question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
97.81% faster using set and set.intersection
|
9781-faster-using-set-and-setintersectio-cg2o
|
\n\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n inter = set(nums[0])\n for i in range(1, len(nums)):\n
|
aissa-laribi
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-27T22:01:24.967129+00:00
|
2022-08-27T22:01:24.967162+00:00
| 223 | false |
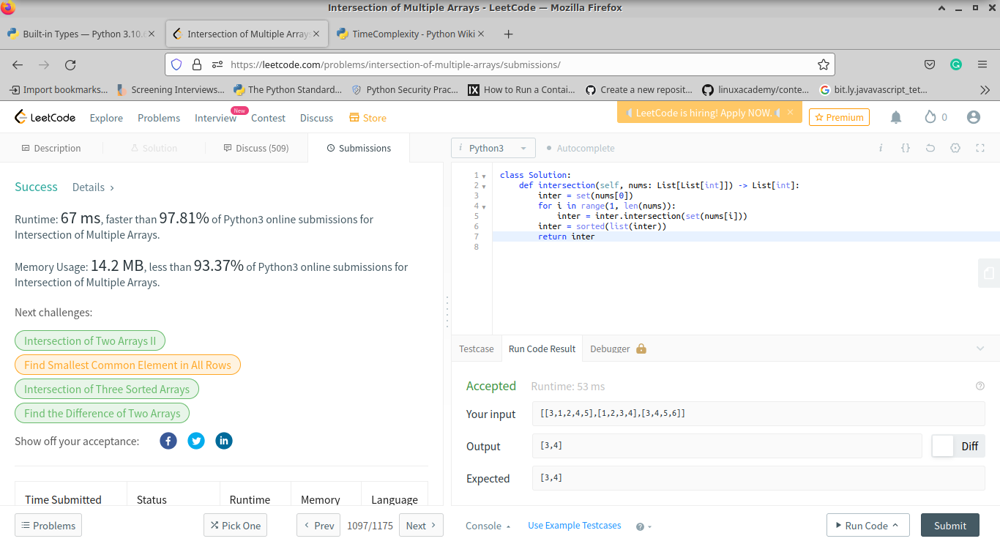\n```\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n inter = set(nums[0])\n for i in range(1, len(nums)):\n inter = inter.intersection(set(nums[i]))\n inter = sorted(list(inter))\n return inter\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Frequency map concept || JAVA || Easy Undestanding :)
|
frequency-map-concept-java-easy-undestan-fwx1
|
Create the frequency map of the integers present in the matrix.\n2. the ans will be the index which has the count equals to the length of the matrix\n\n\nclass
|
Kshitij_Pandey
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-25T09:21:14.877058+00:00
|
2022-08-25T09:21:14.877087+00:00
| 35 | false |
1. Create the frequency map of the integers present in the matrix.\n2. the ans will be the *index which has the count equals to the length of the matrix*\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n int[] frequencyMap = new int[1001];\n \n for(int[] arr: nums){\n for(int x:arr){\n frequencyMap[x]++;\n }\n }\n \n for(int i=0; i< frequencyMap.length; i++){\n if(frequencyMap[i] == nums.length){\n ans.add(i);\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
JAVA STREAM SOLUTION 🧵
|
java-stream-solution-by-sulaymon-dev20-sza0
|
THIS IS NOT FASTER SOLUTION\nBUT 1 LINE CODE\n\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n\t\t//return Arrays.stream(nums).flatMa
|
Sulaymon-Dev20
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-21T14:00:08.542092+00:00
|
2022-08-21T14:00:08.542123+00:00
| 252 | false |
`THIS IS NOT FASTER SOLUTION`\n`BUT 1 LINE CODE `\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n\t\t//return Arrays.stream(nums).flatMapToInt(Arrays::stream).boxed().collect(Collectors.toMap(i -> i, i -> 1, Integer::sum)).entrySet().stream().sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByValue()).filter(item -> item.getValue() == nums.length).map(Map.Entry::getKey).sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());\n\n return Arrays.stream(nums)\n .flatMapToInt(Arrays::stream)\n .boxed()\n .collect(Collectors.toMap(i -> i, i -> 1, Integer::sum))\n .entrySet()\n .stream()\n .sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByValue())\n .filter(item -> item.getValue() == nums.length)\n .map(Map.Entry::getKey)\n .sorted()\n .collect(Collectors.toList());\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Funny solution with Go
|
funny-solution-with-go-by-tuanbieber-8ai7
|
\nfunc intersection(nums [][]int) []int {\n numSet := make([]int, 1001)\n \n for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {\n for j := 0; j < len(nums[i]); j+
|
tuanbieber
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-21T09:15:50.095090+00:00
|
2022-08-21T09:15:50.095157+00:00
| 129 | false |
```\nfunc intersection(nums [][]int) []int {\n numSet := make([]int, 1001)\n \n for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {\n for j := 0; j < len(nums[i]); j++ {\n numSet[nums[i][j]]++\n }\n }\n \n var res []int\n \n for i := 0; i < 1001; i++ {\n if numSet[i] == len(nums) {\n res = append(res, i)\n }\n }\n \n sort.Ints(res)\n \n return res\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Go']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Intersection of Multiple Arrays Solution Java
|
intersection-of-multiple-arrays-solution-2oso
|
class Solution {\n public List intersection(int[][] nums) {\n List ans = new ArrayList<>();\n int[] count = new int[1001];\n\n for (int[] A : nums)\n
|
bhupendra786
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-16T08:50:23.863587+00:00
|
2022-08-16T08:50:23.863625+00:00
| 144 | false |
class Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n int[] count = new int[1001];\n\n for (int[] A : nums)\n for (final int a : A)\n ++count[a];\n\n for (int i = 1; i < 1001; ++i)\n if (count[i] == nums.length)\n ans.add(i);\n\n return ans;\n }\n}\n
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Counting']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Simple JS Solution
|
simple-js-solution-by-user0120v-2ric
|
\tconst intersection = function(nums) {\n\t\tlet map = new Map()\n\t\tlet res = []\n\n\t\tnums.forEach(arr => {\n\t\t\tarr.forEach(num => map.set(num, map.get(n
|
user0120v
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-31T12:09:00.628381+00:00
|
2022-07-31T12:09:00.628412+00:00
| 359 | false |
\tconst intersection = function(nums) {\n\t\tlet map = new Map()\n\t\tlet res = []\n\n\t\tnums.forEach(arr => {\n\t\t\tarr.forEach(num => map.set(num, map.get(num) + 1 || 1))\n\t\t})\n\n\t\tfor(let [key, value] of map) {\n\t\t\tif (value === nums.length) {\n\t\t\t\tres.push(key)\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t}\n\n\t\treturn res.sort((a, b) => a - b)\n\t};
| 2 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Ruby one-liner
|
ruby-one-liner-by-dnnx-1q6z
|
\n# @param {Integer[][]} nums\n# @return {Integer[]}\ndef intersection(nums)\n nums.reduce(:&).sort \nend\n
|
dnnx
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-06T10:15:54.035509+00:00
|
2022-05-06T10:15:54.035549+00:00
| 42 | false |
```\n# @param {Integer[][]} nums\n# @return {Integer[]}\ndef intersection(nums)\n nums.reduce(:&).sort \nend\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Easy, clear and detailed explanation ( faster than 80.96% of Python3 online submissions)
|
easy-clear-and-detailed-explanation-fast-119o
|
FInd the length of the 2D array \n Use hashtable to find out the frequency of each element \n Check whether the frequency of an element equals the length of the
|
haaris272k
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-30T09:10:26.031729+00:00
|
2022-06-29T16:17:33.428705+00:00
| 214 | false |
* FInd the length of the 2D array \n* Use hashtable to find out the frequency of each element \n* Check whether the frequency of an element equals the length of the 2D array ( This would specify that the element occurs in all the array of the 2D array)\n* Store the answer in the list and sort it\n\t\t\n\t\tdef intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n\t\t\n\t\t""" Declarations """\n\t\t\n n_of_lists = len(nums) # finding no. array within 2D array\n\t\t\n hmap = {} # hashmap to map the elements with their frequency\n\t\t\n ans = [] # list to store the final answer\n\t\t\n\t\t""" Finding the frequency of each element """\n\t\t\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n\t\t\n for j in range(len(nums[i])):\n\t\t\t\n if nums[i][j] in hmap:\n\t\t\t\t\n hmap[nums[i][j]] += 1\n\t\t\t\t\t\n else:\n\t\t\t\t\n hmap[nums[i][j]] = 1\n\t\t\n\t\t""" Checking whether the frequency an element equals the no of the array within the 2D array """\n\t\t\n for k, v in hmap.items():\n\t\t\n if v == n_of_lists:\n\t\t\t\n ans.append(k) # appending the result\n\t\t\t\t\n return sorted(ans) # finally sorting the array ( given in the question)\n\t\t\nDo Upvote if you like it :))\n
| 2 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
C++ || EASY SOLUTION || UNOREDERED MAP
|
c-easy-solution-unoredered-map-by-harsh_-iv1u
|
\n\n class Solution {\n public:\n vector intersection(vector>& nums) {\n vectorvect;\n int y=nums.size();\n unordered_mapmp;\n
|
harsh_patell21
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-28T15:43:31.651773+00:00
|
2022-04-28T15:43:31.651798+00:00
| 72 | false |
\n\n class Solution {\n public:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n vector<int>vect;\n int y=nums.size();\n unordered_map<int,int>mp;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n for(int j=0;j<nums[i].size();j++){\n mp[nums[i][j]]++;\n }\n }\n for(auto x:mp){\n if(x.second>=y){\n vect.push_back(x.first);\n }\n }\n sort(vect.begin(),vect.end());\n return vect;\n }\n };\n \n \n \n**IF U FIND IT USEFUL PLEASE UPVOTE IT**
| 2 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Rust solution
|
rust-solution-by-bigmih-atoo
|
\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn intersection(nums: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<i32> {\n let l = nums.len();\n let mut counter = [0; 1001];\n nums.i
|
BigMih
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T14:59:08.345681+00:00
|
2022-04-24T14:59:19.300182+00:00
| 88 | false |
```\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn intersection(nums: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<i32> {\n let l = nums.len();\n let mut counter = [0; 1001];\n nums.iter()\n .flat_map(|v| v.iter())\n .for_each(|v| counter[*v as usize] += 1);\n\n counter\n .iter()\n .zip(0..)\n .filter_map(|(&num, idx)| if num == l { Some(idx) } else { None })\n .collect()\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Rust']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
3 approach JAVA sol
|
3-approach-java-sol-by-anshulpro27-kj0j
|
Using array as HashMap :\n\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] a) {\n List<Integer> ans =new ArrayList<>();\n int dp[]=new int[1001];\n
|
anshulpro27
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-24T07:44:23.412906+00:00
|
2022-04-24T07:44:23.412940+00:00
| 50 | false |
Using array as HashMap :\n```\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] a) {\n List<Integer> ans =new ArrayList<>();\n int dp[]=new int[1001];\n \n for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)\n {\n for(int x: a[i])\n {\n dp[x]++;\n }\n }\n \n for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++) if(dp[i]==a.length)ans.add(i);\n \n return ans;\n }\n```\n\nSimple Hashmap soln :\n```\npublic List<Integer> intersection(int[][] a) {\n List<Integer> ans =new ArrayList<>();\n HashMap<Integer,Integer> hm =new HashMap<>();\n \n for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)\n {\n for(int x : a[i])\n {\n if(!hm.containsKey(x)) hm.put(x,0);\n \n hm.put(x,hm.get(x)+1);\n }\n }\n \n for(int key : hm.keySet())\n {\n if(hm.get(key)==a.length)ans.add(key);\n }\n \n Collections.sort(ans);\n return ans;\n }\n```\nHashSet soln : \n\n```\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] a) {\n List<Integer> ans =new ArrayList<>();\n HashSet<Integer> cur =new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=0;i<a[0].length;i++) cur.add(a[0][i]);\n \n for(int i=1;i<a.length;i++)\n { HashSet<Integer> newcur =new HashSet<>(); \n for(int x : a[i])\n {\n if(cur.contains(x)) newcur.add(x);\n }\n cur=newcur;\n }\n \n for(int x : cur) ans.add(x);\n \n Collections.sort(ans);\n \n return ans;\n }\n```\n
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Simple C solution
|
simple-c-solution-by-mukesh1855-tfdg
|
Code
|
mukesh1855
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-26T16:39:52.386083+00:00
|
2025-03-26T16:39:52.386083+00:00
| 54 | false |
# Code
```c []
int* intersection(int** nums, int size, int* colSize, int* returnSize) {
int hash[1001] = {0};
int count = 0;
int *ans = malloc(4004);
for(int i=0;i<colSize[0];i++){
hash[nums[0][i]]++;
}
for(int i=1;i<size;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<colSize[i];j++)
{
if(hash[nums[i][j]]==i) hash[nums[i][j]]++;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<1001;i++){
if(hash[i]==size) ans[count++] = i;
}
*returnSize = count;
return ans;
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'C']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Python
|
python-by-lathika17-wbnf
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
lathika17
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-03T16:47:30.180452+00:00
|
2025-02-03T16:47:30.180452+00:00
| 112 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
res=[]
for i in range(len(set(nums[0]))):
x = 1
for j in range(1,len(nums)):
if nums[0][i] in nums[j]:
x += 1
if x == len(nums):
res.append(nums[0][i])
return sorted(res)
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Most Easy Solution
|
most-easy-solution-by-who-i-am-blyk
|
Code
|
roniahamed
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-31T06:13:04.642885+00:00
|
2025-01-31T06:13:04.642885+00:00
| 121 | false |
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
set1 = set(nums[0])
for i in nums:
set1 &= set(i)
li = list(set1)
li.sort()
return li
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
easy soln cpp 1ms soln
|
easy-soln-cpp-1ms-soln-by-himkk-4v5q
|
IntuitionApproachUse a Hash Map (mp) to store frequencies of elements across all rows.Traverse each row and insert its elements into mp.
Since each row contains
|
himkkhh
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-30T13:52:55.109251+00:00
|
2025-01-30T13:52:55.109251+00:00
| 128 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
Use a Hash Map (mp) to store frequencies of elements across all rows.
Traverse each row and insert its elements into mp.
Since each row contains unique elements, adding an element from a row only once ensures correctness.
Traverse the map (mp) to find common elements.
If an element appears in all rows, its frequency will be equal to the total number of rows (n).
Add such elements to the answer list.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {
map<int,int>mp;
vector<int>v;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
for(int j=0;j<nums[i].size();j++){
mp[nums[i][j]]++;
}
}
int n=nums.size();
for(auto i=mp.begin();i!=mp.end();i++){
if(i->second==n){
v.push_back(i->first);
}
}
sort(v.begin(),v.end());
return v;
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Easy || Optimized || Efficient Intersection of Multiple Arrays using Sorting and Two Pointers
|
easy-optimized-efficient-intersection-of-bwcu
|
IntuitionTo find the intersection of multiple arrays, we need to identify the common elements that appear in every array.
The key insight here is that sorting e
|
jaspal13
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-24T10:01:50.943063+00:00
|
2025-01-24T10:01:50.943063+00:00
| 89 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
To find the intersection of multiple arrays, we need to identify the common elements that appear in every array.
The key insight here is that sorting each array allows us to efficiently find common elements using the two-pointer technique.
We can progressively reduce the problem size by iterating through each array and updating the intersection based on previously found common elements.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
1. **Sort Each Array:**
- Start by sorting all arrays in nums. Sorting ensures that elements are in ascending order, making it easier to find common elements across arrays using a two-pointer approach.
2. **Two-Pointer Technique:**
- Begin with the intersection being the first array (vec = nums[0]).
