question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
JAVA Easy Beginner Friendly Simple DFS calls with checks Slow but Works Fine.
|
java-easy-beginner-friendly-simple-dfs-c-mh8m
|
\nclass Solution {\n List<List<Integer>> res;\n public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {\n res = new ArrayList<>();\n f
|
bharat194
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-24T03:22:31.701793+00:00
|
2022-02-24T03:22:31.701831+00:00
| 608 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n List<List<Integer>> res;\n public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {\n res = new ArrayList<>();\n for(int i = 0;i<heights.length;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<heights[0].length;j++){\n if((i==heights.length-1 && j==0) || (i==0 && j==heights[0].length-1)){\n res.add(Arrays.asList(i,j));\n continue;\n }\n boolean[] pair = new boolean[2];\n boolean[][] visited = new boolean[heights.length][heights[0].length];\n dfs(heights,i,j,pair,visited,heights[i][j]);\n if(pair[0] && pair[1]) res.add(Arrays.asList(i,j));\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n public void dfs(int[][] heights,int i,int j,boolean[] pair,boolean[][] visited,int prev){\n if(i<0 || j<0 || i>=heights.length || j>=heights[0].length || visited[i][j] == true || heights[i][j] > prev) return;\n if(i == 0 || j==0) pair[0] = true;\n if(i == heights.length-1 || j == heights[0].length-1) pair[1] = true;\n if(pair[0] && pair[1]) return;\n prev = heights[i][j];\n visited[i][j] = true;\n dfs(heights,i-1,j,pair,visited,prev);\n dfs(heights,i,j+1,pair,visited,prev);\n dfs(heights,i+1,j,pair,visited,prev);\n dfs(heights,i,j-1,pair,visited,prev);\n }\n}\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Java']
| 1 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
[Javascript] Idiomatic BFS and DFS
|
javascript-idiomatic-bfs-and-dfs-by-nige-0z84
|
Recursive DFS\n\nconst pacificAtlantic = (heights) => {\n const m = heights.length, n = heights[0].length \n const atlantic = new Array(m).fill().map(()
|
nigelflippo
|
NORMAL
|
2021-12-23T15:58:35.316402+00:00
|
2021-12-29T04:42:13.195754+00:00
| 923 | false |
**Recursive DFS**\n```\nconst pacificAtlantic = (heights) => {\n const m = heights.length, n = heights[0].length \n const atlantic = new Array(m).fill().map(() => new Array(n).fill(false))\n const pacific = new Array(m).fill().map(() => new Array(n).fill(false))\n const directions = [[1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1]]\n const dfs = (x, y, visited) => {\n visited[x][y] = true\n for (let dir of directions) {\n let nx = x + dir[0]\n let ny = y + dir[1]\n if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= m || ny >= n || visited[nx][ny]) continue\n if (heights[nx][ny] >= heights[x][y]) {\n dfs(nx, ny, visited)\n }\n }\n }\n \n for (let x = 0; x < m; x++) {\n for (let y = 0; y < n; y++) {\n if (x === 0 || y === 0) {\n dfs(x, y, pacific)\n }\n if (x === m - 1 || y === n - 1) {\n dfs(x, y, atlantic)\n }\n }\n }\n const paths = []\n for (let x = 0; x < m; x++) {\n for (let y = 0; y < n; y++) {\n if (pacific[x][y] && atlantic[x][y]) {\n paths.push([x, y])\n }\n }\n }\n return paths\n}\n```\n\n**BFS**\n\n```\nconst pacificAtlantic = (heights) => {\n const m = heights.length, n = heights[0].length \n const atlanticQueue = []\n const pacificQueue = []\n \n for (let x = 0; x < m; x++) {\n for (let y = 0; y < n; y++) {\n if (x === m - 1 || y === n - 1) {\n atlanticQueue.push([x, y])\n }\n if (x === 0 || y === 0) {\n pacificQueue.push([x, y])\n }\n }\n } \n const bfs = (queue) => {\n const isValid = (x, y) => x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < m && y < n\n const directions = [[1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1]]\n const visited = new Array(m).fill().map(() => new Array(n).fill(false))\n while (queue.length) {\n const [x, y] = queue.shift()\n visited[x][y] = true\n for (let dir of directions) {\n let nx = x + dir[0]\n let ny = y + dir[1]\n if (!isValid(nx, ny) || visited[nx][ny]) continue\n if (heights[nx][ny] >= heights[x][y]) {\n queue.push([nx, ny])\n }\n }\n }\n return visited\n }\n const pacific = bfs(atlanticQueue)\n const atlantic = bfs(pacificQueue)\n const paths = []\n for (let x = 0; x < m; x++) {\n for (let y = 0; y < n; y++) {\n if (pacific[x][y] && atlantic[x][y]) {\n paths.push([x, y])\n }\n }\n }\n return paths\n}\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Breadth-First Search', 'JavaScript']
| 2 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
javascript easy dfs
|
javascript-easy-dfs-by-cjamm-oyit
|
```\nvar pacificAtlantic = function(matrix) {\n let res = [];\n let min = -Infinity;\n let rows = matrix.length;\n let cols = matrix[0].length; \n
|
Cjamm
|
NORMAL
|
2021-03-31T19:06:44.292197+00:00
|
2021-03-31T19:06:44.292241+00:00
| 804 | false |
```\nvar pacificAtlantic = function(matrix) {\n let res = [];\n let min = -Infinity;\n let rows = matrix.length;\n let cols = matrix[0].length; \n let pacific = new Array(rows).fill().map(() => new Array(cols).fill(0));\n let atlantic = new Array(rows).fill().map(() => new Array(cols).fill(0));\n \n // left & right\n for (let row = 0; row < rows; row ++) {\n dfs(matrix, row, 0, min, pacific)\n dfs(matrix, row, matrix[0].length - 1, min, atlantic)\n }\n // top & bottom\n for (let col = 0; col < cols; col ++) {\n dfs(matrix, 0, col, min, pacific)\n dfs(matrix, matrix.length - 1, col, min, atlantic)\n }\n \n for (let row = 0; row < rows; row ++) {\n for (let col = 0; col < cols; col ++) {\n if (pacific[row][col] == 1 && atlantic[row][col] == 1) {\n res.push([row, col])\n }\n }\n }\n return res;\n \n};\n\nconst dfs = (matrix, r, c, prevVal, ocean) => {\n // 1. Check necessary condition.\n if (r < 0 || c < 0 || r > matrix.length - 1 || c > matrix[0].length - 1) return;\n if (matrix[r][c] < prevVal) return;\n if (ocean[r][c] == 1) return;\n \n // 2. Process call.\n ocean[r][c] = 1;\n \n // 3. Call dfs as needed.\n dfs (matrix, r - 1, c, matrix[r][c], ocean);\n dfs (matrix, r + 1, c, matrix[r][c], ocean);\n dfs (matrix, r, c - 1, matrix[r][c], ocean);\n dfs (matrix, r, c + 1, matrix[r][c], ocean);\n}
| 7 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
C# DFS/BFS solutions
|
c-dfsbfs-solutions-by-newbiecoder1-b4bq
|
DFS\n\npublic class Solution {\n public IList<IList<int>> PacificAtlantic(int[][] matrix) {\n \n List<IList<int>> res = new List<IList<int>>();
|
newbiecoder1
|
NORMAL
|
2021-03-26T15:48:34.531787+00:00
|
2021-03-26T17:41:19.729515+00:00
| 367 | false |
**DFS**\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public IList<IList<int>> PacificAtlantic(int[][] matrix) {\n \n List<IList<int>> res = new List<IList<int>>();\n if(matrix == null || matrix.Length == 0)\n return res;\n \n int m = matrix.Length, n = matrix[0].Length;\n bool[,] pacific = new bool[m,n];\n bool[,] atlantic = new bool[m,n];\n \n for(int row = 0; row < m; row++)\n {\n DFS(row, 0, matrix, pacific, matrix[row][0]);\n DFS(row, n - 1, matrix, atlantic, matrix[row][n - 1]);\n }\n\n for(int col = 0; col < n; col++)\n {\n DFS(0 , col,matrix, pacific, matrix[0][col]);\n DFS(m - 1, col, matrix, atlantic, matrix[m - 1][col]); \n }\n \n for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)\n {\n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)\n {\n if(pacific[i,j] && atlantic[i,j])\n res.Add(new List<int>(){i,j});\n }\n }\n \n return res; \n }\n \n private void DFS(int row, int col, int[][] matrix, bool[,] reach, int prev)\n {\n int m = matrix.Length, n = matrix[0].Length;\n \n if(row < 0 || row >= m || col < 0 || col >= n || reach[row,col] || matrix[row][col] < prev)\n return;\n \n reach[row,col] = true;\n DFS(row, col + 1, matrix, reach, matrix[row][col]);\n DFS(row, col - 1, matrix, reach, matrix[row][col]);\n DFS(row + 1, col, matrix, reach, matrix[row][col]);\n DFS(row - 1, col, matrix, reach, matrix[row][col]);\n }\n}\n```\n\n**BFS**\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public IList<IList<int>> PacificAtlantic(int[][] matrix) {\n \n List<IList<int>> res = new List<IList<int>>();\n if(matrix == null || matrix.Length == 0)\n return res;\n \n int m = matrix.Length, n = matrix[0].Length;\n Queue<(int,int)> queueP = new Queue<(int,int)>();\n Queue<(int,int)> queueA = new Queue<(int,int)>();\n bool[,] pacific = new bool[m,n];\n bool[,] atlantic = new bool[m,n];\n \n for(int row = 0; row < m; row++)\n {\n queueP.Enqueue((row, 0));\n pacific[row,0] = true;\n \n queueA.Enqueue((row, n - 1)); \n atlantic[row,n - 1] = true;\n }\n\n for(int col = 0; col < n; col++)\n {\n queueP.Enqueue((0 , col));\n pacific[0,col] = true;\n \n queueA.Enqueue((m - 1, col));\n atlantic[m - 1,col] = true;\n }\n\n BFS(queueP, matrix, pacific); \n BFS(queueA, matrix, atlantic);\n \n for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)\n {\n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)\n {\n if(pacific[i,j] && atlantic[i,j])\n res.Add(new List<int>(){i,j});\n }\n }\n \n return res; \n }\n \n private void BFS(Queue<(int,int)> queue, int[][] matrix, bool[,] reach)\n {\n int m = matrix.Length, n = matrix[0].Length;\n int[,] dir = new int[,]{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};\n \n while(queue.Count > 0)\n { \n var curr = queue.Dequeue();\n for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)\n {\n int nextRow = curr.Item1 + dir[i,0];\n int nextCol = curr.Item2 + dir[i,1];\n \n if(nextRow >= 0 && nextRow < m && nextCol >= 0 && nextCol < n && !reach[nextRow,nextCol]\n && matrix[curr.Item1][curr.Item2] <= matrix[nextRow][nextCol])\n {\n queue.Enqueue((nextRow,nextCol));\n reach[nextRow, nextCol] = true;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n}\n```
| 7 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Insufficient and incorrect explanation
|
insufficient-and-incorrect-explanation-b-f78b
|
If the starting point is 5 in the midle on the matrix, then we can reach to Atlantic or Pacific ocean. (\nPacific ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ \n ~ 1 2 2 3 (
|
immutablejain
|
NORMAL
|
2021-02-06T16:00:17.996039+00:00
|
2021-02-06T16:00:17.996088+00:00
| 217 | false |
If the starting point is 5 in the midle on the matrix, then we can reach to Atlantic or Pacific ocean. (\nPacific ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ \n ~ 1 2 2 3 (5) *\n ~ 3 2 3 (4) (4) *\n-> ~ 2 4 (5) 3 1 <-\n ~ (6) (7) 1 4 5 *\n ~ (5) 1 1 2 4 *\n * * * * * Atlantic\nAlso, it is mentioned that the water can go either up, down, left or right, then how does flow reach from (7) to (5)\n\nPacific ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ \n ~ 1 2 2 3 (5) *\n ~ 3 2 3 (4) (4) *\n ~ 2 4 (5) 3 1 *\n ~ (6) (7) 1 4 5 *\n ~ (5) 1 1 2 4 *\n * * * * * Atlantic\n\nCan someone please help me with the explanation here?
| 7 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
C++ Implementation (DFS)
|
c-implementation-dfs-by-abhisharma404-5imr
|
C++ Implementation of the following amazing post:\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/pacific-atlantic-water-flow/discuss/90739/Python-DFS-bests-85.-Tips-for-all-DFS
|
abhisharma404
|
NORMAL
|
2020-05-02T14:39:53.538449+00:00
|
2020-05-02T14:39:53.538487+00:00
| 1,191 | false |
C++ Implementation of the following amazing post:\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/pacific-atlantic-water-flow/discuss/90739/Python-DFS-bests-85.-Tips-for-all-DFS-in-matrix-question.\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dx[4] = {0, 1, -1, 0};\n int dy[4] = {1, 0, 0, -1};\n \n void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& v, int i, int j, int height) {\n if (i < 0 || i > grid.size()-1 || j < 0 || j > grid[0].size()-1 || v[i][j]) return;\n if (grid[i][j] < height) return;\n v[i][j] = true;\n for (int k=0; k<4; k++) {\n dfs(grid, v, i+dx[k], j+dy[k], grid[i][j]);\n }\n }\n \n vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {\n vector<vector<int>> ans;\n if (!matrix.size()) return ans;\n vector<vector<bool>> v1(matrix.size(), vector<bool>(matrix[0].size(), false));\n vector<vector<bool>> v2(matrix.size(), vector<bool>(matrix[0].size(), false));\n for (int i=0; i<matrix.size(); i++) {\n dfs(matrix, v1, i, 0, INT_MIN);\n dfs(matrix, v2, i, matrix[0].size()-1, INT_MIN);\n }\n for (int j=0; j<matrix[0].size(); j++) {\n dfs(matrix, v1, 0, j, INT_MIN);\n dfs(matrix, v2, matrix.size()-1, j, INT_MIN);\n }\n for (int i=0; i<matrix.size(); i++) {\n for (int j=0; j<matrix[0].size(); j++) {\n if (v1[i][j] && v2[i][j]) {\n vector<int> temp{i, j};\n ans.push_back(temp);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'C', 'C++']
| 1 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Simple java dfs solution
|
simple-java-dfs-solution-by-yzj1212-rp65
|
Build two sets for Pacific and Atlantic. The result is the intersection of them.\n\n private int[][] direction = new int[][]{{1, 0},{0, 1},{-1, 0},{0, -1}};\n
|
yzj1212
|
NORMAL
|
2016-10-09T15:24:03.711000+00:00
|
2016-10-09T15:24:03.711000+00:00
| 2,276 | false |
Build two sets for Pacific and Atlantic. The result is the intersection of them.\n```\n private int[][] direction = new int[][]{{1, 0},{0, 1},{-1, 0},{0, -1}};\n public List<int[]> pacificAtlantic(int[][] matrix) {\n List<int[]> result = new ArrayList<>();\n if (matrix.length == 0) return result;\n Set<Integer> pacific = new HashSet<>();\n Set<Integer> atlantic = new HashSet<>();\n for (int i = 0; i < matrix[0].length; i++) {\n dfs(matrix, 0, i, pacific);\n dfs(matrix, matrix.length - 1, i, atlantic);\n }\n for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {\n dfs(matrix, i, 0, pacific);\n dfs(matrix, i, matrix[0].length - 1, atlantic);\n }\n \n for (int i: pacific) {\n if (atlantic.contains(i)) {\n result.add(decode(i, matrix));\n }\n }\n return result;\n }\n \n private void dfs(int[][] matrix, int i, int j, Set<Integer> result) {\n if (!result.add(encode(i, j, matrix))) return;\n for (int[] dir: direction) {\n int x = dir[0] + i;\n int y = dir[1] + j;\n if (x >= 0 && x < matrix.length && y >= 0 && y < matrix[0].length && matrix[x][y] >= matrix[i][j]) {\n dfs(matrix, x, y, result);\n }\n }\n }\n \n private int[] decode(int i, int[][] matrix) {\n return new int[]{i / matrix[0].length, i % matrix[0].length};\n }\n \n private int encode(int i, int j, int[][] matrix) {\n return i * matrix[0].length + j;\n }\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Java 28ms BFS solution using one queue
|
java-28ms-bfs-solution-using-one-queue-b-aj2n
|
I use two bits to save the information of pacific ocean and atlantic ocean.\n00: cannot reach any ocean\n01: can reach pacific ocean\n10: can reach atlantic oce
|
kenjichao
|
NORMAL
|
2016-10-15T10:19:10.923000+00:00
|
2016-10-15T10:19:10.923000+00:00
| 2,343 | false |
I use two bits to save the information of pacific ocean and atlantic ocean.\n`00`: cannot reach any ocean\n`01`: can reach pacific ocean\n`10`: can reach atlantic ocean\n`11`: can reach two oceans\n\n**Step 1**: Update the status of border cells and put them into the queue\n**Step 2**: Iterate the queue and explore the four directions. We only put a new cell into the queue if :\n- row and col index are valid\n- the height of the new cell is larger or equals to the height of the current cell\n- the new cell can benifit from the current cell (check status)\n\n```java\npublic class Solution {\n public List<int[]> pacificAtlantic(int[][] matrix) {\n List<int[]> res = new ArrayList<>();\n int m = matrix.length;\n if (m == 0) return res;\n int n = matrix[0].length;\n int[][] state = new int[m][n];\n Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();\n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n state[i][0] |= 1;\n if (i == m - 1 || n == 1) state[i][0] |= 2;\n if (state[i][0] == 3) res.add(new int[]{i, 0});\n q.add(new int[]{i, 0});\n if (n > 1) {\n state[i][n - 1] |= 2;\n if (i == 0) state[i][n - 1] |= 1;\n if (state[i][n - 1] == 3) res.add(new int[]{i, n - 1});\n q.add(new int[]{i, n - 1});\n }\n }\n for (int j = 1; j < n - 1; j++) {\n state[0][j] |= 1;\n if (m == 1) state[0][j] |= 2;\n if (state[0][j] == 3) res.add(new int[]{0, j});\n q.add(new int[]{0, j});\n if (m > 1) {\n state[m - 1][j] |= 2;\n if (state[m - 1][j] == 3) res.add(new int[]{m - 1, j});\n q.add(new int[]{m - 1, j});\n }\n }\n int[][] dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};\n while (!q.isEmpty()) {\n int[] cell = q.poll();\n for (int[] dir : dirs) {\n int row = cell[0] + dir[0];\n int col = cell[1] + dir[1];\n if (row < 0 || col < 0 || row == m || col == n || matrix[row][col] < matrix[cell[0]][cell[1]] || ((state[cell[0]][cell[1]] | state[row][col]) == state[row][col])) continue;\n state[row][col] |= state[cell[0]][cell[1]];\n if (state[row][col] == 3) res.add(new int[]{row, col});\n q.add(new int[]{row, col});\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 7 | 0 |
[]
| 4 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Python: DFS from Ocean, easy to understand
|
python-dfs-from-ocean-easy-to-understand-o1x8
|
Divide the problem into the set of cell where water can run into the Pacific and the set of cell where water can run into the Atlantic. Then we join two sets to
|
duong2016
|
NORMAL
|
2017-12-12T15:26:34.123000+00:00
|
2017-12-12T15:26:34.123000+00:00
| 1,485 | false |
Divide the problem into the set of cell where water can run into the Pacific and the set of cell where water can run into the Atlantic. Then we join two sets to get the result.\nFor the Pacific subset, start running from the ocean (edge where row = 0 or col = 0), and find all the cells which are greater or equal.\nSimilar for the Atlantic.\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def pacificAtlantic(self, matrix):\n """\n :type matrix: List[List[int]]\n :rtype: List[List[int]]\n """\n results = []\n if not len(matrix) or not len(matrix[0]):\n return results\n rows, cols = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])\n directions = [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]\n \n def Pacific(mat):\n visited = set()\n for j in range(cols):\n dfs(mat, 0, j, visited)\n for i in range(rows):\n dfs(mat, i, 0, visited)\n return visited \n \n def Atlantic(mat):\n visited = set()\n for j in reversed(range(cols)):\n dfs(mat, rows-1, j, visited)\n for i in reversed(range(rows)):\n dfs(mat, i, cols-1, visited)\n return visited\n \n def dfs(mat, i, j, visited):\n if (i, j) in visited:\n return\n visited.add((i, j))\n for direction in directions:\n next_i, next_j = i+direction[0],j+direction[1]\n if 0 <= next_i < rows and 0 <= next_j < cols and mat[next_i][next_j] >= mat[i][j]:\n dfs(mat, next_i, next_j, visited)\n \n atlantic = Atlantic(matrix)\n pacific = Pacific(matrix)\n for i, j in atlantic:\n if (i,j) in pacific:\n results.append([i,j])\n return results\n```
| 7 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Simple Solution
|
simple-solution-by-moazmar-56ec
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution:\n def pacificAtlantic(self, h: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:\n n, m = len(h), len(h[0])\n isPacc = [[True
|
moazmar
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-15T17:21:37.880624+00:00
|
2023-04-15T17:21:47.540960+00:00
| 665 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def pacificAtlantic(self, h: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:\n n, m = len(h), len(h[0])\n isPacc = [[True if i == 0 or j == 0 else False for j in range(m)] for i in range(n)]\n isAtl = [[True if i == n - 1 or j == m - 1 else False for j in range(m)] for i in range(n)]\n \n def Pac(i, j, isPac):\n val = h[i][j]\n for x, y in [(i+1, j), (i-1, j), (i, j+1), (i, j-1)]:\n if 0 <= x < n and 0 <= y < m and not isPac[x][y] and h[x][y] >= val:\n isPac[x][y] = True\n Pac(x, y, isPac)\n \n for i in range(n): Pac(i, 0, isPacc)\n for j in range(m): Pac(0, j, isPacc)\n for i in range(n): Pac(i, m-1, isAtl)\n for j in range(m): Pac(n-1, j, isAtl)\n \n return [[i, j] for i in range(n) for j in range(m) if isPacc[i][j] and isAtl[i][j]]\n\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
[C++] Solution || BFS
|
c-solution-bfs-by-dadushiv5-ejdy
|
Language Used: C++\n\nIf you have any questions, feel free to ask. If you like the solution and explanation, please upvote!\n\nTime Complexity: O(nm);\nSpace Co
|
dadushiv5
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-31T05:58:36.699332+00:00
|
2022-08-31T06:21:28.071692+00:00
| 835 | false |
