question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Both 100% | C++ | 58 ms/54.6 MB
|
both-100-c-58-ms546-mb-by-sungod1223-0kp4
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nLet DP[i] represent the farthest distance that can be reached to the right at position
|
SunGod1223
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-10T18:16:33.784502+00:00
|
2023-02-10T18:19:01.716759+00:00
| 323
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nLet DP[i] represent the farthest distance that can be reached to the right at position i. The problem is to find x and y to maximize the sum of DP[x] + DP[y]. Note that the parts covered by x and y cannot overlap.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nUse two sliding windows, one is used to calculate dp[i] (because dp[i]+i is increasing to the right); the other is used to find max(dp[x]) for x<i (the reason is the same as above). Note when x=0, it means that all elements to the left of i are in the range k.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ --> \n\n- Space complexity: $$O(1)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& p, int k) {\n int n=p.size(),ans=0;\n for(int i=0,r=0,l=0,v=0;i<n;++i){\n while(r<n&&p[r]-p[i]<=k)++r;\n p[i]=r-i;\n while(p[l]+l<=i)v=max(v,p[l++]);\n ans=max(ans,l?v+p[i]:p[i]+i);\n if(r==n)return ans;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2
| 0
|
['C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
[Binary Search + DP - With TC & SC & Approach]
|
binary-search-dp-with-tc-sc-approach-by-e204r
|
\n# Approach\n- Pick First_Range_STARTIdx from 0 till n-1\n- Now,START = prizePositions[START] , END = START + k\n- Find First_Range_ENDIdx Using Binary Search(
|
MSJi
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-05T00:11:57.806225+00:00
|
2023-02-05T18:20:35.659320+00:00
| 347
| false
|
\n# Approach\n- Pick First_Range_STARTIdx from 0 till n-1\n- Now,START = prizePositions[START] , END = START + k\n- Find First_Range_ENDIdx Using Binary Search(END) or UpperBound(END) as all values in range [START,END] they are Now a part of First_Range\n- Now, Second_Range_STARTIdx will either start Just from First_Range_ENDIdx OR we will be skipping some and go till n to get maximum Second Range. This is Handled in **nextMaxRange Function** using takeIt OR notTake it LOGIC\n 1. Now, firstRange = First_Range_ENDIdx - First_Range_STARTIdx \n 2. secondRange = nextMaxRange(First_Range_ENDIdx)\n- return max(ans,firstRange+secondRange)\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n*[logn + nextMaxRange])$$ \n= $$O(nlogn]$$\n*here, O[nextMaxRange] ~ logn ,for particular idx ,So overall $$O(nlogn)$$\nBecause Using Memo, we will be going only Once in nextMaxRange Fn*\n\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(n)$$ , *memoized vector*\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int nextMaxRange(int idx,vector<int>& prizePositions,int k,int n,vector<int>& memo){\n if(idx == n){\n return 0;\n }\n\n if(memo[idx] != -1){\n return memo[idx];\n }\n\n //not Take\n int notTakeRange = 0 , takeRange = 0;\n notTakeRange = nextMaxRange(idx+1,prizePositions,k,n,memo);\n\n //Take\n int start = prizePositions[idx];\n int end = start + k;\n int endIdx = upper_bound(prizePositions.begin(),prizePositions.end(),end) - prizePositions.begin(); \n takeRange = endIdx - idx;\n\n return memo[idx] = max(takeRange,notTakeRange);\n\n }\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prizePositions, int k) {\n int n = prizePositions.size();\n vector<int> memo(n,-1);\n int ans = 0;\n\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int start = prizePositions[i];\n int end = start + k;\n //just after Index of end\n int endIdx = upper_bound(prizePositions.begin(),prizePositions.end(),end) - prizePositions.begin(); \n int firstRange = endIdx - i;\n int secondRange = nextMaxRange(endIdx,prizePositions,k,n,memo);\n \n ans = max(ans,firstRange+secondRange);\n\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n\n\n};\n```
| 2
| 0
|
['Binary Search', 'Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 2
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Maximize (left max + right max) for every i || precomputations || O(n)
|
maximize-left-max-right-max-for-every-i-bjsqr
|
Intuition\nThe idea is that as we have to select two segments and making those segments disjoint would always be better. So lets take an index i in the array an
|
yash_karakoti
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-04T19:01:44.758983+00:00
|
2023-02-04T19:08:51.024574+00:00
| 99
| false
|
# Intuition\nThe idea is that as we have to select two segments and making those segments disjoint would always be better. So lets take an index i in the array and take the first segment in the left of i and the second segment in the right of i. \n\n# Approach\nMaximizing the (**left segment** + **right segments**) value over all indexes will give us the answer.\nWe can precompute the prefix and suffix array which stores the maximum prizes we can take from the left and right of some index.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\nO(n) for precomputation + O(n) for calculating final answer\n\n# Code\n```\n#define ll int\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& v, int k) {\n ll n = v.size();\n if(n == 1) return 1;\n vector<ll> pre(n), suff(n);\n ll s = 0;\n for(ll i = 0; i < n; i++){\n while(v[i] - v[s] > k){\n s++;\n }\n ll len = i - s + 1;\n ll prev = (i > 0) ? pre[i-1] : 0;\n pre[i] = max(prev, len);\n }\n s = n-1;\n for(ll i = n-1; i >= 0; i--){\n while(v[s] - v[i] > k){\n s--;\n }\n ll len = s - i + 1;\n ll nx = (i < n-1) ? suff[i + 1] : 0;\n suff[i] = max(nx, len);\n }\n ll ans = 0;\n for(ll i = 0; i < n-1; i++){\n ans = max(ans, pre[i] + suff[i + 1]);\n }\n return ans;\n\n }\n};\n```
| 2
| 0
|
['Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 2
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Recursion + Memoization in Cpp..
|
recursion-memoization-in-cpp-by-sanket_j-ni5w
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n int func(int i,vector<int>&p,int k,int t,vector<vector<int>>&dp){\n\n if(i>=p.size())return 0;\n if(t
|
Sanket_Jadhav
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-04T17:30:17.412402+00:00
|
2023-02-04T17:30:17.412441+00:00
| 381
| false
|
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n int func(int i,vector<int>&p,int k,int t,vector<vector<int>>&dp){\n\n if(i>=p.size())return 0;\n if(t<=0)return 0;\n\n if(dp[i][t]!=-1)return dp[i][t];\n\n int a=0,b=0;\n\n int ind=upper_bound(p.begin(),p.end(),p[i]+k)-p.begin();\n\n // cout<<ind<<" ";\n b=ind-i+func(ind,p,k,t-1,dp);\n\n a=func(i+1,p,k,t,dp);\n \n\n return dp[i][t] = max(a,b);\n }\n\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& p, int k) {\n \n vector<vector<int>>dp(p.size(),vector<int>(3,-1));\n return func(0,p,k,2,dp);\n }\n};\n```
| 2
| 0
|
['C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Python clear solution | Leetcode 2054 - Two Best Non-Overlapping Events
|
python-clear-solution-leetcode-2054-two-cisn2
|
Clearly, maximum score will be achieved with two non-overlapping segments.\nAs a result, we can see the link of this problem to Leetcode 2054.\n\n def maximi
|
vincent_great
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-04T16:17:33.560444+00:00
|
2023-02-04T16:55:07.413348+00:00
| 1,051
| false
|
Clearly, maximum score will be achieved with `two non-overlapping segments`.\nAs a result, we can see the link of this problem to Leetcode 2054.\n\n def maximizeWin(self, ps: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n if max(ps)-min(ps)<=k*2:\n return len(ps)\n\n scores, q, cur, ans = [], [], 0, 0\n\t\t# build the list of (start, end, prize-numbers)\n for i, n in enumerate(ps):\n if not scores or scores[-1][0]!=n:\n idx = bisect.bisect_left(ps, n+k+1)\n scores.append([n, ps[idx-1], idx-i])\n\t\n\t\t# calculate best score of two Non-overlapping segments\n for i, j, v in scores:\n while(q and q[0][0]<i):\n cur = max(cur, heappop(q)[1])\n ans = max(ans, cur+v)\n heappush(q, (j, v))\n return ans
| 2
| 0
|
[]
| 1
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Java | Two Pointer Solution | Simple & Easy Solution using Left max and Right max
|
java-two-pointer-solution-simple-easy-so-4snp
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public int maximizeWin(int[] prizePositions, int k) {\n \n int n = prizePositions.length;\n int leftMax[] = n
|
onefineday01
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-30T14:41:46.257499+00:00
|
2024-03-08T18:33:12.001341+00:00
| 86
| false
|
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximizeWin(int[] prizePositions, int k) {\n \n int n = prizePositions.length;\n int leftMax[] = new int[n];\n int rightMax[] = new int[n];\n\n leftMax[0] = 1;\n for(int i = 1, j = 0; i < n; i++) {\n while(prizePositions[i] - prizePositions[j] > k) {\n j++;\n }\n leftMax[i] = Math.max(leftMax[i-1], i-j+1);\n }\n\n rightMax[n-1] = 1;\n for(int i = n-2, j = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {\n while(prizePositions[j] - prizePositions[i] > k) {\n j--;\n }\n rightMax[i] = Math.max(rightMax[i+1], j-i+1);\n }\n \n int res = 0 ;\n for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {\n res = Math.max(res, (i == 0 ? 0 : leftMax[i - 1]) + (i == n ? 0 : rightMax[i]));\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```\n\n- Do Upvote if this helps \u2B06\uFE0F \uD83D\uDC4D\uD83C\uDFFB \n\n
| 1
| 0
|
['Two Pointers', 'Java']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Python Medium
|
python-medium-by-lucasschnee-0x61
|
\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, prizePositions: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n\n N = len(prizePositions)\n\n dp = [0] * (N + 1)\n\n
|
lucasschnee
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-23T01:52:11.535157+00:00
|
2023-08-23T01:52:11.535176+00:00
| 21
| false
|
```\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, prizePositions: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n\n N = len(prizePositions)\n\n dp = [0] * (N + 1)\n\n l = 0\n\n ans = 0\n\n for r in range(N):\n\n while prizePositions[l] + k < prizePositions[r]:\n l += 1\n\n dp[r + 1] = max(dp[r], r - l + 1)\n\n ans = max(ans, dp[l] + r - l + 1)\n \n\n return ans\n```
| 1
| 0
|
['Python3']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
99% || C++
|
99-c-by-shradhaydham24-zu6m
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
shradhaydham24
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-16T18:59:10.581959+00:00
|
2023-07-16T18:59:10.581979+00:00
| 53
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& A, int k) \n {\n int res = 0, n = A.size(), j = 0;\n vector<int> dp(n + 1, 0);\n for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) \n {\n while (A[j] < A[i] - k)\n ++j;\n dp[i + 1] = max(dp[i], i - j + 1);\n res = max(res, i - j + 1 + dp[j]);\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 1
| 0
|
['C++']
| 1
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
dp || similar to buy and sell stocks with 2 transaction || memoization || binary search
|
dp-similar-to-buy-and-sell-stocks-with-2-im2l
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nwe can use dp to find at most 2 different ranges and return the maximum sum of these ra
|
sarthakrautelanew
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-10T09:17:02.396918+00:00
|
2023-02-10T09:17:39.672064+00:00
| 85
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nwe can use dp to find at most 2 different ranges and return the maximum sum of these ranges. \n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nwe limit ourself to 2 picks .\nwe use the principal of take / not take at a given index.\nwe can take a starting element from the array , then using the fact that array is sorted , we can use binary search to find the last index of range such that , the element is less than or equal to first element +k.\n\n\nwe can do this process at most 2 times.\nthen return maximum number of elements accumulated.\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(2*n*log(n))\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(2n)\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n // this will return index of the last valid element in the range\n \n int search(vector<int>& prize,int s, int key){\nint e=prize.size()-1;\nint mid;\nint ans=-1;\nwhile(s<=e){\n\nmid=(s+e)/2;\nif(prize[mid]<=key){\n ans=mid;\n s=mid+1;\n}\nelse\n e=mid-1;\n\n}\nreturn ans;\n } \n\nint solve(vector<int>& prize, int &k,int idx,int t,int &n,vector<vector<int>>&dp){\n\nif(t==2) // we have used 2 ranges/transactions \nreturn 0;\n\nif(idx>=n) // we are out of the array\nreturn 0;\n\nif(dp[idx][t]!=-1)\nreturn dp[idx][t];\n// memoization\nint l=0,r=0;\n// take \nint range = search(prize,idx,prize[idx]+k); \nl= range-idx+1 + solve(prize,k,range+1,t+1,n,dp);\n// not take\nr=solve(prize,k,idx+1,t,n,dp);\n\nreturn dp[idx][t]=max(l,r);\n}\n\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prize, int k) {\n //take, not take\n // we can take at most 2 times\n\nint n=prize.size();\nvector<vector<int>>dp(n,vector<int>(2,-1));\n// n size of all the indexes from 0- (n-1) and 2 size for atmost 2 transactions.\nreturn solve(prize,k,0,0,n,dp);\n\n }\n};\n```
| 1
| 0
|
['Binary Search', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Javascript - DP + Sliding Window
|
javascript-dp-sliding-window-by-faustale-rizi
|
Code\n\n/**\n * @param {number[]} prizePositions\n * @param {number} k\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar maximizeWin = function (prizePositions, k) {\n const n =
|
faustaleonardo
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-07T01:02:29.310930+00:00
|
2023-02-07T01:02:29.310961+00:00
| 51
| false
|
# Code\n```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} prizePositions\n * @param {number} k\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar maximizeWin = function (prizePositions, k) {\n const n = prizePositions.length;\n const dp = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);\n let ans = 0;\n let start = 0;\n\n for (let end = 0; end < prizePositions.length; end++) {\n while (prizePositions[end] - prizePositions[start] > k) start++;\n\n const currPrize = end - start + 1;\n dp[end + 1] = Math.max(dp[end], currPrize);\n ans = Math.max(ans, currPrize + dp[start]);\n }\n\n return ans;\n};\n\n```
| 1
| 0
|
['JavaScript']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
[C++] Binary Search | DP | Beats 100% | Easy + Intuitive Explanation | Illustration
|
c-binary-search-dp-beats-100-easy-intuit-eryp
|
\n# Solution\nWe Calculate the maximum number of prizes we can collect if we start collecting from index i , using binary search to find the first index that ca
|
braindroid
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-04T23:03:18.229423+00:00
|
2023-02-04T23:03:18.229468+00:00
| 187
| false
|
\n# Solution\n**We Calculate the maximum number of prizes we can collect if we start collecting from index i , using binary search to find the first index that cannot be included if we start at index i.**\n\nAfter that we can just iterate over all index\'s **finding the maximum possible length of segment 1 , which was already calculated in the previous step (DP). For segment 2, we take the maximum possible value of all the remaning indices that remain after inclusion of segment 1 (stored in DP2 using suffix maximum).**\n\n**The answer is the maximum over all index\'s.**\n\n 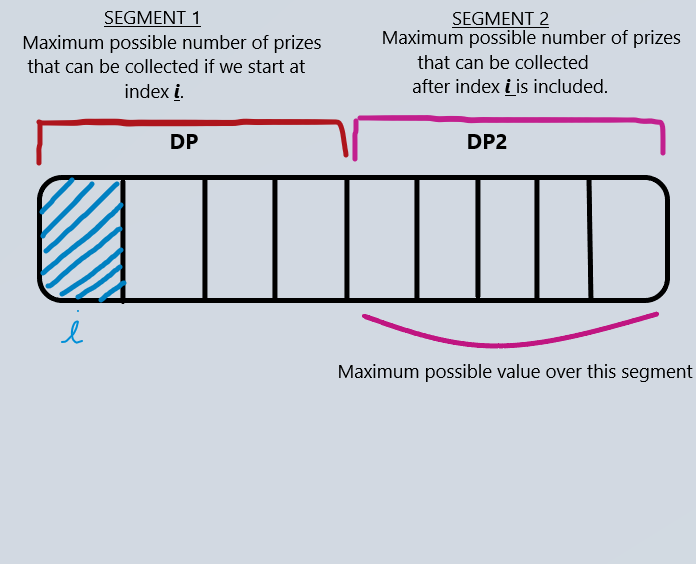\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& a, int k) {\n int n = (int)a.size();\n vector<int>dp(n,0);\n for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {\n //Calculates the maximum number of prizes we can collect if we start at index i.\n\n int p = upper_bound(a.begin(),a.end(),a[i] + k) - a.begin(); // binary search to find the first index that cannot be included\n int len = p - i; // length of the segment that can included we start at index i.\n dp[i] = len; // storing the best possible answer if we start collecting prizes if we start at index i.\n } \n vector<int>dp2 = dp;\n int mx = dp[n-1];\n for(int i = n-1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) {\n mx = max(dp[i],mx);\n dp2[i] = mx; // creating suffix maximum array.\n }\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {\n int res = dp[i]; // gives the maximum number of prizes we can take if we start at index i [Segment 1]. (marked blue & red in picture)\n if(i+dp[i] < n) {\n // Maximum possible value for Segment 2 (marked as pink in picture)\n res += dp2[i+dp[i]]; \n }\n ans = max(ans,res); // maximum possible answer.\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1
| 0
|
['Array', 'Binary Search', 'Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 2
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
very easy and intuitive|| fully explained
|
very-easy-and-intuitive-fully-explained-ed65k
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nsee my first intuition was that , in none of the cases it is ideal for me to take two o
|
sippu
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-04T19:45:02.286196+00:00
|
2023-02-04T19:45:02.286238+00:00
| 158
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nsee my first intuition was that , in none of the cases it is ideal for me to take two overlapping subarrays , if it is possible for me to take two non overlapping subarrays than that would always be better.\nThere is just one case where you need to take overlapping subarrays that is when the number of position on x axis is less than 2*k here you can get all the rewards possible .\n\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nNow this question becomes same as dividing array in two k sized non overlapping subarrays and maximizing our sum , there is just one issue that we can\'t make our right and left dp on positions as it is 10^9 . hence what we will do is we will make dp on the unique pos present in our initial array, that would be in worst case be 10^5,\nnow we just need to take a sliding window approach to fill in these dp\'s and than we can iterate these dp\'s to find our answer.\n\nThere could be two cases on each pos-:\n1) left_max till pos(i)+right_max till pos(i+1);\n2) right_max till pos(i)+left_max till pos(i-1);\nmax of these value should be comapred to our gloabal answer.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(N)\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\no(N) (i.e actually o(2*N));\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& arr, int k) {\n map<int,int> mp;\n vector<int> vec;\n for(int i=0;i<arr.size();i++){\n mp[arr[i]]+=1;\n if(mp[arr[i]]==1){\n vec.push_back(arr[i]);\n }\n }\n \n vector<int> left_max(vec.size(),0);\n int left_max_val=mp[vec[0]];\n int start=0;\n int end=1;\n int sum=mp[vec[0]];\n left_max[0]=mp[vec[0]];\n while(end<vec.size()){\n while(end<vec.size() &&(vec[end]-vec[start])<=k){\n sum+=mp[vec[end]];\n left_max_val=max(sum,left_max_val);\n left_max[end]=left_max_val;\n end++;\n }\n while(end<vec.size() && start<=end && (vec[end]-vec[start])>k){\n sum-=mp[vec[start]];\n start++;\n }\n }\n /*for(int i=0;i<vec.size();i++){\n cout<<left_max[i]<<" ";\n }*/\n \n vector<int> right_max(vec.size(),0);\n int right_max_val=mp[vec[vec.size()-1]];\n start=vec.size()-1;\n end=vec.size()-2;\n sum=mp[vec[vec.size()-1]];\n right_max[vec.size()-1]=mp[vec[vec.size()-1]];\n while(end>=0){\n while(end>=0 &&(vec[start]-vec[end])<=k){\n sum+=mp[vec[end]];\n right_max_val=max(sum,right_max_val);\n right_max[end]=right_max_val;\n end--;\n }\n while(end>=0 && start>=end && (vec[start]-vec[end])>k){\n sum-=mp[vec[start]];\n start--;\n }\n }\n /*for(int i=0;i<vec.size();i++){\n cout<<right_max[i]<<" ";\n }*/\n int ans=INT_MIN;\n for(int i=0;i<vec.size();i++){\n int val=0;\n if(i==0){\n if(i+1<vec.size()){\n val=max(right_max[i],left_max[i]+right_max[i+1]);\n }\n else{\n val=max(right_max[i],left_max[i]);\n }\n }\n else if(i==vec.size()-1){\n if(i-1>=0){\n val=max(left_max[i],right_max[i]+left_max[i-1]);\n }\n else{\n val=max(left_max[i],right_max[i]);\n }\n }\n else{\n val=max(left_max[i]+right_max[i+1],right_max[i]+left_max[i-1]);\n }\n ans=max(ans,val);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
dp || sliding window || o(n) || leftmax + rightmax || faster 100%
|
dp-sliding-window-on-leftmax-rightmax-fa-z1da
|
Intuition\n For every index i, if we can get leftmax[i-1] and rightmax[i], we can iterate through i and get the max result.\n\nleftmax[i]: max on the left of
|
sagar-1209
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-04T18:08:12.527938+00:00
|
2023-02-04T18:08:12.528016+00:00
| 96
| false
|
# Intuition\n For every index i, if we can get leftmax[i-1] and rightmax[i], we can iterate through i and get the max result.\n\nleftmax[i]: max on the left of index i (including i)\nrightmax[i]: max on the right of index i (including i)\n\nTo get leftmax[i]: the max between leftmax[i-1], and the number in the window of size k from i to the left, i.e., i - j + 1, where j is the most left element meeting the window size k requirement for i.\n\nTo get rightmax[i]: the max between rightmax[i+1], and the number in the window of size k from i to the right, i.e., j - i + 1, where j is the most right element meeting the window size k requirement for i.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: o(n)\n- space complexity : o(n)\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& v, int k) {\n int n = v.size();\n vector<int> leftmax(n,1);\n vector<int> rightmax(n,1);\n int j=0;\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++){\n while(v[i]-v[j]>k) j++;\n leftmax[i] = max(leftmax[i-1],i-j+1);\n }\n j = n-1;\n for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--){\n while(v[j]-v[i]>k) j--;\n rightmax[i] = max(rightmax[i+1],j-i+1);\n }\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){\n ans = max((i==0?0:leftmax[i-1])+(i==n?0:rightmax[i]) , ans);\n }\n return ans;\n\n }\n};\n```
| 1
| 0
|
['Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
[Java] DP + sliding window solution
|
java-dp-sliding-window-solution-by-opraj-begp
|
Intuition\nThe intuition behind solving the problem is to use dynamic programming to efficiently keep track of the maximum number of prizes that can be won at e
|
oprajapath
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-04T17:56:46.642098+00:00
|
2023-02-04T17:56:46.642148+00:00
| 542
| false
|
# Intuition\nThe intuition behind solving the problem is to use dynamic programming to efficiently keep track of the maximum number of prizes that can be won at each position.\n\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\nStarting from the first position, the code uses a 2-dimensional DP array dp[][] to store the maximum number of prizes won so far for each position. The DP approach is used to avoid re-computing the same solution multiple times and to ensure that the solution is optimal.\n\nFor each position, the code checks the valid segment (the segment whose difference between the current position and the starting position is less than or equal to k) and updates the dp[][] array to store the maximum number of prizes that can be won. The maximum number of prizes is either the maximum number of prizes won at the previous position or the maximum number of prizes won before the current valid segment plus the length of the valid segment.\n\nThe code continues to do this for each position until the end of the prizePositions array. The final result is stored in dp[2][n], which is the maximum number of prizes that can be won for k jumps starting from the first position and ending at the last position.\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximizeWin(int[] prizePositions, int k) {\n int n = prizePositions.length;\n //dp to store the maximum number of prizes that can be won at each position\n int dp[][] = new int[3][n+1];\n\n for(int i=1;i<3;i++){\n int start = 1;\n for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){\n //if segment becomes greater than k, increase start to make it valid again.\n while(prizePositions[j-1]- prizePositions[start-1] > k){\n start++;\n }\n //update the dp by taking the maximum between the maximum number of prizes at the previous position and the maximum number of prizes in the current valid segment plus the length of the valid segment.\n dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j-1], dp[i-1][start-1] + j-start +1);\n }\n }\n return dp[2][n]; \n }\n}\n```
| 1
