python_code
stringlengths 0
187k
| repo_name
stringlengths 8
46
| file_path
stringlengths 6
135
|
|---|---|---|
import os
from abc import ABC
from typing import Dict, Any, List, Optional, Sequence
import gym
import habitat
import torch
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import MachineParams
from allenact.base_abstractions.preprocessor import SensorPreprocessorGraph
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import SensorSuite
from allenact.embodiedai.sensors.vision_sensors import RGBSensor, DepthSensor
from allenact.base_abstractions.task import TaskSampler
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import evenly_distribute_count_into_bins
from allenact.utils.system import get_logger
from allenact_plugins.habitat_plugin.habitat_constants import (
HABITAT_DATASETS_DIR,
HABITAT_CONFIGS_DIR,
HABITAT_SCENE_DATASETS_DIR,
)
from allenact_plugins.habitat_plugin.habitat_task_samplers import PointNavTaskSampler
from allenact_plugins.habitat_plugin.habitat_tasks import PointNavTask
from allenact_plugins.habitat_plugin.habitat_utils import (
get_habitat_config,
construct_env_configs,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.pointnav_base import PointNavBaseConfig
def create_pointnav_config(
config_yaml_path: str,
mode: str,
scenes_path: str,
simulator_gpu_ids: Sequence[int],
distance_to_goal: float,
rotation_degrees: float,
step_size: float,
max_steps: int,
num_processes: int,
camera_width: int,
camera_height: int,
using_rgb: bool,
using_depth: bool,
) -> habitat.Config:
config = get_habitat_config(config_yaml_path)
config.defrost()
config.NUM_PROCESSES = num_processes
config.SIMULATOR_GPU_IDS = simulator_gpu_ids
config.DATASET.SCENES_DIR = HABITAT_SCENE_DATASETS_DIR
config.DATASET.DATA_PATH = scenes_path
config.SIMULATOR.AGENT_0.SENSORS = []
if using_rgb:
config.SIMULATOR.AGENT_0.SENSORS.append("RGB_SENSOR")
if using_depth:
config.SIMULATOR.AGENT_0.SENSORS.append("DEPTH_SENSOR")
config.SIMULATOR.RGB_SENSOR.WIDTH = camera_width
config.SIMULATOR.RGB_SENSOR.HEIGHT = camera_height
config.SIMULATOR.DEPTH_SENSOR.WIDTH = camera_width
config.SIMULATOR.DEPTH_SENSOR.HEIGHT = camera_height
config.SIMULATOR.TURN_ANGLE = rotation_degrees
config.SIMULATOR.FORWARD_STEP_SIZE = step_size
config.ENVIRONMENT.MAX_EPISODE_STEPS = max_steps
config.TASK.TYPE = "Nav-v0"
config.TASK.SUCCESS_DISTANCE = distance_to_goal
config.TASK.SENSORS = ["POINTGOAL_WITH_GPS_COMPASS_SENSOR"]
config.TASK.POINTGOAL_WITH_GPS_COMPASS_SENSOR.GOAL_FORMAT = "POLAR"
config.TASK.POINTGOAL_WITH_GPS_COMPASS_SENSOR.DIMENSIONALITY = 2
config.TASK.GOAL_SENSOR_UUID = "pointgoal_with_gps_compass"
config.TASK.MEASUREMENTS = ["DISTANCE_TO_GOAL", "SUCCESS", "SPL"]
config.TASK.SPL.TYPE = "SPL"
config.TASK.SPL.SUCCESS_DISTANCE = distance_to_goal
config.TASK.SUCCESS.SUCCESS_DISTANCE = distance_to_goal
config.MODE = mode
config.freeze()
return config
class PointNavHabitatBaseConfig(PointNavBaseConfig, ABC):
"""The base config for all Habitat PointNav experiments."""
FAILED_END_REWARD = -1.0
TASK_DATA_DIR_TEMPLATE = os.path.join(
HABITAT_DATASETS_DIR, "pointnav/gibson/v1/{}/{}.json.gz"
)
BASE_CONFIG_YAML_PATH = os.path.join(
HABITAT_CONFIGS_DIR, "tasks/pointnav_gibson.yaml"
)
NUM_TRAIN_PROCESSES = max(5 * torch.cuda.device_count() - 1, 4)
NUM_VAL_PROCESSES = 1
NUM_TEST_PROCESSES = 10
TRAINING_GPUS = list(range(torch.cuda.device_count()))
VALIDATION_GPUS = [torch.cuda.device_count() - 1]
TESTING_GPUS = [torch.cuda.device_count() - 1]
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def create_config(
mode: str,
scenes_path: str,
num_processes: int,
simulator_gpu_ids: Sequence[int],
):
return create_pointnav_config(
config_yaml_path=self.BASE_CONFIG_YAML_PATH,
mode=mode,
scenes_path=scenes_path,
simulator_gpu_ids=simulator_gpu_ids,
distance_to_goal=self.DISTANCE_TO_GOAL,
rotation_degrees=self.ROTATION_DEGREES,
step_size=self.STEP_SIZE,
max_steps=self.MAX_STEPS,
num_processes=num_processes,
camera_width=self.CAMERA_WIDTH,
camera_height=self.CAMERA_HEIGHT,
using_rgb=any(isinstance(s, RGBSensor) for s in self.SENSORS),
using_depth=any(isinstance(s, DepthSensor) for s in self.SENSORS),
)
self.TRAIN_CONFIG = create_config(
mode="train",
scenes_path=self.train_scenes_path(),
num_processes=self.NUM_TRAIN_PROCESSES,
simulator_gpu_ids=self.TRAINING_GPUS,
)
self.VALID_CONFIG = create_config(
mode="validate",
scenes_path=self.valid_scenes_path(),
num_processes=self.NUM_VAL_PROCESSES,
simulator_gpu_ids=self.VALIDATION_GPUS,
)
self.TEST_CONFIG = create_config(
mode="validate",
scenes_path=self.test_scenes_path(),
num_processes=self.NUM_TEST_PROCESSES,
simulator_gpu_ids=self.TESTING_GPUS,
)
self.TRAIN_CONFIGS_PER_PROCESS = construct_env_configs(
self.TRAIN_CONFIG, allow_scene_repeat=True
)
self.TEST_CONFIG_PER_PROCESS = construct_env_configs(
self.TEST_CONFIG, allow_scene_repeat=False
)
def train_scenes_path(self):
return self.TASK_DATA_DIR_TEMPLATE.format(*(["train"] * 2))
def valid_scenes_path(self):
return self.TASK_DATA_DIR_TEMPLATE.format(*(["val"] * 2))
def test_scenes_path(self):
get_logger().warning("Running tests on the validation set!")
return self.TASK_DATA_DIR_TEMPLATE.format(*(["val"] * 2))
# return self.TASK_DATA_DIR_TEMPLATE.format(*(["test"] * 2))
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "PointNav"
def machine_params(self, mode="train", **kwargs):
has_gpus = torch.cuda.is_available()
if not has_gpus:
gpu_ids = []
nprocesses = 1
elif mode == "train":
gpu_ids = self.TRAINING_GPUS
nprocesses = self.NUM_TRAIN_PROCESSES
elif mode == "valid":
gpu_ids = self.VALIDATION_GPUS
nprocesses = self.NUM_VAL_PROCESSES
elif mode == "test":
gpu_ids = self.TESTING_GPUS
nprocesses = self.NUM_TEST_PROCESSES
else:
raise NotImplementedError("mode must be 'train', 'valid', or 'test'.")
if has_gpus:
nprocesses = evenly_distribute_count_into_bins(nprocesses, len(gpu_ids))
sensor_preprocessor_graph = (
SensorPreprocessorGraph(
source_observation_spaces=SensorSuite(self.SENSORS).observation_spaces,
preprocessors=self.PREPROCESSORS,
)
if mode == "train"
or (
(isinstance(nprocesses, int) and nprocesses > 0)
or (isinstance(nprocesses, Sequence) and sum(nprocesses) > 0)
)
else None
)
return MachineParams(
nprocesses=nprocesses,
devices=gpu_ids,
sensor_preprocessor_graph=sensor_preprocessor_graph,
)
@classmethod
def make_sampler_fn(cls, **kwargs) -> TaskSampler:
return PointNavTaskSampler(
**{"failed_end_reward": cls.FAILED_END_REWARD, **kwargs} # type: ignore
)
def train_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
config = self.TRAIN_CONFIGS_PER_PROCESS[process_ind]
return {
"env_config": config,
"max_steps": self.MAX_STEPS,
"sensors": self.SENSORS,
"action_space": gym.spaces.Discrete(len(PointNavTask.class_action_names())),
"distance_to_goal": self.DISTANCE_TO_GOAL,
}
def valid_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
if total_processes != 1:
raise NotImplementedError(
"In validation, `total_processes` must equal 1 for habitat tasks"
)
return {
"env_config": self.VALID_CONFIG,
"max_steps": self.MAX_STEPS,
"sensors": self.SENSORS,
"action_space": gym.spaces.Discrete(len(PointNavTask.class_action_names())),
"distance_to_goal": self.DISTANCE_TO_GOAL,
}
def test_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
config = self.TEST_CONFIG_PER_PROCESS[process_ind]
return {
"env_config": config,
"max_steps": self.MAX_STEPS,
"sensors": self.SENSORS,
"action_space": gym.spaces.Discrete(len(PointNavTask.class_action_names())),
"distance_to_goal": self.DISTANCE_TO_GOAL,
}
| ask4help-main | projects/pointnav_baselines/experiments/habitat/pointnav_habitat_base.py |
from allenact_plugins.habitat_plugin.habitat_sensors import (
RGBSensorHabitat,
TargetCoordinatesSensorHabitat,
DepthSensorHabitat,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.habitat.debug_pointnav_habitat_base import (
DebugPointNavHabitatBaseConfig,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.pointnav_habitat_mixin_ddppo import (
PointNavHabitatMixInPPOConfig,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.pointnav_mixin_simpleconvgru import (
PointNavMixInSimpleConvGRUConfig,
)
class PointNavHabitatRGBDDeterministiSimpleConvGRUDDPPOExperimentConfig(
DebugPointNavHabitatBaseConfig,
PointNavHabitatMixInPPOConfig,
PointNavMixInSimpleConvGRUConfig,
):
"""An Point Navigation experiment configuration in Habitat with Depth
input."""
SENSORS = [
RGBSensorHabitat(
height=DebugPointNavHabitatBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
width=DebugPointNavHabitatBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
use_resnet_normalization=True,
),
DepthSensorHabitat(
height=DebugPointNavHabitatBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
width=DebugPointNavHabitatBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
use_normalization=True,
),
TargetCoordinatesSensorHabitat(coordinate_dims=2),
]
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "Debug-Pointnav-Habitat-RGBD-SimpleConv-DDPPO"
| ask4help-main | projects/pointnav_baselines/experiments/habitat/debug_pointnav_habitat_rgbd_simpleconvgru_ddppo.py |
from allenact_plugins.habitat_plugin.habitat_sensors import (
RGBSensorHabitat,
TargetCoordinatesSensorHabitat,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.habitat.debug_pointnav_habitat_base import (
DebugPointNavHabitatBaseConfig,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.pointnav_habitat_mixin_ddppo import (
PointNavHabitatMixInPPOConfig,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.pointnav_mixin_simpleconvgru import (
PointNavMixInSimpleConvGRUConfig,
)
class PointNavHabitatDepthDeterministiSimpleConvGRUDDPPOExperimentConfig(
DebugPointNavHabitatBaseConfig,
PointNavHabitatMixInPPOConfig,
PointNavMixInSimpleConvGRUConfig,
):
"""An Point Navigation experiment configuration in Habitat with Depth
input."""
SENSORS = [
RGBSensorHabitat(
height=DebugPointNavHabitatBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
width=DebugPointNavHabitatBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
use_resnet_normalization=True,
),
TargetCoordinatesSensorHabitat(coordinate_dims=2),
]
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "Debug-Pointnav-Habitat-RGB-SimpleConv-DDPPO"
| ask4help-main | projects/pointnav_baselines/experiments/habitat/debug_pointnav_habitat_rgb_simpleconvgru_ddppo.py |
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import LambdaLR
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.imitation import Imitation
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import ExpertActionSensor
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import (
Builder,
PipelineStage,
TrainingPipeline,
LinearDecay,
)
from allenact_plugins.habitat_plugin.habitat_sensors import (
RGBSensorHabitat,
TargetCoordinatesSensorHabitat,
)
from allenact_plugins.habitat_plugin.habitat_tasks import PointNavTask
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.habitat.debug_pointnav_habitat_base import (
DebugPointNavHabitatBaseConfig,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.pointnav_mixin_simpleconvgru import (
PointNavMixInSimpleConvGRUConfig,
)
class PointNavHabitatRGBDeterministiSimpleConvGRUImitationExperimentConfig(
DebugPointNavHabitatBaseConfig, PointNavMixInSimpleConvGRUConfig
):
"""An Point Navigation experiment configuration in Habitat with Depth
input."""
SENSORS = [
RGBSensorHabitat(
height=DebugPointNavHabitatBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
width=DebugPointNavHabitatBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
use_resnet_normalization=True,
),
TargetCoordinatesSensorHabitat(coordinate_dims=2),
ExpertActionSensor(nactions=len(PointNavTask.class_action_names())),
]
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "Debug-Pointnav-Habitat-RGB-SimpleConv-BC"
@classmethod
def training_pipeline(cls, **kwargs):
imitate_steps = int(75000000)
lr = 3e-4
num_mini_batch = 1
update_repeats = 3
num_steps = 30
save_interval = 5000000
log_interval = 10000 if torch.cuda.is_available() else 1
gamma = 0.99
use_gae = True
gae_lambda = 0.95
max_grad_norm = 0.5
return TrainingPipeline(
save_interval=save_interval,
metric_accumulate_interval=log_interval,
optimizer_builder=Builder(optim.Adam, dict(lr=lr)),
num_mini_batch=num_mini_batch,
update_repeats=update_repeats,
max_grad_norm=max_grad_norm,
num_steps=num_steps,
named_losses={"imitation_loss": Imitation()},
gamma=gamma,
use_gae=use_gae,
gae_lambda=gae_lambda,
advance_scene_rollout_period=cls.ADVANCE_SCENE_ROLLOUT_PERIOD,
pipeline_stages=[
PipelineStage(
loss_names=["imitation_loss"],
max_stage_steps=imitate_steps,
# teacher_forcing=LinearDecay(steps=int(1e5), startp=1.0, endp=0.0,),
),
],
lr_scheduler_builder=Builder(
LambdaLR, {"lr_lambda": LinearDecay(steps=imitate_steps)}
),
)
| ask4help-main | projects/pointnav_baselines/experiments/habitat/debug_pointnav_habitat_rgb_simpleconvgru_bc.py |
from allenact_plugins.habitat_plugin.habitat_sensors import (
DepthSensorHabitat,
TargetCoordinatesSensorHabitat,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.habitat.pointnav_habitat_base import (
PointNavHabitatBaseConfig,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.pointnav_habitat_mixin_ddppo import (
PointNavHabitatMixInPPOConfig,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.pointnav_mixin_simpleconvgru import (
PointNavMixInSimpleConvGRUConfig,
)
class PointNavHabitatDepthDeterministiSimpleConvGRUDDPPOExperimentConfig(
PointNavHabitatBaseConfig,
PointNavHabitatMixInPPOConfig,
PointNavMixInSimpleConvGRUConfig,
):
"""An Point Navigation experiment configuration in Habitat with Depth
input."""
SENSORS = [
DepthSensorHabitat(
height=PointNavHabitatBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
width=PointNavHabitatBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
use_normalization=True,
),
TargetCoordinatesSensorHabitat(coordinate_dims=2),
]
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "Pointnav-Habitat-Depth-SimpleConv-DDPPO"
| ask4help-main | projects/pointnav_baselines/experiments/habitat/pointnav_habitat_depth_simpleconvgru_ddppo.py |
import os
from abc import ABC
import habitat
import torch
from allenact_plugins.habitat_plugin.habitat_constants import (
HABITAT_DATASETS_DIR,
HABITAT_CONFIGS_DIR,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.habitat.pointnav_habitat_base import (
PointNavHabitatBaseConfig,
)
class DebugPointNavHabitatBaseConfig(PointNavHabitatBaseConfig, ABC):
"""The base config for all Habitat PointNav experiments."""
FAILED_END_REWARD = -1.0
TASK_DATA_DIR_TEMPLATE = os.path.join(
HABITAT_DATASETS_DIR, "pointnav/habitat-test-scenes/v1/{}/{}.json.gz"
)
BASE_CONFIG_YAML_PATH = os.path.join(
HABITAT_CONFIGS_DIR, "debug_habitat_pointnav.yaml"
)
NUM_TRAIN_PROCESSES = 8 if torch.cuda.is_available() else 4
TRAIN_GPUS = [torch.cuda.device_count() - 1]
VALIDATION_GPUS = [torch.cuda.device_count() - 1]
TESTING_GPUS = [torch.cuda.device_count() - 1]
@staticmethod
def make_easy_dataset(dataset: habitat.Dataset) -> habitat.Dataset:
episodes = [
e for e in dataset.episodes if float(e.info["geodesic_distance"]) < 1.5
]
for i, e in enumerate(episodes):
e.episode_id = str(i)
dataset.episodes = episodes
return dataset
| ask4help-main | projects/pointnav_baselines/experiments/habitat/debug_pointnav_habitat_base.py |
from allenact_plugins.ithor_plugin.ithor_sensors import RGBSensorThor
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_sensors import (
DepthSensorThor,
GPSCompassSensorRoboThor,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.ithor.pointnav_ithor_base import (
PointNaviThorBaseConfig,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.pointnav_mixin_simpleconvgru import (
PointNavMixInSimpleConvGRUConfig,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.pointnav_thor_mixin_ddppo import (
PointNavThorMixInPPOConfig,
)
class PointNaviThorRGBDPPOExperimentConfig(
PointNaviThorBaseConfig,
PointNavThorMixInPPOConfig,
PointNavMixInSimpleConvGRUConfig,
):
"""An Point Navigation experiment configuration in iThor with RGBD
input."""
SENSORS = [
RGBSensorThor(
height=PointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
width=PointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
use_resnet_normalization=True,
uuid="rgb_lowres",
),
DepthSensorThor(
height=PointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
width=PointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
use_normalization=True,
uuid="depth_lowres",
),
GPSCompassSensorRoboThor(),
]
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "Pointnav-iTHOR-RGBD-SimpleConv-DDPPO"
| ask4help-main | projects/pointnav_baselines/experiments/ithor/pointnav_ithor_rgbd_simpleconvgru_ddppo.py |
ask4help-main | projects/pointnav_baselines/experiments/ithor/__init__.py |
|
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_sensors import (
DepthSensorThor,
GPSCompassSensorRoboThor,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.ithor.pointnav_ithor_base import (
PointNaviThorBaseConfig,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.pointnav_mixin_simpleconvgru import (
PointNavMixInSimpleConvGRUConfig,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.pointnav_thor_mixin_ddppo_and_gbc import (
PointNavThorMixInPPOAndGBCConfig,
)
class PointNaviThorDepthPPOExperimentConfig(
PointNaviThorBaseConfig,
PointNavThorMixInPPOAndGBCConfig,
PointNavMixInSimpleConvGRUConfig,
):
"""An Point Navigation experiment configuration in iThor with Depth
input."""
SENSORS = PointNavThorMixInPPOAndGBCConfig.SENSORS + ( # type:ignore
DepthSensorThor(
height=PointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
width=PointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
use_normalization=True,
uuid="depth_lowres",
),
GPSCompassSensorRoboThor(),
)
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "Pointnav-iTHOR-Depth-SimpleConv-DDPPOAndGBC"
| ask4help-main | projects/pointnav_baselines/experiments/ithor/pointnav_ithor_depth_simpleconvgru_ddppo_and_gbc.py |
from allenact_plugins.ithor_plugin.ithor_sensors import RGBSensorThor
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_sensors import GPSCompassSensorRoboThor
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.ithor.pointnav_ithor_base import (
PointNaviThorBaseConfig,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.pointnav_mixin_simpleconvgru import (
PointNavMixInSimpleConvGRUConfig,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.pointnav_thor_mixin_ddppo import (
PointNavThorMixInPPOConfig,
)
class PointNaviThorRGBPPOExperimentConfig(
PointNaviThorBaseConfig,
PointNavThorMixInPPOConfig,
PointNavMixInSimpleConvGRUConfig,
):
"""An Point Navigation experiment configuration in iThor with RGB input."""
SENSORS = [
RGBSensorThor(
height=PointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
width=PointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
use_resnet_normalization=True,
uuid="rgb_lowres",
),
GPSCompassSensorRoboThor(),
]
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "Pointnav-iTHOR-RGB-SimpleConv-DDPPO"
| ask4help-main | projects/pointnav_baselines/experiments/ithor/pointnav_ithor_rgb_simpleconvgru_ddppo.py |
import os
from abc import ABC
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.pointnav_thor_base import (
PointNavThorBaseConfig,
)
class PointNaviThorBaseConfig(PointNavThorBaseConfig, ABC):
"""The base config for all iTHOR PointNav experiments."""
NUM_PROCESSES = 40
TRAIN_DATASET_DIR = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "datasets/ithor-pointnav/train")
VAL_DATASET_DIR = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "datasets/ithor-pointnav/val")
| ask4help-main | projects/pointnav_baselines/experiments/ithor/pointnav_ithor_base.py |
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_sensors import (
DepthSensorThor,
GPSCompassSensorRoboThor,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.ithor.pointnav_ithor_base import (
PointNaviThorBaseConfig,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.pointnav_mixin_simpleconvgru import (
PointNavMixInSimpleConvGRUConfig,
)
from projects.pointnav_baselines.experiments.pointnav_thor_mixin_ddppo import (
PointNavThorMixInPPOConfig,
)
class PointNaviThorDepthPPOExperimentConfig(
PointNaviThorBaseConfig,
PointNavThorMixInPPOConfig,
PointNavMixInSimpleConvGRUConfig,
):
"""An Point Navigation experiment configuration in iThor with Depth
input."""
SENSORS = [
DepthSensorThor(
height=PointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
width=PointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
use_normalization=True,
uuid="depth_lowres",
),
GPSCompassSensorRoboThor(),
]
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "Pointnav-iTHOR-Depth-SimpleConv-DDPPO"
| ask4help-main | projects/pointnav_baselines/experiments/ithor/pointnav_ithor_depth_simpleconvgru_ddppo.py |
from typing import Tuple, Dict, Optional, Union, List, cast
import gym
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from gym.spaces.dict import Dict as SpaceDict
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.policy import ObservationType
from allenact.embodiedai.models.basic_models import SimpleCNN
import allenact.embodiedai.models.resnet as resnet
from allenact.embodiedai.models.visual_nav_models import (
VisualNavActorCritic,
FusionType,
)
class PointNavActorCritic(VisualNavActorCritic):
"""Use raw image as observation to the agent."""
def __init__(
# base params
self,
action_space: gym.spaces.Discrete,
observation_space: SpaceDict,
goal_sensor_uuid: str,
hidden_size=512,
num_rnn_layers=1,
rnn_type="GRU",
add_prev_actions=False,
action_embed_size=4,
multiple_beliefs=False,
beliefs_fusion: Optional[FusionType] = None,
auxiliary_uuids: Optional[List[str]] = None,
# custom params
rgb_uuid: Optional[str] = None,
depth_uuid: Optional[str] = None,
embed_coordinates=False,
coordinate_embedding_dim=8,
coordinate_dims=2,
# perception backbone params,
backbone="gnresnet18",
resnet_baseplanes=32,
):
super().__init__(
action_space=action_space,
observation_space=observation_space,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
multiple_beliefs=multiple_beliefs,
beliefs_fusion=beliefs_fusion,
auxiliary_uuids=auxiliary_uuids,
)
self.goal_sensor_uuid = goal_sensor_uuid
self.embed_coordinates = embed_coordinates
if self.embed_coordinates:
self.coordinate_embedding_size = coordinate_embedding_dim
else:
self.coordinate_embedding_size = coordinate_dims
self.sensor_fusion = False
if rgb_uuid is not None and depth_uuid is not None:
self.sensor_fuser = nn.Linear(hidden_size * 2, hidden_size)
self.sensor_fusion = True
self.backbone = backbone
if backbone == "simple_cnn":
self.visual_encoder = SimpleCNN(
observation_space=observation_space,
output_size=hidden_size,
rgb_uuid=rgb_uuid,
depth_uuid=depth_uuid,
)
else: # resnet family
self.visual_encoder = resnet.GroupNormResNetEncoder(
observation_space=observation_space,
output_size=hidden_size,
rgb_uuid=rgb_uuid,
depth_uuid=depth_uuid,
baseplanes=resnet_baseplanes,
ngroups=resnet_baseplanes // 2,
make_backbone=getattr(resnet, backbone),
)
if self.embed_coordinates:
self.coordinate_embedding = nn.Linear(
coordinate_dims, coordinate_embedding_dim
)
self.create_state_encoders(
obs_embed_size=self.goal_visual_encoder_output_dims,
num_rnn_layers=num_rnn_layers,
rnn_type=rnn_type,
add_prev_actions=add_prev_actions,
prev_action_embed_size=action_embed_size,
)
self.create_actorcritic_head()
self.create_aux_models(
obs_embed_size=self.goal_visual_encoder_output_dims,
action_embed_size=action_embed_size,
)
self.train()
@property
def is_blind(self):
return self.visual_encoder.is_blind
@property
def goal_visual_encoder_output_dims(self):
dims = self.coordinate_embedding_size
if self.is_blind:
return dims
return dims + self.recurrent_hidden_state_size
def get_target_coordinates_encoding(self, observations):
if self.embed_coordinates:
return self.coordinate_embedding(
observations[self.goal_sensor_uuid].to(torch.float32)
)
else:
return observations[self.goal_sensor_uuid].to(torch.float32)
def forward_encoder(self, observations: ObservationType) -> torch.FloatTensor:
target_encoding = self.get_target_coordinates_encoding(observations)
obs_embeds: Union[torch.Tensor, List[torch.Tensor]]
obs_embeds = [target_encoding]
# if observations["rgb"].shape[0] != 1:
# print("rgb", (observations["rgb"][...,0,0,:].unsqueeze(-2).unsqueeze(-2) == observations["rgb"][...,0,0,:]).float().mean())
# if "depth" in observations:
# print("depth", (observations["depth"][...,0,0,:].unsqueeze(-2).unsqueeze(-2) == observations["depth"][...,0,0,:]).float().mean())
if not self.is_blind:
perception_embed = self.visual_encoder(observations)
if self.sensor_fusion:
perception_embed = self.sensor_fuser(perception_embed)
obs_embeds = [perception_embed] + obs_embeds
obs_embeds = torch.cat(obs_embeds, dim=-1)
return obs_embeds
class ResnetTensorPointNavActorCritic(VisualNavActorCritic):
"""Use resnet_preprocessor to generate observations to the agent."""
def __init__(
# base params
self,
action_space: gym.spaces.Discrete,
observation_space: SpaceDict,
goal_sensor_uuid: str,
hidden_size=512,
num_rnn_layers=1,
rnn_type="GRU",
add_prev_actions=False,
action_embed_size=4,
multiple_beliefs=False,
beliefs_fusion: Optional[FusionType] = None,
auxiliary_uuids: Optional[List[str]] = None,
# custom params
rgb_resnet_preprocessor_uuid: Optional[str] = None,
depth_resnet_preprocessor_uuid: Optional[str] = None,
goal_dims: int = 32,
resnet_compressor_hidden_out_dims: Tuple[int, int] = (128, 32),
combiner_hidden_out_dims: Tuple[int, int] = (128, 32),
):
super().__init__(
action_space=action_space,
observation_space=observation_space,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
multiple_beliefs=multiple_beliefs,
beliefs_fusion=beliefs_fusion,
auxiliary_uuids=auxiliary_uuids,
)
if (
rgb_resnet_preprocessor_uuid is None
or depth_resnet_preprocessor_uuid is None
):
resnet_preprocessor_uuid = (
rgb_resnet_preprocessor_uuid
if rgb_resnet_preprocessor_uuid is not None
else depth_resnet_preprocessor_uuid
)
self.goal_visual_encoder = ResnetTensorGoalEncoder(
observation_space,
goal_sensor_uuid,
resnet_preprocessor_uuid,
goal_dims,
resnet_compressor_hidden_out_dims,
combiner_hidden_out_dims,
)
else:
self.goal_visual_encoder = ResnetDualTensorGoalEncoder( # type:ignore
observation_space,
goal_sensor_uuid,
rgb_resnet_preprocessor_uuid,
depth_resnet_preprocessor_uuid,
goal_dims,
resnet_compressor_hidden_out_dims,
combiner_hidden_out_dims,
)
self.create_state_encoders(
obs_embed_size=self.goal_visual_encoder.output_dims,
num_rnn_layers=num_rnn_layers,
rnn_type=rnn_type,
add_prev_actions=add_prev_actions,
prev_action_embed_size=action_embed_size,
)
self.create_actorcritic_head()
self.create_aux_models(
obs_embed_size=self.goal_visual_encoder.output_dims,
action_embed_size=action_embed_size,
)
self.train()
@property
def is_blind(self) -> bool:
"""True if the model is blind (e.g. neither 'depth' or 'rgb' is an
input observation type)."""
return self.goal_visual_encoder.is_blind
def forward_encoder(self, observations: ObservationType) -> torch.FloatTensor:
return self.goal_visual_encoder(observations)
class ResnetTensorGoalEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
observation_spaces: SpaceDict,
goal_sensor_uuid: str,
resnet_preprocessor_uuid: str,
goal_dims: int = 32,
resnet_compressor_hidden_out_dims: Tuple[int, int] = (128, 32),
combiner_hidden_out_dims: Tuple[int, int] = (128, 32),
) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.goal_uuid = goal_sensor_uuid
self.resnet_uuid = resnet_preprocessor_uuid
self.goal_dims = goal_dims
self.resnet_hid_out_dims = resnet_compressor_hidden_out_dims
self.combine_hid_out_dims = combiner_hidden_out_dims
self.embed_goal = nn.Linear(2, self.goal_dims)
self.blind = self.resnet_uuid not in observation_spaces.spaces
if not self.blind:
self.resnet_tensor_shape = observation_spaces.spaces[self.resnet_uuid].shape
self.resnet_compressor = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.resnet_tensor_shape[0], self.resnet_hid_out_dims[0], 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(*self.resnet_hid_out_dims[0:2], 1),
nn.ReLU(),
)
self.target_obs_combiner = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
self.resnet_hid_out_dims[1] + self.goal_dims,
self.combine_hid_out_dims[0],
1,
),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(*self.combine_hid_out_dims[0:2], 1),
)
@property
def is_blind(self):
return self.blind
@property
def output_dims(self):
if self.blind:
return self.goal_dims
else:
return (
self.combine_hid_out_dims[-1]
* self.resnet_tensor_shape[1]
* self.resnet_tensor_shape[2]
)
def get_object_type_encoding(
self, observations: Dict[str, torch.FloatTensor]
) -> torch.FloatTensor:
"""Get the object type encoding from input batched observations."""
return cast(
torch.FloatTensor,
self.embed_goal(observations[self.goal_uuid].to(torch.int64)),
)
def compress_resnet(self, observations):
return self.resnet_compressor(observations[self.resnet_uuid])
def distribute_target(self, observations):
target_emb = self.embed_goal(observations[self.goal_uuid])
return target_emb.view(-1, self.goal_dims, 1, 1).expand(
-1, -1, self.resnet_tensor_shape[-2], self.resnet_tensor_shape[-1]
)
def adapt_input(self, observations):
resnet = observations[self.resnet_uuid]
use_agent = False
nagent = 1
if len(resnet.shape) == 6:
use_agent = True
nstep, nsampler, nagent = resnet.shape[:3]
else:
nstep, nsampler = resnet.shape[:2]
observations[self.resnet_uuid] = resnet.view(-1, *resnet.shape[-3:])
observations[self.goal_uuid] = observations[self.goal_uuid].view(-1, 2)
return observations, use_agent, nstep, nsampler, nagent
@staticmethod
def adapt_output(x, use_agent, nstep, nsampler, nagent):
if use_agent:
return x.view(nstep, nsampler, nagent, -1)
return x.view(nstep, nsampler * nagent, -1)
def forward(self, observations):
observations, use_agent, nstep, nsampler, nagent = self.adapt_input(
observations
)
if self.blind:
return self.embed_goal(observations[self.goal_uuid])
embs = [
self.compress_resnet(observations),
self.distribute_target(observations),
]
x = self.target_obs_combiner(torch.cat(embs, dim=1,))
x = x.reshape(x.size(0), -1) # flatten
return self.adapt_output(x, use_agent, nstep, nsampler, nagent)
class ResnetDualTensorGoalEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
observation_spaces: SpaceDict,
goal_sensor_uuid: str,
rgb_resnet_preprocessor_uuid: str,
depth_resnet_preprocessor_uuid: str,
goal_dims: int = 32,
resnet_compressor_hidden_out_dims: Tuple[int, int] = (128, 32),
combiner_hidden_out_dims: Tuple[int, int] = (128, 32),
) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.goal_uuid = goal_sensor_uuid
self.rgb_resnet_uuid = rgb_resnet_preprocessor_uuid
self.depth_resnet_uuid = depth_resnet_preprocessor_uuid
self.goal_dims = goal_dims
self.resnet_hid_out_dims = resnet_compressor_hidden_out_dims
self.combine_hid_out_dims = combiner_hidden_out_dims
self.embed_goal = nn.Linear(2, self.goal_dims)
self.blind = (
self.rgb_resnet_uuid not in observation_spaces.spaces
or self.depth_resnet_uuid not in observation_spaces.spaces
)
if not self.blind:
self.resnet_tensor_shape = observation_spaces.spaces[
self.rgb_resnet_uuid
].shape
self.rgb_resnet_compressor = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.resnet_tensor_shape[0], self.resnet_hid_out_dims[0], 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(*self.resnet_hid_out_dims[0:2], 1),
nn.ReLU(),
)
self.depth_resnet_compressor = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.resnet_tensor_shape[0], self.resnet_hid_out_dims[0], 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(*self.resnet_hid_out_dims[0:2], 1),
nn.ReLU(),
)
self.rgb_target_obs_combiner = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
self.resnet_hid_out_dims[1] + self.goal_dims,
self.combine_hid_out_dims[0],
1,
),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(*self.combine_hid_out_dims[0:2], 1),
)
self.depth_target_obs_combiner = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
self.resnet_hid_out_dims[1] + self.goal_dims,
self.combine_hid_out_dims[0],
1,
),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(*self.combine_hid_out_dims[0:2], 1),
)
@property
def is_blind(self):
return self.blind
@property
def output_dims(self):
if self.blind:
return self.goal_dims
else:
return (
2
* self.combine_hid_out_dims[-1]
* self.resnet_tensor_shape[1]
* self.resnet_tensor_shape[2]
)
def get_object_type_encoding(
self, observations: Dict[str, torch.FloatTensor]
) -> torch.FloatTensor:
"""Get the object type encoding from input batched observations."""
return cast(
torch.FloatTensor,
self.embed_goal(observations[self.goal_uuid].to(torch.int64)),
)
def compress_rgb_resnet(self, observations):
return self.rgb_resnet_compressor(observations[self.rgb_resnet_uuid])
def compress_depth_resnet(self, observations):
return self.depth_resnet_compressor(observations[self.depth_resnet_uuid])
def distribute_target(self, observations):
target_emb = self.embed_goal(observations[self.goal_uuid])
return target_emb.view(-1, self.goal_dims, 1, 1).expand(
-1, -1, self.resnet_tensor_shape[-2], self.resnet_tensor_shape[-1]
)
def adapt_input(self, observations):
rgb = observations[self.rgb_resnet_uuid]
depth = observations[self.depth_resnet_uuid]
use_agent = False
nagent = 1
if len(rgb.shape) == 6:
use_agent = True
nstep, nsampler, nagent = rgb.shape[:3]
else:
nstep, nsampler = rgb.shape[:2]
observations[self.rgb_resnet_uuid] = rgb.view(-1, *rgb.shape[-3:])
observations[self.depth_resnet_uuid] = depth.view(-1, *depth.shape[-3:])
observations[self.goal_uuid] = observations[self.goal_uuid].view(-1, 2)
return observations, use_agent, nstep, nsampler, nagent
@staticmethod
def adapt_output(x, use_agent, nstep, nsampler, nagent):
if use_agent:
return x.view(nstep, nsampler, nagent, -1)
return x.view(nstep, nsampler, -1)
def forward(self, observations):
observations, use_agent, nstep, nsampler, nagent = self.adapt_input(
observations
)
if self.blind:
return self.embed_goal(observations[self.goal_uuid])
rgb_embs = [
self.compress_rgb_resnet(observations),
self.distribute_target(observations),
]
rgb_x = self.rgb_target_obs_combiner(torch.cat(rgb_embs, dim=1,))
depth_embs = [
self.compress_depth_resnet(observations),
self.distribute_target(observations),
]
depth_x = self.depth_target_obs_combiner(torch.cat(depth_embs, dim=1,))
x = torch.cat([rgb_x, depth_x], dim=1)
x = x.reshape(x.size(0), -1) # flatten
return self.adapt_output(x, use_agent, nstep, nsampler, nagent)
| ask4help-main | projects/pointnav_baselines/models/point_nav_models.py |
ask4help-main | projects/pointnav_baselines/models/__init__.py |
|
import os
from typing import Dict, Any, List, Optional, Sequence
import gym
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import LambdaLR
from torchvision import models
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses import PPO
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.ppo import PPOConfig
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import ExperimentConfig, MachineParams
from allenact.base_abstractions.preprocessor import SensorPreprocessorGraph
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import SensorSuite
from allenact.base_abstractions.task import TaskSampler
from allenact.embodiedai.preprocessors.resnet import ResNetPreprocessor
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import (
Builder,
PipelineStage,
TrainingPipeline,
LinearDecay,
evenly_distribute_count_into_bins,
)
from allenact_plugins.habitat_plugin.habitat_constants import (
HABITAT_DATASETS_DIR,
HABITAT_CONFIGS_DIR,
)
from allenact_plugins.habitat_plugin.habitat_sensors import (
RGBSensorHabitat,
TargetCoordinatesSensorHabitat,
)
from allenact_plugins.habitat_plugin.habitat_task_samplers import PointNavTaskSampler
from allenact_plugins.habitat_plugin.habitat_utils import (
construct_env_configs,
get_habitat_config,
)
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_tasks import PointNavTask
from projects.pointnav_baselines.models.point_nav_models import (
ResnetTensorPointNavActorCritic,
)
class PointNavHabitatRGBPPOTutorialExperimentConfig(ExperimentConfig):
"""A Point Navigation experiment configuration in Habitat."""
# Task Parameters
MAX_STEPS = 500
REWARD_CONFIG = {
"step_penalty": -0.01,
"goal_success_reward": 10.0,
"failed_stop_reward": 0.0,
"shaping_weight": 1.0,
}
DISTANCE_TO_GOAL = 0.2
# Simulator Parameters
CAMERA_WIDTH = 640
CAMERA_HEIGHT = 480
SCREEN_SIZE = 224
# Training Engine Parameters
ADVANCE_SCENE_ROLLOUT_PERIOD: Optional[int] = None
NUM_PROCESSES = max(5 * torch.cuda.device_count() - 1, 4)
TRAINING_GPUS = list(range(torch.cuda.device_count()))
VALIDATION_GPUS = [torch.cuda.device_count() - 1]
TESTING_GPUS = [torch.cuda.device_count() - 1]
task_data_dir_template = os.path.join(
HABITAT_DATASETS_DIR, "pointnav/gibson/v1/{}/{}.json.gz"
)
TRAIN_SCENES = task_data_dir_template.format(*(["train"] * 2))
VALID_SCENES = task_data_dir_template.format(*(["val"] * 2))
TEST_SCENES = task_data_dir_template.format(*(["test"] * 2))
CONFIG = get_habitat_config(
os.path.join(HABITAT_CONFIGS_DIR, "tasks/pointnav_gibson.yaml")
)
CONFIG.defrost()
CONFIG.NUM_PROCESSES = NUM_PROCESSES
CONFIG.SIMULATOR_GPU_IDS = TRAINING_GPUS
CONFIG.DATASET.SCENES_DIR = "habitat/habitat-api/data/scene_datasets/"
CONFIG.DATASET.POINTNAVV1.CONTENT_SCENES = ["*"]
CONFIG.DATASET.DATA_PATH = TRAIN_SCENES
CONFIG.SIMULATOR.AGENT_0.SENSORS = ["RGB_SENSOR"]
CONFIG.SIMULATOR.RGB_SENSOR.WIDTH = CAMERA_WIDTH
CONFIG.SIMULATOR.RGB_SENSOR.HEIGHT = CAMERA_HEIGHT
CONFIG.SIMULATOR.TURN_ANGLE = 30
CONFIG.SIMULATOR.FORWARD_STEP_SIZE = 0.25
CONFIG.ENVIRONMENT.MAX_EPISODE_STEPS = MAX_STEPS
CONFIG.TASK.TYPE = "Nav-v0"
CONFIG.TASK.SUCCESS_DISTANCE = DISTANCE_TO_GOAL
CONFIG.TASK.SENSORS = ["POINTGOAL_WITH_GPS_COMPASS_SENSOR"]
CONFIG.TASK.POINTGOAL_WITH_GPS_COMPASS_SENSOR.GOAL_FORMAT = "POLAR"
CONFIG.TASK.POINTGOAL_WITH_GPS_COMPASS_SENSOR.DIMENSIONALITY = 2
CONFIG.TASK.GOAL_SENSOR_UUID = "pointgoal_with_gps_compass"
CONFIG.TASK.MEASUREMENTS = ["DISTANCE_TO_GOAL", "SUCCESS", "SPL"]
CONFIG.TASK.SPL.TYPE = "SPL"
CONFIG.TASK.SPL.SUCCESS_DISTANCE = DISTANCE_TO_GOAL
CONFIG.TASK.SUCCESS.SUCCESS_DISTANCE = DISTANCE_TO_GOAL
CONFIG.MODE = "train"
SENSORS = [
RGBSensorHabitat(
height=SCREEN_SIZE, width=SCREEN_SIZE, use_resnet_normalization=True,
),
TargetCoordinatesSensorHabitat(coordinate_dims=2),
]
PREPROCESSORS = [
Builder(
ResNetPreprocessor,
{
"input_height": SCREEN_SIZE,
"input_width": SCREEN_SIZE,
"output_width": 7,
"output_height": 7,
"output_dims": 512,
"pool": False,
"torchvision_resnet_model": models.resnet18,
"input_uuids": ["rgb_lowres"],
"output_uuid": "rgb_resnet",
},
),
]
OBSERVATIONS = [
"rgb_resnet",
"target_coordinates_ind",
]
TRAIN_CONFIGS = construct_env_configs(CONFIG)
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "PointNavHabitatRGBPPO"
@classmethod
def training_pipeline(cls, **kwargs):
ppo_steps = int(250000000)
lr = 3e-4
num_mini_batch = 1
update_repeats = 3
num_steps = 30
save_interval = 5000000
log_interval = 10000
gamma = 0.99
use_gae = True
gae_lambda = 0.95
max_grad_norm = 0.5
return TrainingPipeline(
save_interval=save_interval,
metric_accumulate_interval=log_interval,
optimizer_builder=Builder(optim.Adam, dict(lr=lr)),
num_mini_batch=num_mini_batch,
update_repeats=update_repeats,
max_grad_norm=max_grad_norm,
num_steps=num_steps,
named_losses={"ppo_loss": PPO(**PPOConfig)},
gamma=gamma,
use_gae=use_gae,
gae_lambda=gae_lambda,
advance_scene_rollout_period=cls.ADVANCE_SCENE_ROLLOUT_PERIOD,
pipeline_stages=[
PipelineStage(loss_names=["ppo_loss"], max_stage_steps=ppo_steps)
],
lr_scheduler_builder=Builder(
LambdaLR, {"lr_lambda": LinearDecay(steps=ppo_steps)}
),
)
def machine_params(self, mode="train", **kwargs):
if mode == "train":
workers_per_device = 1
gpu_ids = (
[]
if not torch.cuda.is_available()
else self.TRAINING_GPUS * workers_per_device
)
nprocesses = (
1
if not torch.cuda.is_available()
else evenly_distribute_count_into_bins(self.NUM_PROCESSES, len(gpu_ids))
)
elif mode == "valid":
nprocesses = 1
gpu_ids = [] if not torch.cuda.is_available() else self.VALIDATION_GPUS
elif mode == "test":
nprocesses = 1
gpu_ids = [] if not torch.cuda.is_available() else self.TESTING_GPUS
else:
raise NotImplementedError("mode must be 'train', 'valid', or 'test'.")
sensor_preprocessor_graph = (
SensorPreprocessorGraph(
source_observation_spaces=SensorSuite(self.SENSORS).observation_spaces,
preprocessors=self.PREPROCESSORS,
)
if mode == "train"
or (
(isinstance(nprocesses, int) and nprocesses > 0)
or (isinstance(nprocesses, Sequence) and sum(nprocesses) > 0)
)
else None
)
return MachineParams(
nprocesses=nprocesses,
devices=gpu_ids,
sensor_preprocessor_graph=sensor_preprocessor_graph,
)
# Define Model
@classmethod
def create_model(cls, **kwargs) -> nn.Module:
return ResnetTensorPointNavActorCritic(
action_space=gym.spaces.Discrete(len(PointNavTask.class_action_names())),
observation_space=kwargs["sensor_preprocessor_graph"].observation_spaces,
goal_sensor_uuid="target_coordinates_ind",
rgb_resnet_preprocessor_uuid="rgb_resnet",
hidden_size=512,
goal_dims=32,
)
# Define Task Sampler
@classmethod
def make_sampler_fn(cls, **kwargs) -> TaskSampler:
return PointNavTaskSampler(**kwargs)
def train_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
config = self.TRAIN_CONFIGS[process_ind]
return {
"env_config": config,
"max_steps": self.MAX_STEPS,
"sensors": self.SENSORS,
"action_space": gym.spaces.Discrete(len(PointNavTask.class_action_names())),
"distance_to_goal": self.DISTANCE_TO_GOAL, # type:ignore
}
def valid_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
config = self.CONFIG.clone()
config.defrost()
config.DATASET.DATA_PATH = self.VALID_SCENES
config.MODE = "validate"
config.freeze()
return {
"env_config": config,
"max_steps": self.MAX_STEPS,
"sensors": self.SENSORS,
"action_space": gym.spaces.Discrete(len(PointNavTask.class_action_names())),
"distance_to_goal": self.DISTANCE_TO_GOAL, # type:ignore
}
def test_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
raise NotImplementedError("Testing not implemented for this tutorial.")
| ask4help-main | projects/tutorials/pointnav_habitat_rgb_ddppo.py |
# literate: tutorials/running-inference-on-a-pretrained-model.md
# %%
"""# Tutorial: Inference with a pre-trained model."""
# %%
"""
In this tutorial we will run inference on a pre-trained model for the PointNav task
in the RoboTHOR environment. In this task the agent is tasked with going to a specific location
within a realistic 3D environment.
For information on how to train a PointNav Model see [this tutorial](training-a-pointnav-model.md)
We will need to [install the full AllenAct library](../installation/installation-allenact.md#full-library),
the `robothor_plugin` requirements via
```bash
pip install -r allenact_plugins/robothor_plugin/extra_requirements.txt
```
and [download the
RoboTHOR Pointnav dataset](../installation/download-datasets.md) before we get started.
For this tutorial we will download the weights of a model trained on the debug dataset.
This can be done with a handy script in the `pretrained_model_ckpts` directory:
```bash
bash pretrained_model_ckpts/download_navigation_model_ckpts.sh robothor-pointnav-rgb-resnet
```
This will download the weights for an RGB model that has been
trained on the PointNav task in RoboTHOR to `pretrained_model_ckpts/robothor-pointnav-rgb-resnet`
Next we need to run the inference, using the PointNav experiment config from the
[tutorial on making a PointNav experiment](training-a-pointnav-model.md).
We can do this with the following command:
```bash
PYTHONPATH=. python allenact/main.py -o <PATH_TO_OUTPUT> -b <BASE_DIRECTORY_OF_YOUR_EXPERIMENT> -c <PATH_TO_CHECKPOINT> --eval
```
Where `<PATH_TO_OUTPUT>` is the location where the results of the test will be dumped, `<PATH_TO_CHECKPOINT>` is the
location of the downloaded model weights, and `<BASE_DIRECTORY_OF_YOUR_EXPERIMENT>` is a path to the directory where
our experiment definition is stored.
For our current setup the following command would work:
```bash
PYTHONPATH=. python allenact/main.py \
training_a_pointnav_model \
-o pretrained_model_ckpts/robothor-pointnav-rgb-resnet/ \
-b projects/tutorials \
-c pretrained_model_ckpts/robothor-pointnav-rgb-resnet/checkpoints/PointNavRobothorRGBPPO/2020-08-31_12-13-30/exp_PointNavRobothorRGBPPO__stage_00__steps_000039031200.pt \
--eval
```
For testing on all saved checkpoints we pass a directory to `--checkpoint` rather than just a single file:
```bash
PYTHONPATH=. python allenact/main.py \
training_a_pointnav_model \
-o pretrained_model_ckpts/robothor-pointnav-rgb-resnet/ \
-b projects/tutorials \
-c pretrained_model_ckpts/robothor-pointnav-rgb-resnet/checkpoints/PointNavRobothorRGBPPO/2020-08-31_12-13-30
--eval
```
## Visualization
We also show examples of visualizations that can be extracted from the `"valid"` and `"test"` modes. Currently,
visualization is still undergoing design changes and does not support multi-agent tasks, but the available functionality
is sufficient for pointnav in RoboThor.
Following up on the example above, we can make a specialized pontnav `ExperimentConfig` where we instantiate
the base visualization class, `VizSuite`, defined in
[`allenact.utils.viz_utils`](https://github.com/allenai/allenact/tree/master/allenact/utils/viz_utils.py), when in `test` mode.
Each visualization type can be thought of as a plugin to the base `VizSuite`. For example, all `episode_ids` passed to
`VizSuite` will be processed with each of the instantiated visualization types (possibly with the exception of the
`AgentViewViz`). In the example below we show how to instantiate different visualization types from 4 different data
sources.
The data sources available to `VizSuite` are:
* Task output (e.g. 2D trajectories)
* Vector task (e.g. egocentric views)
* Rollout storage (e.g. recurrent memory, taken action logprobs...)
* `ActorCriticOutput` (e.g. action probabilities)
The visualization types included below are:
* `TrajectoryViz`: Generic 2D trajectory view.
* `AgentViewViz`: RGB egocentric view.
* `ActorViz`: Action probabilities from `ActorCriticOutput[CategoricalDistr]`.
* `TensorViz1D`: Evolution of a point from RolloutStorage over time.
* `TensorViz2D`: Evolution of a vector from RolloutStorage over time.
* `ThorViz`: Specialized 2D trajectory view
[for RoboThor](https://github.com/allenai/allenact/tree/master/allenact_plugins/robothor_plugin/robothor_viz.py).
Note that we need to explicitly set the `episode_ids` that we wish to visualize. For `AgentViewViz` we have the option
of using a different (typically shorter) list of episodes or enforce the ones used for the rest of visualizations.
"""
# %% hide
from typing import Optional
from allenact.utils.viz_utils import (
VizSuite,
TrajectoryViz,
ActorViz,
AgentViewViz,
TensorViz1D,
TensorViz2D,
)
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_viz import ThorViz
from projects.tutorials.training_a_pointnav_model import (
PointNavRoboThorRGBPPOExperimentConfig,
)
# %%
class PointNavRoboThorRGBPPOVizExperimentConfig(PointNavRoboThorRGBPPOExperimentConfig):
"""ExperimentConfig used to demonstrate how to set up visualization code.
# Attributes
viz_ep_ids : Scene names that will be visualized.
viz_video_ids : Scene names that will have videos visualizations associated with them.
"""
viz_ep_ids = [
"FloorPlan_Train1_1_3",
"FloorPlan_Train1_1_4",
"FloorPlan_Train1_1_5",
"FloorPlan_Train1_1_6",
]
viz_video_ids = [["FloorPlan_Train1_1_3"], ["FloorPlan_Train1_1_4"]]
viz: Optional[VizSuite] = None
def get_viz(self, mode):
if self.viz is not None:
return self.viz
self.viz = VizSuite(
episode_ids=self.viz_ep_ids,
mode=mode,
# Basic 2D trajectory visualizer (task output source):
base_trajectory=TrajectoryViz(
path_to_target_location=("task_info", "target",),
),
# Egocentric view visualizer (vector task source):
egeocentric=AgentViewViz(
max_video_length=100, episode_ids=self.viz_video_ids
),
# Default action probability visualizer (actor critic output source):
action_probs=ActorViz(figsize=(3.25, 10), fontsize=18),
# Default taken action logprob visualizer (rollout storage source):
taken_action_logprobs=TensorViz1D(),
# Same episode mask visualizer (rollout storage source):
episode_mask=TensorViz1D(rollout_source=("masks",)),
# Default recurrent memory visualizer (rollout storage source):
rnn_memory=TensorViz2D(rollout_source=("memory", "single_belief")),
# Specialized 2D trajectory visualizer (task output source):
thor_trajectory=ThorViz(
figsize=(16, 8),
viz_rows_cols=(448, 448),
scenes=("FloorPlan_Train{}_{}", 1, 1, 1, 1),
),
)
return self.viz
def machine_params(self, mode="train", **kwargs):
res = super().machine_params(mode, **kwargs)
if mode == "test":
res.set_visualizer(self.get_viz(mode))
return res
# %%
"""
Running test on the same downloaded models, but using the visualization-enabled `ExperimentConfig` with
```bash
PYTHONPATH=. python allenact/main.py \
running_inference_tutorial \
-o pretrained_model_ckpts/robothor-pointnav-rgb-resnet/ \
-b projects/tutorials \
-c pretrained_model_ckpts/robothor-pointnav-rgb-resnet/checkpoints/PointNavRobothorRGBPPO/2020-08-31_12-13-30/exp_PointNavRobothorRGBPPO__stage_00__steps_000039031200.pt \
--eval
```
generates different types of visualization and logs them in tensorboard. If everything is properly setup and
tensorboard includes the `robothor-pointnav-rgb-resnet` folder, under the `IMAGES` tab, we should see something similar
to

"""
| ask4help-main | projects/tutorials/running_inference_tutorial.py |
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import LambdaLR
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses import PPO
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.imitation import Imitation
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.ppo import PPOConfig
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import (
Builder,
PipelineStage,
TrainingPipeline,
LinearDecay,
)
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import ExpertActionSensor
from projects.tutorials.object_nav_ithor_ppo_one_object import (
ObjectNavThorPPOExperimentConfig,
ObjectNaviThorGridTask,
)
class ObjectNavThorDaggerThenPPOExperimentConfig(ObjectNavThorPPOExperimentConfig):
"""A simple object navigation experiment in THOR.
Training with DAgger and then PPO.
"""
SENSORS = ObjectNavThorPPOExperimentConfig.SENSORS + [
ExpertActionSensor(
action_space=len(ObjectNaviThorGridTask.class_action_names()),
),
]
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "ObjectNavThorDaggerThenPPO"
@classmethod
def training_pipeline(cls, **kwargs):
dagger_steos = int(1e4)
ppo_steps = int(1e6)
lr = 2.5e-4
num_mini_batch = 2 if not torch.cuda.is_available() else 6
update_repeats = 4
num_steps = 128
metric_accumulate_interval = cls.MAX_STEPS * 10 # Log every 10 max length tasks
save_interval = 10000
gamma = 0.99
use_gae = True
gae_lambda = 1.0
max_grad_norm = 0.5
return TrainingPipeline(
save_interval=save_interval,
metric_accumulate_interval=metric_accumulate_interval,
optimizer_builder=Builder(optim.Adam, dict(lr=lr)),
num_mini_batch=num_mini_batch,
update_repeats=update_repeats,
max_grad_norm=max_grad_norm,
num_steps=num_steps,
named_losses={
"ppo_loss": PPO(clip_decay=LinearDecay(ppo_steps), **PPOConfig),
"imitation_loss": Imitation(), # We add an imitation loss.
},
gamma=gamma,
use_gae=use_gae,
gae_lambda=gae_lambda,
advance_scene_rollout_period=cls.ADVANCE_SCENE_ROLLOUT_PERIOD,
pipeline_stages=[
PipelineStage(
loss_names=["imitation_loss"],
teacher_forcing=LinearDecay(
startp=1.0, endp=0.0, steps=dagger_steos,
),
max_stage_steps=dagger_steos,
),
PipelineStage(loss_names=["ppo_loss"], max_stage_steps=ppo_steps,),
],
lr_scheduler_builder=Builder(
LambdaLR, {"lr_lambda": LinearDecay(steps=ppo_steps)}
),
)
| ask4help-main | projects/tutorials/object_nav_ithor_dagger_then_ppo_one_object.py |
# literate: tutorials/offpolicy-tutorial.md
# %%
"""# Tutorial: Off-policy training."""
# %%
"""
**Note** The provided commands to execute in this tutorial assume you have
[installed the full library](../installation/installation-allenact.md#full-library) and the `extra_requirements`
for the `babyai_plugin` and `minigrid_plugin`. The latter can be installed with:
```bash
pip install -r allenact_plugins/babyai_plugin/extra_requirements.txt; pip install -r allenact_plugins/minigrid_plugin/extra_requirements.txt
```
In this tutorial we'll learn how to train an agent from an external dataset by imitating expert actions via
Behavior Cloning. We'll use a [BabyAI agent](/api/allenact_plugins/babyai_plugin/babyai_models#BabyAIRecurrentACModel) to solve
`GoToLocal` tasks on [MiniGrid](https://github.com/maximecb/gym-minigrid); see the
`projects/babyai_baselines/experiments/go_to_local` directory for more details.
This tutorial assumes `AllenAct`'s [abstractions](../getting_started/abstractions.md) are known.
## The task
In a `GoToLocal` task, the agent immersed in a grid world has to navigate to a specific object in the presence of
multiple distractors, requiring the agent to understand `go to` instructions like "go to the red ball". For further
details, please consult the [original paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.08272).
## Getting the dataset
We will use a large dataset (**more than 4 GB**) including expert demonstrations for `GoToLocal` tasks. To download
the data we'll run
```bash
PYTHONPATH=. python allenact_plugins/babyai_plugin/scripts/download_babyai_expert_demos.py GoToLocal
```
from the project's root directory, which will download `BabyAI-GoToLocal-v0.pkl` and `BabyAI-GoToLocal-v0_valid.pkl` to
the `allenact_plugins/babyai_plugin/data/demos` directory.
We will also generate small versions of the datasets, which will be useful if running on CPU, by calling
```bash
PYTHONPATH=. python allenact_plugins/babyai_plugin/scripts/truncate_expert_demos.py
```
from the project's root directory, which will generate `BabyAI-GoToLocal-v0-small.pkl` under the same
`allenact_plugins/babyai_plugin/data/demos` directory.
## Data iterator
In order to train with an off-policy dataset, we need to define a data `Iterator`.
The `Data Iterator` merges the functionality of the `Dataset` and `Dataloader` in PyTorch,
in that it defines the way to both sample data from the dataset and convert them into batches to be
used for training.
An
example of a `Data Iterator` for BabyAI expert demos might look as follows:
"""
# %% import_summary allenact_plugins.minigrid_plugin.minigrid_offpolicy.ExpertTrajectoryIterator
# %%
"""
A complete example can be found in
[ExpertTrajectoryIterator](/api/allenact_plugins/minigrid_plugin/minigrid_offpolicy#ExpertTrajectoryIterator).
## Loss function
Off-policy losses must implement the
[AbstractOffPolicyLoss](/api/allenact/algorithms/offpolicy_sync/losses/abstract_offpolicy_loss/#abstractoffpolicyloss)
interface. In this case, we minimize the cross-entropy between the actor's policy and the expert action:
"""
# %% import allenact_plugins.minigrid_plugin.minigrid_offpolicy.MiniGridOffPolicyExpertCELoss
# %%
"""
A complete example can be found in
[MiniGridOffPolicyExpertCELoss](/api/allenact_plugins/minigrid_plugin/minigrid_offpolicy#MiniGridOffPolicyExpertCELoss).
Note that in this case we train the entire actor, but it would also be possible to forward data through a different
subgraph of the ActorCriticModel.
## Experiment configuration
For the experiment configuration, we'll build on top of an existing
[base BabyAI GoToLocal Experiment Config](/api/projects/babyai_baselines/experiments/go_to_local/base/#basebabyaigotolocalexperimentconfig).
The complete `ExperimentConfig` file for off-policy training is
[here](/api/projects/tutorials/minigrid_offpolicy_tutorial/#bcoffpolicybabyaigotolocalexperimentconfig), but let's
focus on the most relevant aspect to enable this type of training:
providing an [OffPolicyPipelineComponent](/api/allenact/utils/experiment_utils/#offpolicypipelinecomponent) object as input to a
`PipelineStage` when instantiating the `TrainingPipeline` in the `training_pipeline` method.
"""
# %% hide
import os
from typing import Optional, List, Tuple
import torch
from gym_minigrid.minigrid import MiniGridEnv
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import PipelineStage, OffPolicyPipelineComponent
from allenact_plugins.babyai_plugin.babyai_constants import (
BABYAI_EXPERT_TRAJECTORIES_DIR,
)
from allenact_plugins.minigrid_plugin.minigrid_offpolicy import (
MiniGridOffPolicyExpertCELoss,
create_minigrid_offpolicy_data_iterator,
)
from projects.babyai_baselines.experiments.go_to_local.base import (
BaseBabyAIGoToLocalExperimentConfig,
)
# %%
class BCOffPolicyBabyAIGoToLocalExperimentConfig(BaseBabyAIGoToLocalExperimentConfig):
"""BC Off-policy imitation."""