**Language Used: C++**\n\n*If you have any questions, feel free to ask. If you like the solution and explanation, please **upvote!***\n\nTime Complexity: O(nm);\nSpace Complexity: O(nm);\n\nIntution:\n* When we are at lower level, the water must come in it from a higher level. \n* So for pacific store all the element in the queue which are adjacent to the sea and traverse DFS/BFS to find the higher level.\n* Do the same for atlantic\n* Now the level which is covered by both is our answer.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n typedef pair<int, int> pii; \n vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& h) {\n // Storing the solution\n vector<vector<int>> ans;\n int n = h.size();\n int m = h[0].size();\n // Initializing the Pacific and Atlantic matrices;\n vector<vector<int>> pa(n, vector<int>(m, 0));\n vector<vector<int>> at(n, vector<int>(m, 0));\n \n // BFS for the pacific;\n queue<pii> q;\n for(int i{}; i<n; i++) q.push({i, 0});\n for(int j{}; j<m; j++) q.push({0, j});\n bfs(h, q, pa);\n \n // BFS for the atlantic;\n queue<pii> q2;\n for(int i{}; i<n; i++) q2.push({i, m-1});\n for(int j{}; j<m; j++) q2.push({n-1, j});\n bfs(h, q2, at);\n \n for(int i{}; i<n; i++){\n for(int j{}; j<m; j++){\n if(pa[i][j]==1 && at[i][j]==1) ans.push_back({i, j});\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\nprivate:\n void bfs(vector<vector<int>>& h, queue<pii>&q, vector<vector<int>>& vis){\n int n = h.size(); int m = h[0].size(); // Dimension of the matrix\n int dx[4] = {-1,0,1,0};\n int dy[4] = {0,1,0,-1};\n while(!q.empty()){\n int x = q.front().first; int y = q.front().second;\n q.pop(); vis[x][y] = 1; // Popping the element out ans marking as visited;\n for(int i{}; i<4; i++){\n int cx = x + dx[i]; int cy = y + dy[i];\n\t\t\t\t// Checking feasibility of Current_x & Current_y\n if(cx>=0 && cy>=0 && cx<n && cy<m){\n if(h[cx][cy] >= h[x][y] && vis[cx][cy] == 0) q.push({cx, cy});\n }\n }\n }\n }\n};\n```\nKeep Coding\n**`while(!success){ tryAgain(); } :)`**
| 6 | 0 |
['Breadth-First Search', 'C', 'C++']
| 1 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Easy DFS solution with self-explainatory variable names
|
easy-dfs-solution-with-self-explainatory-49pf
|
\nclass Solution:\n def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:\n ROWS, COLS = len(heights), len(heights[0])\n paci
|
swissnerd
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-19T19:02:20.679144+00:00
|
2022-08-19T19:02:20.679167+00:00
| 485 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:\n ROWS, COLS = len(heights), len(heights[0])\n pacificSet, atlanticSet = set(), set()\n \n def dfs(row, col, visited, prevHeight):\n if (row not in range(ROWS) or\n col not in range(COLS) or\n (row, col) in visited or\n heights[row][col] < prevHeight\n ):\n return\n \n visited.add((row, col))\n dfs(row + 1, col, visited, heights[row][col])\n dfs(row - 1, col, visited, heights[row][col])\n dfs(row, col + 1, visited, heights[row][col])\n dfs(row, col - 1, visited, heights[row][col]) \n \n for row in range(ROWS):\n dfs(row, 0, pacificSet, heights[row][0])\n dfs(row, COLS - 1, atlanticSet, heights[row][COLS - 1])\n \n for col in range(COLS):\n dfs(0, col, pacificSet, heights[0][col])\n dfs(ROWS - 1, col, atlanticSet, heights[ROWS - 1][col])\n \n return pacificSet & atlanticSet\n # Time: O(m * n) where m and n are the dimensions of the grid\n # Space: O(m * n)\n```\n
| 6 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Python']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
EASY DFS SOLUTION || 99.30% FASTER
|
easy-dfs-solution-9930-faster-by-jitendr-agkt
|
\nclass Solution {\n \n int[][] dir = {{0,-1}, {-1,0}, {0,1}, {1,0}};\n public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {\n \n
|
jitendrap1702
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-24T05:59:09.896571+00:00
|
2022-08-31T06:56:29.974760+00:00
| 648 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n \n int[][] dir = {{0,-1}, {-1,0}, {0,1}, {1,0}};\n public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {\n \n int m = heights.length, n = heights[0].length, i, j;\n \n // mark true to all the cells that can flow to pacific ocean\n boolean[][] pacific = new boolean[m][n];\n for(i = 0; i < n; i++) bfs(heights, 0, i, pacific); // first row \n for(i = 0; i < m; i++) bfs(heights, i, 0, pacific); // first column\n \n // mark true to all the cells that can flow to atlantic ocean\n boolean[][] atlantic = new boolean[m][n];\n for(i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) bfs(heights, m-1, i, atlantic); // last row\n for(i = m-1; i >= 0; i--) bfs(heights, i, n-1, atlantic); // last column\n \n // find the cell of rain water that can flow to both ocean\n List<List<Integer>> output = new ArrayList<>();\n for(i = 0; i < m; i++){\n for(j = 0; j < n; j++){\n if(atlantic[i][j] && pacific[i][j])\n output.add(new ArrayList<>(List.of(i, j)));\n }\n }\n return output;\n }\n \n void bfs(int[][] heights, int r, int c, boolean[][] ans){\n \n ans[r][c] = true; // mark reachable\n for(int i = 0; i < dir.length; i++){\n \n int newr = r+dir[i][0];\n int newc = c+dir[i][1];\n if(newr<0 || newc<0 || newr>=heights.length || newc>=heights[0].length || ans[newr][newc] || heights[newr][newc] < heights[r][c])\n continue;\n \n bfs(heights, newr, newc, ans);\n }\n }\n}\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Java']
| 2 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Python [DFS / Beats 99.13%] with full working explanation
|
python-dfs-beats-9913-with-full-working-mvtaa
|
\nclass Solution:\n def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]: # Time: O(mn) and Space: O(mn)\n \n\t rows, cols = len(
|
DanishKhanbx
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-23T11:05:47.251416+00:00
|
2022-07-23T11:06:11.974006+00:00
| 1,102 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]: # Time: O(mn) and Space: O(mn)\n \n\t rows, cols = len(heights), len(heights[0])\n pac, atl = set(), set()\n\n def dfs(r, c, visit, prevHeight): # current location, set of already visited tiles, the value of the tile where we are calling the dfs function\n \n\t\t # we will check if the index[r, c] is not already visited, row and column is inbounds and\n # the current tile should be lower than from we are coming from, it\'s the condition for waterflow mentioned\n # if any one of these conditions fails exit the dfs by returning to from we came from\n if (r, c) in visit or r < 0 or c < 0 or r == rows or c == cols or heights[r][c] < prevHeight:\n return\n\t\t\t\t\n visit.add((r, c)) # mark the tile visited(pac or atl depending on what is passed from the dfs function) when the if conditions true\n\t\t\t\n dfs(r + 1, c, visit, heights[r][c]) # we will next visit the tile down from the current one\n dfs(r - 1, c, visit, heights[r][c]) # up\n dfs(r, c + 1, visit, heights[r][c]) # right\n dfs(r, c - 1, visit, heights[r][c]) # left\n\n for c in range(cols): # we will traverse the first & last row by fixing the r and moving c\n dfs(0, c, pac, heights[0][c]) # first row is just next to pacific\n dfs(rows - 1, c, atl, heights[rows - 1][c]) # last row is just next to atlantic\n\n for r in range(rows): # we will traverse the first & last column by fixing the c and moving r\n dfs(r, 0, pac, heights[r][0]) # first column is just next to pacific\n dfs(r, cols - 1, atl, heights[r][cols - 1]) # last column is just next to atlantic\n\n return list(pac.intersection(atl)) # returns the list which contains the same [i, j] in both the sets\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Sharing my DFS & BFS solution
|
sharing-my-dfs-bfs-solution-by-truongbn_-vs9x
|
Problems that are related to Graph, we usually utilize some classical graph traversal algorithms to work on.\nHere I\'m talking about Depth First Search dfs and
|
truongbn_it
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-09T01:29:38.270452+00:00
|
2022-01-09T01:29:38.270497+00:00
| 1,017 | false |
Problems that are related to `Graph`, we usually utilize some classical graph traversal algorithms to work on.\nHere I\'m talking about Depth First Search `dfs` and Breadth First Search `bfs`\n\nWe\'ll use 2 below options to solve this problem\n1. Recursive dfs, be careful if we have very deep graphs.\n1. Interative bfs, We use Queue\n\n**Idea**\nWe need 2 2D boolean arrays. One is to store capability of any cell `(ri, ci)` that from that cell whether water can flow to the pacific ocean, the other is to store capability of any cell `(ri, ci)` that from that cell whether water can flow to the atlantic ocean\n\nSo water can flow from cell `(ri, ci) ` to both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans, if and only if value of cell `(ri, ci) ` in 2 boolean arrays both are `true`\n\n**BFS**\n```\nclass Solution {\n int[][] dirs = new int[][]{{1,0},{0,1},{-1,0},{0,-1}};\n public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {\n int m = heights.length, n = heights[0].length;\n \n boolean[][] pacific = new boolean[m][n];\n boolean[][] atlantic = new boolean[m][n];\n \n Queue<int[]> pQueue = new LinkedList<>();\n Queue<int[]> aQueue = new LinkedList<>();\n \n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n pQueue.offer(new int[]{i, 0});\n pacific[i][0] = true;\n aQueue.offer(new int[]{i, n-1});\n atlantic[i][n-1] = true;\n }\n \n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n pQueue.offer(new int[]{0, i});\n pacific[0][i] = true;\n aQueue.offer(new int[]{m-1, i});\n atlantic[m-1][i] = true;\n }\n bfs(heights, pQueue, pacific);\n bfs(heights, aQueue, atlantic);\n \n List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();\n \n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n if (pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) {\n res.add(Arrays.asList(i, j));\n }\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n \n private void bfs(int[][] heights, Queue<int[]> queue, boolean[][] visited) {\n int m = heights.length, n = heights[0].length;\n while (!queue.isEmpty()) {\n int[] pos = queue.poll();\n for (int[] dir : dirs) {\n int x = pos[0] + dir[0];\n int y = pos[1] + dir[1];\n if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || \n visited[x][y] || heights[x][y] < heights[pos[0]][pos[1]]) {\n continue;\n }\n visited[x][y] = true;\n queue.offer(new int[]{x, y});\n }\n }\n }\n}\n```\n\n**DFS**\n```\nclass Solution {\n int[][] dirs = new int[][]{{1,0},{0,1},{-1,0},{0,-1}};\n public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {\n int m = heights.length, n = heights[0].length;\n \n boolean[][] pacific = new boolean[m][n];\n boolean[][] atlantic = new boolean[m][n];\n \n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n dfs(heights, pacific, Integer.MIN_VALUE, i, 0);\n dfs(heights, atlantic, Integer.MIN_VALUE, i, n-1);\n }\n \n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n dfs(heights, pacific, Integer.MIN_VALUE, 0, i);\n dfs(heights, atlantic, Integer.MIN_VALUE, m-1, i);\n }\n \n List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();\n \n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n if (pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) {\n res.add(Arrays.asList(i, j));\n }\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n \n private void dfs(int[][] heights, boolean[][] visited, int height, int x, int y) {\n int m = heights.length, n = heights[0].length;\n if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || visited[x][y] || height > heights[x][y]) {\n return;\n }\n visited[x][y] = true;\n dfs(heights, visited, heights[x][y], x+1, y);\n dfs(heights, visited, heights[x][y], x-1, y);\n dfs(heights, visited, heights[x][y], x, y+1);\n dfs(heights, visited, heights[x][y], x, y-1);\n }\n}\n```\n\nTime Complexity: O(4mn)=O(mn) since a cell can be visited at most 4 times.
| 6 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Breadth-First Search', 'Java']
| 1 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Clean python code O(mn) - DFS
|
clean-python-code-omn-dfs-by-arvindn-6un1
|
Naive solution is to do DFS from every other point and see if it reaches both the ocean but the trick to optimisation is to start from the oceans itself and go
|
arvindn
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-16T13:36:29.472920+00:00
|
2021-11-16T13:36:29.472945+00:00
| 1,357 | false |
Naive solution is to do DFS from every other point and see if it reaches both the ocean but the trick to optimisation is to start from the oceans itself and go backwards to every point. Visited ones are all the points that are reachable from ocean so in the end, intersection of points `visited by pacific` and `visited by atlantic` will give you the answer.\n\nAnother thing to note is that the checks always start from the first and last rows/columns for each iteration. For columns, we iterate over each one and keep the row at 0 and m-1 while for rows we keep the column as 0 and n-1 for pacific and atlantic respectively.\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n\n def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:\n m, n = len(heights), len(heights[0])\n v_pac = set()\n v_atl = set()\n \n def dfs(v_set, row, col, curr_height):\n if row < 0 or row >= m or \\\n col < 0 or col >= n or \\\n (row,col) in v_set or \\\n curr_height > heights[row][col]:\n return\n v_set.add((row, col))\n\n curr_height = heights[row][col]\n dfs(v_set, row + 1, col, curr_height)\n dfs(v_set, row - 1, col, curr_height)\n dfs(v_set, row, col + 1, curr_height)\n dfs(v_set, row, col - 1, curr_height)\n\n # Approach is to start from both sides of \n # the oceans and then reach each point that can be \n # reached while maintaining the visited indices\n\n # Iterate over columns and start from both 0, m-1 rows\n for col in range(n):\n dfs(v_pac, 0, col, heights[0][col]) # First row\n dfs(v_atl, m - 1, col, heights[m-1][col]) # Last row\n\n # Iterate over rows and start from both 0, n-1 cols\n for row in range(m):\n dfs(v_pac, row, 0, heights[row][0]) # First column\n dfs(v_atl, row, n-1, heights[row][n-1]) # Last column\n\n # Co-ordinates which can reach both the oceans are the winners\n # so we take intersection\n result = v_atl.intersection(v_pac)\n\n return result\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 1 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
JavaScript 96% | Simple Solution
|
javascript-96-simple-solution-by-casmith-nqxf
|
\n\nDoing the Blind 75 List and posting all solutions.\n\n\nvar pacificAtlantic = function(heights) {\n const oceanMap = Array(heights.length).fill().map(_ =>
|
casmith1987
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-10T23:21:09.610685+00:00
|
2021-10-10T23:59:48.910750+00:00
| 916 | false |
\n\nDoing the Blind 75 List and posting all solutions.\n\n```\nvar pacificAtlantic = function(heights) {\n const oceanMap = Array(heights.length).fill().map(_ => Array(heights[0].length).fill(0))\n const pTrack = new Set(), aTrack = new Set();\n const res = [];\n \n for (let i = 0; i < heights[0].length; i++) {\n traverse(0, i, pTrack)\n traverse(heights.length - 1, i, aTrack)\n }\n \n for (let i = 1; i < heights.length; i++) {\n traverse(i, 0, pTrack)\n traverse(heights.length - 1 - i, heights[i].length - 1, aTrack)\n }\n \n return res\n \n function traverse(row, col, ocean) {\n if (ocean.has(`${row}-${col}`)) return;\n ocean.add(`${row}-${col}`);\n oceanMap[row][col]++;\n if (oceanMap[row][col] === 2) res.push([row, col]);\n (row > 0 && heights[row][col] <= heights[row - 1][col]) && traverse(row - 1, col, ocean);\n (row < heights.length - 1 && heights[row][col] <= heights[row + 1][col]) && traverse(row + 1, col, ocean);\n (col > 0 && heights[row][col] <= heights[row][col - 1]) && traverse(row, col - 1, ocean);\n (col < heights[row].length - 1 && heights[row][col] <= heights[row][col + 1]) && traverse(row, col + 1, ocean)\n }\n};\n```
| 6 | 1 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Help me understand this input -> [[1,2,3],[8,9,4],[7,6,5]]
|
help-me-understand-this-input-123894765-mbtn8
|
The expected output is [[0,2],[1,0],[1,1],[1,2],[2,0],[2,1],[2,2]]\nI don\'t get why [2, 1] is includes\n\n\n Pacific ~ ~ ~\n ~ 1 2 3 *\n
|
neverbe10
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-10T20:17:16.452888+00:00
|
2021-10-10T20:20:55.479151+00:00
| 169 | false |
The expected output is [[0,2],[1,0],[1,1],[1,2],[2,0],[2,1],[2,2]]\nI don\'t get why [2, 1] is includes\n\n```\n Pacific ~ ~ ~\n ~ 1 2 3 *\n ~ 8 9 4 *\n ~ 7 6 5 *\n * * * Atlantic\n\n```\n\nI get that [2, 1] can flows into Atlantic by traveling left, but it\'s blocked by 7 on the left, and 9 on top, how does it flows to Pacific?\n\nI get it now, 6 -> 5 -> 4 -> 3 -> Pacific. Somehow I thought it needs to be travering the same direction, which doesn\'t make sense at all.
| 6 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Java Simple and easy to understand solution, using bfs, clean code with comments
|
java-simple-and-easy-to-understand-solut-3so7
|
PLEASE UPVOTE IF YOU LIKE THIS SOLUTION\n\n\n\nclass Solution {\n private static final int[][] DIRECTIONS = new int[][]{{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};\n
|
satyaDcoder
|
NORMAL
|
2021-03-26T06:30:58.155337+00:00
|
2021-03-26T06:30:58.155370+00:00
| 762 | false |
**PLEASE UPVOTE IF YOU LIKE THIS SOLUTION**\n\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n private static final int[][] DIRECTIONS = new int[][]{{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};\n \n int rows;\n int cols;\n int[][] matrix;\n \n \n public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] matrix) {\n if(matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0)\n return new ArrayList<>();\n \n this.matrix = matrix;\n rows = matrix.length;\n cols = matrix[0].length;\n \n \n \n Queue<int[]> pacificQueue = new LinkedList();\n Queue<int[]> atlanticQueue = new LinkedList();\n \n for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++){\n pacificQueue.add(new int[]{i, 0});\n atlanticQueue.add(new int[]{i, cols - 1});\n }\n \n \n for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++){\n pacificQueue.add(new int[]{0, j});\n atlanticQueue.add(new int[]{rows - 1, j});\n }\n \n \n int[][] pacificReachable = bfs(pacificQueue);\n int[][] altanticReachable = bfs(atlanticQueue);\n \n \n List<List<Integer>> commanCell = new ArrayList();\n for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++){\n //marked\n if(pacificReachable[i][j] == 1 && altanticReachable[i][j] == 1){\n commanCell.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(List.of(i, j)));\n }\n }\n }\n \n \n return commanCell;\n }\n \n \n private int[][] bfs(Queue<int[]> queue){\n \n int[][] reachable = new int[rows][cols];\n \n while(!queue.isEmpty()){\n int[] cell = queue.remove();\n \n \n //mark as reached this cell\n reachable[cell[0]][cell[1]] = 1;\n \n for(int[] dir : DIRECTIONS){\n int newRow = cell[0] + dir[0];\n int newCol = cell[1] + dir[1];\n \n //Boundary check\n if(newRow < 0 || newRow >= rows || newCol < 0 || newCol >= cols)\n continue;\n \n \n //check already reached from pacific ocean or altantic ocean\n if(reachable[newRow][newCol] > 0)\n continue;\n \n //check from.this cell we can reached to ocean or not\n if(matrix[newRow][newCol] < matrix[cell[0]][cell[1]])\n continue;\n \n queue.offer(new int[]{newRow, newCol});\n }\n }\n \n return reachable;\n }\n}\n```
| 6 | 1 |
['Backtracking', 'Breadth-First Search', 'Java']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Beats 💯 % || Optimized DFS solution || Clean & Efficient Code || O(N × M) complexity🔥🔥
|
beats-optimized-dfs-solution-clean-effic-o19h
|
IntuitionThe problem involves finding all grid cells that can flow water to both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. Water can flow from a cell to another cell if
|
ayush_pratap27
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-06T06:45:23.418116+00:00
|
2025-02-06T06:45:23.418116+00:00
| 1,433 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
The problem involves finding all grid cells that can flow water to both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. Water can flow from a cell to another cell if the height of the next cell is greater than or equal to the current cell.
Our first thought is that each cell in the grid should be checked to see if it can reach both oceans. However, instead of checking each cell individually, a more efficient approach is to start from the oceans and move inward, marking all the cells that can flow to them.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
1. Reverse Thinking:
Instead of checking if a cell can reach both oceans, we check which cells can be reached from the oceans.
2. DFS Traversal:
- We treat the Pacific and Atlantic ocean borders as sources and perform Depth First Search (DFS) from them.
- We maintain two 2D boolean arrays (pacific and atlantic) to track which cells can be reached by each ocean.
- We start DFS from:
- Pacific Ocean: The leftmost column and top row.
- Atlantic Ocean: The rightmost column and bottom row.
- DFS explores the neighboring cells if the height condition is satisfied.
3. Result Collection:
- A cell is part of the result if it is marked as reachable in both pacific and atlantic.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
- Each cell is visited at most 4 times (once per direction).
- Since we visit all N × M cells, the worst-case time complexity is $$O(N × M)$$.
- Space complexity:
- We use two 2D matrices (pacific and atlantic) of size N × M, resulting in $$O(N × M)$$ space.
- The recursive DFS stack takes at most $$O(N × M)$$ space in the worst case (if all cells are part of the recursion stack).
- Overall, $$O(N × M)$$ space complexity.
