hexsha
stringlengths 40
40
| size
int64 6
14.9M
| ext
stringclasses 1
value | lang
stringclasses 1
value | max_stars_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_stars_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_stars_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_stars_repo_licenses
list | max_stars_count
int64 1
191k
⌀ | max_stars_repo_stars_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_stars_repo_stars_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_issues_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_issues_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_issues_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_issues_repo_licenses
list | max_issues_count
int64 1
67k
⌀ | max_issues_repo_issues_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_issues_repo_issues_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_forks_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_forks_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_forks_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_forks_repo_licenses
list | max_forks_count
int64 1
105k
⌀ | max_forks_repo_forks_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_forks_repo_forks_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | avg_line_length
float64 2
1.04M
| max_line_length
int64 2
11.2M
| alphanum_fraction
float64 0
1
| cells
list | cell_types
list | cell_type_groups
list |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
cbe57f4a572efd6940781fd3cd7e5e90c8932465
| 624,629 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/colab-github-demo.ipynb
|
magikerwin1993/retinaface-tf2
|
b4a00f751318e433dcff243fae8f488d4984dc9b
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-04-21T05:15:38.000Z
|
2020-04-21T05:15:38.000Z
|
notebooks/colab-github-demo.ipynb
|
magikerwin1993/retinaface-tf2
|
b4a00f751318e433dcff243fae8f488d4984dc9b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/colab-github-demo.ipynb
|
magikerwin1993/retinaface-tf2
|
b4a00f751318e433dcff243fae8f488d4984dc9b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 2,176.407666 | 408,667 | 0.915771 |
[
[
[
"# Demo retinaface-tf2 (MobileNetV2 version) on single image input\nThis notebooks shows the testing results of the Retinaface model trained on Tensorflow2.0+.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Setup Environment\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!git clone https://github.com/peteryuX/retinaface-tf2.git\n%cd retinaface-tf2/\n!pip install -r requirements.txt",
"Cloning into 'retinaface-tf2'...\nremote: Enumerating objects: 9, done.\u001b[K\nremote: Counting objects: 100% (9/9), done.\u001b[K\nremote: Compressing objects: 100% (7/7), done.\u001b[K\nremote: Total 46 (delta 2), reused 6 (delta 2), pack-reused 37\u001b[K\nUnpacking objects: 100% (46/46), done.\n/content/retinaface-tf2\nCollecting tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/0a/93/c7bca39b23aae45cd2e85ad3871c81eccc63b9c5276e926511e2e5b0879d/tensorflow_gpu-2.1.0-cp36-cp36m-manylinux2010_x86_64.whl (421.8MB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 421.8MB 39kB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: numpy in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from -r requirements.txt (line 2)) (1.17.5)\nRequirement already satisfied: opencv-python in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from -r requirements.txt (line 3)) (4.1.2.30)\nRequirement already satisfied: PyYAML in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from -r requirements.txt (line 4)) (3.13)\nRequirement already satisfied: tqdm in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from -r requirements.txt (line 5)) (4.28.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: Pillow in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from -r requirements.txt (line 6)) (6.2.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: Cython in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from -r requirements.txt (line 7)) (0.29.15)\nRequirement already satisfied: ipython in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from -r requirements.txt (line 8)) (5.5.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: termcolor>=1.1.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (1.1.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: keras-applications>=1.0.8 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (1.0.8)\nRequirement already satisfied: six>=1.12.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (1.12.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: absl-py>=0.7.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (0.9.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: protobuf>=3.8.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (3.10.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: wheel>=0.26; python_version >= \"3\" in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (0.34.2)\nCollecting tensorflow-estimator<2.2.0,>=2.1.0rc0\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/18/90/b77c328a1304437ab1310b463e533fa7689f4bfc41549593056d812fab8e/tensorflow_estimator-2.1.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (448kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 450kB 70.4MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: scipy==1.4.1; python_version >= \"3\" in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (1.4.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: google-pasta>=0.1.6 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (0.1.8)\nRequirement already satisfied: astor>=0.6.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (0.8.1)\nCollecting tensorboard<2.2.0,>=2.1.0\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/40/23/53ffe290341cd0855d595b0a2e7485932f473798af173bbe3a584b99bb06/tensorboard-2.1.0-py3-none-any.whl (3.8MB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 3.8MB 57.8MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: keras-preprocessing>=1.1.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (1.1.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: grpcio>=1.8.6 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (1.27.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: wrapt>=1.11.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (1.11.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: opt-einsum>=2.3.2 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (3.1.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: gast==0.2.2 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (0.2.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: pexpect; sys_platform != \"win32\" in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from ipython->-r requirements.txt (line 8)) (4.8.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: simplegeneric>0.8 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from ipython->-r requirements.txt (line 8)) (0.8.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: pickleshare in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from ipython->-r requirements.txt (line 8)) (0.7.5)\nRequirement already satisfied: traitlets>=4.2 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from ipython->-r requirements.txt (line 8)) (4.3.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: prompt-toolkit<2.0.0,>=1.0.4 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from ipython->-r requirements.txt (line 8)) (1.0.18)\nRequirement already satisfied: decorator in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from ipython->-r requirements.txt (line 8)) (4.4.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: setuptools>=18.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from ipython->-r requirements.txt (line 8)) (45.1.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: pygments in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from ipython->-r requirements.txt (line 8)) (2.1.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: h5py in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from keras-applications>=1.0.8->tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (2.8.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: werkzeug>=0.11.15 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorboard<2.2.0,>=2.1.0->tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (1.0.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: markdown>=2.6.8 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorboard<2.2.0,>=2.1.0->tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (3.2.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: requests<3,>=2.21.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorboard<2.2.0,>=2.1.0->tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (2.21.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: google-auth-oauthlib<0.5,>=0.4.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorboard<2.2.0,>=2.1.0->tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (0.4.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: google-auth<2,>=1.6.3 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tensorboard<2.2.0,>=2.1.0->tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (1.7.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: ptyprocess>=0.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from pexpect; sys_platform != \"win32\"->ipython->-r requirements.txt (line 8)) (0.6.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: ipython-genutils in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from traitlets>=4.2->ipython->-r requirements.txt (line 8)) (0.2.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: wcwidth in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from prompt-toolkit<2.0.0,>=1.0.4->ipython->-r requirements.txt (line 8)) (0.1.8)\nRequirement already satisfied: idna<2.9,>=2.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from requests<3,>=2.21.0->tensorboard<2.2.0,>=2.1.0->tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (2.8)\nRequirement already satisfied: certifi>=2017.4.17 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from requests<3,>=2.21.0->tensorboard<2.2.0,>=2.1.0->tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (2019.11.28)\nRequirement already satisfied: chardet<3.1.0,>=3.0.2 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from requests<3,>=2.21.0->tensorboard<2.2.0,>=2.1.0->tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (3.0.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: urllib3<1.25,>=1.21.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from requests<3,>=2.21.0->tensorboard<2.2.0,>=2.1.0->tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (1.24.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: requests-oauthlib>=0.7.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from google-auth-oauthlib<0.5,>=0.4.1->tensorboard<2.2.0,>=2.1.0->tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (1.3.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: cachetools<3.2,>=2.0.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from google-auth<2,>=1.6.3->tensorboard<2.2.0,>=2.1.0->tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (3.1.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: pyasn1-modules>=0.2.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from google-auth<2,>=1.6.3->tensorboard<2.2.0,>=2.1.0->tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (0.2.8)\nRequirement already satisfied: rsa<4.1,>=3.1.4 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from google-auth<2,>=1.6.3->tensorboard<2.2.0,>=2.1.0->tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (4.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: oauthlib>=3.0.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from requests-oauthlib>=0.7.0->google-auth-oauthlib<0.5,>=0.4.1->tensorboard<2.2.0,>=2.1.0->tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (3.1.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: pyasn1<0.5.0,>=0.4.6 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from pyasn1-modules>=0.2.1->google-auth<2,>=1.6.3->tensorboard<2.2.0,>=2.1.0->tensorflow-gpu==2.1.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (0.4.8)\n\u001b[31mERROR: tensorflow 1.15.0 has requirement tensorboard<1.16.0,>=1.15.0, but you'll have tensorboard 2.1.0 which is incompatible.\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31mERROR: tensorflow 1.15.0 has requirement tensorflow-estimator==1.15.1, but you'll have tensorflow-estimator 2.1.0 which is incompatible.\u001b[0m\nInstalling collected packages: tensorflow-estimator, tensorboard, tensorflow-gpu\n Found existing installation: tensorflow-estimator 1.15.1\n Uninstalling tensorflow-estimator-1.15.1:\n Successfully uninstalled tensorflow-estimator-1.15.1\n Found existing installation: tensorboard 1.15.0\n Uninstalling tensorboard-1.15.0:\n Successfully uninstalled tensorboard-1.15.0\nSuccessfully installed tensorboard-2.1.0 tensorflow-estimator-2.1.0 tensorflow-gpu-2.1.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Dowload Pretrained Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from google_drive_downloader import GoogleDriveDownloader as gdd\n\ngdd.download_file_from_google_drive(file_id='1Q8b2vBLafFOr5hy5i4MbgOAoa9tppl3A',\n dest_path='./retinaface_mbv2.zip')\n!mkdir -p checkpoints/retinaface_mbv2\n!unzip retinaface_mbv2.zip -d checkpoints/retinaface_mbv2\n!rm retinaface_mbv2.zip",
"Downloading 1Q8b2vBLafFOr5hy5i4MbgOAoa9tppl3A into ./retinaface_mbv2.zip... Done.\nArchive: retinaface_mbv2.zip\n inflating: checkpoints/retinaface_mbv2/checkpoint \n inflating: checkpoints/retinaface_mbv2/ckpt-81.data-00000-of-00002 \n inflating: checkpoints/retinaface_mbv2/ckpt-81.data-00001-of-00002 \n inflating: checkpoints/retinaface_mbv2/ckpt-81.index \n"
]
],
[
[
"## The Source Image",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from IPython.display import Image\nImage(filename='./data/0_Parade_marchingband_1_149.jpg')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Prediction Result from Testing Script",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!python test.py --cfg_path=\"./configs/retinaface_mbv2.yaml\" --img_path=\"./data/0_Parade_marchingband_1_149.jpg\"\nImage(filename='out_0_Parade_marchingband_1_149.jpg')",