- For each subsequent array in nums, initialize a temporary result array (temp) and use two pointers (j and k) to traverse both the current array and the ongoing intersection (vec).
- If the elements are equal, add it to the temporary result (temp) and move both pointers forward.
- If the current element in the array is smaller, move the pointer for the array forward.
- If the current element in the intersection is smaller, move the pointer for the intersection forward.
- After processing each array, update vec to the temp (intersection of the current array and the previous results).
3. **Final Intersection:**
- After processing all arrays, the result (vec) contains the common elements that appear in every array.
# Complexity
- **Time complexity:**
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
`O(N×MlogM), where 𝑁 is the number of arrays and 𝑀 is the maximum size of the arrays.`
- **Space complexity:** `O(N)`
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> ans;
for (auto& arr : nums) {
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
}
vector<int> vec = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
vector<int> temp;
int j = 0;
int k = 0;
while (j < nums[i].size() && k < vec.size()) {
if (nums[i][j] == vec[k]) {
temp.push_back(vec[k]);
j++;
k++;
} else if (nums[i][j] > vec[k]) {
k++;
} else {
j++;
}
}
vec = temp;
}
ans = vec;
return ans;
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Two Pointers', 'Sorting', 'C++']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Hash Map Solution - Beats 100% Runtime
|
hash-map-solution-beats-100-runtime-by-p-o3q5
|
IntuitionThe problem asks to find the intersection of multiple lists of integers. The goal is to identify the elements that are common to all the lists.A good a
|
premnishok4
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-22T14:04:28.760839+00:00
|
2025-01-22T14:11:19.362370+00:00
| 100 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
The problem asks to find the intersection of multiple lists of integers. The goal is to identify the elements that are common to all the lists.
A good approach to this problem is to count the frequency of each element across all the lists. If an element appears in every list, then it is part of the intersection. This can be achieved using a dictionary (hashmap) to store the frequency of each element. If an element appears in every list (i.e., the frequency is equal to the number of lists), it belongs to the intersection.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
1. Initialization: Start by creating a dictionary, ref, to store the frequency of each element across all the lists.
2. Iterate through each list: For each list in the nums input, iterate through its elements and count how many times each element appears across the lists. This can be done by updating the count of each element in the dictionary.
3. Check frequency: Once the dictionary is populated, iterate over the dictionary to check which elements have a frequency equal to the number of lists. These are the elements that are present in every list.
4. Sort the result: The result needs to be sorted before returning, as the problem might require the intersection to be in ascending order.
5. Return the result: The result will be the list of elements that are common in all the input lists, sorted in ascending order.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: We iterate over each list and each element in the list, which gives a time complexity of O(m * n), where m is the number of lists and n is the average size of the lists. After building the frequency map, we need to check the dictionary, which takes O(k) time, where k is the number of unique elements in the input lists. Sorting the final result will take O(k log k) time.
Hence, the total time complexity is: O(m * n + k log k).
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: The space required for the frequency dictionary is proportional to the number of unique elements across all the lists. In the worst case, this could be all the elements across all lists, giving a space complexity of O(k).
We also use additional space for storing the result, which could have at most k elements.
Hence, the space complexity is: O(k).
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
# Initialize a dictionary to store the frequency of each element
ref = {}
# Iterate over each list in the input
for i in range(len(nums)):
row = nums[i] # Get the current list
# Iterate over each element in the current list
for n in row:
if n in ref:
# If element is already in the dictionary, increment its count
ref[n] += 1
else:
# If element is not in the dictionary, initialize its count to 1
ref[n] = 1
# List to store the intersection result
res = []
# Iterate through the dictionary to find elements that appear in all lists
for key, value in ref.items():
if value == len(nums): # If the element appeared in all lists
res.append(key)
# Return the sorted list of common elements
return sorted(res)
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Simple Python Code Beats 100% 🔥
|
simple-python-code-beats-100-by-suseyizh-cvcl
| null |
suseyizheen
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-15T01:36:38.254577+00:00
|
2024-12-15T01:36:38.254577+00:00
| 124 | false |
```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n from collections import defaultdict\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n counts = defaultdict(int)\n i = 0\n my_set = set()\n while i < len(nums):\n k = 0\n for k in nums[i]:\n counts[k] += 1\n i += 1\n for key, value in counts.items():\n if value == len(nums):\n my_set.add(key)\n ans = sorted(my_set)\n return ans\n\n\n \n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
TC- O(n*m + klogk) 🔥 || SC- O(n*m +k) 🔥 || [With Explanation]
|
tc-onm-klogk-sc-onm-k-with-explanation-b-w7yw
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nTo find the intersection of multiple arrays, the goal is to identify the elements that
|
aayushk0250_
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-22T21:47:08.734275+00:00
|
2024-07-22T21:47:08.734307+00:00
| 234 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nTo find the intersection of multiple arrays, the goal is to identify the elements that are present in all the arrays. A straightforward approach is to use a hash map to count the occurrences of each element across all arrays and then select those elements that appear in all of them.\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nWe can use an unordered map to store the frequency of each element across all arrays. First, we iterate through each element of every array and update its count in the map. After counting the frequencies, we traverse the map to identify the elements whose frequency equals the number of arrays, indicating that these elements are present in every array. Finally, we collect these elements into a result vector and sort it before returning.\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n O(n*m + klogk)\nwhere n*m is to traverse the 2d array of n*m size and k is the list of integers that we need to return and sorting these k element takes klogk time.\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n O(n*m + k)\nn*m to store occurences of all the integers in the 2d array. And k is to store answer elements in vector v.\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n unordered_map<int,int> m;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<nums[i].size();j++)\n {\n m[nums[i][j]]++;\n }\n }\n vector<int> v;\n for(auto i:m)\n {\n if(i.second==nums.size())\n v.push_back(i.first);\n }\n sort(v.begin(),v.end());\n return v;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Sorting', 'Counting', 'C++']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
using hash-map
|
using-hash-map-by-2004sherry-td7d
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nusing hash map\n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \ncountin
|
2004sherry
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-10T15:26:24.535437+00:00
|
2024-04-10T15:26:24.535468+00:00
| 382 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nusing hash map\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\ncounting the frequency of elements\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\no(mn)\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\no(klogk)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n unordered_map<int,int>mp;\n for(auto it:nums)\n {\n for(auto i:it)\n {\n mp[i]++;\n }\n }\n int n= nums.size();\n vector<int>ans;\n for(auto it:mp)\n {\n if(it.second==n)\n {\n ans.push_back(it.first);\n }\n }\n sort(ans.begin(),ans.end());\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
One Pass C++ easy
|
one-pass-c-easy-by-cc_debjyoti-in9r
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n unordered_map<int,int>Map;\n vector<int>ans;\n
|
CC_Debjyoti
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-10T17:07:30.610116+00:00
|
2024-03-10T17:07:30.610150+00:00
| 474 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n unordered_map<int,int>Map;\n vector<int>ans;\n int n=nums.size();\n\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n for(int j=0;j<nums[i].size();j++){\n Map[nums[i][j]]++;\n if(i==n-1 && Map[nums[i][j]]==n)ans.push_back(nums[i][j]);\n }\n }\n\n sort(ans.begin(),ans.end());\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Simple No Map || Count Sort || C++ || Beats 86%
|
simple-no-map-count-sort-c-beats-86-by-b-5eh4
|
Intuition\nif the frequency of an element equals the size of array then it is present in each of the arrays as each array has unique elements.\n Describe your f
|
bhanunegi420
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-24T10:52:21.862856+00:00
|
2024-02-24T10:52:21.862881+00:00
| 285 | false |
# Intuition\nif the frequency of an element equals the size of array then it is present in each of the arrays as each array has unique elements.\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\nJust store the frequency of the elements in an array and return the elements whose frequency is equal to the size of nums.\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n*m)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n*m)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n\n ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(NULL);\n cout.tie(NULL);\n\n vector<int> ans(1001, 0);\n int n = nums.size();\n\n for(int i =0; i < n; i++){\n for(auto it : nums[i]){\n ans[it]++;\n }\n }\n vector<int> finalans;\n for(int i =1; i <= 1000; i++){\n if(ans[i] == n){\n finalans.push_back(i);\n }\n }\n\n return finalans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Simple and easy JS Solution || 53ms ✅✅ ||Beats 93.55%🔥🔥||
|
simple-and-easy-js-solution-53ms-beats-9-vxlr
|
\n# Code\n\n\nvar intersection = function (nums) {\n arr = [];\n for (i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)\n for (j = 0; j < nums[i].length; j++)\n
|
pranjal_ahire
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-02T09:42:55.458908+00:00
|
2024-02-02T09:42:55.458939+00:00
| 259 | false |
\n# Code\n```\n\nvar intersection = function (nums) {\n arr = [];\n for (i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)\n for (j = 0; j < nums[i].length; j++)\n if (arr[nums[i][j]] == undefined)\n arr[nums[i][j]] = 1;\n else\n arr[nums[i][j]]++;\n neww = [];\n for (i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)\n if (arr[i] == undefined)\n continue;\n else if (arr[i] == nums.length)\n neww.push(i);\n return neww;\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Checking distinct positive integers with map in Kotlin
|
checking-distinct-positive-integers-with-mn0c
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n# Co
|
behzodhalil
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-23T01:18:49.287292+00:00
|
2024-01-23T01:18:49.287310+00:00
| 306 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n fun intersection(nums: Array<IntArray>): List<Int> {\n val bucket = nums.flatMap { it.toList() }.groupingBy { it }.eachCount()\n val answer = mutableListOf<Int>()\n \n for(key in bucket.keys) {\n if(bucket[key] == nums.size) {\n answer.add(key)\n }\n }\n\n return answer.sorted()\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Kotlin']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
No set, sort, or hashmap: use Masks
|
no-set-sort-or-hashmap-use-masks-by-nand-4tfl
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n It\'s highlighted that the integers in each sublist are distinct.\n The result must be
|
nandan-helix007
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-22T18:02:09.848379+00:00
|
2023-08-22T18:07:12.865218+00:00
| 198 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n* It\'s highlighted that the integers in each sublist are **distinct**.\n* The result must be sorted in ascending order.\n * I think the point is to build your result in a way that it turns out to be ascending.\n * Not that you build however and finally sort it!\n* Use the constraint: `1 <= nums[i] <= 1000`\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n* For each sublist create a `mask`\n* `mask` is an integer.\n* See it as an array of bits.\n\t* 0-indexed from the right.\n* The length of this array is limited by the range of elements in each sublist of `nums`.\n\t* In this particular problem, `mask` can be, atmost, an array of 1000 bits.\n\t\t* Now that could be a pretty large number. But Python can handle arbitrarily large numbers!\n* Let `arr` be a sublist of `nums`\n* For each `n` in `arr`\n\t* Set the `n-1`-th bit from the right.\t \n\t * The right-most bit is the `0`-th bit.\n\t * When we "set a bit", we mean we set it to `1`.\n\n* Take the intersection of all these masks.\n* The bits that are set in `intersection` correspond to the desired numbers that are common in all the sublists.\n* Iterate over each bit in `intersection` to check if the bit is set or not.\n * If set, add the corresponding element to the result.\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: `O(n)`, where `n = len(nums)`\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: `O(n)`, where `n = len(nums)`\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n minVal = 1 \n \n def generateMask(arr):\n mask = 0\n for n in arr:\n mask |= (1 << (n - minVal))\n return mask\n\n intersection = reduce(lambda x, y: x & y, map(generateMask, nums))\n\n result = []\n ele = 0\n while intersection:\n if intersection & 1:\n result.append(ele + minVal)\n intersection >>= 1\n ele += 1\n\n return result\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Bit Manipulation', 'Python3']
| 1 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Intersection of Multiple Arrays Solution in C++
|
intersection-of-multiple-arrays-solution-62bw
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
The_Kunal_Singh
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-22T18:43:15.122353+00:00
|
2023-03-22T18:43:15.122397+00:00
| 242 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n^2)\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n)\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n int i, j, flag=0;\n vector<int> ans;\n for(i=0 ; i<nums[0].size() ; i++)\n {\n flag=0;\n for(j=1 ; j<nums.size() ; j++)\n {\n if(count(nums[j].begin(), nums[j].end(), nums[0][i])==0)\n {\n flag=1;\n break;\n }\n }\n if(flag==0)\n {\n ans.push_back(nums[0][i]);\n }\n }\n sort(ans.begin(), ans.end());\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
C# with detailed explanation
|
c-with-detailed-explanation-by-fbdaf-sf0a
|
Approach\n1. Using a dictionary, we are going to count the number of occurrences of each integer in ALL ARRAYS.\n2. After that, it checks WHICH NUMBERS have cou
|
FBDAF
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-05T17:01:47.610233+00:00
|
2023-03-05T17:01:47.610286+00:00
| 166 | false |
# Approach\n1. Using a dictionary, we are going to count the number of occurrences of each integer in **ALL ARRAYS**.\n2. After that, it checks WHICH NUMBERS have counts **EQUAL** to the **LENGTH** of the input array, meaning they are present in all subarrays.\n\n# C# Syntax Highlights\n- **IList<int>** instead of a concrete implementation like List<int> in C# allows for more flexibility. A list is a more specific type that implement the interface IList. Problably not make a difference here.\n\n**LINQ FILTERS: Where, Select, OrderBy, ToArray**\n- The Where method is used to filter a collection based on a condition specified by a lambda expression. In this code, it **returns a new collection of key-value pairs where the value of each key is equal to the length of the nums array**.\n- The Select method takes the filtered collection of key-value pairs and **creates a new collection that contains only the keys**.\n- The OrderBy method **sorts the collection** in ascending order by the key.\n- Finally, the ToArray method converts the collection to an array.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n\n The time complexity of this code is O(nmlog(m)). \n n = number of subarrays \n m = maximum length each (so nm). \n \n The sorting adds the logm to the final complexity.\n \n Using a dictionary is generally faster than using a list for counting occurrences of elements, because dictionary lookup and insertion have an average time complexity of O(1), while list lookup and insertion have an average time complexity of O(n).\n\n\n- Space complexity:\n The space complexity of this code is also O(n*m), because the code uses a dictionary to store the counts of each integer.\n\n# Code\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public IList<int> Intersection(int[][] nums) {\n Dictionary<int, int> counts = new Dictionary<int, int>();\n\n foreach (int[] arr in nums) {\n foreach (int n in arr) {\n if (!counts.ContainsKey(n)) {\n counts.Add(n, 1);\n }\n else {\n counts[n]++;\n }\n }\n }\n\n return counts.Where(x => x.Value == nums.Length)\n .Select(x => x.Key)\n .OrderBy(x => x)\n .ToArray();\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
C++ Sol
|
c-sol-by-swish78-s6gi
|
Create an ordered map and vector (dynamic array). \nSurf the vectorvectorint>>nums and store the items present in the map with their frequency. \nCheck to deter
|
swish78
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-17T09:57:18.338731+00:00
|
2023-01-17T09:57:18.338766+00:00
| 22 | false |
Create an ordered map and vector (dynamic array). \nSurf the vectorvectorint>>nums and store the items present in the map with their frequency. \nCheck to determine whether the frequency of the stored element is equal to the size of the vector. If the frequency is the same, then insert that element into the vector. \nFinally, since the specified return type is vector, return the vector.\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n map<int,int>sol;\n int s = nums.size();\n vector<int>ans;\n for(int i = 0;i<nums.size();i++){\n for(int j = 0;j<nums[i].size();j++){\n sol[nums[i][j]]++;\n }\n for(auto x : sol){\n if(x.second == s){\n ans.push_back(x.first);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Python Basic Solution
|
python-basic-solution-by-salonipatadia-xcye
|
\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nRun time =107 ms\nBeats = 76.56%\n\n- Space complexity:\nMemory =14.4 MB \nBeats = 6.15%\n\nUpvote if you find it helpful!!\
|
salonipatadia
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-11T20:32:31.066374+00:00
|
2022-11-13T19:32:20.646678+00:00
| 15 | false |
\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nRun time =107 ms\nBeats = 76.56%\n\n- Space complexity:\nMemory =14.4 MB \nBeats = 6.15%\n\nUpvote if you find it helpful!!\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n i=0\n common_list=[]\n if len(nums)<=1:\n common_list=nums[0]\n return sorted(common_list)\n else:\n while i<len(nums)-1:\n # for i in range(len(nums)):\n for j in range(len(nums[i])):\n common_list = set(nums[i]).intersection(nums[i+1])\n nums[i+1]=common_list\n i+=1\n # result = [i for i in a if i in b]\n return sorted(common_list)\n\n # print(nums[i][j])\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
java easy Solution 100% faster
|
java-easy-solution-100-faster-by-mohd_ak-i2hr
|
\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n ArrayList<Integer> al= new ArrayList<>();\n int[] freq =new int[1001];
|
Mohd_Akib01
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-21T19:40:32.803842+00:00
|
2022-09-21T19:40:32.803869+00:00
| 1,094 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n ArrayList<Integer> al= new ArrayList<>();\n int[] freq =new int[1001];\n for(int r=0;r<nums.length;r++){\n for(int c=0;c<nums[r].length;c++){\n freq[nums[r][c]]++;\n }\n }\n int n=nums.length;\n for(int i=0;i<freq.length;i++){\n if(freq[i]==n) al.add(i);\n }\n return al;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
C++ || Easy Solution || Easy to Understand
|
c-easy-solution-easy-to-understand-by-ya-6zo1
|
class Solution {\npublic:\n vector intersection(vector>& nums) {\n unordered_mapy;\n vectorw;\n int i,j;\n for(i=0;isecond==nums.size
|
yashwardhan24_sharma
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-20T15:54:32.825380+00:00
|
2022-09-20T15:54:32.825424+00:00
| 37 | false |
class Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n unordered_map<int,int>y;\n vector<int>w;\n int i,j;\n for(i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n for(j=0;j<nums[i].size();j++){\n y[nums[i][j]]++;\n \n }}\n for(auto it=y.begin();it!=y.end();it++){\n if(it->second==nums.size()){\n w.push_back(it->first); \n }\n }\n sort(w.begin(),w.end());\n \n return w; }\n};
| 1 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Java | ArrayList | Faster Than 100% Java Submissions
|
java-arraylist-faster-than-100-java-subm-6hm0
|
\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();\n int arr[] = new int[100
|
Divyansh__26
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-19T12:20:26.971261+00:00
|
2022-09-19T12:20:26.971308+00:00
| 513 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();\n int arr[] = new int[1001];\n for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<nums[i].length;j++)\n arr[nums[i][j]]++;\n }\n int num = nums.length;\n for(int k=1;k<arr.length;k++){\n if(arr[k]==num)\n list.add(k);\n }\n return list;\n }\n}\n```\nKindly upvote if you like the code.
