question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
C++ | Clean
|
c-clean-by-haharsh-0j36
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nRecursion + memoization \n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \
|
haharsh
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-09T04:01:46.793574+00:00
|
2024-03-09T04:01:46.793605+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nRecursion + memoization \n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nDP\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N^2)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(N^2)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dp[2001][2001]={0};\n int sameScore(vector<int>& nums,int i,int j,int score)\n {\n if(i>=j)return 0;\n \n if(dp[i][j]!=0)return dp[i][j];\n \n int opt1=0;\n int opt2=0;\n int opt3=0;\n \n if(score==-1)\n {\n opt1=sameScore(nums,i+2,j,nums[i]+nums[i+1]) +1;\n opt2=sameScore(nums,i+1,j-1,nums[i]+nums[j]) +1;\n opt3=sameScore(nums,i,j-2,nums[j]+nums[j-1]) +1;\n }\n else\n { \n if(nums[i]+nums[i+1]==score)opt1=sameScore(nums,i+2,j,nums[i]+nums[i+1]) +1;\n if(nums[i]+nums[j]==score) opt2=sameScore(nums,i+1,j-1,nums[i]+nums[j]) +1;\n if(nums[j]+nums[j-1]==score)opt3=sameScore(nums,i,j-2,nums[j]+nums[j-1]) +1;\n }\n return dp[i][j]=max({opt1,opt2,opt3});\n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n \n return sameScore(nums,0,nums.size()-1,-1);\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Easy Python Solution 🐍 || O(N)
|
easy-python-solution-on-by-arpit_patel_0-wqum
|
Code\n\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, words: List[str]) -> List[int]:\n k,li,ans=0,[],[]\n for i in words:\n if i=
|
Arpit_Patel_07
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T16:02:55.604688+00:00
|
2023-10-14T16:02:55.604720+00:00
| 868 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, words: List[str]) -> List[int]:\n k,li,ans=0,[],[]\n for i in words:\n if i==\'prev\':\n k+=1\n if k>len(li):\n ans.append(-1)\n else:\n ans.append(li[-k])\n else:\n k=0\n li.append(int(i))\n return ans\n```\n***Hope it helps...!!*** \uD83D\uDE07\u270C\uFE0F
| 13 | 0 |
['Array', 'String', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 5 |
last-visited-integers
|
Easiest C++ Solution ?
|
easiest-c-solution-by-aachal5676-rqre
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& words) {\n vector<int>v;\n vector<int>ans;\n int
|
Aachal5676
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T16:01:58.915267+00:00
|
2023-10-14T16:01:58.915295+00:00
| 1,602 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& words) {\n vector<int>v;\n vector<int>ans;\n int count=0;\n for(int i=0;i<words.size();i++){\n if(words[i]=="prev"){\n count++;\n if(count>v.size()){\n ans.push_back(-1);\n }\n else{\n ans.push_back(v[v.size()-count]);\n }\n }\n else{\n count=0;\n v.push_back(stoi(words[i]));\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 13 | 0 |
['C++']
| 5 |
last-visited-integers
|
easy solution using deque 😍❤️🔥
|
easy-solution-using-deque-by-shishirrsia-qkdr
|
if it\'s help, please up \u2B06 vote! \u2764\uFE0F\n\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) \n {\n
|
shishirRsiam
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-11T13:11:39.359487+00:00
|
2024-06-11T13:11:39.359509+00:00
| 177 | false |
# if it\'s help, please up \u2B06 vote! \u2764\uFE0F\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) \n {\n int cnt = 0;\n deque<int>dq, ans;\n for(auto val:nums)\n {\n if(val == -1) \n {\n ans.push_back(cnt < dq.size() ? dq[cnt] : -1);\n cnt++;\n continue;\n }\n cnt = 0;\n dq.push_front(val);\n }\n return vector<int>(ans.begin(), ans.end());\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Array', 'Queue', 'Simulation', 'C++']
| 3 |
last-visited-integers
|
✅☑[C++/C/Java/Python/JavaScript] || EXPLAINED🔥
|
ccjavapythonjavascript-explained-by-mark-jtpi
|
PLEASE UPVOTE IF IT HELPED\n\n---\n\n\n# Approaches\n(Also explained in the code)\n1. The lastVisitedIntegers function takes a vector of strings as input, where
|
MarkSPhilip31
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T16:41:45.069971+00:00
|
2023-10-14T16:41:45.069997+00:00
| 883 | false |
# PLEASE UPVOTE IF IT HELPED\n\n---\n\n\n# Approaches\n**(Also explained in the code)**\n1. The `lastVisitedIntegers` function takes a vector of strings as input, where each string represents either an integer or the word "prev."\n\n1. It initializes two vectors: `ov` to store visited integers and `ans` to store the answers.\n\n1. `ci` is the current index variable, initialized to -1.\n\n1. It iterates through each string in the input `words`.\n\n1. If the current word is "prev," it checks whether there is a previous integer in `ov`:\n\n - If there is no previous integer (ci == -1), it pushes -1 to `ans` to indicate that there is no previous integer.\n - If there is a previous integer, it pushes the previous integer from `ov` to `ans` and decrements the current index `ci`.\n1. If the current word is not `prev`, it converts the string to an integer value:\n\n - It initializes `vv` to 0 to store the integer value.\n - It iterates through the characters of the string, converting them to digits and accumulating the integer value.\n1. After processing each string, it updates the current index `ci` to the last index in the `ov` vector, indicating that the most recently added integer is the current one.\n\n1. The integer value is added to the `ov` vector.\n\n1. Finally, the function returns the `ans` vector containing the answers, which indicate the previous integers corresponding to "prev" words in the input.\n\n\n# Complexity\n- *Time complexity:*\n $$O(N * M)$$\n \n\n- *Space complexity:*\n $$O(1)$$\n \n\n\n# Code\n```C++ []\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& words) {\n vector<int> ov; // Create a vector to store the visited integers.\n vector<int> ans; // Create a vector to store the answers.\n int ci = -1; // Initialize a current index variable to -1.\n\n for (string s : words) {\n if (s == "prev") { // If the word is "prev," we need to handle the previous integer.\n if (ci == -1) {\n ans.push_back(-1); // If there is no previous integer, push -1 to the answers.\n }\n else {\n ans.push_back(ov[ci--]); // Otherwise, push the previous integer and decrement the current index.\n }\n }\n else {\n int vv = 0; // Initialize a variable to store the current integer value.\n for (char c : s) {\n vv *= 10; // Shift digits one position left.\n vv += (c - \'0\'); // Add the current digit value to vv.\n }\n ci = ov.size(); // Update the current index to the last index in ov.\n ov.push_back(vv); // Add the integer to the visited integers vector.\n }\n }\n return ans; // Return the vector containing the answers.\n }\n};\n\n\n```\n\n\n```C []\n\n#include <stdio.h>\n#include <stdlib.h>\n\nint* lastVisitedIntegers(char** words, int n) {\n int* ov = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int)); // Create an array to store the visited integers.\n int* ans = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int)); // Create an array to store the answers.\n int ci = -1; // Initialize a current index variable to -1.\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n char* s = words[i];\n if (strcmp(s, "prev") == 0) { // If the word is "prev," we need to handle the previous integer.\n if (ci == -1) {\n ans[i] = -1; // If there is no previous integer, store -1 in the answers.\n } else {\n ans[i] = ov[ci--]; // Otherwise, store the previous integer and decrement the current index.\n }\n } else {\n int vv = 0; // Initialize a variable to store the current integer value.\n for (int j = 0; s[j] != \'\\0\'; j++) {\n vv *= 10; // Shift digits one position left.\n vv += (s[j] - \'0\'); // Add the current digit value to vv.\n }\n ci = i; // Update the current index to the current position in ov.\n ov[i] = vv; // Store the integer in the visited integers array.\n }\n }\n return ans; // Return the array containing the answers.\n}\n\n\n```\n\n\n\n```Java []\n\nimport java.util.ArrayList;\nimport java.util.List;\n\npublic class Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(List<String> words) {\n List<Integer> ov = new ArrayList<>();\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n int ci = -1;\n\n for (String s : words) {\n if (s.equals("prev")) {\n if (ci == -1) {\n ans.add(-1);\n } else {\n ans.add(ov.get(ci--));\n }\n } else {\n int vv = 0;\n for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {\n vv *= 10;\n vv += (c - \'0\');\n }\n ci = ov.size();\n ov.add(vv);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n\n\n```\n\n\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, words):\n ov = []\n ans = []\n ci = -1\n\n for s in words:\n if s == "prev":\n if ci == -1:\n ans.append(-1)\n else:\n ans.append(ov[ci])\n ci -= 1\n else:\n vv = 0\n for c in s:\n vv *= 10\n vv += int(c)\n ci = len(ov)\n ov.append(vv)\n\n return ans\n\n\n```\n\n```javascript []\n\nclass Solution {\n lastVisitedIntegers(words) {\n const ov = [];\n const ans = [];\n let ci = -1;\n\n for (const s of words) {\n if (s === "prev") {\n if (ci === -1) {\n ans.push(-1);\n } else {\n ans.push(ov[ci]);\n ci--;\n }\n } else {\n let vv = 0;\n for (const c of s) {\n vv *= 10;\n vv += parseInt(c);\n }\n ci = ov.length;\n ov.push(vv);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n\n\n```\n\n\n\n---\n\n\n\n# PLEASE UPVOTE IF IT HELPED\n\n---\n---\n\n\n---
| 4 | 0 |
['String', 'C', 'String Matching', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Most Beginner Approach || yet O(n) || 50% T.C || 78% S.C || CPP
|
most-beginner-approach-yet-on-50-tc-78-s-13d6
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Ganesh_ag10
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-21T05:24:14.873047+00:00
|
2024-03-21T05:24:14.873075+00:00
| 140 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(N)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& v) {\n vector<int>p,a;\n int k=-1;\n for(auto i:v){\n if(i!=-1){\n p.push_back(i);\n k=p.size()-1;\n }\n else if(i==-1&&k>-1){\n a.push_back(p[k]);\n k--;\n }\n else if(i==-1&&k==-1) a.push_back(-1);\n }\n return a;\n\n// if my code helped you then please UpVOTE me, an UpVOTE encourages me to bring some more exciting codes for my coding family. Thank You o((>\u03C9< ))o\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Optimizing Memory and Performance in Last Visited Integers: A Code Solution Exploration || Mr. Robot
|
optimizing-memory-and-performance-in-las-83r4
|
Last Visited Integers\n\n## Approach 1: Tracking and Retrieving\n### Explanation\nIn this approach, we maintain two vectors, st to store the integers we encount
|
LakshayBrejwal_1_0
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T18:17:50.490484+00:00
|
2023-10-14T18:23:07.914818+00:00
| 348 | false |
# Last Visited Integers\n\n## Approach 1: Tracking and Retrieving\n### Explanation\nIn this approach, we maintain two vectors, `st` to store the integers we encounter and `ans` to record the last visited integers when encountering the word "prev." We also keep track of consecutive "prev" words using the `conspre` variable to determine how many positions to go back in `st` when "prev" is encountered.\n\n### Dry Run\nLet\'s dry run the code with a sample input:\n```\nwords = ["3", "5", "prev", "prev", "1", "prev", "prev", "prev"]\n```\n- Initially, `st` and `ans` are empty.\n- Iterating through the words:\n 1. "3" is a number, so it\'s pushed onto `st`.\n 2. "5" is also a number and is pushed onto `st`.\n 3. "prev" is encountered. `conspre` becomes 1. We retrieve the last visited integer at position `st.size() - 1 - 1` (the first "prev") from `st`, which is 5, and push it onto `ans`.\n 4. The next "prev" is encountered, and `conspre` is now 2. We retrieve the last visited integer at position `st.size() - 2 - 1` (the second "prev") from `st`, which is 3, and push it onto `ans`.\n 5. "1" is a number and is pushed onto `st`.\n 6. Another "prev" is encountered, but there are not enough "prev" words to go back 3 positions in `st,` so we push -1 onto `ans`.\n 7. Similarly, the last "prev" also results in -1 being added to `ans`.\n\nThe final value of `ans` is `[5, 3, -1, -1]`.\n\n### Edge Cases\nThis approach handles the following edge cases:\n- Consecutive "prev" words: We track and retrieve the last visited integers accordingly.\n- "prev" words without previous numbers: We return -1 in these cases.\n\n### Complexity Analysis\n- Time Complexity: O(N), where N is the number of words. We iterate through the words once.\n- Space Complexity: O(N), where N is the number of words. We store the last visited integers in the `ans` vector.