# Code
```cpp []
const auto _ = std::cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
#define LC_HACK
#ifdef LC_HACK
const auto __ = []() {
struct ___ {
static void _() { std::ofstream("display_runtime.txt") << 0 << '\n'; }
};
std::atexit(&___::_);
return 0;
}();
#endif
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& heights, vector<vector<int>>& vis, int row, int col) {
int n = heights.size();
int m = heights[0].size();
vis[row][col] = 1;
int delRow[] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
int delCol[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int newRow = row + delRow[i];
int newCol = col + delCol[i];
if(newRow >= 0 && newRow < n && newCol >= 0 && newCol < m && !vis[newRow][newCol] && heights[newRow][newCol] >= heights[row][col]){
dfs(heights, vis, newRow, newCol);
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
int n = heights.size();
int m = heights[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<vector<int>> pac(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
vector<vector<int>> atl(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
dfs(heights, pac, i, 0);
dfs(heights, atl, i, m - 1);
}
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
dfs(heights, pac, 0, j);
dfs(heights, atl, n - 1, j);
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
if(pac[i][j] && atl[i][j]){
result.push_back({i, j});
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
```
``` java []
class Solution {
private void dfs(int[][] heights, boolean[][] ocean, int row, int col) {
int n = heights.length;
int m = heights[0].length;
ocean[row][col] = true;
int[] delRow = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
int[] delCol = {0, 0, -1, 1};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newRow = row + delRow[i];
int newCol = col + delCol[i];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < n && newCol >= 0 && newCol < m &&
!ocean[newRow][newCol] && heights[newRow][newCol] >= heights[row][col]) {
dfs(heights, ocean, newRow, newCol);
}
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {
int n = heights.length;
int m = heights[0].length;
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[][] pacific = new boolean[n][m];
boolean[][] atlantic = new boolean[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dfs(heights, pacific, i, 0);
dfs(heights, atlantic, i, m - 1);
}
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
dfs(heights, pacific, 0, j);
dfs(heights, atlantic, n - 1, j);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) {
result.add(Arrays.asList(i, j));
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
```
``` javascript []
var pacificAtlantic = function(heights) {
let n = heights.length, m = heights[0].length;
let pacific = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(m).fill(false));
let atlantic = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(m).fill(false));
const dfs = (row, col, ocean) => {
ocean[row][col] = true;
let directions = [[-1, 0], [1, 0], [0, -1], [0, 1]];
for (let [dr, dc] of directions) {
let newRow = row + dr, newCol = col + dc;
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < n && newCol >= 0 && newCol < m &&
!ocean[newRow][newCol] && heights[newRow][newCol] >= heights[row][col]) {
dfs(newRow, newCol, ocean);
}
}
};
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dfs(i, 0, pacific);
dfs(i, m - 1, atlantic);
}
for (let j = 0; j < m; j++) {
dfs(0, j, pacific);
dfs(n - 1, j, atlantic);
}
let result = [];
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) result.push([i, j]);
}
}
return result;
};
```
``` python []
class Solution:
def pacificAtlantic(self, heights):
n, m = len(heights), len(heights[0])
pacific, atlantic = set(), set()
def dfs(row, col, ocean):
ocean.add((row, col))
for dr, dc in [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]:
newRow, newCol = row + dr, col + dc
if 0 <= newRow < n and 0 <= newCol < m and (newRow, newCol) not in ocean and heights[newRow][newCol] >= heights[row][col]:
dfs(newRow, newCol, ocean)
for i in range(n):
dfs(i, 0, pacific)
dfs(i, m - 1, atlantic)
for j in range(m):
dfs(0, j, pacific)
dfs(n - 1, j, atlantic)
return list(pacific & atlantic)
```
If this solution helped you, don’t forget to UPVOTE! 🚀💯 Your support keeps me motivated to share more optimized solutions! 🔥🙌
| 5 | 0 |
['Array', 'Depth-First Search', 'Graph', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'JavaScript']
| 2 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
[ C++] | Basic DFS + BFS | Easy Explanation
|
c-basic-dfs-bfs-easy-explanation-by-kshz-tikr
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nLets solve this question backwards\n\nAll the elements at 0th Row and 0th Col can Fall
|
kshzz24
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-23T14:47:29.316136+00:00
|
2023-04-23T14:47:29.316169+00:00
| 200 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nLets solve this question backwards\n\nAll the elements at `0th Row` and `0th Col` can Fall into `Pacific`\nAll the elements at `M-1 th Row` and `N-1 th Col` can Fall into `Atlantic`\n\n\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\nInstead of Traversing from Highest Level to Lower, Use Lower to Higher\nmeaning `Heights[row][col] <= Heights[nrow][ncol]`.\n\nFind all the elements that can be visited and if the element is visited by Both `Atlantic` and `Pacific` Coast then push it in answer\n\n\n# DFS\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> delRow = {1,0,-1,0};\n vector<int> delCol = {0,1,0,-1};\n int m,n;\n void AtlanticFlow(vector<vector<int>>& heights, int row, int col, vector<vector<bool>>& atlantic){\n atlantic[row][col] = true;\n for(int i = 0;i<4;i++){\n int nrow = delRow[i]+row;\n int ncol = delCol[i]+col;\n if(nrow >=0 and ncol >=0 and nrow <m and ncol <n and !atlantic[nrow][ncol] and heights[row][col]<=heights[nrow][ncol]){\n AtlanticFlow(heights, nrow, ncol,atlantic);\n }\n }\n }\n void PacificFlow(vector<vector<int>>& heights, int row, int col, vector<vector<bool>>& pacific){\n pacific[row][col] = true;\n for(int i = 0;i<4;i++){\n int nrow = delRow[i]+row;\n int ncol = delCol[i]+col;\n if(nrow >=0 and ncol >=0 and nrow <m and ncol <n and !pacific[nrow][ncol] and heights[row][col]<=heights[nrow][ncol]){\n PacificFlow(heights, nrow, ncol,pacific);\n }\n }\n }\n vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {\n m = heights.size();\n n = heights[0].size();\n vector<vector<int>> ans;\n vector<vector<bool>> pacific(m, vector<bool>(n,false));\n vector<vector<bool>> atlantic(m, vector<bool>(n,false));\n \n for(int i = 0;i<m;i++){\n AtlanticFlow(heights, i, n-1, atlantic);\n PacificFlow(heights, i, 0, pacific);\n }\n for(int j = 0; j<n; j++){\n AtlanticFlow(heights, m-1, j, atlantic);\n PacificFlow(heights, 0, j, pacific);\n }\n \n for(int i = 0;i<m;i++){\n for(int j = 0; j< n ; j++){\n if(atlantic[i][j] and pacific[i][j]){\n ans.push_back({i,j});\n }\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n# BFS\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> delRow = {1,0,-1,0};\n vector<int> delCol = {0,1,0,-1};\n int m,n;\n \n void bfs(vector<vector<int>>& heights, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, queue<pair<int, int>>& q) {\n while(!q.empty()) {\n pair<int, int> curr = q.front();\n q.pop();\n for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {\n int r = curr.first + delRow[i];\n int c = curr.second + delCol[i];\n if(r>=0 && c>=0 && r<m && c<n && !visited[r][c] && heights[r][c] >= heights[curr.first][curr.second]) {\n visited[r][c] = true;\n q.push(make_pair(r, c));\n }\n }\n }\n }\n \n vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {\n m = heights.size();\n n = heights[0].size();\n vector<vector<int>> ans;\n vector<vector<bool>> pacific(m, vector<bool>(n,false));\n vector<vector<bool>> atlantic(m, vector<bool>(n,false));\n \n queue<pair<int, int>> pq;\n queue<pair<int, int>> aq;\n \n // First and Last row\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {\n pq.push(make_pair(0, i));\n aq.push(make_pair(m-1, i));\n }\n // First and Last column\n for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {\n pq.push(make_pair(i, 0));\n aq.push(make_pair(i, n-1));\n }\n \n bfs(heights, pacific, pq);\n bfs(heights, atlantic, aq);\n \n for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {\n for(int j=0; j<n; j++) {\n if(pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) {\n ans.push_back({i, j});\n }\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n};\n\n```\n
| 5 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Breadth-First Search', 'Matrix', 'C++']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Unique, Compact and Fast (3ms - 99% ) solution with explanation
|
unique-compact-and-fast-3ms-99-solution-kpw4y
|
Intuition\nDFS\n\n# Approach\nHere\'s a step-by-step explanation of the code:\n\n1. The pacificAtlantic method is the entry point of the solution. It takes the
|
shashwat1712
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-12T10:35:36.648391+00:00
|
2023-04-12T10:46:16.526143+00:00
| 1,037 | false |
# Intuition\nDFS\n\n# Approach\nHere\'s a step-by-step explanation of the code:\n\n1. The pacificAtlantic method is the entry point of the solution. It takes the heights matrix as input and returns a list of lists of integers representing the coordinates of the cells where water can flow to both oceans.\n\n2. The visited matrix is a 2D array of integers with the same dimensions as the heights matrix, used to keep track of visited cells. It is initialized with all values set to 0.\n\n3. The ans list is used to store the final result - the list of lists of coordinates.\n\n4. The first two nested loops iterate over the first and last row of the heights matrix, and the dfs method is called for each cell in these rows. The dfs method is called with the row index, column index, heights matrix, visited matrix, mark (1 or 2) representing which ocean the water is flowing to, current height of the cell, and the ans list.\n\n5. The second pair of nested loops iterate over the first and last column of the heights matrix, and the dfs method is called for each cell in these columns, similar to step 4.\n\n6. The dfs method is a recursive function that performs the depth-first search. It takes the current row index, column index, heights matrix, visited matrix, mark, current height of the cell, and the ans list as input.\n\n7. The dfs method starts by checking if the current cell is out of bounds (i.e., row or column index is less than 0 or greater than or equal to the dimensions of the heights matrix), or if the height of the current cell is less than the height of the previous cell (i.e., water can\'t flow uphill), or if the current cell has already been visited by the same ocean (mark) or by both oceans (mark=3). If any of these conditions are true, the function returns early and does not further explore the current cell.\n\n8. If the current cell passes the above checks, it is marked as visited by adding the mark to the visited matrix at the current row and column index.\n\n9. If the current cell has been visited by both oceans (mark=3), its coordinates (row and column index) are added to the ans list as a new list of integers representing the coordinates.\n\n10. The dfs method is then recursively called for the neighboring cells (up, down, left, and right) of the current cell, passing the updated row and column indices, mark, and the height of the current cell.\n\n11. After the DFS traversal is complete, the ans list contains the coordinates of the cells where water can flow to both oceans.\n\n12. Finally, the ans list is returned as the solution to the problem.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(m*n)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(m*n)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {\n int visited[][] = new int[heights.length][heights[0].length];\n List<List<Integer>>ans = new ArrayList<>();\n for(int i=0;i<heights[0].length;i++){\n dfs(0,i,heights,visited,1,heights[0][i],ans);\n dfs(heights.length-1,i,heights,visited,2,heights[heights.length-1][i],ans);\n }\n for(int i=0;i<heights.length;i++){\n dfs(i,0,heights,visited,1,heights[i][0],ans);\n dfs(i,heights[0].length-1,heights,visited,2,heights[i][heights[0].length-1],ans);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n private void dfs(int i , int j ,int[][] heights, int[][] visited, int mark, int ch, List<List<Integer>> ans){\n if(i<0 || j<0 || i>=heights.length || j>=heights[0].length || heights[i][j]<ch || visited[i][j]==mark || visited[i][j]==3) return ;\n visited[i][j]+=mark;\n if(visited[i][j]==3){\n ans.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(i,j)));\n }\n dfs(i+1,j,heights,visited,mark,heights[i][j],ans);\n dfs(i,j+1,heights,visited,mark,heights[i][j],ans);\n dfs(i-1,j,heights,visited,mark,heights[i][j],ans);\n dfs(i,j-1,heights,visited,mark,heights[i][j],ans);\n }\n}\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Array', 'Depth-First Search', 'Matrix', 'Java']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
C++ || DFS using 2d vector of pair || 90% faster code || Beginner friendly code
|
c-dfs-using-2d-vector-of-pair-90-faster-agam1
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dx[4]={0,0,1,-1};\n int dy[4]={1,-1,0,0};\n void paci(vector<vector<int>>& h,vector<vector<pair<bool,bool>>>& ocean,i
|
tanusiwach
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-31T14:19:20.787993+00:00
|
2022-08-31T14:19:20.788036+00:00
| 223 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dx[4]={0,0,1,-1};\n int dy[4]={1,-1,0,0};\n void paci(vector<vector<int>>& h,vector<vector<pair<bool,bool>>>& ocean,int n,int m,int i,int j){\n ocean[i][j].first=true;\n for(int k=0;k<4;k++){\n int nx=i+dx[k];int ny=j+dy[k];\n if(nx>=0 && nx<n && ny>=0 && ny<m && !ocean[nx][ny].first && h[nx][ny]>=h[i][j]){\n paci(h,ocean,n,m,nx,ny);\n }\n }\n }\n void atla(vector<vector<int>>& h,vector<vector<pair<bool,bool>>>& ocean,int n,int m,int i,int j){\n ocean[i][j].second=true;\n for(int k=0;k<4;k++){\n int nx=i+dx[k];int ny=j+dy[k];\n if(nx>=0 && nx<n && ny>=0 && ny<m && !ocean[nx][ny].second && h[nx][ny]>=h[i][j]){\n atla(h,ocean,n,m,nx,ny);\n }\n }\n }\n vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& h) {\n int n=h.size();int m=h[0].size();\n //ocean.first for pacific \n //ocean.second for atlantic\n vector<vector<pair<bool,bool>>> ocean(n,vector<pair<bool,bool>>(m,{false,false}));\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n paci(h,ocean,n,m,i,0);\n atla(h,ocean,n,m,i,m-1);\n }\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n paci(h,ocean,n,m,0,i);\n atla(h,ocean,n,m,n-1,i);\n }\n vector<vector<int>> ans;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++){\n if(ocean[i][j].first && ocean[i][j].second)\n ans.push_back({i,j});\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Graph', 'C++']
| 1 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Runtime: 64 ms, faster than 99.78% of C++ online submissions for Pacific Atlantic Water Flow.
|
runtime-64-ms-faster-than-9978-of-c-onli-t5ff
|
STEP 1- if we start from the cells connected to altantic ocean and visit all cells having height greater than current cell (water can only flow from a cell to a
|
rajat241302
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-09T19:39:16.341175+00:00
|
2022-06-09T19:39:16.341218+00:00
| 427 | false |
**STEP 1**- if we start from the cells connected to altantic ocean and visit all cells having height greater than current cell (**water can only flow from a cell to another one with height equal or lower**), we are able to reach some subset of cells (let\'s call them A).\n \n 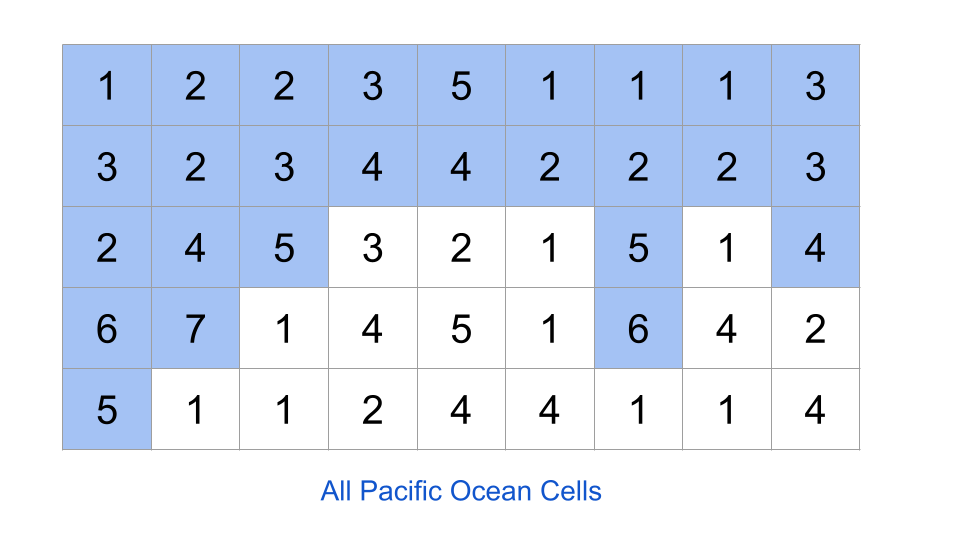\n \n**STEP-2**\n Next, we start from the cells connected to pacific ocean and repeat the same process, we find another subset (let\'s call this one B).\n \n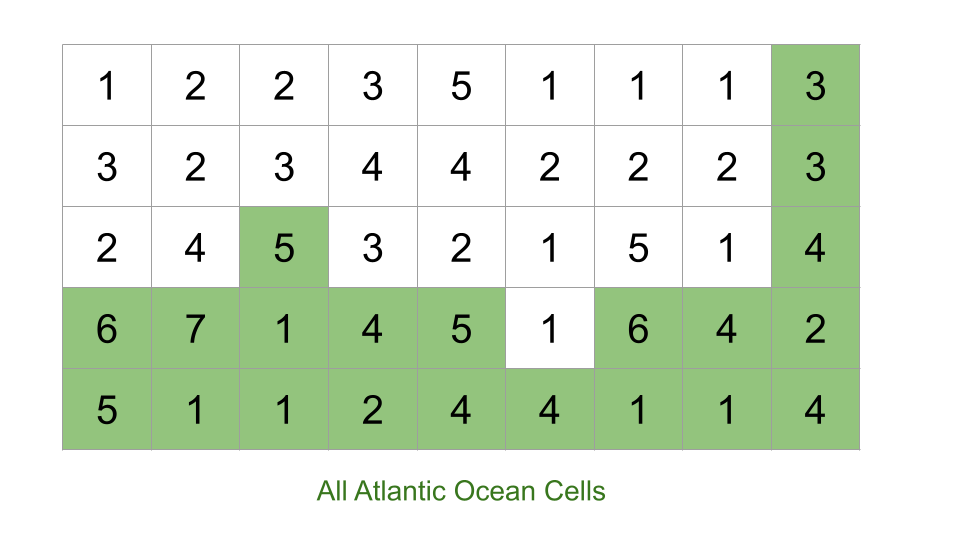\n\n**The final answer we get will be the intersection of sets A and B (A \u2229 B).**\n\n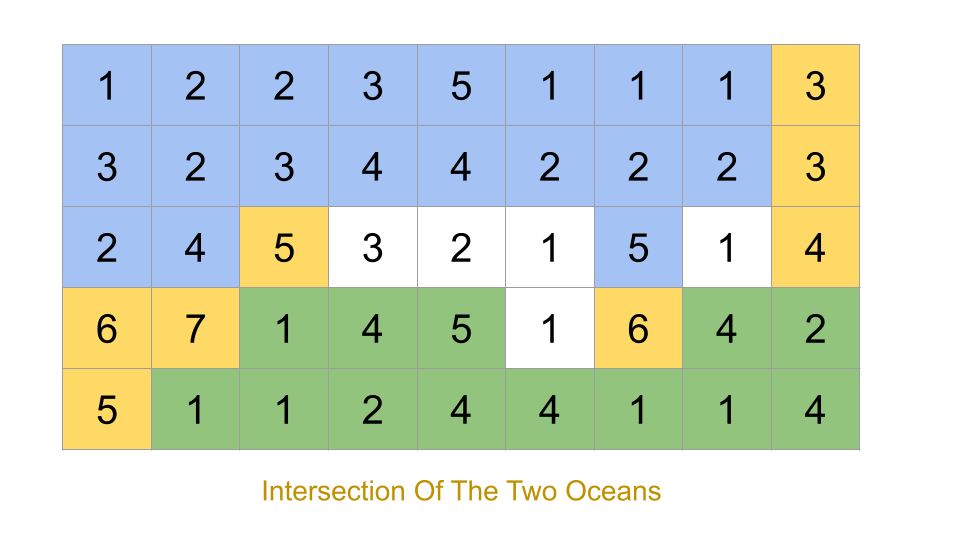\n\n```\nclass Solution\n{\n\n\tvoid bfs(vector<vector<int>> &h, queue<pair<int, int>> q, int n, int m, vector<vector<int>> &visi)\n\t{\n\t\tint ar1[] = {0, 0, 1, -1};\n\t\tint ar2[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};\n\t\twhile (!q.empty())\n\t\t{\n\t\t\tint x = q.front().first;\n\t\t\tint y = q.front().second;\n\t\t\tq.pop();\n\t\t\tfor (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tint xn = x + ar1[i];\n\t\t\t\tint yn = y + ar2[i];\n\t\t\t\tif (xn < 0 || yn < 0 || xn >= n || yn >= m || visi[xn][yn] == 1)\n\t\t\t\t\tcontinue;\n\t\t\t\tif (h[x][y] <= h[xn][yn])\n\t\t\t\t\tq.push({xn, yn}), visi[xn][yn] = 1;\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\npublic:\n\tvector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>> &heights)\n\t{\n int n = heights.size();\n\t\tint m = heights[0].size();\n\t\tvector<vector<int>> visi1(n, vector<int>(m, 0)); // for Pacific Ocean\n\t\tvector<vector<int>> visi2(n, vector<int>(m, 0)); // for Atlantic Ocean\n\n\t\tqueue<pair<int, int>> q;\n\t\t// STEP-1\n\t\tfor (int i = 0; i < m; i++)\n\t\t\tq.push({0, i}), visi1[0][i] = 1;\n\t\tfor (int j = 0; j < n; j++)\n\t\t\tq.push({j, 0}), visi1[j][0] = 1;\n\n\t\tbfs(heights, q, n, m, visi1); // for pacific ocean which are greator and equal to value\n\n\t\t// to empty the queue for atlantic Ocean\n\t\twhile (!q.empty())\n\t\t\tq.pop();\n\t\t// STEP-2\n\t\tfor (int i = 0; i < m; i++)\n\t\t\tq.push({n - 1, i}), visi2[n - 1][i] = 1;\n\t\tfor (int j = 0; j < n; j++)\n\t\t\tq.push({j, m - 1}), visi2[j][m - 1] = 1;\n\n\t\tbfs(heights, q, n, m, visi2); // for Atalantic ocean which are greator and equal to value\n\t // STEP-3\n\t\tvector<vector<int>> ans;\t // to check the common in both visi1 and visi2 vector;\n\n\t\tfor (int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n\t\t{\n\t\t\tfor (int j = 0; j < m; j++)\n\t\t\t\tif (visi1[i][j] == visi2[i][j] and visi1[i][j] == 1)\n\t\t\t\t\tans.push_back({i, j});\n\t\t}\n\t\treturn ans;\n\t}\n};\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Breadth-First Search', 'Graph', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
C++ || DFS || Easiest Explanation || Simple Explanation
|
c-dfs-easiest-explanation-simple-explana-0dmr
|
Tried my level best to explain\nIncase you liked the solution you can upvote it.\n
|
milindguptaji
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-17T19:02:25.952495+00:00
|
2022-04-17T19:02:46.667890+00:00
| 508 | false |
**Tried my level best to explain\nIncase you liked the solution you can upvote it.**\n<iframe src="https://leetcode.com/playground/96uMhG4u/shared" frameBorder="0" width="800" height="600"></iframe>
| 5 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'C', 'C++']
| 2 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Pacific Atlantic
|
pacific-atlantic-by-phoenix2000-8gci
|
i thought it can work with travel in pacific with [i,j + 1] and [i + 1,0] & in atlantic with [ i ,j-1] and [i-1,0].but i was wrong\n\t\n\n\n\tclass Solution
|
phoenix2000
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-02T18:32:49.550030+00:00
|
2022-03-02T18:33:01.921071+00:00
| 173 | false |
i thought it can work with travel in pacific with [i,j + 1] and [i + 1,0] & in atlantic with [ i ,j-1] and [i-1,0].but i was wrong\n\t\n\n\n\tclass Solution {\n\tpublic:\n\t\tvector<vector<int>> dir = {{0,1},{1,0},{-1,0},{0,-1}};\n\n\t\tbool isSafe(int r,int c,int n,int m){\n\t\t\tif( r < 0 or c < 0 or r>=n or c>=m){\n\t\t\t\treturn false;\n\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\treturn true;\n\t\t}\n\t\tvoid dfs(vector<vector<int>>&grid,int r,int c,vector<vector<bool>> &visited) {\n\n\t\t\tint curr = grid[r][c];\n\t\t\tvisited[r][c] = 1;\n\t\t\tfor(int i = 0; i<dir.size();i++){\n\t\t\t\tint r1 = r + dir[i][0];\n\t\t\t\tint c1 = c + dir[i][1];\n\n\n\t\t\t\tif(isSafe(r1,c1,grid.size(),grid[0].size()) and visited[r1][c1]==false and grid[r1][c1] >= curr){\n\t\t\t\t\tdfs(grid,r1,c1,visited);\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t}\n\t\tvector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {\n\n\n\t\t\tint n = heights.size();\n\t\t\tint m = heights[0].size();\n\t\t\tvector<vector<bool>> pacific(n,vector<bool>(m,0));\n\t\t\tvector<vector<bool>> atlantic(n,vector<bool>(m,0));\n\n\t\t\tfor(int i = 0; i<m;i++){\n\t\t\t\tif(pacific[0][i]==false){\n\t\t\t\t\tdfs(heights,0,i,pacific);\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\tfor(int i = 0; i<n;i++){\n\t\t\t\tif(pacific[i][0]==false){\n\t\t\t\t\tdfs(heights,i,0,pacific);\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\tfor(int i = 0; i<m;i++){\n\t\t\t\tif(atlantic[n-1][i]==false){\n\t\t\t\t\tdfs(heights,n-1,i,atlantic);\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\tfor(int i= 0; i<n;i++){\n\t\t\t\tif(atlantic[i][m-1]==false){\n\t\t\t\t\tdfs(heights,i,m-1,atlantic);\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\tvector<vector<int>> ans;\n\n\t\t\tfor(int i = 0; i<n;i++){\n\t\t\t\tfor(int j = 0;j<m;j++){\n\t\t\t\t\tcout<<atlantic[i][j]<<" "<<pacific[i][j]<<" ,";\n\t\t\t\t\tif(atlantic[i][j] and pacific[i][j]){\n\t\t\t\t\t\tans.push_back({i,j});\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\tcout<<endl;\n\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\treturn ans;\n\t\t}
| 5 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Graph']
| 1 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
JAVA 4ms solution | 4ms | with explaination | TC O(M*N) | DFS
|