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Counting', 'Java']
| 1 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
C++ solution
|
c-solution-by-lit2021036_iiitl-jewq
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n vector<int> hsh(1005,0),ans;\n for(auto&_nums:nums)\n
|
lit2021036_iiitl
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-17T11:26:59.838165+00:00
|
2022-09-17T11:26:59.838200+00:00
| 579 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n vector<int> hsh(1005,0),ans;\n for(auto&_nums:nums)\n for(int&x:_nums)\n hsh[x]++;\n for(int i=1; i<hsh.size(); i++)\n if(hsh[i]==nums.size()) ans.push_back(i);\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
java solution with full explanation
|
java-solution-with-full-explanation-by-a-cl3b
|
\'\'\'\nclass Solution {\n public List intersection(int[][] nums) {\n List arr1=new ArrayList<>();\n int maxi=0;\n // find the max
|
agarwal_megha
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-15T15:14:08.989661+00:00
|
2022-09-15T15:14:08.989700+00:00
| 132 | false |
\'\'\'\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n List<Integer> arr1=new ArrayList<>();\n int maxi=0;\n // find the max of the oth index array \n for(int i=0;i<nums[0].length;i++) maxi=Math.max(maxi,nums[0][i]);\n \n //create array with max+1 size\n int arr[]=new int[maxi+1];\n \n //increment elements count in array\n for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++)\n for(int j=0;j<nums[i].length;j++)\n if(nums[i][j]<=maxi) arr[nums[i][j]]++;\n \n // if element count is equal to number of rows that means that particular elements occured in every row ,\n // so put that element in our result list\n for(int i=0;i<=maxi;i++)\n if(arr[i]==nums.length) arr1.add(i);\n \n return arr1;\n \n }\n}\n\'\'\'
| 1 | 0 |
['Array']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Simple solution - 2ms (with comments !!)
|
simple-solution-2ms-with-comments-by-use-4t96
|
\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();\n int count[] = new int[1001];
|
user5717GP
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-11T11:42:11.634651+00:00
|
2022-09-11T11:42:39.236615+00:00
| 189 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();\n int count[] = new int[1001]; // stores the number of array which has that element i\n for(int numsArray[]: nums)\n for(int num: numsArray)\n count[num]++;\n \n int n = nums.length;\n for(int i=0;i<1001;i++)\n if(count[i]==n) // if the count is == size of the array, then it is present in every array\n res.add(i);\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Python fast solution
|
python-fast-solution-by-betaal-i0t7
|
\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n if not nums:\n return []\n a = set(nums[0])\n
|
betaal
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-07T20:58:39.859582+00:00
|
2022-09-07T20:58:39.859617+00:00
| 489 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def intersection(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n if not nums:\n return []\n a = set(nums[0])\n for i in nums[1:]:\n a = a & set(i)\n return sorted(a)\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Ordered Set', 'Python']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Java Solution || 3ms faster && 94.41% faster || easy to understand
|
java-solution-3ms-faster-9441-faster-eas-khhu
|
\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] arr) {\n List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();\n for (int i : arr[0]) {\n
|
beastfake8
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-22T07:15:10.901827+00:00
|
2022-08-22T07:15:10.901857+00:00
| 140 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] arr) {\n List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();\n for (int i : arr[0]) {\n if (helper(i, arr, 1)) list.add(i);\n }\n Collections.sort(list);\n return list;\n }\n\n private static boolean helper(int target, int[][] arr, int start) {\n for (int i = start; i < arr.length; i++) {\n boolean b = false;\n for (int k : arr[i]){\n if (k == target) {\n b = true;\n break;\n }\n }\n if (!b) return false;\n }\n return true;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
C# Solution | Time: O(m*n), Memory: O(m*n) | Easy to understand, Dictionary
|
c-solution-time-omn-memory-omn-easy-to-u-obds
|
C#\npublic class Solution {\n public IList<int> Intersection(int[][] nums) {\n Dictionary<int, int> d = new Dictionary<int, int>();\n for (int
|
tonytroeff
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-20T13:57:29.853359+00:00
|
2022-08-20T13:57:29.853395+00:00
| 37 | false |
```C#\npublic class Solution {\n public IList<int> Intersection(int[][] nums) {\n Dictionary<int, int> d = new Dictionary<int, int>();\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < nums[i].Length; j++) {\n if (!d.ContainsKey(nums[i][j])) d[nums[i][j]] = 0;\n d[nums[i][j]]++;\n }\n }\n \n List<int> ans = new List<int>();\n foreach (var (num, count) in d) {\n if (count == nums.Length) ans.Add(num);\n }\n \n return ans.OrderBy(x => x).ToList();\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Easy✅ JAVA☕ Solution.
|
easy-java-solution-by-hirentimbadiya74-e5ed
|
Please upvote if you understood the solution!!\n\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n List<Integer> list = new Arra
|
hirentimbadiya74
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-20T06:50:46.280122+00:00
|
2022-08-20T06:50:46.280159+00:00
| 100 | false |
**Please upvote if you understood the solution!!**\n```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();\n for (int j = 0; j < nums[0].length; j++) {\n list.add(nums[0][j]);\n }\n for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {\n List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();\n for (int j = 0; j < nums[i].length; j++) {\n if (list.contains(nums[i][j])) {\n list1.add(nums[i][j]);\n }\n }\n list = list1;\n }\n Collections.sort(list);\n return list;\n }\n}\n```\n# upvote
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
[python] Using Counter, faster than 93%
|
python-using-counter-faster-than-93-by-h-9hoz
|
\nclass Solution(object):\n def intersection(self, nums):\n """\n :type nums: List[List[int]]\n :rtype: List[int]\n """\n
|
hhlinwork
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-11T23:46:09.568816+00:00
|
2022-08-11T23:46:09.568848+00:00
| 111 | false |
```\nclass Solution(object):\n def intersection(self, nums):\n """\n :type nums: List[List[int]]\n :rtype: List[int]\n """\n length=len(nums)\n all_nums=[]\n ans=[]\n for num in nums:\n all_nums+=num\n from collections import Counter\n counts=Counter(all_nums)\n for k in counts.keys():\n if counts[k]==length:\n ans.append(k)\n return sorted(ans)\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
Java Simple Brute Force Solution
|
java-simple-brute-force-solution-by-aman-4aea
|
\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n ArrayList<Integer> arrList = new ArrayList<Integer>();\n List<Integer>
|
amankesarwani34
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-31T10:21:25.768054+00:00
|
2022-07-31T10:21:25.768093+00:00
| 91 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public List<Integer> intersection(int[][] nums) {\n ArrayList<Integer> arrList = new ArrayList<Integer>();\n List<Integer> resList = new ArrayList<Integer>();\n \n for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < nums[i].length; j++){\n arrList.add(nums[i][j]); // adding all the elements of nums in arrList\n }\n }\n \n int numLength = nums.length;\n int count = 0;\n \n for(int i = 0; i < nums[0].length; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < arrList.size(); j++){\n if(nums[0][i] == arrList.get(j)){\n count++; //increase count of nums[0][i] \n }\n }\n if(count == numLength){\n resList.add(nums[0][i]); //if nums[0][i] count is equals 3 then add to another array\n }\n count = 0;\n }\n \n Collections.sort(resList);// sort the result array\n \n return resList;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
C++|| 16ms || 68% Bruteforce approach with explanation
|
c-16ms-68-bruteforce-approach-with-expla-okpz
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n map<int,int>sk;\n vector<int>sk1;\n vector<int>res
|
sagarkesharwnnni
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-30T23:04:20.408441+00:00
|
2022-07-30T23:05:20.527283+00:00
| 53 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n map<int,int>sk;\n vector<int>sk1;\n vector<int>res;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){ ///////storing all elements in single array;\n for(int j=0;j<nums[i].size();j++){\n sk1.push_back(nums[i][j]);\n }\n }\n\t\t\n for(int i=0;i<sk1.size();i++){ ////now adding all elements in map\n sk[sk1[i]]++;\n \n }\n \n for(auto i:sk){\n \n if(i.second==nums.size()){ //checking if duplicate element size is equal to nums.size() means it present in all three then pushing into result vector\n res.push_back(i.first);\n }\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
intersection-of-multiple-arrays
|
C++ simple solution using merge algorithm
|
c-simple-solution-using-merge-algorithm-xrb4n
|
\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n vector<int> doIntersection(vector<int> &first, vector<int> &second){\n vector<int> ans;\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n
|
krishnajsw
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-21T10:52:34.326793+00:00
|
2022-07-21T10:52:34.326834+00:00
| 37 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n vector<int> doIntersection(vector<int> &first, vector<int> &second){\n vector<int> ans;\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n sort(first.begin(), first.end());\n sort(second.begin(), second.end());\n while(i < first.size() && j < second.size()){\n if(first[i] < second[j]){\n i++;\n }\n else if(first[i] > second[j]){\n j++;\n }else{\n ans.push_back(first[i]);\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\npublic:\n vector<int> intersection(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n if(nums.size() == 1){\n sort(nums[0].begin(), nums[0].end());\n return nums[0];\n }\n vector<int> ans = doIntersection(nums[0], nums[1]);\n for(int j = 2 ; j < nums.size() ; j++){\n ans = doIntersection(ans, nums[2]);\n }\n return ans;\n\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
JAVA || O(n) solution With Explanation || Range Addition
|
java-on-solution-with-explanation-range-4e3ei
|
Let\'s understand with an example\nSuppose we are given the log [1950, 1961]\nThis means birth year is 1950 and death year is 1961\nTherefore, years from 1950 t
|
vishal_sherawat
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-09T06:21:22.182431+00:00
|
2021-05-10T08:05:41.014209+00:00
| 19,247 | false |
Let\'s understand with an example\nSuppose we are given the log [1950, 1961]\nThis means birth year is 1950 and death year is 1961\nTherefore, years from 1950 to 1960 will be incremented by 1.\n\nWe can do it by iterating from 1950 to 1960 but that will increase time complexity if we have to do it for every query in logs array.\n\nTo do this in O(1), we increment year[1950] by 1 and decrement year[1961] by 1.\nWe can reapeat this for every query in logs array.\n\nWhat will this do ?\n\nFor the case [1950, 1961], let\'s look at how the array will look like\n\n\n\n\nBut this is not the desired result ?\n\nTo get the answer,\nAfter iterating through all the queries, take prefix sum of the array(year)\nThis is how the array will look like\n\n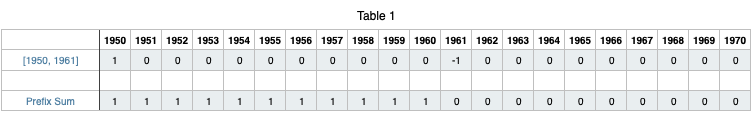\n\nYou can see that the Prefix Sum row will give the desired result as we have incremented the values of array from index 1950 to 1960.\n\nLet\'s try for the test case, logs = [[1950,1961],[1960,1965],[1963,1970]] for a better understanding\n\n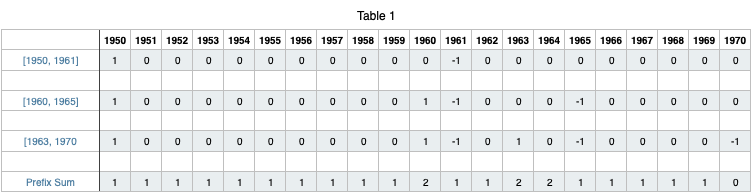\n\nLooking at the Prefix Sum, we can clearly see that the maximum value is 2 and its first occurence is at 1960. Hence, 1960 is the answer.\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n \n int[] year = new int[2051];\n \n\t\t// O(n) -> n is log.length\n\t\t\n for(int[] log : logs){\n \n year[log[0]] += 1;\n year[log[1]] -= 1;\n }\n \n int maxNum = year[1950], maxYear = 1950;\n \n\t\t// O(100) -> 2050 - 1950 = 100\n\n for(int i = 1951; i < year.length; i++){\n year[i] += year[i - 1]; // Generating Prefix Sum\n \n if(year[i] > maxNum){\n maxNum = year[i];\n maxYear = i;\n }\n }\n \n return maxYear;\n }\n}\n```\nTotal time complexity will be O(n + 100) -> O(n)\nIn a general case we can write it as O(n + Range of Year)\n\nYou can also improve the space complexity by taking array of size 101 and not of 2051 because we only consider years from 1950 to 2050.