\n\n## Codes in (C++) (Java) (Python) (C#) (JavaScript)\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& words) {\n vector<int> st;\n vector<int> ans;\n int conspre = 0;\n for (auto i : words) {\n if (i == "prev") {\n conspre++;\n if (conspre <= st.size()) {\n ans.push_back(st[st.size() - conspre]);\n } else {\n ans.push_back(-1);\n }\n } else {\n st.push_back(stoi(i));\n conspre = 0;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n### Java\n```java []\nimport java.util.ArrayList;\nimport java.util.List;\n\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(List<String> words) {\n List<Integer> st = new ArrayList<>();\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n int conspre = 0;\n for (String word : words) {\n if (word.equals("prev")) {\n conspre++;\n if (conspre <= st.size()) {\n ans.add(st.get(st.size() - conspre));\n } else {\n ans.add(-1);\n }\n } else {\n st.add(Integer.parseInt(word));\n conspre = 0;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```\n\n### Python\n```python []\nfrom typing import List\n\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, words: List[str]) -> List[int]:\n st = []\n ans = []\n conspre = 0\n for word in words:\n if word == "prev":\n conspre += 1\n if conspre <= len(st):\n ans.append(st[-conspre])\n else:\n ans.append(-1)\n else:\n st.append(int(word))\n conspre = 0\n return ans\n```\n\n### C#\n```csharp []\nusing System;\nusing System.Collections.Generic;\n\npublic class Solution {\n public IList<int> LastVisitedIntegers(IList<string> words) {\n List<int> st = new List<int>();\n List<int> ans = new List<int>();\n int conspre = 0;\n foreach (string word in words) {\n if (word == "prev") {\n conspre++;\n if (conspre <= st.Count) {\n ans.Add(st[st.Count - conspre]);\n } else {\n ans.Add(-1);\n }\n } else {\n st.Add(int.Parse(word));\n conspre = 0;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```\n\n### JavaScript\n```javascript []\n/**\n * @param {string[]} words\n * @return {number[]}\n */\nvar lastVisitedIntegers = function(words) {\n const st = [];\n const ans = [];\n let conspre = 0;\n for (const word of words) {\n if (word === "prev") {\n conspre++;\n if (conspre <= st.length) {\n ans.push(st[st.length - conspre]);\n } else {\n ans.push(-1);\n }\n } else {\n st.push(parseInt(word));\n conspre = 0;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n};\n``` \n\n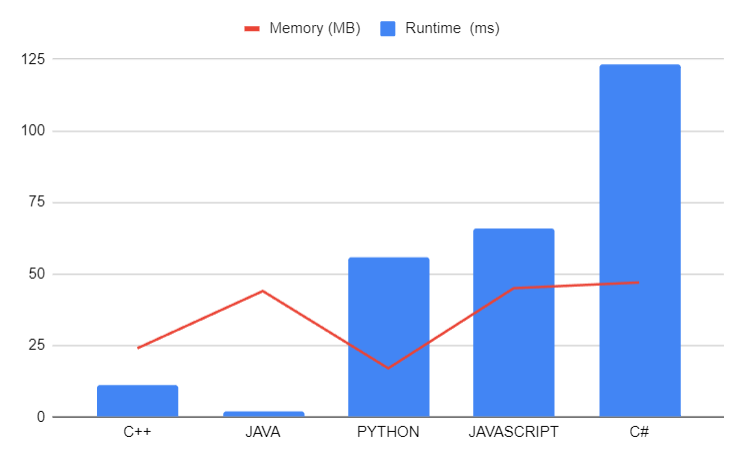\n---\n\n| Language | Runtime (ms) | Memory (MB) |\n|-------------|--------------|-------------|\n| C++ | 11 | 24 |\n| Java | 2 | 44 |\n| Python | 56 | 17 |\n| JavaScript | 66 | 45 |\n| C# | 123 | 47 |\n\n---\n\n\n\n---\n\n# Consider UPVOTING\u2B06\uFE0F\n\n\n\n\n# DROP YOUR SUGGESTIONS IN THE COMMENT\n\n## Keep Coding\uD83E\uDDD1\u200D\uD83D\uDCBB\n\n -- *MR.ROBOT SIGNING OFF*\n
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'JavaScript', 'C#']
| 1 |
last-visited-integers
|
Python Accepted✅
|
python-accepted-by-khacker-x0e5
|
\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, words: List[str]) -> List[int]:\n n = []\n a = []\n p=0\n for w in words:\n
|
khacker
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T16:01:34.773418+00:00
|
2023-10-14T16:01:34.773452+00:00
| 125 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, words: List[str]) -> List[int]:\n n = []\n a = []\n p=0\n for w in words:\n if w=="prev":\n if p<len(n):\n a.append(n[-1-p])\n else:\n a.append(-1)\n p+=1\n \n else:\n i = int(w)\n n.append(i)\n p=0\n \n return a \n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Python']
| 2 |
last-visited-integers
|
❇ last-visited-integers Images👌 🏆O(N)❤️ Javascript🎯 Memory👀73%🕕 ++Explanation✍️🔴🔥✅💪🙏👉
|
last-visited-integers-images-on-javascri-3lmo
|
Time Complexity: O(N)\uD83D\uDD55\nSpace Complexity: O(N)\n\n\nvar lastVisitedIntegers = function (nums) {\n let seenIndex = -1; // \uD83D\uDCCC Tracks the
|
anurag-sindhu
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-23T19:00:37.127444+00:00
|
2024-09-23T19:00:37.127479+00:00
| 35 | false |
**Time Complexity: O(N)\uD83D\uDD55\nSpace Complexity: O(N)**\n\n```\nvar lastVisitedIntegers = function (nums) {\n let seenIndex = -1; // \uD83D\uDCCC Tracks the index of the last seen element in `seen`\n let seen = []; // \uD83D\uDCDD Stores all the elements that have been visited\n let ans = []; // \u2728 The array where we\'ll store our results\n\n for (const iterator of nums) { // \uD83D\uDD04 Loop through each element in the `nums` array\n if (iterator === -1) { // \u26A0\uFE0F If the current element is `-1`...\n ans.push(seen[seenIndex] || -1); // \u21A9\uFE0F Add the last visited number to `ans`\n seenIndex -= 1; // \uD83D\uDD19 Move to the previous element in `seen`\n } else { // \u2705 If it\'s a valid number...\n seen.push(iterator); // \uD83D\uDCE5 Add it to the `seen` array\n seenIndex = seen.length - 1; // \uD83D\uDD04 Update `seenIndex` to point to the new last element\n }\n }\n\n return ans; // \uD83C\uDF89 Return the final result\n};\n\n```\n\n\nPlease upvote \uD83D\uDCAA if like\n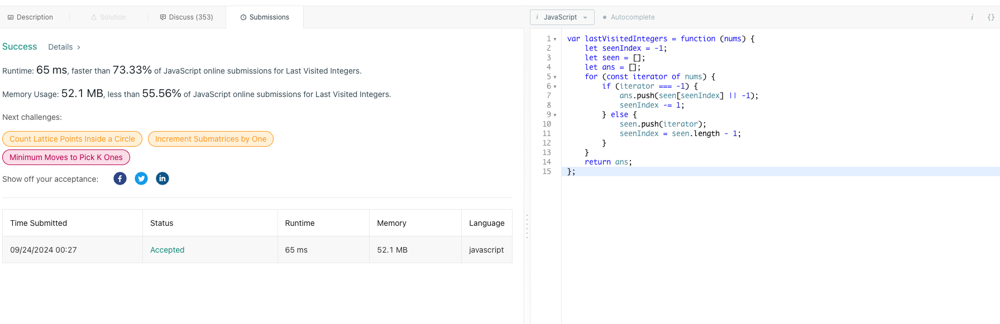\n
| 2 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
o(n) solution
|
on-solution-by-vinuaqua4u-yoxc
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
vinuaqua4u
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-22T14:00:41.484250+00:00
|
2024-04-22T14:00:41.484295+00:00
| 116 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: o(n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: o(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n seen, ans, cur = deque(), [], 0\n for num in nums:\n if num != -1:\n seen.appendleft(num)\n cur = 0\n continue\n\n cur += 1\n ans.append(-1 if cur > len(seen) else seen[cur - 1])\n return ans\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
✅ Best 100% || Only Python || Simple Explanation ✅|| Easy to understand 🔥🔥🔥🔥
|
best-100-only-python-simple-explanation-pb97z
|
\uD83D\uDD3C IF YOU FIND THIS POST HELPFUL PLEASE UPVOTE \uD83D\uDC4D\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n) in the worst case due to the single loop iteratin
|
Kashyap_Gohil
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-08T05:12:01.620401+00:00
|
2024-04-08T05:12:01.620425+00:00
| 103 | false |
# \uD83D\uDD3C IF YOU FIND THIS POST HELPFUL PLEASE UPVOTE \uD83D\uDC4D\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: `O(n)` in the worst case due to the single loop iterating through the `input` list.\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: `O(n)` in the worst case due to the potential size of the `seen` and `ans` lists.\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n seen = []\n ans = []\n k = 0\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n if nums[i] > -1 :\n seen.insert(0, nums[i])\n else:\n if k < len(seen) and nums[i - 1] == -1:\n k += 1\n ans.append(seen[k - 1])\n elif k < len(seen):\n k = 1\n ans.append(seen[0])\n else:\n ans.append(-1)\n return ans\n```\n\n### \uD83D\uDD3C If you found my solution and information helpful, I would greatly appreciate your upvote, as it would motivate me to continue sharing more solutions. \uD83D\uDD3C\n
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Simulation', 'Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
BEAT 91.46% | Shortest, Easiest, Clean & Clear | To the Point & Beginners Friendly Approach(❤️ω❤️)
|
beat-9146-shortest-easiest-clean-clear-t-myk3
|
\n\n# Welcome to My Coding Family\u30FE(\u2267 \u25BD \u2266)\u309D\nThis is my shortest, easiest & to the point approach. This solution mainly aims for purely
|
Nitansh_Koshta
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T03:26:48.575057+00:00
|
2024-02-17T03:26:48.575076+00:00
| 29 | false |
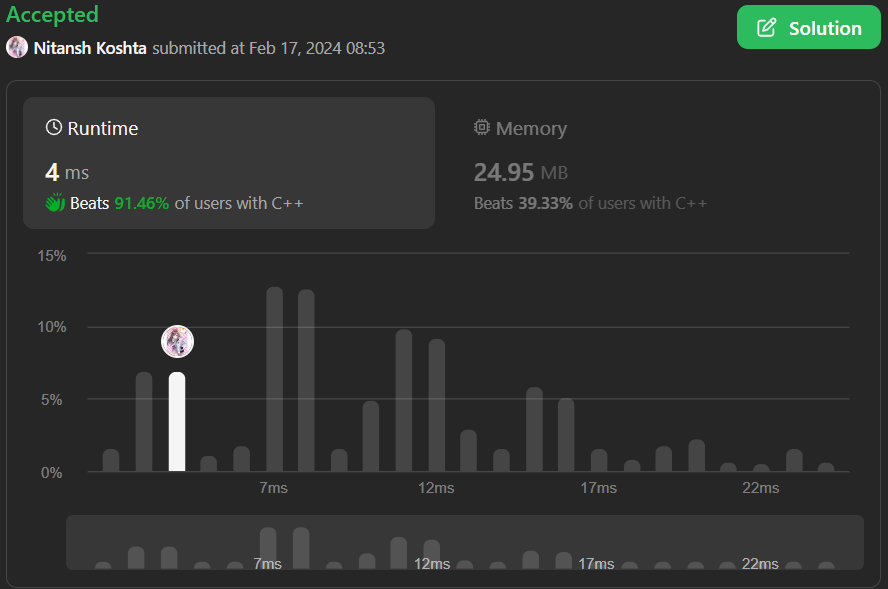\n\n# Welcome to My Coding Family\u30FE(\u2267 \u25BD \u2266)\u309D\n*This is my shortest, easiest & to the point approach. This solution mainly aims for purely beginners so if you\'re new here then too you\'ll be very easily be able to understand my this code. If you like my code then make sure to UpVOTE me. Let\'s start^_~*\n\n**The code is given below(p\u2267w\u2266q)**\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& v) {\n vector<int>p,a;\n int k=-1;\n for(auto i:v){\n if(i!=-1){p.push_back(i);k=p.size()-1;}\n else if(i==-1&&k>-1){a.push_back(p[k]);k--;}\n else if(i==-1&&k==-1)a.push_back(-1);\n }\n return a;\n\n// if my code helped you then please UpVOTE me, an UpVOTE encourages me to bring some more exciting codes for my coding family. Thank You o((>\u03C9< ))o\n }\n};\n```\n\n\n
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
last-visited-integers
|
Simple and clear python3 solution | One pass + stack
|
simple-and-clear-python3-solution-one-pa-w1m0
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n# Co
|
tigprog
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-18T16:11:30.570800+00:00
|
2023-10-18T16:11:38.649025+00:00
| 120 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n``` python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, words: List[str]) -> List[int]:\n stack = []\n position = -1\n result = []\n for elem in words:\n if elem == \'prev\':\n if position == -1:\n result.append(-1)\n else:\n result.append(stack[position])\n position -= 1 \n else:\n stack.append(int(elem))\n position = len(stack) - 1\n \n return result\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Stack', 'Simulation', 'Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
[C++] Simulation
|
c-simulation-by-awesome-bug-x6hf
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n- Keep tracking the visited integers\n- Count the number of consecutive prev strings se
|
pepe-the-frog
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-16T11:08:15.236761+00:00
|
2023-10-16T11:08:15.236789+00:00
| 562 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n- Keep tracking the visited integers\n- Count the number of consecutive `prev` strings seen so far\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n- store the visited integers in `nums`\n- Let `k` be the number of consecutive `prev` strings seen so far\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n // time/space: O(n)/O(n)\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& words) {\n vector<int> nums;\n vector<int> result;\n int k = 0;\n for (const string& word : words) {\n if (word == "prev") {\n k++;\n if (k > nums.size()) result.push_back(-1);\n else result.push_back(nums[nums.size() - k]);\n }\n else {\n k = 0;\n nums.push_back(stoi(word));\n }\n }\n return result;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Simulation', 'C++']
| 1 |
last-visited-integers
|
Simple C++ Solution ✅
|
simple-c-solution-by-akarsh_23-cyt2
|
Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nKeep a count for no of previous till now,\nreset it to 0 whenever you encounter a number.\nKeep a ar
|
akarsh_23
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T17:13:11.748582+00:00
|
2023-10-14T17:13:11.748600+00:00
| 143 | false |
# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nKeep a count for no of previous till now,\nreset it to 0 whenever you encounter a number.\nKeep a array to store the numbers you encounter encounter \n->when encountering a prev \n 1. increment the p_count.\n 2. check if p_count is greater than nums size then push -1 to ans.\n 3. else push the p_count element from last in nums to ans.\n\n-> when encountering a number\n 1. convert the string to num by stoi and push it to nums.\n 2. reset the p_count to 0.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(N)$$\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& words) {\n int n = words.size();\n \n vector<int> ans;\n vector<int> nums; \n int p_Count = 0; \n\n for (int i = 0; i<n; i++) {\n string word = words[i];\n if (word == "prev") {\n p_Count++;\n if (p_Count > nums.size()) {\n ans.push_back(-1);\n } else {\n ans.push_back(nums[nums.size() - p_Count]);\n }\n } else {\n int num = stoi(word);\n nums.push_back(num);\n p_Count = 0;\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
JAVA | Easy code
|
java-easy-code-by-tiwarianand940-l4mq
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(List<String> words) {\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n List<Strin
|
tiwarianand940
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T16:01:32.313044+00:00
|
2023-10-21T09:04:04.608962+00:00
| 585 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(List<String> words) {\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n List<String> digits = new ArrayList<>();\n int k = 0;\n for (String word : words) {\n if (word.equals("prev")) {\n k++;\n ans.add((digits.size() - k < digits.size() && digits.size() - k >= 0) ? Integer.parseInt(digits.get(digits.size() - k)) : -1);\n } else {\n digits.add(word);\n k = 0;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
last-visited-integers
|
Simple C++ Solution || C++ || Beats 100%
|
simple-c-solution-c-beats-100-by-abhinan-9vot
|
IntuitionThe problem requires us to maintain a list of recently visited positive integers and retrieve specific elements based on the number of consecutive -1s
|
Abhinandanpatil02
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-04T12:48:06.947006+00:00
|
2025-03-04T12:48:06.947006+00:00
| 42 | false |
# Intuition
The problem requires us to maintain a list of recently visited positive integers and retrieve specific elements based on the number of consecutive `-1`s encountered. By storing positive integers in a data structure and tracking the count of consecutive `-1`s, we can efficiently determine the last visited integer.
