) -> None:\n nonlocal len_leaves\n d[p.val] = h # Store current node\'s depth\n \n # If leaf node found\n if not p.left and not p.right:\n heights[len_leaves] = h # Store leaf height\n l[p.val] = r[p.val] = len_leaves # Both indices same for leaf\n len_leaves += 1\n return\n \n l[p.val] = len_leaves # Store left index for current node\n \n # Recursively process left and right subtrees\n if p.left:\n search(p.left, h + 1)\n if p.right:\n search(p.right, h + 1)\n \n r[p.val] = len_leaves - 1 # Store right index for current node\n \n # Process the tree starting from root\n search(root, 0)\n \n n = len_leaves # Total number of leaf nodes\n maxl = [0] * n # Max heights from left\n maxr = [0] * n # Max heights from right\n \n # Build prefix and suffix maximum arrays\n for i in range(1, n):\n maxl[i] = max(maxl[i-1], heights[i-1]) # Max height from left\n maxr[n-i-1] = max(maxr[n-i], heights[n-i]) # Max height from right\n \n ret = [] # Result list\n \n # Process each query\n for query in queries:\n # Find maximum height excluding current node\'s subtree\n maxxl = maxl[l[query]] # Max height to the left\n maxxr = maxr[r[query]] # Max height to the right\n # Result is max of (max left height, max right height, current depth-1)\n ret.append(max(max(maxxl, maxxr), d[query]-1))\n \n return ret\n```\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n // Array to store the maximum height of the tree after removing each node\n int maxHeightAfterRemoval[100001];\n int currentMaxHeight = 0;\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n traverseLeftToRight(root, 0);\n currentMaxHeight = 0; // Reset for the second traversal\n traverseRightToLeft(root, 0);\n\n // Process queries and build the result vector\n int queryCount = queries.size();\n vector<int> queryResults(queryCount);\n for (int i = 0; i < queryCount; i++) {\n queryResults[i] = maxHeightAfterRemoval[queries[i]];\n }\n\n return queryResults;\n }\n\nprivate:\n // Left to right traversal\n void traverseLeftToRight(TreeNode* node, int currentHeight) {\n if (node == nullptr) return;\n\n // Store the maximum height if this node were removed\n maxHeightAfterRemoval[node->val] = currentMaxHeight;\n\n // Update the current maximum height\n currentMaxHeight = max(currentMaxHeight, currentHeight);\n\n // Traverse left subtree first, then right\n traverseLeftToRight(node->left, currentHeight + 1);\n traverseLeftToRight(node->right, currentHeight + 1);\n }\n\n // Right to left traversal\n void traverseRightToLeft(TreeNode* node, int currentHeight) {\n if (node == nullptr) return;\n\n // Update the maximum height if this node were removed\n maxHeightAfterRemoval[node->val] =\n max(maxHeightAfterRemoval[node->val], currentMaxHeight);\n\n // Update the current maximum height\n currentMaxHeight = max(currentHeight, currentMaxHeight);\n\n // Traverse right subtree first, then left\n traverseRightToLeft(node->right, currentHeight + 1);\n traverseRightToLeft(node->left, currentHeight + 1);\n }\n};\n```\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n // Arrays to store information about the tree\n private int[] heights; // Stores heights of leaf nodes in order of traversal\n private int[] d; // Stores depth/height of each node by its value\n private int[] l; // Stores left boundary index for each node value\n private int[] r; // Stores right boundary index for each node value\n private int lenLeaves; // Counts number of leaf nodes encountered\n \n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n // Initialize arrays with sufficient size\n heights = new int[50000]; // For storing leaf heights\n d = new int[100001]; // For storing node depths\n l = new int[100001]; // For storing left boundaries\n r = new int[100001]; // For storing right boundaries\n lenLeaves = 0; // Initialize leaf counter\n \n // DFS to process the tree and fill arrays\n search(root, 0);\n \n int n = lenLeaves;\n // Arrays to store maximum heights from left and right\n int[] maxl = new int[n]; // Prefix maximums\n int[] maxr = new int[n]; // Suffix maximums\n \n // Build prefix maximum array (left to right)\n // At each position i, stores max height of all leaves to the left\n for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {\n maxl[i] = Math.max(maxl[i-1], heights[i-1]);\n }\n \n // Build suffix maximum array (right to left)\n // At each position i, stores max height of all leaves to the right\n for (int i = n-2; i >= 0; i--) {\n maxr[i] = Math.max(maxr[i+1], heights[i+1]);\n }\n \n // Process each query\n int[] ret = new int[queries.length];\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {\n int query = queries[i];\n // Find maximum height outside the range of current node\n int maxxl = maxl[l[query]]; // Max height to the left\n int maxxr = maxr[r[query]]; // Max height to the right\n // Result is maximum of left max, right max, and parent height\n ret[i] = Math.max(Math.max(maxxl, maxxr), d[query]-1);\n }\n \n return ret;\n }\n \n // DFS to process the tree\n private void search(TreeNode p, int h) {\n d[p.val] = h; // Store current node\'s height\n \n // If current node is a leaf\n if (p.left == null && p.right == null) {\n heights[lenLeaves] = h; // Store leaf height\n l[p.val] = r[p.val] = lenLeaves; // Both boundaries point to same index\n lenLeaves++; // Increment leaf counter\n return;\n }\n \n l[p.val] = lenLeaves; // Store left boundary\n \n // Recursively process left and right subtrees\n if (p.left != null) {\n search(p.left, h + 1);\n }\n if (p.right != null) {\n search(p.right, h + 1);\n }\n \n r[p.val] = lenLeaves - 1; // Store right boundary\n }\n}\n```\n```csharp []\npublic class Solution {\n // Array to store heights of leaf nodes\n private int[] heights;\n \n // Array to store depth of each node\n private int[] d;\n \n // Arrays to store left and right boundaries of subtrees in the leaf array\n private int[] l;\n private int[] r;\n \n // Counter for number of leaf nodes\n private int lenLeaves;\n \n public int[] TreeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n // Initialize arrays with sufficient size\n // heights stores leaf node heights\n heights = new int[50000];\n // d stores depth of each node (indexed by node value)\n d = new int[100001];\n // l,r store left and right boundaries of subtrees in leaf array\n l = new int[100001];\n r = new int[100001];\n lenLeaves = 0;\n \n // DFS to process the tree and fill arrays\n Search(root, 0);\n \n int n = lenLeaves;\n // Arrays to store maximum heights from left and right\n int[] maxl = new int[n];\n int[] maxr = new int[n];\n \n // Build prefix and suffix maximum arrays\n // maxl[i] stores maximum height from 0 to i-1\n // maxr[i] stores maximum height from i+1 to n-1\n for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {\n maxl[i] = Math.Max(maxl[i-1], heights[i-1]);\n maxr[n-i-1] = Math.Max(maxr[n-i], heights[n-i]);\n }\n \n var ret = new List<int>();\n \n // Process each query\n foreach (int query in queries) {\n // Get maximum height to the left of current node\'s subtree\n int maxxl = maxl[l[query]];\n // Get maximum height to the right of current node\'s subtree\n int maxxr = maxr[r[query]];\n // Result is max of:\n // 1. Maximum height to the left of subtree\n // 2. Maximum height to the right of subtree\n // 3. Depth of current node - 1 (parent\'s depth)\n ret.Add(Math.Max(Math.Max(maxxl, maxxr), d[query]-1));\n }\n \n return ret.ToArray();\n }\n \n private void Search(TreeNode p, int h) {\n // Store current node\'s depth\n d[p.val] = h;\n \n // If leaf node, store its height and boundaries\n if (p.left == null && p.right == null) {\n heights[lenLeaves] = h;\n // For leaf nodes, left and right boundaries are same\n l[p.val] = r[p.val] = lenLeaves;\n lenLeaves++;\n return;\n }\n \n // Store left boundary of current subtree\n l[p.val] = lenLeaves;\n \n // Recursively process left and right children\n if (p.left != null) {\n Search(p.left, h + 1);\n }\n if (p.right != null) {\n Search(p.right, h + 1);\n }\n \n // Store right boundary of current subtree\n r[p.val] = lenLeaves - 1;\n }\n}\n```\n```golang []\ntype Solution struct {\n maxHeightAfterRemoval [100001]int\n currentMaxHeight int\n}\n\nfunc treeQueries(root *TreeNode, queries []int) []int {\n sol := &Solution{}\n \n // First traversal from left to right\n sol.traverseLeftToRight(root, 0)\n \n // Reset current max height for second traversal\n sol.currentMaxHeight = 0\n sol.traverseRightToLeft(root, 0)\n \n // Process queries and build result\n queryResults := make([]int, len(queries))\n for i, query := range queries {\n queryResults[i] = sol.maxHeightAfterRemoval[query]\n }\n \n return queryResults\n}\n\nfunc (s *Solution) traverseLeftToRight(node *TreeNode, currentHeight int) {\n if node == nil {\n return\n }\n \n // Store the maximum height if this node were removed\n s.maxHeightAfterRemoval[node.Val] = s.currentMaxHeight\n \n // Update current maximum height\n s.currentMaxHeight = max(s.currentMaxHeight, currentHeight)\n \n // Traverse left subtree first, then right\n s.traverseLeftToRight(node.Left, currentHeight + 1)\n s.traverseLeftToRight(node.Right, currentHeight + 1)\n}\n\nfunc (s *Solution) traverseRightToLeft(node *TreeNode, currentHeight int) {\n if node == nil {\n return\n }\n \n // Update maximum height if this node were removed\n s.maxHeightAfterRemoval[node.Val] = max(\n s.maxHeightAfterRemoval[node.Val],\n s.currentMaxHeight,\n )\n \n // Update current maximum height\n s.currentMaxHeight = max(currentHeight, s.currentMaxHeight)\n \n // Traverse right subtree first, then left\n s.traverseRightToLeft(node.Right, currentHeight + 1)\n s.traverseRightToLeft(node.Left, currentHeight + 1)\n}\n\nfunc max(a, b int) int {\n if a > b {\n return a\n }\n return b\n}\n```\n```swift []\nclass Solution {\n private var maxHeightAfterRemoval = Array(repeating: 0, count: 100001)\n private var currentMaxHeight = 0\n \n func treeQueries(_ root: TreeNode?, _ queries: [Int]) -> [Int] {\n traverseLeftToRight(root, 0)\n currentMaxHeight = 0 // Reset for second traversal\n traverseRightToLeft(root, 0)\n \n // Process queries and build result array\n return queries.map { maxHeightAfterRemoval[$0] }\n }\n \n private func traverseLeftToRight(_ node: TreeNode?, _ currentHeight: Int) {\n guard let node = node else { return }\n \n // Store maximum height if this node were removed\n maxHeightAfterRemoval[node.val] = currentMaxHeight\n \n // Update current maximum height\n currentMaxHeight = max(currentMaxHeight, currentHeight)\n \n // Traverse left subtree first, then right\n traverseLeftToRight(node.left, currentHeight + 1)\n traverseLeftToRight(node.right, currentHeight + 1)\n }\n \n private func traverseRightToLeft(_ node: TreeNode?, _ currentHeight: Int) {\n guard let node = node else { return }\n \n // Update maximum height if this node were removed\n maxHeightAfterRemoval[node.val] = max(\n maxHeightAfterRemoval[node.val],\n currentMaxHeight\n )\n \n // Update current maximum height\n currentMaxHeight = max(currentHeight, currentMaxHeight)\n \n // Traverse right subtree first, then left\n traverseRightToLeft(node.right, currentHeight + 1)\n traverseRightToLeft(node.left, currentHeight + 1)\n }\n}\n```\n```javascript [JS]\n// JavaScript\n\n\n// Function to process tree queries that finds max height excluding certain nodes\nvar treeQueries = function(root, queries) {\n // Array to store heights of leaf nodes\n const heights = new Array(50000).fill(0);\n \n // Array to store depth of each node (indexed by node value)\n const d = new Array(100001).fill(0);\n \n // Arrays to store left and right boundaries for each node\'s subtree\n const l = new Array(100001).fill(0);\n const r = new Array(100001).fill(0);\n \n // Counter for number of leaf nodes\n let len = 0;\n \n // DFS function to process the tree\n function search(p, h) {\n // Store current node\'s depth\n d[p.val] = h;\n \n // If current node is a leaf node\n if (!p.left && !p.right) {\n heights[len] = h; // Store its height\n l[p.val] = r[p.val] = len; // Set left and right boundaries\n len++; // Increment leaf counter\n return;\n }\n \n // Store left boundary for current node\n l[p.val] = len;\n \n // Recursively process left and right children\n if (p.left) search(p.left, h + 1);\n if (p.right) search(p.right, h + 1);\n \n // Store right boundary for current node\n r[p.val] = len - 1;\n }\n \n // Start DFS from root\n search(root, 0);\n \n const n = len;\n // Arrays to store maximum heights from left and right\n const maxl = new Array(n).fill(0);\n const maxr = new Array(n).fill(0);\n \n // Build prefix and suffix maximum arrays\n for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {\n maxl[i] = Math.max(maxl[i-1], heights[i-1]); // Left to right max\n maxr[n-i-1] = Math.max(maxr[n-i], heights[n-i]); // Right to left max\n }\n \n // Array to store results\n const ret = [];\n const k = queries.length;\n \n // Process each query\n for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {\n // Find maximum height excluding current node\'s subtree\n const maxxl = maxl[l[queries[i]]]; // Max height to the left\n const maxxr = maxr[r[queries[i]]]; // Max height to the right\n // Result is max of left max, right max, and node\'s depth-1\n ret.push(Math.max(Math.max(maxxl, maxxr), d[queries[i]] - 1));\n }\n \n return ret;\n};\n```\n```typescript [TS]\n// TypeScript\n\n\n// Function that processes queries about maximum heights in a binary tree excluding specific nodes\nfunction treeQueries(root: TreeNode | null, queries: number[]): number[] {\n // Arrays to store various tree-related information\n const heights: number[] = new Array(50000).fill(0); // Stores heights of leaf nodes\n const d: number[] = new Array(100001).fill(0); // Stores depth of each node\n const l: number[] = new Array(100001).fill(0); // Stores left boundary index for each node\n const r: number[] = new Array(100001).fill(0); // Stores right boundary index for each node\n let len: number = 0; // Counter for leaf nodes\n \n // DFS function to process the tree\n function search(p: TreeNode, h: number): void {\n // Store current node\'s depth\n d[p.val] = h;\n \n // If current node is a leaf node\n if (!p.left && !p.right) {\n heights[len] = h; // Store its height\n l[p.val] = r[p.val] = len; // Set left and right boundaries to current index\n len++; // Increment leaf counter\n return;\n }\n \n // Store left boundary for current node\n l[p.val] = len;\n \n // Recursively process left and right subtrees\n if (p.left) search(p.left, h + 1);\n if (p.right) search(p.right, h + 1);\n \n // Store right boundary for current node\n r[p.val] = len - 1;\n }\n \n // Handle empty tree case\n if (!root) return [];\n search(root, 0);\n \n const n: number = len;\n // Arrays to store maximum heights from left and right\n const maxl: number[] = new Array(n).fill(0);\n const maxr: number[] = new Array(n).fill(0);\n \n // Compute maximum heights from left to right and right to left\n for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {\n maxl[i] = Math.max(maxl[i-1], heights[i-1]); // Left to right maximums\n maxr[n-i-1] = Math.max(maxr[n-i], heights[n-i]); // Right to left maximums\n }\n \n // Process queries\n const ret: number[] = [];\n const k: number = queries.length;\n \n for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {\n // For each query, find maximum height possible when removing the queried node\n const maxxl: number = maxl[l[queries[i]]]; // Max height to the left\n const maxxr: number = maxr[r[queries[i]]]; // Max height to the right\n // Result is maximum of:\n // 1. Maximum height to the left of node\n // 2. Maximum height to the right of node\n // 3. Node\'s depth minus 1 (representing parent\'s path)\n ret.push(Math.max(Math.max(maxxl, maxxr), d[queries[i]] - 1));\n }\n \n return ret;\n}\n```\n```rust []\nuse std::cell::RefCell;\nuse std::rc::Rc;\n\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn tree_queries(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, queries: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {\n // Initialize storage vectors\n let mut heights = vec![0; 50000]; // Stores heights of leaf nodes\n let mut len = 0; // Tracks number of leaf nodes\n let mut d = vec![0; 100001]; // Stores depth of each node\n let mut l = vec![0; 100001]; // Stores left boundary index for each node\n let mut r = vec![0; 100001]; // Stores right boundary index for each node\n\n // Depth-First Search implementation\n fn search(\n node: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,\n h: i32, // Current height in tree\n heights: &mut Vec<i32>, // Mutable reference to heights vector\n len: &mut usize, // Mutable reference to length counter\n d: &mut Vec<i32>, // Mutable reference to depths vector\n l: &mut Vec<i32>, // Mutable reference to left boundaries\n r: &mut Vec<i32>, // Mutable reference to right boundaries\n ) {\n if let Some(n) = node {\n let node = n.borrow();\n let val = node.val as usize;\n d[val] = h; // Record current node\'s depth\n\n // Handle leaf node case\n if node.left.is_none() && node.right.is_none() {\n heights[*len] = h; // Store leaf height\n l[val] = *len as i32; // Set left boundary\n r[val] = *len as i32; // Set right boundary\n *len += 1; // Increment leaf counter\n return;\n }\n\n l[val] = *len as i32; // Set left boundary for internal node\n\n // Recursively process left and right subtrees\n search(node.left.clone(), h + 1, heights, len, d, l, r);\n search(node.right.clone(), h + 1, heights, len, d, l, r);\n\n r[val] = (*len - 1) as i32; // Set right boundary for internal node\n }\n }\n\n // Process the tree starting from root\n search(\n root,\n 0,\n &mut heights,\n &mut len,\n &mut d,\n &mut l,\n &mut r,\n );\n\n let n = len;\n // Arrays to store maximum heights from left and right\n let mut maxl = vec![0; n];\n let mut maxr = vec![0; n];\n\n // Build prefix (left) and suffix (right) maximum arrays\n for i in 1..n {\n maxl[i] = maxl[i - 1].max(heights[i - 1]); // Maximum height from left\n maxr[n - i - 1] = maxr[n - i].max(heights[n - i]); // Maximum height from right\n }\n\n // Process each query and build result vector\n queries\n .iter()\n .map(|&q| {\n let q = q as usize;\n let maxxl = maxl[l[q] as usize]; // Max height to the left\n let maxxr = maxr[r[q] as usize]; // Max height to the right\n maxxl.max(maxxr).max(d[q] - 1) // Take maximum of left, right, and depth-1\n })\n .collect() // Collect results into vector\n }\n}\n```\n```ruby []\ndef tree_queries(root, queries)\n # Initialize arrays to store tree information\n # @heights: stores heights of leaf nodes\n # @len: tracks number of leaf nodes\n # @d: stores depth of each node\n # @l, @r: store left and right indices for each node\'s subtree range\n @heights = Array.new(50000, 0)\n @len = 0\n @d = Array.new(100001, 0)\n @l = Array.new(100001, 0)\n @r = Array.new(100001, 0)\n \n # Process the tree using DFS\n search(root, 0)\n \n n = @len # Total number of leaf nodes\n # Arrays to store maximum heights from left and right perspectives\n maxl = Array.new(n, 0)\n maxr = Array.new(n, 0)\n \n # Build prefix and suffix maximum arrays\n (1...n).each do |i|\n # maxl[i] stores the maximum height of leaves to the left of index i\n maxl[i] = [maxl[i-1], @heights[i-1]].max\n # maxr[n-i-1] stores the maximum height of leaves to the right of index n-i-1\n maxr[n-i-1] = [maxr[n-i], @heights[n-i]].max\n end\n \n # Process each query\n ret = []\n queries.each do |query|\n # Find maximum height excluding current node\'s subtree\n maxxl = maxl[@l[query]] # Max height to the left of subtree\n maxxr = maxr[@r[query]] # Max height to the right of subtree\n # Result is maximum of: left max, right max, or depth-1\n ret.push([maxxl, maxxr, @d[query]-1].max)\n end\n \n ret\nend\n\n# DFS helper method to process the tree structure\ndef search(p, h)\n @d[p.val] = h # Store current node\'s depth\n \n # If leaf node found\n if !p.left && !p.right\n @heights[@len] = h # Store leaf height\n @l[p.val] = @r[p.val] = @len # Mark leaf node range\n @len += 1\n return\n end\n \n @l[p.val] = @len # Store left boundary of current subtree\n \n # Recursively process left and right children\n search(p.left, h + 1) if p.left\n search(p.right, h + 1) if p.right\n \n @r[p.val] = @len - 1 # Store right boundary of current subtree\nend\n```\n### Without comments\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n heights = [0] * 50000\n d = [0] * 100001\n l = [0] * 100001\n r = [0] * 100001\n len_leaves = 0\n \n def search(p: TreeNode, h: int) -> None:\n nonlocal len_leaves\n d[p.val] = h\n \n if not p.left and not p.right:\n heights[len_leaves] = h\n l[p.val] = r[p.val] = len_leaves\n len_leaves += 1\n return\n \n l[p.val] = len_leaves\n \n if p.left:\n search(p.left, h + 1)\n if p.right:\n search(p.right, h + 1)\n \n r[p.val] = len_leaves - 1\n \n search(root, 0)\n \n n = len_leaves\n maxl = [0] * n\n maxr = [0] * n\n \n for i in range(1, n):\n maxl[i] = max(maxl[i-1], heights[i-1])\n maxr[n-i-1] = max(maxr[n-i], heights[n-i])\n \n ret = []\n \n for query in queries:\n maxxl = maxl[l[query]]\n maxxr = maxr[r[query]]\n ret.append(max(max(maxxl, maxxr), d[query]-1))\n \n return ret\n```\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxHeightAfterRemoval[100001];\n int currentMaxHeight = 0;\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n traverseLeftToRight(root, 0);\n currentMaxHeight = 0;\n traverseRightToLeft(root, 0);\n\n int queryCount = queries.size();\n vector<int> queryResults(queryCount);\n for (int i = 0; i < queryCount; i++) {\n queryResults[i] = maxHeightAfterRemoval[queries[i]];\n }\n\n return queryResults;\n }\n\nprivate:\n void traverseLeftToRight(TreeNode* node, int currentHeight) {\n if (node == nullptr) return;\n\n maxHeightAfterRemoval[node->val] = currentMaxHeight;\n currentMaxHeight = max(currentMaxHeight, currentHeight);\n\n traverseLeftToRight(node->left, currentHeight + 1);\n traverseLeftToRight(node->right, currentHeight + 1);\n }\n\n void traverseRightToLeft(TreeNode* node, int currentHeight) {\n if (node == nullptr) return;\n\n maxHeightAfterRemoval[node->val] = \n max(maxHeightAfterRemoval[node->val], currentMaxHeight);\n currentMaxHeight = max(currentHeight, currentMaxHeight);\n\n traverseRightToLeft(node->right, currentHeight + 1);\n traverseRightToLeft(node->left, currentHeight + 1);\n }\n};\n```\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n private int[] heights;\n private int[] d;\n private int[] l;\n private int[] r;\n private int lenLeaves;\n\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n heights = new int[50000];\n d = new int[100001];\n l = new int[100001];\n r = new int[100001];\n lenLeaves = 0;\n\n search(root, 0);\n\n int n = lenLeaves;\n int[] maxl = new int[n];\n int[] maxr = new int[n];\n\n for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {\n maxl[i] = Math.max(maxl[i-1], heights[i-1]);\n }\n\n for (int i = n-2; i >= 0; i--) {\n maxr[i] = Math.max(maxr[i+1], heights[i+1]);\n }\n\n int[] ret = new int[queries.length];\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {\n int query = queries[i];\n int maxxl = maxl[l[query]];\n int maxxr = maxr[r[query]];\n ret[i] = Math.max(Math.max(maxxl, maxxr), d[query]-1);\n }\n\n return ret;\n }\n\n private void search(TreeNode p, int h) {\n d[p.val] = h;\n\n if (p.left == null && p.right == null) {\n heights[lenLeaves] = h;\n l[p.val] = r[p.val] = lenLeaves;\n lenLeaves++;\n return;\n }\n\n l[p.val] = lenLeaves;\n\n if (p.left != null) {\n search(p.left, h + 1);\n }\n if (p.right != null) {\n search(p.right, h + 1);\n }\n\n r[p.val] = lenLeaves - 1;\n }\n}\n```\n```csharp []\npublic class Solution {\n private int[] heights;\n private int[] d;\n private int[] l;\n private int[] r;\n private int lenLeaves;\n\n public int[] TreeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n heights = new int[50000];\n d = new int[100001];\n l = new int[100001];\n r = new int[100001];\n lenLeaves = 0;\n\n Search(root, 0);\n\n int n = lenLeaves;\n int[] maxl = new int[n];\n int[] maxr = new int[n];\n\n for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {\n maxl[i] = Math.Max(maxl[i-1], heights[i-1]);\n maxr[n-i-1] = Math.Max(maxr[n-i], heights[n-i]);\n }\n\n var ret = new List<int>();\n\n foreach (int query in queries) {\n int maxxl = maxl[l[query]];\n int maxxr = maxr[r[query]];\n ret.Add(Math.Max(Math.Max(maxxl, maxxr), d[query]-1));\n }\n\n return ret.ToArray();\n }\n\n private void Search(TreeNode p, int h) {\n d[p.val] = h;\n\n if (p.left == null && p.right == null) {\n heights[lenLeaves] = h;\n l[p.val] = r[p.val] = lenLeaves;\n lenLeaves++;\n return;\n }\n\n l[p.val] = lenLeaves;\n\n if (p.left != null) {\n Search(p.left, h + 1);\n }\n if (p.right != null) {\n Search(p.right, h + 1);\n }\n\n r[p.val] = lenLeaves - 1;\n }\n}\n```\n```golang []\ntype Solution struct {\n maxHeightAfterRemoval [100001]int\n currentMaxHeight int\n}\n\nfunc treeQueries(root *TreeNode, queries []int) []int {\n sol := &Solution{}\n\n sol.traverseLeftToRight(root, 0)\n\n sol.currentMaxHeight = 0\n sol.traverseRightToLeft(root, 0)\n\n queryResults := make([]int, len(queries))\n for i, query := range queries {\n queryResults[i] = sol.maxHeightAfterRemoval[query]\n }\n\n return queryResults\n}\n\nfunc (s *Solution) traverseLeftToRight(node *TreeNode, currentHeight int) {\n if node == nil {\n return\n }\n\n s.maxHeightAfterRemoval[node.Val] = s.currentMaxHeight\n s.currentMaxHeight = max(s.currentMaxHeight, currentHeight)\n\n s.traverseLeftToRight(node.Left, currentHeight + 1)\n s.traverseLeftToRight(node.Right, currentHeight + 1)\n}\n\nfunc (s *Solution) traverseRightToLeft(node *TreeNode, currentHeight int) {\n if node == nil {\n return\n }\n\n s.maxHeightAfterRemoval[node.Val] = max(\n s.maxHeightAfterRemoval[node.Val],\n s.currentMaxHeight,\n )\n\n s.currentMaxHeight = max(currentHeight, s.currentMaxHeight)\n\n s.traverseRightToLeft(node.Right, currentHeight + 1)\n s.traverseRightToLeft(node.Left, currentHeight + 1)\n}\n\nfunc max(a, b int) int {\n if a > b {\n return a\n }\n return b\n}\n```\n```swift []\nclass Solution {\n private var maxHeightAfterRemoval = Array(repeating: 0, count: 100001)\n private var currentMaxHeight = 0\n \n func treeQueries(_ root: TreeNode?, _ queries: [Int]) -> [Int] {\n traverseLeftToRight(root, 0)\n currentMaxHeight = 0\n traverseRightToLeft(root, 0)\n \n return queries.map { maxHeightAfterRemoval[$0] }\n }\n \n private func traverseLeftToRight(_ node: TreeNode?, _ currentHeight: Int) {\n guard let node = node else { return }\n \n maxHeightAfterRemoval[node.val] = currentMaxHeight\n currentMaxHeight = max(currentMaxHeight, currentHeight)\n \n traverseLeftToRight(node.left, currentHeight + 1)\n traverseLeftToRight(node.right, currentHeight + 1)\n }\n \n private func traverseRightToLeft(_ node: TreeNode?, _ currentHeight: Int) {\n guard let node = node else { return }\n \n maxHeightAfterRemoval[node.val] = max(\n maxHeightAfterRemoval[node.val],\n currentMaxHeight\n )\n \n currentMaxHeight = max(currentHeight, currentMaxHeight)\n \n traverseRightToLeft(node.right, currentHeight + 1)\n traverseRightToLeft(node.left, currentHeight + 1)\n }\n}\n```\n```javascript [JS]\n// JavaScript\n\n\nvar treeQueries = function(root, queries) {\n const heights = new Array(50000).fill(0);\n const d = new Array(100001).fill(0);\n const l = new Array(100001).fill(0);\n const r = new Array(100001).fill(0);\n let len = 0;\n\n function search(p, h) {\n d[p.val] = h;\n\n if (!p.left && !p.right) {\n heights[len] = h;\n l[p.val] = r[p.val] = len;\n len++;\n return;\n }\n\n l[p.val] = len;\n\n if (p.left) search(p.left, h + 1);\n if (p.right) search(p.right, h + 1);\n\n r[p.val] = len - 1;\n }\n\n search(root, 0);\n\n const n = len;\n const maxl = new Array(n).fill(0);\n const maxr = new Array(n).fill(0);\n\n for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {\n maxl[i] = Math.max(maxl[i-1], heights[i-1]);\n maxr[n-i-1] = Math.max(maxr[n-i], heights[n-i]);\n }\n\n const ret = [];\n const k = queries.length;\n\n for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {\n const maxxl = maxl[l[queries[i]]];\n const maxxr = maxr[r[queries[i]]];\n ret.push(Math.max(Math.max(maxxl, maxxr), d[queries[i]] - 1));\n }\n\n return ret;\n};\n```\n```typescript [TS]\n// TypeScript\n\n\nfunction treeQueries(root: TreeNode | null, queries: number[]): number[] {\n const heights: number[] = new Array(50000).fill(0);\n const d: number[] = new Array(100001).fill(0);\n const l: number[] = new Array(100001).fill(0);\n const r: number[] = new Array(100001).fill(0);\n let len: number = 0;\n\n function search(p: TreeNode, h: number): void {\n d[p.val] = h;\n\n if (!p.left && !p.right) {\n heights[len] = h;\n l[p.val] = r[p.val] = len;\n len++;\n return;\n }\n\n l[p.val] = len;\n\n if (p.left) search(p.left, h + 1);\n if (p.right) search(p.right, h + 1);\n\n r[p.val] = len - 1;\n }\n\n if (!root) return [];\n search(root, 0);\n\n const n: number = len;\n const maxl: number[] = new Array(n).fill(0);\n const maxr: number[] = new Array(n).fill(0);\n\n for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {\n maxl[i] = Math.max(maxl[i-1], heights[i-1]);\n maxr[n-i-1] = Math.max(maxr[n-i], heights[n-i]);\n }\n\n const ret: number[] = [];\n const k: number = queries.length;\n\n for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {\n const maxxl: number = maxl[l[queries[i]]];\n const maxxr: number = maxr[r[queries[i]]];\n ret.push(Math.max(Math.max(maxxl, maxxr), d[queries[i]] - 1));\n }\n\n return ret;\n}\n```\n```rust []\nuse std::cell::RefCell;\nuse std::rc::Rc;\n\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn tree_queries(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, queries: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {\n let mut heights = vec![0; 50000];\n let mut len = 0;\n let mut d = vec![0; 100001];\n let mut l = vec![0; 100001];\n let mut r = vec![0; 100001];\n\n fn search(\n node: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,\n h: i32,\n heights: &mut Vec<i32>,\n len: &mut usize,\n d: &mut Vec<i32>,\n l: &mut Vec<i32>,\n r: &mut Vec<i32>,\n ) {\n if let Some(n) = node {\n let node = n.borrow();\n let val = node.val as usize;\n d[val] = h;\n\n if node.left.is_none() && node.right.is_none() {\n heights[*len] = h;\n l[val] = *len as i32;\n r[val] = *len as i32;\n *len += 1;\n return;\n }\n\n l[val] = *len as i32;\n\n search(node.left.clone(), h + 1, heights, len, d, l, r);\n search(node.right.clone(), h + 1, heights, len, d, l, r);\n\n r[val] = (*len - 1) as i32;\n }\n }\n\n search(\n root,\n 0,\n &mut heights,\n &mut len,\n &mut d,\n &mut l,\n &mut r,\n );\n\n let n = len;\n let mut maxl = vec![0; n];\n let mut maxr = vec![0; n];\n\n for i in 1..n {\n maxl[i] = maxl[i - 1].max(heights[i - 1]);\n maxr[n - i - 1] = maxr[n - i].max(heights[n - i]);\n }\n\n queries\n .iter()\n .map(|&q| {\n let q = q as usize;\n let maxxl = maxl[l[q] as usize];\n let maxxr = maxr[r[q] as usize];\n maxxl.max(maxxr).max(d[q] - 1)\n })\n .collect()\n }\n}\n```\n```ruby []\ndef tree_queries(root, queries)\n @heights = Array.new(50000, 0)\n @len = 0\n @d = Array.new(100001, 0)\n @l = Array.new(100001, 0)\n @r = Array.new(100001, 0)\n \n search(root, 0)\n \n n = @len\n maxl = Array.new(n, 0)\n maxr = Array.new(n, 0)\n \n (1...n).each do |i|\n maxl[i] = [maxl[i-1], @heights[i-1]].max\n maxr[n-i-1] = [maxr[n-i], @heights[n-i]].max\n end\n \n ret = []\n queries.each do |query|\n maxxl = maxl[@l[query]]\n maxxr = maxr[@r[query]]\n ret.push([maxxl, maxxr, @d[query]-1].max)\n end\n \n ret\nend\n\ndef search(p, h)\n @d[p.val] = h\n \n if !p.left && !p.right\n @heights[@len] = h\n @l[p.val] = @r[p.val] = @len\n @len += 1\n return\n end\n \n @l[p.val] = @len\n \n search(p.left, h + 1) if p.left\n search(p.right, h + 1) if p.right\n \n @r[p.val] = @len - 1\nend\n\n\n```\n\n\n\n### Complexity \n- Time complexity: O(n)\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n\n\n## Explained step by step\n\n---\n\n1. Data Structure Setup:\n```\n# Arrays initialization\nheights = [0] * 50000 # Store leaf node heights\nd = [0] * 100001 # Store depth of each node\nl = [0] * 100001 # Store left boundary index\nr = [0] * 100001 # Store right boundary index\nlen_leaves = 0 # Track number of leaf nodes\n\n```\n\n2. Tree Traversal Function:\n```\ndef search(p: TreeNode, h: int):\n d[p.val] = h # Record node depth\n \n # Handle leaf node\n if not p.left and not p.right:\n heights[len_leaves] = h\n l[p.val] = r[p.val] = len_leaves\n len_leaves += 1\n return\n \n l[p.val] = len_leaves # Set left boundary\n \n # Traverse children\n if p.left: search(p.left, h + 1)\n if p.right: search(p.right, h + 1)\n \n r[p.val] = len_leaves - 1 # Set right boundary\n\n```\n\n3. Maximum Height Arrays Construction:\n```\nn = len_leaves\nmaxl = [0] * n # Left-to-right maximum heights\nmaxr = [0] * n # Right-to-left maximum heights\n\n\n# Build prefix and suffix maximums\nfor i in range(1, n):\n maxl[i] = max(maxl[i-1], heights[i-1])\n maxr[n-i-1] = max(maxr[n-i], heights[n-i])\n```\n\n4. Query Processing:\n```\nret = []\nfor query in queries:\n # Find max height excluding queried node\'s subtree\n maxxl = maxl[l[query]] # Max height to left\n maxxr = maxr[r[query]] # Max height to right\n ret.append(max(max(maxxl, maxxr), d[query]-1))\n\n```\n- The solution uses DFS to process the tree and record node information\n- For each node, we track:\n - Its depth\n - Left and right boundaries of its subtree in the leaf sequence\n - Heights of leaf nodes\n- We build prefix and suffix maximum arrays to quickly find maximum heights\n- For each query:\n - We find maximum height outside the queried node\'s subtree\n - Compare with (depth-1) to get the final result\n\n\n\n---\n\n\n\n
| 78 | 1 |
['Swift', 'C++', 'Java', 'Go', 'TypeScript', 'Python3', 'Rust', 'Ruby', 'JavaScript', 'C#']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Java 2 pass DFS with HashMaps
|
java-2-pass-dfs-with-hashmaps-by-zadeluc-o6ci
|
\nclass Solution {\n private Map<Integer, Integer> leftMap = new HashMap<>();\n private Map<Integer, Integer> rightMap = new HashMap<>();\n private Map
|
zadeluca
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:11:56.305587+00:00
|
2022-10-30T04:11:56.305618+00:00
| 5,529 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n private Map<Integer, Integer> leftMap = new HashMap<>();\n private Map<Integer, Integer> rightMap = new HashMap<>();\n private Map<Integer, Integer> removed = new HashMap<>();\n \n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n populateHeights(root, 0);\n calculateRemovedHeights(root, 0);\n \n int[] output = new int[queries.length];\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {\n output[i] = removed.get(queries[i]);\n }\n return output;\n }\n \n\t// height is the max tree height with this node removed\n private void calculateRemovedHeights(TreeNode node, int height) {\n if (node == null) {\n return;\n }\n removed.put(node.val, height);\n\t\t\n\t\t// for each child, the height when removed is the max of the the height following\n\t\t// the opposite child, or the passed-in height with this node removed\n calculateRemovedHeights(node.left, Math.max(height, rightMap.get(node.val)));\n calculateRemovedHeights(node.right, Math.max(height, leftMap.get(node.val)));\n }\n \n\t// populate the maps with the total height of the left and right subtree of\n\t// each node, and return the larger of the two values\n private int populateHeights(TreeNode node, int height) {\n if (node == null) {\n return height - 1;\n }\n \n leftMap.put(node.val, populateHeights(node.left, height + 1));\n rightMap.put(node.val, populateHeights(node.right, height + 1));\n \n return Math.max(leftMap.get(node.val), rightMap.get(node.val));\n }\n}\n```
| 60 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Java']
| 8 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
[Python3, C++] Clean 9 lines Dfs
|
python3-c-clean-9-lines-dfs-by-tojuna-b3um
|
Explanation:\n Find height of each node\n Perform a dfs, the parameters are current node, current depth and max height without current node\n Max height without
|
tojuna
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:38:19.960022+00:00
|
2022-10-30T07:26:18.231653+00:00
| 3,201 | false |
**Explanation**:\n* Find height of each node\n* Perform a dfs, the parameters are current node, current depth and max height without current node\n* Max height without current node will be max height elsewhere in the tree or height of sibling node + curr depth\n\n**Python3**\n``` \n def treeQueries(self, root, queries, ans = {}) -> List[int]:\n @cache\n def height(r): return 1 + max(height(r.left), height(r.right)) if r else 0\n def dfs(r, depth, mx):\n if not r: return\n ans[r.val] = mx\n dfs(r.left, depth + 1, max(mx, depth + height(r.right)))\n dfs(r.right, depth + 1, max(mx, depth + height(r.left)))\n dfs(root, 0, 0)\n return [ans[v] for v in queries]\n```\n**C++**\n```\nvector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n\tunordered_map<int, int> ans; unordered_map<TreeNode*, int> hts; vector<int> res;\n\tfunction<int(TreeNode*)> height = [&](TreeNode* r) {\n\t\treturn r ? (hts[r] = 1 + max(height(r->left), height(r->right))) : 0; \n\t};\n\tfunction<void(TreeNode*,int,int)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* r, int depth, int mx) {\n\t\tif (!r) return;\n\t\tans[r->val] = mx;\n\t\tdfs(r->right, depth + 1, max(mx, depth + hts[r->left]));\n\t\tdfs(r->left, depth + 1, max(mx, depth + hts[r->right]));\n\t};\n\theight(root); dfs(root, 0, 0);\n\tfor (int& v: queries) res.push_back(ans[v]);\n\treturn res;\n}\n```\n*Time complexity: O(n)*\n\n**Bonus:**\n**Python3 8 lines**\n ```\n\t def treeQueries(self, root, queries, ans = {}) -> List[int]:\n ht = lru_cache(maxsize = 20000)(lambda r: 1 + max(ht(r.left), ht(r.right)) if r else 0)\n def dfs(r, depth, mx):\n if not r: return\n ans[r.val] = mx\n dfs(r.left, depth + 1, max(mx, depth + ht(r.right)))\n dfs(r.right, depth + 1, max(mx, depth + ht(r.left)))\n dfs(root, 0, 0)\n return [ans[v] for v in queries]\n```
| 53 | 0 |
[]
| 6 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
C++ | DFS
|
c-dfs-by-vaibhavshekhawat-d4sj
|
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n unordered_map l,r,ans;\n int height(TreeNode root){\n if(root==NULL) return 0;\n int le = height(root->left