| 0
|
['Java']
| 1
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
C++ SOLUTION WITH UPPER_BOUND + SUFFIX MAXIMUM ARRAY
|
c-solution-with-upper_bound-suffix-maxim-n9wk
|
Time Complexity: O(nlog(n))\n\n\nclass Solution \n{\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& a, int k) \n {\n int n = a.size();\n vector<pair
|
theILICH
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-04T16:36:45.058032+00:00
|
2023-02-04T16:36:45.058076+00:00
| 894
| false
|
# Time Complexity: $$O(nlog(n))$$\n\n```\nclass Solution \n{\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& a, int k) \n {\n int n = a.size();\n vector<pair<int, int>> b(n), s(n);\n for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)\n {\n int target = a[i] + k;\n int idx = max(0, (int)(upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), target) - a.begin()) - 1);\n b[i] = {i, idx};\n }\n \n int mx = 0;\n pair<int, int> curr;\n for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i)\n {\n if (b[i].second - b[i].first + 1 > mx)\n {\n mx = b[i].second - b[i].first + 1;\n curr = {b[i].first, b[i].second}; \n }\n \n s[i] = curr;\n }\n \n int res = 1;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)\n {\n int j = b[i].second;\n \n res = max(res, b[i].second - b[i].first + 1 + s[j].second - s[j].first + 1 - (s[j].first == b[i].second));\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 1
| 0
|
['C++']
| 1
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Slide Window
|
slide-window-by-linda2024-65e8
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
linda2024
|
NORMAL
|
2025-04-10T17:40:29.581246+00:00
|
2025-04-10T17:40:29.581246+00:00
| 2
| false
|
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```csharp []
public class Solution {
public int MaximizeWin(int[] prizePositions, int k) {
// Pre cal num frequency:
SortedDictionary<int, int> freq = new();
foreach(int n in prizePositions)
{
freq.TryAdd(n, 0);
freq[n]++;
}
List<int> keys = freq.Keys.ToList();
int kLen = keys.Count, sum = 0, start = 0, end = kLen-1;
int[] preSum = new int[kLen], tailSum = new int[kLen];
for(int i = 0; i < kLen; i++)
{
sum += freq[keys[i]];
while(keys[i]-keys[start] > k)
{
sum -= freq[keys[start++]];
}
preSum[i] = Math.Max(i > 0 ? preSum[i-1] : 0, sum);
}
sum = 0;
for(int i = kLen-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
sum += freq[keys[i]];
while(keys[end] - keys[i] > k)
{
sum -= freq[keys[end--]];
}
tailSum[i] = Math.Max(i < kLen-1 ? tailSum[i+1] : 0, sum);
}
int maxSum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < kLen; i++)
{
int curSum = (i > 0 ? preSum[i-1] : 0) + tailSum[i];
maxSum = Math.Max(curSum, maxSum);
}
return maxSum;
}
}
```
| 0
| 0
|
['C#']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
6 lines scala recursion. three pointers, two sliding windows
|
6-lines-scala-recursion-three-pointers-t-5wgq
|
scala []\nobject Solution {\n def maximizeWin(prizePositions: Array[Int], _k: Int): Int =\n def f(i:Int,j:Int,k:Int,mx0:Int, mx:Int): Int =\n if(k>= pr
|
vititov
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-08T19:20:33.413022+00:00
|
2024-12-08T19:20:33.413059+00:00
| 2
| false
|
```scala []\nobject Solution {\n def maximizeWin(prizePositions: Array[Int], _k: Int): Int =\n def f(i:Int,j:Int,k:Int,mx0:Int, mx:Int): Int =\n if(k>= prizePositions.length) mx \n else if(prizePositions(k)-prizePositions(j) <= _k) f(i,j,k+1,mx0,mx max (k-j+1 + mx0))\n else if(prizePositions(j)-prizePositions(i) <= _k) f(i,j+1,k,mx0 max (j-i+1),mx)\n else f(i+1,j,k,mx0,mx)\n f(0,0,0,0,0)\n}\n\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Scala']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
[Python] O(N*LogN) DP with binary search
|
python-onlogn-dp-with-binary-search-by-u-fo5i
|
Eg, k = 2\n\nSuppose we decide to pick current index, lets say item 1. Then we can pick all in range of 1 to 3 inclusive. So we simply binary search to find ind
|
user2292H
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-08T18:50:55.290230+00:00
|
2024-12-08T18:50:55.290256+00:00
| 2
| false
|
Eg, k = 2\n\nSuppose we decide to pick current index, lets say item 1. Then we can pick all in range of 1 to 3 inclusive. So we simply binary search to find index that is strictly greater than 3 in `prizePositions`. This allows to remove the need to keep track of chosen values and reduce time complexity.\n\nWe can also choose not to pick any value at this point as well.\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, prizePositions: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n def binary(arr, find):\n start = 0\n end = len(arr)-1\n res = len(arr)\n while start <= end:\n middle = (start+end)//2\n if arr[middle] > find:\n res = min(res, middle)\n end = middle-1\n else:\n start = middle+1\n return res\n \n @cache\n def dfs(k1, count):\n if k1 >= len(prizePositions) or count == 2:\n return 0\n \n y1 = -float(\'inf\')\n y1 = max(y1, dfs(k1+1, count))\n \n nxtInd = binary(prizePositions, prizePositions[k1] + k)\n y1 = max(y1, dfs(nxtInd, count+1) + nxtInd-k1)\n \n return y1\n return dfs(0, 0)\n \n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'Binary Tree', 'Python']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
|| ✅✅🙏Easiest Solution && Sliding Window Approach🙏✅✅ ||
|
easiest-solution-sliding-window-approach-gd94
|
Thanks for Upvote in Advance\u2B06\uFE0F\uD83D\uDE0A\uD83D\uDC95\n\n\n\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& p, int k) {\
|
Coding_With_Star
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-08T07:17:14.754814+00:00
|
2024-12-08T07:17:14.754863+00:00
| 13
| false
|
# Thanks for Upvote in Advance\u2B06\uFE0F\uD83D\uDE0A\uD83D\uDC95\n\n\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& p, int k) {\n int n = p.size(), ans = 0, s = 0;\n vector<int>v(n);\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n while(p[i] - p[s] > k)s++;\n ans = max(ans, i-s+1 + (s>0? v[s-1] : 0));\n v[i] = max((i>0? v[i-1]:0), i-s+1);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 1
|
['Array', 'Binary Search', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
O(N) Sliding window + DP solution
|
on-sliding-window-dp-solution-by-pipilon-ld8o
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \nO(n)\n- Space complexity:\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n) \nO(n)\n# Code
|
pipilongstocking
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-08T07:08:05.506533+00:00
|
2024-12-08T07:09:31.647080+00:00
| 20
| false
|
# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n)$$\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n)$$\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, prizePositions: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n n = len(prizePositions)\n maxes = [0] * n\n maxes[n-1] = ans = 1\n right = n-1\n for left in range(n-2, -1, -1):\n end = prizePositions[left] + k\n while prizePositions[right] > end:\n right -= 1\n prizes = right - left + 1\n maxes[left] = max(maxes[left+1], prizes)\n ans = max(ans, prizes + (maxes[right+1] if right+1 < n else 0))\n return ans\n\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Sliding Window', 'Python3']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Binary Search + DP
|
binary-search-dp-by-pipilongstocking-wd5i
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
pipilongstocking
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-08T07:04:49.200601+00:00
|
2024-12-08T07:04:49.200634+00:00
| 15
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(nlogn)$$\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n)$$\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, prizePositions: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n n = len(prizePositions)\n maxes = [0] * n\n maxes[n-1] = 1\n ans = 1\n for i in range(n-2, -1, -1):\n end = prizePositions[i] + k\n lo, hi = i, n\n idx = i\n while lo + 1 < hi:\n mid = lo + ((hi - lo)//2)\n if prizePositions[mid] > end:\n hi = mid\n else:\n lo = idx = mid\n prizes = idx - i + 1\n maxes[i] = max(maxes[i+1] if i+1 < n else 0, prizes)\n ans = max(ans, prizes + (maxes[idx+1] if idx+1 < n else 0))\n return ans\n\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Binary Search', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Python3']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Easy Solution
|
easy-solution-by-sunnapu_harshita-3yzs
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe problem asks us to choose two intervals of length k from a sorted list of prize pos
|
Sunnapu_Harshita
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-07T18:08:40.648978+00:00
|
2024-12-07T18:08:40.649017+00:00
| 9
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe problem asks us to choose two intervals of length k from a sorted list of prize positions to maximize the number of prizes we can collect. These intervals can overlap, but we want to find the optimal combination.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nSliding Window for One Interval:\n\nFor each position i, use a sliding window to find the maximum number of prizes that can be collected from an interval ending at position i and having a length of k.\nSimilarly, for each position i, find the maximum number of prizes that can be collected from an interval starting at position i using another sliding window.\nDynamic Programming Arrays:\n\nleftMax[i]: Maximum number of prizes from any interval ending at position i.\nrightMax[i]: Maximum number of prizes from any interval starting at position i.\nCombine the Two Intervals:\n\nFor each possible split between the two intervals, combine the best result from the first interval (leftMax[i-1]) and the best result from the second interval (rightMax[i]).\nMaximize the total number of prizes from these two intervals.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nThe sliding window approach runs in O(n), and combining the intervals also takes O(n), so the total time complexity is O(n).\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maximizeWin(int[] prizePositions, int k) {\n \n int n = prizePositions.length;\n int leftMax[] = new int[n];\n int rightMax[] = new int[n];\n\n leftMax[0] = 1;\n for(int i = 1, j = 0; i < n; i++) {\n while(prizePositions[i] - prizePositions[j] > k) {\n j++;\n }\n leftMax[i] = Math.max(leftMax[i-1], i-j+1);\n }\n\n rightMax[n-1] = 1;\n for(int i = n-2, j = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {\n while(prizePositions[j] - prizePositions[i] > k) {\n j--;\n }\n rightMax[i] = Math.max(rightMax[i+1], j-i+1);\n }\n \n int res = 0 ;\n for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {\n res = Math.max(res, (i == 0 ? 0 : leftMax[i - 1]) + (i == n ? 0 : rightMax[i]));\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Java']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Maximum Win From Two Segments
|
maximum-win-from-two-segments-by-naeem_a-0g9j
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\nAssume dp[j] is the max segment length from (0, i).\ndp[j] = max(dp[j - 1
|
Naeem_ABD
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-06T06:04:37.885656+00:00
|
2024-12-06T06:04:37.885693+00:00
| 6
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\nAssume dp[j] is the max segment length from (0, i).\ndp[j] = max(dp[j - 1], valid(i, j)).\nFor (1,2,3,4) k = 4. If we add a new element 5.\n(1,2,3,4,5)\ndp[4] = range(0, 5) since (5 - 1 <= k) valid range(0, 4).\nIf the new added is value 6.\n(1,2,3,4,6) since 6 - 1 > 5, dp[4] = dp[3].\nFor all valid segment (i, j), max (dp[i - 1] + (j - i + 1)) will be the answer.\n\n# Complexity\nTime complexity:\nSpace complexity:\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maximizeWin(int[] A, int k) {\n //dp[i] means array from [0, i - 1] max segment length;\n int n = A.length, res = 0;\n int[] dp = new int[n];\n for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; ++i){\n while(j < n && A[j] - A[i] <= k){\n int prev = j - 1 >= 0 ? dp[j - 1]: 0;\n dp[j] = Math.max(prev, j - i + 1);\n ++j;\n }\n// int prev = i - 1 >= 0 ? dp[i - 1] : 0;\n// res = Math.max(prev + j - i, res);\n }\n for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; ++i){\n while(j < n && A[j] - A[i] <= k){\n ++j;\n }\n int prev = i - 1 >= 0 ? dp[i - 1] : 0;\n res = Math.max(j - i + prev, res);\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Java']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Intuitive python solution -- Beats 100%
|
intuitive-python-solution-beats-100-by-d-ai2z
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nwe need to:\n- calulate valid segment lengths\n- Find two (non-ovelapping) segments tha
|
dimoka
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-04T00:50:32.879218+00:00
|
2024-12-04T00:50:32.879252+00:00
| 9
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nwe need to:\n- calulate valid segment lengths\n- Find two (non-ovelapping) segments that maximizes the coverage. For each segment, we look back and see what is the longest segment before and add that to the current segment length as a potential answer.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n- Segmenmt length: use sliding window to calculate valid segment length. Note that using sliding window we also count overlapping segments, so we don\'t need to worry about them when doing the next step \n- Max of two (using memorization/DP): We charachtrize a segment by its $$left$$ and $$right$$ index. Once we idnetify a valid segment (by increasing r$$ight$$ pointer to a certain threshold), we can store the longest segment so far up to the index $$right$$. However, we are interested in longest segment ending before $$left$$ index, so we query the memory ($$max_so_far$$) at $$left$$ index (which is set before when we where identifing some earlier valid segment).\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nfrom heapq import heappush, heappop\nfrom bisect import bisect_right\n\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, prizePositions: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n\n # check if having two segment of length k is possible\n if prizePositions[-1] - prizePositions[0] < 2*k:\n return len(prizePositions)\n \n # store max segment length up to the index\n max_so_far = [0] * (len(prizePositions)+1)\n \n left = right = 0\n ans = 0\n \n # dynamic sliding window to calculate valid segments\n for right in range(len(prizePositions)):\n while prizePositions[right] - prizePositions[left] > k :\n left += 1\n \n # a valid segment length\n seg_len = right-left+1\n\n # update max seg len up to the right+1 pointer\n max_so_far[right+1] = max(max_so_far[right], seg_len)\n\n # incorportate the longest segment before current segment\n ans = max(seg_len + max_so_far[left], ans)\n\n # handle ans with two overlapping segments \n return min(ans, len(prizePositions))\n \n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Python3']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
C++ | Sliding Window + Dynamic Programming
|
c-sliding-window-dynamic-programming-by-htsb6
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Sriram8a
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-22T15:59:24.932224+00:00
|
2024-11-22T15:59:24.932282+00:00
| 4
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prizePositions, int k) {\n int i=0;\n int j=0;\n int ans=0;\n vector<int>dp(prizePositions.size()+1,0);\n while(j<prizePositions.size())\n {\n while(prizePositions[j]-prizePositions[i]>k)\n {\n i++;\n }\n dp[j+1]=max(dp[j],j-i+1);\n ans=max(ans,dp[i]+j-i+1);\n j++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Calcualte all right segment win of every position (C++, O(n))
|
calcualte-all-right-segment-win-of-every-gkk6
|
Intuition\nit must be a O(n) complexity\n\n# Approach\nfirstly find out all the max win in the right side of index i (choose a segment in right),\n\nand then it
|
cx3129
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T01:53:46.984845+00:00
|
2024-07-14T01:53:46.984876+00:00
| 4
| false
|
# Intuition\nit must be a O(n) complexity\n\n# Approach\nfirstly find out all the max win in the right side of index i (choose a segment in right),\n\nand then iterate all left segment, find out the max of total win (left side + right side which already calculated as above)\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prizes, int k) {\n int n=int(prizes.size());\n\n //1. calcualte all max win of right segment for each index\n int winTotalRight=0,maxWinRight=0;\n vector<int>maxWinRights(n,0);\n\n for(int i=n-1,j=n-1;i>=0;) {\n if(prizes[j]-prizes[i]<=k) {\n winTotalRight++;\n maxWinRight= max(maxWinRight,winTotalRight);\n maxWinRights[i]=maxWinRight;\n --i;\n }\n else {\n j--;\n winTotalRight--;\n maxWinRights[i]=maxWinRight;\n }\n }\n\n // find out max total win (left side + right side (already calcualted above))\n int winTotalLeft=0,maxWinTotal=0;\n for(int i=0,j=0;i<n;) {\n if(prizes[i]-prizes[j]<=k) {\n winTotalLeft++;\n maxWinTotal = max(maxWinTotal,winTotalLeft+( (i<n-1)?maxWinRights[i+1]:0));\n ++i;\n }\n else {\n winTotalLeft--;\n j++;\n }\n }\n\n return maxWinTotal;\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Java O(n) slide window with dp
|
java-on-slide-window-with-dp-by-qingqian-is97
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nAssume dp[j] is the max
|
qingqianq
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-27T20:48:11.123725+00:00
|
2024-06-27T20:48:11.123744+00:00
| 14
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nAssume dp[j] is the max segment length from (0, i).\ndp[j] = max(dp[j - 1], valid(i, j)).\nFor (1,2,3,4) k = 4. If we add a new element 5.\n(1,2,3,4,5)\ndp[4] = range(0, 5) since (5 - 1 <= k) valid range(0, 4). \nIf the new added is value 6. \n(1,2,3,4,6) since 6 - 1 > 5, dp[4] = dp[3].\nFor all valid segment (i, j), max (dp[i - 1] + (j - i + 1)) will be the answer.\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximizeWin(int[] A, int k) {\n //dp[i] means array from [0, i - 1] max segment length;\n int n = A.length, res = 0;\n int[] dp = new int[n];\n for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; ++i){\n while(j < n && A[j] - A[i] <= k){\n int prev = j - 1 >= 0 ? dp[j - 1]: 0;\n dp[j] = Math.max(prev, j - i + 1);\n ++j;\n }\n// int prev = i - 1 >= 0 ? dp[i - 1] : 0;\n// res = Math.max(prev + j - i, res);\n }\n for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; ++i){\n while(j < n && A[j] - A[i] <= k){\n ++j;\n }\n int prev = i - 1 >= 0 ? dp[i - 1] : 0;\n res = Math.max(j - i + prev, res);\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Java']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Python || O(2N) || Easy Understanding || Left and Right Scan
|
python-o2n-easy-understanding-left-and-r-2f7m
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nWe create two lists to track the max number for one segment from both left and right si
|
liuyunjiahang
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-26T07:41:58.940096+00:00
|
2024-06-26T07:41:58.940118+00:00
| 42
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nWe create two lists to track the max number for one segment from both left and right sides, and there are at least one value.\n```\nleft = [1] * len(p)\nright = [1] * len(p)\n```\nThen max number for two segmens on `ith` element will equal to `left[i]+right[i+1]`. \n\nLastly we can get the max number for two segments on whole array.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, p: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n left = [1] * len(p)\n right = [1] * len(p)\n\n if len(p) <= 1:\n return 1\n i = 0 \n for j in range(1, len(p)):\n while p[j] - k > p[i]:\n i += 1\n left[j] = max(left[j-1], j - i + 1)\n \n i = len(p) - 1\n for j in range(len(p)-2, -1, -1):\n while p[i] - k > p[j]:\n i -= 1\n right[j] = max(right[j+1], i - j + 1)\n\n result = 0\n for i in range(0, len(p)-1):\n result = max(result, left[i]+right[i+1])\n return result\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Python3']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
O(N) Forward/Backward Scan in Python3, Beating 100%
|
on-forwardbackward-scan-in-python3-beati-suy7
|
Approach\nThis problem is about to find a pivot $p$ to split nums into two parts with the maximum value of $(l_2 - l_1 + 1) + (r_2 - r_1 + 1)$ for $l_1 \leq l_2
|
metaphysicalist
|
NORMAL
|
2024-05-22T17:01:15.757050+00:00
|
2024-05-22T17:03:38.043081+00:00
| 22
| false
|
# Approach\nThis problem is about to find a pivot $p$ to split `nums` into two parts with the maximum value of $(l_2 - l_1 + 1) + (r_2 - r_1 + 1)$ for $l_1 \\leq l_2 \\leq p \\leq r_1 \\leq r_2$ and $\\mathrm{nums}[l_2] - \\mathrm{nums}[l_1] \\leq k, \\mathrm{nums}[r_2] - \\mathrm{nums}[r_1] \\leq k$. \nTo speed up, we can precompute the best $(l_1, l_2)$ for each $p$, and loop for the best $(r_1, r_2)$ in the backward direction and find the best value of $(l_2 - l_1 + 1) + (r_2 - r_1 + 1)$. \nFor the two linear scan, the overall complexity is only $O(N)$.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $O(N)$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $O(N)$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, prizes: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n if prizes[-1] - prizes[0] <= k:\n return len(prizes)\n forward = [0, 1]\n offset = 0\n for i in range(1, len(prizes)):\n while prizes[i] - prizes[offset] > k:\n offset += 1\n forward.append(i - offset + 1)\n offset = len(prizes) - 1\n backward = 1\n ans = backward + forward[-1]\n for i in range(offset - 1, -1, -1):\n while prizes[offset] - prizes[i] > k:\n offset -= 1\n backward = max(backward, offset - i + 1)\n ans = max(ans, backward + forward[i])\n return ans```
| 0
| 0
|
['Two Pointers', 'Sliding Window', 'Python3']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
C++ Easy Solution
|
c-easy-solution-by-md_aziz_ali-rc3v
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prizePositions, int k) {\n int n = prizePositions.size();\n vector<int> pre(n,
|
Md_Aziz_Ali
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-05T07:54:53.316077+00:00
|
2024-02-05T07:54:53.316109+00:00
| 17
| false
|
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prizePositions, int k) {\n int n = prizePositions.size();\n vector<int> pre(n, 0);\n\n int j = 0;\n int end = prizePositions[0] + k;\n int count = 0;\n int maxi = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n int curr = prizePositions[i];\n while (curr > end) {\n end = prizePositions[++j] + k;\n count--;\n }\n count++;\n maxi = max(maxi, count);\n pre[i] = maxi;\n }\n\n j = n - 1;\n end = prizePositions[j] - k;\n count = 0;\n maxi = 0;\n int ans = pre[n - 1];\n\n for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {\n int curr = prizePositions[i];\n while (curr < end) {\n end = prizePositions[--j] - k;\n count--;\n }\n count++;\n ans = max(ans, pre[i] + maxi);\n maxi = max(maxi, count);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