| 408 | 5 |
['Java']
| 41 |
maximum-population-year
|
O(n) Line Sweep
|
on-line-sweep-by-votrubac-2yme
|
We can mark the start and end of each life as +1 and -1 on the timeline. Then, we go through timeline from 1950 to 2050 and accumulate the current population fo
|
votrubac
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-09T05:20:29.539544+00:00
|
2021-05-09T05:21:36.187347+00:00
| 16,621 | false |
We can mark the start and end of each life as +1 and -1 on the timeline. Then, we go through timeline from 1950 to 2050 and accumulate the current population for each year.\n\n**C++**\n```cpp\nint maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) {\n int pop[2051] = {}, res = 0;\n for (auto &l : logs) {\n ++pop[l[0]];\n --pop[l[1]];\n }\n for (auto i = 1950; i < 2050; ++i) {\n pop[i] += pop[i - 1];\n res = pop[i] > pop[res] ? i : res;\n }\n return res;\n}\n```\n**Java**\n```java\npublic int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int pop[] = new int[2051], res = 0;\n for (var l : logs) {\n ++pop[l[0]];\n --pop[l[1]];\n }\n for (int i = 1950; i < 2050; ++i) {\n pop[i] += pop[i - 1];\n res = pop[i] > pop[res] ? i : res;\n }\n return res;\n}\n```
| 144 | 9 |
['C', 'Java']
| 27 |
maximum-population-year
|
Python, sorting, max overlapping segments algorithm
|
python-sorting-max-overlapping-segments-3tzql
|
\nclass Solution:\n def maximumPopulation(self, logs: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n dates = []\n for birth, death in logs:\n dates.appe
|
blue_sky5
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-09T12:52:07.462865+00:00
|
2021-05-10T11:47:44.007883+00:00
| 6,633 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def maximumPopulation(self, logs: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n dates = []\n for birth, death in logs:\n dates.append((birth, 1))\n dates.append((death, -1))\n \n dates.sort()\n\n population = max_population = max_year = 0\n for year, change in dates:\n population += change\n if population > max_population:\n max_population = population\n max_year = year\n \n return max_year\n```
| 95 | 1 |
['Python']
| 13 |
maximum-population-year
|
c++ You should learn line sweep algorithm
|
c-you-should-learn-line-sweep-algorithm-imsu5
|
You can do this question in o(n^2) easily but here is a tricky solution which is worth to learn.\n\nstep 1 create an array of 2051 look at constrains to underst
|
sanjeev1709912
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-09T04:23:28.362901+00:00
|
2021-05-09T04:32:25.178875+00:00
| 6,341 | false |
You can do this question in o(n^2) easily but here is a tricky solution which is worth to learn.\n\nstep 1 create an array of 2051 look at constrains to understand why.\n\nstep 2 traverse through the array and mark starting index with +1 and ending index with -1\n\nstep 3 calculate prefix sum of the array\n\nstep 5 then again traverse the array and check the maximum index.\n\nstep 6 return index that contain maximum value.\n\nTime complexity O(N)\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) {\n \n vector<int>v(2051,0);\n \n for(auto a:logs){\n v[a[0]]+=1;\n v[a[1]]-=1;\n }\n for(int i=1;i<2051;i++){\n v[i]+=v[i-1];\n }\n \n int a=INT_MIN,ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<2051;i++){\n if(a<v[i])a=v[i],ans=i;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 45 | 6 |
[]
| 7 |
maximum-population-year
|
Python3 O(N)
|
python3-on-by-signifying-xgrz
|
Steps\n1. For each log, update an array which stores the population changes in each year. The first index corresponds to the year 1950, and the last to the year
|
signifying
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-15T20:19:35.188803+00:00
|
2021-05-17T19:28:36.975994+00:00
| 5,999 | false |
### Steps\n1. For each log, update an array which stores the population changes in each year. The first index corresponds to the year 1950, and the last to the year 2050. \n1. Then, iterate through the years while updating the running sum, max population and year of that max population.\n1. Return that year.\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximumPopulation(self, logs: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n # the timespan 1950-2050 covers 101 years\n\t\tdelta = [0] * 101\n\n\t\t# to make explicit the conversion from the year (1950 + i) to the ith index\n conversionDiff = 1950 \n\t\t\n for l in logs:\n\t\t\t# the log\'s first entry, birth, increases the population by 1\n delta[l[0] - conversionDiff] += 1 \n\t\t\t\n\t\t\t# the log\'s second entry, death, decreases the population by 1\n delta[l[1] - conversionDiff] -= 1\n \n runningSum = 0\n maxPop = 0\n year = 1950\n\t\t\n\t\t# find the year with the greatest population\n for i, d in enumerate(delta):\n runningSum += d\n\t\t\t\n\t\t\t# since we want the first year this population was reached, only update if strictly greater than the previous maximum population\n if runningSum > maxPop:\n maxPop = runningSum\n year = conversionDiff + i\n\t\t\t\t\n return year\n```\n\nThis idea works because we have a limited number of years (101) to track. If this number were higher, we could instead sort then iterate, for an O(nlogn) complexity with O(n) memory solution.
| 42 | 1 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 4 |
maximum-population-year
|
Java || Beginner friendly (with explanation) || Beats 100%
|
java-beginner-friendly-with-explanation-m8w8j
|
Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n1. We want to analyze a range of years from 1950 to 2050, and we\'ll use an array of size 101 to sto
|
dee_pacman
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-31T18:04:35.045198+00:00
|
2023-07-31T18:05:54.210838+00:00
| 1,737 | false |
# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. We want to analyze a range of years from 1950 to 2050, and we\'ll use an array of size 101 to store our data.\n\n2. To work with the array more conveniently, we will shift the input years to the range of 0 to 100. For example, for the year 1950, we will store it at index 0, for 1951 at index 1, and so on.\n\n3. For every log entry [birth, death], increment the value in array at index \'birth\' by 1 and decrement the value at index \'death\' by 1.\n\n4. While doing the prefix sum, we will simultaneously find the year with the maximum number of people alive in the range.\n\n5. Finally, the result will be the year with the maximum number of people alive, but we need to convert it back to the original year by adding 1950 to the index.\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int[] arr = new int[101];\n for(int[] log : logs) {\n int birth = log[0];\n int death = log[1];\n arr[birth-1950]++;\n arr[death-1950]--;\n }\n\n int max = arr[0];\n int year = 1950;\n for(int i = 1 ; i < 101; i++) {\n arr[i] += arr[i-1];\n if(arr[i] > max) {\n max = arr[i];\n year = 1950 + i;\n }\n }\n return year;\n }\n}\n```\n\n\n
| 21 | 0 |
['Java']
| 2 |
maximum-population-year
|
c++ || o(n) || Brute force
|
c-on-brute-force-by-rajat_gupta-zjpy
|
TC : O(n)\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) {\n int arr[101]={0};\n for(vector<int> log : logs){\
|
rajat_gupta_
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-09T05:42:52.688300+00:00
|
2021-05-15T13:31:00.904127+00:00
| 2,578 | false |
**TC : O(n)**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) {\n int arr[101]={0};\n for(vector<int> log : logs){\n arr[log[0]-1950]++;\n arr[log[1]-1950]--;\n }\n int max=0,year,cnt=0;\n for(int i=0;i<101;i++){\n cnt+=arr[i];\n if(cnt>max)\n max=cnt,year=i;\n }\n return year+1950;\n }\n};\n```\n**Brute force**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) { \n vector<int> map(101, 0);\n for(auto &log : logs){\n for(int i = log[0]; i < log[1]; ++i){\n map[i - 1950]++;\n }\n }\n int max = 0, ans;\n for(int i = 0; i <= 100; ++i){\n if(max < map[i]){\n max = map[i];\n ans = i;\n }\n }\n return ans+1950;\n }\n};\n```\n**Feel free to ask any question in the comment section.**\nI hope that you\'ve found the solution useful.\nIn that case, **please do upvote and encourage me** to on my quest to document all leetcode problems\uD83D\uDE03\nHappy Coding :)\n
| 20 | 3 |
['C', 'C++']
| 4 |
maximum-population-year
|
Java Array Solution
|
java-array-solution-by-admin007-28vf
|
\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int[] map = new int[101]; // Based on problem statement: 1950 <= birthi < deathi <= 2050, so we only
|
admin007
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-09T04:46:41.801738+00:00
|
2021-05-09T04:58:16.965919+00:00
| 1,958 | false |
```\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int[] map = new int[101]; // Based on problem statement: 1950 <= birthi < deathi <= 2050, so we only need 101.\n for(int[] l : logs){\n for(int i = l[0]; i < l[1]; i++){\n map[i - 1950]++;\n }\n }\n int max = 0;\n int res = -1;\n for(int i = 0; i < 101; i++){\n if(map[i] > max){\n max = map[i];\n res = i + 1950;\n }\n }\n return res; \n }\n```
| 17 | 2 |
[]
| 1 |
maximum-population-year
|
JavaScript Solution
|
javascript-solution-by-deadication-rvd7
|
First time of learning about line sweep algorithm. I though it was cool so I am posting a solution in JS even though I did not come up with it.\n\n\nvar maximum
|
Deadication
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-19T23:38:03.108915+00:00
|
2021-05-19T23:38:03.108946+00:00
| 1,328 | false |
First time of learning about line sweep algorithm. I though it was cool so I am posting a solution in JS even though I did not come up with it.\n\n```\nvar maximumPopulation = function(logs) {\n const count = new Array(101).fill(0);\n \n for (const [birth, death] of logs) {\n count[birth - 1950]++;\n count[death - 1950]--;\n }\n \n let max = 0;\n \n for (let i = 1; i < 101; i++) {\n count[i] += count[i - 1];\n \n if (count[i] > count[max]) max = i;\n }\n \n return 1950 + max;\n };\n ```
| 16 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
maximum-population-year
|
2 JAVA Solutions with explanation
|
2-java-solutions-with-explanation-by-rah-lc6f
|
i) Naive approach using an array for taking frequency of every year\'s population\n\npublic int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int res[] = new int[1
|
rahultherock955
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-10T08:42:12.293522+00:00
|
2022-09-10T08:42:12.293567+00:00
| 2,391 | false |
i) Naive approach using an array for taking frequency of every year\'s population\n```\npublic int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int res[] = new int[101];\n int max = 0;\n int year = -1;\n for(int i=0; i<logs.length; i++){\n for(int j=logs[i][0]; j<logs[i][1]; j++){\n res[j-1950]++;\n }\n }\n \n for(int i=0; i<101; i++){\n if(res[i] > max){\n max = res[i];\n year = i+1950;\n }\n }\n return year;\n }\n```\n\nii) taking prefix sum\n\n```\npublic int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int res[] = new int[101];\n \n for(int[] log : logs){\n res[log[0]-1950]++;\n res[log[1]-1950]--;\n }\n \n int max = res[0];\n int year = 1950;\n \n for(int i=1; i<101; i++){\n res[i] += res[i-1];\n if(res[i] > max){\n max = res[i];\n year = i+1950;\n }\n }\n return year;\n }\n``` \nplease upvote.
| 13 | 0 |
['Prefix Sum', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
[Python][Sweep Line] Detailed explanation of Sweep Line algorithm
|
pythonsweep-line-detailed-explanation-of-0vxx
|
Decode the problemBeneath the contex of the problem, we are basically given a list of ranges on an axis and we are asked to find the smallest integer with the m
|
lusitian1995
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-09T22:28:02.099202+00:00
|
2025-01-03T09:15:05.212750+00:00
| 3,896 | false |
### Decode the problem
Beneath the contex of the problem, we are basically given a list of ranges on an axis and we are asked to find the smallest integer with the maximum number of overlapping ranges. This is a populate question pattern. One of the most famous problems is meeting room II: https://leetcode.com/problems/meeting-rooms-ii/
---
### Understand the alghorithm
So how do we approach this kind of problems? We use an alghorithm called [sweep line](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sweep_line_algorithm). It is more commonly used in computational geometry processing. But the idea holds same here: We are processing all the range edges in a sorted manner and track the state of our interest.
In the first for loop, we are iterating all the ranges given. And we use an `popluation` array to represent the axis. We are basically doing bucket sort here so all the starting and ending integers will be arranged in sorted order when we iterate it later. Additionally, we are also increment the count when we see starting integer and decrement count when we see ending integer. What we are really repesent here is how many ranges starts / ends at this given year, which is the state of our interest.
*Note in this problem, the range only exist between 1950 - 2050. And most ranges should be in contious fasion. So it makes a lot sense to just do bucket sort. In an open end range problem (imagine there is no limitation of years here) we will need to break up the start and end integers, group them and sort them, which usually requires O(nlogn) time complexity. Otherwise, we will waste a lot of idle meomories just for the bucket sort.*
Now in the second for loop, we are iterating the axis and update the current populations by adding/substracting the # of ranges starts/ends at all the given year. And we just need to keep track of the max Population we got.