|
vaibhavshekhawat
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:05:21.653297+00:00
|
2022-10-30T04:35:27.721146+00:00
| 3,215 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n unordered_map<int,int> l,r,ans;\n int height(TreeNode* root){\n if(root==NULL) return 0;\n int le = height(root->left);\n int re = height(root->right);\n l[root->val] = le; // Storing maximum height in the left side of current node\n r[root->val] = re; // Storing maximum height in the right side of current node\n return max(le,re)+1; \n }\n void fun(TreeNode* root,int MaxSoFar,int depth){\n if(root==NULL) return;\n\n ans[root->val] = MaxSoFar;\n fun(root->left,max(MaxSoFar,depth+r[root->val]),depth+1);\n fun(root->right,max(MaxSoFar,depth+l[root->val]),depth+1);\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& q) {\n height(root);\n \n fun(root->left,r[root->val],1); // Calling on left side and passing the maximum height of right side of root\n fun(root->right,l[root->val],1); // Calling on right side and passing the maximum height of left side of root\n \n vector<int> res(q.size());\n for(int i = 0;i<q.size();i++){\n res[i] = ans[q[i]];\n }\n return res;\n }\n};
| 40 | 1 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Recursion', 'C']
| 10 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
[Tutorial From The Problem Contributor] DFS 1 time converts to a Range Removal Problem
|
tutorial-from-the-problem-contributor-df-gq7o
|
Topic : DFS\n\nAs the contributor to this problem, I\'d like to share the intended solution that I developed while working through it during my Google intervie
|
never_get_piped
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T01:56:44.479167+00:00
|
2024-10-26T04:07:07.016911+00:00
| 9,376 | false |
**Topic** : DFS\n\nAs the **contributor** to this problem, I\'d like to share the intended solution that I developed while working through it during my **Google** interview.\n\n**Contributor**:\n\n\n___\n\n## Solution\nFirst, let\'s consider how to determine the height of a tree **without any removal operations**.\nLet `mp2[i]` represent the height of a single node `i`, defined as the number of nodes along the path from the root node to node `i`. The height of the tree is simply the maximum value in the array `mp2`.\n\nWhen we remove a subtree, we eliminate some values from `mp2`. Consequently, **the height of the remaining tree** will be the **maximum** value among the remaining values in `mp2`. Is there a way to remove those values from `mp2` elegantly?\n\nYes, we can assign each node a unique `ID` to represent its value. **The `ID` will be assigned according to the preorder traversal order of the tree.** Now, `mp2[i]` denotes the number of nodes along the path from the root node to the node with ID `i`.\n\nLet\'s also calculate the size of each subtree. If we remove a subtree rooted at `u`, this means we remove all IDs from `ID[u]` to `ID[u] + subtreeSize[u] - 1` consecutively. By removing a consecutive range from `mp2`, we can easily compute the maximum value among the remaining elements.\n\nWe have an array `left[i]` that represents the maximum value of `mp2` from index `0` to `i`, and an array `right[i]` that represents the maximum value of `mp2` from index `i` to the end. If we remove a range `[l : r]` from `mp2`, the answer will simply be `max(left[l - 1], right[r + 1])`.\n\n\n<br/><br/>\n\n```c++\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n unordered_map<int, int> mp1, mp2, sz;\n int id = 0;\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& q) {\n vector<int> ans;\n dfs(root, 0);\n \n vector<int> left(id), right(id);\n for(int i = 0; i < left.size(); i++) {\n left[i] = mp2[i];\n if(i) left[i] = max(left[i - 1], left[i]);\n }\n \n for(int i = right.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {\n right[i] = mp2[i];\n if(i + 1 < right.size()) right[i] = max(right[i], right[i + 1]);\n }\n \n for(int i = 0; i < q.size(); i++) {\n int nodeid = mp1[q[i]];\n int l = nodeid, r = l + sz[nodeid] - 1;\n int h = 0;\n if(l > 0) h = max(h, left[l - 1]);\n if(r + 1 < right.size()) h = max(h, right[r + 1]);\n ans.push_back(h);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n \n int dfs(TreeNode* root, int h) { //return the size of the subtree\n if(root == NULL) {\n return 0;\n }\n mp1[root -> val] = id;\n mp2[id] = h;\n id++;\n int lz = dfs(root -> left, h + 1);\n int rz = dfs(root -> right, h + 1);\n sz[mp1[root -> val]] = (1 + lz + rz);\n return 1 + lz + rz;\n }\n};\n```\n\n```java\nclass Solution {\n Map<Integer, Integer> mp1 = new HashMap<>(), mp2 = new HashMap<>(), sz = new HashMap<>();\n int id = 0;\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] q) {\n int[] ans = new int[q.length];\n dfs(root, 0);\n \n int[] left = new int[id];\n int[] right = new int[id];\n for (int i = 0; i < id; i++) {\n left[i] = mp2.get(i);\n if (i > 0) left[i] = Math.max(left[i - 1], left[i]);\n }\n \n for (int i = id - 1; i >= 0; i--) {\n right[i] = mp2.get(i);\n if (i + 1 < id) right[i] = Math.max(right[i], right[i + 1]);\n }\n \n for (int i = 0; i < q.length; i++) {\n int nodeId = mp1.get(q[i]);\n int l = nodeId, r = l + sz.get(nodeId) - 1;\n int h = 0;\n if (l > 0) h = Math.max(h, left[l - 1]);\n if (r + 1 < id) h = Math.max(h, right[r + 1]);\n ans[i] = h;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n \n private int dfs(TreeNode root, int h) {\n if (root == null) {\n return 0;\n }\n mp1.put(root.val, id);\n mp2.put(id, h);\n id++;\n int lz = dfs(root.left, h + 1);\n int rz = dfs(root.right, h + 1);\n sz.put(mp1.get(root.val), 1 + lz + rz);\n return 1 + lz + rz;\n }\n}\n```\n\n```python\nclass Solution:\n def __init__(self):\n self.mp1 = {}\n self.mp2 = {}\n self.sz = {}\n self.id = 0\n \n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], q: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n self.dfs(root, 0)\n left = [0] * self.id\n right = [0] * self.id\n \n for i in range(self.id):\n left[i] = self.mp2[i]\n if i > 0:\n left[i] = max(left[i - 1], left[i])\n \n for i in range(self.id - 1, -1, -1):\n right[i] = self.mp2[i]\n if i + 1 < self.id:\n right[i] = max(right[i], right[i + 1])\n \n ans = []\n for node in q:\n nodeid = self.mp1[node]\n l, r = nodeid, nodeid + self.sz[nodeid] - 1\n h = 0\n if l > 0:\n h = max(h, left[l - 1])\n if r + 1 < self.id:\n h = max(h, right[r + 1])\n ans.append(h)\n \n return ans\n \n def dfs(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], h: int) -> int:\n if not root:\n return 0\n self.mp1[root.val] = self.id\n self.mp2[self.id] = h\n self.id += 1\n lz = self.dfs(root.left, h + 1)\n rz = self.dfs(root.right, h + 1)\n self.sz[self.mp1[root.val]] = 1 + lz + rz\n return 1 + lz + rz\n \n```\n\n\n**Complexity**:\n* Time Complexity : `O(n)`.\n* Space Complexity : `O(n)`\n\n**Feel free to leave a comment if something is confusing, or if you have any suggestions on how I can improve the post.**
| 36 | 0 |
['C', 'Python', 'Java']
| 9 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
✅ [Python/C++/Java/Rust] code-as-explanation + BONUS (with detailed comments)
|
pythoncjavarust-code-as-explanation-bonu-qdv3
|
\u2705 IF YOU LIKE THIS SOLUTION, PLEASE UPVOTE.\n*\nThis solution employs a Depth First Search approach to compute heights & depths of tree nodes. Time complex
|
stanislav-iablokov
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-31T07:53:55.735212+00:00
|
2022-10-31T15:04:53.008488+00:00
| 932 | false |
**\u2705 IF YOU LIKE THIS SOLUTION, PLEASE UPVOTE.**\n****\nThis solution employs a Depth First Search approach to compute heights & depths of tree nodes. Time complexity is linear: **O(m+n)**. Space complexity is linear: **O(m+n)**\n\n**Comment**. The strategy here is to pre-compute three maps:\n1. `depths` is a map that stores for each node its depth, i.e., the distance from the top (root) of the tree;\n2. `height` is a map that stores for each node its height, i.e., the maximal length of a path to the bottom of the tree that starts from this node;\n3. `levels` is a map that stores for each level (depth) a list of nodes on that level.\n\nThe idea of the solution is simple: when we remove a node, the maximal height of the resulting tree is the sum of:\n* the depth of removed node\'s parent (i.e., parent\'s level) and\n* the maximal height of the **remaining** nodes on the removed node\'s level.\n\n**Python** self-explanatory (and easy-to-read) code that realizes this strategy is presented below.\n```\nclass Solution:\n \n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n \n height, depths, levels = {}, {}, defaultdict(list)\n \n def dfs(n, d):\n if not n: return 0\n h = 1 + max(dfs(n.left, d+1), dfs(n.right, d+1))\n levels[d].append(n.val)\n height[n.val] = h\n depths[n.val] = d\n return h\n \n @functools.cache\n def query(q):\n max_height = max([height[v] for v in levels[depths[q]] if v != q] or [0])\n return depths[q] - 1 + max_height\n \n dfs(root, 0) \n \n return [query(q) for q in queries]\n```\n\nAs a bonus, I provide a more concise solution in various languages. It turns out that we can precompute the result for each possible query right inside the DFS function by using memoization/cache of height.\n<iframe src="https://leetcode.com/playground/iwDQo4e9/shared" frameBorder="0" width="800" height="640"></iframe>
| 27 | 1 |
[]
| 4 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
find 2 maximum of each level
|
find-2-maximum-of-each-level-by-iamcoder-cccg
|
This Question is Pretty much simple, \nJust read the explanation once,\n\nFirst of All you need to find the level, and height of each node of a tree and store t
|
IAmCoderrr
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:01:14.872741+00:00
|
2022-10-30T11:36:32.353659+00:00
| 2,213 | false |
This Question is Pretty much simple, \nJust read the explanation once,\n\nFirst of All you need to find the level, and height of each node of a tree and store them in a map\nThen store the 2 maximum node of each level\n\nNow start traversing in the queries array, suppose \nthe node you wants to remove is not having the maximum height in its level, \nthen the removal of that node, doesn\'t impact in height of tree,\n\nthe node you wants to remove is having the maximum height in its level, \nthen the removal of that node, impact in height of tree,\nit decrease the height by\n(height of that node - 2nd maximum height of that level)\n\nso in that case queries[i]=heightOf(queries[i])-2nd maximum height of that level;\n\n**Happy coding :)**\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n \n // for storing the height of each node\n Map<Integer,Integer> height=new HashMap<>();\n // for storing the level of each node \n Map<Integer,Integer> level=new HashMap<>();\n // for storing the 2 maximum height of each level \n Map<Integer,Queue<Integer>> twoMaximum=new HashMap<>();\n \n int nodeHeight(TreeNode root,int l){\n \n if(root==null) return -1;\n // adding default priority Queue \n twoMaximum.putIfAbsent(l,new PriorityQueue<>());\n \n int temp=Math.max(nodeHeight(root.left,l+1),nodeHeight(root.right,l+1))+1;\n \n height.put(root.val,temp);\n level.put(root.val,l);\n \n twoMaximum.get(l).add(temp);\n \n // updating priority Queue with the 2 maximum height of current level \n if(twoMaximum.get(l).size()>2) twoMaximum.get(l).remove();\n return temp;\n }\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] q) {\n \n // the height of tree \n int h=nodeHeight(root,0);\n \n for(int i=0;i<q.length;i++){\n int lev=level.get(q[i]);\n int hh=height.get(q[i]); \n int a=-1,b=-1;\n // if there is more then 2 node at the level of query[i]\n if(twoMaximum.get(lev).size()==2){\n b=twoMaximum.get(lev).remove();\n a=twoMaximum.get(lev).remove();\n \n // if current node has maximum height, in his level then the height of tree will be impacted\n // and height of tree will be decrease by heightOf(queries[i])-2nd maximum height of that level;\n if(hh==a) q[i]=h-(a-b);\n \n // else the height of tree remains same \n else q[i]=h;\n \n twoMaximum.get(lev).add(a);\n twoMaximum.get(lev).add(b);\n }\n // if there is only one node at that level \n // then the height of tree will be subtracted by the height of current node\n else q[i]=h-hh-1;\n }\n // returning the updated query array \n return q;\n }\n}\n```\n\n**Time complexity will be O(N) \nSpace complexity will be O(N) + O(h) =O(N)**\n\n**where ,\nN is the number of nodes in a tree \nh is the height of tree**\n\n*Please Upvote the post.*
| 27 | 1 |
[]
| 10 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Java/C++ | DFS | PreorderMirror
|
javac-dfs-preordermirror-by-shenglia-e7x7
|
TWO DFS Preorder Mirror to each other.\nTWO Pass:\n One path start from left child node first.\n The other path start from right child node first.\n\nWhen they
|
shenglia
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T05:05:59.125674+00:00
|
2022-10-31T19:35:44.615283+00:00
| 1,433 | false |
### TWO DFS Preorder Mirror to each other.\nTWO Pass:\n* One path start from left child node first.\n* The other path start from right child node first.\n\nWhen they reach to the same node [6] (for example), \nupdate the max level they saw so far. (Does not include current node [6].)\n\nD[root->val] = max(left_max_level, right_max_level)\n\n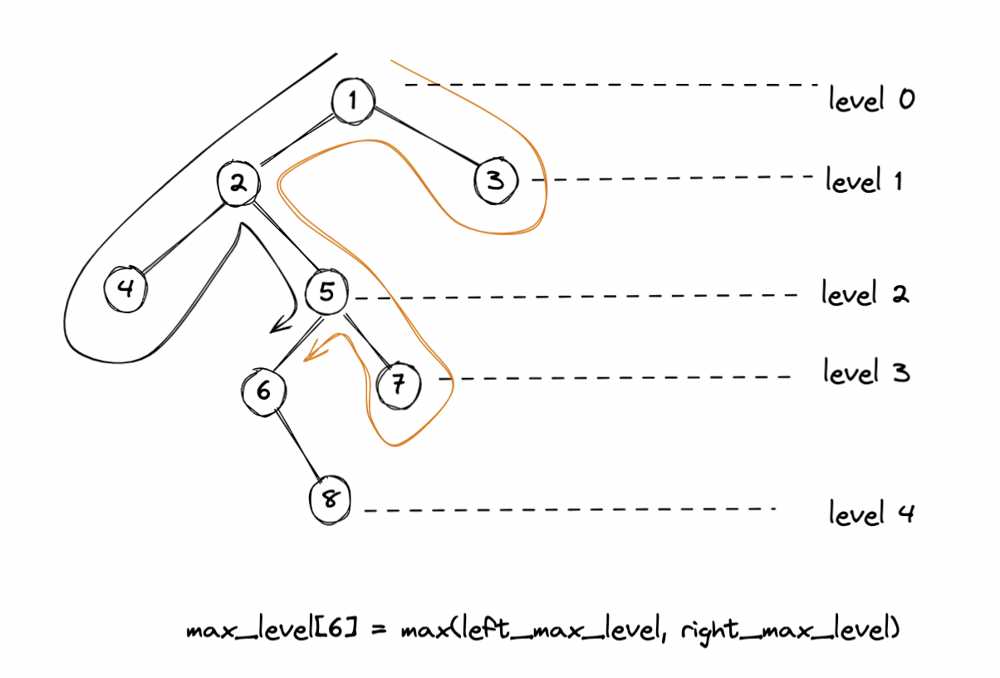\n\n\n\n### 2-Pass DFS preorder: from left and from right, save max level before current node.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> D;\n int lvl_left = 0;\n int lvl_right = 0;\n void preorderLeft(TreeNode* root, int level){\n if (root == nullptr) return;\n D[root->val] = lvl_left;\n lvl_left = max(level,lvl_left);\n preorderLeft(root->left,level+1);\n preorderLeft(root->right,level+1);\n }\n \n void preorderRight(TreeNode* root, int level){\n if (root == nullptr) return;\n D[root->val] = max(D[root->val], lvl_right);\n lvl_right = max(level,lvl_right);\n preorderRight(root->right,level+1);\n preorderRight(root->left,level+1);\n }\n \n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n D.resize(100001,0);\n lvl_left = lvl_right = 0;\n preorderLeft(root,0); preorderRight(root,0);\n int sz = queries.size();\n vector<int> ans(sz,0);\n int i=0;\n for(int val : queries) {\n ans[i++] = D[val];\n }\n return ans;\n } \n};\n```\n\nJava Version\n```\nclass Solution {\n private static int leftmax;\n private static int rightmax;\n private static int[] all_lvl;\n \n private void dfsLeft(TreeNode root, int level){\n if (root==null){\n return;\n }\n all_lvl[root.val] = leftmax;\n leftmax = Math.max(level,leftmax);\n dfsLeft(root.left, level+1);\n dfsLeft(root.right, level+1);\n }\n private void dfsRight(TreeNode root, int level){\n if (root==null){\n return;\n }\n all_lvl[root.val] = Math.max(all_lvl[root.val], rightmax);\n rightmax= Math.max(level,rightmax);\n dfsRight(root.right, level+1);\n dfsRight(root.left, level+1);\n }\n \n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n leftmax=0;\n rightmax=0;\n int n = 100001;\n all_lvl = new int[n];\n dfsLeft(root,0);\n dfsRight(root,0);\n int m = queries.length;\n int [] ans = new int[m];\n for(int i = 0; i < m;i++){\n ans[i]=all_lvl[queries[i]];\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```\n### Compute Height and Depth, save Top 2 Heights at each level\n\n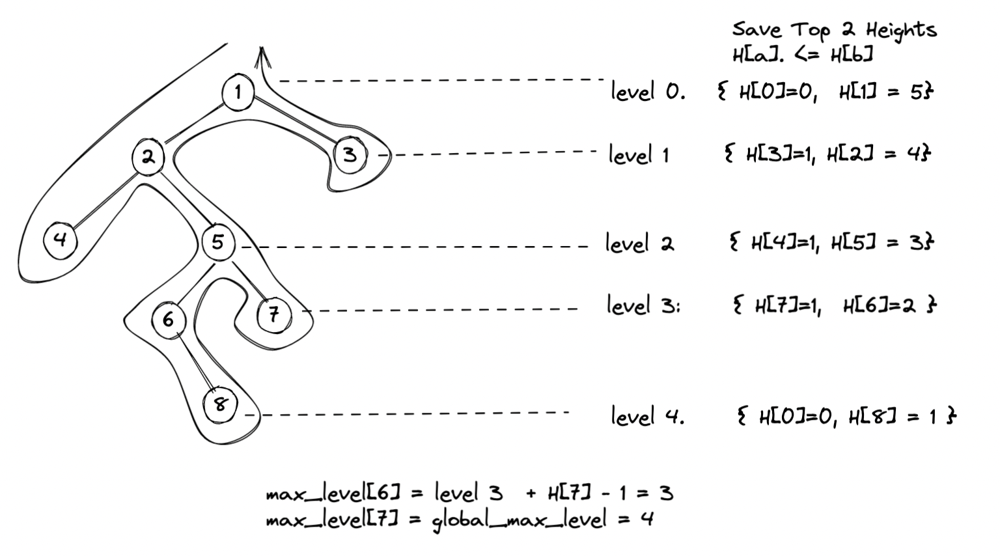\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n vector<int> H;\n vector<int> D;\n vector<vector<int>> lvl; //O(Height)\n // compute height and depth of each nodes.\n int n = 0;\n int dfs(TreeNode* r, int depth) {\n if (r == nullptr) return 0;\n D[r->val] = depth;\n n = max(n, r->val);\n int a = dfs(r->left, depth+1);\n int b = dfs(r->right, depth+1);\n int h = max(a,b)+1;\n H[r->val] = h;\n return h;\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n \n // DFS: save height and depth\n H.resize(100001, 0); //O(N)\n D.resize(100001, 0);\n int max_lvl = dfs(root, 0) - 1;\n \n // Save Top 2 heights at each level.\n lvl.resize(max_lvl+1, vector<int>(2, 0));\n for(int val = 1; val <= n; ++val) {\n int d = D[val];\n auto & v = lvl[d];\n int& a = v[0];\n int& b = v[1];\n // keep H[a] <= H[b]\n if (H[val] > H[a] && H[val] < H[b]) {\n a = val;\n } else if (H[val] >= H[b]) {\n a = b; \n b = val;\n }\n }\n \n int i = 0;\n vector<int> ans(queries.size(), max_lvl);\n for(auto x: queries) {\n int lvl_cnt = D[x]; \n auto& v = lvl[lvl_cnt];\n // x is the max height, update with 2nd heightest at this level.\n if (x == v[1]) {\n ans[i] = lvl_cnt + H[v[0]] - 1;\n }\n ++i;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 21 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search']
| 5 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Python | DFS & Precomputation
|
python-dfs-precomputation-by-khosiyat-dfqj
|
see the Successfully Accepted Submission\n\n# Code\npython3 []\nfrom typing import List, Optional\n\n# Definition for a binary tree node.\nclass TreeNode:\n
|
Khosiyat
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T03:33:38.348289+00:00
|
2024-10-26T03:33:38.348340+00:00
| 1,979 | false |
[see the Successfully Accepted Submission](https://leetcode.com/problems/height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries/submissions/1433872401/?envType=daily-question&envId=2024-10-26)\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nfrom typing import List, Optional\n\n# Definition for a binary tree node.\nclass TreeNode:\n def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):\n self.val = val\n self.left = left\n self.right = right\n\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n depths = {}\n heights = {}\n \n # Step 1: Compute heights and depths using DFS\n def compute_heights(node, depth):\n if not node:\n return -1\n depths[node.val] = depth\n left_height = compute_heights(node.left, depth + 1)\n right_height = compute_heights(node.right, depth + 1)\n heights[node.val] = 1 + max(left_height, right_height)\n return heights[node.val]\n \n compute_heights(root, 0)\n \n # Step 2: Precompute the maximum heights for each level excluding subtrees\n max_height_without_subtree = {}\n level_max_height = {}\n \n # Collect the max heights for each depth level\n def update_level_heights(node):\n if not node:\n return\n depth = depths[node.val]\n if depth not in level_max_height:\n level_max_height[depth] = []\n level_max_height[depth].append(heights[node.val])\n update_level_heights(node.left)\n update_level_heights(node.right)\n \n update_level_heights(root)\n \n # Sort each level\'s heights in descending order to allow easy access to the top two heights\n for depth in level_max_height:\n level_max_height[depth].sort(reverse=True)\n \n # Compute maximum height of the tree excluding each node\'s subtree\n for node_val in heights:\n depth = depths[node_val]\n max_heights = level_max_height[depth]\n \n # Determine the max height excluding the subtree at this node\n if len(max_heights) == 1:\n max_height_without_subtree[node_val] = depth - 1\n elif heights[node_val] == max_heights[0]:\n max_height_without_subtree[node_val] = depth + (max_heights[1] if len(max_heights) > 1 else 0)\n else:\n max_height_without_subtree[node_val] = depth + max_heights[0]\n \n # Step 3: Answer each query\n return [max_height_without_subtree[q] for q in queries]\n\n```\n\n# Step-by-Step Explanation\n\n## Step 1: Compute Heights and Depths of Each Node\n\n### Depth-First Search (DFS) Traversal\nThe `compute_heights` function traverses the tree using DFS to compute the depth and height of each node.\n\n### Depth Storage\n- The `depths` dictionary stores each node\'s depth, where `depths[node.val] = depth`.\n- The `depth` variable tracks the current depth level during traversal, starting from `0` at the root.\n\n### Height Calculation\n- The `heights` dictionary stores the height of each node, where `heights[node.val]` is the maximum depth reachable from that node.\n- Each node\u2019s height is calculated as `1 + max(left_height, right_height)`, where `left_height` and `right_height` are the heights of the left and right subtrees, respectively.\n- If a node is `None` (a leaf node), it returns `-1`, making leaf nodes have a height of `0`.\n\n## Step 2: Precompute Maximum Heights for Each Level Excluding Subtrees\n\n### Collecting Heights by Level\n- The `update_level_heights` function collects heights for each depth level in the dictionary `level_max_height`.\n- For each node, it appends its height to the list associated with its depth level (`level_max_height[depth]`).\n- This function performs a full tree traversal to ensure that every node\u2019s height is collected.\n\n### Sorting Heights\n- After collecting heights for each depth, the algorithm sorts each depth level\u2019s list in descending order (`level_max_height[depth].sort(reverse=True)`).\n- Sorting allows easy access to the two highest subtree heights for each depth level.\n\n### Calculating Maximum Heights Excluding Each Node\u2019s Subtree\n- For each node, the algorithm calculates the maximum height of the tree if the node\u2019s subtree were excluded, storing these values in `max_height_without_subtree`.\n- To determine the maximum height without a specific node\u2019s subtree, two cases are considered:\n - If the node\u2019s height is the highest in its depth level, the next highest height at that level is used.\n - If the node\u2019s height is not the highest, the highest height at that level is used.\n- This allows us to "exclude" the subtree rooted at a particular node by selecting the next tallest subtree.\n\n## Step 3: Answer Queries\n- Finally, for each query in `queries`, the algorithm retrieves the precomputed height from `max_height_without_subtree`.\n- This is done in constant time for each query since the dictionary `max_height_without_subtree` already holds the values needed.\n\n## Complexity Analysis\n\n### Time Complexity\nThe algorithm performs two full traversals of the tree, resulting in \\( O(N) \\) complexity for tree traversal steps. Sorting the heights lists takes \\( O(D \\log D) \\) where \\( D \\) is the depth, but this is typically less significant than the traversal for most balanced trees.\n\n### Space Complexity\nThe space complexity is \\( O(N) \\) due to the storage in `depths`, `heights`, `level_max_height`, and `max_height_without_subtree`.\n\n\n\n\n
| 20 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 3 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
DFS x2 computes heights||24ms Beats 96.70%
|
dfs-x2-computes-heights24ms-beats-9670-b-cz34
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n Hard qestions. Since the constraints\n> 2 <= n <= 10^5\n1 <= Node.val <= n\nAll the va
|
anwendeng
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T00:31:30.914398+00:00
|
2024-10-26T02:16:07.350850+00:00
| 4,163 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n Hard qestions. Since the constraints\n> 2 <= n <= 10^5\n1 <= Node.val <= n\nAll the values in the tree are unique.\n\nC-arrays are used, not the hash maps. 2x DFS, 1 DFS+memo for computing the heights, 2 for the heights with removing subtrees rooted at every tree node.\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. Declare arrays `val2H[N], removal[N]`\n2. Define the 1st DFS function `int h(TreeNode* root)` to compute the height `val2H[x]` for `x=root->val`.(All the values in the tree are unique)\n3. Define the 2nd DFS function `dfs(TreeNode* root, int level, int maxLevel)` to set `removal[root->val]=maxLevel` if removing subtree rooted at the current node `root`. That calls recursively for left-subtree in the parameter for `maxlevel=max(maxLevel, 1+level+h(root->right))`& similar way for the right-subtree.\n4. In `vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) ` set the initial values for `val2H, removal` filled with -1\n5. Proceed `dfs(root, 0, 0)`\n6. Use a loop to assign `ans[i++]=removal[q]` for `q` in `queries`.\n7. return `ans`\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(N+|queries|)$$ \n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$O(100001)$ where `N=max(height)<=100000`\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}\n * };\n */\nconst int N=100001;\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int val2H[N], removal[N];\n int h(TreeNode* root){\n if (!root) return -1;\n int x=root->val;\n if (val2H[x]!=-1) return val2H[x];\n return val2H[x]=1+max(h(root->left), h(root->right));\n }\n\n void dfs(TreeNode* root, int level, int maxLevel){\n if (!root) return;\n int x=root->val;\n removal[x]=maxLevel;\n dfs(root->left, level+1, max(maxLevel, 1+level+h(root->right)));\n dfs(root->right, level+1, max(maxLevel, 1+level+h(root->left)));\n }\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n memset(val2H, -1, sizeof(val2H));\n memset(removal, -1, sizeof(removal));\n dfs(root, 0, 0);\n\n vector<int> ans(queries.size());\n int i=0;\n for(int q: queries)\n ans[i++]=removal[q];\n return ans;\n }\n};\n\n\n\nauto init = []() {\n ios::sync_with_stdio(0);\n cin.tie(0);\n cout.tie(0);\n return \'c\';\n}();\n```\n\n
| 20 | 0 |
['Array', 'Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Memoization', 'Binary Tree', 'C++']
| 5 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Python (Simple DFS)
|
python-simple-dfs-by-rnotappl-y9ix
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
rnotappl
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-18T03:29:13.002392+00:00
|
2023-01-18T03:29:13.002434+00:00
| 1,516 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root, queries):\n @lru_cache(None)\n def height(node):\n if not node:\n return -1\n\n return 1 + max(height(node.left),height(node.right))\n\n dict1 = collections.defaultdict(int)\n\n def dfs(node,depth,max_val):\n if not node: return \n\n dict1[node.val] = max_val\n\n dfs(node.left,depth+1,max(max_val,depth+1+height(node.right)))\n dfs(node.right,depth+1,max(max_val,depth+1+height(node.left)))\n\n dfs(root,0,0)\n\n return [dict1[i] for i in queries]\n\n\n\n \n\n\n \n\n \n\n\n```
| 20 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 7 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
less code beats 100%| single traversal | visualization with added YouTube video
|
less-code-beats-100-single-traversal-vis-792w
|
YouTube explanation :- https://youtu.be/IpES7PqU5QU\n# Intuition and approach\nlets start with certain observations :-\n \n1) at any node in binary tree the dep
|
vinod_aka_veenu
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T02:46:36.449893+00:00
|
2024-10-26T09:26:37.826370+00:00
| 7,870 | false |
# YouTube explanation :- https://youtu.be/IpES7PqU5QU\n# Intuition and approach\nlets start with certain observations :-\n \n**1)** at any node in binary tree the **depth** of the node at given **level** of the node = **1 + max(height(left child, level+1), height(right child, level+1))**\n\n**2)** what if i keep an array that can save the **maximum depth** and **second maximum depth** at every level and also the level of every node at **levelArr[]**, we can keep easily with help of an array.\n\n**now some you might have question, why 2nd maximum as well??**\n\n**3)** the intuition is whenever we are at a query for a node value = val ===> levelArr[val] = level\n depth[val] = 1 + Math.max(height(root.left, level+1), height(root.right, level+1))\n\nnow after removing any node in a given level there are two possiblity\n\n**height of tree = level + max depth of any node on that level -1**\n\nnow **1)**what if the node that make biggest depth is the node itself the one we gonna remove??\n\n==> so in that case we need to pick the second maximum depth.\n\n**2)** otherwise if this is not the biggest height node in that level than we need maximum depth.\n\nso now it should be clear we need to keep trak of**max and 2nd max** in arrays for depth at each level.\n\nso at every query we have return **maxDepth at level** + level -1, accordingly as per case **1** or **2** above.\n\n**still have doubt?? no problem will release YouTube soon**\n\n\n\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode left;\n * TreeNode right;\n * TreeNode() {}\n * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {\n * this.val = val;\n * this.left = left;\n * this.right = right;\n * }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n int depth[];\n int levelArr[];\n int max1[];\n int max2[];\n public int height(TreeNode root, int level)\n {\n if(root==null)\n return 0; \n levelArr[root.val] = level; \n depth[root.val] = 1 + Math.max(height(root.left, level+1), height(root.right, level+1));\n if(max1[level]<depth[root.val]) \n {\n max2[level] = max1[level];\n max1[level] = depth[root.val];\n }\n else if(max2[level]<depth[root.val])\n max2[level] = depth[root.val]; \n return depth[root.val];\n }\n \n \n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n depth = new int[100001];\n levelArr = new int[100001];\n max1 = new int[100001];\n max2 = new int[100001];\n \n height(root, 0);\n for(int i=0; i<queries.length; i++)\n {\n int q = queries[i];\n int level = levelArr[q];\n queries[i] = (max1[level]==depth[q]? max2[level] : max1[level]) + level - 1; \n \n }\n \n return queries; \n }\n}\n```\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> depth, levelArr, max1, max2;\n\n int height(TreeNode* root, int level) {\n if (!root) return 0;\n levelArr[root->val] = level;\n depth[root->val] = 1 + max(height(root->left, level + 1), height(root->right, level + 1));\n\n \n if (max1[level] < depth[root->val]) {\n max2[level] = max1[level];\n max1[level] = depth[root->val];\n } else if (max2[level] < depth[root->val]) {\n max2[level] = depth[root->val];\n }\n\n return depth[root->val];\n }\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n depth.resize(100001, 0);\n levelArr.resize(100001, 0);\n max1.resize(100001, 0);\n max2.resize(100001, 0);\n\n // Compute depths and max depths for each level\n height(root, 0);\n\n // Process each query\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.size(); i++) {\n int q = queries[i];\n int level = levelArr[q];\n queries[i] = (max1[level] == depth[q] ? max2[level] : max1[level]) + level - 1;\n }\n\n return queries;\n }\n};\n\n```\n```python []\n# Definition for a binary tree node.\n# class TreeNode(object):\n# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.left = left\n# self.right = right\n\nclass Solution(object):\n def __init__(self):\n self.depth = [0] * 100001\n self.levelArr = [0] * 100001\n self.max1 = [0] * 100001\n self.max2 = [0] * 100001\n\n def height(self, root, level):\n if not root:\n return 0\n \n # Set the level and calculate depth for the current node\n self.levelArr[root.val] = level\n self.depth[root.val] = 1 + max(self.height(root.left, level + 1), self.height(root.right, level + 1))\n \n # Update the highest and second-highest depths for the current level\n if self.max1[level] < self.depth[root.val]:\n self.max2[level] = self.max1[level]\n self.max1[level] = self.depth[root.val]\n elif self.max2[level] < self.depth[root.val]:\n self.max2[level] = self.depth[root.val]\n \n return self.depth[root.val]\n\n def treeQueries(self, root, queries):\n """\n :type root: Optional[TreeNode]\n :type queries: List[int]\n :rtype: List[int]\n """\n # Compute depths and max depths for each level\n self.height(root, 0)\n\n # Process each query\n result = []\n for q in queries:\n level = self.levelArr[q]\n \n # Calculate the result for each query based on max depths at the level\n result.append((self.max2[level] if self.max1[level] == self.depth[q] else self.max1[level]) + level - 1)\n \n return result\n\n```\n```C# []\npublic class Solution {\n private int[] depth = new int[100001];\n private int[] levelArr = new int[100001];\n private int[] max1 = new int[100001];\n private int[] max2 = new int[100001];\n\n private int Height(TreeNode root, int level) {\n if (root == null) return 0;\n\n // Set the level and calculate depth for the current node\n levelArr[root.val] = level;\n depth[root.val] = 1 + Math.Max(Height(root.left, level + 1), Height(root.right, level + 1));\n\n // Update the highest and second-highest depths for the current level\n if (max1[level] < depth[root.val]) {\n max2[level] = max1[level];\n max1[level] = depth[root.val];\n } else if (max2[level] < depth[root.val]) {\n max2[level] = depth[root.val];\n }\n\n return depth[root.val];\n }\n\n public int[] TreeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n // Compute depths and max depths for each level\n Height(root, 0);\n\n // Process each query\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.Length; i++) {\n int q = queries[i];\n int level = levelArr[q];\n\n // Set result for each query based on max depths at the level\n queries[i] = (max1[level] == depth[q] ? max2[level] : max1[level]) + level - 1;\n }\n\n return queries;\n }\n}\n\n```\n\n\n\n
| 18 | 0 |
['Array', 'Math', 'Tree', 'Memoization', 'Binary Tree', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'C#']
| 4 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
JAVA | Very EASY | DFS | Memoization | 100% Faster
|
java-very-easy-dfs-memoization-100-faste-ps89
|
\tint[] h, l, r;\n\t// Store the height of each node\'s left and right child\n public int height(TreeNode root){\n if(root == null) return 0;\n
|
keshavjoshi_ca
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T07:52:44.550154+00:00
|
2022-10-30T07:53:26.522622+00:00
| 2,562 | false |
\tint[] h, l, r;\n\t// Store the height of each node\'s left and right child\n public int height(TreeNode root){\n if(root == null) return 0;\n \n int lh = height(root.left);\n int rh = height(root.right);\n \n l[root.val] = lh;\n r[root.val] = rh;\n \n return 1+Math.max(lh, rh);\n }\n\t// Store the max height of each node if deleted\n public void solve(TreeNode root, int curmax, int depth){\n if(root == null) return;\n \n h[root.val] = curmax;\n\t\t//max of (current depth + right/left height, maxSoFar)\n solve(root.left, Math.max(curmax, depth+r[root.val]), depth+1);\n solve(root.right, Math.max(curmax, depth+l[root.val]), depth+1);\n }\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n h = new int[100001];\n l = new int[100001];\n r = new int[100001];\n \n height(root);\n solve(root.left, r[root.val], 1);\n solve(root.right, l[root.val], 1);\n \n int n = queries.length;\n int[] q = new int[n];\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++){\n q[i] = h[queries[i]]; //Query in O(1)\n }\n return q;\n }
| 17 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Breadth-First Search', 'Java']
| 4 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
EULERIAN TOUR-USE IN PROBLEMS OF SUBTREE REMOVAL
|
eulerian-tour-use-in-problems-of-subtree-tsmm
|
PLEASE UPVOTE IF U FIND MY SOLUTION HELPFUL :)\n\n\n/*\nEULERIAN TOUR: primarily used while handling problems of subtree removal\nmake a tour during performing
|
chikzz
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T05:52:37.701143+00:00
|
2022-10-30T05:54:34.341711+00:00
| 820 | false |
**PLEASE UPVOTE IF U FIND MY SOLUTION HELPFUL :)**\n\n```\n/*\nEULERIAN TOUR: primarily used while handling problems of subtree removal\nmake a tour during performing a dfs traversal and store it\n\nfor a trivial tree: root\n / \\\n left right\nthe tour will be:root->left->left->right->right->root\nso every node will appear twice in the tour array once when it is visited for the first time(no left or\nright subtree of it is visited earlier) and the other when it is visited for the last time(when both left and right subtrees are visited)\n\nNOW WHEN A SUBTREE IS REMOVED THE REMAINING TREE THAT WE HAVE WOULD BE THE SUBARRAY BEFORE THE FIRST \nOCCURENCE OF ROOT AND THE SUBARRAY AFTER THE LAST OCCURENCE OF ROOT\n\nNow we will make a prefix-max-height and a suffix-max-height for this tour array and after the removal of\na subtree the resultant maximum height will be max(prefix_max(first occurence ofsubtree- root-1),suffix_max(last occurence ofsubtree- root+1))\n*/\n\nclass Solution {\n vector<int>tour,mhl,mhr;\n map<int,int>h,first,last;\n void dfs(TreeNode* root,int height)\n {\n if(!root)return;\n h[root->val]=height;\n first[root->val]=tour.size();\n tour.push_back(root->val);\n dfs(root->left,height+1);\n dfs(root->right,height+1);\n last[root->val]=tour.size();\n tour.push_back(root->val);\n }\npublic:\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n dfs(root,0);\n mhl=vector<int>(tour.size());\n mhr=vector<int>(tour.size());\n mhl[0]=mhr[tour.size()-1]=h[root->val];\n \n for(int i=1;i<tour.size();i++)mhl[i]=max(mhl[i-1],h[tour[i]]);\n for(int i=tour.size()-2;i>=0;i--)mhr[i]=max(mhr[i+1],h[tour[i]]);\n vector<int>res;\n for(int q:queries)\n {\n res.push_back(max(mhl[first[q]-1],mhr[last[q]+1]));\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 17 | 0 |
[]
| 3 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
DFS | C++ | Explained with Picutes
|
dfs-c-explained-with-picutes-by-sunil190-y5ka
|
Explanation:\nAs shown in below picture, we do a pre-order traveral and mark indices.\n\n\n\n\nSimultaneously, store the depths of each node in same order of th
|
sunil1906
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:02:48.103561+00:00
|
2022-10-30T15:03:12.053525+00:00
| 1,377 | false |
Explanation:\nAs shown in below picture, we do a pre-order traveral and mark indices.\n\n\n\n\nSimultaneously, store the depths of each node in same order of their indices.\n\nNow, follow the steps to get the answer:\n1. We calculate the number of nodes under each node using simple dfs in O(n)\n2. Create two arrays left_max, right_max. Store the prefix maximum in left_max and suffix maximum in right_max.\n3. Since we have the index of the node and the number of nodes under it, we can easily calculate the subarray of indices that needs to be excluded.\nFor example, \nIf we queries[i] = 2,\nits index is 2.\n\nSo we query the maximum in the subarray of (0, 1) and (5, 8)\nWe excluded (2, 4) because, 2 is starting index and it has 3 nodes under it.\nFor more calarity, look at picture below:\n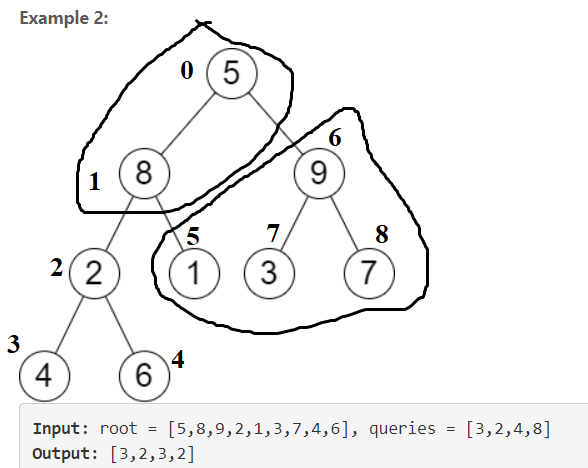\n\nFinally after max query, we store the answer in array and we return it.\n\nCode:\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int n = 0;\n map<int, int> idx_map;\n map<int, int> nodes_under_me;\n vector<int> depths, right_max, left_max;\n void dfs(TreeNode *root, int depth){\n if(!root) return;\n idx_map[root->val] = n++;\n depths.push_back(depth);\n dfs(root -> left, depth + 1);\n dfs(root -> right, depth + 1);\n }\n \n int calc_nodes_under_me(TreeNode *root){\n if(!root) return 0;\n nodes_under_me[root->val] = calc_nodes_under_me(root->left) + calc_nodes_under_me(root->right) + 1;\n return nodes_under_me[root->val];\n }\n \n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n int i, st, en, curr_ans;\n vector<int> ans;\n dfs(root, 0);\n calc_nodes_under_me(root);\n left_max.push_back(depths[0]); right_max.push_back(depths[n-1]);\n for(i=1;i<n;i++) left_max.push_back(max(left_max.back(), depths[i])), right_max.push_back(max(right_max.back(), depths[n-i-1]));\n reverse(right_max.begin(), right_max.end());\n \n for(i=0;i<queries.size();i++){\n en = idx_map[queries[i]] - 1;\n st = en + 1 + nodes_under_me[queries[i]];\n curr_ans = left_max[en];\n if(st < n) curr_ans = max(curr_ans, right_max[st]);\n ans.push_back(curr_ans);\n } \n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\nThank you. Encourage me to post such solutions by upvoting this post.\n