"2020-02-19 14:47:16.419627: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:55] Could not load dynamic library 'libnvinfer.so.6'; dlerror: libnvinfer.so.6: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory; LD_LIBRARY_PATH: /usr/lib64-nvidia\n2020-02-19 14:47:16.419847: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:55] Could not load dynamic library 'libnvinfer_plugin.so.6'; dlerror: libnvinfer_plugin.so.6: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory; LD_LIBRARY_PATH: /usr/lib64-nvidia\n2020-02-19 14:47:16.419871: W tensorflow/compiler/tf2tensorrt/utils/py_utils.cc:30] Cannot dlopen some TensorRT libraries. If you would like to use Nvidia GPU with TensorRT, please make sure the missing libraries mentioned above are installed properly.\nI0219 14:47:17.700846 140334969730944 utils.py:30] Detect 1 Physical GPUs, 1 Logical GPUs.\n/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/keras_applications/mobilenet_v2.py:294: UserWarning: `input_shape` is undefined or non-square, or `rows` is not in [96, 128, 160, 192, 224]. Weights for input shape (224, 224) will be loaded as the default.\n warnings.warn('`input_shape` is undefined or non-square, '\nDownloading data from https://github.com/JonathanCMitchell/mobilenet_v2_keras/releases/download/v1.1/mobilenet_v2_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_1.0_224_no_top.h5\n9412608/9406464 [==============================] - 1s 0us/step\n[*] load ckpt from ./checkpoints/retinaface_mbv2/ckpt-81.\n[*] Processing on single image ./data/0_Parade_marchingband_1_149.jpg\n[*] save result at out_0_Parade_marchingband_1_149.jpg\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
cbe5823ebf17c670ae4762fffed8be2f5fc297d4
| 570,655 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
unsupervised/04_anomaly_detection/01_local_outlier_factor.ipynb
|
krakowiakpawel9/machine-learning-bootcamp
|
1c65405e56a302228581998e699d4705d3660249
|
[
"MIT"
] | 7 |
2020-04-04T15:55:40.000Z
|
2021-12-28T12:44:04.000Z
|
unsupervised/04_anomaly_detection/01_local_outlier_factor.ipynb
|
krakowiakpawel9/machine-learning-bootcamp
|
1c65405e56a302228581998e699d4705d3660249
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
unsupervised/04_anomaly_detection/01_local_outlier_factor.ipynb
|
krakowiakpawel9/machine-learning-bootcamp
|
1c65405e56a302228581998e699d4705d3660249
|
[
"MIT"
] | 20 |
2020-03-02T10:54:52.000Z
|
2022-02-27T18:12:28.000Z
| 886.110248 | 193,776 | 0.899668 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/krakowiakpawel9/machine-learning-bootcamp/blob/master/unsupervised/04_anomaly_detection/01_local_outlier_factor.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### scikit-learn\nStrona biblioteki: [https://scikit-learn.org](https://scikit-learn.org) \n\nDokumentacja/User Guide: [https://scikit-learn.org/stable/user_guide.html](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/user_guide.html)\n\nPodstawowa biblioteka do uczenia maszynowego w języku Python.\n\nAby zainstalować bibliotekę scikit-learn, użyj polecenia poniżej:\n```\n!pip install scikit-learn\n```\nAby zaktualizować do najnowszej wersji bibliotekę scikit-learn, użyj polecenia poniżej:\n```\n!pip install --upgrade scikit-learn\n```\nKurs stworzony w oparciu o wersję `0.22.1`\n\n### Spis treści:\n1. [Import bibliotek](#0)\n2. [Wygenerowanie danych](#1)\n3. [Wizualizacja danych](#2)\n4. [Algorytm K-średnich](#3)\n5. [Wizualizacja klastrów](#4)\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### <a name='0'></a> Import bibliotek",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nfrom sklearn.datasets import make_blobs\nimport plotly.express as px\nimport plotly.graph_objects as go\n\nsns.set(font_scale=1.2)\nnp.random.seed(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### <a name='1'></a> Wygenerowanie danych",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data = make_blobs(n_samples=300, cluster_std=2.0, random_state=10)[0]\ndata[:5]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### <a name='2'></a> Wizualizacja danych",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tmp = pd.DataFrame(data=data, columns={'x1', 'x2'})\npx.scatter(tmp, x='x1', y='x2', width=950, title='Local Outlier Factor', template='plotly_dark')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = go.Figure()\nfig1 = px.density_heatmap(tmp, x='x1', y='x2', width=700, title='Outliers', nbinsx=20, nbinsy=20)\nfig2 = px.scatter(tmp, x='x1', y='x2', width=700, title='Outliers', opacity=0.5)\n\nfig.add_trace(fig1['data'][0])\nfig.add_trace(fig2['data'][0])\nfig.update_traces(marker=dict(size=4, line=dict(width=2, color='white')), selector=dict(mode='markers'))\nfig.update_layout(template='plotly_dark', width=950)\nfig.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(12, 7))\nplt.scatter(data[:, 0], data[:, 1], label='data', cmap='tab10')\nplt.title('Local Outlier Factor')\nplt.legend()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.neighbors import LocalOutlierFactor \n\nlof = LocalOutlierFactor(n_neighbors=20)\ny_pred = lof.fit_predict(data)\ny_pred[:10]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"all_data = np.c_[data, y_pred]\nall_data[:5]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tmp['y_pred'] = y_pred\npx.scatter(tmp, x='x1', y='x2', color='y_pred', width=950, \n title='Local Outlier Factor', template='plotly_dark')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(12, 7))\nplt.scatter(all_data[:, 0], all_data[:, 1], c=all_data[:, 2], cmap='tab10', label='data')\nplt.title('Local Outlier Factor')\nplt.legend()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"LOF_scores = lof.negative_outlier_factor_\nradius = (LOF_scores.max() - LOF_scores) / (LOF_scores.max() - LOF_scores.min())\nradius[:5]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(12, 7))\nplt.scatter(all_data[:, 0], all_data[:, 1], label='data', cmap='tab10')\nplt.scatter(all_data[:, 0], all_data[:, 1], s=2000 * radius, edgecolors='r', facecolors='none', label='outlier scores')\nplt.title('Local Outlier Factor')\nlegend = plt.legend()\nlegend.legendHandles[1]._sizes = [40]\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(12, 7))\nplt.scatter(all_data[:, 0], all_data[:, 1], c=all_data[:, 2], cmap='tab10', label='data')\nplt.scatter(all_data[:, 0], all_data[:, 1], s=2000 * radius, edgecolors='r', facecolors='none', label='outlier scores')\nplt.title('Local Outlier Factor')\nlegend = plt.legend()\nlegend.legendHandles[1]._sizes = [40]\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe58a8a4a7837e16adc8fb51ddc2bbeefc488d8
| 18,072 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
experimental_data_scripts/preprocess_data.ipynb
|
jpzwolak/quantum-ml
|
aebe3496516be3bc0fc4392aaf7805ab5faf98dc
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2018-06-27T17:20:19.000Z
|
2021-05-30T06:21:01.000Z
|
experimental_data_scripts/preprocess_data.ipynb
|
jpzwolak/quantum-ml
|
aebe3496516be3bc0fc4392aaf7805ab5faf98dc
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
experimental_data_scripts/preprocess_data.ipynb
|
jpzwolak/quantum-ml
|
aebe3496516be3bc0fc4392aaf7805ab5faf98dc
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2018-11-30T20:34:17.000Z
|
2022-02-16T23:06:37.000Z
| 207.724138 | 15,824 | 0.905434 |
[
[
[
"# This notebook is intended to display experimental data and preprocess it to be fed to the neural network\n\n# This box is used to create png files of the data and store it in a folder\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport glob\nimport os\n%matplotlib\n\ndata_folder_path = \"/Users/sandesh/exp_data/\"\nmap_folder_path = \"/Users/sandesh/exp_data/maps/\"\nfiles = glob.glob(data_folder_path + \"*.dat\")\n\n# Data format is V_LGD I_DC(nA) V_LGS I_AC(nA) t(sec)\n# The format of the loaded array is [num_points,5]\nfor file in files:\n plt.clf()\n dat = np.loadtxt(file)\n plt.tricontourf(dat[:,0],dat[:,2],dat[:,1])\n plt.xlabel(r'$V_{LGD}$ (V)',fontsize=16)\n plt.ylabel(r'$V_{LGS}$ (V)',fontsize=16)\n cbar = plt.colorbar()\n cbar.set_label(r'$I_{DC}$ (nA)',fontsize=16)\n # -3 is a simple way to remove the dat extension\n # . is already present in the filename, so only png needs to be appended\n plt.savefig(os.path.join(map_folder_path,os.path.basename(file)[:-3] + \"png\"))",
"Using matplotlib backend: MacOSX\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
]
] |
cbe58aa8381078c36625e91535933c27f7ffbbd1
| 43,939 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
playground/DevianceInformationCriteria.ipynb
|
adamamiller/ztf_early_Ia_2018
|
4caf7660a3971fa32b63a1d41f82e78fc0599982
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2019-02-24T22:34:02.000Z
|
2019-10-17T16:01:03.000Z
|
playground/DevianceInformationCriteria.ipynb
|
adamamiller/ztf_early_Ia_2018
|
4caf7660a3971fa32b63a1d41f82e78fc0599982
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
playground/DevianceInformationCriteria.ipynb
|
adamamiller/ztf_early_Ia_2018
|
4caf7660a3971fa32b63a1d41f82e78fc0599982
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-05-09T23:16:21.000Z
|
2021-05-09T23:16:21.000Z
| 41.886559 | 340 | 0.532534 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport glob\nimport emcee\nimport corner\nimport scipy.stats\nfrom scipy.ndimage import gaussian_filter1d\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom matplotlib.ticker import MultipleLocator\n\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV\nfrom sklearn.neighbors import KernelDensity\n\nfrom fit_just_early_lc import prep_light_curve, multifcqfid_lnlike_big_unc, multifcqfid_lnprior_big_unc, multifcqfid_lnposterior_big_unc, lnlike_big_unc\n\nfrom multiprocessing import Pool\nimport time\n\nfrom corner_hack import corner_hack\nfrom light_curve_plot import f_t, plot_both_filt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%matplotlib notebook",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"info_path = \"../../forced_lightcurves/sample_lc_v2/\"\nsalt_df = pd.read_csv(info_path + \"../../Nobs_cut_salt2_spec_subtype_pec.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Measure the Deviance Information Criterion\n\n$$DIC = 2 \\bar{D(\\theta)} - D(\\bar{\\theta})$$\n\nwhere, $D(\\theta) = -2 \\log P(x|\\theta)$.\n\nThus, we need to calculate the mean posterior parameters, AND, the mean likelihood for the posterior parameters. This requires the `multifcqfid_lnlike_big_unc` function. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"thin_by = 100\nrel_flux_cutoff = 0.4\n\nsn = 'ZTF18abauprj'\n\nh5_file = info_path + 'big_unc/{}_emcee_40_varchange.h5'.format(sn)\nreader = emcee.backends.HDFBackend(h5_file)\nnsteps = thin_by*np.shape(reader.get_chain())[0]\ntau = reader.get_autocorr_time(tol=0)\nburnin = int(5*np.max(tau))\nsamples = reader.get_chain(discard=burnin, thin=np.max([int(np.max(tau)), 1]), flat=True)\nlnpost = reader.get_log_prob(discard=burnin, thin=np.max([int(np.max(tau)), 1]), flat=True)\n\n\nt_max = float(salt_df['t0_g_adopted'][salt_df['name'] == sn].values)\nz = float(salt_df['z_adopt'][salt_df['name'] == sn].values)\ng_max = float(salt_df['fratio_gmax_2adam'][salt_df['name'] == sn].values)\nr_max = float(salt_df['fratio_rmax_2adam'][salt_df['name'] == sn].values)\n\nt_data, f_data, f_unc_data, fcqfid_data = prep_light_curve(info_path+\"{}_force_phot.h5\".format(sn),\n t_max=t_max, \n z=z,\n g_max=g_max,\n r_max=r_max,\n rel_flux_cutoff=rel_flux_cutoff)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"loglike_samples = np.zeros(len(samples))\n\nfor samp_num, sample in enumerate(samples):\n loglike_samples[samp_num] = multifcqfid_lnlike_big_unc(sample, f_data, t_data, f_unc_data, fcqfid_data)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dhat = -2*multifcqfid_lnlike_big_unc(np.mean(samples, axis=0), f_data, t_data, f_unc_data, fcqfid_data)\n\ndbar = -2*np.mean(loglike_samples)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dic = 2*dbar - dhat\nprint(dic)",
"-359.9673406752178\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### What about for the $t^2$ model?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"h5_file = info_path + 'big_unc/{}_emcee_40_tsquared.h5'.format(sn)\nreader = emcee.backends.HDFBackend(h5_file)\nnsteps = thin_by*np.shape(reader.get_chain())[0]\ntau = reader.get_autocorr_time(tol=0)\nburnin = int(5*np.max(tau))\nsamples_tsquared = reader.get_chain(discard=burnin, thin=np.max([int(np.max(tau)), 1]), flat=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"loglike_samples_tsquared = np.zeros(len(samples))\n\nfor samp_num, sample in enumerate(samples_tsquared):\n loglike_samples_tsquared[samp_num] = multifcqfid_lnlike_big_unc(sample, f_data, t_data, f_unc_data, fcqfid_data, \n prior='delta2')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dhat = -2*multifcqfid_lnlike_big_unc(np.mean(samples_tsquared, axis=0), f_data, t_data, f_unc_data, fcqfid_data, \n prior='delta2')\n\ndbar = np.mean(-2*loglike_samples_tsquared)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dic_tsquared = 2*dbar_tsquared - dhat_tsquared\nprint(dic_tsquared)",