##### Time complexity: O(n)
---
### Full Implementation
```
class Solution(object):
def maximumPopulation(self, logs):
"""
:type logs: List[List[int]]
:rtype: int
"""
totalYears = 2050 - 1950 + 1
population = [0] * totalYears
for log in logs:
birthYear = log[0]
deathYear = log[1]
population[birthYear - 1950] += 1
population[deathYear - 1950] -= 1
currPop = maxPop = result = 0
for year in range(totalYears):
currPop += population[year]
if currPop > maxPop:
maxPop = currPop
result = year
return result + 1950
```
| 13 | 0 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 1 |
maximum-population-year
|
[Python 3] 5-line defaultdict, simple, no hardcoding
|
python-3-5-line-defaultdict-simple-no-ha-0kuf
|
```\ndef maximumPopulation(self, logs: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n d = collections.defaultdict(int)\n \n # Count the live population for each ye
|
zhouxu_ds
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-13T16:05:28.991145+00:00
|
2021-05-13T16:22:47.409107+00:00
| 1,097 | false |
```\ndef maximumPopulation(self, logs: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n d = collections.defaultdict(int)\n \n # Count the live population for each year in the dict\n for y_b, y_d in logs:\n for y in range(y_b, y_d):\n d[y] += 1\n \n # return the earliest maxinum population year\n return max(d.items(), key=lambda x: (x[1], -x[0]))[0]
| 11 | 0 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
[Python3] greedy
|
python3-greedy-by-ye15-d7zt
|
\n\nclass Solution:\n def maximumPopulation(self, logs: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n vals = []\n for x, y in logs: \n vals.append((x,
|
ye15
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-09T04:05:32.629357+00:00
|
2021-05-10T02:07:38.776963+00:00
| 1,840 | false |
\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximumPopulation(self, logs: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n vals = []\n for x, y in logs: \n vals.append((x, 1))\n vals.append((y, -1))\n ans = prefix = most = 0\n for x, k in sorted(vals): \n prefix += k\n if prefix > most: \n ans = x\n most = prefix \n return ans \n```
| 10 | 1 |
['Python3']
| 2 |
maximum-population-year
|
C++ easy solution
|
c-easy-solution-by-srinivasteja18-6kfa
|
\nint maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) {\n vector<int>v(101,0);\n for(vector<int>cur :logs){\n for(int i=cur[0];i<cur[1];i+
|
srinivasteja18
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-09T04:00:33.425778+00:00
|
2021-05-09T04:00:33.425862+00:00
| 713 | false |
```\nint maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) {\n vector<int>v(101,0);\n for(vector<int>cur :logs){\n for(int i=cur[0];i<cur[1];i++){\n v[i-1950]++;\n }\n }\n int maxi =0,ind;\n for(int i=0;i<101;i++){\n if(maxi < v[i]){\n maxi = v[i];\n ind = i+1950;\n }\n }\n return ind;\n }\n```
| 8 | 3 |
[]
| 2 |
maximum-population-year
|
JAVA SOLUTION EASY and EXPLAINED
|
java-solution-easy-and-explained-by-deep-y0xu
|
JAVA SOLUTION @DeepakKumar\n# In Case of Any Doubt Feel Free to ASK .....\n\n\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n // De
|
Deepak2002
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-02T13:06:00.308275+00:00
|
2021-11-02T13:07:10.861513+00:00
| 1,550 | false |
# JAVA SOLUTION @DeepakKumar\n# In Case of Any Doubt Feel Free to ASK .....\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n // Declaring Array of Size 101\n int [] arr = new int[101]; // Initializing of 101 BECAUSE OF Constraint 1950 <= birthi < deathi <= 2050\n for (int[] log : logs) { // For Every row in logs\n for (int j = log[0]; j < log[1]; j++) { // Range is from [birthi, deathi - 1] Both Inclusive\n arr[j - 1950]++; \n /*\n During j = 1950 \n arr[1950-1950] = arr[0] will be incremented\n Similarly During j = 1951\n arr[1] will be incremented ..... and so on..\n */\n }\n }\n // System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));\n int maxValue = 0; // Initialize maxValue of Population as 0\n int maxYear = 1950; // Let Initially YEAR with Maximum Population is 1950\n for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ // Now compare maxValue with all the Elements of arr\n if(arr[i]> maxValue){ // If any Element is Greater than it\n maxValue = arr[i]; // update maxValue\n maxYear = i+1950; // Once maxValue is Incremented then Also Increment the year \n /*\n EXAMPLE \n Suppose i = 2 has MAX VALUE\n so YEAR is 2+1950 = 1952\n */\n }\n }\n return maxYear;\n }\n}\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
maximum-population-year
|
Python simple solution
|
python-simple-solution-by-zara_gh-saej
|
\nclass Solution(object):\n def maximumPopulation(self, logs):\n """\n :type logs: List[List[int]]\n :rtype: int\n """\n\t\tbirth
|
Zara_Gh
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-13T18:24:01.125673+00:00
|
2021-05-13T18:24:34.354147+00:00
| 944 | false |
```\nclass Solution(object):\n def maximumPopulation(self, logs):\n """\n :type logs: List[List[int]]\n :rtype: int\n """\n\t\tbirth_years = sorted([i[0] for i in logs])\n\t\tmax_pop = 0\n\t\toutput = 0\n\n\t\tfor year in birth_years: #It can be easily proved that the answer would be one of the birth years. So we do not need to go over the whole range of years!\n\t\t\tpopulation= 0\n\t\t\tfor dates in logs:\n\t\t\t\tif dates[0]<=year and dates[1]>year: #If the person is born before or the same year, and died after this year\n\t\t\t\t\tpopulation+=1\n\n\t\t\tif population>max_pop:\n\t\t\t\toutput = year\n\t\t\t\tmax_pop = population\n\n\t\treturn output\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
C++ Hashmap Solution
|
c-hashmap-solution-by-its_gupta_ananya-kkgk
|
Approach :- Iterate over the array and store the frequencies of the years in range [birth,year). Iterate over the hashmap to find the year with maximum count (A
|
its_gupta_ananya
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-09T07:17:59.533724+00:00
|
2021-05-09T07:17:59.533767+00:00
| 892 | false |
Approach :- Iterate over the array and store the frequencies of the years in range [birth,year). Iterate over the hashmap to find the year with maximum count (Also store the last saved count value along with the year for comparison).\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) {\n \n int n = logs.size();\n \n unordered_map<int,int> s;\n for(int i=0;i<n;++i){\n for(int k = logs[i][0]; k != logs[i][1];++k){\n s[k]++ ;\n }\n }\n \n int year = 0; //Stores the last year with maximum count\n int count = 0; //Stores count of last encountered max value\n \n for(auto it:s){\n if(it.second > count){\n count = it.second;\n year = it.first;\n }\n if(it.second == count){\n year = min(year,it.first);\n }\n } \n return year; \n }\n \n};\n```\n\nHope this helps!\nStay safe.
| 7 | 1 |
['C']
| 2 |
maximum-population-year
|
Prefix Sum with Range Updates
|
prefix-sum-with-range-updates-by-dixon_n-4thw
|
\n\n# Code\njava []\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n \n int[] year = new int[2051];\n \n\t\t// O(n) ->
|
Dixon_N
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-27T03:11:25.847615+00:00
|
2024-09-27T03:11:25.847642+00:00
| 682 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n \n int[] year = new int[2051];\n \n\t\t// O(n) -> n is log.length\n\t\t\n for(int[] log : logs){\n \n year[log[0]] += 1;\n year[log[1]] -= 1;\n }\n \n int maxNum = year[1950], maxYear = 1950;\n \n\t\t// O(100) -> 2050 - 1950 = 100\n\n for(int i = 1951; i < year.length; i++){\n year[i] += year[i - 1]; // Generating Prefix Sum\n \n if(year[i] > maxNum){\n maxNum = year[i];\n maxYear = i;\n }\n }\n \n return maxYear;\n }\n}\n```\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n Map<Integer, Integer> populationChange = new TreeMap<>();\n\n // Iterate through logs and record population changes\n for (int[] log : logs) {\n populationChange.put(log[0], populationChange.getOrDefault(log[0], 0) + 1); // +1 for birth year\n populationChange.put(log[1], populationChange.getOrDefault(log[1], 0) - 1); // -1 for death year\n }\n\n int maxNum = 0, maxYear = 0, currentPopulation = 0;\n\n // Traverse the TreeMap to calculate cumulative population and find the max\n for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : populationChange.entrySet()) {\n currentPopulation += entry.getValue();\n if (currentPopulation > maxNum) {\n maxNum = currentPopulation;\n maxYear = entry.getKey();\n }\n }\n\n return maxYear;\n }\n}\n\n```\n<br/>\n<br/><br/>\n\n---\n\n<br/><br/>\n\n\n### Difference Array or Prefix Sum with Range Updates Technique\n\nThis technique is called the **"Difference Array"** or **"Prefix Sum with Range Updates"**. It is commonly used to efficiently handle range updates and compute cumulative effects over a period.\n\n#### How it works:\nIn problems where we need to track changes over a range (e.g., years), this technique allows marking the beginning and the end of an effect (like population increase or decrease). \n\n#### Steps:\n1. **Range Update**: \n - For an event that starts at `yearStart` and ends at `yearEnd`, you:\n - Increase the value at `yearStart` by a certain amount (e.g., population `+1` for a birth year).\n - Decrease the value at `yearEnd` by the same amount (e.g., population `-1` for a death year).\n\n2. **Prefix Sum Calculation**: \n - After marking the changes, you calculate the prefix sum (cumulative effect) to get the actual values year by year. This accumulates the effect from previous years and applies it progressively.\n\n#### Why Use This Technique?\nInstead of updating every year between `yearStart` and `yearEnd` individually (which would be inefficient), you mark only the boundaries and compute the cumulative sum afterward. This reduces the time complexity of range updates to **O(1)** per event, followed by a **single pass** to calculate the final values.\n\n#### Use Cases:\n- **Population Change Problems** (like the problem shared).\n- **Range Addition Problems** (adding values to a subarray or interval).\n- **Scheduling Problems** (tracking activity over a period of time).\n\n#### In Your Code:\n- We marked the population changes by increasing the population by `+1` for births and decreasing it by `-1` for deaths.\n- Then, we used a prefix sum to accumulate population changes and find the year with the maximum population efficiently.\n\nBy using this technique, we optimized the solution for tracking changes over a range of years.\n
| 6 | 0 |
['Counting', 'Prefix Sum', 'Java']
| 5 |
maximum-population-year
|
Python || 97.44% Faster || O(N) Solution || Hashmap
|
python-9744-faster-on-solution-hashmap-b-moqk
|
\nclass Solution:\n def maximumPopulation(self, logs: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n a,n=[0]*101,len(logs)\n for birth,death in logs:\n
|
pulkit_uppal
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-07T22:05:17.732694+00:00
|
2022-12-07T22:06:39.618204+00:00
| 1,567 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def maximumPopulation(self, logs: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n a,n=[0]*101,len(logs)\n for birth,death in logs:\n a[birth-1950]+=1\n a[death-1950]-=1\n c=m=year=0\n for i in range(101):\n c+=a[i]\n if c>m:\n m=c\n year=i+1950\n return year\n```\n\n**An upvote will be encouraging**
| 6 | 0 |
['Array', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
Clear Java 0ms implementation with comments
|
clear-java-0ms-implementation-with-comme-5u26
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n final int[] popChange = new int[2050-1950+1];\n for (int i = 0; i < logs.le
|
53296
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-09T04:05:14.331813+00:00
|
2021-05-09T04:43:22.952428+00:00
| 346 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n final int[] popChange = new int[2050-1950+1];\n for (int i = 0; i < logs.length; i++) {\n popChange[logs[i][0]-1950] += 1;\n popChange[logs[i][1]-1950] -= 1;\n }\n \n // Find the year that maximizes the sum of popChange from 0 to the year\n // i.e. max_x(popChange[0..x])\n int maxPop = -1;\n int bestYear = -1;\n int lastYearPop = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < popChange.length; i++) {\n final int currentYearPop = lastYearPop + popChange[i];\n if (currentYearPop > maxPop) {\n maxPop = currentYearPop;\n bestYear = 1950 + i;\n }\n lastYearPop = currentYearPop;\n }\n return bestYear;\n }\n}\n```
| 6 | 4 |
[]
| 1 |
maximum-population-year
|
Hindi Explanation with Comments | Prefix Sum
|
hindi-explanation-with-comments-prefix-s-1jh1
|
\n# Code\njava []\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int[] arr = new int[101];\n for(int[] log : logs) {\n
|
btwitsrohit
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-31T13:20:43.680524+00:00
|
2024-09-05T00:28:07.891932+00:00
| 273 | false |
\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int[] arr = new int[101];\n for(int[] log : logs) {\n int birth = log[0];\n int death = log[1];\n arr[birth-1950]++;\n arr[death-1950]--;\n }\n\n int max = arr[0];\n int year = 1950;\n for(int i = 1 ; i < 101; i++) {\n arr[i] += arr[i-1];\n if(arr[i] > max) {\n max = arr[i];\n year = 1950 + i;\n }\n }\n return year;\n }\n}\n```\n\n# Let\'s Understand\n\n class Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n // Step 1: Array initialize karte hain, size 101 hai kyunki 1950 se le kar 2050 tak ke saal cover karne hain\n int[] arr = new int[101];\n \n // Step 2: Logs ko iterate karke population changes track karte hain\n for (int[] log : logs) {\n int birth = log[0]; // Birth year ko fetch karte hain\n int death = log[1]; // Death year ko fetch karte hain\n arr[birth - 1950]++; // Birth year ke corresponding index ko increment karte hain\n arr[death - 1950]--; // Death year ke corresponding index ko decrement karte hain\n }\n\n // Step 3: Maximum population find karne ke liye initialization\n int max = arr[0]; // 1950 ka population initial maximum population hai\n int year = 1950; // Initial year 1950 hai\n // Year-by-year cumulative sum nikal kar maximum population find karte hain\n for (int i = 1; i < 101; i++) {\n arr[i] += arr[i - 1]; // Current year ki population calculate karte hain previous year ki population se\n // Agar current year ka population maximum se zyada hai, to update karte hain maximum aur year\n if (arr[i] > max) {\n max = arr[i];\n year = 1950 + i;\n }\n }\n\n // Step 4: Maximum population wale year ko return karte hain\n return year;\n }\n }\n
| 5 | 0 |
['Prefix Sum', 'Java']
| 1 |
maximum-population-year
|
Java Simple solution with explanation in comments
|
java-simple-solution-with-explanation-in-ok5o
|
Please up vote if you like :)\n\nBrute force approach :\nTime Complexity : O(n^2)\nSpace Complexity : O(n)\n\n\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulati
|
SahilRathod
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-27T14:20:52.503094+00:00
|
2022-08-27T14:48:50.902507+00:00
| 781 | false |
Please up vote if you like :)\n\nBrute force approach :\nTime Complexity : O(n^2)\nSpace Complexity : O(n)\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n \n //constraints 1 <= logs.length <= 100 and 1950 <= birthi < deathi <= 2050\n //so max years we can have is 2050 - 1950 = 100\n //so create an array for storing population in given years\n int[] arr = new int[101];\n \n //first check logs\n for(int i=0;i<logs.length;i++){\n //checking only birthi to deathi(excluding)\n for(int j =logs[i][0];j<logs[i][1];j++){\n //counting population\n arr[j-1950]++;\n }\n }\n \n \n int maxPopulationYear = 0;\n int maxPopulation = 0;\n //now checking in arr \n for(int i = 0;i<101;i++){\n //highest and earliest arr[i] will be our maximum population , and i wil be year \n if(maxPopulation < arr[i]){\n maxPopulation = arr[i];\n //max population year + 1950\n maxPopulationYear = i + 1950;\n }\n }\n return maxPopulationYear;\n }\n}\n```\n\nUsing running sum of array :\nTime Complexity : O(n)\nSpace Complexity : O(1)\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n \n int [] arr = new int[101];\n \n for(int i=0;i<logs.length;i++){\n arr[logs[i][0] - 1950]++;\n arr[logs[i][1] - 1950]--;\n }\n \n for(int i = 1;i<101;i++){\n arr[i] += arr[i-1];\n }\n \n int maxPopulation = 0;\n int year = 0;\n for(int i = 0;i<101;i++){\n if(arr[i] > maxPopulation){\n maxPopulation = arr[i];\n year = i + 1950;\n }\n }\n return year;\n }\n}\n```\n
| 5 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
maximum-population-year
|
JAVA Solution | Short and simple
|
java-solution-short-and-simple-by-mahita-bbn9
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) \n {\n int[] arr = new int[101];\n for(int i=0;i<logs.length;i++)\n {
|
mahitakhandelwal
|
NORMAL
|
2021-08-23T16:53:05.384426+00:00
|
2021-08-23T16:53:05.384491+00:00
| 366 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) \n {\n int[] arr = new int[101];\n for(int i=0;i<logs.length;i++)\n {\n for(int s=logs[i][0];s<logs[i][1];s++)\n {\n arr[s-1950]++;\n } \n }\n \n int max=0;\n for(int i=0;i<101;i++)\n {\n if(arr[i]>arr[max])\n max=i;\n }\n return max+1950;\n }\n}\n\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
C++ simple & fast solution (faster than 100%)
|
c-simple-fast-solution-faster-than-100-b-wyuk
|
\n// Elharem Soufiane\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) {\n int max = 0, earliest_year;\n vector<in
|
selharem
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-13T16:48:09.501669+00:00
|
2021-05-13T16:48:09.501715+00:00
| 777 | false |
```\n// Elharem Soufiane\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) {\n int max = 0, earliest_year;\n vector<int> years(101);\n for(vector<int> log : logs){\n for(int year = log[0]; year< log[1]; year++)\n years[year - 1950]++;\n }\n for(int year=0 ; year <= 100; year++){\n if(years[year] > max){\n max = years[year] ;\n earliest_year = year;\n } \n }\n return earliest_year + 1950;\n }\n};\n```
| 5 | 1 |
['Array', 'C', 'C++']
| 1 |
maximum-population-year
|
Sweep Line Algorithm with Explanation
|
sweep-line-algorithm-with-explanation-by-rryf
|
This is a clasic sweep line algorithm.\n\n1. Get all births and deaths in sorted array/map;\n2. Now if its a birth, then increment and if its a death then decre
|
randomguid
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-09T04:51:50.090300+00:00
|
2021-05-09T04:51:50.090337+00:00
| 3,454 | false |
This is a clasic sweep line algorithm.\n\n1. Get all births and deaths in sorted array/map;\n2. Now if its a birth, then increment and if its a death then decrement;\n3. And keep count of the population while doing so. Result is the max population.\n\nAs a reference, here are few more problems that could be solved by sweep line:\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/my-calendar-iii/submissions/\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/employee-free-time/submissions/\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/meeting-scheduler/submissions/\n\n\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public int MaximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n \n var map = new SortedDictionary<int, int>();\n var res = 0;\n var maxPop = 0;\n var sum = 0;\n \n foreach(var log in logs) {\n if(!map.ContainsKey(log[0])) map.Add(log[0], 0);\n map[log[0]]++;\n if(!map.ContainsKey(log[1])) map.Add(log[1], 0);\n map[log[1]]--;\n }\n\n foreach(var key in map.Keys){\n \n sum += map[key];\n \n if(sum > maxPop) {\n maxPop = sum;\n res = key;\n }\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 5 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
Java Line Sweep
|
java-line-sweep-by-wushangzhen-hbfc
|
Similiar to the meeting room problem\n\nclass Pair {\n public int year;\n public int birth;\n public Pair(int year, int birth) {\n this.year = y
|
wushangzhen
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-09T04:04:58.804456+00:00
|
2021-05-09T04:07:11.255699+00:00
| 403 | false |
Similiar to the `meeting room` problem\n```\nclass Pair {\n public int year;\n public int birth;\n public Pair(int year, int birth) {\n this.year = year;\n this.birth = birth;\n }\n}\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n ArrayList<Pair> list = new ArrayList<>();\n for (int[] log : logs) {\n list.add(new Pair(log[0], 1));\n list.add(new Pair(log[1], -1));\n }\n Collections.sort(list, (a, b) -> (a.year == b.year ? a.birth - b.birth : a.year - b.year));\n int max = 0;\n int year = 0;\n int count = 0;\n for (Pair p : list) {\n if (p.birth == 1) {\n count++;\n } else {\n count--;\n }\n if (count > max) {\n max = count;\n year = p.year;\n }\n }\n return year;\n }\n}\n```
| 5 | 3 |
[]
| 2 |
maximum-population-year
|
Simple LOGIC : Brute Force : Easy To Understand
|
simple-logic-brute-force-easy-to-underst-nk7t
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe problem at hand is to find the year with the maximum population based on a given se
|
Haari_Johns
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-27T17:45:53.428785+00:00
|
2023-11-27T17:45:53.428812+00:00
| 195 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe problem at hand is to find the year with the maximum population based on a given set of birth and death logs. The solution approaches this by simulating the population growth and decline over the years.\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1.Initialization:\nint[] population = new int[101];: Initializes an array called population with 101 elements to represent the population count for each year from 1950 to 2050.\n\n2.Population Counting:\n-> for(int i=0; i<logs.length; i++) { ... }: Iterates through each log entry in the logs array.\n-> int x = logs[i][0] - 1950; int y = logs[i][1] - 1950;: Calculates the birth and death years relative to 1950.\n-> for(int a=x; a<y; a++) { population[a]++; }: Increments the population count for each year within the lifespan of an individual.\n\n3.Finding Maximum Population:\n-> int populationCount = 0; int maxYear = 0;: Initializes variables to store the maximum population count and the year with the maximum population.\n-> for(int i=0; i<101; i++) { ... }: Iterates through each year in the population array.\n-> if(population[i] > populationCount) { populationCount = population[i]; maxYear = i + 1950; }: Updates populationCount and maxYear if the population count for the current year is greater than the current maximum.\n\n4.Result:\n->return maxYear;: Returns the year with the maximum population based on the processed logs.\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int[] population=new int[101];\n for(int i=0;i<logs.length;i++){\n int x=logs[i][0]-1950;\n int y=logs[i][1]-1950;\n for(int a=x;a<y;a++){\n population[a]++;\n }\n }\n int populationcount=0,maxyear=0;\n for(int i=0;i<101;i++){\n if(population[i]>populationcount){\n populationcount=population[i];\n maxyear=i+1950;\n }\n }\n return maxyear;\n }\n}\n\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
maximum-population-year
|
Python3 O(N)
|
python3-on-by-jbirara-ufii
|
Intuition\nThe "Maximum Population Year" problem involves finding the year with the maximum population based on a list of birth and death years of individuals.