| 14 | 0 |
[]
| 3 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
2-pass preorder traversal
|
2-pass-preorder-traversal-by-theabbie-s09n
|
\nfrom collections import defaultdict\n\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n dp = de
|
theabbie
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:00:37.433748+00:00
|
2022-10-30T04:00:37.433789+00:00
| 1,259 | false |
```\nfrom collections import defaultdict\n\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n dp = defaultdict(int)\n def preorder(root, h):\n if root:\n dp[root.val] = max(dp[root.val], self.maxheight)\n self.maxheight = max(self.maxheight, h)\n preorder(root.left, h + 1)\n preorder(root.right, h + 1)\n def preorderrev(root, h):\n if root:\n dp[root.val] = max(dp[root.val], self.maxheight)\n self.maxheight = max(self.maxheight, h)\n preorderrev(root.right, h + 1)\n preorderrev(root.left, h + 1)\n self.maxheight = 0\n preorder(root, 0)\n self.maxheight = 0\n preorderrev(root, 0)\n res = []\n for q in queries:\n res.append(dp[q])\n return res\n```
| 10 | 0 |
['Python']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
✅C++|| Height and Depth || Easy Solution
|
c-height-and-depth-easy-solution-by-indr-ls38
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n map<int,int> l,r,h;\n int height(TreeNode *root)\n {\n if(!root) return 0;\n \n int lh = height(root
|
indresh149
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-02T06:35:18.332593+00:00
|
2022-11-02T06:35:18.332633+00:00
| 876 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n map<int,int> l,r,h;\n int height(TreeNode *root)\n {\n if(!root) return 0;\n \n int lh = height(root->left);\n int rh = height(root->right);\n \n l[root->val] = lh;\n r[root->val] = rh;\n \n return max(lh,rh)+1;\n }\n void solve(TreeNode *root,int maxa,int depth){\n if(!root) return;\n \n h[root->val] = maxa;\n \n solve(root->left, max(maxa, depth+r[root->val]), depth+1);\n solve(root->right, max(maxa, depth+l[root->val]),depth+1);\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n height(root);\n solve(root->left, r[root->val], 1);\n solve(root->right, l[root->val], 1);\n \n vector<int> ans;\n \n for(int i=0;i<queries.size();i++){\n ans.push_back(h[queries[i]]);\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n**Please upvote if it was helpful for you, thank you!**
| 8 | 0 |
['Tree', 'C']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Runtime beats 93.33%, memory 54.51 MB Beats 82.82% [w/ comments and explained]
|
runtime-beats-9333-memory-5451-mb-beats-lmiko
|
Intuition\nWe want to know how the tree\u2019s shape changes if we \u201Cremove\u201D certain nodes. For each node, we find the height of its subtree (how far i
|
r9n
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T02:35:36.935372+00:00
|
2024-10-26T02:35:36.935392+00:00
| 35 | false |
# Intuition\nWe want to know how the tree\u2019s shape changes if we \u201Cremove\u201D certain nodes. For each node, we find the height of its subtree (how far it goes down) and also keep track of the new \u201Cmax height\u201D of the entire tree if that node disappears, adjusting to account for whichever child subtree would remain.\n\n# Approach\nTraverse the tree to calculate and store heights for each node\u2019s subtree, then perform a depth-first traversal to find the \u201Cnew height\u201D of the tree for each node as if it were removed by updating heights using the remaining child subtrees, and finally retrieve the \u201Cnew height\u201D for each node in the query list.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n) \u2014 where n is the number of nodes \u2014 since we visit each node a few times for height and depth-first calculations.\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n) due to storing subtree heights and \u201Cnew heights\u201D for each node in arrays.\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nfrom typing import List, Optional\n\nclass TreeNode:\n # Definition for a binary tree node\n def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):\n self.val = val\n self.left = left\n self.right = right\n\nclass Solution:\n # Define a large enough constant N to cover possible node values\n N = 100001\n\n def __init__(self):\n # Initialize height and removal arrays\n # val2H stores height of each node, initialized to -1\n # removal stores the maximum depth if that node were removed, initialized to -1\n self.val2H = [-1] * self.N\n self.removal = [-1] * self.N\n\n def h(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:\n # Calculate the height of the node\'s subtree rooted at \'root\'\n if not root:\n return -1 # Return -1 if root is None (no height for empty nodes)\n x = root.val # Get the value of the current node\n\n # Return the cached height if already calculated\n if self.val2H[x] != -1:\n return self.val2H[x]\n \n # Recursively calculate the height as 1 + max height of left and right children\n self.val2H[x] = 1 + max(self.h(root.left), self.h(root.right))\n return self.val2H[x]\n\n def dfs(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], level: int, maxLevel: int):\n # Perform depth-first search to calculate removal depths\n if not root:\n return # Base case: return if node is None\n x = root.val # Get the value of the current node\n\n # Set the removal depth of the current node to maxLevel\n self.removal[x] = maxLevel\n\n # Recurse on the left child with an updated maxLevel that includes the right subtree height\n self.dfs(root.left, level + 1, max(maxLevel, 1 + level + self.h(root.right)))\n\n # Recurse on the right child with an updated maxLevel that includes the left subtree height\n self.dfs(root.right, level + 1, max(maxLevel, 1 + level + self.h(root.left)))\n\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n # Prepare height and removal arrays\n self.val2H = [-1] * self.N\n self.removal = [-1] * self.N\n\n # Compute removal depths for each node using DFS traversal\n self.dfs(root, 0, 0)\n\n # Retrieve the removal depths for each query\n ans = [self.removal[q] for q in queries]\n return ans\n\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Recursion', 'Python3']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Javascript Easy to Understand DFS
|
javascript-easy-to-understand-dfs-by-rha-quwe
|
Inspired by this solution and re-written in JS: https://leetcode.com/problems/height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries/discuss/2758375/Python3-C%2B%2
|
rhattab
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-06T03:36:13.195543+00:00
|
2023-07-06T03:36:13.195567+00:00
| 417 | false |
Inspired by this solution and re-written in JS: https://leetcode.com/problems/height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries/discuss/2758375/Python3-C%2B%2B-Clean-9-lines-Dfs\n\n```\nvar treeQueries = function(root, queries) {\n if (!root) return [];\n \n let ans = {};\n let heights = {}\n \n function maxHeight(node) {\n if (!node) return 0;\n \n if (heights[node.val]) return heights[node.val];\n \n heights[node.val] = 1 + Math.max(maxHeight(node.left), maxHeight(node.right));\n \n return heights[node.val];\n }\n \n function dfs(node, depth, maxDepthWithoutCurrentNode) {\n if (!node) return 0;\n \n ans[node.val] = maxDepthWithoutCurrentNode;\n \n // depth + height(node.right)\n // Add current depth + depth of opposite child (since we act as if we remove one of the children)\n dfs(node.left, depth + 1, Math.max(maxDepthWithoutCurrentNode, depth + maxHeight(node.right)));\n dfs(node.right, depth + 1, Math.max(maxDepthWithoutCurrentNode, depth + maxHeight(node.left)));\n }\n \n dfs(root, 0, 0);\n \n return queries.map(q => ans[q]);\n};\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Python | Two pass solution | Beats 98% 🚀| O(n)
|
python-two-pass-solution-beats-98-on-by-3q3eb
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe approach leverages a two-step process where it first calculates the height of subtr
|
shivamtld
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T04:00:27.667795+00:00
|
2024-10-26T04:13:34.119521+00:00
| 988 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe approach leverages a two-step process where it first calculates the height of subtrees for each node and stores these in a dictionary. It then iteratively updates this dictionary to ensure that each node\'s value reflects the maximum height observable from that node\'s position, using a depth-first traversal to propagate the maximum heights from the root downwards to all descendants. This ensures efficient query responses by precomputing necessary values.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n- **Initialize Helper Functions**: The solution defines two helper functions within the treeQueries method. The first function, calcHeight, calculates the height of the tree from any given node and populates treeDict where each node\'s value is mapped to the height of its opposite subtree (left child\'s value maps to the right subtree height and vice versa). The second function, updateTreeDict, propagates the maximum heights found in the subtrees downward through the tree to potentially update the values in treeDict.\n\n- **Populate Tree Dictionary**: Using the calcHeight function, the algorithm first populates treeDict with initial values based on subtree heights. Each node\'s value is associated with the maximum height of the subtree opposite its child. For instance, if a node has a left child, the left child\'s value in treeDict is set to the height of the right subtree of the parent node.\n\n- **Update Tree Dictionary**: After the initial population, the updateTreeDict function is called to revise treeDict. This function ensures that each node in the tree has the correct maximum height value from its subtree by checking and updating treeDict values downward from the root, adjusting them based on the greater of the current value or the inherited maximum height from ancestor nodes.\n\n- **Answer Queries**: Finally, the method returns a list of heights for the nodes specified in the queries list by accessing the values in treeDict for each queried node value. This step directly uses the prepared treeDict to fetch and return the results efficiently.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n \n def calcHeight(node, height):\n if not node:\n return height-1\n leftH, rightH = calcHeight(node.left, height+1), calcHeight(node.right, height+1)\n if node.left:\n treeDict[node.left.val] = rightH\n if node.right:\n treeDict[node.right.val]=leftH\n return max(leftH, rightH)\n\n def updateTreeDict(node, maxheight):\n if not node: return \n if maxheight ==-2 or treeDict[node.val]>maxheight:\n maxheight = treeDict[node.val]\n if node.left and maxheight>treeDict[node.left.val]:\n treeDict[node.left.val] = maxheight\n if node.right and maxheight>treeDict[node.right.val]:\n treeDict[node.right.val]= maxheight\n updateTreeDict(node.left, maxheight)\n updateTreeDict(node.right, maxheight)\n \n treeDict=defaultdict(int)\n calcHeight(root, 0)\n updateTreeDict(root, -2)\n return [treeDict[i] for i in queries]\n```\n\n\n\n
| 6 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Depth-First Search', 'Binary Tree', 'Python3']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Very Stupid C++ Solution (Eulerian Tour on Trees)
|
very-stupid-c-solution-eulerian-tour-on-gh27m
|
Warning\nThis is definitely not the most optimal solution, not just in time/memory complexity (both O(NlogN)), but also in implementation (as you can see below,
|
aqxa2k
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:02:10.422071+00:00
|
2022-10-30T17:48:19.622412+00:00
| 2,269 | false |
# Warning\nThis is definitely not the most optimal solution, not just in time/memory complexity (both O(NlogN)), but also in implementation (as you can see below, it isnt pretty, but I tried to explain it). \nI used the Euler tour technique on trees, which seems and likely is overkill\n\n \n# Algorithm\nNow, what the Euler tour technique does on a tree is flatten it into an array. Converting that array into a segtree, you can efficiently make queries on subtrees. \n\nI won\'t go into detail but essentially you order the array indexes (node # -> array index) by the order nodes are visited in a simple dfs. Therefore, for every subtree in the tree, each element in that subtree will lie in a continuous subsegment. (Draw a few examples and try it out).\n\nNext, you would make that array into a segtree, so you can query and modfiy values on the array. \n*In this case, those values are the max depth within the subtree we are querying, and since we arent modfiying, even an RMQ would suffice.\nhttps://usaco.guide/CPH.pdf#page=174 \nThis is a nice resource for learning this algorithm, as it becomes trivial for some advanced graph problems. \n\n# Intuition \nThe question is asking us what is the deepest node that is not in the subtree we are querying. Notice that there is only a left and a right we have to query (find the max from), and also notice if you compress the tree into an array, then the nodes that we may get the answer from will lie either to the left or right (or both) from the subsegment that represents the subtree we removed.\n\nWe will flatten our tree into an array/RMQ/segtree, and process each query in O(logN)\n\n\nWith a clear idea of our algorithm, the challenge now lies in implementation.\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}\n * };\n */\n\nint mxn = 1e5 + 5; \nint n, timer = 0; \nvector<vector<int>> adj(mxn); \nvector<int> st(mxn), en(mxn), d(mxn), to(mxn); \n//to[x] = time x is processed (order) in the dfs, index in the array\n//set the timer and compute st[x], en[x] = starting index\n//and ending index of the subtree with head of x\nvoid dfs(int node, int parent) {\n st[to[node]] = timer++;\n for (int i : adj[node]) {\n if (i != parent) {\n dfs(i, node);\n }\n }\n en[to[node]] = timer-1;\n}\n\n//converting each node to the array index\nvoid make(TreeNode* x, int depth) {\n to[x -> val - 1] = n; \n n++; \n d[to[x -> val - 1]] = depth; \n \n if (x -> right) {\n make(x -> right, depth + 1); \n } if (x -> left) {\n make(x -> left, depth + 1); \n }\n}\n\n//creating the adjacency list for the dfs \n//This is redundant, you could combine the dfs into this \n//recursive function to make it more elegant\nvoid make2(TreeNode* x) {\n if (x -> right) {\n adj[x -> val - 1].push_back(x -> right -> val - 1);\n make2(x -> right); \n } if (x -> left) {\n adj[x -> val - 1].push_back(x -> left -> val - 1);\n make2(x -> left); \n }\n}\n\n//This is your classical segtree \n//Segtree: initialize, make, build, modify, query; \ntemplate <class T> \nclass St {\n private: \n vector<T> t;\n int tn; T def = 0; \n //operation and initial value\n T op(T a, T b) {\n return max(a, b); \n } \n public:\n St(T N) { \n t = vector<T>(2 * N, 0); \n tn = N; \n }\n\n void make(vector<T> & a) { \n for (int i = 0; i < tn; ++i) t[n+i] = a[i]; \n } \n\n void build() {\n for (int i = tn - 1; i > 0; --i) t[i] = op(t[i<<1], t[i<<1|1]);\n }\n\n void modify(int p, T val) {\n for (t[p += tn] = val; p > 1; p >>= 1) t[p>>1] = op(t[p], t[p^1]);\n }\n\n //query on [l, r)\n T query(int l, int r) { \n T res = def;\n for (l += tn, r += tn; l < r; l >>= 1, r >>= 1) {\n if (l&1) res = op(res, t[l++]);\n if (r&1) res = op(res, t[--r]);\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n //initialize and prepare for making segtree\n n = 0; \n timer = 0; \n make(root, 0);\n for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {\n adj[i].clear();\n }\n //compress into array\n make2(root); \n dfs(root -> val - 1, -1); \n \n //make segtree\n St s(n); \n vector<int> vd(n); \n for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {\n vd[i] = d[i];\n }\n s.make(vd);\n s.build(); \n \n vector<int> ans; \n\n //process online queries\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.size(); ++i) {\n int x = queries[i]; \n x--; \n int mx = 0; \n //if the left of the removed subtree exists, maximise the depth from the [0, left)\n if (st[to[x]] > 0) {\n mx = max(mx, s.query(0, st[to[x]])); \n } \n //if the right of the removed subtree exists, maximise the depth from the (right, n)\n if (en[to[x]] < n - 1) {\n mx = max(mx, s.query(en[to[x]] + 1, n));\n }\n ans.push_back(mx); \n }\n \n return ans; \n }\n};\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['C++']
| 3 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
C++ || DFS || Two Largest Heights || Intuitive
|
c-dfs-two-largest-heights-intuitive-by-a-w32j
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nIf we are removing any node at some level, then tree\'s overall height will be determin
|
akash92
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T04:15:50.794955+00:00
|
2024-10-26T04:15:50.794984+00:00
| 1,380 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nIf we are removing any node at some level, then tree\'s overall height will be determined by the other nodes at the same level.\n\nNow the problem reduces to 3 cases :\n1. If the largest height node is being removed, then 2nd largest height node will determine the height of the remaining tree\n2. If only one node at that level exists, then height of the tree reduces by the height of that node\n3. In all other cases height does not change\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nPrecompute nodeToLevel (maps node to the level it belongs) and levelToHeight (stores top 2 heights and corresponding nodes at every level)\nNow process each query according to the above cases and store the height for every query.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n+q)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\n map<int, int> nodeToLevel;\n map<int, priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>>> levelToHeight;\n\n int fillMap(TreeNode* root, int level = 0) {\n if (!root) return 0;\n\n nodeToLevel[root->val] = level;\n\n int lh = fillMap(root->left, level + 1);\n int rh = fillMap(root->right, level + 1);\n \n int height = max(lh, rh);\n\n levelToHeight[level].push({height, root->val});\n if (levelToHeight[level].size() > 2) {\n levelToHeight[level].pop();\n }\n\n return 1+height;\n }\n\npublic:\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n nodeToLevel.clear();\n levelToHeight.clear();\n int h = fillMap(root)-1;\n\n vector<int> ans;\n for (auto q : queries) {\n int level = nodeToLevel[q];\n\n auto pq = levelToHeight[level];\n auto top2 = pq.top(); pq.pop();\n auto top1 = pq.empty() ? make_pair(0, -1) :pq.top(); pq.push(top2);\n\n if (q == top1.second) {\n ans.push_back(h - top1.first + top2.first);\n }\n else if(pq.size()==1 && q == top2.second){\n ans.push_back(h - top2.first - 1);\n }\n else {\n ans.push_back(h);\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\nauto speedup = [](){ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); return 0;}();\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Array', 'Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Binary Tree', 'C++']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Java Clean Solution
|
java-clean-solution-by-shree_govind_jee-o0dc
|
Code\njava []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode left;\n * TreeNode right;\n * TreeNode() {}\n *
|
Shree_Govind_Jee
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T04:10:36.373658+00:00
|
2024-10-26T04:10:36.373684+00:00
| 973 | false |
# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode left;\n * TreeNode right;\n * TreeNode() {}\n * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {\n * this.val = val;\n * this.left = left;\n * this.right = right;\n * }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n int[] po = new int[100001];\n int[] po_ = new int[100001];\n int maxH = 0;\n\n private void preOrder(TreeNode root, int height) {\n // edge\n if (root == null) {\n return;\n }\n\n po[root.val] = maxH;\n maxH = Math.max(maxH, height);\n preOrder(root.left, height + 1);\n preOrder(root.right, height + 1);\n }\n\n private void postOrder(TreeNode root, int height) {\n // edge\n if (root == null) {\n return;\n }\n\n po_[root.val] = maxH;\n maxH = Math.max(maxH, height);\n postOrder(root.right, height + 1);\n postOrder(root.left, height + 1);\n }\n\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n preOrder(root, 0);\n maxH = 0;\n postOrder(root, 0);\n\n int[] res = new int[queries.length];\n for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {\n res[i] = Math.max(po[queries[i]], po_[queries[i]]);\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Array', 'Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Breadth-First Search', 'Binary Indexed Tree', 'Binary Search Tree', 'Binary Tree', 'Java']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Simple || C++ || Using Map
|
simple-c-using-map-by-yc06311-uj50
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
yc06311
|
NORMAL
|
2023-09-29T11:28:04.047913+00:00
|
2023-09-29T11:28:04.047935+00:00
| 1,166 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n map<int, int> l, r, h;\n int height (TreeNode *root)\n {\n if(!root) return 0;\n int lh = height (root->left);\n int rh = height (root->right);\n l[root->val] = lh;\n r[root->val] = rh;\n return max(lh, rh)+1;\n }\n void solve(TreeNode *root, int maxa, int depth)\n {\n if(!root) return;\n h[root->val] = maxa;\n solve(root->left, max(maxa, depth+r[root->val]), depth+1);\n solve(root->right, max(maxa, depth+l[root->val]), depth+1);\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries (TreeNode* root, vector<int>& q)\n {\n height (root);\n solve(root->left, r[root->val], 1);\n solve(root->right, l[root->val], 1);\n vector<int> ans;\n for (int i=0; i<q.size(); i++) ans.push_back(h[q[i]]);\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
[With Drawing] C++ Single DFS, Record Each Level's Nodes
|
with-drawing-c-single-dfs-record-each-le-sjxi
|
Intuition\n- depth is how many levels are beneath this node. Height is how many levels are above.\n- First, use DFS to find each node\'s{height, depth} and reco
|
faradawn
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-02T00:11:51.655664+00:00
|
2023-07-02T00:11:51.655682+00:00
| 247 | false |
# Intuition\n- `depth` is how many levels are beneath this node. `Height` is how many levels are above.\n- First, use DFS to find each node\'s`{height, depth}` and record in a map `mp`.\n- Second, loop through `mp`, and for each node, we add it to the corresponding height level. The map `nei[height]` records the nodes / neighbors with the same height. \n - For example, `nei[2]` has the nodes `[2, 1, 3, 7]`:\n\n\n\n- Each of the nodes has a depth, which are inserted in the `nei[2]`.\n- Finally, to remove `node 2`, we index into the corresponding height level and pop `node 2` in that level. So, nodes `[1, 3, 7]` remains. Among them, the max depth is `0`. So the result is `height + remaining max depth`. \n- For optimization, we only keep the top two depth for each `nei` height level. Then, when sorting each level, we only sort two elements.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $O(n)$\n\n- Space complexity: $O(n)$\n\n# Code C++\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n unordered_map<int, pair<int,int>> mp; // {height, depth}\n int depth(TreeNode* cur, int cur_h){\n if(cur == NULL){\n return -1;\n }\n int left = depth(cur->left, cur_h + 1);\n int right = depth(cur->right, cur_h + 1);\n int cur_d = max(left, right) + 1;\n mp[cur->val] = {cur_h, cur_d};\n // cout << "Mp " << cur->val << ", h " << cur_h << ", d " << cur_d << endl;\n return cur_d;\n }\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n depth(root, 0);\n unordered_map<int, vector<int>> nei;\n\n for(auto& [key, val] : mp){\n int h = val.first;\n int d = val.second;\n nei[h].push_back(d);\n sort(nei[h].begin(), nei[h].end(), greater<int>());\n if(nei[h].size() > 2){\n nei[h].pop_back();\n }\n }\n\n\n vector<int> res(queries.size());\n for(int i = 0; i < queries.size(); i++){\n int h = mp[queries[i]].first;\n int d = mp[queries[i]].second;\n if(nei[h].size() == 1){\n res[i] = h - 1;\n }else{\n if(nei[h][0] == d){\n res[i] = h + nei[h][1];\n }else{\n res[i] = h + nei[h][0];\n }\n }\n }\n\n return res;\n \n }\n};\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Beats 100% | 0 ms | 16 ms
|
beats-100-0-ms-16-ms-by-user4256be-xcqd
|
Code\n\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode left;\n * TreeNode right;\n * TreeNode(
|
user4256bE
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-20T20:01:02.427457+00:00
|
2023-01-20T20:01:02.427496+00:00
| 964 | false |
# Code\n```\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode left;\n * TreeNode right;\n * TreeNode() {}\n * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {\n * this.val = val;\n * this.left = left;\n * this.right = right;\n * }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n int leftMax;\n int rightMax;\n // HashMap<Integer, Integer> allLevel;\n int[] allL;\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n leftMax = 0;\n rightMax = 0;\n // allLevel = new HashMap<>();\n allL = new int[100001];\n int[] res = new int[queries.length];\n dfsLeft(root, 0);\n dfsRight(root, 0);\n for(int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++){\n res[i] = allL[queries[i]];\n }\n return res;\n }\n \n public void dfsLeft(TreeNode root, int level){\n if(root == null) return;\n allL[root.val] = leftMax;\n leftMax = Math.max(leftMax, level);\n dfsLeft(root.left, level + 1);\n dfsLeft(root.right, level + 1);\n }\n \n public void dfsRight(TreeNode root, int level){\n if(root == null) return;\n allL[root.val] = Math.max(rightMax, allL[root.val]);\n rightMax = Math.max(rightMax, level);\n dfsRight(root.right, level + 1);\n dfsRight(root.left, level + 1);\n }\n}\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Java']
| 2 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Java | Custom Tree Node + Height impact
|
java-custom-tree-node-height-impact-by-n-jdb5
|
Intuition\nFirst of all we are going to created a CustomTreeNode that will add the following data for every tree node:\n Parent pointer\n Right subtree height\n
|
nadaralp
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T17:15:19.835433+00:00
|
2022-10-30T17:19:52.451227+00:00
| 1,215 | false |
# Intuition\nFirst of all we are going to created a `CustomTreeNode` that will add the following data for every tree node:\n* Parent pointer\n* Right subtree height\n* Left subtree height\n\nWe are also going to create a `Map<Integer, CustomTreeNode>` so we can get direct access of the deleted node.\n\nFrom here we are going to traverse upwards and check if by deleting the current node we impacted the parent node maximum height. If we did, we calculate the `deltaOfDeletion` which is basically a number representing how much of the max-height to remove from the next parent.\n\nWe do this the whole way up the tree (we have reference to parents) and get the root node height.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n Map<Integer, CustomTreeNode> valToCustomNode = new HashMap<>();\n\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n CustomTreeNode customRoot = buildCustomTree(null, root); // also sets valToCustomNode - side effect for efficiency\n setNodeHeights(customRoot);\n int m = queries.length;\n int[] res = new int[m];\n\n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n int query = queries[i];\n\n CustomTreeNode impactedNode = valToCustomNode.get(query);\n int deltaOfDeletion = impactedNode.treeHeight();\n\n while (impactedNode.parent != null) {\n CustomTreeNode parent = impactedNode.parent;\n int curNewMaxHeight = 0;\n\n\t\t\t\t// Indicates impactedNode is the *right* node of parent\n if (parent.right != null && parent.right.val == impactedNode.val) {\n int newRightHeight = parent.rightTreeHeight - deltaOfDeletion;\n curNewMaxHeight = Math.max(parent.leftTreeHeight, newRightHeight);\n\n\t\t\t\t// Indicates impactedNode is the *left* node of parent\n } else {\n int newLeftHeight = parent.leftTreeHeight - deltaOfDeletion;\n curNewMaxHeight = Math.max(newLeftHeight, parent.rightTreeHeight);\n }\n\n deltaOfDeletion = parent.treeHeight() - curNewMaxHeight;\n impactedNode = parent;\n\t\n\t\t\t\t// There is no more impact to the deletion. (example: deleted left subtree but right subtree was bigger)\n if (deltaOfDeletion == 0) break; // Optimization\n }\n\n res[i] = customRoot.treeHeight() - deltaOfDeletion - 1;\n\n }\n\n return res;\n }\n\n private CustomTreeNode buildCustomTree(CustomTreeNode parent, TreeNode root) {\n if (root == null) return null;\n\n CustomTreeNode node = new CustomTreeNode(root.val, parent);\n node.setRightTree(buildCustomTree(node, root.right));\n node.setLeftTree(buildCustomTree(node, root.left));\n valToCustomNode.put(node.val, node);\n\n return node;\n }\n\n private int setNodeHeights(CustomTreeNode node) {\n if (node == null) return 0;\n\n int leftNodeHeight = setNodeHeights(node.left);\n int rightNodeHeight = setNodeHeights(node.right);\n node.leftTreeHeight = 1 + leftNodeHeight;\n node.rightTreeHeight = 1 + rightNodeHeight;\n return node.treeHeight();\n\n }\n\n\n class CustomTreeNode {\n public int val;\n public CustomTreeNode parent;\n public CustomTreeNode left;\n public CustomTreeNode right;\n public int leftTreeHeight;\n public int rightTreeHeight;\n\n public CustomTreeNode(int val, CustomTreeNode parent) {\n this.val = val;\n this.parent = parent;\n }\n\n public void setRightTree(CustomTreeNode rightNode) {\n this.right = rightNode;\n }\n\n public void setLeftTree(CustomTreeNode leftNode) {\n this.left = leftNode;\n }\n\n public int treeHeight() {\n return Math.max(leftTreeHeight, rightTreeHeight);\n }\n\n @Override\n public String toString() {\n return "CustomTreeNode{" +\n "val=" + val +\n ", leftTreeHeight=" + leftTreeHeight +\n ", rightTreeHeight=" + rightTreeHeight +\n \'}\';\n }\n }\n}\n```\n\n# Complexity\nm - queries\nn - number of nodes\n\nAverage case - `m * log(n)`\nWorst case - `m * n`
| 5 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Video Explanation (Euler Tour)
|
video-explanation-euler-tour-by-codingmo-px16
|
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s62a0uxeRkE
|
codingmohan
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T05:10:15.489848+00:00
|
2022-10-30T05:10:15.489887+00:00
| 195 | false |
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s62a0uxeRkE
| 5 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Euler Tour Based Solution
|
euler-tour-based-solution-by-hustler2-xhdv
|
So Basically we create with euler tour array with elements and its depth from root, like for tree as shown : \n\t "1"\n\t\t " / \"\n\t\t "2
|
Hustler2
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:26:40.577882+00:00
|
2022-10-30T05:01:53.166236+00:00
| 577 | false |
* So Basically we create with euler tour array with elements and its depth from root, like for tree as shown : \n\t* "1"\n\t\t " / \\"\n\t\t "2 3"\n\t\t "/"\n\t\t "4"\n* euler tour array is [(1,0),(2,1),(4,2),(4,2),(2,1),(3,1),(3,1),(1,0)]\n* now lets say if we remove subtree 2 than array from index 1 to 4 is removed so now what is maximum height of tree so basically is the maximum height till from index 0 to 1 (not included) and maximum height from index(5 to 7) so we can maintain a prefix and suffix maximum array upto a particular point \n* LET ME EXPLAIN THE MY ROUGH ALGO NOW\n* create a euler tour array as u can see\n* for each node maintain its starting and ending index in euler tour array \n* pre and suf have the maximum in prefix till i and suffix from i to end \n* So for a particular query we find starting and ending point of subtree with the element and find prefix maxium till start and suffix maximum till end \nIf u like the explanation please do upvote it motivates me a lot \n```py\n# Definition for a binary tree node.\n# class TreeNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.left = left\n# self.right = right\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n def solve(node,level):\n euler_tour.append((node.val,level))\n if node.left:\n solve(node.left,level+1)\n if node.right:\n solve(node.right,level+1)\n euler_tour.append((node.val,level))\n euler_tour=[]\n solve(root,1)\n d={}\n for i,el in enumerate(euler_tour):\n if el[0] in d:\n d[el[0]].append(i)\n else:\n d[el[0]]=[i]\n pre=[0]\n for el,l in euler_tour:\n pre.append(max(pre[-1],l))\n suf=[0]\n for el,l in euler_tour[::-1]:\n suf.append(max(suf[-1],l))\n suf=suf[::-1]\n ans=[]\n \n for el in queries:\n start,end=d[el]\n ans.append(max(pre[start],suf[end+1])-1)\n return ans\n\t\t```
| 5 | 0 |
['Python']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Time(100%)|Memo(100%)|preorder , Reverse PreOrder (Node,Right,Left)
|
time100memo100preorder-reverse-preorder-o9kh4
|
The explantion is for preorder we will be storing the maximum height we till its predecessor.\nsame goes to the reverse preorder. and we are stroing the values
|
Priyanshu_Chaudhary_
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:16:10.911242+00:00
|
2022-10-30T05:34:03.723396+00:00
| 481 | false |
The explantion is for preorder we will be storing the maximum height we till its predecessor.\nsame goes to the reverse preorder. and we are stroing the values in an array\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n int dp[100001]={0};\n int maxi1=0,maxi2=0;\n void dfs(TreeNode *root,int height=0)\n {\n if(root==NULL)\n return;\n dp[root->val]=max(maxi2,dp[root->val]); \n maxi2=max(maxi2,height); \n dfs(root->left,height+1);\n dfs(root->right,height+1); \n }\n \n void reversedfs(TreeNode *root,int height=0)\n {\n \n if(root==NULL)\n return ; \n dp[root->val]=max(maxi1,dp[root->val]);\n maxi1=max(maxi1,height);\n reversedfs(root->right,height+1);\n reversedfs(root->left,height+1); \n return; \n }\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) \n {\n vector<int>ans;\n dfs(root,0);\n reversedfs(root,0);\n \n for(int i=0;i<queries.size();i++)\n {\n ans.push_back(dp[queries[i]]);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
[Python] Simple traverse + DP, O(n)
|
python-simple-traverse-dp-on-by-zsk99881-3sdv
|
The idea is simple, say a node A has left child B and right child C, max depth in the tree after removing C is either:\n\n X\n A X
|
zsk99881
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:11:04.233733+00:00
|
2022-10-30T04:48:57.707737+00:00
| 507 | false |
The idea is simple, say a node A has left child B and right child C, max depth in the tree after removing C is either:\n```\n X\n A X\n B C X X\n X X X X \n```\n(1) the max depth within the sub tree of B, or \n(2) the max depth in the tree after removing A\n\nmax_depth_without_subtree(val) returns max depth in the tree after removing subtree at node with value val. then (1) is done through recursion (with cache/dp to avoid re-computation) while (2) is done by simply storing every node\'s depth and max depth of its left/right sub tree in one pass by dfs(node, parent, depth).\n\ncomplexity is O(n) for 1 pass preprocessing and O(n + #queries) for max_depth_without_subtree(val) on all queries due to the cache, and eventually O(n) since #queries <= n.\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n node_to_parent = {}\n value_to_node = {}\n # node to its depth\n node_to_depth = {}\n # node to max depth of its left and right subtree\n node_to_subtree_max_depths = {}\n \n def traverse(node, parent, depth):\n if not node:\n return 0\n value_to_node[node.val] = node\n node_to_parent[node] = parent\n node_to_depth[node] = depth\n l = dfs(node.left, node, depth+1)\n r = dfs(node.right, node, depth+1)\n node_to_subtree_max_depths[node] = [l, r]\n return max(l, r)+1\n \n traverse(root, None, 0)\n \n @cache\n def max_depth_without_subtree(val):\n node = value_to_node[val]\n if node == root:\n return -1\n parent = node_to_parent[node]\n if parent.left == node:\n max_depth = node_to_depth[parent] + node_to_subtree_max_depths[parent][1]\n else:\n max_depth = node_to_depth[parent] + node_to_subtree_max_depths[parent][0]\n return max(max_depth, max_depth_without_subtree(parent.val))\n \n return [max_depth_without_subtree(q) for q in queries] \n```
| 5 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Segment Tree | O(nlogn)
|
segment-tree-onlogn-by-toubatbrian-6nbn
|
Approach\nDo a dfs traversal to append each depth (from root to leaf) to compute a list depth. \n\npre and post determine the range of element in depth list so
|
toubatbrian
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:01:31.404085+00:00
|
2022-10-30T04:01:31.404117+00:00
| 1,623 | false |