java-4ms-solution-4ms-with-explaination-15xc7
|
```\nclass Solution {\n int dir[][] = {{0,1}, {0,-1}, {1,0}, {-1,0}};\n public List> pacificAtlantic(int[][] matrix) {\n List> res = new ArrayList<
|
varun_singh_01
|
NORMAL
|
2021-08-24T00:38:35.560798+00:00
|
2021-08-24T00:38:35.560843+00:00
| 468 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n int dir[][] = {{0,1}, {0,-1}, {1,0}, {-1,0}};\n public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] matrix) {\n List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); // create a new list to store result \n if(matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) //if matrix is etiehr null or 1d\n return res;\n \n // create 2 boolean arrays for pacific and atlantic\n int row = matrix.length, col = matrix[0].length;\n boolean[][] pacific = new boolean[row][col];\n boolean[][] atlantic = new boolean[row][col];\n \n // call upon the dfs ,s.t. pacific starts from top and left and atlantic starts from bottom and right \n //DFS\n for(int i = 0; i < col; i++){\n dfs(matrix, 0, i, Integer.MIN_VALUE, pacific);\n dfs(matrix, row-1, i, Integer.MIN_VALUE, atlantic);\n }\n for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){\n dfs(matrix, i, 0, Integer.MIN_VALUE, pacific);\n dfs(matrix, i, col-1, Integer.MIN_VALUE, atlantic);\n }\n \n //Ceheck for conditions where both pacific[i][j] and atlantic[i][j] are true \n //preparing the result\n for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < col; j++) {\n if(pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) {\n res.add(Arrays.asList(i,j));\n }\n }\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n \n public void dfs(int[][] matrix, int i, int j, int prev, boolean[][] ocean){\n if(i < 0 || i >= ocean.length || j < 0 || j >= ocean[0].length) return; // checking edge cases here\n if(matrix[i][j] < prev || ocean[i][j]) return; // if either current cell is already visited or the current cell is < prev\n ocean[i][j] = true; // set cell as true\n // move into hte 4 directions\n for(int[] d : dir){\n dfs(matrix, i+d[0], j+d[1], matrix[i][j], ocean);\n }\n \n }\n}
| 5 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Java']
| 2 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
[Python] 3 Approaches (brute-force, flood-fill) with explanations
|
python-3-approaches-brute-force-flood-fi-hal0
|
----------------------------------\nApproach 1: Brute-force\nTLE : 111 / 113 test cases passed.\n----------------------------------\n---------------------------
|
Hieroglyphs
|
NORMAL
|
2021-06-30T13:07:14.485176+00:00
|
2021-06-30T13:08:31.485127+00:00
| 466 | false |
----------------------------------\nApproach 1: Brute-force\nTLE : 111 / 113 test cases passed.\n----------------------------------\n----------------------------------\n\n**Idea:**\n\n- For each cell:\n\t- see if I can reach pacific \n\t- see if I can reach atlantic\n\t- if the answer is True for both -> add to result\n\n\n- Time: \n\t- main function : `O(m*n) `\n\t- helper : `O(E+V) `\n\t- Overall => `O(E^2 + V)` => `O((M*N)^2)`\n\t- Iterating over cells and trigger 2 bfs searchs on each cell. We could do better!\n\n\n```\ndef pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:\n \n # bfs helper 1:\n def reachPacific(x,y): # - O(E+V)\n if x == 0 or y == 0:\n return True\n \n from collections import deque\n q = deque()\n q.append((x,y))\n dirs = [(1,0), (0,1), (-1,0), (0,-1)]\n visited = set()\n while q:\n for i in range(len(q)):\n x, y = q.popleft()\n if x == 0 or y == 0:\n return True # found my way to \n visited.add((x,y))\n \n for dir in dirs: # must only add nei that have less height - so that water falls to them\n newX, newY = x+dir[0], y+dir[1]\n if newX >= 0 and newX <= len(grid)-1 and newY >= 0 and newY <= len(grid[0])-1: \n if (newX, newY) not in visited:\n if grid[newX][newY] <= grid[x][y]: # water can flow\n q.append((newX, newY))\n return False \n \n\t\t# bfs helper 2:\n def reachAtlantic(x,y): # - O(E+V)\n grid = heights\n \n if x == len(grid)-1 or y == len(grid[0])-1:\n return True\n \n from collections import deque\n q = deque()\n q.append((x,y))\n dirs = [(1,0), (0,1), (-1,0), (0,-1)]\n visited = set()\n while q:\n for i in range(len(q)):\n x, y = q.popleft()\n if x == len(grid)-1 or y == len(grid[0])-1:\n return True # found my way to \n visited.add((x,y))\n \n for dir in dirs: # must only add nei that have less height - so that water falls to them\n newX, newY = x+dir[0], y+dir[1]\n if newX >= 0 and newX <= len(grid)-1 and newY >= 0 and newY <= len(grid[0])-1: \n if (newX, newY) not in visited:\n if grid[newX][newY] <= grid[x][y]: # water can flow\n q.append((newX, newY))\n return False \n \n # main:\n grid = heights\n res = []\n for r in range(len(grid)): # - O(V) or O(M*N)\n for c in range(len(grid[0])):\n if reachPacific(r,c) and reachAtlantic(r,c):\n res.append([r,c])\n return res\n\n``` \n\n----------------------------------------------\nApproach 2: Enhanced BFS (aka Flood-fill style BFS)\n----------------------------------\n----------------------------------\n\n**Idea:**\n1- flood-fill-style, simaltanous BFS from all pacific ocean cells\n2- flood-fill-style, simaltanous BFS from all atlantic ocean cells\n\n- start with 2 qeue : one for each ocean/cost\n- In order for a cell to flush its share of rain into the ocean, the cell has to have a higher altitude.\n- Hence, if a cell is higher than ocean cell -> include in ocean cell\nperform intersect between atlantic cells and pacific cells\n\n- Time: \n\t- `O(M*N)`\n\n``` \n\ndef pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:\n \n\tgrid = heights\n \n # helper 1:\n def findPacificCells(grid):\n from collections import deque\n q = deque()\n visited = set()\n \n # num_rows, num_cols\n numRows, numCols = len(grid), len(grid[0])\n \n # add all pacific cells\n for i in range(numCols): # top row\n q.append((0,i))\n visited.add((0,i))\n \n for i in range(numRows): # left most col\n q.append((i,0))\n visited.add((i,0))\n \n dirs = [(1,0), (0,1), (-1,0), (0,-1)]\n while q:\n for i in range(len(q)):\n x, y = q.popleft()\n visited.add((x,y))\n \n for dir in dirs:\n newX, newY = x+dir[0], y+dir[1]\n if newX >= 0 and newX <= len(grid)-1 and newY >= 0 and newY <= len(grid[0])-1:\n if grid[newX][newY] >= grid[x][y]: # -- note [1]\n if (newX, newY) not in visited:\n q.append((newX, newY))\n \n # note [1]\n # if new cell is higher -> means rain can flow from it to pacific -> hence include new cell in pacific\n return visited\n \n # helper 2\n def findAtlanticCells(grid):\n \n from collections import deque\n q = deque()\n visited = set()\n \n # num_rows, num_cols\n numRows, numCols = len(grid), len(grid[0])\n \n # add all atlantic cells\n for i in range(numCols): # bottom row\n q.append((numRows-1,i))\n visited.add((numRows-1,i))\n \n for i in range(len(grid)): # right most col\n q.append((i,numCols-1))\n visited.add((i,numCols-1))\n \n dirs = [(1,0), (0,1), (-1,0), (0,-1)]\n while q:\n for i in range(len(q)):\n x, y = q.popleft()\n visited.add((x,y))\n \n for dir in dirs:\n newX, newY = x+dir[0], y+dir[1]\n if newX >= 0 and newX <= len(grid)-1 and newY >= 0 and newY <= len(grid[0])-1:\n if grid[newX][newY] >= grid[x][y]: # -- note [1]\n if (newX, newY) not in visited:\n q.append((newX, newY))\n \n # note [1]\n # if new cell is higher -> means rain can flow from it to pacific -> hence include new cell in pacific\n return visited\n \n # main:\n pacific = findPacificCells(grid)\n atlantic = findAtlanticCells(grid)\n mutual = pacific.intersection(atlantic)\n \n return list(mutual)\n``` \n \n--------------------------------------------\nApproach 3 : Enhanced Flood-fill BFS\n--------------------------------------------\n--------------------------------------------\n- Instead of having 2 seperate functions: `findPacificCells` and `findAtlanticCells`\n- Use one bfs helper function on 2 different queues\n- Time: \n\t- `O(M*N)`\n \n``` \n def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:\n \n # bfs helper\n def bfs(q):\n dirs = [(1,0), (0,1), (-1,0), (0,-1)]\n visited = set()\n while q:\n for i in range(len(q)):\n x, y = q.popleft()\n visited.add((x,y))\n \n # expand to nei cell if nei cell is higher in atltitude\n for dir in dirs:\n newX, newY = x+dir[0], y+dir[1]\n if newX >= 0 and newX <= len(grid)-1 and newY >= 0 and newY <= len(grid[0])-1:\n if (newX, newY) not in visited:\n if grid[newX][newY] >= grid[x][y]: # water can flow from nei to x,y to ocean\n q.append((newX, newY))\n return visited\n \n \n # main\n # initial queues - one for each cost/ocean\n from collections import deque\n qp = deque()\n qa = deque()\n \n grid = heights\n \n # num_rows, num_cols\n numRows, numCols = len(grid), len(grid[0])\n \n # 1) pacific:\n for i in range(numCols): # top row\n qp.append((0,i))\n \n for i in range(numRows): # left most col\n qp.append((i,0))\n \n # 2) atlantic\n for i in range(numRows): # right most col\n qa.append((i,numCols-1))\n \n for i in range(numCols): # bottom row\n qa.append((numRows-1, i))\n \n pacific = bfs(qp)\n atlantic = bfs(qa)\n mutual = pacific.intersection(atlantic)\n return mutual\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Python easy to understand BFS
|
python-easy-to-understand-bfs-by-mxmb-bh1b
|
python\n\tdef pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:\n m, n = len(heights), len(heights[0])\n pacific = deque([[0,j]
|
mxmb
|
NORMAL
|
2021-04-30T19:29:50.062846+00:00
|
2021-04-30T19:29:50.062883+00:00
| 786 | false |
```python\n\tdef pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:\n m, n = len(heights), len(heights[0])\n pacific = deque([[0,j] for j in range(n)] + [[i,0] for i in range(m)])\n atlantic = deque([[i,n-1] for i in range(m)] + [[m-1, i] for i in range(n)])\n \n def bfs(queue):\n visited = set()\n while queue:\n x,y = queue.popleft()\n visited.add((x,y))\n for dx,dy in [[1,0],[0,1],[-1,0],[0,-1]]:\n if 0 <= x+dx < m and 0 <= y+dy < n:\n if (x+dx, y+dy) not in visited:\n if heights[x+dx][y+dy] >= heights[x][y]:\n queue.append((x+dx, y+dy))\n return visited\n \n p, a = bfs(pacific), bfs(atlantic)\n \n return p.intersection(a)\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
BFS | C++
|
bfs-c-by-tanyarajhans7-y5ys
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int m,n;\n int dx[4]={1,0,-1,0};\n int dy[4]={0,1,0,-1};\n queue<pair<int,int>> pac;\n queue<pair<int,int>> atl;\n
|
tanyarajhans7
|
NORMAL
|
2021-03-25T11:04:17.160104+00:00
|
2021-03-25T11:04:17.160133+00:00
| 252 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int m,n;\n int dx[4]={1,0,-1,0};\n int dy[4]={0,1,0,-1};\n queue<pair<int,int>> pac;\n queue<pair<int,int>> atl;\n \n bool isValid(int x, int y){\n return x>=0 && x<m && y>=0 && y<n;\n }\n \n void bfs(queue<pair<int,int>> &q, vector<vector<int>> &vis, vector<vector<int>>& matrix){\n while(!q.empty()){\n int x=q.front().first;\n int y=q.front().second;\n vis[x][y]=1;\n q.pop();\n for(int k=0;k<4;k++){\n int xx=x+dx[k];\n int yy=y+dy[k];\n if(isValid(xx,yy) && matrix[x][y]<=matrix[xx][yy] && vis[xx][yy]==0){\n q.push({xx,yy});\n }\n }\n }\n }\n \n \n vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {\n vector<vector<int>> ans;\n m=matrix.size();\n if(m==0)\n return ans;\n n=matrix[0].size();\n if(n==0)\n return ans;\n vector<vector<int>> visp(m, vector<int>(n,0));\n vector<vector<int>> visq(m, vector<int>(n,0));\n for(int i=m-1;i>=0;i--)\n pac.push({i,0});\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)\n pac.push({0,i});\n for(int i=m-1;i>=0;i--)\n atl.push({i,n-1});\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)\n atl.push({m-1,i});\n bfs(pac,visp,matrix);\n bfs(atl,visq,matrix);\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n if(visp[i][j]==1 && visq[i][j]==1)\n ans.push_back({i,j});\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 5 | 1 |
[]
| 1 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Straightforward efficient C++ solution using stack
|
straightforward-efficient-c-solution-usi-rwau
|
The code is rather long, but very easy to understand.\nBasically, we use two tables to record if the water can flow to pacific or atlantic. To determine the ele
|
liyouvane
|
NORMAL
|
2016-10-09T04:52:19.860000+00:00
|
2016-10-09T04:52:19.860000+00:00
| 2,078 | false |
The code is rather long, but very easy to understand.\nBasically, we use two tables to record if the water can flow to pacific or atlantic. To determine the element, we use a stack structure to search the element on the four sides of a certain element.\nIn the test the runtime is 55ms.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<pair<int, int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {\n vector<pair<int,int>> result;\n int m=matrix.size();\n if (m==0) return result;\n int n=matrix[0].size();\n int pacific[m][n];\n int atlantic[m][n];\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n pacific[i][j]=0;\n atlantic[i][j]=0;\n }\n }\n stack<pair<int,int>> sp;\n stack<pair<int,int>> sa;\n for (int i=0;i<m;i++){\n pacific[i][0]=1;\n sp.push(make_pair(i,0));\n }\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++){\n pacific[0][i]=1;\n sp.push(make_pair(0,i));\n }\n while(!sp.empty()){\n pair<int, int> index=sp.top();\n int x=index.first;\n int y=index.second;\n sp.pop();\n if (x-1>=0&&pacific[x-1][y]==0&&matrix[x-1][y]>=matrix[x][y]){\n sp.push(make_pair(x-1,y));\n pacific[x-1][y]=1;\n }\n if (x+1<m&&pacific[x+1][y]==0&&matrix[x+1][y]>=matrix[x][y]){\n sp.push(make_pair(x+1,y));\n pacific[x+1][y]=1;\n }\n if (y-1>=0&&pacific[x][y-1]==0&&matrix[x][y-1]>=matrix[x][y]){\n sp.push(make_pair(x,y-1));\n pacific[x][y-1]=1;\n }\n if (y+1<n&&pacific[x][y+1]==0&&matrix[x][y+1]>=matrix[x][y]){\n sp.push(make_pair(x,y+1));\n pacific[x][y+1]=1;\n }\n }\n for (int i=0;i<m;i++){\n atlantic[i][n-1]=1;\n sa.push(make_pair(i,n-1));\n }\n for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){\n atlantic[m-1][i]=1;\n sa.push(make_pair(m-1,i));\n }\n while(!sa.empty()){\n pair<int, int> index=sa.top();\n int x=index.first;\n int y=index.second;\n sa.pop();\n if (x-1>=0&&atlantic[x-1][y]==0&&matrix[x-1][y]>=matrix[x][y]){\n sa.push(make_pair(x-1,y));\n atlantic[x-1][y]=1;\n }\n if (x+1<m&&atlantic[x+1][y]==0&&matrix[x+1][y]>=matrix[x][y]){\n sa.push(make_pair(x+1,y));\n atlantic[x+1][y]=1;\n }\n if (y-1>=0&&atlantic[x][y-1]==0&&matrix[x][y-1]>=matrix[x][y]){\n sa.push(make_pair(x,y-1));\n atlantic[x][y-1]=1;\n }\n if (y+1<n&&atlantic[x][y+1]==0&&matrix[x][y+1]>=matrix[x][y]){\n sa.push(make_pair(x,y+1));\n atlantic[x][y+1]=1;\n }\n }\n for(int i=0; i<m;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n if (atlantic[i][j]==1&&pacific[i][j]==1){\n result.push_back(make_pair(i,j));\n }\n }\n }\n return result;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 5 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Clean BFS(Breadth-First Search) Solution
|
clean-bfsbreadth-first-search-solution-b-mhsj
|
Summary\nVery simple easy to understand beginner friendly BFS code. In this cod we have to basically run BFS two times for the opposite sets of edges and mark t
|
sir1us
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-22T15:17:32.887476+00:00
|
2024-06-22T15:17:32.887532+00:00
| 1,341 | false |
# Summary\nVery simple easy to understand beginner friendly BFS code. In this cod we have to basically run BFS two times for the opposite sets of edges and mark the visited array for each bfs. Once that is done we can just iterate and check if a node was tagged by both the BFS, if so we can put it in our ans. Finally return the ans.\n\nIf any doubt please ask, will be happy to help, Happy coding :).\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n const string PACIFIC_OCEAN = "pacific";\n const string ATLANTIC_OCEAN = "atlantic";\n \n bool checkVisited(string ocean, pair<int, int> p){\n if(ocean == ATLANTIC_OCEAN)\n return p.second == 1;\n return p.first == 1;\n }\n\n void bfs(string ocean, vector<vector<int>>& heights, vector<vector<pair<int, int>>>& visited, queue<pair<int, int>>& q, vector<pair<int, int>>& directions, int n, int m){\n while(!q.empty()){\n int row = q.front().first;\n int col = q.front().second;\n q.pop();\n\n for(auto it : directions){\n int x = row + it.first;\n int y = col + it.second;\n\n if(x<0 || x>=n || y<0 || y>=m || heights[x][y] < heights[row][col] || checkVisited(ocean, visited[x][y]))\n continue;\n\n if(ocean == ATLANTIC_OCEAN)\n visited[x][y].second = 1;\n else\n visited[x][y].first = 1;\n\n q.push(make_pair(x, y));\n }\n }\n }\n\n vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {\n int n = heights.size();\n int m = heights[0].size();\n\n vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> visited(n, vector<pair<int, int>> (m, {0, 0}));\n vector<pair<int, int>> directions = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};\n\n queue<pair<int, int>> q;\n for(int i=0; i<m; i++){\n visited[n-1][i].second = 1;\n q.push({n-1, i});\n } \n for(int i=0; i<n; i++){\n visited[i][m-1].second = 1;\n q.push({i, m-1});\n } \n\n bfs(ATLANTIC_OCEAN ,heights, visited, q, directions, n, m);\n\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++){\n visited[i][0].first = 1;\n q.push({i, 0});\n } \n for(int i=0; i<m; i++){\n visited[0][i].first = 1;\n q.push({0, i});\n }\n\n bfs(PACIFIC_OCEAN, heights, visited, q, directions, n, m);\n\n vector<vector<int>> ans;\n\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++){\n for(int j=0; j<m; j++){\n pair<int, int> it = visited[i][j];\n if(it.first && it.second)\n ans.push_back({i, j});\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n\n }\n};\n\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Breadth-First Search', 'C++']
| 2 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
[Python] Explaining Common Pitfalls and Nuanced Tricks Along with the Problem Patterns
|
python-explaining-common-pitfalls-and-nu-1e3p
|
1. Problem Statement Breakdown\n\nIn this problem, we are given a m x n matrix named heights, where each cell represents the height above sea level. The grid bo
|
chitralpatil
|
NORMAL
|
2023-12-11T18:57:59.195379+00:00
|
2023-12-11T18:57:59.195397+00:00
| 237 | false |
### 1. Problem Statement Breakdown\n\nIn this problem, we are given a `m x n` matrix named `heights`, where each cell represents the height above sea level. The grid borders two oceans: the Pacific Ocean on the top and left edges, and the Atlantic Ocean on the right and bottom edges. The rule for water flow is that it can only move from a cell to another neighboring cell (north, south, east, or west) if the neighboring cell\'s height is less than or equal to the current cell\'s height. We need to find all cells from which water can flow to both oceans.\n\n### 2. Solution Rationale\n\nThe approach involves conducting depth-first searches (DFS) from the edges of the matrix that touch each ocean, marking cells as reachable from that ocean. Specifically, we start from the cells adjacent to the oceans and perform DFS, moving to adjacent cells if they are higher or equal in height. This process is done twice: once for the Pacific (top and left edges) and once for the Atlantic (right and bottom edges). The intersection of the cells reachable by both oceans is the solution.\n\n### 3. Python Code Explanation\n\nThe Python solution involves defining a DFS helper function and applying it to the edge cells for both oceans. The function marks visited cells and proceeds recursively to adjacent cells that meet the height requirement.\n\n```python\ndef pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:\n \n rows, cols = len(heights), len(heights[0])\n pacific, atlantic = set(), set()\n\n def dfs(r, c, visited, prev):\n if not ((0 <= r < rows) and (0 <= c < cols)):\n return \n \n if (r, c) in visited or heights[r][c] < prev:\n return \n \n visited.add((r, c))\n \n directions = [(1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]\n for dr, dc in directions:\n nr, nc = r + dr, c + dc\n dfs(nr, nc, visited, heights[r][c])\n\n for r in range(rows):\n dfs(r, 0, pacific, heights[r][0])\n dfs(r, cols-1, atlantic, heights[r][cols-1])\n \n for c in range(cols):\n dfs(0, c, pacific, heights[0][c])\n dfs(rows-1, c, atlantic, heights[rows-1][c])\n \n return list(pacific & atlantic)\n```\n\n\n\n### 4. Time and Space Complexity Analysis\n\n- **Time Complexity:** O(m*n) where m and n are the dimensions of the matrix. Each cell is visited at most twice (once for each ocean).\n- **Space Complexity:** O(m*n) for the storage of the visited sets and the recursion stack in the worst case.\n\n### 5. Common Pitfalls and Nuanced Tricks\n\n- **Pitfall:** Forgetting to check for previous height in DFS can lead to incorrect traversal. Passing some other value instead of calling first dfs with the value of the same row index and column index. \n- **Trick:** Using sets for visited cells for efficient lookup and avoiding duplicates.\n\n### 6. Problem Pattern\n\nThis problem is a classic example of graph traversal using Depth-First Search (DFS) from multiple sources (edge cells in this case). It demonstrates how to use DFS to propagate conditions (height constraints) through a grid.\n\n### 7. Similar LeetCode Problems\n\n- [200. Number of Islands](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-islands/)\n- [695. Max Area of Island](https://leetcode.com/problems/max-area-of-island/)\n- [130. Surrounded Regions](https://leetcode.com/problems/surrounded-regions/)\n\nEach of these problems involves traversing a grid with DFS or BFS, applying similar principles to different scenarios.