"-311.7311584562079\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Loop over all SNe",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"salt_df.name.values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dic_uniformative_arr = np.zeros(len(salt_df))\ndic_tsquared_arr = np.zeros(len(salt_df))\ndic_alpha_r_plus_colors_arr = np.zeros(len(salt_df))\n\ndef get_dic(sn):\n\n# sn, bw = tup\n sn_num = np.where(salt_df.name == sn)[0]\n \n h5_file = info_path + 'big_unc/{}_emcee_40_varchange.h5'.format(sn)\n reader = emcee.backends.HDFBackend(h5_file)\n thin_by = 100\n nsteps = thin_by*np.shape(reader.get_chain())[0]\n tau = reader.get_autocorr_time(tol=0)\n burnin = int(5*np.max(tau))\n samples = reader.get_chain(discard=burnin, thin=np.max(int(np.max(tau)), 0), flat=True)\n\n rel_flux_cutoff = 0.4\n t_max = float(salt_df['t0_g_adopted'][salt_df['name'] == sn].values)\n z = float(salt_df['z_adopt'][salt_df['name'] == sn].values)\n g_max = float(salt_df['fratio_gmax_2adam'][salt_df['name'] == sn].values)\n r_max = float(salt_df['fratio_rmax_2adam'][salt_df['name'] == sn].values)\n\n t_data, f_data, f_unc_data, fcqfid_data = prep_light_curve(info_path+\"{}_force_phot.h5\".format(sn),\n t_max=t_max, \n z=z,\n g_max=g_max,\n r_max=r_max,\n rel_flux_cutoff=rel_flux_cutoff)\n\n loglike_samples = np.zeros(len(samples))\n\n for samp_num, sample in enumerate(samples):\n loglike_samples[samp_num] = multifcqfid_lnlike_big_unc(sample, f_data, t_data, f_unc_data, fcqfid_data)\n \n dhat = -2*multifcqfid_lnlike_big_unc(np.mean(samples, axis=0), f_data, t_data, f_unc_data, fcqfid_data)\n dbar = -2*np.mean(loglike_samples)\n dic = 2*dbar - dhat\n \n h5_file = info_path + 'big_unc/{}_emcee_40_tsquared.h5'.format(sn)\n reader = emcee.backends.HDFBackend(h5_file)\n nsteps = thin_by*np.shape(reader.get_chain())[0]\n tau = reader.get_autocorr_time(tol=0)\n burnin = int(5*np.max(tau))\n samples_tsquared = reader.get_chain(discard=burnin, thin=np.max([int(np.max(tau)), 1]), flat=True)\n \n loglike_samples_tsquared = np.zeros(len(samples_tsquared))\n\n for samp_num, sample in enumerate(samples_tsquared):\n loglike_samples_tsquared[samp_num] = multifcqfid_lnlike_big_unc(sample, f_data, t_data, f_unc_data, fcqfid_data, \n prior='delta2')\n\n dhat_tsquared = -2*multifcqfid_lnlike_big_unc(np.mean(samples_tsquared, axis=0), f_data, t_data, f_unc_data, fcqfid_data, \n prior='delta2')\n\n dbar_tsquared = np.mean(-2*loglike_samples_tsquared)\n dic_tsquared = 2*dbar_tsquared - dhat_tsquared\n\n dic_uniformative_arr[sn_num] = dic\n dic_tsquared_arr[sn_num] = dic_tsquared\n \n h5_file = info_path + 'big_unc/{}_emcee_40_alpha_r_plus_colors.h5'.format(sn)\n reader = emcee.backends.HDFBackend(h5_file)\n nsteps = thin_by*np.shape(reader.get_chain())[0]\n tau = reader.get_autocorr_time(tol=0)\n burnin = int(5*np.max(tau))\n samples_alpha_r_plus_colors = reader.get_chain(discard=burnin, thin=np.max([int(np.max(tau)), 1]), flat=True)\n \n loglike_samples_alpha_r_plus_colors = np.zeros(len(samples_alpha_r_plus_colors))\n\n for samp_num, sample in enumerate(samples_alpha_r_plus_colors):\n loglike_samples_alpha_r_plus_colors[samp_num] = multifcqfid_lnlike_big_unc(sample, f_data, t_data, f_unc_data, fcqfid_data, \n prior='alpha_r_plus_colors')\n\n dhat_alpha_r_plus_colors = -2*multifcqfid_lnlike_big_unc(np.mean(samples_alpha_r_plus_colors, axis=0), f_data, t_data, f_unc_data, fcqfid_data, \n prior='alpha_r_plus_colors')\n\n dbar_alpha_r_plus_colors = np.mean(-2*loglike_samples_alpha_r_plus_colors)\n dic_alpha_r_plus_colors = 2*dbar_alpha_r_plus_colors - dhat_alpha_r_plus_colors\n\n dic_uniformative_arr[sn_num] = dic\n dic_alpha_r_plus_colors_arr[sn_num] = dic_alpha_r_plus_colors\n \n return (dic, dic_tsquared, dic_alpha_r_plus_colors)\n\npool = Pool()\n\ndic_res = pool.map(get_dic, salt_df.name.values)",
"/Users/adamamiller/astronomy/ZTF/early_Ia/2018/ztf_early_Ia_2018/playground/fit_just_early_lc.py:516: RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in power\n weights=f_zp_unc_tonight[g_tonight]**(-2))\n/Users/adamamiller/miniconda3/envs/emcee3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/numpy/lib/function_base.py:388: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in multiply\n avg = np.multiply(a, wgt, dtype=result_dtype).sum(axis)/scl\n/Users/adamamiller/astronomy/ZTF/early_Ia/2018/ztf_early_Ia_2018/playground/fit_just_early_lc.py:519: RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in power\n weights=f_zp_unc_tonight[~g_tonight]**(-2))\n/Users/adamamiller/astronomy/ZTF/early_Ia/2018/ztf_early_Ia_2018/playground/fit_just_early_lc.py:521: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in greater\n cutoff_g = np.where((mean_rf < 0) & (mean_g > 0) &\n/Users/adamamiller/astronomy/ZTF/early_Ia/2018/ztf_early_Ia_2018/playground/fit_just_early_lc.py:522: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in less\n (mean_g < rel_flux_cutoff))\n/Users/adamamiller/astronomy/ZTF/early_Ia/2018/ztf_early_Ia_2018/playground/fit_just_early_lc.py:525: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in greater\n cutoff_r = np.where((mean_rf < 0) & (mean_r > 0) &\n/Users/adamamiller/astronomy/ZTF/early_Ia/2018/ztf_early_Ia_2018/playground/fit_just_early_lc.py:526: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in less\n (mean_r < rel_flux_cutoff))\n"
],
[
"dic_res",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dic_uninformative_arr = np.array(dic_res)[:,0]\ndic_tsquared_arr = np.array(dic_res)[:,1]\ndic_alpha_r_plus_colors_arr = np.array(dic_res)[:,2]\n\n\ndic_df = pd.DataFrame(salt_df.name.values, columns=['ztf_name'])\ndic_df['dic_uninformative'] = dic_uninformative_arr\ndic_df['dic_delta2'] = dic_tsquared_arr\ndic_df['dic_alpha_r_plus'] = dic_alpha_r_plus_colors_arr",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(np.where(np.exp((dic_tsquared_arr - dic_alpha_r_plus_colors_arr)/2) > 30)[0])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dic_evidence = np.array(['very strong']*len(salt_df))\ndic_evidence[np.where((np.exp((dic_tsquared_arr - dic_uninformative_arr)/2) <= 1))] = 'negative'\ndic_evidence[np.where((np.exp((dic_tsquared_arr - dic_uninformative_arr)/2) > 1) & \n (np.exp((dic_tsquared_arr - dic_uninformative_arr)/2) <= 3))] = 'weak'\ndic_evidence[np.where((np.exp((dic_tsquared_arr - dic_uninformative_arr)/2) > 3) & \n (np.exp((dic_tsquared_arr - dic_uninformative_arr)/2) <= 10))] = 'substantial'\ndic_evidence[np.where((np.exp((dic_tsquared_arr - dic_uninformative_arr)/2) > 10) & \n (np.exp((dic_tsquared_arr - dic_uninformative_arr)/2) <= 30))] = 'strong'\ndic_evidence[np.where((np.exp((dic_tsquared_arr - dic_uninformative_arr)/2) > 30) & \n (np.exp((dic_tsquared_arr - dic_uninformative_arr)/2) <= 100))] = 'very strong'\ndic_evidence[np.where((np.exp((dic_tsquared_arr - dic_uninformative_arr)/2) > 100))] = 'decisive'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dic_evidence",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.unique(dic_evidence, return_counts=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dic_df['dic_evidence'] = dic_evidence\ndic_df.to_csv('dic_results.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Analyze which SN prefer $t^2$ model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dic_df = pd.read_csv('dic_results.csv')\ndic_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"res = pd.read_csv('results_40percent.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"decisive = np.where(dic_df.dic_evidence == 'decisive')\nvstrong = np.where(dic_df.dic_evidence == 'very strong')\nstrong = np.where(dic_df.dic_evidence == 'strong')\nsubstantial = np.where(dic_df.dic_evidence == 'substantial')\nweak = np.where(dic_df.dic_evidence == 'weak')\n\nres[['ztf_name','final_selection', 't_rise_95', 't_rise_05', 'n_nights_gr_post']].iloc[decisive]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"res_tsquared = pd.read_csv('results_40_tsquared.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"colors_sample = np.where( (((dic_df.dic_evidence == 'decisive') | (dic_df.dic_evidence == 'very strong')) \n & (res.final_selection == 1)))\n\ntsquared_sample = np.where( (((dic_df.dic_evidence == 'decisive') | (dic_df.dic_evidence == 'very strong')) \n & (res.final_selection == 0) & (res_tsquared.final_selection == 1)) | \n (((dic_df.dic_evidence != 'decisive') & (dic_df.dic_evidence != 'very strong')) \n & (res_tsquared.final_selection == 1)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The upshot here is that the very best models (i.e. low $z$, high $N_\\mathrm{det}$, and low $CR_{90}$) and the very worst, opposite of this, are the ones that show significant evidence for a departure from $\\alpha = 2$ according to the DIC. These models, therefore, should not be \"lumped in\" with a uniform $\\alpha = 2$ analysis. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe58b95b2de90ca3f39cf266c1c3833861c3172
| 113,827 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/Rigetti_XY_demo.ipynb
|
lebassman/ArQTiC
|
23d9877dfb0a8c5c10da2865abaf9ca830298199
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause-LBNL"
] | 3 |
2021-06-10T01:23:24.000Z
|
2021-08-13T06:29:45.000Z
|
examples/Rigetti_XY_demo.ipynb
|
lebassman/ArQTiC
|
23d9877dfb0a8c5c10da2865abaf9ca830298199
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause-LBNL"
] | null | null | null |
examples/Rigetti_XY_demo.ipynb
|
lebassman/ArQTiC
|
23d9877dfb0a8c5c10da2865abaf9ca830298199
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause-LBNL"
] | null | null | null | 482.317797 | 30,473 | 0.76886 |
[
[
[
"import sys\nsys.path.append('/Users/cdp/Documents/GitHub/ArQTiC')\nfrom arqtic.simulation_generator import Simulation_Generator\nimport numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#create simulation object\nsim_obj = Simulation_Generator(\"ibm_control.txt\")\nsim_obj.connect_IBM()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sim_obj.generate_circuits()",
"Generating timestep 0 program\nGenerating timestep 1 program\nGenerating timestep 2 program\nGenerating timestep 3 program\nGenerating timestep 4 program\nGenerating timestep 5 program\nGenerating timestep 6 program\nGenerating timestep 7 program\nGenerating timestep 8 program\nGenerating timestep 9 program\nGenerating timestep 10 program\nGenerating timestep 11 program\nGenerating timestep 12 program\nGenerating timestep 13 program\nGenerating timestep 14 program\nGenerating timestep 15 program\nGenerating timestep 16 program\nGenerating timestep 17 program\nGenerating timestep 18 program\nGenerating timestep 19 program\nGenerating timestep 20 program\nCreating IBM quantum circuit objects...\nIBM quantum circuit objects created\nTranspiling circuits...\nCircuits transpiled successfully\n"
],
[
"#run circuits on backend\nsim_obj.run_circuits()",
"Running noiseless simulator job...\nNoiseless simulator job successful\n"
],
[
"noiseless_results=sim_obj.result_matrix\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nplt.plot(noiseless_results)\n#plt.ylim(-1,1)\n#plt.xlim(0,sim_obj.steps)\n\nplt.xlabel(\"Simulation Timestep\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Staggered Magnetization\")\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sim_obj2=Simulation_Generator(\"rigetti_demo.txt\")\nsim_obj2.generate_circuits()",
"Generating timestep 0 program\nGenerating timestep 1 program\nGenerating timestep 2 program\nGenerating timestep 3 program\nGenerating timestep 4 program\nGenerating timestep 5 program\nGenerating timestep 6 program\nGenerating timestep 7 program\nGenerating timestep 8 program\nGenerating timestep 9 program\nGenerating timestep 10 program\nGenerating timestep 11 program\nGenerating timestep 12 program\nGenerating timestep 13 program\nGenerating timestep 14 program\nGenerating timestep 15 program\nGenerating timestep 16 program\nGenerating timestep 17 program\nGenerating timestep 18 program\nGenerating timestep 19 program\nGenerating timestep 20 program\nCreating Pyquil program list...\nTranspiling circuits...\nCircuits transpiled successfully\nPyquil program list created successfully\n"
],
[
"sim_obj2.run_circuits()",
"Running Pyquil programs...\n"
],
[
"noiseless_results=sim_obj2.result_matrix\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nplt.plot(noiseless_results)\n#plt.ylim(-1,1)\n#plt.xlim(0,sim_obj.steps)\n\nplt.xlabel(\"Simulation Timestep\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Staggered Magnetization\")\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe594f207d748409a55419f534008a54d6bb28d
| 8,960 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
exampleNotebooks/calculationExamples_Ngen1and3.ipynb
|
jnhoward/SU2LDM_public
|
67db9142cbb67946e273ac940d13906d0a39bf58
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
exampleNotebooks/calculationExamples_Ngen1and3.ipynb
|
jnhoward/SU2LDM_public
|
67db9142cbb67946e273ac940d13906d0a39bf58
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
exampleNotebooks/calculationExamples_Ngen1and3.ipynb
|
jnhoward/SU2LDM_public
|
67db9142cbb67946e273ac940d13906d0a39bf58
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 27.739938 | 348 | 0.51317 |
[
[
[
"This notebook demonstrates how to use this code to calculate various quantities for both Ngen=1 and Ngen=3.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport time\n\n#-- Change working directory to the main one with omegaH2.py and omegaH2_ulysses.py--#\nimport os\n#print(os.getcwd())\nos.chdir('../')\n#print(os.getcwd())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Define input variables",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The inputs depend on whether you are using omegaH2.py directly or the SU2LDM class defined in omegaH2_ulysses.py. \n\n\n###### For the SU2LDM class defined in omegaH2_ulysses.py:\n\nSince the ulysses scan is performed in log(parameters), the inputs here are the powers of the variables. For example for BP1,\n\ngs_pow = log(0.8) $\\Rightarrow$ gs = 10**(gs_pow) = 0.8\n\n###### For omegaH2.py directly:\n\nHere the variables are their true values. For example, for BP1,\n\ngs = 0.8\n\n\nThe input variables below match those in data/test.dat and correspond to BP1.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#-- Define input variables (standard) --#\nkwargs = {}\n\n# Scan parameters \nkwargs[\"gs\"] = 0.8\nkwargs[\"eQ\"] = 0.5\nkwargs[\"sQsq\"] = 0.3\nkwargs[\"kappa\"] = 1.\n\nkwargs[\"fpi\"] = 60000. # GeV\nmDM_GeV = 5000. # GeV\nkwargs[\"bsmall\"] = (1./(4.*np.pi*kwargs[\"fpi\"]))*mDM_GeV \n\n# NOTE: \n# The input parameter bsmall is related to the mass of the DM constituent. \n# This controls how far the mass is below the weak confinement scale (lamW).\n# Namely: mDM = bsmall*lamW\n# Since lamW is also assumed to be related to fpi (namely lamW = 4*np.pi*fpi GeV) we get\n# bsmall = (1/(4*np.pi*fpi))*mDM_GeV\n\nprint(kwargs)",
"{'gs': 0.8, 'eQ': 0.5, 'sQsq': 0.3, 'kappa': 1.0, 'fpi': 60000.0, 'bsmall': 0.006631455962162305}\n"
],
[
"#-- Define input variables (powers) --#\n\n# Note that there are 16 extra parameters necessary for interfacing with ulysses\n# We set these all to have a power of zero\nkwargs_pow = { \"m\":0.000000, \"M1\":0.000000, \"M2\":0.000000, \"M3\":0.000000, \"delta\":0.000000,\n \"a21\":0.000000, \"a31\":0.000000, \"x1\":0.000000, \"x2\":0.000000, \"x3\":0.000000,\n \"y1\":0.000000, \"y2\":0.000000, \"y3\":0.000000, \"t12\":0.000000, \"t13\":0.000000,\n \"t23\":0.000000}\n\n# Scan parameters\nkwargs_pow[\"gs\"] = np.log10(kwargs[\"gs\"])\nkwargs_pow[\"fpi\"] = np.log10(kwargs[\"fpi\"])\nkwargs_pow[\"kappa\"] = np.log10(kwargs[\"kappa\"])\nkwargs_pow[\"eQ\"] = np.log10(kwargs[\"eQ\"])\nkwargs_pow[\"bsmall\"] = np.log10(kwargs[\"bsmall\"])\nkwargs_pow[\"sQsq\"] = np.log10(kwargs[\"sQsq\"])\n\nprint(kwargs_pow)",