# Approach\nDo a dfs traversal to append each depth (from root to leaf) to compute a list `depth`. \n\n`pre` and `post` determine the range of element in `depth` list so that all values inside this range are from path rooted at this node. \n\nFor each queries, we want to find out the max depth without choosing element from this range, so we use segment tree to query max depth before pre[node] and max depth after pre node, as well as the depth of the parent of this node.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(nlogn)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n# Definition for a binary tree node.\n# class TreeNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.left = left\n# self.right = right\n\nclass SegmentTree:\n def __init__(self, n, fn): # fn is transformation function\n self.n = n\n self.fn = fn\n self.tree = [0] * (2 * self.n)\n \n def update(self, idx, val):\n idx += self.n\n \n self.tree[idx] = val\n while idx > 1:\n idx >>= 1\n self.tree[idx] = self.fn(self.tree[2 * idx], self.tree[2 * idx + 1])\n \n def query(self, lo, hi):\n lo += self.n\n hi += self.n + 1\n res = 0\n \n while lo < hi:\n if lo & 1 == 1:\n res = self.fn(res, self.tree[lo])\n lo += 1\n if hi & 1 == 1:\n hi -= 1\n res = self.fn(res, self.tree[hi])\n lo >>= 1\n hi >>= 1\n \n return res \n \nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n pre = defaultdict(int)\n post = defaultdict(int)\n height = defaultdict(int)\n depth = []\n \n def dfs(node, curr):\n if not node: return\n \n height[node.val] = curr\n pre[node.val] = len(depth)\n dfs(node.left, curr + 1)\n dfs(node.right, curr + 1)\n \n if len(depth) == pre[node.val]: # node is leaf\n post[node.val] = pre[node.val]\n depth.append(curr)\n else:\n post[node.val] = len(depth) - 1\n \n dfs(root, 0)\n seg = SegmentTree(len(depth), max)\n for i in range(len(depth)):\n seg.update(i, depth[i])\n \n res = []\n for q in queries:\n lo, hi = pre[q], post[q]\n \n d = 0\n if lo == 0 and hi == len(depth) - 1:\n res.append(height[q] - 1)\n elif lo == 0:\n res.append(max(seg.query(hi + 1, len(depth) - 1), height[q] - 1))\n elif hi == len(depth) - 1:\n res.append(max(seg.query(0, lo - 1), height[q] - 1))\n else:\n res.append(max(seg.query(0, lo - 1), seg.query(hi + 1, len(depth) - 1), height[q] - 1))\n \n return res \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Simple DFS
|
simple-dfs-by-kanna-naveen-2f77
|
Intuition\nDepth of a node-> maximum number of edges from the node to any leaf node.\nlevel of a node-> number of edges from root node to the node.\nFind the de
|
kanna-naveen
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T08:22:06.111958+00:00
|
2024-10-26T08:22:06.112002+00:00
| 44 | false |
# Intuition\nDepth of a node-> maximum number of edges from the node to any leaf node.\nlevel of a node-> number of edges from root node to the node.\nFind the depth and level of each node. For each level, We just need two nodes in the level with 1st maximum of level+depth and 2nd maximum of level+depth of those nodes in that level.\nFor each query, if current node is the node that contains maximum of level+depth, then return 2nd maximum. If there is only one node in that level, then return level-1;\n\n# Approach\nAs we know max node value is 100000.\nStep -1: Take two arrays level[], depth[] of max size and consider those indices as node.val.\nStep-2: Store level and depth of each node while travering the tree using DFS.\nStep-3: Take another 2d array leveldDepth[] of "maxDepth" rows, 2 columns. Consider teach row index as level. \na. First column (index 0) contains first maximum level+depth for that level.\nb. 2nd column(index 1) contains 2nd maximum level+depth.\nStep-4: Store depth of the tree in each leevl for each specific node i.e, level+depth of a node.\nStep-5: \na. Iterate over the given queries. For each query i.e, for each node val, take level and depth of the node from the level[], depth[] arrays.\nb. Comapre it with first maximum of level+depth in levelDepth array using the node level.\ncase-i (only one node in the level): the its previous level will be the answer for the query\ncase - ii (more than one node in the level): if curr node is the one that conatains the 1st maximum level+depth in that level, 2nd maximum will be answer otherwise first maximum will be answer for that query\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(N) = N+100000+N = 2N+100000= 300000 (N= 100000 in worst case)= 3N\n\nN -> Number of node in the given tree.\nTraversing the tree = N nodes.\nTraversing from 1 to 100000 = 100000\nTraversing the queries = Q (N in worst case)\n- Space complexity:\nO(N)=100000+100000+ maxDepth (100000 in worst case) = 300000 (N=100000 in worst case) = 3N\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode left;\n * TreeNode right;\n * TreeNode() {}\n * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {\n * this.val = val;\n * this.left = left;\n * this.right = right;\n * }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n private int height(TreeNode root,int l,int[] depth,int[] level){\n if(root==null) return 0;\n int left=0;\n int right=0;\n level[root.val]=l;\n if(root.left!=null) left=1+height(root.left,l+1,depth,level);\n if(root.right!=null) right=1+height(root.right,l+1,depth,level);\n return depth[root.val]= Math.max(left,right);\n }\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n final int n=(int)(1e5)+1;\n int[] depth=new int[n];\n int[] level=new int[n];\n int maxDepth=height(root,0,depth,level);\n int[][] levelDepth=new int[maxDepth+1][2];\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int l=level[i];\n int h=depth[i];\n if(l+h>levelDepth[l][0]){\n levelDepth[l][1]=levelDepth[l][0];\n levelDepth[l][0]=l+h;\n }\n else if(l+h>levelDepth[l][1]){\n levelDepth[l][1]=l+h;\n }\n }\n int[] queryAns=new int[queries.length];\n for(int i=0;i<queries.length;i++){\n int nodeVal=queries[i];\n int l=level[nodeVal];\n if(levelDepth[l][1]==0){\n queryAns[i]=l-1;\n }\n else{\n int d=depth[nodeVal];\n if(l+d==levelDepth[l][0]){\n queryAns[i]=levelDepth[l][1];\n }\n else{\n queryAns[i]=levelDepth[l][0];\n }\n }\n }\n return queryAns;\n }\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Recursion', 'Java']
| 2 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Solved..........🔥🔥🔥🔥
|
solved-by-pritambanik-mub3
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
PritamBanik
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T06:52:31.387567+00:00
|
2024-10-26T06:52:31.387585+00:00
| 351 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: 100%\u2705\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```c []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * struct TreeNode *left;\n * struct TreeNode *right;\n * };\n */\n\ntypedef struct TreeNode NODE;\n\nvoid compute(NODE * curr, int * comp, int * hlist, NODE* p, int height, NODE* sibnode, int level)\n{\n if (curr == NULL)\n return;\n \n if (p == NULL)\n comp[curr->val] = -1;\n else if ((comp[p->val] == height) ||\n ((sibnode != NULL) &&\n (hlist[sibnode->val] >= hlist[curr->val])))\n comp[curr->val] = height; \n else\n {\n /* (sibling height + parent node level + 1) > computed value of parent \n * then "v1"" else "comp[parent]""\n * Parent level = level -1\n * Hence sh + (level -1) + 1 ==> sh + level */\n int v1 = ((sibnode == NULL) ? -1 : (hlist[sibnode->val])) + level;\n comp[curr->val] = comp[p->val] > v1 ? comp[p->val] : v1;\n }\n\n compute(curr->left, comp, hlist, curr, height, curr->right, level + 1);\n compute(curr->right, comp, hlist, curr, height, curr->left, level + 1);\n}\n\nint traverse(NODE * curr, int * hlist)\n{\n if (curr == NULL)\n return -1;\n\n int h1 = traverse(curr->left, hlist);\n int h2 = traverse(curr->right, hlist);\n\n hlist[curr->val] = ((h1 > h2) ? (h1) : (h2)) + 1;\n\n return hlist[curr->val];\n}\n\n/**\n * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().\n */\nint* treeQueries(struct TreeNode* root, int* queries, int queriesSize, int* returnSize)\n{\n * returnSize = 0;\n\n int * answer = malloc(sizeof(int) * queriesSize);\n int * hlist = malloc(sizeof(int) * 100001);\n int * comp = malloc(sizeof(int) * 100001);\n\n int h = traverse(root, hlist);\n\n compute(root, comp, hlist, NULL, h, NULL, 0);\n\n for (int i = 0; i < queriesSize; i++)\n {\n (*returnSize) ++;\n answer[i] = comp[queries[i]];\n }\n\n free(hlist);\n free(comp);\n\n return answer;\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Array', 'Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Breadth-First Search', 'C', 'Binary Tree']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Java and C Solution using level order (O(n))
|
java-and-c-solution-using-level-order-on-ciok
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n1. Arrays left, right,
|
rajnarayansharma110
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T06:05:28.893799+00:00
|
2024-10-26T06:11:28.962898+00:00
| 305 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. Arrays left, right, and remove:\n - left[i]: Maximum height of the left subtree of node i.\n - right[i]: Maximum height of the right subtree of node i.\n - remove[i]: Tree height after removing the subtree rooted at node i.\n2. storeMaxDepth Method:\nCalculates and stores the maximum depth for each node\u2019s left and right subtrees.\n3. depthAfterRemove Method:\nCalculates the maximum height of the remaining tree if each node\u2019s subtree is removed.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n int[] left;\n int[] right;\n int[] remove;\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n left = new int[100001];\n right = new int[100001];\n remove = new int[100001];\n storeMaxDepth(root, 0);\n depthAfterRemove(root, 0);\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {\n queries[i] = remove[queries[i]];\n }\n return queries;\n }\n private int storeMaxDepth(TreeNode root, int level) {\n if (root == null) return level - 1;\n int leftVal = storeMaxDepth(root.left, level + 1);\n int rightVal = storeMaxDepth(root.right, level + 1);\n left[root.val] = leftVal;\n right[root.val] = rightVal;\n return Math.max(leftVal, rightVal);\n }\n private void depthAfterRemove(TreeNode root, int level) {\n if (root == null) return;\n remove[root.val] = level;\n depthAfterRemove(root.left, Math.max(right[root.val], level));\n depthAfterRemove(root.right, Math.max(left[root.val], level));\n }\n}\n```\n```C []\n#define MAX_NODES 100001\nint left[MAX_NODES];\nint right[MAX_NODES];\nint removeDepth[MAX_NODES];\nint storeMaxDepth(struct TreeNode* root, int level);\nvoid depthAfterRemove(struct TreeNode* root, int level);\n\nint* treeQueries(struct TreeNode* root, int* queries, int queriesSize, int* returnSize) {\n *returnSize = queriesSize;\n int* result = (int*)malloc(queriesSize * sizeof(int));\n for (int i = 0; i < MAX_NODES; i++) {\n left[i] = right[i] = removeDepth[i] = 0;\n }\n storeMaxDepth(root, 0);\n depthAfterRemove(root, 0);\n for (int i = 0; i < queriesSize; i++) {\n result[i] = removeDepth[queries[i]];\n }\n return result;\n}\n\nint storeMaxDepth(struct TreeNode* root, int level) {\n if (root == NULL) return level - 1;\n int leftVal = storeMaxDepth(root->left, level + 1);\n int rightVal = storeMaxDepth(root->right, level + 1);\n left[root->val] = leftVal;\n right[root->val] = rightVal;\n return (leftVal > rightVal) ? leftVal : rightVal;\n}\n\nvoid depthAfterRemove(struct TreeNode* root, int level) {\n if (root == NULL) return;\n removeDepth[root->val] = level;\n depthAfterRemove(root->left, (right[root->val] > level) ? right[root->val] : level);\n depthAfterRemove(root->right, (left[root->val] > level) ? left[root->val] : level);\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Easy Intuitive (BFS+DFS)|| top->bottom height|| bottom->top height✅ ✅
|
easy-intuitive-bfsdfs-top-bottom-height-i1opm
|
\n\n# Approach\n> Pre Computations:\n1. First I find the level of each node from bottom.(using dfs)\n2. Then I find the level of each node from the top.(using b
|
arunk_leetcode
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T05:16:11.089950+00:00
|
2024-10-26T05:16:11.089985+00:00
| 1,190 | false |
\n\n# Approach\n> **Pre Computations:**\n1. First I find the level of each node from bottom.(using `dfs`)\n2. Then I find the level of each node from the top.(using `bfs` using function `f`)\n3. Now i find the path along the max height using `dfs2`.\n>**Query Processing**:\n - For each query:\n - If the node is in the main path, calculate the height based on the second-highest height at that level.\n - If it\u2019s not on the main path, reduce the height by 1.\n\n# Complexity\n- **Time Complexity**:\n - `O(n)` for calculating node heights and performing level-order traversal.\n - Each query takes `O(log n)` due to priority queue operations.\n- **Space Complexity**:\n - `O(n)` for storing node heights, main path, and levels.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n map<int, int> mp, path;\n map<int, priority_queue<int>> level;\n void f(TreeNode* root) {\n queue<TreeNode*> q;\n q.push(root);\n int lvl = 0;\n while (!q.empty()) {\n int s = q.size();\n lvl++;\n while (s--) {\n auto it = q.front();\n q.pop();\n level[lvl].push(mp[it->val]);\n if (it->right)\n q.push(it->right);\n if (it->left)\n q.push(it->left);\n }\n }\n }\n int dfs(TreeNode* root) {\n if (!root)\n return 0;\n int left = 0, right = 0;\n if (root->left)\n left = dfs(root->left);\n if (root->right)\n right = dfs(root->right);\n\n return mp[root->val] = 1 + max(left, right);\n }\n void dfs2(TreeNode* root) {\n if (!root)\n return;\n path[root->val]++;\n if (root->left && root->right) {\n if (mp[root->left->val] > mp[root->right->val]) {\n dfs2(root->left);\n } else\n dfs2(root->right);\n } else if (!root->right) {\n dfs2(root->left);\n } else if (!root->left) {\n dfs2(root->right);\n }\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n dfs(root);\n dfs2(root);\n // for (auto it : mp) {\n // cout << it.first << " " << it.second << endl;\n // }\n vector<int> ans;\n int h = mp[root->val];\n f(root);\n for (auto it : queries) {\n int nh = h;\n if (path.find(it) != path.end()) {\n // the node removed is from the path of the max height\n int lvl = h-mp[it]+1;//find the level from top\n if(level[lvl].size() <= 1){\n ans.push_back(h-mp[it]-1);//if not other node on same level\n }\n else{\n int t = level[lvl].top();\n level[lvl].pop();\n ans.push_back(lvl+level[lvl].top()-2)\n //the new height using the second max. height\n level[lvl].push(t);\n }\n } else {\n ans.push_back(nh - 1);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Breadth-First Search', 'Binary Tree', 'C++']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
JAVA|segment tree|DFS|
|
javasegment-treedfs-by-rkroy-t4nj
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
RkRoy
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-24T19:37:20.585325+00:00
|
2024-03-24T19:37:20.585379+00:00
| 75 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode left;\n * TreeNode right;\n * TreeNode() {}\n * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {\n * this.val = val;\n * this.left = left;\n * this.right = right;\n * }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n\n //graph;\n ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<>();\n for(int i = 0; i <= 100000 + 5; i++) adj.add(new ArrayList<>());\n Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();\n q.offer(root);\n while(!q.isEmpty()) {\n int len = q.size();\n for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {\n if(q.peek().left != null) {\n q.offer(q.peek().left);\n int u = q.peek().val;\n int v = q.peek().left.val;\n adj.get(u).add(v);\n adj.get(v).add(u);\n }\n if(q.peek().right != null) {\n q.offer(q.peek().right);\n int u = q.peek().val;\n int v = q.peek().right.val;\n adj.get(u).add(v);\n adj.get(v).add(u);\n }\n q.poll();\n }\n }\n\n int depth[] = new int[100000 + 5];\n ArrayList<Integer> flat = new ArrayList<>();\n dfs(root.val,-1, adj, flat, depth);\n \n\n int len = flat.size();\n int res[] = new int[len];\n int first[] = new int[100000 + 1];\n int last[] = new int[100000 + 1];\n Arrays.fill(first, -1); Arrays.fill(last, -1);\n for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {\n res[i] = depth[flat.get(i)];\n }\n\n for(int i = 0; i < flat.size(); i++) {\n int current = flat.get(i);\n if(first[current] == -1) first[current] = i;\n else last[current] = i;\n }\n\n\n \n int seg[] = new int[4 * len + 10];\n build(res, seg, 0, 0, len - 1);\n\n int ans[] = new int[queries.length];\n for(int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {\n int current = queries[i];\n if(current == root.val) {\n ans[i] = 0;\n continue;\n }\n int x = query(res, seg, 0, 0, len - 1, 0 , first[current] - 1);\n int y = query(res, seg , 0 , 0, len - 1, last[current] + 1, len - 1);\n ans[i] = Math.max(x, y);\n\n\n }\n return ans; \n }\n\n public static void dfs(int u , int par, ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj , ArrayList<Integer> flat,int depth[]) {\n flat.add(u);\n for(int v : adj.get(u)) {\n if(v != par) {\n depth[v] = 1 + depth[u];\n dfs(v, u, adj, flat,depth);\n }\n }\n flat.add(u);\n }\n\n\n //segment tree implementation;\n\n public static void build(int arr[] , int seg[] , int ind, int low, int high) {\n if(low == high) {\n seg[ind] = arr[low];\n return;\n }\n int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;\n build(arr, seg, 2 * ind + 1, low, mid);\n build(arr, seg, 2 * ind + 2, mid + 1, high);\n seg[ind] = Math.max(seg[2 * ind + 1] , seg[2 * ind + 2]);\n }\n\n public static int query(int arr[] ,int seg[] , int ind, int low ,int high, int l , int r) {\n if(low >= l && high <= r) return seg[ind];\n if(low > r || high < l) return Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;\n int left = query(arr, seg, 2 * ind + 1, low, mid, l , r);\n int right = query(arr, seg, 2 * ind + 2, mid + 1, high, l , r);\n return Math.max(left, right);\n }\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
simple and fast - DFS + heap
|
simple-and-fast-dfs-heap-by-ikrenji13-vso5
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nEach node has a height and a depth associated with it. Height is the number of levels a
|
ikrenji13
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-31T00:11:21.595384+00:00
|
2023-07-31T00:11:49.747561+00:00
| 772 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nEach node has a height and a depth associated with it. Height is the number of levels above the node and depth is the number of levels below the node. So the nodes potential contribution to the maximum height of the binary tree is its height + depth (+/- 1 depending on how you track these variables). We will have a max heap for each level of the tree. We will calculate the potential contribution of each nodes height+depth to the max height of the tree and put this value into its levels heap. We put this into the max_heap (depth + height, height, node.val). Finally we have three situations to consider:\n\n1, q is the only node on this level. We return the HEIGHT of any of the nodes one level above our level.\n\n2, we have more than one node in our lvl, but q is on the top of the heap. We simply lookup the next biggest HEIGHT + DEPTH value in the heap.\n\n3, we have more than one node in our lvl and q is not on the top of the heap. We simply add the HEIGHT + DEPTH value from the top of the heap.\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(N) + q * O(logN)\nO(N) - to precompute the answers\nO(logN) - per query to look up the answer\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(N) - the combined heaps hold N nodes\n\n\n# Code\n```\n# Definition for a binary tree node.\n# class TreeNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.left = left\n# self.right = right\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n node_to_lvl = {}\n lvls = defaultdict(list)\n\n def dfs(node, height):\n if not node:\n return 0\n height += 1\n left = dfs(node.left, height) + 1\n right = dfs(node.right, height) + 1\n node_to_lvl[node.val] = height\n heapq.heappush(lvls[height], (-max(left, right) - height + 1, height, node.val))\n return max(left, right)\n \n dfs(root, -1)\n res = []\n\n for q in queries:\n lvl = node_to_lvl[q]\n if q == root.val:\n res.append(0)\n elif len(lvls[lvl]) == 1:\n res.append(lvls[lvl - 1][0][1])\n elif lvls[lvl][0][2] == q:\n temp = heapq.heappop(lvls[lvl])\n res.append(-lvls[lvl][0][0])\n heapq.heappush(lvls[lvl], temp)\n elif lvls[lvl][0][2] != q:\n res.append(-lvls[lvl][0][0])\n \n return res\n \n\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Heap (Priority Queue)', 'Python3']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
✅Easy C++|| Height and Depth || Preorder Traversal
|
easy-c-height-and-depth-preorder-travers-hotd
|
Code\n\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() :
|
black_pearl98
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-19T16:24:45.009845+00:00
|
2023-07-19T16:24:45.009870+00:00
| 519 | false |
# Code\n```\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n unordered_map<int,int> lheight;\n unordered_map<int,int> rheight;\n unordered_map<int,int> res;\n int findHeight(TreeNode* root)\n {\n if(root==NULL)\n return 0;\n\n int left= findHeight(root->left);\n int right= findHeight(root->right);\n\n lheight[root->val]= left;\n rheight[root->val]= right;\n\n return 1+ max(left, right);\n\n }\n void newHeight(TreeNode* root, int maxi, int level)\n {\n if(root==NULL)\n return;\n res[root->val]= maxi;\n newHeight(root->left, max(maxi, level + rheight[root->val]), level+1);\n newHeight(root->right, max(maxi, level + lheight[root->val]), level+1);\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n int m= queries.size();\n lheight.clear();\n rheight.clear();\n res.clear();\n vector<int> answer(m, 0);\n if(root==NULL) return answer;\n findHeight(root);\n newHeight(root, 0, 0);\n\n for(int i=0; i<m; i++)\n {\n answer[i]=res[queries[i]];\n }\n return answer;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['C++']
| 2 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
C# | Detailed Explanation + Dry Run | Level Order Traversal
|
c-detailed-explanation-dry-run-level-ord-14ba
|
Intuition\nFor this problem my first intuition was to iterate over the queries array and call a RemoveNode function for each of the query nodes. The Remove func
|
anaken
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-16T10:15:46.600645+00:00
|
2023-07-23T09:56:28.661436+00:00
| 137 | false |
# Intuition\nFor this problem my first intuition was to iterate over the queries array and call a RemoveNode function for each of the query nodes. The Remove function would mark the node as null at its parent and calculate the tree\'s new height after that action. But the problem statement mentions that the state of the tree resets to the original after every query operation. That presented a problem with my initial approach. After this I decided to store multiple deep copies of the original array for every index i in queries array. I did that and ran the code. The code worked for all but last 5 test cases. I changed my approach to not modify the original array but just return the control from the calculateHeight function when finding the query node, but that too required a full travsersal every time a query node is called and hence a time complexity of O(m*n) where m is the query array length and n is the tree node count. \nI was stuck at this stage for quite some time and decided to see the existing submitted solutions. I found Bakerston\'s submission here \nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries/solutions/2757990/python-3-explanation-with-pictures-dfs/\n\nI am using his logic but tried to code it in a slighly different way using Level Order Traversal. \n \n\n# Approach\n\nUsed the below example for dry run :- \n\nroot =\n[5,8,9,2,1,3,7,4,6]\n\nqueries =\n[3,4,2,8]\n\n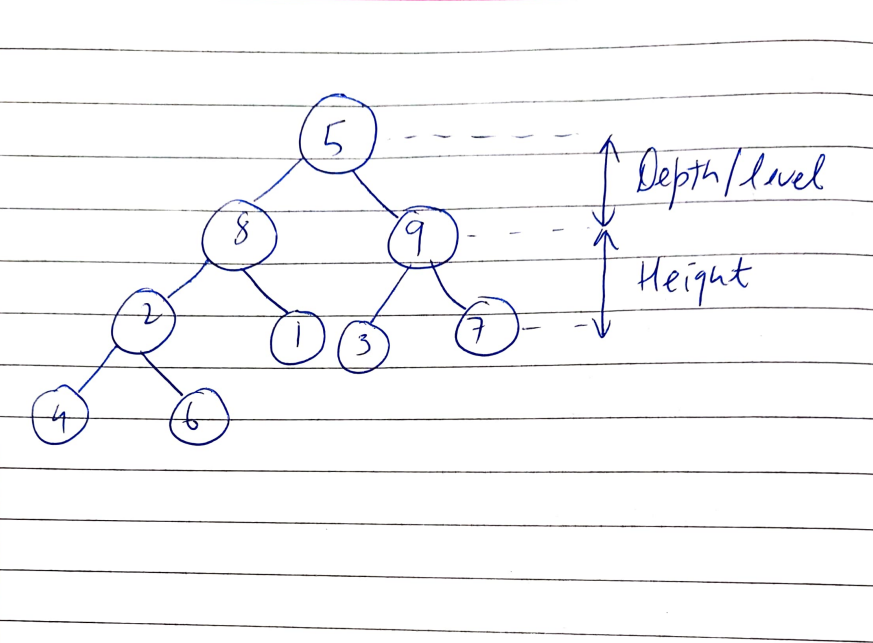\n\n\nThe approach I took here makes use of precomputed values which would help us reduce the time complexity from O(m*n) where m = length of queries, n = nodes in tree using the stabdard DFS approach to a time complexity of O(N) where N = node count in the original tree.\n\nFirst we populate the structure \'nodeHeightsMap\'. It stores the map of tree node to its corresponding height. It makes use of the standard Height finding algorithm. \n\nSecond we call the standard \'Level Order Traversal\' also known as the Breadth First Search in case of Graphs. Here by making use of the Queue structure we store all the nodes at a particular level in a map structure called \'LevelByChildren\', where key is the current level and value is the list of all nodes at that particular level.\nWhile iterating doing this traversal we also store a mapping of node to level so that we know that what level does a particular node belong to, so that we can later do a look up on that.\n\n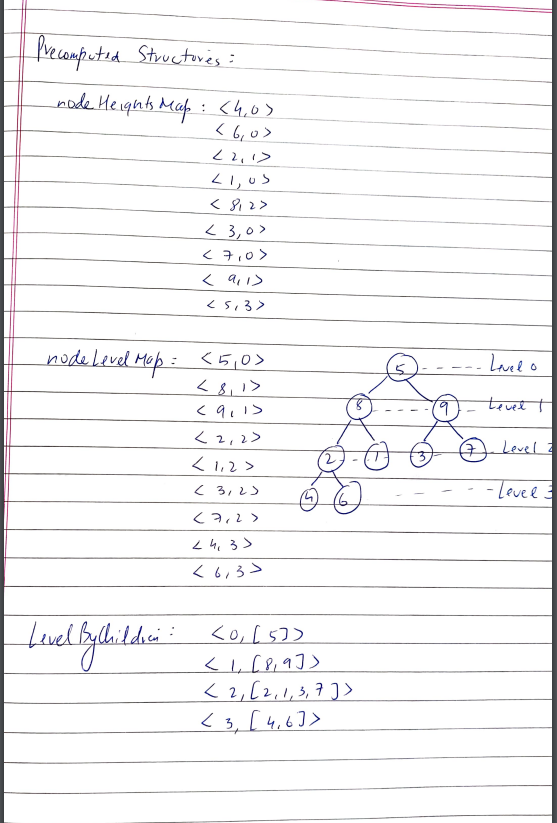\n\n\nThirdly we will need sort each list in the \'LevelByChildrenMap\' structure by height since we need just 2 largest values for our calculation. You will understand this by going over the point b) in the below passage. \n\n\n\n\nOnce we have all these precomputed values stored it is time for the logic of the problem. \na) We find all the cousins for that query node. What that means is we pull all the nodes which are at the same level as this node from the map structure \'LevelByChildrenMap\'.\nb) What we are trying to do is if there are more that one cousins at the same level we will use its height to calculate the height of the tree. We do this by adding the node\'s height + node\'s depth that would effectively give us the totol tree height.\nc) In case there is only one node at that level which is the query node, and since we need to remove this, we return \'level-1\' level essentially here is the depth of the node. \nd) One thing to remember here is at every level we just need to maintain just two nodes with max height since both will never be deleted together.\n\n**Dry Run** **:-**\n\n\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N) N is the node count \n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(N) N is the node count\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# **If you found my solution and explanation helpful, please consider upvoting it. Your upvote will help rank it higher among other solutions, making it easier for people seeking assistance to find. Feel free to ask any follow-up questions in the comment section. Thank you for reading!**\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * public int val;\n * public TreeNode left;\n * public TreeNode right;\n * public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) {\n * this.val = val;\n * this.left = left;\n * this.right = right;\n * }\n * }\n */\npublic class Solution {\n public int[] TreeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) \n {\n int[] result = new int[queries.Length];\n \n Dictionary<int,int> nodeHeightsMap = new();\n Dictionary<int,int> nodeLevelMap = new();\n Dictionary<int,List<int>> LevelByChildrenMap = new();\n\n CalculateHeightsOfAllNodes(root,nodeHeightsMap);\n\n LevelOrderTravsersal(root,LevelByChildrenMap,nodeLevelMap);\n\n foreach(KeyValuePair<int,List<int>> entry in LevelByChildrenMap)\n {\n entry.Value.Sort((a, b) =>\n {\n if (nodeHeightsMap[a] > nodeHeightsMap[b])\n {\n return -1;\n }\n else if (nodeHeightsMap[a] < nodeHeightsMap[b])\n {\n return 1;\n }\n else\n {\n return 0;\n }\n });\n }\n\n for(int i = 0 ; i < queries.Length ; i++)\n {\n int level = nodeLevelMap[queries[i]];\n List<int> ChildrenAtLevel = LevelByChildrenMap[level];\n\n if(ChildrenAtLevel.Count == 1)\n {\n result[i] = level-1;\n }\n else\n {\n foreach(int child in ChildrenAtLevel)\n {\n if(child != queries[i])\n {\n result[i] = nodeLevelMap[child]+nodeHeightsMap[child];\n break; \n }\n }\n }\n }\n\n return result;\n }\n public int CalculateHeightsOfAllNodes(TreeNode root,Dictionary<int,int> heights)\n {\n if(root == null) return -1;\n\n int height = Math.Max(CalculateHeightsOfAllNodes(root.left,heights),CalculateHeightsOfAllNodes(root.right,heights))+1;\n\n heights.Add(root.val,height);\n\n return height;\n }\n private void LevelOrderTravsersal(TreeNode root,Dictionary<int,List<int>> LevelByChildren,Dictionary<int,int> nodeLevelMap)\n {\n Queue<TreeNode> queue = new Queue<TreeNode>();\n queue.Enqueue(root);\n queue.Enqueue(null);\n int level = 0;\n List<int> curr = new List<int>();\n while(queue.Count != 0)\n {\n TreeNode temp = queue.Dequeue(); \n if(temp != null)\n {\n curr.Add(temp.val);\n nodeLevelMap.Add(temp.val,level);\n if(temp.left != null) queue.Enqueue(temp.left);\n\n if(temp.right != null) queue.Enqueue(temp.right);\n }\n else\n {\n List<int> newList = new List<int>(curr);\n LevelByChildren.Add(level,newList);\n level++; \n curr.Clear();\n if(queue.Count != 0)\n {\n queue.Enqueue(null);\n }\n }\n }\n }\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Tree', 'Breadth-First Search', 'C#']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Well-explained || C++ || Height+Level ||O(N)
|
well-explained-c-heightlevel-on-by-night-l4af
|
Intuition\nWhat we need to think is that in what cases will the height of the overall tree be affected by deleting the given node.This leads us to realizing tha
|
night_sky-02
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-13T18:16:31.284223+00:00
|
2024-01-08T06:35:31.020397+00:00
| 1,115 | false |
# Intuition\nWhat we need to think is that in what cases will the height of the overall tree be affected by deleting the given node.This leads us to realizing that it depends on the heights of the other nodes at the same level as the given node.It\'ll become clearer when you see the code\n\n# Approach\nThe code uses a recursive function, height, to traverse the binary tree and calculate the height of each node.\nIt maintains two vectors, levels and lev, to store information about the levels and heights of the nodes.\nThe levels vector is a 2D vector, where each row represents a level in the tree. Each row consists of two pairs: the first pair stores the maximum height and its corresponding node value, and the second pair stores the second maximum height and its corresponding node value.\nThe lev vector is used to store the level of each node.\nThe height function recursively calculates the height of each node and updates the levels and lev vectors accordingly.\nOnce the height function has traversed the entire tree, the code processes the queries.\nFor each query, it retrieves the level and node value.\nIf the queried node is the left child of its parent (i.e., it is stored in the first pair of the levels vector for its level), the code calculates the height of the node from the root using the heights stored in the first and second pairs of the levels vector.\nIf the queried node is the right child of its parent (i.e., it is stored in the second pair of the levels vector for its level), the code simply calculates the height of the node from the root as ht - 1, where ht represents the overall height of the tree.\nThe calculated heights are stored in the ans vector, which is then returned as the result.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(N+Q) \nLet\'s analyze the main operations:\nTraversing the binary tree to calculate heights: This process has a time complexity of O(N), where N is the number of nodes in the tree.\nProcessing queries: The code iterates through the queries, and for each query, it performs a constant number of operations. Therefore, the time complexity for processing queries is O(Q), where Q is the number of queries.\nOverall, the time complexity of the solution is O(N + Q), considering the traversal and query processing steps.\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(N+Q)\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> levels(1e5,vector<pair<int,int>>(2,{0,0}));\n vector<int> lev(1e5+1,0);\n int ht=height(root,0,levels,lev);\n vector<int> ans;\n for(int i=0;i<queries.size();i++)\n {\n int node=queries[i];\n int level=lev[node];\n if(levels[level][0].second==node)\n {\n ans.push_back(ht-levels[level][0].first+levels[level][1].first-1);\n }\n else\n {\n ans.push_back(ht-1);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n \n }\n int height(TreeNode* root,int level,vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> &levels,vector<int> &lev)\n {\n if(root==NULL)\n return 0;\n lev[root->val]=level;\n int hleft=height(root->left,level+1,levels,lev);\n int hright=height(root->right,level+1,levels,lev);\n int tmp=1+max(hleft,hright);\n if(tmp>levels[level][0].first)\n {\n levels[level][1]=levels[level][0];\n levels[level][0]={tmp,root->val};\n }\n else if(tmp>levels[level][1].first)\n levels[level][1]={tmp,root->val};\n return 1+max(hleft,hright);\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Binary Tree', 'C++']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
3 unique solutions
|
3-unique-solutions-by-heisenberg2003-h7g1
|
Using Tree DP\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n void dfs1(TreeNode* root,unordered_map<int,int>&maxdepth)\n {\n if(root->right==NULL &&
|
Heisenberg2003
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-31T06:22:02.409087+00:00
|
2024-10-31T06:22:02.409119+00:00
| 32 | false |
# Using Tree DP\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n void dfs1(TreeNode* root,unordered_map<int,int>&maxdepth)\n {\n if(root->right==NULL && root->left==NULL)\n {\n maxdepth[root->val]=1;\n return;\n }\n if(root->left!=NULL)\n {\n dfs1(root->left,maxdepth);\n maxdepth[root->val]=max(maxdepth[root->val],1+maxdepth[root->left->val]);\n }\n if(root->right!=NULL)\n {\n dfs1(root->right,maxdepth);\n maxdepth[root->val]=max(maxdepth[root->val],1+maxdepth[root->right->val]);\n }\n return;\n }\n void dfs2(TreeNode* root,unordered_map<int,int>&maxdepth,int maxoutdepth,int depth,unordered_map<int,int>&ans)\n {\n ans[root->val]=max(maxoutdepth,depth-1);\n if(root->left!=NULL)\n {\n if(root->right!=NULL)\n {\n dfs2(root->left,maxdepth,max(maxoutdepth,depth+maxdepth[root->right->val]),depth+1,ans);\n }\n else\n {\n dfs2(root->left,maxdepth,maxoutdepth,depth+1,ans); \n }\n }\n if(root->right!=NULL)\n {\n if(root->left!=NULL)\n {\n dfs2(root->right,maxdepth,max(maxoutdepth,depth+maxdepth[root->left->val]),depth+1,ans);\n }\n else\n {\n dfs2(root->right,maxdepth,maxoutdepth,depth+1,ans); \n }\n }\n return;\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root,vector<int>&queries) \n {\n // Tree DP\n vector<int>anstoquery;\n unordered_map<int,int>querynum,maxdepth,ans;\n dfs1(root,maxdepth);\n dfs2(root,maxdepth,0,0,ans);\n for(auto j:queries)\n {\n anstoquery.push_back(ans[j]);\n }\n return anstoquery;\n }\n};\n```\n\n# Using Timer Approach\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n // Timer Approach + PrefixSuffix Max\n void assigntime(int& timer,int level,unordered_map<int,int>&in,unordered_map<int,int>&out,unordered_map<int,int>&depth,TreeNode* root)\n {\n if(root==NULL)\n {\n return;\n }\n in[root->val]=timer;\n depth[timer]=level;\n timer++;\n assigntime(timer,level+1,in,out,depth,root->left);\n assigntime(timer,level+1,in,out,depth,root->right);\n out[root->val]=timer;\n return;\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) \n {\n unordered_map<int,int>in,out,depth;\n int timer=0,level=0;\n assigntime(timer,level,in,out,depth,root);\n vector<int>prefmax(timer),suffmax(timer);\n for(int i=0;i<timer;i++)\n {\n prefmax[i]=depth[i];\n if(i)\n {\n prefmax[i]=max(prefmax[i],prefmax[i-1]);\n }\n }\n for(int i=timer-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n suffmax[i]=depth[i];\n if(i<(timer-1))\n {\n suffmax[i]=max(suffmax[i],suffmax[i+1]);\n }\n }\n vector<int>ans;\n for(auto j:queries)\n {\n int x=INT_MIN;\n if((in[j]-1)>=0)\n {\n x=prefmax[in[j]-1];\n }\n if(out[j]<timer)\n {\n x=max(x,suffmax[out[j]]);\n }\n ans.push_back(x);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n# Using Max 2 down-depths at a level\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n // Consider at any level max two depths available\n void dfs(TreeNode* root,int level,map<int,int>&depth,map<int,int>&downdepth,map<int,vector<int>>&maxdepths)\n {\n depth[root->val]=level;\n if(root->left!=NULL)\n {\n dfs(root->left,level+1,depth,downdepth,maxdepths);\n downdepth[root->val]=max(downdepth[root->val],1+downdepth[root->left->val]);\n }\n if(root->right!=NULL)\n {\n dfs(root->right,level+1,depth,downdepth,maxdepths);\n downdepth[root->val]=max(downdepth[root->val],1+downdepth[root->right->val]);\n }\n if(maxdepths[level].size()<2)\n {\n maxdepths[level].push_back(downdepth[root->val]);\n if(maxdepths[level].size()==2)\n {\n if(maxdepths[level][0]>maxdepths[level][1])\n {\n swap(maxdepths[level][0],maxdepths[level][1]);\n }\n }\n }\n else\n {\n if(maxdepths[level][0]<downdepth[root->val])\n {\n maxdepths[level][0]=downdepth[root->val];\n if(maxdepths[level][0]>maxdepths[level][1])\n {\n swap(maxdepths[level][0],maxdepths[level][1]);\n }\n }\n }\n return;\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n map<int,int>depth,downdepth;\n map<int,vector<int>>maxdepths;\n dfs(root,0,depth,downdepth,maxdepths);\n vector<int>ans;\n for(auto j:queries)\n {\n if(maxdepths[depth[j]].size()==2 && maxdepths[depth[j]][1]==downdepth[j])\n {\n ans.push_back(depth[j]+maxdepths[depth[j]][0]);\n }\n else\n {\n if(maxdepths[depth[j]].size()==1)\n {\n ans.push_back(depth[j]-1);\n }\n else\n {\n ans.push_back(depth[j]+maxdepths[depth[j]][1]);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Compute once, O(n)
|
compute-once-on-by-dzmtr-y7qy
|
\nDfs to calculate and store the maximum depth reachable from each node.\nThen answer each query with the precomputed maximum depth for the specified node.\n\nk
|
dzmtr
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T09:08:09.174033+00:00
|
2024-10-26T09:52:36.160356+00:00
| 23 | false |
\nDfs to calculate and store the maximum depth reachable from each node.\nThen answer each query with the precomputed maximum depth for the specified node.\n\n```kotlin []\nclass Solution {\n val heightMap = mutableMapOf<TreeNode?, Int>(null to 0)\n val res = mutableMapOf<Int, Int>()\n \n fun treeQueries(root: TreeNode?, queries: IntArray): IntArray {\n dfs(root, 0, 0)\n return queries.map { res[it] ?: 0 }.toIntArray()\n }\n\n fun dfs(node: TreeNode?, depth: Int, max: Int) {\n if (node == null) return\n res[node.`val`] = max\n\n dfs(node.left, depth + 1, max(max, depth + height(node.right)))\n dfs(node.right, depth + 1, max(max, depth + height(node.left)))\n }\n\n fun height(node: TreeNode?): Int = heightMap.getOrPut(node) { \n 1 + maxOf(height(node?.left), height(node?.right)) }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Kotlin']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Easy To Understand Solution TC: O(N).