| 4 | 1 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Graph', 'Recursion', 'Python3']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Diagram and code Explanation 👍..
|
diagram-and-code-explanation-by-ankit147-mk37
|
Example \n \n\n\n# blue color represent pacific water that in matrix \n\n\n\n\n# Green color represent atlantic water\n\n\n\n# Orange color represent common p
|
ankit1478
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-26T21:02:52.160192+00:00
|
2023-11-26T21:03:32.824407+00:00
| 461 | false |
# Example \n \n\n\n# blue color represent pacific water that in matrix \n\n\n\n\n# Green color represent atlantic water\n\n\n\n# Orange color represent common part that connect pacific and atlantic water .. which is our answer \n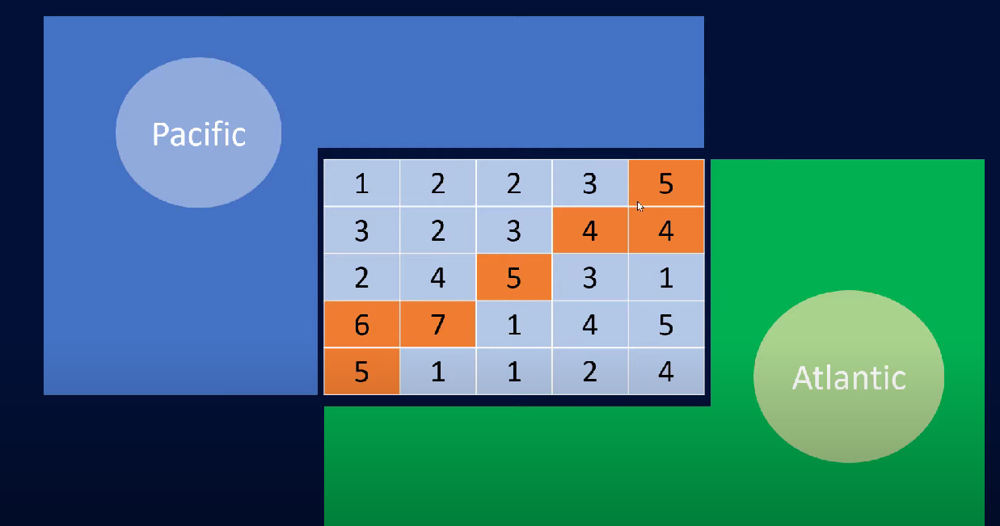\n\n### Initialization:\n\nTwo boolean matrices, \'pacific\' and \'Atlantic,\' are created to mark cells that are reachable from the Pacific and Atlantic oceans, respectively.\n\nTwo queues, \'qpacific\' and \'qAtlantic,\' are created to perform Breadth-First Search (BFS) traversal from the ocean edges.\n\n### BFS for Pacific:\n\nStarting from the top and left edges of the matrix, BFS is performed to mark cells that are reachable from the Pacific Ocean. The BFS function is called with the \'qpacific\' queue.\nDuring BFS, if a cell is reachable from the Pacific Ocean, it is marked in the \'pacific\' matrix.\n\n\n### BFS for Atlantic:\n\nStarting from the bottom and right edges of the matrix, BFS is performed to mark cells that are reachable from the Atlantic Ocean. The BFS function is called with the \'qAtlantic\' queue.\nDuring BFS, if a cell is reachable from the Atlantic Ocean, it is marked in the \'Atlantic\' matrix.\n\n### Check Common Cells:\n\nAfter both BFS operations, the code iterates through all cells in the matrix and checks if a cell is marked as reachable from both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.\nIf a cell satisfies this condition, its coordinates are added to the \'ans\' list.\n\n### Return Result:\n\nThe final result is a list of cell coordinates (\'ans\') representing the cells that are reachable from both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n * m)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n * m)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n static class Pair {\n int row;\n int col;\n\n Pair(int row, int col) {\n this.row = row;\n this.col = col;\n }\n }\n\n public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {\n List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n int n = heights.length; // row\n int m = heights[0].length; // col\n\n boolean pacific[][] = new boolean[n][m];\n boolean Atlantic[][] = new boolean[n][m];\n\n Queue<Pair> qpacific = new LinkedList<>();\n Queue<Pair> qAtlantic = new LinkedList<>();\n\n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n qpacific.add(new Pair(0, i));\n pacific[0][i] = true;\n qAtlantic.add(new Pair(n - 1, i));\n Atlantic[n - 1][i] = true;\n }\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n qpacific.add(new Pair(i, 0));\n pacific[i][0] = true;\n qAtlantic.add(new Pair(i, m - 1)); \n Atlantic[i][m - 1] = true;\n }\n\n bfs(heights, pacific, qpacific);\n bfs(heights, Atlantic, qAtlantic);\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {\n if (pacific[i][j] && Atlantic[i][j]) {\n ans.add(Arrays.asList(i, j));\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\n static void bfs(int height[][], boolean[][] vis, Queue<Pair>q) {\n int n = height.length;\n int m = height[0].length;\n\n int[] delrow = {-1, 0, 0, 1};\n int[] delcol = {0, -1, 1, 0};\n\n while (!q.isEmpty()) {\n int row = q.peek().row;\n int col = q.peek().col;\n\n q.poll();\n\n for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {\n int nrow = row + delrow[i];\n int ncol = col + delcol[i];\n\n if (nrow >= 0 && ncol >= 0 && nrow < n && ncol < m && !vis[nrow][ncol]\n && height[nrow][ncol] >= height[row][col]) {\n q.add(new Pair(nrow, ncol));\n vis[nrow][ncol] = true;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n}\n\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Breadth-First Search', 'Graph', 'Java']
| 1 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
C++ || Clean and Simple || Beginner Friendly || Easy to Understand
|
c-clean-and-simple-beginner-friendly-eas-mmbs
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
chicken_rice
|
NORMAL
|
2023-06-13T17:43:13.021413+00:00
|
2023-06-13T17:43:13.021433+00:00
| 1,003 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {\n int m = heights.size();\n int n = heights[0].size();\n\n vector<vector<int>> visited_p(m, vector<int> (n, 0));\n vector<vector<int>> visited_a(m, vector<int> (n, 0));\n queue<pair<int, int>> q_pacific;\n queue<pair<int, int>> q_atlantic;\n\n\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n visited_p[0][i] = 1;\n q_pacific.push({0, i});\n visited_a[m-1][i] = 1; \n q_atlantic.push({m-1, i});\n }\n\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n visited_p[i][0] = 1;\n q_pacific.push({i, 0});\n visited_a[i][n-1] = 1;\n q_atlantic.push({i, n-1});\n }\n\n vector<int> di = {+1, 0, 0, -1};\n vector<int> dj = {0, +1, -1, 0};\n\n while(!q_pacific.empty()){\n int row = q_pacific.front().first;\n int col = q_pacific.front().second;\n q_pacific.pop();\n\n for(int i=0;i<4;i++){\n int n_row = row + di[i];\n int n_col = col + dj[i];\n\n if(n_row >= 0 && n_row < m && n_col >= 0 && n_col < n && visited_p[n_row][n_col] == 0){\n if(heights[n_row][n_col] >= heights[row][col]){\n visited_p[n_row][n_col] = 1;\n q_pacific.push({n_row, n_col});\n }\n }\n }\n }\n\n while(!q_atlantic.empty()){\n int row = q_atlantic.front().first;\n int col = q_atlantic.front().second;\n q_atlantic.pop();\n\n for(int i=0;i<4;i++){\n int n_row = row + di[i];\n int n_col = col + dj[i];\n\n if(n_row >= 0 && n_row < m && n_col >= 0 && n_col < n && visited_a[n_row][n_col] == 0){\n if(heights[n_row][n_col] >= heights[row][col]){\n visited_a[n_row][n_col] = 1;\n q_atlantic.push({n_row, n_col});\n }\n }\n }\n }\n\n vector<vector<int>> ans;\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n if(visited_p[i][j] == 1 && visited_a[i][j] == 1)\n ans.push_back({i, j});\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Breadth-First Search', 'C++']
| 1 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
✅Accepted || ✅Short & Simple || ✅Best Method || ✅Easy-To-Understand
|
accepted-short-simple-best-method-easy-t-50tw
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n void bfs(vector<vector<int>>& heights, queue<pair<int, int>>& q, vector<vector<bool>>& v)\n {\n int x[5]={0
|
sanjaydwk8
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-27T08:08:12.333857+00:00
|
2023-01-27T08:08:12.333900+00:00
| 1,856 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n void bfs(vector<vector<int>>& heights, queue<pair<int, int>>& q, vector<vector<bool>>& v)\n {\n int x[5]={0, 1, 0, -1, 0};\n int m=heights.size();\n int n=heights[0].size();\n while(!q.empty())\n {\n // cout<<"d";\n auto p=q.front();\n q.pop();\n int i=p.first;\n int j=p.second;\n for(int k=0;k<4;k++)\n {\n int r=i+x[k];\n int c=j+x[k+1];\n if(r>=0 && r<m && c>=0 && c<n && heights[r][c]>=heights[i][j] && v[r][c]==false)\n {\n v[r][c]=true;\n q.push({r, c});\n }\n }\n }\n // for(int i=0;i<m;i++)\n // {\n // for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n // cout<<v[i][j]<<" ";\n // cout<<"\\n";\n // }\n }\n vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {\n int m=heights.size();\n int n=heights[0].size();\n vector<vector<bool>> p(m, vector<bool>(n, false));\n vector<vector<bool>> a(m, vector<bool>(n, false));\n queue<pair<int, int>> q1, q2;\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n {\n q1.push({0, j});\n p[0][j]=true;\n q2.push({m-1, j});\n a[m-1][j]=true;\n }\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++)\n {\n q1.push({i, 0});\n p[i][0]=true;\n q2.push({i, n-1});\n a[i][n-1]=true;\n }\n bfs(heights, q1, p);\n cout<<"\\n";\n bfs(heights, q2, a);\n vector<vector<int>> ans;\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n if(p[i][j] && a[i][j])\n ans.push_back({i, j});\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\nPlease **UPVOTE** if it helps \u2764\uFE0F\uD83D\uDE0A\nThank You and Happy To Help You!!
| 4 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Readable JavaScript DFS Solution
|
readable-javascript-dfs-solution-by-kevh-pgkb
|
Code\n\n/**\n * @param {number[][]} heights\n * @return {number[][]}\n */\nvar pacificAtlantic = function(heights) {\n let ROWS = heights.length \n let CO
|
kevhnh
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-22T21:23:45.042856+00:00
|
2022-11-22T21:23:45.042891+00:00
| 471 | false |
# Code\n```\n/**\n * @param {number[][]} heights\n * @return {number[][]}\n */\nvar pacificAtlantic = function(heights) {\n let ROWS = heights.length \n let COLS = heights[0].length\n let pac = new Set()\n let atl = new Set()\n let res = []\n\n function dfs(r, c, visit, prevHeight) {\n if (Math.min(r,c) < 0 || r >= ROWS || c >= COLS || heights[r][c] < prevHeight || visit.has(r + \'-\' + c)) { //Checks for invalid entries\n return \n }\n\n visit.add(r + \'-\' + c) //Valid entries gets added to set\n dfs(r + 1, c, visit, heights[r][c]) //Checks neighbors\n dfs(r - 1, c, visit, heights[r][c])\n dfs(r, c + 1, visit, heights[r][c])\n dfs(r, c - 1, visit, heights[r][c])\n }\n\n for (let c = 0; c < COLS; c++) { \n dfs(0, c, pac, heights[0][c]) //Top\n dfs(ROWS - 1, c, atl, heights[ROWS - 1][c]) //Bottom\n }\n\n for (let r = 0; r < ROWS; r++) { \n dfs(r, 0, pac, heights[r][0]) //Left\n dfs(r, COLS - 1, atl, heights[r][COLS - 1]) //Right\n }\n\n for (let r = 0; r < ROWS; r++) { //Checks for collisions\n for (let c = 0; c < COLS; c++) {\n if (pac.has(r + \'-\' + c) && atl.has(r + \'-\' + c)) { //If both sets have the same values\n res.push([r,c]) //Push coord to res\n }\n }\n }\n\n return res\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
C++ || DFS || Easy Approach
|
c-dfs-easy-approach-by-mrigank_2003-30ms
|
Here is my c++ code for this problem.\n\'\'\'\n\n\tclass Solution {\n\tpublic:\n\t\tvoid dfs(int x, int y, int num, vector>& v, vector>& heights){\n\t\t\tif(x<0
|
mrigank_2003
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-20T15:43:13.926574+00:00
|
2022-11-20T15:43:13.926604+00:00
| 655 | false |
Here is my c++ code for this problem.\n\'\'\'\n\n\tclass Solution {\n\tpublic:\n\t\tvoid dfs(int x, int y, int num, vector<vector<int>>& v, vector<vector<int>>& heights){\n\t\t\tif(x<0 || x>=heights.size() || y<0 || y>=heights[0].size() || heights[x][y]<num || v[x][y]){return;}\n\t\t\tv[x][y]=1;\n\t\t\tdfs(x-1, y, heights[x][y], v, heights);\n\t\t\tdfs(x, y-1, heights[x][y], v, heights);\n\t\t\tdfs(x+1, y, heights[x][y], v, heights);\n\t\t\tdfs(x, y+1, heights[x][y], v, heights);\n\t\t}\n\t\tvector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {\n\t\t\tvector<vector<int>>v1(heights.size(), vector<int>(heights[0].size(), 0));\n\t\t\tvector<vector<int>>v2(heights.size(), vector<int>(heights[0].size(), 0));\n\t\t\tfor(int i=0; i<heights.size(); i++){\n\t\t\t\tif(!v1[i][0]){dfs(i, 0, heights[i][0], v1, heights);}\n\t\t\t\tif(!v2[i][heights[0].size()-1]){dfs(i, heights[0].size()-1, heights[i][heights[0].size()-1], v2, heights);}\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\tfor(int i=0; i<heights[0].size(); i++){\n\t\t\t\tif(!v1[0][i]){dfs(0, i, heights[0][i], v1, heights);}\n\t\t\t\tif(!v2[heights.size()-1][i]){dfs(heights.size()-1, i, heights[heights.size()-1][i], v2, heights);}\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t// for(int i=0; i<heights.size(); i++){\n\t\t\t// for(int j=0; j<heights[0].size(); j++){\n\t\t\t// cout<<v1[i][j]<<" ";\n\t\t\t// }cout<<endl;\n\t\t\t// }cout<<endl;\n\t\t\t// for(int i=0; i<heights.size(); i++){\n\t\t\t// for(int j=0; j<heights[0].size(); j++){\n\t\t\t// cout<<v2[i][j]<<" ";\n\t\t\t// }cout<<endl;\n\t\t\t// }\n\t\t\tvector<vector<int>>ans;\n\t\t\tfor(int i=0; i<heights.size(); i++){\n\t\t\t\tfor(int j=0; j<heights[0].size(); j++){\n\t\t\t\t\tif(v1[i][j] && v2[i][j]){\n\t\t\t\t\t\tans.push_back({i, j});\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\treturn ans;\n\t\t}\n\t};\n\'\'\'
| 4 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Graph', 'C']
| 1 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Python | BFS
|
python-bfs-by-samdak-1bj8
|
Intuition\n- BFS from cells that are beside pacific ocean to find reachable cells.\n- BFS from cells that are beside atlantic ocean to find reachable cells.\n-
|
samdak
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-12T14:50:17.303593+00:00
|
2022-10-26T02:47:36.029400+00:00
| 580 | false |
# Intuition\n- BFS from cells that are beside pacific ocean to find reachable cells.\n- BFS from cells that are beside atlantic ocean to find reachable cells.\n- Take the intersection of the reachable cells to get cells that can reach both oceans.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. First, create the starting queues for BFS by adding cells beside ocean.\n - `pacificQueue` takes those cells with `row == 0` and `col == 0`\n - `atlanticQueue` takes those cells with `row == ROWS - 1` and `cols == COLS - 1`\n - Add their `level` from `heights` as a third param in the tuple\n1. Perform BFS on each `queue` (Use a function)\n - Create a `reachable` set\n - For each cell, go through the adjacent cells\n - If cell is in bounds, not in `reachable` set and has `height` greater than the `level` of the current cell, we add it to the `queue`.\n - Notice we add all the popped cells to `reachable` set as from our previous condition, we only add reachable cells to the `reachable` set.\n - Return the `reachable` set\n1. Get the intersection of the `atlanticReachable` and `pacificReachable` sets to get the cells that can reach both oceans. Remember to return as a `list`\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: `O(M*N)`\n- Space complexity: `O(M*N)`\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:\n ROWS, COLS = len(heights), len(heights[0])\n \n pacificQueue, atlanticQueue = deque(), deque()\n \n for col in range(COLS):\n pacificQueue.append((0, col, heights[0][col]))\n atlanticQueue.append((ROWS-1, col, heights[ROWS-1][col]))\n \n for row in range(ROWS):\n pacificQueue.append((row, 0, heights[row][0]))\n atlanticQueue.append((row, COLS-1, heights[row][COLS-1]))\n \n directions = [(0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0)]\n \n def bfs(queue):\n reachable = set()\n while queue:\n for _ in range(len(queue)):\n r, c, level = queue.popleft()\n reachable.add((r, c))\n\n for dr, dc in directions:\n nr, nc = r + dr, c + dc\n\n if (nr < 0 or nr >= ROWS or \n nc < 0 or nc >= COLS or \n heights[nr][nc] < level or \n (nr, nc) in reachable):\n continue\n\n queue.append((nr, nc, heights[nr][nc]))\n return reachable\n \n atlanticReachable = bfs(atlanticQueue)\n pacificReachable = bfs(pacificQueue)\n\n return list(atlanticReachable.intersection(pacificReachable))\n```\n\n### Bonus: DFS Approach\n```\nclass Solution:\n def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:\n ROWS, COLS = len(heights), len(heights[0])\n \n def dfs(r, c, prev_height):\n if r < 0 or c < 0 or r == ROWS or c == COLS or heights[r][c] < prev_height or (r, c) in reachable:\n return\n reachable.add((r, c))\n for dr, dc in [(0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0)]:\n dfs(r + dr, c + dc, heights[r][c])\n \n reachable = set()\n for r in range(ROWS):\n for c in range(COLS):\n if r == 0 or c == 0:\n dfs(r, c, -1)\n pacific_reachable = reachable\n \n reachable = set()\n for r in range(ROWS):\n for c in range(COLS):\n if r == ROWS - 1 or c == COLS - 1:\n dfs(r, c, -1)\n atlantic_reachable = reachable\n \n return list(pacific_reachable.intersection(atlantic_reachable))\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Clean DFS solution with minimum number of recursive calls in C++
|
clean-dfs-solution-with-minimum-number-o-wlj7
|
Time Complexity = O(N * M)\nSpace Complexity = O(N * M)\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n/*\n TC: O(N*M)\n SC: O(N*M)\n*/\n \n vector<int> dx = {-1,
|
asamir
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-03T21:13:45.886369+00:00
|
2022-09-03T21:13:45.886412+00:00
| 201 | false |
Time Complexity = O(N * M)\nSpace Complexity = O(N * M)\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n/*\n TC: O(N*M)\n SC: O(N*M)\n*/\n \n vector<int> dx = {-1, 1, 0, 0};\n vector<int> dy = {0, 0, 1, -1};\n \n bool valid(int i, int j, int n, int m){\n return i >= 0 && i < n && j >= 0 && j < m;\n }\n \n void DFS(vector<vector<int>>& heights, int i, int j, int prev,vector<vector<bool>>& anyOcean){\n if(heights[i][j] < prev || anyOcean[i][j]) return;\n anyOcean[i][j] = true;\n for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++){\n int row = dx[k] + i;\n int col = dy[k] + j;\n if(valid(row, col, heights.size(), heights[0].size()) && !anyOcean[row][col])\n DFS(heights, row, col, heights[i][j], anyOcean);\n }\n }\n vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {\n int n = heights.size(), m = heights[0].size();\n vector<vector<int>> res;\n vector<vector<bool>> atlantic(n, vector<bool>(m)), pacific(n, vector<bool>(m));\n \n // check for columns\n for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){\n DFS(heights, 0, i, INT_MIN, pacific);\n DFS(heights, n-1, i, INT_MIN, atlantic);\n }\n \n // check for rows\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n DFS(heights, i, 0, INT_MIN, pacific);\n DFS(heights, i, m-1, INT_MIN, atlantic);\n }\n \n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){\n if(atlantic[i][j] && pacific[i][j])\n res.push_back({i, j});\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Graph', 'C']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
Python Fastest Queue Solution
|
python-fastest-queue-solution-by-day_tri-n7in
|
\nfrom collections import deque\n\nclass Solution:\n def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:\n # construct a BFS tree
|
Day_Tripper
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-31T05:40:10.746466+00:00
|
2022-08-31T05:40:10.746492+00:00
| 83 | false |
```\nfrom collections import deque\n\nclass Solution:\n def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:\n # construct a BFS tree rooted at the pacific ocean and record what nodes we can reach\n # construct a BFS tree rooted at the atlantic ocean and record what nodes we can reach\n\n m = len(heights)\n n = len(heights[0])\n\n \n def BFS(grid, startingNodes):\n # return a list of reachable cells\n nonlocal m,n\n \n Q = deque()\n Q.extend(startingNodes)\n visited = set(startingNodes)\n while Q:\n r,c = Q.popleft()\n h = grid[r][c]\n \n # north\n if r>0 and grid[r-1][c]>=h and (r-1,c) not in visited:\n visited.add((r-1,c))\n Q.append((r-1,c))\n \n # south\n if r<m-1 and grid[r+1][c]>=h and (r+1,c) not in visited:\n visited.add((r+1,c))\n Q.append((r+1,c))\n \n # east\n if c>0 and grid[r][c-1]>=h and (r,c-1) not in visited:\n visited.add((r,c-1))\n Q.append((r,c-1))\n\n # east\n if c<n-1 and grid[r][c+1]>=h and (r,c+1) not in visited:\n visited.add((r,c+1))\n Q.append((r,c+1))\n \n return visited\n \n \n pacificNeighbours = [(0,0)]\n for i in range(1,n):\n pacificNeighbours.append((0,i))\n for i in range(1,m):\n pacificNeighbours.append((i,0))\n\n atlanticNeighbours = [(m-1,n-1)]\n for i in range(n-1):\n atlanticNeighbours.append((m-1,i))\n for i in range(m-1):\n atlanticNeighbours.append((i,n-1))\n \n pCells = BFS(heights, pacificNeighbours)\n aCells = BFS(heights, atlanticNeighbours)\n \n X = pCells.intersection(aCells)\n return list(X)\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Recursion', 'Queue']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
C++ || DFS || EASY SOLUTION
|
c-dfs-easy-solution-by-njyotiprakash189-b85i
|
class Solution {\n public:\n\n int DR[4]={1,0,-1,0};\n int DC[4]={0,-1,0,1};\n void dfs(int i,int j,int prev, vector> &ocean, vector> &height){\n
|
njyotiprakash189
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-31T04:47:20.949017+00:00
|
2022-08-31T04:47:44.767311+00:00
| 121 | false |