"{'m': 0.0, 'M1': 0.0, 'M2': 0.0, 'M3': 0.0, 'delta': 0.0, 'a21': 0.0, 'a31': 0.0, 'x1': 0.0, 'x2': 0.0, 'x3': 0.0, 'y1': 0.0, 'y2': 0.0, 'y3': 0.0, 't12': 0.0, 't13': 0.0, 't23': 0.0, 'gs': -0.09691001300805639, 'fpi': 4.778151250383644, 'kappa': 0.0, 'eQ': -0.3010299956639812, 'bsmall': -2.1783911100697213, 'sQsq': -0.5228787452803376}\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Calculate with omegaH2.py",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#-- Ngen=1 --#\nkwargs[\"Ngen\"] = 1\n\n#-- Calculate oh2 and therm values --#\nfrom omegaH2 import omegaH2\nstart = time.process_time()\noh2, therm = omegaH2(**kwargs, DEBUG=False)\nend = time.process_time()\nprint(\"oh2 = \", oh2, therm)\nprint(\"TIME = \", end - start)\nprint(\"\")\n\n#-- Calculate m1 and aeff values (demonstration of RETURN option) --#\nstart = time.process_time()\nm1, aeff = omegaH2(**kwargs, DEBUG=False, RETURN='m1_aeff')\nend = time.process_time()\nprint(\"m1, aeff = \", m1, aeff)\nprint(\"TIME = \", end - start)\nprint(\"\")\n",
"oh2 = 0.1001053678842274 5.390028794795367\nTIME = 11.531341999999999\n\nm1, aeff = 771570.1602976598 (1.8923857077963512e-11+0j)\nTIME = 0.0752469999999974\n\n"
],
[
"#-- Ngen=3 --#\nkwargs[\"Ngen\"] = 3\n\n#-- Calculate oh2 and therm values --#\nfrom omegaH2 import omegaH2\nstart = time.process_time()\noh2, therm = omegaH2(**kwargs, DEBUG=False)\nend = time.process_time()\nprint(\"oh2 = \", oh2, therm)\nprint(\"TIME = \", end - start)\nprint(\"\")\n\n#-- Calculate m1 and aeff values (demonstration of RETURN option) --#\nstart = time.process_time()\nm1, aeff = omegaH2(**kwargs, DEBUG=False, RETURN='m1_aeff')\nend = time.process_time()\nprint(\"m1, aeff = \", m1, aeff)\nprint(\"TIME = \", end - start)\nprint(\"\")",
"oh2 = 0.07767697146334929 4.1824042179652485\nTIME = 118.55119200000001\n\nm1, aeff = 771570.1602976598 (2.471915617766557e-11+0j)\nTIME = 110.78659200000001\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Calculate with SU2LDM class defined in omegaH2_ulysses.py",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"NOTE: Ngen argument must be changed in the omegaH2_ulysses.py file and the kernel must be restarted. Run cells 1-3, and then run the cell below. #! Fix this later",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from omegaH2_ulysses import SU2LDM\n\nstart = time.process_time()\nobjectSU2LDM = SU2LDM()\nobjectSU2LDM.setParams(pdict=kwargs_pow)\noh2 = objectSU2LDM.EtaB #EtaB is treated like a property of the class not a function\nend = time.process_time()\nprint(\"oh2 = \", oh2)\nprint(\"TIME = \", end - start)",
"oh2 = 0.10010536788423431\nTIME = 10.036499000000001\n"
],
[
"#-- Ngen=1 Result --#\n\n# oh2 = 0.10010536788423431\n# TIME = 10.036499000000001 \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#-- Ngen=3 Result --#\n\n# oh2 = 0.07774433729213447\n# TIME = 119.14895899999999\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe5a447be99208b6b44805f02885c8f3e504eac
| 5,543 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
experiments/Untitled.ipynb
|
alpha-nome/style-transfer
|
cd57de92901635d7cc7be5477eeae2bb9439927d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-02-03T07:17:57.000Z
|
2021-02-03T07:17:57.000Z
|
experiments/Untitled.ipynb
|
alpha-nome/style-transfer
|
cd57de92901635d7cc7be5477eeae2bb9439927d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
experiments/Untitled.ipynb
|
alpha-nome/style-transfer
|
cd57de92901635d7cc7be5477eeae2bb9439927d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 31.494318 | 104 | 0.515966 |
[
[
[
"import gradio as gr\nimport torch\nfrom torchvision import transforms\nimport requests\nfrom PIL import Image\nfrom net import Net, Vgg16\nimport numpy as np\n\n\nmodel = torch.hub.load('pytorch/vision:v0.6.0', 'resnet18', pretrained=True).eval()\n\n# Download human-readable labels for ImageNet.\nresponse = requests.get(\"https://git.io/JJkYN\")\nlabels = response.text.split(\"\\n\")\n\ndef preprocess_batch(batch):\n batch = batch.transpose(0, 1)\n (r, g, b) = torch.chunk(batch, 3)\n batch = torch.cat((b, g, r))\n batch = batch.transpose(0, 1)\n return batch\n\ndef tensor_load_rgbimage(filename, size=None, scale=None, keep_asp=False):\n\n img = Image.open(filename).convert('RGB')\n if size is not None:\n if keep_asp:\n size2 = int(size * 1.0 / img.size[0] * img.size[1])\n img = img.resize((size, size2), Image.ANTIALIAS)\n else:\n img = img.resize((size, size), Image.ANTIALIAS)\n\n elif scale is not None:\n img = img.resize((int(img.size[0] / scale), int(img.size[1] / scale)), Image.ANTIALIAS)\n img = np.array(img).transpose(2, 0, 1)\n img = torch.from_numpy(img).float()\n return img\n\ndef tensor_load_rgbimage_2(filename, size=None, scale=None, keep_asp=False):\n\n img = Image.fromarray(filename).convert('RGB')\n if size is not None:\n if keep_asp:\n size2 = int(size * 1.0 / img.size[0] * img.size[1])\n img = img.resize((size, size2), Image.ANTIALIAS)\n else:\n img = img.resize((size, size), Image.ANTIALIAS)\n\n elif scale is not None:\n img = img.resize((int(img.size[0] / scale), int(img.size[1] / scale)), Image.ANTIALIAS)\n img = np.array(img).transpose(2, 0, 1)\n img = torch.from_numpy(img).float()\n return img\n\n\ndef evaluate(img):\n content_image = tensor_load_rgbimage_2(img, size=1024, keep_asp=True)\n #content_image = img\n content_image = content_image.unsqueeze(0)\n style = tensor_load_rgbimage(\"images/21styles/candy.jpg\", size=512)\n style = style.unsqueeze(0) \n style = preprocess_batch(style)\n \n style_model = Net(ngf=128)\n model_dict = torch.load(\"models/21styles.model\")\n model_dict_clone = model_dict.copy()\n for key, value in model_dict_clone.items():\n if key.endswith(('running_mean', 'running_var')):\n del model_dict[key]\n style_model.load_state_dict(model_dict, False)\n\n style_v = Variable(style)\n\n content_image = Variable(preprocess_batch(content_image))\n style_model.setTarget(style_v)\n\n output = style_model(content_image)\n img = output.data[0].clone().clamp(0, 255).numpy()\n img = img.transpose(1, 2, 0).astype('uint8')\n img = Image.fromarray(img)\n #output = utils.color_match(output, style_v)\n return img\n\ndef predict(inp):\n return inp\ninputs = gr.inputs.Image()\noutputs = gr.outputs.Image()\ngr.Interface(fn=evaluate, inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs).launch(share=False)",
"Using cache found in /Users/sachinchandra/.cache/torch/hub/pytorch_vision_v0.6.0\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
]
] |
cbe5f4d99d9777c4299ba1ba777d5e496b660825
| 794,038 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/stephan_notebooks/01-Initial_EDA.ipynb
|
raspstephan/nwp-downscale
|
dbb6d560126a8d13a2748bc088f382e68fa7c0b3
|
[
"MIT"
] | 7 |
2020-12-14T02:57:39.000Z
|
2022-03-29T08:32:36.000Z
|
notebooks/stephan_notebooks/01-Initial_EDA.ipynb
|
raspstephan/nwp-downscale
|
dbb6d560126a8d13a2748bc088f382e68fa7c0b3
|
[
"MIT"
] | 39 |
2020-12-03T11:39:11.000Z
|
2021-09-28T09:57:33.000Z
|
notebooks/stephan_notebooks/01-Initial_EDA.ipynb
|
raspstephan/nwp-downscale
|
dbb6d560126a8d13a2748bc088f382e68fa7c0b3
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-09-21T23:57:36.000Z
|
2021-09-21T23:57:36.000Z
| 274.848737 | 440,220 | 0.903155 |
[
[
[
"# Initial data and problem exploration\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import xarray as xr\nimport pandas as pd\nimport urllib.request\nimport numpy as np\nfrom glob import glob\nimport cartopy.crs as ccrs\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport os",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import cartopy.feature as cfeature\nstates_provinces = cfeature.NaturalEarthFeature(\n category='cultural',\n name='admin_1_states_provinces_lines',\n scale='50m',\n facecolor='none')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Data preprocessing",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## TIGGE ECMWF",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Control run",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tigge_ctrl = xr.open_mfdataset(\"/datadrive/tigge/16km/2m_temperature/2019-10.nc\")\ntigge_ctrl",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tigge_ctrl.lat.min()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tigge_2dslice = tigge_ctrl.t2m.isel(lead_time=4, init_time=0)\np = tigge_2dslice.plot( \n subplot_kws=dict(projection=ccrs.Orthographic(-80, 35), facecolor=\"gray\"),\n transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(),)\n#p.axes.set_global()\np.axes.coastlines()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### TIGGE CTRL precip",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prec = xr.open_mfdataset(\"/datadrive/tigge/raw/total_precipitation/*.nc\")\nprec # aggregated precipitation ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"prec.tp.mean('init_time').diff('lead_time').plot(col='lead_time', col_wrap=3) # that takes a while! ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Checking regridding",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"t2m_raw = xr.open_mfdataset(\"/datadrive/tigge/raw/2m_temperature/2019-10.nc\")\nt2m_32 = xr.open_mfdataset(\"/datadrive/tigge/32km/2m_temperature/2019-10.nc\")\nt2m_16 = xr.open_mfdataset(\"/datadrive/tigge/16km/2m_temperature/2019-10.nc\")\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for ds in [t2m_raw, t2m_16, t2m_32]: \n tigge_2dslice = ds.t2m.isel(lead_time=4, init_time=-10)\n plt.figure()\n p = tigge_2dslice.plot(levels=np.arange(270,305),\n subplot_kws=dict(projection=ccrs.Orthographic(-80, 35), facecolor=\"gray\"),\n transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(),)\n p.axes.coastlines()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Ensemble",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!ls -lh ../data/tigge/2020-10-23_ens2.grib",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tigge = xr.open_mfdataset('../data/tigge/2020-10-23_ens2.grib', engine='pynio').isel()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tigge = tigge.rename({\n 'tp_P11_L1_GGA0_acc': 'tp', \n 'initial_time0_hours': 'init_time',\n 'forecast_time0': 'lead_time',\n 'lat_0': 'latitude',\n 'lon_0': 'longitude',\n 'ensemble0' : 'member'\n}).diff('lead_time').tp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tigge = tigge.where(tigge >= 0, 0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# tigge = tigge * 1000 # m to mm",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tigge.coords['valid_time'] = xr.concat([i + tigge.lead_time for i in tigge.init_time], 'init_time')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tigge",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tigge.to_netcdf('../data/tigge/2020-10-23_ens_preprocessed.nc')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Deterministic",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tigge = xr.open_mfdataset('../data/tigge/2020-10-23.grib', engine='pynio')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tigge = tigge.rename({\n 'tp_P11_L1_GGA0_acc': 'tp', \n 'initial_time0_hours': 'init_time',\n 'forecast_time0': 'lead_time',\n 'lat_0': 'latitude',\n 'lon_0': 'longitude',\n}).diff('lead_time').tp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tigge = tigge.where(tigge >= 0, 0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tigge.coords['valid_time'] = xr.concat([i + tigge.lead_time for i in tigge.init_time], 'init_time')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tigge",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tigge.to_netcdf('../data/tigge/2020-10-23_preprocessed.nc')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## YOPP",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"yopp = xr.open_dataset('../data/yopp/2020-10-23.grib', engine='pynio').TP_GDS4_SFC\nyopp2 = xr.open_dataset('../data/yopp/2020-10-23_12.grib', engine='pynio').TP_GDS4_SFC",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"yopp = xr.merge([yopp, yopp2]).rename({\n 'TP_GDS4_SFC': 'tp', \n 'initial_time0_hours': 'init_time',\n 'forecast_time1': 'lead_time',\n 'g4_lat_2': 'latitude',\n 'g4_lon_3': 'longitude'\n})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"yopp = yopp.diff('lead_time').tp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"yopp = yopp.where(yopp >= 0, 0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"yopp = yopp * 1000 # m to mm",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"yopp.coords['valid_time'] = xr.concat([i + yopp.lead_time for i in yopp.init_time], 'init_time')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"yopp.to_netcdf('../data/yopp/2020-10-23_preprocessed.nc')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## NRMS data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def time_from_fn(fn):\n s = fn.split('/')[-1].split('_')[-1]\n year = s[:4]\n month = s[4:6]\n day = s[6:8]\n hour = s[9:11]\n return np.datetime64(f'{year}-{month}-{day}T{hour}')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def open_nrms(path):\n fns = sorted(glob(f'{path}/*'))\n dss = [xr.open_dataset(fn, engine='pynio') for fn in fns]\n times = [time_from_fn(fn) for fn in fns]\n times = xr.DataArray(times, name='time', dims=['time'], coords={'time': times})\n ds = xr.concat(dss, times).rename({'lat_0': 'latitude', 'lon_0': 'longitude'})\n da = ds[list(ds)[0]].rename('tp')\n return da",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_mrms_fn(path, source, year, month, day, hour):\n month, day, hour = [str(x).zfill(2) for x in [month, day, hour]]\n fn = f'{path}/{source}/MRMS_{source}_00.00_{year}{month}{day}-{hour}0000.grib2'\n# print(fn)\n return fn",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def load_mrms_data(path, start_time, stop_time, accum=3):\n times = pd.to_datetime(np.arange(start_time, stop_time, np.timedelta64(accum, 'h'), dtype='datetime64[h]'))\n das = []\n for t in times:\n if os.path.exists(get_mrms_fn(path, f'MultiSensor_QPE_0{accum}H_Pass1', t.year, t.month, t.day, t.hour)):\n ds = xr.open_dataset(get_mrms_fn(path, f'MultiSensor_QPE_0{accum}H_Pass1', t.year, t.month, t.day, t.hour), engine='pynio')\n elif os.path.exists(get_mrms_fn(path, f'MultiSensor_QPE_0{accum}H_Pass2', t.year, t.month, t.day, t.hour)):\n ds = xr.open_dataset(get_mrms_fn(path, f'MultiSensor_QPE_0{accum}H_Pass2', t.year, t.month, t.day, t.hour), engine='pynio')\n elif os.path.exists(get_mrms_fn(path, f'RadarOnly_QPE_0{accum}H', t.year, t.month, t.day, t.hour)):\n ds = xr.open_dataset(get_mrms_fn(path, f'RadarOnly_QPE_0{accum}H', t.year, t.month, t.day, t.hour), engine='pynio')\n else:\n raise Exception(f'No data found for {t}')\n ds = ds.rename({'lat_0': 'latitude', 'lon_0': 'longitude'})\n da = ds[list(ds)[0]].rename('tp')\n das.append(da)\n times = xr.DataArray(times, name='time', dims=['time'], coords={'time': times})\n da = xr.concat(das, times)\n return da",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mrms = load_mrms_data('../data/', '2020-10-23', '2020-10-25')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mrms6h = mrms.rolling(time=2).sum().isel(time=slice(0, None, 2))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mrms.to_netcdf('../data/mrms/mrms_preprocessed.nc')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mrms6h.to_netcdf('../data/mrms/mrms6_preprocessed.nc')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!ls ../data",