---
# Approach
- Use a `list<int>` (`li`) to store positive integers in reverse order (most recent at the front).
- Maintain a variable `k` to track the count of consecutive `-1`s.
- Iterate through `nums`:
- If `nums[i]` is positive, add it to the front of `li`.
- If `nums[i]` is `-1`:
- If it's consecutive to a previous `-1`, increment `k`.
- Otherwise, reset `k` to `1`.
- If `k` is within the bounds of `li`, retrieve the `k-th` most recent integer; otherwise, return `-1`.
---
# Complexity
- **Time complexity:** \(O(n)\), since each element is processed once, and `advance(it, k-1)` runs in \(O(k)\) in the worst case but is overall efficient.
- **Space complexity:** \(O(n)\), as we store up to `n` elements in `li`.
---
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) {
int prev=-1;
vector<int>ans;
list<int>li;
int k=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
if(nums[i]!=-1){
li.push_front(nums[i]);
}
else{
if(prev==-1||prev+1==i){
k++;
if(k>li.size()){
ans.push_back(-1);
}
else{
list<int>:: iterator it =li.begin();
advance(it,k-1);
ans.push_back(*it);
}
prev=i;
}
else{
k=1;
list<int>::iterator it =li.begin();
advance(it,k-1);
ans.push_back(*it);
prev=i;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
☑️ Finding Last Visited Integers. ☑️
|
finding-last-visited-integers-by-abdusal-n9s4
|
Code
|
Abdusalom_16
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-11T04:53:55.893903+00:00
|
2025-02-11T04:53:55.893903+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Code
```dart []
class Solution {
List<int> lastVisitedIntegers(List<int> nums) {
List<int> seen = [];
List<int> ans = [];
int count = 0;
for(int elem in nums){
if(elem == -1){
count++;
if(count > seen.length){
ans.add(-1);
}else{
ans.add(seen[count-1]);
}
}else{
count = 0;
seen.insert(0, elem);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Simulation', 'Dart']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
O(n) | | C++ 🔥
|
on-c-by-varuntyagig-r7xq
|
Complexity
Time complexity:
O(n)
Space complexity:
O(n)
Code
|
varuntyagig
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-24T08:07:03.323406+00:00
|
2025-01-24T08:07:23.982985+00:00
| 43 | false |
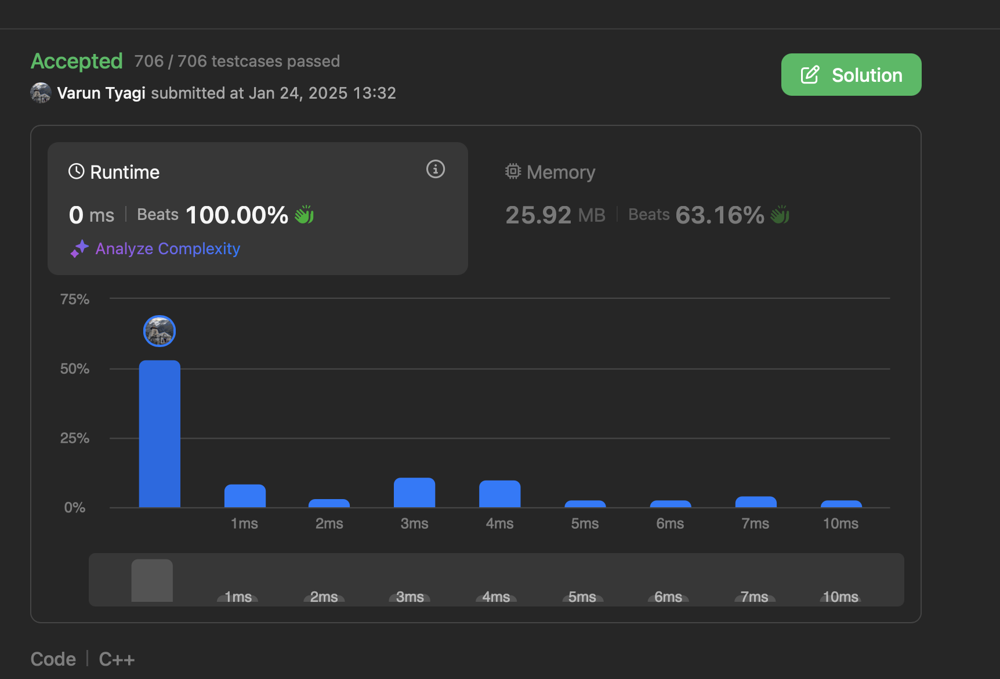
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
$$O(n)$$
- Space complexity:
$$O(n)$$
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> seen, ans;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (nums[i] > 0) {
// reset k to 0
k = 0;
// prepend element in front of array
reverse(seen.begin(), seen.end());
seen.push_back(nums[i]);
reverse(seen.begin(), seen.end());
} else if (nums[i] == -1) {
k += 1;
if (k <= seen.size()) {
ans.push_back(seen[k - 1]);
} else {
ans.push_back(-1);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Math', 'C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
:D
|
d-by-yesyesem-lf5k
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
yesyesem
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-22T12:02:19.323230+00:00
|
2024-10-22T12:02:19.323255+00:00
| 32 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) {\n vector<int>seen;\n vector<int>ans;\n int k=0;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)\n {\n if(nums[i]>0)\n { \n seen.insert(seen.begin(),nums[i]);\n k=0;\n }\n else if(nums[i]==-1)\n { \n k++;\n if(k>seen.size())\n {\n ans.push_back(-1);\n }\n else\n ans.push_back(seen[k-1]);\n\n }\n }\n for(int i=0;i<seen.size();i++)\n cout<<seen[i]<<" ";\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Beats 100% O(n) solution
|
beats-100-on-solution-by-shreedev-6cb8
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Shreedev
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-22T04:03:04.424943+00:00
|
2024-10-22T04:03:04.424968+00:00
| 16 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```typescript []\nfunction lastVisitedIntegers(nums: number[]): number[] {\n let seen = []\n let ans = []\n let k = 0;\n for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {\n if(nums[i] === -1) {\n k++;\n if(k > seen.length) ans.push(-1)\n else ans.push(seen[k - 1])\n } else {\n seen.unshift(nums[i])\n k = 0;\n }\n }\n \n return ans\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['TypeScript', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
A beginner friendly C++ Solution || Straight Forward approach
|
a-beginner-friendly-c-solution-straight-7tfju
|
Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) {\n vector<int> seen;\n vector<int> ans;\n
|
johnk4590
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-11T07:12:19.657675+00:00
|
2024-10-11T07:12:19.657707+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) {\n vector<int> seen;\n vector<int> ans;\n int k = 0;\n for(int i = 0;i<nums.size();i++)\n {\n if(nums[i] > 0)\n {\n seen.insert(seen.begin(),nums[i]);\n k = 0;\n }\n else if(nums[i] == -1)\n {\n k++;\n if(k<= seen.size())\n {\n ans.push_back(seen[k-1]);\n }\n else if(k > 0)\n {\n ans.push_back(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
C# solution 100% runtime
|
c-solution-100-runtime-by-cvalingam-jhe1
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
cvalingam
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-08T06:15:35.723186+00:00
|
2024-03-08T06:15:35.723229+00:00
| 54 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(2n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public IList<int> LastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n var ans = new List<int>();\n var seen = new List<int>();\n int k = 0;\n int n = nums.Length;\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n if(nums[i] != -1)\n {\n k = 0;\n seen.Insert(0, nums[i]);\n }\n else\n {\n k++;\n if(k <= seen.Count)\n ans.Add(seen[k - 1]);\n else\n ans.Add(-1);\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Easy beginner Friendly Solution🔥
|
easy-beginner-friendly-solution-by-sumo2-xcq4
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n List<Integer> seen=new ArrayList<>();\n List<Integer>
|
sumo25
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-20T15:30:10.780606+00:00
|
2024-02-20T15:30:10.780638+00:00
| 140 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n List<Integer> seen=new ArrayList<>();\n List<Integer> ans=new ArrayList<>();\n int k=0;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){\n if(nums[i]>0){\n seen.add(0,nums[i]);\n }\n else{\n if(i!=0 && nums[i-1]!=-1){\n k=1;\n }\n else{\n k++;\n }\n \n if(k<=seen.size()){\n ans.add(seen.get(k-1));\n }\n else{\n ans.add(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Java || Runtime 2ms || Beat 98% || With detailed explanation
|
java-runtime-2ms-beat-98-with-detailed-e-feaj
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(List<String> words) {\n List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); // List for final r
|
shiyang2575326696
|
NORMAL
|
2023-12-21T01:48:56.798905+00:00
|
2023-12-21T01:48:56.798934+00:00
| 67 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(List<String> words) {\n List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); // List for final results\n List<Integer> numbersSeen = new ArrayList<>(); // List to store numbers seen so far\n int consecutivePrevCount = 0; // Counts consecutive "prev" strings\n\n for (String word : words) {\n if (!word.equals("prev")) {\n // If it\'s a number, reset consecutivePrevCount and add to numbersSeen\n consecutivePrevCount = 0;\n numbersSeen.add(Integer.parseInt(word));\n } else {\n // Increment consecutivePrevCount for each "prev"\n consecutivePrevCount++;\n\n if (consecutivePrevCount > numbersSeen.size()) {\n // If more "prev" than numbers, add -1\n res.add(-1);\n } else {\n // Add the number corresponding to the count of "prev" from the end\n res.add(numbersSeen.get(numbersSeen.size() - consecutivePrevCount));\n }\n }\n }\n\n return res; // Return the result list\n }\n}\n\n```\n\n
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Python | O(N) time, O(1) space
|
python-on-time-o1-space-by-aljipa-d2n3
|
Code\n\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, words: List[str]) -> List[int]:\n res = []\n prv = e = 0\n for i, w in enumerate
|
aljipa
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-17T01:59:37.388913+00:00
|
2023-11-17T01:59:37.388934+00:00
| 34 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, words: List[str]) -> List[int]:\n res = []\n prv = e = 0\n for i, w in enumerate(words):\n if w == "prev":\n res.append(int(words[e - 1 - prv]) if e - 1 - prv >= 0 else -1)\n prv += 1\n else:\n words[e] = w\n e += 1\n prv = 0\n return res\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Brute➡️Optimal | 2 Solutions | 🔥Intuitive - Self Explanatory Comments🔥 | C++ Clean Code✅
|
bruteoptimal-2-solutions-intuitive-self-atw58
|
\uD83D\uDE0A ~ \uD835\uDE52\uD835\uDE5E\uD835\uDE69\uD835\uDE5D \u2764\uFE0F \uD835\uDE57\uD835\uDE6E \uD835\uDE43\uD835\uDE5E\uD835\uDE67\uD835\uDE5A\uD835\uDE
|
hirenjoshi
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-16T06:30:14.267588+00:00
|
2024-07-13T13:49:16.960805+00:00
| 218 | false |
\uD83D\uDE0A ~ \uD835\uDE52\uD835\uDE5E\uD835\uDE69\uD835\uDE5D \u2764\uFE0F \uD835\uDE57\uD835\uDE6E \uD835\uDE43\uD835\uDE5E\uD835\uDE67\uD835\uDE5A\uD835\uDE63\n# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n***Hey There! It\'s Easy As Heaven, Just Take A Look At The Code And Comments Within It, You\'ll Get It.\nStill Have Doubts! Feel Free To Comment, I\'ll Definitely Reply!***\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n***Two Solutions : Both Accepted***\n\n# Complexity\n- *Time complexity: Mentioned in the code*\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- *Space complexity: Mentioned in the code*\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n**Solution 1 :**\n```\n// #1 Method to find the last visited integers - O(N*N) & O(N) \nvector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& words) {\n vector<int> output; // Stores the last visited integers (resultant values).\n vector<int> nums; // Stores the integers seen so far, in reverse order.\n\n // Tracks the number of consecutive "prev" strings encountered up to and including the current string.\n int k = 0; \n \n for(int i=0; i<words.size(); i++) {\n // If the ith string is a digit, then insert it as a digit at the beginning of the "nums" array. \n if(words[i] != "prev") {\n nums.insert(begin(nums), stoi(words[i])); \n }\n // Else when the ith string is "prev".\n else {\n // If the "prev" strings is seen consecutively, then increase the consecutive count by 1.\n if(i > 0 && words[i-1] == "prev") {\n k += 1;\n }\n // Else when the "prev" strings is not seen consecutively, reset the consecutive count by 1.\n else {\n k = 1;\n }\n \n // If the (k-1) is a valid index, then store the index element of "nums" to "output".\n if(nums.size() > 0 && k-1 < nums.size()) {\n output.push_back(nums[k-1]);\n }\n // If the (k-1) is not a valid index, then store the value -1 to the "output".\n else {\n output.push_back(-1);\n }\n } \n }\n \n // Return the array containing the last visited integers.\n return output;\n}\n```\n**Solution 2 :**\n```\n// #2 Method to find the last visited integers - O(N) & O(N) \nvector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& words) {\n vector<int> output; // Stores the resultant values.\n vector<int> nums; // Stores the integers seen so far, in original order.\n\n // Tracks the number of consecutive "prev" strings encountered up to and including the current string.\n int k = 0; \n \n for(int i=0; i<words.size(); i++) {\n // If the ith string is a digit, then insert it as a digit to the "nums" array. \n if(words[i] != "prev") {\n nums.push_back(stoi(words[i])); \n }\n // Else when the ith string is "prev".\n else {\n // If the "prev" strings is seen consecutively, then increase the consecutive count by 1.\n if(i > 0 && words[i-1] == "prev") {\n k += 1;\n }\n // Else when the "prev" strings is not seen consecutively, reset the consecutive count by 1.\n else {\n k = 1;\n }\n \n // If the (k-1) is a valid index, then store the index element of "nums" to "output".\n if(nums.size() > 0 && k-1 < nums.size()) {\n // Assume the index element is in the reverse of the "nums", then calculate the index based on the reverse array.\n int idx = nums.size() - k;\n // If the calcuated index is valid, then store the index element to the "output". \n if(idx >= 0 && idx < nums.size())\n output.push_back(nums[idx]);\n }\n // If the (k-1) is not a valid index, then store the value -1 to the "output".\n else {\n output.push_back(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n \n // Return the array containing the last visited integers.\n return output;\n}\n```\n\uD835\uDDE8\uD835\uDDE3\uD835\uDDE9\uD835\uDDE2\uD835\uDDE7\uD835\uDDD8 \uD835\uDDDC\uD835\uDDD9 \uD835\uDDEC\uD835\uDDE2\uD835\uDDE8 \uD835\uDDDF\uD835\uDDDC\uD835\uDDDE\uD835\uDDD8 \uD835\uDDE7\uD835\uDDDB\uD835\uDDD8 \uD835\uDDE6\uD835\uDDE2\uD835\uDDDF\uD835\uDDE8\uD835\uDDE7\uD835\uDDDC\uD835\uDDE2\uD835\uDDE1 \uD83D\uDC4D