The Only DP Solution || Sliding Window
|
the-only-dp-solution-sliding-window-by-v-ily1
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Verma_03
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-13T12:55:45.688069+00:00
|
2024-01-13T12:55:45.688088+00:00
| 11
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& p, int k) {\n int n = p.size();\n vector<int> dp(n,0);\n int ans = 0;\n\n int i = 0,j = 0;\n\n while(j < p.size()){\n while(p[j]-p[i] > k){\n i++;\n }\n\n if(i > 0){\n ans = max(ans,j-i+1+dp[i-1]);\n }\n else{\n ans = max(ans,j-i+1);\n }\n \n if(j > 0){\n dp[j] = max(dp[j-1],j-i+1);\n }\n else{\n dp[j] = j-i+1;\n }\n j++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
rust: simple partition_point and max array, beats 100%
|
rust-simple-partition_point-and-max-arra-mra4
|
\n# Code\n\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn maximize_win(prize_positions: Vec<i32>, k: i32) -> i32 {\n let mut i = 0;\n let mut cmax = vec![0; prize_p
|
happysings
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-07T09:01:38.240968+00:00
|
2024-01-07T09:01:38.241005+00:00
| 3
| false
|
\n# Code\n```\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn maximize_win(prize_positions: Vec<i32>, k: i32) -> i32 {\n let mut i = 0;\n let mut cmax = vec![0; prize_positions.len() + 1];\n let mut max = 0; // result\n while i < prize_positions.len() {\n let curr = prize_positions[i];\n // locate the largest segment with k from i\n let r = prize_positions.partition_point(|&x| x <= curr + k);\n // length of segment\n let wt = (r - i) as i32;\n // update cmax for r - max of segment ending at r\n // max of last max, current, or already ending ar r\n cmax[r] = cmax[i].max(cmax[r].max(wt));\n // update max with the max of last non overlapping segment\n max = max.max(cmax[i] + wt);\n // bubble up the max to all equal values for prizes\n while i < prize_positions.len() && prize_positions[i] == curr {\n i += 1;\n cmax[i] = cmax[i].max(cmax[i - 1]);\n }\n }\n max\n }\n}\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Rust']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Simple DP 🚀 || C++ || TC: O(N*3)
|
simple-dp-c-tc-on3-by-_maityamit-0rjc
|
\nint const N = 1e5;\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dp[N+1][3];\n int helper(int idx,int k,vector<int> &pp,int kk){\n if(idx==pp.size()||k==0) re
|
_maityamit
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-06T09:26:35.459514+00:00
|
2024-01-06T09:26:35.459550+00:00
| 8
| false
|
```\nint const N = 1e5;\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dp[N+1][3];\n int helper(int idx,int k,vector<int> &pp,int kk){\n if(idx==pp.size()||k==0) return 0;\n if(dp[idx][k]!=-1) return dp[idx][k];\n int ntk = helper(idx+1,k,pp,kk);\n int index = lower_bound(pp.begin(),pp.end(),pp[idx]+1+kk)-pp.begin();\n int tk = index-idx;\n tk+= helper(index,k-1,pp,kk);\n return dp[idx][k]=max(tk,ntk);\n }\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& pp, int k) {\n memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));\n return helper(0,2,pp,k);\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Recursive || 2D dp
|
recursive-2d-dp-by-sh1n0b1-ne35
|
When skipping, we skip all the occurances of current element.\nWhen picking, we pick till the indx where the element is greater than current element + k.\n\n# C
|
sh1n0b1
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-03T18:00:48.935661+00:00
|
2024-01-03T18:00:48.935698+00:00
| 12
| false
|
When skipping, we skip all the occurances of current element.\nWhen picking, we pick till the indx where the element is greater than current element + k.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int solve(vector<int>& prizePositions, vector<vector<int>>& dp, int k, int indx, int segments) {\n if(indx == prizePositions.size())\n return 0;\n if(segments == 0)\n return 0;\n\n if(dp[indx][segments] != -1)\n return dp[indx][segments]; \n\n int skipToIndex = lower_bound(prizePositions.begin(), prizePositions.end(), prizePositions[indx]+1) - prizePositions.begin();\n int skipped = solve(prizePositions, dp, k, skipToIndex, segments);\n\n int pickTillIndex = lower_bound(prizePositions.begin(), prizePositions.end(), prizePositions[indx]+k+1) - prizePositions.begin();\n int picked = pickTillIndex - indx + solve(prizePositions, dp, k, pickTillIndex, segments-1);\n\n return dp[indx][segments] = max(skipped, picked);\n }\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prizePositions, int k) {\n vector<vector<int>> dp(prizePositions.size() + 1, vector<int> (3, -1));\n return solve(prizePositions, dp, k, 0, 2);\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Recursion', 'C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
[C] sliding window, suffixMax, two ptrs | Time: O(n), Space: O(n)
|
c-sliding-window-suffixmax-two-ptrs-time-zr5n
|
C []\nint maximizeWin(\n\tconst int * const posArr,\n\tconst int posArrLen,\n\n\tconst int len\n){\n\tassert(posArrLen >= 1 && len >= 0);\n\n\tstruct {\n\t\tint
|
zhang_jiabo
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-25T12:50:21.858404+00:00
|
2023-11-25T12:50:21.858433+00:00
| 4
| false
|
```C []\nint maximizeWin(\n\tconst int * const posArr,\n\tconst int posArrLen,\n\n\tconst int len\n){\n\tassert(posArrLen >= 1 && len >= 0);\n\n\tstruct {\n\t\tint start;\n\t\tint cnt;\n\t} intervalArr[posArrLen];\n\tint intervalArrLen = 0;\n\tfor (int left = 0, right = 0; left < posArrLen; ){\n\t\twhile (right < posArrLen && posArr[right] <= posArr[left] + len){\n\t\t\tright += 1;\n\t\t}\n\n\t\tintervalArr[intervalArrLen].start = posArr[left];\n\t\tintervalArr[intervalArrLen].cnt = right - left;\n\t\tintervalArrLen += 1;\n\n\t\tconst int leftVal = posArr[left];\n\t\twhile (left < posArrLen && posArr[left] == leftVal){\n\t\t\tleft += 1;\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\n\tint suffixMaxArr[intervalArrLen];\n\tsuffixMaxArr[intervalArrLen - 1] = intervalArr[intervalArrLen - 1].cnt;\n\tfor (int i = intervalArrLen - 2; i >= 0; i -= 1){\n\t\tsuffixMaxArr[i] = suffixMaxArr[i + 1];\n\t\tif (intervalArr[i].cnt > suffixMaxArr[i]){\n\t\t\tsuffixMaxArr[i] = intervalArr[i].cnt;\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\n\tint maxPairSum = 0;\n\tfor (int i = 0, j = 0; i < intervalArrLen; i += 1){\n\t\twhile (j < intervalArrLen && intervalArr[j].start <= intervalArr[i].start + len){\n\t\t\tj += 1;\n\t\t}\n\n\t\tconst int curPairSum = intervalArr[i].cnt +\n\t\t\t( (j < intervalArrLen)? suffixMaxArr[j] : 0 );\n\t\tif (curPairSum > maxPairSum){\n\t\t\tmaxPairSum = curPairSum;\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\treturn maxPairSum;\n}\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['C']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Linear time using monotonic queue + sliding window
|
linear-time-using-monotonic-queue-slidin-39zw
|
Intuition\nMight as well be greedy with placement of two intervals and make them disjoint. Why make them overlapping and risk missing out on some prizes?\n\n# A
|
c-m-d-
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-17T00:52:50.915985+00:00
|
2023-11-17T00:52:50.916006+00:00
| 4
| false
|
# Intuition\nMight as well be greedy with placement of two intervals and make them disjoint. Why make them overlapping and risk missing out on some prizes?\n\n# Approach\nThought about binary search but realized we can solve it in linear time with a sliding window approach and monotonic queue. Straightforward sliding window approach yields the max number of prizes for any interval of size k starting at some index i in the input array.\n\nAs we iterate, we throw those results into a queue. This allows us to keep track of the best interval we\'ve already seen -- when a previously seen interval ends before our current interval begins, we update `best_single` to denote the best interval to the left that\'s disjoint from the current one. Because it\'s disjoint we don\'t need to worry about double counting prizes.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n), the queue can never have more than n elements, and we iterate once over the input array.\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n) due to queue\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& ps, int k) {\n const int n = ps.size();\n auto right = 0;\n auto best_single = 0;\n queue<pair<int, int>> q;\n auto best = 0;\n for (auto left = 0; left < n; ++left) {\n while (!q.empty() && q.front().first < ps[left]) {\n const auto [r, count] = q.front();\n q.pop();\n best_single = max(best_single, count);\n }\n while (right < n && ps[right] - ps[left] <= k) ++right;\n best = max(best, best_single + right - left);\n q.emplace(ps[right - 1], right - left);\n }\n return best;\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Rust Solution using Sliidng Window and DP
|
rust-solution-using-sliidng-window-and-d-dv8x
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n)\n\n# Code\n\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn maximize_win(prize_positions: Vec<i32>, k: i32) -> i32
|
rchaser53
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-04T08:09:35.841732+00:00
|
2023-11-04T08:09:35.841751+00:00
| 9
| false
|
# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn maximize_win(prize_positions: Vec<i32>, k: i32) -> i32 {\n let n = prize_positions.len();\n if n == 1 {\n return 1\n }\n\n let mut memo = vec![0;n];\n let mut max = 0;\n let mut ri = 0;\n for li in 0..n {\n while ri < n && prize_positions[ri] - prize_positions[li] <= k {\n ri += 1;\n let score = ri - li;\n max = max.max(score);\n memo[ri-1] = memo[ri-1].max(max);\n }\n\n if ri == n {\n break\n }\n }\n\n let mut result = 0;\n let mut li = (n-1) as i32;\n for ri in (1..n).rev() {\n while 0 <= li && prize_positions[ri] - prize_positions[li as usize] <= k {\n li -= 1;\n let score = ri - li as usize;\n if 0 <= li {\n result = result.max(score + memo[li as usize]);\n }\n }\n }\n\n result as i32\n }\n}\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Sliding Window', 'Rust']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
maximize win from two segments
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments-by-2020ku-cd3b
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
2020kucp1032
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-27T03:46:51.844610+00:00
|
2023-10-27T03:46:51.844642+00:00
| 33
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, prizePositions: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n\n intval=[]\n max_before=[]\n start=0\n count=0\n\n for index,pos in enumerate(prizePositions):\n count+=1\n while pos-k>prizePositions[start]:\n count-=1\n start+=1\n intval.append((count,pos))\n if not max_before or max_before[-1][0]<count:\n max_before.append((count,pos))\n\n max_sol=0\n while intval:\n count,pos=intval.pop()\n while max_before and max_before[-1][-1]>=pos-k:\n max_before.pop()\n\n candidate=count+(0 if not max_before else max_before[-1][0])\n max_sol=max(candidate,max_sol)\n\n return max_sol\n\n \n \n```
| 0
| 1
|
['Python3']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
C++ Implementation using Binary Search + Brute Force
|
c-implementation-using-binary-search-bru-tzin
|
Key Points\n- Find the unique segment till the length k using Binary Search\n- Then sort these segments according to the highest length\n- Then Brute Force by P
|
ayushnautiyal1110
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-24T18:38:15.301814+00:00
|
2023-10-24T18:38:15.301831+00:00
| 14
| false
|
**Key Points**\n- Find the unique segment till the length k using Binary Search\n- Then sort these segments according to the highest length\n- Then Brute Force by Picking one of the greatest no till 100 times and matching with the other greatest no\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n static bool cmp(pair<int,int> &p1,pair<int,int> &p2){\n return p1.second-p1.first>p2.second-p2.first; \n }\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prizePositions, int k) {\n \n set<int>st;\n vector<pair<int,int>>vp;\n for(int i=0;i<prizePositions.size();i++){\n if(st.find(prizePositions[i])==st.end()){\n st.insert(prizePositions[i]);\n int ind=upper_bound(prizePositions.begin(),prizePositions.end(),prizePositions[i]+k)-prizePositions.begin();\n // ind--;\n vp.push_back({i,ind-1});\n st.insert(prizePositions[i]);\n }\n }\n sort(vp.begin(),vp.end(),cmp);\n int n=vp.size();\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<min(100,n);i++){\n pair<int,int>p=vp[i];\n for(int j=0;j<vp.size();j++){\n \n pair<int,int>p1=vp[j];\n if(p.second>=p1.first && p1.first>=p.first || p1.second>=p.first &&p.first>=p1.first){\n int u=min(p.first,p1.first);\n int v=max(p.second,p1.second);\n ans=max(ans,v-u+1);\n }\n else{\n ans=max(ans,p.second-p.first+p1.second-p1.first+2);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Binary Search', 'C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Golang sliding solution
|
golang-sliding-solution-by-tjucoder-zcba
|
Code\ngo\nfunc maximizeWin(prizePositions []int, k int) int {\n\thash := make(map[int]int)\n\tfor _, p := range prizePositions {\n\t\thash[p]++\n\t}\n\tkeys :=
|
tjucoder
|
NORMAL
|
2023-09-14T16:52:22.264517+00:00
|
2023-09-14T16:52:22.264541+00:00
| 10
| false
|
# Code\n```go\nfunc maximizeWin(prizePositions []int, k int) int {\n\thash := make(map[int]int)\n\tfor _, p := range prizePositions {\n\t\thash[p]++\n\t}\n\tkeys := make([]int, 0, len(hash))\n\tfor k := range hash {\n\t\tkeys = append(keys, k)\n\t}\n\tsort.Ints(keys)\n\tl1, r1 := 0, 0\n\tmaxWinScore := hash[keys[0]]\n\tfor r1+1 < len(keys) && keys[r1+1] - keys[l1] <= k {\n\t\tr1++\n\t\tmaxWinScore += hash[keys[r1]]\n\t}\n\tif r1 + 1 >= len(keys) {\n\t\treturn maxWinScore\n\t}\n\tmaxLine1 := maxWinScore\n\tcurLine1 := maxWinScore\n\tmaxWinScore += hash[keys[r1+1]]\n\tl2, r2 := r1+1, r1+1\n\tfor r2+1 < len(keys) && keys[r2+1] - keys[l2] <= k {\n\t\tr2++\n\t\tmaxWinScore += hash[keys[r2]]\n\t}\n\tcurLine2 := maxWinScore - curLine1\n\tfor r2 + 1 < len(keys) {\n\t\tr2++\n\t\tcurLine2 += hash[keys[r2]]\n\t\tfor keys[r2] - keys[l2] > k {\n\t\t\tcurLine2 -= hash[keys[l2]]\n\t\t\tl2++\n\t\t}\n\t\tfor r1 + 1 < l2 {\n\t\t\tr1++\n\t\t\tcurLine1 += hash[keys[r1]]\n\t\t\tfor keys[r1] - keys[l1] > k {\n\t\t\t\tcurLine1 -= hash[keys[l1]]\n\t\t\t\tl1++\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\tif curLine1 > maxLine1 {\n\t\t\t\tmaxLine1 = curLine1\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t}\n\t\tif maxLine1 + curLine2 > maxWinScore {\n\t\t\tmaxWinScore = maxLine1 + curLine2\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\treturn maxWinScore\n}\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Sliding Window', 'Go']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Python Sliding Window O(N). Clean Code + Intuition + Similar problem
|
python-sliding-window-on-clean-code-intu-la19
|
Intuition\nThis is the same problem as:\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iii/editorial, Approach 1: Bidirectional Dynamic Programm
|
bwindsor22
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-20T18:05:38.242036+00:00
|
2023-08-20T18:23:35.897638+00:00
| 43
| false
|
# Intuition\nThis is the same problem as:\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iii/editorial, Approach 1: Bidirectional Dynamic Programming, where you want a max to the left of i and a max to the right of i.\n\n# Approach\n1. Use a counter to get a num -> count mapping so the distance to iterate becomes less\n2. Make an array in_span_l which is the maximum possible score making a span to the left of this index. Use a sliding window to compute this, tracking all numbers within k span of the index. \n3. Similarly, make an array in_span_r is the maximum possible to the right of this index. \n4. The max is max(in_span_l[i] + in_span_r[i + 1]) for any i \n```\n1 2 3 5 7 num\n2 2 2 1 2 count of num\n2 4 6 6 6 in_span_l\n6 4 3 3 2 in_span_r\n```\n\n# Code\n```\n\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, prizePositions: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n\n counts = Counter(prizePositions)\n counts_arr = [(num, count) for num, count in counts.items()]\n if len(counts_arr) == 1:\n return counts_arr[0][1]\n num_ind = list(counts.keys())\n in_span = []\n rolling_count = 0\n j = 0\n pre = -inf\n for i in range(len(counts_arr)):\n rolling_count += counts_arr[i][1]\n while num_ind[i] - num_ind[j] > k:\n rolling_count -= counts_arr[j][1]\n j += 1\n in_span.append(max(rolling_count, pre))\n pre = max(rolling_count, pre)\n\n in_span_r = []\n rolling_count = 0\n j = len(counts_arr) - 1\n pre = -inf\n for i in range(len(counts_arr) - 1, -1, -1):\n rolling_count += counts_arr[i][1]\n while num_ind[j] - num_ind[i] > k:\n rolling_count -= counts_arr[j][1]\n j -= 1\n in_span_r.append(max(rolling_count, pre))\n pre = max(rolling_count, pre)\n in_span_r = list(reversed(in_span_r))\n # print(list(range(len(counts_arr))), \'i\')\n # print(list(counts.keys()), \'num\')\n # print(list(counts.values()), \'count of num\')\n # print(in_span, \'span_l\')\n # print(in_span_r, \'span_r\')\n max_all = -inf\n for i in range(len(in_span) - 1):\n max_all = max(max_all, in_span[i] + in_span_r[i + 1])\n return max_all\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Python3']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Swift, DP + Sliding Segment, O(n)
|
swift-dp-sliding-segment-on-by-sergeyles-3ey6
|
Intuition\nThe problem of maximizing wins from one segment, can be effectively solved using a sliding window approach. By utilizing this approach, we can calcul
|
sergeyleschev
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-19T15:40:41.002907+00:00
|
2023-08-19T15:41:21.073763+00:00
| 1
| false
|
# Intuition\nThe problem of maximizing wins from one segment, can be effectively solved using a sliding window approach. By utilizing this approach, we can calculate the outcome by considering the dynamic programming (dp) values.\n\n# Approach\nTo solve this problem, we establish a sliding segment, resembling a sliding window, where the difference between A[i] and A[j] is less than or equal to k.\n\nThe dp array dp[k] signifies the maximum number of elements we can encompass if we optimally choose a single segment within the first k elements.\n\nAs we shift a segment from the left to the right, the count of elements covered by this segment is given by i - j + 1. Additionally, within the initial j elements, we are capable of covering at most dp[j] elements.\n\nIn total, we can cover i - j + 1 + dp[j] elements. Continuously update the result res during this process. Ultimately, return the value of res.\n\nThis approach offers a clear way to maximize the count of prizes won through strategically selecting two segments while adhering to the specified conditions.\n\n# Complexity\n\n- Time complexity: `O(n)`\n\n- Space complexity: `O(n)`\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n func maximizeWin(_ prizePositions: [Int], _ k: Int) -> Int {\n var res = 0\n let n = prizePositions.count\n var j = 0\n var dp = Array(repeating: 0, count: n + 1)\n \n for i in 0..<n {\n while j < n && prizePositions[j] < prizePositions[i] - k {\n j += 1\n }\n dp[i + 1] = max(dp[i], i - j + 1)\n res = max(res, i - j + 1 + dp[j])\n }\n \n return res\n }\n}\n\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Swift']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
python O(N) runtime O(1) space
|
python-on-runtime-o1-space-by-sroninio-za2q
|
Approach\nIterate with head right to left.\nAt any iteration maintain the following:\n- longest segment that ends exactly at head on the right side of the segme
|
sroninio
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-08T08:19:08.985433+00:00
|
2023-08-08T08:19:08.985451+00:00
| 17
| false
|
# Approach\n$$Iterate$$ with $$head$$ right to left.\nAt any iteration maintain the following:\n- longest segment that ends exactly at $$head$$ on the right side of the segment: $$currLeft$$ stands for the number of prizes in this segment and $$leftEdge$$ stands for the left edge of the segment\n- longest segment that ends exactly at $$head$$ on the left side of the segment : $$currRight$$ stands for the number of prizes in this segment and $$rightEdge$$ stands for the right edge of the segment\n- number of prizes in the longest segment that ends at some indx larger or equal than $$head$$ on the left side of the segment: $$bestRight$$\n- best result until now: $$best$$\n\nat any iteration of $$head$$ we:\n - update $$currLeft$$ and $$leftEdge$$ by iterating left with $$leftEdge$$ as long as the segment is valid.\n - update $$currRight$$ and $$rightEdge$$ by iterating left with $$rightEdge$$ as long as the segment is not valid.\n - update $$bestRight$$ as max($$bestRight$$, $$currRight$$)\n - update $best$ as max($best$, $$currLeft$$ + $$bestRight$$)\n\nat the end return $best$.\ncorrectness follows straight forward from the algorithm description\nLets say for example that the best segments to pick are [10,30], [80,100] so by the time head got to 30 we already accounted for [80,100]\nand now we have [10,30] in our hands, so we will account for this solution. (obviously we will never account a non existing solution so all good)\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(N)$$\n$$leftEdge$$, $$rightEdge$$, $$head$$ always advance left and at each advnacment we do O(1) operations so all good.\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(1)$$: we simply hold 7 variables \n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def maximizeWin(self, prizePositions, k):\n """\n :type prizePositions: List[int]\n :type k: int\n :rtype: int\n """\n N = len(prizePositions)\n head, left_edge, right_edge, curr_left, curr_right, best_right, best = N-1, N, N-1, 1, 0, 0, 0\n \n while head >= 0:\n curr_left -= 1\n while (left_edge > 0) and (prizePositions[head] - prizePositions[left_edge - 1] <= k):\n left_edge -= 1\n curr_left += 1\n best = max(best, best_right + curr_left)\n curr_right += 1\n while prizePositions[right_edge] - prizePositions[head] > k:\n curr_right -= 1\n right_edge -= 1\n best_right = max(best_right, curr_right)\n head -= 1\n return best\n\n\n\n \n\n\n\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Python']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Ruby O(N)
|
ruby-on-by-fnkwjgsm3qruaf-7lod
|
\nruby\n# @param {Integer[]} prize_positions\n# @param {Integer} k\n# @return {Integer}\ndef maximize_win(prize_positions, k)\n # dp[idx] := max prize if one o
|
FNkWJgsm3QruaF
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-05T21:53:00.507839+00:00
|
2023-08-05T21:53:00.507860+00:00
| 1
| false
|
\n```ruby\n# @param {Integer[]} prize_positions\n# @param {Integer} k\n# @return {Integer}\ndef maximize_win(prize_positions, k)\n # dp[idx] := max prize if one optimal segment is chosen among the first k prizes\n dp = Array.new(prize_positions.length + 1, 0)\n res, left = 0, 0\n for right in 0...prize_positions.length\n while prize_positions[right] - prize_positions[left] > k\n left += 1\n end\n dp[right + 1] = [dp[right], right - left + 1].max\n res = [res, right - left + 1 + dp[left]].max\n end\n res\nend\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Ruby']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
fully explained c++ solution
|
fully-explained-c-solution-by-deviltrek-znuv
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