"ls: cannot access '../data': No such file or directory\n"
],
[
"tigge_det = xr.open_dataarray('../data/tigge/2020-10-23_preprocessed.nc').rename({'latitude': 'lat', 'longitude': 'lon'})\ntigge_ens = xr.open_dataarray('../data/tigge/2020-10-23_ens_preprocessed.nc').rename({'latitude': 'lat', 'longitude': 'lon'})\nyopp = xr.open_dataarray('../data/yopp/2020-10-23_preprocessed.nc').rename({'latitude': 'lat', 'longitude': 'lon'})\nmrms = xr.open_dataarray('../data/mrms/mrms_preprocessed.nc').rename({'latitude': 'lat', 'longitude': 'lon'})\nmrms6h = xr.open_dataarray('../data/mrms/mrms6_preprocessed.nc').rename({'latitude': 'lat', 'longitude': 'lon'})",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Regrid",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import xesmf as xe",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lons = slice(260, 280)\nlats = slice(45, 25)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def regrid(ds, km, lats, lons):\n deg = km/100.\n grid = xr.Dataset(\n {\n 'lat': (['lat'], np.arange(lats.start, lats.stop, -deg)),\n 'lon': (['lon'], np.arange(lons.start, lons.stop, deg))\n }\n )\n regridder = xe.Regridder(ds.sel(lat=lats, lon=lons), grid, 'bilinear')\n return regridder(ds.sel(lat=lats, lon=lons), keep_attrs=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mrms4km = regrid(mrms, 4, lats, lons)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mrms2km = regrid(mrms, 2, lats, lons)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mrms4km6h = regrid(mrms6h, 4, lats, lons)\nmrms2km6h = regrid(mrms6h, 2, lats, lons)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mrms4km6h = mrms4km6h.rename('tp')\nmrms2km6h =mrms2km6h.rename('tp')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"yopp16km = regrid(yopp, 16, lats, lons)\nyopp32km = regrid(yopp, 32, lats, lons)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tigge_det16km = regrid(tigge_det, 16, lats, lons)\ntigge_det32km = regrid(tigge_det, 32, lats, lons)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tigge_ens16km = regrid(tigge_ens, 16, lats, lons)\ntigge_ens32km = regrid(tigge_ens, 32, lats, lons)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!mkdir ../data/regridded",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mrms2km.to_netcdf('../data/regridded/mrms2km.nc')\nmrms4km.to_netcdf('../data/regridded/mrms4km.nc')\nmrms2km6h.to_netcdf('../data/regridded/mrms2km6h.nc')\nmrms4km6h.to_netcdf('../data/regridded/mrms4km6h.nc')\nyopp16km.to_netcdf('../data/regridded/yopp16km.nc')\nyopp32km.to_netcdf('../data/regridded/yopp32km.nc')\ntigge_det16km.to_netcdf('../data/regridded/tigge_det16km.nc')\ntigge_det32km.to_netcdf('../data/regridded/tigge_det32km.nc')\ntigge_ens16km.to_netcdf('../data/regridded/tigge_ens16km.nc')\ntigge_ens32km.to_netcdf('../data/regridded/tigge_ens32km.nc')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mrms2km = xr.open_dataarray('../data/regridded/mrms2km.nc')\nmrms4km = xr.open_dataarray('../data/regridded/mrms4km.nc')\nmrms2km6h = xr.open_dataarray('../data/regridded/mrms2km6h.nc')\nmrms4km6h = xr.open_dataarray('../data/regridded/mrms4km6h.nc')\nyopp16km = xr.open_dataarray('../data/regridded/yopp16km.nc')\nyopp32km = xr.open_dataarray('../data/regridded/yopp32km.nc')\ntigge_det16km = xr.open_dataarray('../data/regridded/tigge_det16km.nc')\ntigge_det32km = xr.open_dataarray('../data/regridded/tigge_det32km.nc')\ntigge_ens16km = xr.open_dataarray('../data/regridded/tigge_ens16km.nc')\ntigge_ens32km = xr.open_dataarray('../data/regridded/tigge_ens32km.nc')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Matplotlib",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Compare different resolutions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mrms4km",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.arange(lons.start, lons.stop, 512/100)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def add_grid(axs):\n for ax in axs:\n ax.set_xticks(np.arange(lons.start, lons.stop, 512/100))\n ax.set_yticks(np.arange(lats.start, lats.stop, -512/100))\n ax.grid(True)\n ax.set_aspect('equal')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"yopp16km",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"yopp16km.isel(init_time=i, lead_time=slice(0, 3)).valid_time",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"i = 3\nvalid_time = yopp16km.isel(init_time=i, lead_time=slice(0, 3)).valid_time\nfigsize = (16, 5)\naxs = mrms4km.sel(time=valid_time.values).plot(vmin=0, vmax=50, col='time', cmap='gist_ncar_r', figsize=figsize).axes[0]\nadd_grid(axs)\naxs = yopp16km.isel(init_time=i, lead_time=slice(0, 3)).plot(vmin=0, vmax=50, col='lead_time', cmap='gist_ncar_r', figsize=figsize).axes[0]\nadd_grid(axs)\naxs = yopp32km.isel(init_time=i, lead_time=slice(0, 3)).plot(vmin=0, vmax=50, col='lead_time', cmap='gist_ncar_r', figsize=figsize).axes[0]\nadd_grid(axs)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"i = 2\nvalid_time = tigge_det16km.isel(init_time=i, lead_time=slice(0, 3)).valid_time\nfigsize = (16, 5)\naxs = mrms4km6h.sel(time=valid_time.values, method='nearest').assign_coords({'time': valid_time.values}).plot(vmin=0, vmax=50, col='time', cmap='gist_ncar_r', figsize=figsize).axes[0]\nadd_grid(axs)\naxs = tigge_det16km.isel(init_time=i, lead_time=slice(0, 3)).plot(vmin=0, vmax=50, col='lead_time', cmap='gist_ncar_r', figsize=figsize).axes[0]\nadd_grid(axs)\naxs = tigge_det32km.isel(init_time=i, lead_time=slice(0, 3)).plot(vmin=0, vmax=50, col='lead_time', cmap='gist_ncar_r', figsize=figsize).axes[0]\nadd_grid(axs)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tigge_ens16km.isel(init_time=i, lead_time=l)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"i = 3\nl = 0\nt = tigge_ens16km.isel(init_time=i, lead_time=slice(l, l+2)).valid_time.values\naxs = mrms4km6h.sel(time=t, method='nearest').assign_coords({'time': t}).plot(vmin=0, vmax=50, cmap='gist_ncar_r', figsize=(10, 4), col='time').axes[0]\nadd_grid(axs)\naxs = tigge_ens16km.isel(init_time=i, lead_time=l, member=slice(0, 6)).plot(vmin=0, vmax=50, cmap='gist_ncar_r', figsize=(24, 4), col='member').axes[0]\nadd_grid(axs)\naxs = tigge_ens16km.isel(init_time=i, lead_time=l+1, member=slice(0, 6)).plot(vmin=0, vmax=50, cmap='gist_ncar_r', figsize=(24, 4), col='member').axes[0]\nadd_grid(axs)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Holoviews",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import holoviews as hv\nhv.extension('bokeh')\nhv.config.image_rtol = 1\n# from holoviews import opts\n# opts.defaults(opts.Scatter3D(color='Value', cmap='viridis', edgecolor='black', s=50))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lons2 = slice(268, 273)\nlats2 = slice(40, 35)\nlons2 = lons\nlats2 = lats",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def to_hv(da, dynamic=False, opts={'clim': (1, 50)}):\n hv_ds = hv.Dataset(da)\n img = hv_ds.to(hv.Image, kdims=[\"lon\", \"lat\"], dynamic=dynamic)\n return img.opts(**opts)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"valid_time = yopp16km.isel(lead_time=slice(0, 4), init_time=slice(0, 3)).valid_time\nvalid_time2 = tigge_det16km.isel(lead_time=slice(0, 3), init_time=slice(0, 3)).valid_time",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mrms2km_hv = to_hv(mrms2km.sel(time=valid_time, method='nearest').sel(lat=lats2, lon=lons2))\nmrms4km_hv = to_hv(mrms4km.sel(time=valid_time, method='nearest').sel(lat=lats2, lon=lons2))\nmrms2km6h_hv = to_hv(mrms2km6h.sel(time=valid_time2, method='nearest').sel(lat=lats2, lon=lons2))\nmrms4km6h_hv = to_hv(mrms4km6h.sel(time=valid_time2, method='nearest').sel(lat=lats2, lon=lons2))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"yopp16km_hv = to_hv(yopp16km.isel(lead_time=slice(0, 4), init_time=slice(0, 3)).sel(lat=lats2, lon=lons2))\nyopp32km_hv = to_hv(yopp32km.isel(lead_time=slice(0, 4), init_time=slice(0, 3)).sel(lat=lats2, lon=lons2))\ntigge_det16km_hv = to_hv(tigge_det16km.isel(lead_time=slice(0, 3), init_time=slice(0, 3)).sel(lat=lats2, lon=lons2))\ntigge_det32km_hv = to_hv(tigge_det32km.isel(lead_time=slice(0, 3), init_time=slice(0, 3)).sel(lat=lats2, lon=lons2))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Which resolution for MRMS?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%output holomap='widgets'\n%%opts Image style(cmap='gist_ncar_r') [width=600, height=600]\n# mrms4km6h_hv + tigge_det16km_hv + tigge_det32km_hv\n# mrms4km_hv + yopp16km_hv + yopp32km_hv",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%output holomap='widgets'\n%%opts Image style(cmap='gist_ncar_r') [width=600, height=600]\nmrms4km_hv + mrms4km6h_hv",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hv_yopp = yopp.isel(init_time=0).sel(latitude=lats, longitude=lons)\nhv_yopp.coords['time'] = hv_yopp.init_time + hv_yopp.lead_time\nhv_yopp = hv_yopp.swap_dims({'lead_time': 'time'})\n# hv_yopp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hv_mrms = hv.Dataset(mrms.sel(latitude=lats, longitude=lons)[1:])\nhv_yopp = hv.Dataset(hv_yopp.sel(time=mrms.time[1:]))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"img1 = hv_mrms.to(hv.Image, kdims=[\"longitude\", \"latitude\"], dynamic=False)\nimg2 = hv_yopp.to(hv.Image, kdims=[\"longitude\", \"latitude\"], dynamic=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%output holomap='widgets'\n%%opts Image style(cmap='gist_ncar_r') plot[colorbar=True]\n%%opts Image [width=500, height=400]\nimg1 + img2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hv_yopp = yopp.sel(latitude=lats, longitude=lons)\nhv_yopp = hv.Dataset(hv_yopp)\nimg1 = hv_yopp.to(hv.Image, kdims=[\"longitude\", \"latitude\"], dynamic=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%output holomap='widgets'\n%%opts Image style(cmap='gist_ncar_r') plot[colorbar=True]\n%%opts Image [width=500, height=400]\nimg1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hv_ds = hv.Dataset(da.sel(latitude=lats, longitude=lons))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hv_ds",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = hv_ds.to(hv.Image, kdims=[\"longitude\", \"latitude\"], dynamic=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a.opts(colorbar=True, fig_size=200, cmap='viridis')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Old",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"path = '../data/MultiSensor_QPE_01H_Pass1/'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"da1 = open_nrms('../data/MultiSensor_QPE_01H_Pass1/')\nda3 = open_nrms('../data/MultiSensor_QPE_03H_Pass1/')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dar = open_nrms('../data/RadarOnly_QPE_03H/')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"da3p = open_nrms('../data/MultiSensor_QPE_03H_Pass2/')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"da1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"da3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"da13 = da1.rolling(time=3).sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"(da13 - da3).isel(time=3).sel(latitude=lats, longitude=lons).plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"da13.isel(time=slice(0, 7)).sel(latitude=slice(44, 40), longitude=slice(268, 272)).plot(col='time', vmin=0, vmax=50)\nplt.suptitle('1h accumulation with rolling(time=3).sum()', y=1.05)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"da3.isel(time=slice(0, 7)).sel(latitude=slice(44, 40), longitude=slice(268, 272)).plot(col='time', vmin=0, vmax=50)\nplt.suptitle('3h accumulation', y=1.05)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dar.isel(time=slice(0, 7)).sel(latitude=slice(44, 40), longitude=slice(268, 272)).plot(col='time', vmin=0, vmax=50)\nplt.suptitle('3h accumulation radar', y=1.05)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"da3.isel(time=slice(0, 7)).sel(latitude=slice(44, 43), longitude=slice(269, 270)).plot(col='time', vmin=0, vmax=50)\nplt.suptitle('3h accumulation', y=1.05)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dar.isel(time=slice(0, 7)).sel(latitude=slice(44, 43), longitude=slice(269, 270)).plot(col='time', vmin=0, vmax=50)\nplt.suptitle('3h accumulation radar', y=1.05)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for t in np.arange('2020-10-23', '2020-10-25', np.timedelta64(3, 'h'), dtype='datetime64[h]'):\n print(t)\n print('Radar', (dar.time.values == t).sum() > 0)\n print('Pass1', (da3.time.values == t).sum() > 0)\n print('Pass2', (da3p.time.values == t).sum() > 0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"t",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"(dar.time.values == t).sum() > 0",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"da3.time.values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def plot_facet(da, title='', **kwargs):\n p = da.plot(\n col='time', col_wrap=3,\n subplot_kws={'projection': ccrs.PlateCarree()},\n transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(),\n figsize=(15, 15), **kwargs\n )\n for ax in p.axes.flat:\n ax.coastlines()\n ax.add_feature(states_provinces, edgecolor='gray')\n# ax.set_extent([113, 154, -11, -44], crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())\n plt.suptitle(title);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_facet(da.isel(time=slice(0, 9)).sel(latitude=lats, longitude=lons), vmin=0, vmax=10, add_colorbar=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import holoviews as hv\nhv.extension('matplotlib')\nfrom holoviews import opts\nopts.defaults(opts.Scatter3D(color='Value', cmap='fire', edgecolor='black', s=50))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hv_ds = hv.Dataset(da.sel(latitude=lats, longitude=lons))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hv_ds",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = hv_ds.to(hv.Image, kdims=[\"longitude\", \"latitude\"], dynamic=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a.opts(colorbar=True, fig_size=200, cmap='viridis')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"da.longitude.diff('longitude').min()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!cp ../data/yopp/2020-10-23.nc ../data/yopp/2020-10-23.grib",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = xr.open_dataset('../data/yopp/2020-10-23.grib', engine='pynio')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a.g4_lat_2.diff('g4_lat_2')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a.g4_lon_3.diff('g4_lon_3')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!cp ../data/tigge/2020-10-23.nc ../data/tigge/2020-10-23.grib",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"b = xr.open_dataset('../data/tigge/2020-10-23.grib', engine='pynio')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"b",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe5fcbef1e35f236e476f6b6bce39513ae6f257