|
easy-to-understand-solution-tc-on-by-abh-5349
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\nTO Solve this Question ASK YOUR SELF:\n\nQ1: How can i find the level of any node in
|
AbhisheK_Dogra_9
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T07:46:45.205430+00:00
|
2024-10-26T10:10:11.704432+00:00
| 661 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\nTO Solve this Question ASK YOUR SELF:\n\nQ1: How can i find the level of any node in O(1) by using extra space.\n\nQ2:How can i find all the nodes at a particular level and their depths in O(1) by precomputation.\n\nQ3: If I am deleting a node at particular level and that node has the highest / largest depth in that level then what will be the new height of tree.\n\n{RE THINK} Q2: In a particular node Do i need to find (all the nodes and their depths) or (only the node with highest and second Highest depths)\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(N)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(N)+O(2N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n int mp[100001]={0};\n\n int dfs(TreeNode* curr,int level,vector<vector<pair<int,int>>>&vec)\n {\n if(!curr)\n return -1;\n\n //later using this mp you can find the level of any node in O(1)\n mp[curr->val]=level;\n\n int l=1+dfs(curr->left,level+1,vec);\n int r=1+dfs(curr->right,level+1,vec);\n int h=max(l,r);\n\n //store the highest and second highest depth of each level in vec\n if(vec[level][0].second<=h)\n {\n auto pr=vec[level][0];\n vec[level][0]={curr->val,h};\n vec[level][1]=pr;\n }\n else if(vec[level][1].second<=h)\n {\n vec[level][1]={curr->val,h};\n }\n \n //maximum depth of a node is maximum of its left and right child\n return max(l,r);\n }\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n int n=100001;\n \n memset(mp,-1,sizeof(mp));\n\n vector<vector<pair<int,int>>>vec(n,vector<pair<int,int>>(2,{0,0}));\n\n //mxht means Maximum height\n int mxht=dfs(root,0,vec);\n\n vector<int>ans;\n\n for(auto nd:queries)\n {\n auto &v=vec[mp[nd]];\n\n int x=mxht;\n \n //(v[0].first==nd) means => If the node i am deleting has the highest depth in this level. \n //Then the new max height of the tree will be the level i am standing at (mp[v[1].first]) + second highest depth in that level (v[1].second)\n\n\n // if(v[0].first != nd) means => If the node i am deleting is not the node with highest depth in the level then the height will not change at all.\n\n\n // (v[1].first==0) means=> If the level has only one node then the new height will be maximum height - the level of the node where i am standing now\n\n if(v[0].first==nd)\n {\n x=(v[1].first==0)?(mp[v[0].first]-1):mp[v[1].first]+v[1].second;\n }\n ans.push_back(x); \n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Using Precomputed Heights to Efficiently Handle Tree Queries
|
using-precomputed-heights-to-efficiently-3m52
|
Intuition\nThe problem requires calculating the height of a binary tree after removing the subtree rooted at a given node for each query. Since each query is in
|
RohanRPM
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T06:08:09.724830+00:00
|
2024-10-26T06:08:09.724869+00:00
| 261 | false |
# Intuition\nThe problem requires calculating the height of a binary tree after removing the subtree rooted at a given node for each query. Since each query is independent, recalculating the height from scratch each time would be inefficient. A better approach is to precompute each node\'s height and store this information in a way that allows us to quickly adjust the height for each query based on the subtree removal.\n\n# Approach\n1. **Calculate Heights and Levels**:\n - Use a recursive `height` function to calculate the height of each node from the root. \n - While calculating the height, store each node\u2019s height and level (distance from the root) in a map `mp`.\n - Another map `mp2` groups nodes by level, associating each level with a list of nodes and their heights.\n\n2. **Precompute Maximum Heights at Each Level**:\n - For each level, find the two tallest nodes (i.e., nodes with the largest heights). This allows us to quickly adjust the tree\'s height if the subtree of the tallest node at a level is removed.\n\n3. **Process Each Query**:\n - For each query, find the level of the queried node and retrieve the maximum and second maximum heights at that level.\n - If the queried node is the tallest node in its level, adjust the tree height by replacing it with the second maximum height.\n - Otherwise, the tree height remains the same.\n\n4. **Return Results**:\n - For each query, add the adjusted height to the result list.\n\n# Complexity\n- **Time complexity**:\n - Calculating heights and levels for each node takes $$O(n)$$ time.\n - Processing each query by finding the maximum and second maximum height at each level also takes $$O(n)$$ in total.\n - So, the overall time complexity is $$O(n)$$.\n\n- **Space complexity**:\n - Storing heights and levels in maps `mp` and `mp2` requires $$O(n)$$ space.\n - Thus, the space complexity is $$O(n)$$.\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left),\n * right(right) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n unordered_map<int, pair<int, int>> mp;\n unordered_map<int, vector<pair<int, int>>> mp2;\n\n int height(TreeNode* root, int level = 0) \n {\n if (!root)\n return 0;\n if (mp.find(root->val) != mp.end())\n return mp[root->val].first;\n\n int l = height(root->left, level + 1);\n int r = height(root->right, level + 1);\n int curr = 1 + max(l, r);\n\n mp[root->val] = {curr, level};\n\n mp2[level].push_back({root->val, curr});\n\n return curr;\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n int H = height(root) - 1;\n int m = queries.size();\n\n vector<int> ans(m, H);\n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)\n {\n int q = queries[i];\n int lev = mp[q].second;\n int maxi = 0;\n int secondMaxi = 0;\n for (auto a : mp2[lev]) \n {\n if (a.second > maxi) \n {\n secondMaxi = maxi;\n maxi = a.second;\n } \n else if (a.second > secondMaxi) \n {\n secondMaxi = a.second;\n }\n }\n\n if (maxi == mp[q].first) ans[i] = H - maxi + secondMaxi;\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Depth-First Search', 'Breadth-First Search', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'Binary Tree', 'C++']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
DFS | One pass solution | Very Detail Explanation ✅
|
dfs-one-pass-solution-very-detail-explan-1q5t
|
\n# Approach\nUsing DFS to travel for each level of tree. When travel, remember to store these important information of each level:\n- Number of node with same
|
manmapi
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-16T07:14:20.720801+00:00
|
2024-10-16T07:14:20.720836+00:00
| 440 | false |
\n# Approach\nUsing DFS to travel for each level of tree. When travel, remember to store these important information of each level:\n- Number of node with same level\n- Max value among these node\n- Second max value among these node.\n\nAnother thing to save is a hash map, linking a node val to level and depth of subnode. \n```\nlevel_map = dict() => value: (level, depth_of_subnode)\n```\n\nNow, for each of queries. These are some step to do:\n- Find the level using `level_map`\n- If this level has number of node is 1 return `level - 1`\n- If the depth of current query is equal `max_` of its level return `level + second_max`. Else return `level + max_`\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n Travel each node: $$O(n)$$\n Travel each query: $$O(m) < O(n)$$\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n Store depth_map: $$O(n)$$ (n is the worst case for 1 side tree)\n Store level_map: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\n# Definition for a binary tree node.\n# class TreeNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.left = left\n# self.right = right\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n depth_map = defaultdict(lambda :(-1, -1, 0))\n level_map = {}\n def travel(root, level):\n if not root:\n return 0\n depth = max(travel(root.left, level + 1), travel(root.right, level + 1))\n level_map[root.val] = (level, depth)\n max_, second_max, size = depth_map[level]\n if depth >= max_:\n depth_map[level] = (depth, max_, size + 1)\n elif depth > second_max:\n depth_map[level] = (max_, depth, size + 1)\n else:\n depth_map[level] = (max_, second_max, size + 1)\n return depth + 1\n travel(root, 0)\n result = []\n for q in queries:\n level, depth = level_map[q]\n max_, second_max, size = depth_map[level]\n if size == 1:\n result.append(level - 1)\n continue\n if depth == max_:\n result.append(level + second_max)\n else:\n result.append(level + max_) \n return result\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Depth-First Search', 'Python3']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Java Solution with comments
|
java-solution-with-comments-by-z0pchur-q010
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \nTime complexity of preprocessing: O(n * log(n))\nTime complexity of each query: O(lo
|
z0pchur
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-14T09:04:30.186618+00:00
|
2024-04-14T09:04:30.186662+00:00
| 552 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nTime complexity of preprocessing: $$O(n * log(n))$$\nTime complexity of each query: $$O(log(n))$$\nTotal time complexity: $$O(n*log(n) + q*log(n))$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode left;\n * TreeNode right;\n * TreeNode() {}\n * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {\n * this.val = val;\n * this.left = left;\n * this.right = right;\n * }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n\n int dfs(TreeNode root, Map<Integer, int[]> heights, int level) {\n if(root == null) return 0;\n heights.put(root.val, new int[] {1 + Math.max(dfs(root.left, heights, level + 1), dfs(root.right, heights, level + 1)), level});\n return heights.get(root.val)[0];\n }\n\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n // map for storing height and level of each node\n Map<Integer, int[]> heights = new HashMap<>();\n // map for storing heights at each level\n Map<Integer, PriorityQueue<Integer>> levelOrderHeights = new HashMap<>();\n\n // dfs to calculate the height and level of each node\n dfs(root, heights, 0);\n\n int rootHeight = heights.get(root.val)[0];\n for(int i = 0; i < heights.get(root.val)[0]; ++i) levelOrderHeights.put(i, new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> Integer.compare(b, a)));\n\n // BFS to calculate heights and each level\n Queue<TreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<>();\n q.add(root);\n int level = 0;\n while(!q.isEmpty()) {\n int size = q.size();\n while(size -- != 0) {\n TreeNode node = q.poll();\n levelOrderHeights.get(level).add(heights.get(node.val)[0]);\n if(node.left != null) q.add(node.left);\n if(node.right != null) q.add(node.right);\n }\n level ++;\n }\n\n int ans[] = new int[queries.length];\n int i = 0;\n for(int query: queries) {\n int height = heights.get(query)[0];\n int curlevel = heights.get(query)[1];\n PriorityQueue<Integer> curheights = levelOrderHeights.get(curlevel);\n \n // if height of the deleted node is not the maximum at that level, then it will have no impact on the root height\n if(height != curheights.peek()) ans[i++] = rootHeight - 1;\n \n // if it is the only node at that level, means height of the root will get reduced by height of the node subtree\n else if(curheights.size() == 1) ans[i++] = rootHeight - height - 1;\n\n // if deleted node has the max height at that level then the height of the root get reduced by the difference of max and second max height at that level\n else {\n int curHeight = curheights.poll();\n int res = rootHeight - curHeight + curheights.peek();\n curheights.add(curHeight);\n ans[i++] = res - 1;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
C++| Euler tour
|
c-euler-tour-by-kumarabhi98-wlsr
|
Prerequisite: Eular Tour\n\nFor every node, store the following things:\n1. Time of discovery (TOD)\n1. Height of node\n1. No. of nodes/children in its subtree\
|
kumarabhi98
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T07:19:28.973280+00:00
|
2022-10-30T07:19:28.973321+00:00
| 172 | false |
**Prerequisite: Eular Tour**\n\nFor every node, store the following things:\n1. Time of discovery (**TOD**)\n1. Height of node\n1. No. of nodes/children in its subtree\n\n* Once the above parameters are stored, we can find the range of TOD of every node present in any subtree of some node. Ex: suppose that for a node `x`, TOD is `in` and no. of children are `y`, then all the node with TOD between **in** to **in+y** lies in the subtree of node `x`. To find the height of tree, we have to avoid these nodes for any `queries[i] = x`.\n* To do the above operation and find height in O(1), We need to maintain prefix and suffix array. For each TOD, store its height and compute max height of TOD from `0 to i` in preffix and store max of height of TOD from `i to n` in suffix. Rest will be clear from code.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dfs(TreeNode* root,map<int,vector<int>> &mp,int h,int &n){\n if(!root) return 0;\n int no = n++;\n int sum = dfs(root->left,mp,h+1,n)+dfs(root->right,mp,h+1,n);\n mp[root->val] = {no,h,sum}; // {time of discovery, height of node, no. of children}\n return sum+1;\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& q) {\n map<int,vector<int>> mp;\n int x = 0;\n dfs(root,mp,0,x);\n int n = mp.size();\n vector<int> left(n+1,0),right(n+1,0);\n \n for(auto it = mp.begin(); it!=mp.end();++it){\n left[it->second[0]] = it->second[1];\n right[it->second[0]] = it->second[1];\n }\n \n for(int i = 1; i<n;++i) left[i] = max(left[i-1],left[i]);\n for(int i = n-1;i>=0;--i) right[i] = max(right[i],right[i+1]);\n \n vector<int> re(q.size(),0);\n for(int i = 0; i<q.size();++i){\n int l = mp[q[i]][0]-1, h = mp[q[i]][0]+mp[q[i]][2]+1;\n if(l>=0) re[i] = left[l];\n if(h<n) re[i] = max(re[i],right[h]);\n }\n return re;\n }\n};\n```\n**Upvote if it helps **
| 3 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'C']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Java Segment Tree
|
java-segment-tree-by-gautamsw5-6h0t
|
The maximum depth after removal of a subtree will be max of depths of all nodes that are not in that subtree\n\nWe find the max by using 2 queries: 1st to find
|
gautamsw5
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T05:35:59.436138+00:00
|
2022-10-30T07:27:37.598731+00:00
| 1,177 | false |
The maximum depth after removal of a subtree will be max of depths of all nodes that are not in that subtree\n\nWe find the max by using 2 queries: 1st to find max of depths of all nodes that occur before the current node in preorder traversal and 2nd to find max of depths of all nodes that occur after the subtree in the preorder traversal\n\nThe answer is the max of the results of these queries\n\nIn preorder traversal, each subtree can be represented by a subarray\n\nEg.\n\n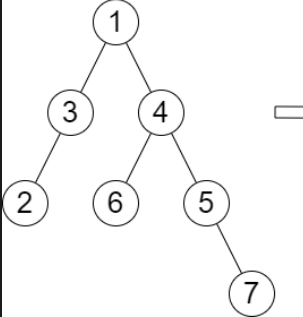\n```\nlet size(x) be size of subtree rooted at x\npreorder = [1, 3, 2, 4, 6, 5, 7]\nsubtree(1) = [1, 3, 2, 4, 6, 5, 7] which is preorder[index(1):index(1)+size(1)]\nsubtree(3) = [3, 2] which is preorder[index(3):index(3)+size(3)]\nsubtree(2) = [2] which is preorder[index(2):index(2)+size(2)]\nsubtree(4) = [4, 6, 5, 7] which is preorder[index(4):index(4)+size(4)]\nsubtree(6) = [6] which is preorder[index(6):index(6)+size(6)]\nsubtree(5) = [5, 7] which is preorder[index(5):index(5)+size(5)]\nsubtree(7) = [7] which is preorder[index(7):index(7)+size(7)]\n```\nSegment tree with range maximum query can be used to find max of any subarray in O(log n)\n<iframe src="https://leetcode.com/playground/AHsCYdo9/shared" frameBorder="0" width="1000" height="1000"></iframe>
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Rust | DFS | With Comments
|
rust-dfs-with-comments-by-wallicent-psof
|
I attempted to solve this for the 2022-10-30 Weekly Contest 317. Collect a map of the tree node levels, keyed by node value. At the same time, we make another m
|
wallicent
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:47:43.246386+00:00
|
2022-10-30T04:47:43.246419+00:00
| 1,262 | false |
I attempted to solve this for the 2022-10-30 Weekly Contest 317. Collect a map of the tree node levels, keyed by node value. At the same time, we make another map of the maximum levels of the tree nodes under each node, keyed by level (`levels`). For each query, we can then look up the level of that node. We use the level to look up the other nodes on that level in `levels`. If the queried node is the only node on that level, the resulting tree is `level - 1` high, since we will remove all levels below. If there are other nodes, the result is the maximum of the maximum levels of those nodes.\n\nComments:\n* I first went down the wrong path and had to restart. I was five minutes late when I had a working solution. Too bad, but it was a nice exercise.\n\n```\nuse std::rc::Rc;\nuse std::cell::RefCell;\nuse std::collections::HashMap;\nimpl Solution {\n fn map(node: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, levels: &mut Vec<Vec<(i32, usize)>>, map: &mut HashMap<i32, usize>, level: usize) -> usize {\n if let Some(node_rc) = node {\n let node_ref = node_rc.borrow();\n if levels.len() == level {\n levels.push(vec![]);\n }\n let max_level = Self::map(node_ref.left.clone(), levels, map, level + 1)\n .max(Self::map(node_ref.right.clone(), levels, map, level + 1));\n levels[level].push((node_ref.val, max_level));\n map.insert(node_ref.val, level);\n max_level\n } else {\n level - 1\n }\n }\n\n pub fn tree_queries(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, queries: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {\n let mut levels = vec![];\n let mut map = HashMap::new();\n Self::map(root, &mut levels, &mut map, 0);\n queries.into_iter().map(|q| {\n let &level = map.get(&q).unwrap();\n if levels[level].len() == 1 {\n (level - 1) as i32\n } else {\n levels[level].iter().filter_map(|(val, l)| (*val != q).then(|| {\n *l\n })).max().unwrap() as i32\n }\n }).collect()\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 1 |
['Rust']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
[Java] Simply traverse the tree twice
|
java-simply-traverse-the-tree-twice-by-w-0t2x
|
Intuition & Approach\n\nJust traverse the tree twice. First time calculate the height of subtrees, and second time calculate the max height without a node.\n\nF
|
wddd
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:34:45.780464+00:00
|
2022-10-30T07:56:59.655770+00:00
| 1,134 | false |
# Intuition & Approach\n\nJust traverse the tree twice. First time calculate the height of subtrees, and second time calculate the max height without a node.\n\nFirst traversal is trivial.\nSecond traversal is a bit tricky. If we remove left child of root, then the possible max height of the new tree is the height of right child + 1. We can recursively get this "possible max height".\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode left;\n * TreeNode right;\n * TreeNode() {}\n * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {\n * this.val = val;\n * this.left = left;\n * this.right = right;\n * }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n Map<Integer, Integer> heightsRooted = new HashMap<>();\n getHeightRootedAt(root, heightsRooted);\n\n int[] heightsWithout = new int[heightsRooted.size() + 1];\n getHeightsWithoutNode(root, 0, 0, heightsWithout, heightsRooted);\n\n int[] result = new int[queries.length];\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {\n result[i] = heightsWithout[queries[i]];\n }\n\n return result;\n }\n\n private void getHeightsWithoutNode(TreeNode node, int height, int possibleMaxHeight, int[] heightsWithout, Map<Integer, Integer> heightsRooted) {\n if (node == null) {\n return;\n }\n\n int leftHeight = node.left == null ? -1 : heightsRooted.get(node.left.val);\n int rightHeight = node.right == null ? -1 : heightsRooted.get(node.right.val);\n\n getHeightsWithoutNode(node.left, height + 1, Math.max(possibleMaxHeight, rightHeight + height + 1), heightsWithout, heightsRooted);\n getHeightsWithoutNode(node.right, height + 1, Math.max(possibleMaxHeight, leftHeight + height + 1), heightsWithout, heightsRooted);\n\n heightsWithout[node.val] = Math.max(height - 1, possibleMaxHeight);\n }\n\n private int getHeightRootedAt(TreeNode node, Map<Integer, Integer> heightsRooted) {\n if (node == null) {\n return -1;\n }\n\n int maxHeight = 1 + Math.max(getHeightRootedAt(node.left, heightsRooted), getHeightRootedAt(node.right, heightsRooted));\n heightsRooted.put(node.val, maxHeight);\n return maxHeight;\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
[Segment Tree][C++][Euler Path] Explained
|
segment-treeceuler-path-explained-by-bre-fkki
|
Run a euler tour on the tree to find the start time and end time of each node.\nStore the depth of each node in it\'s start time. \nBuild a Segment Tree contain
|
brehampie
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:33:36.320320+00:00
|
2022-10-30T04:38:42.137856+00:00
| 991 | false |
Run a euler tour on the tree to find the start time and end time of each node.\nStore the depth of each node in it\'s start time. \nBuild a Segment Tree containing the maximum of ranges.\nNow for each query node <b>\'x\'</b> then answer will be the maximum of the maximum of range\n<b>(1, start[x]-1)</b> and <b>(end[x]+1,totalTime)</b>.\n\nSample Code:\n```\nstruct SegmentTree {\n#define lc (C << 1)\n#define rc (C << 1 | 1)\n#define M ((L+R)>>1)\n struct data {\n int sum;\n data() :sum(0) {};\n };\n vector<data>st;\n int N;\n SegmentTree(int _N) :N(_N) {\n st.resize(4 * N);\n }\n void combine(data& cur, data& l, data& r) {\n cur.sum = max(l.sum,r.sum);\n }\n data Query(int i, int j, int C, int L, int R) {\n if (j < L || i > R || L > R) return data();\n if (i <= L && R <= j) return st[C];\n data ret;\n data d1 = Query(i, j, lc, L, M);\n data d2 = Query(i, j, rc, M + 1, R);\n combine(ret, d1, d2);\n return ret;\n }\n void Update(int i, int j, int val, int C, int L, int R) {\n if (j < L || i > R || L > R) return;\n if (i <= L && R <= j) {\n st[C].sum = val;\n return;\n }\n Update(i, j, val, lc, L, M);\n Update(i, j, val, rc, M + 1, R);\n combine(st[C], st[lc], st[rc]);\n }\n void Update(int i, int j, int val) {\n Update(i, j, val, 1, 1, N);\n }\n int Query(int i, int j) {\n return Query(i, j, 1, 1, N).sum;\n }\n};\nclass Solution {\npublic: \n int startTime[100001],endTime[100001];\n int arr[100001];\n int T;\n void dfs(TreeNode* root,int d){\n ++T;\n startTime[root->val] = T;\n arr[T] = d;\n if(root->left!=nullptr)dfs(root->left,d+1);\n if(root->right!=nullptr) dfs(root->right,d+1);\n endTime[root->val] = T;\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n T = 0;\n dfs(root,0);\n SegmentTree st(T);\n for(int i=1;i<=T;i++){\n st.Update(i,i,arr[i]);\n }\n vector<int>ret;\n for(int&x:queries){\n int from = startTime[x];\n int till = endTime[x];\n int a = st.Query(1,from-1);\n int b = st.Query(till+1,T);\n ret.push_back(max(a,b));\n }\n return ret;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Tree', 'C']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Single traversal | Level-Order | CPP
|
single-traversal-level-order-cpp-by-scof-15m3
|
Traverse the tree and compute the height of each node, level of each node and in each level store the max 2 heights.\nIf you remove a node, we have two possibil
|
scofield24
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:15:57.033686+00:00
|
2022-10-30T04:15:57.033719+00:00
| 582 | false |
Traverse the tree and compute the height of each node, level of each node and in each level store the max 2 heights.\nIf you remove a node, we have two possibilities. \n1. It\'s in the longest path\n2. It\'s not in the longest path\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n unordered_map<int, int> nodeLevel;\n unordered_map<int, pair<int,int>> heights;\n unordered_map<int,int> height;\npublic:\n int getHeight(TreeNode* root, int level) {\n if (root == nullptr) return 0;\n int lh = getHeight(root->left, level + 1);\n int rh = getHeight(root->right, level + 1);\n int h = 1 + max(lh, rh);\n \n nodeLevel[root->val] = level;\n height[root->val] = h;\n \n if (heights.count(level)) {\n if (heights[level].first <= h) {\n pair<int,int> p = {h, heights[level].first};\n heights[level] = p;\n } else if (heights[level].second < h) {\n heights[level].second = h;\n }\n } else {\n heights[level] = {h, 0};\n }\n return h;\n }\n \n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n getHeight(root, 0);\n vector<int> result;\n for (auto node: queries) {\n int level = nodeLevel[node];\n if (height[node] == heights[level].first) {\n result.push_back(heights[level].second + level - 1);\n } else {\n result.push_back(heights[level].first + level - 1);\n }\n }\n return result;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['C++']
| 2 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
O(N) solution
|
on-solution-by-sampath_17-3na0
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \npreprocess everything\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nsa
|
Sampath_17
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-27T09:46:51.936889+00:00
|
2024-10-27T09:46:51.936924+00:00
| 29 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\npreprocess everything\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nsave the height and depth of all nodes at every level\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}\n * };\n */\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n unordered_map<int,vector<int>> mp;\n unordered_map<int,int> mp_row;\n unordered_map<int,int> mp_depth;\n unordered_map<int,pair<int,int>> lvl;\n void prep(){\n for(int i=0;mp[i].size()!=0;i++){\n lvl[i].first=0;\n lvl[i].second=0;\n for(int j:mp[i]){\n if(lvl[i].first<=i+mp_depth[j]){\n lvl[i].second = lvl[i].first;\n lvl[i].first = i+mp_depth[j];\n }else if(lvl[i].second<i+mp_depth[j])\n lvl[i].second = i+mp_depth[j];\n }\n }\n }\n\n int height(TreeNode* root, int level) {\n if(!root) return 0;\n\n mp_row[root->val] = level;\n mp[level].push_back(root->val);\n\n int l = height(root->left, level + 1);\n int r = height(root->right, level + 1);\n int curr = 1 + max(l, r);\n\n mp_depth[root->val] = curr-1;\n\n return curr;\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n int h=height(root,0);\n prep();\n vector<int> ans;\n for(auto k:queries){\n int row = mp_row[k];\n if(mp[row].size()==1){\n ans.push_back(row-1);\n continue;\n }else{\n if(lvl[row].first==row+mp_depth[k]) ans.push_back(lvl[row].second);\n else ans.push_back(lvl[row].first);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Breadth-First Search', 'Binary Tree', 'C++']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
One pass dfs
|
one-pass-dfs-by-teja-b_v_s-w63s
|
Intuition\npreprocess to pass the time and space limits\n# Approach\n hint: store nodes in given level, heights and depths of every node\n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
teja-b_v_s
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-27T09:22:07.214266+00:00
|
2024-10-27T09:22:07.214286+00:00
| 22 | false |
# Intuition\npreprocess to pass the time and space limits\n# Approach\n hint: store nodes in given level, heights and depths of every node\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n)\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int ht[100001];\n int depth[100001];\n int lvl[100001][2];\n unordered_map<int,vector<int>>mp;\n int dfs(TreeNode* root,int d){\n if(!root) return 0;\n depth[root->val] = d;\n mp[d].push_back(root->val);\n return ht[root->val] = 1+max(dfs(root->left,d+1), dfs(root->right,d+1));\n }\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n int q = queries.size();\n mp.clear();\n dfs(root,0);\n for(auto [l,k]:mp){\n int maxi = 0, mini = 0;\n for(auto v:k){\n int temp = (ht[v]+depth[v]-1); \n if(maxi<=temp){\n mini = maxi;\n maxi = temp;\n }\n else if(mini<temp){\n mini = temp;\n }\n }\n lvl[l][0] = maxi;\n lvl[l][1] = mini;\n }\n vector<int>ans;\n for(int i=0;i<q;i++){\n int node = queries[i];\n if(mp[depth[node]].size()==1) ans.push_back(depth[node]-1);\n else{\n if(lvl[depth[node]][0]==depth[node]+ht[node]-1) \n ans.push_back(lvl[depth[node]][1]);\n else ans.push_back(lvl[depth[node]][0]);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
O(N) Time and Space by doing Preprocessing of level and maxHeight
|
on-time-and-space-by-doing-preprocessing-0w4n
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nO(N) Time and Space by
|
Ashutosh_1114
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T14:45:36.379953+00:00
|
2024-10-26T14:45:36.379971+00:00