deviltrek
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-20T15:41:49.721479+00:00
|
2023-07-20T15:41:49.721509+00:00
| 13
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic: \n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& nums, int k) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<int>v(n);\n // this vector store how much element if take nums[i] starting x-cordinates\n // That means number of element between [nums[i],nums[i]+k];\n for(int i = 0;i<nums.size();i++){\n int x = upper_bound(nums.begin()+i,nums.end(),nums[i]+k) - nums.begin(); \n v[i] = x - i;\n cout<<v[i]<<" ";\n // as i mention above we store element between[nums[i],nums[i]+k]\n // suppose we take nums[i] = 1 at i = 0 in example 1 1 2 2 3 3 5\n //then x will be index = 6\n // we store at i = 0 in vector v; 6 that is number of element between [nums[i],nums[i]+k] (1 , 3);\n } \n\n //now v vector : - 6 5 5 3 3 2 1\n\n\n vector<int>suff(n);\n suff[n-1] = 1;\n // suff vector store maximum number of prize we get if we chhose index i;\n long long ans = 0;\n for(int i = n-2;i>=0;i--){\n suff[i] = max(suff[i+1],v[i]);\n }\n //now suff vector : - 1 2 3 3 4 5 6\n\n\n //now for getting answer\n for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){\n //suppose you chhose index i = 1,then v[i] = 5 means it have prize so 1 + 5 = 6 \n // first segment is at i = 1 and second at 6\n // and suff vector store maximum prize you can get at index 6 suff[i+v[i]] \n if(i+v[i]<n){\n ans = max(ans,1ll*(suff[i+v[i]]+v[i]));\n }\n ans = max(ans,1ll*(v[i]));\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Python3 Dynamic programming
|
python3-dynamic-programming-by-wxli3388-ok5f
|
Approach\n- Need to choose at most two segment, the dfs function should go through all index or run out of two segments.\n- There are two states in each index,
|
wxli3388
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-16T15:31:29.437668+00:00
|
2023-07-16T16:00:40.265955+00:00
| 18
| false
|
# Approach\n- Need to choose at most two segment, the dfs function should go through all index or run out of two segments.\n- There are two states in each index, pick or not pick\n- If pick the idx, skip the value less or equal than the value plus k. \n ex: `prize[idx] = 1 and k = 2`\n It can cover from value 1 to 3, so find the next first index larger than 3, using binary search to find next index\n- If skip the index, skip all the index with the same value.\n ex: `prize = [1,1,1,1,2,2,2,3,3]`\n If skip index 0, should also skip other index with the same value `1`, it won\'t bring larget answer, using binary search to find the next first index of value larger than 1d\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO( n * log(n) *2)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO( n )\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, prizePositions: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n @cache\n def dfs(idx, n):\n if idx==len(prizePositions) or n==0:\n return 0\n left = bisect.bisect_right(prizePositions, prizePositions[idx]+k)\n i = bisect.bisect_right(prizePositions, prizePositions[idx])\n a = dfs(left, n-1)+left-idx\n b = dfs(i, n)\n return max(a,b)\n return dfs(0, 2)\n```\n\nIterator\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, prizePositions: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n dp = [0 for _ in range(len(prizePositions)+1)]\n ans = 0\n for i in range(len(prizePositions)):\n if i>0:\n dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[i-1])\n left = bisect.bisect_right(prizePositions, prizePositions[i]+k)\n dp[left] = max(dp[left], left-i)\n ans = max(ans, dp[i]+left-i)\n return ans\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python3']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
DP. Time: O(3*n), Space: O(2*n)
|
dp-time-o3n-space-o2n-by-iitjsagar-e5lj
|
class Solution(object):\n def maximizeWin(self, prizePositions, k):\n """\n :type prizePositions: List[int]\n :type k: int\n :rty
|
iitjsagar
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-15T20:51:36.734321+00:00
|
2023-07-15T20:51:36.734348+00:00
| 2
| false
|
class Solution(object):\n def maximizeWin(self, prizePositions, k):\n """\n :type prizePositions: List[int]\n :type k: int\n :rtype: int\n """\n \n n = len(prizePositions)\n \n jump_arr = [0 for i in range(n)]\n r = n-1\n \n for i in range(n-1,-1,-1):\n while prizePositions[r] > prizePositions[i] + k:\n r -= 1\n \n jump_arr[i] = r\n \n \n dp_prev = [0 for i in range(n)]\n \n max_so_far = 0\n for i in range(n-1,-1,-1):\n dp_prev[i] = max(jump_arr[i] - i + 1, max_so_far)\n max_so_far = dp_prev[i]\n \n res = 0\n for i in range(n-1,-1,-1):\n cur = jump_arr[i] - i + 1\n \n if jump_arr[i] + 1 < n:\n cur += dp_prev[jump_arr[i] + 1]\n \n res = max(res, cur)\n \n return res\n\n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n
| 0
| 0
|
[]
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Best DP + Binary search solution(c++ solution)
|
best-dp-binary-search-solutionc-solution-biio
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
jishudip389
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-15T20:11:28.353486+00:00
|
2023-07-15T20:11:28.353510+00:00
| 4
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n int f(int ind,int k,vector<int>&arr,int l,vector<vector<int>>&dp){\n if(k == 0)return 0;\n if(ind == arr.size())return 0;\n\n if(dp[ind][k]!=-1)return dp[ind][k];\n int nottake = f(ind+1,k,arr,l,dp);\n int take = -1e9;\n if(k>0){\n int findind = lower_bound(arr.begin(),arr.end(),arr[ind]+l+1) - arr.begin();\n take = (findind - ind) + f(findind,k-1,arr,l,dp);\n }\n return dp[ind][k] = max(take,nottake);\n }\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prizePositions, int k) {\n int n = prizePositions.size();\n vector<vector<int>>dp(n+1,vector<int>(3,-1));//we can take at most 2 segment \n //DP + Binary search solution(c++ solution)\n return f(0,2,prizePositions,k,dp);\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Simple 1D dp C++
|
simple-1d-dp-c-by-user0592e-vqd8
|
\n\nVariables:\n\nn represents the size of the input array nums.\nstart keeps track of the starting index of the segment.\nans stores the maximum number of priz
|
user0592E
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-04T09:12:10.940755+00:00
|
2023-07-04T09:12:10.940783+00:00
| 24
| false
|
\n\nVariables:\n\nn represents the size of the input array nums.\nstart keeps track of the starting index of the segment.\nans stores the maximum number of prizes won.\ndp is an auxiliary array that keeps track of the maximum number of prizes that can be won up to the current index.\n\n\nIterate through the elements of prizePositions using the variable i:\n\nInside the loop, we find the maximum value of start such that prizePositions[i] - prizePositions[start] <= k. This means we find the leftmost element within k distance from prizePositions[i].\nUpdate ans by comparing the current maximum with the length of the current segment (i - start + 1) plus the maximum number of prizes won from the previous segment (start > 0 ? dp[start - 1] : 0).\nUpdate dp[i] by comparing the maximum number of prizes won up to the previous index (i > 0 ? dp[i - 1] : 0) with the length of the current segment (i - start + 1).\nReturn the maximum number of prizes won, which is stored in ans.\n\nThe main idea behind this approach is to find the maximum number of prizes that can be won by selecting two segments of length k or less. By keeping track of the starting index start and updating the dp array, the algorithm efficiently finds the optimal solution in a single pass through the prizePositions array.\n\nThe time complexity of this code is O(n), where n is the size of the input array prizePositions. The space complexity is O(n) as well, due to the dp array.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prizePositions, int k) \n {\n int n=prizePositions.size();\n int start =0; int ans=0;\n vector<int> dp(n);\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n //find leftmost element with k segement\n while(prizePositions[i]-prizePositions[start]>k) start++;\n //calculate this segment length\n int segmentLength = i-start+1;\n //maintain ans, sum of two segemtn, curr+ use dp for previous one \n ans = max(ans,segmentLength+(start>0?dp[start-1]:0));\n //update dp[i] which store maxlenght upto this index\n dp[i] = max((i>0 ? dp[i-1]:0),segmentLength);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n \n// int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prizePositions, int k) {\n// //FIrst to intersect na hi kr to theek , But kabhi forceful krana pdega\n// //maintain two max\n \n// int max1=INT_MIN,max2 =INT_MIN;\n// for(int i=0;i<prizePositions.size();i++)\n// {\n// int val =prizePositions[i];\n// int target = val+k-1; //isse bade wala pinter nikalo\n// int len = upper_bound(prizePositions.begin()+i,prizePositions.end(),target) - (prizePositions.begin()+i) ;\n// if(len>=max1)\n// {\n// max2 =max1;\n// max1 = len;\n// }\n// //update i to the pointer iterator \n// i=i+len; //But yhn cases miss honge overlap wale\n// }\n// return max1+max2;\n// }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
2p+dp ^^
|
2pdp-by-andrii_khlevniuk-63jl
|
time: O(N); space: O(N)\n\nint maximizeWin(vector<int>& x, int k) \n{\n\tint out{}; \n\tfor(int i{}, j{}, d[100002]{}; i<size(x); )\n\t\tif(x[i]-x[j]<=k)\n\t\t\
|
andrii_khlevniuk
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-03T12:26:35.201906+00:00
|
2023-07-03T15:22:45.930874+00:00
| 13
| false
|
**time: `O(N)`; space: `O(N)`**\n```\nint maximizeWin(vector<int>& x, int k) \n{\n\tint out{}; \n\tfor(int i{}, j{}, d[100002]{}; i<size(x); )\n\t\tif(x[i]-x[j]<=k)\n\t\t\t++i,\n\t\t\td[i] = max(d[i-1], i-j),\n out = max(out, i-j+d[j]);\n\t\telse\n\t\t\t++j;\n\treturn out; \n}\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['C', 'C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
O(N) approach using dynamic programming and sliding window
|
on-approach-using-dynamic-programming-an-2usj
|
Approach\nDynamic Programming with Sliding Window\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution(object):\n
|
the_first_avenger_2023
|
NORMAL
|
2023-06-02T09:27:41.362149+00:00
|
2023-06-02T09:29:07.824076+00:00
| 33
| false
|
# Approach\nDynamic Programming with Sliding Window\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def maximizeWin(self, P, k):\n #Have a dp array to record the max length of the first segment at i:\n dp = [0] * len(P)\n res = 0\n left = 0 # first pointer of the sliding window\n for right in range(len(P)):\n while P[right] - P[left] > k:\n # sliding window, contract left if (P[left],P[right]) is not a valid segment\n left += 1\n\n # now, (left, right) is valid\n # calculate this segment length starts from left to right\n this_segment = right - left + 1\n\n # first max segment length is the dp[left-1] because this segment starts from left\n first_segment = dp[left-1]\n\n # result is the max of current res or (first_segment + second segment(this_segment))\n res = max(res, first_segment + this_segment)\n\n # dp[right] is the max of dp[right-1] or this_segment\n dp[right] = max(dp[right-1], this_segment)\n\n return res\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Python']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Store longest range in left and right using sliding window
|
store-longest-range-in-left-and-right-us-113v
|
\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, pos, k):\n n = len(pos)\n l = [0] * n\n r = [0] * n\n i = 0\n for j in range(n):
|
theabbie
|
NORMAL
|
2023-05-12T01:23:07.829380+00:00
|
2023-05-12T01:23:07.829422+00:00
| 21
| false
|
```\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, pos, k):\n n = len(pos)\n l = [0] * n\n r = [0] * n\n i = 0\n for j in range(n):\n while i < j and pos[j] - pos[i] > k:\n i += 1\n if pos[j] - pos[i] <= k:\n l[j] = j - i + 1\n i = n - 1\n for j in range(n - 1, -1, -1):\n while i > j and pos[i] - pos[j] > k:\n i -= 1\n if pos[i] - pos[j] <= k:\n r[j] = i - j + 1\n res = 0\n maxleft = 0\n for i in range(n):\n res = max(res, maxleft + r[i])\n maxleft = max(maxleft, l[i])\n return res\n```
| 0
| 0
|
[]
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
C++||DP||Sliding window approaches🔥🚀🔥✨💖
|
cdpsliding-window-approaches-by-curious_-4gp2
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prizePositions, int k) {\n int res =0;;\n int n = prizePositions.size();\n
|
Curious_hritik
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-09T09:23:51.139225+00:00
|
2023-04-09T09:23:51.139271+00:00
| 42
| false
|
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prizePositions, int k) {\n int res =0;;\n int n = prizePositions.size();\n int j=0;\n\n vector<int>dp(n+1,0);\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n while(prizePositions[j]<prizePositions[i]-k)\n j++;\n \n dp[i+1] = max(dp[i],i-j+1);\n res = max(res,i-j+1+dp[j]);\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Use two points cleverly
|
use-two-points-cleverly-by-fredrick_li-n2y2
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Fredrick_LI
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-10T21:04:47.478566+00:00
|
2023-03-10T21:04:47.478618+00:00
| 87
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, p: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n i,n = 0,len(p)\n if p[-1] - p[0] <= k:\n return n\n pre = [0]\n i = 0\n for j in range(1,n):\n if p[j] - p[i] > k:\n i += 1\n else:\n pre.append(j)\n sub = [n-1]\n j = n-1\n for i in range(n-2,-1,-1):\n if p[j] - p[i] > k:\n j -= 1\n else:\n sub.append(i)\n \n sub = sub[::-1]\n i,j = 0,0\n ans = -len(sub)\n while i < len(pre) and j < len(sub):\n if pre[i] >= sub[j]:\n j += 1\n else:\n ans = max(i-j,ans)\n i += 1\n return ans + len(sub) + 1\n\n\n\n \n \n\n \n\n\n\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Python3']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Python (Simple DP + Sliding Window)
|
python-simple-dp-sliding-window-by-rnota-68qj
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
rnotappl
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-03T16:16:02.938882+00:00
|
2023-03-03T16:16:02.938912+00:00
| 79
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, prizePositions, k):\n n = len(prizePositions)\n\n left, dp, max_val = 0, [0]*(n+1), 0\n\n for right in range(n):\n while prizePositions[right] - prizePositions[left] > k:\n left += 1\n\n dp[right+1] = max(dp[right],right-left+1)\n\n max_val = max(max_val,dp[left] + right - left + 1)\n\n return max_val\n\n\n\n\n\n \n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Python3']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
[1Sentence] Slide a window saving best solution so far, return max(sum(window) + best to the left)
|
1sentence-slide-a-window-saving-best-sol-0l1c
|
Upvote if you like the simplicity\n\n\ndef maximizeWin(self, prizes: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n bestBefore = [0] * (len(prizes) + 1)\n bestBeforeSoFar =
|
Balwierz
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-18T13:45:31.484905+00:00
|
2023-02-18T13:45:31.484938+00:00
| 63
| false
|
# Upvote if you like the simplicity\n\n```\ndef maximizeWin(self, prizes: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n bestBefore = [0] * (len(prizes) + 1)\n bestBeforeSoFar = 0\n ret = 0\n runSum = 0\n i, j = 0, 0\n while j<len(prizes):\n x = prizes[j]\n while j<len(prizes) and prizes[j] == x:\n runSum += 1\n j += 1\n while prizes[i] + k < prizes[j-1]:\n runSum -= 1\n i += 1 # i points to the first included price index\n bestBeforeSoFar = max(bestBeforeSoFar, runSum)\n bestBefore[j] = bestBeforeSoFar\n ret = max(ret, runSum + bestBefore[i])\n return ret\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Python3']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Python DP
|
python-dp-by-dinar-q4g2
|
\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, prizePositions: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n\n prefix = [0] * len(prizePositions)\n sufix = [0] * len
|
dinar
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-18T11:46:33.837388+00:00
|
2023-02-18T11:46:33.837434+00:00
| 30
| false
|
```\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, prizePositions: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n\n prefix = [0] * len(prizePositions)\n sufix = [0] * len(prizePositions)\n prefix[0] = 1\n sufix[-1] = 1\n left, right = 0, 1\n while right < len(prizePositions):\n if prizePositions[right] - prizePositions[left] <= k:\n prefix[right] = max(prefix[right - 1], right - left + 1)\n right += 1\n else:\n left += 1\n\n left, right = len(prizePositions) - 2, len(prizePositions) - 1\n while left >= 0:\n if prizePositions[right] - prizePositions[left] <= k:\n sufix[left] = max(sufix[left + 1], right - left + 1)\n left -= 1\n else:\n right -= 1\n \n \n ans = 0\n print(prefix)\n print(sufix)\n for border in range(len(prizePositions) + 1):\n p = prefix[border - 1] if border > 0 else 0\n s = sufix[border] if border < len(prizePositions) else 0\n l = p + s\n ans = max(ans, l)\n \n return ans\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Prefix+Suffix+BS using python
|
prefixsuffixbs-using-python-by-venkataak-k2tb
|
Code\n\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, pp: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n n=len(pp)\n \n pre=[0]*(n)\n suff=[0]*(n)\n
|
venkataakhil4518
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-18T10:11:45.997676+00:00
|
2023-02-18T10:11:45.997722+00:00
| 46
| false
|
# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, pp: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n n=len(pp)\n \n pre=[0]*(n)\n suff=[0]*(n)\n \n for i in range(n-1,-1,-1):\n pos=bisect_right(pp,pp[i]+k)\n if i==n-1:\n suff[i]=pos-i\n else:\n suff[i]=max(pos-i,suff[i+1])\n \n pos=bisect_right(pp,pp[i]-k-1)\n pre[i]=i-pos+1\n \n for i in range(1,n):\n pre[i]=max(pre[i-1],pre[i])\n \n ans=pre[0]\n # for i in range(n-2,-1,-1):\n # suff[i]=max(suff[i+1],suff[i])\n for i in range(n-1):\n ans=max(ans,pre[i]+suff[i+1])\n \n return ans\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Python3']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Python solution using DP
|
python-solution-using-dp-by-pradoshsahoo-3rgi
|
Code\n\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, A: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n dp = [0] * (len(A) + 1)\n res = j = 0\n for i, a in enum
|
pradoshsahoo81
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-18T06:29:37.553573+00:00
|
2023-02-18T06:29:37.553619+00:00
| 38
| false
|
# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximizeWin(self, A: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n dp = [0] * (len(A) + 1)\n res = j = 0\n for i, a in enumerate(A):\n while A[j] < A[i] - k: j += 1\n res = max(res, i - j + 1 + dp[j])\n dp[i + 1] = max(dp[i], i - j + 1)\n return res\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Python3']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Swift | One-Liner
|
swift-one-liner-by-upvotethispls-ul1a
|
One-Liner, terse (accepted answer)\n\nclass Solution {\n func maximizeWin(_ p: [Int], _ k: Int) -> Int {\n p.indices.reduce(into:(0,0,[0])){while p[$0.0]<p
|
UpvoteThisPls
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-16T23:15:26.185660+00:00
|
2023-02-16T23:21:16.576116+00:00
| 21
| false
|
**One-Liner, terse (accepted answer)**\n```\nclass Solution {\n func maximizeWin(_ p: [Int], _ k: Int) -> Int {\n p.indices.reduce(into:(0,0,[0])){while p[$0.0]<p[$1]-k{$0.0+=1};let x=$1-$0.0+1;$0.1=max($0.1,x+$0.2[$0.0]);$0.2+=[max($0.2[$1],x)]}.1\n }\n}\n```\n\n---\n\n**One-Liner, expanded and annotated (accepted answer)**\n```\nclass Solution {\n func maximizeWin(_ prizePositions: [Int], _ k: Int) -> Int {\n prizePositions.indices.reduce(into: (\n result: 0,\n trailingSegLower: 0, // lower bounds of second segment\n dp: [0] // each element is max prize count (delta X) for the prize at this location\n )) { data, leadingSegLower in\n while prizePositions[data.trailingSegLower] < prizePositions[leadingSegLower] - k {\n data.trailingSegLower += 1\n }\n let leadingSegPrizeCount = leadingSegLower - data.trailingSegLower + 1\n let trailingSegPrizeCount = data.dp[data.trailingSegLower]\n data.result = max(data.result, leadingSegPrizeCount + trailingSegPrizeCount)\n data.dp.append(max(data.dp[leadingSegLower], leadingSegPrizeCount))\n }.result\n }\n}\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Swift']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Easy C++ O(N) solution || sliding segment
|
easy-c-on-solution-sliding-segment-by-sa-xjjc
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& arr, int k) {\n //for every index store the result\n vector<int> dp(arr.size());\n
|
saiteja_balla0413
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-14T10:29:11.680224+00:00
|
2023-02-14T10:29:11.680270+00:00
| 71
| false
|
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& arr, int k) {\n //for every index store the result\n vector<int> dp(arr.size());\n \n //dp[i] stores the max pos covered by any single segment of length k\n int res=0;\n int i=0;\n int maxiSingle=0;\n \n for(int j=0;j<arr.size();j++)\n {\n while(arr[i]< arr[j]-k)\n i++;\n int dist=j-i+1;\n maxiSingle=max(maxiSingle,dist);\n dp[j]=maxiSingle; \n //arr[i..j] consits of one segment and add the max ans for subarray [0..i-1] \n int curr=dist;\n if(i>0)\n curr+=dp[i-1];\n res=max(res,curr);\n \n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
[]
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
C++ Solution Queue
|
c-solution-queue-by-retire-xpr7
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prizePositions, int k) \n {\n int f[3];\n f[0]=f[1]=f[2]=0;\n queue<
|
Retire
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-13T15:40:35.572041+00:00
|
2023-02-13T15:40:35.572080+00:00
| 29
| false
|
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prizePositions, int k) \n {\n int f[3];\n f[0]=f[1]=f[2]=0;\n queue<int>q1;\n queue<pair<int,int>>q2;\n for(auto &x:prizePositions)\n {\n f[0]+=1;\n q1.push(x);\n while(q1.size()&&q1.front()<x-k)\n {\n f[0]-=1;\n q1.pop();\n }\n q2.push({x,f[0]});\n while(q2.size()&&q2.front().first<x-k)\n {\n f[1]=max(f[1],q2.front().second);\n q2.pop();\n }\n f[2]=max(f[2],f[1]+f[0]);\n }\n return max({f[0],f[1],f[2]});\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Queue', 'C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
easy short efficient clean code
|
easy-short-efficient-clean-code-by-maver-rqvs
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\ntypedef long long ll;\n#define vi(x) vector<x>\nint maximizeWin(vector<int>&v, int k) {\n ll n=v.size(), ans=0;\n vi(ll)dp(n)
|
maverick09
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-12T05:40:41.735876+00:00
|
2023-02-12T05:40:41.735915+00:00
| 38
| false
|
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\ntypedef long long ll;\n#define vi(x) vector<x>\nint maximizeWin(vector<int>&v, int k) {\n ll n=v.size(), ans=0;\n vi(ll)dp(n);\n for(ll i=0, j=0;i<n;++i){\n while(j<i && v[i]-v[j]>k){\n ++j;\n }\n dp[i]=max(i?dp[i-1]:0, i-j+1);\n ans=max(ans, i-j+1+(j?dp[j-1]:0));\n }\n return ans;\n}\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'Sliding Window']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
[Python] Maximize Left and Right Segments, The Best
|
python-maximize-left-and-right-segments-53hqh
|
Intuition\nSplit the prizes list such that the number of maximum-count prizes segment of length k in left and right part of the split is maximized.\n\nThe Best!