class Solution {\n public:\n\n int DR[4]={1,0,-1,0};\n int DC[4]={0,-1,0,1};\n void dfs(int i,int j,int prev, vector<vector<int>> &ocean, vector<vector<int>> &height){\n int n=height.size();\n int m=height[0].size();\n \n ocean[i][j]=1;\n \n for(int k=0;k<4;k++){\n int ci=i+DR[k];\n int cj=j+DC[k];\n \n if(ci>=0 && ci<n && cj>=0 && cj<m && !ocean[ci][cj] && prev <= height[ci][cj]){\n dfs(ci,cj,height[ci][cj],ocean,height);\n }\n }\n \n }\n vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {\n int n=heights.size();\n int m=heights[0].size();\n \n vector<vector<int>> ans;\n vector<vector<int>> pacificVis(n,vector<int>(m,0));\n vector<vector<int>> atlanticVis(n,vector<int>(m,0));\n \n for(int j=0;j<m;j++){\n //1st row\n dfs(0,j,heights[0][j],pacificVis,heights);\n //last row\n dfs(n-1,j,heights[n-1][j],atlanticVis,heights);\n }\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n //1st col\n dfs(i,0,heights[i][0],pacificVis,heights);\n //last col\n dfs(i,m-1,heights[i][m-1],atlanticVis,heights);\n }\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++){\n if(pacificVis[i][j] && atlanticVis[i][j]){\n ans.push_back({i,j});\n }\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n};
| 4 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'C']
| 0 |
pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
✔ Simple java solution
|
simple-java-solution-by-shwetaa-tf2f
|
\nclass Solution {\n int dir[][] = {{0,1}, {0,-1}, {1,0}, {-1,0}};\n public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] matrix) {\n List<List<Integer
|
shwetaa_
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-31T04:36:52.307685+00:00
|
2022-08-31T04:37:09.561407+00:00
| 564 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n int dir[][] = {{0,1}, {0,-1}, {1,0}, {-1,0}};\n public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] matrix) {\n List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();\n if(matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) \n return res;\n \n int row = matrix.length, col = matrix[0].length;\n boolean[][] pacific = new boolean[row][col];\n boolean[][] atlantic = new boolean[row][col];\n \n //DFS\n for(int i = 0; i < col; i++){\n dfs(matrix, 0, i, Integer.MIN_VALUE, pacific);\n dfs(matrix, row-1, i, Integer.MIN_VALUE, atlantic);\n }\n for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){\n dfs(matrix, i, 0, Integer.MIN_VALUE, pacific);\n dfs(matrix, i, col-1, Integer.MIN_VALUE, atlantic);\n }\n \n //preparing the result\n for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < col; j++) {\n if(pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) {\n res.add(Arrays.asList(i,j));\n }\n }\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n \n public void dfs(int[][] matrix, int i, int j, int prev, boolean[][] ocean){\n if(i < 0 || i >= ocean.length || j < 0 || j >= ocean[0].length) return;\n if(matrix[i][j] < prev || ocean[i][j]) return;\n ocean[i][j] = true;\n for(int[] d : dir){\n dfs(matrix, i+d[0], j+d[1], matrix[i][j], ocean);\n }\n \n }\n}\n```\n\n**113 / 113 test cases passed.\nStatus: Accepted\nRuntime: 6 ms\nMemory Usage: 55.4 MB**
| 4 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
java easy solution
|
java-easy-solution-by-anukulsaini-dk6r
|
\n\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n \n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n \n int[] c
|
anukulSaini
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T04:07:26.043935+00:00
|
2022-04-24T04:07:26.043966+00:00
| 8,665 | false |
```\n\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n \n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n \n int[] count = new int[1001];\n \n for(int[] arr : nums){\n for(int i : arr){\n count[i]++;\n }\n }\n \n for(int i=0;i<count.length;i++){\n if(count[i]==nums.length){\n ans.add(i);\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n}\n\n```
| 67 | 0 |
['Array', 'Java']
| 8 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
94.58% faster using set and & operator in Python
|
9458-faster-using-set-and-operator-in-py-qynl
|
\n\n\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n res = set(nums[0])\n for i in range(1, len(nums)):\n
|
ankurbhambri
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-15T08:46:57.384688+00:00
|
2022-08-15T08:46:57.384738+00:00
| 3,057 | false |
\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n res = set(nums[0])\n for i in range(1, len(nums)):\n res &= set(nums[i])\n res = list(res)\n res.sort()\n return res\n \n```
| 55 | 0 |
['Ordered Set', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 2 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
[Python3] - 1 LINE Solution || Simple Explanation
|
python3-1-line-solution-simple-explanati-hngd
|
Idea\n\n\n##### To solve this question easily, we can take advantage of one of the specifications:\n\nnums[i] is a non-empty array of distinct positive integers
|
drknzz
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T07:59:55.391048+00:00
|
2022-04-24T08:18:28.583129+00:00
| 6,180 | false |
# **Idea**\n<br>\n\n##### To solve this question easily, we can take advantage of one of the specifications:\n\n*nums[i] is a non-empty array of **distinct** positive integers*\n\n<br>\n\n##### Since the integers in each sub-list of nums are distinct (i.e. unique), we can count the number of occurences of every integer in nums.\n<br>\n\n##### Suppose it happens that the number of occurences for some integer x is equal to the length of nums (the number of sub-lists).\n##### It would mean, that x must have appeared in every single sub-list of nums (because it could appear in each of the sub-lists at most 1 time).\n\n<br>\n\n##### Notice, that the result is a list of integers like x, so we just need to find all of them.\n\n<br>\n<br>\n\n# **Code**\n<br>\n\n```\n\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, A: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n return sorted([k for k,v in Counter([x for l in A for x in l]).items() if v==len(A)])\n\t\t\n```\n\n<br>\n<br>\n\n# **Breakdown**\n\n##### Here\'s a breakdown of each operation that\'s happening in the line above:\n\n<br>\n\n```\n\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, A: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n # Flattening the list A\n # For example, if A = [[3, 5, 1], [2, 3, 1]] then flat_list = [3, 5, 1, 2, 3, 1]\n flat_list = [x for lst in A for x in lst]\n\n # Counter - a container from the collections module\n # Here, it is pretty much a dictionary, where:\n # keys - the integers from flat_list\n # values - the number of occurences of the keys\n\n # counts from the above flat_list would be equal to {3: 2, 5: 1, 1: 2, 2: 1}\n counts = Counter(flat_list)\n\n # dict.items() is a method that returns a list of pairs that look like (key, value)\n # Here, items would be equal to [(3, 2), (5, 1), (1, 2), (2, 1)]\n items = counts.items()\n\n # result array created by taking every key from items array\n # which has the value (number of key\'s occurences) equal to the length of A (here, 2)\n # The result would be equal to [3, 1]\n result = [key for (key, value) in items if value == len(A)]\n\n # Sort the result array and return it\n # The result is [1, 3]\n return sorted(result)\n\t\t\n```\n\n<br>\n\n---\n\n<br>\n\n\n### Thanks for reading, and have an amazing day! \uFF3C(\uFF3E\u25BD\uFF3E)\uFF0F\n\n<br>
| 46 | 1 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 6 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
✅C++ || EXPLAINED || BEATS 100% || OPTIMIZED
|
c-explained-beats-100-optimized-by-ayush-uyvc
|
PLEASE UPVOTE IF YOU FIND MY APPROACH HELPFUL, MEANS A LOT \uD83D\uDE0A\n\nExplanation:\n\n Initialize an ordered map mp and vector vec.\n\n Traverse the 2D arr
|
ayushsenapati123
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-25T12:27:29.839988+00:00
|
2022-06-25T12:27:29.840018+00:00
| 6,054 | false |
**PLEASE UPVOTE IF YOU FIND MY APPROACH HELPFUL, MEANS A LOT \uD83D\uDE0A**\n\n**Explanation:**\n\n* Initialize an ordered map mp and vector vec.\n\n* Traverse the 2D array and store the elements present with their frequency.\n* Now check if the element.second (frequency) stored in the map is equal to the no. of rows in the array.\n* If element.second == no. of rows then it implies that the element is present in every array.\n* Push all the elements which satisfy this condition.\n* Return the vector vec as it now contains the intersecting elements.\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size(); // gives the no. of rows\n map<int,int> mp; // we don\'t need unordered_map because we need the elements to be in sorted format.\n vector<int> vec;\n \n // traverse through the 2D array and store the frequency of each element\n for(int row=0;row<n;row++)\n {\n for(int col=0;col<nums[row].size();col++)\n {\n mp[nums[row][col]]++;\n }\n }\n \n // In the 2D array, intersection occurs when the elements are present in every row.\n // So the frequency of the element should match with the no. or rows in the 2D array.\n for(auto element : mp)\n if(element.second == n)\n vec.push_back(element.first);\n \n // return the intersecting elements\n return vec;\n }\n};\n```\n
| 34 | 1 |
['C', 'C++']
| 6 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Java / C++ Clean && Short
|
java-c-clean-short-by-fllght-wvd8
|
Java \n\npublic List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n Map<Integer, Integer> countMap = new HashMap<>();\n List<Integer> inEachArray = new A
|
FLlGHT
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T05:37:36.670320+00:00
|
2023-05-12T05:21:43.573172+00:00
| 3,778 | false |
### Java \n```\npublic List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n Map<Integer, Integer> countMap = new HashMap<>();\n List<Integer> inEachArray = new ArrayList<>();\n for (int[] num : nums) {\n for (int x : num) {\n countMap.put(x, countMap.getOrDefault(x, 0) + 1);\n if (countMap.get(x) == nums.length) inEachArray.add(x);\n }\n }\n inEachArray.sort(Comparator.naturalOrder());\n return inEachArray;\n }\n```\n### C++\n```\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>&nums) {\n map<int, int> countMap;\n vector<int> inEachArray;\n for (auto num : nums) {\n for (auto x : num) {\n countMap[x]++;\n if (countMap[x] == nums.size())\n inEachArray.push_back(x);\n }\n }\n sort(inEachArray.begin(), inEachArray.end());\n return inEachArray;\n }\n```\n\n### + 3-Line Java\n```\npublic List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n Map<Integer, Integer> countMap = new HashMap<>();\n Arrays.stream(nums).forEach(a -> Arrays.stream(a).forEach(x -> countMap.put(x, countMap.getOrDefault(x, 0) + 1)));\n return countMap.entrySet().stream().filter(e -> e.getValue() == nums.length).map(Map.Entry::getKey).sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());\n }\n```\n\nMy repositories with leetcode problems solving - [Java](https://github.com/FLlGHT/algorithms/tree/master/j-algorithms/src/main/java), [C++](https://github.com/FLlGHT/algorithms/tree/master/c-algorithms/src/main/c%2B%2B)
| 27 | 1 |
['C', 'Java']
| 1 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Counter
|
counter-by-votrubac-p3zv
|
Since numbers in each array are unique, we can just count all numbers.\n\nNumbers that are present in each array will be counted nums.size() number of times.\n\
|
votrubac
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-25T20:56:38.892052+00:00
|
2022-04-25T21:05:44.486379+00:00
| 2,181 | false |
Since numbers in each array are unique, we can just count all numbers.\n\nNumbers that are present in each array will be counted `nums.size()` number of times.\n\n**C++**\n```cpp\nvector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n vector<int> cnt(1001), res;\n for (auto &arr: nums)\n for (int n : arr)\n ++cnt[n];\n for (int i = 0; i < cnt.size(); ++i)\n if (cnt[i] == nums.size())\n res.push_back(i);\n return res;\n}\n```
| 19 | 0 |
['C']
| 2 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
100% BEAT Java Easy ✅
|
100-beat-java-easy-by-omjethva24-h7j9
|
Time complexity: O(NM\nSpace complexity: O(1)\n- We simply count freq of each elements.\n- And each array is distinct elements so if elements freq is equal to l
|
omjethva24
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-16T07:10:52.383450+00:00
|
2023-12-30T11:33:40.685503+00:00
| 656 | false |
***Time complexity***: O(N*M\n***Space complexity***: O(1)\n- We simply count `freq` of each elements.\n- And each array is `distinct` elements so if elements freq is equal to len it means it ocuur in all array. And each array is `distinct` elements.\n- And we make freq array `1001` size because `1 <= sum(nums[i].length) <= 1000`.\n- and we don\'t have -1 every time so that\'s why i make `1001` size instead of `1000` because index start from `0`.\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n int freq[] = new int[1001];\n int len = nums.length;\n \n for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < nums[i].length; j++){\n freq[nums[i][j]]++;\n }\n }\n\n List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();\n\n for(int i = 1; i < 1001; i++){\n if(freq[i] == len) list.add(i);\n }\n return list;\n }\n}\n```\n\n\n\n**HAPPY CODING !**\n\n
| 11 | 0 |
['Java']
| 5 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
[JAVA] 3LINES // BEATS 100.00% MEMORY/SPEED 0ms // APRIL 2022
|
java-3lines-beats-10000-memoryspeed-0ms-gxeov
|
\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] aa){\n int[] counts = new int[1_001];\n Arrays.stream(aa).forEach(a -> Arrays.strea
|
darian-catalin-cucer
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T06:50:46.068135+00:00
|
2022-04-24T06:50:46.068171+00:00
| 930 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] aa){\n int[] counts = new int[1_001];\n Arrays.stream(aa).forEach(a -> Arrays.stream(a).forEach(n -> counts[n]++));\n return IntStream.range(0, counts.length).filter(n -> counts[n] == aa.length).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList());\n }\n}\n```\n\n***Consider upvote if useful!***
| 10 | 0 |
['Java']
| 3 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
✅ One Solution if elements in arrays are => { DISTINCT or DUPLICATE }
|
one-solution-if-elements-in-arrays-are-d-pvd2
|
Similar Question: 2032. Two Out of Three\n\nExplanation:\nJust Resisit the increase of count of same elements multiple times in an array.\n\nFot this We use: pa
|
xxvvpp
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T04:14:01.743235+00:00
|
2022-04-24T16:20:24.284651+00:00
| 1,773 | false |
**Similar Question**: [2032. Two Out of Three](https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-262/problems/two-out-of-three/)\n\n**Explanation:**\nJust Resisit the increase of count of same elements multiple times in an array.\n\n**Fot this We use**: `pair<int,int>`\n`First int`- Count of arrays in which we have seen this element\n`Second int` - Array number in which it was last found. **{This will help in preventing from increase in count of same element muliple times in a single array}**\n\n> This Solution will also work if elements across the arrays are not distinct. **[BOTH TYPES USES SAME SPACE i.e if all are {distinct or not-distinct}]**\n\n**Type A**\nWe simply use a `map` and return the answer as map gives a `sorted sequence`.\n**Runtime - 24ms**\n# C++\n \n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n map<int,pair<int,int>> mp; \n int cnt=1;\n for(auto i:nums){\n\t\t for(auto j:i) if(mp[j].second!=cnt) mp[j].first++, mp[j].second=cnt;\n\t\t cnt++;\n\t }\n vector<int> res;\n for(auto i:mp) if(i.second.first==size(nums)) res.push_back(i.first);\n return res;\n }\n\t\n**Type B**\nWe simply use a `unordered_map` and return the answer after `sorting manually`.\n**Runtime - 7ms**\n# C++\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n unordered_map<int,pair<int,int>> mp; \n int cnt=1;\n for(auto i:nums){\n\t for(auto j:i) if(mp[j].second!=cnt) mp[j].first++, mp[j].second=cnt;\n\t cnt++;\n }\n vector<int> res;\n for(auto i:mp) if(i.second.first==size(nums)) res.push_back(i.first);\n sort(begin(res),end(res));\n return res; \n }\n\n
| 10 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
✅✅C++ || Easy Solution
|
c-easy-solution-by-himanshu_52-m2gx
|
\nMethod-1(Simple Searching)\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n vector intersection(vector>& nums) {\n vector sol;\n for(int i=0;i<nums[0].size(
|
himanshu_52
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T04:10:16.173257+00:00
|
2022-04-24T04:35:53.918577+00:00
| 1,662 | false |
\n**Method-1(Simple Searching)**\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n vector<int> sol;\n for(int i=0;i<nums[0].size();i++)\n {\n int f1=1;\n for(int j=1;j<nums.size();j++)\n {\n int f2=0;\n for(int p=0;p<nums[j].size();p++)\n if(nums[j][p]==nums[0][i]) {f2=1; break;}\n if(f2==0) {f1=0; break;}\n } \n if(f1==1) sol.push_back(nums[0][i]);\n }\n sort(sol.begin(),sol.end());\n return sol;\n }\n};\n\n\n\n\n**Method-2** (Using Map)\n\'\'\'\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n vector<int> ans;\n map<int,int> mp;\n int m=nums.size();\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n int n=nums[i].size();\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n mp[nums[i][j]]++;\n }\n \n for(auto i=mp.begin();i!=mp.end();i++)\n if(i->second==m) ans.push_back(i->first);\n \n return ans;\n }\n};\n\'\'\'
| 10 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Short JavaScript Solution Using a Set Object
|
short-javascript-solution-using-a-set-ob-7g88
|
\nconst intersection = nums => {\n if (nums.length === 1) return nums[0].sort((a, b) => a - b)\n\t\n let initSet = new Set(nums[0]) //Initial Set \n\n
|
sronin
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-26T01:46:55.802410+00:00
|
2022-04-26T01:47:54.098524+00:00
| 1,074 | false |
```\nconst intersection = nums => {\n if (nums.length === 1) return nums[0].sort((a, b) => a - b)\n\t\n let initSet = new Set(nums[0]) //Initial Set \n\n for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {\n initSet = new Set([...nums[i]].filter(x => initSet.has(x)))\n }\n\t\n return Array.from(initSet).sort((a, b) => a - b)\n};\n```
| 8 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 2 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Hashmap Accepted solution to make it easily Understandable
|
hashmap-accepted-solution-to-make-it-eas-q0wa
|
\nclass Solution {\n public static List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n\t\tList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();\n\t\tHashMap<Integer, Integer> map
|
Aditya_jain_2584550188
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-25T12:56:13.835678+00:00
|
2022-04-25T12:56:13.835710+00:00
| 649 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public static List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n\t\tList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();\n\t\tHashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();\n\n\t\tfor (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {\n\t\t\tfor (int j = 0; j < nums[i].length; j++) {\n\t\t\t\tif (map.containsKey(nums[i][j])) {\n\t\t\t\t\tmap.put(nums[i][j], map.get(nums[i][j]) + 1);\n\t\t\t\t} else {\n\t\t\t\t\tmap.put(nums[i][j], 1);\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t}\n for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> ans : map.entrySet()) {\n\t\t\tif (ans.getValue() == nums.length) {\n\t\t\t\tlist.add(ans.getKey());\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t}\t\tCollections.sort(list);\n\t\treturn list;\n\t}\n}\n```
| 8 | 0 |
['Java']
| 2 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Easy Python
|
easy-python-by-thoyajkiran-dv4n
|
\t\tres=[]\n arr=[]\n n=len(nums)\n for num in nums:\n arr.extend(num)\n count=Counter(arr)\n for i in count:\n
|
Thoyajkiran
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T04:43:51.376642+00:00
|
2022-04-24T04:43:51.376667+00:00
| 1,189 | false |
\t\tres=[]\n arr=[]\n n=len(nums)\n for num in nums:\n arr.extend(num)\n count=Counter(arr)\n for i in count:\n if(count[i]==n):\n res.append(i)\n return sorted(res) if res else res
| 8 | 1 |
['Python']
| 1 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Python Solution || Hashmap
|
python-solution-hashmap-by-garviel77-88yv
|