| 86 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nO(N) Time and Space by doing Preprocessing of level and maxHeight\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(N)\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(N)\n# Code\n```golang []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * type TreeNode struct {\n * Val int\n * Left *TreeNode\n * Right *TreeNode\n * }\n */\n\nfunc findHeightOfNodes(root *TreeNode, l int, height, levelMaxHeight, levelSecondMaxHeight, level []int) int{\n\n if root == nil {\n return 0\n }\n\n level[root.Val] = l //level Population / preprocessing\n height[root.Val] = max(findHeightOfNodes(root.Left, l+1, height, levelMaxHeight, levelSecondMaxHeight, level), findHeightOfNodes(root.Right, l+1, height, levelMaxHeight, levelSecondMaxHeight, level)) + 1\n\n //max and second max height calculation as if node that is to be deleted has the max height from that node\n\n if levelMaxHeight[l] < height[root.Val]{\n levelSecondMaxHeight[l] = levelMaxHeight[l]\n levelMaxHeight[l] = height[root.Val]\n } else if levelSecondMaxHeight[l] < height[root.Val]{\n levelSecondMaxHeight[l] = height[root.Val]\n }\n\n return height[root.Val]\n}\nfunc treeQueries(root *TreeNode, queries []int) []int {\n const n = 1000001\n height := make([]int, n)\n levelMaxHeight := make([]int, n)\n levelSecondMaxHeight := make([]int, n)\n level := make([]int, n)\n\n findHeightOfNodes(root, 0, height, levelMaxHeight, levelSecondMaxHeight, level)\n\n ans := make([]int, len(queries))\n\n for i, query := range queries{\n levelOfNode := level[query]\n\n if levelMaxHeight[levelOfNode] == height[query]{ //node to be deleted is max height node so use height as secondMaxHeight node\n ans[i] = levelOfNode + levelSecondMaxHeight[levelOfNode] - 1\n }else{\n ans[i] = levelOfNode + levelMaxHeight[levelOfNode] - 1\n }\n }\n\n return ans\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Go']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
✅ Simple Java Solution
|
simple-java-solution-by-harsh__005-tgn5
|
CODE\nJava []\nclass Solution {\n class Pair {\n TreeNode node;\n int level;\n Pair(TreeNode n, int l) {\n node = n;\n
|
Harsh__005
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T13:37:13.600502+00:00
|
2024-10-26T13:37:13.600544+00:00
| 95 | false |
## **CODE**\n```Java []\nclass Solution {\n class Pair {\n TreeNode node;\n int level;\n Pair(TreeNode n, int l) {\n node = n;\n level = l;\n }\n }\n \n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n Map<Integer, Pair> valueMap = new HashMap<>();\n Map<Integer, Integer> levelMap = new HashMap<>();\n \n Queue<TreeNode> bfs = new LinkedList<>();\n bfs.add(root);\n \n int levelCount=0, size = 0;\n while(!bfs.isEmpty()) {\n size = bfs.size();\n levelMap.put(levelCount, size);\n \n while(size-- > 0) {\n TreeNode top = bfs.remove();\n valueMap.put(top.val, new Pair(top, levelCount));\n if(top.left != null) bfs.add(top.left);\n if(top.right != null) bfs.add(top.right);\n }\n levelCount++;\n }\n levelMap.put(levelCount, 0);\n \n int n = queries.length, i = 0;\n int res[] = new int[n];\n for(int query : queries) {\n Pair p = valueMap.get(query);\n TreeNode curr = p.node;\n \n if(levelMap.get(p.level) == 1) {\n res[i++] = p.level-1;\n continue;\n }\n \n bfs.clear();\n bfs.add(curr);\n int currLevel = p.level;\n boolean flag = true;\n \n while(!bfs.isEmpty()) {\n int nodeCounts = levelMap.get(currLevel+1);\n size = bfs.size();\n \n while(size-- > 0) {\n TreeNode top = bfs.remove();\n if(top.left != null) {\n bfs.add(top.left);\n nodeCounts--;\n }\n if(top.right != null) {\n bfs.add(top.right);\n nodeCounts--;\n }\n }\n \n if(nodeCounts == 0) {\n res[i++] = currLevel;\n flag=false;\n break;\n }\n currLevel++;\n }\n \n if(flag) {\n res[i++] = levelCount-1;\n }\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Breadth-First Search', 'Java']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
C# Solution for Height of Binary Tree After Subtree Removal Queries Problem
|
c-solution-for-height-of-binary-tree-aft-0dy2
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe problem requires us to efficiently determine the maximum depth of a binary tree aft
|
Aman_Raj_Sinha
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T09:29:27.092763+00:00
|
2024-10-26T09:29:27.092803+00:00
| 72 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe problem requires us to efficiently determine the maximum depth of a binary tree after removing a node specified in the queries. Simply performing a depth-first search (DFS) for each query would be inefficient, especially for large trees and multiple queries. Instead, we can preprocess the tree to gather necessary information and then respond to each query in constant time.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1.\tPreprocessing with DFS:\n\t\u2022\tWe perform a DFS on the tree to calculate two key pieces of information:\n\t\u2022\tNode Depths: Store the depth of each node in a list.\n\t\u2022\tNode Index Mapping: Create a mapping from each node\u2019s value to its index in the depth list.\n\t\u2022\tDuring the DFS, we also calculate the size of the subtree for each node, which tells us how many nodes are in the subtree rooted at that node.\n2.\tCalculating Maximum Depths:\n\t\u2022\tAfter the DFS, we construct two lists:\n\t\u2022\tMax Depth from Left: This maintains the maximum depth encountered when traversing from the root to the left of each node.\n\t\u2022\tMax Depth from Right: This is similar but maintains the maximum depth encountered when traversing from the root to the right.\n\t\u2022\tWe fill these lists by iterating through the node depths.\n3.\tProcessing Queries:\n\t\u2022\tFor each query, which specifies a node to be removed:\n\t\u2022\tDetermine the index of the node in the nodeDepths list.\n\t\u2022\tCalculate the maximum depth that can be achieved after removing that node by considering:\n\t\u2022\tThe maximum depth of the subtree on the left side of the node.\n\t\u2022\tThe maximum depth of the subtree on the right side of the node (if any).\n\t\u2022\tThis is done in constant time for each query, leveraging the preprocessed information.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\u2022\tDFS Traversal: O(n) - Each node is visited once during the DFS to gather depths and subtree sizes.\n\u2022\tBuilding Maximum Depth Lists: O(n) - We compute the max depths for each node using the depth list.\n\u2022\tQuery Processing: O(1) for each query. If there are q queries, this step takes O(q).\n\nThus, the total time complexity is: O(n + q) \nwhere n is the number of nodes in the tree and q is the number of queries.\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\u2022\tNode Depths and Index Maps: O(n) - We use lists and dictionaries to store depths and subtree sizes, both of which scale with the number of nodes.\n\u2022\tAuxiliary Space: The DFS call stack may take O(h) space, where h is the height of the tree (in the worst case, this could be O(n) for skewed trees).\n\nThus, the total space complexity is: O(n) \n\n# Code\n```csharp []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * public int val;\n * public TreeNode left;\n * public TreeNode right;\n * public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) {\n * this.val = val;\n * this.left = left;\n * this.right = right;\n * }\n * }\n */\npublic class Solution {\n public int[] TreeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n // Maps to store the index of each node value and the number of nodes in subtree for each node\n Dictionary<int, int> nodeIndexMap = new Dictionary<int, int>();\n Dictionary<int, int> subtreeSize = new Dictionary<int, int>();\n\n // Lists to store node depths and maximum depths from left and right\n List<int> nodeDepths = new List<int>();\n List<int> maxDepthFromLeft = new List<int>();\n List<int> maxDepthFromRight = new List<int>();\n\n // Perform DFS to populate nodeIndexMap and nodeDepths\n DFS(root, 0, nodeIndexMap, nodeDepths);\n\n int totalNodes = nodeDepths.Count;\n\n // Calculate subtree sizes\n CalculateSubtreeSize(root, subtreeSize);\n\n // Calculate maximum depths from left and right\n maxDepthFromLeft.Add(nodeDepths[0]);\n maxDepthFromRight.Add(nodeDepths[totalNodes - 1]);\n\n for (int i = 1; i < totalNodes; i++) {\n maxDepthFromLeft.Add(Math.Max(maxDepthFromLeft[i - 1], nodeDepths[i]));\n maxDepthFromRight.Add(Math.Max(maxDepthFromRight[i - 1], nodeDepths[totalNodes - i - 1]));\n }\n maxDepthFromRight.Reverse();\n\n // Process queries\n int[] results = new int[queries.Length];\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.Length; i++) {\n int queryNode = queries[i];\n int startIndex = nodeIndexMap[queryNode] - 1;\n int endIndex = startIndex + 1 + subtreeSize[queryNode];\n\n int maxDepth = maxDepthFromLeft[startIndex];\n if (endIndex < totalNodes) {\n maxDepth = Math.Max(maxDepth, maxDepthFromRight[endIndex]);\n }\n\n results[i] = maxDepth;\n }\n\n return results;\n }\n\n // Depth-first search to populate nodeIndexMap and nodeDepths\n private void DFS(TreeNode root, int depth, Dictionary<int, int> nodeIndexMap, List<int> nodeDepths) {\n if (root == null) return;\n\n nodeIndexMap[root.val] = nodeDepths.Count;\n nodeDepths.Add(depth);\n\n DFS(root.left, depth + 1, nodeIndexMap, nodeDepths);\n DFS(root.right, depth + 1, nodeIndexMap, nodeDepths);\n }\n\n // Calculate the size of subtree for each node\n private int CalculateSubtreeSize(TreeNode root, Dictionary<int, int> subtreeSize) {\n if (root == null) return 0;\n\n int leftSize = CalculateSubtreeSize(root.left, subtreeSize);\n int rightSize = CalculateSubtreeSize(root.right, subtreeSize);\n\n int totalSize = leftSize + rightSize + 1;\n subtreeSize[root.val] = totalSize;\n\n return totalSize;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
CPP BFS DFS Easy Solution 🚀
|
cpp-bfs-dfs-easy-solution-by-vijay-mali-mang
|
\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n1. First calculate level of each node using DFS/BFS any method.\n\n2. Then Calculate What is max
|
vijay-mali
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T09:29:16.963983+00:00
|
2024-10-26T09:34:05.175273+00:00
| 411 | false |
\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. First calculate level of each node using DFS/BFS any method.\n\n2. Then Calculate What is maxDepth from current node i can achieve, for that i used DFS.\n\n3. After that just create an map which can store vector of all pairs of node with their corresponding maxDepth for each level.\n\n4. After that just traverse on that vector and sort all pairs in descending order as we want max Height.\n\n5. Then just traverse on queries vector and find level of that node and traverse the vector for that level to see what is maxDepth i can go with that level.\n\n6. If there is no node for that level simply my ans will be current level of node - 1.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}\n * };\n */\nmap<int,int> mp,maxmp;\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n static bool cmp(pair<int,int> & a, pair<int,int> &b){\n return a.first > b.first;\n }\n void dfs(TreeNode* tmp, int lvl){\n if(!tmp){\n return;\n }\n\n maxmp[tmp -> val] = lvl;\n dfs(tmp -> left, lvl + 1);\n dfs(tmp -> right, lvl + 1);\n int lft = 0, rgt = 0;\n lft = tmp -> left ? maxmp[tmp -> left -> val] : 0;\n rgt = tmp -> right ? maxmp[tmp -> right -> val] : 0;\n maxmp[tmp -> val] = max({lft,rgt,maxmp[tmp->val]});\n\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n\n mp.clear();\n maxmp.clear();\n map<int,vector<pair<int,int>>> allLvl;\n\n queue<pair<TreeNode*,int>> q;\n q.push({root,0});\n\n while(!q.empty()){\n TreeNode* tmp = q.front().first;\n int lvl = q.front().second;\n q.pop();\n mp[tmp -> val] = lvl;\n\n if(tmp -> left){\n q.push({tmp -> left, lvl+1});\n }\n if(tmp -> right){\n q.push({tmp -> right, lvl+1});\n }\n\n }\n dfs(root,0);\n\n for(auto it : maxmp){\n int node = it.first;\n int maxdepth = it.second;\n int lvl = mp[node];\n allLvl[lvl].push_back({maxdepth,node});\n // cout<<it.first<< " "<<it.second<<endl;\n }\n\n for(auto &it : allLvl){\n // auto v = it.second;\n sort(it.second.begin(),it.second.end(),cmp);\n }\n vector<int> ans;\n for(int i : queries){\n int lvl = mp[i];\n bool printed = 0;\n for(auto h : allLvl[lvl]){\n int depth = h.first;\n int node = h.second;\n if(node != i){\n ans.push_back(depth);\n printed = 1;\n break;\n }\n // cout<<h\n }\n if(!printed){\n ans.push_back(lvl-1);\n }\n }\n\n for(auto i : allLvl[2]){\n cout<<i.first<<" "<<i.second<<endl;\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Java Solution for Height of Binary Tree After Subtree Removal Queries Problem
|
java-solution-for-height-of-binary-tree-p2xcr
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe goal is to determine the maximum height of the tree after hypothetically removing t
|
Aman_Raj_Sinha
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T09:13:31.750002+00:00
|
2024-10-26T09:13:31.750034+00:00
| 169 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe goal is to determine the maximum height of the tree after hypothetically removing the subtree rooted at each queried node. Calculating this efficiently for a large number of nodes requires precomputing information about the structure of the tree so that we avoid repeated traversals\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1.\tDFS Traversal for Heights and Depths: Perform a DFS traversal of the tree to calculate the height and depth of each node. For each node:\n\t\u2022\tStore its depth and height in maps for fast access during query processing.\n2.\tStore Maximum Heights by Depth: To efficiently determine the maximum height after removing a subtree rooted at a specific node:\n\t\u2022\tStore the two highest heights of nodes at each depth level in a map. This enables us to quickly find the maximum height for a level after removing a node.\n3.\tAnswer Each Query Efficiently: For each query (removal of a subtree rooted at a specific node):\n\t\u2022\tLook up the depth and height of the node to be \u201Cremoved.\u201D\n\t\u2022\tCheck the heights at that depth level using the precomputed values. If the height of the queried node is the highest, use the second-highest height as the new maximum; otherwise, use the current highest height.\n\t\u2022\tThis results in an efficient, constant-time computation per query.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n1.\tDFS Traversal for Heights and Depths: O(n), where n is the number of nodes, since each node is visited once.\n2.\tBuilding Depth Heights Map: O(n log n), as we sort the list of heights at each depth level. In the worst case, we would sort n nodes in total.\n3.\tQuery Processing: O(q), where q is the number of queries, since each query is processed in constant time by accessing precomputed information.\n\nTotal Time Complexity: O(n log n + q)\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n1.\tHeights and Depths Maps: O(n), as we store depth and height for each node.\n2.\tDepth Heights Map: O(n), as each node\u2019s height is stored in the list corresponding to its depth.\n3.\tResult Array for Queries: O(q), where q is the number of queries.\n\nTotal Space Complexity: O(n + q)\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode left;\n * TreeNode right;\n * TreeNode() {}\n * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {\n * this.val = val;\n * this.left = left;\n * this.right = right;\n * }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n private Map<Integer, Integer> heights = new HashMap<>(); \n private Map<Integer, Integer> depths = new HashMap<>(); \n private Map<Integer, List<Integer>> depthHeights = new HashMap<>();\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n calculateHeightAndDepth(root, 0);\n\n for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : heights.entrySet()) {\n int nodeValue = entry.getKey();\n int height = entry.getValue();\n int depth = depths.get(nodeValue);\n depthHeights.computeIfAbsent(depth, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(height);\n }\n for (List<Integer> heightList : depthHeights.values()) {\n Collections.sort(heightList, Collections.reverseOrder());\n }\n\n int[] result = new int[queries.length];\n \n for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {\n int nodeValue = queries[i];\n int depth = depths.get(nodeValue);\n int nodeHeight = heights.get(nodeValue);\n List<Integer> heightList = depthHeights.get(depth);\n \n int maxHeightWithoutNode;\n if (heightList.size() == 1) {\n maxHeightWithoutNode = depth - 1;\n } else if (heightList.get(0) == nodeHeight) {\n maxHeightWithoutNode = depth + heightList.get(1);\n } else {\n maxHeightWithoutNode = depth + heightList.get(0);\n }\n\n result[i] = maxHeightWithoutNode;\n }\n\n return result;\n }\n\n private int calculateHeightAndDepth(TreeNode node, int depth) {\n if (node == null) return -1;\n\n depths.put(node.val, depth);\n int leftHeight = calculateHeightAndDepth(node.left, depth + 1);\n int rightHeight = calculateHeightAndDepth(node.right, depth + 1);\n\n int height = 1 + Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight);\n heights.put(node.val, height);\n\n return height;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
✅ DFS | Short & Straightforward
|
dfs-short-straightforward-by-eleev-tqj8
|
\n\n# Solution\nswift []\nstruct Solution {\n func treeQueries(_ root: TreeNode?, _ queries: [Int]) -> [Int] {\n var heights = [Int](repeating: 0, cou
|
eleev
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T08:26:21.424282+00:00
|
2024-10-26T08:26:21.424302+00:00
| 45 | false |
\n\n# Solution\n```swift []\nstruct Solution {\n func treeQueries(_ root: TreeNode?, _ queries: [Int]) -> [Int] {\n var heights = [Int](repeating: 0, count: 100001)\n var maxHeight = 0\n\n func preorder(_ node: TreeNode?, _ height: Int = 0, isLeftToRight: Bool) {\n guard let node else { return }\n heights[node.val] = max(heights[node.val], maxHeight)\n maxHeight = max(maxHeight, height)\n let nodes = isLeftToRight ? (node.left, node.right) : (node.right, node.left)\n preorder(nodes.0, height + 1, isLeftToRight: isLeftToRight)\n preorder(nodes.1, height + 1, isLeftToRight: isLeftToRight)\n }\n preorder(root, isLeftToRight: true)\n maxHeight = 0\n preorder(root, isLeftToRight: false)\n return queries.reduce(into: [Int]()) { r, q in\n r.append(heights[q])\n }\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Depth-First Search', 'Swift', 'Binary Tree']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
🏆 Preorder & Postorder | 🥇 Beats 100% | ✨ Most Efficient & Readable | ✔ Explained | C++
|
preorder-postorder-beats-100-most-effici-sqdk
|
\uD83C\uDFC6 Preorder & Postorder | \uD83E\uDD47 Beats 100% | \u2728 Most Efficient & Readable | \u2714 Explained | C++\n\n\n\n# Intuition\nTo solve this proble
|
AhmadMzayekCS
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T07:44:55.687063+00:00
|
2024-10-26T07:48:44.558595+00:00
| 202 | false |
# \uD83C\uDFC6 Preorder & Postorder | \uD83E\uDD47 Beats 100% | \u2728 Most Efficient & Readable | \u2714 Explained | C++\n\n\n\n# Intuition\nTo solve this problem **efficiently**, we need to determine the `height` of the binary tree after removing the subtree rooted at each node specified in the **queries** array. Since the queries are independent, **the original tree structure is restored** after each query.\n\nOur approach leverages the properties of `preorder` and `postorder` traversals. By `storing heights at each node` in both traversal orders, we can **quickly** calculate the **height** of the tree after removing each subtree.\n\n# Approach\n1. `Traversals:`\n - Performing both **preorder** and **postorder** traversals, which helps **store heights** for each node **efficiently**.\n\n2. `Pre-calculated Heights:`\n - For each node, storing the **maximum height** reached in both traversals.\n\n3. `Efficient Query Processing:`\n - Using the stored heights for **quick lookups** in response to each query, giving us **constant-time complexity per query**.\n\n# Complexity\n- `Let:`\n - $$m = nbNodes$$.\n - $$n = nbQueries$$.\n - $$MAX\\_VALUE = 100,001$$.\n\n- `Time complexity:` $$O(m + n)$$.\n\n- `Space complexity:` $$O(MAX\\_VALUE)$$.\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n#define MAX_VALUE 100001\n\n#pragma GCC target("avx, mmx, sse2, sse3, sse4")\n#pragma GCC optimize("Ofast,no-stack-protector")\n\nstatic const int disableSync = [](void) noexcept -> int\n{\n std::cin.tie(nullptr);\n std::cout.tie(nullptr);\n std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);\n return 0;\n}();\n\nusing NodeBT_t = TreeNode;\n\nclass Solution final\n{\nprivate:\n int maxHeight;\n std::array<int, MAX_VALUE> preorderHeights, postorderHeights;\n\npublic:\n std::vector<int> treeQueries(const NodeBT_t* const root, std::vector<int>& queries) noexcept\n {\n this->setHeights(root);\n for (int& query : queries)\n query = std::max(this->preorderHeights[query], this->postorderHeights[query]);\n return queries;\n }\n\nprivate:\n inline void setHeights(const NodeBT_t* const root) noexcept\n {\n this->maxHeight = 0;\n this->setPreorderHeights(root, 0);\n this->maxHeight = 0;\n this->setPostorderHeights(root, 0);\n }\n\n void setPreorderHeights(const NodeBT_t* const root, const int height) noexcept\n {\n if (!root)\n return;\n this->preorderHeights[root->val] = this->maxHeight;\n this->maxHeight = std::max(this->maxHeight, height);\n this->setPreorderHeights(root->left, height + 1);\n this->setPreorderHeights(root->right, height + 1);\n }\n\n void setPostorderHeights(const NodeBT_t* const root, const int height) noexcept\n {\n if (!root)\n return;\n this->postorderHeights[root->val] = this->maxHeight;\n this->maxHeight = std::max(this->maxHeight, height);\n this->setPostorderHeights(root->right, height + 1);\n this->setPostorderHeights(root->left, height + 1);\n }\n};\n```\n\n
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Recursion', 'C', 'Binary Tree', 'C++']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
DFS for subtree heights + BFS for level search
|
dfs-for-subtree-heights-bfs-for-level-se-3amo
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nConsider nodes on the same level.\nIf a node is being removed, the max height after rem
|
kenkyng
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T04:35:23.237553+00:00
|
2024-10-26T04:35:23.237585+00:00
| 107 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nConsider nodes on the same level.\nIf a node is being removed, the max height after removal is the depth of the level and the max height of the remaining subtrees.\n\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nFirst generate subtree heights recursively (DFS) and store them in a hashmap (taking advantage of unique values).\nIterate node removal by BFS and keep track of level depth. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n+q)$$ in total, for $$n$$ and $$q$$ being the number of nodes and number of queries, respectively.\n$$O(n)$$ for DFS and BFS.\n$$O(q)$$ for $$q \\times O(1)$$ queries.\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n)$$ for storing max heights before and after removal.\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\n# Definition for a binary tree node.\n# class TreeNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.left = left\n# self.right = right\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n heights = {}\n\n # get subtree\'s heights by dfs\n def get_height(node):\n if not node:\n return -1\n if node in heights:\n return heights[node.val]\n \n height = 1 + max(get_height(node.left), get_height(node.right))\n heights[node.val] = height\n return height\n get_height(root)\n\n # bfs approach:\n # on each level, find two subtrees with the largest heights, h1 >= h2\n # each node on the same level is being cut.\n # if node.val = h1, max_height = depth + h2, else depth + h1\n # h1, h2 = -1, -1 at initialisation since a null child implies a step back to parent\n max_heights = {root.val: 0}\n queue = deque([root])\n depth = 0\n while queue:\n k = len(queue)\n # get first and second max heights\n h1, h2 = -1, -1\n for i in range(k):\n h = heights[queue[i].val]\n if h > h1:\n h1, h2 = h, h1\n elif h > h2:\n h2 = h\n while k:\n k -= 1\n node = queue.popleft()\n h = heights[node.val]\n if h == h1:\n max_heights[node.val] = h2 + depth\n else:\n max_heights[node.val] = h1 + depth\n if node.left:\n queue.append(node.left)\n if node.right:\n queue.append(node.right)\n depth += 1\n \n return [max_heights[q] for q in queries]\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Depth-First Search', 'Breadth-First Search', 'Python3']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Flattening the depth of tree and using range query
|
flattening-the-depth-of-tree-and-using-r-mjqc
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nWe calculate the depth of every node and build a tree out of those nodes depths as thei
|
hgharshop
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T02:48:20.890564+00:00
|
2024-10-26T02:59:31.923888+00:00
| 85 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nWe calculate the depth of every node and build a tree out of those nodes depths as their respective values. flatten the tree and calculate the maximum value of array while excluding the subarray which is the subtree of the given node.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O( N*log(N) )\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n\n- Space complexity: O( N )\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n vector<int> flatten, flatten_depth;\n map<int,pair<int,int>> childCount;\n\n int dfs( TreeNode* node, int depth ){\n if( node == NULL ) return 0;\n int left = dfs( node->left, depth + 1 );\n flatten.push_back(node->val);\n flatten_depth.push_back(depth);\n int right = dfs(node->right, depth + 1 );\n childCount[node->val] = {left, right};\n return left + right + 1;\n }\n\n class SegmentTree{\n int N;\n vector<int> tree;\n \n public:\n \n SegmentTree(int _N){\n N = _N;\n int TREE_SIZE = 4 * N + 1;\n tree.resize(TREE_SIZE);\n }\n \n int build( int l, int r, int idx, vector<int> &v ){\n if( l > r ) return INT_MIN;\n if( l == r ) return tree[idx] = v[l];\n int mid = l + ( r - l ) / 2;\n int left = build( l , mid, idx * 2, v );\n int right = build( mid + 1, r, idx * 2 + 1, v );\n return tree[idx] = max( left, right );\n }\n\n int query( int l, int r, int idx, int left_bound, int right_bound ){\n if( l > r ) return INT_MIN;\n if( right_bound < l || r < left_bound ) return INT_MIN;\n if( left_bound <= l && r <= right_bound ) return tree[idx];\n int mid = l + ( r - l ) / 2;\n int left = query( l, mid, idx * 2, left_bound, right_bound );\n int right = query( mid+1, r, idx * 2 + 1, left_bound, right_bound );\n return max( left, right );\n }\n\n };\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n dfs(root, 0);\n\n int n = flatten.size();\n map<int,int> nodeLoc;\n for( int i = 0; i < n; i++ ){\n nodeLoc[flatten[i]] = i;\n }\n\n SegmentTree tree = SegmentTree(n);\n tree.build(0, n-1, 1, flatten_depth);\n\n int m = queries.size();\n vector<int> ans(m);\n\n for( int i = 0; i < m; i++ ){\n int node = queries[i];\n int index = nodeLoc[node];\n auto childs = childCount[node];\n int left_bound = index - childs.first;\n int right_bound = index + childs.second;\n int left_val = tree.query( 0, n-1, 1, 0, left_bound-1 );\n int right_val = tree.query( 0, n-1, 1, right_bound+1, n-1 );\n int val = max( left_val, right_val );\n ans[i] = val;\n }\n\n return ans;\n\n }\n};\n```\n\n# Optimised by using prefix and suffix\n\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n vector<int> flatten, flattenDepth;\n map<int,pair<int,int>> childCount;\n\n int dfs( TreeNode* node, int depth ){\n if( node == NULL ) return 0;\n int left = dfs( node->left, depth + 1 );\n flatten.push_back(node->val);\n flattenDepth.push_back(depth);\n int right = dfs(node->right, depth + 1 );\n childCount[node->val] = {left, right};\n return left + right + 1;\n }\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n dfs(root, 0);\n\n int n = flatten.size();\n map<int,int> nodeLoc;\n for( int i = 0; i < n; i++ ){\n nodeLoc[flatten[i]] = i;\n }\n\n vector<int> left(n), right(n);\n int maxi = INT_MIN;\n for( int i = 0; i < n; i++ ) left[i] = (maxi = max( maxi, flattenDepth[i] ));\n maxi = INT_MIN;\n for( int i = n-1; i >= 0 ; i-- ) right[i] = (maxi = max( maxi, flattenDepth[i] ));\n\n int m = queries.size();\n vector<int> ans(m);\n\n for( int i = 0; i < m; i++ ){\n int node = queries[i];\n int index = nodeLoc[node];\n auto childs = childCount[node];\n int left_bound = index - childs.first;\n int right_bound = index + childs.second;\n int left_val = left_bound > 0 ? left[left_bound-1] : INT_MIN;\n int right_val = right_bound < n-1 ? right[right_bound+1] : INT_MIN ;\n int val = max( left_val, right_val );\n ans[i] = val;\n }\n\n return ans;\n\n }\n};\n```\n\n\n\n
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Simple DFS solution with Pre-calculation.