| 19,336 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Linear Model.ipynb
|
farukeryilmaz/deep-learning-machine-learning-examples
|
9073f4b8f5fc598ea3800e4d57edd615a7394382
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Linear Model.ipynb
|
farukeryilmaz/deep-learning-machine-learning-examples
|
9073f4b8f5fc598ea3800e4d57edd615a7394382
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Linear Model.ipynb
|
farukeryilmaz/deep-learning-machine-learning-examples
|
9073f4b8f5fc598ea3800e4d57edd615a7394382
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 62.576052 | 6,236 | 0.759981 |
[
[
[
"import tensorflow as tf\nfrom tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport random\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('data/MNIST/', one_hot=True) #onhot=true -> y=5 ise => on tane eleman olan vektore cevirdi -> y=[0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0]",
"Extracting data/MNIST/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz\nExtracting data/MNIST/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz\nExtracting data/MNIST/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz\nExtracting data/MNIST/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz\n"
],
[
"def show_digit(pixels):\n img = pixels.reshape(28, 28)\n plt.axis('off')\n plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray_r')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sample = random.choice(mnist.train.images)\n\nshow_digit(sample)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(u\"Training data set: %d\" % len(mnist.train.images))\nprint(u\"Test data set: %d\" % len(mnist.test.images))",
"Training data set: 55000\nTest data set: 10000\n"
],
[
"#veri setini iclerine koymak icin\nX = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) #yertutucu tersorfow degiskeni, yertutucunun veri tipi float32, matrix formatinda kac satir oldugunu bilmiyoruz o yuzden none, 784 deger\ny = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10]) #onhot=true -> y=5 ise => on tane eleman olan vektore cevirdi -> y=[0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0]\n\nW = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[784, 10], stddev=0.1)) #rastgele sayilar olustur, boyutu 784x4. 0.1 -> elemanlar arasi sicrama\nb = tf.Variable(tf.constant(shape=[10], value=0.1)) #basta sabit bir deger=0.1, boyutu 10",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_pred = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(X, W) + b) #y_pred=[0.01, 0.2.., 0.75, ...,0.1] en yuksek 5inci index, y ile karsilastirmasi kolay eger onehot true ise\n\nloss = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y * tf.log(y_pred),\n reduction_indices=[1])) # probleme gore maliyet fonksiyonlari vardir, bu fonksiyon cross entropy. fonksiyona gore deger ne kadar buyuk ise o kadar kotu\n# loss un minimum oldugu noktayi ariyoruz\n\noptimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.05).minimize(loss) # 0.05 -> learning rate \n\ncorrect_predictions = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(y_pred, 1)) # liste halinde true false cikaracak\naccuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_predictions, tf.float32)) # dogrular 1.0, yanlislar 0. reduce_mean -> listenin icindeki m tane sayiyi topla ve m ye bol (yani ortalama al)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sess = tf.Session() # calisirabilmek icin session olusturduk\nsess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())\n\nfor i in range(10000):\n xs, ys = mnist.train.next_batch(150) # 128 resim. tek seferde tek resim gondermek maliyeti yukseltir o yuzden 128 tane resmi paket halinde gonder. sistem gucune gore sayi artabilir azaltilabilir\n \n sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={X: xs, y: ys})\n \n if i % 500 == 0: #her 500 adimda accuracy calistir, test veri setinin hepsini gonder, modelin basarisini olc\n acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images,\n y: mnist.test.labels})\n print(\"[*] Step: %d, test accuracy: %.2f%%\" % (i, acc * 100))\n ",
"[*] Step: 0, test accuracy: 6.90%\n[*] Step: 500, test accuracy: 88.45%\n[*] Step: 1000, test accuracy: 89.79%\n[*] Step: 1500, test accuracy: 90.39%\n[*] Step: 2000, test accuracy: 90.73%\n[*] Step: 2500, test accuracy: 90.99%\n[*] Step: 3000, test accuracy: 91.14%\n[*] Step: 3500, test accuracy: 91.29%\n[*] Step: 4000, test accuracy: 91.29%\n[*] Step: 4500, test accuracy: 91.47%\n[*] Step: 5000, test accuracy: 91.61%\n[*] Step: 5500, test accuracy: 91.63%\n[*] Step: 6000, test accuracy: 91.67%\n[*] Step: 6500, test accuracy: 91.60%\n[*] Step: 7000, test accuracy: 91.79%\n[*] Step: 7500, test accuracy: 91.84%\n[*] Step: 8000, test accuracy: 91.88%\n[*] Step: 8500, test accuracy: 91.77%\n[*] Step: 9000, test accuracy: 92.03%\n[*] Step: 9500, test accuracy: 91.88%\n"
],
[
"weig = tf.Print(W,[W])\nbia = tf.Print(b,[b])\n# print sess.run(weig), sess.run(bia)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sample = random.choice(mnist.test.images)\n\npredict = sess.run(y_pred, feed_dict={X: [sample]})[0]\n\nfor i, v in enumerate(predict):\n print(\"Probability of being %d: %.2f%%\" % (i, v * 100))\n \nshow_digit(sample)",
"Probability of being 0: 0.00%\nProbability of being 1: 0.00%\nProbability of being 2: 0.00%\nProbability of being 3: 0.00%\nProbability of being 4: 99.73%\nProbability of being 5: 0.00%\nProbability of being 6: 0.12%\nProbability of being 7: 0.01%\nProbability of being 8: 0.01%\nProbability of being 9: 0.11%\n"
],
[
"random_img = np.random.rand(784)\n\npredict = sess.run(y_pred, feed_dict={X: [random_img]})[0]\n\nfor i, v in enumerate(predict):\n print(\"Probability of being %d: %.2f%%\" % (i, v * 100))\n \nshow_digit(random_img)",
"Probability of being 0: 0.00%\nProbability of being 1: 0.00%\nProbability of being 2: 31.93%\nProbability of being 3: 64.93%\nProbability of being 4: 0.00%\nProbability of being 5: 3.00%\nProbability of being 6: 0.00%\nProbability of being 7: 0.00%\nProbability of being 8: 0.14%\nProbability of being 9: 0.00%\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe60a00208d21a806a01c0e45366a131fe01d4f
| 388,200 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/PCA.ipynb
|
ttsuchi/ttsuchi.github.io
|
45ee147e7bc8597510778b0f5cb46df3940ed9f1
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/PCA.ipynb
|
ttsuchi/ttsuchi.github.io
|
45ee147e7bc8597510778b0f5cb46df3940ed9f1
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/PCA.ipynb
|
ttsuchi/ttsuchi.github.io
|
45ee147e7bc8597510778b0f5cb46df3940ed9f1
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 560.17316 | 138,260 | 0.929652 |
[
[
[
"%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2\n%matplotlib inline\n\nfrom numpy import *\nfrom IPython.html.widgets import *\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom IPython.core.display import clear_output",
":0: FutureWarning: IPython widgets are experimental and may change in the future.\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Principal Component Analysis and EigenFaces\n\nIn this notebook, I will go through the basic concepts behind the principal component analysis (PCA). I will then apply PCA to a face dataset to find the characteristic faces (\"eigenfaces\").",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## What is PCA?\n\nPCA is a **linear** transformation. Suppose I have a $N \\times P$ data matrix ${\\bf X}$, where $N$ is the number of samples and $P$ is the dimension of each sample. Then PCA will find you a $K \\times P$ matrix ${\\bf V}$ such that\n\n$$ \\underbrace{{\\bf X}}_{N \\times P} = \\underbrace{{\\bf S}}_{P \\times K} \\underbrace{{\\bf V}}_{K \\times P}. $$\n\nHere, $K$ is the number of **principal components** with $K \\le P$.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## But what does the V matrix do?\n\n\n${\\bf V}$ can be though of in many different ways.\n\nThe first way is to think of it as a de-correlating transformation: originally, each variable (or dimension) in ${\\bf X}$ - there are $P$ of them - may be *correlated*. That is, if I take any two column vectors of ${\\bf X}$, say ${\\bf x}_0$ and ${\\bf x}_1$, their covariance is not going to be zero.\n\nLet's try this in a randomly generated data:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from numpy.random import standard_normal # Gaussian variables\nN = 1000; P = 5\nX = standard_normal((N, P))\nW = X - X.mean(axis=0,keepdims=True)\nprint(dot(W[:,0], W[:,1]))",
"-70.7565800526\n"
]
],
[
[
"I'll skip ahead and use a pre-canned PCA routine from `scikit-learn` (but I'll dig into it a bit later!) Let's see what happens to the transformed variables, ${\\bf S}$:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.decomposition import PCA\nS=PCA(whiten=True).fit_transform(X)\nprint(dot(S[:,0], S[:,1]))",
"4.68958205602e-13\n"
]
],
[
[
"Another way to look at ${\\bf V}$ is to think of them as **projections**. Since the row vectors of ${\\bf V}$ is *orthogonal* to each other, the projected data ${\\bf S}$ lines in a new \"coordinate system\" specified by ${\\bf V}$. Furthermore, the new coordinate system is sorted in the decreasing order of *variance* in the original data. So, PCA can be thought of as calculating a new coordinate system where the basis vectors point toward the direction of largest variances first.\n\n<img src=\"files/images/PCA/pca.png\" style=\"margin:auto; width: 483px;\"/>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Exercise 1. Let's get a feel for this in the following interactive example. Try moving the sliders around to generate the data, and see how the principal component vectors change.\n\nIn this demo, `mu_x` and `mu_y` specifies the center of the data, `sigma_x` and `sigma_y` the standard deviations, and everything is rotated by the angle `theta`. The two blue arrows are the rows of ${\\bf V}$ that gets calculated.\n\nWhen you click on `center`, the data is first centered (mean is subtracted from the data) first. (Question: why is it necessary to \"center\" data when `mu_x` and `mu_y` are not zero?)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from numpy.random import standard_normal\nfrom matplotlib.patches import Ellipse\nfrom numpy.linalg import svd\n@interact\ndef plot_2d_pca(mu_x=FloatSlider(min=-3.0, max=3.0, value=0), \n mu_y=FloatSlider(min=-3.0, max=3.0, value=0), \n sigma_x=FloatSlider(min=0.2, max=1.8, value=1.8),\n sigma_y=FloatSlider(min=0.2, max=1.8, value=0.3),\n theta=FloatSlider(min=0.0, max=pi, value=pi/6), center=False):\n mu=array([mu_x, mu_y])\n sigma=array([sigma_x, sigma_y])\n R=array([[cos(theta),-sin(theta)],[sin(theta),cos(theta)]])\n X=dot(standard_normal((1000, 2)) * sigma[newaxis,:],R.T) + mu[newaxis,:]\n\n # Plot the points and the ellipse\n fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,8))\n ax.scatter(X[:200,0], X[:200,1], marker='.')\n ax.grid()\n M=8.0\n ax.set_xlim([-M,M])\n ax.set_ylim([-M,M])\n e=Ellipse(xy=array([mu_x, mu_y]), width=sigma_x*3, height=sigma_y*3, angle=theta/pi*180, \n facecolor=[1.0,0,0], alpha=0.3)\n ax.add_artist(e)\n \n # Perform PCA and plot the vectors\n if center:\n X_mean=X.mean(axis=0,keepdims=True)\n else:\n X_mean=zeros((1,2))\n\n # Doing PCA here... I'm using svd instead of scikit-learn PCA, I'll come back to this.\n U,s,V =svd(X-X_mean, full_matrices=False)\n for v in dot(diag(s/sqrt(X.shape[0])),V): # Each eigenvector\n ax.arrow(X_mean[0,0],X_mean[0,1],-v[0],-v[1], \n head_width=0.5, head_length=0.5, fc='b', ec='b')\n Ustd=U.std(axis=0)\n ax.set_title('std(U*s) [%f,%f]' % (Ustd[0]*s[0],Ustd[1]*s[1]))\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Yet another use for ${\\bf V}$ is to perform a **dimensionality reduction**. In many scenarios you encounter in image manipulation (as I'll see soon), Imight want to have a more concise representation of the data ${\\bf X}$. PCA with $K < P$ is one way to *reduce the dimesionality*: because PCA picks the directions with highest data variances, if a small number of top $K$ rows are sufficient to approximate (reconstruct) ${\\bf X}$.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## How do Iactually *perform* PCA?\n\nWell, we can use `from sklearn.decomposition import PCA`. But for learning, let's dig just one step into what it acutally does.\n\nOne of the easiest way to perform PCA is to use the singular value decomposition (SVD). SVD decomposes a matrix ${\\bf X}$ into a unitary matrix ${\\bf U}$, rectangular diagonal matrix ${\\bf \\Sigma}$ (called \"singular values\"), and another unitary matrix ${\\bf W}$ such that\n\n$$ {\\bf X} = {\\bf U} {\\bf \\Sigma} {\\bf W}$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"So how can Iuse that to do PCA? Well, it turns out ${\\bf \\Sigma} {\\bf W}$ of SVD, are exactly what Ineed to calculate the ${\\bf V}$ matrix for the PCA, so I just have to run SVD and set ${\\bf V} = {\\bf \\Sigma} {\\bf W}$.\n\n(Note: `svd` of `numpy` returns only the diagonal elements of ${\\bf \\Sigma}$.)\n\nExercise 2. Generate 1000 10-dimensional data and perform PCA this way. Plot the squares of the singular values.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To reduce the the $P$-dimesional data ${\\bf X}$ to a $K$-dimensional data, I just need to pick the top $K$ row vectors of ${\\bf V}$ - let's call that ${\\bf W}$ - then calcuate ${\\bf T} = {\\bf X} {\\bf W}^\\intercal$. ${\\bf T}$ then has the dimension $N \\times K$.\n\nIf I want to reconstruct the data ${\\bf T}$, Isimply do ${\\hat {\\bf X}} = {\\bf T} {\\bf W}$ (and re-add the means for ${\\bf X}$, if necessary).\n\nExercise 3. Reduce the same data to 5 dimensions, then based on the projected data ${\\bf T}$, reconstruct ${\\bf X}$. What's the mean squared error of the reconstruction?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Performing PCA on a face dataset\n\nNow that I have a handle on the PCA method, let's try applying it to a dataset consisting of face data. I will use the CAlifornia FAcial expressions dataset (CAFE) from http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~gary/CAFE/ . The following code loads the dataset into the `dataset` variable:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pickle\ndataset=pickle.load(open('data/cafe.pkl','r'))\ndisp('dataset.images shape is %s' % str(dataset.images.shape))\ndisp('dataset.data shape is %s' % str(dataset.data.shape))\n\n@interact\ndef plot_face(image_id=(0, dataset.images.shape[0]-1)):\n plt.imshow(dataset.images[image_id],cmap='gray')\n plt.title('Image Id = %d, Gender = %d' % (dataset.target[image_id], dataset.gender[image_id]))\n plt.axis('off')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Preprocessing\n\nI'll center the data by subtracting the mean. The first axis (`axis=0`) is the `n_samples` dimension.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X=dataset.data.copy() # So that Iwon't mess up the data in the dataset\\\nX_mean=X.mean(axis=0,keepdims=True) # Mean for each dimension across sample (centering)\nX_std=X.std(axis=0,keepdims=True)\nX-=X_mean\ndisp(all(abs(X.mean(axis=0))<1e-12)) # Are means for all dimensions very close to zero?",