\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n d = {}\n \n for i in range(len(nums)):\n fo
|
Garviel77
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-08T18:52:56.025440+00:00
|
2022-10-08T18:52:56.025487+00:00
| 1,277 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n d = {}\n \n for i in range(len(nums)):\n for j in nums[i]:\n if j not in d:\n d[j] = 1\n else:\n d[j]+=1\n \n res = []\n for k,v in d.items():\n if v == len(nums):\n res.append(k)\n \n return sorted(res)\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 1 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Easy to Understand for beginners || c++
|
easy-to-understand-for-beginners-c-by-sh-s386
|
class Solution {\npublic:\n vector intersection(vector>& a) {\n unordered_mapmp;\n for(int i=0;i<a.size();i++)\n {\n for(int
|
Shivam_sahal
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T14:16:32.935001+00:00
|
2022-04-24T14:16:32.935040+00:00
| 616 | false |
class Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& a) {\n unordered_map<int,int>mp;\n for(int i=0;i<a.size();i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<a[i].size();j++)\n {\n mp[a[i][j]]++;\n }\n }\n vector<int>res;\n for(auto it :mp)\n {\n if(it.second ==a.size())\n {\n res.push_back(it.first);\n }\n \n }\n sort(res.begin(),res.end());\n return res;\n }\n};
| 7 | 0 |
['C']
| 3 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Simple solution using unordered map | c++
|
simple-solution-using-unordered-map-c-by-g853
|
Take an unordered map and simply store the values with their number of occurences in the array. Now check if the second value (ie number of occurences) stored i
|
anjani_1507
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T13:35:00.705960+00:00
|
2022-04-24T13:35:00.705996+00:00
| 531 | false |
Take an unordered map and simply store the values with their number of occurences in the array. Now check if the second value (ie number of occurences) stored in the map is equal to the size of vector (ie nums) then it implies that the value corresponding to this is present in every array. So just push this value in the vector \'v\'. The finally made vector v will be the answer.\n\n```\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n \n int n=nums.size();\n unordered_map<int, int> mp;\n vector<int> v;\n \n for(int i=0; i<n; i++){\n for(int j=0; j<nums[i].size(); j++){\n mp[nums[i][j]]++;\n }\n }\n \n for(auto x: mp){\n if(x.second == n){\n v.push_back(x.first);\n }\n }\n \n sort(v.begin(), v.end());\n \n return v;\n }\n\t\n\t```
| 5 | 0 |
['C']
| 4 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
✅ Python Simple Solution using reduce and set
|
python-simple-solution-using-reduce-and-3e5e1
|
As its an interesection operation, I am using the set intersect using & operator to find the common elements. So basically, the code converts each list to set a
|
constantine786
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T09:32:19.632702+00:00
|
2022-04-25T14:38:39.920098+00:00
| 511 | false |
As its an interesection operation, I am using the set intersect using `&` operator to find the common elements. So basically, the code converts each list to set and then performs the intersect between adjacent sets.\n\nBelow is my python code for the same:\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n return sorted(reduce(lambda x,y: set(x) & set(y), nums))\n```\n\n---\n\n***Please upvote if you find it useful***\n\n
| 5 | 0 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Java Solution with Comments || HashMap
|
java-solution-with-comments-hashmap-by-a-9915
|
\npublic List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n HashMap<Integer,Integer> hm=new HashMap(); //To store the count of number\n List<Integer> li
|
m0rnings8ar
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T04:03:17.924275+00:00
|
2022-04-24T04:03:17.924309+00:00
| 566 | false |
```\npublic List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n HashMap<Integer,Integer> hm=new HashMap(); //To store the count of number\n List<Integer> li=new ArrayList(); // To store the result\n for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<nums[i].length;j++){\n int val=hm.getOrDefault(nums[i][j],0);\n hm.put(nums[i][j],val+1);\n if(val+1==nums.length) li.add(nums[i][j]); //whenever we get the count of number equal to row length that mean it is present in every rows.\n }\n }\n Collections.sort(li); //Sort the number in result list.\n return li;\n }\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Python Elegant & Short | 1-Line
|
python-elegant-short-1-line-by-kyrylo-kt-c72u
|
Complexity
Time complexity: O(n∗m)
Space complexity: O(m)
Code
|
Kyrylo-Ktl
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-07T17:27:55.398022+00:00
|
2025-02-07T17:27:55.398022+00:00
| 431 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity: $$O(n*m)$$
- Space complexity: $$O(m)$$
# Code
```python3 []
from functools import reduce
from operator import and_
class Solution:
def intersection(self, arrays: list[list[int]]) -> list[int]:
return sorted(reduce(and_, map(set, arrays)))
```
| 4 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Sorting', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
easy solution
|
easy-solution-by-leet1101-w4r8
|
Intuition\nTo find the integers present in each array of a 2D integer array nums, we need to identify elements that appear in all the subarrays.\n\n# Approach\n
|
leet1101
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-02T10:08:25.118630+00:00
|
2024-07-02T10:08:25.118662+00:00
| 321 | false |
# Intuition\nTo find the integers present in each array of a 2D integer array `nums`, we need to identify elements that appear in all the subarrays.\n\n# Approach\n1. Create a frequency array `freq` to count the occurrences of each integer across all subarrays.\n2. Iterate through each subarray in `nums` and update the frequency count for each element.\n3. After counting, iterate through the frequency array and collect integers that have a frequency equal to the number of subarrays (i.e., they appear in all subarrays).\n4. Return the list of these integers sorted in ascending order.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n \\times m)$$\n - Where $$n$$ is the number of subarrays and $$m$$ is the average number of elements in each subarray. We iterate through each element of each subarray.\n- Space complexity: $$O(1)$$\n - We use a fixed-size frequency array with size 1001 to store counts of elements.\n\n# Code\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n vector<int> freq(1001, 0);\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < nums[i].size(); j++) {\n freq[nums[i][j]]++;\n }\n }\n vector<int> ans;\n for (int i = 0; i <= 1000; i++) {\n if (freq[i] == nums.size()) ans.push_back(i);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Counting', 'C++']
| 2 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Similar Problems + Hints | Beats 99% | Clean Code
|
similar-problems-hints-beats-99-clean-co-ilhy
|
Similar Problem:\nIf you have premium you should definately solve this one after you\'ve solved the current problem.\n\n1198. Find Smallest Common Element in Al
|
hridoy100
|
NORMAL
|
2023-09-03T20:01:49.986841+00:00
|
2023-09-03T20:03:48.602595+00:00
| 490 | false |
# Similar Problem:\nIf you have premium you should definately solve this one after you\'ve solved the current problem.\n\n[1198. Find Smallest Common Element in All Rows (Premium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-smallest-common-element-in-all-rows/description/)\n\n# Hints:\n\nClick to open the hints. Try it yourself!\n\n<details open>\n <summary>Hint 1</summary>\n Notice that each row has no duplicates.\n</details>\n<br>\n<details>\n <summary>Hint 2</summary>\n Is counting the frequency of elements enough to find the answer?\n</details>\n<br>\n<details>\n <summary>Hint 3</summary>\n Use a data structure to count the frequency of elements.\n</details>\n<br>\n<details>\n <summary>Hint 3</summary>\n Iterate for each element in freqMap array. Find an element whose frequency equals the number of rows.\n</details>\n\n# Code\n``` java []\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n int ROW = nums.length;\n int M = 1001;\n int[] freq = new int[M];\n for(int i=0; i<ROW; i++) {\n for(int j=0; j<nums[i].length; j++) {\n int num = nums[i][j];\n freq[num]++;\n }\n }\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n for(int i=1; i<M; i++) {\n if(freq[i] == ROW) {\n ans.add(i);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```\n\n
| 4 | 0 |
['Array', 'Counting', 'Java']
| 1 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Python 2 beginner friendly approaches
|
python-2-beginner-friendly-approaches-by-2wxc
|
Method 1\n\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n res = []\n concat = []\n for i in range(len(
|
elefant1805
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-28T04:13:43.299373+00:00
|
2022-04-28T04:13:43.299399+00:00
| 691 | false |
### Method 1\n```\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n res = []\n concat = []\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n concat += nums[i]\n for i in set(concat):\n if concat.count(i) == len(nums):\n res.append(i)\n return sorted(res)\n```\n\n### Method 2\n```\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n res = []\n nums = sorted(nums, key=len)\n check = 0\n for i in nums[0]:\n for j in nums:\n if i in j:\n check += 1\n if check == len(nums):\n res.append(i)\n check = 0\n return sorted(res)\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
very easy cpp solution using map
|
very-easy-cpp-solution-using-map-by-varc-h5tp
|
\'\'\'\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector intersection(vector>& nums) {\n unordered_mapmp;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n for(
|
varchirag
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-27T13:42:51.553841+00:00
|
2022-04-27T13:42:51.553883+00:00
| 542 | false |
\'\'\'\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n unordered_map<int,int>mp;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n for(int j=0;j<nums[i].size();j++){\n mp[nums[i][j]]++;\n }\n }\n vector<int>ans;\n for(auto i:mp){\n if(i.second==nums.size()) ans.push_back(i.first);\n }\n sort(ans.begin(),ans.end());\n return ans;\n }\n};
| 4 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 1 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Beginners Friendly || Unordered_map || C++ Solution || Easy to Understand
|
beginners-friendly-unordered_map-c-solut-0ju3
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<int> result;\n unorder
|
Shishir_Sharma
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T04:16:36.829078+00:00
|
2022-04-24T04:16:36.829106+00:00
| 608 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<int> result;\n unordered_map<int,int> umap;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<nums[i].size();j++)\n {\n if(umap[nums[i][j]]<i+1)\n {\n umap[nums[i][j]]++;\n }\n }\n }\n \n for(auto i=umap.begin();i!=umap.end();i++)\n {\n if(i->second==n)\n {\n result.push_back(i->first);\n }\n }\n sort(result.begin(),result.end());\n return result;\n }\n};\n```\n**Like it? Please Upvote ;-)**
| 4 | 1 |
['C', 'C++']
| 1 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Hashmap Solution || Easy to understand C++
|
hashmap-solution-easy-to-understand-c-by-xtsz
|
The idea is to traverse through complete 2d array and count the frequency of every element and at last if the size of outer array is equal to the frequency we r
|
NeerajSati
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T04:03:22.592319+00:00
|
2022-04-24T04:05:08.546453+00:00
| 567 | false |
The idea is to traverse through complete 2d array and count the frequency of every element and at last if the size of outer array is equal to the frequency we return the value.\n\n\uD83D\uDE42\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n map<int,int> hm;\n int n = 0;\n for(auto it: nums){\n for(auto x: it){\n hm[x]++;\n }\n n++;\n }\n vector<int> ans;\n for(auto it: hm){\n if(it.second == n){\n ans.push_back(it.first);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['C']
| 2 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
JAVA | Running | EASY & FAST | HashMap Frequency | Explained in detail
|
java-running-easy-fast-hashmap-frequency-xgsz
|
IntuitionApproachHere’s the approach for solving the problem of finding the intersection of all rows in a 2D array (nums):Problem ExplanationGiven a 2D array nu
|
atreya_sengar
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-27T04:26:32.598935+00:00
|
2025-01-27T04:26:32.598935+00:00
| 338 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
Here’s the approach for solving the problem of finding the intersection of all rows in a 2D array (`nums`):
---
### **Problem Explanation**
Given a 2D array `nums`, find the elements that are present in every row of `nums`. The result should be a sorted list of these elements.
---
### **Approach**
1. **Use a HashMap to Track Frequencies:**
- Traverse through all rows and track how many rows each element appears in using a `HashMap`.
- For each element in a row, increment its count in the map.
2. **Filter Elements Present in All Rows:**
- After building the `HashMap`, iterate over its entries.
- If an element’s count matches the total number of rows (`m`), it means the element is present in every row.
3. **Sort the Result:**
- Collect all elements that are present in every row into a list.
- Sort the list before returning it as the final result.
---
### **Steps**
1. **Initialization:**
- Create a `HashMap` to store the frequency of each element across all rows.
- Initialize a `List` to hold the result.
2. **Traverse the 2D Array:**
- For each row in `nums`:
- Iterate through its elements.
- If the element is already in the `HashMap`, increment its frequency.
- Otherwise, add it to the map with an initial count of `1`.
3. **Filter and Collect Results:**
- Iterate through the entries of the `HashMap`.
- If the frequency of an element equals the number of rows (`m`), add it to the result list.
4. **Sort the Result List:**
- Sort the result list in ascending order.
5. **Return the Result:**
- Return the sorted list as the final output.
---
### Example Walkthrough
#### Input:
```java
nums = [
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 2],
[6, 2, 7]
]
```
#### Execution:
1. **Initialize `HashMap`:**
- Start with an empty map: `{}`.
2. **First Row `[1, 2, 3]`:**
- Add `1`, `2`, `3` to the map: `{1: 1, 2: 1, 3: 1}`.
3. **Second Row `[4, 5, 2]`:**
- Increment count for `2` and add `4`, `5`: `{1: 1, 2: 2, 3: 1, 4: 1, 5: 1}`.
4. **Third Row `[6, 2, 7]`:**
- Increment count for `2` and add `6`, `7`: `{1: 1, 2: 3, 3: 1, 4: 1, 5: 1, 6: 1, 7: 1}`.
5. **Filter Results:**
- Only `2` appears in all 3 rows (`frequency == 3`).
6. **Sort and Return:**
- Result list: `[2]`.
#### Output:
```java
[2]
```
---
### Complexity Analysis
#### **Time Complexity:**
1. **Building the HashMap:**
- Each element in `nums` is processed once. Let \( n \) be the total number of elements across all rows. This step takes \( O(n) \).
2. **Filtering Results:**
- Iterating through the `HashMap` takes \( O(k) \), where \( k \) is the number of unique elements.
3. **Sorting the Result:**
- Sorting the final list takes \( O(x \log x) \), where \( x \) is the size of the result list.
**Total Time Complexity:**
\[
O(n + k + x \log x)
\]
In the worst case, \( k = n \) and \( x = k \), making the complexity \( O(n \log n) \).
#### **Space Complexity:**
1. **HashMap:**
- Stores up to \( k \) unique elements. \( O(k) \).
2. **Result List:**
- Stores up to \( k \) elements. \( O(k) \).
**Total Space Complexity:** \( O(k) \).
---
- This approach ensures efficiency by processing each element once and using a single map to track frequencies.
# Complexity
Let’s analyze the **time complexity** and **space complexity** of the given solution:
---
### Time Complexity:
#### 1. **Building the HashMap:**
- The outer loop iterates through each subarray in `nums`, and the inner loop iterates through the elements of the current subarray.
- Let \( n \) be the total number of elements across all subarrays (i.e., \( n = \text{sum of lengths of all subarrays} \)).
- Each element is processed once to either insert or update its frequency in the `HashMap`.
- **Time for this step:** \( O(n) \).
#### 2. **Iterating Through the HashMap:**
- The `HashMap` contains at most \( n \) keys (one for each distinct number in the input).
- For each key, we check its frequency to see if it matches the number of subarrays \( m \). This operation takes \( O(k) \), where \( k \) is the number of distinct elements in the input.
- **Time for this step:** \( O(k) \).
#### 3. **Sorting the Result List:**
- After filtering the elements that appear in all \( m \) subarrays, the resulting list \( a \) (with size \( x \)) is sorted.
- **Time for this step:** \( O(x \log x) \), where \( x \leq k \).
---
#### Total Time Complexity:
The total time complexity is:
\[
O(n) + O(k) + O(x \log x)
\]
- In the worst case, all elements are distinct and appear in all subarrays, so \( k = n \) and \( x = k \).
- Thus, the worst-case time complexity simplifies to:
\[
O(n + n \log n) = O(n \log n)
\]
---
### Space Complexity:
#### 1. **HashMap:**
- The `HashMap` stores frequencies of up to \( k \) distinct elements, which requires \( O(k) \) space.
#### 2. **Result List:**
- The result list stores at most \( k \) elements, so it requires \( O(k) \) space.
#### 3. **Other Variables:**
- A few auxiliary variables (e.g., `a`, loop counters) use \( O(1) \) space.
---
#### Total Space Complexity:
The total space complexity is:
\[
O(k)
\]
where \( k \) is the number of distinct elements in the input.
---
### Final Complexity:
- **Time Complexity:** \( O(n \log n) \)
- **Space Complexity:** \( O(k) \)
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums)
{
HashMap<Integer,Integer> h=new HashMap<>();
List<Integer> a=new ArrayList<>();
int m=nums.length;//number of arrays
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)//iterating array to array
{
for(int j=0;j<nums[i].length;j++)//iterating through array elements
{
if(h.containsKey(nums[i][j]))
{
h.put(nums[i][j],h.get(nums[i][j])+1);//taking frequency
}
else
{
h.put(nums[i][j],1);
}
}
}
for(Map.Entry er:h.entrySet())
{
if((int)er.getValue()==m)//if freq is equal to number of arrays
{
a.add((int)er.getKey());//then,add in list
}
}
Collections.sort(a);//sorting the list
return a;
}
} // please upvote ;)
```

| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Sorting', 'Counting', 'Java']
| 1 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
leetcodedaybyday -Beats 61.63% with Python3 and Beats 30.29% with C++
|
leetcodedaybyday-beats-6163-with-python3-hm9x
|
IntuitionThe goal is to identify elements that are present in all subarrays of the 2D list nums. By counting the occurrences of elements in each subarray and ch
|
tuanlong1106
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T07:25:43.979614+00:00
|
2024-12-27T07:25:43.979614+00:00
| 224 | false |
# Intuition
The goal is to identify elements that are present in all subarrays of the 2D list `nums`. By counting the occurrences of elements in each subarray and checking if they appear in all subarrays, we can efficiently solve the problem.
# Approach
1. **Frequency Counting**:
- Use a hash map or dictionary to count the occurrences of each element across all subarrays.
- Ensure each element is counted only once per subarray by using a `set` for each subarray.
2. **Filter Common Elements**:
- After populating the hash map, select elements that appear exactly as many times as the number of subarrays. These are the common elements.
3. **Sort the Result**:
- Return the sorted list of common elements.
# Complexity
- **Time Complexity**:
- Let `N` be the total number of elements across all subarrays and `K` the size of the result:
- Counting occurrences: `O(N)`.
- Sorting the result: `O(K * log(K))`.
- **Overall**: `O(N + K * log(K))`.
- **Space Complexity**:
- `O(U)`, where `U` is the total number of unique elements across all subarrays, used for the hash map.