|
simple-dfs-solution-with-pre-calculation-ivg9
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
samiul_bu
|
NORMAL
|
2023-12-08T11:17:37.140683+00:00
|
2023-12-08T11:17:37.140726+00:00
| 410 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dp[100002];\n int ans[100002];\n int calculateDepth(TreeNode* root, int currentDepth) {\n if(root == nullptr) {\n return 0;\n }\n int left = calculateDepth(root->left, currentDepth+1);\n int right = calculateDepth(root->right, currentDepth+1);\n dp[root->val] = max(left, right);\n return dp[root->val] + 1;\n\n }\n void calculateAnswer(TreeNode* root, int maxOfPrev, int depthFormTop) {\n if(root == nullptr) {\n return;\n }\n int leftMax = root->left == nullptr ? 0 : dp[root->left->val] + 1;\n int rightMax = root->right == nullptr ? 0 : dp[root->right->val] + 1;\n ans[root->val] = maxOfPrev;\n calculateAnswer(root->left, max(maxOfPrev, rightMax + depthFormTop), depthFormTop + 1);\n calculateAnswer(root->right, max(maxOfPrev, leftMax + depthFormTop), depthFormTop + 1);\n return;\n\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));\n calculateDepth(root, 0);\n calculateAnswer(root, 0, 0);\n vector<int>fAns;\n for(int i=0;i<queries.size();i++) {\n fAns.push_back(ans[queries[i]]);\n }\n return fAns;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'C++']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Think from scratch to optimised solution ||c++
|
think-from-scratch-to-optimised-solution-vkkx
|
the first thing is it involves removal so segment tree can be implimented?\nbut the thing is if tree is branched it works well bcz updatation in segment tree co
|
demon_code
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-02T16:03:57.593389+00:00
|
2024-06-30T09:42:42.696983+00:00
| 1,350 | false |
the first thing is it involves removal so segment tree can be implimented?\nbut the thing is if tree is branched it works well bcz updatation in segment tree cost = hight of tree \nbut in worst case it may happen that tree is like a linkedlist so hight = no of nodes so it will fail for \nqueries of order of 10^4\n\n\nin segment tree we will use inorder indexing to figur out the node which need to removed is on the left or right side of current root it will help to get new hight in O(h) complexcity \n\n**Intutive but failed Approach \uD83D\uDE42**\n//using segment tree to find affected branch and then recalculate the hight \n``` complexcity for each query = O(h) ```\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n unordered_map<int,int> m;\n int t=0;\n unordered_map<TreeNode*,int> seg;\n int update(TreeNode* root, int tg) // tg here is index of root to be removed from inorder traversal\n {\n if(m[root->val]==tg) // node to be removed is found \n {\n // seg[idx]=0;\n return 0; // return 0 as this is removed so no contribution from this subtree\n }\n if(m[root->val]<tg)// if target node is on the right side\n {\n int r=update(root->right, tg); // we only need to check right side as left side is uneffected same for left side as well\n \n int l=0;\n if(root->left) l=seg[root->left];\n return max(l,r)+1;\n }\n else // if target node is on left side \n {\n\t\t \n int l=update(root->left,tg);\n int r=0;\n if(root->right) r=seg[root->right];\n return max(l,r)+1;\n }\n \n }\n\t\n int solve(TreeNode* root) // for inorder indexing and intialisation of segment tree\n {\n if(root==NULL) return 0;\n \n int l=solve(root->left);\n m[root->val] =t; t++;\n int r= solve(root->right);\n return seg[root]=max(l,r)+1;\n }\n \n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& q) \n {\n solve(root);\n vector<int> ans;\n for(auto i: q)\n {\n ans.push_back(update(root,m[i])-1);\n }\n return ans;\n \n }\n};\n```\n\n```\n37 / 40 test cases passed.\n```\n\n**Optimised approach** \n\nto get rid of this one sided branched tree which fails segment tree idea bcz the hight is same as no of nodes \nso now we can think some thing about in & out time\n\nany root node will have lesser in time and higher out time than any of it bellow child nodes till leaf node why? bcz u enter from root so let\'s say in time is t then u keep increment timer when u go for childs so when u go for left timer is t+1 and so on.... so ``` intime of root is always smaller than child ``` \n\nand similarly when u leave from child and go to parent u incrment timer so ``` parent node (root ) ``` will have always ``` more out time ``` than any of it ``` child node ```\n\nwe store all nodes on hight basis like level oreder traversal hight is 0 at root node and increses by +1 as we move down \nhere insted of storing nodes we store inout time of those nodes in sorted order \nso now if we need to remove any root we will take it\'s ``` intime and out time values ``` and apply a binary search on hight (it works bcz intime increases& out time decreases down the tree ) and we check is their any node at hight h such that ``` it\'s intime is less that root or out time more than this root ``` this means their is atlease one branch which is not a child branch of our root (which is going to be removed) has atleast a node on this hight ``` ( so our hight is ovisly >=h ) ``` so we can now go down or if their is no such node then we need to go up side using binary search method\n\n\n\n\n```\n\n\nusing pii = pair<int,int>;\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n // in out time pairs at particular depth\n vector<pii> g[100005];\n \n int in[100005];\n int out[100005];\n int timer = 0;\n \n // Max Depth Overall\n int mx;\n\n \n // Calculating in out times for each vertex\n // postorder assignment\n void dfs(TreeNode* root, int depth)\n {\n if(root == nullptr)return;\n \n in[root -> val] = timer++;\n\n dfs(root -> left,depth + 1);\n dfs(root -> right, depth + 1);\n\n out[root -> val] = timer++;\n\n g[depth].push_back({in[root -> val], out[root -> val]});\n mx = max(mx,depth);\n }\n\n // check for particular height\n int check(int mid, int src)\n {\n if(g[mid].size() == 0) return 0;\n\n // check if first vertex don\'t lie in subtree of src means this hight is safe and be counted\n if(g[mid][0].first < in[src] || g[mid][0].second > out[src]) return 1;\n\n // check if last vertex don\'t lies in subtree of src\n\t\t// Checking first and last is sufficient becase other middle vartices are in range of timings\n if(g[mid].back().first < in[src] || g[mid].back().second > out[src]) return 1;\n\n\n return 0;\n }\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n\n for(int i=0;i;i++)\n {\n if(g[i].size() == 0)break;\n g[i].clear();\n }\n\n // resetting \n timer = 0;\n mx = 0;\n dfs(root,0);\n \n \n vector<int> ans;\n\n for(int q:queries)\n {\n int lo = 0;\n int hi = mx;\n int h = 1;\n\n while(lo <= hi)\n {\n int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;\n\n if(check(mid,q))\n {\n h = mid;\n lo = mid + 1;\n }\n else\n {\n hi = mid - 1;\n }\n }\n\n ans.push_back(h);\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n
| 2 | 0 |
['C']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Python3 | 100% T | 85% S | O(N) Time and Space | Explained for Beginner Friendly
|
python3-100-t-85-s-on-time-and-space-exp-a3l1
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nWe can think of solving offline query. \nNot all nodes will affect the height of tree,
|
bajrangcomder
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-08T05:15:16.141754+00:00
|
2023-08-08T05:15:16.141773+00:00
| 472 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nWe can think of solving offline query. \nNot all nodes will affect the height of tree, only those node who are in path of maximum height will affect the height of tree\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nLet\'s say leaf node <code> X</code> is giving the longest height. Now let\'s say path from root to <code> X</code> is like n1 -> n2 -> n3 -> n4 -> <code> X</code>.\nSo removing only these node will alter your height. \nSo we start from root, check the level of left and right, and whichever is greater, removing that will affect the answer. Whichever is lower, removing that won\'t change our height. \nWe do recursively to all nodes. \n<code> curmx </code> is the current maximum height if we remove the curent node.\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(N)\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\nO(N)\n# Code\n```\n# Definition for a binary tree node.\n# class TreeNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.left = left\n# self.right = right\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], q : List[int]) -> List[int]:\n lvl = defaultdict(int)\n mx = 0\n def level(node):\n nonlocal mx\n if not node:\n return 0\n l = level(node.left)\n r = level(node.right)\n lvl[node.val] = max(l,r) +1\n mx = max(mx, lvl[node.val])\n return lvl[node.val]\n level(root)\n n = len(lvl) + 3\n ans = [mx-1 for i in range(n+1)]\n curmx = 0\n def helper(node, cur):\n if not node:\n return \n nonlocal curmx\n # print(node.val)\n l,r = 0,0\n if node.left:\n l = lvl[node.left.val] \n if node.right:\n r = lvl[node.right.val] \n if r > l:\n right = node.right.val\n curmx = max(curmx, cur + l)\n ans[right] = curmx\n helper(node.right, cur + 1)\n elif l > r:\n left = node.left.val\n curmx = max(curmx, cur + r)\n ans[left] = curmx\n helper(node.left, cur + 1)\n else:\n return\n helper(root, 0)\n return [ans[i] for i in q]\n\n \n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Appraoch:Usingdfs
|
appraochusingdfs-by-arunraghavssreeragam-hgpy
|
Intuition\nHere we can get the max height after remobing a node by storing the height and depth od each node in the tree and then using this info to \ncreate a
|
arunraghavssreeragam
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-25T11:48:54.439812+00:00
|
2023-07-25T11:48:54.439831+00:00
| 52 | false |
# Intuition\nHere we can get the max height after remobing a node by storing the height and depth od each node in the tree and then using this info to \ncreate a cousins map which basically takes current depth(level) as the key and the top 2 nodes with the maximum height in that level. The ideology ios that if we delete a node in a level, \n- The max path can be = height of Tree if the node deleted is not the node with maxHeight in that level\n- The max path can be = depth of current Level+ height of second best node\n- The max Path can be= depth of current level-1 if only one node in that level\nSo by this way we can get maxPath for each queries\n# Approach\n- in ```height_depthDFS``` we store the hight and depth of each node\n- first we calculate height of Tree ```height_depthDFS(root,0)```\n- Now we create and store the top2 nodes with maxHeight in each level\n - ```cousins[depth].push_back({heightNodes[node],node});```\n - We sort these in descending order\n - then remove nodes outside top3 in each iteration as they are not needed\n- Finally we consder 3 cases which i discussed above\n - ```if(cousins[depthQ].size()==1)```\n - ```else if(cousins[depthQ][0].second==q)```\n - ```else result.push_back(heightTree);```\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(N)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n unordered_map<int,int>depthNodes;\n unordered_map<int,int>heightNodes;\n int height_depthDFS(TreeNode*root,int level){\n if(!root) return-1;\n depthNodes[root->val]=level;\n heightNodes[root->val]=1+max(height_depthDFS(root->left,level+1),height_depthDFS(root->right,level+1));\n return heightNodes[root->val];\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n int heightTree=height_depthDFS(root,0);\n vector<int>result;\n unordered_map<int,vector<pair<int,int>>>cousins;\n for(auto&[node,depth]:depthNodes){\n cousins[depth].push_back({heightNodes[node],node});\n sort(cousins[depth].begin(),cousins[depth].end(),greater<pair<int,int>>());\n if(cousins[depth].size()>2) cousins[depth].pop_back();\n }\n for(auto&q:queries){\n int depthQ=depthNodes[q];\n if(cousins[depthQ].size()==1) result.push_back(depthQ-1);\n else if(cousins[depthQ][0].second==q) result.push_back(cousins[depthQ][1].first+depthQ);\n else result.push_back(heightTree);\n }\n return result;\n\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Euler Tour O(N)
|
euler-tour-on-by-jessup-1001
|
Intuition\nEuler Sandwich to Precompute the Maximum Tree Levels\n\n# Approach\nEuler Tour is a sandwich list of the root node of a tree surrounding the sub-node
|
jessup
|
NORMAL
|
2023-06-30T20:13:59.246836+00:00
|
2023-07-07T03:53:03.794660+00:00
| 352 | false |
# Intuition\nEuler Sandwich to Precompute the Maximum Tree Levels\n\n# Approach\nEuler Tour is a sandwich list of the root node of a tree surrounding the sub-nodes within that tree.\n\ntour: you first create a list of sandwiching Euler Tour list\nmap_indices: you map the indices of where the starting and ending indices are\nmap_prefix_suffix: you calculate the prefix and suffix maximum levels.\ngive_answer: easily computes the maximum level when the subtree is removed.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(N)\n\nCalculating the tour, indices, prefix, and suffix takes O(N). After that, each iteration of query takes O(1), a simple calculation based on indexing pre-computed numbers.\n\n\n# Code\n```\n# Definition for a binary tree node.\n# class TreeNode(object):\n# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.left = left\n# self.right = right\n\n# Map (list) node reference, height, other_node_height (if enone, -1)\n\ndef tour(euler_tour, node, level):\n """\n This function performs an Euler tour (DFS) on the tree.\n :param euler_tour: list that stores the tour (node value, level)\n :param node: current node being visited\n :param level: level of the current node\n :return: None\n """\n if not node:\n return\n\n euler_tour.append((node.val, level))\n tour(euler_tour, node.left, level + 1)\n tour(euler_tour, node.right, level + 1)\n euler_tour.append((node.val, level))\n\ndef map_indices(indices, euler_tour):\n """\n This function maps node values to their indices in the Euler tour.\n :param indices: dictionary that stores node values as keys and a list of indices as values\n :param euler_tour: list that stores the Euler tour (node value, level)\n :return: None\n """\n for i, item in enumerate(euler_tour):\n indices[item[0]] = indices.get(item[0], []) + [i]\n\ndef map_prefix_suffix(prefix_max, suffix_max, euler_tour):\n """\n This function creates prefix and suffix maximum arrays based on the levels in the Euler tour.\n :param prefix_max: list that stores the maximum level from the start to each index\n :param suffix_max: list that stores the maximum level from each index to the end\n :param euler_tour: list that stores the Euler tour (node value, level)\n :return: None\n """\n max_ind = len(euler_tour) - 1\n for i, (_, level) in enumerate(euler_tour):\n prefix_max[i] = max(prefix_max[i - 1], level)\n\n _, suffix_level = euler_tour[max_ind - i]\n suffix_max[max_ind - i] = max(suffix_max[max_ind - i + 1], suffix_level)\n\ndef give_answer(queries, indices, prefix_max, suffix_max):\n """\n This function calculates the answers for the queries.\n :param queries: list of queries (node values)\n :param indices: dictionary that maps node values to their indices in the Euler tour\n :param prefix_max: list that stores the maximum level from the start to each index\n :param suffix_max: list that stores the maximum level from each index to the end\n :return: list of answers for the queries\n """\n return_answer = []\n for query in queries:\n start, end = indices[query]\n # this includes possibility of list spillover\n return_answer += [max(prefix_max[start - 1], suffix_max[end + 1])]\n return return_answer\n\nclass Solution(object):\n def treeQueries(self, root, queries):\n """\n :type root: Optional[TreeNode]\n :type queries: List[int]\n :rtype: List[int]\n """\n euler_tour = []\n indices = {} \n \n tour(euler_tour, root, 0)\n\n map_indices(indices, euler_tour)\n\n prefix_max = [0 for i in range(len(euler_tour) + 1)]\n suffix_max = [0 for i in range(len(euler_tour) + 1)]\n\n map_prefix_suffix(prefix_max, suffix_max, euler_tour)\n\n return give_answer(queries, indices, prefix_max, suffix_max)\n\n\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python']
| 2 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Precompute height (level) & Depth for each node | Beats 83%
|
precompute-height-level-depth-for-each-n-8r40
|
\n# Definition for a binary tree node.\n# class TreeNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.lef
|
rktayal
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-21T04:28:11.081568+00:00
|
2023-01-21T04:28:11.081604+00:00
| 722 | false |
```\n# Definition for a binary tree node.\n# class TreeNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.left = left\n# self.right = right\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n """\n for every node, store the level and max depth of it\'s subtree\n for every level, store the highest and second highest depth\n """\n depth = {}\n level = {}\n max_depth_at_each_level = {}\n def compute(root, height):\n if not root:\n return 0\n level[root.val] = height\n left = compute(root.left, height+1)\n right = compute(root.right, height+1)\n depth[root.val] = max(left, right)\n return 1 + max(left, right)\n compute(root, 0)\n\n def compute_max_depth_at_each_level(root):\n que = deque([root])\n level = 0\n while len(que):\n for _ in range(len(que)):\n node = que.popleft()\n x = depth[node.val]\n if level in max_depth_at_each_level:\n max_depth_at_each_level[level].append(x)\n else:\n max_depth_at_each_level[level] = [x]\n if node.left:\n que.append(node.left)\n if node.right:\n que.append(node.right)\n max_depth_at_each_level[level].sort(reverse=True)\n level+=1\n compute_max_depth_at_each_level(root)\n\n ans = []\n for query in queries:\n del_lev = level[query]\n if len(max_depth_at_each_level[del_lev]) == 1:\n ans.append(del_lev-1)\n continue\n if depth[query] == max_depth_at_each_level[del_lev][0]:\n ans.append(del_lev + max_depth_at_each_level[del_lev][1])\n else:\n ans.append(del_lev + max_depth_at_each_level[del_lev][0])\n return ans\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Breadth-First Search', 'Python3']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
DMS two times
|
dms-two-times-by-hayglx-ydl7
|
Intuition\nsource:0x3f\n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n)\n Add your time complexity here,
|
hayglx
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-09T10:21:07.427957+00:00
|
2022-12-09T10:21:07.428000+00:00
| 89 | false |
# Intuition\nsource:0x3f\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * type TreeNode struct {\n * Val int\n * Left *TreeNode\n * Right *TreeNode\n * }\n */\nfunc treeQueries(root *TreeNode, queries []int) []int {\n height:=map[*TreeNode]int{}//tree node height\n var dfsheight func(*TreeNode)int\n dfsheight=func(node *TreeNode) int{\n if node==nil{\n return 0\n }\n height[node]=max(dfsheight(node.Left),dfsheight(node.Right))+1\n return height[node]\n }\n dfsheight(root)\n\n ans:=make([]int,len(height)+1)\n var dfs func(*TreeNode,int,int)\n dfs=func(node *TreeNode,deep,val int){\n if node==nil{\n return\n }\n deep+=1\n ans[node.Val]=val\n dfs(node.Left,deep,max(val,height[node.Right]+deep-1))\n dfs(node.Right,deep,max(val,height[node.Left]+deep-1))\n }\n dfs(root,0,0)\n\n for i,v := range(queries){\n queries[i]=ans[v]\n }\n return queries\n}\nfunc max(a,b int)int{if a>b {return a}; return b}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Go']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Simple Solution using DFS and Hashmap || C++ Fully Explained
|
simple-solution-using-dfs-and-hashmap-c-ptvx2
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nStore levels of nodes and height of its subtree \n# Approach\n Describe your approach t
|
rkkumar421
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-16T19:30:41.824513+00:00
|
2022-11-16T19:30:41.824536+00:00
| 1,308 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nStore levels of nodes and height of its subtree \n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int N; // total nodes\n vector<vector<int>> lv; // this will store level and it\'s maximum heights and only 2 of its point\n vector<int> nlv; // this will store value of nodes level \n vector<int> nheg; // this will store height of n node\n // this function will init all above vectors recursively\n int trverse(TreeNode* r,int l){\n if(r == NULL) return 0;\n // find N \n N = max(N,r->val);\n // nlv array will contain r->val level\n nlv[r->val] = l;\n // call for left and right\n int lt = trverse(r->left,l+1);\n int rt = trverse(r->right,l+1);\n // nheg will store height of nth node as root node\n nheg[r->val] = max(lt,rt);\n // push this node in this level\n lv[l].push_back(nheg[r->val]);\n if(lv[l].size() == 3){\n // find min and remove it\n int mi = min({lv[l][0],lv[l][1],lv[l][2]});\n if(lv[l][0] == mi) swap(lv[l][2],lv[l][0]);\n else if(lv[l][1] == mi) swap(lv[l][2],lv[l][1]);\n lv[l].pop_back();\n }\n return nheg[r->val] + 1;\n }\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n // initalizing size of vectors\n lv.resize(1e5);\n nheg.resize(1e5+1,0);\n nlv.resize(1e5+1,0);\n // we can store tree node with their value\n N = 0;\n nheg[0] = -1;\n trverse(root,0); // fill all vectors\n vector<int> t(N+1,0); // store values of height if every node is deleted one time\n vector<int> ans(queries.size(),0);\n for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){\n // try removing i\n // we are going to search that level\n if(nlv[i] == 0) continue; // if i is root node\n int new_maxh = -1; // we have to find new max height\n bool cnt = 1; // if we have same value for 2 time then avoid only one time\n // traverse level of i\'th node\n for(int j : lv[nlv[i]]){\n if(j == nheg[i] && cnt){ cnt = 0; continue;}\n new_maxh = max(new_maxh, j);\n }\n // if new max is -1 means no other node at this level so this means we can only have tree height \n // if we found another max then add that max height to this level\n t[i] = new_maxh == -1 ? nlv[i] - 1 : nlv[i] + new_maxh;\n }\n // Now just fill answer for queries\n for(int i=0;i<queries.size();i++){\n ans[i] = t[queries[i]];\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Depth-First Search', 'C++']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
C# || Solution
|
c-solution-by-vdmhunter-oxsi
|
\n# Code\n\npublic class Solution\n{\n private readonly int[] _seen = new int[100001];\n private int _maxHeight;\n\n public int[] TreeQueries(TreeNode
|
vdmhunter
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-09T00:15:48.609485+00:00
|
2022-11-09T00:15:48.609521+00:00
| 121 | false |
\n# Code\n```\npublic class Solution\n{\n private readonly int[] _seen = new int[100001];\n private int _maxHeight;\n\n public int[] TreeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries)\n {\n _maxHeight = 0;\n Dfs(root, 0);\n\n _maxHeight = 0;\n Dfs(root, 0);\n\n return queries.Select(q => _seen[q]).ToArray();\n }\n\n private void Dfs(TreeNode root, int h)\n {\n if (root == null)\n return;\n \n _seen[root.val] = Math.Max(_seen[root.val], _maxHeight);\n _maxHeight = Math.Max(_maxHeight, h);\n \n Dfs(root.left, h + 1);\n Dfs(root.right, h + 1);\n \n (root.right, root.left) = (root.left, root.right);\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Explaination With Dry Run C++ well commented code DFS+Hashmap
|
explaination-with-dry-run-c-well-comment-yn0f
|
Solution:\n1. For removing any node we need to keep track of height of CurrNode(Node that is supposed to be removed) and two max heights at same level of that n
|
sarthak_045
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-02T05:49:43.907709+00:00
|
2022-11-02T06:24:54.718353+00:00
| 321 | false |
Solution:\n1. For removing any node we need to keep track of height of CurrNode(Node that is supposed to be removed) and two max heights at same level of that node.\n\n2. Now there can be two cases\n\t1. \tCurrNode has the maxHeight at that level- removing currNode will affect the total height(Node is in the longest path to leaf i.e EULER TOUR). \n\t**ans[queries[i]]=totalHeight-Height(currNode)+Height(2nd max height at L)**.\n\t**if there is only one node at Level L then consider maxHeight at L-1.**\n\t\n\t2. \tSome other Node has maxheight- removing currNode will not affect the total height beacuse currNode is not in the euler tour(Longest path to leaf) **ans[queries[i]]=totalHeight**\n\n3.Now we need **height**(longest path from currNode to leaf) and **level**(depth from root node) of currNode.\n\n4.Also we need two values {maxHeight , 2nd maxHeight } at level L. (use minheap priority queue)\n5.we can compute above values using single DFS call\n6.one IMP thing to understand for beginner is top element of minheap will always be 2nd maxHeight we need to swap (a,b) where **a=maxheight and b=2nd MaxHeight**\n\n\n\n\n\n\n**Please Upvote if you like the solution**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n map<int,int>height;//node ->height\n map<int,int>depth;//node ->depth\n map<int,priority_queue <int, vector<int>, greater<int>> >twomax;//level-> <firstmax,secondmax (H)>\n\n int dfsHeightDepth(TreeNode* root,int level){\n\n if(!root) return -1;\n //recursive calls for calculating height for left and right subtree\n int lheight=dfsHeightDepth(root->left,level+1);\n int rheight=dfsHeightDepth(root->right,level+1);\n \n //store max heigit and depth(level) in map\n height[root->val]=max(lheight,rheight)+1;\n depth[root->val]=level;\n \n //maitain priority queue with only 2 elements in it top element will be Node with 2nd max height at perticular level\n //2nd node will be max height at peritcular level because it is minheap\n twomax[level].push(height[root->val]);\n //remove extra nodes from pq\n if(twomax[level].size()>2) twomax[level].pop();\n \n //return computed height\n return height[root->val];\n \n\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n \n //ans vector\n vector<int>ans(queries.size());\n \n //compute height and depth(level) of tree\n int h=dfsHeightDepth(root,0);//calculates height and depth of each node\n \n for(int i=0;i<queries.size();i++){\n //for each query Node calculate level and height\n int level=depth[queries[i]];\n int heightOfcurrentNode=height[queries[i]];\n \n int a=-1,b=-1;\n if(twomax[level].size()==2){\n //beacuse it is minheap top element will be smaller\n b=twomax[level].top();twomax[level].pop();\n a=twomax[level].top();twomax[level].pop();\n \n // if currentNode has maxheight then remove its height from total height and add height of 2nd Max Node to total height\n if(heightOfcurrentNode==a) ans[i]=h-(a-b); \n \n //if it is not maxheight node then it should not affect total height computation\n else ans[i]=h; \n \n //again add popped element back to priority queue\n twomax[level].push(b);\n twomax[level].push(a);\n }\n \n // if only one node present at that level subtract the heightOfcurrentNode and consider height of (level-1)th max height\n else ans[i]=h-heightOfcurrentNode-1;\n \n \n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n**Please Upvote if you like the solution**
| 2 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'C', 'Heap (Priority Queue)']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
[Python 3]Topological sort + Hashmap
|
python-3topological-sort-hashmap-by-ches-xmgd
|
```\n# Definition for a binary tree node.\n# class TreeNode:\n# def init(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.left
|
chestnut890123
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T14:38:37.798744+00:00
|
2022-10-30T14:39:03.385131+00:00
| 641 | false |
```\n# Definition for a binary tree node.\n# class TreeNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.left = left\n# self.right = right\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n par = {} # keep track of parent nodes\n height = {} # height for each node\n \n def dfs(node, level):\n if not node:\n return\n height[node.val] = level\n if node.left:\n par[node.left.val] = node.val\n dfs(node.left, level+1)\n if node.right:\n par[node.right.val] = node.val\n dfs(node.right, level+1)\n \n dfs(root, 0)\n \n # Topological sort\n deg = defaultdict(int)\n for k in par:\n deg[par[k]] += 1\n # starts from leaf nodes \n q = [k for k in height if not deg[k]]\n h = height.copy() # propagate depth to parent nodes\n \n while q:\n cur = q.pop()\n if cur not in par: continue\n p = par[cur]\n deg[p] -= 1\n h[p] = max(h[p], h[cur])\n if not deg[p]:\n q.append(p)\n \n # for each level, only store top 2 nodes with deepest path\n h_node = defaultdict(list)\n for k in height:\n heappush(h_node[height[k]], (h[k], k))\n if len(h_node[height[k]]) > 2:\n heappop(h_node[height[k]])\n \n \n ans = []\n for q in queries:\n # if current level only one node then whole level gone, the height will minus 1\n if len(h_node[height[q]]) == 1:\n ans.append(height[q] - 1)\n # if deleted node equals the node with deepest path at current level, then chose the second deepest\n elif q == h_node[height[q]][1][1]:\n ans.append(h_node[height[q]][0][0])\n # otherwise select the top one\n else:\n ans.append(h_node[height[q]][1][0])\n\n \n return ans
| 2 | 0 |
['Topological Sort', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Simple DFS Solution using TreeMap JAVA Code with Video Explanation in Hindi
|
simple-dfs-solution-using-treemap-java-c-pip8
|
Time Complexity :- O(n.log(n));\n\nExplanation :- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=doCIdDHxgbw\n\nJAVA Code :-\n\n\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n
|
VIVEK_8877
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T08:42:52.209064+00:00
|
2022-10-30T08:42:52.209092+00:00
| 1,065 | false |
**Time Complexity :- O(n.log(n));**\n\n**Explanation :-** https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=doCIdDHxgbw\n\n**JAVA Code :-**\n\n```\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode left;\n * TreeNode right;\n * TreeNode() {}\n * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {\n * this.val = val;\n * this.left = left;\n * this.right = right;\n * }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n // Time Complexity :- O(n.log(n));\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n int m = maximum_value(root);\n int[] depth = new int[m+1];\n int[] level = new int[m+1];\n \n dfs(root,0,depth,level);\n \n // level -> (depth -> frequency)\n TreeMap<Integer,TreeMap<Integer,Integer>> map = new TreeMap<>();\n for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) {\n int l = level[i];\n int v = i;\n TreeMap<Integer,Integer> m1;\n if(map.containsKey(l)) {\n m1 = map.get(l);\n if(m1.containsKey(depth[v])) {\n m1.put(depth[v],m1.get(depth[v])+1);\n } else {\n m1.put(depth[v],1);\n }\n } else {\n m1 = new TreeMap<>();\n m1.put(depth[v],1);\n }\n map.put(l,m1);\n }\n \n \n // System.out.println(map);\n for(int i=0;i<queries.length;i++) {\n int q = queries[i];\n int ans = level[q]-1;\n TreeMap<Integer,Integer> m1 = map.get(level[q]);\n \n if(m1.get(depth[q])==1) {\n m1.remove(depth[q]);\n } else {\n m1.put(depth[q],m1.get(depth[q])-1);\n }\n \n if(m1.size()>0) {\n ans+=m1.lastKey();\n }\n \n if(m1.containsKey(depth[q])) {\n m1.put(depth[q],m1.get(depth[q])+1);\n } else {\n m1.put(depth[q],1);\n }\n \n queries[i]=ans;\n }\n return queries;\n \n }\n \n public static int maximum_value(TreeNode root) {\n if(root==null) return 0;\n int a1 = maximum_value(root.left);\n int a2 = maximum_value(root.right);\n \n return Math.max(a1,Math.max(a2,root.val));\n }\n \n \n public static int dfs(TreeNode root,int lvl,int[] depth,int[] level) {\n if(root==null) {\n return 0;\n }\n \n \n level[root.val]=lvl;\n \n int a1 =dfs(root.left,lvl+1,depth,level);\n int a2 =dfs(root.right,lvl+1,depth,level);\n \n return depth[root.val]=Math.max(a1,a2)+1;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Breadth-First Search', 'Recursion', 'Java']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
DFS IN and OUT timers | Binary Search | C++ | Comments
|
dfs-in-and-out-timers-binary-search-c-co-05yp
|
```\nusing pii = pair;\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n // in out time pairs at particular depth\n vector g[100005];\n \n int in[100005];\n int out
|
dpw4112001
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T05:53:41.441400+00:00
|
2022-10-30T06:26:17.911704+00:00
| 1,071 | false |
```\nusing pii = pair<int,int>;\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n // in out time pairs at particular depth\n vector<pii> g[100005];\n \n int in[100005];\n int out[100005];\n int timer = 0;\n \n // Max Depth Overall\n int mx;\n\n \n // Calculating in out times for each vertex\n // postorder assignment\n void dfs(TreeNode* root, int depth)\n {\n if(root == nullptr)return;\n \n in[root -> val] = timer++;\n\n dfs(root -> left,depth + 1);\n dfs(root -> right, depth + 1);\n\n out[root -> val] = timer++;\n\n g[depth].push_back({in[root -> val], out[root -> val]});\n mx = max(mx,depth);\n }\n\n // check for particular height\n int check(int mid, int src)\n {\n if(g[mid].size() == 0) return 0;\n\n // check if first vertex don\'t lie in subtree of src\n if(!(g[mid][0].first >= in[src] && g[mid][0].second <= out[src])) return 1;\n\n // check if last vertex don\'t lies in subtree of src\n\t\t// Checking first and last is sufficient becase other middle vartices are in range of timings\n if(!(g[mid].back().first >= in[src] && g[mid].back().second <= out[src])) return 1;\n\n\n return 0;\n }\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n\n for(int i=0;i;i++)\n {\n if(g[i].size() == 0)break;\n g[i].clear();\n }\n\n // resetting \n timer = 0;\n mx = 0;\n dfs(root,0);\n \n \n vector<int> ans;\n\n for(int q:queries)\n {\n int lo = 0;\n int hi = mx;\n int h = 1;\n\n while(lo <= hi)\n {\n int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;\n\n if(check(mid,q))\n {\n h = mid;\n lo = mid + 1;\n }\n else\n {\n hi = mid - 1;\n }\n }\n\n ans.push_back(h);\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};
| 2 | 0 |
['Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Graph', 'Binary Tree']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
[java] Preorder + Level order to build look up cache
|
java-preorder-level-order-to-build-look-q676h
|
\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode left;\n * TreeNode right;\n * TreeNode() {}\n
|
liyun1988
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:04:59.014366+00:00
|
2022-10-30T04:14:59.115097+00:00
| 310 | false |
```\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode left;\n * TreeNode right;\n * TreeNode() {}\n * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {\n * this.val = val;\n * this.left = left;\n * this.right = right;\n * }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n HashMap<Integer, Integer> nodeToHeight = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();\n dfsPopulate(root, nodeToHeight);\n \n HashMap<Integer, Integer> nodeToLevel = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();\n // level to nodeIds sorted by subHeights\n HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>> levelToNodeIds = new HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>>();\n // populate those caches through level order traverse.\n int level = 0;\n Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();\n queue.offer(root);\n while(queue.size() > 0) {\n ++level;\n int size = queue.size();\n List<Integer> nodeIdsAtCurLevel = new ArrayList<Integer>();\n for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {\n TreeNode cur = queue.poll();\n if(cur.left != null) {\n nodeIdsAtCurLevel.add(cur.left.val);\n nodeToLevel.put(cur.left.val, level);\n queue.offer(cur.left);\n }\n if(cur.right != null) {\n nodeIdsAtCurLevel.add(cur.right.val);\n nodeToLevel.put(cur.right.val, level);\n queue.offer(cur.right);\n }\n }\n \n nodeIdsAtCurLevel = sort(nodeIdsAtCurLevel, nodeToHeight);\n levelToNodeIds.put(level, nodeIdsAtCurLevel);\n }\n \n int[] res = new int[queries.length];\n for(int i = 0; i < queries.length; ++i) {\n Integer curLevel = nodeToLevel.get(queries[i]);\n List<Integer> nodeIds = levelToNodeIds.get(curLevel);\n int additionalHeight = 0;\n for(Integer nodeId : nodeIds) {\n if(nodeId != queries[i]) {\n additionalHeight = nodeToHeight.get(nodeId);\n\t\t\t\t\t// no longer need to iterate all list since this is in revere order by sub-height.\n break;\n }\n }\n \n res[i] = additionalHeight + curLevel - 1;\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n \n private List<Integer> sort(List<Integer>nodeIdsAtCurLevel, HashMap<Integer, Integer>nodeToHeight) {\n Collections.sort(nodeIdsAtCurLevel, new Comparator<Integer>() {\n @Override\n public int compare(Integer i1, Integer i2) {\n return nodeToHeight.get(i2) - nodeToHeight.get(i1);\n }\n });\n \n return nodeIdsAtCurLevel;\n }\n \n \n \n private int dfsPopulate(TreeNode root, HashMap<Integer, Integer> nodeToHeight) {\n if(root == null) {\n return 0;\n }\n \n int left = dfsPopulate(root.left, nodeToHeight);\n int right = dfsPopulate(root.right, nodeToHeight);\n int height = 1 + Math.max(left, right);\n nodeToHeight.put(root.val, height);\n return height;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
C++|Maps|Set|Preorder Traversal
|
cmapssetpreorder-traversal-by-charitrame-j4fs
|
\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0)
|
charitramehlawat
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T04:00:55.939367+00:00
|
2022-10-30T04:00:55.939405+00:00
| 623 | false |
```\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n map<int,int>mp;\n map<int,int>height;\n map<int,set<pair<int,int>>>mp1;\n int check(TreeNode*root,int count)\n {\n if(!root)return 0;\n mp[root->val] = count;\n int a = check(root->left,count+1);\n int b = check(root->right,count+1);\n int c = 1+max(a,b);\n int d = count+max(a,b);// This is to find total height of tree because of this node\n height[root->val] = d;\n mp1[count].insert({d,root->val});\n return c;\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n mp.clear();\n mp1.clear();\n height.clear();\n check(root,0);\n vector<int>ans;\n for(auto x:queries)\n {\n int a = mp[x];\n if(mp1[a].size()>1)\n {\n int x1 = height[x];\n auto it = mp1[a].lower_bound({x1,-1});\n pair<int,int>p = *it;\n mp1[a].erase(it);\n auto y = *(mp1[a].rbegin());\n ans.push_back(y.first);\n mp1[a].insert(p);\n }\n else\n {\n ans.push_back(a-1);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C', 'Ordered Set']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
C++ | DFS + BFS | O(n)
|
c-dfs-bfs-on-by-kena7-32he
|
Code
|
kenA7
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-15T10:06:27.129394+00:00
|
2025-03-15T10:06:27.129394+00:00
| 21 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<int,int>height;
int dfs(TreeNode *root, int level)
{
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
int leftHeight=dfs(root->left, level+1);
int rightHeight=dfs(root->right, level+1);
int currMax=max(level, leftHeight);
currMax=max(currMax, rightHeight);
height[root->val]=currMax;
return currMax;
}
vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries)
{
dfs(root, 0);
unordered_map<int,int>heightAfterRemoval;
queue<TreeNode *>q;
int level=0;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int size=q.size(),levelMaxHeight=level-1, levelSecondMaxHeight=0;
vector<int>nodes;
while(size--)
{
TreeNode *node=q.front();
q.pop();
nodes.push_back(node->val);
if(height[node->val]>levelMaxHeight)
{
levelSecondMaxHeight=levelMaxHeight;
levelMaxHeight=height[node->val];
}
else if(height[node->val]>levelSecondMaxHeight)
levelSecondMaxHeight=height[node->val];
if(node->left)
q.push(node->left);
if(node->right)
q.push(node->right);
}
for(auto node:nodes)
{
if(height[node]!=levelMaxHeight)
heightAfterRemoval[node]=levelMaxHeight;
else
heightAfterRemoval[node]=levelSecondMaxHeight;
}
level++;
}
vector<int> res;
for(auto &q:queries)
res.push_back(heightAfterRemoval[q]);
return res;
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
C#
|
c-by-adchoudhary-rcqg
|
Code
|
adchoudhary
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-04T05:03:46.533713+00:00
|
2025-03-04T05:03:46.533713+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Code
```csharp []
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left;
* public TreeNode right;
* public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
private int[] depth = new int[100001];
private int[] levelArr = new int[100001];
private int[] max1 = new int[100001];
private int[] max2 = new int[100001];
private int Height(TreeNode root, int level)
{
if (root == null) return 0;
// Set the level and calculate depth for the current node
levelArr[root.val] = level;
depth[root.val] = 1 + Math.Max(Height(root.left, level + 1), Height(root.right, level + 1));
// Update the highest and second-highest depths for the current level
if (max1[level] < depth[root.val])
{
max2[level] = max1[level];
max1[level] = depth[root.val];
}
else if (max2[level] < depth[root.val])
{
max2[level] = depth[root.val];
}
return depth[root.val];
}
public int[] TreeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries)
{
// Compute depths and max depths for each level
Height(root, 0);
// Process each query
for (int i = 0; i < queries.Length; i++)
{
int q = queries[i];
int level = levelArr[q];
// Set result for each query based on max depths at the level
queries[i] = (max1[level] == depth[q] ? max2[level] : max1[level]) + level - 1;
}
return queries;
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
C++ || O(N) TC || O(N) SC
|
c-on-tc-on-sc-by-shikharsrivastava2002-p9l2
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
ShikharSrivastava2002
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-02T10:35:00.848914+00:00
|
2024-11-02T10:35:00.848952+00:00
| 21 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(N) where N = number of nodes\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(N) where N = number of nodes\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int computeHeight(TreeNode* root,int level,unordered_map<int,int> &nodeLevel,unordered_map<int,int> &nodeHeight,unordered_map<int,pair<int,int>> &top2height)\n {\n if(!root)\n {\n return 0;\n }\n int v1= computeHeight(root->left,level+1,nodeLevel,nodeHeight,top2height);\n int v2= computeHeight(root->right,level+1,nodeLevel,nodeHeight,top2height);\n nodeLevel[root->val]=level;\n int height= (v1>v2)?v1+1:v2+1;\n nodeHeight[root->val]=height;\n pair<int,int> temp= top2height[level];\n \n if(temp.first<height)\n {\n temp.second= temp.first;\n temp.first =height; \n }\n else\n if(temp.second<height)\n {\n temp.second = height;\n } \n top2height[level]= temp;\n return height;\n }\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n int n=queries.size();\n unordered_map<int,int> nodeLevel;\n unordered_map<int,int> nodeHeight;\n unordered_map<int,pair<int,int>> top2height;\n //preFillHeight(root,0,top2height);\n computeHeight(root,0,nodeLevel,nodeHeight,top2height);\n vector<int> ans(n,0);\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n int node=queries[i];\n int h=nodeHeight[node];\n int l =nodeLevel[node];\n auto x= top2height[l];\n if(h == x.first)\n {\n ans[i]= l+x.second-1;\n \n }\n else\n {\n ans[i]= l+x.first-1; \n }\n }\n return ans;\n\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Simple Approach | Without tree flattening
|