|
Triquetra
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-11T19:38:20.243427+00:00
|
2023-02-11T19:38:20.243490+00:00
| 41
| false
|
# Intuition\nSplit the prizes list such that the number of maximum-count prizes segment of length $$k$$ in left and right part of the split is maximized.\n\nThe Best!\n\n# Approach\nUse a sliding window to build two aggregated maximums of $$k$$-length prizes counts when moving from left and from right.\n\nHandle a special case of singleton input array by providing a default value to the final `max()` iterator.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```py\ndef maximizeWin(self, prizes: list[int], k: int) -> int:\n n, i, j = len(prizes), 0, 0\n left, right = [0] * n, [0] * n\n\n while j != n:\n while prizes[j]-prizes[i] > k:\n i += 1\n left[j] = max(j-i+1, left[j-1] if j != 0 else 0)\n j += 1\n \n i = j = n-1\n while i != -1:\n while prizes[j]-prizes[i] > k:\n j -= 1\n right[i] = max(j-i+1, right[i+1] if i != n-1 else 0)\n i -= 1\n\n return max((left[i] + right[i+1] for i in range(n-1)), default=n)\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Python3']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
C++ || Binary Search || Lower bound || Suffix Max
|
c-binary-search-lower-bound-suffix-max-b-4zd9
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(NlogN+N+N)\n\n- Space complexity: O(3N)\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n //find last value of val\n //1 2 2 3
|
sangramsinh
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-11T04:41:05.834640+00:00
|
2023-02-11T04:41:05.834677+00:00
| 97
| false
|
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(NlogN+N+N)\n\n- Space complexity: O(3N)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n //find last value of val\n //1 2 2 3 4 5\n //2 3 3 4 5 5\n int lowerBound(vector<int>& nums, int &ws,int &n, int lo , int hi, int val){\n int j = -1;\n while(lo<=hi){\n int mid = lo+(hi-lo)/2;\n\n if( nums[mid] <= val ){\n lo = mid+1;\n j = mid;\n }\n else{\n hi = mid-1;\n }\n }\n\n if(j == -1){\n return n-1;\n }\n return j;\n }\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& nums, int k) {\n int n = nums.size();\n\n int ws = k;\n vector<pair<int,int>> endidx(n);//{endIdx,max no.of prices}\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int val = nums[i]+k;\n int j = lowerBound(nums,ws,n,0,n-1,val);\n endidx[i].first = j;\n endidx[i].second = j-i+1;\n }\n\n\n vector<int> suffixMax(n);\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){\n if(i == n-1){\n suffixMax[n-1] = endidx[n-1].second;\n }\n else{\n suffixMax[i] = max(suffixMax[i+1],endidx[i].second);\n }\n }\n\n \n int ans = 0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int j = endidx[i].first;\n // int t = endidx[i].second + (i==n-1? 0: suffixMax[j+1]);\n int t;\n \n if(j == n-1){\n t = endidx[i].second;\n }\n else{\n t = endidx[i].second + suffixMax[j+1];\n }\n ans = max(ans,t);\n }\n\n return ans;\n\n }\n};\n\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Binary Search', 'C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
My Solution
|
my-solution-by-hope_ma-treu
|
\n/**\n * Time Complexity: O(n)\n * Space Complexity: O(n)\n * where `n` is the length of the vector `prizePositions`\n */\nclass Solution {\n public:\n int ma
|
hope_ma
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-10T12:57:15.170446+00:00
|
2023-02-10T12:57:15.170482+00:00
| 5
| false
|
```\n/**\n * Time Complexity: O(n)\n * Space Complexity: O(n)\n * where `n` is the length of the vector `prizePositions`\n */\nclass Solution {\n public:\n int maximizeWin(const vector<int> &prizePositions, const int k) {\n const int n = static_cast<int>(prizePositions.size());\n int left[n];\n for (int max_prices = 0, start = 0, end = 0; end < n; ++end) {\n while (prizePositions[end] - prizePositions[start] > k) {\n ++start;\n }\n max_prices = max(max_prices, end - start + 1);\n left[end] = max_prices;\n }\n \n int right[n];\n for (int max_prices = 0, start = n - 1, end = n - 1; end > -1; --end) {\n while (prizePositions[start] - prizePositions[end] > k) {\n --start;\n }\n max_prices = max(max_prices, start - end + 1);\n right[end] = max_prices;\n }\n \n int ret = 0;\n for (int separator = 0; separator < n; ++separator) {\n ret = max(ret, left[separator] + (separator + 1 < n ? right[separator + 1] : 0));\n }\n return ret;\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
[]
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
[Java Solution Using Segment Tree ]
|
java-solution-using-segment-tree-by-gane-tmu2
|
Consider array arr[1,1,2,2,3,3,5] and k=2 and make an array grtrOrEq which stores at index i , index of least element greater than arr[i]+k . For example grtrOr
|
Ganesha_
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-10T09:17:07.912124+00:00
|
2023-02-10T09:17:07.912153+00:00
| 69
| false
|
Consider array arr[1,1,2,2,3,3,5] and k=2 and make an array grtrOrEq which stores at index i , index of least element greater than arr[i]+k . For example grtrOrEq will look like [6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7]. Now make an array ans where at any index i ans[i]=grtrOrEq[i]-i.\nCode for grtrOrEq array\n```\nfor(int i=0;i<grtrOrEq.length;i++){\n grtrOrEq[i]=grtrOrEq(arr,arr[i]+k);\n}\n```\n\nCode for function grtrOrEq\n```\npublic int grtrOrEq(long []arr,long k){\n int l=-1;\n int r=arr.length;\n while(l+1<r){\n int mid=(l+r)/2;\n if(arr[mid]<=k){\n l=mid;\n }else{\n r=mid;\n }\n\t}\n return r;\n}\n```\n\nCode for making ans array\n```\nfor(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n ans[i]=grtrOrEq[i]-i;\n}\n```\n\nMake a class segment tree that has two functions build and query in which build preprocesses the segment tree and query finds maximum in some range.\nNow make a variable st of class Segment Tree and a variable sum\nNow for each index i sum is either\n1. Maximum of sum or ans[i] which means we are selecting two segments and they completely overlap\n2. Maximum of sum or ans[i]+maximum in ans from index grtrOrEq[i] to last index.\n\n```\nsegTree st=new segTree(n);\nst.build(0,0,n-1,ans);\nlong sum=0;\nfor(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n sum=Math.max(ans[i],sum);\n sum=Math.max(sum,ans[i]+st.query(0,0,n-1,grtrOrEq[i],n-1));\n}\n```\n\nCode for Segment Tree \n```\npublic class segTree {\n private long[] seg;\n\n public segTree(int size) {\n seg = new long[4 * size];\n }\n\n // segment_index (0) ,low_for_arr (0), high_for_arr,arr (arr.length-1)\n public void build(int ind, int low, int high, long[] arr) {\n if (low == high) {\n seg[ind] = arr[low];\n\t\t return;\n\t\t}\n\t\tint mid = (low + high) / 2;\n\t\tbuild(2 * ind + 1, low, mid, arr);\n\t\tbuild(2 * ind + 2, mid + 1, high, arr);\n\t\tseg[ind] = mer(seg[2 * ind + 1], seg[2 * ind + 2]);\n\t}\n\n // ind_for_seg (0) , low_for_arr (0) , high_for_arr (arr.length-1) , l=>given\n // query left, r=>given query right\n public long query(int ind, int low, int high, int l, int r) {\n // NO OVERLAP\n if (r < low || high < l) {\n return Long.MIN_VALUE;\n }\n if (low >= l && high <= r) {\n return seg[ind];\n }\n int mid = (low + high) / 2;\n long left = query(2 * ind + 1, low, mid, l, r);\n long right = query(2 * ind + 2, mid + 1, high, l, r);\n return mer(left, right);\n\t }\n\n public long mer(long left, long right) {\n return Math.max(left, right);\n }\n}\n```\n\n
| 0
| 0
|
['Tree', 'Binary Tree', 'Java']
| 1
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Easy c++ solution 100% faster in binarySearch+dp
|
easy-c-solution-100-faster-in-binarysear-3cky
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nif use the the array then you find that it is sorted so we can apply binary search over
|
Balram_54321
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-08T15:16:23.636117+00:00
|
2023-02-08T15:17:37.557980+00:00
| 15
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nif use the the array then you find that it is sorted so we can apply binary search over here\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nbinary search and dynamic programing\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(nlogn)\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n)\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prize, int k) {\n int n=prize.size();\n \n \n vector<int> dp(n);\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int lb=i;\n int ub=n-1;\n \n while(lb<=ub){\n int mid=(lb+ub)/2;\n \n if(prize[i]+k>=prize[mid]){\n dp[i]=(mid-i)+1;\n lb=mid+1;\n }else{\n ub=mid-1;\n }\n }\n }\n int ans=0;\n vector<int> maxArr(n);\n int maxVal=dp[n-1];\n for(int i=n-1;i>-1;i--){\n maxVal=max(maxVal,dp[i]);\n maxArr[i]=maxVal;\n }\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int next=dp[i]+i<n?maxArr[dp[i]+i]:0;\n ans=max(ans,dp[i]+next);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
C++ | Dp | Binary Search | Sliding Window
|
c-dp-binary-search-sliding-window-by-ari-g506
|
i) First create all ranges i.e take all values as starting points and again all of them as ending points using sliding window. Store all these ranges and their
|
arindombora_ug
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-08T09:02:03.172071+00:00
|
2023-02-08T09:02:03.172124+00:00
| 67
| false
|
i) First create all ranges i.e take all values as starting points and again all of them as ending points using sliding window. Store all these ranges and their sums.\nii) Sort the values according to starting index and apply dp to choose 2 non-overlapping intervals with maximum sum. Use Binary search to avoid overlapping intervals. Note here we consider all non-overlapping ranges whose starting point is greater than ending point of given range.\niii) Sort the values according to ending index and apply dp to choose 2 non-overlapping intervals with maximum sum. Use Binary search to avoid overlapping intervals. Note here we consider all non-overlapping ranges whose ending point is smaller than starting point of given range.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n static bool sortcol(const vector<long>& v1, const vector<long>& v2){\n return v1[1] > v2[1];\n }\n int maxiW1(vector<vector<long>>& pq,int k,int ind,vector<vector<int>>& dp1,vector<long>& v1){\n if(k==0)\n return 0;\n if(ind==pq.size())\n return 0;\n if(dp1[ind][k]!=-1)\n return dp1[ind][k];\n int tk=0;\n int ntk=0;\n if(k==2){\n int t=upper_bound(v1.begin(),v1.end(),pq[ind][1])-v1.begin();\n tk=pq[ind][2]+maxiW1(pq,k-1,t,dp1,v1);\n ntk=maxiW1(pq,k,ind+1,dp1,v1);\n }\n else if(k==1){\n tk=pq[ind][2]+maxiW1(pq,0,ind+1,dp1,v1);\n ntk=maxiW1(pq,k,ind+1,dp1,v1);\n }\n return dp1[ind][k]=max(tk,ntk);\n }\n int maxiW2(vector<vector<long>>& pq1,int k,int ind,vector<vector<int>>& dp2,vector<long>& v2){\n if(k==0)\n return 0;\n if(ind==pq1.size())\n return 0;\n if(dp2[ind][k]!=-1)\n return dp2[ind][k];\n int tk=0;\n int ntk=0;\n if(k==2){\n int t=upper_bound(v2.begin(),v2.end(),pq1[ind][1],greater<long>())-v2.begin();\n tk=pq1[ind][2]+maxiW2(pq1,k-1,t,dp2,v2);\n ntk=maxiW2(pq1,k,ind+1,dp2,v2);\n }\n else if(k==1){\n tk=pq1[ind][2]+maxiW2(pq1,0,ind+1,dp2,v2);\n ntk=maxiW2(pq1,k,ind+1,dp2,v2);\n }\n return dp2[ind][k]=max(tk,ntk);\n }\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& pp, int k) {\n vector<vector<long>>pq;\n map<long,long>m1;\n int i;\n for(i=0;i<pp.size();i++)\n m1[pp[i]]++;\n long start=pp[0]-k;\n long end=pp[0];\n long sum=0;\n sum+=m1[end];\n vector<long>v2,v4;\n v2.push_back(start);\n v2.push_back(end);\n v2.push_back(sum);\n pq.push_back(v2);\n long t2=end;\n int ind=upper_bound(pp.begin(),pp.end(),end)-pp.begin();\n if(ind==pp.size())\n return sum;\n long temp=start;\n while(ind<pp.size()){\n end=pp[ind];\n start=end-k;\n while(temp<start){\n sum=sum-m1[temp];\n int ind1=upper_bound(pp.begin(),pp.end(),temp)-pp.begin();\n temp=pp[ind1];\n }\n sum+=m1[end];\n vector<long>v3;\n v3.push_back(start);\n v3.push_back(end);\n v3.push_back(sum);\n pq.push_back(v3);\n ind=upper_bound(pp.begin(),pp.end(),end)-pp.begin();\n }\n reverse(pp.begin(),pp.end());\n start=pp[0]+k;\n end=pp[0];\n sum=0;\n sum+=m1[end];\n v4.push_back(end);\n v4.push_back(start);\n v4.push_back(sum);\n pq.push_back(v4);\n ind=upper_bound(pp.begin(),pp.end(),end,greater<int>())-pp.begin();\n temp=start;\n while(ind<pp.size()){\n end=pp[ind];\n start=end+k;\n while(temp>start){\n sum=sum-m1[temp];\n int ind1=upper_bound(pp.begin(),pp.end(),temp,greater<int>())-pp.begin();\n temp=pp[ind1];\n }\n sum+=m1[end];\n vector<long>v3;\n v3.push_back(end);\n v3.push_back(start);\n v3.push_back(sum);\n pq.push_back(v3);\n ind=upper_bound(pp.begin(),pp.end(),end,greater<int>())-pp.begin();\n }\n sort(pq.begin(),pq.end());\n vector<vector<long>>pq1(pq.size(),vector<long>(3));\n vector<long>v1,v5;\n for(i=0;i<pq.size();i++){\n v1.push_back(pq[i][0]);\n pq1[i][0]=pq[i][1];\n pq1[i][1]=pq[i][0];\n pq1[i][2]=pq[i][2];\n }\n sort(pq1.begin(),pq1.end(),sortcol);\n for(i=0;i<pq.size();i++)\n v5.push_back(pq1[i][0]);\n vector<vector<int>>dp1(pq.size()+1,vector<int>(3,-1));\n vector<vector<int>>dp2(pq.size()+1,vector<int>(3,-1));\n int ans1=maxiW1(pq,2,0,dp1,v1);\n int ans2=maxiW2(pq1,2,0,dp2,v5);\n return max(ans1,ans2);\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'Sliding Window', 'Binary Tree']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
C++ Easy solution BS
|
c-easy-solution-bs-by-fagun06-s3nf
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int n;\n int bns(int x,vector<int>&v) {\n int l=0,r=n-1;\n int res;\n while(l<=r) {\n
|
Fagun06
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-08T05:22:05.436406+00:00
|
2023-02-08T05:22:05.436435+00:00
| 16
| false
|
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int n;\n int bns(int x,vector<int>&v) {\n int l=0,r=n-1;\n int res;\n while(l<=r) {\n int md=(l+r)/2;\n if(v[md]<=x) res=md,l=md+1;\n else r=md-1;\n }\n return res;\n }\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& v, int k) {\n n=v.size();\n int ans=0;\n int aa[n+5],bb[n+5];\n \n for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {\n int x=k+v[i];\n int y=bns(x,v)+1;\n int p=i;\n //cout<<y-p<<endl;\n aa[i]=y-p;\n \n }\n for(int i=n-1; i>=0; i--) {\n int x;\n if(i==n-1) x=0;\n else x=bb[i+1];\n bb[i]=max(aa[i],x);\n }\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {\n int x=0;\n if(i+aa[i]<n) {\n x=bb[i+aa[i]];\n }\n ans=max(ans,aa[i]+x);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Worst Implementation of Binary Search
|
worst-implementation-of-binary-search-by-23pe
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int maximizeWin(int[] arr, int k) {\n int n = arr.length;\n int[] pre = new int[n];\n int count = 0;\n
|
MaawanAhmad
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-07T19:25:47.777623+00:00
|
2023-02-07T19:25:47.777667+00:00
| 20
| false
|
```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximizeWin(int[] arr, int k) {\n int n = arr.length;\n int[] pre = new int[n];\n int count = 0;\n for(int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i++){\n pre[i] = count;\n count++;\n }\n for(int i = arr.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--){\n int index = getIndex(0 , i , arr[i] - k , arr);\n pre[i] = pre[i] +1 - pre[index];\n }\n // for(int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i++){\n // System.out.print(pre[i] + " ");\n // }\n count = 0;\n int[] suffix = new int[n];\n for(int i = arr.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--){\n suffix[i] = count;\n count++;\n }\n for(int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i++){\n int index = getIndex2(i , arr.length - 1 , arr[i] + k , arr);\n suffix[i] = - suffix[index] + suffix[i] + 1;\n }\n //System.out.println();\n // for(int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i++){\n // System.out.print(suffix[i] + " ");\n // }\n int cur = 0;\n for(int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i++){\n cur = Math.max(cur , pre[i]);\n pre[i] = cur;\n }\n cur = 0;\n for(int i = arr.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--){\n cur = Math.max(cur , suffix[i]);\n suffix[i] = cur;\n }\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i = 0 ; i < arr.length - 1 ; i++){\n ans = Math.max(ans , pre[i]+suffix[i+1]);\n }\n if(arr.length == 1){\n return pre[0];\n }\n return ans;\n }\n private int getIndex2(int i , int j , int target ,int[] arr){\n int index = -1000000;\n while(i <= j){\n int mid = (i+j) >> 1;\n if(arr[mid] <= target){\n index = Math.max(mid , index);\n i = mid + 1;\n }else{\n j = mid - 1; \n }\n }\n return index == -1000000 ? arr.length - 1 : index;\n }\n private int getIndex(int i , int j , int target ,int[] arr){\n int index = 1000000;\n while(i <= j){\n int mid = (i+j) >> 1;\n if(arr[mid] >= target){\n index = Math.min(mid , index);\n j = mid - 1;\n }else{\n i = mid + 1; \n }\n }\n return index == 1000000 ? 0 : index;\n }\n}\n```
| 0
| 0
|
[]
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
C++ || easy solution || DP + Sliding Window || beats 88%
|
c-easy-solution-dp-sliding-window-beats-5rzjp
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prizePositions, int k) {\n int n = prizePositions.size(), start = 0, ans = 0;\n
|
Madhur_Jain
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-07T18:31:54.617484+00:00
|
2023-02-07T18:32:45.921576+00:00
| 36
| false
|
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prizePositions, int k) {\n int n = prizePositions.size(), start = 0, ans = 0;\n vector<int>dp(n);\n for(int end=0; end<n; end++) {\n while(prizePositions[end] - prizePositions[start] > k)\n start++;\n\n int curr_ans = end-start + 1; \n if(start > 0) {\n curr_ans += dp[start-1];\n }\n ans = max(ans, curr_ans);\n\n int prev = 0;\n if(end > 0) prev = dp[end-1];\n \n dp[end] = max(prev, end-start+1);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
C++
|
c-by-tlu22-j9k0
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
tlu22
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-07T15:36:45.462968+00:00
|
2023-02-07T15:36:45.491918+00:00
| 23
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& prizePositions, int k) {\n //It is meaningless to let the two interval to overlap\n int l = prizePositions.size();\n if(prizePositions[l-1] - prizePositions[0] <= 2*k+1) return l;\n //now we can assume they don\'t overlap. \n //so we search the interval through [m,m+k] to [M-k,M]\n //and use Mi,Mj to mark the first interval that we can get most prizes from prizePisitions[Mi] to prizePositions[Mj-1], where prizePositions[Mj-1]+k <= curi, and curi to curj is the second interval\n //if we find more prizes in the second interval, we will renew the Mi and Mj to the new ones as soon as they don\'t overlap\n int Mi=0,Mj=0;//mark our first interval\n queue<pair<int, int>> previousIntervals;//stores possible larger intervals for our first interval\n int ans = 0;\n int curi=0,curj=Mj;\n for(;curi<l;curi++)\n {\n //find interval\n while(curj < l && prizePositions[curj] - prizePositions[curi] <= k)\n {\n curj++;\n }\n //If there are no overlap we can replace the old first interval with the new first interval.\n while(!previousIntervals.empty() && previousIntervals.front().second <= curi)\n {\n if(previousIntervals.front().second - previousIntervals.front().first > Mj - Mi)\n {\n Mj = previousIntervals.front().second;\n Mi = previousIntervals.front().first;\n }\n previousIntervals.pop();\n }\n if(curj-curi > Mj - Mi)//If we find a larger interval\n {\n previousIntervals.push(make_pair(curi,curj));\n }\n if(curj - curi + Mj - Mi > ans) ans = curj-curi+Mj-Mi;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Sliding window O(N)
|
sliding-window-on-by-sandeep_003-aipq
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& v, int k) {\n int n=v.size(),ans=0;\n\n // sliding window from right\n
|
sandeep_003
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-07T07:10:28.561952+00:00
|
2023-02-07T07:10:28.561995+00:00
| 67
| false
|