DATASET: Optional[List[Tuple[str, bytes, List[int], MiniGridEnv.Actions]]] = None
GPU_ID = 0 if torch.cuda.is_available() else None
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "BabyAIGoToLocalBCOffPolicy"
@classmethod
def METRIC_ACCUMULATE_INTERVAL(cls):
# See BaseBabyAIGoToLocalExperimentConfig for how this is used.
return 1
@classmethod
def training_pipeline(cls, **kwargs):
total_train_steps = cls.TOTAL_IL_TRAIN_STEPS
ppo_info = cls.rl_loss_default("ppo", steps=-1)
num_mini_batch = ppo_info["num_mini_batch"]
update_repeats = ppo_info["update_repeats"]
# fmt: off
return cls._training_pipeline(
named_losses={
"offpolicy_expert_ce_loss": MiniGridOffPolicyExpertCELoss(
total_episodes_in_epoch=int(1e6)
),
},
pipeline_stages=[
# Single stage, only with off-policy training
PipelineStage(
loss_names=[], # no on-policy losses
max_stage_steps=total_train_steps, # keep sampling episodes in the stage
# Enable off-policy training:
offpolicy_component=OffPolicyPipelineComponent(
# Pass a method to instantiate data iterators
data_iterator_builder=lambda **extra_kwargs: create_minigrid_offpolicy_data_iterator(
path=os.path.join(
BABYAI_EXPERT_TRAJECTORIES_DIR,
"BabyAI-GoToLocal-v0{}.pkl".format(
"" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "-small"
),
),
nrollouts=cls.NUM_TRAIN_SAMPLERS // num_mini_batch, # per trainer batch size
rollout_len=cls.ROLLOUT_STEPS,
instr_len=cls.INSTR_LEN,
**extra_kwargs,
),
loss_names=["offpolicy_expert_ce_loss"], # off-policy losses
updates=num_mini_batch * update_repeats, # number of batches per rollout
),
),
],
# As we don't have any on-policy losses, we set the next
# two values to zero to ensure we don't attempt to
# compute gradients for on-policy rollouts:
num_mini_batch=0,
update_repeats=0,
total_train_steps=total_train_steps,
)
# fmt: on
# %%
"""
You'll have noted that it is possible to combine on-policy and off-policy training in the same stage, even though here
we apply pure off-policy training.
## Training
We recommend using a machine with a CUDA-capable GPU for this experiment. In order to start training, we just need to
invoke
```bash
PYTHONPATH=. python allenact/main.py -b projects/tutorials minigrid_offpolicy_tutorial -m 8 -o <OUTPUT_PATH>
```
Note that with the `-m 8` option we limit to 8 the number of on-policy task sampling processes used between off-policy
updates.
If everything goes well, the training success should quickly reach values around 0.7-0.8 on GPU and converge to values
close to 1 if given sufficient time to train.
If running tensorboard, you'll notice a separate group of scalars named `offpolicy` with losses, approximate frame rate
and other tracked values in addition to the standard `train` used for on-policy training.
A view of the training progress about 5 minutes after starting on a CUDA-capable GPU should look similar to

"""
| ask4help-main | projects/tutorials/minigrid_offpolicy_tutorial.py |
from math import ceil
from typing import Dict, Any, List, Optional
import gym
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import LambdaLR
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses import PPO
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.ppo import PPOConfig
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import ExperimentConfig
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import SensorSuite
from allenact.base_abstractions.task import TaskSampler
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import (
Builder,
PipelineStage,
TrainingPipeline,
LinearDecay,
)
from allenact.utils.multi_agent_viz_utils import MultiTrajectoryViz
from allenact.utils.viz_utils import VizSuite, AgentViewViz
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_models import (
NavToPartnerActorCriticSimpleConvRNN,
)
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_sensors import RGBSensorMultiRoboThor
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_task_samplers import (
NavToPartnerTaskSampler,
)
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_tasks import NavToPartnerTask
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_viz import ThorMultiViz
class NavToPartnerRoboThorRGBPPOExperimentConfig(ExperimentConfig):
"""A Multi-Agent Navigation experiment configuration in RoboThor."""
# Task Parameters
MAX_STEPS = 500
REWARD_CONFIG = {
"step_penalty": -0.01,
"max_success_distance": 0.75,
"success_reward": 5.0,
}
# Simulator Parameters
CAMERA_WIDTH = 300
CAMERA_HEIGHT = 300
SCREEN_SIZE = 224
# Training Engine Parameters
ADVANCE_SCENE_ROLLOUT_PERIOD: Optional[int] = None
NUM_PROCESSES = 20
TRAINING_GPUS: List[int] = [0]
VALIDATION_GPUS: List[int] = [0]
TESTING_GPUS: List[int] = [0]
SENSORS = [
RGBSensorMultiRoboThor(
agent_count=2,
height=SCREEN_SIZE,
width=SCREEN_SIZE,
use_resnet_normalization=True,
uuid="rgb",
),
]
OBSERVATIONS = [
"rgb",
]
ENV_ARGS = dict(
width=CAMERA_WIDTH,
height=CAMERA_HEIGHT,
rotateStepDegrees=30.0,
visibilityDistance=1.0,
gridSize=0.25,
agentCount=2,
)
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "NavToPartnerRobothorRGBPPO"
@classmethod
def training_pipeline(cls, **kwargs):
ppo_steps = int(1000000)
lr = 3e-4
num_mini_batch = 1
update_repeats = 3
num_steps = 30
save_interval = 200000
log_interval = 1
gamma = 0.99
use_gae = True
gae_lambda = 0.95
max_grad_norm = 0.5
return TrainingPipeline(
save_interval=save_interval,
metric_accumulate_interval=log_interval,
optimizer_builder=Builder(optim.Adam, dict(lr=lr)),
num_mini_batch=num_mini_batch,
update_repeats=update_repeats,
max_grad_norm=max_grad_norm,
num_steps=num_steps,
named_losses={"ppo_loss": PPO(**PPOConfig)},
gamma=gamma,
use_gae=use_gae,
gae_lambda=gae_lambda,
advance_scene_rollout_period=cls.ADVANCE_SCENE_ROLLOUT_PERIOD,
pipeline_stages=[
PipelineStage(loss_names=["ppo_loss"], max_stage_steps=ppo_steps)
],
lr_scheduler_builder=Builder(
LambdaLR, {"lr_lambda": LinearDecay(steps=ppo_steps)}
),
)
def split_num_processes(self, ndevices):
assert self.NUM_PROCESSES >= ndevices, "NUM_PROCESSES {} < ndevices {}".format(
self.NUM_PROCESSES, ndevices
)
res = [0] * ndevices
for it in range(self.NUM_PROCESSES):
res[it % ndevices] += 1
return res
viz: Optional[VizSuite] = None
def get_viz(self, mode):
if self.viz is not None:
return self.viz
self.viz = VizSuite(
mode=mode,
# Basic 2D trajectory visualizer (task output source):
base_trajectory=MultiTrajectoryViz(), # plt_colormaps=["cool", "cool"]),
# Egocentric view visualizer (vector task source):
egeocentric=AgentViewViz(max_video_length=100, max_episodes_in_group=1),
# Specialized 2D trajectory visualizer (task output source):
thor_trajectory=ThorMultiViz(
figsize=(16, 8),
viz_rows_cols=(448, 448),
scenes=("FloorPlan_Train{}_{}", 1, 1, 1, 1),
),
)
return self.viz
def machine_params(self, mode="train", **kwargs):
visualizer = None
if mode == "train":
devices = (
["cpu"] if not torch.cuda.is_available() else list(self.TRAINING_GPUS)
)
nprocesses = (
4
if not torch.cuda.is_available()
else self.split_num_processes(len(devices))
)
elif mode == "valid":
nprocesses = 0
devices = ["cpu"] if not torch.cuda.is_available() else self.VALIDATION_GPUS
elif mode == "test":
nprocesses = 1
devices = ["cpu"] if not torch.cuda.is_available() else self.TESTING_GPUS
visualizer = self.get_viz(mode=mode)
else:
raise NotImplementedError("mode must be 'train', 'valid', or 'test'.")
return {
"nprocesses": nprocesses,
"devices": devices,
"visualizer": visualizer,
}
# TODO Define Model
@classmethod
def create_model(cls, **kwargs) -> nn.Module:
return NavToPartnerActorCriticSimpleConvRNN(
action_space=gym.spaces.Tuple(
[
gym.spaces.Discrete(len(NavToPartnerTask.class_action_names())),
gym.spaces.Discrete(len(NavToPartnerTask.class_action_names())),
]
),
observation_space=SensorSuite(cls.SENSORS).observation_spaces,
hidden_size=512,
)
# Define Task Sampler
@classmethod
def make_sampler_fn(cls, **kwargs) -> TaskSampler:
return NavToPartnerTaskSampler(**kwargs)
# Utility Functions for distributing scenes between GPUs
@staticmethod
def _partition_inds(n: int, num_parts: int):
return np.round(np.linspace(0, n, num_parts + 1, endpoint=True)).astype(
np.int32
)
def _get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
self,
scenes: List[str],
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
if total_processes > len(scenes): # oversample some scenes -> bias
if total_processes % len(scenes) != 0:
print(
"Warning: oversampling some of the scenes to feed all processes."
" You can avoid this by setting a number of workers divisible by the number of scenes"
)
scenes = scenes * int(ceil(total_processes / len(scenes)))
scenes = scenes[: total_processes * (len(scenes) // total_processes)]
else:
if len(scenes) % total_processes != 0:
print(
"Warning: oversampling some of the scenes to feed all processes."
" You can avoid this by setting a number of workers divisor of the number of scenes"
)
inds = self._partition_inds(len(scenes), total_processes)
return {
"scenes": scenes[inds[process_ind] : inds[process_ind + 1]],
"max_steps": self.MAX_STEPS,
"sensors": self.SENSORS,
"action_space": gym.spaces.Tuple(
[
gym.spaces.Discrete(len(NavToPartnerTask.class_action_names())),
gym.spaces.Discrete(len(NavToPartnerTask.class_action_names())),
]
),
"seed": seeds[process_ind] if seeds is not None else None,
"deterministic_cudnn": deterministic_cudnn,
"rewards_config": self.REWARD_CONFIG,
}
def train_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
scenes = ["FloorPlan_Train1_1"]
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
scenes,
process_ind,
total_processes,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
)
res["env_args"] = {
**self.ENV_ARGS,
"x_display": ("0.%d" % devices[process_ind % len(devices)])
if devices is not None and len(devices) > 0
else None,
}
return res
def valid_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
scenes = ["FloorPlan_Train1_1"]
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
scenes,
process_ind,
total_processes,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
)
res["env_args"] = {
**self.ENV_ARGS,
"x_display": ("0.%d" % devices[process_ind % len(devices)])
if devices is not None and len(devices) > 0
else None,
}
res["max_tasks"] = 20
return res
def test_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
scenes = ["FloorPlan_Train1_1"]
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
scenes,
process_ind,
total_processes,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
)
res["env_args"] = {
**self.ENV_ARGS,
"x_display": ("0.%d" % devices[process_ind % len(devices)])
if devices is not None and len(devices) > 0
else None,
}
res["max_tasks"] = 4
return res
| ask4help-main | projects/tutorials/navtopartner_robothor_rgb_ppo.py |
# literate: tutorials/gym-tutorial.md
# %%
"""# Tutorial: OpenAI gym for continuous control."""
# %%
"""
**Note** The provided commands to execute in this tutorial assume you have
[installed the full library](../installation/installation-allenact.md#full-library) and the requirements for the
`gym_plugin`. The latter can be installed by
```bash
pip install -r allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/extra_requirements.txt
```
In this tutorial, we:
1. Introduce the `gym_plugin`, which enables some of the tasks in [OpenAI's gym](https://gym.openai.com/) for training
and inference within AllenAct.
1. Show an example of continuous control with an arbitrary action space covering 2 policies for one of the `gym` tasks.
## The task
For this tutorial, we'll focus on one of the continuous-control environments under the `Box2D` group of `gym`
environments: [LunarLanderContinuous-v2](https://gym.openai.com/envs/LunarLanderContinuous-v2/). In this task, the goal
is to smoothly land a lunar module in a landing pad, as shown below.
.
To achieve this goal, we need to provide continuous control for a main engine and directional one (2 real values). In
order to solve the task, the expected reward is of at least 200 points. The controls for main and directional engines
are both in the range [-1.0, 1.0] and the observation space is composed of 8 scalars indicating `x` and `y` positions,
`x` and `y` velocities, lander angle and angular velocity, and left and right ground contact. Note that these 8 scalars
provide a full observation of the state.
## Implementation
For this tutorial, we'll use the readily available `gym_plugin`, which includes a
[wrapper for `gym` environments](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_environment.md#gymenvironment), a
[task sampler](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_tasks.md#gymtasksampler) and
[task definition](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_tasks.md#gymcontinuousbox2dtask), a
[sensor](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_sensors.md#gymbox2dsensor) to wrap the observations provided by the `gym`
environment, and a simple [model](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_models.md#memorylessactorcritic).
The experiment config, similar to the one used for the
[Navigation in MiniGrid tutorial](../tutorials/minigrid-tutorial.md), is defined as follows:
"""
# %%
from typing import Dict, Optional, List, Any, cast
import gym
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import LambdaLR
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.ppo import PPO
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import ExperimentConfig, TaskSampler
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import SensorSuite
from allenact_plugins.gym_plugin.gym_models import MemorylessActorCritic
from allenact_plugins.gym_plugin.gym_sensors import GymBox2DSensor
from allenact_plugins.gym_plugin.gym_tasks import GymTaskSampler
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import (
TrainingPipeline,
Builder,
PipelineStage,
LinearDecay,
)
from allenact.utils.viz_utils import VizSuite, AgentViewViz
class GymTutorialExperimentConfig(ExperimentConfig):
@classmethod
def tag(cls) -> str:
return "GymTutorial"
# %%
"""
### Sensors and Model
As mentioned above, we'll use a [GymBox2DSensor](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_sensors.md#gymbox2dsensor) to provide
full observations from the state of the `gym` environment to our model.
"""
# %%
SENSORS = [
GymBox2DSensor("LunarLanderContinuous-v2", uuid="gym_box_data"),
]
# %%
"""
We define our `ActorCriticModel` agent using a lightweight implementation with separate MLPs for actors and critic,
[MemorylessActorCritic](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_models.md#memorylessactorcritic). Since
this is a model for continuous control, note that the superclass of our model is `ActorCriticModel[GaussianDistr]`
instead of `ActorCriticModel[CategoricalDistr]`, since we'll use a
[Gaussian distribution](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_distributions.md#gaussiandistr) to sample actions.
"""
# %%
@classmethod
def create_model(cls, **kwargs) -> nn.Module:
return MemorylessActorCritic(
input_uuid="gym_box_data",
action_space=gym.spaces.Box(
-1.0, 1.0, (2,)
), # 2 actors, each in the range [-1.0, 1.0]
observation_space=SensorSuite(cls.SENSORS).observation_spaces,
action_std=0.5,
)
# %%
"""
### Task samplers
We use an available `TaskSampler` implementation for `gym` environments that allows to sample
[GymTasks](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_tasks.md#gymtask):
[GymTaskSampler](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_tasks.md#gymtasksampler). Even though it is possible to let the task
sampler instantiate the proper sensor for the chosen task name (by passing `None`), we use the sensors we created
above, which contain a custom identifier for the actual observation space (`gym_box_data`) also used by the model.
"""
# %%
@classmethod
def make_sampler_fn(cls, **kwargs) -> TaskSampler:
return GymTaskSampler(**kwargs)
# %%
"""
For convenience, we will use a `_get_sampler_args` method to generate the task sampler arguments for all three
modes, `train, valid, test`:
"""
# %%
def train_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return self._get_sampler_args(
process_ind=process_ind, mode="train", seeds=seeds
)
def valid_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return self._get_sampler_args(
process_ind=process_ind, mode="valid", seeds=seeds
)
def test_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return self._get_sampler_args(process_ind=process_ind, mode="test", seeds=seeds)
# %%
"""
Similarly to what we do in the Minigrid navigation tutorial, the task sampler samples random tasks for ever, while,
during testing (or validation), we sample a fixed number of tasks.
"""
# %%
def _get_sampler_args(
self, process_ind: int, mode: str, seeds: List[int]
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Generate initialization arguments for train, valid, and test
TaskSamplers.
# Parameters
process_ind : index of the current task sampler
mode: one of `train`, `valid`, or `test`
"""
if mode == "train":
max_tasks = None # infinite training tasks
task_seeds_list = None # no predefined random seeds for training
deterministic_sampling = False # randomly sample tasks in training
else:
max_tasks = 3
# one seed for each task to sample:
# - ensures different seeds for each sampler, and
# - ensures a deterministic set of sampled tasks.
task_seeds_list = list(
range(process_ind * max_tasks, (process_ind + 1) * max_tasks)
)
deterministic_sampling = (
True # deterministically sample task in validation/testing
)
return dict(
gym_env_types=["LunarLanderContinuous-v2"],
sensors=self.SENSORS, # sensors used to return observations to the agent
max_tasks=max_tasks, # see above
task_seeds_list=task_seeds_list, # see above
deterministic_sampling=deterministic_sampling, # see above
seed=seeds[process_ind],
)
# %%
"""
Note that we just sample 3 tasks for validation and testing in this case, which suffice to illustrate the model's
success.
### Machine parameters
Given the simplicity of the task and model, we can just train the model on the CPU. During training, success should
reach 100% in less than 10 minutes, whereas solving the task (evaluation reward > 200) might take about 20 minutes
(on a laptop CPU).
We allocate a larger number of samplers for training (8) than for validation or testing (just 1), and we default to
CPU usage by returning an empty list of `devices`. We also include a video visualizer (`AgentViewViz`) in test mode.
"""
# %%
@classmethod
def machine_params(cls, mode="train", **kwargs) -> Dict[str, Any]:
visualizer = None
if mode == "test":
visualizer = VizSuite(
mode=mode,
video_viz=AgentViewViz(
label="episode_vid",
max_clip_length=400,
vector_task_source=("render", {"mode": "rgb_array"}),
fps=30,
),
)
return {
"nprocesses": 8 if mode == "train" else 1,
"devices": [],
"visualizer": visualizer,
}
# %%
"""
### Training pipeline
The last definition is the training pipeline. In this case, we use a PPO stage with linearly decaying learning rate
and 80 single-batch update repeats per rollout:
"""
# %%
@classmethod
def training_pipeline(cls, **kwargs) -> TrainingPipeline:
ppo_steps = int(1.2e6)
return TrainingPipeline(
named_losses=dict(
ppo_loss=PPO(clip_param=0.2, value_loss_coef=0.5, entropy_coef=0.0,),
), # type:ignore
pipeline_stages=[
PipelineStage(loss_names=["ppo_loss"], max_stage_steps=ppo_steps),
],
optimizer_builder=Builder(cast(optim.Optimizer, optim.Adam), dict(lr=1e-3)),
num_mini_batch=1,
update_repeats=80,
max_grad_norm=100,
num_steps=2000,
gamma=0.99,
use_gae=False,
gae_lambda=0.95,
advance_scene_rollout_period=None,
save_interval=200000,
metric_accumulate_interval=50000,
lr_scheduler_builder=Builder(
LambdaLR, {"lr_lambda": LinearDecay(steps=ppo_steps)}, # type:ignore
),
)
# %%
"""
## Training and validation
We have a complete implementation of this experiment's configuration class in `projects/tutorials/gym_tutorial.py`.
To start training from scratch, we just need to invoke
```bash
PYTHONPATH=. python allenact/main.py gym_tutorial -b projects/tutorials -m 8 -o /PATH/TO/gym_output -s 54321 -e
```
from the `allenact` root directory. Note that we include `-e` to enforce deterministic evaluation. Please refer to the
[Navigation in MiniGrid tutorial](../tutorials/minigrid-tutorial.md) if in doubt of the meaning of the rest of parameters.
If we have Tensorboard installed, we can track progress with
```bash
tensorboard --logdir /PATH/TO/gym_output
```
which will default to the URL [http://localhost:6006/](http://localhost:6006/).
After 1,200,000 steps, the script will terminate. If everything went well, the `valid` success rate should quickly
converge to 1 and the mean reward to above 250, while the average episode length should stay below or near 300.
## Testing
The training start date for the experiment, in `YYYY-MM-DD_HH-MM-SS` format, is used as the name of one of the
subfolders in the path to the checkpoints, saved under the output folder.
In order to evaluate (i.e. test) a collection of checkpoints, we need to pass the `--eval` flag and specify the
directory containing the checkpoints with the `--checkpoint CHECKPOINT_DIR` option:
```bash
PYTHONPATH=. python allenact/main.py gym_tutorial \
-b projects/tutorials \
-m 1 \
-o /PATH/TO/gym_output \
-s 54321 \
-e \
--eval \
--checkpoint /PATH/TO/gym_output/checkpoints/GymTutorial/YOUR_START_DATE \
--approx_ckpt_step_interval 800000 # Skip some checkpoints
```
The option `--approx_ckpt_step_interval 800000` tells AllenAct that we only want to evaluate checkpoints
which were saved every ~800000 steps, this lets us avoid evaluating every saved checkpoint. If everything went well,
the `test` success rate should converge to 1, the episode length below or near 300 steps, and the mean reward to above
250. The images tab in tensorboard will contain videos for the sampled test episodes.
.
If the test command fails with `pyglet.canvas.xlib.NoSuchDisplayException: Cannot connect to "None"`, e.g. when running
remotely, try prepending `DISPLAY=:0.0` to the command above, assuming you have an xserver running with such display
available:
```bash
DISPLAY=:0.0 PYTHONPATH=. python allenact/main.py gym_tutorial \
-b projects/tutorials \
-m 1 \
-o /PATH/TO/gym_output \
-s 54321 \
-e \
--eval \
--checkpoint /PATH/TO/gym_output/checkpoints/GymTutorial/YOUR_START_DATE \
--approx_ckpt_step_interval 800000
```
"""
| ask4help-main | projects/tutorials/gym_tutorial.py |
# literate: tutorials/gym-mujoco-tutorial.md
# %%
"""# Tutorial: OpenAI gym MuJoCo environment."""
# %%
"""
**Note** The provided commands to execute in this tutorial assume you have
[installed the full library](../installation/installation-allenact.md#full-library) and the requirements for the
`gym_plugin`. The latter can be installed by
```bash
pip install -r allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/extra_requirements.txt
```
The environments for this tutorial use [MuJoCo](http://www.mujoco.org/)(**Mu**lti-**Jo**int dynamics in **Co**ntact)
physics simulator, which is also required to be installed properly with instructions
[here](https://github.com/openai/mujoco-py).
## The task
For this tutorial, we'll focus on one of the continuous-control environments under the `mujoco` group of `gym`
environments: [Ant-v2](https://gym.openai.com/envs/Ant-v2/). In this task, the goal
is to make a four-legged creature, "ant", walk forward as fast as possible. A random agent of "Ant-v2" is shown below.
.
To achieve the goal, we need to provide continuous control for the agent moving forward with four legs with the
`x` velocity as high as possible for at most 1000 episodes steps. The agent is failed, or done, if the `z` position
is out of the range [0.2, 1.0]. The dimension of the action space is 8 and 111 for the dimension of the observation
space that maps to different body parts, including 3D position `(x,y,z)`, orientation(quaternion `x`,`y`,`z`,`w`)
of the torso, and the joint angles, 3D velocity `(x,y,z)`, 3D angular velocity `(x,y,z)`, and joint velocities.
The rewards for the agent "ant" are composed of the forward rewards, healthy rewards, control cost, and contact cost.
## Implementation
For this tutorial, we'll use the readily available `gym_plugin`, which includes a
[wrapper for `gym` environments](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_environment.md#gymenvironment), a
[task sampler](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_tasks.md#gymtasksampler) and
[task definition](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_tasks.md#gymcontinuousbox2dtask), a
[sensor](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_sensors.md#gymbox2dsensor) to wrap the observations provided by the `gym`
environment, and a simple [model](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_models.md#memorylessactorcritic).
The experiment config, similar to the one used for the
[Navigation in MiniGrid tutorial](../tutorials/minigrid-tutorial.md), is defined as follows:
"""
# %%
from typing import Dict, Optional, List, Any, cast
import gym
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import LambdaLR
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.ppo import PPO
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import ExperimentConfig, TaskSampler
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import SensorSuite
from allenact_plugins.gym_plugin.gym_models import MemorylessActorCritic
from allenact_plugins.gym_plugin.gym_sensors import GymMuJoCoSensor
from allenact_plugins.gym_plugin.gym_tasks import GymTaskSampler
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import (
TrainingPipeline,
Builder,
PipelineStage,
LinearDecay,
)
from allenact.utils.viz_utils import VizSuite, AgentViewViz
class HandManipulateTutorialExperimentConfig(ExperimentConfig):
@classmethod
def tag(cls) -> str:
return "GymMuJoCoTutorial"
# %%
"""
### Sensors and Model
As mentioned above, we'll use a [GymBox2DSensor](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_sensors.md#gymbox2dsensor) to provide
full observations from the state of the `gym` environment to our model.
"""
# %%
SENSORS = [
GymMuJoCoSensor("Ant-v2", uuid="gym_mujoco_data"),
]
# %%
"""
We define our `ActorCriticModel` agent using a lightweight implementation with separate MLPs for actors and critic,
[MemorylessActorCritic](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_models.md#memorylessactorcritic). Since
this is a model for continuous control, note that the superclass of our model is `ActorCriticModel[GaussianDistr]`
instead of `ActorCriticModel[CategoricalDistr]`, since we'll use a
[Gaussian distribution](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_distributions.md#gaussiandistr) to sample actions.
"""
# %%
@classmethod
def create_model(cls, **kwargs) -> nn.Module:
"""We define our `ActorCriticModel` agent using a lightweight
implementation with separate MLPs for actors and critic,
MemorylessActorCritic.
Since this is a model for continuous control, note that the
superclass of our model is `ActorCriticModel[GaussianDistr]`
instead of `ActorCriticModel[CategoricalDistr]`, since we'll use
a Gaussian distribution to sample actions.
"""
return MemorylessActorCritic(
input_uuid="gym_mujoco_data",
action_space=gym.spaces.Box(
-3.0, 3.0, (8,), "float32"
), # 8 actors, each in the range [-3.0, 3.0]
observation_space=SensorSuite(cls.SENSORS).observation_spaces,
action_std=0.5,
)
# %%
"""
### Task samplers
We use an available `TaskSampler` implementation for `gym` environments that allows to sample
[GymTasks](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_tasks.md#gymtask):
[GymTaskSampler](../api/allenact_plugins/gym_plugin/gym_tasks.md#gymtasksampler). Even though it is possible to let the task
sampler instantiate the proper sensor for the chosen task name (by passing `None`), we use the sensors we created
above, which contain a custom identifier for the actual observation space (`gym_mujoco_data`) also used by the model.
"""
# %%
@classmethod
def make_sampler_fn(cls, **kwargs) -> TaskSampler:
return GymTaskSampler(gym_env_type="Ant-v2", **kwargs)
# %%
"""
For convenience, we will use a `_get_sampler_args` method to generate the task sampler arguments for all three
modes, `train, valid, test`:
"""
# %%
def train_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return self._get_sampler_args(
process_ind=process_ind, mode="train", seeds=seeds
)
def valid_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return self._get_sampler_args(
process_ind=process_ind, mode="valid", seeds=seeds
)
def test_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return self._get_sampler_args(process_ind=process_ind, mode="test", seeds=seeds)
# %%
"""
Similarly to what we do in the Minigrid navigation tutorial, the task sampler samples random tasks for ever, while,
during testing (or validation), we sample a fixed number of tasks.
"""
# %%
def _get_sampler_args(
self, process_ind: int, mode: str, seeds: List[int]
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Generate initialization arguments for train, valid, and test
TaskSamplers.
# Parameters
process_ind : index of the current task sampler
mode: one of `train`, `valid`, or `test`
"""
if mode == "train":
max_tasks = None # infinite training tasks
task_seeds_list = None # no predefined random seeds for training
deterministic_sampling = False # randomly sample tasks in training
else:
max_tasks = 4
# one seed for each task to sample:
# - ensures different seeds for each sampler, and
# - ensures a deterministic set of sampled tasks.
task_seeds_list = list(
range(process_ind * max_tasks, (process_ind + 1) * max_tasks)
)
deterministic_sampling = (
True # deterministically sample task in validation/testing
)
return dict(
gym_env_types=["Ant-v2"],
sensors=self.SENSORS, # sensors used to return observations to the agent
max_tasks=max_tasks, # see above
task_seeds_list=task_seeds_list, # see above
deterministic_sampling=deterministic_sampling, # see above
seed=seeds[process_ind],
)
# %%
"""
Note that we just sample 4 tasks for validation and testing in this case, which suffice to illustrate the model's
success.
### Machine parameters
In this tutorial, we just train the model on the CPU. We allocate a larger number of samplers for training (8) than
for validation or testing (just 1), and we default to CPU usage by returning an empty list of `devices`. We also
include a video visualizer (`AgentViewViz`) in test mode.
"""
# %%
@classmethod
def machine_params(cls, mode="train", **kwargs) -> Dict[str, Any]:
visualizer = None
if mode == "test":
visualizer = VizSuite(
mode=mode,
video_viz=AgentViewViz(
label="episode_vid",
max_clip_length=400,
vector_task_source=("render", {"mode": "rgb_array"}),
fps=30,
),
)
return {
"nprocesses": 8 if mode == "train" else 1, # rollout
"devices": [],
"visualizer": visualizer,
}
# %%
"""
### Training pipeline
The last definition is the training pipeline. In this case, we use a PPO stage with linearly decaying learning rate
and 10 single-batch update repeats per rollout. The reward should exceed 4,000
in 20M steps in the test. In order to make the "ant" run with an obvious fast speed, we train the agents using PPO
with 3e7 steps.
"""
# %%
@classmethod
def training_pipeline(cls, **kwargs) -> TrainingPipeline:
lr = 3e-4
ppo_steps = int(3e7)
clip_param = 0.2
value_loss_coef = 0.5
entropy_coef = 0.0
num_mini_batch = 4 # optimal 64
update_repeats = 10
max_grad_norm = 0.5
num_steps = 2048
gamma = 0.99
use_gae = True
gae_lambda = 0.95
advance_scene_rollout_period = None
save_interval = 200000
metric_accumulate_interval = 50000
return TrainingPipeline(
named_losses=dict(
ppo_loss=PPO(
clip_param=clip_param,
value_loss_coef=value_loss_coef,
entropy_coef=entropy_coef,
),
), # type:ignore
pipeline_stages=[
PipelineStage(loss_names=["ppo_loss"], max_stage_steps=ppo_steps),
],
optimizer_builder=Builder(cast(optim.Optimizer, optim.Adam), dict(lr=lr)),
num_mini_batch=num_mini_batch,
update_repeats=update_repeats,
max_grad_norm=max_grad_norm,
num_steps=num_steps,
gamma=gamma,
use_gae=use_gae,
gae_lambda=gae_lambda,
advance_scene_rollout_period=advance_scene_rollout_period,
save_interval=save_interval,
metric_accumulate_interval=metric_accumulate_interval,
lr_scheduler_builder=Builder(
LambdaLR, {"lr_lambda": LinearDecay(steps=ppo_steps, startp=1, endp=0)},
),
)
# %%
"""
## Training and validation
We have a complete implementation of this experiment's configuration class in `projects/tutorials/gym_mujoco_tutorial.py`.
To start training from scratch, we just need to invoke
```bash
PYTHONPATH=. python allenact/main.py gym_mujoco_tutorial -b projects/tutorials -m 8 -o /PATH/TO/gym_mujoco_output -s 0 -e
```
from the `allenact` root directory. Note that we include `-e` to enforce deterministic evaluation. Please refer to the
[Navigation in MiniGrid tutorial](../tutorials/minigrid-tutorial.md) if in doubt of the meaning of the rest of parameters.
If we have Tensorboard installed, we can track progress with
```bash
tensorboard --logdir /PATH/TO/gym_mujoco_output
```
which will default to the URL [http://localhost:6006/](http://localhost:6006/).
After 30,000,000 steps, the script will terminate. If everything went well, the `valid` success rate should be 1
and the mean reward to above 4,000 in 20,000,000 steps, while the average episode length should stay or a
little below 1,000.
## Testing
The training start date for the experiment, in `YYYY-MM-DD_HH-MM-SS` format, is used as the name of one of the
subfolders in the path to the checkpoints, saved under the output folder.
In order to evaluate (i.e. test) a collection of checkpoints, we need to pass the `--eval` flag and specify the
directory containing the checkpoints with the `--checkpoint CHECKPOINT_DIR` option:
```bash
PYTHONPATH=. python allenact/main.py gym_mujoco_tutorial \
-b projects/tutorials \
-m 1 \
-o /PATH/TO/gym_mujoco_output \
-s 0 \
-e \
--eval \
--checkpoint /PATH/TO/gym_mujoco_output/checkpoints/GymMuJoCoTutorial/YOUR_START_DATE
```
If everything went well, the `test` success rate should converge to 1, the `test` success rate should be 1
and the mean reward to above 4,000 in 20,000,000 steps, while the average episode length should stay or a
little below 1,000. The `gif` results can be seen in the image tab of Tensorboard while testing.
The output should be something like this:
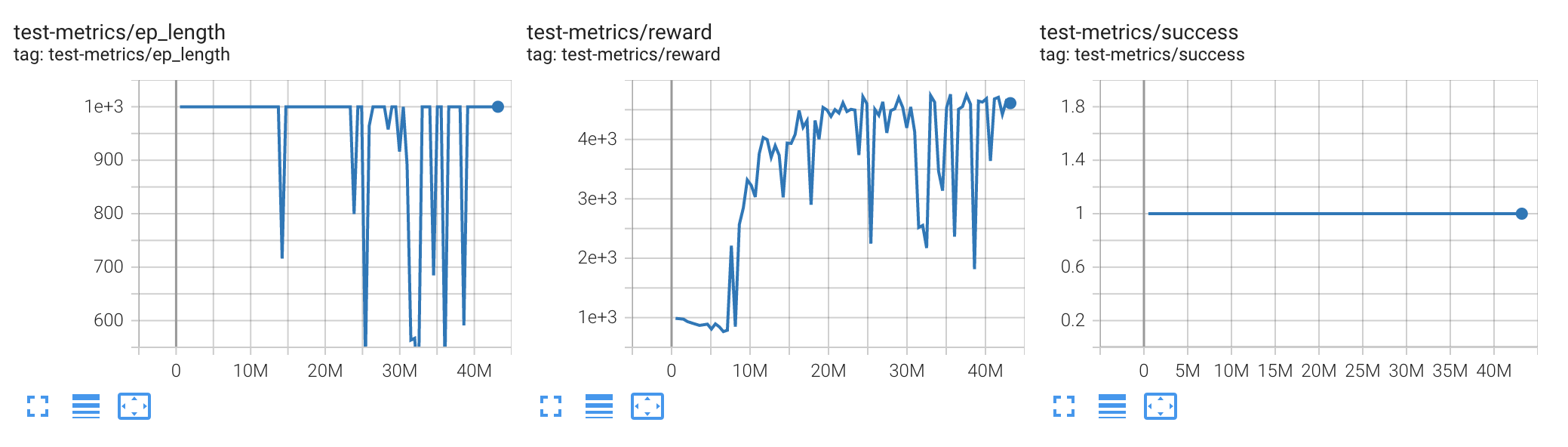.
And the `gif` results can be seen in the image tab of Tensorboard while testing.
If the test command fails with `pyglet.canvas.xlib.NoSuchDisplayException: Cannot connect to "None"`, e.g. when running
remotely, try prepending `DISPLAY=:0.0` to the command above, assuming you have an xserver running with such display
available:
```bash
DISPLAY=:0.0 PYTHONPATH=. python allenact/main.py gym_mujoco_tutorial \
-b projects/tutorials \
-m 1 \
-o /PATH/TO/gym_mujoco_output \
-s 0 \
-e \
--eval \
--checkpoint /PATH/TO/gym_mujoco_output/checkpoints/GymMuJoCoTutorial/YOUR_START_DATE
```
"""
| ask4help-main | projects/tutorials/gym_mujoco_tutorial.py |
ask4help-main | projects/tutorials/__init__.py |
|
import glob
import os
from math import ceil
from typing import Dict, Any, List, Optional, Sequence
import gym
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import LambdaLR
from torchvision import models
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses import PPO
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.ppo import PPOConfig
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import ExperimentConfig, MachineParams
from allenact.base_abstractions.preprocessor import SensorPreprocessorGraph
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import SensorSuite
from allenact.base_abstractions.task import TaskSampler
from allenact.embodiedai.preprocessors.resnet import ResNetPreprocessor
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import (
Builder,
PipelineStage,
TrainingPipeline,
LinearDecay,
evenly_distribute_count_into_bins,
)
from allenact_plugins.ithor_plugin.ithor_sensors import RGBSensorThor
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_sensors import GPSCompassSensorRoboThor
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_task_samplers import (
PointNavDatasetTaskSampler,
)
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_tasks import PointNavTask
from projects.pointnav_baselines.models.point_nav_models import (
ResnetTensorPointNavActorCritic,
)
class PointNaviThorRGBPPOExperimentConfig(ExperimentConfig):
"""A Point Navigation experiment configuration in iTHOR."""
# Task Parameters
MAX_STEPS = 500
REWARD_CONFIG = {
"step_penalty": -0.01,
"goal_success_reward": 10.0,
"failed_stop_reward": 0.0,
"shaping_weight": 1.0,
}
# Simulator Parameters
CAMERA_WIDTH = 640
CAMERA_HEIGHT = 480
SCREEN_SIZE = 224
# Training Engine Parameters
ADVANCE_SCENE_ROLLOUT_PERIOD: Optional[int] = None
NUM_PROCESSES = 60
TRAINING_GPUS = list(range(torch.cuda.device_count()))
VALIDATION_GPUS = [torch.cuda.device_count() - 1]
TESTING_GPUS = [torch.cuda.device_count() - 1]
# Dataset Parameters
TRAIN_DATASET_DIR = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "datasets/ithor-objectnav/train")
VAL_DATASET_DIR = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "datasets/ithor-objectnav/val")
SENSORS = [
RGBSensorThor(
height=SCREEN_SIZE,
width=SCREEN_SIZE,
use_resnet_normalization=True,
uuid="rgb_lowres",
),
GPSCompassSensorRoboThor(),
]
PREPROCESSORS = [
Builder(
ResNetPreprocessor,
{
"input_height": SCREEN_SIZE,
"input_width": SCREEN_SIZE,
"output_width": 7,
"output_height": 7,
"output_dims": 512,
"pool": False,
"torchvision_resnet_model": models.resnet18,
"input_uuids": ["rgb_lowres"],
"output_uuid": "rgb_resnet",
},
),
]
OBSERVATIONS = [
"rgb_resnet",
"target_coordinates_ind",
]
ENV_ARGS = dict(
width=CAMERA_WIDTH,
height=CAMERA_HEIGHT,
rotateStepDegrees=30.0,
visibilityDistance=1.0,
gridSize=0.25,
)
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "PointNavithorRGBPPO"
@classmethod
def training_pipeline(cls, **kwargs):
ppo_steps = int(250000000)
lr = 3e-4
num_mini_batch = 1
update_repeats = 3
num_steps = 30
save_interval = 5000000
log_interval = 10000
gamma = 0.99
use_gae = True
gae_lambda = 0.95
max_grad_norm = 0.5
return TrainingPipeline(
save_interval=save_interval,
metric_accumulate_interval=log_interval,
optimizer_builder=Builder(optim.Adam, dict(lr=lr)),
num_mini_batch=num_mini_batch,
update_repeats=update_repeats,
max_grad_norm=max_grad_norm,
num_steps=num_steps,
named_losses={"ppo_loss": PPO(**PPOConfig)},
gamma=gamma,
use_gae=use_gae,
gae_lambda=gae_lambda,
advance_scene_rollout_period=cls.ADVANCE_SCENE_ROLLOUT_PERIOD,
pipeline_stages=[
PipelineStage(loss_names=["ppo_loss"], max_stage_steps=ppo_steps)
],
lr_scheduler_builder=Builder(
LambdaLR, {"lr_lambda": LinearDecay(steps=ppo_steps)}
),
)
def machine_params(self, mode="train", **kwargs):
sampler_devices: Sequence[int] = []
if mode == "train":
workers_per_device = 1
gpu_ids = (
[]
if not torch.cuda.is_available()
else self.TRAINING_GPUS * workers_per_device
)
nprocesses = (
1
if not torch.cuda.is_available()
else evenly_distribute_count_into_bins(self.NUM_PROCESSES, len(gpu_ids))
)
sampler_devices = self.TRAINING_GPUS
elif mode == "valid":
nprocesses = 1
gpu_ids = [] if not torch.cuda.is_available() else self.VALIDATION_GPUS
elif mode == "test":
nprocesses = 1
gpu_ids = [] if not torch.cuda.is_available() else self.TESTING_GPUS
else:
raise NotImplementedError("mode must be 'train', 'valid', or 'test'.")
sensor_preprocessor_graph = (
SensorPreprocessorGraph(
source_observation_spaces=SensorSuite(self.SENSORS).observation_spaces,
preprocessors=self.PREPROCESSORS,
)
if mode == "train"
or (
(isinstance(nprocesses, int) and nprocesses > 0)
or (isinstance(nprocesses, Sequence) and sum(nprocesses) > 0)
)
else None
)
return MachineParams(
nprocesses=nprocesses,
devices=gpu_ids,
sampler_devices=sampler_devices
if mode == "train"
else gpu_ids, # ignored with > 1 gpu_ids
sensor_preprocessor_graph=sensor_preprocessor_graph,
)
# Define Model
@classmethod
def create_model(cls, **kwargs) -> nn.Module:
return ResnetTensorPointNavActorCritic(
action_space=gym.spaces.Discrete(len(PointNavTask.class_action_names())),
observation_space=kwargs["sensor_preprocessor_graph"].observation_spaces,
goal_sensor_uuid="target_coordinates_ind",
rgb_resnet_preprocessor_uuid="rgb_resnet",
hidden_size=512,
goal_dims=32,
)
# Define Task Sampler
@classmethod
def make_sampler_fn(cls, **kwargs) -> TaskSampler:
return PointNavDatasetTaskSampler(**kwargs)
# Utility Functions for distributing scenes between GPUs
@staticmethod
def _partition_inds(n: int, num_parts: int):
return np.round(np.linspace(0, n, num_parts + 1, endpoint=True)).astype(
np.int32
)
def _get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
self,
scenes_dir: str,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
path = os.path.join(scenes_dir, "*.json.gz")
scenes = [scene.split("/")[-1].split(".")[0] for scene in glob.glob(path)]
if len(scenes) == 0:
raise RuntimeError(
(
"Could find no scene dataset information in directory {}."
" Are you sure you've downloaded them? "
" If not, see https://allenact.org/installation/download-datasets/ information"
" on how this can be done."
).format(scenes_dir)
)
if total_processes > len(scenes): # oversample some scenes -> bias
if total_processes % len(scenes) != 0:
print(
"Warning: oversampling some of the scenes to feed all processes."
" You can avoid this by setting a number of workers divisible by the number of scenes"
)
scenes = scenes * int(ceil(total_processes / len(scenes)))
scenes = scenes[: total_processes * (len(scenes) // total_processes)]
else:
if len(scenes) % total_processes != 0:
print(
"Warning: oversampling some of the scenes to feed all processes."
" You can avoid this by setting a number of workers divisor of the number of scenes"
)
inds = self._partition_inds(len(scenes), total_processes)
return {
"scenes": scenes[inds[process_ind] : inds[process_ind + 1]],
"max_steps": self.MAX_STEPS,
"sensors": self.SENSORS,
"action_space": gym.spaces.Discrete(len(PointNavTask.class_action_names())),
"seed": seeds[process_ind] if seeds is not None else None,
"deterministic_cudnn": deterministic_cudnn,
"rewards_config": self.REWARD_CONFIG,
}
def train_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
os.path.join(self.TRAIN_DATASET_DIR, "episodes"),
process_ind,
total_processes,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
)
res["scene_directory"] = self.TRAIN_DATASET_DIR
res["loop_dataset"] = True
res["env_args"] = {}
res["env_args"].update(self.ENV_ARGS)
res["env_args"]["x_display"] = (
("0.%d" % devices[process_ind % len(devices)])
if devices is not None and len(devices) > 0
else None
)
res["allow_flipping"] = True
return res
def valid_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
os.path.join(self.VAL_DATASET_DIR, "episodes"),
process_ind,
total_processes,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
)
res["scene_directory"] = self.VAL_DATASET_DIR
res["loop_dataset"] = False
res["env_args"] = {}
res["env_args"].update(self.ENV_ARGS)
res["env_args"]["x_display"] = (
("0.%d" % devices[process_ind % len(devices)])
if devices is not None and len(devices) > 0
else None
)
return res
def test_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
os.path.join(self.VAL_DATASET_DIR, "episodes"),
process_ind,
total_processes,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
)
res["scene_directory"] = self.VAL_DATASET_DIR
res["loop_dataset"] = False
res["env_args"] = {}
res["env_args"].update(self.ENV_ARGS)
return res
| ask4help-main | projects/tutorials/pointnav_ithor_rgb_ddppo.py |
from projects.tutorials.object_nav_ithor_dagger_then_ppo_one_object import (
ObjectNavThorDaggerThenPPOExperimentConfig,
)
from allenact.utils.viz_utils import (
VizSuite,
TrajectoryViz,
AgentViewViz,
ActorViz,
TensorViz1D,
)
from allenact_plugins.ithor_plugin.ithor_viz import ThorViz
class ObjectNavThorDaggerThenPPOVizExperimentConfig(
ObjectNavThorDaggerThenPPOExperimentConfig
):
"""A simple object navigation experiment in THOR.
Training with DAgger and then PPO + using viz for test.
"""
TEST_SAMPLES_IN_SCENE = 4
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "ObjectNavThorDaggerThenPPOViz"
viz = None
def get_viz(self, mode):
if self.viz is not None:
return self.viz
self.viz = VizSuite(
mode=mode,
base_trajectory=TrajectoryViz(
path_to_target_location=None, path_to_rot_degrees=("rotation",),
),
egeocentric=AgentViewViz(max_video_length=100),
action_probs=ActorViz(figsize=(3.25, 10), fontsize=18),
taken_action_logprobs=TensorViz1D(),
episode_mask=TensorViz1D(rollout_source=("masks",)),
thor_trajectory=ThorViz(
path_to_target_location=None, figsize=(8, 8), viz_rows_cols=(448, 448),
),
)
return self.viz
def machine_params(self, mode="train", **kwargs):
params = super().machine_params(mode, **kwargs)
if mode == "test":
params.set_visualizer(self.get_viz(mode))
return params
| ask4help-main | projects/tutorials/object_nav_ithor_dagger_then_ppo_one_object_viz.py |
# literate: tutorials/training-a-pointnav-model.md
# %%
"""# Tutorial: PointNav in RoboTHOR."""
# %%
"""

## Introduction
One of the most obvious tasks that an embodied agent should master is navigating the world it inhabits.
Before we can teach a robot to cook or clean it first needs to be able to move around. The simplest
way to formulate "moving around" into a task is by making your agent find a beacon somewhere in the environment.
This beacon transmits its location, such that at any time, the agent can get the direction and euclidian distance
to the beacon. This particular task is often called Point Navigation, or **PointNav** for short.
#### PointNav
At first glance, this task seems trivial. If the agent is given the direction and distance of the target at
all times, can it not simply follow this signal directly? The answer is no, because agents are often trained
on this task in environments that emulate real-world buildings which are not wide-open spaces, but rather
contain many smaller rooms. Because of this, the agent has to learn to navigate human spaces and use doors
and hallways to efficiently navigate from one side of the building to the other. This task becomes particularly
difficult when the agent is tested in an environment that it is not trained in. If the agent does not know
how the floor plan of an environment looks, it has to learn to predict the design of man-made structures,
to efficiently navigate across them, much like how people instinctively know how to move around a building
they have never seen before based on their experience navigating similar buildings.
#### What is an environment anyways?
Environments are worlds in which embodied agents exist. If our embodied agent is simply a neural network that is being
trained in a simulator, then that simulator is its environment. Similarly, if our agent is a
physical robot then its environment is the real world. The agent interacts with the environment by taking one
of several available actions (such as "move forward", or "turn left"). After each action, the environment
produces a new frame that the agent can analyze to determine its next step. For many tasks, including PointNav
the agent also has a special "stop" action which indicates that the agent thinks it has reached the target.
After this action is called the agent will be reset to a new location, regardless if it reached the
target. The hope is that after enough training the agent will learn to correctly assess that it has successfully
navigated to the target.

There are many simulators designed for the training
of embodied agents. In this tutorial, we will be using a simulator called [RoboTHOR](https://ai2thor.allenai.org/robothor/),
which is designed specifically to train models that can easily be transferred to a real robot, by providing a
photo-realistic virtual environment and a real-world replica of the environment that researchers can have access to.
RoboTHOR contains 60 different virtual scenes with different floor plans and furniture and 15 validation scenes.
It is also important to mention that **AllenAct**
has a class abstraction called Environment. This is not the actual simulator game engine or robotics controller,
but rather a shallow wrapper that provides a uniform interface to the actual environment.
#### Learning algorithm
Finally, let us briefly touch on the algorithm that we will use to train our embodied agent to navigate. While
*AllenAct* offers us great flexibility to train models using complex pipelines, we will be using a simple
pure reinforcement learning approach for this tutorial. More specifically, we will be using DD-PPO,
a decentralized and distributed variant of the ubiquitous PPO algorithm. For those unfamiliar with Reinforcement
Learning we highly recommend [this tutorial](http://karpathy.github.io/2016/05/31/rl/) by Andrej Karpathy, and [this
book](http://www.incompleteideas.net/book/the-book-2nd.html) by Sutton and Barto. Essentially what we are doing
is letting our agent explore the environment on its own, rewarding it for taking actions that bring it closer
to its goal and penalizing it for actions that take it away from its goal. We then optimize the agent's model
to maximize this reward.
## Requirements
To train the model on the PointNav task, we need to [install the RoboTHOR environment](../installation/installation-framework.md)
and [download the RoboTHOR PointNav dataset](../installation/download-datasets.md)
The dataset contains a list of episodes with thousands of randomly generated starting positions and target locations for each of the scenes
as well as a precomputed cache of distances, containing the shortest path from each point in a scene, to every other point in that scene.
This is used to reward the agent for moving closer to the target in terms of geodesic distance - the actual path distance (as opposed to a
straight line distance).
## Config File Setup
Now comes the most important part of the tutorial, we are going to write an experiment config file.
If this is your first experience with experiment config files in AllenAct, we suggest that you
first see our how-to on [defining an experiment](../howtos/defining-an-experiment.md) which will
walk you through creating a simplified experiment config file.
Unlike a library that can be imported into python, **AllenAct** is structured as a framework with a runner script called
`main.py` which will run the experiment specified in a config file. This design forces us to keep meticulous records of
exactly which settings were used to produce a particular result,
which can be very useful given how expensive RL models are to train.
The `projects/` directory is home to different projects using `AllenAct`. Currently it is populated with baselines
of popular tasks and tutorials.
We already have all the code for this tutorial stored in `projects/tutorials/training_a_pointnav_model.py`. We will
be using this file to run our experiments, but you can create a new directory in `projects/` and start writing your
experiment there.
We start off by importing everything we will need:
"""
# %%
import glob
import os
from math import ceil
from typing import Dict, Any, List, Optional, Sequence
import gym
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import LambdaLR
from torchvision import models
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses import PPO
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.ppo import PPOConfig
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import ExperimentConfig, MachineParams
from allenact.base_abstractions.preprocessor import SensorPreprocessorGraph
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import SensorSuite
from allenact.base_abstractions.task import TaskSampler
from allenact.embodiedai.preprocessors.resnet import ResNetPreprocessor
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import (
Builder,
PipelineStage,
TrainingPipeline,
LinearDecay,
evenly_distribute_count_into_bins,
)
from allenact_plugins.ithor_plugin.ithor_sensors import RGBSensorThor
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_sensors import GPSCompassSensorRoboThor
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_task_samplers import (
PointNavDatasetTaskSampler,
)
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_tasks import PointNavTask
from projects.pointnav_baselines.models.point_nav_models import (
ResnetTensorPointNavActorCritic,
)
# %%
"""Next we define a new experiment config class:"""
# %%
class PointNavRoboThorRGBPPOExperimentConfig(ExperimentConfig):
"""A Point Navigation experiment configuration in RoboThor."""
# %%
"""
We then define the task parameters. For PointNav, these include the maximum number of steps our agent
can take before being reset (this prevents the agent from wandering on forever), and a configuration
for the reward function that we will be using.
"""
# %%
# Task Parameters
MAX_STEPS = 500
REWARD_CONFIG = {
"step_penalty": -0.01,
"goal_success_reward": 10.0,
"failed_stop_reward": 0.0,
"shaping_weight": 1.0,
}
# %%
"""
In this case, we set the maximum number of steps to 500.
We give the agent a reward of -0.01 for each action that it takes (this is to encourage it to reach the goal
in as few actions as possible), and a reward of 10.0 if the agent manages to successfully reach its destination.
If the agent selects the `stop` action without reaching the target we do not punish it (although this is
sometimes useful for preventing the agent from stopping prematurely). Finally, our agent gets rewarded if it moves
closer to the target and gets punished if it moves further away. `shaping_weight` controls how strong this signal should
be and is here set to 1.0. These parameters work well for training an agent on PointNav, but feel free to play around
with them.
Next, we set the parameters of the simulator itself. Here we select a resolution at which the engine will render
every frame (640 by 480) and a resolution at which the image will be fed into the neural network (here it is set
to a 224 by 224 box).
"""
# %%
# Simulator Parameters
CAMERA_WIDTH = 640
CAMERA_HEIGHT = 480
SCREEN_SIZE = 224
# %%
"""
Next, we set the hardware parameters for the training engine. `NUM_PROCESSES` sets the total number of parallel
processes that will be used to train the model. In general, more processes result in faster training,
but since each process is a unique instance of the environment in which we are training they can take up a
lot of memory. Depending on the size of the model, the environment, and the hardware we are using, we may
need to adjust this number, but for a setup with 8 GTX Titans, 60 processes work fine. 60 also happens to
be the number of training scenes in RoboTHOR, which allows each process to load only a single scene into
memory, saving time and space.
`TRAINING_GPUS` takes the ids of the GPUS on which
the model should be trained. Similarly `VALIDATION_GPUS` and `TESTING_GPUS` hold the ids of the GPUS on which
the validation and testing will occur. During training, a validation process is constantly running and evaluating
the current model, to show the progress on the validation set, so reserving a GPU for validation can be a good idea.
If our hardware setup does not include a GPU, these fields can be set to empty lists, as the codebase will default
to running everything on the CPU with only 1 process.
"""
# %%
ADVANCE_SCENE_ROLLOUT_PERIOD: Optional[int] = None
NUM_PROCESSES = 20
TRAINING_GPUS: Sequence[int] = [0]
VALIDATION_GPUS: Sequence[int] = [0]
TESTING_GPUS: Sequence[int] = [0]
# %%
"""
Since we are using a dataset to train our model we need to define the path to where we have stored it. If we
download the dataset instructed above we can define the path as follows
"""
# %%
TRAIN_DATASET_DIR = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "datasets/robothor-pointnav/debug")
VAL_DATASET_DIR = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "datasets/robothor-pointnav/debug")
# %%
"""
Next, we define the sensors. `RGBSensorThor` is the environment's implementation of an RGB sensor. It takes the
raw image outputted by the simulator and resizes it, to the input dimensions for our neural network that we
specified above. It also performs normalization if we want. `GPSCompassSensorRoboThor` is a sensor that tracks
the point our agent needs to move to. It tells us the direction and distance to our goal at every time step.
"""
# %%
SENSORS = [
RGBSensorThor(
height=SCREEN_SIZE,
width=SCREEN_SIZE,
use_resnet_normalization=True,
uuid="rgb_lowres",
),
GPSCompassSensorRoboThor(),
]
# %%
"""
For the sake of this example, we are also going to be using a preprocessor with our model. In *AllenAct*
the preprocessor abstraction is designed with large models with frozen weights in mind. These models often
hail from the ResNet family and transform the raw pixels that our agent observes in the environment, into a
complex embedding, which then gets stored and used as input to our trainable model instead of the original image.
Most other preprocessing work is done in the sensor classes (as we just saw with the RGB
sensor scaling and normalizing our input), but for the sake of efficiency, all neural network preprocessing should
use this abstraction.
"""
# %%
PREPROCESSORS = [
Builder(
ResNetPreprocessor,
{
"input_height": SCREEN_SIZE,
"input_width": SCREEN_SIZE,
"output_width": 7,
"output_height": 7,
"output_dims": 512,
"pool": False,
"torchvision_resnet_model": models.resnet18,
"input_uuids": ["rgb_lowres"],
"output_uuid": "rgb_resnet",
},
),
]
# %%
"""
Next, we must define all of the observation inputs that our model will use. These are just
the hardcoded ids of the sensors we are using in the experiment.
"""
# %%
OBSERVATIONS = [
"rgb_resnet",
"target_coordinates_ind",
]
# %%
"""
Finally, we must define the settings of our simulator. We set the camera dimensions to the values
we defined earlier. We set rotateStepDegrees to 30 degrees, which means that every time the agent takes a
turn action, they will rotate by 30 degrees. We set grid size to 0.25 which means that every time the
agent moves forward, it will do so by 0.25 meters.
"""
# %%
ENV_ARGS = dict(
width=CAMERA_WIDTH,
height=CAMERA_HEIGHT,
rotateStepDegrees=30.0,
visibilityDistance=1.0,
gridSize=0.25,
)
# %%
"""
Now we move on to the methods that we must define to finish implementing an experiment config. Firstly we
have a simple method that just returns the name of the experiment.
"""
# %%
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "PointNavRobothorRGBPPO"
# %%
"""
Next, we define the training pipeline. In this function, we specify exactly which algorithm or algorithms
we will use to train our model. In this simple example, we are using the PPO loss with a learning rate of 3e-4.
We specify 250 million steps of training and a rollout length of 30 with the `ppo_steps` and `num_steps` parameters
respectively. All the other standard PPO parameters are also present in this function. `metric_accumulate_interval`
sets the frequency at which data is accumulated from all the processes and logged while `save_interval` sets how
often we save the model weights and run validation on them.
"""
# %%
@classmethod
def training_pipeline(cls, **kwargs):
ppo_steps = int(250000000)
lr = 3e-4
num_mini_batch = 1
update_repeats = 3
num_steps = 30
save_interval = 5000000
log_interval = 1000
gamma = 0.99
use_gae = True
gae_lambda = 0.95
max_grad_norm = 0.5
return TrainingPipeline(
save_interval=save_interval,
metric_accumulate_interval=log_interval,
optimizer_builder=Builder(optim.Adam, dict(lr=lr)),
num_mini_batch=num_mini_batch,
update_repeats=update_repeats,
max_grad_norm=max_grad_norm,
num_steps=num_steps,
named_losses={"ppo_loss": PPO(**PPOConfig)},
gamma=gamma,
use_gae=use_gae,
gae_lambda=gae_lambda,
advance_scene_rollout_period=cls.ADVANCE_SCENE_ROLLOUT_PERIOD,
pipeline_stages=[
PipelineStage(loss_names=["ppo_loss"], max_stage_steps=ppo_steps)
],
lr_scheduler_builder=Builder(
LambdaLR, {"lr_lambda": LinearDecay(steps=ppo_steps)}
),
)
# %%
"""
The `machine_params` method returns the hardware parameters of each
process, based on the list of devices we defined above.
"""
# %%
def machine_params(self, mode="train", **kwargs):
sampler_devices: List[int] = []
if mode == "train":
workers_per_device = 1
gpu_ids = (
[]
if not torch.cuda.is_available()
else list(self.TRAINING_GPUS) * workers_per_device
)
nprocesses = (
8
if not torch.cuda.is_available()
else evenly_distribute_count_into_bins(self.NUM_PROCESSES, len(gpu_ids))
)
sampler_devices = list(self.TRAINING_GPUS)
elif mode == "valid":
nprocesses = 1
gpu_ids = [] if not torch.cuda.is_available() else self.VALIDATION_GPUS
elif mode == "test":
nprocesses = 1
gpu_ids = [] if not torch.cuda.is_available() else self.TESTING_GPUS
else:
raise NotImplementedError("mode must be 'train', 'valid', or 'test'.")
sensor_preprocessor_graph = (
SensorPreprocessorGraph(
source_observation_spaces=SensorSuite(self.SENSORS).observation_spaces,
preprocessors=self.PREPROCESSORS,
)
if mode == "train"
or (
(isinstance(nprocesses, int) and nprocesses > 0)
or (isinstance(nprocesses, Sequence) and sum(nprocesses) > 0)
)
else None
)
return MachineParams(
nprocesses=nprocesses,
devices=gpu_ids,
sampler_devices=sampler_devices
if mode == "train"
else gpu_ids, # ignored with > 1 gpu_ids
sensor_preprocessor_graph=sensor_preprocessor_graph,
)
# %%
"""
Now we define the actual model that we will be using. **AllenAct** offers first-class support for PyTorch,
so any PyTorch model that implements the provided `ActorCriticModel` class will work here. Here we borrow a modelfrom the `pointnav_baselines` project (which
unsurprisingly contains several PointNav baselines). It is a small convolutional network that expects the output of a ResNet as its rgb input followed by a single-layered GRU. The model accepts as input the number of different
actions our agent can perform in the environment through the `action_space` parameter, which we get from the task definition. We also define the shape of the inputs we are going to be passing to the model with `observation_space`
We specify the names of our sensors with `goal_sensor_uuid` and `rgb_resnet_preprocessor_uuid`. Finally, we define
the size of our RNN with `hidden_layer` and the size of the embedding of our goal sensor data (the direction and
distance to the target) with `goal_dims`.
"""
# %%
@classmethod
def create_model(cls, **kwargs) -> nn.Module:
return ResnetTensorPointNavActorCritic(
action_space=gym.spaces.Discrete(len(PointNavTask.class_action_names())),
observation_space=kwargs["sensor_preprocessor_graph"].observation_spaces,
goal_sensor_uuid="target_coordinates_ind",
rgb_resnet_preprocessor_uuid="rgb_resnet",
hidden_size=512,
goal_dims=32,
)
# %%
"""
We also need to define the task sampler that we will be using. This is a piece of code that generates instances
of tasks for our agent to perform (essentially starting locations and targets for PointNav). Since we are getting
our tasks from a dataset, the task sampler is a very simple code that just reads the specified file and sets
the agent to the next starting locations whenever the agent exceeds the maximum number of steps or selects the
`stop` action.
"""
# %%
@classmethod
def make_sampler_fn(cls, **kwargs) -> TaskSampler:
return PointNavDatasetTaskSampler(**kwargs)
# %%
"""
You might notice that we did not specify the task sampler's arguments, but are rather passing them in. The
reason for this is that each process will have its own task sampler, and we need to specify exactly which scenes
each process should work with. If we have several GPUS and many scenes this process of distributing the work can be rather complicated so we define a few helper functions to do just this.