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'String', 'C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Easy O(N) solution
|
easy-on-solution-by-harshsantoshi-08b1
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& words) {\n //array to store the numbers encountered while trav
|
HarshSantoshi
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-15T11:36:24.249149+00:00
|
2023-10-15T11:36:24.249185+00:00
| 229 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& words) {\n //array to store the numbers encountered while traversing\n vector<int>numbers;\n //An iterator for accessing the prev number\n int i=-1 ;\n vector<int>ans;\n for(auto it: words){\n string curr = it ; \n if(curr=="prev"){\n if(i==-1){\n // if no number comes before this prev store -1 \n ans.push_back(-1);\n }\n else{\n //adding the prev number to ans then decrementing i\n ans.push_back(numbers[i]);\n i--;\n }\n }\n else{\n // converting string to number and pushing it into numbers array \n int num = stoi(curr);\n numbers.push_back(num);\n //updating i \n i=numbers.size()-1;\n }\n }\n return ans ;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
[C++] State Machine Approach, 0ms, 23.5MB
|
c-state-machine-approach-0ms-235mb-by-aj-lkub
|
This problem will require us to create a state machine that performs two different tasks:\n for numerical strings, it will store the number in a container;\n fo
|
Ajna2
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-15T10:58:09.385622+00:00
|
2023-10-15T10:58:09.385643+00:00
| 104 | false |
This problem will require us to create a state machine that performs two different tasks:\n* for numerical strings, it will store the number in a container;\n* for `"prev"` strings, it will:\n * if it is the first `"prev"` we meet, check when we last wrote in and take the last element and then write it down in our result variable;\n * in all the other cases, it will take the `n`th last element we wrote in our container, with `n` being the number of consecutive `"prev"`s we encountered in a row.\n\nNow, to code our solution, let\'s get started with a few support variables:\n* `len` will store the size of `words`;\n* `pos` will be our pointer to know where to write in `res`;\n* `w` and `r` are going to be our write and read poitners, respectively;\n* `res` is going to be our result variable, initialised to be `len` elements already, to avoid reallocations.\n\nWe will loop through each `word` in `words` and handle two base cases:\n* if `word == "prev"`, we will:\n * decrease `r` by `1`;\n * compute a value that equals the `seen[r]` if `r >= 0`, `-1` otherwise;\n * write said value in `res[pos]`;\n * increase `pos` by `1`;\n* otherwise, we will:\n * convert `word` to a number and store its value in `seen[w]`\n * increase `w` by `1`;\n * reset `r` to be `w`; \n\nAfter that, we can `resize` `res` to be only `pos` cells and finally `return` it :)\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string> &words) {\n // support variables\n int len = words.size(), pos = 0, seen[len], w = 0, r = 0;\n vector<int> res(len);\n for (auto &word: words) {\n // 1st case:\n if (word == "prev") {\n res[pos++] = (--r) >= 0 ? seen[r] : -1;\n }\n // 2nd case:\n else {\n seen[w++] = stoi(word);\n r = w;\n }\n }\n res.resize(pos);\n return res;\n }\n};\n```\n\nAn alternative way to write this would be by replacing `r` with a counter variable `cnt` that counts how many `"prev"`s in a row we have encountered.\n\nI like it a bit less since with it we will make one extra operation (`w - cnt`) per loop:\n\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string> &words) {\n // support variables\n int len = words.size(), pos = 0, seen[len], w = 0, cnt = 0;\n vector<int> res(len);\n for (auto &word: words) {\n // 1st case:\n if (word == "prev") {\n cnt++;\n res[pos++] = w >= cnt ? seen[w - cnt] : -1;\n }\n // 2nd case:\n else {\n seen[w++] = stoi(word);\n cnt = 0;\n }\n }\n res.resize(pos);\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Python Easy Solution | O(N) | 23ms | Beats 100% Users in Runtime & Memory
|
python-easy-solution-on-23ms-beats-100-u-xzh6
|
Intuition\nThe intuition behind this approach is to keep track of the integers visited using a stack, and when a "prev" word is encountered, determine the last
|
actually_sam
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T21:08:28.191136+00:00
|
2023-10-14T21:09:15.015468+00:00
| 101 | false |
# Intuition\nThe intuition behind this approach is to keep track of the integers visited using a stack, and when a "prev" word is encountered, determine the last visited integer based on the count of consecutive "prev" words and the total count of integers visited so far. If there are more "prev" words than integers on the stack, it appends -1 to the result list; otherwise, it retrieves the appropriate integer from the stack and appends it to the result list. This approach ensures that the last visited integers are correctly identified when encountering "prev" words in the input list.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nThis solution solves the problem in O(N) time \n\n- Space complexity:\nSpace Complecity of this code is O(N)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, words):\n """\n :type words: List[str]\n :rtype: List[int]\n """\n stack = []\n res = []\n total_visited_integers = 0\n consecutive_prevs = 0\n for word in words:\n if word != "prev":\n consecutive_prevs = 0\n total_visited_integers += 1\n stack.append(int(word))\n else:\n consecutive_prevs += 1\n if consecutive_prevs > total_visited_integers:\n res.append(-1)\n else:\n res.append(stack[-consecutive_prevs])\n \n return res\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python']
| 1 |
last-visited-integers
|
C++ implementation easy
|
c-implementation-easy-by-rounaq_khandelw-txy2
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& words) {\n vector<int> ans;\n vector<int> prev;\n
|
rounaq_khandelwal
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T19:28:39.094022+00:00
|
2023-10-14T19:28:39.094053+00:00
| 13 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& words) {\n vector<int> ans;\n vector<int> prev;\n for(int i=0;i<words.size();i++){\n if(words[i]=="prev"){\n int noOfPrev=1;\n int j=i-1;\n while(j>=0 && words[j]=="prev"){\n noOfPrev++;\n j--;\n }\n int n=prev.size();\n if(n-noOfPrev>=0){\n ans.push_back(prev[n-noOfPrev]);\n }\n else ans.push_back(-1);\n }\n else{\n prev.push_back(stoi(words[i]));\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Best Java Solution || Beats 100%
|
best-java-solution-beats-100-by-ravikuma-ryha
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
ravikumar50
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T17:26:05.241129+00:00
|
2023-10-14T17:26:05.241156+00:00
| 403 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(List<String> arr) {\n\n List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n\n int count = -1;\n\n for(int i=0; i<arr.size(); i++){\n if(arr.get(i).equals("prev")){\n if(count==-1) ans.add(-1);\n else ans.add(nums.get(count--));\n }else{\n int a = 0;\n String s = arr.get(i);\n for(int j=0; j<s.length(); j++){\n a *= 10;\n a += (s.charAt(j)-\'0\');\n }\n count = nums.size();\n nums.add(a);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
C++ || Brute Force ||
|
c-brute-force-by-neon772-g6tg
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
neon772
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T17:01:40.681360+00:00
|
2023-10-14T17:01:40.681380+00:00
| 24 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& words) {\n int n=words.size();\n vector<int>ans;\n vector<int>temp;\n int count=0;\n int t=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n if(words[i]!="prev"){\n temp.push_back(stoi(words[i]));\n t++;\n count=0;\n }else{\n count++;\n vector<int>temp2;\n for(auto x: temp){\n if(x!=-1)\n temp2.push_back(x);\n }\n reverse(temp2.begin(),temp2.end());\n if(((count<=t))and (count-1)>=0)\n ans.push_back(temp2[count-1]);\n else ans.push_back(-1);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Last Visited Integers - O(n) Java | Beats 100%
|
last-visited-integers-on-java-beats-100-ibi5l
|
Intuition\nThe code essentially maintains a list of integers encountered, and when the word "prev" is encountered, it looks back a certain number of positions i
|
baltuky
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T16:37:38.205462+00:00
|
2023-10-14T16:43:59.448102+00:00
| 231 | false |
# Intuition\nThe code essentially maintains a list of integers encountered, and when the word "prev" is encountered, it looks back a certain number of positions in the list to find the last visited integer(s) and adds them to the result list. If "prev" is not encountered, it adds the current integer to the list for future reference.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(List<String> words) {\n final List<Integer> answers = new LinkedList<>();\n final List<Integer> numbers = new ArrayList<>();\n \n int prevSeen = 0;\n \n for(String word: words){\n if("prev".equals(word)){\n prevSeen++;\n \n int i = numbers.size() - prevSeen;\n \n answers.add(0 <= i ? numbers.get(i) : -1);\n } else {\n prevSeen = 0;\n numbers.add(Integer.valueOf(word));\n }\n }\n \n return answers;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'String', 'Java']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Detailed C++ solution || O(n) complexity || Easy and Straight-forward approach
|
detailed-c-solution-on-complexity-easy-a-0du3
|
\n# Approach\n I am traversing through the array words.\n -If the array element is not "prev", it must be a number.I am converting the string "2" to integer
|
hachimaan_03
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T16:32:05.735356+00:00
|
2023-10-14T16:33:25.250962+00:00
| 137 | false |