|
jbirara
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-29T09:41:53.814756+00:00
|
2023-10-29T09:41:53.814776+00:00
| 427 | false |
# Intuition\nThe "Maximum Population Year" problem involves finding the year with the maximum population based on a list of birth and death years of individuals. The intuition is to create a timeline and track the changes in population over the years to determine the year with the highest population.\n\n# Approach\nTo solve this problem, we adopt the following approach:\n\n1. Initialize a list `res` of size 101 (representing years from 1950 to 2050) with all elements set to 0. This list will be used to track population changes.\n\n2. Iterate through each pair of birth and death years in the `logs` list. For each pair, perform the following steps:\n - Adjust the birth year by subtracting 1950 to map it to the index in the `res` list (e.g., 1950 maps to index 0).\n - Adjust the death year similarly.\n - Increment the population count at the birth year index in the `res` list.\n - Decrement the population count at the death year index in the `res` list.\n\n3. Create a variable `num` and initialize it to 0. This variable will store the maximum population count.\n\n4. Iterate through the `res` list from index 1 to 100 (representing years 1951 to 2050). For each year, update the population count by adding the population count from the previous year. This step effectively creates a cumulative population count over the years.\n\n5. Find the maximum population count in the `res` list and store it in the `num` variable.\n\n6. Return the year corresponding to the maximum population count by finding its index in the `res` list and adding 1950 to map it back to the actual year.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: The time complexity is O(n), where \'n\' is the number of pairs in the `logs` list. We iterate through the list once to calculate population changes.\n- Space complexity: The space complexity is O(1) because the `res` list has a fixed size of 101, and we use a constant amount of extra space.\n\n# Code\n```python\nclass Solution:\n def maximumPopulation(self, logs: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n res = [0] * (100 + 1)\n\n for birth, death in logs:\n birth -= 1950\n death -= 1950\n\n res[birth] += 1\n res[death] -= 1\n\n for i in range(1, 100):\n res[i] += res[i - 1]\n\n num = max(res)\n\n return res.index(num) + 1950\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Line Sweep', 'Prefix Sum', 'Python3']
| 1 |
maximum-population-year
|
C++ || 0 ms || Line Sweep Algorithm
|
c-0-ms-line-sweep-algorithm-by-prabhashb-pfls
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) \n {\n // make a population array to store the number of peopl
|
prabhashbhajani
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-04T10:35:36.572004+00:00
|
2023-10-04T10:37:23.350590+00:00
| 686 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) \n {\n // make a population array to store the number of people alive in the given year\n vector<int> population(101, 0);\n int sum = 0;\n int maxi = INT_MIN;\n int ans;\n\n for(int i=0; i<logs.size(); i++)\n {\n // adding 1 to the birth year of the person\n population[logs[i][0] - 1950] += 1;\n // subtracting 1 from the death year of the person\n population[logs[i][1] - 1950] -= 1;\n }\n\n // same as the prefix sum\n // if a person was born in a specific year then he will be counted in the population till the year he dies.\n for(int i=0; i<population.size(); i++)\n {\n sum += population[i];\n \n if(sum > maxi)\n {\n maxi = sum;\n ans = i + 1950;\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Line Sweep', 'C++']
| 1 |
maximum-population-year
|
O(N) Optimized And Easy To Understand Code
|
on-optimized-and-easy-to-understand-code-jyz5
|
1. O(n) Optimized Code\n#### Approach\nStoring the population of all the year in an array of size 101 from year=1950 to year=2050. Now finding the earliest year
|
Aman__Bhardwaj
|
NORMAL
|
2023-05-28T12:52:53.611311+00:00
|
2023-05-28T12:52:53.611340+00:00
| 1,419 | false |
# 1. O(n) Optimized Code\n#### Approach\nStoring the population of all the year in an array of size 101 from year=1950 to year=2050. Now finding the earliest year having the maximum population.\n\n#### Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n * 101)\n\n- Space complexity: O(101) ~ O(1)\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int[] population = new int[101];\n for(int year=1950;year<=2050;year++){\n population[year-1950] = countPopulation(logs,year);\n }\n int minYear = Integer.MAX_VALUE, maxPopulation = Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n for(int index=100;index>=0;index--){\n int population_ = population[index];\n if(population_>=maxPopulation){\n minYear = index+1950;\n maxPopulation = population_;\n }\n }\n return minYear;\n }\n\n // Method to find the population in any given year. ...... O(n)\n private static int countPopulation(int[][] logs, int year){\n int count = 0;\n for(int[] person : logs){\n int birth = person[0], death = person[1];\n if(birth<=year && year<death) count++;\n }\n return count;\n }\n}\n\n// Time Complexity : O(n*100)\n// Space Complecity : O(101) ~ O(1)\n\n// 1950 - 2050\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Counting Sort', 'Java']
| 1 |
maximum-population-year
|
Runs 100% - easy understanding solution with comments
|
runs-100-easy-understanding-solution-wit-h36c
|
Always try to bring the complexity down by gathering requirements, here we used arrays of size 101, as the year is from 1950 to 2050\n\nUpvote if you like this
|
v_suresh
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-09T04:23:59.421409+00:00
|
2022-04-09T04:23:59.421450+00:00
| 442 | false |
Always try to bring the complexity down by gathering requirements, here we used arrays of size 101, as the year is from 1950 to 2050\n\nUpvote if you like this solution!\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n \n //we know the input is from 1950 to 2050\n //index 0 is 1950, 1 is 1951 and so on..\n int[] populationAtYear = new int[101];\n \n \n //max year population setting it to 1950, as thats the starting year as per question\n int maxYearPopulation=1950;\n \n //maintaining no. of people born and dead at a particular year\n //if its positive we have people alive, if negative we have more death in that year\n for(int i=0;i<logs.length;i++){\n \n int birthYear = logs[i][0];\n int deathYear = logs[i][1];\n \n populationAtYear[birthYear-1950]++;\n populationAtYear[deathYear-1950]--;\n }\n \n //Set maxPopulation to 1st value\n int maxPopulation=populationAtYear[0];\n \n //lets start from index 1 and iterate over the array we formed which has total people alive/dead at a year\n for(int i=1;i<populationAtYear.length;i++){\n \n //accumulate the sum at each year and see if maxPopulation is less than newly commuted population \n populationAtYear[i]=populationAtYear[i]+populationAtYear[i-1];\n \n \n //keep tracking year and population\n if(maxPopulation<populationAtYear[i]){\n maxPopulation=populationAtYear[i];\n maxYearPopulation=1950+i;\n }\n }\n \n return maxYearPopulation;\n }\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Array', 'Prefix Sum', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
C++ Line Sweep O(N) 4 Lines (Using std::algorithm)
|
c-line-sweep-on-4-lines-using-stdalgorit-mpsf
|
Let\'s use this as an input:\n Input: logs = [[1993, 1995],[1994, 1996]]\n\tOutput: 1994\n\nIn the first line of code, I made an array of 101 elements initia
|
andrew_macatangay
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-17T02:25:34.645765+00:00
|
2021-06-09T19:47:03.695822+00:00
| 223 | false |
Let\'s use this as an input:\n Input: logs = [[1993, 1995],[1994, 1996]]\n\tOutput: 1994\n\nIn the first line of code, I made an array of 101 elements initialized to 0 since the years are given as 1950 <= birth_i < death_i <= 2050 as given in the constraints.\n\nThe second line of code will increment the index of logs[x][0] - 1950 if we have a birth, and decrement the index of logs[x][1] - 1950 if we have a death.\n\nIn our example above, we would end up with a table like this:\n```\n0 ... 1 1 -1 -1 ... 0\n1950 ... 1993 1994 1995 1996 ... 2050\n```\n\nSince a single person was born in 1993 and 1994, we mark those years as 1. Since those people died in 1995 and 1996, we mark those years as -1.\n\nThe third line of code will get the prefix sum; also known as the [partial sum](https://www.cplusplus.com/reference/numeric/partial_sum/). Our table will look like this afterwards:\n```\n0 ... 1 2 1 0 ... 0\n1950 ... 1993 1994 1995 1996 ... 2050\n```\n\nBy doing this, we are able to see which year the maximum number of people were alive in.\n\nThe last line will find the [max element](https://www.cplusplus.com/reference/algorithm/max_element/) of the array (an iterator to the first maximum element will be returned), and it\'s distance from the beginning of the array will be found. In our example, max_element would point to index 44. The distance from the beginning (index 0) to index 44, is 44. We then add this to 1950 to get 1994, which is our solution.\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) {\n vector<int> arr(101, 0);\n for (int x = 0; x < logs.size(); arr[logs[x][0] - 1950]++, arr[logs[x][1] - 1950]--, x++);\n partial_sum(arr.begin(), arr.end(), arr.begin());\n return 1950 + distance(arr.begin(), max_element(arr.begin(), arr.end()));\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 1 |
[]
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
Solution that beasts 100% in javascript
|
solution-that-beasts-100-in-javascript-b-r3wy
|
So I submitted a solution for this problem which beats 100% (Maybe because it is the first solution submitted written in javascript?)\n\nSo here is my thought
|
Boubaker93
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-09T16:08:13.441153+00:00
|
2021-05-09T19:45:20.411222+00:00
| 395 | false |
So I submitted a solution for this problem which beats 100% (Maybe because it is the first solution submitted written in javascript?)\n\nSo here is my thought process of how i solved this problem: If we look deeply into the problem, we can find that if we draw the timeline of the persons on top of each others we will notice that the **earliest year of the maximum population will always be the birthday of a person.**\n\nFor example given logs : [[1950,1960],[1955,1970],[1945,1958],[1953,1970]] we can get this graph:\n\n\n\n\n\n\nThe solution that I came up with is pretty easy; now all we need to do is to **iterate through the birthdays** and **calculate how many people are alive in that particular year.** then we save that information in an object containing the year as a key and the number of persons alive as a value.\n\nThe **result** then will be **the minimum key with the biggest value**.\n\nWe also need to be carful to not iterate through the same year twice.\n\nThe best result for the code below is **72ms / 38.9 MB** (beats 100% / 100%).\n```\nvar maximumPopulation = function (logs) {\n let results = {};\n for (let i = 0; i < logs.length; i++)\n if (!results[logs[i][0]])\n for (let j = 0; j < logs.length; j++)\n if (logs[i][0] >= logs[j][0] && logs[i][0] < logs[j][1])\n results[logs[i][0]] = (results[logs[i][0]] ? results[logs[i][0]] : 0) + 1;\n\n return Object.keys(results).sort((a, b) => results[b] - results[a])[0];\n};\n```\nAnd please give me feedback about the solution and how to improve it!\nThanks.
| 4 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
c++, easy using array
|
c-easy-using-array-by-krishnendra007-pb6u
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumPopulation(vector>& log) {\n int arr[2051]={0};\n \n for(int i=0;i<log.size();i++){\n
|
krishnendra007
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-09T04:16:12.558887+00:00
|
2021-05-09T06:27:54.732736+00:00
| 325 | false |
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& log) {\n int arr[2051]={0};\n \n for(int i=0;i<log.size();i++){\n int a=log[i][0];\n int b=log[i][1];\n \n for(int j=a;j<b;j++) arr[j]++;\n }\n \n int maxv=0;\n int val=-1;\n for(int i=1950;i<=2050;i++) {\n if(arr[i]>maxv){\n maxv=arr[i];\n val=i;\n }\n }\n \n return val;\n }\n};\n
| 4 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
maximum-population-year
|
Easiest SOlution Ever
|
easiest-solution-ever-by-ameyapradippotd-lj6q
|
\nclass Solution\n{\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) \n {\n int[] ans = new int[2050];\n for(int[] log : logs)\n {\n
|
ameyapradippotdar
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-09T04:00:53.241225+00:00
|
2021-05-09T04:00:53.241274+00:00
| 451 | false |
```\nclass Solution\n{\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) \n {\n int[] ans = new int[2050];\n for(int[] log : logs)\n {\n ans[log[0] - 1950] += 1;\n ans[log[1] - 1950] -= 1;\n }\n int max_pop=0;\n int max_pop_idx=0;\n int population=0;\n for(int i=0;i<ans.length;i++)\n {\n population += ans[i];\n if(population > max_pop)\n {\n max_pop = population;\n max_pop_idx = i;\n }\n }\n return (1950 + max_pop_idx);\n }\n}\n```
| 4 | 3 |
[]
| 1 |
maximum-population-year
|
Python3 || Beats 100% 🌟🔥|| Prefix Sum || Line sweep algorithm 💡
|
python3-beats-100-prefix-sum-line-sweep-5twmh
|
IntuitionThe problem asks us to find the year with the most people alive based on their birth and death years. Instead of counting the population year by year (
|
anushkambtech
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-05T07:55:57.139630+00:00
|
2025-01-05T07:56:38.582694+00:00
| 579 | false |
### **Intuition**
The problem asks us to find the year with the most people alive based on their birth and death years. Instead of counting the population year by year (which is slow), we can track how the population changes at each year using an array. This way, we calculate the population in one pass.