"""
# %%
@staticmethod
def _partition_inds(n: int, num_parts: int):
return np.round(np.linspace(0, n, num_parts + 1, endpoint=True)).astype(
np.int32
)
def _get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
self,
scenes_dir: str,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
path = os.path.join(scenes_dir, "*.json.gz")
scenes = [scene.split("/")[-1].split(".")[0] for scene in glob.glob(path)]
if len(scenes) == 0:
raise RuntimeError(
(
"Could find no scene dataset information in directory {}."
" Are you sure you've downloaded them? "
" If not, see https://allenact.org/installation/download-datasets/ information"
" on how this can be done."
).format(scenes_dir)
)
if total_processes > len(scenes): # oversample some scenes -> bias
if total_processes % len(scenes) != 0:
print(
"Warning: oversampling some of the scenes to feed all processes."
" You can avoid this by setting a number of workers divisible by the number of scenes"
)
scenes = scenes * int(ceil(total_processes / len(scenes)))
scenes = scenes[: total_processes * (len(scenes) // total_processes)]
else:
if len(scenes) % total_processes != 0:
print(
"Warning: oversampling some of the scenes to feed all processes."
" You can avoid this by setting a number of workers divisor of the number of scenes"
)
inds = self._partition_inds(len(scenes), total_processes)
return {
"scenes": scenes[inds[process_ind] : inds[process_ind + 1]],
"max_steps": self.MAX_STEPS,
"sensors": self.SENSORS,
"action_space": gym.spaces.Discrete(len(PointNavTask.class_action_names())),
"seed": seeds[process_ind] if seeds is not None else None,
"deterministic_cudnn": deterministic_cudnn,
"rewards_config": self.REWARD_CONFIG,
}
# %%
"""
The very last things we need to define are the sampler arguments themselves. We define them separately for a train,
validation, and test sampler, but in this case, they are almost the same. The arguments need to include the location
of the dataset and distance cache as well as the environment arguments for our simulator, both of which we defined above
and are just referencing here. The only consequential differences between these task samplers are the path to the dataset
we are using (train or validation) and whether we want to loop over the dataset or not (we want this for training since
we want to train for several epochs, but we do not need this for validation and testing). Since the test scenes of
RoboTHOR are private we are also testing on our validation set.
"""
# %%
def train_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
os.path.join(self.TRAIN_DATASET_DIR, "episodes"),
process_ind,
total_processes,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
)
res["scene_directory"] = self.TRAIN_DATASET_DIR
res["loop_dataset"] = True
res["env_args"] = {}
res["env_args"].update(self.ENV_ARGS)
res["env_args"]["x_display"] = (
("0.%d" % devices[process_ind % len(devices)])
if devices is not None and len(devices) > 0
else None
)
res["allow_flipping"] = True
return res
def valid_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
os.path.join(self.VAL_DATASET_DIR, "episodes"),
process_ind,
total_processes,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
)
res["scene_directory"] = self.VAL_DATASET_DIR
res["loop_dataset"] = False
res["env_args"] = {}
res["env_args"].update(self.ENV_ARGS)
res["env_args"]["x_display"] = (
("0.%d" % devices[process_ind % len(devices)])
if devices is not None and len(devices) > 0
else None
)
return res
def test_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
os.path.join(self.VAL_DATASET_DIR, "episodes"),
process_ind,
total_processes,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
)
res["scene_directory"] = self.VAL_DATASET_DIR
res["loop_dataset"] = False
res["env_args"] = {}
res["env_args"].update(self.ENV_ARGS)
return res
# %%
"""
This is it! If we copy all of the code into a file we should be able to run our experiment!
## Training Model On Debug Dataset
We can test if our installation worked properly by training our model on a small dataset of 4 episodes. This
should take about 20 minutes on a computer with a NVIDIA GPU.
We can now train a model by running:
```bash
PYTHONPATH=. python allenact/main.py -o <PATH_TO_OUTPUT> -c -b <BASE_DIRECTORY_OF_YOUR_EXPERIMENT> <EXPERIMENT_NAME>
```
If using the same configuration as we have set up, the following command should work:
```bash
PYTHONPATH=. python allenact/main.py training_a_pointnav_model -o storage/robothor-pointnav-rgb-resnet-resnet -b projects/tutorials
```
If we start up a tensorboard server during training and specify that `output_dir=storage` the output should look
something like this:

## Training Model On Full Dataset
We can also train the model on the full dataset by changing back our dataset path and running the same command as above.
But be aware, training this takes nearly 2 days on a machine with 8 GPU.
## Testing Model
To test the performance of a model please refer to [this tutorial](running-inference-on-a-pretrained-model.md).
## Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned how to create a new PointNav experiment using **AllenAct**. There are many simple
and obvious ways to modify the experiment from here - changing the model, the learning algorithm and the environment
each requires very few lines of code changed in the above file, allowing us to explore our embodied ai research ideas
across different frameworks with ease.
"""
| ask4help-main | projects/tutorials/training_a_pointnav_model.py |
from math import ceil
from typing import Dict, Any, List, Optional
import gym
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import LambdaLR
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses import PPO
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.ppo import PPOConfig
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import ExperimentConfig, MachineParams
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import SensorSuite
from allenact.base_abstractions.task import TaskSampler
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import (
Builder,
PipelineStage,
TrainingPipeline,
LinearDecay,
)
from allenact_plugins.ithor_plugin.ithor_sensors import (
RGBSensorThor,
GoalObjectTypeThorSensor,
)
from allenact_plugins.ithor_plugin.ithor_task_samplers import ObjectNavTaskSampler
from allenact_plugins.ithor_plugin.ithor_tasks import ObjectNaviThorGridTask
from projects.objectnav_baselines.models.object_nav_models import (
ObjectNavBaselineActorCritic,
)
class ObjectNavThorPPOExperimentConfig(ExperimentConfig):
"""A simple object navigation experiment in THOR.
Training with PPO.
"""
# A simple setting, train/valid/test are all the same single scene
# and we're looking for a single object
OBJECT_TYPES = ["Tomato"]
TRAIN_SCENES = ["FloorPlan1_physics"]
VALID_SCENES = ["FloorPlan1_physics"]
TEST_SCENES = ["FloorPlan1_physics"]
# Setting up sensors and basic environment details
SCREEN_SIZE = 224
SENSORS = [
RGBSensorThor(
height=SCREEN_SIZE, width=SCREEN_SIZE, use_resnet_normalization=True,
),
GoalObjectTypeThorSensor(object_types=OBJECT_TYPES),
]
ENV_ARGS = {
"player_screen_height": SCREEN_SIZE,
"player_screen_width": SCREEN_SIZE,
"quality": "Very Low",
}
MAX_STEPS = 128
ADVANCE_SCENE_ROLLOUT_PERIOD: Optional[int] = None
VALID_SAMPLES_IN_SCENE = 10
TEST_SAMPLES_IN_SCENE = 100
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "ObjectNavThorPPO"
@classmethod
def training_pipeline(cls, **kwargs):
ppo_steps = int(1e6)
lr = 2.5e-4
num_mini_batch = 2 if not torch.cuda.is_available() else 6
update_repeats = 4
num_steps = 128
metric_accumulate_interval = cls.MAX_STEPS * 10 # Log every 10 max length tasks
save_interval = 10000
gamma = 0.99
use_gae = True
gae_lambda = 1.0
max_grad_norm = 0.5
return TrainingPipeline(
save_interval=save_interval,
metric_accumulate_interval=metric_accumulate_interval,
optimizer_builder=Builder(optim.Adam, dict(lr=lr)),
num_mini_batch=num_mini_batch,
update_repeats=update_repeats,
max_grad_norm=max_grad_norm,
num_steps=num_steps,
named_losses={
"ppo_loss": PPO(clip_decay=LinearDecay(ppo_steps), **PPOConfig),
},
gamma=gamma,
use_gae=use_gae,
gae_lambda=gae_lambda,
advance_scene_rollout_period=cls.ADVANCE_SCENE_ROLLOUT_PERIOD,
pipeline_stages=[
PipelineStage(loss_names=["ppo_loss"], max_stage_steps=ppo_steps,),
],
lr_scheduler_builder=Builder(
LambdaLR, {"lr_lambda": LinearDecay(steps=ppo_steps)}
),
)
@classmethod
def machine_params(cls, mode="train", **kwargs):
num_gpus = torch.cuda.device_count()
has_gpu = num_gpus != 0
if mode == "train":
nprocesses = 20 if has_gpu else 4
gpu_ids = [0] if has_gpu else []
elif mode == "valid":
nprocesses = 1
gpu_ids = [1 % num_gpus] if has_gpu else []
elif mode == "test":
nprocesses = 1
gpu_ids = [0] if has_gpu else []
else:
raise NotImplementedError("mode must be 'train', 'valid', or 'test'.")
return MachineParams(nprocesses=nprocesses, devices=gpu_ids,)
@classmethod
def create_model(cls, **kwargs) -> nn.Module:
return ObjectNavBaselineActorCritic(
action_space=gym.spaces.Discrete(
len(ObjectNaviThorGridTask.class_action_names())
),
observation_space=SensorSuite(cls.SENSORS).observation_spaces,
rgb_uuid=cls.SENSORS[0].uuid,
depth_uuid=None,
goal_sensor_uuid="goal_object_type_ind",
hidden_size=512,
object_type_embedding_dim=8,
)
@classmethod
def make_sampler_fn(cls, **kwargs) -> TaskSampler:
return ObjectNavTaskSampler(**kwargs)
@staticmethod
def _partition_inds(n: int, num_parts: int):
return np.round(np.linspace(0, n, num_parts + 1, endpoint=True)).astype(
np.int32
)
def _get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
self,
scenes: List[str],
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
if total_processes > len(scenes): # oversample some scenes -> bias
if total_processes % len(scenes) != 0:
print(
"Warning: oversampling some of the scenes to feed all processes."
" You can avoid this by setting a number of workers divisible by the number of scenes"
)
scenes = scenes * int(ceil(total_processes / len(scenes)))
scenes = scenes[: total_processes * (len(scenes) // total_processes)]
else:
if len(scenes) % total_processes != 0:
print(
"Warning: oversampling some of the scenes to feed all processes."
" You can avoid this by setting a number of workers divisor of the number of scenes"
)
inds = self._partition_inds(len(scenes), total_processes)
return {
"scenes": scenes[inds[process_ind] : inds[process_ind + 1]],
"object_types": self.OBJECT_TYPES,
"env_args": self.ENV_ARGS,
"max_steps": self.MAX_STEPS,
"sensors": self.SENSORS,
"action_space": gym.spaces.Discrete(
len(ObjectNaviThorGridTask.class_action_names())
),
"seed": seeds[process_ind] if seeds is not None else None,
"deterministic_cudnn": deterministic_cudnn,
}
def train_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
self.TRAIN_SCENES,
process_ind,
total_processes,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
)
res["scene_period"] = "manual"
res["env_args"] = {}
res["env_args"].update(self.ENV_ARGS)
res["env_args"]["x_display"] = (
("0.%d" % devices[process_ind % len(devices)])
if devices is not None and len(devices) > 0
else None
)
return res
def valid_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
self.VALID_SCENES,
process_ind,
total_processes,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
)
res["scene_period"] = self.VALID_SAMPLES_IN_SCENE
res["max_tasks"] = self.VALID_SAMPLES_IN_SCENE * len(res["scenes"])
res["env_args"] = {}
res["env_args"].update(self.ENV_ARGS)
res["env_args"]["x_display"] = (
("0.%d" % devices[process_ind % len(devices)])
if devices is not None and len(devices) > 0
else None
)
return res
def test_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
self.TEST_SCENES,
process_ind,
total_processes,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
)
res["scene_period"] = self.TEST_SAMPLES_IN_SCENE
res["max_tasks"] = self.TEST_SAMPLES_IN_SCENE * len(res["scenes"])
res["env_args"] = {}
res["env_args"].update(self.ENV_ARGS)
res["env_args"]["x_display"] = (
("0.%d" % devices[process_ind % len(devices)])
if devices is not None and len(devices) > 0
else None
)
return res
| ask4help-main | projects/tutorials/object_nav_ithor_ppo_one_object.py |
# literate: tutorials/distributed-objectnav-tutorial.md
# %%
"""# Tutorial: Distributed training across multiple nodes."""
# %%
"""
**Note** The provided commands to execute in this tutorial assume include a configuration script to
[clone the full library](../installation/installation-allenact.md#full-library). Setting up headless THOR might
require superuser privileges. We also assume [NCCL](https://developer.nvidia.com/nccl) is available for communication
across computation nodes and all nodes have a running `ssh` server.
The below introduced experimental tools and commands for distributed training assume a Linux OS (tested on Ubuntu
18.04).
In this tutorial, we:
1. Introduce the available API for training across multiple nodes, as well as experimental scripts for distributed
configuration, training start and termination, and remote command execution.
1. Introduce the headless mode for [AI2-THOR](https://ai2thor.allenai.org/) in `AllenAct`. Note that, in contrast with
previous tutorials using AI2-THOR, this time we don't require an xserver (in Linux) to be active.
1. Show a training example for RoboTHOR ObjectNav on a cluster, with each node having sufficient GPUs and GPU memory to
host 60 experience samplers collecting rollout data.
Thanks to the massive parallelization of experience collection and model training enabled by
[DD-PPO](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.00357), we can greatly speed up training by scaling across multiple nodes:

## The task: ObjectNav
In ObjectNav, the goal for the agent is to navigate to an object (possibly unseen during training) of a known given
class and signal task completion when it determines it has reached the goal.
## Implementation
For this tutorial, we'll use the readily available `objectnav_baselines` project, which includes configurations for
a wide variety of object navigation experiments for both iTHOR and RoboTHOR. Since those configuration files are
defined for a single-node setup, we will mainly focus on the changes required in the `machine_params` and
`training_pipeline` methods.
Note that, in order to use the headless version of AI2-THOR, we currently need to install a specific THOR commit,
different from the default one in `robothor_plugin`. Note that this command is included in the configuration script
below, so **we don't need to run this**:
```bash
pip install --extra-index-url https://ai2thor-pypi.allenai.org ai2thor==0+91139c909576f3bf95a187c5b02c6fd455d06b48
```
The experiment config starts as follows:
"""
# %%
import math
from typing import Optional, Sequence
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import LambdaLR
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses import PPO
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.ppo import PPOConfig
from projects.objectnav_baselines.experiments.robothor.objectnav_robothor_rgb_resnetgru_ddppo import (
ObjectNavRoboThorRGBPPOExperimentConfig as BaseConfig,
)
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import (
Builder,
LinearDecay,
MultiLinearDecay,
TrainingPipeline,
PipelineStage,
)
class DistributedObjectNavRoboThorRGBPPOExperimentConfig(BaseConfig):
def tag(self) -> str:
return "DistributedObjectNavRoboThorRGBPPO"
# %%
"""We override ObjectNavRoboThorBaseConfig's THOR_COMMIT_ID to match the installed headless one:"""
# %%
THOR_COMMIT_ID = "91139c909576f3bf95a187c5b02c6fd455d06b48"
# %%
"""Also indicate that we're using headless THOR (for `task_sampler_args` methods):"""
# %%
THOR_IS_HEADLESS = True
# %%
"""**Temporary hack** Disable the `commit_id` argument passed to the THOR `Controller`'s `init` method:"""
# %%
def env_args(self):
res = super().env_args()
res.pop("commit_id", None)
return res
# %%
"""
And, of course, define the number of nodes. This will be used by `machine_params` and `training_pipeline` below.
We override the existing `ExperimentConfig`'s `init` method to include control on the number of nodes:
"""
# %%
def __init__(
self,
distributed_nodes: int = 1,
num_train_processes: Optional[int] = None,
train_gpu_ids: Optional[Sequence[int]] = None,
val_gpu_ids: Optional[Sequence[int]] = None,
test_gpu_ids: Optional[Sequence[int]] = None,
):
super().__init__(num_train_processes, train_gpu_ids, val_gpu_ids, test_gpu_ids)
self.distributed_nodes = distributed_nodes
# %%
"""
### Machine parameters
**Note:** We assume that all nodes are identical (same number and model of GPUs and drivers).
The `machine_params` method will be invoked by `runner.py` with different arguments, e.g. to determine the
configuration for validation or training.
When working in distributed settings, `AllenAct` needs to know the total number of trainers across all nodes as well
as the local number of trainers. This is accomplished through the introduction of a `machine_id` keyword argument,
which will be used to define the training parameters as follows:
"""
# %%
def machine_params(self, mode="train", **kwargs):
params = super().machine_params(mode, **kwargs)
if mode == "train":
params.devices = params.devices * self.distributed_nodes
params.nprocesses = params.nprocesses * self.distributed_nodes
params.sampler_devices = params.sampler_devices * self.distributed_nodes
if "machine_id" in kwargs:
machine_id = kwargs["machine_id"]
assert (
0 <= machine_id < self.distributed_nodes
), f"machine_id {machine_id} out of range [0, {self.distributed_nodes - 1}]"
local_worker_ids = list(
range(
len(self.train_gpu_ids) * machine_id,
len(self.train_gpu_ids) * (machine_id + 1),
)
)
params.set_local_worker_ids(local_worker_ids)
# Confirm we're setting up train params nicely:
print(
f"devices {params.devices}"
f"\nnprocesses {params.nprocesses}"
f"\nsampler_devices {params.sampler_devices}"
f"\nlocal_worker_ids {params.local_worker_ids}"
)
elif mode == "valid":
# Use all GPUs at their maximum capacity for training
# (you may run validation in a separate machine)
params.nprocesses = (0,)
return params
# %%
"""
In summary, we need to specify which indices in `devices`, `nprocesses` and `sampler_devices` correspond to the
local `machine_id` node (whenever a `machine_id` is given as a keyword argument), otherwise we specify the global
configuration.
### Training pipeline
In preliminary ObjectNav experiments, we observe that small batches are useful during the initial training steps in
terms of sample efficiency, whereas large batches are preferred during the rest of training.
In order to scale to the larger amount of collected data in multi-node settings, we will proceed with a two-stage
pipeline:
1. In the first stage, we'll enforce a number of updates per amount of collected data similar to the
configuration with a single node by enforcing more batches per rollout (for about 30 million steps).
1. In the second stage we'll switch to a configuration with larger learning rate and batch size to be
used up to the grand total of 300 million experience steps.
We first define a helper method to generate a learning rate curve with decay for each stage:
"""
# %%
@staticmethod
def lr_scheduler(small_batch_steps, transition_steps, ppo_steps, lr_scaling):
safe_small_batch_steps = int(small_batch_steps * 1.02)
large_batch_and_lr_steps = ppo_steps - safe_small_batch_steps - transition_steps
# Learning rate after small batch steps (assuming decay to 0)
break1 = 1.0 - safe_small_batch_steps / ppo_steps
# Initial learning rate for large batch (after transition from initial to large learning rate)
break2 = lr_scaling * (
1.0 - (safe_small_batch_steps + transition_steps) / ppo_steps
)
return MultiLinearDecay(
[
# Base learning rate phase for small batch (with linear decay towards 0)
LinearDecay(steps=safe_small_batch_steps, startp=1.0, endp=break1,),
# Allow the optimizer to adapt its statistics to the changes with a larger learning rate
LinearDecay(steps=transition_steps, startp=break1, endp=break2,),
# Scaled learning rate phase for large batch (with linear decay towards 0)
LinearDecay(steps=large_batch_and_lr_steps, startp=break2, endp=0,),
]
)
# %%
"""
The training pipeline looks like:
"""
# %%
def training_pipeline(self, **kwargs):
# These params are identical to the baseline configuration for 60 samplers (1 machine)
ppo_steps = int(300e6)
lr = 3e-4
num_mini_batch = 1
update_repeats = 4
num_steps = 128
save_interval = 5000000
log_interval = 10000 if torch.cuda.is_available() else 1
gamma = 0.99
use_gae = True
gae_lambda = 0.95
max_grad_norm = 0.5
# We add 30 million steps for small batch learning
small_batch_steps = int(30e6)
# And a short transition phase towards large learning rate
# (see comment in the `lr_scheduler` helper method
transition_steps = int(2 / 3 * self.distributed_nodes * 1e6)
# Find exact number of samplers per GPU
assert (
self.num_train_processes % len(self.train_gpu_ids) == 0
), "Expected uniform number of samplers per GPU"
samplers_per_gpu = self.num_train_processes // len(self.train_gpu_ids)
# Multiply num_mini_batch by the largest divisor of
# samplers_per_gpu to keep all batches of same size:
num_mini_batch_multiplier = [
i
for i in reversed(
range(1, min(samplers_per_gpu // 2, self.distributed_nodes) + 1)
)
if samplers_per_gpu % i == 0
][0]
# Multiply update_repeats so that the product of this factor and
# num_mini_batch_multiplier is >= self.distributed_nodes:
update_repeats_multiplier = int(
math.ceil(self.distributed_nodes / num_mini_batch_multiplier)
)
return TrainingPipeline(
save_interval=save_interval,
metric_accumulate_interval=log_interval,
optimizer_builder=Builder(optim.Adam, dict(lr=lr)),
num_mini_batch=num_mini_batch,
update_repeats=update_repeats,
max_grad_norm=max_grad_norm,
num_steps=num_steps,
named_losses={"ppo_loss": PPO(**PPOConfig, show_ratios=False)},
gamma=gamma,
use_gae=use_gae,
gae_lambda=gae_lambda,
advance_scene_rollout_period=self.ADVANCE_SCENE_ROLLOUT_PERIOD,
pipeline_stages=[
# We increase the number of batches for the first stage to reach an
# equivalent number of updates per collected rollout data as in the
# 1 node/60 samplers setting
PipelineStage(
loss_names=["ppo_loss"],
max_stage_steps=small_batch_steps,
num_mini_batch=num_mini_batch * num_mini_batch_multiplier,
update_repeats=update_repeats * update_repeats_multiplier,
),
# The we proceed with the base configuration (leading to larger
# batches due to the increased number of samplers)
PipelineStage(
loss_names=["ppo_loss"],
max_stage_steps=ppo_steps - small_batch_steps,
),
],
# We use the MultiLinearDecay curve defined by the helper function,
# setting the learning rate scaling as the square root of the number
# of nodes. Linear scaling might also works, but we leave that
# check to the reader.
lr_scheduler_builder=Builder(
LambdaLR,
{
"lr_lambda": self.lr_scheduler(
small_batch_steps=small_batch_steps,
transition_steps=transition_steps,
ppo_steps=ppo_steps,
lr_scaling=math.sqrt(self.distributed_nodes),
)
},
),
)
# %%
"""
## Multi-node configuration
**Note:** In the following, we'll assume you don't have an available setup for distributed execution, such as
[slurm](https://slurm.schedmd.com/documentation.html). If you do have access to a better alternative to setup and run
distributed processes, we encourage you to use that. The experimental distributed tools included here are intended for
a rather basic usage pattern that might not suit your needs.
If we haven't set up AllenAct with the headless version of Ai2-THOR in our nodes, we can define a configuration script
similar to:
```bash
#!/bin/bash
# Prepare a virtualenv for allenact
sudo apt-get install -y python3-venv
python3 -mvenv ~/allenact_venv
source ~/allenact_venv/bin/activate
pip install -U pip wheel
# Install AllenAct
cd ~
git clone https://github.com/allenai/allenact.git
cd allenact
# Install AllenaAct + RoboTHOR plugin dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install -r allenact_plugins/robothor_plugin/extra_requirements.txt
# Download + setup datasets
bash datasets/download_navigation_datasets.sh robothor-objectnav
# Install headless AI2-THOR and required libvulkan1
sudo apt-get install -y libvulkan1
pip install --extra-index-url https://ai2thor-pypi.allenai.org ai2thor==0+91139c909576f3bf95a187c5b02c6fd455d06b48
# Download AI2-THOR binaries
python -c "from ai2thor.controller import Controller; c=Controller(); c.stop()"
echo DONE
```
and save it as `headless_robothor_config.sh`. Note that some of the configuration steps in the script assume you have
superuser privileges.
Then, we can just copy this file to the first node in our cluster and run it with:
```bash
source <PATH/TO/headless_robothor_config.sh>
```
If everything went well, we should be able to
```bash
cd ~/allenact && source ~/allenact_venv/bin/activate
```
Note that we might need to install `libvulkan1` in each node (even if the AllenAct setup is shared across nodes) if it
is not already available.
### Local filesystems
If our cluster does not use a shared filesystem, we'll need to propagate the setup to the rest of nodes. Assuming
we can just `ssh` with the current user to all nodes, we can propagate our config with
```bash
scripts/dconfig.py --runs_on <COMMA_SEPARATED_LIST_OF_IP_ADDRESSES> \
--config_script <PATH/TO/headless_robothor_config.sh>
```
and we can check the state of the installation with the `scripts/dcommand.py` tool:
```bash
scripts/dcommand.py --runs_on <COMMA_SEPARATED_LIST_OF_IP_ADDRESSES> \
--command 'tail -n 5 ~/log_allenact_distributed_config'
```
If everything went fine, all requirements are ready to start running our experiment.
## Run your experiment
**Note:** In this section, we again assume you don't have an available setup for distributed execution, such as
[slurm](https://slurm.schedmd.com/documentation.html). If you do have access to a better alternative to setup/run
distributed processes, we encourage you to use that. The experimental distributed tools included here are intended for
a rather basic usage pattern that might not suit your needs.
Our experimental extension to AllenAct's `main.py` script allows using practically identical commands to the ones
used in a single-node setup to start our experiments. From the root `allenact` directory, we can simply invoke
```bash
scripts/dmain.py projects/tutorials/distributed_objectnav_tutorial.py \
--config_kwargs '{"distributed_nodes":3}' \
--runs_on <COMMA_SEPARATED_LIST_OF_IP_ADDRESSES> \
--env_activate_path ~/allenact_venv/bin/activate \
--allenact_path ~/allenact \
--distributed_ip_and_port <FIRST_IP_ADDRESS_IN_RUNS_ON_LIST>:<FREE_PORT_NUMBER_FOR_THIS_IP_ADDRESS>
```
This script will do several things for you, including synchronization of the changes in the `allenact` directory
to all machines, enabling virtual environments in each node, sharing the same random seed for all `main.py` instances,
assigning `--machine_id` parameters required for multi-node training, and redirecting the process output to a log file
under the output results folder.
Note that by changing the value associated with the `distributed_nodes` key in the `config_kwargs` map and the `runs_on`
list of IPs, we can easily scale our training to e.g. 1, 3, or 8 nodes as shown in the chart above. Note that for this
call to work unmodified, you should have sufficient GPUs/GPU memory to host 60 samplers per node.
## Track and stop your experiment
You might have noticed that, when your experiment started with the above command, a file was created under
`~/.allenact`. This file includes IP addresses and screen session IDs for all nodes. It can be used
by the already introduced `scripts/dcommand.py` script, if we omit the `--runs_on` argument, to call a command on each
node via ssh; but most importantly it is used by the `scripts/dkill.py` script to terminate all screen sessions hosting
our training processes.
### Experiment tracking
A simple way to check all machines are training, assuming you have `nvidia-smi` installed in all nodes, is to just call
```bash
scripts/dcommand.py
```
from the root `allenact` directory. If everything is working well, the GPU usage stats from `nvidia-smi` should reflect
ongoing activity. You can also add different commands to be executed by each node. It is of course also possible to run
tensorboard on any of the nodes, if that's your preference.
### Experiment termination
Just call
```bash
scripts/dkill.py
```
After killing all involved screen sessions, you will be asked about whether you also want to delete the "killfile"
stored under the `~/.allenact` directory (which might be your preferred option once all processes are terminated).
We hope this tutorial will help you start quickly testing new ideas! Even if we've only explored moderates settings of
up to 480 experience samplers, you might want to consider some additional changes (like the
[choice for the optimizer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.07013)) if you plan to run at larger scale.
"""
| ask4help-main | projects/tutorials/distributed_objectnav_tutorial.py |
# literate: tutorials/minigrid-tutorial.md
# %%
"""# Tutorial: Navigation in MiniGrid."""
# %%
"""
In this tutorial, we will train an agent to complete the `MiniGrid-Empty-Random-5x5-v0` task within the
[MiniGrid](https://github.com/maximecb/gym-minigrid) environment. We will demonstrate how to:
* Write an experiment configuration file with a simple training pipeline from scratch.
* Use one of the supported environments with minimal user effort.
* Train, validate and test your experiment from the command line.
This tutorial assumes the [installation instructions](../installation/installation-allenact.md) have already been
followed and that, to some extent, this framework's [abstractions](../getting_started/abstractions.md) are known.
The `extra_requirements` for `minigrid_plugin` and `babyai_plugin` can be installed with.
```bash
pip install -r allenact_plugins/minigrid_plugin/extra_requirements.txt; pip install -r allenact_plugins/babyai_plugin/extra_requirements.txt
```
## The task
A `MiniGrid-Empty-Random-5x5-v0` task consists of a grid of dimensions 5x5 where an agent spawned at a random
location and orientation has to navigate to the visitable bottom right corner cell of the grid by sequences of three
possible actions (rotate left/right and move forward). A visualization of the environment with expert steps in a random
`MiniGrid-Empty-Random-5x5-v0` task looks like

The observation for the agent is a subset of the entire grid, simulating a simplified limited field of view, as
depicted by the highlighted rectangle (observed subset of the grid) around the agent (red arrow). Gray cells correspond
to walls.
## Experiment configuration file
Our complete experiment consists of:
* Training a basic actor-critic agent with memory to solve randomly sampled navigation tasks.
* Validation on a fixed set of tasks (running in parallel with training).
* A second stage where we test saved checkpoints with a larger fixed set of tasks.
The entire configuration for the experiment, including training, validation, and testing, is encapsulated in a single
class implementing the `ExperimentConfig` abstraction. For this tutorial, we will follow the config under
`projects/tutorials/minigrid_tutorial.py`.
The `ExperimentConfig` abstraction is used by the
[OnPolicyTrainer](../api/allenact/algorithms/onpolicy_sync/engine.md#onpolicytrainer) class (for training) and the
[OnPolicyInference](../api/allenact/algorithms/onpolicy_sync/engine.md#onpolicyinference) class (for validation and testing)
invoked through the entry script `main.py` that calls an orchestrating
[OnPolicyRunner](../api/allenact/algorithms/onpolicy_sync/runner.md#onpolicyrunner) class. It includes:
* A `tag` method to identify the experiment.
* A `create_model` method to instantiate actor-critic models.
* A `make_sampler_fn` method to instantiate task samplers.
* Three `{train,valid,test}_task_sampler_args` methods describing initialization parameters for task samplers used in
training, validation, and testing; including assignment of workers to devices for simulation.
* A `machine_params` method with configuration parameters that will be used for training, validation, and testing.
* A `training_pipeline` method describing a possibly multi-staged training pipeline with different types of losses,
an optimizer, and other parameters like learning rates, batch sizes, etc.
### Preliminaries
We first import everything we'll need to define our experiment.
"""
# %%
from typing import Dict, Optional, List, Any, cast
import gym
from gym_minigrid.envs import EmptyRandomEnv5x5
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import LambdaLR
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.ppo import PPO, PPOConfig
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import ExperimentConfig, TaskSampler
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import SensorSuite
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import (
TrainingPipeline,
Builder,
PipelineStage,
LinearDecay,
)
from allenact_plugins.minigrid_plugin.minigrid_models import MiniGridSimpleConvRNN
from allenact_plugins.minigrid_plugin.minigrid_sensors import EgocentricMiniGridSensor
from allenact_plugins.minigrid_plugin.minigrid_tasks import (
MiniGridTaskSampler,
MiniGridTask,
)
# %%
"""
We now create the `MiniGridTutorialExperimentConfig` class which we will use to define our experiment.
For pedagogical reasons, we will add methods to this class one at a time below with a description of what
these classes do.
"""
# %%
class MiniGridTutorialExperimentConfig(ExperimentConfig):
# %%
"""An experiment is identified by a `tag`."""
# %%
@classmethod
def tag(cls) -> str:
return "MiniGridTutorial"
# %%
"""
### Sensors and Model
A readily available Sensor type for MiniGrid,
[EgocentricMiniGridSensor](../api/allenact_plugins/minigrid_plugin/minigrid_sensors.md#egocentricminigridsensor),
allows us to extract observations in a format consumable by an `ActorCriticModel` agent:
"""
# %%
SENSORS = [
EgocentricMiniGridSensor(agent_view_size=5, view_channels=3),
]
# %%
"""
The three `view_channels` include objects, colors and states corresponding to a partial observation of the environment
as an image tensor, equivalent to that from `ImgObsWrapper` in
[MiniGrid](https://github.com/maximecb/gym-minigrid#wrappers). The
relatively large `agent_view_size` means the view will only be clipped by the environment walls in the forward and
lateral directions with respect to the agent's orientation.
We define our `ActorCriticModel` agent using a lightweight implementation with recurrent memory for MiniGrid
environments, [MiniGridSimpleConvRNN](../api/allenact_plugins/minigrid_plugin/minigrid_models.md#minigridsimpleconvrnn):
"""
# %%
@classmethod
def create_model(cls, **kwargs) -> nn.Module:
return MiniGridSimpleConvRNN(
action_space=gym.spaces.Discrete(len(MiniGridTask.class_action_names())),
observation_space=SensorSuite(cls.SENSORS).observation_spaces,
num_objects=cls.SENSORS[0].num_objects,
num_colors=cls.SENSORS[0].num_colors,
num_states=cls.SENSORS[0].num_states,
)
# %%
"""
### Task samplers
We use an available TaskSampler implementation for MiniGrid environments that allows to sample both random and
deterministic `MiniGridTasks`,
[MiniGridTaskSampler](../api/allenact_plugins/minigrid_plugin/minigrid_tasks.md#minigridtasksampler):
"""
# %%
@classmethod
def make_sampler_fn(cls, **kwargs) -> TaskSampler:
return MiniGridTaskSampler(**kwargs)
# %%
"""
This task sampler will during training (or validation/testing), randomly initialize new tasks for the agent to complete.
While it is not quite as important for this task type (as we test our agent in the same setting it is trained on) there
are a lot of good reasons we would like to sample tasks differently during training than during validation or testing.
One good reason, that is applicable in this tutorial, is that, during training, we would like to be able to sample tasks
forever while, during testing, we would like to sample a fixed number of tasks (as otherwise we would never finish
testing!). In `allenact` this is made possible by defining different arguments for the task sampler:
"""
# %%
def train_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return self._get_sampler_args(process_ind=process_ind, mode="train")
def valid_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return self._get_sampler_args(process_ind=process_ind, mode="valid")
def test_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return self._get_sampler_args(process_ind=process_ind, mode="test")
# %%
"""
where, for convenience, we have defined a `_get_sampler_args` method:
"""
# %%
def _get_sampler_args(self, process_ind: int, mode: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Generate initialization arguments for train, valid, and test
TaskSamplers.
# Parameters
process_ind : index of the current task sampler
mode: one of `train`, `valid`, or `test`
"""
if mode == "train":
max_tasks = None # infinite training tasks
task_seeds_list = None # no predefined random seeds for training
deterministic_sampling = False # randomly sample tasks in training
else:
max_tasks = 20 + 20 * (mode == "test") # 20 tasks for valid, 40 for test
# one seed for each task to sample:
# - ensures different seeds for each sampler, and
# - ensures a deterministic set of sampled tasks.
task_seeds_list = list(
range(process_ind * max_tasks, (process_ind + 1) * max_tasks)
)
deterministic_sampling = (
True # deterministically sample task in validation/testing
)
return dict(
max_tasks=max_tasks, # see above
env_class=self.make_env, # builder for third-party environment (defined below)
sensors=self.SENSORS, # sensors used to return observations to the agent
env_info=dict(), # parameters for environment builder (none for now)
task_seeds_list=task_seeds_list, # see above
deterministic_sampling=deterministic_sampling, # see above
)
@staticmethod
def make_env(*args, **kwargs):
return EmptyRandomEnv5x5()
# %%
"""
Note that the `env_class` argument to the Task Sampler is the one determining which task type we are going to train the
model for (in this case, `MiniGrid-Empty-Random-5x5-v0` from
[gym-minigrid](https://github.com/maximecb/gym-minigrid#empty-environment))
. The sparse reward is
[given by the environment](https://github.com/maximecb/gym-minigrid/blob/6e22a44dc67414b647063692258a4f95ce789161/gym_minigrid/minigrid.py#L819)
, and the maximum task length is 100. For training, we opt for a default random sampling, whereas for validation and
test we define fixed sets of randomly sampled tasks without needing to explicitly define a dataset.
In this toy example, the maximum number of different tasks is 32. For validation we sample 320 tasks using 16 samplers,
or 640 for testing, so we can be fairly sure that all possible tasks are visited at least once during evaluation.
### Machine parameters
Given the simplicity of the task and model, we can quickly train the model on the CPU:
"""
# %%
@classmethod
def machine_params(cls, mode="train", **kwargs) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return {
"nprocesses": 128 if mode == "train" else 16,
"devices": [],
}
# %%
"""
We allocate a larger number of samplers for training (128) than for validation or testing (16), and we default to CPU
usage by returning an empty list of `devices`.
### Training pipeline
The last definition required before starting to train is a training pipeline. In this case, we just use a single PPO
stage with linearly decaying learning rate:
"""
# %%
@classmethod
def training_pipeline(cls, **kwargs) -> TrainingPipeline:
ppo_steps = int(150000)
return TrainingPipeline(
named_losses=dict(ppo_loss=PPO(**PPOConfig)), # type:ignore
pipeline_stages=[
PipelineStage(loss_names=["ppo_loss"], max_stage_steps=ppo_steps)
],
optimizer_builder=Builder(cast(optim.Optimizer, optim.Adam), dict(lr=1e-4)),
num_mini_batch=4,
update_repeats=3,
max_grad_norm=0.5,
num_steps=16,
gamma=0.99,
use_gae=True,
gae_lambda=0.95,
advance_scene_rollout_period=None,
save_interval=10000,
metric_accumulate_interval=1,
lr_scheduler_builder=Builder(
LambdaLR, {"lr_lambda": LinearDecay(steps=ppo_steps)} # type:ignore
),
)
# %%
"""
You can see that we use a `Builder` class to postpone the construction of some of the elements, like the optimizer,
for which the model weights need to be known.
## Training and validation
We have a complete implementation of this experiment's configuration class in `projects/tutorials/minigrid_tutorial.py`.
To start training from scratch, we just need to invoke
```bash
PYTHONPATH=. python allenact/main.py minigrid_tutorial -b projects/tutorials -m 8 -o /PATH/TO/minigrid_output -s 12345
```
from the `allenact` root directory.
* With `-b projects/tutorials` we tell `allenact` that `minigrid_tutorial` experiment config file
will be found in the `projects/tutorials` directory.
* With `-m 8` we limit the number of subprocesses to 8 (each subprocess will run 16 of the 128 training task samplers).
* With `-o minigrid_output` we set the output folder into which results and logs will be saved.
* With `-s 12345` we set the random seed.
If we have Tensorboard installed, we can track progress with
```bash
tensorboard --logdir /PATH/TO/minigrid_output
```
which will default to the URL [http://localhost:6006/](http://localhost:6006/).
After 150,000 steps, the script will terminate and several checkpoints will be saved in the output folder.
The training curves should look similar to:

If everything went well, the `valid` success rate should converge to 1 and the mean episode length to a value below 4.
(For perfectly uniform sampling and complete observation, the expectation for the optimal policy is 3.75 steps.) In the
not-so-unlikely event of the run failing to converge to a near-optimal policy, we can just try to re-run (for example
with a different random seed). The validation curves should look similar to:

## Testing
The training start date for the experiment, in `YYYY-MM-DD_HH-MM-SS` format, is used as the name of one of the
subfolders in the path to the checkpoints, saved under the output folder.
In order to evaluate (i.e. test) a particular checkpoint, we need to pass the `--eval` flag and specify the checkpoint with the
`--checkpoint CHECKPOINT_PATH` option:
```bash
PYTHONPATH=. python allenact/main.py minigrid_tutorial \
-b projects/tutorials \
-m 1 \
-o /PATH/TO/minigrid_output \
-s 12345 \
--eval \
--checkpoint /PATH/TO/minigrid_output/checkpoints/MiniGridTutorial/YOUR_START_DATE/exp_MiniGridTutorial__stage_00__steps_000000151552.pt
```
Again, if everything went well, the `test` success rate should converge to 1 and the mean episode length to a value
below 4. Detailed results are saved under a `metrics` subfolder in the output folder.
The test curves should look similar to:

"""
| ask4help-main | projects/tutorials/minigrid_tutorial.py |
from typing import Dict, Optional, List, Any, cast, Callable, Union, Tuple
import gym
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from gym_minigrid.envs import EmptyRandomEnv5x5
from gym_minigrid.minigrid import MiniGridEnv
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import LambdaLR
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.imitation import Imitation
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.ppo import PPO, PPOConfig
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.policy import ActorCriticModel, DistributionType
from allenact.base_abstractions.distributions import (
CategoricalDistr,
ConditionalDistr,
SequentialDistr,
)
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import ExperimentConfig, TaskSampler
from allenact.base_abstractions.misc import ActorCriticOutput, Memory, RLStepResult
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import SensorSuite, ExpertActionSensor
from allenact.embodiedai.models.basic_models import RNNStateEncoder
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import (
TrainingPipeline,
Builder,
PipelineStage,
LinearDecay,
)
from allenact.utils.misc_utils import prepare_locals_for_super
from allenact_plugins.minigrid_plugin.minigrid_models import MiniGridSimpleConvBase
from allenact_plugins.minigrid_plugin.minigrid_sensors import EgocentricMiniGridSensor
from allenact_plugins.minigrid_plugin.minigrid_tasks import (
MiniGridTaskSampler,
MiniGridTask,
)
class ConditionedLinearActorCriticHead(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self, input_size: int, master_actions: int = 2, subpolicy_actions: int = 2
):
super().__init__()
self.input_size = input_size
self.master_and_critic = nn.Linear(input_size, master_actions + 1)
self.embed_higher = nn.Embedding(num_embeddings=2, embedding_dim=input_size)
self.actor = nn.Linear(2 * input_size, subpolicy_actions)
nn.init.orthogonal_(self.master_and_critic.weight)
nn.init.constant_(self.master_and_critic.bias, 0)
nn.init.orthogonal_(self.actor.weight)
nn.init.constant_(self.actor.bias, 0)
def lower_policy(self, *args, **kwargs):
assert "higher" in kwargs
assert "state_embedding" in kwargs
emb = self.embed_higher(kwargs["higher"])
logits = self.actor(torch.cat([emb, kwargs["state_embedding"]], dim=-1))
return CategoricalDistr(logits=logits)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.master_and_critic(x)
master_logits = out[..., :-1]
values = out[..., -1:]
# noinspection PyArgumentList
cond1 = ConditionalDistr(
distr_conditioned_on_input_fn_or_instance=CategoricalDistr(
logits=master_logits
),
action_group_name="higher",
)
cond2 = ConditionalDistr(
distr_conditioned_on_input_fn_or_instance=lambda *args, **kwargs: ConditionedLinearActorCriticHead.lower_policy(
self, *args, **kwargs
),
action_group_name="lower",
state_embedding=x,
)
return (
SequentialDistr(cond1, cond2),
values.view(*values.shape[:2], -1), # [steps, samplers, flattened]
)
class ConditionedLinearActorCritic(ActorCriticModel[SequentialDistr]):
def __init__(
self,
input_uuid: str,
action_space: gym.spaces.Dict,
observation_space: gym.spaces.Dict,
):
super().__init__(action_space=action_space, observation_space=observation_space)
assert (
input_uuid in observation_space.spaces
), "ConditionedLinearActorCritic expects only a single observational input."
self.input_uuid = input_uuid
box_space: gym.spaces.Box = observation_space[self.input_uuid]
assert isinstance(box_space, gym.spaces.Box), (
"ConditionedLinearActorCritic requires that"
"observation space corresponding to the input uuid is a Box space."
)
assert len(box_space.shape) == 1
self.in_dim = box_space.shape[0]
self.head = ConditionedLinearActorCriticHead(
input_size=self.in_dim,
master_actions=action_space["higher"].n,
subpolicy_actions=action_space["lower"].n,
)
# noinspection PyMethodMayBeStatic
def _recurrent_memory_specification(self):
return None
def forward(self, observations, memory, prev_actions, masks):
dists, values = self.head(observations[self.input_uuid])
# noinspection PyArgumentList
return (
ActorCriticOutput(distributions=dists, values=values, extras={},),
None,
)
class ConditionedRNNActorCritic(ActorCriticModel[SequentialDistr]):
def __init__(
self,
input_uuid: str,
action_space: gym.spaces.Dict,
observation_space: gym.spaces.Dict,
hidden_size: int = 128,
num_layers: int = 1,
rnn_type: str = "GRU",
head_type: Callable[
..., ActorCriticModel[SequentialDistr]
] = ConditionedLinearActorCritic,
):
super().__init__(action_space=action_space, observation_space=observation_space)
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.rnn_type = rnn_type
assert (
input_uuid in observation_space.spaces
), "LinearActorCritic expects only a single observational input."
self.input_uuid = input_uuid
box_space: gym.spaces.Box = observation_space[self.input_uuid]
assert isinstance(box_space, gym.spaces.Box), (
"RNNActorCritic requires that"
"observation space corresponding to the input uuid is a Box space."
)
assert len(box_space.shape) == 1
self.in_dim = box_space.shape[0]
self.state_encoder = RNNStateEncoder(
input_size=self.in_dim,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
num_layers=num_layers,
rnn_type=rnn_type,
trainable_masked_hidden_state=True,
)
self.head_uuid = "{}_{}".format("rnn", input_uuid)
self.ac_nonrecurrent_head: ActorCriticModel[SequentialDistr] = head_type(
input_uuid=self.head_uuid,
action_space=action_space,
observation_space=gym.spaces.Dict(
{
self.head_uuid: gym.spaces.Box(
low=np.float32(0.0), high=np.float32(1.0), shape=(hidden_size,)
)
}
),
)
self.memory_key = "rnn"
@property
def recurrent_hidden_state_size(self) -> int:
return self.hidden_size
@property
def num_recurrent_layers(self) -> int:
return self.state_encoder.num_recurrent_layers
def _recurrent_memory_specification(self):
return {
self.memory_key: (
(
("layer", self.num_recurrent_layers),
("sampler", None),
("hidden", self.recurrent_hidden_state_size),
),
torch.float32,
)
}
def forward( # type:ignore
self,
observations: Dict[str, Union[torch.FloatTensor, Dict[str, Any]]],
memory: Memory,
prev_actions: torch.Tensor,
masks: torch.FloatTensor,
) -> Tuple[ActorCriticOutput[DistributionType], Optional[Memory]]:
rnn_out, mem_return = self.state_encoder(
x=observations[self.input_uuid],
hidden_states=memory.tensor(self.memory_key),
masks=masks,
)
# noinspection PyCallingNonCallable
out, _ = self.ac_nonrecurrent_head(
observations={self.head_uuid: rnn_out},
memory=None,
prev_actions=prev_actions,
masks=masks,
)
# noinspection PyArgumentList
return (
out,
memory.set_tensor(self.memory_key, mem_return),
)
class ConditionedMiniGridSimpleConvRNN(MiniGridSimpleConvBase):
def __init__(
self,
action_space: gym.spaces.Dict,
observation_space: gym.spaces.Dict,
num_objects: int,
num_colors: int,
num_states: int,
object_embedding_dim: int = 8,
hidden_size=512,
num_layers=1,
rnn_type="GRU",
head_type: Callable[
..., ActorCriticModel[SequentialDistr]
] = ConditionedLinearActorCritic,
**kwargs,
):
super().__init__(**prepare_locals_for_super(locals()))
self._hidden_size = hidden_size
agent_view_x, agent_view_y, view_channels = observation_space[
"minigrid_ego_image"
].shape
self.actor_critic = ConditionedRNNActorCritic(
input_uuid=self.ac_key,
action_space=action_space,
observation_space=gym.spaces.Dict(
{
self.ac_key: gym.spaces.Box(
low=np.float32(-1.0),
high=np.float32(1.0),
shape=(
self.object_embedding_dim
* agent_view_x
* agent_view_y
* view_channels,
),
)
}
),
hidden_size=hidden_size,
num_layers=num_layers,
rnn_type=rnn_type,
head_type=head_type,
)
self.memory_key = "rnn"
self.train()
@property
def num_recurrent_layers(self):
return self.actor_critic.num_recurrent_layers
@property
def recurrent_hidden_state_size(self):
return self._hidden_size
def _recurrent_memory_specification(self):
return {
self.memory_key: (
(
("layer", self.num_recurrent_layers),
("sampler", None),
("hidden", self.recurrent_hidden_state_size),
),
torch.float32,
)
}
class ConditionedMiniGridTask(MiniGridTask):
_ACTION_NAMES = ("left", "right", "forward", "pickup")
_ACTION_IND_TO_MINIGRID_IND = tuple(
MiniGridEnv.Actions.__members__[name].value for name in _ACTION_NAMES
)
@property
def action_space(self) -> gym.spaces.Dict:
return gym.spaces.Dict(
higher=gym.spaces.Discrete(2), lower=gym.spaces.Discrete(2)
)
def _step(self, action: Dict[str, int]) -> RLStepResult:
assert len(action) == 2, "got action={}".format(action)
minigrid_obs, reward, self._minigrid_done, info = self.env.step(
action=(
self._ACTION_IND_TO_MINIGRID_IND[action["lower"] + 2 * action["higher"]]
)
)
# self.env.render()
return RLStepResult(
observation=self.get_observations(minigrid_output_obs=minigrid_obs),
reward=reward,
done=self.is_done(),
info=info,
)
def query_expert(self, **kwargs) -> Tuple[int, bool]:
if kwargs["expert_sensor_group_name"] == "higher":
if self._minigrid_done:
raise ValueError("Episode is completed, but expert is still queried.")
# return 0, False
self.cached_expert = super().query_expert(**kwargs)
if self.cached_expert[1]:
return self.cached_expert[0] // 2, True
else:
return 0, False
else:
assert hasattr(self, "cached_expert")
if self.cached_expert[1]:
res = (self.cached_expert[0] % 2, True)
else:
res = (0, False)
del self.cached_expert
return res
class MiniGridTutorialExperimentConfig(ExperimentConfig):
@classmethod
def tag(cls) -> str:
return "MiniGridTutorial"
SENSORS = [
EgocentricMiniGridSensor(agent_view_size=5, view_channels=3),
ExpertActionSensor(
action_space=gym.spaces.Dict(
higher=gym.spaces.Discrete(2), lower=gym.spaces.Discrete(2)
)
),
]
@classmethod
def create_model(cls, **kwargs) -> nn.Module:
return ConditionedMiniGridSimpleConvRNN(
action_space=gym.spaces.Dict(
higher=gym.spaces.Discrete(2), lower=gym.spaces.Discrete(2)
),
observation_space=SensorSuite(cls.SENSORS).observation_spaces,
num_objects=cls.SENSORS[0].num_objects,
num_colors=cls.SENSORS[0].num_colors,
num_states=cls.SENSORS[0].num_states,
)
@classmethod
def make_sampler_fn(cls, **kwargs) -> TaskSampler:
return MiniGridTaskSampler(**kwargs)
def train_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return self._get_sampler_args(process_ind=process_ind, mode="train")
def valid_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return self._get_sampler_args(process_ind=process_ind, mode="valid")
def test_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return self._get_sampler_args(process_ind=process_ind, mode="test")
def _get_sampler_args(self, process_ind: int, mode: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Generate initialization arguments for train, valid, and test
TaskSamplers.
# Parameters
process_ind : index of the current task sampler
mode: one of `train`, `valid`, or `test`
"""
if mode == "train":
max_tasks = None # infinite training tasks
task_seeds_list = None # no predefined random seeds for training
deterministic_sampling = False # randomly sample tasks in training
else:
max_tasks = 20 + 20 * (
mode == "test"
) # 20 tasks for valid, 40 for test (per sampler)
# one seed for each task to sample:
# - ensures different seeds for each sampler, and
# - ensures a deterministic set of sampled tasks.
task_seeds_list = list(
range(process_ind * max_tasks, (process_ind + 1) * max_tasks)
)
deterministic_sampling = (
True # deterministically sample task in validation/testing
)
return dict(
max_tasks=max_tasks, # see above
env_class=self.make_env, # builder for third-party environment (defined below)
sensors=self.SENSORS, # sensors used to return observations to the agent
env_info=dict(), # parameters for environment builder (none for now)
task_seeds_list=task_seeds_list, # see above
deterministic_sampling=deterministic_sampling, # see above
task_class=ConditionedMiniGridTask,
)
@staticmethod
def make_env(*args, **kwargs):
return EmptyRandomEnv5x5()
@classmethod
def machine_params(cls, mode="train", **kwargs) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return {
"nprocesses": 128 if mode == "train" else 16,
"devices": [],
}
@classmethod
def training_pipeline(cls, **kwargs) -> TrainingPipeline:
ppo_steps = int(150000)
return TrainingPipeline(
named_losses=dict(
imitation_loss=Imitation(
cls.SENSORS[1]
), # 0 is Minigrid, 1 is ExpertActionSensor
ppo_loss=PPO(**PPOConfig, entropy_method_name="conditional_entropy"),
), # type:ignore
pipeline_stages=[
PipelineStage(
teacher_forcing=LinearDecay(
startp=1.0, endp=0.0, steps=ppo_steps // 2,
),
loss_names=["imitation_loss", "ppo_loss"],
max_stage_steps=ppo_steps,
)
],
optimizer_builder=Builder(cast(optim.Optimizer, optim.Adam), dict(lr=1e-4)),
num_mini_batch=4,
update_repeats=3,
max_grad_norm=0.5,
num_steps=16,
gamma=0.99,
use_gae=True,
gae_lambda=0.95,
advance_scene_rollout_period=None,
save_interval=10000,
metric_accumulate_interval=1,
lr_scheduler_builder=Builder(
LambdaLR, {"lr_lambda": LinearDecay(steps=ppo_steps)} # type:ignore
),
)
| ask4help-main | projects/tutorials/minigrid_tutorial_conds.py |
ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/__init__.py |
|
ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/__init__.py |
|
import platform
from abc import ABC
from math import ceil
from typing import Dict, Any, List, Optional, Sequence
import gym
import numpy as np
import torch
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import MachineParams
from allenact.base_abstractions.preprocessor import SensorPreprocessorGraph
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import SensorSuite, ExpertActionSensor
from allenact.base_abstractions.task import TaskSampler
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import evenly_distribute_count_into_bins
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.manipulathor_constants import ENV_ARGS
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.manipulathor_task_samplers import (
SimpleArmPointNavGeneralSampler,
)
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.manipulathor_viz import (
ImageVisualizer,
TestMetricLogger,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.experiments.armpointnav_base import (
ArmPointNavBaseConfig,
)
class ArmPointNavThorBaseConfig(ArmPointNavBaseConfig, ABC):
"""The base config for all iTHOR PointNav experiments."""
TASK_SAMPLER = SimpleArmPointNavGeneralSampler
VISUALIZE = False
if platform.system() == "Darwin":
VISUALIZE = True
NUM_PROCESSES: Optional[int] = None
TRAIN_GPU_IDS = list(range(torch.cuda.device_count()))
SAMPLER_GPU_IDS = TRAIN_GPU_IDS
VALID_GPU_IDS = [torch.cuda.device_count() - 1]
TEST_GPU_IDS = [torch.cuda.device_count() - 1]
TRAIN_DATASET_DIR: Optional[str] = None
VAL_DATASET_DIR: Optional[str] = None
CAP_TRAINING = None
TRAIN_SCENES: str = None
VAL_SCENES: str = None
TEST_SCENES: str = None
OBJECT_TYPES: Optional[Sequence[str]] = None
VALID_SAMPLES_IN_SCENE = 1
TEST_SAMPLES_IN_SCENE = 1
NUMBER_OF_TEST_PROCESS = 10
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
assert (
self.CAMERA_WIDTH == 224
and self.CAMERA_HEIGHT == 224
and self.VISIBILITY_DISTANCE == 1
and self.STEP_SIZE == 0.25
)
self.ENV_ARGS = ENV_ARGS
def machine_params(self, mode="train", **kwargs):
sampler_devices: Sequence[int] = []
if mode == "train":
workers_per_device = 1
gpu_ids = (
[]
if not torch.cuda.is_available()
else self.TRAIN_GPU_IDS * workers_per_device
)
nprocesses = (
1
if not torch.cuda.is_available()
else evenly_distribute_count_into_bins(self.NUM_PROCESSES, len(gpu_ids))
)
sampler_devices = self.SAMPLER_GPU_IDS
elif mode == "valid":
nprocesses = 1
gpu_ids = [] if not torch.cuda.is_available() else self.VALID_GPU_IDS
elif mode == "test":
nprocesses = self.NUMBER_OF_TEST_PROCESS if torch.cuda.is_available() else 1
gpu_ids = [] if not torch.cuda.is_available() else self.TEST_GPU_IDS
else:
raise NotImplementedError("mode must be 'train', 'valid', or 'test'.")
sensors = [*self.SENSORS]
if mode != "train":
sensors = [s for s in sensors if not isinstance(s, ExpertActionSensor)]
sensor_preprocessor_graph = (
SensorPreprocessorGraph(
source_observation_spaces=SensorSuite(sensors).observation_spaces,
preprocessors=self.preprocessors(),
)
if mode == "train"
or (
(isinstance(nprocesses, int) and nprocesses > 0)
or (isinstance(nprocesses, Sequence) and sum(nprocesses) > 0)
)
else None
)
return MachineParams(
nprocesses=nprocesses,
devices=gpu_ids,
sampler_devices=sampler_devices
if mode == "train"
else gpu_ids, # ignored with > 1 gpu_ids
sensor_preprocessor_graph=sensor_preprocessor_graph,
)
@classmethod
def make_sampler_fn(cls, **kwargs) -> TaskSampler:
from datetime import datetime
now = datetime.now()
exp_name_w_time = cls.__name__ + "_" + now.strftime("%m_%d_%Y_%H_%M_%S_%f")
if cls.VISUALIZE:
visualizers = [
ImageVisualizer(exp_name=exp_name_w_time),
TestMetricLogger(exp_name=exp_name_w_time),
]
kwargs["visualizers"] = visualizers
kwargs["objects"] = cls.OBJECT_TYPES
kwargs["exp_name"] = exp_name_w_time
return cls.TASK_SAMPLER(**kwargs)
@staticmethod
def _partition_inds(n: int, num_parts: int):
return np.round(np.linspace(0, n, num_parts + 1, endpoint=True)).astype(
np.int32
)
def _get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
self,
scenes: List[str],
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
if total_processes > len(scenes): # oversample some scenes -> bias
if total_processes % len(scenes) != 0:
print(
"Warning: oversampling some of the scenes to feed all processes."
" You can avoid this by setting a number of workers divisible by the number of scenes"
)
scenes = scenes * int(ceil(total_processes / len(scenes)))
scenes = scenes[: total_processes * (len(scenes) // total_processes)]
else:
if len(scenes) % total_processes != 0:
print(
"Warning: oversampling some of the scenes to feed all processes."
" You can avoid this by setting a number of workers divisor of the number of scenes"
)
inds = self._partition_inds(len(scenes), total_processes)
return {
"scenes": scenes[inds[process_ind] : inds[process_ind + 1]],
"env_args": self.ENV_ARGS,
"max_steps": self.MAX_STEPS,
"sensors": self.SENSORS,
"action_space": gym.spaces.Discrete(
len(self.TASK_SAMPLER._TASK_TYPE.class_action_names())
),
"seed": seeds[process_ind] if seeds is not None else None,
"deterministic_cudnn": deterministic_cudnn,
"rewards_config": self.REWARD_CONFIG,
}
def train_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
self.TRAIN_SCENES,
process_ind,
total_processes,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
)
res["scene_period"] = "manual"
res["sampler_mode"] = "train"
res["cap_training"] = self.CAP_TRAINING
res["env_args"] = {}
res["env_args"].update(self.ENV_ARGS)
res["env_args"]["x_display"] = (
("0.%d" % devices[process_ind % len(devices)]) if len(devices) > 0 else None
)
return res
def valid_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]],
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
self.VALID_SCENES,
process_ind,
total_processes,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
)
res["scene_period"] = self.VALID_SAMPLES_IN_SCENE
res["sampler_mode"] = "val"
res["cap_training"] = self.CAP_TRAINING
res["max_tasks"] = self.VALID_SAMPLES_IN_SCENE * len(res["scenes"])
res["env_args"] = {}
res["env_args"].update(self.ENV_ARGS)
res["env_args"]["x_display"] = (
("0.%d" % devices[process_ind % len(devices)]) if len(devices) > 0 else None
)
return res
def test_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]],
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
self.TEST_SCENES,
process_ind,
total_processes,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
)
res["scene_period"] = self.TEST_SAMPLES_IN_SCENE
res["sampler_mode"] = "test"
res["env_args"] = {}
res["cap_training"] = self.CAP_TRAINING
res["env_args"].update(self.ENV_ARGS)
res["env_args"]["x_display"] = (
("0.%d" % devices[process_ind % len(devices)]) if len(devices) > 0 else None
)
return res
| ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/experiments/armpointnav_thor_base.py |
from abc import ABC
from typing import Optional, Sequence, Union
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import ExperimentConfig
from allenact.base_abstractions.preprocessor import Preprocessor
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import Sensor
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import Builder
class ArmPointNavBaseConfig(ExperimentConfig, ABC):
"""The base object navigation configuration file."""