"True\n"
]
],
[
[
"Then I perform SVD to calculate the projection matrix $V$. By default, `U,s,V=svd(...)` returns full matrices, which will return $n \\times n$ matrix `U`, $n$-dimensional vector of singular values `s`, and $d \\times d$ matrix `V`. But here, I don't really need $d \\times d$ matrix `V`; with `full_matrices=False`, `svd` only returns $n \\times d$ matrix for `V`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from numpy.linalg import svd\nU,s,V=svd(X,compute_uv=True, full_matrices=False)\ndisp(str(U.shape))\ndisp(str(s.shape))\ndisp(str(V.shape))",
"(80, 80)\n(80,)\n(80, 5700)\n"
]
],
[
[
"I can also plot how much each eigenvector in `V` contributes to the overall variance by plotting `variance_ratio` = $\\frac{s^2}{\\sum s^2}$. (Notice that `s` is already in the decreasing order.) The `cumsum` (cumulative sum) of `variance_ratio` then shows how much of the variance is explained by components up to `n_components`. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"variance_ratio=s**2/(s**2).sum() # Normalized so that they add to one.\n@interact\ndef plot_variance_ratio(n_components=(1, len(variance_ratio))):\n n=n_components-1\n fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 5))\n \n axs[0].plot(variance_ratio)\n axs[0].set_title('Explained Variance Ratio')\n axs[0].set_xlabel('n_components')\n axs[0].axvline(n, color='r', linestyle='--')\n axs[0].axhline(variance_ratio[n], color='r', linestyle='--')\n \n axs[1].plot(cumsum(variance_ratio))\n axs[1].set_xlabel('n_components')\n axs[1].set_title('Cumulative Sum')\n \n captured=cumsum(variance_ratio)[n]\n axs[1].axvline(n, color='r', linestyle='--')\n axs[1].axhline(captured, color='r', linestyle='--')\n axs[1].annotate(s='%f%% with %d components' % (captured * 100, n_components), xy=(n, captured), \n xytext=(10, 0.5), arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle=\"->\")) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Since I'm dealing with face data, each row vector of ${\\bf V}$ is called an \"eigenface\". The first \"eigenface\" is the one that explains a lot of variances in the data, whereas the last one explains the least.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"image_shape=dataset.images.shape[1:] # (H x W)\n@interact\ndef plot_eigenface(eigenface=(0, V.shape[0]-1)):\n v=V[eigenface]*X_std\n \n plt.imshow(v.reshape(image_shape), cmap='gray')\n plt.title('Eigenface %d (%f to %f)' % (eigenface, v.min(), v.max()))\n plt.axis('off')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now I'll try reconstructing faces with different number of principal components (PCs)! Now, the transformed `X` is reconstructed by multiplying by the sample standard deviations for each dimension and adding the sample mean. For this reason, even for zero components, you get a face-like image!\n\nThe rightmost plot is the \"relative\" reconstruction error (image minus the reconstruction squared, divided by the data standard deviations). White is where the error is close to zero, and black is where the relative error is large (1 or more). As you increase the number of PCs, you should see the error mostly going to zero (white).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"@interact\ndef plot_reconstruction(image_id=(0,dataset.images.shape[0]-1), n_components=(0, V.shape[0]-1),\n pc1_multiplier=FloatSlider(min=-2,max=2, value=1)):\n # This is where Iperform the projection and un-projection\n Vn=V[:n_components]\n M=ones(n_components)\n if n_components > 0:\n M[0]=pc1_multiplier\n X_hat=dot(multiply(dot(X[image_id], Vn.T), M), Vn)\n \n # Un-center\n I=X[image_id] + X_mean\n I_hat = X_hat + X_mean\n D=multiply(I-I_hat,I-I_hat) / multiply(X_std, X_std)\n \n # And plot\n fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(10, 10))\n \n axs[0].imshow(I.reshape(image_shape), cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=1)\n axs[0].axis('off')\n axs[0].set_title('Original')\n \n axs[1].imshow(I_hat.reshape(image_shape), cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=1)\n axs[1].axis('off')\n axs[1].set_title('Reconstruction')\n\n axs[2].imshow(1-D.reshape(image_shape), cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=1)\n axs[2].axis('off')\n axs[2].set_title('Difference^2 (mean = %f)' % sqrt(D.mean()))\n \n plt.tight_layout()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Image morphing\n\nAs a fun exercise, I'll morph two images by taking averages of the two images within the transformed data space. How is it different than simply morphing them in the pixel space?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plot_morph(left=0, right=1, mix=0.5):\n # Projected images\n x_lft=dot(X[left], V.T)\n x_rgt=dot(X[right], V.T)\n \n # Mix\n x_avg = x_lft * (1.0-mix) + x_rgt * (mix)\n \n # Un-project\n X_hat = dot(x_avg[newaxis,:], V)\n I_hat = X_hat + X_mean\n \n # And plot\n fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(10, 10))\n \n axs[0].imshow(dataset.images[left], cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=1)\n axs[0].axis('off')\n axs[0].set_title('Left')\n \n axs[1].imshow(I_hat.reshape(image_shape), cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=1)\n axs[1].axis('off')\n axs[1].set_title('Morphed (%.2f %% right)' % (mix * 100))\n\n axs[2].imshow(dataset.images[right], cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=1)\n axs[2].axis('off')\n axs[2].set_title('Right')\n \n plt.tight_layout()\n\ninteract(plot_morph,\n left=IntSlider(max=dataset.images.shape[0]-1),\n right=IntSlider(max=dataset.images.shape[0]-1,value=1),\n mix=FloatSlider(value=0.5, min=0, max=1.0))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"(The answer: not very much...)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe60c861951dfa0721efd3c7c38d4a92abb60be
| 293,976 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Notebooks/knn2e.ipynb
|
eacunafer/DataMining-Machine-Learning-Py3
|
e97f32720412c61ea406bc5dcc44edf97f16e2bd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Notebooks/knn2e.ipynb
|
eacunafer/DataMining-Machine-Learning-Py3
|
e97f32720412c61ea406bc5dcc44edf97f16e2bd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Notebooks/knn2e.ipynb
|
eacunafer/DataMining-Machine-Learning-Py3
|
e97f32720412c61ea406bc5dcc44edf97f16e2bd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 381.291829 | 246,466 | 0.923222 |
[
[
[
"## Data Mining and Machine Learning\n### k-nn Classification\n#### Edgar Acuna \n#### November 2018",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Example 1. Predicting the final grade in a course based on Ex1 and Ex2 scores",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df=pd.read_csv(\"c://PW-PR/eje1dis.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Convirtiendo en matriz la tabla de predictoras y la columna de clases\ny=df['Nota']\nX=df.iloc[:,0:2]\n#creando una columna \"pass\" numerica para representar las clases\nlb_make = LabelEncoder()\ndf[\"pass\"] = lb_make.fit_transform(df[\"Nota\"])\n#Tambien se puede usar y.as_matrix() para la clasificacion\ny2=df['pass']\ny1=y2.as_matrix()\nX1=X.as_matrix()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Applying knn with k=3 and finding the accuracy\nneigh = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)\nneigh.fit(X1, y1) \nneigh.score(X1, y1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Finding the predictions\npred=neigh.predict(X1)\nprint pred",
"[1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]\n"
],
[
"#Finding the number of errors\nerror=(y!=pred).sum()\nprint \"This is the number of errors=\", error",
"This is the number of errors= 32\n"
],
[
"#Visualizing the decision boundary with k=1\nfrom matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap\nneigh = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=1)\nneigh.fit(X1,y1)\neje1=np.arange(start = X1[:, 0].min()-1, stop = X1[:, 0].max() + 1, step = 0.1)\neje2=np.arange(start = X1[:, 1].min()-1, stop = X1[:, 1].max() + 1, step = 0.11)\nY1, Y2 = np.meshgrid(eje1,eje2)\npred2=neigh.predict(np.c_[Y1.ravel(), Y2.ravel()]).reshape(Y1.shape)\nprint pred2\nplt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))\nplt.pcolormesh(Y1, Y2, pred2,cmap=plt.cm.Paired)\n# Plot also the training points#\nplt.scatter(X1[:, 0], X1[:, 1], c=y2, edgecolors='k')\nplt.xlabel('Ex1')\nplt.ylabel('Ex2')\nplt.xlim(Y1.min(), Y1.max())\nplt.ylim(Y2.min(), Y2.max())\nplt.xticks(())\nplt.yticks(())\n\nplt.show()",
"[[0 0 0 ... 1 1 1]\n [0 0 0 ... 1 1 1]\n [0 0 0 ... 1 1 1]\n ...\n [1 1 1 ... 1 1 1]\n [1 1 1 ... 1 1 1]\n [1 1 1 ... 1 1 1]]\n"
],
[
"#Visualizing the decision boundary with k=7\nfrom matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap\nneigh = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=7)\nneigh.fit(X1,y1)\neje1=np.arange(start = X1[:, 0].min()-1, stop = X1[:, 0].max() + 1, step = 0.1)\neje2=np.arange(start = X1[:, 1].min()-1, stop = X1[:, 1].max() + 1, step = 0.11)\nY1, Y2 = np.meshgrid(eje1,eje2)\npred2=neigh.predict(np.c_[Y1.ravel(), Y2.ravel()]).reshape(Y1.shape)\nplt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))\nplt.pcolormesh(Y1, Y2, pred2,cmap=plt.cm.Paired)\n# Plot also the training points#\nplt.scatter(X1[:, 0], X1[:, 1], c=y2, edgecolors='k')\nplt.xlabel('Ex1')\nplt.ylabel('Ex2')\nplt.xlim(Y1.min(), Y1.max())\nplt.ylim(Y2.min(), Y2.max())\nplt.xticks(())\nplt.yticks(())\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Example 2. K-nn applied to Diabetes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"url= \"http://academic.uprm.edu/eacuna/diabetes.dat\"\nnames = ['preg', 'plas', 'pres', 'skin', 'test', 'mass', 'pedi', 'age', 'class']\ndata = pd.read_table(url, names=names)\nprint(data.shape)\ndata.head()",
"(768, 9)\n"
],
[
"y=data['class']\nX=data.iloc[:,0:8]\ny1=y.as_matrix()\nX1=X.as_matrix()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Estimacion de la precision con k=3 vecinos por el metodo \"holdout \nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X1,y1, test_size=0.4, random_state=0)\nX_train, y_train\n\nX_test, y_test\n\nneigh = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)\nneigh.fit(X_train, y_train) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pred=neigh.predict(X_test)\n(pred==1).sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"(pred==2).sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"neigh.score(X_test, y_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(classification_report(y_test, pred))",
" precision recall f1-score support\n\n 1 0.76 0.82 0.79 205\n 2 0.57 0.49 0.53 103\n\n micro avg 0.71 0.71 0.71 308\n macro avg 0.67 0.65 0.66 308\nweighted avg 0.70 0.71 0.70 308\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"Precision is the ratio tp / (tp + fp) where tp=168 is the number of true positives and fp=53 is the number of false positives. It measures the cspsbility of the classifier to do not label as positives intances that have negative as label. \n\nRecall or sensitivity is the ratio tp / (tp + fn) where y fp=37 is the number of false negatives. It measures the capability of the classifier to find all the positive instancias.\n\nThe f1-score is the harmonic mean of the precision and recall.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Estimacion de la precision usando k=5 vecinos usando validacion cruzada\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score\nneigh = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)\nscores = cross_val_score(neigh, X1, y1, cv=10)\nscores",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(\"Accuracy using k=5 neighbors: %0.2f (+/- %0.2f)\" % (scores.mean(), scores.std() * 2))",
"Accuracy using k=5 neighbors: 0.72 (+/- 0.09)\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Ejemplo 3. Dataset Landsat visualizando con Componentes principales",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Cargando el conjunto de datos Landsat\nurl='http://academic.uprm.edu/eacuna/landsat.txt'\ndata = pd.read_table(url, header=None,delim_whitespace=True)\ny=data.iloc[:,36]\nX=data.iloc[:,0:36]\ny1=y.as_matrix()\nX1=X.as_matrix()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Estimacion de la precision con k=3 vecinos por el metodo \"holdout \nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X1,y1, test_size=0.4, random_state=0)\nX_train, y_train\n\nX_test, y_test\n\nneigh = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)\nneigh.fit(X_train, y_train) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pred=neigh.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"neigh.score(X_test, y_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(classification_report(y_test, pred))",
" precision recall f1-score support\n\n 1 0.98 0.97 0.98 427\n 2 0.97 0.97 0.97 197\n 3 0.88 0.92 0.90 396\n 4 0.60 0.60 0.60 161\n 5 0.92 0.85 0.88 183\n 6 0.89 0.87 0.88 410\n\n micro avg 0.89 0.89 0.89 1774\n macro avg 0.87 0.87 0.87 1774\nweighted avg 0.89 0.89 0.89 1774\n\n"
],
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nfrom sklearn.decomposition import PCA\npca = PCA(n_components=2)\nX = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X)\nprincipalComponents = pca.fit_transform(X)\npcaDF=pd.DataFrame(data = principalComponents, columns = ['PC1', 'PC2'])\nprint pca.explained_variance_\nprint pca.explained_variance_ratio_\nprint pca.explained_variance_ratio_.cumsum()",