\n# Approach\n I am traversing through the array **words**.\n -If the array element is not **"prev"**, it must be a number.I am **converting** the string **"2"** to integer **2** using **stoi()** function.\n - I have a **temp** vector which stores the converted number.\n - I am keeping a **count** variable which will be **0** initially. This **increases** by 1 everytime I get a "**prev**". When I **don\'t** get a **"prev"**, I initialise count **back to 0**.\n - Now, if **count <=temp.size()**, my desired number is **temp[temp.size()-count]** which will be pushed into my final ans vector.(*dry run to understand better*);\n - if **count >temp.size()** it means there are more **"prev"** than numbers and thus, we **push_back(-1)** into ans.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n**O(n)**\n\n- Space complexity:\n**O(n)**\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& words) {\n vector<int>temp;\n vector<int>ans;\n int count=0;\n int n=words.size(),num;\n for(int i=0;i<words.size();i++){\n if(words[i]!="prev"){\n count=0;\n num=stoi(words[i]);\n temp.push_back(num);\n }\n else{\n count++;\n if(count<=temp.size()){\n ans.push_back(s[temp.size()-count]);\n }\n else {\n ans.push_back(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Easy java solution
|
easy-java-solution-by-kirtisahu683-8tqw
|
\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(List<String> list) {\n List<Integer> num=new ArrayList<>();\n List<Integer> res=n
|
kirtisahu683
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T16:18:25.635616+00:00
|
2023-10-14T16:25:58.371556+00:00
| 589 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(List<String> list) {\n List<Integer> num=new ArrayList<>();\n List<Integer> res=new ArrayList<>();\n int c=0;\n for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++)\n {\n if(list.get(i).equals("prev"))\n {\n if (c < num.size())\n {\n res.add(num.get(num.size()-1-c));\n }\n else\n {\n res.add(-1);\n }\n c++;\n }\n else {\n int nums = Integer.valueOf(list.get(i));\n num.add(nums);\n c = 0;\n } \n \n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
last-visited-integers
|
✅[cpp || Self Explanatory, Intuitive & Easy to Understand || O(n) TC || O(n) SC]✅
|
cpp-self-explanatory-intuitive-easy-to-u-nv82
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& word
|
mayanksinghchouhan
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T16:07:27.987025+00:00
|
2023-10-14T16:07:27.987059+00:00
| 32 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& words) {\n vector<int> ans, nums;\n int cc = 0;\n \n for(string val : words){\n int n = nums.size();\n \n if(val == "prev"){\n cc++;\n if(cc > n) ans.push_back(-1); \n else ans.push_back(nums[n - cc]);\n }else{\n cc = 0;\n int number;\n istringstream iss(val);\n iss >> number;\n nums.push_back(number);\n }\n } \n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Easy to understand Solution || Explained
|
easy-to-understand-solution-explained-by-1kta
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n) \n\n- Space complexity: O(1)\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& wor
|
coder_rastogi_21
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T16:04:05.770187+00:00
|
2023-10-14T16:31:46.340799+00:00
| 112 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$ \n\n- Space complexity: $$O(1)$$\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& words) {\n vector<int> ans;\n vector<int> integers;\n int prev = 0;\n for(int i=0; i<words.size(); i++)\n {\n if(words[i] != "prev")\n { //push all the integers in a vector\n integers.push_back(stoi(words[i]));\n prev = 0;\n }\n else\n {\n prev++; //count consecutive "prev" occurences\n int n = integers.size(); \n int insert = n >= prev ? integers[n-prev] : -1; //get previous kth element, if it exists\n ans.push_back(insert);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
[Python] brute force
|
python-brute-force-by-pbelskiy-fcf7
|
python\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, words: List[str]) -> List[int]:\n nums = []\n res = []\n idx = -1\n\n for
|
pbelskiy
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T16:02:57.712312+00:00
|
2023-10-14T16:02:57.712334+00:00
| 59 | false |
```python\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, words: List[str]) -> List[int]:\n nums = []\n res = []\n idx = -1\n\n for w in words:\n if w != \'prev\':\n nums.append(int(w))\n idx = len(nums) - 1\n continue\n \n if idx < 0:\n res.append(-1)\n continue\n\n res.append(nums[idx])\n idx -= 1\n \n return res\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
python3: easy solution
|
python3-easy-solution-by-nkrishk-hbqr
|
\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n
|
nkrishk
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-14T16:02:02.746568+00:00
|
2023-10-14T22:31:25.767636+00:00
| 251 | false |
\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# C++\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<string>& words) {\n vector<int> ans, num;\n int k = 0, len;\n for (auto word : words) {\n if ( word == "prev") {\n k += 1;\n len = num.size();\n if (k > len)\n ans.push_back(-1);\n else\n ans.push_back(num[len-k]);\n } else {\n num.push_back(stoi(word));\n k = 0;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n# Python3\n```\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, words: List[str]) -> List[int]:\n ans = []\n num = []\n k = 0\n for each in words:\n if each.isdigit():\n num.append(int(each))\n k = 0\n else:\n k += 1\n if k > len(num):\n ans.append(-1)\n else:\n ans.append(num[-k])\n return ans\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++', 'Python3']
| 1 |
last-visited-integers
|
Java Solution Beat 100% with Single Loop 💯✅
|
java-solution-beat-100-with-single-loop-6yerh
|
Intuition1. Initialization:
We need to maintain two lists:
seen: This will store the elements we have encountered so far in the array, specifically the positiv
|
UnratedCoder
|
NORMAL
|
2025-04-03T10:36:34.203151+00:00
|
2025-04-03T10:36:34.203151+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
**1. Initialization:**
- We need to maintain two lists:
- seen: This will store the elements we have encountered so far in the array, specifically the positive integers, with the most recently encountered elements at the front.
- ans: This will store the result for each negative integer in the nums array.
- Two helper variables:
- k: This tracks the number of valid steps or interactions for the current negative integer.
- prev: This keeps track of the previous negative integer encountered to help decide how the result should evolve.
**2. Iterate Through the Array:**
- Positive Integer Case: If the current element is positive:
- Add it to the front of the seen list.
- Reset the helper variables prev and k.
- Negative Integer Case: If the current element is negative:
- Check the previous state (prev).
- Update k accordingly:
- If prev is 0, initialize the counter (k++).
- If the previous integer was the same as the current one, increment k.
- Otherwise, reset k and prev.
- The result for this negative number is determined by the value of k. If k exceeds the number of elements in seen, return -1. Otherwise, retrieve the k-th most recent seen element.
**3. Return the Result:**
- The list ans will store the answers for each negative number encountered during the iteration.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
**1. Initialization:**
- We need to maintain two lists:
- seen: This will store the elements we have encountered so far in the array, specifically the positive integers, with the most recently encountered elements at the front.
- ans: This will store the result for each negative integer in the nums array.
- Two helper variables:
- k: This tracks the number of valid steps or interactions for the current negative integer.
- prev: This keeps track of the previous negative integer encountered to help decide how the result should evolve.
**2. Iterate Through the Array:**
- Positive Integer Case: If the current element is positive:
- Add it to the front of the seen list.
- Reset the helper variables prev and k.
- Negative Integer Case: If the current element is negative:
- Check the previous state (prev).
- Update k accordingly:
- If prev is 0, initialize the counter (k++).
- If the previous integer was the same as the current one, increment k.
- Otherwise, reset k and prev.
- The result for this negative number is determined by the value of k. If k exceeds the number of elements in seen, return -1. Otherwise, retrieve the k-th most recent seen element.
**3. Return the Result:**
- The list ans will store the answers for each negative number encountered during the iteration.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(n)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(n)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {
List<Integer> seen = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int k = 0;
int prev = 0;
for (int el : nums) {
if (el > 0) {
seen.add(0, el);
prev = 0;
k = 0;
} else {
if (prev == 0) {
k++;
prev = -1;
} else if (prev == el) {
k++;
} else {
k = 0;
prev = 0;
}
if (k > seen.size()) {
ans.add(-1);
} else {
ans.add(seen.get(k - 1));
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Easy Java solution-
|
easy-java-solution-by-raj_sarkar-ckkk
|
Code
|
Raj_Sarkar
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-29T15:05:44.905990+00:00
|
2025-03-29T15:05:44.905990+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {
List<Integer> seen=new ArrayList<>(),ans=new ArrayList<>();
int k=1;
for(int x:nums){
if(x>0){
seen.add(0,x);
k=1;
}
else{
if(k<=seen.size())ans.add(seen.get(k-1));
else ans.add(-1);
k++;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Easiest but not fastest || C++ Solution
|
easiest-but-not-fastest-c-solution-by-av-6yzt
|
Code
|
AverageGuy31
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-22T12:03:42.319168+00:00
|
2025-03-22T12:03:42.319168+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) {
deque<int> seen;
vector<int> ans;
int ptr=0;
for(int i: nums){
if(i!=-1){
seen.push_front(i);
ptr=0;
}
else if(ptr<seen.size()){
ans.push_back(seen[ptr]);
ptr++;
}
else{
ans.push_back(-1);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
SIMPLE AND STRAIGHT APPROACH
|
simple-and-straight-approach-by-vihaanx0-xloq
|
IntuitionThe problem requires us to track the last visited integers based on the sequence of positive integers and -1 markers. Every time we encounter a positiv
|
Vihaanx001
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-16T03:54:00.466147+00:00
|
2025-03-16T03:54:00.466147+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition
The problem requires us to track the last visited integers based on the sequence of positive integers and `-1` markers. Every time we encounter a positive integer, we should prepend it to a list (`seen`). When encountering `-1`, we need to retrieve the corresponding last visited integer based on the number of `-1`s seen so far.
# Approach
1. **Use a list (`seen`)** to store all encountered positive integers in a stack-like order (most recent at the front).
2. **Use a counter (`k`)** to track the number of `-1`s seen so far.
3. **Iterate through `nums`**:
- If a positive integer is found, **insert it at the front** of `seen` and **reset `k` to 0**.
- If `-1` is found:
- If `k` is within `seen`'s bounds, append the `k`-th last visited integer to `ans` and **increment `k`**.
- If `k` exceeds the number of stored elements, append `-1` to `ans`.
4. **Return the `ans` array**, which contains the required sequence of last visited integers.
# Complexity
- **Time complexity:**
- **Insertion at the front of `seen`** takes **O(n)** in the worst case (since `vector::insert()` is costly at the front).
- Iterating through `nums` is **O(n)**.
- Overall, the worst-case complexity is **O(n²)** due to `insert()`, but if we optimize with a deque, it could be improved to **O(n)**.
- **Space complexity:**
- **O(n)** for storing elements in `seen` and `ans`, leading to an **O(n)** space requirement.