ADVANCE_SCENE_ROLLOUT_PERIOD: Optional[int] = None
SENSORS: Optional[Sequence[Sensor]] = None
STEP_SIZE = 0.25
ROTATION_DEGREES = 45.0
VISIBILITY_DISTANCE = 1.0
STOCHASTIC = False
CAMERA_WIDTH = 224
CAMERA_HEIGHT = 224
SCREEN_SIZE = 224
MAX_STEPS = 200
def __init__(self):
self.REWARD_CONFIG = {
"step_penalty": -0.01,
"goal_success_reward": 10.0,
"pickup_success_reward": 5.0,
"failed_stop_reward": 0.0,
"shaping_weight": 1.0, # we are not using this
"failed_action_penalty": -0.03,
}
@classmethod
def preprocessors(cls) -> Sequence[Union[Preprocessor, Builder[Preprocessor]]]:
return tuple()
| ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/experiments/armpointnav_base.py |
import torch.optim as optim
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses import PPO
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.ppo import PPOConfig
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import (
Builder,
PipelineStage,
TrainingPipeline,
LinearDecay,
)
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import LambdaLR
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.experiments.armpointnav_base import (
ArmPointNavBaseConfig,
)
class ArmPointNavMixInPPOConfig(ArmPointNavBaseConfig):
def training_pipeline(self, **kwargs):
ppo_steps = int(300000000)
lr = 3e-4
num_mini_batch = 1
update_repeats = 4
num_steps = self.MAX_STEPS
save_interval = 500000 # from 50k
log_interval = 1000
gamma = 0.99
use_gae = True
gae_lambda = 0.95
max_grad_norm = 0.5
return TrainingPipeline(
save_interval=save_interval,
metric_accumulate_interval=log_interval,
optimizer_builder=Builder(optim.Adam, dict(lr=lr)),
num_mini_batch=num_mini_batch,
update_repeats=update_repeats,
max_grad_norm=max_grad_norm,
num_steps=num_steps,
named_losses={"ppo_loss": PPO(**PPOConfig)},
gamma=gamma,
use_gae=use_gae,
gae_lambda=gae_lambda,
advance_scene_rollout_period=self.ADVANCE_SCENE_ROLLOUT_PERIOD,
pipeline_stages=[
PipelineStage(loss_names=["ppo_loss"], max_stage_steps=ppo_steps)
],
lr_scheduler_builder=Builder(
LambdaLR, {"lr_lambda": LinearDecay(steps=ppo_steps)}
),
)
| ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/experiments/armpointnav_mixin_ddppo.py |
ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/experiments/__init__.py |
|
from typing import Sequence, Union
import gym
import torch.nn as nn
from allenact.base_abstractions.preprocessor import Preprocessor
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import Builder
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.experiments.armpointnav_base import (
ArmPointNavBaseConfig,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.models.arm_pointnav_models import (
ArmPointNavBaselineActorCritic,
)
class ArmPointNavMixInSimpleGRUConfig(ArmPointNavBaseConfig):
@classmethod
def preprocessors(cls) -> Sequence[Union[Preprocessor, Builder[Preprocessor]]]:
preprocessors = []
return preprocessors
@classmethod
def create_model(cls, **kwargs) -> nn.Module:
return ArmPointNavBaselineActorCritic(
action_space=gym.spaces.Discrete(
len(cls.TASK_SAMPLER._TASK_TYPE.class_action_names())
),
observation_space=kwargs["sensor_preprocessor_graph"].observation_spaces,
hidden_size=512,
)
| ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/experiments/armpointnav_mixin_simplegru.py |
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.manipulathor_constants import ENV_ARGS
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.manipulathor_sensors import (
NoVisionSensorThor,
RelativeAgentArmToObjectSensor,
RelativeObjectToGoalSensor,
PickedUpObjSensor,
)
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.manipulathor_task_samplers import (
ArmPointNavTaskSampler,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.experiments.armpointnav_mixin_ddppo import (
ArmPointNavMixInPPOConfig,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.experiments.armpointnav_mixin_simplegru import (
ArmPointNavMixInSimpleGRUConfig,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.experiments.ithor.armpointnav_ithor_base import (
ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig,
)
class ArmPointNavNoVision(
ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig,
ArmPointNavMixInPPOConfig,
ArmPointNavMixInSimpleGRUConfig,
):
"""An Object Navigation experiment configuration in iThor with RGB
input."""
SENSORS = [
NoVisionSensorThor(
height=ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
width=ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
use_resnet_normalization=False,
uuid="rgb_lowres",
),
RelativeAgentArmToObjectSensor(),
RelativeObjectToGoalSensor(),
PickedUpObjSensor(),
]
MAX_STEPS = 200
TASK_SAMPLER = ArmPointNavTaskSampler #
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
assert (
self.CAMERA_WIDTH == 224
and self.CAMERA_HEIGHT == 224
and self.VISIBILITY_DISTANCE == 1
and self.STEP_SIZE == 0.25
)
self.ENV_ARGS = {**ENV_ARGS, "renderDepthImage": False}
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return cls.__name__
| ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/experiments/ithor/armpointnav_no_vision.py |
from abc import ABC
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.armpointnav_constants import (
TRAIN_OBJECTS,
TEST_OBJECTS,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.experiments.armpointnav_thor_base import (
ArmPointNavThorBaseConfig,
)
class ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig(ArmPointNavThorBaseConfig, ABC):
"""The base config for all iTHOR ObjectNav experiments."""
NUM_PROCESSES = 40
# add all the arguments here
TOTAL_NUMBER_SCENES = 30
TRAIN_SCENES = [
"FloorPlan{}_physics".format(str(i))
for i in range(1, TOTAL_NUMBER_SCENES + 1)
if (i % 3 == 1 or i % 3 == 0) and i != 28
] # last scenes are really bad
TEST_SCENES = [
"FloorPlan{}_physics".format(str(i))
for i in range(1, TOTAL_NUMBER_SCENES + 1)
if i % 3 == 2 and i % 6 == 2
]
VALID_SCENES = [
"FloorPlan{}_physics".format(str(i))
for i in range(1, TOTAL_NUMBER_SCENES + 1)
if i % 3 == 2 and i % 6 == 5
]
ALL_SCENES = TRAIN_SCENES + TEST_SCENES + VALID_SCENES
assert (
len(ALL_SCENES) == TOTAL_NUMBER_SCENES - 1
and len(set(ALL_SCENES)) == TOTAL_NUMBER_SCENES - 1
)
OBJECT_TYPES = tuple(sorted(TRAIN_OBJECTS))
UNSEEN_OBJECT_TYPES = tuple(sorted(TEST_OBJECTS))
| ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/experiments/ithor/armpointnav_ithor_base.py |
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.manipulathor_constants import ENV_ARGS
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.manipulathor_sensors import (
DepthSensorThor,
RelativeAgentArmToObjectSensor,
RelativeObjectToGoalSensor,
PickedUpObjSensor,
)
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.manipulathor_task_samplers import (
ArmPointNavTaskSampler,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.experiments.armpointnav_mixin_ddppo import (
ArmPointNavMixInPPOConfig,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.experiments.armpointnav_mixin_simplegru import (
ArmPointNavMixInSimpleGRUConfig,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.experiments.ithor.armpointnav_ithor_base import (
ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig,
)
class ArmPointNavDepth(
ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig,
ArmPointNavMixInPPOConfig,
ArmPointNavMixInSimpleGRUConfig,
):
"""An Object Navigation experiment configuration in iThor with RGB
input."""
SENSORS = [
DepthSensorThor(
height=ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
width=ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
use_normalization=True,
uuid="depth_lowres",
),
RelativeAgentArmToObjectSensor(),
RelativeObjectToGoalSensor(),
PickedUpObjSensor(),
]
MAX_STEPS = 200
TASK_SAMPLER = ArmPointNavTaskSampler
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
assert (
self.CAMERA_WIDTH == 224
and self.CAMERA_HEIGHT == 224
and self.VISIBILITY_DISTANCE == 1
and self.STEP_SIZE == 0.25
)
self.ENV_ARGS = {**ENV_ARGS, "renderDepthImage": True}
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return cls.__name__
| ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/experiments/ithor/armpointnav_depth.py |
ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/experiments/ithor/__init__.py |
|
from allenact_plugins.ithor_plugin.ithor_sensors import RGBSensorThor
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.manipulathor_constants import ENV_ARGS
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.manipulathor_sensors import (
RelativeAgentArmToObjectSensor,
RelativeObjectToGoalSensor,
PickedUpObjSensor,
)
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.manipulathor_task_samplers import (
ArmPointNavTaskSampler,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.experiments.armpointnav_mixin_ddppo import (
ArmPointNavMixInPPOConfig,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.experiments.armpointnav_mixin_simplegru import (
ArmPointNavMixInSimpleGRUConfig,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.experiments.ithor.armpointnav_ithor_base import (
ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig,
)
class ArmPointNavRGB(
ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig,
ArmPointNavMixInPPOConfig,
ArmPointNavMixInSimpleGRUConfig,
):
"""An Object Navigation experiment configuration in iThor with RGB
input."""
SENSORS = [
RGBSensorThor(
height=ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
width=ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
use_resnet_normalization=True,
uuid="rgb_lowres",
),
RelativeAgentArmToObjectSensor(),
RelativeObjectToGoalSensor(),
PickedUpObjSensor(),
]
MAX_STEPS = 200
TASK_SAMPLER = ArmPointNavTaskSampler #
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
assert (
self.CAMERA_WIDTH == 224
and self.CAMERA_HEIGHT == 224
and self.VISIBILITY_DISTANCE == 1
and self.STEP_SIZE == 0.25
)
self.ENV_ARGS = {**ENV_ARGS}
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return cls.__name__
| ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/experiments/ithor/armpointnav_rgb.py |
from allenact_plugins.ithor_plugin.ithor_sensors import RGBSensorThor
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.manipulathor_constants import ENV_ARGS
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.manipulathor_sensors import (
DepthSensorThor,
RelativeAgentArmToObjectSensor,
RelativeObjectToGoalSensor,
PickedUpObjSensor,
)
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.manipulathor_task_samplers import (
ArmPointNavTaskSampler,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.experiments.armpointnav_mixin_ddppo import (
ArmPointNavMixInPPOConfig,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.experiments.armpointnav_mixin_simplegru import (
ArmPointNavMixInSimpleGRUConfig,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.experiments.ithor.armpointnav_ithor_base import (
ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig,
)
class ArmPointNavRGBDepth(
ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig,
ArmPointNavMixInPPOConfig,
ArmPointNavMixInSimpleGRUConfig,
):
"""An Object Navigation experiment configuration in iThor with RGB
input."""
SENSORS = [
DepthSensorThor(
height=ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
width=ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
use_normalization=True,
uuid="depth_lowres",
),
RGBSensorThor(
height=ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
width=ArmPointNaviThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
use_resnet_normalization=True,
uuid="rgb_lowres",
),
RelativeAgentArmToObjectSensor(),
RelativeObjectToGoalSensor(),
PickedUpObjSensor(),
]
MAX_STEPS = 200
TASK_SAMPLER = ArmPointNavTaskSampler #
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
assert (
self.CAMERA_WIDTH == 224
and self.CAMERA_HEIGHT == 224
and self.VISIBILITY_DISTANCE == 1
and self.STEP_SIZE == 0.25
)
self.ENV_ARGS = {**ENV_ARGS, "renderDepthImage": True}
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return cls.__name__
| ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/experiments/ithor/armpointnav_rgbdepth.py |
import gym
import torch.nn as nn
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.manipulathor_constants import ENV_ARGS
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.manipulathor_task_samplers import (
ArmPointNavTaskSampler,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.experiments.ithor.armpointnav_depth import (
ArmPointNavDepth,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.models.disjoint_arm_pointnav_models import (
DisjointArmPointNavBaselineActorCritic,
)
class ArmPointNavDisjointDepth(ArmPointNavDepth):
"""An Object Navigation experiment configuration in iThor with RGB
input."""
TASK_SAMPLER = ArmPointNavTaskSampler
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
assert (
self.CAMERA_WIDTH == 224
and self.CAMERA_HEIGHT == 224
and self.VISIBILITY_DISTANCE == 1
and self.STEP_SIZE == 0.25
)
self.ENV_ARGS = {**ENV_ARGS, "renderDepthImage": True}
@classmethod
def create_model(cls, **kwargs) -> nn.Module:
return DisjointArmPointNavBaselineActorCritic(
action_space=gym.spaces.Discrete(
len(cls.TASK_SAMPLER._TASK_TYPE.class_action_names())
),
observation_space=kwargs["sensor_preprocessor_graph"].observation_spaces,
hidden_size=512,
)
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return cls.__name__
| ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/experiments/ithor/armpointnav_disjoint_depth.py |
"""Baseline models for use in the Arm Point Navigation task.
Arm Point Navigation is currently available as a Task in ManipulaTHOR.
"""
from typing import Tuple, Optional
import gym
import torch
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.policy import (
ActorCriticModel,
LinearCriticHead,
LinearActorHead,
DistributionType,
Memory,
ObservationType,
)
from allenact.base_abstractions.distributions import CategoricalDistr
from allenact.base_abstractions.misc import ActorCriticOutput
from allenact.embodiedai.models.basic_models import SimpleCNN, RNNStateEncoder
from gym.spaces.dict import Dict as SpaceDict
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.models.manipulathor_net_utils import (
input_embedding_net,
)
class ArmPointNavBaselineActorCritic(ActorCriticModel[CategoricalDistr]):
"""Baseline recurrent actor critic model for armpointnav task.
# Attributes
action_space : The space of actions available to the agent. Currently only discrete
actions are allowed (so this space will always be of type `gym.spaces.Discrete`).
observation_space : The observation space expected by the agent. This observation space
should include (optionally) 'rgb' images and 'depth' images.
hidden_size : The hidden size of the GRU RNN.
object_type_embedding_dim: The dimensionality of the embedding corresponding to the goal
object type.
"""
def __init__(
self,
action_space: gym.spaces.Discrete,
observation_space: SpaceDict,
hidden_size=512,
obj_state_embedding_size=512,
trainable_masked_hidden_state: bool = False,
num_rnn_layers=1,
rnn_type="GRU",
):
"""Initializer.
See class documentation for parameter definitions.
"""
super().__init__(action_space=action_space, observation_space=observation_space)
self._hidden_size = hidden_size
self.object_type_embedding_size = obj_state_embedding_size
sensor_names = self.observation_space.spaces.keys()
self.visual_encoder = SimpleCNN(
self.observation_space,
self._hidden_size,
rgb_uuid="rgb_lowres" if "rgb_lowres" in sensor_names else None,
depth_uuid="depth_lowres" if "depth_lowres" in sensor_names else None,
)
if "rgb_lowres" in sensor_names and "depth_lowres" in sensor_names:
input_visual_feature_num = 2
elif "rgb_lowres" in sensor_names:
input_visual_feature_num = 1
elif "depth_lowres" in sensor_names:
input_visual_feature_num = 1
self.state_encoder = RNNStateEncoder(
(self._hidden_size) * input_visual_feature_num + obj_state_embedding_size,
self._hidden_size,
trainable_masked_hidden_state=trainable_masked_hidden_state,
num_layers=num_rnn_layers,
rnn_type=rnn_type,
)
self.actor = LinearActorHead(self._hidden_size, action_space.n)
self.critic = LinearCriticHead(self._hidden_size)
relative_dist_embedding_size = torch.Tensor([3, 100, obj_state_embedding_size])
self.relative_dist_embedding = input_embedding_net(
relative_dist_embedding_size.long().tolist(), dropout=0
)
self.train()
@property
def recurrent_hidden_state_size(self) -> int:
"""The recurrent hidden state size of the model."""
return self._hidden_size
@property
def num_recurrent_layers(self) -> int:
"""Number of recurrent hidden layers."""
return self.state_encoder.num_recurrent_layers
def _recurrent_memory_specification(self):
return dict(
rnn=(
(
("layer", self.num_recurrent_layers),
("sampler", None),
("hidden", self.recurrent_hidden_state_size),
),
torch.float32,
)
)
def get_relative_distance_embedding(
self, state_tensor: torch.Tensor
) -> torch.FloatTensor:
return self.relative_dist_embedding(state_tensor)
def forward( # type:ignore
self,
observations: ObservationType,
memory: Memory,
prev_actions: torch.Tensor,
masks: torch.FloatTensor,
) -> Tuple[ActorCriticOutput[DistributionType], Optional[Memory]]:
"""Processes input batched observations to produce new actor and critic
values. Processes input batched observations (along with prior hidden
states, previous actions, and masks denoting which recurrent hidden
states should be masked) and returns an `ActorCriticOutput` object
containing the model's policy (distribution over actions) and
evaluation of the current state (value).
# Parameters
observations : Batched input observations.
memory : `Memory` containing the hidden states from initial timepoints.
prev_actions : Tensor of previous actions taken.
masks : Masks applied to hidden states. See `RNNStateEncoder`.
# Returns
Tuple of the `ActorCriticOutput` and recurrent hidden state.
"""
arm2obj_dist = self.get_relative_distance_embedding(
observations["relative_agent_arm_to_obj"]
)
obj2goal_dist = self.get_relative_distance_embedding(
observations["relative_obj_to_goal"]
)
perception_embed = self.visual_encoder(observations)
pickup_bool = observations["pickedup_object"]
after_pickup = pickup_bool == 1
distances = arm2obj_dist
distances[after_pickup] = obj2goal_dist[after_pickup]
x = [distances, perception_embed]
x_cat = torch.cat(x, dim=-1)
x_out, rnn_hidden_states = self.state_encoder(
x_cat, memory.tensor("rnn"), masks
)
actor_out = self.actor(x_out)
critic_out = self.critic(x_out)
actor_critic_output = ActorCriticOutput(
distributions=actor_out, values=critic_out, extras={}
)
updated_memory = memory.set_tensor("rnn", rnn_hidden_states)
return (
actor_critic_output,
updated_memory,
)
| ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/models/arm_pointnav_models.py |
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class LinearActorHeadNoCategory(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_inputs: int, num_outputs: int):
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(num_inputs, num_outputs)
nn.init.orthogonal_(self.linear.weight, gain=0.01)
nn.init.constant_(self.linear.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x: torch.FloatTensor): # type: ignore
x = self.linear(x) # type:ignore
assert len(x.shape) == 3
return x
| ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/models/base_models.py |
ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/models/__init__.py |
|
"""Baseline models for use in the Arm Point Navigation task.
Arm Point Navigation is currently available as a Task in ManipulaTHOR.
"""
from typing import Tuple, Optional
import gym
import torch
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.policy import (
ActorCriticModel,
LinearCriticHead,
DistributionType,
Memory,
ObservationType,
)
from allenact.base_abstractions.distributions import CategoricalDistr
from allenact.base_abstractions.misc import ActorCriticOutput
from allenact.embodiedai.models.basic_models import SimpleCNN, RNNStateEncoder
from gym.spaces.dict import Dict as SpaceDict
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.models.base_models import (
LinearActorHeadNoCategory,
)
from projects.manipulathor_baselines.armpointnav_baselines.models.manipulathor_net_utils import (
input_embedding_net,
)
class DisjointArmPointNavBaselineActorCritic(ActorCriticModel[CategoricalDistr]):
"""Disjoint Baseline recurrent actor critic model for armpointnav.
# Attributes
action_space : The space of actions available to the agent. Currently only discrete
actions are allowed (so this space will always be of type `gym.spaces.Discrete`).
observation_space : The observation space expected by the agent. This observation space
should include (optionally) 'rgb' images and 'depth' images and is required to
have a component corresponding to the goal `goal_sensor_uuid`.
goal_sensor_uuid : The uuid of the sensor of the goal object. See `GoalObjectTypeThorSensor`
as an example of such a sensor.
hidden_size : The hidden size of the GRU RNN.
object_type_embedding_dim: The dimensionality of the embedding corresponding to the goal
object type.
"""
def __init__(
self,
action_space: gym.spaces.Discrete,
observation_space: SpaceDict,
hidden_size=512,
obj_state_embedding_size=512,
trainable_masked_hidden_state: bool = False,
num_rnn_layers=1,
rnn_type="GRU",
):
"""Initializer.
See class documentation for parameter definitions.
"""
super().__init__(action_space=action_space, observation_space=observation_space)
self._hidden_size = hidden_size
self.object_type_embedding_size = obj_state_embedding_size
self.visual_encoder_pick = SimpleCNN(
self.observation_space,
self._hidden_size,
rgb_uuid=None,
depth_uuid="depth_lowres",
)
self.visual_encoder_drop = SimpleCNN(
self.observation_space,
self._hidden_size,
rgb_uuid=None,
depth_uuid="depth_lowres",
)
self.state_encoder = RNNStateEncoder(
(self._hidden_size) + obj_state_embedding_size,
self._hidden_size,
trainable_masked_hidden_state=trainable_masked_hidden_state,
num_layers=num_rnn_layers,
rnn_type=rnn_type,
)
self.actor_pick = LinearActorHeadNoCategory(self._hidden_size, action_space.n)
self.critic_pick = LinearCriticHead(self._hidden_size)
self.actor_drop = LinearActorHeadNoCategory(self._hidden_size, action_space.n)
self.critic_drop = LinearCriticHead(self._hidden_size)
# self.object_state_embedding = nn.Embedding(num_embeddings=6, embedding_dim=obj_state_embedding_size)
relative_dist_embedding_size = torch.Tensor([3, 100, obj_state_embedding_size])
self.relative_dist_embedding_pick = input_embedding_net(
relative_dist_embedding_size.long().tolist(), dropout=0
)
self.relative_dist_embedding_drop = input_embedding_net(
relative_dist_embedding_size.long().tolist(), dropout=0
)
self.train()
@property
def recurrent_hidden_state_size(self) -> int:
"""The recurrent hidden state size of the model."""
return self._hidden_size
@property
def num_recurrent_layers(self) -> int:
"""Number of recurrent hidden layers."""
return self.state_encoder.num_recurrent_layers
def _recurrent_memory_specification(self):
return dict(
rnn=(
(
("layer", self.num_recurrent_layers),
("sampler", None),
("hidden", self.recurrent_hidden_state_size),
),
torch.float32,
)
)
def forward( # type:ignore
self,
observations: ObservationType,
memory: Memory,
prev_actions: torch.Tensor,
masks: torch.FloatTensor,
) -> Tuple[ActorCriticOutput[DistributionType], Optional[Memory]]:
"""Processes input batched observations to produce new actor and critic
values. Processes input batched observations (along with prior hidden
states, previous actions, and masks denoting which recurrent hidden
states should be masked) and returns an `ActorCriticOutput` object
containing the model's policy (distribution over actions) and
evaluation of the current state (value).
# Parameters
observations : Batched input observations.
memory : `Memory` containing the hidden states from initial timepoints.
prev_actions : Tensor of previous actions taken.
masks : Masks applied to hidden states. See `RNNStateEncoder`.
# Returns
Tuple of the `ActorCriticOutput` and recurrent hidden state.
"""
arm2obj_dist = self.relative_dist_embedding_pick(
observations["relative_agent_arm_to_obj"]
)
obj2goal_dist = self.relative_dist_embedding_drop(
observations["relative_obj_to_goal"]
)
perception_embed_pick = self.visual_encoder_pick(observations)
perception_embed_drop = self.visual_encoder_drop(observations)
pickup_bool = observations["pickedup_object"]
after_pickup = pickup_bool == 1
distances = arm2obj_dist
distances[after_pickup] = obj2goal_dist[after_pickup]
perception_embed = perception_embed_pick
perception_embed[after_pickup] = perception_embed_drop[after_pickup]
x = [distances, perception_embed]
x_cat = torch.cat(x, dim=-1) # type: ignore
x_out, rnn_hidden_states = self.state_encoder(
x_cat, memory.tensor("rnn"), masks
)
actor_out_pick = self.actor_pick(x_out)
critic_out_pick = self.critic_pick(x_out)
actor_out_drop = self.actor_drop(x_out)
critic_out_drop = self.critic_drop(x_out)
actor_out = actor_out_pick
actor_out[after_pickup] = actor_out_drop[after_pickup]
critic_out = critic_out_pick
critic_out[after_pickup] = critic_out_drop[after_pickup]
actor_out = CategoricalDistr(logits=actor_out)
actor_critic_output = ActorCriticOutput(
distributions=actor_out, values=critic_out, extras={}
)
updated_memory = memory.set_tensor("rnn", rnn_hidden_states)
return (
actor_critic_output,
updated_memory,
)
| ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/models/disjoint_arm_pointnav_models.py |
import pdb
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
def upshuffle(
in_planes, out_planes, upscale_factor, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1
):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
in_planes,
out_planes * upscale_factor ** 2,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride,
padding=padding,
),
nn.PixelShuffle(upscale_factor),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
)
def upshufflenorelu(
in_planes, out_planes, upscale_factor, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1
):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
in_planes,
out_planes * upscale_factor ** 2,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride,
padding=padding,
),
nn.PixelShuffle(upscale_factor),
)
def combine_block_w_bn(in_planes, out_planes):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, 1, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_planes),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
)
def conv2d_block(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=1):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_planes),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(out_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_planes),
)
def combine_block_w_do(in_planes, out_planes, dropout=0.0):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, 1, 1), nn.LeakyReLU(), nn.Dropout(dropout),
)
def combine_block_no_do(in_planes, out_planes):
return nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, 1, 1), nn.LeakyReLU(),)
def linear_block(in_features, out_features, dropout=0.0):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features, out_features), nn.LeakyReLU(), nn.Dropout(dropout),
)
def linear_block_norelu(in_features, out_features):
return nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(in_features, out_features),)
def input_embedding_net(list_of_feature_sizes, dropout=0.0):
modules = []
for i in range(len(list_of_feature_sizes) - 1):
input_size, output_size = list_of_feature_sizes[i : i + 2]
if i + 2 == len(list_of_feature_sizes):
modules.append(linear_block_norelu(input_size, output_size))
else:
modules.append(linear_block(input_size, output_size, dropout=dropout))
return nn.Sequential(*modules)
def _upsample_add(x, y):
_, _, H, W = y.size()
return F.upsample(x, size=(H, W), mode="bilinear") + y
def replace_all_relu_w_leakyrelu(model):
pdb.set_trace()
print("Not sure if using this is a good idea")
modules = model._modules
for m in modules.keys():
module = modules[m]
if isinstance(module, nn.ReLU):
model._modules[m] = nn.LeakyReLU()
elif isinstance(module, nn.Module):
model._modules[m] = replace_all_relu_w_leakyrelu(module)
return model
def replace_all_leakyrelu_w_relu(model):
modules = model._modules
for m in modules.keys():
module = modules[m]
if isinstance(module, nn.LeakyReLU):
model._modules[m] = nn.ReLU()
elif isinstance(module, nn.Module):
model._modules[m] = replace_all_leakyrelu_w_relu(module)
return model
def replace_all_bn_w_groupnorm(model):
pdb.set_trace()
print("Not sure if using this is a good idea")
modules = model._modules
for m in modules.keys():
module = modules[m]
if isinstance(module, nn.BatchNorm2d) or isinstance(module, nn.BatchNorm1d):
feature_number = module.num_features
model._modules[m] = nn.GroupNorm(32, feature_number)
elif isinstance(module, nn.BatchNorm3d):
raise Exception("Not implemented")
elif isinstance(module, nn.Module):
model._modules[m] = replace_all_bn_w_groupnorm(module)
return model
def flat_temporal(tensor, batch_size, sequence_length):
tensor_shape = [s for s in tensor.shape]
assert tensor_shape[0] == batch_size and tensor_shape[1] == sequence_length
result_shape = [batch_size * sequence_length] + tensor_shape[2:]
return tensor.contiguous().view(result_shape)
def unflat_temporal(tensor, batch_size, sequence_length):
tensor_shape = [s for s in tensor.shape]
assert tensor_shape[0] == batch_size * sequence_length
result_shape = [batch_size, sequence_length] + tensor_shape[1:]
return tensor.contiguous().view(result_shape)
| ask4help-main | projects/manipulathor_baselines/armpointnav_baselines/models/manipulathor_net_utils.py |
### THIS FILE ORIGINALLY LOCATED AT '/home/kunals/eai_proj/clip_model/allenact/projects/objectnav_baselines/experiments/robothor/objectnav_robothor_rgb_resnet50gru_ddppo.py'
from allenact_plugins.ithor_plugin.ithor_sensors import (
RGBSensorThor,
GoalObjectTypeThorSensor,
)
from projects.objectnav_baselines.experiments.objectnav_mixin_ddppo import (
ObjectNavMixInPPOConfig,
)
from projects.objectnav_baselines.experiments.objectnav_mixin_resnetgru import (
ObjectNavMixInResNetGRUConfig,
)
from projects.objectnav_baselines.experiments.robothor.objectnav_robothor_base import (
ObjectNavRoboThorBaseConfig,
)
class ObjectNavRoboThorRGBPPOExperimentConfig(
ObjectNavRoboThorBaseConfig, ObjectNavMixInPPOConfig, ObjectNavMixInResNetGRUConfig,
):
"""An Object Navigation experiment configuration in RoboThor with RGB
input."""
RESNET_TYPE = "RN50"
SENSORS = [
RGBSensorThor(
height=ObjectNavRoboThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
width=ObjectNavRoboThorBaseConfig.SCREEN_SIZE,
use_resnet_normalization=True,
uuid="rgb_lowres",
),
GoalObjectTypeThorSensor(
object_types=ObjectNavRoboThorBaseConfig.TARGET_TYPES,
),
]
@classmethod
def tag(cls):
return "Objectnav-RoboTHOR-RGB-ResNet50GRU-DDPPO"
| ask4help-main | experiment_output/used_configs/Objectnav-RoboTHOR-RGB-ResNet50GRU-DDPPO/2022-02-10_14-00-37/objectnav_robothor_rgb_resnet50gru_ddppo.py |
### THIS FILE ORIGINALLY LOCATED AT '/home/kunals/eai_proj/clip_model/allenact/projects/objectnav_baselines/experiments/robothor/objectnav_robothor_base.py'
import os
from abc import ABC
from typing import Optional, List, Any, Dict
import torch
from allenact.utils.misc_utils import prepare_locals_for_super
from projects.objectnav_baselines.experiments.objectnav_thor_base import (
ObjectNavThorBaseConfig,
)
class ObjectNavRoboThorBaseConfig(ObjectNavThorBaseConfig, ABC):
"""The base config for all RoboTHOR ObjectNav experiments."""
THOR_COMMIT_ID = "bad5bc2b250615cb766ffb45d455c211329af17e"
THOR_COMMIT_ID_FOR_RAND_MATERIALS = "9549791ce2e7f472063a10abb1fb7664159fec23"
AGENT_MODE = "locobot"
DEFAULT_NUM_TRAIN_PROCESSES = 1 if torch.cuda.is_available() else 1
TRAIN_DATASET_DIR = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "datasets/robothor-objectnav/train")
VAL_DATASET_DIR = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "datasets/robothor-objectnav/val")
TEST_DATASET_DIR = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "datasets/robothor-objectnav/test")
TARGET_TYPES = tuple(
sorted(
[
"AlarmClock",
"Apple",
"BaseballBat",
"BasketBall",
"Bowl",
"GarbageCan",
"HousePlant",
"Laptop",
"Mug",
"SprayBottle",
"Television",
"Vase",
]
)
)
def train_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
kwargs = super(ObjectNavRoboThorBaseConfig, self).train_task_sampler_args(
**prepare_locals_for_super(locals())
)
if self.randomize_train_materials:
kwargs["env_args"]["commit_id"] = self.THOR_COMMIT_ID_FOR_RAND_MATERIALS
return kwargs
| ask4help-main | experiment_output/used_configs/Objectnav-RoboTHOR-RGB-ResNet50GRU-DDPPO/2022-02-10_14-00-37/objectnav_robothor_base.py |
### THIS FILE ORIGINALLY LOCATED AT '/home/kunals/eai_proj/clip_model/allenact/projects/objectnav_baselines/experiments/objectnav_thor_base.py'
import glob
import os
import platform
from abc import ABC
from math import ceil
from typing import Dict, Any, List, Optional, Sequence, Tuple, cast
import gym
import numpy as np
import torch
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import MachineParams
from allenact.base_abstractions.preprocessor import SensorPreprocessorGraph
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import SensorSuite, ExpertActionSensor
from allenact.base_abstractions.task import TaskSampler
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import evenly_distribute_count_into_bins
from allenact.utils.system import get_logger
from allenact_plugins.ithor_plugin.ithor_util import (
horizontal_to_vertical_fov,
get_open_x_displays,
)
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_sensors import DepthSensorThor
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_task_samplers import (
ObjectNavDatasetTaskSampler,
)
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_tasks import ObjectNavTask
from projects.objectnav_baselines.experiments.objectnav_base import ObjectNavBaseConfig
import ai2thor
from packaging import version
if ai2thor.__version__ not in ["0.0.1", None] and version.parse(
ai2thor.__version__
) < version.parse("3.2.0"):
raise ImportError(
"To run the AI2-THOR ObjectNav baseline experiments you must use"
" ai2thor version 3.2.0 or higher."
)
class ObjectNavThorBaseConfig(ObjectNavBaseConfig, ABC):
"""The base config for all AI2-THOR ObjectNav experiments."""
DEFAULT_NUM_TRAIN_PROCESSES: Optional[int] = None
DEFAULT_TRAIN_GPU_IDS = tuple(range(torch.cuda.device_count()))
DEFAULT_VALID_GPU_IDS = (torch.cuda.device_count() - 1,)
DEFAULT_TEST_GPU_IDS = (torch.cuda.device_count() - 1,)
TRAIN_DATASET_DIR: Optional[str] = None
VAL_DATASET_DIR: Optional[str] = None
TEST_DATASET_DIR: Optional[str] = None
AGENT_MODE = "default"
TARGET_TYPES: Optional[Sequence[str]] = None
THOR_COMMIT_ID: Optional[str] = None
THOR_IS_HEADLESS: bool = False
def __init__(
self,
num_train_processes: Optional[int] = None,
num_test_processes: Optional[int] = None,
test_on_validation: bool = False,
train_gpu_ids: Optional[Sequence[int]] = None,
val_gpu_ids: Optional[Sequence[int]] = None,
test_gpu_ids: Optional[Sequence[int]] = None,
randomize_train_materials: bool = False,
):
super().__init__()
def v_or_default(v, default):
return v if v is not None else default
self.num_train_processes = v_or_default(
num_train_processes, self.DEFAULT_NUM_TRAIN_PROCESSES
)
self.num_test_processes = v_or_default(
num_test_processes, (10 if torch.cuda.is_available() else 1)
)
self.test_on_validation = test_on_validation
self.train_gpu_ids = v_or_default(train_gpu_ids, self.DEFAULT_TRAIN_GPU_IDS)
self.val_gpu_ids = v_or_default(val_gpu_ids, self.DEFAULT_VALID_GPU_IDS)
self.test_gpu_ids = v_or_default(test_gpu_ids, self.DEFAULT_TEST_GPU_IDS)
self.sampler_devices = self.train_gpu_ids
self.randomize_train_materials = randomize_train_materials
@classmethod
def env_args(cls):
assert cls.THOR_COMMIT_ID is not None
return dict(
width=cls.CAMERA_WIDTH,
height=cls.CAMERA_HEIGHT,
commit_id=cls.THOR_COMMIT_ID,
continuousMode=True,
applyActionNoise=cls.STOCHASTIC,
rotateStepDegrees=cls.ROTATION_DEGREES,
visibilityDistance=cls.VISIBILITY_DISTANCE,
gridSize=cls.STEP_SIZE,
snapToGrid=False,
agentMode=cls.AGENT_MODE,
fieldOfView=horizontal_to_vertical_fov(
horizontal_fov_in_degrees=cls.HORIZONTAL_FIELD_OF_VIEW,
width=cls.CAMERA_WIDTH,
height=cls.CAMERA_HEIGHT,
),
include_private_scenes=False,
renderDepthImage=any(isinstance(s, DepthSensorThor) for s in cls.SENSORS),
)
def machine_params(self, mode="train", **kwargs):
sampler_devices: Sequence[torch.device] = []
devices: Sequence[torch.device]
if mode == "train":
workers_per_device = 1
devices = (
[torch.device("cpu")]
if not torch.cuda.is_available()
else cast(Tuple, self.train_gpu_ids) * workers_per_device
)
nprocesses = evenly_distribute_count_into_bins(
self.num_train_processes, max(len(devices), 1)
)
sampler_devices = self.sampler_devices
elif mode == "valid":
nprocesses = 1
devices = (
[torch.device("cpu")]
if not torch.cuda.is_available()
else self.val_gpu_ids
)
elif mode == "test":
devices = (
[torch.device("cpu")]
if not torch.cuda.is_available()
else self.test_gpu_ids
)
nprocesses = evenly_distribute_count_into_bins(
self.num_test_processes, max(len(devices), 1)
)
else:
raise NotImplementedError("mode must be 'train', 'valid', or 'test'.")
sensors = [*self.SENSORS]
if mode != "train":
sensors = [s for s in sensors if not isinstance(s, ExpertActionSensor)]
sensor_preprocessor_graph = (
SensorPreprocessorGraph(
source_observation_spaces=SensorSuite(sensors).observation_spaces,
preprocessors=self.preprocessors(),
)
if mode == "train"
or (
(isinstance(nprocesses, int) and nprocesses > 0)
or (isinstance(nprocesses, Sequence) and sum(nprocesses) > 0)
)
else None
)
return MachineParams(
nprocesses=nprocesses,
devices=devices,
sampler_devices=sampler_devices
if mode == "train"
else devices, # ignored with > 1 gpu_ids
sensor_preprocessor_graph=sensor_preprocessor_graph,
)
@classmethod
def make_sampler_fn(cls, **kwargs) -> TaskSampler:
return ObjectNavDatasetTaskSampler(**kwargs)
@staticmethod
def _partition_inds(n: int, num_parts: int):
return np.round(np.linspace(0, n, num_parts + 1, endpoint=True)).astype(
np.int32
)
def _get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
self,
scenes_dir: str,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]],
seeds: Optional[List[int]],
deterministic_cudnn: bool,
include_expert_sensor: bool = True,
allow_oversample: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
path = os.path.join(scenes_dir, "*.json.gz")
scenes = [scene.split("/")[-1].split(".")[0] for scene in glob.glob(path)]
if len(scenes) == 0:
raise RuntimeError(
(
"Could find no scene dataset information in directory {}."
" Are you sure you've downloaded them? "
" If not, see https://allenact.org/installation/download-datasets/ information"
" on how this can be done."
).format(scenes_dir)
)
oversample_warning = (
f"Warning: oversampling some of the scenes ({scenes}) to feed all processes ({total_processes})."
" You can avoid this by setting a number of workers divisible by the number of scenes"
)
if total_processes > len(scenes): # oversample some scenes -> bias
if not allow_oversample:
raise RuntimeError(
f"Cannot have `total_processes > len(scenes)`"
f" ({total_processes} > {len(scenes)}) when `allow_oversample` is `False`."
)
if total_processes % len(scenes) != 0:
get_logger().warning(oversample_warning)
scenes = scenes * int(ceil(total_processes / len(scenes)))
scenes = scenes[: total_processes * (len(scenes) // total_processes)]
elif len(scenes) % total_processes != 0:
get_logger().warning(oversample_warning)
inds = self._partition_inds(len(scenes), total_processes)
if not self.THOR_IS_HEADLESS:
x_display: Optional[str] = None
if platform.system() == "Linux":
x_displays = get_open_x_displays(throw_error_if_empty=True)
if len([d for d in devices if d != torch.device("cpu")]) > len(
x_displays
):
get_logger().warning(
f"More GPU devices found than X-displays (devices: `{x_displays}`, x_displays: `{x_displays}`)."
f" This is not necessarily a bad thing but may mean that you're not using GPU memory as"
f" efficiently as possible. Consider following the instructions here:"
f" https://allenact.org/installation/installation-framework/#installation-of-ithor-ithor-plugin"
f" describing how to start an X-display on every GPU."
)
x_display = x_displays[process_ind % len(x_displays)]
device_dict = dict(x_display=x_display)
else:
device_dict = dict(gpu_device=devices[process_ind % len(devices)])
return {
"scenes": scenes[inds[process_ind] : inds[process_ind + 1]],
"object_types": self.TARGET_TYPES,
"max_steps": self.MAX_STEPS,
"sensors": [
s
for s in self.SENSORS
if (include_expert_sensor or not isinstance(s, ExpertActionSensor))
],
"action_space": gym.spaces.Discrete(
len(ObjectNavTask.class_action_names())
),
"seed": seeds[process_ind] if seeds is not None else None,
"deterministic_cudnn": deterministic_cudnn,
"rewards_config": self.REWARD_CONFIG,
"env_args": {**self.env_args(), **device_dict},
}
def train_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
scenes_dir=os.path.join(self.TRAIN_DATASET_DIR, "episodes"),
process_ind=process_ind,
total_processes=total_processes,
devices=devices,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
allow_oversample=True,
)
res["scene_directory"] = self.TRAIN_DATASET_DIR
res["loop_dataset"] = True
res["allow_flipping"] = True
res["randomize_materials_in_training"] = self.randomize_train_materials
return res
def valid_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
scenes_dir=os.path.join(self.VAL_DATASET_DIR, "episodes"),
process_ind=process_ind,
total_processes=total_processes,
devices=devices,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
include_expert_sensor=False,
allow_oversample=False,
)
res["scene_directory"] = self.VAL_DATASET_DIR
res["loop_dataset"] = False
return res
def test_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
if self.test_on_validation or self.TEST_DATASET_DIR is None:
if not self.test_on_validation:
get_logger().warning(
"`test_on_validation` is set to `True` and thus we will run evaluation on the validation set instead."
" Be careful as the saved metrics json and tensorboard files **will still be labeled as"
" 'test' rather than 'valid'**."
)
else:
get_logger().warning(
"No test dataset dir detected, running test on validation set instead."
" Be careful as the saved metrics json and tensorboard files *will still be labeled as"
" 'test' rather than 'valid'**."
)
return self.valid_task_sampler_args(
process_ind=process_ind,
total_processes=total_processes,
devices=devices,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
)
else:
res = self._get_sampler_args_for_scene_split(
scenes_dir=os.path.join(self.TEST_DATASET_DIR, "episodes"),
process_ind=process_ind,
total_processes=total_processes,
devices=devices,
seeds=seeds,
deterministic_cudnn=deterministic_cudnn,
include_expert_sensor=False,
allow_oversample=False,
)
res["env_args"]["all_metadata_available"] = False
res["rewards_config"] = {**res["rewards_config"], "shaping_weight": 0}
res["scene_directory"] = self.TEST_DATASET_DIR
res["loop_dataset"] = False
return res
| ask4help-main | experiment_output/used_configs/Objectnav-RoboTHOR-RGB-ResNet50GRU-DDPPO/2022-02-10_14-00-37/objectnav_thor_base.py |
### THIS FILE ORIGINALLY LOCATED AT '/home/kunals/eai_proj/clip_model/allenact/projects/objectnav_baselines/experiments/objectnav_mixin_resnetgru.py'
from typing import Sequence, Union
import gym
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision import models
from allenact.base_abstractions.preprocessor import Preprocessor
from allenact.embodiedai.preprocessors.resnet import ResNetPreprocessor
from allenact.embodiedai.sensors.vision_sensors import RGBSensor, DepthSensor
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import Builder
from allenact_plugins.ithor_plugin.ithor_sensors import GoalObjectTypeThorSensor
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_tasks import ObjectNavTask
from projects.objectnav_baselines.experiments.objectnav_base import ObjectNavBaseConfig
from projects.objectnav_baselines.experiments.robothor.objectnav_robothor_base import (
ObjectNavRoboThorBaseConfig,
)
from projects.objectnav_baselines.models.object_nav_models import (
ResnetTensorObjectNavActorCritic,
)
class ObjectNavMixInResNetGRUConfig(ObjectNavBaseConfig):
RESNET_TYPE: str
@classmethod
def preprocessors(cls) -> Sequence[Union[Preprocessor, Builder[Preprocessor]]]:
if not hasattr(cls, "RESNET_TYPE"):
raise RuntimeError(
"When subclassing `ObjectNavMixInResNetGRUConfig` we now expect that you have specified `RESNET_TYPE`"
" as a class variable of your subclass (e.g. `RESNET_TYPE = 'RN18'` to use a ResNet18 model)."
" Alternatively you can instead subclass `ObjectNavMixInResNet18GRUConfig` which does this"
" specification for you."
)
preprocessors = []
if cls.RESNET_TYPE in ["RN18", "RN34"]:
output_shape = (512, 7, 7)
elif cls.RESNET_TYPE in ["RN50", "RN101", "RN152"]:
output_shape = (2048, 7, 7)
else:
raise NotImplementedError(
f"`RESNET_TYPE` must be one 'RNx' with x equaling one of"
f" 18, 34, 50, 101, or 152."
)
rgb_sensor = next((s for s in cls.SENSORS if isinstance(s, RGBSensor)), None)
if rgb_sensor is not None:
preprocessors.append(
ResNetPreprocessor(
input_height=cls.SCREEN_SIZE,
input_width=cls.SCREEN_SIZE,
output_width=output_shape[2],
output_height=output_shape[1],
output_dims=output_shape[0],
pool=False,
torchvision_resnet_model=getattr(
models, f"resnet{cls.RESNET_TYPE.replace('RN', '')}"
),
input_uuids=[rgb_sensor.uuid],
output_uuid="rgb_resnet_imagenet",
)
)
depth_sensor = next(
(s for s in cls.SENSORS if isinstance(s, DepthSensor)), None
)
if depth_sensor is not None:
preprocessors.append(
ResNetPreprocessor(
input_height=cls.SCREEN_SIZE,
input_width=cls.SCREEN_SIZE,
output_width=output_shape[2],
output_height=output_shape[1],
output_dims=output_shape[0],
pool=False,
torchvision_resnet_model=getattr(
models, f"resnet{cls.RESNET_TYPE.replace('RN', '')}"
),
input_uuids=[depth_sensor.uuid],
output_uuid="depth_resnet_imagenet",
)
)
return preprocessors
@classmethod
def create_model(cls, **kwargs) -> nn.Module:
has_rgb = any(isinstance(s, RGBSensor) for s in cls.SENSORS)
has_depth = any(isinstance(s, DepthSensor) for s in cls.SENSORS)
goal_sensor_uuid = next(
(s.uuid for s in cls.SENSORS if isinstance(s, GoalObjectTypeThorSensor)),
None,
)
return ResnetTensorObjectNavActorCritic(
action_space=gym.spaces.Discrete(len(ObjectNavTask.class_action_names())),
observation_space=kwargs["sensor_preprocessor_graph"].observation_spaces,
goal_sensor_uuid=goal_sensor_uuid,
rgb_resnet_preprocessor_uuid="rgb_resnet_imagenet" if has_rgb else None,
depth_resnet_preprocessor_uuid="depth_resnet_imagenet"
if has_depth
else None,
hidden_size=512,
goal_dims=32,
)
| ask4help-main | experiment_output/used_configs/Objectnav-RoboTHOR-RGB-ResNet50GRU-DDPPO/2022-02-10_14-00-37/objectnav_mixin_resnetgru.py |
### THIS FILE ORIGINALLY LOCATED AT '/home/kunals/eai_proj/clip_model/allenact/projects/objectnav_baselines/experiments/objectnav_base.py'
from abc import ABC
from typing import Optional, Sequence, Union
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import ExperimentConfig
from allenact.base_abstractions.preprocessor import Preprocessor
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import Sensor
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import Builder
class ObjectNavBaseConfig(ExperimentConfig, ABC):
"""The base object navigation configuration file."""
STEP_SIZE = 0.25
ROTATION_DEGREES = 30.0
VISIBILITY_DISTANCE = 1.0
STOCHASTIC = True
HORIZONTAL_FIELD_OF_VIEW = 79
CAMERA_WIDTH = 400
CAMERA_HEIGHT = 300
SCREEN_SIZE = 224
MAX_STEPS = 500
ADVANCE_SCENE_ROLLOUT_PERIOD: Optional[int] = None
SENSORS: Sequence[Sensor] = []
def __init__(self):
self.REWARD_CONFIG = {
"step_penalty": -0.01,
"goal_success_reward": 10.0,
"failed_stop_reward": 0.0,
"shaping_weight": 1.0,
}
@classmethod
def preprocessors(cls) -> Sequence[Union[Preprocessor, Builder[Preprocessor]]]:
return tuple()
| ask4help-main | experiment_output/used_configs/Objectnav-RoboTHOR-RGB-ResNet50GRU-DDPPO/2022-02-10_14-00-37/objectnav_base.py |
### THIS FILE ORIGINALLY LOCATED AT '/home/kunals/eai_proj/clip_model/allenact/projects/objectnav_baselines/experiments/objectnav_mixin_ddppo.py'
from typing import Dict, Tuple
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import LambdaLR
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.abstract_loss import (
AbstractActorCriticLoss,
)
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses import PPO
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.ppo import PPOConfig
from allenact.embodiedai.aux_losses.losses import (
MultiAuxTaskNegEntropyLoss,
InverseDynamicsLoss,
TemporalDistanceLoss,
CPCA1Loss,
CPCA2Loss,
CPCA4Loss,
CPCA8Loss,
CPCA16Loss,
)
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
from allenact.embodiedai.models.fusion_models import (
AverageFusion,
SoftmaxFusion,
AttentiveFusion,
)
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import (
Builder,
PipelineStage,
TrainingPipeline,
LinearDecay,
)
from projects.objectnav_baselines.experiments.objectnav_base import ObjectNavBaseConfig
class ObjectNavMixInPPOConfig(ObjectNavBaseConfig):
# selected auxiliary uuids
## if comment all the keys, then it's vanilla DD-PPO
AUXILIARY_UUIDS = [
# InverseDynamicsLoss.UUID,
# TemporalDistanceLoss.UUID,
# CPCA1Loss.UUID,
# CPCA4Loss.UUID,
# CPCA8Loss.UUID,
# CPCA16Loss.UUID,
]
ADD_PREV_ACTIONS = False
MULTIPLE_BELIEFS = False
BELIEF_FUSION = ( # choose one
None
# AttentiveFusion.UUID
# AverageFusion.UUID
# SoftmaxFusion.UUID
)
def training_pipeline(self, **kwargs):
# PPO
ppo_steps = int(300000000)
lr = 3e-4
num_mini_batch = 1
update_repeats = 4
num_steps = 128
save_interval = 5000000
log_interval = 10000 if torch.cuda.is_available() else 1
gamma = 0.99
use_gae = True
gae_lambda = 0.95
max_grad_norm = 0.5
named_losses = {"ppo_loss": (PPO(**PPOConfig), 1.0)}
named_losses = self._update_with_auxiliary_losses(named_losses)
return TrainingPipeline(
save_interval=save_interval,
metric_accumulate_interval=log_interval,
optimizer_builder=Builder(optim.Adam, dict(lr=lr)),
num_mini_batch=num_mini_batch,
update_repeats=update_repeats,
max_grad_norm=max_grad_norm,
num_steps=num_steps,
named_losses={key: val[0] for key, val in named_losses.items()},
gamma=gamma,
use_gae=use_gae,
gae_lambda=gae_lambda,
advance_scene_rollout_period=self.ADVANCE_SCENE_ROLLOUT_PERIOD,
pipeline_stages=[
PipelineStage(
loss_names=list(named_losses.keys()),
max_stage_steps=ppo_steps,
loss_weights=[val[1] for val in named_losses.values()],
)
],
lr_scheduler_builder=Builder(
LambdaLR, {"lr_lambda": LinearDecay(steps=ppo_steps)}
),
)
@classmethod
def _update_with_auxiliary_losses(cls, named_losses):
# auxliary losses
aux_loss_total_weight = 2.0
# Total losses
total_aux_losses: Dict[str, Tuple[AbstractActorCriticLoss, float]] = {
InverseDynamicsLoss.UUID: (
InverseDynamicsLoss(
subsample_rate=0.2, subsample_min_num=10, # TODO: test its effects
),
0.05 * aux_loss_total_weight, # should times 2
),
TemporalDistanceLoss.UUID: (
TemporalDistanceLoss(
num_pairs=8, epsiode_len_min=5, # TODO: test its effects
),
0.2 * aux_loss_total_weight, # should times 2
),
CPCA1Loss.UUID: (
CPCA1Loss(subsample_rate=0.2,), # TODO: test its effects
0.05 * aux_loss_total_weight, # should times 2
),
CPCA2Loss.UUID: (
CPCA2Loss(subsample_rate=0.2,), # TODO: test its effects
0.05 * aux_loss_total_weight, # should times 2
),
CPCA4Loss.UUID: (
CPCA4Loss(subsample_rate=0.2,), # TODO: test its effects
0.05 * aux_loss_total_weight, # should times 2
),
CPCA8Loss.UUID: (
CPCA8Loss(subsample_rate=0.2,), # TODO: test its effects
0.05 * aux_loss_total_weight, # should times 2
),
CPCA16Loss.UUID: (
CPCA16Loss(subsample_rate=0.2,), # TODO: test its effects
0.05 * aux_loss_total_weight, # should times 2
),
}
named_losses.update(
{uuid: total_aux_losses[uuid] for uuid in cls.AUXILIARY_UUIDS}
)
if cls.MULTIPLE_BELIEFS: # add weight entropy loss automatically
named_losses[MultiAuxTaskNegEntropyLoss.UUID] = (
MultiAuxTaskNegEntropyLoss(cls.AUXILIARY_UUIDS),
0.01,
)
return named_losses
| ask4help-main | experiment_output/used_configs/Objectnav-RoboTHOR-RGB-ResNet50GRU-DDPPO/2022-02-10_14-00-37/objectnav_mixin_ddppo.py |
### THIS FILE ORIGINALLY LOCATED AT '/usr/lib/python3.8/abc.py'
# Copyright 2007 Google, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
# Licensed to PSF under a Contributor Agreement.
"""Abstract Base Classes (ABCs) according to PEP 3119."""
def abstractmethod(funcobj):
"""A decorator indicating abstract methods.
Requires that the metaclass is ABCMeta or derived from it. A
class that has a metaclass derived from ABCMeta cannot be
instantiated unless all of its abstract methods are overridden.
The abstract methods can be called using any of the normal
'super' call mechanisms. abstractmethod() may be used to declare
abstract methods for properties and descriptors.
Usage:
class C(metaclass=ABCMeta):
@abstractmethod
def my_abstract_method(self, ...):
...
"""
funcobj.__isabstractmethod__ = True
return funcobj
class abstractclassmethod(classmethod):
"""A decorator indicating abstract classmethods.
Deprecated, use 'classmethod' with 'abstractmethod' instead.
"""
__isabstractmethod__ = True
def __init__(self, callable):
callable.__isabstractmethod__ = True
super().__init__(callable)
class abstractstaticmethod(staticmethod):
"""A decorator indicating abstract staticmethods.
Deprecated, use 'staticmethod' with 'abstractmethod' instead.
"""
__isabstractmethod__ = True
def __init__(self, callable):
callable.__isabstractmethod__ = True
super().__init__(callable)
class abstractproperty(property):
"""A decorator indicating abstract properties.
Deprecated, use 'property' with 'abstractmethod' instead.
"""
__isabstractmethod__ = True
try:
from _abc import (get_cache_token, _abc_init, _abc_register,
_abc_instancecheck, _abc_subclasscheck, _get_dump,
_reset_registry, _reset_caches)
except ImportError:
from _py_abc import ABCMeta, get_cache_token
ABCMeta.__module__ = 'abc'
else:
class ABCMeta(type):
"""Metaclass for defining Abstract Base Classes (ABCs).
Use this metaclass to create an ABC. An ABC can be subclassed
directly, and then acts as a mix-in class. You can also register
unrelated concrete classes (even built-in classes) and unrelated
ABCs as 'virtual subclasses' -- these and their descendants will
be considered subclasses of the registering ABC by the built-in
issubclass() function, but the registering ABC won't show up in
their MRO (Method Resolution Order) nor will method
implementations defined by the registering ABC be callable (not
even via super()).
"""
def __new__(mcls, name, bases, namespace, **kwargs):
cls = super().__new__(mcls, name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
_abc_init(cls)
return cls
def register(cls, subclass):
"""Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
"""
return _abc_register(cls, subclass)
def __instancecheck__(cls, instance):
"""Override for isinstance(instance, cls)."""
return _abc_instancecheck(cls, instance)
def __subclasscheck__(cls, subclass):
"""Override for issubclass(subclass, cls)."""
return _abc_subclasscheck(cls, subclass)
def _dump_registry(cls, file=None):
"""Debug helper to print the ABC registry."""
print(f"Class: {cls.__module__}.{cls.__qualname__}", file=file)
print(f"Inv. counter: {get_cache_token()}", file=file)
(_abc_registry, _abc_cache, _abc_negative_cache,
_abc_negative_cache_version) = _get_dump(cls)
print(f"_abc_registry: {_abc_registry!r}", file=file)
print(f"_abc_cache: {_abc_cache!r}", file=file)
print(f"_abc_negative_cache: {_abc_negative_cache!r}", file=file)
print(f"_abc_negative_cache_version: {_abc_negative_cache_version!r}",
file=file)
def _abc_registry_clear(cls):
"""Clear the registry (for debugging or testing)."""
_reset_registry(cls)
def _abc_caches_clear(cls):
"""Clear the caches (for debugging or testing)."""
_reset_caches(cls)
class ABC(metaclass=ABCMeta):
"""Helper class that provides a standard way to create an ABC using
inheritance.
"""
__slots__ = ()
| ask4help-main | experiment_output/used_configs/Objectnav-RoboTHOR-RGB-ResNet50GRU-DDPPO/2022-02-10_14-00-37/abc.py |
import json
import os
import re
import shutil
import sys
from pathlib import Path
from urllib.request import urlopen
from more_itertools import all_equal
DATASET_DIR = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(Path(__file__)))
def get_habitat_download_info(allow_create: bool = False):
"""Get a dictionary giving a specification of where habitat data lives
online.
# Parameters
allow_create: Whether or not we should try to regenerate the json file that represents
the above dictionary. This is potentially unsafe so please only set this to `True`
if you're sure it will download what you want.
"""
json_save_path = os.path.join(DATASET_DIR, ".habitat_datasets_download_info.json")
if allow_create and not os.path.exists(json_save_path):
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/facebookresearch/habitat-lab/master/README.md"
output = urlopen(url).read().decode("utf-8")
lines = [l.strip() for l in output.split("\n")]
task_table_started = False
table_lines = []
for l in lines:
if l.count("|") > 3 and l[0] == l[-1] == "|":
if task_table_started:
table_lines.append(l)
elif "Task" in l and "Link" in l:
task_table_started = True
table_lines.append(l)
elif task_table_started:
break
url_pat = re.compile("\[.*\]\((.*)\)")
def get_url(in_str: str):
match = re.match(pattern=url_pat, string=in_str)
if match:
return match.group(1)
else:
return in_str
header = None
rows = []
for i, l in enumerate(table_lines):
l = l.strip("|")
entries = [get_url(e.strip().replace("`", "")) for e in l.split("|")]
if i == 0:
header = [e.lower().replace(" ", "_") for e in entries]
elif not all_equal(entries):
rows.append(entries)
link_ind = header.index("link")
extract_ind = header.index("extract_path")
config_ind = header.index("config_to_use")
assert link_ind >= 0
data_info = {}
for row in rows:
id = row[link_ind].split("/")[-1].replace(".zip", "").replace("_", "-")
data_info[id] = {
"link": row[link_ind],
"rel_path": row[extract_ind],
"config_url": row[config_ind],
}
with open(json_save_path, "w") as f:
json.dump(data_info, f)
with open(json_save_path, "r") as f:
return json.load(f)
if __name__ == "__main__":
habitat_dir = os.path.join(DATASET_DIR, "habitat")
os.makedirs(habitat_dir, exist_ok=True)
os.chdir(habitat_dir)
download_info = get_habitat_download_info(allow_create=False)
if len(sys.argv) != 2 or sys.argv[1] not in download_info:
print(
"Incorrect input, expects a single input where this input is one of "
f" {['test-scenes', *sorted(download_info.keys())]}."
)
quit(1)
task_key = sys.argv[1]
task_dl_info = download_info[task_key]
output_archive_name = "__TO_OVERWRITE__.zip"
deletable_dir_name = "__TO_DELETE__"
cmd = f"wget {task_dl_info['link']} -O {output_archive_name}"
if os.system(cmd):
print(f"ERROR: `{cmd}` failed.")
quit(1)
cmd = f"unzip {output_archive_name} -d {deletable_dir_name}"
if os.system(cmd):
print(f"ERROR: `{cmd}` failed.")
quit(1)
download_to_path = task_dl_info["rel_path"].replace("data/", "")
if download_to_path[-1] == "/":
download_to_path = download_to_path[:-1]
os.makedirs(download_to_path, exist_ok=True)
cmd = f"rsync -avz {deletable_dir_name}/ {download_to_path}/"
if os.system(cmd):
print(f"ERROR: `{cmd}` failed.")
quit(1)
os.remove(output_archive_name)
shutil.rmtree(deletable_dir_name)
| ask4help-main | datasets/.habitat_downloader_helper.py |
ask4help-main | tests/__init__.py |
|
ask4help-main | tests/mapping/__init__.py |
|
import os
import platform
import random
import sys
import urllib
import urllib.request
import warnings
from collections import defaultdict
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
from tempfile import mkdtemp
from typing import Dict, List, Tuple, cast
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
import ai2thor
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
import ai2thor.wsgi_server
import compress_pickle
import numpy as np
import torch
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.storage import RolloutStorage
from allenact.base_abstractions.misc import Memory, ActorCriticOutput
from allenact.embodiedai.mapping.mapping_utils.map_builders import SemanticMapBuilder
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import set_seed
from allenact.utils.system import get_logger
from allenact.utils.tensor_utils import batch_observations
from allenact_plugins.ithor_plugin.ithor_sensors import (
RelativePositionChangeTHORSensor,
ReachableBoundsTHORSensor,
BinnedPointCloudMapTHORSensor,
SemanticMapTHORSensor,
)
from allenact_plugins.ithor_plugin.ithor_util import get_open_x_displays
from allenact_plugins.robothor_plugin.robothor_sensors import DepthSensorThor
from constants import ABS_PATH_OF_TOP_LEVEL_DIR
class TestAI2THORMapSensors(object):
def setup_path_for_use_with_rearrangement_project(self) -> bool:
if platform.system() != "Darwin" and len(get_open_x_displays()) == 0:
wrn_msg = "Cannot run tests as there seem to be no open displays!"
warnings.warn(wrn_msg)
get_logger().warning(wrn_msg)
return False
os.chdir(ABS_PATH_OF_TOP_LEVEL_DIR)
sys.path.append(
os.path.join(ABS_PATH_OF_TOP_LEVEL_DIR, "projects/ithor_rearrangement")
)
try:
import rearrange
except ImportError:
wrn_msg = (
"Could not import `rearrange`. Is it possible you have"
" not initialized the submodules (i.e. by running"
" `git submodule init; git submodule update;`)?"