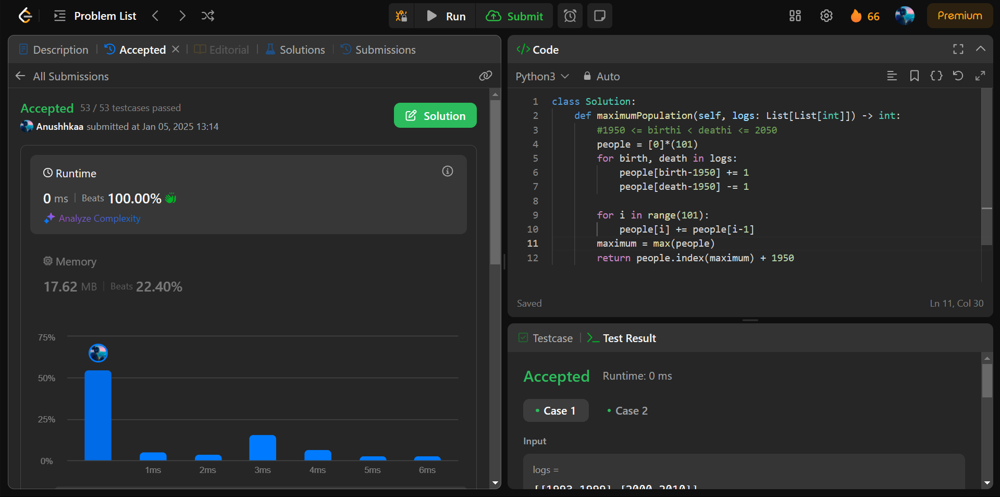
---
### **Approach**
1. **Create an Array for Years:**
- Use an array `people` of size 101, where each index represents the years from 1950 to 2050. For example, index `0` is 1950, index `1` is 1951, and so on.
2. **Mark Population Changes:**
- For each log `[birth, death]`, add `1` to the year of birth (`people[birth - 1950]`) and subtract `1` from the year of death (`people[death - 1950]`). This marks when people are born and when they die.
3. **Calculate Total Population:**
- Use a prefix sum to calculate the total population for each year. This means adding up the changes year by year so that each index in the array shows the total population for that year.
4. **Find the Year with the Most People:**
- Find the maximum value in the array. The index of this value tells us which year had the most people. Convert it back to the actual year (`index + 1950`).
---
### **Complexity**
- **Time Complexity:**
- \(O(n)\) to update the array for all logs.
- \(O(101)\) to calculate the prefix sum and find the maximum.
- Overall: \(O(n)\) for large \(n\).
- **Space Complexity:**
- \(O(101)\) for the `people` array.
- This is small and treated as \(O(1)\) constant space.
---
### **Code**
```python
class Solution:
def maximumPopulation(self, logs: List[List[int]]) -> int:
# Create an array to track population changes
people = [0] * 101 # 1950 to 2050 = 101 years
# Mark population changes for each log
for birth, death in logs:
people[birth - 1950] += 1 # A person is born
people[death - 1950] -= 1 # A person dies
# Calculate the total population for each year
for i in range(1, 101):
people[i] += people[i - 1]
# Find the year with the maximum population
max_population = max(people)
return people.index(max_population) + 1950
```
---
Happy coding
:)
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Prefix Sum', 'Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
SIMPLE PREFIX SUM + DIFFERENCE ARRAY C++ SOLUTION
|
simple-prefix-sum-difference-array-c-sol-tggs
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Jeffrin2005
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-30T08:55:28.719451+00:00
|
2024-07-30T08:55:28.719477+00:00
| 574 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:o(m) where m is the no of logs \n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:o(1)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs){\n vector<int>pref(2054);\n for(auto&x : logs){\n pref[x[0]]++;\n pref[x[1]]--;\n }\n int maxi = 0;\n int year = 0; \n pref[0] = 0;\n for(int i=1; i<pref.size(); i++){\n pref[i]+=pref[i-1];\n }\n for(int i=1950; i<=2050; i++){\n if(pref[i] > maxi){\n maxi = pref[i];\n year = i; \n }\n }\n return year;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['C++']
| 3 |
maximum-population-year
|
❇ maximum-population-year👌 🏆O(N)❤️ Javascript🎯 Memory👀16.15%🕕 ++Explanation✍️ 🔴🔥 ✅ 👉 💪🙏
|
maximum-population-year-on-javascript-me-3683
|
Time Complexity: O(N)\nSpace Complexity: O(100) =~ O(1)\n\n\n\nvar maximumPopulation = function (logs) {\n const yearToFrequencyMapping = {};\n const freq
|
anurag-sindhu
|
NORMAL
|
2024-05-20T08:42:10.308361+00:00
|
2024-05-20T08:42:10.308386+00:00
| 395 | false |
Time Complexity: O(N)\nSpace Complexity: O(100) =~ O(1)\n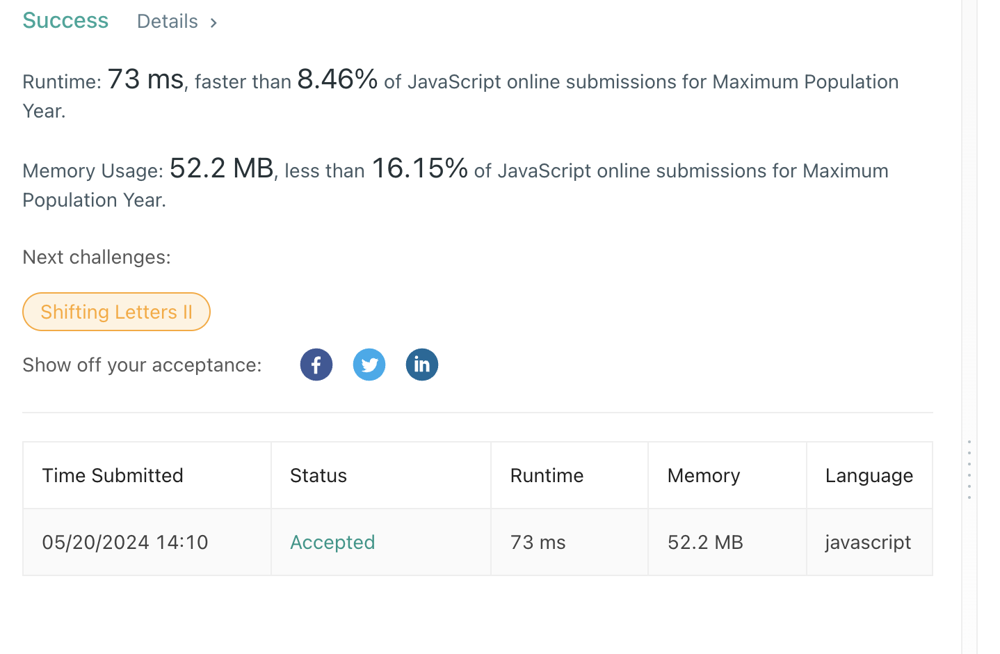\n\n```\nvar maximumPopulation = function (logs) {\n const yearToFrequencyMapping = {};\n const frequencyToLowestYearMapping = {};\n let maxFrequency = -Infinity;\n for (const iterator of logs) {\n const [from, to] = iterator;\n for (let index = from; index < to; index++) {\n const element = yearToFrequencyMapping[index];\n if (!yearToFrequencyMapping[index]) {\n yearToFrequencyMapping[index] = 0;\n }\n yearToFrequencyMapping[index] += 1;\n }\n }\n\n for (const key in yearToFrequencyMapping) {\n if (maxFrequency < yearToFrequencyMapping[key]) {\n maxFrequency = yearToFrequencyMapping[key];\n }\n if (!frequencyToLowestYearMapping[yearToFrequencyMapping[key]]) {\n frequencyToLowestYearMapping[yearToFrequencyMapping[key]] = Infinity;\n }\n let temp = Number(key);\n if (frequencyToLowestYearMapping[yearToFrequencyMapping[key]] > temp) {\n frequencyToLowestYearMapping[yearToFrequencyMapping[key]] = temp;\n }\n }\n\n return frequencyToLowestYearMapping[maxFrequency];\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
C++ solution || Beginner-friendly approach || Line-sweep
|
c-solution-beginner-friendly-approach-li-h1lv
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nWe first put +1 and -1 for birth and death year of a person. We then traverse the array
|
prathams29
|
NORMAL
|
2023-06-24T05:14:09.768670+00:00
|
2023-06-24T05:14:09.768710+00:00
| 664 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nWe first put +1 and -1 for birth and death year of a person. We then traverse the array and sum the values to find the year with maximum population.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) {\n int pop[2051] = {}, res = 0;\n for (auto &l : logs) {\n ++pop[l[0]];\n --pop[l[1]];\n }\n for (auto i = 1950; i < 2050; ++i) {\n pop[i] += pop[i - 1];\n res = pop[i] > pop[res] ? i : res;\n }\n return res;\n}\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
Simple prefix-sum solution | C# | +96% efficient
|
simple-prefix-sum-solution-c-96-efficien-eo9l
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nEvery log indicates a birth and death year of a person. We need to calculate for every
|
Baymax_
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-27T08:57:43.159803+00:00
|
2023-03-27T08:58:22.780306+00:00
| 116 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nEvery log indicates a birth and death year of a person. We need to calculate for every year how many people are alive.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nWe\'ll create a prefix sum of population over the years - in a given year how many people are alive (B-D -> born on same year or previous year - died this year)\n\n### Please upvote if you liked the simplicity of the solution\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n)\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(1)\n\n# Code\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public int MaximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int[] population = new int[101];\n foreach (var log in logs)\n {\n population[log[0] - 1950]++;\n population[log[1] - 1950]--;\n }\n Console.WriteLine("here..");\n\n int maxYear = 0;\n for (int i = 1; i < population.Length; i++)\n {\n population[i] += population[i - 1];\n maxYear = population[i] > population[maxYear] ? i : maxYear;\n }\n\n return (1950 + maxYear);\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Counting', 'C#']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
Maximum overlapping intervals
|
maximum-overlapping-intervals-by-jerry42-hqor
|
\nLogic is pretty simple\n\n- Create a Min heap with an Int[] array. This will be a 2 dimentional array which will store the year and population increment/decre
|
Jerry420
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-25T00:18:52.678258+00:00
|
2022-08-25T00:19:08.687451+00:00
| 169 | false |
\nLogic is pretty simple\n\n- Create a Min heap with an `Int[]` array. This will be a 2 dimentional array which will store the `year` and `population increment/decrement`\n- Go through the list of intervals (all the people) and follow these \n\t* When an interval starts (Person is born) add `[Year, +1]` to min heap\n\t* When an interval ends (Person is dead) add `[Year, -1]` to min heap\n\nAfter this, we iterate through the heap and calculate the population like\n```java\n public int solution(List<Person> people) {\n\n Queue<int[]> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();\n for (Person p : people) {\n // When interval starts we add 1 to total interval count\n queue.add(new int[]{p.birth, 1});\n // When interval ends we remove 1 from total interval count\n queue.add(new int[]{p.death, -1});\n }\n\n int currentPopulation = 0;\n int maxPopulation = 0;\n int year = 0;\n\n while (!queue.isEmpty()) {\n int[] poll = queue.poll();\n currentPopulation += poll[1];\n if (currentPopulation > maxPopulation) {\n maxPopulation = currentPopulation;\n year = poll[0];\n }\n }\n return year;\n\n }\n```\n
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
JAVA 2ms 99.53% less memory easy solution O(1) space
|
java-2ms-9953-less-memory-easy-solution-8qsha
|
\nPlease Upvote if you find this helpful\n\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int recentMaxPopulation = 0;\n in
|
nesarptr
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-03T14:04:52.503206+00:00
|
2022-04-03T14:04:52.503250+00:00
| 195 | false |
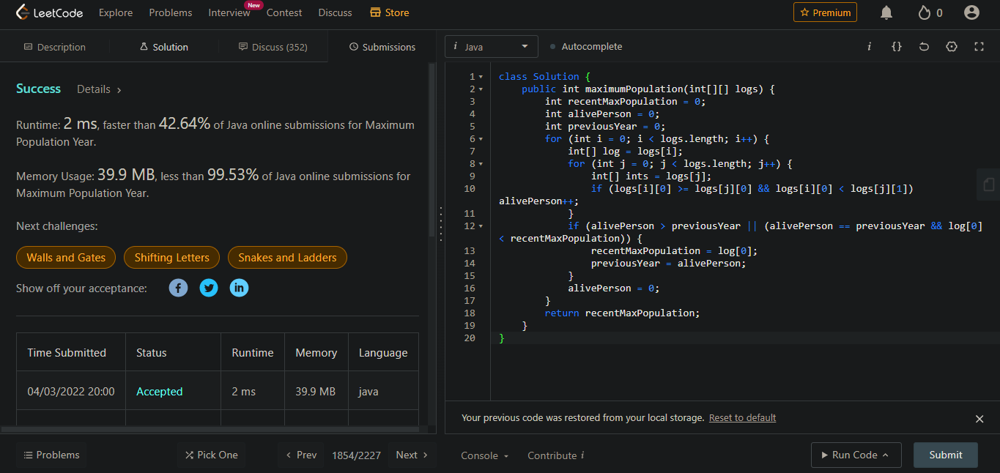\n***Please Upvote if you find this helpful***\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int recentMaxPopulation = 0;\n int alivePerson = 0;\n int previousYear = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < logs.length; i++) {\n int[] log = logs[i];\n for (int j = 0; j < logs.length; j++) {\n int[] ints = logs[j];\n if (logs[i][0] >= logs[j][0] && logs[i][0] < logs[j][1]) alivePerson++;\n }\n if (alivePerson > previousYear || (alivePerson == previousYear && log[0] < recentMaxPopulation)) {\n recentMaxPopulation = log[0];\n previousYear = alivePerson;\n }\n alivePerson = 0;\n }\n return recentMaxPopulation;\n }\n}\n```\n***please Upvote if you find this helpful***\n
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Java']
| 1 |
maximum-population-year
|
0 ms, faster than 100.00% of Java online submissions o(n) Solution
|
0-ms-faster-than-10000-of-java-online-su-1htt
|
Runtime: 0 ms, faster than 100.00% of Java online submissions for Maximum Population Year.\nMemory Usage: 36.6 MB, less than 96.04% of Java online submissions f
|
gautammali_740
|
NORMAL
|
2021-08-25T10:15:03.371535+00:00
|
2021-09-11T11:11:30.814496+00:00
| 685 | false |
**Runtime: 0 ms, faster than 100.00% of Java online submissions for Maximum Population Year.\nMemory Usage: 36.6 MB, less than 96.04% of Java online submissions for Maximum Population Year.**\nhere is the expalnation :\nhere the array is given of [[1993,1999],[2000,2010]]\nso what i do is according to this \n1 <= logs.length <= 100\n1950 <= birthi < deathi <= 2050\nlogs[0] and log[1] is bitween 1950 t0 2050 that mean 2050-1950 =100;\nso i ceated year array of 101 size;\nthan \nlog[0]=1993\nso year[1993-1950]=43 so year[43]=1;\nlog[1]=1999\nyear[1999-1950]=49 so year[49]= -1;\nfor second array \nlog[0]=2000\nyear[2000-1950]=50 so year[50]=1;\nlog[1]=2010\nyear[2010-1950]=60 year[60]=-1;\nnow i took maxnum=year[0] and maxYear=1950\nbecause posibility is the maximmum year can not after tha 1950 and maxnum can\'t less than 0\nthan start from 1 and add previsous value and check if max \nand i started from 1 and go till 100 and add 1950 so i get that exget year\n```\npublic int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int[] year=new int[101];\n for(int[] log:logs){\n year[log[0]-1950]++;\n year[log[1]-1950]--;\n }\n int maxNum=year[0],maxYear=1950;\n for(int i=1;i<year.length;i++){\n year[i] += year[i-1];\n if(year[i]>maxNum){\n maxNum=year[i];\n maxYear=i+1950;\n }\n }\n return maxYear;\n }\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 2 |
maximum-population-year
|
Range Addition
|
range-addition-by-himanshuchhikara-f8fi
|
CODE:\n\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int[] year=new int[2051];\n \n for(int[] log:logs){\n year[log[0]]+=1;
|
himanshuchhikara
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-13T05:56:36.564260+00:00
|
2021-05-13T05:56:36.564295+00:00
| 214 | false |
CODE:\n```\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int[] year=new int[2051];\n \n for(int[] log:logs){\n year[log[0]]+=1;\n year[log[1]]-=1;\n }\n \n int maxPopulation=year[1950];\n int maxYear=1950;\n \n for(int i=1950;i<year.length;i++){\n year[i]+=year[i-1]; // prefixSum\n \n if(year[i]>maxPopulation){\n maxPopulation=year[i];\n maxYear=i;\n }\n }\n return maxYear;\n }\n```\n\nComplexity:\n\t`time:O(n) and space:O(2051)`
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
Python || Easy To Understand || Short ||
|
python-easy-to-understand-short-by-deepc-lzoj
|
Here we know that all years in input lies in a range of 1950-2050, so we can make an array of 101 size and for every persons lifespan increment the count by 1 f
|
deepcoder1
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-09T14:36:23.026247+00:00
|
2021-05-09T14:36:23.026281+00:00
| 121 | false |
**Here we know that all years in input lies in a range of 1950-2050, so we can make an array of 101 size and for every persons lifespan increment the count by 1 for his span in that range.\nIn the end we will return the index of max val + 1950**\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximumPopulation(self, logs: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n \n # As we have only 101 possible years, make an array for them.\n arr = [0]*101\n \n for x,y in logs:\n for i in range(x,y):\n # for a person living range increment array count by 1; accounting the life span of that person.\n arr[i-1950] += 1\n \n index = arr.index(max(arr))\n return index + 1950\n\t\t\n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
Rust - Sweep Line