simple-approach-without-tree-flattening-r34xs
|
Intuition\nThink in terms of levels - what could be done if we remove a particular subtree?\n\n# Approach\n1. We can precompute the heights of each subtree root
|
shruti066
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T20:39:19.119229+00:00
|
2024-10-26T20:39:19.119257+00:00
| 20 | false |
# Intuition\nThink in terms of levels - what could be done if we remove a particular subtree?\n\n# Approach\n1. We can precompute the heights of each subtree rooted at every node and store them in a vector or array, where the ith element represents the height of the subtree rooted at the ith node.\n \n2. Maintain a map of vectors to store nodes present at each level, where each level contains a vector of nodes present in that level.\n\n3. Create a map that associates each node with its level, allowing easy lookup of the level for any given node.\n\n4. a. If any node at a specific level has a subtree height greater than the subtree height of the given node, the height of the entire tree remains unchanged.\n\n b. If the given node has the maximum subtree height at that level, find the second highest subtree height in that level. Subtract the difference between these heights from the original tree height to get the updated height.\n\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n unordered_map<int,vector<int>>m; // level , node values\n unordered_map<int,int>levelMap; // value , level\n vector<int>h;\n int heightOfSubTree(TreeNode*root,int level){\n if(root==NULL)return 0;\n\n int l=0,r=0;\n l=heightOfSubTree(root->left,level+1);\n r=heightOfSubTree(root->right,level+1);\n\n m[level].push_back(root->val);\n levelMap[root->val]=level;\n h[root->val]=max(l,r)+1;\n\n return h[root->val];\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& q) {\n h.assign(1e5+1,0); // height of sub tree\n\n heightOfSubTree(root,0);\n\n vector<int>ans;\n\n for(int i=0;i<q.size();i++){\n int val=q[i];\n int l=levelMap[val];\n int mini=h[val];\n for(int i=0;i<m[l].size();i++){\n if(val!=m[l][i]){\n if(h[m[l][i]]>=h[val]){\n mini=0;\n break;\n }\n else mini=min(mini,h[val]-h[m[l][i]]);\n }\n }\n ans.push_back(h[root->val]-1-mini);\n }\n\n return ans;\n\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Python. beats 95%. DFS bases solution
|
python-beats-95-dfs-bases-solution-by-de-x9sm
|
Intuition\nThe key is to Group nodes per level.\nfor instance we have nodes [3, 5, 6 ] on level 3.\nqeustion if we cut node = 3. We need extra piece of informa
|
dev_lvl_80
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T19:27:19.699428+00:00
|
2024-10-26T19:29:52.221522+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\nThe key is to Group nodes per level.\nfor instance we have nodes [3, 5, 6 ] on level 3.\nqeustion if we cut node = 3. We need extra piece of information here to answer what would be tree height after. That info is depth of being cut children.\nSo the sctructure of information stored along node is maximum depth.\nAs result we might have on level such dataset [ [3,10], [5,11], [6,7]]\nHaving said that if we still want to cut node=3, tree height will remain 11. and so on\n\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nDFS - O(N)\nAnswering Queries O(N)\nSorting - O(NLogN)\n\nSo solution has time complexity O(NlogN)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(N)\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\n# Definition for a binary tree node.\n# class TreeNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.left = left\n# self.right = right\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n # mapping level: List[nodes]\n nodes_on_level = {}\n # node 2 level mapping as val:level\n n2l = {}\n\n # traverse tree to identify\n # - level of each node\n # - group nodes on the same level\n def dfs(node, lvl):\n if not node:\n return lvl-1\n \n n2l[node.val]=lvl # we need to know level of each node for fast lookup\n max_depth_of_children = max(dfs(node.left, lvl+1), dfs(node.right, lvl+1)) \n if not lvl in nodes_on_level:\n nodes_on_level[lvl] = {}\n nodes_on_level[lvl][node.val]=max_depth_of_children\n \n return max_depth_of_children\n \n dfs(root,1)\n\n # sort all this crazieness\n for lvl in nodes_on_level.keys():\n nodes_on_level[lvl] = sorted(nodes_on_level[lvl].items(), key = lambda x:x[1]) # sort by depth\n \n ret = []\n # answer queries\n for q in queries: \n on_level = nodes_on_level[n2l[q]]\n if on_level[-1][0] == q: # we cut most deepest branch\n if len(on_level) == 1:\n ret.append(n2l[q]-2)\n else:\n ret.append(on_level[-2][1] -1)\n else:\n ret.append(on_level[-1][1] -1)\n\n return ret\n \n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
✅ Explained step by step easy to understand | 8 ms Beats 99.79% ✨
|
explained-step-by-step-easy-to-understan-z5ag
|
Intuition\nThe problem revolves around finding the height of subtrees after removing a specified node. Observing that the subtree height heavily depends on the
|
Ansh_811
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T18:55:02.724999+00:00
|
2024-10-26T18:55:02.725023+00:00
| 15 | false |
# Intuition\nThe problem revolves around finding the height of subtrees after removing a specified node. Observing that the subtree height heavily depends on the tree\'s structure and levels, we can preprocess the tree to store the height of each node. This allows us to quickly compute the new height when a node is removed. Additionally, by maintaining the highest and second-highest subtree heights at each level, we can efficiently handle the height adjustments when a particular node is removed.\n\n\n\n\n# Approach\n1. **Preprocessing Heights:**\n - We define arrays height, maxHt, and secondMaxHt to keep track of the height of each node and the two highest heights at each level of the tree.\n - Using DFS, traverse the tree to calculate the height of each node and store it in the height array.\n2. **Track Maximum Heights:**\n - While traversing, update maxHt and secondMaxHt at each level based on the node\'s height. This helps us quickly determine the new height of the tree if the current node is removed.\n\n3. **Query Processing:**\n - For each query, get the level of the queried node.\n - Calculate the new height by using either maxHt or secondMaxHt based on whether the queried node\'s height matches the maximum height at that level.\n\n4. **Return Results:**\n - Update each query with the computed result and return the modified query list.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(N+Q)\n - Where N is the number of nodes in the tree, as we traverse it once to compute heights.\n - Q is the number of queries, each processed in constant time.\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(N)\n - Due to the storage arrays for heights, levels, and max heights.\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int level[100001];\n int height[100001];\n int maxHt[100001];\n int secondMaxHt[100001];\n\n int findHeight(TreeNode* root, int lvl)\n {\n if(root == NULL) return 0;\n\n level[root->val] = lvl;\n height[root->val] = max(findHeight(root->left, lvl+1), findHeight(root->right, lvl+1)) + 1;\n if(maxHt[lvl] < height[root->val])\n {\n secondMaxHt[lvl] = maxHt[lvl];\n maxHt[lvl] = height[root->val];\n }\n else if(secondMaxHt[lvl] < height[root->val])\n {\n secondMaxHt[lvl] = height[root->val];\n }\n\n return height[root->val];\n }\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n findHeight(root, 0);\n // vector<int> result;\n\n for(int i=0; i<queries.size(); i++)\n {\n int temp = queries[i];\n int L = level[temp];\n int tempRes = L + (maxHt[L] == height[temp] ? secondMaxHt[L] : maxHt[L]) - 1;\n\n queries[i] = tempRes;\n }\n\n return queries;\n }\n};\n```\n``` java []\nclass Solution {\n int[] level = new int[100001];\n int[] height = new int[100001];\n int[] maxHt = new int[100001];\n int[] secondMaxHt = new int[100001];\n\n public int findHeight(TreeNode root, int lvl) {\n if (root == null) return 0;\n\n level[root.val] = lvl;\n height[root.val] = Math.max(findHeight(root.left, lvl + 1), findHeight(root.right, lvl + 1)) + 1;\n\n if (maxHt[lvl] < height[root.val]) {\n secondMaxHt[lvl] = maxHt[lvl];\n maxHt[lvl] = height[root.val];\n } else if (secondMaxHt[lvl] < height[root.val]) {\n secondMaxHt[lvl] = height[root.val];\n }\n\n return height[root.val];\n }\n\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n findHeight(root, 0);\n\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {\n int temp = queries[i];\n int L = level[temp];\n int tempRes = L + (maxHt[L] == height[temp] ? secondMaxHt[L] : maxHt[L]) - 1;\n\n queries[i] = tempRes;\n }\n\n return queries;\n }\n}\n```\n\n
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Binary Tree', 'C++', 'Java']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Best Solution completely intuition based: C++, Java and Python Solutions
|
best-solution-completely-intuition-based-xto3
|
Intuition\nTo solve this problem, we need to determine the height of the binary tree after a node and its subtree are removed. When a node is removed, there are
|
nikhil_kumar_1
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T17:47:35.271447+00:00
|
2024-10-26T17:57:25.185258+00:00
| 62 | false |
# Intuition\nTo solve this problem, we need to determine the height of the binary tree after a node and its subtree are removed. When a node is removed, there are two possibilities:\n1. **The node is not the tallest in its level:** If the removed node does not contribute to the current maximum height at its level, then the height remains unchanged.\n2. **The node is the tallest in its level:** If the removed node contributes to the maximum height at its level, we need to update the height using the second-tallest node\'s height at the same level.\n\n# Approach\n1. **Tree Traversal for Height Calculation:**\n - Perform a depth-first search (DFS) to compute the height of each node and store this information in a `level` array, where each entry holds the level and height of the node.\n - While traversing, update the maximum and second-maximum heights at each level using a `maxHeights` array.\n\n2. **Processing Queries:**\n - For each query, check the node\u2019s height and its level.\n - If the queried node determines the current maximum height, use the second-highest height at that level as the new maximum height after removal; otherwise, use the original maximum.\n - Compute the tree height based on the updated maximum height at the level.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n + q)$$, where $$n$$ is the number of nodes in the tree, and $$q$$ is the number of queries. We traverse the tree once for height calculation and then process each query.\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$ for storing the level and height information.\n\n# Code\n\n## C++\n\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\n int getHeight(TreeNode* root, int lev, vector<pair<int, int>>& level, vector<pair<int, int>>& maxHeights) {\n if (root == nullptr) return 0;\n int left = getHeight(root->left, lev + 1, level, maxHeights);\n int right = getHeight(root->right, lev + 1, level, maxHeights);\n int currentHeight = max(left, right) + 1;\n \n level[root->val] = {lev, currentHeight};\n \n auto& [firstMax, secondMax] = maxHeights[lev];\n if (currentHeight > firstMax) {\n secondMax = firstMax;\n firstMax = currentHeight;\n } else if (currentHeight >= secondMax) {\n secondMax = currentHeight;\n }\n \n return currentHeight;\n }\n\npublic:\n Solution() {\n std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);\n std::cin.tie(NULL);\n std::cout.tie(NULL);\n }\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n const int MAX_LEVEL = 1e5 + 7;\n vector<pair<int, int>> level(MAX_LEVEL);\n vector<pair<int, int>> maxHeights(MAX_LEVEL, {0, 0});\n int maxH = getHeight(root, 0, level, maxHeights);\n vector<int> ans;\n for (auto& it : queries) {\n int nodeHeight = level[it].second;\n int i = level[it].first;\n auto& [firstMax, secondMax] = maxHeights[i];\n int maxOtherHeight = (nodeHeight == firstMax && firstMax == secondMax) ? firstMax : \n (nodeHeight == firstMax ? secondMax : firstMax);\n \n ans.push_back(i + maxOtherHeight - 1);\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n## Java\n\n```java []\n\nclass Solution {\n private int getHeight(TreeNode root, int lev, Map<Integer, int[]> level, Map<Integer, int[]> maxHeights) {\n if (root == null) return 0;\n int left = getHeight(root.left, lev + 1, level, maxHeights);\n int right = getHeight(root.right, lev + 1, level, maxHeights);\n int currentHeight = Math.max(left, right) + 1;\n \n level.put(root.val, new int[]{lev, currentHeight});\n \n int[] heights = maxHeights.getOrDefault(lev, new int[]{0, 0});\n int firstMax = heights[0], secondMax = heights[1];\n if (currentHeight > firstMax) {\n secondMax = firstMax;\n firstMax = currentHeight;\n } else if (currentHeight >= secondMax) {\n secondMax = currentHeight;\n }\n \n maxHeights.put(lev, new int[]{firstMax, secondMax});\n return currentHeight;\n }\n\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n final int MAX_LEVEL = 100007;\n Map<Integer, int[]> level = new HashMap<>();\n Map<Integer, int[]> maxHeights = new HashMap<>();\n getHeight(root, 0, level, maxHeights);\n \n int[] ans = new int[queries.length];\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {\n int nodeHeight = level.get(queries[i])[1];\n int lev = level.get(queries[i])[0];\n int[] heights = maxHeights.get(lev);\n int firstMax = heights[0], secondMax = heights[1];\n int maxOtherHeight = nodeHeight == firstMax ? secondMax : firstMax;\n \n ans[i] = lev + maxOtherHeight - 1;\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n}\n\n```\n\n## Python\n\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def __init__(self):\n import sys\n sys.setrecursionlimit(10**6)\n\n def getHeight(self, root, lev, level, maxHeights):\n if root is None:\n return 0\n left = self.getHeight(root.left, lev + 1, level, maxHeights)\n right = self.getHeight(root.right, lev + 1, level, maxHeights)\n currentHeight = max(left, right) + 1\n \n level[root.val] = (lev, currentHeight)\n \n firstMax, secondMax = maxHeights[lev]\n if currentHeight > firstMax:\n secondMax = firstMax\n firstMax = currentHeight\n elif currentHeight >= secondMax:\n secondMax = currentHeight\n \n maxHeights[lev] = (firstMax, secondMax)\n return currentHeight\n\n def treeQueries(self, root, queries):\n MAX_LEVEL = 10**5 + 7\n level = [None] * MAX_LEVEL\n maxHeights = [(0, 0)] * MAX_LEVEL\n self.getHeight(root, 0, level, maxHeights)\n \n ans = []\n for node in queries:\n nodeHeight = level[node][1]\n i = level[node][0]\n firstMax, secondMax = maxHeights[i]\n maxOtherHeight = firstMax if nodeHeight != firstMax else secondMax\n ans.append(i + maxOtherHeight - 1)\n \n return ans\n\n```\n
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Python3
|
python3-by-toniliu672-thqr
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
toniliu672
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T17:42:07.108075+00:00
|
2024-10-26T17:42:07.108101+00:00
| 51 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\n# Definition for a binary tree node.\n# Uncomment and use the following if needed for testing.\n# class TreeNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.left = left\n# self.right = right\n\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[\'TreeNode\'], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n depth = {}\n height = {}\n nodes = {}\n\n\n def dfs(node, d):\n if not node:\n return -1\n depth[node.val] = d\n nodes[node.val] = node\n left_height = dfs(node.left, d + 1)\n right_height = dfs(node.right, d + 1)\n h = max(left_height, right_height) + 1\n height[node.val] = h\n return h\n\n dfs(root, 0)\n\n\n depth_to_heights = defaultdict(list)\n\n\n for node_val, d in depth.items():\n h = height[node_val]\n depth_to_heights[d].append((h, node_val))\n\n max_total_height = max(depth.values())\n\n\n for d in depth_to_heights:\n depth_to_heights[d].sort(reverse=True)\n\n res = []\n for q in queries:\n q_depth = depth[q]\n heights_nodes = depth_to_heights[q_depth]\n if heights_nodes[0][1] != q:\n\n new_height = max_total_height\n else:\n if len(heights_nodes) > 1:\n\n second_height = heights_nodes[1][0]\n new_height = second_height + q_depth\n else:\n new_height = q_depth - 1\n res.append(new_height)\n return res\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
easy to understand, beats 95% in Python3
|
easy-to-understand-beats-95-in-python3-b-axxb
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
lehaulm007
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T16:50:20.706474+00:00
|
2024-10-26T16:50:20.706497+00:00
| 30 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\n# Definition for a binary tree node.\n# class TreeNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.left = left\n# self.right = right\nclass Solution:\n def treeQueries(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n n = len(queries)\n ans = [-1 for _ in range(n)] \n \n mp = {}\n for i, query in enumerate(queries):\n if query not in mp:\n mp[query] = [i]\n else:\n mp[query].append(i)\n \n max_depth = [-1]\n def travelLeft(root: Optional[TreeNode], lv: int):\n if not root:\n max_depth[0] = max(max_depth[0], lv - 1)\n return\n \n if root.val in mp:\n for i in mp[root.val]:\n ans[i] = max(ans[i], max_depth[0])\n \n travelLeft(root.left, lv + 1)\n travelLeft(root.right, lv + 1) \n \n def travelRight(root: Optional[TreeNode], lv: int):\n if not root:\n max_depth[0] = max(max_depth[0], lv - 1)\n return\n \n if root.val in mp:\n for i in mp[root.val]:\n ans[i] = max(ans[i], max_depth[0])\n \n travelRight(root.right, lv + 1)\n travelRight(root.left, lv + 1)\n \n travelLeft(root, 0)\n max_depth[0] = -1 \n travelRight(root, 0)\n\n for i in range(n):\n if ans[i] == -1:\n ans[i] = max_depth[0]\n\n return ans\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Tree', 'Python3']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Beats 99.79% | 3 Code
|
beats-9979-3-code-by-b_i_t-yoqj
|
\n# Solution - 1 (TLE)\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n int getDepth(TreeNode * & root,int & nodeForRemove){\n if(nodeForRemove==root->val) retur
|
B_I_T
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T16:47:58.544769+00:00
|
2024-10-26T16:47:58.544793+00:00
| 20 | false |
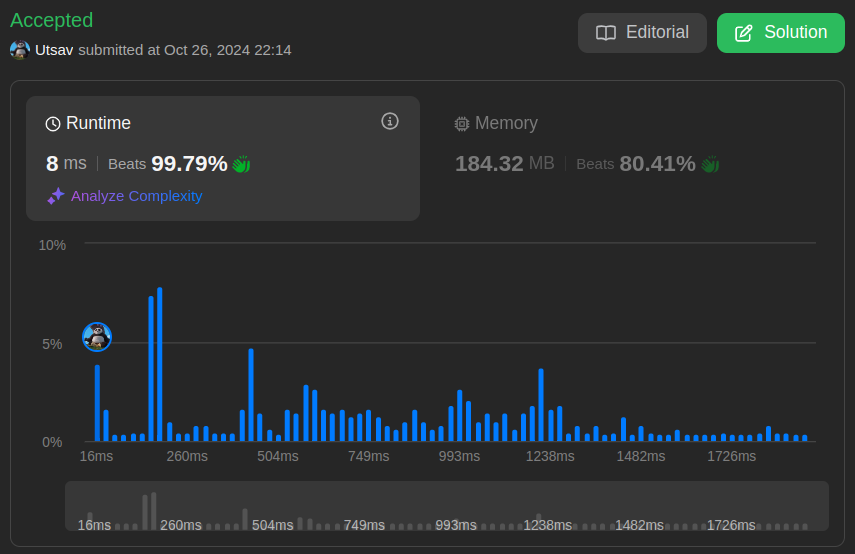\n# Solution - 1 (TLE)\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n int getDepth(TreeNode * & root,int & nodeForRemove){\n if(nodeForRemove==root->val) return 0;\n int depth=0;\n queue<pair<TreeNode*,int>> q;\n q.push({root,0});\n while(!q.empty()){\n TreeNode * node = q.front().first;\n int currDepth = q.front().second;\n q.pop();\n\n depth = max(depth,currDepth);\n\n if(node->left && node->left->val != nodeForRemove){\n q.push({node->left,currDepth+1});\n } \n if(node->right && node->right->val != nodeForRemove){\n q.push({node->right,currDepth+1});\n } \n }\n return depth;\n }\npublic:\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n vector<int> res;\n for(int & q : queries){\n res.push_back(getDepth(root,q));\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```\n# Solution - 2 (Runtime 1671ms)\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n vector<unordered_map<int,int>> levelOf;\n unordered_map<int,int> depthOf;\n\n int getDepth(TreeNode * root,int depth){\n if(!root) return 0;\n \n // store maximum depth in maxDepth\n int maxDepth = depth;\n\n // store depth value wise \n depthOf[root->val] = depth;\n\n // increase size\n if(levelOf.size() < depth+1){\n levelOf.push_back(unordered_map<int,int>());\n }\n\n maxDepth = max(maxDepth,getDepth(root->left,depth+1));\n maxDepth = max(maxDepth,getDepth(root->right,depth+1));\n\n // store maximum depth\n levelOf[depth][root->val] = maxDepth;\n\n return maxDepth;\n }\npublic:\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n // clear old data\n levelOf.clear();\n depthOf = unordered_map<int,int>();\n\n // perform dfs\n getDepth(root,0);\n\n // store depth in res\n vector<int> res;\n int depth,maxDepth;\n\n for(int q : queries){\n depth = depthOf[q];\n maxDepth = max(0,depth-1);\n // check all the nodes on that level \n for(const auto & [node,nodeMaxDepth] : levelOf[depth]){\n if(node == q) continue;\n if(maxDepth == levelOf.size()-1) break;\n maxDepth = max(maxDepth,nodeMaxDepth);\n }\n\n res.push_back(maxDepth);\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```\n# Solution - 3 (Runtime - 8 ms)\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n int depthAfterRemoveOf[100001],maxDepth=0;\n\n void dfsFromLeft(TreeNode * root,int currDepth){\n if(!root) return ;\n \n depthAfterRemoveOf[root->val] = maxDepth;\n\n maxDepth = max(maxDepth,currDepth);\n\n dfsFromLeft(root->left,currDepth+1);\n dfsFromLeft(root->right,currDepth+1);\n }\n void dfsFromRight(TreeNode * root,int currDepth){\n if(!root) return ;\n \n depthAfterRemoveOf[root->val] = max(depthAfterRemoveOf[root->val],maxDepth);\n\n maxDepth = max(maxDepth,currDepth);\n\n dfsFromRight(root->right,currDepth+1);\n dfsFromRight(root->left,currDepth+1);\n }\npublic:\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n dfsFromLeft(root,0);\n maxDepth = 0;\n dfsFromRight(root,0);\n \n // store depth in res\n vector<int> res;\n\n for(int q : queries){\n res.push_back(depthAfterRemoveOf[q]);\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```\n\n
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Breadth-First Search', 'Binary Tree', 'C++']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
very easy code using reccursion concept
|
very-easy-code-using-reccursion-concept-bj2nj
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
__agrim__chauhan__
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T16:40:13.332839+00:00
|
2024-10-26T16:40:13.332861+00:00
| 104 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int max_height_after_removal[100001];\n int current_max_height = 0;\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n traverse_left_to_right(root, 0);\n current_max_height = 0;\n traverse_right_to_left(root, 0);\n\n vector<int> query_results(queries.size());\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.size(); i++) \n query_results[i] = max_height_after_removal[queries[i]];\n\n return query_results;\n }\n\nprivate:\n void traverse_left_to_right(TreeNode* node, int height) {\n if (node == nullptr) return;\n\n max_height_after_removal[node->val] = current_max_height;\n current_max_height = max(current_max_height, height);\n\n traverse_left_to_right(node->left, height + 1);\n traverse_left_to_right(node->right, height + 1);\n }\n\n void traverse_right_to_left(TreeNode* node, int height) {\n if (node == nullptr) return;\n\n max_height_after_removal[node->val] = max(max_height_after_removal[node->val], current_max_height);\n current_max_height = max(current_max_height, height);\n\n traverse_right_to_left(node->right, height + 1);\n traverse_right_to_left(node->left, height + 1);\n }\n};\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Java
|
java-by-siyadhri-3lan
|
\n\n# Code\njava []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode left;\n * TreeNode right;\n * TreeNode() {
|
siyadhri
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T15:06:52.236158+00:00
|
2024-10-26T15:06:52.236180+00:00
| 11 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode left;\n * TreeNode right;\n * TreeNode() {}\n * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {\n * this.val = val;\n * this.left = left;\n * this.right = right;\n * }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n int[] po = new int[100001];\n int[] po_ = new int[100001];\n int maxH = 0;\n\n private void preOrder(TreeNode root, int height) {\n // edge\n if (root == null) {\n return;\n }\n\n po[root.val] = maxH;\n maxH = Math.max(maxH, height);\n preOrder(root.left, height + 1);\n preOrder(root.right, height + 1);\n }\n\n private void postOrder(TreeNode root, int height) {\n // edge\n if (root == null) {\n return;\n }\n\n po_[root.val] = maxH;\n maxH = Math.max(maxH, height);\n postOrder(root.right, height + 1);\n postOrder(root.left, height + 1);\n }\n\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n preOrder(root, 0);\n maxH = 0;\n postOrder(root, 0);\n\n int[] res = new int[queries.length];\n for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {\n res[i] = Math.max(po[queries[i]], po_[queries[i]]);\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Efficiently Calculating Tree Heights with Node Exclusions in a Binary Tree
|
efficiently-calculating-tree-heights-wit-mwpm
|
Intuition\nThe task involves calculating the height of subtrees in a binary tree and determining the height of the tree if certain nodes are excluded. The idea
|
amanbisht_359
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T14:12:52.388739+00:00
|
2024-10-26T14:12:52.388765+00:00
| 71 | false |
# Intuition\nThe task involves calculating the height of subtrees in a binary tree and determining the height of the tree if certain nodes are excluded. The idea is to calculate the height of each subtree rooted at each node first, then find a way to compute the height of the tree if specific nodes are omitted. This approach allows us to answer queries efficiently.\n\n# Approach\n1. Calculate Subtree Heights: Use a recursive function to calculate the height of each subtree, storing results in each_subtree_height.\n\n2. Calculate Height Excluding Nodes: Traverse each level and, for each node, use the subtree height data to determine the height of the tree when this node is excluded. Store results in height_excluding_node.\n\n3. Answer Queries: For each query, use height_excluding_node to get the tree height when a specified node is excluded.\n\n# Complexity\n- ***Time complexity: O(n log n + m)***\n\n1. Calculating subtree heights: O(n).\n2. Calculating height excluding nodes: O(n log n) (due to the use of a priority queue for each level)\n3. Answering queries: O(m) m, where is the number of queries\n\n- **Space complexity: O(n)** for storing heights and intermediate results.\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}\n * };\n */\n\n// This solution efficiently handles each query by precomputing and storing relevant heights, making each query \uD835\uDC42(1) to access. \n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int calculate_each_subtrees_height(TreeNode* root, unordered_map<TreeNode*, int> &each_subtree_height){\n if(root == nullptr){\n return 0;\n }\n\n int left_subtree_height = calculate_each_subtrees_height(root->left, each_subtree_height);\n int right_subtree_height = calculate_each_subtrees_height(root->right, each_subtree_height);\n\n each_subtree_height[root] = 1 + max(left_subtree_height, right_subtree_height);\n\n return each_subtree_height[root];\n }\n\n void calculate_height_exclu_node( TreeNode* root, unordered_map<TreeNode*, int> each_subtree_height, unordered_map<int, int> &height_excluding_node){\n queue<TreeNode*> q;\n q.push(root);\n\n int height = 0;\n\n while(!q.empty()){\n int n = q.size();\n \n priority_queue<pair<int, int>> pq;\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++){\n TreeNode* node = q.front();\n q.pop();\n\n pq.push({each_subtree_height[node], node->val});\n if(node->left){\n q.push(node->left);\n }\n\n if(node->right){\n q.push(node->right);\n }\n }\n\n pair<int, int> ele = pq.top();\n pq.pop();\n\n height_excluding_node[ele.second] = height + (pq.empty() ? 0 : pq.top().first);\n\n while(!pq.empty()){\n int a = pq.top().second;\n height_excluding_node[a] = height + ele.first;\n pq.pop();\n }\n\n height++;\n\n }\n\n\n return;\n\n }\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n \n unordered_map<TreeNode*, int> each_subtree_height;\n\n calculate_each_subtrees_height(root, each_subtree_height);\n\n unordered_map<int, int> height_excluding_node;\n\n calculate_height_exclu_node(root, each_subtree_height, height_excluding_node);\n\n\n int m = queries.size();\n vector<int> ans(m, 0);\n\n for(int i=0; i<m; i++){\n ans[i] = height_excluding_node[queries[i]] - 1;\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Depth-First Search', 'Breadth-First Search', 'Heap (Priority Queue)', 'Binary Tree', 'C++']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Easy solution beats 100%
|
easy-solution-beats-100-by-anonymous6996-1usx
|
\n\n# Code\njavascript []\n\nvar treeQueries = function(root, queries) {\n const heights = new Array(50000).fill(0);\n const d = new Array(100001).fill(0)
|
Anonymous6996
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T13:34:59.777582+00:00
|
2024-10-26T13:34:59.777611+00:00
| 27 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\n\nvar treeQueries = function(root, queries) {\n const heights = new Array(50000).fill(0);\n const d = new Array(100001).fill(0);\n const l = new Array(100001).fill(0);\n const r = new Array(100001).fill(0);\n let len = 0;\n\n function search(p, h) {\n d[p.val] = h;\n\n if (!p.left && !p.right) {\n heights[len] = h;\n l[p.val] = r[p.val] = len;\n len++;\n return;\n }\n\n l[p.val] = len;\n\n if (p.left) search(p.left, h + 1);\n if (p.right) search(p.right, h + 1);\n\n r[p.val] = len - 1;\n }\n\n search(root, 0);\n\n const n = len;\n const maxl = new Array(n).fill(0);\n const maxr = new Array(n).fill(0);\n\n for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {\n maxl[i] = Math.max(maxl[i-1], heights[i-1]);\n maxr[n-i-1] = Math.max(maxr[n-i], heights[n-i]);\n }\n\n const ret = [];\n const k = queries.length;\n\n for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {\n const maxxl = maxl[l[queries[i]]];\n const maxxr = maxr[r[queries[i]]];\n ret.push(Math.max(Math.max(maxxl, maxxr), d[queries[i]] - 1));\n }\n\n return ret;\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-querie
|
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-remo-mqcc
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Narendra_Sai
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T13:00:30.172618+00:00
|
2024-10-26T13:00:30.172712+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode left;\n * TreeNode right;\n * TreeNode() {}\n * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {\n * this.val = val;\n * this.left = left;\n * this.right = right;\n * }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n private Map<Integer, Integer> heights = new HashMap<>(); \n private Map<Integer, Integer> depths = new HashMap<>(); \n private Map<Integer, List<Integer>> depthHeights = new HashMap<>();\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n calculateHeightAndDepth(root, 0);\n\n for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : heights.entrySet()) {\n int nodeValue = entry.getKey();\n int height = entry.getValue();\n int depth = depths.get(nodeValue);\n depthHeights.computeIfAbsent(depth, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(height);\n }\n for (List<Integer> heightList : depthHeights.values()) {\n Collections.sort(heightList, Collections.reverseOrder());\n }\n\n int[] result = new int[queries.length];\n \n for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {\n int nodeValue = queries[i];\n int depth = depths.get(nodeValue);\n int nodeHeight = heights.get(nodeValue);\n List<Integer> heightList = depthHeights.get(depth);\n \n int maxHeightWithoutNode;\n if (heightList.size() == 1) {\n maxHeightWithoutNode = depth - 1;\n } else if (heightList.get(0) == nodeHeight) {\n maxHeightWithoutNode = depth + heightList.get(1);\n } else {\n maxHeightWithoutNode = depth + heightList.get(0);\n }\n\n result[i] = maxHeightWithoutNode;\n }\n\n return result;\n }\n\n private int calculateHeightAndDepth(TreeNode node, int depth) {\n if (node == null) return -1;\n\n depths.put(node.val, depth);\n int leftHeight = calculateHeightAndDepth(node.left, depth + 1);\n int rightHeight = calculateHeightAndDepth(node.right, depth + 1);\n\n int height = 1 + Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight);\n heights.put(node.val, height);\n\n return height;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Kotlin | Rust
|
kotlin-rust-by-samoylenkodmitry-ng0u
|
\n\nhttps://youtu.be/Y4Uurs3uKVE\n\n#### Join me on Telegram\n\nhttps://t.me/leetcode_daily_unstoppable/780\n\n#### Problem TLDR\n\nn new heights by cutting nod
|
SamoylenkoDmitry
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T09:14:54.023170+00:00
|
2024-10-26T09:23:53.532870+00:00
| 70 | false |
\n\nhttps://youtu.be/Y4Uurs3uKVE\n\n#### Join me on Telegram\n\nhttps://t.me/leetcode_daily_unstoppable/780\n\n#### Problem TLDR\n\n`n` new heights by cutting nodes in a Tree #hard #dfs\n\n#### Intuition\n\nAfter cut, check the sibling: if it has the bigger depth, we are good, otherwise update and go up. This will take O(log(n)) for each call.\n\nWe can speed it up by tracking the `level` from the node to upwards the root.\n\n\nThe catch is the siblings of each level: there are can be more than one of them. Check if cutting node is the current level maximum depth, and if so, take the second maximum of the depth.\n\n#### Approach\n\n* can be done in a single DFS traversal\n* in Rust `let m = ld[lvl]` makes a `copy`, do `&mut ld[lvl]` instead (silent bug) \n* arrays are faster than HashMap (in the leetcode tests runner)\n\n#### Complexity\n\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n + q)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(n + q)$$\n\n#### Code\n\n```kotlin []\n\n fun treeQueries(root: TreeNode?, queries: IntArray): IntArray {\n val lToD = Array(100001) { intArrayOf(-1, -1) }; val vToLD = lToD.clone()\n fun dfs(n: TreeNode?, lvl: Int): Int = n?.run {\n val d = 1 + max(dfs(left, lvl + 1), dfs(right, lvl + 1))\n vToLD[`val`] = intArrayOf(lvl, d); val m = lToD[lvl]\n if (d > m[0]) { m[1] = m[0]; m[0] = d } else m[1] = max(m[1], d); d\n } ?: -1\n dfs(root, 0)\n return IntArray(queries.size) { i ->\n val (lvl, d) = vToLD[queries[i]]; val (d1, d2) = lToD[lvl]\n lvl + if (d < d1) d1 else d2\n }\n }\n\n```\n```rust []\n\n pub fn tree_queries(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, queries: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {\n type D = [(i32, i32); 100001]; \n let mut ld = [(-1, -1); 100001]; let mut vld = ld.clone();\n fn dfs(ld: &mut D, vld: &mut D, n: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, lvl: i32) -> i32 {\n let Some(n) = n else { return -1 }; let mut n = n.borrow_mut();\n let d = 1 + dfs(ld, vld, &n.left, lvl + 1).max(dfs(ld, vld, &n.right, lvl + 1));\n vld[n.val as usize] = (lvl, d); let m = &mut ld[lvl as usize];\n if d > m.0 { m.1 = m.0; m.0 = d } else { m.1 = m.1.max(d) }; d\n }\n dfs(&mut ld, &mut vld, &root, 0);\n queries.iter().map(|&q| { \n let (lvl, d) = vld[q as usize]; let (d1, d2) = ld[lvl as usize]; \n lvl + if d < d1 { d1 } else { d2 }}).collect()\n }\n\n```\n```c++ []\n\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n array<pair<int, int>, 100001> ld{}, vld = ld;\n function<int(TreeNode*,int)> f = [&](TreeNode* n, int l) {\n if (!n) return 0;\n int d = 1 + max(f(n->left, l + 1), f(n->right, l + 1));\n vld[n->val] = {l, d}; auto& [d1, d2] = ld[l];\n if (d > d1) d2 = d1, d1 = d; else d2 = max(d2, d);\n return d;\n };\n f(root,0);\n transform(begin(queries), end(queries), begin(queries), [&](int q){\n auto [l, d] = vld[q]; auto [d1, d2] = ld[l]; return l - 1 + (d < d1 ? d1 : d2);\n });\n return queries;\n }\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Breadth-First Search', 'C++', 'Rust', 'Kotlin']
| 0 |
height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
|
Simple Intiutive Solution | 2 Passes | 97.11% beats | Beginner Friendly
|
simple-intiutive-solution-2-passes-9711-f4ue2
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nTo solve this problem, we need to understand how removing a node affects the height of
|
chiragp1u2p3
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-26T08:52:15.612699+00:00
|
2024-10-26T08:52:15.612744+00:00
| 248 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nTo solve this problem, we need to understand how removing a node affects the height of a binary tree. The main idea is to find out the maximum height of the remaining tree when a node is removed. For each node in the tree, if we remove it, the new tree\'s height can be determined based on the heights of its sibling nodes and parent nodes.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. Calculate Heights: Use DFS to find the height of each subtree.\n2. BFS Traversal: Perform a level-order traversal, tracking the maximum and second maximum heights at each level.\n3. Update Heights: Update each node\'s height based on whether it is the maximum or not at its level.\n4. Answer Queries: Return the precomputed heights for each queried node.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n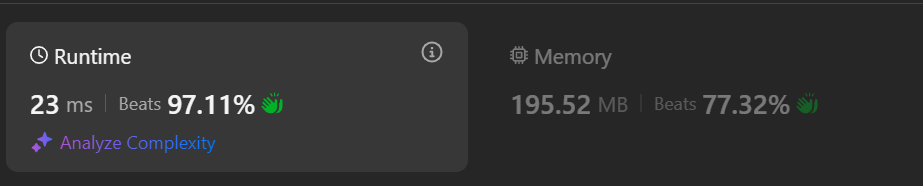\n\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * struct TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode *left;\n * TreeNode *right;\n * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}\n * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\n //height array\n int height[100001];\n // function to calculate heights of all substrees \n int calHeight(TreeNode* root){\n if(root==NULL)return 0;\n int lef=calHeight(root->left);\n int rig=calHeight(root->right);\n height[root->val]=max(lef,rig);\n return max(lef,rig)+1;\n }\npublic:\n vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {\n // array for storing height of tree if that index node is deleted \n int newheight[100001];\n calHeight(root);\n // BFS queue\n queue<TreeNode*>q;\n q.push(root);\n // count of level\n int lev=0;\n while(!q.empty()){\n int n=q.size();\n // if only one node\n if(n==1){\n TreeNode* curr=q.front();\n q.pop();\n // store the level of upper tree as removing this node we\'ll not include this level so that\'s why level-1\n newheight[curr->val]=lev-1;\n lev++;\n if(curr->left)q.push(curr->left);\n if(curr->right)q.push(curr->right);\n continue;\n }\n // calculate the nodes havng max and second max value\n int maxi=0,secmaxi=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n TreeNode* curr=q.front();\n if(height[curr->val]>height[maxi]){\n secmaxi=maxi;\n maxi=curr->val;\n }\n else if(height[curr->val]>height[secmaxi]){\n secmaxi=curr->val;\n }\n q.pop();\n q.push(curr);\n }\n while(n--){\n TreeNode* curr=q.front();\n q.pop();\n // node is max and then add level of 2nd max\n if(curr->val==maxi){\n newheight[curr->val]=lev+height[secmaxi];\n }\n else newheight[curr->val]=lev+height[maxi];\n if(curr->left)q.push(curr->left);\n if(curr->right)q.push(curr->right);\n }\n lev++;\n }\n // store the ans\n for(int &i:queries){\n i=newheight[i];\n }\n return queries;\n }\n};\n```\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for a binary tree node.\n * public class TreeNode {\n * int val;\n * TreeNode left;\n * TreeNode right;\n * TreeNode() {}\n * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {\n * this.val = val;\n * this.left = left;\n * this.right = right;\n * }\n * }\n */\nimport java.util.*;\n\nclass Solution {\n //height array\n private int[] height = new int[100001];\n\n // Function to calculate the height of each subtree\n private int calHeight(TreeNode root) {\n if (root == null) return 0;\n int leftHeight = calHeight(root.left);\n int rightHeight = calHeight(root.right);\n height[root.val] = Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight);\n return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;\n }\n\n public int[] treeQueries(TreeNode root, int[] queries) {\n // array for storing height of tree if that index node is deleted \n int[] newHeight = new int[100001];\n calHeight(root); // Calculate initial heights\n\n Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();\n q.offer(root);\n int level = 0;\n\n while (!q.isEmpty()) {\n int n = q.size();\n // if only one node\n if (n == 1) {\n TreeNode curr = q.poll();\n newHeight[curr.val] = level - 1;\n level++;\n if (curr.left != null) q.offer(curr.left);\n if (curr.right != null) q.offer(curr.right);\n continue;\n }\n \n int maxIdx = 0, secondMaxIdx = 0;\n // Find maximum and second maximum heights\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n TreeNode curr = q.poll();\n if (height[curr.val] > height[maxIdx]) {\n secondMaxIdx = maxIdx;\n maxIdx = curr.val;\n } else if (height[curr.val] > height[secondMaxIdx]) {\n secondMaxIdx = curr.val;\n }\n q.offer(curr);\n }\n\n // Update newHeight for each node in the current level\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n TreeNode curr = q.poll();\n if (curr.val == maxIdx) {\n newHeight[curr.val] = level + height[secondMaxIdx];\n } else {\n newHeight[curr.val] = level + height[maxIdx];\n }\n if (curr.left != null) q.offer(curr.left);\n if (curr.right != null) q.offer(curr.right);\n }\n level++;\n }\n\n // Process the queries\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {\n queries[i] = newHeight[queries[i]];\n }\n\n return queries;\n }\n}\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Breadth-First Search', 'Binary Tree', 'C++', 'Java']
| 0 |
smallest-subtree-with-all-the-deepest-nodes
|
[C++/Java/Python] One Pass
|
cjavapython-one-pass-by-lee215-or32
|
Explanatoin\nWrite a sub function deep(TreeNode root).\nReturn a pair(int depth, TreeNode subtreeWithAllDeepest)\n\nIn sub function deep(TreeNode root):\n\nif r
|
lee215
|
NORMAL
|
2018-07-08T03:22:28.222760+00:00
|
2020-09-27T08:01:51.068960+00:00
| 31,371 | false |
# Explanatoin\nWrite a sub function `deep(TreeNode root)`.\nReturn a `pair(int depth, TreeNode subtreeWithAllDeepest)`\n\nIn sub function `deep(TreeNode root)`:\n\n**if root == null**,\nreturn pair(0, null)\n\n**if left depth == right depth**,\ndeepest nodes both in the left and right subtree,\nreturn pair (left.depth + 1, root)\n\n**if left depth > right depth**,\ndeepest nodes only in the left subtree,\nreturn pair (left.depth + 1, left subtree)\n\n**if left depth < right depth**,\ndeepest nodes only in the right subtree,\nreturn pair (right.depth + 1, right subtree)\n<br>\n\n# Complexity\nTime `O(N)`\nSpace `O(height)`\n\n**C++**\n```cpp\n TreeNode* subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode* root) {\n return deep(root).second;\n }\n\n pair<int, TreeNode*> deep(TreeNode* root) {\n if (!root) return {0, NULL};\n pair<int, TreeNode*> l = deep(root->left), r = deep(root->right);\n\n int d1 = l.first, d2 = r.first;\n return {max(d1, d2) + 1, d1 == d2 ? root : d1 > d2 ? l.second : r.second};\n }\n```\n\n**Java**\n```java\n public TreeNode subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode root) {\n return deep(root).getValue();\n }\n\n public Pair<Integer, TreeNode> deep(TreeNode root) {\n if (root == null) return new Pair(0, null);\n Pair<Integer, TreeNode> l = deep(root.left), r = deep(root.right);\n\n int d1 = l.getKey(), d2 = r.getKey();\n return new Pair(Math.max(d1, d2) + 1, d1 == d2 ? root : d1 > d2 ? l.getValue() : r.getValue());\n }\n```\n**Python**\n```py\n def subtreeWithAllDeepest(self, root):\n def deep(root):\n if not root: return 0, None\n l, r = deep(root.left), deep(root.right)\n if l[0] > r[0]: return l[0] + 1, l[1]\n elif l[0] < r[0]: return r[0] + 1, r[1]\n else: return l[0] + 1, root\n return deep(root)[1]\n```\n
| 466 | 11 |
[]
| 49 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.