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& v, int k) {\n int n=v.size(),ans=0;\n\n // sliding window from right\n int cnt=0,j=n-1;\n vector<int> res(n+2,0);\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){\n cnt++;\n while(v[j]-v[i]>k){ \n j--;\n cnt--;\n }\n res[i]=max(res[i+1],cnt);\n }\n\n // sliding window from left\n j=0,cnt=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n cnt++;\n while(v[i]-v[j]>k){\n j++;\n cnt--;\n }\n ans=max(ans,cnt+res[i+1]);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Memoization -> Tabulation | DP + BS | C++
|
memoization-tabulation-dp-bs-c-by-tushar-6y2o
|
Memoization\n\nclass Solution {\n int dfs(int i, int n, int k, int cnt, vector<int> &pp, vector<vector<int>> &dp) {\n if(i == n) return 0;\n if
|
TusharBhart
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-06T17:14:32.190708+00:00
|
2023-02-06T17:14:32.190755+00:00
| 69
| false
|
# Memoization\n```\nclass Solution {\n int dfs(int i, int n, int k, int cnt, vector<int> &pp, vector<vector<int>> &dp) {\n if(i == n) return 0;\n if(dp[i][cnt] != -1) return dp[i][cnt];\n\n int notPick = dfs(i + 1, n, k, cnt, pp, dp), pick = 0;\n if(cnt) {\n int pos = lower_bound(pp.begin() + i, pp.end(), pp[i] + k + 1) - pp.begin() - 1;\n pick = pos - i + 1 + dfs(pos + 1, n, k, cnt - 1, pp, dp);\n }\n return dp[i][cnt] = max(pick, notPick);\n }\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& pp, int k) {\n int n = pp.size();\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int>(3, -1));\n\n return dfs(0, n, k, 2, pp, dp);\n }\n};\n```\n\n# Tabulation\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& pp, int k) {\n int n = pp.size();\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n + 1, vector<int>(3));\n\n for(int i=n-1; i>=0; i--) {\n for(int cnt=1; cnt<=2; cnt++) {\n int notPick = dp[i + 1][cnt], pick = 0;\n int pos = lower_bound(pp.begin() + i, pp.end(), pp[i] + k + 1) - pp.begin() - 1;\n pick = pos - i + 1 + dp[pos + 1][cnt - 1];\n dp[i][cnt] = max(pick, notPick);\n }\n }\n return dp[0][2];\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Binary Search', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
[Java] Prefix MAX + Binary Search, O(nlogn) solution
|
java-prefix-max-binary-search-onlogn-sol-qfk6
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int maximizeWin(int[] a, int k) {\n int max_till_here=0;\n int maxans=0;\n for(int j=0;j<a.length;j++)\n
|
kritikmodi
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-06T13:46:53.068183+00:00
|
2023-03-28T10:05:45.745930+00:00
| 39
| false
|
```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximizeWin(int[] a, int k) {\n int max_till_here=0;\n int maxans=0;\n for(int j=0;j<a.length;j++)\n {\n int end=j;\n int l=0;\n int r=a.length-1;\n while(l<=r)\n {\n int mid=l+(r-l)/2;\n if(a[mid]<=a[j]+k)\n {\n end=mid;\n l=mid+1;\n }\n else\n r=mid-1;\n }\n maxans=Math.max(maxans,max_till_here+(end-j)+1);\n int start=j;\n l=0;\n r=a.length-1;\n while(l<=r)\n {\n int mid=l+(r-l)/2;\n if(a[mid]>=a[j]-k)\n {\n start=mid;\n r=mid-1;\n }\n else\n l=mid+1;\n }\n max_till_here=Math.max(max_till_here,(j-start)+1);\n }\n return maxans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['Binary Search', 'Sliding Window']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Clean prefix solution || C++
|
clean-prefix-solution-c-by-_pinocchio-511m
|
Approach\nCode size is huge but not logic is\n- Left array : At every index find no. of prizes in a window of k (idx to left)\n- Right array : At every index fi
|
_Pinocchio
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-06T09:07:11.702679+00:00
|
2023-02-06T16:34:21.870108+00:00
| 43
| false
|
# Approach\nCode size is huge but not logic is\n- Left array : At every index find no. of prizes in a window of k (idx to left)\n- Right array : At every index find no. of prizes in a window of k (idx to right)\n- prefix array : keep track of maximum no. of prize till this point from right\n- Last for loop : at every index take the no. of prizes from left array and take the just next index of prefix array as we are storing maximum in prefix array\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N)\n- Space complexity: O(4N)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximizeWin(vector<int>& arr, int k) {\n vector<pair<int,int>> vp;\n for(int i=0;i<arr.size();){\n int j = i;\n while(j < arr.size() and arr[j] == arr[i]) j++;\n vp.push_back({arr[i],j-i});\n i = j;\n }\n int i=0,j=0,sum=0;\n vector<int> left;\n while(j < vp.size()){\n int diff = vp[j].first - vp[i].first;\n sum += vp[j].second;\n if(diff <= k){\n left.push_back(sum);\n }else{\n while(i <= j){\n sum -= vp[i].second;\n int diff = vp[j].first - vp[++i].first;\n if(diff <= k){\n left.push_back(sum); break;\n }\n }\n }\n j++;\n }\n i=vp.size()-1,j=vp.size()-1,sum=0;\n vector<int> right;\n while(j >= 0){\n int diff = vp[i].first - vp[j].first;\n sum += vp[j].second;\n if(diff <= k){\n right.push_back(sum);\n }else{\n while(i >= j){\n sum -= vp[i].second;\n int diff = vp[--i].first - vp[j].first;\n if(diff <= k){\n right.push_back(sum); break;\n }\n }\n }\n j--;\n } \n reverse(right.begin(),right.end());\n vector<int> pref(left.size());\n int maxi = right.back();\n for(int i=right.size()-1;i>=0;i--){\n maxi = max(maxi,right[i]);\n pref[i] = maxi;\n }\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i=0;i<left.size();i++){\n ans = max(ans,left[i]+(i+1 < left.size() ? pref[i+1] : 0));\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['C++']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Detailed solution with comments | Sliding Window | Prefix Sum | Suffix Sum | O(N)
|
detailed-solution-with-comments-sliding-rpy4z
|
\nclass Solution\n{\n public:\n \t// basically for ant index i, (0,i) will give me one segment out of all segments possible\n \t//in this range (
|
Dark_kryptonian23
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-06T08:34:10.817082+00:00
|
2023-02-06T08:36:19.751321+00:00
| 36
| false
|
```\nclass Solution\n{\n public:\n \t// basically for ant index i, (0,i) will give me one segment out of all segments possible\n \t//in this range (0,i) in such a way that it will give me max. prize. Similarly (i+1,n-1)\n \t// will give me one segment out of all segments possible in this range (i+1,n-1) in such\n \t// way that it will give me max.prize. So adding up their values will give me max.prize\n \t// possible for any index i and i have to do that for every index. out of thsese whichever \n \t// will give maximum answer, would be my answer.\n int maximizeWin(vector<int> &prizePositions, int k)\n {\n int n = prizePositions.size();\n vector<int> pref(n), suff(n);\n```\n\n \t// Find maximum count of prize for(0,i). It can be[1,3], [2,4], [3,5]...out of these\n \t// segments whichever will give me max count, i will choose it. For this example it \n \t// is[1,3]\n\n int count = 0, maxCount = 0;\n int st = 0;\n int end = prizePositions[0] + k;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n int curr = prizePositions[i];\n\n if (curr <= end) count++;\n else\n {\n \t// i will keep contracting my window until my curr is in range or so to say\n \t// find a new range\n while (curr > end)\n {\n st++;\n end = prizePositions[st] + k;\n count--;\n }\n\n count++;\n }\n maxCount = max(maxCount, count);\n pref[i] = maxCount;\t// store the max count for (0,i);\n }\n\n count = 0, maxCount = 0;\n st = n - 1;\n end = prizePositions[n - 1] - k;\n\n for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)\n {\n int curr = prizePositions[i];\n\n if (curr >= end) count++;\n else\n {\n \t// i will keep contracting my window until my curr is in range or so to say\n \t// find a new range\n while (curr < end)\n {\n st--;\n end = prizePositions[st] - k;\n count--;\n }\n\n count++;\n }\n maxCount = max(maxCount, count);\n suff[i] = maxCount;\t// store the max count for (i,n-1)\n }\n\n int maxPrize = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n int prize = pref[i];\n if (i + 1 < n) prize += suff[i + 1];\n maxPrize = max(maxPrize, prize);\n }\n return maxPrize;\n }\n};\n\n**If you find this explanation helpful, make sure you upvote this!**\n**For more such solution, you can follow this:** https://github.com/tanmoyheritage23/Leetcode-GFG\n**Find me on LinkedIn:** https://www.linkedin.com/in/tanmoysahaofficial/
| 0
| 0
|
['Prefix Sum']
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
Problem with the Problem Description
|
problem-with-the-problem-description-by-ryj4k
|
Anybody else read this problem wrong to where they thought a segment must contain both the left and the right endpoints to be valid? What led me to think this i
|
throwaway1973
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-06T00:47:55.925254+00:00
|
2023-02-06T00:52:55.221313+00:00
| 34
| false
|
Anybody else read this problem wrong to where they thought a segment must contain both the left and the right endpoints to be valid? What led me to think this is the fact it said the \'The length of each segment must be k\', which made me think that the right endpoint of the segment should always be contained within the segment, else the segment is not of length k technically. Of course this ends up being a harder problem if so, and could maybe be considered a a valid follow up.
| 0
| 0
|
[]
| 0
|
maximize-win-from-two-segments
|
JavaScript (DP)
|
javascript-dp-by-swseverance-kirg
|
javascript\nvar maximizeWin = function(prizePositions, k) {\n const dp = {};\n \n for (const position of prizePositions)\n dp[position] = Array(3).fill(0)
|
swseverance
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-05T22:02:33.761193+00:00
|
2023-02-08T14:07:30.376792+00:00
| 59
| false
|
```javascript\nvar maximizeWin = function(prizePositions, k) {\n const dp = {};\n \n for (const position of prizePositions)\n dp[position] = Array(3).fill(0);\n \n for (let i = 0, j = 0; i < prizePositions.length; ++i) {\n const position = prizePositions[i];\n \n // range of prizes we can collect is [position - k, position];\n while (prizePositions[j] < position - k)\n ++j;\n \n for (let interval = 1; interval <= 2; ++interval) {\n // we have two options:\n\n // 1) we place the interval so that it ends at `position`\n // in doing so we collect i - j + 1 prizes plus \n // dp[prizePositions[j - 1]][interval - 1]\n const maxFromPlacingIntervalAtPosition =\n i - j + 1 + (j > 0 ? dp[prizePositions[j - 1]][interval - 1] : 0);\n \n // 2) we do not place the interval and use the max we got\n // at the previous position\n const maxFromPrevious = i > 0 ? dp[prizePositions[i - 1]][interval] : 0;\n \n dp[position][interval] = Math.max(\n maxFromPlacingIntervalAtPosition, maxFromPrevious\n );\n }\n }\n \n return dp[prizePositions[prizePositions.length - 1]][2];\n};\n```
| 0
| 0
|
['JavaScript']
| 0
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
[Java/C++/Python] Top-down DP solution
|
javacpython-top-down-dp-solution-by-lee2-qk4e
|
Intuition\nTop down dynamic programming.\nAlso noticed that some people already get accepted, a dp program.\n\n\n# Explanation\ndp[i,k] means picking k elements
|
lee215
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-27T04:03:57.397740+00:00
|
2022-03-27T04:56:36.321129+00:00
| 22,547
| false
|
# **Intuition**\nTop down dynamic programming.\nAlso noticed that some people already get accepted, a dp program.\n<br>\n\n# **Explanation**\n`dp[i,k]` means picking `k` elements from `pile[i]` to `pile[n-1]`.\nWe can pick 0,1,2,3... elements from the current `pile[i]` one by one.\nIt asks for the maximum total value of coins we can have,\nso we need to return `max` of all the options.\n<br>\n\n# **Complexity**\nTime `O(nm)`\nSpace `O(nk)`\nwhere `m = sum(piles[i].length) <= 2000`\n<br>\n\n**Java**\nFrom @ssmegentle\n```java\n public int maxValueOfCoins(List<List<Integer>> piles, int k) {\n Integer[][] memo = new Integer[piles.size() + 1][k + 1];\n\n return dp(piles, memo, 0, k);\n }\n public int dp(List<List<Integer>> piles, Integer[][] memo, int i, int k) {\n if (k == 0 || i == piles.size()) return 0;\n if (memo[i][k] != null) return memo[i][k];\n\n int res = dp(piles, memo, i + 1, k);\n int cur = 0;\n\n for (int j = 0; j < Math.min(piles.get(i).size(), k); ++j) {\n cur += piles.get(i).get(j);\n res = Math.max(res, cur + dp(piles, memo, i + 1, k - j - 1));\n }\n return memo[i][k] = res;\n }\n```\n**C++**\n```cpp\n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& A, int K) {\n int n = A.size();\n vector<vector<int>> memo(n + 1, vector<int>(K + 1, 0));\n function<int(int, int)> dp = [&](int i, int k) {\n if (memo[i][k] > 0) return memo[i][k];\n if (i == n || k == 0) return 0;\n int res = dp(i + 1, k), cur = 0;\n for (int j = 0; j < A[i].size() && j < k; ++j) {\n cur += A[i][j];\n res = max(res, dp(i + 1, k - j - 1) + cur);\n }\n memo[i][k] = res;\n return res;\n };\n return dp(0, K);\n }\n```\n**Python**\n```py\n def maxValueOfCoins(self, A, K):\n \n @functools.lru_cache(None)\n def dp(i, k):\n if k == 0 or i == len(A): return 0\n res, cur = dp(i + 1, k), 0\n for j in range(min(len(A[i]), k)):\n cur += A[i][j]\n res = max(res, cur + dp(i+1, k-j-1))\n return res\n \n return dp(0, K)\n```\n
| 183
| 3
|
['C', 'Python', 'Java']
| 32
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
Image Explanation🏆- [Top Down DP - Easy & Concise] - C++/Java/Python
|
image-explanation-top-down-dp-easy-conci-iutw
|
Video Solution (Aryan Mittal) - Link in LeetCode Profile\nMaximum Value of K Coins From Piles by Aryan Mittal\n\n\n\n# Approach & Intution\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n#
|
aryan_0077
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-15T01:36:20.982860+00:00
|
2023-04-15T12:50:52.382700+00:00
| 19,424
| false
|
# Video Solution (`Aryan Mittal`) - Link in LeetCode Profile\n`Maximum Value of K Coins From Piles` by `Aryan Mittal`\n\n\n\n# Approach & Intution\n\n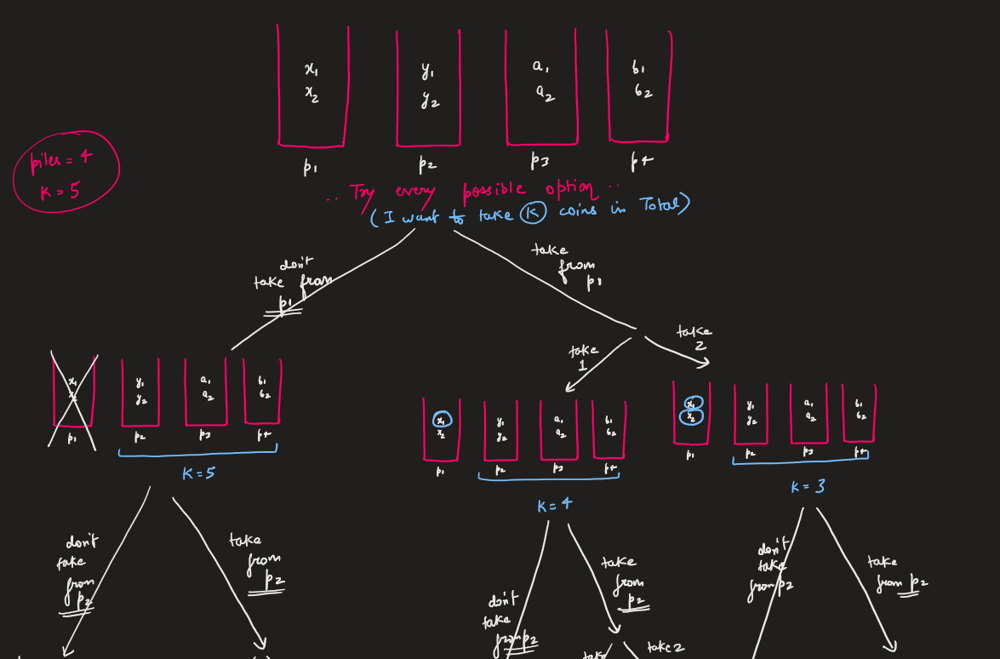\n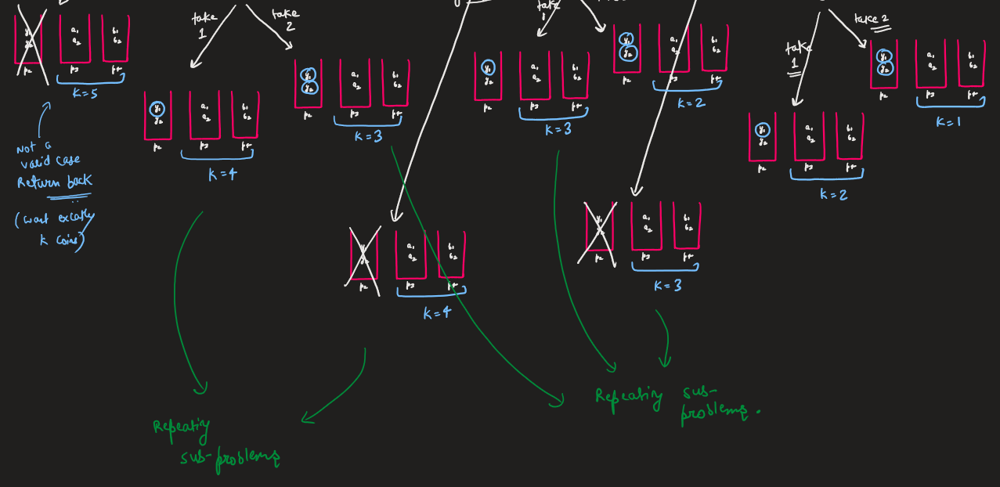\n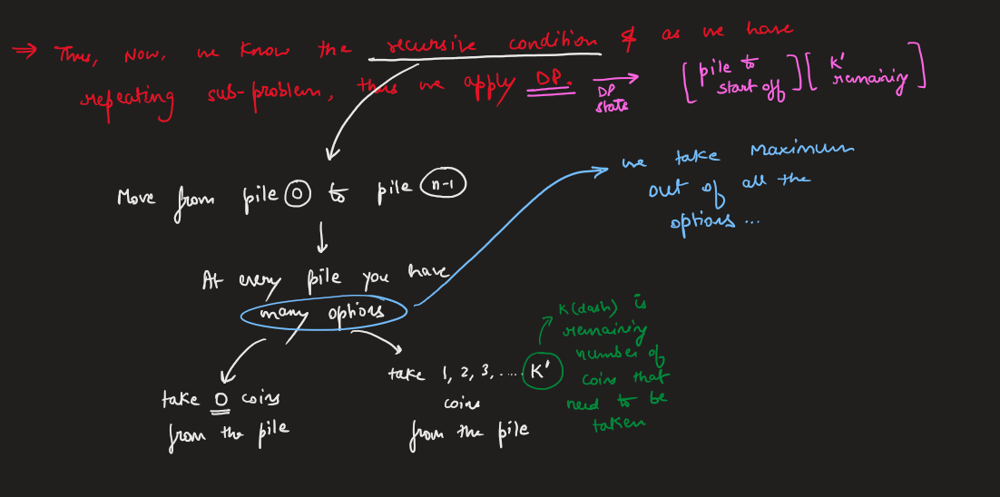\n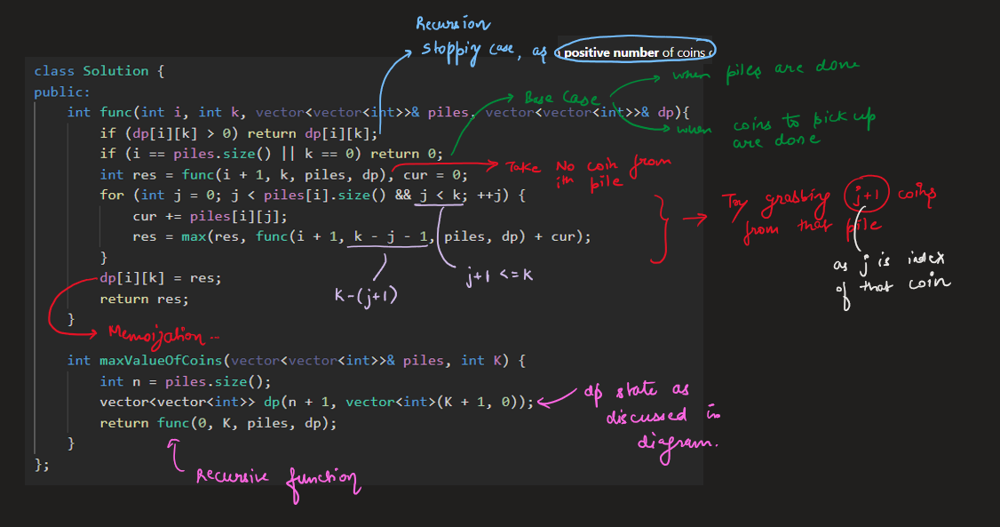\n\n\n\n\n# Code\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int func(int i, int k, vector<vector<int>>& piles, vector<vector<int>>& dp){\n if (dp[i][k] > 0) return dp[i][k];\n if (i == piles.size() || k == 0) return 0;\n int res = func(i + 1, k, piles, dp), cur = 0;\n for (int j = 0; j < piles[i].size() && j < k; ++j) {\n cur += piles[i][j];\n res = max(res, func(i + 1, k - j - 1, piles, dp) + cur);\n }\n dp[i][k] = res;\n return res;\n }\n\n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& piles, int K) {\n int n = piles.size();\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n + 1, vector<int>(K + 1, 0));\n return func(0, K, piles, dp);\n }\n};\n```\n```Java []\nclass Solution {\n public int func(int i, int k, List<List<Integer>> piles, int[][] dp) {\n if (dp[i][k] > 0) return dp[i][k];\n if (i == piles.size() || k == 0) return 0;\n int res = func(i + 1, k, piles, dp), cur = 0;\n for (int j = 0; j < piles.get(i).size() && j < k; ++j) {\n cur += piles.get(i).get(j);\n res = Math.max(res, func(i + 1, k - j - 1, piles, dp) + cur);\n }\n dp[i][k] = res;\n return res;\n }\n\n public int maxValueOfCoins(List<List<Integer>> piles, int K) {\n int n = piles.size();\n int[][] dp = new int[n + 1][K + 1];\n return func(0, K, piles, dp);\n }\n}\n```\n```Python []\nclass Solution:\n def maxValueOfCoins(self, piles: List[List[int]], k: int) -> int:\n \n @functools.lru_cache(None)\n def _search(rest_k: int, pile_pos: int) -> int:\n """Searches for best accumulated coin value starting from pile at position `pile_pos`.\n \n Args:\n - rest_k: The rest of coins we could pick.\n - pile_pos: The starting position of pile we are working on.\n """\n if rest_k == 0 or pile_pos == len(piles): return 0\n\n # Ignore the current pile and moving to next pile\n current_mv_found = _search(rest_k, pile_pos+1)\n\n # Start looking solution with current pile being involved\n current_pile = piles[pile_pos]\n accum_coin_value = 0\n for i in range(min(rest_k, len(current_pile))):\n # Accumulate the coins\n accum_coin_value += current_pile[i]\n\n # Moving to next pile with accumulated coin value in current pile\n current_mv_found = max(\n current_mv_found, \n accum_coin_value + _search(rest_k-i-1, pile_pos+1))\n\n # Return the maximum accumulated coin value found from current pile.\n return current_mv_found\n\n # Start searching with initial `k` and first pile\n return _search(k, 0)\n```\nCredits: Python Solution commented beautifully by @puremonkey2001\n
| 124
| 6
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 7
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
✔️✔️Easy Solutions in Java ✔️✔️, Python ✔️, and C++ ✔️🧐Look at once 💻 with Exaplanation
|
easy-solutions-in-java-python-and-c-look-er9k
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe problem can be approached using dynamic programming by breaking it down into subpro
|
Vikas-Pathak-123
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-15T03:42:12.162520+00:00
|
2023-04-15T03:42:12.162558+00:00
| 9,897
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe problem can be approached using dynamic programming by breaking it down into subproblems. We can create a 2D array dp[i][j] to store the maximum value of coins for choosing j coins from the first i piles. Then, we can iterate through the array and compute the maximum value of coins for each subproblem by trying all possible choices for the current pile and updating the maximum result.\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. Create a 2D array dp[i][j] to store the maximum value of coins for choosing j coins from the first i piles.\n2. Fill the first row and column of the array with zeros.\n3. Iterate through the array and compute the maximum value of coins for each subproblem by trying all possible choices for the current pile and updating the maximum result.\n4. If not choosing any coin from the current pile gives a better result, use that instead.\n5. The last element of the array is the maximum value of coins for choosing k coins from all the piles.\n\n \n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n^3), where n is the maximum number of coins in a pile. The outer loop runs n times, the inner loop runs k times, and the innermost loop runs n times in the worst case.\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(nk), since we are using a 2D array of size (n+1) x (k+1) to store the results.\n\n\n\n\n# Please Upvote\uD83D\uDC4D\uD83D\uDC4D\n```\nThanks for visiting my solution.\uD83D\uDE0A Keep Learning\nPlease give my solution an upvote! \uD83D\uDC4D\nIt\'s a simple way to show your appreciation and\nkeep me motivated. Thank you! \uD83D\uDE0A\n```\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxValueOfCoins(List<List<Integer>> piles, int k) {\n // create a 2D array to store the maximum value of coins for choosing j coins from the first i piles\n int[][] dp = new int[piles.size() + 1][k + 1];\n // fill the first row of the array with zeros\n Arrays.fill(dp[0], 0);\n // fill the first column of the array with zeros\n for (int i = 1; i <= piles.size(); i++) {\n dp[i][0] = 0;\n }\n // iterate through the array and compute the maximum value of coins for each subproblem\n for (int i = 1; i <= piles.size(); i++) {\n for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {\n int cur = 0;\n // try all possible choices for the current pile and update the maximum result\n for (int x = 0; x < Math.min(piles.get(i - 1).size(), j); x++) {\n cur += piles.get(i - 1).get(x);\n dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j], cur + dp[i - 1][j - x - 1]);\n }\n // if not choosing any coin from the current pile gives a better result, use that instead\n dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j]);\n }\n }\n // the last element of the array is the maximum value of coins for choosing k coins from all the piles\n return dp[piles.size()][k];\n }\n}\n```\n```javascript []\n/**\n * @param {number[][]} piles\n * @param {number} k\n * @return {number}\n */\n \nvar maxValueOfCoins = function(piles, k) {\n // Initialize a 2D array dp with dimensions (n+1) x (k+1) to store the maximum value of coins\n // for choosing j coins from the first i piles\n const n = piles.length;\n const dp = Array(n + 1).fill().map(() => Array(k + 1).fill(0));\n \n // Iterate through the rows of dp and compute the maximum value of coins for each subproblem\n for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) {\n // Iterate through the columns of dp and compute the maximum value of coins for each subproblem\n for (let j = 1; j <= k; j++) {\n let cur = 0;\n // Iterate through the first j coins of the ith pile and compute the maximum value of coins\n // for choosing x coins from the ith pile and (j-x) coins from the first (i-1) piles\n for (let x = 0; x < Math.min(j, piles[i-1].length); x++) {\n cur += piles[i-1][x];\n dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j], cur + dp[i-1][j-x-1]);\n }\n // Take the maximum value of coins for choosing j coins from the first (i-1) piles\n dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j], dp[i-1][j]);\n }\n }\n // Return the maximum value of coins for choosing k coins from all the piles\n return dp[n][k];\n};\n\n```\n```python []\nclass Solution(object):\n def maxValueOfCoins(self, piles, k):\n """\n :type piles: List[List[int]]\n :type k: int\n :rtype: int\n """\n dp = [[0] * (k + 1) for _ in range(len(piles) + 1)]\n for i in range(1, len(piles) + 1):\n for j in range(1, k + 1):\n cur = 0\n for x in range(min(len(piles[i - 1]), j)):\n cur += piles[i - 1][x]\n dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], cur + dp[i - 1][j - x - 1])\n dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j])\n return dp[len(piles)][k]\n```\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& piles, int k) {\n int n = piles.size();\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n + 1, vector<int>(k + 1, 0));\n \n for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {\n for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {\n int cur = 0;\n for (int x = 0; x < min(j, (int)piles[i-1].size()); x++) {\n cur += piles[i-1][x];\n dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], cur + dp[i-1][j-x-1]);\n }\n dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i-1][j]);\n }\n }\n return dp[n][k];\n }\n};\n```\n# Please Comment\uD83D\uDC4D\uD83D\uDC4D\n```\nThanks for visiting my solution comment below if you like it.\uD83D\uDE0A\n```