)
warnings.warn(wrn_msg)
get_logger().warning(wrn_msg)
return False
return True
def test_binned_and_semantic_mapping(self, tmpdir):
try:
if not self.setup_path_for_use_with_rearrangement_project():
return
from baseline_configs.rearrange_base import RearrangeBaseExperimentConfig
from baseline_configs.walkthrough.walkthrough_rgb_base import (
WalkthroughBaseExperimentConfig,
)
from rearrange.constants import (
FOV,
PICKUPABLE_OBJECTS,
OPENABLE_OBJECTS,
)
from datagen.datagen_utils import get_scenes
ORDERED_OBJECT_TYPES = list(sorted(PICKUPABLE_OBJECTS + OPENABLE_OBJECTS))
map_range_sensor = ReachableBoundsTHORSensor(margin=1.0)
map_info = dict(
map_range_sensor=map_range_sensor,
vision_range_in_cm=40 * 5,
map_size_in_cm=1050,
resolution_in_cm=5,
)
map_sensors = [
RelativePositionChangeTHORSensor(),
map_range_sensor,
DepthSensorThor(
height=224, width=224, use_normalization=False, uuid="depth",
),
BinnedPointCloudMapTHORSensor(fov=FOV, ego_only=False, **map_info,),
SemanticMapTHORSensor(
fov=FOV,
ego_only=False,
ordered_object_types=ORDERED_OBJECT_TYPES,
**map_info,
),
]
all_sensors = [*WalkthroughBaseExperimentConfig.SENSORS, *map_sensors]
open_x_displays = []
try:
open_x_displays = get_open_x_displays()
except (AssertionError, IOError):
pass
walkthrough_task_sampler = WalkthroughBaseExperimentConfig.make_sampler_fn(
stage="train",
sensors=all_sensors,
scene_to_allowed_rearrange_inds={s: [0] for s in get_scenes("train")},
force_cache_reset=True,
allowed_scenes=None,
seed=1,
x_display=open_x_displays[0] if len(open_x_displays) != 0 else None,
thor_controller_kwargs={
**RearrangeBaseExperimentConfig.THOR_CONTROLLER_KWARGS,
# "server_class": ai2thor.wsgi_server.WsgiServer, # Only for debugging
},
)
targets_path = os.path.join(tmpdir, "rearrange_mapping_examples.pkl.gz")
urllib.request.urlretrieve(
"https://ai2-prior-allenact-public-test.s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/ai2thor_mapping/rearrange_mapping_examples.pkl.gz",
targets_path,
)
goal_obs_dict = compress_pickle.load(targets_path)
def compare_recursive(obs, goal_obs, key_list: List):
if isinstance(obs, Dict):
for k in goal_obs:
compare_recursive(
obs=obs[k], goal_obs=goal_obs[k], key_list=key_list + [k]
)
elif isinstance(obs, (List, Tuple)):
for i in range(len(goal_obs)):
compare_recursive(
obs=obs[i], goal_obs=goal_obs[i], key_list=key_list + [i]
)
else:
# Should be a numpy array at this point
assert isinstance(obs, np.ndarray) and isinstance(
goal_obs, np.ndarray
), f"After {key_list}, not numpy arrays, obs={obs}, goal_obs={goal_obs}"
obs = 1.0 * obs
goal_obs = 1.0 * goal_obs
where_nan = np.isnan(goal_obs)
obs[where_nan] = 0.0
goal_obs[where_nan] = 0.0
assert (
np.abs(1.0 * obs - 1.0 * goal_obs).mean() < 1e-4
), f"Difference of {np.abs(1.0 * obs - 1.0 * goal_obs).mean()} at {key_list}."
observations_dict = defaultdict(lambda: [])
for i in range(5): # Why 5, why not 5?
set_seed(i)
task = walkthrough_task_sampler.next_task()
obs_list = observations_dict[i]
obs_list.append(task.get_observations())
k = 0
compare_recursive(
obs=obs_list[0], goal_obs=goal_obs_dict[i][0], key_list=[i, k]
)
while not task.is_done():
obs = task.step(
action=task.action_names().index(
random.choice(
3
* [
"move_ahead",
"rotate_right",
"rotate_left",
"look_up",
"look_down",
]
+ ["done"]
)
)
).observation
k += 1
obs_list.append(obs)
compare_recursive(
obs=obs,
goal_obs=goal_obs_dict[i][task.num_steps_taken()],
key_list=[i, k],
)
# Free space metric map in RGB using pointclouds coming from depth images. This
# is built iteratively after every step.
# R - is used to encode points at a height < 0.02m (i.e. the floor)
# G - is used to encode points at a height between 0.02m and 2m, i.e. objects the agent would run into
# B - is used to encode points higher than 2m, i.e. ceiling
# Uncomment if you wish to visualize the observations:
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# plt.imshow(
# np.flip(255 * (obs["binned_pc_map"]["map"] > 0), 0)
# ) # np.flip because we expect "up" to be -row
# plt.title("Free space map")
# plt.show()
# plt.close()
# See also `obs["binned_pc_map"]["egocentric_update"]` to see the
# the metric map from the point of view of the agent before it is
# rotated into the world-space coordinates and merged with past observations.
# Semantic map in RGB which is iteratively revealed using depth maps to figure out what
# parts of the scene the agent has seen so far.
# This map has shape 210x210x72 with the 72 channels corresponding to the 72
# object types in `ORDERED_OBJECT_TYPES`
semantic_map = obs["semantic_map"]["map"]
# We can't display all 72 channels in an RGB image so instead we randomly assign
# each object a color and then just allow them to overlap each other
colored_semantic_map = SemanticMapBuilder.randomly_color_semantic_map(
semantic_map
)
# Here's the full semantic map with nothing masked out because the agent
# hasn't seen it yet
colored_semantic_map_no_fog = SemanticMapBuilder.randomly_color_semantic_map(
map_sensors[-1].semantic_map_builder.ground_truth_semantic_map
)
# Uncomment if you wish to visualize the observations:
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# plt.imshow(
# np.flip( # np.flip because we expect "up" to be -row
# np.concatenate(
# (
# colored_semantic_map,
# 255 + 0 * colored_semantic_map[:, :10, :],
# colored_semantic_map_no_fog,
# ),
# axis=1,
# ),
# 0,
# )
# )
# plt.title("Semantic map with and without exploration fog")
# plt.show()
# plt.close()
# See also
# * `obs["semantic_map"]["egocentric_update"]`
# * `obs["semantic_map"]["explored_mask"]`
# * `obs["semantic_map"]["egocentric_mask"]`
# To save observations for comparison against future runs, uncomment the below.
# os.makedirs("tmp_out", exist_ok=True)
# compress_pickle.dump(
# {**observations_dict}, "tmp_out/rearrange_mapping_examples.pkl.gz"
# )
finally:
try:
walkthrough_task_sampler.close()
except NameError:
pass
def test_pretrained_rearrange_walkthrough_mapping_agent(self, tmpdir):
try:
if not self.setup_path_for_use_with_rearrangement_project():
return
from baseline_configs.rearrange_base import RearrangeBaseExperimentConfig
from baseline_configs.walkthrough.walkthrough_rgb_mapping_ppo import (
WalkthroughRGBMappingPPOExperimentConfig,
)
from rearrange.constants import (
FOV,
PICKUPABLE_OBJECTS,
OPENABLE_OBJECTS,
)
from datagen.datagen_utils import get_scenes
open_x_displays = []
try:
open_x_displays = get_open_x_displays()
except (AssertionError, IOError):
pass
walkthrough_task_sampler = WalkthroughRGBMappingPPOExperimentConfig.make_sampler_fn(
stage="train",
scene_to_allowed_rearrange_inds={s: [0] for s in get_scenes("train")},
force_cache_reset=True,
allowed_scenes=None,
seed=2,
x_display=open_x_displays[0] if len(open_x_displays) != 0 else None,
)
named_losses = (
WalkthroughRGBMappingPPOExperimentConfig.training_pipeline().named_losses
)
ckpt_path = os.path.join(
tmpdir, "pretrained_walkthrough_mapping_agent_75mil.pt"
)
if not os.path.exists(ckpt_path):
urllib.request.urlretrieve(
"https://prior-model-weights.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/embodied-ai/rearrangement/walkthrough/pretrained_walkthrough_mapping_agent_75mil.pt",
ckpt_path,
)
state_dict = torch.load(ckpt_path, map_location="cpu",)
walkthrough_model = WalkthroughRGBMappingPPOExperimentConfig.create_model()
walkthrough_model.load_state_dict(state_dict["model_state_dict"])
rollout_storage = RolloutStorage(
num_steps=1,
num_samplers=1,
actor_critic=walkthrough_model,
only_store_first_and_last_in_memory=True,
)
memory = rollout_storage.pick_memory_step(0)
masks = rollout_storage.masks[:1]
binned_map_losses = []
semantic_map_losses = []
for i in range(5):
masks = 0 * masks
set_seed(i + 1)
task = walkthrough_task_sampler.next_task()
def add_step_dim(input):
if isinstance(input, torch.Tensor):
return input.unsqueeze(0)
elif isinstance(input, Dict):
return {k: add_step_dim(v) for k, v in input.items()}
else:
raise NotImplementedError
batch = add_step_dim(batch_observations([task.get_observations()]))
while not task.is_done():
ac_out, memory = cast(
Tuple[ActorCriticOutput, Memory],
walkthrough_model.forward(
observations=batch,
memory=memory,
prev_actions=None,
masks=masks,
),
)
binned_map_losses.append(
named_losses["binned_map_loss"]
.loss(
step_count=0, # Not used in this loss
batch={"observations": batch},
actor_critic_output=ac_out,
)[0]
.item()
)
assert (
binned_map_losses[-1] < 0.16
), f"Binned map loss to large at ({i}, {task.num_steps_taken()})"
semantic_map_losses.append(
named_losses["semantic_map_loss"]
.loss(
step_count=0, # Not used in this loss
batch={"observations": batch},
actor_critic_output=ac_out,
)[0]
.item()
)
assert (
semantic_map_losses[-1] < 0.004
), f"Semantic map loss to large at ({i}, {task.num_steps_taken()})"
masks = masks.fill_(1.0)
obs = task.step(
action=ac_out.distributions.sample().item()
).observation
batch = add_step_dim(batch_observations([obs]))
if task.num_steps_taken() >= 10:
break
# To save observations for comparison against future runs, uncomment the below.
# os.makedirs("tmp_out", exist_ok=True)
# compress_pickle.dump(
# {**observations_dict}, "tmp_out/rearrange_mapping_examples.pkl.gz"
# )
finally:
try:
walkthrough_task_sampler.close()
except NameError:
pass
if __name__ == "__main__":
TestAI2THORMapSensors().test_binned_and_semantic_mapping(mkdtemp()) # type:ignore
# TestAI2THORMapSensors().test_binned_and_semantic_mapping("tmp_out") # Used for local debugging
# TestAI2THORMapSensors().test_pretrained_rearrange_walkthrough_mapping_agent(
# "tmp_out"
# ) # Used for local debugging
| ask4help-main | tests/mapping/test_ai2thor_mapping.py |
from typing import Dict, Any
import torch.multiprocessing as mp
import torch.nn as nn
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import ExperimentConfig
from allenact.base_abstractions.task import TaskSampler
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import TrainingPipeline
# noinspection PyAbstractClass,PyTypeChecker
class MyConfig(ExperimentConfig):
MY_VAR: int = 3
@classmethod
def tag(cls) -> str:
return ""
@classmethod
def training_pipeline(cls, **kwargs) -> TrainingPipeline:
return None
@classmethod
def create_model(cls, **kwargs) -> nn.Module:
return None
@classmethod
def make_sampler_fn(cls, **kwargs) -> TaskSampler:
return None
def my_var_is(self, val):
assert self.MY_VAR == val
# noinspection PyAbstractClass
class MySpecConfig(MyConfig):
MY_VAR = 6
@classmethod
def machine_params(cls, mode="train", **kwargs) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return {}
@classmethod
def tag(cls) -> str:
return "SpecTag"
scfg = MySpecConfig()
class TestFrozenAttribs(object):
def test_frozen_inheritance(self):
from abc import abstractmethod
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import FrozenClassVariables
class SomeBase(metaclass=FrozenClassVariables):
yar = 3
@abstractmethod
def use(self):
raise NotImplementedError()
class SomeDerived(SomeBase):
yar = 33
def use(self):
return self.yar
failed = False
try:
SomeDerived.yar = 6 # Error
except Exception as _:
failed = True
assert failed
inst = SomeDerived()
inst2 = SomeDerived()
inst.yar = 12 # No error
assert inst.use() == 12
assert inst2.use() == 33
@staticmethod
def my_func(config, val):
config.my_var_is(val)
def test_frozen_experiment_config(self):
val = 5
failed = False
try:
MyConfig()
except (RuntimeError, TypeError):
failed = True
assert failed
scfg.MY_VAR = val
scfg.my_var_is(val)
failed = False
try:
MyConfig.MY_VAR = val
except RuntimeError:
failed = True
assert failed
failed = False
try:
MySpecConfig.MY_VAR = val
except RuntimeError:
failed = True
assert failed
for fork_method in ["forkserver", "fork"]:
ctxt = mp.get_context(fork_method)
p = ctxt.Process(target=self.my_func, kwargs=dict(config=scfg, val=val))
p.start()
p.join()
if __name__ == "__main__":
TestFrozenAttribs().test_frozen_inheritance() # type:ignore
TestFrozenAttribs().test_frozen_experiment_config() # type:ignore
| ask4help-main | tests/multiprocessing/test_frozen_attribs.py |
ask4help-main | tests/multiprocessing/__init__.py |
|
ask4help-main | tests/utils/__init__.py |
|
import warnings
from collections import OrderedDict
from typing import Tuple
import numpy as np
import torch
from gym import spaces as gyms
from allenact.utils import spaces_utils as su
class TestSpaces(object):
space = gyms.Dict(
{
"first": gyms.Tuple(
[
gyms.Box(-10, 10, (3, 4)),
gyms.MultiDiscrete([2, 3, 4]),
gyms.Box(-1, 1, ()),
]
),
"second": gyms.Tuple(
[gyms.Dict({"third": gyms.Discrete(11)}), gyms.MultiBinary(8),]
),
}
)
@staticmethod
def same(a, b, bidx=None):
if isinstance(a, OrderedDict):
for key in a:
if not TestSpaces.same(a[key], b[key], bidx):
return False
return True
elif isinstance(a, Tuple):
for it in range(len(a)):
if not TestSpaces.same(a[it], b[it], bidx):
return False
return True
else:
# np.array_equal also works for torch tensors and scalars
if bidx is None:
return np.array_equal(a, b)
else:
return np.array_equal(a, b[bidx])
def test_conversion(self):
gsample = self.space.sample()
asample = su.torch_point(self.space, gsample)
back = su.numpy_point(self.space, asample)
assert self.same(back, gsample)
def test_flatten(self):
# We flatten Discrete to 1 value
assert su.flatdim(self.space) == 25
# gym flattens Discrete to one-hot
assert gyms.flatdim(self.space) == 35
asample = su.torch_point(self.space, self.space.sample())
flattened = su.flatten(self.space, asample)
unflattened = su.unflatten(self.space, flattened)
assert self.same(asample, unflattened)
# suppress `UserWarning: WARN: Box bound precision lowered by casting to float32`
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter("ignore")
flattened_space = su.flatten_space(self.space)
assert flattened_space.shape == (25,)
# The maximum comes from Discrete(11)
assert flattened_space.high.max() == 11.0
assert flattened_space.low.min() == -10.0
gym_flattened_space = gyms.flatten_space(self.space)
assert gym_flattened_space.shape == (35,)
# The maximum comes from Box(-10, 10, (3, 4))
assert gym_flattened_space.high.max() == 10.0
assert gym_flattened_space.low.min() == -10.0
def test_batched(self):
samples = [self.space.sample() for _ in range(10)]
flattened = [
su.flatten(self.space, su.torch_point(self.space, sample))
for sample in samples
]
stacked = torch.stack(flattened, dim=0)
unflattened = su.unflatten(self.space, stacked)
for bidx, refsample in enumerate(samples):
# Compare each torch-ified sample to the corresponding unflattened from the stack
assert self.same(su.torch_point(self.space, refsample), unflattened, bidx)
assert self.same(su.flatten(self.space, unflattened), stacked)
def test_tolist(self):
space = gyms.MultiDiscrete([3, 3])
actions = su.torch_point(space, space.sample()) # single sampler
actions = actions.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0) # add [step, sampler]
flat_actions = su.flatten(space, actions)
al = su.action_list(space, flat_actions)
assert len(al) == 1
assert len(al[0]) == 2
space = gyms.Tuple([gyms.MultiDiscrete([3, 3]), gyms.Discrete(2)])
actions = su.torch_point(space, space.sample()) # single sampler
actions = (
actions[0].unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0),
torch.tensor(actions[1]).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0),
) # add [step, sampler]
flat_actions = su.flatten(space, actions)
al = su.action_list(space, flat_actions)
assert len(al) == 1
assert len(al[0][0]) == 2
assert isinstance(al[0][1], int)
space = gyms.Dict(
{"tuple": gyms.MultiDiscrete([3, 3]), "scalar": gyms.Discrete(2)}
)
actions = su.torch_point(space, space.sample()) # single sampler
actions = OrderedDict(
[
("tuple", actions["tuple"].unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0)),
("scalar", torch.tensor(actions["scalar"]).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0)),
]
)
flat_actions = su.flatten(space, actions)
al = su.action_list(space, flat_actions)
assert len(al) == 1
assert len(al[0]["tuple"]) == 2
assert isinstance(al[0]["scalar"], int)
if __name__ == "__main__":
TestSpaces().test_conversion() # type:ignore
TestSpaces().test_flatten() # type:ignore
TestSpaces().test_batched() # type:ignore
TestSpaces().test_tolist() # type:ignore
| ask4help-main | tests/utils/test_spaces.py |
import hashlib
import os
import imageio
import numpy as np
from torchvision.transforms import transforms
from allenact.utils.tensor_utils import ScaleBothSides
from constants import ABS_PATH_OF_TOP_LEVEL_DIR
to_pil = transforms.ToPILImage() # Same as used by the vision sensors
class TestPillowRescaling(object):
def _load_thor_img(self) -> np.ndarray:
img_path = os.path.join(
ABS_PATH_OF_TOP_LEVEL_DIR, "docs/img/iTHOR_framework.jpg"
)
img = imageio.imread(img_path)
return img
def _get_img_hash(self, img: np.ndarray) -> str:
img_hash = hashlib.sha1(np.ascontiguousarray(img))
return img_hash.hexdigest()
def _random_rgb_image(self, width: int, height: int, seed: int) -> np.ndarray:
s = np.random.get_state()
np.random.seed(seed)
img = np.random.randint(
low=0, high=256, size=(width, height, 3), dtype=np.uint8
)
np.random.set_state(s)
return img
def _random_depthmap(
self, width: int, height: int, max_depth: float, seed: int
) -> np.ndarray:
s = np.random.get_state()
np.random.seed(seed)
img = max_depth * np.random.rand(width, height, 1)
np.random.set_state(s)
return np.float32(img)
def test_scaler_rgb_thor(self):
thor_img_arr = np.uint8(self._load_thor_img())
assert (
self._get_img_hash(thor_img_arr)
== "80ff8a342b4f74966796eee91babde31409d0457"
)
img = to_pil(thor_img_arr)
scaler = ScaleBothSides(width=75, height=75)
scaled_img = np.array(scaler(img))
assert (
self._get_img_hash(scaled_img) == "2c47057aa188240cb21b2edc39e0f269c1085bac"
)
scaler = ScaleBothSides(width=500, height=600)
scaled_img = np.array(scaler(img))
assert (
self._get_img_hash(scaled_img) == "faf0be2b9ec9bfd23a1b7b465c86ad961d03c259"
)
def test_scaler_rgb_random(self):
arr = self._random_rgb_image(width=100, height=100, seed=1)
assert self._get_img_hash(arr) == "d01bd8ba151ab790fde9a8cc29aa8a3c63147334"
img = to_pil(arr)
scaler = ScaleBothSides(width=60, height=60)
scaled_img = np.array(scaler(img))
assert (
self._get_img_hash(scaled_img) == "22473537e50d5e39abeeec4f92dbfde51c754010"
)
scaler = ScaleBothSides(width=1000, height=800)
scaled_img = np.array(scaler(img))
assert (
self._get_img_hash(scaled_img) == "5e5b955981e4ee3b5e22287536040d001a31fbd3"
)
def test_scaler_depth_thor(self):
thor_depth_arr = 5 * np.float32(self._load_thor_img()).sum(-1)
thor_depth_arr /= thor_depth_arr.max()
assert (
self._get_img_hash(thor_depth_arr)
== "d3c1474400ba57ed78f52cf4ba6a4c2a1d90516c"
)
img = to_pil(thor_depth_arr)
scaler = ScaleBothSides(width=75, height=75)
scaled_img = np.array(scaler(img))
assert (
self._get_img_hash(scaled_img) == "6a879beb6bed49021e438c1e3af7a62c428a44d8"
)
scaler = ScaleBothSides(width=500, height=600)
scaled_img = np.array(scaler(img))
assert (
self._get_img_hash(scaled_img) == "79f11fb741ae638afca40125e4c501f54b22cc01"
)
def test_scaler_depth_random(self):
depth_arr = self._random_depthmap(width=96, height=103, max_depth=5.0, seed=1)
assert (
self._get_img_hash(depth_arr) == "cbd8ca127951ffafb6848536d9d731970a5397e9"
)
img = to_pil(depth_arr)
scaler = ScaleBothSides(width=60, height=60)
scaled_img = np.array(scaler(img))
assert (
self._get_img_hash(scaled_img) == "5bed173f2d783fb2badcde9b43904ef85a1a5820"
)
scaler = ScaleBothSides(width=1000, height=800)
scaled_img = np.array(scaler(img))
assert (
self._get_img_hash(scaled_img) == "9dceb7f77d767888f24a84c00913c0cf4ccd9d49"
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
TestPillowRescaling().test_scaler_rgb_thor()
TestPillowRescaling().test_scaler_rgb_random()
TestPillowRescaling().test_scaler_depth_thor()
TestPillowRescaling().test_scaler_depth_random()
| ask4help-main | tests/vision/test_pillow_rescaling.py |
ask4help-main | tests/vision/__init__.py |
|
import math
import os
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.runner import OnPolicyRunner
from projects.babyai_baselines.experiments.go_to_obj.ppo import (
PPOBabyAIGoToObjExperimentConfig,
)
class TestGoToObjTrains(object):
def test_ppo_trains(self, tmpdir):
cfg = PPOBabyAIGoToObjExperimentConfig()
output_dir = tmpdir.mkdir("experiment_output")
train_runner = OnPolicyRunner(
config=cfg,
output_dir=output_dir,
loaded_config_src_files=None,
seed=1,
mode="train",
deterministic_cudnn=True,
)
start_time_str = train_runner.start_train(max_sampler_processes_per_worker=1)
test_runner = OnPolicyRunner(
config=cfg,
output_dir=output_dir,
loaded_config_src_files=None,
seed=1,
mode="test",
deterministic_cudnn=True,
)
test_results = test_runner.start_test(
checkpoint_path_dir_or_pattern=os.path.join(
output_dir, "checkpoints", "**", start_time_str, "*.pt"
),
max_sampler_processes_per_worker=1,
)
assert (
len(test_results) == 1
), f"Too many or too few test results ({test_results})"
tr = test_results[0]
assert (
tr["training_steps"]
== round(
math.ceil(
cfg.TOTAL_RL_TRAIN_STEPS
/ (cfg.ROLLOUT_STEPS * cfg.NUM_TRAIN_SAMPLERS)
)
)
* cfg.ROLLOUT_STEPS
* cfg.NUM_TRAIN_SAMPLERS
), "Incorrect number of training steps"
assert len(tr["tasks"]) == cfg.NUM_TEST_TASKS, "Incorrect number of test tasks"
assert tr["success"] == sum(task["success"] for task in tr["tasks"]) / len(
tr["tasks"]
), "Success counts don't seem to match"
assert (
tr["success"] > 0.95
), "PPO did not seem to converge for the go_to_obj task (success {}).".format(
tr["success"]
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
import pathlib
TestGoToObjTrains().test_ppo_trains(pathlib.Path("testing")) # type:ignore
| ask4help-main | tests/sync_algs_cpu/test_to_to_obj_trains.py |
ask4help-main | tests/sync_algs_cpu/__init__.py |
|
from allenact_plugins.manipulathor_plugin.arm_calculation_utils import (
world_coords_to_agent_coords,
)
class TestArmCalculationUtils(object):
def test_translation_functions(self):
agent_coordinate = {
"position": {"x": 1, "y": 0, "z": 2},
"rotation": {"x": 0, "y": -45, "z": 0},
}
obj_coordinate = {
"position": {"x": 0, "y": 1, "z": 0},
"rotation": {"x": 0, "y": 0, "z": 0},
}
rotated = world_coords_to_agent_coords(obj_coordinate, agent_coordinate)
eps = 0.01
assert (
abs(rotated["position"]["x"] - (-2.12)) < eps
and abs(rotated["position"]["y"] - (1.0)) < eps
and abs(rotated["position"]["z"] - (-0.70)) < eps
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
TestArmCalculationUtils().test_translation_functions()
| ask4help-main | tests/manipulathor_plugin/test_utils.py |
from typing import Dict, Optional, List, Any, cast
import os
import gym
from gym_minigrid.envs import EmptyRandomEnv5x5
from torch import nn
from torch import optim
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import LambdaLR
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.ppo import PPO, PPOConfig
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import ExperimentConfig, TaskSampler
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import SensorSuite, ExpertActionSensor
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import (
TrainingPipeline,
Builder,
PipelineStage,
LinearDecay,
)
from allenact_plugins.minigrid_plugin.minigrid_sensors import EgocentricMiniGridSensor
from allenact_plugins.minigrid_plugin.minigrid_tasks import MiniGridTaskSampler
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.imitation import Imitation
from tempfile import mkdtemp
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.runner import OnPolicyRunner
from projects.tutorials.minigrid_tutorial_conds import (
ConditionedMiniGridSimpleConvRNN,
ConditionedMiniGridTask,
)
class MiniGridCondTestExperimentConfig(ExperimentConfig):
@classmethod
def tag(cls) -> str:
return "MiniGridCondTest"
SENSORS = [
EgocentricMiniGridSensor(agent_view_size=5, view_channels=3),
ExpertActionSensor(
action_space=gym.spaces.Dict(
higher=gym.spaces.Discrete(2), lower=gym.spaces.Discrete(2)
)
),
]
@classmethod
def create_model(cls, **kwargs) -> nn.Module:
return ConditionedMiniGridSimpleConvRNN(
action_space=gym.spaces.Dict(
higher=gym.spaces.Discrete(2), lower=gym.spaces.Discrete(2)
),
observation_space=SensorSuite(cls.SENSORS).observation_spaces,
num_objects=cls.SENSORS[0].num_objects,
num_colors=cls.SENSORS[0].num_colors,
num_states=cls.SENSORS[0].num_states,
)
@classmethod
def make_sampler_fn(cls, **kwargs) -> TaskSampler:
return MiniGridTaskSampler(**kwargs)
def train_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return self._get_sampler_args(process_ind=process_ind, mode="train")
def valid_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return self._get_sampler_args(process_ind=process_ind, mode="valid")
def test_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return self._get_sampler_args(process_ind=process_ind, mode="test")
def _get_sampler_args(self, process_ind: int, mode: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Generate initialization arguments for train, valid, and test
TaskSamplers.
# Parameters
process_ind : index of the current task sampler
mode: one of `train`, `valid`, or `test`
"""
if mode == "train":
max_tasks = None # infinite training tasks
task_seeds_list = None # no predefined random seeds for training
deterministic_sampling = False # randomly sample tasks in training
else:
max_tasks = 20 + 20 * (
mode == "test"
) # 20 tasks for valid, 40 for test (per sampler)
# one seed for each task to sample:
# - ensures different seeds for each sampler, and
# - ensures a deterministic set of sampled tasks.
task_seeds_list = list(
range(process_ind * max_tasks, (process_ind + 1) * max_tasks)
)
deterministic_sampling = (
True # deterministically sample task in validation/testing
)
return dict(
max_tasks=max_tasks, # see above
env_class=self.make_env, # builder for third-party environment (defined below)
sensors=self.SENSORS, # sensors used to return observations to the agent
env_info=dict(), # parameters for environment builder (none for now)
task_seeds_list=task_seeds_list, # see above
deterministic_sampling=deterministic_sampling, # see above
task_class=ConditionedMiniGridTask,
)
@staticmethod
def make_env(*args, **kwargs):
return EmptyRandomEnv5x5()
@classmethod
def machine_params(cls, mode="train", **kwargs) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return {
"nprocesses": 4 if mode == "train" else 1,
"devices": [],
}
@classmethod
def training_pipeline(cls, **kwargs) -> TrainingPipeline:
ppo_steps = int(512)
return TrainingPipeline(
named_losses=dict(
imitation_loss=Imitation(
cls.SENSORS[1]
), # 0 is Minigrid, 1 is ExpertActionSensor
ppo_loss=PPO(**PPOConfig, entropy_method_name="conditional_entropy"),
), # type:ignore
pipeline_stages=[
PipelineStage(
teacher_forcing=LinearDecay(
startp=1.0, endp=0.0, steps=ppo_steps // 2,
),
loss_names=["imitation_loss", "ppo_loss"],
max_stage_steps=ppo_steps,
)
],
optimizer_builder=Builder(cast(optim.Optimizer, optim.Adam), dict(lr=1e-4)),
num_mini_batch=4,
update_repeats=3,
max_grad_norm=0.5,
num_steps=16,
gamma=0.99,
use_gae=True,
gae_lambda=0.95,
advance_scene_rollout_period=None,
save_interval=10000,
metric_accumulate_interval=1,
lr_scheduler_builder=Builder(
LambdaLR, {"lr_lambda": LinearDecay(steps=ppo_steps)} # type:ignore
),
)
class TestMiniGridCond:
def test_train(self, tmpdir):
cfg = MiniGridCondTestExperimentConfig()
train_runner = OnPolicyRunner(
config=cfg,
output_dir=tmpdir,
loaded_config_src_files=None,
seed=12345,
mode="train",
deterministic_cudnn=False,
deterministic_agents=False,
extra_tag="",
disable_tensorboard=True,
disable_config_saving=True,
)
start_time_str, valid_results = train_runner.start_train(
checkpoint=None,
restart_pipeline=False,
max_sampler_processes_per_worker=1,
collect_valid_results=True,
)
assert len(valid_results) > 0
test_runner = OnPolicyRunner(
config=cfg,
output_dir=tmpdir,
loaded_config_src_files=None,
seed=12345,
mode="test",
deterministic_cudnn=False,
deterministic_agents=False,
extra_tag="",
disable_tensorboard=True,
disable_config_saving=True,
)
test_results = test_runner.start_test(
checkpoint_path_dir_or_pattern=os.path.join(
tmpdir, "checkpoints", "**", start_time_str, "*.pt"
),
max_sampler_processes_per_worker=1,
inference_expert=True,
)
assert test_results[-1]["ep_length"] < 4
if __name__ == "__main__":
TestMiniGridCond().test_train(mkdtemp()) # type:ignore
| ask4help-main | tests/hierarchical_policies/test_minigrid_conditional.py |
ask4help-main | tests/hierarchical_policies/__init__.py |
|
import os
from pathlib import Path
ALLENACT_INSTALL_DIR = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(Path(__file__)))
| ask4help-main | allenact/_constants.py |
try:
from allenact._version import __version__
except ModuleNotFoundError:
__version__ = None
| ask4help-main | allenact/__init__.py |
import os
from pathlib import Path
from setuptools import find_packages, setup
def parse_req_file(fname, initial=None):
"""Reads requires.txt file generated by setuptools and outputs a
new/updated dict of extras as keys and corresponding lists of dependencies
as values.
The input file's contents are similar to a `ConfigParser` file, e.g.
pkg_1
pkg_2
pkg_3
[extras1]
pkg_4
pkg_5
[extras2]
pkg_6
pkg_7
"""
reqs = {} if initial is None else initial
cline = None
with open(fname, "r") as f:
for line in f.readlines():
line = line[:-1].strip()
if len(line) == 0:
continue
if line[0] == "[":
# Add new key for current extras (if missing in dict)
cline = line[1:-1]
if cline not in reqs:
reqs[cline] = []
else:
# Only keep dependencies from extras
if cline is not None:
reqs[cline].append(line)
return reqs
def get_version(fname):
"""Reads PKG-INFO file generated by setuptools and extracts the Version
number."""
res = "UNK"
with open(fname, "r") as f:
for line in f.readlines():
line = line[:-1]
if line.startswith("Version:"):
res = line.replace("Version:", "").strip()
break
if res in ["UNK", ""]:
raise ValueError(f"Missing Version number in {fname}")
return res
if __name__ == "__main__":
base_dir = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(Path(__file__)))
if not os.path.exists(
os.path.join(base_dir, "allenact.egg-info/dependency_links.txt")
):
# Build mode for sdist
os.chdir(os.path.join(base_dir, ".."))
with open(".VERSION", "r") as f:
__version__ = f.readline().strip()
# Extra dependencies for development (actually unnecessary)
extras = {
"dev": [
l.strip()
for l in open("dev_requirements.txt", "r").readlines()
if l.strip() != ""
]
}
else:
# Install mode from sdist
__version__ = get_version(os.path.join(base_dir, "allenact.egg-info/PKG-INFO"))
extras = parse_req_file(
os.path.join(base_dir, "allenact.egg-info/requires.txt")
)
setup(
name="allenact",
version=__version__,
description="AllenAct framework",
long_description=(
"AllenAct is a modular and flexible learning framework designed with"
" a focus on the unique requirements of Embodied-AI research."
),
classifiers=[
"Intended Audience :: Science/Research",
"Development Status :: 3 - Alpha",
"License :: OSI Approved :: MIT License",
"Topic :: Scientific/Engineering :: Artificial Intelligence",
"Programming Language :: Python",
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3.6",
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3.7",
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3.8",
],
keywords=["reinforcement learning", "embodied-AI", "AI", "RL", "SLAM"],
url="https://github.com/allenai/allenact",
author="Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence",
author_email="[email protected]",
license="MIT",
packages=find_packages(include=["allenact", "allenact.*"]),
install_requires=[
"gym>=0.17.0,<0.18.0",
"torch>=1.6.0,!=1.8.0,<1.9.0",
"tensorboardx>=2.1",
"torchvision>=0.7.0,<0.10.0",
"setproctitle",
"moviepy>=1.0.3",
"filelock",
"numpy>=1.19.1",
"Pillow==8.2.0",
"matplotlib>=3.3.1",
"networkx",
"opencv-python",
"wheel>=0.36.2",
],
setup_requires=["pytest-runner"],
tests_require=["pytest", "pytest-cov", "compress_pickle"],
entry_points={"console_scripts": ["allenact=allenact.main:main"]},
extras_require=extras,
)
| ask4help-main | allenact/setup.py |
"""Entry point to training/validating/testing for a user given experiment
name."""
import argparse
import ast
import importlib
import inspect
import json
import os
from typing import Dict, Tuple, List, Optional, Type
from setproctitle import setproctitle as ptitle
from allenact import __version__
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.runner import (
OnPolicyRunner,
_CONFIG_KWARGS_STR,
SaveDirFormat,
)
from allenact.base_abstractions.experiment_config import ExperimentConfig
from allenact.utils.system import get_logger, init_logging, HUMAN_LOG_LEVELS
def get_argument_parser():
"""Creates the argument parser."""
# noinspection PyTypeChecker
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description="allenact", formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter,
)
parser.add_argument(
"experiment",
type=str,
help="the path to experiment config file relative the 'experiment_base' directory"
" (see the `--experiment_base` flag).",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--eval",
dest="eval",
action="store_true",
required=False,
help="if you pass the `--eval` flag, AllenAct will run inference on your experiment configuration."
" You will need to specify which experiment checkpoints to run evaluation using the `--checkpoint`"
" flag.",
)
parser.set_defaults(eval=False)
parser.add_argument(
"--config_kwargs",
type=str,
default=None,
required=False,
help="sometimes it is useful to be able to pass additional key-word arguments"
" to `__init__` when initializing an experiment configuration. This flag can be used"
" to pass such key-word arugments by specifying them with json, e.g."
'\n\t--config_kwargs \'{"gpu_id": 0, "my_important_variable": [1,2,3]}\''
"\nTo see which arguments are supported for your experiment see the experiment"
" config's `__init__` function. If the value passed to this function is a file path"
" then we will try to load this file path as a json object and use this json object"
" as key-word arguments.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--extra_tag",
type=str,
default="",
required=False,
help="Add an extra tag to the experiment when trying out new ideas (will be used"
" as a subdirectory of the tensorboard path so you will be able to"
" search tensorboard logs using this extra tag). This can also be used to add an extra"
" organization when running evaluation (e.g. `--extra_tag running_eval_on_great_idea_12`)",
)
parser.add_argument(
"-o",
"--output_dir",
required=False,
type=str,
default="experiment_output",
help="experiment output folder",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--save_dir_fmt",
required=False,
type=lambda s: SaveDirFormat[s.upper()],
default="flat",
help="The file structure to use when saving results from allenact."
" See documentation o f`SaveDirFormat` for more details."
" Allowed values are ('flat' and 'nested'). Default: 'flat'.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"-s", "--seed", required=False, default=None, type=int, help="random seed",
)
parser.add_argument(
"-b",
"--experiment_base",
required=False,
default=os.getcwd(),
type=str,
help="experiment configuration base folder (default: working directory)",
)
parser.add_argument(
"-c",
"--checkpoint",
required=False,
default=None,
type=str,
help="optional checkpoint file name to resume training on or run testing with. When testing (see the `--eval` flag) this"
" argument can be used very flexibly as:"
"\n(1) the path to a particular individual checkpoint file,"
"\n(2) the path to a directory of checkpoint files all of which you'd like to be evaluated"
" (checkpoints are expected to have a `.pt` file extension),"
'\n(3) a "glob" pattern (https://tldp.org/LDP/abs/html/globbingref.html) that will be expanded'
" using python's `glob.glob` function and should return a collection of checkpoint files."
"\nIf you'd like to only evaluate a subset of the checkpoints specified by the above directory/glob"
" (e.g. every checkpoint saved after 5mil steps) you'll likely want to use the `--approx_ckpt_step_interval`"
" flag.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--infer_output_dir",
dest="infer_output_dir",
action="store_true",
required=False,
help="applied when evaluating checkpoint(s) in nested save_dir_fmt: if specified, the output dir will be inferred from checkpoint path.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--approx_ckpt_step_interval",
required=False,
default=None,
type=float,
help="if running tests on a collection of checkpoints (see the `--checkpoint` flag) this argument can be"
" used to skip checkpoints. In particular, if this value is specified and equals `n` then we will"
" only evaluate checkpoints whose step count is closest to each of `0*n`, `1*n`, `2*n`, `3*n`, ... "
" n * ceil(max training steps in ckpts / n). Note that 'closest to' is important here as AllenAct does"
" not generally save checkpoints at exact intervals (doing so would result in performance degregation"
" in distributed training).",
)
parser.add_argument(
"-r",
"--restart_pipeline",
dest="restart_pipeline",
action="store_true",
required=False,
help="for training, if checkpoint is specified, DO NOT continue the training pipeline from where"
" training had previously ended. Instead restart the training pipeline from scratch but"
" with the model weights from the checkpoint.",
)
parser.set_defaults(restart_pipeline=False)
parser.add_argument(
"-d",
"--deterministic_cudnn",
dest="deterministic_cudnn",
action="store_true",
required=False,
help="sets CuDNN to deterministic mode",
)
parser.set_defaults(deterministic_cudnn=False)
parser.add_argument(
"-m",
"--max_sampler_processes_per_worker",
required=False,
default=None,
type=int,
help="maximal number of sampler processes to spawn for each worker",
)
parser.add_argument(
"-e",
"--deterministic_agents",
dest="deterministic_agents",
action="store_true",
required=False,
help="enable deterministic agents (i.e. always taking the mode action) during validation/testing",
)
parser.set_defaults(deterministic_agents=False)
parser.add_argument(
"-l",
"--log_level",
default="info",
type=str,
required=False,
help="sets the log_level. it must be one of {}.".format(
", ".join(HUMAN_LOG_LEVELS)
),
)
parser.add_argument(
"-i",
"--disable_tensorboard",
dest="disable_tensorboard",
action="store_true",
required=False,
help="disable tensorboard logging",
)
parser.set_defaults(disable_tensorboard=False)
parser.add_argument(
"-a",
"--disable_config_saving",
dest="disable_config_saving",
action="store_true",
required=False,
help="disable saving the used config in the output directory",
)
parser.set_defaults(disable_config_saving=False)
parser.add_argument(
"--collect_valid_results",
dest="collect_valid_results",
action="store_true",
required=False,
help="enables returning and saving valid results during training",
)
parser.set_defaults(collect_valid_results=False)
parser.add_argument(
"--test_expert",
dest="test_expert",
action="store_true",
required=False,
help="use expert during test",
)
parser.set_defaults(test_expert=False)
parser.add_argument(
"--version", action="version", version=f"allenact {__version__}"
)
parser.add_argument(
"--distributed_ip_and_port",
dest="distributed_ip_and_port",
required=False,
type=str,
default="127.0.0.1:0",
help="IP address and port of listener for distributed process with rank 0."
" Port number 0 lets runner choose a free port. For more details, please follow the"
" tutorial https://allenact.org/tutorials/distributed-objectnav-tutorial/.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--machine_id",
dest="machine_id",
required=False,
type=int,
default=0,
help="ID for machine in distributed runs. For more details, please follow the"
" tutorial https://allenact.org/tutorials/distributed-objectnav-tutorial/",
)
### DEPRECATED FLAGS
parser.add_argument(
"-t",
"--test_date",
default=None,
type=str,
required=False,
help="`--test_date` has been deprecated. Please use `--eval` instead.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--approx_ckpt_steps_count",
required=False,
default=None,
type=float,
help="`--approx_ckpt_steps_count` has been deprecated."
" Please specify the checkpoint directly using the '--checkpoint' flag.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"-k",
"--skip_checkpoints",
required=False,
default=0,
type=int,
help="`--skip_checkpoints` has been deprecated. Please use `--approx_ckpt_steps_count` instead.",
)
### END DEPRECATED FLAGS
return parser
def get_args():
"""Creates the argument parser and parses any input arguments."""
parser = get_argument_parser()
args = parser.parse_args()
# check for deprecated
deprecated_flags = ["test_date", "skip_checkpoints", "approx_ckpt_steps_count"]
for df in deprecated_flags:
df_info = parser._option_string_actions[f"--{df}"]
if getattr(args, df) is not df_info.default:
raise RuntimeError(df_info.help)
return args
def _config_source(config_type: Type) -> Dict[str, str]:
if config_type is ExperimentConfig:
return {}
try:
module_file_path = inspect.getfile(config_type)
module_dot_path = config_type.__module__
sources_dict = {module_file_path: module_dot_path}
for super_type in config_type.__bases__:
sources_dict.update(_config_source(super_type))
return sources_dict
except TypeError as _:
return {}
def find_sub_modules(path: str, module_list: Optional[List] = None):
if module_list is None:
module_list = []
path = os.path.abspath(path)
if path[-3:] == ".py":
module_list.append(path)
elif os.path.isdir(path):
contents = os.listdir(path)
if any(key in contents for key in ["__init__.py", "setup.py"]):
new_paths = [os.path.join(path, f) for f in os.listdir(path)]
for new_path in new_paths:
find_sub_modules(new_path, module_list)
return module_list
def load_config(args) -> Tuple[ExperimentConfig, Dict[str, str]]:
assert os.path.exists(
args.experiment_base
), "The path '{}' does not seem to exist (your current working directory is '{}').".format(
args.experiment_base, os.getcwd()
)
rel_base_dir = os.path.relpath( # Normalizing string representation of path
os.path.abspath(args.experiment_base), os.getcwd()
)
rel_base_dot_path = rel_base_dir.replace("/", ".")
if rel_base_dot_path == ".":
rel_base_dot_path = ""
exp_dot_path = args.experiment
if exp_dot_path[-3:] == ".py":
exp_dot_path = exp_dot_path[:-3]
exp_dot_path = exp_dot_path.replace("/", ".")
module_path = (
f"{rel_base_dot_path}.{exp_dot_path}"
if len(rel_base_dot_path) != 0
else exp_dot_path
)
try:
importlib.invalidate_caches()
module = importlib.import_module(module_path)
except ModuleNotFoundError as e:
if not any(isinstance(arg, str) and module_path in arg for arg in e.args):
raise e
all_sub_modules = set(find_sub_modules(os.getcwd()))
desired_config_name = module_path.split(".")[-1]
relevant_submodules = [
sm for sm in all_sub_modules if desired_config_name in os.path.basename(sm)
]
raise ModuleNotFoundError(
f"Could not import experiment '{module_path}', are you sure this is the right path?"
f" Possibly relevant files include {relevant_submodules}."
f" Note that the experiment must be reachable along your `PYTHONPATH`, it might"
f" be helpful for you to run `export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:$PWD` in your"
f" project's top level directory."
) from e
experiments = [
m[1]
for m in inspect.getmembers(module, inspect.isclass)
if m[1].__module__ == module.__name__ and issubclass(m[1], ExperimentConfig)
]
assert (
len(experiments) == 1
), "Too many or two few experiments defined in {}".format(module_path)
config_kwargs = {}
if args.config_kwargs is not None:
if os.path.exists(args.config_kwargs):
with open(args.config_kwargs, "r") as f:
config_kwargs = json.load(f)
else:
try:
config_kwargs = json.loads(args.config_kwargs)
except json.JSONDecodeError:
get_logger().warning(
f"The input for --config_kwargs ('{args.config_kwargs}')"
f" does not appear to be valid json. Often this is due to"
f" json requiring very specific syntax (e.g. double quoted strings)"
f" we'll try to get around this by evaluating with `ast.literal_eval`"
f" (a safer version of the standard `eval` function)."
)
config_kwargs = ast.literal_eval(args.config_kwargs)
assert isinstance(
config_kwargs, Dict
), "`--config_kwargs` must be a json string (or a path to a .json file) that evaluates to a dictionary."
config = experiments[0](**config_kwargs)
sources = _config_source(config_type=experiments[0])
sources[_CONFIG_KWARGS_STR] = json.dumps(config_kwargs)
return config, sources
def main():
args = get_args()
init_logging(args.log_level)
get_logger().info("Running with args {}".format(args))
ptitle("Master: {}".format("Training" if args.eval is None else "Evaluation"))
cfg, srcs = load_config(args)
if not args.eval:
OnPolicyRunner(
config=cfg,
output_dir=args.output_dir,
save_dir_fmt=args.save_dir_fmt,
loaded_config_src_files=srcs,
seed=args.seed,
mode="train",
deterministic_cudnn=args.deterministic_cudnn,
deterministic_agents=args.deterministic_agents,
extra_tag=args.extra_tag,
disable_tensorboard=args.disable_tensorboard,
disable_config_saving=args.disable_config_saving,
distributed_ip_and_port=args.distributed_ip_and_port,
machine_id=args.machine_id,
).start_train(
checkpoint=args.checkpoint,
restart_pipeline=args.restart_pipeline,
max_sampler_processes_per_worker=args.max_sampler_processes_per_worker,
collect_valid_results=args.collect_valid_results,
)
else:
OnPolicyRunner(
config=cfg,
output_dir=args.output_dir,
save_dir_fmt=args.save_dir_fmt,
loaded_config_src_files=srcs,
seed=args.seed,
mode="test",
deterministic_cudnn=args.deterministic_cudnn,
deterministic_agents=args.deterministic_agents,
extra_tag=args.extra_tag,
disable_tensorboard=args.disable_tensorboard,
disable_config_saving=args.disable_config_saving,
distributed_ip_and_port=args.distributed_ip_and_port,
machine_id=args.machine_id,
).start_test(
checkpoint_path_dir_or_pattern=args.checkpoint,
infer_output_dir=args.infer_output_dir,
approx_ckpt_step_interval=args.approx_ckpt_step_interval,
max_sampler_processes_per_worker=args.max_sampler_processes_per_worker,
inference_expert=args.test_expert,
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
| ask4help-main | allenact/main.py |
ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/__init__.py |
|
ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/mapping/__init__.py |
|
import torch
from torch.nn import functional as F
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.abstract_loss import (
AbstractActorCriticLoss,
)
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.policy import ObservationType
from allenact.base_abstractions.distributions import CategoricalDistr
from allenact.base_abstractions.misc import ActorCriticOutput
class BinnedPointCloudMapLoss(AbstractActorCriticLoss):
"""A (binary cross entropy) loss for training metric maps for free space
prediction."""
def __init__(
self, binned_pc_uuid: str, map_logits_uuid: str,
):
"""Initializer.
# Parameters
binned_pc_uuid : The uuid of a sensor returning
a dictionary with an "egocentric_update"
key with the same format as returned by
`allenact.embodied_ai.mapping_utils.map_builders.BinnedPointCloudMapBuilder`. Such a sensor
can be found in the `allenact_plugins` library: see
`allenact_plugins.ithor_plugin.ithor_sensors.BinnedPointCloudMapTHORSensor`.
map_logits_uuid : key used to index into `actor_critic_output.extras` (returned by the model)
whose value should be a tensor of the same shape as the tensor corresponding to the above
"egocentric_update" key.
"""
super().__init__()
self.binned_pc_uuid = binned_pc_uuid
self.map_logits_uuid = map_logits_uuid
def loss( # type: ignore
self,
step_count: int,
batch: ObservationType,
actor_critic_output: ActorCriticOutput[CategoricalDistr],
*args,
**kwargs,
):
ego_map_gt = batch["observations"][self.binned_pc_uuid][
"egocentric_update"
].float()
*_, h, w, c = ego_map_gt.shape
ego_map_gt = ego_map_gt.view(-1, h, w, c).permute(0, 3, 1, 2).contiguous()
ego_map_logits = actor_critic_output.extras[self.map_logits_uuid]
vision_range = ego_map_logits.shape[-1]
ego_map_logits = ego_map_logits.view(-1, c, vision_range, vision_range)
assert ego_map_gt.shape == ego_map_logits.shape
ego_map_gt_thresholded = (ego_map_gt > 0.5).float()
total_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(
ego_map_logits, ego_map_gt_thresholded
)
return (
total_loss,
{"binned_pc_map_ce": total_loss.item()},
)
# FOR DEBUGGING: Save all the ground-truth & predicted maps side by side
# import numpy as np
# import imageio
# for i in range(ego_map_gt_thresholded.shape[0]):
# a = ego_map_gt_thresholded[i].permute(1, 2, 0).flip(0).detach().numpy()
# b = torch.sigmoid(ego_map_logits)[i].permute(1, 2, 0).flip(0).detach().numpy()
#
# imageio.imwrite(
# f"z_occupancy_maps/{i}.png",
# np.concatenate((a, 1 + 0 * a[:, :10], b), axis=1),
# )
class SemanticMapFocalLoss(AbstractActorCriticLoss):
"""A (focal-loss based) loss for training metric maps for free space
prediction.
As semantic maps tend to be quite sparse this loss uses the focal
loss (https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.02002) rather than binary cross
entropy (BCE). If the `gamma` parameter is 0.0 then this is just the
normal BCE, larger values of `gamma` result less and less emphasis
being paid to examples that are already well classified.
"""
def __init__(
self, semantic_map_uuid: str, map_logits_uuid: str, gamma: float = 2.0
):
"""Initializer.
# Parameters
semantic_map_uuid : The uuid of a sensor returning
a dictionary with an "egocentric_update"
key with the same format as returned by
`allenact.embodied_ai.mapping_utils.map_builders.SemanticMapBuilder`. Such a sensor
can be found in the `allenact_plugins` library: see
`allenact_plugins.ithor_plugin.ithor_sensors.SemanticMapTHORSensor`.
map_logits_uuid : key used to index into `actor_critic_output.extras` (returned by the model)
whose value should be a tensor of the same shape as the tensor corresponding to the above
"egocentric_update" key.
"""
super().__init__()
assert gamma >= 0, f"`gamma` (=={gamma}) must be >= 0"
self.semantic_map_uuid = semantic_map_uuid
self.map_logits_uuid = map_logits_uuid
self.gamma = gamma
def loss( # type: ignore
self,
step_count: int,
batch: ObservationType,
actor_critic_output: ActorCriticOutput[CategoricalDistr],
*args,
**kwargs,
):
ego_map_gt = batch["observations"][self.semantic_map_uuid]["egocentric_update"]
ego_map_gt = (
ego_map_gt.view(-1, *ego_map_gt.shape[-3:]).permute(0, 3, 1, 2).contiguous()
)
ego_map_logits = actor_critic_output.extras[self.map_logits_uuid]
ego_map_logits = ego_map_logits.view(-1, *ego_map_logits.shape[-3:])
assert ego_map_gt.shape == ego_map_logits.shape
p = torch.sigmoid(ego_map_logits)
one_minus_p = torch.sigmoid(-ego_map_logits)
log_p = F.logsigmoid(ego_map_logits)
log_one_minus_p = F.logsigmoid(-ego_map_logits)
ego_map_gt = ego_map_gt.float()
total_loss = -(
ego_map_gt * (log_p * (one_minus_p ** self.gamma))
+ (1 - ego_map_gt) * (log_one_minus_p * (p ** self.gamma))
).mean()
return (
total_loss,
{"sem_map_focal_loss": total_loss.item()},
)
# FOR DEBUGGING: Save all the ground-truth & predicted maps side by side
# import numpy as np
# import imageio
# from allenact.embodiedai.mapping.mapping_utils.map_builders import SemanticMapBuilder
#
# print("\n" * 3)
# for i in range(ego_map_gt.shape[0]):
# pred_sem_map = torch.sigmoid(ego_map_logits)[i].permute(1, 2, 0).flip(0).detach()
# a = SemanticMapBuilder.randomly_color_semantic_map(ego_map_gt[i].permute(1, 2, 0).flip(0).detach())
# b = SemanticMapBuilder.randomly_color_semantic_map(pred_sem_map)
# imageio.imwrite(
# f"z_semantic_maps/{i}.png",
# np.concatenate((a, 255 + a[:, :10] * 0, b), axis=1),
# )
#
| ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/mapping/mapping_losses.py |
ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/mapping/mapping_utils/__init__.py |
|
# MIT License
#
# Original Copyright (c) 2020 Devendra Chaplot
#
# Modified work Copyright (c) 2021 Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence
#
# Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
# of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
# in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
# to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
# copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
# furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
#
# The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
# copies or substantial portions of the Software.
#
# THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
# IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
# FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
# AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
# LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
# OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
# SOFTWARE.
import random
from typing import Optional, Sequence, Union, Dict
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from allenact.embodiedai.mapping.mapping_utils.point_cloud_utils import (
depth_frame_to_world_space_xyz,
project_point_cloud_to_map,
)
class BinnedPointCloudMapBuilder(object):
"""Class used to iteratively construct a map of "free space" based on input
depth maps (i.e. pointclouds).
Adapted from https://github.com/devendrachaplot/Neural-SLAM
This class can be used to (iteratively) construct a metric map of free space in an environment as
an agent moves around. After every step the agent takes, you should call the `update` function and
pass the agent's egocentric depth image along with the agent's new position. This depth map will
be converted into a pointcloud, binned along the up/down axis, and then projected
onto a 3-dimensional tensor of shape (HxWxC) whose where HxW represent the ground plane
and where C equals the number of bins the up-down coordinate was binned into. This 3d map counts the
number of points in each bin. Thus a lack of points within a region can be used to infer that
that region is free space.
# Attributes
fov : FOV of the camera used to produce the depth images given when calling `update`.
vision_range_in_map_units : The maximum distance (in number of rows/columns) that will
be updated when calling `update`, points outside of this map vision range are ignored.
map_size_in_cm : Total map size in cm.
resolution_in_cm : Number of cm per row/column in the map.
height_bins : The bins used to bin the up-down coordinate (for us the y-coordinate). For example,
if `height_bins = [0.1, 1]` then
all y-values < 0.1 will be mapped to 0, all y values in [0.1, 1) will be mapped to 1, and
all y-values >= 1 will be mapped to 2.
**Importantly:** these y-values will first be recentered by the `min_xyz` value passed when
calling `reset(...)`.
device : A `torch.device` on which to run computations. If this device is a GPU you can potentially
obtain significant speed-ups.
"""
def __init__(
self,
fov: float,
vision_range_in_cm: int,
map_size_in_cm: int,
resolution_in_cm: int,
height_bins: Sequence[float],
device: torch.device = torch.device("cpu"),
):
assert vision_range_in_cm % resolution_in_cm == 0
self.fov = fov
self.vision_range_in_map_units = vision_range_in_cm // resolution_in_cm
self.map_size_in_cm = map_size_in_cm
self.resolution_in_cm = resolution_in_cm
self.height_bins = height_bins
self.device = device
self.binned_point_cloud_map = np.zeros(
(
self.map_size_in_cm // self.resolution_in_cm,
self.map_size_in_cm // self.resolution_in_cm,
len(self.height_bins) + 1,
),
dtype=np.float32,
)
self.min_xyz: Optional[np.ndarray] = None
def update(
self,
depth_frame: np.ndarray,
camera_xyz: np.ndarray,
camera_rotation: float,
camera_horizon: float,
) -> Dict[str, np.ndarray]:
"""Updates the map with the input depth frame from the agent.
See the `allenact.embodiedai.mapping.mapping_utils.point_cloud_utils.project_point_cloud_to_map`
function for more information input parameter definitions. **We assume that the input
`depth_frame` has depths recorded in meters**.
# Returns
Let `map_size = self.map_size_in_cm // self.resolution_in_cm`. Returns a dictionary with keys-values:
* `"egocentric_update"` - A tensor of shape
`(vision_range_in_map_units)x(vision_range_in_map_units)x(len(self.height_bins) + 1)` corresponding
to the binned pointcloud after having been centered on the agent and rotated so that
points ahead of the agent correspond to larger row indices and points further to the right of the agent
correspond to larger column indices. Note that by "centered" we mean that one can picture
the agent as being positioned at (0, vision_range_in_map_units/2) and facing downward. Each entry in this tensor
is a count equaling the number of points in the pointcloud that, once binned, fell into this
entry. This is likely the output you want to use if you want to build a model to predict free space from an image.
* `"allocentric_update"` - A `(map_size)x(map_size)x(len(self.height_bins) + 1)` corresponding
to `"egocentric_update"` but rotated to the world-space coordinates. This `allocentric_update`
is what is used to update the internally stored representation of the map.
* `"map"` - A `(map_size)x(map_size)x(len(self.height_bins) + 1)` tensor corresponding
to the sum of all `"allocentric_update"` values since the last `reset()`.
```
"""
with torch.no_grad():
assert self.min_xyz is not None, "Please call `reset` before `update`."
camera_xyz = (
torch.from_numpy(camera_xyz - self.min_xyz).float().to(self.device)
)
depth_frame = torch.from_numpy(depth_frame).to(self.device)
depth_frame[
depth_frame
> self.vision_range_in_map_units * self.resolution_in_cm / 100
] = np.NaN
world_space_point_cloud = depth_frame_to_world_space_xyz(
depth_frame=depth_frame,
camera_world_xyz=camera_xyz,
rotation=camera_rotation,
horizon=camera_horizon,
fov=self.fov,
)
world_binned_map_update = project_point_cloud_to_map(
xyz_points=world_space_point_cloud,
bin_axis="y",
bins=self.height_bins,
map_size=self.binned_point_cloud_map.shape[0],
resolution_in_cm=self.resolution_in_cm,
flip_row_col=True,
)
# Center the cloud on the agent
recentered_point_cloud = world_space_point_cloud - (
torch.FloatTensor([1.0, 0.0, 1.0]).to(self.device) * camera_xyz
).reshape((1, 1, 3))
# Rotate the cloud so that positive-z is the direction the agent is looking
theta = (
np.pi * camera_rotation / 180
) # No negative since THOR rotations are already backwards
cos_theta = np.cos(theta)
sin_theta = np.sin(theta)
rotation_transform = torch.FloatTensor(
[
[cos_theta, 0, -sin_theta],
[0, 1, 0], # unchanged
[sin_theta, 0, cos_theta],
]
).to(self.device)
rotated_point_cloud = recentered_point_cloud @ rotation_transform.T
xoffset = (self.map_size_in_cm / 100) / 2
agent_centric_point_cloud = rotated_point_cloud + torch.FloatTensor(
[xoffset, 0, 0]
).to(self.device)
allocentric_update_numpy = world_binned_map_update.cpu().numpy()
self.binned_point_cloud_map = (
self.binned_point_cloud_map + allocentric_update_numpy
)
agent_centric_binned_map = project_point_cloud_to_map(
xyz_points=agent_centric_point_cloud,
bin_axis="y",
bins=self.height_bins,
map_size=self.binned_point_cloud_map.shape[0],
resolution_in_cm=self.resolution_in_cm,
flip_row_col=True,
)
vr = self.vision_range_in_map_units
vr_div_2 = self.vision_range_in_map_units // 2
width_div_2 = agent_centric_binned_map.shape[1] // 2
agent_centric_binned_map = agent_centric_binned_map[
:vr, (width_div_2 - vr_div_2) : (width_div_2 + vr_div_2), :
]
return {
"egocentric_update": agent_centric_binned_map.cpu().numpy(),
"allocentric_update": allocentric_update_numpy,
"map": self.binned_point_cloud_map,
}
def reset(self, min_xyz: np.ndarray):
"""Reset the map.
Resets the internally stored map.
# Parameters
min_xyz : An array of size (3,) corresponding to the minimum possible x, y, and z values that will be observed
as a point in a pointcloud when calling `.update(...)`. The (world-space) maps returned by calls to `update`
will have been normalized so the (0,0,:) entry corresponds to these minimum values.
"""
self.min_xyz = min_xyz
self.binned_point_cloud_map = np.zeros_like(self.binned_point_cloud_map)
class ObjectHull2d:
def __init__(
self,
object_id: str,
object_type: str,
hull_points: Union[np.ndarray, Sequence[Sequence[float]]],
):
"""A class used to represent 2d convex hulls of objects when projected
to the ground plane.
# Parameters
object_id : A unique id for the object.
object_type : The type of the object.
hull_points : A Nx2 matrix with `hull_points[:, 0]` being the x coordinates and `hull_points[:, 1]` being
the `z` coordinates (this is using the Unity game engine conventions where the `y` axis is up/down).
"""
self.object_id = object_id
self.object_type = object_type
self.hull_points = (
hull_points
if isinstance(hull_points, np.ndarray)
else np.array(hull_points)
)
class SemanticMapBuilder(object):
"""Class used to iteratively construct a semantic map based on input depth
maps (i.e. pointclouds).
Adapted from https://github.com/devendrachaplot/Neural-SLAM
This class can be used to (iteratively) construct a semantic map of objects in the environment.
This map is similar to that generated by `BinnedPointCloudMapBuilder` (see its documentation for
more information) but the various channels correspond to different object types. Thus
if the `(i,j,k)` entry of a map generated by this function is `True`, this means that an
object of type `k` is present in position `i,j` in the map. In particular, by "present" we mean that,
after projecting the object to the ground plane and taking the convex hull of the resulting
2d object, a non-trivial portion of this convex hull overlaps the `i,j` position.
For attribute information, see the documentation of the `BinnedPointCloudMapBuilder` class. The
only attribute present in this class that is not present in `BinnedPointCloudMapBuilder` is
`ordered_object_types` which corresponds to a list of unique object types where
object type `ordered_object_types[i]` will correspond to the `i`th channel of the map
generated by this class.