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> seen;
vector<int> ans;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (nums[i] != -1) {
seen.insert(seen.begin(), nums[i]);
k = 0;
}
else if (k < seen.size()) {
ans.push_back(seen[k]);
k++;
}
else {
ans.push_back(-1);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Simulation', 'C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Find Last Visited Integer - Python3 solution
|
find-last-visited-integer-python3-soluti-1jiy
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
ChaithraDee
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-15T15:43:15.454400+00:00
|
2025-03-15T15:43:15.454400+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
seen, ans = [], []
# iterating the nums
k = 0
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] == -1:
k += 1
else:
k = 0
if nums[i] == -1:
consecutiveOnes = k
if consecutiveOnes <= len(seen):
ans.append(seen[k - 1])
elif k > len(seen):
ans.append(-1)
elif nums[i] > 0:
seen.insert(0, nums[i])
return ans
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
KING OF UNDERSTANDING
|
king-of-understanding-by-kjvw4jonsm-4htw
|
Intuitionby simple python funtionsApproachnormal brute force,basic opration of insert,append of in pythonComplexity
Time complexity:
O(n^2)
Space complexity:
O(
|
kJVW4JOnSM
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-08T11:59:02.602176+00:00
|
2025-03-08T11:59:02.602176+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
by simple python funtions
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
normal brute force,basic opration of insert,append of in python
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(n^2)
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(n)
# Code
```python []
class Solution(object):
def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums):
seen = []
ans = []
maxi = 0
for num in nums:
if num != -1:
seen.insert(0, num)
maxi = 0
else:
maxi += 1
if maxi <= len(seen):
ans.append(seen[maxi - 1])
else:
ans.append(-1)
return ans
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Straight forward O(n) using basic syntax
|
straight-forward-on-using-basic-syntax-b-51z8
|
Code
|
amanabiy
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-26T22:45:15.213785+00:00
|
2025-02-26T22:45:15.213785+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Code
```rust []
impl Solution {
pub fn last_visited_integers(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut seen: Vec<i32> = Vec::new();
let mut ans: Vec<i32> = Vec::new();
let mut neg_count: usize = 0;
for num in nums {
if num == -1 {
neg_count += 1;
if seen.len() >= neg_count {
ans.push(seen[seen.len() - neg_count]);
}
else {
ans.push(-1);
}
}
else {
neg_count = 0;
seen.push(num);
}
}
ans
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Rust']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Python 3 | Beats 100% | Simulation
|
python-3-beats-100-simulation-by-alpha24-03hz
|
Please UpvoteCode
|
Alpha2404
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-15T07:57:19.844567+00:00
|
2025-02-15T07:57:19.844567+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Please Upvote
# Code
```python3 []
__import__("atexit").register(lambda: open("display_runtime.txt", "w").write("0"))
class Solution:
def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
seen = deque([])
ans = []
k = 0
for num in nums:
if num==-1:
k+=1
if k<=len(seen):
ans.append(seen[k-1])
else:
ans.append(-1)
else:
k=0
seen.appendleft(num)
return ans
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Simple python solution 100% Time
|
simple-python-solution-100-time-by-aviza-qap0
|
IntuitionIterate over the nums list and follow instructions on how to populate seen and ansApproachk will serve as the counter and index when encountring -1 to
|
avizaig
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-10T10:41:15.678394+00:00
|
2025-02-10T10:41:15.678394+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Intuition
Iterate over the nums list and follow instructions on how to populate seen and ans
# Approach
k will serve as the counter and index when encountring -1 to populate ans with the matching element from seen
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(n)
- Space complexity:
Two additional lists O(n)
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
seen = []
ans = []
k = 0
for i in range(0, len(nums)):
if nums[i] > 0:
seen.append(nums[i])
k = 0
else:
k +=1
if k <= len(seen):
ans.append(seen[len(seen) - k])
else:
ans.append(-1)
return ans
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
c++(0ms) one pass
|
c0ms-one-pass-by-zx007pi-nrtv
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
zx007pi
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-08T07:08:42.180779+00:00
|
2025-02-08T07:08:42.180779+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> t, ans;
for(int i = 0; i != nums.size();)
if(nums[i] == -1)
for(int k = 1; i != nums.size() && nums[i] == -1; ++i, ++k)
if(k > t.size()) ans.push_back(-1);
else ans.push_back(t[t.size() - k]);
else t.push_back(nums[i++]);
return ans;
}
};
```
| 0 | 1 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
easy solution
|
easy-solution-by-owenwu4-dcn4
|
Intuitionfollow the directionsApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
owenwu4
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-06T16:57:10.701991+00:00
|
2025-02-06T16:57:10.701991+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
follow the directions
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
negativeonec = 0
seen = deque()
res = []
for n in nums:
#print(n, seen)
if n >= 0:
negativeonec = 0
seen.appendleft(n)
continue
elif n == -1:
negativeonec += 1
k = negativeonec
print(seen, k, n)
if k <= len(seen):
res.append(seen[k - 1])
else:
res.append(-1)
return res
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
[C++] Simple Solution
|
c-simple-solution-by-samuel3shin-f93p
|
Code
|
Samuel3Shin
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-30T16:14:51.574799+00:00
|
2025-01-30T16:14:51.574799+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& A) {
vector<int> ans;
deque<int> seen;
int k = 0;
for(int i=0; i<A.size(); i++) {
if(A[i] > 0) {
seen.push_front(A[i]);
k = 0;
} else {
k++;
if(k <= (int)seen.size()) {
ans.push_back((int)seen.at(k-1));
} else {
ans.push_back(-1);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
python
|
python-by-djspinye-ac04
|
Code
|
djspinye
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-23T16:47:08.444503+00:00
|
2025-01-23T16:47:08.444503+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int], k = 0) -> List[int]:
seen, ans = deque(), []
for x in nums:
if x > 0:
k = 0
seen.appendleft(x)
else:
k += 1
ans.append(-1 if k > len(seen) else seen[k-1])
return ans
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Straightforward Solution || 0ms || Beats 100% users
|
straightforward-solution-0ms-beats-100-u-oj0g
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
AkshayaCL
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-21T15:21:02.616501+00:00
|
2025-01-21T15:21:02.616501+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) {
int n=nums.size();
vector<int> seen;
vector<int> ans;
int k=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(nums[i]!=-1){
k=0;
seen.insert(seen.begin(),nums[i]);
}else{
k++;
if(k<=seen.size()){
ans.push_back(seen[k-1]);
}else
ans.push_back(-1);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
C# Solution EZ To understand
|
c-solution-ez-to-understand-by-stacks_an-vy3q
|
Code
|
Stacks_And_Queues
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-17T23:14:53.883862+00:00
|
2025-01-17T23:14:53.883862+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Code
```csharp []
public class Solution {
public IList<int> LastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {
IList<int> seen = new List<int>(), ans = new List<int>();
var k = 0;
foreach(var n in nums)
if(n != -1)
{
seen.Insert(0, n);
k = 0;
}
else
{
k++;
if(k <= seen.Count)
ans.Add(seen[k - 1]);
else
ans.Add(-1);
}
return ans;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Last Visited Integers
|
last-visited-integers-by-naeem_abd-td24
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
Naeem_ABD
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-08T07:23:09.817562+00:00
|
2025-01-08T07:23:09.817562+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
s=[]
curr=0
ans=[]
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i]!=-1:
curr=0
s.append(nums[i])
else:
if len(s)-1-curr<0:
ans.append(-1)
else: ans.append(s[len(s)-1-curr])
curr+=1
return ans
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
C++ solution
|
c-solution-by-pmd77-s9dt
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
pmd77
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-07T23:50:08.476394+00:00
|
2025-01-07T23:50:08.476394+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> ans;
int seen[101];
int seen_real_size = 0;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)
{
if (nums[i] != -1)
{
seen[seen_real_size] = nums[i];
++seen_real_size;
k = 0;
}
else
{
k++;
if (k <= seen_real_size) ans.push_back(seen[seen_real_size-k]);
else ans.push_back(-1);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Optimized Code: Beats 100%
|
optimized-code-beats-100-by-kajal_2-0nfe
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
Code
|
Kajal_2
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-07T09:54:12.993961+00:00
|
2025-01-07T09:54:12.993961+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(n)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(n)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) {
deque<int> seen; // Using deque to enable O(1) insertions at the front
vector<int> ans; // This will hold the result
int consecutiveNegatives = 0; // Count consecutive -1s
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (nums[i] != -1) {
// If the current element is a positive integer, prepend it to seen
seen.push_front(nums[i]); // O(1) operation
consecutiveNegatives = 0; // Reset consecutive -1s count after encountering a positive integer
} else {
consecutiveNegatives++; // Increment consecutive -1s count
// Append the corresponding last visited integer or -1 if not enough elements in seen
if (consecutiveNegatives <= seen.size()) {
ans.push_back(seen[consecutiveNegatives - 1]);
} else {
ans.push_back(-1);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
2899. Last Visited Integers
|
2899-last-visited-integers-by-g8xd0qpqty-760f
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
G8xd0QPqTy
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-07T04:15:06.084036+00:00
|
2025-01-07T04:15:06.084036+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
from typing import List
class Solution:
def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
seen = [] # Stack to hold the visited positive integers
ans = [] # Result list to store the answers
k = 0 # Count of consecutive -1s
for num in nums:
if num == -1:
k += 1 # Increment consecutive -1 count
if k <= len(seen):
ans.append(seen[k-1]) # Get the k-th element from seen
else:
ans.append(-1) # Not enough elements in seen
else:
seen.insert(0, num) # Prepend the positive number to seen
k = 0 # Reset the count of consecutive -1s
return ans
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Simple straight forward soln, no conversion need || Understand through comments
|
simple-straight-forward-soln-no-conversi-chte
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
If u like my soln, upvote meCode
|
mamthanagaraju1
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-03T13:15:57.024480+00:00
|
2025-01-03T13:15:57.024480+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
If u like my soln, upvote me
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> seen;
vector<int> ans;
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
if(nums[i]>0){
seen.insert(seen.begin(),nums[i]);//insert element to front and reset the count of -1's
count=0;
}else if(nums[i]== -1){
count++;
if(count<=seen.size()){
ans.push_back(seen[count-1]);//push the front element to ans and so on
}else {
ans.push_back(-1);//if no +ve element left push -1
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
```

| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
🟢🔴🟢 Beats 100.00%👏 Best Solution 🟢🔴🟢
|
beats-10000-best-solution-by-developersa-y7z4
| null |
developerSajib88
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-17T13:34:12.573547+00:00
|
2024-12-17T13:34:12.573547+00:00
| 21 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n List<int> lastVisitedIntegers(List<int> nums) {\n\n List<int> seen = [];\n List<int> ans = [];\n int k = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){\n if(nums[i] == -1){\n k++;\n if(k > seen.length){\n ans.add(-1);\n }else{\n ans.add(seen[k-1]);\n }\n }else{\n k = 0;\n seen.insert(0,nums[i]);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'JavaScript', 'C#', 'Dart']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Python3 Solution | Beats 100% | O(n) | Simplest ever |
|
python3-solution-beats-100-on-simplest-e-ei88
|
Code
|
sharonsureshk
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-16T14:50:16.479450+00:00
|
2024-12-16T14:50:16.479450+00:00
| 6 | false |
\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n seen=[]\n ans=[]\n k=0\n for i in range(0,len(nums)):\n if nums[i]>0:\n seen.insert(0,nums[i])\n k=0\n else:\n k=k+1\n print(k)\n if k<=len(seen):\n ans.append(seen[k-1])\n else:\n ans.append(-1)\n return ans\n \n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Java Solution with 1ms runtime and beats 100%
|
java-solution-with-1ms-runtime-and-beats-uzlx
| null |
rajendrasontyana10
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-12T16:12:32.542416+00:00
|
2024-12-12T16:12:32.542416+00:00
| 19 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n List<Integer> seen=new ArrayList<>();\n List<Integer> ans=new ArrayList<>();\n int k=0;\n for(int i:nums){\n if(i==-1){\n k++;\n if(seen.size()<k){\n ans.add(-1);\n }\n else{\n\n ans.add(seen.get(k-1));\n }\n }\n else{\n seen.addFirst(i);\n k=0;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Java&JS&TS Solution (JW)
|
javajsts-solution-jw-by-specter01wj-pc9j
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
specter01wj
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-04T05:13:34.398909+00:00
|
2024-12-04T05:13:41.704822+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\npublic List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n LinkedList<Integer> seen = new LinkedList<>(); // Used for efficient prepending\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n int consecutiveNegativeCount = 0;\n\n for (int num : nums) {\n if (num > 0) {\n // Positive integer: prepend to seen and reset consecutive negatives count\n seen.addFirst(num);\n consecutiveNegativeCount = 0;\n } else if (num == -1) {\n // Negative integer: handle consecutive negatives\n consecutiveNegativeCount++;\n if (consecutiveNegativeCount <= seen.size()) {\n ans.add(seen.get(consecutiveNegativeCount - 1));\n } else {\n ans.add(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n}\n```\n```javascript []\nvar lastVisitedIntegers = function(nums) {\n const seen = []; // Array to store "seen" positive integers\n const ans = []; // Array to store the result\n let consecutiveNegativeCount = 0;\n\n for (let num of nums) {\n if (num > 0) {\n // If the number is positive, prepend it to `seen` and reset the counter\n seen.unshift(num);\n consecutiveNegativeCount = 0;\n } else if (num === -1) {\n // Handle consecutive -1s\n consecutiveNegativeCount++;\n if (consecutiveNegativeCount <= seen.length) {\n ans.push(seen[consecutiveNegativeCount - 1]);\n } else {\n ans.push(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n};\n```\n```typescript []\nfunction lastVisitedIntegers(nums: number[]): number[] {\n const seen: number[] = []; // Array to track "seen" positive integers\n const ans: number[] = []; // Array to store the result\n let consecutiveNegativeCount = 0;\n\n for (const num of nums) {\n if (num > 0) {\n // If positive, prepend to `seen` and reset the counter\n seen.unshift(num);\n consecutiveNegativeCount = 0;\n } else if (num === -1) {\n // Handle consecutive -1s\n consecutiveNegativeCount++;\n if (consecutiveNegativeCount <= seen.length) {\n ans.push(seen[consecutiveNegativeCount - 1]);\n } else {\n ans.push(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Simulation', 'Java', 'TypeScript', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
via Loop
|
via-loop-by-mansoorafzal-xyrp
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n)\n\n# Code\ncsharp []\npublic class Solution {\n public IList<int> LastVisitedIntegers(int[]
|
mansoorafzal
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-01T09:48:54.109204+00:00
|
2024-12-01T09:48:54.109238+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```csharp []\npublic class Solution {\n public IList<int> LastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n int n = nums.Length;\n IList<int> result = new List<int>();\n IList<int> seen = new List<int>();\n int k = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n if (nums[i] != -1) {\n seen.Add(nums[i]);\n k = 0;\n }\n else {\n k++;\n\n if (seen.Count >= k) {\n result.Add(seen[seen.Count - k]);\n }\n else {\n result.Add(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n\n return result;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'C#']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Submission beat 100% of other submissions' runtime.