| 69
| 5
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'JavaScript']
| 1
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
[Python] dp solution (complexity updated), explained
|
python-dp-solution-complexity-updated-ex-1l4n
|
Let use dp with states dp(n, k), where it is (current index of pile, nubmer of elements we still need to take). Then on each state we can try to take 0, ..., mi
|
dbabichev
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-27T04:00:38.532221+00:00
|
2022-03-27T16:51:47.516775+00:00
| 5,876
| false
|
Let use dp with states `dp(n, k)`, where it is `(current index of pile, nubmer of elements we still need to take)`. Then on each state we can try to take `0, ..., min(k, len(piles[m]))` elements from pile `m`. Also if `n == N`, that is we reached the last pile and `k == 0`, we are happy, return `0`. If `k > 0`, it means that we reached the last pile and did not take `k` elements, we are not happy, return `-inf`.\n\n#### Complexity\nImagine, that piles have `x1, ..., xn` elements in them. Then for state `(1, k)` we have `x1` possible transactions, for state `(2, k)` we have `x2` possible transactions and so on. In total we have `x1 + ... + xn` transactions for every value of `k`. So, in total we have time complexity `O(M * K)`, where `M = x1 + ... + xn`. Space is `O(n * K)`.\n\n#### Code\n```python\nclass Solution:\n def maxValueOfCoins(self, piles, K):\n N = len(piles)\n @lru_cache(None)\n def dp(n, k):\n if n == N:\n if k == 0: return 0\n if k > 0: return -float("inf")\n ans = dp(n + 1, k)\n sm = 0\n for i in range(min(k, len(piles[n]))):\n sm += piles[n][i]\n ans = max(ans, dp(n + 1, k - i - 1) + sm)\n return ans\n\n return dp(0, K)\n```\n\nIf you have any questions, feel free to ask. If you like solution and explanations, please **Upvote!**
| 68
| 1
|
['Dynamic Programming']
| 13
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
Again Knapsack Variation | Easy to understand
|
again-knapsack-variation-easy-to-underst-ifa0
|
TC - O(NM) n=size of piles, m=size of piles[i]\nJAVA\n\nclass Solution {\n Integer dp[][];\n\n public int maxValueOfCoins(List<List<Integer>> piles, int k
|
surajthapliyal
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-27T04:00:46.268121+00:00
|
2022-03-28T06:42:10.756937+00:00
| 5,563
| false
|
TC - O(N*M) n=size of piles, m=size of piles[i]\n**JAVA**\n```\nclass Solution {\n Integer dp[][];\n\n public int maxValueOfCoins(List<List<Integer>> piles, int k) {\n this.dp = new Integer[piles.size() + 1][k + 1];\n return solve(0, piles, k);\n }\n\n private int solve(int index, List<List<Integer>> p, int k) {\n if (index >= p.size()) return 0;\n int max = 0, sum = 0;\n if (dp[index][k] != null) return dp[index][k];\n //either dont take from that pile\n max = Math.max(max, solve(index + 1, p, k));\n for (int i = 0; i < p.get(index).size(); i++) {\n sum += p.get(index).get(i);\n //or take some certain prefix from that pile, if we can take that much elements.\n if (k - (i + 1) >= 0) max = Math.max(max, sum + solve(index + 1, p, k - (i + 1)));\n }\n return dp[index][k] = max; // return max\n }\n}\n```\n**CPP**\n```\nclass Solution {\n public:\n int dp[2001][2001] = { 0 };\n int maxValueOfCoins(vector < vector < int >> & piles, int k) {\n return solve(0, piles, k);\n }\n int solve(int index, vector < vector < int >> & piles, int k) {\n if (index >= piles.size()) return 0;\n if (dp[index][k] != 0) return dp[index][k];\n int maxi = 0, sum = 0;\n //either dont take from that pile\n maxi = max(maxi, solve(index + 1, piles, k));\n for (int i = 0; i < piles[index].size(); i++) {\n sum += piles[index][i];\n //or take some certain prefix from that pile, if we can take that much elements.\n if (k - (i + 1) >= 0) maxi = max(maxi, sum + solve(index + 1, piles, k - (i + 1)));\n }\n return dp[index][k] = maxi;\n }\n};\n```
| 37
| 1
|
['Memoization']
| 2
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
✅ C++ | DP + Memoization
|
c-dp-memoization-by-chandanagrawal23-zglu
|
\nclass Solution\n{\n public:\n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector < int>> &p, int k)\n {\n int n = p.size();\n vector<vec
|
chandanagrawal23
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-27T04:15:03.112649+00:00
|
2022-03-27T04:18:59.196394+00:00
| 5,153
| false
|
```\nclass Solution\n{\n public:\n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector < int>> &p, int k)\n {\n int n = p.size();\n vector<vector < int>> dp(n + 1, vector<int> (k + 1, -1));\n return solve(0, dp, p, k);\n }\n int solve(int index, vector<vector < int>> &dp, vector< vector< int>> &p, int k)\n {\n if (index >= p.size())\n return 0;\n\n int maxi = 0, sum = 0;\n\n if (dp[index][k] != -1)\n return dp[index][k];\n \n //dont take from that pile\n maxi = max(maxi, solve(index + 1, dp, p, k));\n\n for (int i = 0; i < p[index].size(); i++)\n {\n sum += p[index][i];\n \n //take some certain prefix from that pile, if we can take that much elements.\n if (k - (i + 1) >= 0)\n maxi = max(maxi, sum + solve(index + 1, dp, p, k - (i + 1)));\n }\n return dp[index][k] = maxi;\t// return max\n }\n};\n```\n\nC++ version of @x21svage \'s code
| 31
| 3
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization']
| 5
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
Recursion->Top Down-> Bottom Up || Easy to understand code
|
recursion-top-down-bottom-up-easy-to-und-xlqb
|
RECURSION, TLE\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n //startPileIdx is always 0\n //piles under consideration for each call ==> [pileIdx = 0 to pileIdx = endPile
|
mohakharjani
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-15T01:00:16.009637+00:00
|
2023-04-15T04:02:37.948115+00:00
| 6,698
| false
|
### RECURSION, TLE\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n //startPileIdx is always 0\n //piles under consideration for each call ==> [pileIdx = 0 to pileIdx = endPileIdx]\n int solve(vector<vector<int>>&piles, int endPileIdx, int k)\n {\n if (endPileIdx < 0 || k == 0) return 0;\n \n int currPileSize = piles[endPileIdx].size(); \n int maxCanPick = min(k, currPileSize);\n \n //consider \'not picking\' any coin\n int maxSum = solve(piles, endPileIdx - 1, k); //DON\'T PICK ANY COIN FROM CURR PILE\n int pickedSum = 0;\n //===============================================================================\n //now consider picking some coins\n for (int i = 0; i < maxCanPick; i++)\n {\n int coinValue = piles[endPileIdx][i];\n pickedSum += coinValue;\n \n int nextMaxSum = solve(piles, endPileIdx - 1, k - i - 1); \n maxSum = max(maxSum, pickedSum + nextMaxSum);\n }\n //=================================================================================\n return maxSum;\n \n }\n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& piles, int k) \n {\n int n = piles.size();\n int ans = solve(piles, n - 1, k);\n return ans;\n \n }\n};\n```\n//====================================================================================================================\n\n### TOP DOWN [Memoization], Accepted\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n //startPileIdx is always 0\n //piles under consideration for each call ==> [pileIdx = 0 to pileIdx = endPileIdx]\n int solve(vector<vector<int>>&piles, vector<vector<int>>&dp, int endPileIdx, int k)\n {\n if (endPileIdx < 0 || k == 0) return 0;\n if (dp[endPileIdx][k] != -1) return dp[endPileIdx][k];\n \n int currPileSize = piles[endPileIdx].size(); \n int maxCanPick = min(k, currPileSize);\n \n //consider \'not picking\' any coin\n int maxSum = solve(piles, dp, endPileIdx - 1, k); //DON\'T PICK ANY COIN FROM CURR PILE\n int pickedSum = 0;\n //===============================================================================\n //now consider picking some coins\n for (int i = 0; i < maxCanPick; i++)\n {\n int coinValue = piles[endPileIdx][i];\n pickedSum += coinValue;\n \n int nextMaxSum = solve(piles, dp, endPileIdx - 1, k - i - 1); \n maxSum = max(maxSum, pickedSum + nextMaxSum);\n }\n //=================================================================================\n return dp[endPileIdx][k] = maxSum;\n \n }\n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& piles, int k) \n {\n int n = piles.size();\n vector<vector<int>>dp(n, vector<int>(k + 1, -1));\n int ans = solve(piles, dp, n - 1, k);\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n//================================================================================================================================\n\n### BOTTOM UP, Accepted\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& piles, int k) \n {\n int n = piles.size();\n vector<vector<int>>dp(n, vector<int>(k + 1, 0)); \n //for considering [number of piles = n]\n //we must already have answers for [number of piles = (n - 1)]\n //thus we need to go bottom up\n //we need to go from [no. of piles under consideration = 1 to n]\n \n //consider only (endPileIdx + 1) number of piles at a time\n for (int endPileIdx = 0; endPileIdx < n; endPileIdx++) //count of piles = endPileIdx + 1\n {\n int currPileSize = piles[endPileIdx].size();\n for (int coinsToPick = 1; coinsToPick <= k; coinsToPick++)\n {\n //=============================================================================\n //DON\'T PICK ANY COIN FROM CURR PILE\n int maxSum = (endPileIdx - 1 < 0)? 0 : dp[endPileIdx - 1][coinsToPick]; \n \n int maxCanPick = min(coinsToPick, currPileSize);\n int pickedSum = 0;\n //now consider picking some coins\n for (int i = 0; i < maxCanPick; i++)\n {\n int coinValue = piles[endPileIdx][i];\n pickedSum += coinValue;\n \n int nextMaxSum = 0;\n if (endPileIdx > 0) \n nextMaxSum = dp[endPileIdx - 1][coinsToPick - i - 1];\n maxSum = max(maxSum, pickedSum + nextMaxSum);\n }\n //=======================================================================================\n dp[endPileIdx][coinsToPick] = maxSum;\n }\n }\n return dp[n - 1][k];\n }\n};\n````\n\n
| 24
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'C++']
| 3
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
[Java] Bottom up DP with clear explanation and code
|
java-bottom-up-dp-with-clear-explanation-53n5
|
Either pick all k from previous piles, or choose j from current pile and pick k-j from previous piles\nRecurrence relation:\nf(n,k) represents the max sum of co
|
gonpachiro
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-27T04:03:09.065420+00:00
|
2022-03-30T11:35:18.862281+00:00
| 2,319
| false
|
Either pick all k from previous piles, or choose j from current pile and pick k-j from previous piles\n**Recurrence relation**:\n`f(n,k)` represents the max sum of coins collected from first `n` piles and choosing `k` top coins.\n```\nf(n,k) = max(\n\t\t\tf(n-1,k) // pick k from previous n-1 piles\n\t\t\t,max(f(n-1,k-j-1)+sum(0 to j) for j = 0 to min(k,p[n-1].size())) // pick j+1 from current pile and k-j-1 from previous n-1 piles\n\t\t)\n```\nif k = 0, i.e. you can\'t pick any coin then ans = 0\nif n = 0, i.e. you don\'t have any piles then ans = 0\n**Base cases** :\n`f(0,k) = 0`\n`f(n,0) = 0`\n\n```\n/*\nf(i,k) = max(f(i-1,k),max(f(i-1,k-j-1)+sum(j) for j = 0 to max(k,p[i-1].length)))\nf(i,0) = 0\nf(0,k) = 0\n*/\nclass Solution {\n public int maxValueOfCoins(List<List<Integer>> piles, int K) {\n int n = piles.size();\n int[][] dp = new int[n+1][K+1];\n \n for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {\n for(int k = 1; k <= K; k ++) {\n dp[i][k] = dp[i-1][k];\n int sum = 0;\n int picked = 1;\n for(int v: piles.get(i-1)) {\n if(k-picked < 0) {\n break;\n }\n sum += v;\n dp[i][k] = Math.max(dp[i][k], dp[i-1][k-picked]+sum);\n picked ++;\n }\n }\n }\n return dp[n][K];\n }\n}\n```
| 24
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 3
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
✅ Easy DP Solution/Approach Explained 📝 | Beginner Friendly
|
easy-dp-solutionapproach-explained-begin-xyxl
|
Intuition\nThe intuition here is to understand that when we are on any currentPile we have two choices\n- either to exclude that pile and move on to next one or
|
nikeMafia
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-15T05:47:29.096829+00:00
|
2023-05-01T06:29:27.399271+00:00
| 3,566
| false
|
# Intuition\nThe intuition here is to understand that when we are on any currentPile we have two choices\n- either to exclude that pile and move on to next one or\n- pick from currentPile one or two or three coins and so on till <= K(coinsLeft to pick) and currentPile is not exhausted of coins and then move on to new pile if coins are left\n\nNow when we try to solve with above approach, we see that there are repeating sub problems so we will go ahead and store results of repeating subproblems in a 2D DP array.\n\nDP[i][j] represent the max-value of coins(or sum) from j coins, when we are on ith pile.\n\n---\n\n\n# Approach\n1) We declare dp[n+1][k+1], we need to intialise DP with some variable so that we know if we have solved that subproblem so either intialise all elements *by -1* or i have made *dp = new Integer[][]* so that by default it is intialised *to null values*.\n\n2) Following top down approach we start iterating from last pile\n- check base conditions\n- return if we have already solved for that case already\n\n3) If above coditions don\'t pass then we calcualte what is coinPickLimit\n```\nint coinsPickLimit = Math.min(coinsLeft, piles.get(currentPile).size());\n```\nminmium we are taking since the each piles coins can get exhausted if we plan to take multiple coins from it.\n\n4) for currentPile either we \n- exclude it and move on to next pile \n```\nint excludeCurrentPile = helper(piles, currentPile-1, coinsLeft);\n```\n- or we include the currentPile and take 1 or 2 or .. coins from it(so for loop), we calculate sum and move onto next pile. Each time we pick a coin from curretPile we add to sum and move on to next pile get the result, we can repeat this till cointsLeftLimit.\n\nSo we calculate all possiblities of currentPile if we take one coint move on to next pile, then if we took 2 coins from currentPile and moved on to next pile and so on\n\nNow we have both result from excludeCurrentPile, includeCurentPile we do\n```\nMath.max(includeCurentPile, excludeCurrentPile)\n```\nand set it to dp[currentPile][coinsLeft]\n\nTry dry the code with 3 piles you will get the idea and why dp is imp as we are reusing our results.\n\n---\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n*k) where n is the total number of coins in all the piles\n\n---\nHope it is easy to understand.\nLet me know if there is something unclear and i can fix it.\n\nOtherwise, please upvote if you like the solution, it would be encouraging\n\n----\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n private Integer dp[][];\n private int helper(List<List<Integer>> piles, int currentPile, int coinsLeft){\n if(currentPile<0 || coinsLeft == 0)\n return 0;\n if(dp[currentPile][coinsLeft]!=null)\n return dp[currentPile][coinsLeft];\n\n int coinsPickLimit = Math.min(coinsLeft, piles.get(currentPile).size());\n\n //not including that currentPile, so coinsLeft remain same\n int excludeCurrentPile = helper(piles, currentPile-1, coinsLeft);\n \n int includeCurentPile=0;\n for(int j=0, sum=0; j<coinsPickLimit ; j++){\n sum+= piles.get(currentPile).get(j);\n //doing coinsLeft-(j+1) as we are starting from index 0 and coin picked cannot pe 0 if we pick it is > 0\n includeCurentPile = Math.max(sum + helper(piles, currentPile-1, coinsLeft-(j+1)), includeCurentPile);\n }\n \n int res = Math.max(includeCurentPile, excludeCurrentPile);\n dp[currentPile][coinsLeft] = res;\n return res;\n\n } \n\n public int maxValueOfCoins(List<List<Integer>> piles, int K) {\n int n = piles.size();\n dp = new Integer[n + 1][K + 1];\n return helper(piles, n-1, K);\n }\n}\n```
| 23
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'Java']
| 2
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
C++ | Recursive DP + Memoization | Prefix Sum | Commented Code
|
c-recursive-dp-memoization-prefix-sum-co-ib9e
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n const int inf = 1e9;\n int dp[1001][2001];\n int help(int idx, int k, vector<vector<int>> &piles)\n {\n /
|
jatin1510
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-15T06:11:49.347353+00:00
|
2023-04-15T06:42:30.471228+00:00
| 4,009
| false
|
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n const int inf = 1e9;\n int dp[1001][2001];\n int help(int idx, int k, vector<vector<int>> &piles)\n {\n // if no coins left then return 0\n if (k == 0)\n return 0;\n\n // if we have processed all the piles\n if (idx == piles.size())\n {\n // if k is 0 then we have chosen all the coins so return 0\n if (k == 0)\n return 0; \n // if k is not 0, then this is not valid so return -infinity\n return -inf;\n }\n\n // if we have calculated the state before then return it\n if (dp[idx][k] != -1)\n return dp[idx][k];\n \n // for the current state initialize answer as 0\n int ans = -inf;\n\n // case1: take coins from the current prices {we can choose maximum \'min(k, current pile size)\' coins from the current pile}\n for (int i = 0; i < min(k, (int)piles[idx].size()); i++)\n ans = max(ans, piles[idx][i] + help(idx + 1, k - (i + 1), piles));\n\n // -----------------max(take,nottake)----------------\n return dp[idx][k] = max(ans, help(idx + 1, k, piles));\n }\n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>> &piles, int k)\n {\n memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));\n int n = piles.size();\n\n // storing pref in the piles itself\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n for (int j = 1; j < piles[i].size(); j++)\n piles[i][j] += piles[i][j - 1];\n\n // answer\n return help(0, k, piles);\n }\n};\n```\n\n### Please UPVOTE if you liked.