"""
def __init__(
self,
fov: float,
vision_range_in_cm: int,
map_size_in_cm: int,
resolution_in_cm: int,
ordered_object_types: Sequence[str],
device: torch.device = torch.device("cpu"),
):
self.fov = fov
self.vision_range_in_map_units = vision_range_in_cm // resolution_in_cm
self.map_size_in_cm = map_size_in_cm
self.resolution_in_cm = resolution_in_cm
self.ordered_object_types = tuple(ordered_object_types)
self.device = device
self.object_type_to_index = {
ot: i for i, ot in enumerate(self.ordered_object_types)
}
self.ground_truth_semantic_map = np.zeros(
(
self.map_size_in_cm // self.resolution_in_cm,
self.map_size_in_cm // self.resolution_in_cm,
len(self.ordered_object_types),
),
dtype=np.uint8,
)
self.explored_mask = np.zeros(
(
self.map_size_in_cm // self.resolution_in_cm,
self.map_size_in_cm // self.resolution_in_cm,
1,
),
dtype=bool,
)
self.min_xyz: Optional[np.ndarray] = None
@staticmethod
def randomly_color_semantic_map(
map: Union[np.ndarray, torch.Tensor], threshold: float = 0.5, seed: int = 1
) -> np.ndarray:
if not isinstance(map, np.ndarray):
map = np.array(map)
rnd = random.Random(seed)
semantic_int_mat = (
(map >= threshold)
* np.array(list(range(1, map.shape[-1] + 1))).reshape((1, 1, -1))
).max(-1)
# noinspection PyTypeChecker
return np.uint8(
np.array(
[(0, 0, 0)]
+ [
tuple(rnd.randint(0, 256) for _ in range(3))
for _ in range(map.shape[-1])
]
)[semantic_int_mat]
)
def _xzs_to_colrows(self, xzs: np.ndarray):
height, width, _ = self.ground_truth_semantic_map.shape
return np.clip(
np.int32(
(
(100 / self.resolution_in_cm)
* (xzs - np.array([[self.min_xyz[0], self.min_xyz[2]]]))
)
),
a_min=0,
a_max=np.array(
[width - 1, height - 1]
), # width then height as we're returns cols then rows
)
def build_ground_truth_map(self, object_hulls: Sequence[ObjectHull2d]):
self.ground_truth_semantic_map.fill(0)
height, width, _ = self.ground_truth_semantic_map.shape
for object_hull in object_hulls:
ot = object_hull.object_type
if ot in self.object_type_to_index:
ind = self.object_type_to_index[ot]
self.ground_truth_semantic_map[
:, :, ind : (ind + 1)
] = cv2.fillConvexPoly(
img=np.array(
self.ground_truth_semantic_map[:, :, ind : (ind + 1)],
dtype=np.uint8,
),
points=self._xzs_to_colrows(np.array(object_hull.hull_points)),
color=255,
)
def update(
self,
depth_frame: np.ndarray,
camera_xyz: np.ndarray,
camera_rotation: float,
camera_horizon: float,
) -> Dict[str, np.ndarray]:
"""Updates the map with the input depth frame from the agent.
See the documentation for `BinnedPointCloudMapBuilder.update`,
the inputs and outputs are similar except that channels are used
to represent the presence/absence of objects of given types.
Unlike `BinnedPointCloudMapBuilder.update`, this function also
returns two masks with keys `"egocentric_mask"` and `"mask"`
that can be used to determine what portions of the map have been
observed by the agent so far in the egocentric and world-space
reference frames respectively.
"""
with torch.no_grad():
assert self.min_xyz is not None
camera_xyz = torch.from_numpy(camera_xyz - self.min_xyz).to(self.device)
map_size = self.ground_truth_semantic_map.shape[0]
depth_frame = torch.from_numpy(depth_frame).to(self.device)
depth_frame[
depth_frame
> self.vision_range_in_map_units * self.resolution_in_cm / 100
] = np.NaN
world_space_point_cloud = depth_frame_to_world_space_xyz(
depth_frame=depth_frame,
camera_world_xyz=camera_xyz,
rotation=camera_rotation,
horizon=camera_horizon,
fov=self.fov,
)
world_newly_explored = (
project_point_cloud_to_map(
xyz_points=world_space_point_cloud,
bin_axis="y",
bins=[],
map_size=map_size,
resolution_in_cm=self.resolution_in_cm,
flip_row_col=True,
)
> 0.001
)
world_update_and_mask = torch.cat(
(
torch.logical_and(
torch.from_numpy(self.ground_truth_semantic_map).to(
self.device
),
world_newly_explored,
),
world_newly_explored,
),
dim=-1,
).float()
world_update_and_mask_for_sample = world_update_and_mask.unsqueeze(
0
).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
# We now use grid sampling to rotate world_update_for_sample into the egocentric coordinate
# frame of the agent so that the agent's forward direction is downwards in the tensor
# (and it's right side is to the right in the image, this means that right/left
# when taking the perspective of the agent in the image). This convention aligns with
# what's expected by grid_sample where +x corresponds to +cols and +z corresponds to +rows.
# Here also the rows/cols have been normalized so that the center of the image is at (0,0)
# and the bottom right is at (1,1).
# Mentally you can think of the output from the F.affine_grid function as you wanting
# rotating/translating an axis-aligned square on the image-to-be-sampled and then
# copying whatever is in this square to a new image. Note that the translation always
# happens in the global reference frame after the rotation. We'll start by rotating
# the square so that the the agent's z direction is downwards in the image.
# Since the global axis of the map and the grid sampling are aligned, this requires
# rotating the square by the rotation of the agent. As rotation is negative the usual
# standard in THOR, we need to negate the rotation of the agent.
theta = -np.pi * camera_rotation / 180
# Here form the rotation matrix
cos_theta = np.cos(theta)
sin_theta = np.sin(theta)
rot_mat = torch.FloatTensor(
[[cos_theta, -sin_theta], [sin_theta, cos_theta]]
).to(self.device)
# Now we need to figure out the translation. For an intuitive understanding, we break this
# translation into two different "offsets". The first offset centers the square on the
# agent's current location:
scaler = 2 * (100 / (self.resolution_in_cm * map_size))
offset_to_center_the_agent = (
scaler
* torch.FloatTensor([camera_xyz[0], camera_xyz[2]])
.unsqueeze(-1)
.to(self.device)
- 1
)
# The second offset moves the square in the direction of the agent's z direction
# so that the output image will have the agent's view starting directly at the
# top of the image.
offset_to_top_of_image = rot_mat @ torch.FloatTensor([0, 1.0]).unsqueeze(
1
).to(self.device)
rotation_and_translate_mat = torch.cat(
(rot_mat, offset_to_top_of_image + offset_to_center_the_agent,), dim=1,
)
ego_update_and_mask = F.grid_sample(
world_update_and_mask_for_sample.to(self.device),
F.affine_grid(
rotation_and_translate_mat.to(self.device).unsqueeze(0),
world_update_and_mask_for_sample.shape,
align_corners=False,
),
align_corners=False,
)
# All that's left now is to crop out the portion of the transformed tensor that we actually
# care about (i.e. the portion corresponding to the agent's `self.vision_range_in_map_units`.
vr = self.vision_range_in_map_units
half_vr = vr // 2
center = self.map_size_in_cm // (2 * self.resolution_in_cm)
cropped = ego_update_and_mask[
:, :, :vr, (center - half_vr) : (center + half_vr)
]
np.logical_or(
self.explored_mask,
world_newly_explored.cpu().numpy(),
out=self.explored_mask,
)
return {
"egocentric_update": cropped[0, :-1].permute(1, 2, 0).cpu().numpy(),
"egocentric_mask": (cropped[0, -1:].view(vr, vr, 1) > 0.001)
.cpu()
.numpy(),
"explored_mask": np.array(self.explored_mask),
"map": np.logical_and(
self.explored_mask, (self.ground_truth_semantic_map > 0)
),
}
def reset(self, min_xyz: np.ndarray, object_hulls: Sequence[ObjectHull2d]):
"""Reset the map.
Resets the internally stored map.
# Parameters
min_xyz : An array of size (3,) corresponding to the minimum possible x, y, and z values that will be observed
as a point in a pointcloud when calling `.update(...)`. The (world-space) maps returned by calls to `update`
will have been normalized so the (0,0,:) entry corresponds to these minimum values.
object_hulls : The object hulls corresponding to objects in the scene. These will be used to
construct the map.
"""
self.min_xyz = min_xyz
self.build_ground_truth_map(object_hulls=object_hulls)
| ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/mapping/mapping_utils/map_builders.py |
# MIT License
#
# Original Copyright (c) 2020 Devendra Chaplot
#
# Modified work Copyright (c) 2021 Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence
#
# Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
# of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
# in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
# to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
# copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
# furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
#
# The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
# copies or substantial portions of the Software.
#
# THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
# IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
# FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
# AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
# LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
# OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
# SOFTWARE.
import math
from typing import Optional, Sequence, cast
import numpy as np
import torch
def camera_space_xyz_to_world_xyz(
camera_space_xyzs: torch.Tensor,
camera_world_xyz: torch.Tensor,
rotation: float,
horizon: float,
) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Transforms xyz coordinates in the camera's coordinate frame to world-
space (global) xyz frame.
This code has been adapted from https://github.com/devendrachaplot/Neural-SLAM.
**IMPORTANT:** We use the conventions from the Unity game engine. In particular:
* A rotation of 0 corresponds to facing north.
* Positive rotations correspond to CLOCKWISE rotations. That is a rotation of 90 degrees corresponds
to facing east. **THIS IS THE OPPOSITE CONVENTION OF THE ONE GENERALLY USED IN MATHEMATICS.**
* When facing NORTH (rotation==0) moving ahead by 1 meter results in the the z coordinate
increasing by 1. Moving to the right by 1 meter corresponds to increasing the x coordinate by 1.
Finally moving upwards by 1 meter corresponds to increasing the y coordinate by 1.
**Having x,z as the ground plane in this way is common in computer graphics but is different than
the usual mathematical convention of having z be "up".**
* The horizon corresponds to how far below the horizontal the camera is facing. I.e. a horizon
of 30 corresponds to the camera being angled downwards at an angle of 30 degrees.
# Parameters
camera_space_xyzs : A 3xN matrix of xyz coordinates in the camera's reference frame.
Here `x, y, z = camera_space_xyzs[:, i]` should equal the xyz coordinates for the ith point.
camera_world_xyz : The camera's xyz position in the world reference frame.
rotation : The world-space rotation (in degrees) of the camera.
horizon : The horizon (in degrees) of the camera.
# Returns
3xN tensor with entry [:, i] is the xyz world-space coordinate corresponding to the camera-space
coordinate camera_space_xyzs[:, i]
"""
# Adapted from https://github.com/devendrachaplot/Neural-SLAM.
# First compute the transformation that points undergo
# due to the camera's horizon
psi = -horizon * np.pi / 180
cos_psi = np.cos(psi)
sin_psi = np.sin(psi)
# fmt: off
horizon_transform = camera_space_xyzs.new(
[
[1, 0, 0], # unchanged
[0, cos_psi, sin_psi],
[0, -sin_psi, cos_psi,],
],
)
# fmt: on
# Next compute the transformation that points undergo
# due to the agent's rotation about the y-axis
phi = -rotation * np.pi / 180
cos_phi = np.cos(phi)
sin_phi = np.sin(phi)
# fmt: off
rotation_transform = camera_space_xyzs.new(
[
[cos_phi, 0, -sin_phi],
[0, 1, 0], # unchanged
[sin_phi, 0, cos_phi],],
)
# fmt: on
# Apply the above transformations
view_points = (rotation_transform @ horizon_transform) @ camera_space_xyzs
# Translate the points w.r.t. the camera's position in world space.
world_points = view_points + camera_world_xyz[:, None]
return world_points
def depth_frame_to_camera_space_xyz(
depth_frame: torch.Tensor, mask: Optional[torch.Tensor], fov: float = 90
) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Transforms a input depth map into a collection of xyz points (i.e. a
point cloud) in the camera's coordinate frame.
# Parameters
depth_frame : A square depth map, i.e. an MxM matrix with entry `depth_frame[i, j]` equaling
the distance from the camera to nearest surface at pixel (i,j).
mask : An optional boolean mask of the same size (MxM) as the input depth. Only values
where this mask are true will be included in the returned matrix of xyz coordinates. If
`None` then no pixels will be masked out (so the returned matrix of xyz points will have
dimension 3x(M*M)
fov: The field of view of the camera.
# Returns
A 3xN matrix with entry [:, i] equalling a the xyz coordinates (in the camera's coordinate
frame) of a point in the point cloud corresponding to the input depth frame.
"""
assert (
len(depth_frame.shape) == 2 and depth_frame.shape[0] == depth_frame.shape[1]
), f"depth has shape {depth_frame.shape}, we only support (N, N) shapes for now."
resolution = depth_frame.shape[0]
if mask is None:
mask = torch.ones_like(depth_frame, dtype=bool)
# pixel centers
camera_space_yx_offsets = (
torch.stack(torch.where(mask))
+ 0.5 # Offset by 0.5 so that we are in the middle of the pixel
)
# Subtract center
camera_space_yx_offsets -= resolution / 2.0
# Make "up" in y be positive
camera_space_yx_offsets[0, :] *= -1
# Put points on the clipping plane
camera_space_yx_offsets *= (2.0 / resolution) * math.tan((fov / 2) / 180 * math.pi)
camera_space_xyz = torch.cat(
[
camera_space_yx_offsets[1:, :], # This is x
camera_space_yx_offsets[:1, :], # This is y
torch.ones_like(camera_space_yx_offsets[:1, :]),
],
axis=0,
)
return camera_space_xyz * depth_frame[mask][None, :]
def depth_frame_to_world_space_xyz(
depth_frame: torch.Tensor,
camera_world_xyz: torch.Tensor,
rotation: float,
horizon: float,
fov: float,
):
"""Transforms a input depth map into a collection of xyz points (i.e. a
point cloud) in the world-space coordinate frame.
**IMPORTANT:** We use the conventions from the Unity game engine. In particular:
* A rotation of 0 corresponds to facing north.
* Positive rotations correspond to CLOCKWISE rotations. That is a rotation of 90 degrees corresponds
to facing east. **THIS IS THE OPPOSITE CONVENTION OF THE ONE GENERALLY USED IN MATHEMATICS.**
* When facing NORTH (rotation==0) moving ahead by 1 meter results in the the z coordinate
increasing by 1. Moving to the right by 1 meter corresponds to increasing the x coordinate by 1.
Finally moving upwards by 1 meter corresponds to increasing the y coordinate by 1.
**Having x,z as the ground plane in this way is common in computer graphics but is different than
the usual mathematical convention of having z be "up".**
* The horizon corresponds to how far below the horizontal the camera is facing. I.e. a horizon
of 30 corresponds to the camera being angled downwards at an angle of 30 degrees.
# Parameters
depth_frame : A square depth map, i.e. an MxM matrix with entry `depth_frame[i, j]` equaling
the distance from the camera to nearest surface at pixel (i,j).
mask : An optional boolean mask of the same size (MxM) as the input depth. Only values
where this mask are true will be included in the returned matrix of xyz coordinates. If
`None` then no pixels will be masked out (so the returned matrix of xyz points will have
dimension 3x(M*M)
camera_space_xyzs : A 3xN matrix of xyz coordinates in the camera's reference frame.
Here `x, y, z = camera_space_xyzs[:, i]` should equal the xyz coordinates for the ith point.
camera_world_xyz : The camera's xyz position in the world reference frame.
rotation : The world-space rotation (in degrees) of the camera.
horizon : The horizon (in degrees) of the camera.
fov: The field of view of the camera.
# Returns
A 3xN matrix with entry [:, i] equalling a the xyz coordinates (in the world coordinate
frame) of a point in the point cloud corresponding to the input depth frame.
"""
camera_space_xyz = depth_frame_to_camera_space_xyz(
depth_frame=depth_frame, mask=None, fov=fov
)
world_points = camera_space_xyz_to_world_xyz(
camera_space_xyzs=camera_space_xyz,
camera_world_xyz=camera_world_xyz,
rotation=rotation,
horizon=horizon,
)
return world_points.view(3, *depth_frame.shape).permute(1, 2, 0)
def project_point_cloud_to_map(
xyz_points: torch.Tensor,
bin_axis: str,
bins: Sequence[float],
map_size: int,
resolution_in_cm: int,
flip_row_col: bool,
):
"""Bins an input point cloud into a map tensor with the bins equaling the
channels.
This code has been adapted from https://github.com/devendrachaplot/Neural-SLAM.
# Parameters
xyz_points : (x,y,z) pointcloud(s) as a torch.Tensor of shape (... x height x width x 3).
All operations are vectorized across the `...` dimensions.
bin_axis : Either "x", "y", or "z", the axis which should be binned by the values in `bins`.
If you have generated your point clouds with any of the other functions in the `point_cloud_utils`
module you almost certainly want this to be "y" as this is the default upwards dimension.
bins: The values by which to bin along `bin_axis`, see the `bins` parameter of `np.digitize`
for more info.
map_size : The axes not specified by `bin_axis` will be be divided by `resolution_in_cm / 100`
and then rounded to the nearest integer. They are then expected to have their values
within the interval [0, ..., map_size - 1].
resolution_in_cm: The resolution_in_cm, in cm, of the map output from this function. Every
grid square of the map corresponds to a (`resolution_in_cm`x`resolution_in_cm`) square
in space.
flip_row_col: Should the rows/cols of the map be flipped? See the 'Returns' section below for more
info.
# Returns
A collection of maps of shape (... x map_size x map_size x (len(bins)+1)), note that bin_axis
has been moved to the last index of this returned map, the other two axes stay in their original
order unless `flip_row_col` has been called in which case they are reversed (useful as often
rows should correspond to y or z instead of x).
"""
bin_dim = ["x", "y", "z"].index(bin_axis)
start_shape = xyz_points.shape
xyz_points = xyz_points.reshape([-1, *start_shape[-3:]])
num_clouds, h, w, _ = xyz_points.shape
if not flip_row_col:
new_order = [i for i in [0, 1, 2] if i != bin_dim] + [bin_dim]
else:
new_order = [i for i in [2, 1, 0] if i != bin_dim] + [bin_dim]
uvw_points = cast(
torch.Tensor, torch.stack([xyz_points[..., i] for i in new_order], dim=-1)
)
num_bins = len(bins) + 1
isnotnan = ~torch.isnan(xyz_points[..., 0])
uvw_points_binned: torch.Tensor = torch.cat(
(
torch.round(100 * uvw_points[..., :-1] / resolution_in_cm).long(),
torch.bucketize(
uvw_points[..., -1:].contiguous(), boundaries=uvw_points.new(bins)
),
),
dim=-1,
)
maxes = (
xyz_points.new()
.long()
.new([map_size, map_size, num_bins])
.reshape((1, 1, 1, 3))
)
isvalid = torch.logical_and(
torch.logical_and(
(uvw_points_binned >= 0).all(-1), (uvw_points_binned < maxes).all(-1),
),
isnotnan,
)
uvw_points_binned_with_index_mat = torch.cat(
(
torch.repeat_interleave(
torch.arange(0, num_clouds).to(xyz_points.device), h * w
).reshape(-1, 1),
uvw_points_binned.reshape(-1, 3),
),
dim=1,
)
uvw_points_binned_with_index_mat[~isvalid.reshape(-1), :] = 0
ind = (
uvw_points_binned_with_index_mat[:, 0] * (map_size * map_size * num_bins)
+ uvw_points_binned_with_index_mat[:, 1] * (map_size * num_bins)
+ uvw_points_binned_with_index_mat[:, 2] * num_bins
+ uvw_points_binned_with_index_mat[:, 3]
)
ind[~isvalid.reshape(-1)] = 0
count = torch.bincount(
ind.view(-1),
isvalid.view(-1).long(),
minlength=num_clouds * map_size * map_size * num_bins,
)
return count.view(*start_shape[:-3], map_size, map_size, num_bins)
################
# FOR DEBUGGNG #
################
# The below functions are versions of the above which, because of their reliance on
# numpy functions, cannot use GPU acceleration. These are possibly useful for debugging,
# performance comparisons, or for validating that the above GPU variants work properly.
def _cpu_only_camera_space_xyz_to_world_xyz(
camera_space_xyzs: np.ndarray,
camera_world_xyz: np.ndarray,
rotation: float,
horizon: float,
):
# Adapted from https://github.com/devendrachaplot/Neural-SLAM.
# view_position = 3, world_points = 3 x N
# NOTE: camera_position is not equal to agent_position!!
# First compute the transformation that points undergo
# due to the camera's horizon
psi = -horizon * np.pi / 180
cos_psi = np.cos(psi)
sin_psi = np.sin(psi)
# fmt: off
horizon_transform = np.array(
[
[1, 0, 0], # unchanged
[0, cos_psi, sin_psi],
[0, -sin_psi, cos_psi,],
],
np.float64,
)
# fmt: on
# Next compute the transformation that points undergo
# due to the agent's rotation about the y-axis
phi = -rotation * np.pi / 180
cos_phi = np.cos(phi)
sin_phi = np.sin(phi)
# fmt: off
rotation_transform = np.array(
[
[cos_phi, 0, -sin_phi],
[0, 1, 0], # unchanged
[sin_phi, 0, cos_phi],],
np.float64,
)
# fmt: on
# Apply the above transformations
view_points = (rotation_transform @ horizon_transform) @ camera_space_xyzs
# Translate the points w.r.t. the camera's position in world space.
world_points = view_points + camera_world_xyz[:, None]
return world_points
def _cpu_only_depth_frame_to_camera_space_xyz(
depth_frame: np.ndarray, mask: Optional[np.ndarray], fov: float = 90
):
""""""
assert (
len(depth_frame.shape) == 2 and depth_frame.shape[0] == depth_frame.shape[1]
), f"depth has shape {depth_frame.shape}, we only support (N, N) shapes for now."
resolution = depth_frame.shape[0]
if mask is None:
mask = np.ones(depth_frame.shape, dtype=bool)
# pixel centers
camera_space_yx_offsets = (
np.stack(np.where(mask))
+ 0.5 # Offset by 0.5 so that we are in the middle of the pixel
)
# Subtract center
camera_space_yx_offsets -= resolution / 2.0
# Make "up" in y be positive
camera_space_yx_offsets[0, :] *= -1
# Put points on the clipping plane
camera_space_yx_offsets *= (2.0 / resolution) * math.tan((fov / 2) / 180 * math.pi)
camera_space_xyz = np.concatenate(
[
camera_space_yx_offsets[1:, :], # This is x
camera_space_yx_offsets[:1, :], # This is y
np.ones_like(camera_space_yx_offsets[:1, :]),
],
axis=0,
)
return camera_space_xyz * depth_frame[mask][None, :]
def _cpu_only_depth_frame_to_world_space_xyz(
depth_frame: np.ndarray,
camera_world_xyz: np.ndarray,
rotation: float,
horizon: float,
fov: float,
):
camera_space_xyz = _cpu_only_depth_frame_to_camera_space_xyz(
depth_frame=depth_frame, mask=None, fov=fov
)
world_points = _cpu_only_camera_space_xyz_to_world_xyz(
camera_space_xyzs=camera_space_xyz,
camera_world_xyz=camera_world_xyz,
rotation=rotation,
horizon=horizon,
)
return world_points.reshape((3, *depth_frame.shape)).transpose((1, 2, 0))
def _cpu_only_project_point_cloud_to_map(
xyz_points: np.ndarray,
bin_axis: str,
bins: Sequence[float],
map_size: int,
resolution_in_cm: int,
flip_row_col: bool,
):
"""Bins points into bins.
Adapted from https://github.com/devendrachaplot/Neural-SLAM.
# Parameters
xyz_points : (x,y,z) point clouds as a np.ndarray of shape (... x height x width x 3). (x,y,z)
should be coordinates specified in meters.
bin_axis : Either "x", "y", or "z", the axis which should be binned by the values in `bins`
bins: The values by which to bin along `bin_axis`, see the `bins` parameter of `np.digitize`
for more info.
map_size : The axes not specified by `bin_axis` will be be divided by `resolution_in_cm / 100`
and then rounded to the nearest integer. They are then expected to have their values
within the interval [0, ..., map_size - 1].
resolution_in_cm: The resolution_in_cm, in cm, of the map output from this function. Every
grid square of the map corresponds to a (`resolution_in_cm`x`resolution_in_cm`) square
in space.
flip_row_col: Should the rows/cols of the map be flipped
# Returns
A collection of maps of shape (... x map_size x map_size x (len(bins)+1)), note that bin_axis
has been moved to the last index of this returned map, the other two axes stay in their original
order unless `flip_row_col` has been called in which case they are reversed (useful if you give
points as often rows should correspond to y or z instead of x).
"""
bin_dim = ["x", "y", "z"].index(bin_axis)
start_shape = xyz_points.shape
xyz_points = xyz_points.reshape([-1, *start_shape[-3:]])
num_clouds, h, w, _ = xyz_points.shape
if not flip_row_col:
new_order = [i for i in [0, 1, 2] if i != bin_dim] + [bin_dim]
else:
new_order = [i for i in [2, 1, 0] if i != bin_dim] + [bin_dim]
uvw_points: np.ndarray = np.stack([xyz_points[..., i] for i in new_order], axis=-1)
num_bins = len(bins) + 1
isnotnan = ~np.isnan(xyz_points[..., 0])
uvw_points_binned = np.concatenate(
(
np.round(100 * uvw_points[..., :-1] / resolution_in_cm).astype(np.int32),
np.digitize(uvw_points[..., -1:], bins=bins).astype(np.int32),
),
axis=-1,
)
maxes = np.array([map_size, map_size, num_bins]).reshape((1, 1, 1, 3))
isvalid = np.logical_and.reduce(
(
(uvw_points_binned >= 0).all(-1),
(uvw_points_binned < maxes).all(-1),
isnotnan,
)
)
uvw_points_binned_with_index_mat = np.concatenate(
(
np.repeat(np.arange(0, num_clouds), h * w).reshape(-1, 1),
uvw_points_binned.reshape(-1, 3),
),
axis=1,
)
uvw_points_binned_with_index_mat[~isvalid.reshape(-1), :] = 0
ind = np.ravel_multi_index(
uvw_points_binned_with_index_mat.transpose(),
(num_clouds, map_size, map_size, num_bins),
)
ind[~isvalid.reshape(-1)] = 0
count = np.bincount(
ind.ravel(),
isvalid.ravel().astype(np.int32),
minlength=num_clouds * map_size * map_size * num_bins,
)
return count.reshape([*start_shape[:-3], map_size, map_size, num_bins])
| ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/mapping/mapping_utils/point_cloud_utils.py |
# MIT License
#
# Original Copyright (c) 2020 Devendra Chaplot
#
# Modified work Copyright (c) 2021 Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence
#
# Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
# of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
# in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
# to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
# copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
# furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
#
# The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
# copies or substantial portions of the Software.
#
# THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
# IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
# FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
# AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
# LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
# OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
# SOFTWARE.
import math
from typing import Optional, Tuple, Dict, Any
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.models as models
import torch.nn.functional as F
from allenact.utils.model_utils import simple_conv_and_linear_weights_init
DEGREES_TO_RADIANS = np.pi / 180.0
RADIANS_TO_DEGREES = 180.0 / np.pi
def _inv_sigmoid(x: torch.Tensor):
return torch.log(x) - torch.log1p(-x)
class ActiveNeuralSLAM(nn.Module):
"""Active Neural SLAM module.
This is an implementation of the Active Neural SLAM module
from:
```
Chaplot, D.S., Gandhi, D., Gupta, S., Gupta, A. and Salakhutdinov, R., 2020.
Learning To Explore Using Active Neural SLAM.
In International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR).
```
Note that this is purely the mapping component and does not include the planning
components from the above paper.
This implementation is adapted from `https://github.com/devendrachaplot/Neural-SLAM`,
we have extended this implementation to allow for an arbitrary number of output map
channels (enabling semantic mapping).
At a high level, this model takes as input RGB egocentric images and outputs metric
map tensors of shape (# channels) x height x width where height/width correspond to the
ground plane of the environment.
"""
def __init__(
self,
frame_height: int,
frame_width: int,
n_map_channels: int,
resolution_in_cm: int = 5,
map_size_in_cm: int = 2400,
vision_range_in_cm: int = 300,
use_pose_estimation: bool = False,
pretrained_resnet: bool = True,
freeze_resnet_batchnorm: bool = True,
use_resnet_layernorm: bool = False,
):
"""Initialize an Active Neural SLAM module.
# Parameters
frame_height : The height of the RGB images given to this module on calls to `forward`.
frame_width : The width of the RGB images given to this module on calls to `forward`.
n_map_channels : The number of output channels in the output maps.
resolution_in_cm : The resolution of the output map, see `map_size_in_cm`.
map_size_in_cm : The height & width of the map in centimeters. The size of the map
tensor returned on calls to forward will be `map_size_in_cm/resolution_in_cm`. Note
that `map_size_in_cm` must be an divisible by resolution_in_cm.
vision_range_in_cm : Given an RGB image input, this module will transform this image into
an "egocentric map" with height and width equaling `vision_range_in_cm/resolution_in_cm`.
This egocentr map corresponds to the area of the world directly in front of the agent.
This "egocentric map" will be rotated/translated into the allocentric reference frame and
used to update the larger, allocentric, map whose
height and width equal `map_size_in_cm/resolution_in_cm`. Thus this parameter controls
how much of the map will be updated on every step.
use_pose_estimation : Whether or not we should estimate the agent's change in position/rotation.
If `False`, you'll need to provide the ground truth changes in position/rotation.
pretrained_resnet : Whether or not to use ImageNet pre-trained model weights for the ResNet18
backbone.
freeze_resnet_batchnorm : Whether or not the batch normalization layers in the ResNet18 backbone
should be frozen and batchnorm updates disabled. You almost certainly want this to be `True`
as using batch normalization during RL training results in all sorts of issues unless you're
very careful.
use_resnet_layernorm : If you've enabled `freeze_resnet_batchnorm` (recommended) you'll likely want
to normalize the output from the ResNet18 model as we've found that these values can otherwise
grow quite large harming learning.
"""
super(ActiveNeuralSLAM, self).__init__()
self.frame_height = frame_height
self.frame_width = frame_width
self.n_map_channels = n_map_channels
self.resolution_in_cm = resolution_in_cm
self.map_size_in_cm = map_size_in_cm
self.input_channels = 3
self.vision_range_in_cm = vision_range_in_cm
self.dropout = 0.5
self.use_pose_estimation = use_pose_estimation
self.freeze_resnet_batchnorm = freeze_resnet_batchnorm
self.max_abs_map_logit_value = 20
# Visual Encoding
resnet = models.resnet18(pretrained=pretrained_resnet)
self.resnet_l5 = nn.Sequential(*list(resnet.children())[0:8])
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
*filter(bool, [nn.Conv2d(512, 64, (1, 1), stride=(1, 1)), nn.ReLU()])
)
self.bn_modules = [
module
for module in self.resnet_l5.modules()
if "BatchNorm" in type(module).__name__
]
if freeze_resnet_batchnorm:
for bn in self.bn_modules:
bn.momentum = 0
# Layernorm (if requested)
self.use_resnet_layernorm = use_resnet_layernorm
if self.use_resnet_layernorm:
assert (
self.freeze_resnet_batchnorm
), "When using layernorm, we require that set `freeze_resnet_batchnorm` to True."
self.resnet_normalizer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 1),
nn.LayerNorm(normalized_shape=[512, 7, 7], elementwise_affine=True,),
)
self.resnet_normalizer.apply(simple_conv_and_linear_weights_init)
else:
self.resnet_normalizer = nn.Identity()
# convolution output size
input_test = torch.randn(
1, self.input_channels, self.frame_height, self.frame_width
)
# Have to explicitly call .forward to get past LGTM checks as it thinks nn.Sequential isn't callable
conv_output = self.conv.forward(self.resnet_l5.forward(input_test))
self.conv_output_size = conv_output.view(-1).size(0)
# projection layer
self.proj1 = nn.Linear(self.conv_output_size, 1024)
assert self.vision_range % 8 == 0
self.deconv_in_height = self.vision_range // 8
self.deconv_in_width = self.deconv_in_height
self.n_input_channels_for_deconv = 64
proj2_out_size = 64 * self.deconv_in_height * self.deconv_in_width
self.proj2 = nn.Linear(1024, proj2_out_size)
if self.dropout > 0:
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(self.dropout)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(self.dropout)
# Deconv layers to predict map
self.deconv = nn.Sequential(
*filter(
bool,
[
nn.ConvTranspose2d(
self.n_input_channels_for_deconv,
32,
(4, 4),
stride=(2, 2),
padding=(1, 1),
),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.ConvTranspose2d(32, 16, (4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.ConvTranspose2d(
16, self.n_map_channels, (4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1)
),
],
)
)
# Pose Estimator
self.pose_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(2 * self.n_map_channels, 64, (4, 4), stride=(2, 2)),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, 32, (4, 4), stride=(2, 2)),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(32, 16, (3, 3), stride=(1, 1)),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Flatten(),
)
self.pose_conv_output_dim = (
self.pose_conv.forward(
torch.zeros(
1, 2 * self.n_map_channels, self.vision_range, self.vision_range
)
)
.view(-1)
.size(0)
)
# projection layer
self.pose_proj1 = nn.Linear(self.pose_conv_output_dim, 1024)
self.pose_proj2_x = nn.Linear(1024, 128)
self.pose_proj2_z = nn.Linear(1024, 128)
self.pose_proj2_o = nn.Linear(1024, 128)
self.pose_proj3_x = nn.Linear(128, 1)
self.pose_proj3_y = nn.Linear(128, 1)
self.pose_proj3_o = nn.Linear(128, 1)
if self.dropout > 0:
self.pose_dropout1 = nn.Dropout(self.dropout)
self.train()
@property
def device(self):
d = self.pose_proj1.weight.get_device()
if d < 0:
return torch.device("cpu")
return torch.device(d)
def train(self, mode: bool = True):
super().train(mode=mode)
if mode and self.freeze_resnet_batchnorm:
for module in self.bn_modules:
module.eval()
@property
def map_size(self):
return self.map_size_in_cm // self.resolution_in_cm
@property
def vision_range(self):
return self.vision_range_in_cm // (self.resolution_in_cm)
def image_to_egocentric_map_logits(
self,
images: Optional[torch.Tensor],
resnet_image_features: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
):
if resnet_image_features is None:
bs, _, _, _ = images.size()
resnet_image_features = self.resnet_normalizer(
self.resnet_l5(images[:, :3, :, :])
)
else:
bs = resnet_image_features.shape[0]
conv_output = self.conv(resnet_image_features)
proj1 = F.relu(self.proj1(conv_output.reshape(-1, self.conv_output_size)))
if self.dropout > 0:
proj1 = self.dropout1(proj1)
proj3 = F.relu(self.proj2(proj1))
deconv_input = proj3.view(
bs,
self.n_input_channels_for_deconv,
self.deconv_in_height,
self.deconv_in_width,
)
deconv_output = self.deconv(deconv_input)
return deconv_output
def allocentric_map_to_egocentric_view(
self, allocentric_map: torch.Tensor, xzr: torch.Tensor, padding_mode: str
):
# Index the egocentric viewpoints at the given xzr locations
with torch.no_grad():
allocentric_map = allocentric_map.float()
xzr = xzr.float()
theta = xzr[:, 2].float() * float(np.pi / 180)
# Here form the rotation matrix
cos_theta = torch.cos(theta)
sin_theta = torch.sin(theta)
rot_mat = torch.stack(
(
torch.stack((cos_theta, -sin_theta), -1),
torch.stack((sin_theta, cos_theta), -1),
),
1,
)
scaler = 2 * (100 / (self.resolution_in_cm * self.map_size))
offset_to_center_the_agent = scaler * xzr[:, :2].unsqueeze(-1) - 1
offset_to_top_of_image = rot_mat @ torch.FloatTensor([0, 1.0]).unsqueeze(
1
).to(self.device)
rotation_and_translate_mat = torch.cat(
(rot_mat, offset_to_top_of_image + offset_to_center_the_agent,), dim=-1,
)
ego_map = F.grid_sample(
allocentric_map,
F.affine_grid(
rotation_and_translate_mat.to(self.device), allocentric_map.shape,
),
padding_mode=padding_mode,
align_corners=False,
)
vr = self.vision_range
half_vr = vr // 2
center = self.map_size_in_cm // (2 * self.resolution_in_cm)
cropped = ego_map[:, :, :vr, (center - half_vr) : (center + half_vr)]
return cropped
def estimate_egocentric_dx_dz_dr(
self,
map_probs_egocentric: torch.Tensor,
last_map_probs_egocentric: torch.Tensor,
):
assert last_map_probs_egocentric.shape == map_probs_egocentric.shape
pose_est_input = torch.cat(
(map_probs_egocentric.detach(), last_map_probs_egocentric.detach()), dim=1
)
pose_conv_output = self.pose_conv(pose_est_input)
proj1 = F.relu(self.pose_proj1(pose_conv_output))
if self.dropout > 0:
proj1 = self.pose_dropout1(proj1)
proj2_x = F.relu(self.pose_proj2_x(proj1))
pred_dx = self.pose_proj3_x(proj2_x)
proj2_z = F.relu(self.pose_proj2_z(proj1))
pred_dz = self.pose_proj3_y(proj2_z)
proj2_o = F.relu(self.pose_proj2_o(proj1))
pred_do = self.pose_proj3_o(proj2_o)
return torch.cat((pred_dx, pred_dz, pred_do), dim=1)
@staticmethod
def update_allocentric_xzrs_with_egocentric_movement(
last_xzrs_allocentric: torch.Tensor, dx_dz_drs_egocentric: torch.Tensor,
):
new_xzrs_allocentric = last_xzrs_allocentric.clone()
theta = new_xzrs_allocentric[:, 2] * DEGREES_TO_RADIANS
sin_theta = torch.sin(theta)
cos_theta = torch.cos(theta)
new_xzrs_allocentric[:, :2] += torch.matmul(
torch.stack([cos_theta, -sin_theta, sin_theta, cos_theta], dim=-1).view(
-1, 2, 2
),
dx_dz_drs_egocentric[:, :2].unsqueeze(-1),
).squeeze(-1)
new_xzrs_allocentric[:, 2] += dx_dz_drs_egocentric[:, 2]
new_xzrs_allocentric[:, 2] = (
torch.fmod(new_xzrs_allocentric[:, 2] - 180.0, 360.0) + 180.0
)
new_xzrs_allocentric[:, 2] = (
torch.fmod(new_xzrs_allocentric[:, 2] + 180.0, 360.0) - 180.0
)
return new_xzrs_allocentric
def forward(
self,
images: Optional[torch.Tensor],
last_map_probs_allocentric: Optional[torch.Tensor],
last_xzrs_allocentric: Optional[torch.Tensor],
dx_dz_drs_egocentric: Optional[torch.Tensor],
last_map_logits_egocentric: Optional[torch.Tensor],
return_allocentric_maps=True,
resnet_image_features: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Create allocentric/egocentric maps predictions given RGB image
inputs.
Here it is assumed that `last_xzrs_allocentric` has been re-centered so that (x, z) == (0,0)
corresponds to the top left of the returned map (with increasing x/z moving to the bottom right of the map).
Note that all maps are oriented so that:
* **Increasing x values** correspond to **increasing columns** in the map(s).
* **Increasing z values** correspond to **increasing rows** in the map(s).
Note that this may seem a bit weird as:
* "north" is pointing downwards in the map,
* if you picture yourself as the agent facing north (i.e. down) in the map, then moving to the right from
the agent's perspective will correspond to **increasing** which column the agent is at:
```
agent facing downwards - - > (dir. to the right of the agent, i.e. moving right corresponds to +cols)
|
|
v (dir. agent faces, i.e. moving ahead corresponds to +rows)
```
This may be the opposite of what you expect.
# Parameters
images : A (# batches) x 3 x height x width tensor of RGB images. These should be
normalized for use with a resnet model. See [here](https_DOC_COLON_//pytorch.org/vision/stable/models.html)
for information (see also the `use_resnet_normalization` parameter of the
`allenact.base_abstractions.sensor.RGBSensor` sensor).
last_map_probs_allocentric : A (# batches) x (map channels) x (map height) x (map width)
tensor representing the colllection of allocentric maps to be updated.
last_xzrs_allocentric : A (# batches) x 3 tensor where `last_xzrs_allocentric[_DOC_COLON_, 0]`
are the agent's (allocentric) x-coordinates on the previous step,
`last_xzrs_allocentric[_DOC_COLON_, 1]` are the agent's (allocentric) z-coordinates from the previous
step, and `last_xzrs_allocentric[_DOC_COLON_, 2]` are the agent's rotations (allocentric, in degrees)
from the prevoius step.
dx_dz_drs_egocentric : A (# batches) x 3 tensor representing the agent's change in x (in meters), z (in meters),
and rotation (in degrees) from the previous step. Note that these changes are "egocentric" so that if the
agent moved 1 meter ahead from it's perspective this should correspond to a dz of +1.0 regardless of
the agent's orientation (similarly moving right would result in a dx of +1.0). This
is ignored (and thus can be `None`) if you are using pose estimation
(i.e. `self.use_pose_estimation` is `True`) or if `return_allocentric_maps` is `False`.
last_map_logits_egocentric : The "egocentric_update" output when calling this function
on the last agent's step. I.e. this should be the egocentric map view of the agent
from the last step. This is used to compute the change in the agent's position rotation.
This is ignored (and thus can be `None`) if you do not wish to estimate the agent's pose
(i.e. `self.use_pose_estimation` is `False`).
return_allocentric_maps : Whether or not to generate new allocentric maps given `last_map_probs_allocentric`
and the new map estimates. Creating these new allocentric maps is expensive so better avoided when
not needed.
resnet_image_features : Sometimes you may wish to compute the ResNet image features yourself for use
in another part of your model. Rather than having to recompute them multiple times, you can
instead compute them once and pass them into this forward call (in this case the input `images`
parameter is ignored). Note that if you're using the `self.resnet_l5` module to compute these
features, be sure to also normalize them with `self.resnet_normalizer` if you have opted to
`use_resnet_layernorm` when initializing this module).
# Returns
A dictionary with keys/values:
* "egocentric_update" - The egocentric map view for the given RGB image. This is what should
be used for computing losses in general.
* "map_logits_probs_update_no_grad" - The egocentric map view after it has been
rotated, translated, and moved into a full-sized allocentric map. This map has been
detached from the computation graph and so should not be used for gradient computations.
This will be `None` if `return_allocentric_maps` was `False`.
* "map_logits_probs_no_grad" - The newly updated allocentric map, this corresponds to
performing a pointwise maximum between `last_map_probs_allocentric` and the
above returned `map_probs_allocentric_update_no_grad`.
This will be `None` if `return_allocentric_maps` was `False`.
* "dx_dz_dr_egocentric_preds" - The predicted change in x, z, and rotation of the agent (from the
egocentric perspective of the agent).
* "xzr_allocentric_preds" - The (predicted if `self.use_pose_estimation == True`) allocentric
(x, z) position and rotation of the agent. This will equal `None` if `self.use_pose_estimation == False`
and `dx_dz_drs_egocentric` is `None`.
"""
# TODO: For consistency we should update things so that:
# "Furthermore, the rotation component of `last_xzrs_allocentric` and `dx_dz_drs_egocentric`
# should be specified in **degrees* with positive rotation corresponding to a **CLOCKWISE**
# rotation (this is the default used by the many game engines)."
map_logits_egocentric = self.image_to_egocentric_map_logits(
images=images, resnet_image_features=resnet_image_features
)
map_probs_egocentric = torch.sigmoid(map_logits_egocentric)
dx_dz_dr_egocentric_preds = None
if last_map_logits_egocentric is not None:
dx_dz_dr_egocentric_preds = self.estimate_egocentric_dx_dz_dr(
map_probs_egocentric=map_probs_egocentric,
last_map_probs_egocentric=torch.sigmoid(last_map_logits_egocentric),
)
if self.use_pose_estimation:
updated_xzrs_allocentrc = self.update_allocentric_xzrs_with_egocentric_movement(
last_xzrs_allocentric=last_xzrs_allocentric,
dx_dz_drs_egocentric=dx_dz_dr_egocentric_preds,
)
elif dx_dz_drs_egocentric is not None:
updated_xzrs_allocentrc = self.update_allocentric_xzrs_with_egocentric_movement(
last_xzrs_allocentric=last_xzrs_allocentric,
dx_dz_drs_egocentric=dx_dz_drs_egocentric,
)
else:
updated_xzrs_allocentrc = None
if return_allocentric_maps:
# Aggregate egocentric map prediction in the allocentric map
# using the predicted pose (if `self.use_pose_estimation`) or the ground
# truth pose (if not `self.use_pose_estimation`)
with torch.no_grad():
# Rotate and translate the egocentric map view, we do this grid sampling
# at the level of probabilities as bad results can occur at the logit level
full_size_allocentric_map_probs_update = _move_egocentric_map_view_into_allocentric_position(
map_probs_egocentric=map_probs_egocentric,
xzrs_allocentric=updated_xzrs_allocentrc,
allocentric_map_height_width=(self.map_size, self.map_size),
resolution_in_cm=self.resolution_in_cm,
)
map_probs_allocentric = torch.max(
last_map_probs_allocentric, full_size_allocentric_map_probs_update
)
else:
full_size_allocentric_map_probs_update = None
map_probs_allocentric = None
return {
"egocentric_update": map_logits_egocentric,
"map_probs_allocentric_update_no_grad": full_size_allocentric_map_probs_update,
"map_probs_allocentric_no_grad": map_probs_allocentric,
"dx_dz_dr_egocentric_preds": dx_dz_dr_egocentric_preds,
"xzr_allocentric_preds": updated_xzrs_allocentrc,
}
def _move_egocentric_map_view_into_allocentric_position(
map_probs_egocentric: torch.Tensor,
xzrs_allocentric: torch.Tensor,
allocentric_map_height_width: Tuple[int, int],
resolution_in_cm: float,
):
"""Translate/rotate an egocentric map view into an allocentric map.
Let's say you have a collection of egocentric maps in a tensor of shape
`(# batches) x (# channels) x (# ego rows) x (# ego columns)`
where these are "egocentric" as we assume the agent is always
at the center of the map and facing "downwards", namely
* **ahead** of the agent should correspond to **increasing rows** in the map(s).
* **right** of the agent should correspond to **increasing columns** in the map(s).
Note that the above is a bit weird as, if you picture yourself as the agent facing
downwards in the map, then moving to the right from the agent perspective. Here's how things
should look if you plotted one of these egocentric maps:
```
center of map - - > (dir. to the right of the agent, i.e. moving right corresponds to +cols)
|
|
v (dir. agent faces, i.e. moving ahead corresponds to +rows)
```
This function is used to translate/rotate the above ego maps so that
they are in the right position/rotation in an allocentric map of size
`(# batches) x (# channels) x (# allocentric_map_height_width[0]) x (# allocentric_map_height_width[1])`.
Adapted from the get_grid function in https://github.com/devendrachaplot/Neural-SLAM.
# Parameters
map_probs_egocentric : Egocentric map views.
xzrs_allocentric : (# batches)x3 tensor with `xzrs_allocentric[:, 0]` being the x-coordinates (in meters),
`xzrs_allocentric[:, 1]` being the z-coordinates (in meters), and `xzrs_allocentric[:, 2]` being the rotation
(in degrees) of the agent in the allocentric reference frame. Here it is assumed that `xzrs_allocentric` has
been re-centered so that (x, z) == (0,0) corresponds to the top left of the returned map (with increasing
x/z moving to the bottom right of the map). Note that positive rotations are in the counterclockwise direction.
allocentric_map_height_width : Height/width of the allocentric map to be returned
resolution_in_cm : Resolution (in cm) of map to be returned (and of map_probs_egocentric). I.e.
`map_probs_egocentric[0,0,0:1,0:1]` should correspond to a `resolution_in_cm x resolution_in_cm`
square on the ground plane in the world.
# Returns
`(# batches) x (# channels) x (# allocentric_map_height_width[0]) x (# allocentric_map_height_width[1])`
tensor where the input `map_probs_egocentric` maps have been rotated/translated so that they
are in the positions specified by `xzrs_allocentric`.
"""
# TODO: For consistency we should update the rotations so they are in the clockwise direction.
# First we place the egocentric map view into the center
# of a map that has the same size as the allocentric map
nbatch, c, ego_h, ego_w = map_probs_egocentric.shape
allo_h, allo_w = allocentric_map_height_width
max_view_range = math.sqrt((ego_w / 2.0) ** 2 + ego_h ** 2)
if min(allo_h, allo_w) / 2.0 < max_view_range:
raise NotImplementedError(
f"The shape of your egocentric view (ego_h, ego_w)==({ego_h, ego_w})"
f" is too large relative the size of the allocentric map (allo_h, allo_w)==({allo_h}, {allo_w})."
f" The height/width of your allocentric map should be at least {2 * max_view_range} to allow"
f" for no information to be lost when rotating the egocentric map."
)
full_size_ego_map_update_probs = map_probs_egocentric.new(
nbatch, c, *allocentric_map_height_width
).fill_(0)
assert (ego_h % 2, ego_w % 2, allo_h % 2, allo_w % 2) == (
0,
) * 4, "All map heights/widths should be divisible by 2."
x1 = allo_w // 2 - ego_w // 2
x2 = x1 + ego_w
z1 = allo_h // 2
z2 = z1 + ego_h
full_size_ego_map_update_probs[:, :, z1:z2, x1:x2] = map_probs_egocentric
# Now we'll rotate and translate `full_size_ego_map_update_probs`
# so that the egocentric map view is positioned where it should be
# in the allocentric coordinate frame
# To do this we first need to rescale our allocentric xz coordinates
# so that the center of the map is (0,0) and the top left corner is (-1, -1)
# as this is what's expected by the `affine_grid` function below.
rescaled_xzrs_allocentric = xzrs_allocentric.clone().detach().float()
rescaled_xzrs_allocentric[:, :2] *= (
100.0 / resolution_in_cm
) # Put x / z into map units rather than meters
rescaled_xzrs_allocentric[:, 0] /= allo_w / 2 # x corresponds to columns
rescaled_xzrs_allocentric[:, 1] /= allo_h / 2 # z corresponds to rows
rescaled_xzrs_allocentric[:, :2] -= 1.0 # Re-center
x = rescaled_xzrs_allocentric[:, 0]
z = rescaled_xzrs_allocentric[:, 1]
theta = (
-rescaled_xzrs_allocentric[:, 2] * DEGREES_TO_RADIANS
) # Notice the negative sign
cos_theta = theta.cos()
sin_theta = theta.sin()
zeroes = torch.zeros_like(cos_theta)
ones = torch.ones_like(cos_theta)
theta11 = torch.stack([cos_theta, -sin_theta, zeroes], 1)
theta12 = torch.stack([sin_theta, cos_theta, zeroes], 1)
theta1 = torch.stack([theta11, theta12], 1)
theta21 = torch.stack([ones, zeroes, x], 1)
theta22 = torch.stack([zeroes, ones, z], 1)
theta2 = torch.stack([theta21, theta22], 1)
grid_size = (nbatch, c, allo_h, allo_w)
rot_grid = F.affine_grid(theta1, grid_size)
trans_grid = F.affine_grid(theta2, grid_size)
return F.grid_sample(
F.grid_sample(
full_size_ego_map_update_probs,
rot_grid,
padding_mode="zeros",
align_corners=False,
),
trans_grid,
padding_mode="zeros",
align_corners=False,
)
| ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/mapping/mapping_models/active_neural_slam.py |
ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/mapping/mapping_models/__init__.py |
|
ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/preprocessors/__init__.py |
|
from typing import List, Callable, Optional, Any, cast, Dict
import gym
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision import models
from allenact.base_abstractions.preprocessor import Preprocessor
from allenact.utils.misc_utils import prepare_locals_for_super
class ResNetEmbedder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, resnet, pool=True):
super().__init__()
self.model = resnet
self.pool = pool
self.eval()
def forward(self, x):
with torch.no_grad():
x = self.model.conv1(x)
x = self.model.bn1(x)
x = self.model.relu(x)
x = self.model.maxpool(x)
x = self.model.layer1(x)
x = self.model.layer2(x)
x = self.model.layer3(x)
x = self.model.layer4(x)
if not self.pool:
return x
else:
x = self.model.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
return x
class ResNetPreprocessor(Preprocessor):
"""Preprocess RGB or depth image using a ResNet model."""
def __init__(
self,
input_uuids: List[str],
output_uuid: str,
input_height: int,
input_width: int,
output_height: int,
output_width: int,
output_dims: int,
pool: bool,
torchvision_resnet_model: Callable[..., models.ResNet] = models.resnet18,
device: Optional[torch.device] = None,
device_ids: Optional[List[torch.device]] = None,
**kwargs: Any
):
def f(x, k):
assert k in x, "{} must be set in ResNetPreprocessor".format(k)
return x[k]
def optf(x, k, default):
return x[k] if k in x else default
self.input_height = input_height
self.input_width = input_width
self.output_height = output_height
self.output_width = output_width
self.output_dims = output_dims
self.pool = pool
self.make_model = torchvision_resnet_model
self.device = torch.device("cpu") if device is None else device
self.device_ids = device_ids or cast(
List[torch.device], list(range(torch.cuda.device_count()))
)
self._resnet: Optional[ResNetEmbedder] = None
low = -np.inf
high = np.inf
shape = (self.output_dims, self.output_height, self.output_width)
assert (
len(input_uuids) == 1
), "resnet preprocessor can only consume one observation type"
observation_space = gym.spaces.Box(low=low, high=high, shape=shape)
super().__init__(**prepare_locals_for_super(locals()))
@property
def resnet(self) -> ResNetEmbedder:
if self._resnet is None:
self._resnet = ResNetEmbedder(
self.make_model(pretrained=True).to(self.device), pool=self.pool
)
return self._resnet
def to(self, device: torch.device) -> "ResNetPreprocessor":
self._resnet = self.resnet.to(device)
self.device = device
return self
def process(self, obs: Dict[str, Any], *args: Any, **kwargs: Any) -> Any:
x = obs[self.input_uuids[0]].to(self.device).permute(0, 3, 1, 2) # bhwc -> bchw
# If the input is depth, repeat it across all 3 channels
if x.shape[1] == 1:
x = x.repeat(1, 3, 1, 1)
return self.resnet(x.to(self.device))
| ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/preprocessors/resnet.py |
from abc import abstractmethod, ABC
from typing import Optional, Tuple, Any, cast, Union, Sequence
import PIL
import gym
import numpy as np
from torchvision import transforms
from allenact.base_abstractions.misc import EnvType
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import Sensor
from allenact.base_abstractions.task import SubTaskType
from allenact.utils.misc_utils import prepare_locals_for_super
from allenact.utils.tensor_utils import ScaleBothSides
class VisionSensor(Sensor[EnvType, SubTaskType]):
def __init__(
self,
mean: Optional[np.ndarray] = None,
stdev: Optional[np.ndarray] = None,
height: Optional[int] = None,
width: Optional[int] = None,
uuid: str = "vision",
output_shape: Optional[Tuple[int, ...]] = None,
output_channels: Optional[int] = None,
unnormalized_infimum: float = -np.inf,
unnormalized_supremum: float = np.inf,
scale_first: bool = True,
**kwargs: Any
):
"""Initializer.
# Parameters
mean : The images will be normalized with the given mean
stdev : The images will be normalized with the given standard deviations.
height : If it's a non-negative integer and `width` is also non-negative integer, the image returned from the
environment will be rescaled to have `height` rows and `width` columns using bilinear sampling.
width : If it's a non-negative integer and `height` is also non-negative integer, the image returned from the
environment will be rescaled to have `height` rows and `width` columns using bilinear sampling.
uuid : The universally unique identifier for the sensor.
output_shape : Optional observation space shape (alternative to `output_channels`).
output_channels : Optional observation space number of channels (alternative to `output_shape`).
unnormalized_infimum : Lower limit(s) for the observation space range.
unnormalized_supremum : Upper limit(s) for the observation space range.
scale_first : Whether to scale image before normalization (if needed).
kwargs : Extra kwargs. Currently unused.
"""
self._norm_means = mean
self._norm_sds = stdev
assert (self._norm_means is None) == (self._norm_sds is None), (
"In VisionSensor's config, "
"either both mean/stdev must be None or neither."
)
self._should_normalize = self._norm_means is not None
self._height = height
self._width = width
assert (self._width is None) == (self._height is None), (
"In VisionSensor's config, "
"either both height/width must be None or neither."
)
self._scale_first = scale_first
self.scaler: Optional[ScaleBothSides] = None
if self._width is not None:
self.scaler = ScaleBothSides(
width=cast(int, self._width), height=cast(int, self._height)
)
self.to_pil = transforms.ToPILImage() # assumes mode="RGB" for 3 channels
self._observation_space = self._make_observation_space(
output_shape=output_shape,
output_channels=output_channels,
unnormalized_infimum=unnormalized_infimum,
unnormalized_supremum=unnormalized_supremum,
)
assert int(PIL.__version__.split(".")[0]) != 7, (
"We found that Pillow version >=7.* has broken scaling,"
" please downgrade to version 6.2.1 or upgrade to >=8.0.0"
)
observation_space = self._get_observation_space()
super().__init__(**prepare_locals_for_super(locals()))
def _make_observation_space(
self,
output_shape: Optional[Tuple[int, ...]],
output_channels: Optional[int],
unnormalized_infimum: float,
unnormalized_supremum: float,
) -> gym.spaces.Box:
assert output_shape is None or output_channels is None, (
"In VisionSensor's config, "
"only one of output_shape and output_channels can be not None."
)
shape: Optional[Tuple[int, ...]] = None
if output_shape is not None:
shape = output_shape
elif self._height is not None and output_channels is not None:
shape = (
cast(int, self._height),
cast(int, self._width),
cast(int, output_channels),
)
if not self._should_normalize or shape is None or len(shape) == 1:
return gym.spaces.Box(
low=np.float32(unnormalized_infimum),
high=np.float32(unnormalized_supremum),
shape=shape,
)
else:
out_shape = shape[:-1] + (1,)
low = np.tile(
(unnormalized_infimum - cast(np.ndarray, self._norm_means))
/ cast(np.ndarray, self._norm_sds),
out_shape,
)
high = np.tile(
(unnormalized_supremum - cast(np.ndarray, self._norm_means))
/ cast(np.ndarray, self._norm_sds),
out_shape,
)
return gym.spaces.Box(low=np.float32(low), high=np.float32(high))
def _get_observation_space(self):
return self._observation_space
@property
def height(self) -> Optional[int]:
"""Height that input image will be rescale to have.
# Returns
The height as a non-negative integer or `None` if no rescaling is done.
"""
return self._height
@property
def width(self) -> Optional[int]:
"""Width that input image will be rescale to have.
# Returns
The width as a non-negative integer or `None` if no rescaling is done.
"""
return self._width
@abstractmethod
def frame_from_env(self, env: EnvType, task: Optional[SubTaskType]) -> np.ndarray:
raise NotImplementedError
def get_observation(
self, env: EnvType, task: Optional[SubTaskType], *args: Any, **kwargs: Any
) -> Any:
im = self.frame_from_env(env=env, task=task)
assert (
im.dtype == np.float32 and (len(im.shape) == 2 or im.shape[-1] == 1)
) or (im.shape[-1] == 3 and im.dtype == np.uint8), (
"Input frame must either have 3 channels and be of"
" type np.uint8 or have one channel and be of type np.float32"
)
if self._scale_first:
if self.scaler is not None and im.shape[:2] != (self._height, self._width):
im = np.array(self.scaler(self.to_pil(im)), dtype=im.dtype) # hwc
assert im.dtype in [np.uint8, np.float32]
if im.dtype == np.uint8:
im = im.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
if self._should_normalize:
im -= self._norm_means
im /= self._norm_sds
if not self._scale_first:
if self.scaler is not None and im.shape[:2] != (self._height, self._width):
im = np.array(self.scaler(self.to_pil(im)), dtype=np.float32) # hwc
return im
class RGBSensor(VisionSensor[EnvType, SubTaskType], ABC):
IMAGENET_RGB_MEANS: Tuple[float, float, float] = (0.485, 0.456, 0.406)
IMAGENET_RGB_STDS: Tuple[float, float, float] = (0.229, 0.224, 0.225)
def __init__(
self,
use_resnet_normalization: bool = False,
mean: Optional[Union[np.ndarray, Sequence[float]]] = IMAGENET_RGB_MEANS,
stdev: Optional[Union[np.ndarray, Sequence[float]]] = IMAGENET_RGB_STDS,
height: Optional[int] = None,
width: Optional[int] = None,
uuid: str = "rgb",
output_shape: Optional[Tuple[int, ...]] = None,
output_channels: int = 3,
unnormalized_infimum: float = 0.0,
unnormalized_supremum: float = 1.0,
scale_first: bool = True,
**kwargs: Any
):
"""Initializer.
# Parameters
use_resnet_normalization : Whether to apply image normalization with the given `mean` and `stdev`.
mean : The images will be normalized with the given mean if `use_resnet_normalization` is True (default
`[0.485, 0.456, 0.406]`, i.e. the standard resnet normalization mean).
stdev : The images will be normalized with the given standard deviation if `use_resnet_normalization` is True
(default `[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]`, i.e. the standard resnet normalization standard deviation).
height: If it's a non-negative integer and `width` is also non-negative integer, the image returned from the
environment will be rescaled to have `height` rows and `width` columns using bilinear sampling.
width: If it's a non-negative integer and `height` is also non-negative integer, the image returned from the
environment will be rescaled to have `height` rows and `width` columns using bilinear sampling.
uuid: The universally unique identifier for the sensor.
output_shape: Optional observation space shape (alternative to `output_channels`).
output_channels: Optional observation space number of channels (alternative to `output_shape`).
unnormalized_infimum: Lower limit(s) for the observation space range.
unnormalized_supremum: Upper limit(s) for the observation space range.
scale_first: Whether to scale image before normalization (if needed).
kwargs : Extra kwargs. Currently unused.
"""
if not use_resnet_normalization:
mean, stdev = None, None
if isinstance(mean, tuple):
mean = np.array(mean, dtype=np.float32).reshape(1, 1, len(mean))
if isinstance(stdev, tuple):
stdev = np.array(stdev, dtype=np.float32).reshape(1, 1, len(stdev))
super().__init__(**prepare_locals_for_super(locals()))
class DepthSensor(VisionSensor[EnvType, SubTaskType], ABC):
def __init__(
self,
use_normalization: bool = False,
mean: Optional[Union[np.ndarray, float]] = 0.5,
stdev: Optional[Union[np.ndarray, float]] = 0.25,
height: Optional[int] = None,
width: Optional[int] = None,
uuid: str = "depth",
output_shape: Optional[Tuple[int, ...]] = None,
output_channels: int = 1,
unnormalized_infimum: float = 0.0,
unnormalized_supremum: float = 5.0,
scale_first: bool = True,
**kwargs: Any
):
"""Initializer.