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
counts = defaultdict(int)
i = 0
my_set = set()
while i < len(nums):
k = 0
for k in nums[i]:
counts[k] += 1
i += 1
for key, value in counts.items():
if value == len(nums):
my_set.add(key)
ans = sorted(my_set)
return ans
```
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
map<int, int> count;
vector<int> matrix;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < nums[i].size(); j++){
count[nums[i][j]]++;
}
}
for (auto idx : count)
if (idx.second == n)
matrix.push_back(idx.first);
return matrix;
}
};
```
| 3 | 0 |
['C++', 'Python3']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
🌟 Beats 100.00% || Python One Line 💯🔥
|
beats-10000-python-one-line-by-emmanuel0-swpf
|
Intuition\nThe intuition for this problem is to first collect all the elements from the input lists into a single list, then count the frequency of each element
|
emmanuel011
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-06T18:03:07.895872+00:00
|
2024-11-06T18:03:07.895899+00:00
| 188 | false |
# Intuition\nThe intuition for this problem is to first collect all the elements from the input lists into a single list, then count the frequency of each element. Elements that appear in all the input lists (i.e. have a frequency equal to the number of input lists) are the final result.\n\n# Approach\n1. Initialize an empty list `my_list` to store all the elements from the input lists.\n2. Iterate through each input list and extend `my_list` with the elements from that list.\n3. Create a `Counter` object to count the frequency of each element in `my_list`.\n4. Iterate through the `Counter` object and add any elements with a frequency equal to the number of input lists to the result list `res`.\n5. Return the sorted result list `res`.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$, where n is the total number of elements in all the input lists. We iterate through the input lists once to build `my_list`, then iterate through the `Counter` object once to build the result.\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$, where n is the total number of elements in all the input lists. We store all the elements in `my_list` and the frequency counts in the `Counter` object.\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n my_list=[]\n for i in nums:\n my_list.extend(i)\n c=Counter(my_list)\n res=[]\n for k, v in c.items():\n if v>=len(nums):\n res.append(k)\n return sorted(res)\n```\n\n# Code in one line \n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n return return sorted([k for k, v in Counter([x for sublist in nums for x in sublist]).items() if v >= len(nums)])\n1``
| 3 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 1 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
📌Map | 📌Simple & Neat Explanation | 📌 Clean C++, Java code
|
map-simple-neat-explanation-clean-c-java-r399
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nWe need to find the intersection of elements present in all the sub-arrays of the given
|
mnk17arts
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-01T06:13:13.321832+00:00
|
2023-03-01T06:13:13.321881+00:00
| 427 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nWe need to find the intersection of elements present in all the sub-arrays of the given 2D integer array nums. For this, we can create a hashmap where we store the frequency of each element present in any sub-array of nums. Then, we traverse the hashmap and if the frequency of any element is equal to the number of sub-arrays, we add that element to the result vector.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. We create an `unordered_map<int, int> map` to store the frequency of each element.\n1. We traverse the `nums` 2D array and for each element in each sub-array, we increment its frequency in `map`.\n1. We traverse the `map` and for each element whose frequency is equal to the number of sub-arrays, we add that element to the result vector.\n1. We sort the result vector in ascending order and return it.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n log n)$$, We traverse the nums 2D array once and then the map hashmap once. Both of these operations take O(n) time, where n is the total number of elements in all sub-arrays of nums. Sorting the result vector takes O(k log k) time, where k is the number of elements in the result vector. Since k can be at most equal to the number of elements in any sub-array of nums, which is also equal to n, the time complexity of this algorithm is O(n log n).\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$, We store the frequency of each element in the map hashmap, which can contain at most all the elements in all sub-arrays of nums. Therefore, the space complexity of this algorithm is O(n).\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n unordered_map<int, int> map;\n for(const auto &arr: nums) {\n for(const auto &num: arr) {\n map[num]++;\n }\n }\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<int> res;\n for(const auto &it: map) {\n if(it.second == n) {\n res.push_back(it.first);\n }\n }\n sort(res.begin(), res.end());\n return res;\n }\n};\n```\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();\n for (int[] arr : nums) {\n for (int num : arr) {\n map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);\n }\n }\n int n = nums.length;\n List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();\n for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {\n if (entry.getValue() == n) {\n res.add(entry.getKey());\n }\n }\n Collections.sort(res);\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Sorting', 'C++', 'Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
easy short fast solution
|
easy-short-fast-solution-by-hurshidbek-9yc6
|
\nPLEASE UPVOTE IF YOU LIKE\n\n```\n int[] arr = new int[1001];\n\n for (int i = 0; i <nums.length; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < nums[i
|
Hurshidbek
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-30T05:14:33.680854+00:00
|
2022-08-30T05:14:33.680900+00:00
| 197 | false |
```\nPLEASE UPVOTE IF YOU LIKE\n```\n```\n int[] arr = new int[1001];\n\n for (int i = 0; i <nums.length; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < nums[i].length; j++) {\n arr[ nums[i][j] ]++;\n }\n }\n\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {\n if (arr[i] == nums.length){\n ans.add(i);\n }\n }\n return ans;
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Python - Short & Simple - Set
|
python-short-simple-set-by-siddheshsagar-x8os
|
\ndef intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n temp = set(nums[0])\n for i in range(1,len(nums)):\n temp = (temp & set
|
SiddheshSagar
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-26T14:53:59.511950+00:00
|
2022-07-26T14:53:59.511975+00:00
| 796 | false |
```\ndef intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n temp = set(nums[0])\n for i in range(1,len(nums)):\n temp = (temp & set(nums[i]))\n \n return list(sorted(temp))\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Ordered Set', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Python Easy Understanding
|
python-easy-understanding-by-thereal007-8mqi
|
\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n \n intersection = nums[0]\n \n for i in range(1
|
theReal007
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-04T04:06:28.582128+00:00
|
2022-07-04T04:06:28.582155+00:00
| 207 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n \n intersection = nums[0]\n \n for i in range(1,len(nums)):\n intersection = set(nums[i]) & set(intersection)\n \n return sorted(list(intersection))\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Javascript Solution no map or set 70 ms, 4.1 MB
|
javascript-solution-no-map-or-set-70-ms-o2tiz
|
\nvar intersection = function(nums) {\n let ref = [...nums[0]]\n for(let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++){\n ref = ref.filter(n => nums[i].includes(
|
ahmedelbessfy
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-12T07:50:57.405145+00:00
|
2022-05-12T07:50:57.405173+00:00
| 439 | false |
```\nvar intersection = function(nums) {\n let ref = [...nums[0]]\n for(let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++){\n ref = ref.filter(n => nums[i].includes(n))\n }\n return ref.sort((a,b) => a-b)\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
JavaScript - JS
|
javascript-js-by-mlienhart-4pz5
|
\n/**\n * @param {number[][]} nums\n * @return {number[]}\n */\nvar intersection = function (nums) {\n const result = [];\n\n for (let i = 0; i < nums[0].leng
|
mlienhart
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T10:07:38.027558+00:00
|
2023-03-20T21:53:01.663652+00:00
| 551 | false |
```\n/**\n * @param {number[][]} nums\n * @return {number[]}\n */\nvar intersection = function (nums) {\n const result = [];\n\n for (let i = 0; i < nums[0].length; i++) {\n if (nums.every((x) => x.includes(nums[0][i]))) {\n result.push(nums[0][i]);\n }\n }\n\n return result.sort((a, b) => a - b);\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
frequency count / count sort w/ array || C++ || 100% fast (3ms)
|
frequency-count-count-sort-w-array-c-100-m1sn
|
Since the numbers in each array are distinct and the range these numbers are in is limited to 1 to 1000 we can just use a frequency count. The answer is all the
|
heder
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T08:54:21.877293+00:00
|
2022-04-24T08:57:54.187880+00:00
| 130 | false |
Since the numbers in each array are distinct and the range these numbers are in is limited to 1 to 1000 we can just use a frequency count. The answer is all these numbers that are found as often as the number of arrays.\n\n```\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n array<int, 1001> counts = {};\n for (const auto& as : nums) {\n for (int a : as) {\n ++counts[a];\n }\n }\n vector<int> ans;\n for (int i = 0; i < size(counts); ++i) {\n if (counts[i] == size(nums)) ans.push_back(i);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'C', 'Counting Sort']
| 1 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
c++ easy solution || beginners friendly
|
c-easy-solution-beginners-friendly-by-as-i5yb
|
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector intersection(vector>& nums) {\n unordered_map mp;\n int k = 0;\n int n = nums.size();\n f
|
Ashutosh_Anand_Sharma
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T04:31:46.213349+00:00
|
2022-04-24T04:31:46.213380+00:00
| 379 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n unordered_map<int,int> mp;\n int k = 0;\n int n = nums.size();\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<nums[i].size();j++)\n {\n mp[nums[i][j]]++;\n }\n }\n vector<int> v;\n for(auto it : mp)\n {\n if(it.second == n)\n {\n v.push_back(it.first);\n }\n }\n sort(v.begin(),v.end());\n return v;\n }\n};\n
| 3 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Python solution 3 line
|
python-solution-3-line-by-amannarayansin-lyoc
|
\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n a=set(nums[0])\n inters=a.intersection(*nums)\n return
|
amannarayansingh10
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T04:15:17.070934+00:00
|
2022-04-24T04:15:17.070974+00:00
| 402 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n a=set(nums[0])\n inters=a.intersection(*nums)\n return sorted(list(inters))\n\n\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Ordered Set', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 1 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Python3, Set Intersection
|
python3-set-intersection-by-silvia42-rnso
|
\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n return sorted(set.intersection(*[set(nums[i]) for i in range(len(num
|
silvia42
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T04:07:07.673323+00:00
|
2022-04-24T04:07:07.673351+00:00
| 337 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n return sorted(set.intersection(*[set(nums[i]) for i in range(len(nums))]))\n```\n\nExplanation:\n```\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n answ=set(nums[0])\n for i in range(1,len(nums)):\n answ=answ.intersection(set(nums[i]))\n return sorted(answ) \n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
2MS 🥇|| BEATS 100% 🏆 || 🌟JAVA ☕
|
2ms-beats-100-java-by-galani_jenis-nfjs
|
Code
|
Galani_jenis
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-19T05:47:43.270068+00:00
|
2025-01-19T05:47:43.270068+00:00
| 177 | false |
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int[] count = new int[1001];
for(int[] arr : nums){
for(int i : arr){
count[i]++;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<count.length;i++){
if(count[i]==nums.length){
ans.add(i);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
```

| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Java || Solution
|
java-solution-by-itsanuragpal-izn4
|
Code
|
ItsAnuragPal
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-13T17:44:17.346811+00:00
|
2024-12-13T17:44:17.346811+00:00
| 185 | false |
\n# Code\n```java []\nimport java.util.*;\n\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n Map<Integer, Integer> freqMap = new HashMap<>();\n int n = nums.length;\n\n // Count the frequency of each element in all arrays\n for (int[] arr : nums) {\n for (int num : arr) {\n freqMap.put(num, freqMap.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);\n }\n }\n\n // Filter elements that occur in all arrays\n List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();\n for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : freqMap.entrySet()) {\n if (entry.getValue() == n) {\n result.add(entry.getKey());\n }\n }\n\n Collections.sort(result);\n return result;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Intersection of Multiple Arrays
|
intersection-of-multiple-arrays-by-gokul-5rr6
|
Intuition\nThe goal is to find elements that appear in every array. To achieve this, we can use a HashMap to count the occurrences of each element across all ar
|
Gokulnathan_Thanapal
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-07T16:46:31.170552+00:00
|
2024-10-07T16:46:31.170585+00:00
| 53 | false |
# Intuition\nThe goal is to find elements that appear in every array. To achieve this, we can use a HashMap to count the occurrences of each element across all arrays. Once we know the frequency of each element, we can check which elements appear in every array and return them as the intersection.\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\nUse a HashMap:\n- We traverse each array and for each element, we update its count in the HashMap.\n- The key in the map is the element, and the value is the count of how many arrays it appears in.\n\nFilter Common Elements:\n- After counting, we check the map. If an element\'s count equals the number of arrays (nums.length), it means the element is present in all arrays.\n\nSort the Result:\n- The elements that are common in all arrays are then added to a list and sorted.\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nTime complexity: O(n * m), where n is the number of arrays, and m is the average length of each array. We iterate through every element once while counting and sorting.\n\n\n- Space complexity:\n\nSpace complexity: O(m), where m is the number of unique elements across all arrays. This space is used by the HashMap to store the count of each element.\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();\n List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();\n\n int n = nums.length;\n for (int[] num : nums) {\n for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {\n map.put(num[i], map.getOrDefault(num[i], 0) + 1);\n }\n }\n for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {\n if (map.get(key) == nums.length) {\n list.add(key);\n }\n }\n Collections.sort(list);\n return list;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Sorting', 'Java']
| 1 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
🔢 21. 2 Approaches || Using Counting & Unordered Map || C++ Code Reference !!
|
21-2-approaches-using-counting-unordered-uuvf
|
\n# \ncpp [Using Count Vector]\n\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& A) {\n \n int k=1001,n=A.size();\n vector<int>C(k,0),V;
|
Amanzm00
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-13T12:56:26.137520+00:00
|
2024-07-13T12:56:26.137564+00:00
| 170 | false |
\n# \n```cpp [Using Count Vector]\n\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& A) {\n \n int k=1001,n=A.size();\n vector<int>C(k,0),V;\n\n for(auto& v: A)\n for(auto& x:v)\n C[x]++;\n\n for(int i=0;i<k;i++)\n if(C[i]==n)\n V.push_back(i);\n \n return V;\n }\n```\n```cpp [Using Map]\n\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& A) {\n \n unordered_map<int,int>m;\n vector<int>V;\n int n=A.size();\n\n for(auto& v: A)\n for(auto& x:v)\n m[x]++;\n\n for(auto& i: m)\n if(i.second==n)\n V.push_back(i.first);\n\n sort(V.begin(),V.end());\n\n return V;\n }\n\n```\n\n---\n# *Guy\'s Upvote Pleasee !!* \n\n\n# ***(\u02E3\u203F\u02E3 \u035C)***\n\n\n
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Design', 'Sorting', 'Counting', 'C++']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
really easy to understandable solution guy's ->
|
really-easy-to-understandable-solution-g-sxmz
|
\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n^2)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity:\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n#
|
mantosh_kumar04
|
NORMAL
|
2024-05-03T16:16:03.454423+00:00
|
2024-05-03T16:16:03.454448+00:00
| 358 | false |
\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n^2)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n HashMap<Integer, Integer>map=new HashMap<>();\n for( int i=0; i<nums.length; i++)\n {\n for( int j=0; j<nums[i].length; j++)\n {\n if(map.containsKey(nums[i][j]))\n {\n map.put(nums[i][j], map.get(nums[i][j])+1);\n }\n else\n {\n map.put(nums[i][j], 1);\n }\n }\n }\n List<Integer>list=new ArrayList<>();\n for( int i=0; i<nums[0].length; i++)\n {\n // System.out.println(nums[0][i]+" "+map.get(nums[0][i]));\n if(map.get(nums[0][i])==nums.length)\n {\n list.add(nums[0][i]);\n }\n }\n Collections.sort(list);\n return list;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Easiest C /C++ / Python3 / Java / Python With Hash or without beats 100%
|
easiest-c-c-python3-java-python-with-has-alat
|
Intuition\n\n\n\n\n\nC++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n map<int, int> mp;\n int len =
|
Edwards310
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-13T02:09:33.769591+00:00
|
2024-03-13T02:09:33.769622+00:00
| 113 | false |
# Intuition\n\n\n\n\n\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n map<int, int> mp;\n int len = nums.size();\n for (auto& x : nums)\n for (auto& y : x)\n mp[y]++;\n vector<int> res;\n for (auto& [key, value] : mp)\n if (value == len)\n res.push_back(key);\n return res;\n }\n};\n```\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n n = len(nums)\n ans = set(nums[0])\n for i in range(1, n):\n ans = ans.intersection(set(nums[i]))\n \n ans_lst = list(ans)\n ans_lst.sort()\n return ans_lst\n```\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(NULL);\n cout.tie(NULL);\n vector<int> ans(1001, 0);\n int n = nums.size();\n for(int i =0; i < n; i++)\n for(auto it : nums[i])\n ans[it]++;\n\n vector<int> finalans;\n for(int i =1; i <= 1000; i++)\n if(ans[i] == n)\n finalans.push_back(i); \n \n return finalans;\n }\n};\n```\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n int[] count = new int[1001];\n for(int[] arr : nums)\n for(int i : arr)\n count[i]++;\n\n for(int i = 0; i <count.length; i++)\n if(count[i] == nums.length)\n ans.add(i); \n\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```\n```python []\nclass Solution(object):\n def intersection(self, nums):\n """\n :type nums: List[List[int]]\n :rtype: List[int]\n """\n ans = set(nums[0])\n for row in nums:\n row_set = set(row)\n ans = row_set & ans\n\n return sorted(list(ans))\n```\n```C []\n/**\n * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().\n */\nint* intersection(int** nums, int numsSize, int* numsColSize, int* returnSize) {\n int arr[1001] = {0};\n for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++)\n for (int c = 0; c < numsColSize[i]; c++)\n arr[nums[i][c]]++;\n int* res = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 1001);\n int t = 0;\n for (int x = 0; x < 1001; x++)\n if (arr[x] == numsSize)\n res[t++] = x;\n *returnSize = t;\n return res;\n}\n```\n\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n O(n)\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n O(1001) --> O(1)\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().\n */\nint* intersection(int** nums, int numsSize, int* numsColSize, int* returnSize) {\n int arr[1001] = {0};\n for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++)\n for (int c = 0; c < numsColSize[i]; c++)\n arr[nums[i][c]]++;\n int* res = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 1001);\n int t = 0;\n for (int x = 0; x < 1001; x++)\n if (arr[x] == numsSize)\n res[t++] = x;\n *returnSize = t;\n return res;\n}\n```\n# Please Upvote if it\'s useful for you .. Thanks..\n\n
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'C', 'Sorting', 'Counting', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'C#']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Simple and easy solutions, beats 90% ✅✅
|
simple-and-easy-solutions-beats-90-by-va-6uvc
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n map<int,int> m; // use mao because we need result in
|
vaibhav2112
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-10T13:35:00.453078+00:00
|
2024-03-10T13:35:00.453159+00:00
| 276 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n map<int,int> m; // use mao because we need result in sorted order\n\n // keep count of each element\n for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.size(); i++){\n for(int &x : nums[i]){\n m[x]++;\n }\n }\n\n vector<int> ans;\n\n // if frequency of element == size of vector, means it is present in all\n for(auto &x : m){\n if(x.second == nums.size()){\n ans.push_back(x.first);\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
simple python solution
|
simple-python-solution-by-kabshaansariya-y080
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
kabshaansariya
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-09T09:46:43.669795+00:00
|
2023-11-09T09:46:43.669824+00:00
| 759 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n l=[]\n for i in nums:\n l.extend(i)\n s=[]\n k=len(nums)\n for i in l:\n if l.count(i)==k:\n s.append(i)\n s=list(set(s))\n s.sort()\n return s\n\n\n \n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
✅100% Easy Java Solution
|
100-easy-java-solution-by-kartik_ksk7-57ej
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
kartik_ksk7
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-08T08:27:54.945633+00:00
|
2023-07-08T08:27:54.945657+00:00
| 287 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n List<Integer>list=new ArrayList<>();\n for(int j=0;j<nums[0].length;j++)\n {\n list.add(nums[0][j]);\n }\n\n for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++)\n {\n List<Integer>list1=new ArrayList<>();\n for(int j=0;j<nums[i].length;j++)\n {\n if(list.contains(nums[i][j]))\n list1.add(nums[i][j]);\n }\n list=list1;\n }\n Collections.sort(list);\n return list;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Beginners Friendly solution
|
beginners-friendly-solution-by-bhaskarku-s00j
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n // add 1st row to set\n HashSet<Integer> common= new HashSet
|
bhaskarkumar07
|
NORMAL
|
2023-05-11T02:32:49.674770+00:00
|
2023-05-11T02:32:49.674809+00:00
| 1,310 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n // add 1st row to set\n HashSet<Integer> common= new HashSet<>();\n\n for(int i=0;i<nums[0].length;i++){\n common.add(nums[0][i]);\n }\n //now add other rows and retain only those in common if it present in current set;\n\n for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){\n HashSet<Integer> current= new HashSet<>();\n for(int j=0;j<nums[i].length;j++){\n if(common.contains(nums[i][j]))\n current.add(nums[i][j]);\n }\n common.retainAll(current);\n }\n\n List<Integer> ls= new ArrayList<>(common);\n Collections.sort(ls);\n\n return ls;\n\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
[Python] good looking solution, easy to understand
|
python-good-looking-solution-easy-to-und-lorg
|
\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n^2)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity: O(n^2)\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n)
|
8uziak
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-17T18:56:40.997701+00:00
|
2023-04-17T18:56:40.997741+00:00
| 1,220 | false |
\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n^2)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n^2)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n\n ll = []\n sortedNums = sorted(nums)\n\n for num in sortedNums[0]:\n cou = 1\n\n for listNums in sortedNums[1:]:\n if num not in listNums:\n cou = 0\n break\n \n if cou:\n ll.append(num)\n\n return sorted(ll)\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 2 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Simplest possible ruby solution
|
simplest-possible-ruby-solution-by-gabeh-rpwh
|
\n# @param {Integer[][]} nums\n# @return {Integer[]}\ndef intersection(nums)\n nums.reduce(:&).sort\nend\n
|
gabehblack
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-29T13:48:14.297959+00:00
|
2023-03-29T13:48:14.298005+00:00
| 21 | false |
```\n# @param {Integer[][]} nums\n# @return {Integer[]}\ndef intersection(nums)\n nums.reduce(:&).sort\nend\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Ruby']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
C#| 1 line LINQ using Aggregate. Beats 100% Runtime
|
c-1-line-linq-using-aggregate-beats-100-pknfc
|
\n\n\n# Code\n\npublic class Solution \n{\n public IList<int> Intersection(int[][] nums) \n {\n return nums.Skip(1)\n .Aggregate(nums[0]
|
neerex
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-04T08:32:22.815533+00:00
|
2023-03-04T08:32:22.815558+00:00
| 88 | false |
\n\n\n# Code\n```\npublic class Solution \n{\n public IList<int> Intersection(int[][] nums) \n {\n return nums.Skip(1)\n .Aggregate(nums[0].AsEnumerable(), (s, v) => s.Intersect(v))\n .OrderBy(x => x)\n .ToList();\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Easy Approach // Java
|
easy-approach-java-by-kiet7uke-1n4l
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n int[] count = new
|
KIET7UKE
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-12T20:07:32.586382+00:00
|
2022-12-12T20:07:32.586422+00:00
| 1,098 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n int[] count = new int[1001];\n \n for(int[] arr : nums) {\n for(int i : arr) {\n count[i]++;\n }\n }\n\n for(int i = 0; i < count.length; i++) {\n if(count[i] == nums.length) {\n ans.add(i);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Java Solution
|
java-solution-by-tbekpro-j4ue
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();\n for (int i = 0; i
|
tbekpro
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-19T16:14:28.355458+00:00
|
2022-11-19T16:14:28.355490+00:00
| 933 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < nums[i].length; j++) {\n if (map.containsKey(nums[i][j])) {\n map.put(nums[i][j], map.get(nums[i][j]) + 1);\n } else {\n map.put(nums[i][j], 1);\n }\n }\n }\n List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();\n for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {\n if (map.get(key) == nums.length) {\n list.add(key);\n }\n }\n Collections.sort(list);\n return list;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 2 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Python3 one line solution
|
python3-one-line-solution-by-tryit163281-lyrp
|
\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n return sorted(reduce(lambda x,y: set(x) & set(y),nums))\n\nYou don\'
|
tryit163281
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-19T08:43:23.004438+00:00
|
2022-11-19T08:43:23.004478+00:00
| 183 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n return sorted(reduce(lambda x,y: set(x) & set(y),nums))\n```\nYou don\'t have to use Counter , just set and reduce.\nIt\'s easier than Counter.
| 2 | 0 |
['Ordered Set', 'Python3']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Python3
|
python3-by-sneh713-v8cn
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Sneh713
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-20T10:43:33.518350+00:00
|
2022-10-20T10:43:33.518390+00:00
| 616 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n d = {}\n \n for i in range(len(nums)):\n for j in nums[i]:\n if j not in d:\n d[j] = 1\n else:\n d[j]+=1\n \n res = []\n for k,v in d.items():\n if v == len(nums):\n res.append(k)\n \n return sorted(res)\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
JAVA solution | Count sort | No hashing | Easy
|
java-solution-count-sort-no-hashing-easy-qf76
|
Please Upvote !!! (\u25E0\u203F\u25E0)\n\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n int[] freq = new int[1001];\n\n
|
sourin_bruh
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-28T07:26:53.970677+00:00
|
2022-09-28T07:28:18.250991+00:00
| 656 | false |
### ***Please Upvote !!!*** **(\u25E0\u203F\u25E0)**\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n int[] freq = new int[1001];\n\n for (int[] row : nums) {\n for (int n : row) {\n freq[n]++;\n }\n }\n\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n\t\t\n for (int i = 1; i < freq.length; i++) {\n if (freq[i] == nums.length) {\n ans.add(i);\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n}\n\n// TC: O(m * n), SC: O(1) - ignoring the output array\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Using Map | C++
|
using-map-c-by-nehagupta_09-mg5b
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n map<int,int>mp1;\n vector<int>ans;\n for(int i=0;i
|
NehaGupta_09
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-25T10:12:11.368598+00:00
|
2022-09-25T10:12:11.368650+00:00
| 904 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n map<int,int>mp1;\n vector<int>ans;\n for(int i=0;i<nums[0].size();i++)\n {\n mp1[nums[0][i]]++;\n }\n for(int i=1;i<nums.size();i++)\n {\n vector<int>temp=nums[i];\n for(int j=0;j<temp.size();j++)\n {\n if(mp1.find(temp[j])!=mp1.end())\n {\n mp1[temp[j]]++;\n }\n }\n }\n for(auto it=mp1.begin();it!=mp1.end();it++)\n {\n if(it->second==nums.size())\n {\n ans.push_back(it->first);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.