| 18
| 4
|
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Prefix Sum', 'C++']
| 1
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
Explained Solution by relating it to coin change problem || Memoisation || C++
|
explained-solution-by-relating-it-to-coi-z9sd
|
Intution and Relation with Coin Change\nLets try to recall what do we do in coin change , we go to every index and either pick or not pick the element.\nSimilar
|
ankursharma6084
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-27T09:12:47.695705+00:00
|
2022-03-27T17:17:00.214713+00:00
| 1,459
| false
|
### **Intution and Relation with Coin Change**\nLets try to recall what do we do in coin change , we go to every index and either pick or not pick the element.\nSimilarly , in this question , we go to every index and because we can pick atmost k elements so , we try all the possibilities of picking elements from 0 to min(piles[idx].size() , k ) and we have to take max of all the possibilities \nwe tried and return . As simple as that. For the memoisation part , the two parameters that are changing are memoised to reduce the \n**Time complexity from O(K^n) to (O(k*n)**\nIf you dont understand any part , try to recall coin change problem thoroughly or comment below. I would be happy to explain further.\n\n\n```\n int fun(vector<vector<int>>& piles, vector<vector<int>>& dp , int idx , int k)\n {\n if(idx == piles.size() || k==0) return 0;\n \n if(dp[idx][k]!= -1) return dp[idx][k] ;\n \n int ans = fun(piles, dp , idx+1 , k ) ;\n int sum = 0;\n \n for(int i=0; i< min(int(piles[idx].size()) , k) ; i++)\n {\n sum+=piles[idx][i] ;\n ans = max(ans , sum + fun(piles , dp , idx+1 , k-i-1)) ;\n }\n \n return dp[idx][k] = ans ;\n \n }\n \n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& piles, int k) {\n \n int n = piles.size();\n vector<vector<int> > dp(n+1 , vector<int>(k+1 , -1)) ;\n \n return fun(piles , dp , 0 , k) ;\n \n \n }
| 18
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C']
| 10
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
2D DP
|
2d-dp-by-votrubac-n06k
|
We search and memoize the maximum value for k coins and i piles. \n\nC++\ncpp\nint dp[1001][2001] = {};\nint maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& piles, int k,
|
votrubac
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-27T04:01:13.115225+00:00
|
2022-03-27T04:35:25.570635+00:00
| 2,736
| false
|
We search and memoize the maximum value for `k` coins and `i` piles. \n\n**C++**\n```cpp\nint dp[1001][2001] = {};\nint maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& piles, int k, int i = 0) {\n if (i == piles.size() || k == 0)\n return 0;\n if (dp[i][k] == 0)\n for (int j = 0, sum = 0; j <= piles[i].size() && k - j >= 0; ++j) {\n dp[i][k] = max(dp[i][k], sum + maxValueOfCoins(piles, k - j, i + 1));\n if (j < piles[i].size())\n sum += piles[i][j];\n }\n return dp[i][k];\n}\n```
| 17
| 1
|
['C']
| 4
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
C++,Top-Down(Memoization) with Explanation.
|
ctop-downmemoization-with-explanation-by-wyzw
|
Approach:-\n-->This is the DP Approach with Memoization.\n-->We have Choices for any i\'th index Pile. :-\n 1)Either We should not take any Coin from i\'th ind
|
bnb_2001
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-27T13:27:09.794152+00:00
|
2023-04-15T03:31:37.935521+00:00
| 1,300
| false
|
**Approach:-**\n-->This is the **DP Approach with Memoization.**\n-->We have Choices for any i\'th index Pile. :-\n 1)Either We should not take any Coin from i\'th index pile.\n 2)Either we take one top coin from it.\n 3)Either we take 2 consecutive top coin from that pile.\n And So ...on \n -->And After that We call for (i+1)th index Pile.\n ```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dp[1001][2001]; //Dp array For Memoization.\n int solve(vector<vector<int>>&v,int index,int coin)\n {\n if(index>=v.size()||coin==0) //Base Condition\n return 0;\n if(dp[index][coin]!=-1) //Check wheather It is Already Calculated Or not.\n return dp[index][coin];\n \n \n /* Our 1st choice :- We not take any Coin from that pile*/\n int ans=solve(v,index+1,coin); //Just Call function for next Pile.\n \n \n /*Otherwise we can take Coins from that Pile.*/\n int loop=v[index].size()-1;\n int sum=0;\n \n for(int j=0;j<=min(coin-1,loop);j++) //\n {\n sum=sum+v[index][j];\n ans=max(ans,sum+solve(v,index+1,coin-(j+1)));\n \n /*Above we Pass coin-(j+1). Because till j\'th index we have taken j+1 coin from that pile.*/\n }\n \n return dp[index][coin]=ans;\n }\n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& piles, int k) {\n memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));\n return solve(piles,0,k);\n }\n};\n```\n*If you find it Helpful .Please Upvote.*
| 16
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C']
| 1
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
✅Simple DP Solution | Go | C#✅
|
simple-dp-solution-go-c-by-shukhratutabo-o3lr
|
Go\n\nfunc maxValueOfCoins(piles [][]int, k int) int {\n\tmemo := make([][]int, len(piles)+1)\n\tfor i := range memo {\n\t\tmemo[i] = make([]int, k+1)\n\t}\n\n\
|
shukhratutaboev
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-15T00:47:04.514923+00:00
|
2023-04-15T05:58:27.279561+00:00
| 1,102
| false
|
Go\n```\nfunc maxValueOfCoins(piles [][]int, k int) int {\n\tmemo := make([][]int, len(piles)+1)\n\tfor i := range memo {\n\t\tmemo[i] = make([]int, k+1)\n\t}\n\n\treturn dp(piles, memo, 0, k)\n}\n\nfunc dp(piles [][]int, memo [][]int, i int, k int) int {\n\tif k == 0 || i == len(piles) {\n\t\treturn 0\n\t}\n\tif memo[i][k] != 0 {\n\t\treturn memo[i][k]\n\t}\n\n\tres := dp(piles, memo, i+1, k)\n\tcur := 0\n\n\tfor j := 0; j < min(len(piles[i]), k); j++ {\n\t\tcur += piles[i][j]\n\t\tres = max(res, cur+dp(piles, memo, i+1, k-j-1))\n\t}\n\n\tmemo[i][k] = res\n\treturn res\n}\n\nfunc min(a, b int) int {\n\tif a < b {\n\t\treturn a\n\t}\n\treturn b\n}\n\nfunc max(a, b int) int {\n\tif a > b {\n\t\treturn a\n\t}\n\treturn b\n}\n```\nC#\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public int MaxValueOfCoins(IList<IList<int>> piles, int k) {\n int n = piles.Count;\n int[][] memo = new int[n + 1][];\n for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {\n memo[i] = new int[k + 1];\n Array.Fill(memo[i], -1);\n }\n\n return DP(piles, memo, 0, k);\n }\n\n public int DP(IList<IList<int>> piles, int[][] memo, int i, int k) {\n if (k == 0 || i == piles.Count) return 0;\n if (memo[i][k] != -1) return memo[i][k];\n\n int res = DP(piles, memo, i + 1, k);\n int cur = 0;\n\n for (int j = 0; j < Math.Min(piles[i].Count, k); ++j) {\n cur += piles[i][j];\n res = Math.Max(res, cur + DP(piles, memo, i + 1, k - j - 1));\n }\n return memo[i][k] = res;\n }\n}\n```\n
| 13
| 1
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'Go', 'C#']
| 0
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
C++ Top-down DP
|
c-top-down-dp-by-lzl124631x-7le5
|
See my latest update in repo LeetCode\n\n\n## Solution 1. Top-down DP\n\nLet dp[i][j] be the max value of j coins using piles i ~ N-1. The answer is dp[0][k].\n
|
lzl124631x
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-27T04:00:44.368247+00:00
|
2022-03-27T04:00:44.368275+00:00
| 1,816
| false
|
See my latest update in repo [LeetCode](https://github.com/lzl124631x/LeetCode)\n\n\n## Solution 1. Top-down DP\n\nLet `dp[i][j]` be the max value of `j` coins using piles `i ~ N-1`. The answer is `dp[0][k]`.\n\nFor `dp[i][j]`, we can try using `t` elements from `A[i]` (`0 <= t <= min(j, A[i].size())`), getting `A[i][0] + ... + A[i][t-1]` value plus `dp[i+1][j-t]` value (the max value of `j-t` coins using piles `i+1 ~ N-1`). We try different `t`s and assign the max value to `dp[i][j]`.\n\n```\ndp[i][j] = max( dp[i+1][j-t] + sum(i, t) | 0 <= t <= min(j, A[i].size()) )\n where sum(i, t) = A[i][0] + ... + A[i][t-1]\n```\n\nTrivial case is `dp[N][j] = 0`, i.e. we can\'t get any value from the nonexistent `A[N]`.\n\n```cpp\n// OJ: https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-286/problems/maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles/\n// Author: github.com/lzl124631x\n// Time: O(NK)\n// Space: O(NK)\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& A, int k) {\n int N = A.size(), m[1001][2001] = {};\n memset(m, -1, sizeof(m));\n function<int(int, int)> dp =[&](int i, int j) {\n if (m[i][j] != -1) return m[i][j];\n if (i == N) return 0;\n int ans = dp(i + 1, j), sum = 0;\n for (int t = 1; t <= j && t <= A[i].size(); ++t) {\n sum += A[i][t - 1];\n ans = max(ans, dp(i + 1, j - t) + sum);\n }\n return m[i][j] = ans;\n };\n return dp(0, k);\n }\n};\n```
| 12
| 1
|
[]
| 3
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
✅ Recursion | Memoization | Tabulation | C++ | Striver | Beginner friendly solution ✅
|
recursion-memoization-tabulation-c-striv-7chq
|
Intuition\nSimple pick or not pick approach. For pick we run a for loop through the array. \n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n#
|
warrior0331
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-15T06:31:49.463450+00:00
|
2023-04-15T11:14:28.332655+00:00
| 1,120
| false
|
# Intuition\nSimple pick or not pick approach. For pick we run a for loop through the array. \n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n\n```\n# Recusive code which will give you TLE\n\nint sumi(int ind, vector<vector<int>> &piles, int k, int n){\n if(ind==n or k==0) return 0;\n int notPick=sumi(ind+1,piles,k,n);\n int pick=0,coins=k,sum=0;\n for(int i=0;i<piles[ind].size() and coins>0;i++){\n sum+=piles[ind][i];\n coins--;\n int x=sum+sumi(ind+1,piles,coins,n);\n pick=max(pick,x);\n }\n return max(pick,notPick);\n}\n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& piles, int k) {\n int n=piles.size();\n int ind=0;\n return sumi(ind,piles,k,n);\n }\n```\n\n\n\n\n```\n# Memoized Solution of above\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\nint sumi(int ind, vector<vector<int>> &piles, int k, int n, vector<vector<int>> &dp){\n if(ind==n or k==0) return 0;\n if(dp[ind][k]!=-1) return dp[ind][k];\n int notPick=sumi(ind+1,piles,k,n,dp);\n int pick=0,coins=k,sum=0;\n for(int i=0;i<piles[ind].size() and coins>0;i++){\n sum+=piles[ind][i];\n coins--;\n int x=sum+sumi(ind+1,piles,coins,n,dp);\n pick=max(pick,x);\n }\n return dp[ind][k]=max(pick,notPick);\n}\n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& piles, int k) {\n int n=piles.size();\n int ind=0;\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int> (k+1,-1));\n return sumi(ind,piles,k,n,dp);\n }\n};\n```\n```\n# Tabulation\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& piles, int k) {\n int n=piles.size();\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int> (k+1,0));\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n dp[i][0]=0;\n }\n int sum=0;\n for(int i=1;i<=k and i<=piles[0].size();i++){\n sum+=piles[0][i-1];\n dp[0][i]=sum;\n }\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=1;j<=k;j++){\n int notPick=dp[i-1][j];\n int pick=0;\n int sum=0;\n for(int k=1;k<=j and k<=piles[i].size();k++){\n sum+=piles[i][k-1];\n pick=max(pick,sum+dp[i-1][j-k]);\n }\n dp[i][j]=max(pick,notPick);\n }\n }\n return dp[n-1][k];\n }\n};\n```\n# ***Please upvote if it helped!***
| 11
| 1
|
['C++']
| 1
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
[Python] Bottom-up DP solution
|
python-bottom-up-dp-solution-by-xil899-9e7f
|
Intuition\nBottom-up dynamic programming.\n\n\nExplanation\nTop-down DP solution is well-explained in @lee215\'s post. Here we present the Bottom-up DP solution
|
xil899
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-27T18:54:07.552028+00:00
|
2022-09-20T04:25:13.884128+00:00
| 1,397
| false
|
**Intuition**\nBottom-up dynamic programming.\n\n\n**Explanation**\nTop-down DP solution is well-explained in @lee215\'s [post](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles/discuss/1887010/JavaC%2B%2BPython-Top-down-DP-solution). Here we present the Bottom-up DP solution.\n`dp[i][j]` is the maximum total value from `pile[0]` to `pile[i]`, if choosing exactly `j` coins optimally.\nWe can pick `0, 1, 2, 3, ... , len(pile[i])` elements from the current `pile[i]` one by one.\nIt asks for the maximum total value of coins we can have, so we need to return max of all the options.\n\n\n**Complexity**\nTime `O(m * k)`\nSpace `O(n * k)`\nwhere `m = sum(piles[i].length) <= 2000`.\nTime complexity is well-explained in @DBabichev\'s [post](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles/discuss/1886905/Python-dp-solution-(complexity-updated)-explained), don\'t be scared by the triple for-loop here.\n\n\n**Python 3 solution**\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxValueOfCoins(self, piles: List[List[int]], k: int) -> int:\n n, m = len(piles), 0\n prefixSum = []\n for i in range(n):\n temp = [0]\n for j in range(len(piles[i])):\n temp.append(temp[-1] + piles[i][j])\n m += 1\n prefixSum.append(temp)\n if m == k:\n return sum(temp[-1] for temp in prefixSum)\n \n dp = [[0] * (k + 1) for _ in range(n)]\n for j in range(1, k + 1):\n if j < len(prefixSum[0]):\n dp[0][j] = prefixSum[0][j]\n \n for i in range(1, n):\n for j in range(1, k + 1):\n for l in range(len(prefixSum[i])):\n if l > j:\n break\n dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], prefixSum[i][l] + dp[i - 1][j - l])\n return dp[n - 1][k]\n```\nPlease upvote if you find this solution helpful.
| 11
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 4
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
🔥 [LeetCode The Hard Way] 🔥 DP + Memo Explained
|
leetcode-the-hard-way-dp-memo-explained-5ttjk
|
Let dp[i][j] be the maximum total value we can have if we pick j elements starting from piles[i]. The answer is dp[0][k]. First we calculate the value if we pic
|
__wkw__
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-15T04:02:25.439230+00:00
|
2023-04-26T15:21:26.348675+00:00
| 842
| false
|
Let `dp[i][j]` be the maximum total value we can have if we pick `j` elements starting from `piles[i]`. The answer is `dp[0][k]`. First we calculate the value if we pick any elements in the current pile. Then we try to pick at most `min((int) piles[i].size(), k)` elements and find out the max result.\n\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& piles, int k) {\n int n = piles.size();\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int>(k + 1, -1));\n function<int(int,int)> dfs = [&](int i, int k) {\n // reach the end - return 0\n if (i == n || k == 0) return 0;\n // calculated previously - return immediately\n if (dp[i][k] != -1) return dp[i][k];\n // do not take \n int res = dfs(i + 1, k), val = 0;\n // try to take it one by one \n // calculate the value we could have\n for (int j = 0; j < min((int) piles[i].size(), k); j++) {\n // take this element\n val += piles[i][j];\n res = max(res, dfs(i + 1, k - 1 - j) + val);\n }\n return dp[i][k] = res;\n };\n return dfs(0, k);\n }\n};\n```\n\n```py\nclass Solution:\n def maxValueOfCoins(self, piles: List[List[int]], k: int) -> int:\n @lru_cache(None)\n def dp(i, k):\n # reach the end - return 0\n if i == len(piles) or k == 0:\n return 0\n res = 0\n # do not take \n res += dp(i + 1, k)\n # try to take it one by one \n # calculate the value we could have\n take = 0\n for j in range(min(k, len(piles[i]))):\n # take this element\n take += piles[i][j]\n res = max(res, dp(i + 1, k - 1 - j) + take)\n return res\n return dp(0, k)\n```
| 9
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'Python', 'C++']
| 0
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
JAVA || Easy Solution || DP ||
|
java-easy-solution-dp-by-shivrastogi-aegf
|
\n\n# Code\nPLEASE UPVOTE IF YOU LIKE.\n\nclass Solution {\n public int maxValueOfCoins(List<List<Integer>> piles, int k) {\n int numPiles = piles.siz
|
shivrastogi
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-15T00:58:03.735431+00:00
|
2023-04-15T00:58:03.735463+00:00
| 1,701
| false
|
\n\n# Code\nPLEASE UPVOTE IF YOU LIKE.\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxValueOfCoins(List<List<Integer>> piles, int k) {\n int numPiles = piles.size();\n \n int[][] dp = new int[numPiles+1][k+1];\n \n for(int i=1; i<=numPiles; i++){\n for(int j=1; j<=k; j++){\n dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]; \n List<Integer> currPile = piles.get(i-1);\n int coinSum = 0;\n for(int l=0; l < Math.min(currPile.size(), j); l++){\n coinSum += currPile.get(l);\n dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j], coinSum + dp[i-1][j - l - 1]); \n }\n }\n }\n \n return dp[numPiles][k];\n }\n}\n```
| 9
| 2
|
['Java']
| 1
|
maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles
|
DP | Memoization | Easy to understand
|
dp-memoization-easy-to-understand-by-nim-i8ug
|
In the problem, we have to select *K coins from the given piles of coins. In one step we can select one coin from the top of the n piles.\nOur task is to maximi
|
nimitdidwania27
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-10T19:01:00.539051+00:00
|
2022-06-10T19:02:24.583220+00:00
| 695
| false
|
In the problem, we have to select ****K**** coins from the given piles of coins. In one step we can select one coin from the top of the n piles.\nOur task is to ****maximize the total money we can get****.\nFrom the ith pile, we can select between 0 to k coins.\nTherefore, for every pile we have choice to take 0 coin to k coins. Simply, we can write the recursive code exploring all the choices.\n\n**Recursive Solution-**\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int fun(vector<vector<int>>& piles,int ind,int k)\n {\n if(k==0 )return 0; // no more coins can be taken\n if(ind==piles.size())return INT_MIN;// no more piles are left\n int ans=fun(piles,ind+1,k); // if we take 0 coin from the pile\n int score=0;\n int secAns=INT_MIN;\n for(int i=0;i<k && i<piles[ind].size();i++)// taking 1 to k coins from the pile\n {\n score+=piles[ind][i];\n secAns=max(secAns,score+fun(piles,ind+1,k-i-1));\n }\n return max(ans,secAns); \n }\n \n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& piles, int k) {\n int n=piles.size();\n return fun(piles,0,k);\n }\n};\n```\nAs we can clearly see, we have overlapping subproblems, therefore, we can solve the problem with the help of Dynamic Programming. \nThe state variables for the given dynamic programming problem are ind(index) and k. \nWe can create a **dp[n][k+1]** and store the answer for the problem with i and k state variables.\n\n**Dynamic Programming (Memoization)-**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int fun(vector<vector<int>>& piles,int ind,int k,vector<vector<int>>&dp)\n {\n if(k==0 )return 0; //no more coins can be taken \n if(ind==piles.size())return INT_MIN; // no more piles are left\n if(dp[ind][k]!=-1)return dp[ind][k]; // if already calculated, simply return\n int ans=fun(piles,ind+1,k,dp); // if we take 0 coin from the pile\n int score=0;\n int secAns=INT_MIN;\n for(int i=0;i<k && i<piles[ind].size();i++) // taking 1 to k coins from the pile\n {\n score+=piles[ind][i];\n secAns=max(secAns,score+fun(piles,ind+1,k-i-1,dp));\n }\n return dp[ind][k] = max(ans,secAns); \n }\n \n int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& piles, int k) {\n int n=piles.size();\n vector<vector<int>>dp(n,vector<int>(k+1,-1));\n return fun(piles,0,k,dp);\n }\n};\n```\nThe above is the memoized dynamic programming solution.
| 9
| 0
|
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C']
| 0
|
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.