# Parameters
config : If `config["use_normalization"]` is `True` then the depth images will be normalized
with mean 0.5 and standard deviation 0.25. If both `config["height"]` and `config["width"]` are
non-negative integers then the depth image returned from the environment will be rescaled to have shape
(config["height"], config["width"]) using bilinear sampling.
use_normalization : Whether to apply image normalization with the given `mean` and `stdev`.
mean : The images will be normalized with the given mean if `use_normalization` is True (default 0.5).
stdev : The images will be normalized with the given standard deviation if `use_normalization` is True
(default 0.25).
height: If it's a non-negative integer and `width` is also non-negative integer, the image returned from the
environment will be rescaled to have `height` rows and `width` columns using bilinear sampling.
width: If it's a non-negative integer and `height` is also non-negative integer, the image returned from the
environment will be rescaled to have `height` rows and `width` columns using bilinear sampling.
uuid: The universally unique identifier for the sensor.
output_shape: Optional observation space shape (alternative to `output_channels`).
output_channels: Optional observation space number of channels (alternative to `output_shape`).
unnormalized_infimum: Lower limit(s) for the observation space range.
unnormalized_supremum: Upper limit(s) for the observation space range.
scale_first: Whether to scale image before normalization (if needed).
kwargs : Extra kwargs. Currently unused.
"""
if not use_normalization:
mean, stdev = None, None
if isinstance(mean, float):
mean = np.array(mean, dtype=np.float32).reshape(1, 1)
if isinstance(stdev, float):
stdev = np.array(stdev, dtype=np.float32).reshape(1, 1)
super().__init__(**prepare_locals_for_super(locals()))
def get_observation( # type: ignore
self, env: EnvType, task: Optional[SubTaskType], *args: Any, **kwargs: Any
) -> Any:
depth = super().get_observation(env, task, *args, **kwargs)
depth = np.expand_dims(depth, 2)
return depth
| ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/sensors/vision_sensors.py |
ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/sensors/__init__.py |
|
# Original work Copyright (c) Facebook, Inc. and its affiliates.
# Modified work Copyright (c) Allen Institute for AI
# This source code is licensed under the MIT license found in the
# LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree.
"""Several of the models defined in this file are modified versions of those
found in https://github.com/joel99/habitat-pointnav-
aux/blob/master/habitat_baselines/"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from allenact.utils.model_utils import FeatureEmbedding
from allenact.embodiedai.aux_losses.losses import (
InverseDynamicsLoss,
TemporalDistanceLoss,
CPCALoss,
FrequencyLoss,
SupImitationLoss
)
class AuxiliaryModel(nn.Module):
"""The class of defining the models for all kinds of self-supervised
auxiliary tasks."""
def __init__(
self,
aux_uuid: str,
action_dim: int,
obs_embed_dim: int,
belief_dim: int,
action_embed_size: int = 4,
cpca_classifier_hidden_dim: int = 32,
):
super().__init__()
self.aux_uuid = aux_uuid
self.action_dim = action_dim
self.obs_embed_dim = obs_embed_dim
self.belief_dim = belief_dim
if self.aux_uuid == InverseDynamicsLoss.UUID:
self.decoder = nn.Linear(
2 * self.obs_embed_dim + self.belief_dim, self.action_dim
)
elif self.aux_uuid == TemporalDistanceLoss.UUID:
self.decoder = nn.Linear(2 * self.obs_embed_dim + self.belief_dim, 1)
elif CPCALoss.UUID in self.aux_uuid: # the CPCA family with various k
## Auto-regressive model to predict future context
self.action_embedder = FeatureEmbedding(
self.action_dim + 1, action_embed_size
)
# NOTE: add extra 1 in embedding dict cuz we will pad zero actions?
self.context_model = nn.GRU(action_embed_size, self.belief_dim)
## Classifier to estimate mutual information
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(
self.belief_dim + self.obs_embed_dim, cpca_classifier_hidden_dim
),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(cpca_classifier_hidden_dim, 1),
)
elif FrequencyLoss.UUID in self.aux_uuid:
pass
elif SupImitationLoss.UUID in self.aux_uuid:
pass
else:
raise ValueError("Unknown Auxiliary Loss UUID")
def forward(self, features: torch.FloatTensor):
if self.aux_uuid in [InverseDynamicsLoss.UUID, TemporalDistanceLoss.UUID]:
return self.decoder(features)
else:
raise NotImplementedError(
f"Auxiliary model with UUID {self.aux_uuid} does not support `forward` call."
)
| ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/models/aux_models.py |
ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/models/__init__.py |
|
"""Basic building block torch networks that can be used across a variety of
tasks."""
from typing import (
Sequence,
Dict,
Union,
cast,
List,
Callable,
Optional,
Tuple,
Any,
)
import gym
import numpy as np
import torch
from gym.spaces.dict import Dict as SpaceDict
import torch.nn as nn
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.policy import ActorCriticModel, DistributionType
from allenact.base_abstractions.distributions import CategoricalDistr, Distr
from allenact.base_abstractions.misc import ActorCriticOutput, Memory
from allenact.utils.model_utils import make_cnn, compute_cnn_output
from allenact.utils.system import get_logger
class SimpleCNN(nn.Module):
"""A Simple N-Conv CNN followed by a fully connected layer. Takes in
observations (of type gym.spaces.dict) and produces an embedding of the
`rgb_uuid` and/or `depth_uuid` components.
# Attributes
observation_space : The observation_space of the agent, should have `rgb_uuid` or `depth_uuid` as
a component (otherwise it is a blind model).
output_size : The size of the embedding vector to produce.
"""
def __init__(
self,
observation_space: SpaceDict,
output_size: int,
rgb_uuid: Optional[str],
depth_uuid: Optional[str],
layer_channels: Sequence[int] = (32, 64, 32),
kernel_sizes: Sequence[Tuple[int, int]] = ((8, 8), (4, 4), (3, 3)),
layers_stride: Sequence[Tuple[int, int]] = ((4, 4), (2, 2), (1, 1)),
paddings: Sequence[Tuple[int, int]] = ((0, 0), (0, 0), (0, 0)),
dilations: Sequence[Tuple[int, int]] = ((1, 1), (1, 1), (1, 1)),
flatten: bool = True,
output_relu: bool = True,
):
"""Initializer.
# Parameters
observation_space : See class attributes documentation.
output_size : See class attributes documentation.
"""
super().__init__()
self.rgb_uuid = rgb_uuid
if self.rgb_uuid is not None:
assert self.rgb_uuid in observation_space.spaces
self._n_input_rgb = observation_space.spaces[self.rgb_uuid].shape[2]
assert self._n_input_rgb >= 0
else:
self._n_input_rgb = 0
self.depth_uuid = depth_uuid
if self.depth_uuid is not None:
assert self.depth_uuid in observation_space.spaces
self._n_input_depth = observation_space.spaces[self.depth_uuid].shape[2]
assert self._n_input_depth >= 0
else:
self._n_input_depth = 0
if not self.is_blind:
# hyperparameters for layers
self._cnn_layers_channels = list(layer_channels)
self._cnn_layers_kernel_size = list(kernel_sizes)
self._cnn_layers_stride = list(layers_stride)
self._cnn_layers_paddings = list(paddings)
self._cnn_layers_dilations = list(dilations)
if self._n_input_rgb > 0:
input_rgb_cnn_dims = np.array(
observation_space.spaces[self.rgb_uuid].shape[:2], dtype=np.float32
)
self.rgb_cnn = self.make_cnn_from_params(
output_size=output_size,
input_dims=input_rgb_cnn_dims,
input_channels=self._n_input_rgb,
flatten=flatten,
output_relu=output_relu,
)
if self._n_input_depth > 0:
input_depth_cnn_dims = np.array(
observation_space.spaces[self.depth_uuid].shape[:2],
dtype=np.float32,
)
self.depth_cnn = self.make_cnn_from_params(
output_size=output_size,
input_dims=input_depth_cnn_dims,
input_channels=self._n_input_depth,
flatten=flatten,
output_relu=output_relu,
)
def make_cnn_from_params(
self,
output_size: int,
input_dims: np.ndarray,
input_channels: int,
flatten: bool,
output_relu: bool,
) -> nn.Module:
output_dims = input_dims
for kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation in zip(
self._cnn_layers_kernel_size,
self._cnn_layers_stride,
self._cnn_layers_paddings,
self._cnn_layers_dilations,
):
# noinspection PyUnboundLocalVariable
output_dims = self._conv_output_dim(
dimension=output_dims,
padding=np.array(padding, dtype=np.float32),
dilation=np.array(dilation, dtype=np.float32),
kernel_size=np.array(kernel_size, dtype=np.float32),
stride=np.array(stride, dtype=np.float32),
)
# noinspection PyUnboundLocalVariable
cnn = make_cnn(
input_channels=input_channels,
layer_channels=self._cnn_layers_channels,
kernel_sizes=self._cnn_layers_kernel_size,
strides=self._cnn_layers_stride,
paddings=self._cnn_layers_paddings,
dilations=self._cnn_layers_dilations,
output_height=output_dims[0],
output_width=output_dims[1],
output_channels=output_size,
flatten=flatten,
output_relu=output_relu,
)
self.layer_init(cnn)
return cnn
@staticmethod
def _conv_output_dim(
dimension: Sequence[int],
padding: Sequence[int],
dilation: Sequence[int],
kernel_size: Sequence[int],
stride: Sequence[int],
) -> Tuple[int, ...]:
"""Calculates the output height and width based on the input height and
width to the convolution layer. For parameter definitions see.
[here](https://pytorch.org/docs/master/nn.html#torch.nn.Conv2d).
# Parameters
dimension : See above link.
padding : See above link.
dilation : See above link.
kernel_size : See above link.
stride : See above link.
"""
assert len(dimension) == 2
out_dimension = []
for i in range(len(dimension)):
out_dimension.append(
int(
np.floor(
(
(
dimension[i]
+ 2 * padding[i]
- dilation[i] * (kernel_size[i] - 1)
- 1
)
/ stride[i]
)
+ 1
)
)
)
return tuple(out_dimension)
@staticmethod
def layer_init(cnn) -> None:
"""Initialize layer parameters using Kaiming normal."""
for layer in cnn:
if isinstance(layer, (nn.Conv2d, nn.Linear)):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(layer.weight, nn.init.calculate_gain("relu"))
if layer.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(layer.bias, val=0)
@property
def is_blind(self):
"""True if the observation space doesn't include `self.rgb_uuid` or
`self.depth_uuid`."""
return self._n_input_rgb + self._n_input_depth == 0
def forward(self, observations: Dict[str, torch.Tensor]): # type: ignore
if self.is_blind:
return None
def check_use_agent(new_setting):
if use_agent is not None:
assert (
use_agent is new_setting
), "rgb and depth must both use an agent dim or none"
return new_setting
cnn_output_list: List[torch.Tensor] = []
use_agent: Optional[bool] = None
if self.rgb_uuid is not None:
use_agent = check_use_agent(len(observations[self.rgb_uuid].shape) == 6)
cnn_output_list.append(
compute_cnn_output(self.rgb_cnn, observations[self.rgb_uuid])
)
if self.depth_uuid is not None:
use_agent = check_use_agent(len(observations[self.depth_uuid].shape) == 6)
cnn_output_list.append(
compute_cnn_output(self.depth_cnn, observations[self.depth_uuid])
)
if use_agent:
channels_dim = 3 # [step, sampler, agent, channel (, height, width)]
else:
channels_dim = 2 # [step, sampler, channel (, height, width)]
return torch.cat(cnn_output_list, dim=channels_dim)
class RNNStateEncoder(nn.Module):
"""A simple RNN-based model playing a role in many baseline embodied-
navigation agents.
See `seq_forward` for more details of how this model is used.
"""
def __init__(
self,
input_size: int,
hidden_size: int,
num_layers: int = 1,
rnn_type: str = "GRU",
trainable_masked_hidden_state: bool = False,
):
"""An RNN for encoding the state in RL. Supports masking the hidden
state during various timesteps in the forward lass.
# Parameters
input_size : The input size of the RNN.
hidden_size : The hidden size.
num_layers : The number of recurrent layers.
rnn_type : The RNN cell type. Must be GRU or LSTM.
trainable_masked_hidden_state : If `True` the initial hidden state (used at the start of a Task)
is trainable (as opposed to being a vector of zeros).
"""
super().__init__()
self._num_recurrent_layers = num_layers
self._rnn_type = rnn_type
self.rnn = getattr(torch.nn, rnn_type)(
input_size=input_size, hidden_size=hidden_size, num_layers=num_layers
)
self.trainable_masked_hidden_state = trainable_masked_hidden_state
if trainable_masked_hidden_state:
self.init_hidden_state = nn.Parameter(
0.1 * torch.randn((num_layers, 1, hidden_size)), requires_grad=True
)
self.layer_init()
def layer_init(self):
"""Initialize the RNN parameters in the model."""
for name, param in self.rnn.named_parameters():
if "weight" in name:
nn.init.orthogonal_(param)
elif "bias" in name:
nn.init.constant_(param, 0)
@property
def num_recurrent_layers(self) -> int:
"""The number of recurrent layers in the network."""
return self._num_recurrent_layers * (2 if "LSTM" in self._rnn_type else 1)
def _pack_hidden(
self, hidden_states: Union[torch.FloatTensor, Sequence[torch.FloatTensor]]
) -> torch.FloatTensor:
"""Stacks hidden states in an LSTM together (if using a GRU rather than
an LSTM this is just the identity).
# Parameters
hidden_states : The hidden states to (possibly) stack.
"""
if "LSTM" in self._rnn_type:
hidden_states = cast(
torch.FloatTensor,
torch.cat([hidden_states[0], hidden_states[1]], dim=0),
)
return cast(torch.FloatTensor, hidden_states)
def _unpack_hidden(
self, hidden_states: torch.FloatTensor
) -> Union[torch.FloatTensor, Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor]]:
"""Partial inverse of `_pack_hidden` (exact if there are 2 hidden
layers)."""
if "LSTM" in self._rnn_type:
new_hidden_states = (
hidden_states[0 : self._num_recurrent_layers],
hidden_states[self._num_recurrent_layers :],
)
return cast(Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor], new_hidden_states)
return cast(torch.FloatTensor, hidden_states)
def _mask_hidden(
self,
hidden_states: Union[Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, ...], torch.FloatTensor],
masks: torch.FloatTensor,
) -> Union[Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, ...], torch.FloatTensor]:
"""Mask input hidden states given `masks`. Useful when masks represent
steps on which a task has completed.
# Parameters
hidden_states : The hidden states.
masks : Masks to apply to hidden states (see seq_forward).
# Returns
Masked hidden states. Here masked hidden states will be replaced with
either all zeros (if `trainable_masked_hidden_state` was False) and will
otherwise be a learnable collection of parameters.
"""
if not self.trainable_masked_hidden_state:
if isinstance(hidden_states, tuple):
hidden_states = tuple(
cast(torch.FloatTensor, v * masks) for v in hidden_states
)
else:
hidden_states = cast(torch.FloatTensor, masks * hidden_states)
else:
if isinstance(hidden_states, tuple):
# noinspection PyTypeChecker
hidden_states = tuple(
v * masks # type:ignore
+ (1.0 - masks) * (self.init_hidden_state.repeat(1, v.shape[1], 1)) # type: ignore
for v in hidden_states # type:ignore
) # type: ignore
else:
# noinspection PyTypeChecker
hidden_states = masks * hidden_states + (1 - masks) * ( # type: ignore
self.init_hidden_state.repeat(1, hidden_states.shape[1], 1)
)
return hidden_states
def single_forward(
self,
x: torch.FloatTensor,
hidden_states: torch.FloatTensor,
masks: torch.FloatTensor,
) -> Tuple[
torch.FloatTensor, Union[torch.FloatTensor, Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, ...]]
]:
"""Forward for a single-step input."""
(
x,
hidden_states,
masks,
mem_agent,
obs_agent,
nsteps,
nsamplers,
nagents,
) = self.adapt_input(x, hidden_states, masks)
unpacked_hidden_states = self._unpack_hidden(hidden_states)
x, unpacked_hidden_states = self.rnn(
x,
self._mask_hidden(
unpacked_hidden_states, cast(torch.FloatTensor, masks[0].view(1, -1, 1))
),
)
return self.adapt_result(
x,
self._pack_hidden(unpacked_hidden_states),
mem_agent,
obs_agent,
nsteps,
nsamplers,
nagents,
)
def adapt_input(
self,
x: torch.FloatTensor,
hidden_states: torch.FloatTensor,
masks: torch.FloatTensor,
) -> Tuple[
torch.FloatTensor,
torch.FloatTensor,
torch.FloatTensor,
bool,
bool,
int,
int,
int,
]:
nsteps, nsamplers = masks.shape[:2]
assert len(hidden_states.shape) in [
3,
4,
], "hidden_states must be [layer, sampler, hidden] or [layer, sampler, agent, hidden]"
assert len(x.shape) in [
3,
4,
], "observations must be [step, sampler, data] or [step, sampler, agent, data]"
nagents = 1
mem_agent: bool
if len(hidden_states.shape) == 4: # [layer, sampler, agent, hidden]
mem_agent = True
nagents = hidden_states.shape[2]
else: # [layer, sampler, hidden]
mem_agent = False
obs_agent: bool
if len(x.shape) == 4: # [step, sampler, agent, dims]
obs_agent = True
else: # [step, sampler, dims]
obs_agent = False
# Flatten (nsamplers, nagents)
x = x.view(nsteps, nsamplers * nagents, -1) # type:ignore
masks = masks.expand(-1, -1, nagents).reshape( # type:ignore
nsteps, nsamplers * nagents
)
# Flatten (nsamplers, nagents) and remove step dim
hidden_states = hidden_states.view( # type:ignore
self.num_recurrent_layers, nsamplers * nagents, -1
)
# noinspection PyTypeChecker
return x, hidden_states, masks, mem_agent, obs_agent, nsteps, nsamplers, nagents
def adapt_result(
self,
outputs: torch.FloatTensor,
hidden_states: torch.FloatTensor,
mem_agent: bool,
obs_agent: bool,
nsteps: int,
nsamplers: int,
nagents: int,
) -> Tuple[
torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor,
]:
output_dims = (nsteps, nsamplers) + ((nagents, -1) if obs_agent else (-1,))
hidden_dims = (self.num_recurrent_layers, nsamplers) + (
(nagents, -1) if mem_agent else (-1,)
)
outputs = cast(torch.FloatTensor, outputs.view(*output_dims))
hidden_states = cast(torch.FloatTensor, hidden_states.view(*hidden_dims),)
return outputs, hidden_states
def seq_forward( # type: ignore
self,
x: torch.FloatTensor,
hidden_states: torch.FloatTensor,
masks: torch.FloatTensor,
) -> Tuple[
torch.FloatTensor, Union[torch.FloatTensor, Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, ...]]
]:
"""Forward for a sequence of length T.
# Parameters
x : (Steps, Samplers, Agents, -1) tensor.
hidden_states : The starting hidden states.
masks : A (Steps, Samplers, Agents) tensor.
The masks to be applied to hidden state at every timestep, equal to 0 whenever the previous step finalized
the task, 1 elsewhere.
"""
(
x,
hidden_states,
masks,
mem_agent,
obs_agent,
nsteps,
nsamplers,
nagents,
) = self.adapt_input(x, hidden_states, masks)
# steps in sequence which have zero for any episode. Assume t=0 has
# a zero in it.
has_zeros = (masks[1:] == 0.0).any(dim=-1).nonzero().squeeze().cpu()
# +1 to correct the masks[1:]
if has_zeros.dim() == 0:
# handle scalar
has_zeros = [has_zeros.item() + 1] # type: ignore
else:
has_zeros = (has_zeros + 1).numpy().tolist()
# add t=0 and t=T to the list
has_zeros = cast(List[int], [0] + has_zeros + [nsteps])
unpacked_hidden_states = self._unpack_hidden(
cast(torch.FloatTensor, hidden_states)
)
outputs = []
for i in range(len(has_zeros) - 1):
# process steps that don't have any zeros in masks together
start_idx = int(has_zeros[i])
end_idx = int(has_zeros[i + 1])
# noinspection PyTypeChecker
rnn_scores, unpacked_hidden_states = self.rnn(
x[start_idx:end_idx],
self._mask_hidden(
unpacked_hidden_states,
cast(torch.FloatTensor, masks[start_idx].view(1, -1, 1)),
),
)
outputs.append(rnn_scores)
return self.adapt_result(
cast(torch.FloatTensor, torch.cat(outputs, dim=0)),
self._pack_hidden(unpacked_hidden_states),
mem_agent,
obs_agent,
nsteps,
nsamplers,
nagents,
)
def forward( # type: ignore
self,
x: torch.FloatTensor,
hidden_states: torch.FloatTensor,
masks: torch.FloatTensor,
) -> Tuple[
torch.FloatTensor, Union[torch.FloatTensor, Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, ...]]
]:
nsteps = masks.shape[0]
if nsteps == 1:
return self.single_forward(x, hidden_states, masks)
return self.seq_forward(x, hidden_states, masks)
class LinearActorCritic(ActorCriticModel[CategoricalDistr]):
def __init__(
self,
input_uuid: str,
action_space: gym.spaces.Discrete,
observation_space: SpaceDict,
):
super().__init__(action_space=action_space, observation_space=observation_space)
assert (
input_uuid in observation_space.spaces
), "LinearActorCritic expects only a single observational input."
self.input_uuid = input_uuid
box_space: gym.spaces.Box = observation_space[self.input_uuid]
assert isinstance(box_space, gym.spaces.Box), (
"LinearActorCritic requires that"
"observation space corresponding to the input uuid is a Box space."
)
assert len(box_space.shape) == 1
self.in_dim = box_space.shape[0]
self.linear = nn.Linear(self.in_dim, action_space.n + 1)
nn.init.orthogonal_(self.linear.weight)
nn.init.constant_(self.linear.bias, 0)
# noinspection PyMethodMayBeStatic
def _recurrent_memory_specification(self):
return None
def forward(self, observations, memory, prev_actions, masks):
out = self.linear(observations[self.input_uuid])
# noinspection PyArgumentList
return (
ActorCriticOutput(
# ensure [steps, samplers, ...]
distributions=CategoricalDistr(logits=out[..., :-1]),
# ensure [steps, samplers, flattened]
values=cast(torch.FloatTensor, out[..., -1:].view(*out.shape[:2], -1)),
extras={},
),
None,
)
class RNNActorCritic(ActorCriticModel[Distr]):
def __init__(
self,
input_uuid: str,
action_space: gym.spaces.Discrete,
observation_space: SpaceDict,
hidden_size: int = 128,
num_layers: int = 1,
rnn_type: str = "GRU",
head_type: Callable[..., ActorCriticModel[Distr]] = LinearActorCritic,
):
super().__init__(action_space=action_space, observation_space=observation_space)
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.rnn_type = rnn_type
assert (
input_uuid in observation_space.spaces
), "LinearActorCritic expects only a single observational input."
self.input_uuid = input_uuid
box_space: gym.spaces.Box = observation_space[self.input_uuid]
assert isinstance(box_space, gym.spaces.Box), (
"RNNActorCritic requires that"
"observation space corresponding to the input uuid is a Box space."
)
assert len(box_space.shape) == 1
self.in_dim = box_space.shape[0]
self.state_encoder = RNNStateEncoder(
input_size=self.in_dim,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
num_layers=num_layers,
rnn_type=rnn_type,
trainable_masked_hidden_state=True,
)
self.head_uuid = "{}_{}".format("rnn", input_uuid)
self.ac_nonrecurrent_head: ActorCriticModel[Distr] = head_type(
input_uuid=self.head_uuid,
action_space=action_space,
observation_space=SpaceDict(
{
self.head_uuid: gym.spaces.Box(
low=np.float32(0.0), high=np.float32(1.0), shape=(hidden_size,)
)
}
),
)
self.memory_key = "rnn"
@property
def recurrent_hidden_state_size(self) -> int:
return self.hidden_size
@property
def num_recurrent_layers(self) -> int:
return self.state_encoder.num_recurrent_layers
def _recurrent_memory_specification(self):
return {
self.memory_key: (
(
("layer", self.num_recurrent_layers),
("sampler", None),
("hidden", self.recurrent_hidden_state_size),
),
torch.float32,
)
}
def forward( # type:ignore
self,
observations: Dict[str, Union[torch.FloatTensor, Dict[str, Any]]],
memory: Memory,
prev_actions: torch.Tensor,
masks: torch.FloatTensor,
) -> Tuple[ActorCriticOutput[DistributionType], Optional[Memory]]:
if self.memory_key not in memory:
get_logger().warning(
f"Key {self.memory_key} not found in memory,"
f" initializing this as all zeros."
)
obs = observations[self.input_uuid]
memory.check_append(
key=self.memory_key,
tensor=obs.new(
self.num_recurrent_layers,
obs.shape[1],
self.recurrent_hidden_state_size,
)
.float()
.zero_(),
sampler_dim=1,
)
rnn_out, mem_return = self.state_encoder(
x=observations[self.input_uuid],
hidden_states=memory.tensor(self.memory_key),
masks=masks,
)
# noinspection PyCallingNonCallable
out, _ = self.ac_nonrecurrent_head(
observations={self.head_uuid: rnn_out},
memory=None,
prev_actions=prev_actions,
masks=masks,
)
# noinspection PyArgumentList
return (
out,
memory.set_tensor(self.memory_key, mem_return),
)
| ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/models/basic_models.py |
# Original work Copyright (c) Facebook, Inc. and its affiliates.
# Modified work Copyright (c) Allen Institute for AI
# This source code is licensed under the MIT license found in the
# LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree.
# Adapted from https://github.com/joel99/habitat-pointnav-aux/blob/master/habitat_baselines/
from typing import Optional
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from gym.spaces.dict import Dict as SpaceDict
from allenact.utils.model_utils import Flatten
from allenact.utils.system import get_logger
def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1, groups=1):
"""3x3 convolution with padding."""
return nn.Conv2d(
in_planes,
out_planes,
kernel_size=3,
stride=stride,
padding=1,
bias=False,
groups=groups,
)
def conv1x1(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
"""1x1 convolution."""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
resneXt = False
def __init__(
self, inplanes, planes, ngroups, stride=1, downsample=None, cardinality=1,
):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.convs = nn.Sequential(
conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride, groups=cardinality),
nn.GroupNorm(ngroups, planes),
nn.ReLU(True),
conv3x3(planes, planes, groups=cardinality),
nn.GroupNorm(ngroups, planes),
)
self.downsample = downsample
self.relu = nn.ReLU(True)
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.convs(x)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
return self.relu(out + residual)
def _build_bottleneck_branch(inplanes, planes, ngroups, stride, expansion, groups=1):
return nn.Sequential(
conv1x1(inplanes, planes),
nn.GroupNorm(ngroups, planes),
nn.ReLU(True),
conv3x3(planes, planes, stride, groups=groups),
nn.GroupNorm(ngroups, planes),
nn.ReLU(True),
conv1x1(planes, planes * expansion),
nn.GroupNorm(ngroups, planes * expansion),
)
class SE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, planes, r=16):
super().__init__()
self.squeeze = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.excite = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(planes, int(planes / r)),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(int(planes / r), planes),
nn.Sigmoid(),
)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
x = self.squeeze(x)
x = x.view(b, c)
x = self.excite(x)
return x.view(b, c, 1, 1)
def _build_se_branch(planes, r=16):
return SE(planes, r)
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
resneXt = False
def __init__(
self, inplanes, planes, ngroups, stride=1, downsample=None, cardinality=1,
):
super().__init__()
self.convs = _build_bottleneck_branch(
inplanes, planes, ngroups, stride, self.expansion, groups=cardinality,
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
def _impl(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.convs(x)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
return self.relu(out + identity)
def forward(self, x):
return self._impl(x)
class SEBottleneck(Bottleneck):
def __init__(
self, inplanes, planes, ngroups, stride=1, downsample=None, cardinality=1,
):
super().__init__(inplanes, planes, ngroups, stride, downsample, cardinality)
self.se = _build_se_branch(planes * self.expansion)
def _impl(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.convs(x)
out = self.se(out) * out
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
return self.relu(out + identity)
class SEResNeXtBottleneck(SEBottleneck):
expansion = 2
resneXt = True
class ResNeXtBottleneck(Bottleneck):
expansion = 2
resneXt = True
class GroupNormResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, base_planes, ngroups, block, layers, cardinality=1):
super(GroupNormResNet, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
in_channels,
base_planes,
kernel_size=7,
stride=2,
padding=3,
bias=False,
),
nn.GroupNorm(ngroups, base_planes),
nn.ReLU(True),
)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.cardinality = cardinality
self.inplanes = base_planes
if block.resneXt:
base_planes *= 2
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, ngroups, base_planes, layers[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(
block, ngroups, base_planes * 2, layers[1], stride=2
)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(
block, ngroups, base_planes * 2 * 2, layers[2], stride=2
)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(
block, ngroups, base_planes * 2 * 2 * 2, layers[3], stride=2
)
self.final_channels = self.inplanes
self.final_spatial_compress = 1.0 / (2 ** 5)
def _make_layer(self, block, ngroups, planes, blocks, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
conv1x1(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion, stride),
nn.GroupNorm(ngroups, planes * block.expansion),
)
layers = []
layers.append(
block(
self.inplanes,
planes,
ngroups,
stride,
downsample,
cardinality=self.cardinality,
)
)
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for i in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, ngroups))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
return x
def gnresnet18(in_channels, base_planes, ngroups):
model = GroupNormResNet(in_channels, base_planes, ngroups, BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2])
return model
def gnresnet50(in_channels, base_planes, ngroups):
model = GroupNormResNet(in_channels, base_planes, ngroups, Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3])
return model
def gnresneXt50(in_channels, base_planes, ngroups):
model = GroupNormResNet(
in_channels,
base_planes,
ngroups,
ResNeXtBottleneck,
[3, 4, 6, 3],
cardinality=int(base_planes / 2),
)
return model
def se_gnresnet50(in_channels, base_planes, ngroups):
model = GroupNormResNet(
in_channels, base_planes, ngroups, SEBottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3]
)
return model
def se_gnresneXt50(in_channels, base_planes, ngroups):
model = GroupNormResNet(
in_channels,
base_planes,
ngroups,
SEResNeXtBottleneck,
[3, 4, 6, 3],
cardinality=int(base_planes / 2),
)
return model
def se_gnresneXt101(in_channels, base_planes, ngroups):
model = GroupNormResNet(
in_channels,
base_planes,
ngroups,
SEResNeXtBottleneck,
[3, 4, 23, 3],
cardinality=int(base_planes / 2),
)
return model
class GroupNormResNetEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
observation_space: SpaceDict,
rgb_uuid: Optional[str],
depth_uuid: Optional[str],
output_size: int,
baseplanes=32,
ngroups=32,
spatial_size=128,
make_backbone=None,
):
super().__init__()
self._inputs = []
self.rgb_uuid = rgb_uuid
if self.rgb_uuid is not None:
assert self.rgb_uuid in observation_space.spaces
self._n_input_rgb = observation_space.spaces[self.rgb_uuid].shape[2]
assert self._n_input_rgb >= 0
self._inputs.append(self.rgb_uuid)
else:
self._n_input_rgb = 0
self.depth_uuid = depth_uuid
if self.depth_uuid is not None:
assert self.depth_uuid in observation_space.spaces
self._n_input_depth = observation_space.spaces[self.depth_uuid].shape[2]
assert self._n_input_depth >= 0
self._inputs.append(self.depth_uuid)
else:
self._n_input_depth = 0
if not self.is_blind:
spatial_size = (
observation_space.spaces[self._inputs[0]].shape[0] // 2
) # H (=W) / 2
# RGBD into one model
input_channels = self._n_input_rgb + self._n_input_depth # C
self.backbone = make_backbone(input_channels, baseplanes, ngroups)
final_spatial = int(
np.ceil(spatial_size * self.backbone.final_spatial_compress)
) # fix bug in habitat that uses int()
after_compression_flat_size = 2048
num_compression_channels = int(
round(after_compression_flat_size / (final_spatial ** 2))
)
self.compression = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
self.backbone.final_channels,
num_compression_channels,
kernel_size=3,
padding=1,
bias=False,
),
nn.GroupNorm(1, num_compression_channels),
nn.ReLU(True),
)
self.output_shape = (
num_compression_channels,
final_spatial,
final_spatial,
)
self.head = nn.Sequential(
Flatten(),
nn.Linear(np.prod(self.output_shape), output_size),
nn.ReLU(True),
)
self.layer_init()
@property
def is_blind(self):
return self._n_input_rgb + self._n_input_depth == 0
def layer_init(self):
for layer in self.modules():
if isinstance(layer, (nn.Conv2d, nn.Linear)):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(layer.weight, nn.init.calculate_gain("relu"))
if layer.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(layer.bias, val=0)
get_logger().info("initialize resnet encoder")
def forward(self, observations):
if self.is_blind:
return None
# TODO: the reshape follows compute_cnn_output()
# but it's hard to make the forward as a nn.Module as cnn param
cnn_input = []
for mode in self._inputs:
mode_obs = observations[mode]
assert len(mode_obs.shape) in [
5,
6,
], "CNN input must have shape [STEP, SAMPLER, (AGENT,) dim1, dim2, dim3]"
nagents: Optional[int] = None
if len(mode_obs.shape) == 6:
nsteps, nsamplers, nagents = mode_obs.shape[:3]
else:
nsteps, nsamplers = mode_obs.shape[:2]
# Make FLAT_BATCH = nsteps * nsamplers (* nagents)
mode_obs = mode_obs.view(
(-1,) + mode_obs.shape[2 + int(nagents is not None) :]
)
# permute tensor to dimension [BATCH x CHANNEL x HEIGHT X WIDTH]
mode_obs = mode_obs.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
cnn_input.append(mode_obs)
x = torch.cat(cnn_input, dim=1)
x = F.avg_pool2d(x, 2) # 2x downsampling
x = self.backbone(x) # (256, 4, 4)
x = self.compression(x) # (128, 4, 4)
x = self.head(x) # (2048) -> (hidden_size)
if nagents is not None:
x = x.reshape((nsteps, nsamplers, nagents,) + x.shape[1:])
else:
x = x.reshape((nsteps, nsamplers,) + x.shape[1:])
return x
| ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/models/resnet.py |
# Original work Copyright (c) Facebook, Inc. and its affiliates.
# Modified work Copyright (c) Allen Institute for AI
# This source code is licensed under the MIT license found in the
# LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree.
# Adapted from https://github.com/joel99/habitat-pointnav-aux/blob/master/habitat_baselines/
from typing import Tuple
import math
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class Fusion(nn.Module):
"""Base class of belief fusion model from Auxiliary Tasks Speed Up Learning
PointGoal Navigation (Ye, 2020) Child class should implement
`get_belief_weights` function to generate weights to fuse the beliefs from
all the auxiliary task into one."""
def __init__(self, hidden_size, obs_embed_size, num_tasks):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size # H
self.obs_embed_size = obs_embed_size # Z
self.num_tasks = num_tasks # k
def forward(
self,
all_beliefs: torch.FloatTensor, # (T, N, H, K)
obs_embeds: torch.FloatTensor, # (T, N, Z)
) -> Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor]: # (T, N, H), (T, N, K)
num_steps, num_samplers, _, _ = all_beliefs.shape
all_beliefs = all_beliefs.view(
num_steps * num_samplers, self.hidden_size, self.num_tasks
)
obs_embeds = obs_embeds.view(num_steps * num_samplers, -1)
weights = self.get_belief_weights(
all_beliefs=all_beliefs, obs_embeds=obs_embeds, # (T*N, H, K) # (T*N, Z)
).unsqueeze(
-1
) # (T*N, K, 1)
beliefs = torch.bmm(all_beliefs, weights) # (T*N, H, 1)
beliefs = beliefs.squeeze(-1).view(num_steps, num_samplers, self.hidden_size)
weights = weights.squeeze(-1).view(num_steps, num_samplers, self.num_tasks)
return beliefs, weights
def get_belief_weights(
self,
all_beliefs: torch.FloatTensor, # (T*N, H, K)
obs_embeds: torch.FloatTensor, # (T*N, Z)
) -> torch.FloatTensor: # (T*N, K)
raise NotImplementedError()
class AverageFusion(Fusion):
UUID = "avg"
def get_belief_weights(
self,
all_beliefs: torch.FloatTensor, # (T*N, H, K)
obs_embeds: torch.FloatTensor, # (T*N, Z)
) -> torch.FloatTensor: # (T*N, K)
batch_size = all_beliefs.shape[0]
weights = torch.ones(batch_size, self.num_tasks).to(all_beliefs)
weights /= self.num_tasks
return weights
class SoftmaxFusion(Fusion):
"""Situational Fusion of Visual Representation for Visual Navigation
https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.09073."""
UUID = "smax"
def __init__(self, hidden_size, obs_embed_size, num_tasks):
super().__init__(hidden_size, obs_embed_size, num_tasks)
# mapping from rnn input to task
# ignore beliefs
self.linear = nn.Linear(obs_embed_size, num_tasks)
def get_belief_weights(
self,
all_beliefs: torch.FloatTensor, # (T*N, H, K)
obs_embeds: torch.FloatTensor, # (T*N, Z)
) -> torch.FloatTensor: # (T*N, K)
scores = self.linear(obs_embeds) # (T*N, K)
weights = torch.softmax(scores, dim=-1)
return weights
class AttentiveFusion(Fusion):
"""Attention is All You Need https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762 i.e. scaled
dot-product attention."""
UUID = "attn"
def __init__(self, hidden_size, obs_embed_size, num_tasks):
super().__init__(hidden_size, obs_embed_size, num_tasks)
self.linear = nn.Linear(obs_embed_size, hidden_size)
def get_belief_weights(
self,
all_beliefs: torch.FloatTensor, # (T*N, H, K)
obs_embeds: torch.FloatTensor, # (T*N, Z)
) -> torch.FloatTensor: # (T*N, K)
queries = self.linear(obs_embeds).unsqueeze(1) # (T*N, 1, H)
scores = torch.bmm(queries, all_beliefs).squeeze(1) # (T*N, K)
weights = torch.softmax(
scores / math.sqrt(self.hidden_size), dim=-1
) # (T*N, K)
return weights
| ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/models/fusion_models.py |
from typing import Tuple, Dict, Optional, List
from allenact.utils.system import get_logger
from collections import OrderedDict
import os
import gym
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from gym.spaces.dict import Dict as SpaceDict
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.policy import (
ActorCriticModel,
LinearCriticHead,
LinearActorHead,
ObservationType,
DistributionType,
)
from allenact.base_abstractions.misc import ActorCriticOutput, Memory
from allenact.utils.model_utils import FeatureEmbedding
from allenact.embodiedai.models.basic_models import RNNStateEncoder
from allenact.embodiedai.models.aux_models import AuxiliaryModel
from allenact.embodiedai.aux_losses.losses import MultiAuxTaskNegEntropyLoss
from allenact.base_abstractions.distributions import CategoricalDistr
from typing import TypeVar
from allenact.embodiedai.models.fusion_models import Fusion
from allenact.base_abstractions.distributions import Distr
FusionType = TypeVar("FusionType", bound=Fusion)
class succ_pred_model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,input_size):
super(succ_pred_model,self).__init__()
self.rnn_unit = RNNStateEncoder(input_size=input_size,hidden_size=512)
self.linear_layer = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(512,128),nn.ReLU(),nn.Linear(128,32),nn.ReLU(),nn.Linear(32,8),nn.ReLU(),nn.Linear(8,1))
def forward(self,x,hidden_states,masks):
out,rnn_hidden_state = self.rnn_unit(x,hidden_states,masks)
out = self.linear_layer(out)
return out,rnn_hidden_state
# succ_pred_model= succ_pred_model(512)#.load_state_dict('./')
# succ_pred_model.load_state_dict('./')
class MultiDimActionDistr(Distr):
'''
Takes two categorical distributions and outputs a joint multidimensional distributions
'''
def __init__(self,actor_distr,label_distr):
super().__init__()
self.actor_distr = actor_distr
self.label_distr = label_distr
def sample(self):
actor_out = self.actor_distr.sample()
label_out = self.label_distr.sample()
return {"nav_action": actor_out, "ask_action": label_out}
def log_prob(self,value):
return self.label_distr.log_prob(value["ask_action"]) #+ self.actor_distr.log_prob(value["nav_action"])
def entropy(self):
return self.label_distr.entropy() #+ self.actor_distr.entropy()
def mode(self):
return {"nav_action":self.actor_distr.mode(),"ask_action":self.label_distr.mode()}
class VisualNavActorCritic(ActorCriticModel[CategoricalDistr]):
"""Base class of visual navigation / manipulation (or broadly, embodied AI)
model.
`forward_encoder` function requires implementation.
"""
def __init__(
self,
action_space: gym.spaces.Discrete,
observation_space: SpaceDict,
hidden_size=512,
multiple_beliefs=False,
beliefs_fusion: Optional[FusionType] = None,
auxiliary_uuids: Optional[List[str]] = None,
):
super().__init__(action_space=action_space, observation_space=observation_space)
self._hidden_size = hidden_size
assert multiple_beliefs == (beliefs_fusion is not None)
self.multiple_beliefs = multiple_beliefs
self.beliefs_fusion = beliefs_fusion
self.auxiliary_uuids = auxiliary_uuids
if isinstance(self.auxiliary_uuids, list) and len(self.auxiliary_uuids) == 0:
self.auxiliary_uuids = None
self.nav_action_space = action_space['nav_action']
self.ask_action_space = action_space['ask_action']
self.succ_pred_rnn_hidden_state = None
self.succ_pred_model = None
'''
mlp_input_size = self._hidden_size+48+6 ## 6 for prev action embedding
self.ask_actor_head = LinearActorHead(mlp_input_size,self.ask_action_space.n) ## concatenating frozen beliefs with success prediction output
self.ask_critic_head = LinearCriticHead(mlp_input_size) ## 6 for prev action embedding
self.ask_policy_mlp = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(mlp_input_size,mlp_input_size//2),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(mlp_input_size//2,mlp_input_size//4),
)
self.ask_policy_gru = RNNStateEncoder(mlp_input_size//4,128,
num_layers=1,
rnn_type="GRU",
trainable_masked_hidden_state=False,) ##restore to run gru variant
self.ask_policy_gru_hidden_state = None
self.ask_actor_head = LinearActorHead(128,self.ask_action_space.n) ## concatenating frozen beliefs with success prediction output
self.ask_critic_head = LinearCriticHead(128)
'''
self.end_action_idx = 3
# self.succ_pred_model = succ_pred_model(512)#.load_state_dict('./')
# Define the placeholders in init function
self.state_encoders: nn.ModuleDict
self.aux_models: nn.ModuleDict
self.actor: LinearActorHead
self.critic: LinearCriticHead
def create_state_encoders(
self,
obs_embed_size: int,
prev_action_embed_size: int,
num_rnn_layers: int,
rnn_type: str,
add_prev_actions: bool,
trainable_masked_hidden_state=False,
):
rnn_input_size = obs_embed_size
self.prev_action_embedder = FeatureEmbedding(
input_size=self.nav_action_space.n,
output_size=prev_action_embed_size if add_prev_actions else 0,
)
if add_prev_actions:
rnn_input_size += prev_action_embed_size
state_encoders = OrderedDict() # perserve insertion order in py3.6
if self.multiple_beliefs: # multiple belief model
for aux_uuid in self.auxiliary_uuids:
state_encoders[aux_uuid] = RNNStateEncoder(
rnn_input_size,
self._hidden_size,
num_layers=num_rnn_layers,
rnn_type=rnn_type,
trainable_masked_hidden_state=trainable_masked_hidden_state,
)
# create fusion model
self.fusion_model = self.beliefs_fusion(
hidden_size=self._hidden_size,
obs_embed_size=obs_embed_size,
num_tasks=len(self.auxiliary_uuids),
)
else: # single belief model
state_encoders["single_belief"] = RNNStateEncoder(
rnn_input_size,
self._hidden_size,
num_layers=num_rnn_layers,
rnn_type=rnn_type,
trainable_masked_hidden_state=trainable_masked_hidden_state,
)
self.state_encoders = nn.ModuleDict(state_encoders)
self.belief_names = list(self.state_encoders.keys())
get_logger().info(
"there are {} belief models: {}".format(
len(self.belief_names), self.belief_names
)
)
def create_expert_encoder(self,
input_size: int,
prev_action_embed_size: int,
num_rnn_layers: int,
rnn_type: str,
trainable_masked_hidden_state=False,):
self.prev_expert_action_embedder = FeatureEmbedding(
input_size=self.nav_action_space.n,
output_size=prev_action_embed_size,
)
self.expert_encoder = RNNStateEncoder(input_size+prev_action_embed_size,
self._hidden_size,
num_layers=num_rnn_layers,
rnn_type=rnn_type,
trainable_masked_hidden_state=trainable_masked_hidden_state,
)
def create_ask4_help_module(self,
prev_action_embed_size: int,
num_rnn_layers: int,
rnn_type:str,
ask_gru_hidden_size=128,
trainable_masked_hidden_state=False,
adaptive_reward=False,
):
self.prev_ask_action_embedder = FeatureEmbedding(
input_size=self.ask_action_space.n,
output_size=prev_action_embed_size,
)
self.expert_mask_embedder = FeatureEmbedding(input_size=2,output_size=prev_action_embed_size)
if adaptive_reward:
self.reward_function_embedder = FeatureEmbedding(input_size=30,output_size=prev_action_embed_size*2)
else:
self.reward_function_embedder = None
if adaptive_reward:
mlp_input_size = self._hidden_size + 48 + prev_action_embed_size + prev_action_embed_size + prev_action_embed_size*2
## ask_action + expert_action embedding + reward_function_embed
else:
mlp_input_size = self._hidden_size + 48 + prev_action_embed_size + prev_action_embed_size
self.ask_policy_mlp = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(mlp_input_size,mlp_input_size//2),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(mlp_input_size//2,mlp_input_size//4),
)
self.ask_policy_gru = RNNStateEncoder(mlp_input_size//4,
ask_gru_hidden_size,
num_layers=num_rnn_layers,
rnn_type="GRU",
trainable_masked_hidden_state=False,)
self.ask_actor_head = LinearActorHead(ask_gru_hidden_size,self.ask_action_space.n) ## concatenating frozen beliefs with success prediction output
self.ask_critic_head = LinearCriticHead(ask_gru_hidden_size)
def load_state_dict(self, state_dict):
new_state_dict = OrderedDict()
for key in state_dict.keys():
if "state_encoder." in key: # old key name
new_key = key.replace("state_encoder.", "state_encoders.single_belief.")
else:
new_key = key
new_state_dict[new_key] = state_dict[key]
return super().load_state_dict(new_state_dict,strict=False) # compatible in keys
def create_actorcritic_head(self):
self.actor = LinearActorHead(self._hidden_size, self.nav_action_space.n)
self.critic = LinearCriticHead(self._hidden_size)
def create_aux_models(self, obs_embed_size: int, action_embed_size: int):
if self.auxiliary_uuids is None:
return
aux_models = OrderedDict()
for aux_uuid in self.auxiliary_uuids:
aux_models[aux_uuid] = AuxiliaryModel(
aux_uuid=aux_uuid,
action_dim=self.nav_action_space.n,
obs_embed_dim=obs_embed_size,
belief_dim=self._hidden_size,
action_embed_size=action_embed_size,
)
self.aux_models = nn.ModuleDict(aux_models)
@property
def num_recurrent_layers(self):
"""Number of recurrent hidden layers."""
return list(self.state_encoders.values())[0].num_recurrent_layers
@property
def recurrent_hidden_state_size(self):
"""The recurrent hidden state size of a single model."""
return {'single_belief':self._hidden_size,'residual_gru':self._hidden_size,'ask4help_gru':128,'succ_pred_gru':512}
# return self._hidden_size
def _recurrent_memory_specification(self):
if self.is_finetuned:
self.belief_names.append('ask4help_gru')
self.belief_names.append('succ_pred_gru')
if self.adapt_belief:
self.belief_names.append('residual_gru')
return {
memory_key: (
(
("layer", self.num_recurrent_layers),
("sampler", None),
("hidden", self.recurrent_hidden_state_size[memory_key]),
),
torch.float32,
)
for memory_key in self.belief_names
}
def forward_encoder(self, observations: ObservationType) -> torch.FloatTensor:
raise NotImplementedError("Obs Encoder Not Implemented")
def fuse_beliefs(
self, beliefs_dict: Dict[str, torch.FloatTensor], obs_embeds: torch.FloatTensor,
) -> Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, Optional[torch.FloatTensor]]:
all_beliefs = torch.stack(list(beliefs_dict.values()), dim=-1) # (T, N, H, k)
if self.multiple_beliefs: # call the fusion model
return self.fusion_model(all_beliefs=all_beliefs, obs_embeds=obs_embeds)
# single belief
beliefs = all_beliefs.squeeze(-1) # (T,N,H)
return beliefs, None
def forward( # type:ignore
self,
observations: ObservationType,
memory: Memory,
prev_actions: torch.Tensor,
masks: torch.FloatTensor,
) -> Tuple[ActorCriticOutput[DistributionType], Optional[Memory]]:
"""Processes input batched observations to produce new actor and critic
values. Processes input batched observations (along with prior hidden
states, previous actions, and masks denoting which recurrent hidden
states should be masked) and returns an `ActorCriticOutput` object
containing the model's policy (distribution over actions) and
evaluation of the current state (value).
# Parameters
observations : Batched input observations.
memory : `Memory` containing the hidden states from initial timepoints.
prev_actions : Tensor of previous actions taken.
masks : Masks applied to hidden states. See `RNNStateEncoder`.
# Returns
Tuple of the `ActorCriticOutput` and recurrent hidden state.
"""
if self.is_finetuned:
expert_action_obs = observations['expert_action']
expert_action = expert_action_obs[:,:,0]
expert_action_mask = expert_action_obs[:,:,1]
nactions = self.nav_action_space.n
with torch.no_grad():
# 1.1 use perception model (i.e. encoder) to get observation embeddings
obs_embeds = self.forward_encoder(observations)
nsteps,nsamplers,_ = obs_embeds.shape
prev_actions_embeds = self.prev_action_embedder(prev_actions['nav_action'])
joint_embeds = torch.cat((obs_embeds, prev_actions_embeds), dim=-1) # (T, N, *)
if not self.adapt_belief:
beliefs_dict = {}
for key, model in self.state_encoders.items():
beliefs_dict[key], rnn_hidden_states = model(
joint_embeds, memory.tensor(key), masks
)
memory.set_tensor(key, rnn_hidden_states) # update memory here
# 3. fuse beliefs for multiple belief models
beliefs, task_weights = self.fuse_beliefs(
beliefs_dict, obs_embeds
)
beliefs_combined = beliefs
if self.adapt_belief:
### only done when adaptation is switched on###
joint_embeds_all = torch.cat((obs_embeds, prev_actions_embeds), dim=-1)
beliefs_combined = None
for step in range(nsteps):
# 1.2 use embedding model to get prev_action embeddings
joint_embeds = joint_embeds_all[step,:,:].unsqueeze(0)
masks_step = masks[step,:,:].unsqueeze(0)
# 2. use RNNs to get single/multiple beliefs
with torch.no_grad():
beliefs_dict = {}
for key, model in self.state_encoders.items():
beliefs_dict[key], rnn_hidden_states = model(
joint_embeds, memory.tensor(key), masks_step
)
memory.set_tensor(key, rnn_hidden_states) # update memory here
# 3. fuse beliefs for multiple belief models
beliefs, task_weights = self.fuse_beliefs(
beliefs_dict, obs_embeds
) # fused beliefs
if beliefs_combined is None:
beliefs_combined = beliefs
else:
beliefs_combined = torch.cat((beliefs_combined,beliefs),dim=0)
expert_action_embedding = self.prev_expert_action_embedder(expert_action[step,:].unsqueeze(0))
res_input = torch.cat((beliefs,expert_action_embedding),dim=-1)
beliefs_residual,residual_hidden_states = self.expert_encoder(res_input,memory.tensor('residual_gru'),masks_step)
memory.set_tensor('residual_gru',residual_hidden_states)
beliefs_residual = beliefs_residual * expert_action_mask.unsqueeze(-1)[step,:,:].unsqueeze(0)
beliefs = beliefs + beliefs_residual
# if beliefs_combined is None:
# beliefs_combined = beliefs
# else:
# beliefs_combined = torch.cat((beliefs_combined,beliefs),dim=0)
memory.set_tensor('single_belief',beliefs)
beliefs = beliefs_combined
with torch.no_grad():
actor_pred_distr = self.actor(beliefs)
if self.end_action_in_ask:
## making logits of end so small that it's never picked by the agent.
actor_pred_distr.logits[:,:,self.end_action_idx] -= 999
if self.succ_pred_model is None:
self.succ_pred_model = succ_pred_model(512).to(beliefs.device)
self.succ_pred_model.load_state_dict(
torch.load('./storage/best_auc_clip_run_belief_480_rollout_len.pt',
map_location=beliefs.device))
succ_pred_out, succ_rnn_hidden_states = self.succ_pred_model(beliefs, memory.tensor('succ_pred_gru'),masks)
memory.set_tensor('succ_pred_gru', succ_rnn_hidden_states)
succ_prob = torch.sigmoid(succ_pred_out)
succ_prob_inp = succ_prob.repeat(1,1,48)
ask_policy_input = torch.cat((beliefs,succ_prob_inp),dim=-1)
prev_ask_action_embed = self.prev_ask_action_embedder(prev_actions['ask_action'])
expert_mask_embed = self.expert_mask_embedder(expert_action_mask)
if self.adaptive_reward:
reward_config_embed = self.reward_function_embedder(observations['reward_config_sensor'])
ask_policy_input = torch.cat((ask_policy_input,prev_ask_action_embed,expert_mask_embed,reward_config_embed),dim=-1)
else:
ask_policy_input = torch.cat((ask_policy_input,prev_ask_action_embed,expert_mask_embed),dim=-1)
if self.ask_actor_head is None:
print ('initialisation error')
exit()
self.ask_actor_head = LinearActorHead(self._hidden_size+48,self.ask_action_space.n).to(beliefs.device) ## concatenating frozen beliefs with success prediction output
self.ask_critic_head = LinearCriticHead(self._hidden_size+48).to(beliefs.device)
ask_policy_input = self.ask_policy_mlp(ask_policy_input)
ask_policy_input,ask_hidden_states = self.ask_policy_gru(ask_policy_input,memory.tensor('ask4help_gru'),masks)
memory.set_tensor('ask4help_gru', ask_hidden_states)
ask_pred_distr = self.ask_actor_head(ask_policy_input)
ask_pred_value = self.ask_critic_head(ask_policy_input)
expert_logits = (torch.zeros(nsteps, nsamplers, nactions) + 1e-3).to(beliefs.device)
for step in range(nsteps):
for samp in range(nsamplers):
expert_action_idx = expert_action[step,samp].item()
expert_logits[step,samp,expert_action_idx] = 999
expert_action_mask = expert_action_mask.unsqueeze(-1)
action_logits = expert_logits * expert_action_mask + (1 - expert_action_mask) * actor_pred_distr.logits
actor_distr = CategoricalDistr(logits=action_logits)
output_distr = MultiDimActionDistr(actor_distr, ask_pred_distr)
# 4. prepare output
extras = (
{
aux_uuid: {
"beliefs": (
beliefs_dict[aux_uuid] if self.multiple_beliefs else beliefs_combined
),
"obs_embeds": obs_embeds,
"ask_action_logits":ask_pred_distr.logits,
"model_action_logits":actor_pred_distr.logits,
"expert_actions":observations['expert_action'],
"prev_actions":prev_actions,
"aux_model": (
self.aux_models[aux_uuid]
if aux_uuid in self.aux_models
else None
),
}
for aux_uuid in self.auxiliary_uuids
}
if self.auxiliary_uuids is not None
else {}
)
if self.multiple_beliefs:
extras[MultiAuxTaskNegEntropyLoss.UUID] = task_weights
actor_critic_output = ActorCriticOutput(
distributions=output_distr,
values=ask_pred_value,
extras=extras,
)
return actor_critic_output,memory
print ('logic error model')
exit()
# 1.1 use perception model (i.e. encoder) to get observation embeddings
obs_embeds = self.forward_encoder(observations)
# 1.2 use embedding model to get prev_action embeddings
prev_actions_embeds = self.prev_action_embedder(prev_actions)
joint_embeds = torch.cat((obs_embeds, prev_actions_embeds), dim=-1) # (T, N, *)
# 2. use RNNs to get single/multiple beliefs
beliefs_dict = {}
for key, model in self.state_encoders.items():
beliefs_dict[key], rnn_hidden_states = model(
joint_embeds, memory.tensor(key), masks
)
memory.set_tensor(key, rnn_hidden_states) # update memory here
# 3. fuse beliefs for multiple belief models
beliefs, task_weights = self.fuse_beliefs(
beliefs_dict, obs_embeds
) # fused beliefs
# 4. prepare output
extras = (
{
aux_uuid: {
"beliefs": (
beliefs_dict[aux_uuid] if self.multiple_beliefs else beliefs
),
"obs_embeds": obs_embeds,
"aux_model": (
self.aux_models[aux_uuid]
if aux_uuid in self.aux_models
else None
),
}
for aux_uuid in self.auxiliary_uuids
}
if self.auxiliary_uuids is not None
else {}
)
if self.multiple_beliefs:
extras[MultiAuxTaskNegEntropyLoss.UUID] = task_weights
'''
expert_action_obs = observations['expert_action'].squeeze()
expert_action = expert_action_obs[0]
expert_action_mask = expert_action_obs[1]
nsteps,nsamplers,_ = beliefs.shape
nactions = self.nav_action_space.n
actor_pred_distr = self.actor(beliefs)
with torch.no_grad():
if self.succ_pred_model is None:
self.succ_pred_model = succ_pred_model(512).to(beliefs.device)
self.succ_pred_model.load_state_dict(torch.load('./storage/best_auc_clip_run_belief_480_rollout_len.pt',map_location=beliefs.device))
if self.succ_pred_rnn_hidden_state is None:
self.succ_pred_rnn_hidden_state = torch.zeros(1,1,512).to(beliefs.device)
succ_pred_out,rnn_hidden_states = self.succ_pred_model(beliefs,self.succ_pred_rnn_hidden_state,masks)
self.succ_pred_rnn_hidden_state = rnn_hidden_states
succ_prob = torch.sigmoid(succ_pred_out).squeeze()
expert_logits = torch.zeros(nsteps,nsamplers,nactions) + 1e-3
expert_logits[:,:,expert_action.item()] = 999
action_logits = expert_logits*expert_action_mask + (1-expert_action_mask) * actor_pred_distr.logits
actor_distr = CategoricalDistr(logits=action_logits)
threshold = 0.2 ## To be updated
if succ_prob<threshold:
succ_pred_logit = torch.tensor([0.001,999]).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0).to(beliefs.device)
else:
succ_pred_logit = torch.tensor([999,0.001]).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0).to(beliefs.device)
# succ_pred_logit = torch.tensor([0.001,999]).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0).to(beliefs.device)
output_distr = MultiDimActionDistr(actor_distr,CategoricalDistr(logits=succ_pred_logit))
'''
actor_critic_output = ActorCriticOutput(
distributions=self.actor(beliefs),
values=self.critic(beliefs),
extras=extras,
)
return actor_critic_output, memory
| ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/models/visual_nav_models.py |
ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/aux_losses/__init__.py |
|
# Original work Copyright (c) Facebook, Inc. and its affiliates.
# Modified work Copyright (c) Allen Institute for AI
# This source code is licensed under the MIT license found in the
# LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree.
"""Defining the auxiliary loss for actor critic type models.
Several of the losses defined in this file are modified versions of those found in
https://github.com/joel99/habitat-pointnav-aux/blob/master/habitat_baselines/
"""
from typing import Dict, cast, Tuple, List
import abc
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from allenact.algorithms.onpolicy_sync.losses.abstract_loss import (
AbstractActorCriticLoss,
ObservationType,
)
from allenact.base_abstractions.distributions import CategoricalDistr
from allenact.base_abstractions.misc import ActorCriticOutput
def _bernoulli_subsample_mask_like(masks, p=0.1):
return (torch.rand_like(masks) <= p).float()
class MultiAuxTaskNegEntropyLoss(AbstractActorCriticLoss):
"""Used in multiple auxiliary tasks setting.
Add a negative entropy loss over all the task weights.
"""
UUID = "multitask_entropy" # make sure this is unique
def __init__(self, task_names: List[str], *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.num_tasks = len(task_names)
self.task_names = task_names
def loss( # type: ignore
self,
step_count: int,
batch: ObservationType,
actor_critic_output: ActorCriticOutput[CategoricalDistr],
*args,
**kwargs
) -> Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, Dict[str, float]]:
task_weights = actor_critic_output.extras[self.UUID]
task_weights = task_weights.view(-1, self.num_tasks)
entropy = CategoricalDistr(task_weights).entropy()
avg_loss = (-entropy).mean()
avg_task_weights = task_weights.mean(dim=0) # (K)
outputs = {"entropy_loss": cast(torch.Tensor, avg_loss).item()}
for i in range(self.num_tasks):
outputs["weight_" + self.task_names[i]] = cast(
torch.Tensor, avg_task_weights[i]
).item()
return (
avg_loss,
outputs,
)
class AuxiliaryLoss(AbstractActorCriticLoss):
"""Base class of auxiliary loss.
Any auxiliary task loss should inherit from it, and implement
the `get_aux_loss` function.