|
rust-sweep-line-by-idiotleon-obg2
|
Solution - github\n\nProblem List related to #SweepLine - github\n\nProblem List related to #Greedy - github\n\n\n/// @author: Leon\n/// https://leetcode.com/pr
|
idiotleon
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-09T06:13:18.578951+00:00
|
2022-03-24T06:50:33.514540+00:00
| 251 | false |
Solution - [github](https://github.com/An7One/leetcode-solutions-rust-an7one/tree/main/src/leetcode/lvl2/lc1854)\n\nProblem List related to #SweepLine - [github](https://github.com/An7One/leetcode-problems-by-tag-an7one/blob/main/txt/by_algorithm/greedy/by_topic/sweep_line.txt)\n\nProblem List related to #Greedy - [github](https://github.com/An7One/leetcode-problems-by-tag-an7one/tree/main/txt/by_algorithm/greedy)\n\n```\n/// @author: Leon\n/// https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-population-year/\n/// Time Complexity: O(`RANGE`)\n/// Space Complexity: O(`RANGE`) ~ O(1)\n/// Reference:\n/// https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-population-year/discuss/1198838/Java-Array-Solution\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn maximum_population(logs: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {\n const RANGE: usize = 2050 - 1950 + 1;\n const YEAR_BASE: usize = 1950;\n let timeline: Vec<i32> = {\n let mut timeline = vec![0; RANGE];\n for log in logs{\n let start: usize = log[0] as usize;\n let end: usize = log[1] as usize;\n for i in start..end {\n timeline[i - YEAR_BASE] += 1;\n }\n }\n timeline\n };\n let mut max: i32 = 0;\n let mut max_year: usize = 0;\n for (idx_year, population) in timeline.into_iter().enumerate() {\n if population > max {\n max = population;\n max_year = idx_year + YEAR_BASE;\n }\n }\n max_year as i32\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Greedy', 'Rust']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
Simple Prefix Sum Approach || Java
|
simple-prefix-sum-approach-java-by-dsury-78et
|
Code
|
dsuryaprakash89
|
NORMAL
|
2025-04-12T05:08:08.497076+00:00
|
2025-04-12T05:08:08.497076+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {
if(logs.length==1)return logs[0][0];
int p[]= new int[101];
for(int [] log:logs){
p[log[0]-1950]++;
p[log[1]-1950]--;
}
int []res=new int[101];
res[0]=p[0];
int maxi=0;
for(int i=1;i<101;i++){
res[i]=res[i-1]+p[i];
maxi=Math.max(res[i],maxi);
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<101;i++){
if(res[i]==maxi) {
ans= i+1950;
break;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Prefix Sum', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
JAVA | Line Sweep | 100% | Prefix Sum
|
java-clean-sweep-100-prefix-sum-by-akash-j3lx
|
IntuitionWe will maintain entire timeline of years(1950-2050) in an array.
Line Sweep: It involves sweeping a line (or point) across a plane or sequence, proces
|
akashBisht
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-06T17:21:28.889214+00:00
|
2025-01-06T17:21:54.659659+00:00
| 261 | false |
# Intuition
We will maintain entire timeline of years(1950-2050) in an array.
Line Sweep: It involves sweeping a line (or point) across a plane or sequence, processing events as they are encountered.
# Approach
Instead of finding total population of each year, we will find number of births and deaths for a year.
Then to find population for each year we will just use prefix sum to find cumulative sum at that year.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(N)
->Iterating over all intervals of logs array: O(N)
->Iterating over the 101 years in pop: O(101)=O(1) constant because the range is fixed.
->Overall: O(n+101)=O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)
->Fixed size of 101: O(101)=O(1)
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {
int pop[]=new int[101];
for(int i=0;i<logs.length;i++){
pop[logs[i][0]-1950]++;
pop[logs[i][1]-1950]--;
}
int maxPop=pop[0];
int maxYear=1950;
for(int i=1;i<101;i++){
pop[i]+=pop[i-1];
if(pop[i]>maxPop){
maxPop=pop[i];
maxYear=i+1950;
}
}
return maxYear;
}
}
```
| 2 | 0 |
['Prefix Sum', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
use diff array and prefix sum !!
|
use-diff-array-and-prefix-sum-by-goodluc-1uwm
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
goodluck8
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-05T06:12:22.123503+00:00
|
2025-01-05T06:12:22.123503+00:00
| 394 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) {
vector<int> diff(101);
for(auto x:logs){
int birth = x[0]-1950;
int end = x[1]-1950;
diff[birth] +=1;
diff[end]-=1;
}
partial_sum(diff.begin(),diff.end(),diff.begin());
int maxi = INT_MIN;
int maxiyear = 1950;
for(int i=0;i<101;i++){
if(diff[i] > maxi){
maxiyear = 1950+i;
maxi = diff[i];
}
}
return maxiyear;
}
};
```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
maximum-population-year
|
[Java] Easy 100% solution - Line sweep
|
java-easy-100-solution-line-sweep-by-ytc-li7i
|
java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(final int[][] logs) {\n final int[] dates = new int[101];\n\n for(final int[] log : lo
|
YTchouar
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-27T03:46:20.820756+00:00
|
2024-11-27T03:46:20.820787+00:00
| 206 | false |
```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(final int[][] logs) {\n final int[] dates = new int[101];\n\n for(final int[] log : logs) {\n dates[log[0] - 1950]++;\n dates[log[1] - 1950]--;\n }\n\n int prefix = 0, maxCount = 0, date = 0;\n\n for(int i = 0; i < 101; ++i) {\n prefix += dates[i];\n\n if(prefix > maxCount) {\n maxCount = prefix;\n date = i;\n }\n }\n\n return date + 1950;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
C++ constant space
|
c-constant-space-by-iamnot_coder-wlus
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
iamnot_coder
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-18T12:31:59.769162+00:00
|
2024-01-18T12:31:59.769184+00:00
| 995 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) {\n int ans =0;\n int pop =0;\n for(int i =1950;i<2050;i++){\n int temp = 0;\n for(auto j:logs){\n if(j[0]<=i) temp++;\n if(j[1]<=i) temp--;\n }\n if(temp>pop){\n ans =i;\n pop = temp;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
C++ || Line sweep || O(N) || Very easy
|
c-line-sweep-on-very-easy-by-shiv2708200-mcwb
|
Approach : Line sweep\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n
|
shiv27082002
|
NORMAL
|
2023-09-03T02:34:58.002690+00:00
|
2023-09-03T02:34:58.002709+00:00
| 478 | false |
# Approach : Line sweep\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) {\n int p[101] = {0};\n \n for(int i = 0; i<logs.size(); i++){\n int l = logs[i][0] % 1950;\n int r = logs[i][1] % 1950;\n\n p[l]+=1;\n p[r]-=1;\n }\n \n int indx = 0;\n for(int i = 1; i<101; i++){\n p[i] = p[i-1] + p[i];\n if(p[i] > p[indx]){\n indx = i;\n }\n }\n return 1950+indx;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
Easy Python Solution for beginners
|
easy-python-solution-for-beginners-by-os-3khl
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n- This solution iterates through each year in the range of birth years to death years a
|
oshine_chan
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-09T17:56:53.256840+00:00
|
2023-08-09T17:56:53.256862+00:00
| 651 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n- This solution iterates through each year in the range of birth years to death years and counts the population by checking if the year falls within the inclusive range for each individual. \n- It then keeps track of the maximum population and the corresponding year. \n- While this solution is less efficient for larger input data, it\'s easy to understand.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximumPopulation(self, logs: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n min_year = float(\'inf\') # To find the minimum birth year\n max_year = float(\'-inf\') # To find the maximum death year\n \n # Find the minimum birth year and maximum death year\n for birth, death in logs:\n min_year = min(min_year, birth)\n max_year = max(max_year, death - 1)\n \n max_population = 0\n max_population_year = None\n \n # Iterate through each year and count the population\n for year in range(min_year, max_year + 1):\n population = 0\n for birth, death in logs:\n if birth <= year <= death - 1:\n population += 1\n if population > max_population:\n max_population = population\n max_population_year = year\n \n return max_population_year\n```\n\n
| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 2 |
maximum-population-year
|
Maximum Population Year Solution in C++
|
maximum-population-year-solution-in-c-by-fvgj
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
The_Kunal_Singh
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-05T08:01:04.541361+00:00
|
2023-04-27T16:53:39.910637+00:00
| 431 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n^2)\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(1)\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumPopulation(vector<vector<int>>& logs) {\n int i, j, count=0, max=0, year=logs[0][0];\n for(i=0 ; i<logs.size() ; i++)\n {\n count=0;\n for(j=0 ; j<logs.size() ; j++)\n {\n if(logs[j][0]<=logs[i][0] && logs[i][0]<logs[j][1])\n {\n count++;\n }\n }\n if(count>max)\n {\n max = count;\n year = logs[i][0];\n }\n else if(count==max && logs[i][0]<year)\n {\n year = logs[i][0];\n }\n }\n return year;\n }\n};\n```\n
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
JAVA Counting solution using Prefix Sum | Beats 100%
|
java-counting-solution-using-prefix-sum-216rk
|
\npublic int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n\tint[] ppl = new int[101]; \n\tint max = 0, idx = 0, lastSum = 0;;\n\tfor ( int i = 0; i < logs.length; i++ ) {
|
user5869CS
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-11T12:01:31.690821+00:00
|
2022-09-11T12:01:31.690864+00:00
| 735 | false |
```\npublic int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n\tint[] ppl = new int[101]; \n\tint max = 0, idx = 0, lastSum = 0;;\n\tfor ( int i = 0; i < logs.length; i++ ) {\n\t\tppl[logs[i][0] - 1950]++;\n\t\tppl[logs[i][1] - 1950]--;\n\t}\n\tfor ( int i = 0; i < ppl.length; i++ ) {\n\t\tlastSum += ppl[i];\n\t\tif ( lastSum > max ) {\n\t\t\tmax = lastSum;\n\t\t\tidx = i;\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\treturn idx + 1950;\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Counting', 'Iterator', 'Prefix Sum', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
Go simple
|
go-simple-by-caochanhduong-kep5
|
```\nfunc maximumPopulation(logs [][]int) int {\n yearSet := make(map[int]int)\n ans := math.MaxInt\n for , v := range logs {\n yearSet[v[0]] =
|
caochanhduong
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-27T04:31:39.003699+00:00
|
2022-08-27T04:31:39.003734+00:00
| 149 | false |
```\nfunc maximumPopulation(logs [][]int) int {\n yearSet := make(map[int]int)\n ans := math.MaxInt\n for _, v := range logs {\n yearSet[v[0]] = 0\n yearSet[v[1]] = 0\n }\n \n for k := range yearSet {\n for _, v := range logs {\n if k >= v[0] && k <= v[1]-1 {\n yearSet[k]++\n }\n }\n }\n \n maxPopulation := 0\n for year, population := range yearSet {\n if population > maxPopulation {\n maxPopulation = population\n ans = year\n } else if population == maxPopulation && year < ans {\n ans = year\n }\n }\n \n return ans\n}
| 2 | 0 |
['Go']
| 0 |
maximum-population-year
|
Java solution (both brute force and optimized)
|
java-solution-both-brute-force-and-optim-2qo8
|
\n// Brute force approach: O(N^2)\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int[] arr = new int[101];\n\n for(int i =
|
sourin_bruh
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-28T08:54:48.773115+00:00
|
2022-07-28T08:54:48.773147+00:00
| 286 | false |
```\n// Brute force approach: O(N^2)\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int[] arr = new int[101];\n\n for(int i = 0; i<logs.length; ++i){\n for(int j=logs[i][0]; j<logs[i][1]; j++){\n arr[j-1950]++;\n }\n }\n\n int maxYear = 1950;\n int maxVal = 0;\n for(int i=0; i<arr.length; ++i){\n if(arr[i]>maxVal) {\n maxVal = arr[i];\n maxYear = i + 1950;\n }\n }\n return maxYear;\n }\n}\n\n\n// Optimised solution: O(N)\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumPopulation(int[][] logs) {\n int[] arr = new int[101];\n\n for(int i=0; i<logs.length; ++i){\n arr[logs[i][0] - 1950]++;\n arr[logs[i][1] - 1950]--;\n }\n\n for(int i = 1; i<101; ++i){\n arr[i] += arr[i-1];\n }\n\n int maxYear = 1950;\n int maxVal = 0;\n for(int i=0; i<arr.length; ++i){\n if(arr[i]>maxVal) {\n maxVal = arr[i];\n maxYear = i + 1950;\n }\n }\n return maxYear;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.