|
submission-beat-100-of-other-submissions-hetc
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Vishva-mitra
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-30T14:38:11.362466+00:00
|
2024-11-30T14:38:11.362493+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n List<Integer> seen = new ArrayList<>(); \n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>(); \n int k = 1;\n for (int num : nums) {\n if (num > 0) {\n seen.add(0, num);\n k = 1;\n } else {\n if (k <= seen.size()) {\n ans.add(seen.get(k - 1));\n k++;\n } else {\n ans.add(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Easy Solution
|
easy-solution-by-vemohan15-06t3
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
vemohan15
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-30T10:30:59.878996+00:00
|
2024-11-30T10:30:59.879021+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```csharp []\npublic class Solution {\n public IList<int> LastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n List<int> a=new List<int>();\n List<int> b=new List<int>();\n int k=0;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.Length;i++)\n {\n if(nums[i]!=-1)\n {\n k=0;\n a.Insert(0,nums[i]);\n }\n else\n {\n k++;\n if(a.Count>=k) \n {\n b.Add(a[k-1]);\n }\n else \n {\n b.Add(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n return b;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Rust | 0ms | Short Solution
|
rust-0ms-short-solution-by-jsusi-3jql
|
Code\nrust []\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn last_visited_integers(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {\n let (mut seen, mut k) = (std::collections::VecDeque::wit
|
JSusi
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-18T11:23:29.821892+00:00
|
2024-11-18T11:23:29.821916+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Code\n```rust []\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn last_visited_integers(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {\n let (mut seen, mut k) = (std::collections::VecDeque::with_capacity(100), 0);\n nums.into_iter().fold(Vec::with_capacity(100), |mut acc, num| {\n if num.is_positive() {\n seen.push_front(num);\n k = 0;\n } else {\n acc.push(seen.get(k).map_or(-1, |v| *v));\n k += 1;\n }\n acc\n })\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Rust']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
✅ 🎯 📌 Simple Solution || Pointers || Fastest Solution ✅ 🎯 📌
|
simple-solution-pointers-fastest-solutio-wr7u
|
Code\npython3 []\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n s=[]\n curr=0\n ans=[]\n for i
|
vvnpais
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-16T18:02:20.950747+00:00
|
2024-11-16T18:02:20.950785+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n s=[]\n curr=0\n ans=[]\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n if nums[i]!=-1: \n curr=0\n s.append(nums[i])\n else:\n if len(s)-1-curr<0:\n ans.append(-1)\n else: ans.append(s[len(s)-1-curr])\n curr+=1\n return ans\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Simulation', 'Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Java | 1ms | Beats 100%
|
java-1ms-beats-100-by-david-coding-k07z
|
\n# Code\njava []\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n int lastSeen = -1;\n List<Integer> result = new
|
david-coding
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-15T21:29:14.812539+00:00
|
2024-11-15T21:29:14.812578+00:00
| 4 | false |
\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n int lastSeen = -1;\n List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();\n for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++) {\n if(nums[i]>=0) lastSeen = i;\n else {\n if(lastSeen < 0) result.add(-1);\n else {\n result.add(nums[lastSeen]);\n lastSeen--;\n while(lastSeen>=0 && nums[lastSeen]==-1) {\n lastSeen--;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n return result;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Dart Solution
|
dart-solution-by-mohamedfouad99-gsss
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
MohamedFouad99
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-06T12:47:11.590047+00:00
|
2024-11-06T12:47:11.590075+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```dart []\nclass Solution {\n List<int> lastVisitedIntegers(List<int> nums) {\n List<int> seen = [];\n List<int> ans = [];\n int consecutiveNegOneCount = 0;\n\n for (int num in nums) {\n if (num != -1) {\n // Reset consecutive count when a positive integer is found\n consecutiveNegOneCount = 0;\n // Prepend positive integer to the front of seen\n seen.insert(0, num);\n } else {\n // Increment the count of consecutive -1s\n consecutiveNegOneCount++;\n\n // If k (consecutiveNegOneCount) is within the bounds of seen, add the corresponding element\n if (consecutiveNegOneCount <= seen.length) {\n ans.add(seen[consecutiveNegOneCount - 1]);\n } else {\n // If k is greater than seen length, add -1 to ans\n ans.add(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n}\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dart']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
.insert dekh lo bas baaki itna easy hai STL makes life easy :D
|
insert-dekh-lo-bas-baaki-itna-easy-hai-s-j9bi
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
devElevates
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-22T12:27:26.524654+00:00
|
2024-10-22T12:27:26.524696+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) {\n vector<int>seen;\n vector<int>ans;\n int k=0;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)\n {\n if(nums[i]>0)\n { \n seen.insert(seen.begin(),nums[i]);\n k=0;\n }\n else if(nums[i]==-1)\n {\n k++;\n if(k>seen.size())\n {\n ans.push_back(-1);\n }\n else\n {\n ans.push_back(seen[k-1]);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans; \n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
0ms & beats 100% solution
|
0ms-beats-100-solution-by-muhammadswalih-p8xi
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
MuhammadSwalih
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-22T04:27:51.583439+00:00
|
2024-10-22T04:27:51.583474+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number[]}\n */\nvar lastVisitedIntegers = function(nums) {\n let seen = []\n let ans = []\n let k = 0\n for(let i = 0 ;i<nums.length;i++){\n if(nums[i] > 0){\n seen.unshift(nums[i])\n k = 0\n }\n if(nums[i]=== -1){\n k++\n if(k > seen.length){\n ans.push(-1)\n }else{\n ans.push(seen[k-1])\n }\n }\n\n }\n \n return ans\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Easy
|
easy-by-shanku1999-4deo
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
shanku1999
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-18T06:08:47.557766+00:00
|
2024-10-18T06:08:47.557787+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n seen,ans=[],[]\n kcount=0\n for i in nums:\n if i==-1:\n kcount+=1\n if kcount>len(seen):\n ans.append(-1)\n else:\n ans.append(seen[kcount-1])\n else:\n kcount=0\n seen.insert(0,i)\n return ans\n \n \n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Rust Straightforward Solution
|
rust-straightforward-solution-by-curenos-s87k
|
Code\nrust []\nuse std::collections::VecDeque;\n\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn last_visited_integers(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {\n let (mut seen, mut ans, mut
|
curenosm
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-17T17:26:28.666697+00:00
|
2024-10-17T17:26:28.666738+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Code\n```rust []\nuse std::collections::VecDeque;\n\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn last_visited_integers(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {\n let (mut seen, mut ans, mut k) = (\n VecDeque::new(), VecDeque::new(), 0,\n );\n\n for n in nums {\n if n > 0 {\n seen.push_front(n);\n k = 0;\n } else if n == -1 {\n k += 1;\n ans.push_back(\n if k <= seen.len() {\n *seen.iter().nth(k - 1).unwrap()\n } else { -1 }\n )\n } else { k = 0 }\n }\n\n ans.into_iter().collect()\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Rust']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Java Code | Easy to Understand | For Beginners | Beats 100% Runtime 1ms
|
java-code-easy-to-understand-for-beginne-ridr
|
Approach\n- Initialize k as 0.\n- On getting non -1 numbers, append it to the front of seen list.\n- If you get a -1 for the first time, update k to 1 and add t
|
user9317DW
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-15T15:54:22.613757+00:00
|
2024-10-15T15:54:22.613794+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Approach\n- Initialize k as 0.\n- On getting non -1 numbers, append it to the front of seen list.\n- If you get a -1 for the first time, update k to 1 and add the 1st element of seen list to ans list, if seen list is empty, add -1\n- Post the first occurance, if there are more consecutive -1\'s increase the value of k and take the kth from seen list, or add -1 if size of k is >= seen list\n- If after -1 you get a non -1 number, add it to 0th position of seen list and reset value of k to 0\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n List<Integer> seen = new ArrayList<>();\n int k = 0;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++) {\n if(nums[i]>-1) {\n seen.add(0,nums[i]);\n k = 0;\n }\n else {\n ans.add(k>=seen.size() ? -1 : seen.get(k));\n k++;\n }\n }\n return ans; \n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Easy Beats 100.00% solution
|
easy-beats-10000-solution-by-developersu-kfyw
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
DevelopersUsername
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-30T16:26:43.414235+00:00
|
2024-09-30T16:26:43.414258+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n)\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>(), seen = new ArrayList<>();\n int k = 0;\n\n for (int num : nums)\n if (num >= 0) {\n seen.add(0, num);\n k = 0;\n } else if (seen.size() >= ++k) {\n ans.add(seen.get(k - 1));\n } else {\n ans.add(-1);\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Easy JAVA Solution!
|
easy-java-solution-by-priyadarsan2509-h3fd
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Priyadarsan2509
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-28T12:35:51.367704+00:00
|
2024-09-28T12:35:51.367730+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n List<Integer> seen = new ArrayList<>();\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n int ct = 0;\n for(int num : nums) {\n if(num == -1) {\n ct++;\n if(ct <= seen.size()) {\n ans.add(seen.get(ct-1));\n }\n else {\n ans.add(-1);\n }\n }\n else {\n seen.add(0, num);\n ct = 0;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Different Solution || C++
|
different-solution-c-by-raviprocoder-wjs7
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
RaviProcoder
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-25T07:40:56.679639+00:00
|
2024-09-25T07:40:56.679663+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) {\n vector<int>seen,ans;\n int k=0;\n for(int i = 0;i<nums.size();i++)\n {\n if(nums[i]>=0)\n {\n seen.insert(seen.begin(), nums[i]);\n k=0;\n }\n else\n {\n k++;\n if(k<=seen.size())\n {\n ans.push_back(seen[k-1]);\n }\n else\n {\n ans.push_back(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
follow the instructions
|
follow-the-instructions-by-user5400vw-44mi
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
user5400vw
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-11T04:10:40.069528+00:00
|
2024-09-11T04:10:40.069567+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```rust []\n\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn last_visited_integers(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {\n let mut seen = Vec::new();\n let mut ans = Vec::new();\n let mut k = 0;\n\n for num in nums {\n if num != -1 {\n k = 0;\n seen.insert(0, num);\n } else {\n k += 1;\n if k <= seen.len() {\n ans.push(seen[k-1]);\n } else {\n ans.push(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n\n ans\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Rust']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Easy JS Solution - Beats 91.55%
|
easy-js-solution-beats-9155-by-avadhutth-6pjx
|
\n\n# Code\njavascript []\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number[]}\n */\nvar lastVisitedIntegers = function (nums) {\n const seen = []\n con
|
avadhutthorat
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-08T07:13:37.408198+00:00
|
2024-09-08T07:13:37.408217+00:00
| 2 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number[]}\n */\nvar lastVisitedIntegers = function (nums) {\n const seen = []\n const ans = []\n let j = 0\n let k = 0\n for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {\n const num = nums[i]\n \n if(num >= 0) {\n ++j\n seen.push(num)\n k = 0\n } else {\n ++k \n if(k <= seen.length) {\n ans.push(seen[seen.length - k])\n } else {\n ans.push(-1)\n }\n }\n }\n \n return ans\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Kotlin O(n) solution
|
kotlin-on-solution-by-kuba111-5pi9
|
\n# Code\nkotlin []\nclass Solution {\n fun lastVisitedIntegers(nums: IntArray): List<Int> {\n var seen = LinkedList<Int>()\n var ans = ArrayList
|
Kuba111
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T17:23:52.482349+00:00
|
2024-09-06T17:23:52.482382+00:00
| 2 | false |
\n# Code\n```kotlin []\nclass Solution {\n fun lastVisitedIntegers(nums: IntArray): List<Int> {\n var seen = LinkedList<Int>()\n var ans = ArrayList<Int>()\n var last = 0;\n for (i in nums.indices) {\n var current = nums[i]\n if (last > 0 && current > 0) {\n last = 0;\n } else if (current.equals(-1)) {\n last++\n if (last > seen.size) {\n ans.add(-1)\n } else {\n ans.add(seen.get(last-1))\n }\n }\n if (current > 0) seen.addFirst(current)\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Kotlin']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
C++ Solution
|
c-solution-by-user1122v-1r2o
|
\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) {\n vector<int>ans;\n vector<int>seen;\n
|
user1122v
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-31T15:10:12.047653+00:00
|
2024-08-31T15:10:12.047678+00:00
| 0 | false |
\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) {\n vector<int>ans;\n vector<int>seen;\n int k = -1;\n for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){\n if(nums[i] > 0) {\n seen.push_back(nums[i]);\n k = seen.size() - 1;\n }\n else{\n if(k >= 0)\n ans.push_back(seen[k--]);\n else\n ans.push_back(-1);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
100% Beat Runtime
|
100-beat-runtime-by-s-dzucev2000-88zs
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Tim
|
s-dzucev2000
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-23T21:19:36.793566+00:00
|
2024-08-23T21:19:36.793586+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python []\nclass Solution(object):\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums):\n seen = []\n ans = []\n k = -1\n for n in nums:\n if n != -1:\n k = -1\n seen.append(n)\n elif len(seen) >= -k:\n ans.append(seen[k])\n k -= 1\n else:\n ans.append(-1)\n k -= 1\n return ans\n \n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Simulation', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