"""
def __init__(self, auxiliary_uuid: str, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.auxiliary_uuid = auxiliary_uuid
def loss( # type: ignore
self,
step_count: int,
batch: ObservationType,
actor_critic_output: ActorCriticOutput[CategoricalDistr],
*args,
**kwargs
) -> Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, Dict[str, float]]:
# auxiliary loss
return self.get_aux_loss(
**actor_critic_output.extras[self.auxiliary_uuid],
observations=batch["observations"],
actions=batch["actions"],
masks=batch["masks"],
)
@abc.abstractmethod
def get_aux_loss(
self,
aux_model: nn.Module,
observations: ObservationType,
obs_embeds: torch.FloatTensor,
actions: torch.FloatTensor,
beliefs: torch.FloatTensor,
masks: torch.FloatTensor,
*args,
**kwargs
):
raise NotImplementedError()
def _propagate_final_beliefs_to_all_steps(
beliefs: torch.Tensor, masks: torch.Tensor, num_sampler: int, num_steps: int,
):
final_beliefs = torch.zeros_like(beliefs) # (T, B, *)
start_locs_list = []
end_locs_list = []
for i in range(num_sampler):
# right shift: to locate the 1 before 0 and ignore the 1st element
end_locs = torch.where(masks[1:, i] == 0)[0] # maybe [], dtype=torch.Long
start_locs = torch.cat(
[torch.tensor([0]).to(end_locs), end_locs + 1]
) # add the first element
start_locs_list.append(start_locs)
end_locs = torch.cat(
[end_locs, torch.tensor([num_steps - 1]).to(end_locs)]
) # add the last element
end_locs_list.append(end_locs)
for st, ed in zip(start_locs, end_locs):
final_beliefs[st : ed + 1, i] = beliefs[ed, i]
return final_beliefs, start_locs_list, end_locs_list
class FrequencyLoss(AuxiliaryLoss):
"""
Frequency loss to encourage contiguous chunks of help
"""
UUID = "FreqLoss"
def __init__(self,*args,**kwargs):
super().__init__(auxiliary_uuid=self.UUID,**kwargs)
def get_aux_loss(
self,
aux_model: nn.Module,
observations: ObservationType,
obs_embeds: torch.FloatTensor,
ask_action_logits,
model_action_logits,
expert_actions,
prev_actions,
actions: torch.FloatTensor,
beliefs: torch.FloatTensor,
masks: torch.FloatTensor,
*args,
**kwargs):
nsteps,nsamplers,_ = ask_action_logits.shape
softmax_logits = torch.softmax(ask_action_logits,dim=-1)
loss = torch.zeros(nsteps,nsamplers).to(beliefs.device)
for step in range(nsteps):
for samp in range(nsamplers):
prev_action_idx = prev_actions['ask_action'][step,samp].item()
loss[step,samp] = 1-softmax_logits[step,samp,prev_action_idx]
num_valid_losses = masks.sum()
loss = loss.unsqueeze(-1)
loss = loss*masks
loss = loss.squeeze(-1)
avg_loss = (loss.sum(0).sum(0)) / torch.clamp(num_valid_losses, min=1.0)
return (
avg_loss,
{"total": cast(torch.Tensor, avg_loss).item(),},
)
class SupImitationLoss(AuxiliaryLoss):
"""
Supervised Imitation Loss for adaptation from expert supervision
"""
UUID = "IMITATION_ADAPT"
def __init__(self,*args,**kwargs):
super().__init__(auxiliary_uuid=self.UUID,**kwargs)
self.cross_entropy_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none')
def get_aux_loss(
self,
aux_model: nn.Module,
observations: ObservationType,
obs_embeds: torch.FloatTensor,
ask_action_logits,
model_action_logits,
expert_actions,
actions: torch.FloatTensor,
beliefs: torch.FloatTensor,
masks: torch.FloatTensor,
*args,
**kwargs):
## add agent logits to extras dict.
nsteps,nsamplers,_ = ask_action_logits.shape
expert_action_masks = expert_actions[:,:,1]
expert_action_seq = expert_actions[:,:,0]
softmax_logits = torch.log_softmax(model_action_logits,dim=-1)
softmax_logits = softmax_logits.view(nsteps*nsamplers,-1)
expert_action_seq = expert_action_seq.view(nsteps*nsamplers)
loss = self.cross_entropy_loss(softmax_logits,expert_action_seq)
loss = loss.view(nsteps,nsamplers)
num_valid_losses = expert_action_masks.sum()
loss = loss*expert_action_masks
avg_loss = (loss.sum(0).sum(0)) / torch.clamp(num_valid_losses, min=1.0)
return (
avg_loss,
{"total": cast(torch.Tensor, avg_loss).item(),},
)
class InverseDynamicsLoss(AuxiliaryLoss):
"""Auxiliary task of Inverse Dynamics from Auxiliary Tasks Speed Up
Learning PointGoal Navigation (Ye, 2020) https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.04561
originally from Curiosity-driven Exploration by Self-supervised Prediction
(Pathak, 2017) https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.05363."""
UUID = "InvDyn"
def __init__(
self, subsample_rate: float = 0.2, subsample_min_num: int = 10, *args, **kwargs
):
"""Subsample the valid samples by the rate of `subsample_rate`, if the
total num of the valid samples is larger than `subsample_min_num`."""
super().__init__(auxiliary_uuid=self.UUID, *args, **kwargs)
self.cross_entropy_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction="none")
self.subsample_rate = subsample_rate
self.subsample_min_num = subsample_min_num
def get_aux_loss(
self,
aux_model: nn.Module,
observations: ObservationType,
obs_embeds: torch.FloatTensor,
actions: torch.FloatTensor,
beliefs: torch.FloatTensor,
masks: torch.FloatTensor,
*args,
**kwargs
):
## we discard the last action in the batch
num_steps, num_sampler = actions.shape # T, B
actions = cast(torch.LongTensor, actions)
actions = actions[:-1] # (T-1, B)
## find the final belief state based on masks
# we did not compute loss here as model.forward is compute-heavy
masks = masks.squeeze(-1) # (T, B)
final_beliefs, _, _ = _propagate_final_beliefs_to_all_steps(
beliefs, masks, num_sampler, num_steps,
)
## compute CE loss
decoder_in = torch.cat(
[obs_embeds[:-1], obs_embeds[1:], final_beliefs[:-1]], dim=2
) # (T-1, B, *)
preds = aux_model(decoder_in) # (T-1, B, A)
# cross entropy loss require class dim at 1
loss = self.cross_entropy_loss(
preds.view((num_steps - 1) * num_sampler, -1), # ((T-1)*B, A)
actions.flatten(), # ((T-1)*B,)
)
loss = loss.view(num_steps - 1, num_sampler) # (T-1, B)
# def vanilla_valid_losses(loss, num_sampler, end_locs_batch):
# ## this is just used to verify the vectorized version works correctly.
# ## not used for experimentation
# valid_losses = []
# for i in range(num_sampler):
# end_locs = end_locs_batch[i]
# for j in range(len(end_locs)):
# if j == 0:
# start_loc = 0
# else:
# start_loc = end_locs[j - 1] + 1
# end_loc = end_locs[j]
# if end_loc - start_loc <= 0: # the episode only 1-step
# continue
# valid_losses.append(loss[start_loc:end_loc, i])
# if len(valid_losses) == 0:
# valid_losses = torch.zeros(1, dtype=torch.float).to(loss)
# else:
# valid_losses = torch.cat(valid_losses) # (sum m, )
# return valid_losses
# valid_losses = masks[1:] * loss # (T-1, B)
# valid_losses0 = vanilla_valid_losses(loss, num_sampler, end_locs_batch)
# assert valid_losses0.sum() == valid_losses.sum()
num_valid_losses = torch.count_nonzero(masks[1:])
if num_valid_losses < self.subsample_min_num: # don't subsample
subsample_rate = 1.0
else:
subsample_rate = self.subsample_rate
loss_masks = masks[1:] * _bernoulli_subsample_mask_like(
masks[1:], subsample_rate
)
num_valid_losses = torch.count_nonzero(loss_masks)
avg_loss = (loss * loss_masks).sum() / torch.clamp(num_valid_losses, min=1.0)
return (
avg_loss,
{"total": cast(torch.Tensor, avg_loss).item(),},
)
class TemporalDistanceLoss(AuxiliaryLoss):
"""Auxiliary task of Temporal Distance from Auxiliary Tasks Speed Up
Learning PointGoal Navigation (Ye, 2020)
https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.04561."""
UUID = "TempDist"
def __init__(self, num_pairs: int = 8, epsiode_len_min: int = 5, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(auxiliary_uuid=self.UUID, *args, **kwargs)
self.num_pairs = num_pairs
self.epsiode_len_min = float(epsiode_len_min)
def get_aux_loss(
self,
aux_model: nn.Module,
observations: ObservationType,
obs_embeds: torch.FloatTensor,
actions: torch.FloatTensor,
beliefs: torch.FloatTensor,
masks: torch.FloatTensor,
*args,
**kwargs
):
## we discard the last action in the batch
num_steps, num_sampler = actions.shape # T, B
## find the final belief state based on masks
# we did not compute loss here as model.forward is compute-heavy
masks = masks.squeeze(-1) # (T, B)
(
final_beliefs,
start_locs_list,
end_locs_list,
) = _propagate_final_beliefs_to_all_steps(
beliefs, masks, num_sampler, num_steps,
)
## also find the locs_batch of shape (M, 3)
# the last dim: [0] is on num_sampler loc, [1] and [2] is start and end locs
# of one episode
# in other words: at locs_batch[m, 0] in num_sampler dim, there exists one episode
# starting from locs_batch[m, 1], ends at locs_batch[m, 2] (included)
locs_batch = []
for i in range(num_sampler):
locs_batch.append(
torch.stack(
[
i * torch.ones_like(start_locs_list[i]),
start_locs_list[i],
end_locs_list[i],
],
dim=-1,
)
) # shape (M[i], 3)
locs_batch = torch.cat(locs_batch) # shape (M, 3)
temporal_dist_max = (
locs_batch[:, 2] - locs_batch[:, 1]
).float() # end - start, (M)
# create normalizer that ignores too short episode, otherwise 1/T
normalizer = torch.where(
temporal_dist_max > self.epsiode_len_min,
1.0 / temporal_dist_max,
torch.tensor([0]).to(temporal_dist_max),
) # (M)
# sample valid pairs: sampled_pairs shape (M, num_pairs, 3)
# where M is the num of total episodes in the batch
locs = locs_batch.cpu().numpy() # as torch.randint only support int, not tensor
sampled_pairs = np.random.randint(
np.repeat(locs[:, [1]], 2 * self.num_pairs, axis=-1), # (M, 2*k)
np.repeat(locs[:, [2]] + 1, 2 * self.num_pairs, axis=-1), # (M, 2*k)
).reshape(
-1, self.num_pairs, 2
) # (M, k, 2)
sampled_pairs_batch = torch.from_numpy(sampled_pairs).to(
locs_batch
) # (M, k, 2)
num_sampler_batch = locs_batch[:, [0]].expand(
-1, 2 * self.num_pairs
) # (M, 1) -> (M, 2*k)
num_sampler_batch = num_sampler_batch.reshape(
-1, self.num_pairs, 2
) # (M, k, 2)
sampled_obs_embeds = obs_embeds[
sampled_pairs_batch, num_sampler_batch
] # (M, k, 2, H1)
sampled_final_beliefs = final_beliefs[
sampled_pairs_batch, num_sampler_batch
] # (M, k, 2, H2)
features = torch.cat(
[
sampled_obs_embeds[:, :, 0],
sampled_obs_embeds[:, :, 1],
sampled_final_beliefs[:, :, 0],
],
dim=-1,
) # (M, k, 2*H1 + H2)
pred_temp_dist = aux_model(features).squeeze(-1) # (M, k)
true_temp_dist = (
sampled_pairs_batch[:, :, 1] - sampled_pairs_batch[:, :, 0]
).float() # (M, k)
pred_error = (pred_temp_dist - true_temp_dist) * normalizer.unsqueeze(1)
loss = 0.5 * (pred_error).pow(2)
avg_loss = loss.mean()
return (
avg_loss,
{"total": cast(torch.Tensor, avg_loss).item(),},
)
class CPCALoss(AuxiliaryLoss):
"""Auxiliary task of CPC|A from Auxiliary Tasks Speed Up Learning PointGoal
Navigation (Ye, 2020) https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.04561 originally from
Neural Predictive Belief Representations (Guo, 2018)
https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.06407."""
UUID = "CPCA"
def __init__(
self, planning_steps: int = 8, subsample_rate: float = 0.2, *args, **kwargs
):
super().__init__(auxiliary_uuid=self.UUID, *args, **kwargs)
self.planning_steps = planning_steps
self.subsample_rate = subsample_rate
self.cross_entropy_loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(reduction="none")
def get_aux_loss(
self,
aux_model: nn.Module,
observations: ObservationType,
obs_embeds: torch.FloatTensor,
actions: torch.FloatTensor,
beliefs: torch.FloatTensor,
masks: torch.FloatTensor,
*args,
**kwargs
):
# prepare for autoregressive inputs: c_{t+1:t+k} = GRU(b_t, a_{t:t+k-1}) <-> z_{t+k}
## where b_t = RNN(b_{t-1}, z_t, a_{t-1}), prev action is optional
num_steps, num_sampler, obs_embed_size = obs_embeds.shape # T, N, H_O
assert 0 < self.planning_steps <= num_steps
## prepare positive and negatives that sample from all the batch
positives = obs_embeds # (T, N, -1)
negative_inds = torch.randperm(num_steps * num_sampler).to(positives.device)
negatives = torch.gather( # input[index[i,j]][j]
positives.view(num_steps * num_sampler, -1),
dim=0,
index=negative_inds.view(num_steps * num_sampler, 1).expand(
num_steps * num_sampler, positives.size(-1)
),
).view(
num_steps, num_sampler, -1
) # (T, N, -1)
## prepare action sequences and initial beliefs
action_embedding = aux_model.action_embedder(actions) # (T, N, -1)
action_embed_size = action_embedding.size(-1)
action_padding = torch.zeros(
self.planning_steps - 1, num_sampler, action_embed_size
).to(
action_embedding
) # (k-1, N, -1)
action_padded = torch.cat(
(action_embedding, action_padding), dim=0
) # (T+k-1, N, -1)
## unfold function will create consecutive action sequences
action_seq = (
action_padded.unfold(dimension=0, size=self.planning_steps, step=1)
.permute(3, 0, 1, 2)
.view(self.planning_steps, num_steps * num_sampler, action_embed_size)
) # (k, T*N, -1)
beliefs = beliefs.view(num_steps * num_sampler, -1).unsqueeze(0) # (1, T*N, -1)
# get future contexts c_{t+1:t+k} = GRU(b_t, a_{t:t+k-1})
future_contexts_all, _ = aux_model.context_model(
action_seq, beliefs
) # (k, T*N, -1)
## NOTE: future_contexts_all starting from next step t+1 to t+k, not t to t+k-1
future_contexts_all = future_contexts_all.view(
self.planning_steps, num_steps, num_sampler, -1
).permute(
1, 0, 2, 3
) # (k, T, N, -1)
# get all the classifier scores I(c_{t+1:t+k}; z_{t+1:t+k})
positives_padding = torch.zeros(
self.planning_steps, num_sampler, obs_embed_size
).to(
positives
) # (k, N, -1)
positives_padded = torch.cat(
(positives[1:], positives_padding), dim=0
) # (T+k-1, N, -1)
positives_expanded = positives_padded.unfold(
dimension=0, size=self.planning_steps, step=1
).permute(
0, 3, 1, 2
) # (T, k, N, -1)
positives_logits = aux_model.classifier(
torch.cat([positives_expanded, future_contexts_all], -1)
) # (T, k, N, 1)
positive_loss = self.cross_entropy_loss(
positives_logits, torch.ones_like(positives_logits)
) # (T, k, N, 1)
negatives_padding = torch.zeros(
self.planning_steps, num_sampler, obs_embed_size
).to(
negatives
) # (k, N, -1)
negatives_padded = torch.cat(
(negatives[1:], negatives_padding), dim=0
) # (T+k-1, N, -1)
negatives_expanded = negatives_padded.unfold(
dimension=0, size=self.planning_steps, step=1
).permute(
0, 3, 1, 2
) # (T, k, N, -1)
negatives_logits = aux_model.classifier(
torch.cat([negatives_expanded, future_contexts_all], -1)
) # (T, k, N, 1)
negative_loss = self.cross_entropy_loss(
negatives_logits, torch.zeros_like(negatives_logits)
) # (T, k, N, 1)
# Masking to get valid scores
## masks: Note which timesteps [1, T+k+1] could have valid queries, at distance (k) (note offset by 1)
## we will extract the **diagonals** as valid_masks from masks later as below
## the vertical axis is (absolute) real timesteps, the horizontal axis is (relative) planning timesteps
## | - - - - - |
## | . |
## | , . |
## | . , . |
## | , . , . |
## | , . , . |
## | , . , |
## | , . |
## | , |
## | - - - - - |
masks = masks.squeeze(-1) # (T, N)
pred_masks = torch.ones(
num_steps + self.planning_steps,
self.planning_steps,
num_sampler,
1,
dtype=torch.bool,
).to(
beliefs.device
) # (T+k, k, N, 1)
pred_masks[
num_steps - 1 :
] = False # GRU(b_t, a_{t:t+k-1}) is invalid when t >= T, as we don't have real z_{t+1}
for j in range(1, self.planning_steps + 1): # for j-step predictions
pred_masks[
: j - 1, j - 1
] = False # Remove the upper triangle above the diagnonal (but I think this is unnecessary for valid_masks)
for n in range(num_sampler):
has_zeros_batch = torch.where(masks[:, n] == 0)[0]
# in j-step prediction, timesteps z -> z + j are disallowed as those are the first j timesteps of a new episode
# z-> z-1 because of pred_masks being offset by 1
for z in has_zeros_batch:
pred_masks[
z - 1 : z - 1 + j, j - 1, n
] = False # can affect j timesteps
# instead of the whole range, we actually are only comparing a window i:i+k for each query/target i - for each, select the appropriate k
# we essentially gather diagonals from this full mask, t of them, k long
valid_diagonals = [
torch.diagonal(pred_masks, offset=-i) for i in range(num_steps)
] # pull the appropriate k per timestep
valid_masks = (
torch.stack(valid_diagonals, dim=0).permute(0, 3, 1, 2).float()
) # (T, N, 1, k) -> (T, k, N, 1)
# print(valid_masks.int().squeeze(-1)); print(masks) # verify its correctness
loss_masks = valid_masks * _bernoulli_subsample_mask_like(
valid_masks, self.subsample_rate
) # (T, k, N, 1)
num_valid_losses = torch.count_nonzero(loss_masks)
avg_positive_loss = (positive_loss * loss_masks).sum() / torch.clamp(
num_valid_losses, min=1.0
)
avg_negative_loss = (negative_loss * loss_masks).sum() / torch.clamp(
num_valid_losses, min=1.0
)
avg_loss = avg_positive_loss + avg_negative_loss
return (
avg_loss,
{
"total": cast(torch.Tensor, avg_loss).item(),
"positive_loss": cast(torch.Tensor, avg_positive_loss).item(),
"negative_loss": cast(torch.Tensor, avg_negative_loss).item(),
},
)
class CPCA1Loss(CPCALoss):
UUID = "CPCA_1"
def __init__(self, subsample_rate: float = 0.2, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(
planning_steps=1, subsample_rate=subsample_rate, *args, **kwargs
)
class CPCA2Loss(CPCALoss):
UUID = "CPCA_2"
def __init__(self, subsample_rate: float = 0.2, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(
planning_steps=2, subsample_rate=subsample_rate, *args, **kwargs
)
class CPCA4Loss(CPCALoss):
UUID = "CPCA_4"
def __init__(self, subsample_rate: float = 0.2, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(
planning_steps=4, subsample_rate=subsample_rate, *args, **kwargs
)
class CPCA8Loss(CPCALoss):
UUID = "CPCA_8"
def __init__(self, subsample_rate: float = 0.2, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(
planning_steps=8, subsample_rate=subsample_rate, *args, **kwargs
)
class CPCA16Loss(CPCALoss):
UUID = "CPCA_16"
def __init__(self, subsample_rate: float = 0.2, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(
planning_steps=16, subsample_rate=subsample_rate, *args, **kwargs
)
| ask4help-main | allenact/embodiedai/aux_losses/losses.py |
"""Defines the `ExperimentConfig` abstract class used as the basis of all
experiments."""
import abc
from typing import Dict, Any, Optional, List, Union, Sequence, Tuple, cast
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from allenact.base_abstractions.preprocessor import SensorPreprocessorGraph
from allenact.base_abstractions.task import TaskSampler
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import TrainingPipeline, Builder
from allenact.utils.system import get_logger
from allenact.utils.viz_utils import VizSuite
def split_processes_onto_devices(nprocesses: int, ndevices: int):
assert (
nprocesses == 0 or nprocesses >= ndevices
), "NUM_PROCESSES {} < ndevices {}".format(nprocesses, ndevices)
res = [0] * ndevices
for it in range(nprocesses):
res[it % ndevices] += 1
return res
class MachineParams(object):
def __init__(
self,
nprocesses: Union[int, Sequence[int]],
devices: Union[
None, int, str, torch.device, Sequence[Union[int, str, torch.device]]
] = None,
sensor_preprocessor_graph: Optional[
Union[SensorPreprocessorGraph, Builder[SensorPreprocessorGraph]]
] = None,
sampler_devices: Union[
None, int, str, torch.device, Sequence[Union[int, str, torch.device]]
] = None,
visualizer: Optional[Union[VizSuite, Builder[VizSuite]]] = None,
gpu_ids: Union[int, Sequence[int]] = None,
local_worker_ids: Optional[List[int]] = None,
):
assert (
gpu_ids is None or devices is None
), "only one of `gpu_ids` or `devices` should be set."
if gpu_ids is not None:
get_logger().warning(
"The `gpu_ids` parameter will be deprecated, use `devices` instead."
)
devices = gpu_ids
self.nprocesses = (
nprocesses if isinstance(nprocesses, Sequence) else (nprocesses,)
)
self.devices: Tuple[torch.device, ...] = self._standardize_devices(
devices=devices, nworkers=len(self.nprocesses)
)
self._sensor_preprocessor_graph_maybe_builder = sensor_preprocessor_graph
self.sampler_devices: Tuple[torch.device, ...] = (
None
if sampler_devices is None
else self._standardize_devices(
devices=sampler_devices, nworkers=len(self.nprocesses)
)
)
self._visualizer_maybe_builder = visualizer
self._sensor_preprocessor_graph_cached: Optional[SensorPreprocessorGraph] = None
self._visualizer_cached: Optional[VizSuite] = None
self.local_worker_ids: Optional[List[int]] = None
self.set_local_worker_ids(local_worker_ids)
def set_local_worker_ids(self, local_worker_ids: Optional[List[int]]):
self.local_worker_ids = local_worker_ids or list(range(len(self.devices)))
assert all(0 <= id < len(self.devices) for id in self.local_worker_ids), (
f"Passed {len(self.local_worker_ids)} local worker ids {self.local_worker_ids}"
f" for {len(self.devices)} total devices (workers)"
)
@classmethod
def instance_from(
cls, machine_params: Union["MachineParams", Dict[str, Any]]
) -> "MachineParams":
if isinstance(machine_params, cls):
return machine_params
assert isinstance(machine_params, Dict)
return cls(**machine_params)
@staticmethod
def _standardize_devices(
devices: Optional[
Union[int, str, torch.device, Sequence[Union[int, str, torch.device]]]
],
nworkers: int,
) -> Tuple[torch.device, ...]:
if devices is None or (isinstance(devices, Sequence) and len(devices) == 0):
devices = torch.device("cpu")
if not isinstance(devices, Sequence):
devices = (devices,) * nworkers
assert len(devices) == nworkers, (
f"The number of devices (len({devices})={len(devices)})"
f" must equal the number of workers ({nworkers})"
)
devices = tuple(
torch.device("cpu") if d == -1 else torch.device(d) for d in devices # type: ignore
)
for d in devices:
if d != torch.device("cpu"):
try:
torch.cuda.get_device_capability(d) # type: ignore
except Exception:
raise RuntimeError(
f"It appears the cuda device {d} is not available on your system."
)
return cast(Tuple[torch.device, ...], devices)
@property
def sensor_preprocessor_graph(self) -> Optional[SensorPreprocessorGraph]:
if self._sensor_preprocessor_graph_maybe_builder is None:
return None
if self._sensor_preprocessor_graph_cached is None:
if isinstance(self._sensor_preprocessor_graph_maybe_builder, Builder):
self._sensor_preprocessor_graph_cached = (
self._sensor_preprocessor_graph_maybe_builder()
)
else:
self._sensor_preprocessor_graph_cached = (
self._sensor_preprocessor_graph_maybe_builder
)
return self._sensor_preprocessor_graph_cached
def set_visualizer(self, viz: VizSuite):
if self._visualizer_cached is None:
self._visualizer_maybe_builder = viz
else:
get_logger().warning("Ignoring viz (already instantiated)")
@property
def visualizer(self) -> Optional[VizSuite]:
if self._visualizer_maybe_builder is None:
return None
if self._visualizer_cached is None:
if isinstance(self._visualizer_maybe_builder, Builder):
self._visualizer_cached = self._visualizer_maybe_builder()
else:
self._visualizer_cached = self._visualizer_maybe_builder
return self._visualizer_cached
class FrozenClassVariables(abc.ABCMeta):
"""Metaclass for ExperimentConfig.
Ensures ExperimentConfig class-level attributes cannot be modified.
ExperimentConfig attributes can still be modified at the object
level.
"""
def __setattr__(cls, attr, value):
if isinstance(cls, type) and (
attr != "__abstractmethods__" and not attr.startswith("_abc_")
):
raise RuntimeError(
"Cannot edit class-level attributes.\n"
"Changing the values of class-level attributes is disabled in ExperimentConfig classes.\n"
"This is to prevent problems that can occur otherwise when using multiprocessing.\n"
"If you wish to change the value of a configuration, please do so for an instance of that"
" configuration.\nTriggered by attempting to modify {}".format(
cls.__name__
)
)
else:
super().__setattr__(attr, value)
class ExperimentConfig(metaclass=FrozenClassVariables):
"""Abstract class used to define experiments.
Instead of using yaml or text files, experiments in our framework
are defined as a class. In particular, to define an experiment one
must define a new class inheriting from this class which implements
all of the below methods. The below methods will then be called when
running the experiment.
"""
@abc.abstractmethod
def tag(self) -> str:
"""A string describing the experiment."""
raise NotImplementedError()
@abc.abstractmethod
def training_pipeline(self, **kwargs) -> TrainingPipeline:
"""Creates the training pipeline.
# Parameters
kwargs : Extra kwargs. Currently unused.
# Returns
An instantiate `TrainingPipeline` object.
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
@abc.abstractmethod
def machine_params(
self, mode="train", **kwargs
) -> Union[MachineParams, Dict[str, Any]]:
"""Parameters used to specify machine information.
Machine information includes at least (1) the number of processes
to train with and (2) the gpu devices indices to use.
mode : Whether or not the machine parameters should be those for
"train", "valid", or "test".
kwargs : Extra kwargs.
# Returns
A dictionary of the form `{"nprocesses": ..., "gpu_ids": ..., ...}`.
Here `nprocesses` must be a non-negative integer, `gpu_ids` must
be a sequence of non-negative integers (if empty, then everything
will be run on the cpu).
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
@abc.abstractmethod
def create_model(self, **kwargs) -> nn.Module:
"""Create the neural model."""
raise NotImplementedError()
@abc.abstractmethod
def make_sampler_fn(self, **kwargs) -> TaskSampler:
"""Create the TaskSampler given keyword arguments.
These `kwargs` will be generated by one of
`ExperimentConfig.train_task_sampler_args`,
`ExperimentConfig.valid_task_sampler_args`, or
`ExperimentConfig.test_task_sampler_args` depending on whether
the user has chosen to train, validate, or test.
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
def train_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Specifies the training parameters for the `process_ind`th training
process.
These parameters are meant be passed as keyword arguments to `ExperimentConfig.make_sampler_fn`
to generate a task sampler.
# Parameters
process_ind : The unique index of the training process (`0 ≤ process_ind < total_processes`).
total_processes : The total number of training processes.
devices : Gpu devices (if any) to use.
seeds : The seeds to use, if any.
deterministic_cudnn : Whether or not to use deterministic cudnn.
# Returns
The parameters for `make_sampler_fn`
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
def valid_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Specifies the validation parameters for the `process_ind`th
validation process.
See `ExperimentConfig.train_task_sampler_args` for parameter
definitions.
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
def test_task_sampler_args(
self,
process_ind: int,
total_processes: int,
devices: Optional[List[int]] = None,
seeds: Optional[List[int]] = None,
deterministic_cudnn: bool = False,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Specifies the test parameters for the `process_ind`th test process.
See `ExperimentConfig.train_task_sampler_args` for parameter
definitions.
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
| ask4help-main | allenact/base_abstractions/experiment_config.py |
import abc
from typing import (
Dict,
Any,
TypeVar,
Sequence,
NamedTuple,
Optional,
List,
Union,
Generic,
)
import torch
EnvType = TypeVar("EnvType")
DistributionType = TypeVar("DistributionType")
class RLStepResult(NamedTuple):
observation: Optional[Any]
reward: Optional[Union[float, List[float]]]
done: Optional[bool]
info: Optional[Dict[str, Any]]
def clone(self, new_info: Dict[str, Any]):
return RLStepResult(
observation=self.observation
if "observation" not in new_info
else new_info["observation"],
reward=self.reward if "reward" not in new_info else new_info["reward"],
done=self.done if "done" not in new_info else new_info["done"],
info=self.info if "info" not in new_info else new_info["info"],
)
def merge(self, other: "RLStepResult"):
return RLStepResult(
observation=self.observation
if other.observation is None
else other.observation,
reward=self.reward if other.reward is None else other.reward,
done=self.done if other.done is None else other.done,
info={
**(self.info if self.info is not None else {}),
**(other.info if other is not None else {}),
},
)
class ActorCriticOutput(tuple, Generic[DistributionType]):
distributions: DistributionType
values: torch.FloatTensor
extras: Dict[str, Any]
# noinspection PyTypeChecker
def __new__(
cls,
distributions: DistributionType,
values: torch.FloatTensor,
extras: Dict[str, Any],
):
self = tuple.__new__(cls, (distributions, values, extras))
self.distributions = distributions
self.values = values
self.extras = extras
return self
def __repr__(self) -> str:
return (
f"Group(distributions={self.distributions},"
f" values={self.values},"
f" extras={self.extras})"
)
class Loss(abc.ABC):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
pass
@abc.abstractmethod
def loss(self, *args, **kwargs):
raise NotImplementedError()
class Memory(Dict):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
if len(args) > 0:
assert len(args) == 1, (
"Only one of Sequence[Tuple[str, Tuple[torch.Tensor, int]]]"
"or Dict[str, Tuple[torch.Tensor, int]] accepted as unnamed args"
)
if isinstance(args[0], Sequence):
for key, tensor_dim in args[0]:
assert (
len(tensor_dim) == 2
), "Only Tuple[torch.Tensor, int]] accepted as second item in Tuples"
tensor, dim = tensor_dim
self.check_append(key, tensor, dim)
elif isinstance(args[0], Dict):
for key in args[0]:
assert (
len(args[0][key]) == 2
), "Only Tuple[torch.Tensor, int]] accepted as values in Dict"
tensor, dim = args[0][key]
self.check_append(key, tensor, dim)
elif len(kwargs) > 0:
for key in kwargs:
assert (
len(kwargs[key]) == 2
), "Only Tuple[torch.Tensor, int]] accepted as keyword arg"
tensor, dim = kwargs[key]
self.check_append(key, tensor, dim)
def check_append(
self, key: str, tensor: torch.Tensor, sampler_dim: int
) -> "Memory":
"""Appends a new memory type given its identifier, its memory tensor
and its sampler dim.
# Parameters
key: string identifier of the memory type
tensor: memory tensor
sampler_dim: sampler dimension
# Returns
Updated Memory
"""
assert isinstance(key, str), "key {} must be str".format(key)
assert isinstance(
tensor, torch.Tensor
), "tensor {} must be torch.Tensor".format(tensor)
assert isinstance(sampler_dim, int), "sampler_dim {} must be int".format(
sampler_dim
)
assert key not in self, "Reused key {}".format(key)
assert (
0 <= sampler_dim < len(tensor.shape)
), "Got sampler_dim {} for tensor with shape {}".format(
sampler_dim, tensor.shape
)
self[key] = (tensor, sampler_dim)
return self
def tensor(self, key: str) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Returns the memory tensor for a given memory type.
# Parameters
key: string identifier of the memory type
# Returns
Memory tensor for type `key`
"""
assert key in self, "Missing key {}".format(key)
return self[key][0]
def sampler_dim(self, key: str) -> int:
"""Returns the sampler dimension for the given memory type.
# Parameters
key: string identifier of the memory type
# Returns
The sampler dim
"""
assert key in self, "Missing key {}".format(key)
return self[key][1]
def sampler_select(self, keep: Sequence[int]) -> "Memory":
"""Equivalent to PyTorch index_select along the `sampler_dim` of each
memory type.
# Parameters
keep: a list of sampler indices to keep
# Returns
Selected memory
"""
res = Memory()
valid = False
for name in self:
sampler_dim = self.sampler_dim(name)
tensor = self.tensor(name)
assert len(keep) == 0 or (
0 <= min(keep) and max(keep) < tensor.shape[sampler_dim]
), "Got min(keep)={} max(keep)={} for memory type {} with shape {}, dim {}".format(
min(keep), max(keep), name, tensor.shape, sampler_dim
)
if tensor.shape[sampler_dim] > len(keep):
tensor = tensor.index_select(
dim=sampler_dim,
index=torch.as_tensor(
list(keep), dtype=torch.int64, device=tensor.device
),
)
res.check_append(name, tensor, sampler_dim)
valid = True
if valid:
return res
return self
def set_tensor(self, key: str, tensor: torch.Tensor) -> "Memory":
"""Replaces tensor for given key with an updated version.
# Parameters
key: memory type identifier to update
tensor: updated tensor
# Returns
Updated memory
"""
assert key in self, "Missing key {}".format(key)
assert (
tensor.shape == self[key][0].shape
), "setting tensor with shape {} for former {}".format(
tensor.shape, self[key][0].shape
)
self[key] = (tensor, self[key][1])
return self
def step_select(self, step: int) -> "Memory":
"""Equivalent to slicing with length 1 for the `step` (i.e first)
dimension in rollouts storage.
# Parameters
step: step to keep
# Returns
Sliced memory with a single step
"""
res = Memory()
for key in self:
tensor = self.tensor(key)
assert (
tensor.shape[0] > step
), "attempting to access step {} for memory type {} of shape {}".format(
step, key, tensor.shape
)
if step != -1:
res.check_append(
key, self.tensor(key)[step : step + 1, ...], self.sampler_dim(key)
)
else:
res.check_append(
key, self.tensor(key)[step:, ...], self.sampler_dim(key)
)
return res
def step_squeeze(self, step: int) -> "Memory":
"""Equivalent to simple indexing for the `step` (i.e first) dimension
in rollouts storage.
# Parameters
step: step to keep
# Returns
Sliced memory with a single step (and squeezed step dimension)
"""
res = Memory()
for key in self:
tensor = self.tensor(key)
assert (
tensor.shape[0] > step
), "attempting to access step {} for memory type {} of shape {}".format(
step, key, tensor.shape
)
res.check_append(
key, self.tensor(key)[step, ...], self.sampler_dim(key) - 1
)
return res
def slice(
self,
dim: int,
start: Optional[int] = None,
stop: Optional[int] = None,
step: int = 1,
) -> "Memory":
"""Slicing for dimensions that have same extents in all memory types.
It also accepts negative indices.
# Parameters
dim: the dimension to slice
start: the index of the first item to keep if given (default 0 if None)
stop: the index of the first item to discard if given (default tensor size along `dim` if None)
step: the increment between consecutive indices (default 1)
# Returns
Sliced memory
"""
checked = False
total: Optional[int] = None
res = Memory()
for key in self:
tensor = self.tensor(key)
assert (
len(tensor.shape) > dim
), "attempting to access dim {} for memory type {} of shape {}".format(
dim, key, tensor.shape
)
if not checked:
total = tensor.shape[dim]
checked = True
assert (
total == tensor.shape[dim]
), "attempting to slice along non-uniform dimension {}".format(dim)
if start is not None or stop is not None or step != 1:
slice_tuple = (
(slice(None),) * dim
+ (slice(start, stop, step),)
+ (slice(None),) * (len(tensor.shape) - (1 + dim))
)
sliced_tensor = tensor[slice_tuple]
res.check_append(
key=key, tensor=sliced_tensor, sampler_dim=self.sampler_dim(key),
)
else:
res.check_append(
key, tensor, self.sampler_dim(key),
)
return res
def to(self, device: torch.device) -> "Memory":
for key in self:
tensor = self.tensor(key)
if tensor.device != device:
self.set_tensor(key, tensor.to(device))
return self
| ask4help-main | allenact/base_abstractions/misc.py |
# Original work Copyright (c) Facebook, Inc. and its affiliates.
# Modified work Copyright (c) Allen Institute for AI
# This source code is licensed under the MIT license found in the
# LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree.
"""Defines the primary data structures by which agents interact with their
environment."""
import abc
from typing import Dict, Any, Tuple, Generic, Union, Optional, TypeVar, Sequence, List
import gym
import numpy as np
from gym.spaces.dict import Dict as SpaceDict
from allenact.base_abstractions.misc import RLStepResult
from allenact.base_abstractions.sensor import Sensor, SensorSuite
from allenact.utils.misc_utils import deprecated
EnvType = TypeVar("EnvType")
class Task(Generic[EnvType]):
"""An abstract class defining a, goal directed, 'task.' Agents interact
with their environment through a task by taking a `step` after which they
receive new observations, rewards, and (potentially) other useful
information.
A Task is a helpful generalization of the OpenAI gym's `Env` class
and allows for multiple tasks (e.g. point and object navigation) to
be defined on a single environment (e.g. AI2-THOR).
# Attributes
env : The environment.
sensor_suite: Collection of sensors formed from the `sensors` argument in the initializer.
task_info : Dictionary of (k, v) pairs defining task goals and other task information.
max_steps : The maximum number of steps an agent can take an in the task before it is considered failed.
observation_space: The observation space returned on each step from the sensors.
"""
env: EnvType
sensor_suite: SensorSuite[EnvType]
task_info: Dict[str, Any]
max_steps: int
observation_space: SpaceDict
def __init__(
self,
env: EnvType,
sensors: Union[SensorSuite, Sequence[Sensor]],
task_info: Dict[str, Any],
max_steps: int,
**kwargs
) -> None:
self.env = env
self.sensor_suite = (
SensorSuite(sensors) if not isinstance(sensors, SensorSuite) else sensors
)
self.task_info = task_info
self.max_steps = max_steps
self.observation_space = self.sensor_suite.observation_spaces
self._num_steps_taken = 0
self._total_reward: Union[float, List[float]] = 0.0
def get_observations(self, **kwargs) -> Any:
return self.sensor_suite.get_observations(env=self.env, task=self, **kwargs)
@property
@abc.abstractmethod
def action_space(self) -> gym.Space:
"""Task's action space.
# Returns
The action space for the task.
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
@abc.abstractmethod
def render(self, mode: str = "rgb", *args, **kwargs) -> np.ndarray:
"""Render the current task state.
Rendered task state can come in any supported modes.
# Parameters
mode : The mode in which to render. For example, you might have a 'rgb'
mode that renders the agent's egocentric viewpoint or a 'dev' mode
returning additional information.
args : Extra args.
kwargs : Extra kwargs.
# Returns
An numpy array corresponding to the requested render.
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
def _increment_num_steps_taken(self) -> None:
"""Helper function that increases the number of steps counter by
one."""
self._num_steps_taken += 1
def step(self, action: Any) -> RLStepResult:
"""Take an action in the environment (one per agent).
Takes the action in the environment and returns
observations (& rewards and any additional information)
corresponding to the agent's new state. Note that this function
should not be overwritten without care (instead
implement the `_step` function).
# Parameters
action : The action to take, should be of the same form as specified by `self.action_space`.
# Returns
A `RLStepResult` object encoding the new observations, reward, and
(possibly) additional information.
"""
assert not self.is_done()
sr = self._step(action=action)
# If reward is Sequence, it's assumed to follow the same order imposed by spaces' flatten operation
if isinstance(sr.reward, Sequence):
if isinstance(self._total_reward, Sequence):
for it, rew in enumerate(sr.reward):
self._total_reward[it] += float(rew)
else:
self._total_reward = [float(r) for r in sr.reward]
else:
self._total_reward += float(sr.reward) # type:ignore
self._increment_num_steps_taken()
# TODO: We need a better solution to the below. It's not a good idea
# to pre-increment the step counter as this might play poorly with `_step`
# if it relies on some aspect of the current number of steps taken.
return sr.clone({"done": sr.done or self.is_done()})
@abc.abstractmethod
def _step(self, action: Any) -> RLStepResult:
"""Helper function called by `step` to take a step by each agent in the
environment.
Takes the action in the environment and returns
observations (& rewards and any additional information)
corresponding to the agent's new state. This function is called
by the (public) `step` function and is what should be implemented
when defining your new task. Having separate `_step` be separate from `step`
is useful as this allows the `step` method to perform bookkeeping (e.g.
keeping track of the number of steps), without having `_step` as a separate
method, everyone implementing `step` would need to copy this bookkeeping code.
# Parameters
action : The action to take.
# Returns
A `RLStepResult` object encoding the new observations, reward, and
(possibly) additional information.
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
def reached_max_steps(self) -> bool:
"""Has the agent reached the maximum number of steps."""
return self.num_steps_taken() >= self.max_steps
@abc.abstractmethod
def reached_terminal_state(self) -> bool:
"""Has the agent reached a terminal state (excluding reaching the
maximum number of steps)."""
raise NotImplementedError()
def is_done(self) -> bool:
"""Did the agent reach a terminal state or performed the maximum number
of steps."""
return self.reached_terminal_state() or self.reached_max_steps()
def num_steps_taken(self) -> int:
"""Number of steps taken by the agent in the task so far."""
return self._num_steps_taken
@deprecated
def action_names(self) -> Tuple[str, ...]:
"""Action names of the Task instance.
This function has been deprecated and will be removed.
This function is a hold-over from when the `Task`
abstraction only considered `gym.space.Discrete` action spaces (in which
case it makes sense name these actions).
This implementation of `action_names` requires that a `class_action_names`
method has been defined. This method should be overwritten if `class_action_names`
requires key word arguments to determine the number of actions.
"""
if hasattr(self, "class_action_names"):
return self.class_action_names()
else:
raise NotImplementedError(
"`action_names` requires that a function `class_action_names` be defined."
" This said, please do not use this functionality as it has been deprecated and will be removed."
" If you would like an `action_names` function for your task, feel free to define one"
" with the knowledge that the AllenAct internals will ignore it."
)
@abc.abstractmethod
def close(self) -> None:
"""Closes the environment and any other files opened by the Task (if
applicable)."""
raise NotImplementedError()
def metrics(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Computes metrics related to the task after the task's completion.
By default this function is automatically called during training
and the reported metrics logged to tensorboard.
# Returns
A dictionary where every key is a string (the metric's
name) and the value is the value of the metric.
"""
return {
"ep_length": self.num_steps_taken(),
"reward": self.cumulative_reward,
"task_info": self.task_info,
}
def query_expert(self, **kwargs) -> Tuple[Any, bool]:
"""(Deprecated) Query the expert policy for this task.
The new correct way to include this functionality is through the definition of a class
derived from `allenact.base_abstractions.sensor.AbstractExpertActionSensor` or
`allenact.base_abstractions.sensor.AbstractExpertPolicySensor`, where a
`query_expert` method must be defined.
# Returns
A tuple (x, y) where x is the expert action (or policy) and y is False \
if the expert could not determine the optimal action (otherwise True). Here y \
is used for masking. Even when y is False, x should still lie in the space of \
possible values (e.g. if x is the expert policy then x should be the correct length, \
sum to 1, and have non-negative entries).
"""
return None, False
@property
def cumulative_reward(self) -> float:
"""Mean per-agent total cumulative in the task so far.
# Returns
Mean per-agent cumulative reward as a float.
"""
return (
np.mean(self._total_reward).item()
if isinstance(self._total_reward, Sequence)
else self._total_reward
)
SubTaskType = TypeVar("SubTaskType", bound=Task)
class TaskSampler(abc.ABC):
"""Abstract class defining a how new tasks are sampled."""
@property
@abc.abstractmethod
def length(self) -> Union[int, float]:
"""Length.
# Returns
Number of total tasks remaining that can be sampled. Can be
float('inf').
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
@property
@abc.abstractmethod
def last_sampled_task(self) -> Optional[Task]:
"""Get the most recently sampled Task.
# Returns
The most recently sampled Task.
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
@abc.abstractmethod
def next_task(self, force_advance_scene: bool = False) -> Optional[Task]:
"""Get the next task in the sampler's stream.
# Parameters
force_advance_scene : Used to (if applicable) force the task sampler to
use a new scene for the next task. This is useful if, during training,
you would like to train with one scene for some number of steps and
then explicitly control when you begin training with the next scene.
# Returns
The next Task in the sampler's stream if a next task exists. Otherwise None.
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
@abc.abstractmethod
def close(self) -> None:
"""Closes any open environments or streams.
Should be run when done sampling.
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
@property
@abc.abstractmethod
def all_observation_spaces_equal(self) -> bool:
"""Checks if all observation spaces of tasks that can be sampled are
equal.
This will almost always simply return `True`. A case in which it should
return `False` includes, for example, a setting where you design
a `TaskSampler` that can generate different types of tasks, i.e.
point navigation tasks and object navigation tasks. In this case, these
different tasks may output different types of observations.
# Returns
True if all Tasks that can be sampled by this sampler have the
same observation space. Otherwise False.
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
@abc.abstractmethod
def reset(self) -> None:
"""Resets task sampler to its original state (except for any seed)."""
raise NotImplementedError()
@abc.abstractmethod
def set_seed(self, seed: int) -> None:
"""Sets new RNG seed.
# Parameters
seed : New seed.
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
| ask4help-main | allenact/base_abstractions/task.py |
# Original work Copyright (c) Facebook, Inc. and its affiliates.
# Modified work Copyright (c) Allen Institute for AI
# This source code is licensed under the MIT license found in the
# LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree.
from collections import OrderedDict
from typing import (
Generic,
Dict,
Any,
Optional,
TYPE_CHECKING,
TypeVar,
Sequence,
Union,
Tuple,
cast,
)
import abc
import gym
import gym.spaces as gyms
import numpy as np
from torch.distributions.utils import lazy_property
from allenact.base_abstractions.misc import EnvType
from allenact.utils import spaces_utils as su
from allenact.utils.misc_utils import prepare_locals_for_super
from allenact.utils.system import get_logger
if TYPE_CHECKING:
from allenact.base_abstractions.task import SubTaskType
else:
SubTaskType = TypeVar("SubTaskType", bound="Task")
SpaceDict = gyms.Dict
class Sensor(Generic[EnvType, SubTaskType]):
"""Represents a sensor that provides data from the environment to agent.
The user of this class needs to implement the get_observation method and
the user is also required to set the below attributes:
# Attributes
uuid : universally unique id.
observation_space : ``gym.Space`` object corresponding to observation of
sensor.
"""
uuid: str
observation_space: gym.Space
def __init__(self, uuid: str, observation_space: gym.Space, **kwargs: Any) -> None:
self.uuid = uuid
self.observation_space = observation_space
def get_observation(
self, env: EnvType, task: Optional[SubTaskType], *args: Any, **kwargs: Any
) -> Any:
"""Returns observations from the environment (or task).
# Parameters
env : The environment the sensor is used upon.
task : (Optionally) a Task from which the sensor should get data.
# Returns
Current observation for Sensor.
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
class SensorSuite(Generic[EnvType]):
"""Represents a set of sensors, with each sensor being identified through a
unique id.
# Attributes
sensors: list containing sensors for the environment, uuid of each
sensor must be unique.
"""
sensors: Dict[str, Sensor[EnvType, Any]]
observation_spaces: gyms.Dict
def __init__(self, sensors: Sequence[Sensor]) -> None:
"""Initializer.
# Parameters
param sensors: the sensors that will be included in the suite.
"""
self.sensors = OrderedDict()
spaces: OrderedDict[str, gym.Space] = OrderedDict()
for sensor in sensors:
assert (
sensor.uuid not in self.sensors
), "'{}' is duplicated sensor uuid".format(sensor.uuid)
self.sensors[sensor.uuid] = sensor
spaces[sensor.uuid] = sensor.observation_space
self.observation_spaces = SpaceDict(spaces=spaces)
def get(self, uuid: str) -> Sensor:
"""Return sensor with the given `uuid`.
# Parameters
uuid : The unique id of the sensor
# Returns
The sensor with unique id `uuid`.
"""
return self.sensors[uuid]
def get_observations(
self, env: EnvType, task: Optional[SubTaskType], **kwargs: Any
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Get all observations corresponding to the sensors in the suite.
# Parameters
env : The environment from which to get the observation.
task : (Optionally) the task from which to get the observation.
# Returns
Data from all sensors packaged inside a Dict.
"""
return {
uuid: sensor.get_observation(env=env, task=task, **kwargs) # type: ignore
for uuid, sensor in self.sensors.items()
}
class AbstractExpertSensor(Sensor[EnvType, SubTaskType], abc.ABC):
"""Base class for sensors that obtain the expert action for a given task
(if available)."""
ACTION_POLICY_LABEL: str = "action_or_policy"
EXPERT_SUCCESS_LABEL: str = "expert_success"
_NO_GROUPS_LABEL: str = "__dummy_expert_group__"
def __init__(
self,
action_space: Optional[Union[gym.Space, int]] = None,
uuid: str = "expert_sensor_type_uuid",
expert_args: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None,
nactions: Optional[int] = None,
use_dict_as_groups: bool = True,
**kwargs: Any,
) -> None:
"""Initialize an `ExpertSensor`.
# Parameters
action_space : The action space of the agent. This is necessary in order for this sensor
to know what its output observation space is.
uuid : A string specifying the unique ID of this sensor.
expert_args : This sensor obtains an expert action from the task by calling the `query_expert`
method of the task. `expert_args` are any keyword arguments that should be passed to the
`query_expert` method when called.
nactions : [DEPRECATED] The number of actions available to the agent, corresponds to an `action_space`
of `gym.spaces.Discrete(nactions)`.
use_dict_as_groups : Whether to use the top-level action_space of type `gym.spaces.Dict` as action groups.
"""
if isinstance(action_space, int):
action_space = gym.spaces.Discrete(action_space)
elif action_space is None:
assert (
nactions is not None
), "One of `action_space` or `nactions` must be not `None`."
get_logger().warning(
"The `nactions` parameter to `AbstractExpertSensor` is deprecated and will be removed, please use"
" the `action_space` parameter instead."
)
action_space = gym.spaces.Discrete(nactions)
self.action_space = action_space
self.use_groups = (
isinstance(action_space, gym.spaces.Dict) and use_dict_as_groups
)
self.group_spaces = (
self.action_space
if self.use_groups
else OrderedDict([(self._NO_GROUPS_LABEL, self.action_space,)])
)
self.expert_args: Dict[str, Any] = expert_args or {}
assert (
"expert_sensor_group_name" not in self.expert_args
), "`expert_sensor_group_name` is reserved for `AbstractExpertSensor`"
observation_space = self._get_observation_space()
super().__init__(**prepare_locals_for_super(locals()))
@classmethod
@abc.abstractmethod
def flagged_group_space(cls, group_space: gym.spaces.Space) -> gym.spaces.Dict:
"""gym space resulting from wrapping the given action space (or a
derived space, as in `AbstractExpertPolicySensor`) together with a
binary action space corresponding to an expert success flag, in a Dict
space.
# Parameters
group_space : The source action space to be (optionally used to derive a policy space,) flagged and wrapped
"""
raise NotImplementedError
@classmethod
def flagged_space(
cls, action_space: gym.spaces.Space, use_dict_as_groups: bool = True
) -> gym.spaces.Dict:
"""gym space resulting from wrapping the given action space (or every
highest-level entry in a Dict action space), together with binary
action space corresponding to an expert success flag, in a Dict space.
# Parameters
action_space : The agent's action space (to be flagged and wrapped)
use_dict_as_groups : Flag enabling every highest-level entry in a Dict action space to be independently flagged.
"""
use_groups = isinstance(action_space, gym.spaces.Dict) and use_dict_as_groups
if not use_groups:
return cls.flagged_group_space(action_space)
else:
return gym.spaces.Dict(
[
(group_space, cls.flagged_group_space(action_space[group_space]),)
for group_space in cast(gym.spaces.Dict, action_space)
]
)
def _get_observation_space(self) -> gym.spaces.Dict:
"""The observation space of the expert sensor.
For the most basic discrete agent's ExpertActionSensor, it will
equal `gym.spaces.Dict([ (self.ACTION_POLICY_LABEL,
self.action_space), (self.EXPERT_SUCCESS_LABEL,
gym.spaces.Discrete(2))])`, where the first entry hosts the
expert action index and the second equals 0 if and only if the
expert failed to generate a true expert action.
"""
return self.flagged_space(self.action_space, use_dict_as_groups=self.use_groups)
@lazy_property
def _zeroed_observation(self) -> Union[OrderedDict, Tuple]:
# AllenAct-style flattened space (to easily generate an all-zeroes action as an array)
flat_space = su.flatten_space(self.observation_space)
# torch point to correctly unflatten `Discrete` for zeroed output
flat_zeroed = su.torch_point(flat_space, np.zeros_like(flat_space.sample()))
# unflatten zeroed output and convert to numpy
return su.numpy_point(
self.observation_space, su.unflatten(self.observation_space, flat_zeroed)
)
def flatten_output(self, unflattened):
return (
su.flatten(
self.observation_space,
su.torch_point(self.observation_space, unflattened),
)
.cpu()
.numpy()
)
@abc.abstractmethod
def query_expert(
self, task: SubTaskType, expert_sensor_group_name: Optional[str],
) -> Tuple[Any, bool]:
"""Query the expert for the given task (and optional group name).
# Returns
A tuple (x, y) where x is the expert action or policy and y is False \
if the expert could not determine the optimal action (otherwise True). Here y \
is used for masking. Even when y is False, x should still lie in the space of \
possible values (e.g. if x is the expert policy then x should be the correct length, \
sum to 1, and have non-negative entries).
"""
raise NotImplementedError
def get_observation(
self, env: EnvType, task: SubTaskType, *args: Any, **kwargs: Any
) -> Union[OrderedDict, Tuple]:
# If the task is completed, we needn't (perhaps can't) find the expert
# action from the (current) terminal state.
if task.is_done():
return self.flatten_output(self._zeroed_observation)
actions_or_policies = OrderedDict()
for group_name in self.group_spaces:
action_or_policy, expert_was_successful = self.query_expert(
task=task, expert_sensor_group_name=group_name
)
actions_or_policies[group_name] = OrderedDict(
[
(self.ACTION_POLICY_LABEL, action_or_policy),
(self.EXPERT_SUCCESS_LABEL, expert_was_successful),
]
)
return self.flatten_output(
actions_or_policies
if self.use_groups
else actions_or_policies[self._NO_GROUPS_LABEL]
)
class AbstractExpertActionSensor(AbstractExpertSensor, abc.ABC):
def __init__(
self,
action_space: Optional[Union[gym.Space, int]] = None,
uuid: str = "expert_action",
expert_args: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None,
nactions: Optional[int] = None,
use_dict_as_groups: bool = True,
**kwargs: Any,
) -> None:
super().__init__(**prepare_locals_for_super(locals()))
@classmethod
def flagged_group_space(cls, group_space: gym.spaces.Space) -> gym.spaces.Dict:
"""gym space resulting from wrapping the given action space, together
with a binary action space corresponding to an expert success flag, in
a Dict space.
# Parameters
group_space : The action space to be flagged and wrapped
"""
return gym.spaces.Dict(
[
(cls.ACTION_POLICY_LABEL, group_space),
(cls.EXPERT_SUCCESS_LABEL, gym.spaces.Discrete(2)),
]
)
class ExpertActionSensor(AbstractExpertActionSensor):
"""(Deprecated) A sensor that obtains the expert action from a given task
(if available)."""
def query_expert(
self, task: SubTaskType, expert_sensor_group_name: Optional[str]
) -> Tuple[Any, bool]:
return task.query_expert(
**self.expert_args, expert_sensor_group_name=expert_sensor_group_name
)
class AbstractExpertPolicySensor(AbstractExpertSensor, abc.ABC):
def __init__(
self,
action_space: Optional[Union[gym.Space, int]] = None,
uuid: str = "expert_policy",
expert_args: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None,
nactions: Optional[int] = None,
use_dict_as_groups: bool = True,
**kwargs: Any,
) -> None:
super().__init__(**prepare_locals_for_super(locals()))
@classmethod
def flagged_group_space(cls, group_space: gym.spaces.Space) -> gym.spaces.Dict:
"""gym space resulting from wrapping the policy space corresponding to
`allenact.utils.spaces_utils.policy_space(group_space)` together with a
binary action space corresponding to an expert success flag, in a Dict
space.
# Parameters
group_space : The source action space to be used to derive a policy space, flagged and wrapped
"""
return gym.spaces.Dict(
[
(cls.ACTION_POLICY_LABEL, su.policy_space(group_space)),
(cls.EXPERT_SUCCESS_LABEL, gym.spaces.Discrete(2)),
]
)
class ExpertPolicySensor(AbstractExpertPolicySensor):
"""(Deprecated) A sensor that obtains the expert policy from a given task
(if available)."""
def query_expert(
self, task: SubTaskType, expert_sensor_group_name: Optional[str]
) -> Tuple[Any, bool]:
return task.query_expert(
**self.expert_args, expert_sensor_group_name=expert_sensor_group_name
)
| ask4help-main | allenact/base_abstractions/sensor.py |
ask4help-main | allenact/base_abstractions/__init__.py |
|
import abc
from typing import List, Any, Dict
from typing import Sequence
from typing import Union
import gym
import networkx as nx
import torch
from gym.spaces import Dict as SpaceDict
from allenact.utils.experiment_utils import Builder
class Preprocessor(abc.ABC):
"""Represents a preprocessor that transforms data from a sensor or another
preprocessor to the input of agents or other preprocessors. The user of
this class needs to implement the process method and the user is also
required to set the below attributes:
# Attributes:
input_uuids : List of input universally unique ids.
uuid : Universally unique id.
observation_space : ``gym.Space`` object corresponding to processed observation spaces.
"""
input_uuids: List[str]
uuid: str
observation_space: gym.Space
def __init__(
self,
input_uuids: List[str],
output_uuid: str,
observation_space: gym.Space,
**kwargs: Any
) -> None:
self.uuid = output_uuid
self.input_uuids = input_uuids
self.observation_space = observation_space
@abc.abstractmethod
def process(self, obs: Dict[str, Any], *args: Any, **kwargs: Any) -> Any:
"""Returns processed observations from sensors or other preprocessors.
# Parameters
obs : Dict with available observations and processed observations.
# Returns
Processed observation.
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
@abc.abstractmethod
def to(self, device: torch.device) -> "Preprocessor":
raise NotImplementedError()
class SensorPreprocessorGraph:
"""Represents a graph of preprocessors, with each preprocessor being
identified through a universally unique id.
Allows for the construction of observations that are a function of
sensor readings. For instance, perhaps rather than giving your agent
a raw RGB image, you'd rather first pass that image through a pre-trained
convolutional network and only give your agent the resulting features
(see e.g. the `ResNetPreprocessor` class).
# Attributes
preprocessors : List containing preprocessors with required input uuids, output uuid of each
sensor must be unique.
observation_spaces: The observation spaces of the values returned when calling `get_observations`.
By default (see the `additionally_exposed_uuids` parameter to to change this default) the observations
returned by the `SensorPreprocessorGraph` **include only the sink nodes** of the graph (i.e.
those that are not used by any other preprocessor).
Thus if one of the input preprocessors takes as input the `'YOUR_SENSOR_UUID'` sensor, then
`'YOUR_SENSOR_UUID'` will not be returned when calling `get_observations`.
device: The `torch.device` upon which the preprocessors are run.
"""
preprocessors: Dict[str, Preprocessor]
observation_spaces: SpaceDict
device: torch.device
def __init__(
self,
source_observation_spaces: SpaceDict,
preprocessors: Sequence[Union[Preprocessor, Builder[Preprocessor]]],
additional_output_uuids: Sequence[str] = tuple(),
) -> None:
"""Initializer.
# Parameters
source_observation_spaces : The observation spaces of all sensors before preprocessing.
This generally should be the output of `SensorSuite.observation_spaces`.
preprocessors : The preprocessors that will be included in the graph.
additional_output_uuids: As described in the documentation for this class, the observations
returned when calling `get_observations` only include, by default, those observations
that are not processed by any preprocessor. If you'd like to include observations that
would otherwise not be included, the uuids of these sensors should be included as
a sequence of strings here.
"""
self.device: torch.device = torch.device("cpu")
obs_spaces: Dict[str, gym.Space] = {
k: source_observation_spaces[k] for k in source_observation_spaces
}
self.preprocessors: Dict[str, Preprocessor] = {}
for preprocessor in preprocessors:
if isinstance(preprocessor, Builder):
preprocessor = preprocessor()
assert (
preprocessor.uuid not in self.preprocessors
), "'{}' is duplicated preprocessor uuid".format(preprocessor.uuid)
self.preprocessors[preprocessor.uuid] = preprocessor
obs_spaces[preprocessor.uuid] = preprocessor.observation_space
g = nx.DiGraph()
for k in obs_spaces:
g.add_node(k)
for k in self.preprocessors:
for j in self.preprocessors[k].input_uuids:
g.add_edge(j, k)
assert nx.is_directed_acyclic_graph(
g
), "preprocessors do not form a direct acyclic graph"
self.observation_spaces = SpaceDict(
spaces={
uuid: obs_spaces[uuid]
for uuid in obs_spaces
if uuid in additional_output_uuids or g.out_degree(uuid) == 0
}
)
# ensure dependencies are precomputed
self.compute_order = [n for n in nx.dfs_postorder_nodes(g)]
def get(self, uuid: str) -> Preprocessor:
"""Return preprocessor with the given `uuid`.
# Parameters
uuid : The unique id of the preprocessor.
# Returns
The preprocessor with unique id `uuid`.
"""
return self.preprocessors[uuid]
def to(self, device: torch.device) -> "SensorPreprocessorGraph":
for k, v in self.preprocessors.items():
self.preprocessors[k] = v.to(device)
self.device = device
return self
def get_observations(
self, obs: Dict[str, Any], *args: Any, **kwargs: Any
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Get processed observations.
# Returns
Collect observations processed from all sensors and return them packaged inside a Dict.
"""
for uuid in self.compute_order:
if uuid not in obs:
obs[uuid] = self.preprocessors[uuid].process(obs)
return {uuid: obs[uuid] for uuid in self.observation_spaces}
class PreprocessorGraph(SensorPreprocessorGraph):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
raise DeprecationWarning(
"`PreprocessorGraph` has been deprecated, use `SensorPreprocessorGraph` instead."
)
class ObservationSet:
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs) -> None:
raise DeprecationWarning(
"`ObservationSet` has been deprecated. Use `SensorPreprocessorGraph` instead."
)
| ask4help-main | allenact/base_abstractions/preprocessor.py |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.