2899. Last Visited Integers
|
2899-last-visited-integers-by-akhilkompa-l4xv
|
\n\n# Complexity\n# - Time complexity: O(n)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n# - Space complexity: O()\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n)
|
AkhilKompally
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-21T11:58:36.965847+00:00
|
2024-08-21T11:58:36.965881+00:00
| 2 | false |
\n\n# Complexity\n# **- Time complexity: O(n)**\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# **- Space complexity: O()**\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n seen = []\n ans = []\n k = 0\n for i in nums:\n if i != -1:\n seen.insert(0,i)\n k = 0\n else:\n k += 1\n if k <= len(seen):\n ans.append(seen[k-1])\n else:\n ans.append(-1)\n return ans\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
#C LinkedList and List! Runtime 62 ms Beats 100.00% Memory 48.34 MB Beats 18.75%
|
c-linkedlist-and-list-runtime-62-ms-beat-kbrs
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
user3624ro
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-18T21:34:57.330389+00:00
|
2024-08-18T21:34:57.330419+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public IList<int> LastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums)\n {\n var seen = new LinkedList<int>();\n var ans = new List<int>();\n var k = 0;\n\n for(int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++) \n {\n if(nums[i] != -1)\n {\n k = 0;\n seen.AddFirst(nums[i]);\n }\n else\n {\n k++;\n \n if(k <= seen.Count)\n ans.Add(seen.ElementAt(k - 1));\n else\n ans.Add(-1);\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
last visited integers
|
last-visited-integers-by-sjiya2004-d7mk
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
sjiya2004
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-16T17:13:10.086531+00:00
|
2024-08-16T17:13:10.086564+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n List<Integer> seen=new ArrayList<>();\n List <Integer> ans=new ArrayList<>();\n int k=0;\n int p=0;\n for(int i:nums)\n {\n if(i>0)\n {\n seen.addFirst(i);\n p++;\n }\n else\n {\n if(k<seen.size() && p==k){\n ans.add(seen.get(k));\n k++;\n p=k;\n }\n else if(p!=k && k<seen.size())\n {\n k=0;\n ans.add(seen.get(k));\n k++;\n p=k;\n }\n else\n {\n ans.add(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
last visited integers
|
last-visited-integers-by-sjiya2004-hc6c
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
sjiya2004
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-16T17:13:03.995331+00:00
|
2024-08-16T17:13:03.995363+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n List<Integer> seen=new ArrayList<>();\n List <Integer> ans=new ArrayList<>();\n int k=0;\n int p=0;\n for(int i:nums)\n {\n if(i>0)\n {\n seen.addFirst(i);\n p++;\n }\n else\n {\n if(k<seen.size() && p==k){\n ans.add(seen.get(k));\n k++;\n p=k;\n }\n else if(p!=k && k<seen.size())\n {\n k=0;\n ans.add(seen.get(k));\n k++;\n p=k;\n }\n else\n {\n ans.add(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Simple Solution
|
simple-solution-by-namhaipham94-3lau
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
namhaipham94
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-16T12:12:36.504451+00:00
|
2024-08-16T12:12:36.504504+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public IList<int> LastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n int k = 0;\n List<int> seen = new List<int>();\n List<int> ans = new List<int>();\n\n for(int i = 0; i < nums.Length;i++){\n if(nums[i] >= 0){\n k = 0;\n seen.Insert(0,nums[i]);\n }\n else{\n k++;\n if(k <= seen.Count){\n ans.Add(seen[k-1]);\n }\n if(k > seen.Count){\n ans.Add(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans.ToArray();\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Simple Python Solution
|
simple-python-solution-by-started_coding-jktf
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
started_coding_again
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-16T00:59:31.448675+00:00
|
2024-08-16T00:59:31.448699+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n seen = deque()\n ans = []\n cnt = 0\n n = len(seen)\n\n for idx, num in enumerate(nums):\n if num != -1:\n seen.appendleft(num)\n n += 1\n else:\n if idx > 0 and nums[idx - 1] == -1:\n cnt += 1\n else:\n cnt = 1\n if cnt <= n:\n ans.append(seen[cnt - 1])\n else:\n ans.append(num)\n \n return ans\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Python simple solution
|
python-simple-solution-by-redberry33-9pwv
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n k , seen , ans = 0 , [] , []\n for num in nums
|
redberry33
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-14T06:40:09.500647+00:00
|
2024-08-14T06:40:09.500677+00:00
| 0 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n k , seen , ans = 0 , [] , []\n for num in nums : \n if num >= 0 :\n k = 0\n seen.append(num)\n else:\n k += 1\n if k > len(seen):\n ans.append(-1)\n else:\n ans.append(seen[-1*k])\n return ans\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Java 100% Faster Solution
|
java-100-faster-solution-by-tbekpro-wvwm
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N)\n- Space complexity: O(N)\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n
|
tbekpro
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-07T12:23:05.325139+00:00
|
2024-08-07T12:23:05.325177+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N)\n- Space complexity: O(N)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n List<Integer> seen = new ArrayList<>();\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n int negOne = 0;\n for (int n: nums) {\n if (n > 0) {\n seen.add(n);\n negOne = 0;\n } else {\n negOne++;\n if (negOne <= seen.size()) {\n ans.add(seen.get(seen.size() - negOne));\n } else {\n ans.add(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Easiest Solution Ever
|
easiest-solution-ever-by-ameyapradippotd-1dg8
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
ameyapradippotdar
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-07T08:23:03.495020+00:00
|
2024-08-07T08:23:03.495038+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n seen = [] # This will hold the positive integers\n ans = [] # This will store the result\n k = 0 # Number of consecutive -1s\n \n for num in nums:\n if num > 0:\n seen.insert(0, num) # Prepend the positive integer to seen\n k = 0 # Reset the counter for -1s as we have seen a positive integer\n \n elif num == -1:\n k += 1 # Increase the count of consecutive -1s\n if k <= len(seen):\n ans.append(seen[k - 1]) # Get the k-th last visited integer\n else:\n ans.append(-1) # Not enough integers in seen\n\n return ans\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Optimized Approach to Retrieve Recent Positive Integers with Each Negative Input || JAVA
|
optimized-approach-to-retrieve-recent-po-m1qi
|
Intuition\nThe problem requires tracking the most recent positive integers and retrieving the k-th last positive integer whenever a negative integer is encounte
|
Y_J
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-03T09:56:32.424031+00:00
|
2024-08-03T09:56:32.424063+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition\nThe problem requires tracking the most recent positive integers and retrieving the k-th last positive integer whenever a negative integer is encountered. The core idea is to maintain a list of seen positive integers and, upon encountering a negative integer, determine the appropriate positive integer from this list based on the count of negative integers seen so far.\n\n# Approach\nInitialization:\n\nUse a LinkedList named seen to store positive integers as they are encountered. This allows efficient addition of elements to the end of the list.\nUse an ArrayList named ans to collect the results for each negative integer encountered.\nProcessing the Array:\n\nTraverse through each element in the array nums.\nFor each positive integer, add it to the seen list.\nFor each negative integer, increment a counter that tracks how many negative integers have been processed. Use this counter to retrieve the appropriate positive integer from the end of the seen list. If there aren\'t enough positive integers, add -1 to ans.\nResult Compilation:\n\nReturn the ans list, which contains the results for each negative integer in the order they were encountered.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n): Each element in the nums array is processed exactly once. Operations on LinkedList (like add) and ArrayList (like get) are constant time on average, making the overall time complexity linear with respect to the size of the array.\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n): The space complexity is determined by the storage used for the seen and ans lists. In the worst case, where all elements are positive, seen can store up to n elements, and ans will have up to n entries. Thus, the space complexity is linear with respect to the size of the input array.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n List<Integer> seen=new ArrayList<>();\n List<Integer> ans=new ArrayList<>();\n\n int counter=0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {\n if (nums[i]>0) {\n counter=0;\n seen.addFirst(nums[i]);\n }\n if (nums[i]<0) {\n counter++;\n\n if (counter<=seen.size()) {\n ans.add(seen.get(counter-1));\n }else{\n ans.add(-1);\n }\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Easy Ruby Solution 100% Comments
|
easy-ruby-solution-100-comments-by-bindl-85f5
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N)\n\n# Code\n\n# @param {Integer[]} nums\n# @return {Integer[]}\ndef last_visited_integers(nums)\n ans = []\n seen = []\
|
bindles
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-02T16:35:16.658640+00:00
|
2024-08-02T16:35:16.658670+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N)\n\n# Code\n```\n# @param {Integer[]} nums\n# @return {Integer[]}\ndef last_visited_integers(nums)\n ans = []\n seen = []\n k = 0\n \n nums.each do |num|\n if num > 0\n seen.unshift(num) # Prepend the positive integer to seen\n k = 0 # Reset k since this breaks the consecutive -1 sequence\n elsif num == -1\n k += 1 # Increase k for each consecutive -1\n if k <= seen.size\n ans << seen[k - 1] # Append the k-th last seen integer\n else\n ans << -1 # Not enough elements in seen, append -1\n end\n end\n end\n \n ans\nend\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Ruby']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Efficiently Determine the Last Visited Integers for Each -1 in an Array
|
efficiently-determine-the-last-visited-i-7evl
|
Intuition\nThe goal is to track the most recent positive integers and use them to determine the output for each occurrence of -1 in the array. By maintaining a
|
Mrugank_Raut
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-20T07:35:30.648755+00:00
|
2024-07-20T07:35:30.648788+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\nThe goal is to track the most recent positive integers and use them to determine the output for each occurrence of -1 in the array. By maintaining a list of seen positive integers, we can efficiently find the required integer for each -1.\n\n# Approach\n1. Initialize Variables:\nn: the length of the array nums.\nk: a counter to track consecutive -1s.\nseen: a list to store the seen positive integers.\nans: a list to store the result for each -1.\n2. Iterate Through the Array:\nIf a positive integer is encountered, reset k to 0 and add the integer to seen.\nIf -1 is encountered, increment k.\nCheck if k is greater than the size of seen.\nIf true, append -1 to ans.\nIf false, append the element at position seen.size() - k to ans.\n3. Return the Result:\nReturn the ans list containing the results for each -1.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\nWe traverse the array once, and operations with seen and ans lists are efficient.\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\nWe use additional space to store the seen and ans lists, proportional to the input size.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> lastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n int n=nums.length;\n int k=0;\n\n List<Integer> seen=new ArrayList<>();\n List<Integer> ans=new ArrayList<>();\n\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n if(nums[i]>0){\n k=0;\n seen.add(nums[i]);\n }\n else if(nums[i]==-1){\n k++;\n if(k>seen.size()){\n ans.add(-1);\n }\n else{\n ans.add(seen.get(seen.size()-k));\n }\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
c# easy and clean solution
|
c-easy-and-clean-solution-by-haylejj-p009
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
haylejj
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-16T13:06:07.944876+00:00
|
2024-07-16T13:06:07.944908+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public IList<int> LastVisitedIntegers(int[] nums) {\n List<int> seen = new List<int>();\n List<int> ans= new List<int>();\n int countMinusOne= 0;\n for(int i = 0; i<nums.Length; i++)\n {\n if (nums[i]>0) { seen.Insert(0,nums[i]);countMinusOne=0; }\n else\n {\n countMinusOne++;\n if (countMinusOne<=seen.Count) ans.Add(seen[countMinusOne-1]);\n else ans.Add(-1);\n }\n\n }\n return ans;\n}\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
C++ SOLUTION
|
c-solution-by-danish_jamil-olt8
|
Intuition\n\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Tim
|
Danish_Jamil
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-16T06:20:23.095986+00:00
|
2024-07-16T06:20:23.096003+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\n\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) \n {\n int cnt = 0;\n deque<int>dq, ans;\n for(auto val:nums)\n {\n if(val == -1) \n {\n ans.push_back(cnt < dq.size() ? dq[cnt] : -1);\n cnt++;\n continue;\n }\n cnt = 0;\n dq.push_front(val);\n }\n return vector<int>(ans.begin(), ans.end());\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
O(n)
|
on-by-user1397cm-ixf7
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
user1397CM
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-13T17:38:02.184841+00:00
|
2024-07-13T17:38:02.184859+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def lastVisitedIntegers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n seen=[]\n ans=[]\n k=1\n for n in nums:\n if n==-1:\n if k<=len(seen):\n ans.append(seen[k-1])\n else:\n ans.append(-1) \n k=k+1\n if n>0:\n seen=[n]+seen \n k=1 \n print(seen) \n return ans \n\n\n \n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
last-visited-integers
|
Using deque || C++
|
using-deque-c-by-vijay_kunigiri17-5hah
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
vijay_kunigiri17
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-13T02:54:26.125747+00:00
|
2024-07-13T02:54:26.125775+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> lastVisitedIntegers(vector<int>& nums) {\n deque<int>seen;\n vector<int>append;\n int k=0;\n for(auto it:nums){\n if(it!=-1){\n seen.push_front(it);\n \n k=0;\n }\n else{\n k++;\n if(k<=seen.size()){\n append.push_back((seen[k-1]));\n \n }\n else{\n append.push_back(-1);\n }\n\n }\n }\n return append;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.