"C:\\Users\\edgar2017\\Anaconda2\\envs\\ipykernel_py2\\lib\\site-packages\\sklearn\\preprocessing\\data.py:617: DataConversionWarning: Data with input dtype int64 were all converted to float64 by StandardScaler.\n return self.partial_fit(X, y)\nC:\\Users\\edgar2017\\Anaconda2\\envs\\ipykernel_py2\\lib\\site-packages\\sklearn\\base.py:462: DataConversionWarning: Data with input dtype int64 were all converted to float64 by StandardScaler.\n return self.fit(X, **fit_params).transform(X)\n"
],
[
"#Aplicando el clasificador knn con k=9 y calculando el porcentaje de precision\nneigh = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=9)\nneigh.fit(principalComponents, y) \npcaDF['class']=y\nfinalDf=pcaDF\n#Tasa de precision\nypred=neigh.predict(principalComponents)\nprecision=(y==ypred).sum()/float(len(y))\nprint \"Este la precision con dos PC=\", precision",
"Este la precision con dos PC= 0.8622322435174746\n"
],
[
"from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap\neje1=np.arange(start = finalDf['PC1'].min()-1, stop = finalDf['PC1'].max() + 1, step = 0.1)\neje2=np.arange(start = finalDf['PC2'].min()-1, stop = finalDf['PC2'].max() + 1, step = 0.11)\nY1, Y2 = np.meshgrid(eje1,eje2)\npred2=neigh.predict(np.c_[Y1.ravel(), Y2.ravel()]).reshape(Y1.shape)\nplt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))\nplt.pcolormesh(Y1, Y2, pred2,cmap=plt.cm.Paired)\n# Plot also the training points#\nplt.scatter(finalDf['PC1'], finalDf['PC2'], c=y)\nplt.xlabel('PC1')\nplt.ylabel('PC2')\nplt.xlim(Y1.min(), Y1.max())\nplt.ylim(Y2.min(), Y2.max())\nplt.xticks(())\nplt.yticks(())\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe61d31d6d1c6907be5076d181f2f2fede09917
| 6,346 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Python Absolute Beginner/Module_4.2_Required_Code.ipynb
|
mlane52/pythonteachingcode
|
46f007a94dfc6afcc22b41952f9c486d5c4c145e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Python Absolute Beginner/Module_4.2_Required_Code.ipynb
|
mlane52/pythonteachingcode
|
46f007a94dfc6afcc22b41952f9c486d5c4c145e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Python Absolute Beginner/Module_4.2_Required_Code.ipynb
|
mlane52/pythonteachingcode
|
46f007a94dfc6afcc22b41952f9c486d5c4c145e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 39.416149 | 421 | 0.512922 |
[
[
[
"# Module 4 Required Coding Activity \nIntroduction to Python Unit 1 \n\nThe activity is based on modules 1 - 4 and is similar to the Jupyter Notebooks **`Practice_MOD04_1-6_IntroPy.ipynb`** and **`Practice_MOD04_1-7_IntroPy.ipynb`** which you may have completed as practice. This activity is a new version of the str_analysis() function.\n\n| Some Assignment Requirements |\n|:-------------------------------|\n|This program requires the use of<ul><li>**`while`** loop to get non-empty input</li><li>**`if, else`**</li><li>**`if, else`** (nested)</li><li>**`.isdigit()`** check for integer only input</li><li>**`.isalpha()`** check for alphabetic only input</li></ul><br/>The program should **only** use code syntax covered in modules 1 - 4.<br/><br/>The program must result in printed message analysis of the input. |\n\n\n \n## Program: `str_analysis()` Function \n\nCreate the str_analysis() function that takes 1 string argument and returns a string message. The message will be an analysis of a test string that is passed as an argument to str_analysis(). The function should respond with messages such as: \n- \"big number\"\n- \"small number\"\n- \"all alphabetic\"\n- \"multiple character types\"\n\nThe program will call str_analysis() with a string argument from input collected within a while loop. The while loop will test if input is empty (an empty string \"\") and continue to loop and gather input until the user submits at least 1 character (input cannot be empty). \n\nThe program then calls the str_analysis() function and prints the **return** message.\n\n\n\n#### Sample input and output: \nenter nothing (twice) then enter a word \n```\nenter word or integer: \nenter word or integer: \nenter word or integer: Hello\n\"Hello\" is all alphabetical characters!\n \n``` \n----- \n \nalphabetical word input \n```\nenter word or integer: carbonization\n\"carbonization\" is all alphabetical characters!\n \n``` \n----- \n \nnumeric inputs\n```\nenter word or integer: 30\n30 is a smaller number than expected\n\nenter word or integer: 1024\n1024 is a pretty big number\n``` \n----- \n\n\n### loop until non-empty input is submitted \nThis diagram represents the input part of the assignment - it is the loop to keep prompting the user for input until they submit some input (non-empty). \n\n \n\nOnce the user gives input with characters use the input in calling the str_analysis() function.\n\n### Additional Details\nIn the body of the str_analysis() function:\n- Check `if` string is digits \n - if digits: convert to `int` and check `if` greater than 99 \n - if greater than 99 print a message about a \"big number\" \n - if not greater than 99 print message about \"small number\" \n - check if string isalpha then (since not digits)\n - if isalpha print message about being all alpha\n - if not isalpha print a message about being neither all alpha nor all digit \n \ncall the function with a string from user input \n- Run and test your code before submitting",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# [ ] create, call and test the str_analysis() function \n\ndef str_analysis(string):\n if string.isdigit(): \n string = int(string) \n\n if string > 99: \n return str(string) + \" That's a big number.\"\n else:\n return str(string) + \" That's small number.\"\n else: \n if string.isalpha(): \n return string + \" uses all alpha characters.\"\n else: \n return string + \" neither all alpha nor digit.\"\n\nprint(\"StringTester\\n\") \n\nwhile True:\n user_input = input(\"Input string for testing: \") \n if user_input == \"\": \n print(\"No input detected.\")\n else: \n print(str_analysis(user_input)) \n break \n\n",
"StringTester\n\n100 That's a big number.\n"
]
],
[
[
"Submit this by creating a python file (.py) and submitting it in D2L. Be sure to test that it works.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe61d8a3f13c6989bed9df40bd522ca911cca86
| 25,867 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
src/py/5-descriptive-analysis.ipynb
|
TheYuanLiao/individual_mobility_model
|
3026b8d51e50ffe24a398b22789c86230cd971ce
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2022-03-26T01:34:42.000Z
|
2022-03-26T01:34:42.000Z
|
src/py/5-descriptive-analysis.ipynb
|
TheYuanLiao/individual_mobility_model
|
3026b8d51e50ffe24a398b22789c86230cd971ce
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
src/py/5-descriptive-analysis.ipynb
|
TheYuanLiao/individual_mobility_model
|
3026b8d51e50ffe24a398b22789c86230cd971ce
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2021-10-05T15:19:18.000Z
|
2022-03-26T01:34:38.000Z
| 69.910811 | 2,748 | 0.597557 |
[
[
[
"# Descriptive analysis for the manuscript\n\nSummarize geotagged tweets of the multiple regions used for the experiment and the application.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import os\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport yaml\nimport scipy.stats as stats\nfrom tqdm import tqdm\n\ndef load_region_tweets(region=None):\n df = pd.read_csv(f'../../dbs/{region}/geotweets.csv')\n df['day'] = df['createdat'].apply(lambda x: x.split(' ')[0])\n df['createdat'] = pd.to_datetime(df['createdat'], infer_datetime_format=True)\n t_max, t_min = df.createdat.max(), df.createdat.min()\n time_span = f'{t_min} - {t_max}'\n num_users = len(df.userid.unique())\n num_geo = len(df)\n num_days = np.median(df.groupby(['userid'])['day'].nunique())\n num_geo_freq = np.median(df.groupby(['userid']).size() / df.groupby(['userid'])['day'].nunique())\n return region, time_span, num_users, num_geo, num_days, num_geo_freq\n\ndef user_stats_cal(data):\n time_span = data.createdat.max() - data.createdat.min()\n time_span = time_span.days\n if time_span == 0:\n time_span += 1\n num_days = data['day'].nunique()\n num_geo = len(data)\n geo_freq = num_geo / num_days\n share_active = num_days / time_span\n return pd.DataFrame.from_dict({'time_span': [time_span],\n 'num_days': [num_days],\n 'num_geo': [num_geo],\n 'geo_freq': [geo_freq],\n 'share_active': [share_active]\n })\n\ndef region_tweets_stats_per_user(region=None):\n df = pd.read_csv(f'../../dbs/{region}/geotweets.csv')\n df['day'] = df['createdat'].apply(lambda x: x.split(' ')[0])\n df['createdat'] = pd.to_datetime(df['createdat'], infer_datetime_format=True)\n tqdm.pandas(desc=region)\n df_users = df.groupby('userid').progress_apply(user_stats_cal).reset_index()\n df_users.loc[:, 'region'] = region\n df_users.drop(columns=['level_1'], inplace=True)\n return df_users\n\nregion_list = ['sweden', 'netherlands', 'saopaulo', 'australia', 'austria', 'barcelona',\n 'capetown', 'cebu', 'egypt', 'guadalajara', 'jakarta',\n 'johannesburg', 'kualalumpur', 'lagos', 'madrid', 'manila', 'mexicocity', 'moscow', 'nairobi',\n 'rio', 'saudiarabia', 'stpertersburg', 'surabaya']\n\nwith open('../../lib/regions.yaml', encoding='utf8') as f:\n region_manager = yaml.load(f, Loader=yaml.FullLoader)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 1 Summarize the geotagged tweets used as input to the model\nGeotagged tweets: Time span, No. of Twitter users, No. of geotagged tweets,\nDays covered/user, No. of geotagged tweets/day/user",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = pd.DataFrame([load_region_tweets(region=x) for x in region_list],\n columns=('region', 'time_span', 'num_users', 'num_geo', 'num_days', 'num_geo_freq'))\ndf.loc[:, 'gdp_capita'] = df.loc[:, 'region'].apply(lambda x: region_manager[x]['gdp_capita'])\ndf.loc[:, 'country'] = df.loc[:, 'region'].apply(lambda x: region_manager[x]['country'])\ndf.loc[:, 'pop'] = df.loc[:, 'region'].apply(lambda x: region_manager[x]['pop'])\ndf.loc[:, 'time_span'] = df.loc[:, 'time_span'].apply(lambda x: ' - '.join([x_t.split(' ')[0] for x_t in x.split(' - ')]))\ndf.loc[:, 'region'] = df.loc[:, 'region'].apply(lambda x: region_manager[x]['name'])\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.to_clipboard(index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 1-extra Summarize the geotagged tweets used as input to the model - by user\nThis is for dissertation presentation - sparsity issue.\n\nGeotagged tweets: Time span, No. of Twitter users, No. of geotagged tweets,\nDays covered/user, No. of geotagged tweets/day/user",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = pd.concat([region_tweets_stats_per_user(region=x) for x in region_list])\ndf.loc[:, 'gdp_capita'] = df.loc[:, 'region'].apply(lambda x: region_manager[x]['gdp_capita'])\ndf.loc[:, 'country'] = df.loc[:, 'region'].apply(lambda x: region_manager[x]['country'])\ndf.loc[:, 'pop'] = df.loc[:, 'region'].apply(lambda x: region_manager[x]['pop'])\ndf.loc[:, 'region'] = df.loc[:, 'region'].apply(lambda x: region_manager[x]['name'])\ndf.to_csv(f'../../dbs/regional_stats.csv', index=False)",
"sweden: 100%|██████████| 3961/3961 [00:05<00:00, 778.29it/s]\nnetherlands: 100%|██████████| 5375/5375 [00:06<00:00, 793.24it/s]\nsaopaulo: 100%|██████████| 10943/10943 [00:14<00:00, 766.58it/s] \naustralia: 100%|██████████| 3310/3310 [00:04<00:00, 756.92it/s]\naustria: 100%|██████████| 729/729 [00:00<00:00, 820.02it/s]\nbarcelona: 100%|██████████| 1891/1891 [00:02<00:00, 728.01it/s]\ncapetown: 100%|██████████| 1092/1092 [00:01<00:00, 760.97it/s]\ncebu: 100%|██████████| 1486/1486 [00:01<00:00, 754.36it/s]\negypt: 100%|██████████| 1464/1464 [00:01<00:00, 779.08it/s]\nguadalajara: 100%|██████████| 684/684 [00:00<00:00, 767.69it/s]\njakarta: 100%|██████████| 13088/13088 [00:17<00:00, 754.31it/s]\njohannesburg: 100%|██████████| 1268/1268 [00:01<00:00, 820.29it/s]\nkualalumpur: 100%|██████████| 4663/4663 [00:05<00:00, 838.44it/s]\nlagos: 100%|██████████| 812/812 [00:01<00:00, 795.90it/s]\nmadrid: 100%|██████████| 3172/3172 [00:03<00:00, 868.21it/s]\nmanila: 100%|██████████| 11997/11997 [00:14<00:00, 817.76it/s]\nmexicocity: 100%|██████████| 15615/15615 [00:18<00:00, 822.62it/s]\nmoscow: 100%|██████████| 4206/4206 [00:05<00:00, 809.16it/s]\nnairobi: 100%|██████████| 644/644 [00:00<00:00, 879.42it/s]\nrio: 100%|██████████| 6063/6063 [00:07<00:00, 824.33it/s]\nsaudiarabia: 100%|██████████| 3117/3117 [00:03<00:00, 869.21it/s]\nstpertersburg: 100%|██████████| 1386/1386 [00:01<00:00, 839.37it/s]\nsurabaya: 100%|██████████| 2414/2414 [00:02<00:00, 807.53it/s]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 2 Merge ODMs for visualisation\nThis part applies to Sweden, The Netherlands, and Sao Paulo, Brazil.\n\nSeparate files will be deleted.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for region in ['sweden', 'netherlands', 'saopaulo']:\n df = pd.read_csv(f'../../dbs/{region}/odm_gt.csv')\n df_c = pd.read_csv(f'../../dbs/{region}/odm_calibration.csv')\n df_v = pd.read_csv(f'../../dbs/{region}/odm_validation.csv')\n df_cb = pd.read_csv(f'../../dbs/{region}/odm_benchmark_c.csv')\n df_vb = pd.read_csv(f'../../dbs/{region}/odm_benchmark_v.csv')\n df = pd.merge(df, df_c, on=['ozone', 'dzone'])\n df = df.rename(columns={'model': 'model_c'})\n df = pd.merge(df, df_v, on=['ozone', 'dzone'])\n df = df.rename(columns={'model': 'model_v'})\n df = pd.merge(df, df_cb, on=['ozone', 'dzone'])\n df = df.rename(columns={'benchmark': 'benchmark_c'})\n df = pd.merge(df, df_vb, on=['ozone', 'dzone'])\n df = df.rename(columns={'benchmark': 'benchmark_v'})\n df.loc[:, ['ozone', 'dzone',\n 'gt', 'model_c', 'model_v',\n 'benchmark_c', 'benchmark_v']].to_csv(f'../../dbs/{region}/odms.csv', index=False)\n os.remove(f'../../dbs/{region}/odm_gt.csv')\n os.remove(f'../../dbs/{region}/odm_calibration.csv')\n os.remove(f'../../dbs/{region}/odm_validation.csv')\n os.remove(f'../../dbs/{region}/odm_benchmark_c.csv')\n os.remove(f'../../dbs/{region}/odm_benchmark_v.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 3 Quantify the od-pair similarity\nThis part applies to Sweden, The Netherlands, and Sao Paulo, Brazil.\n\nThe overall similarity.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"quant_list = []\nfor region in ['sweden', 'netherlands', 'saopaulo']:\n df = pd.read_csv(f'../../dbs/{region}/odms.csv')\n df_c = df.loc[(df.gt != 0) & (df.model_c != 0) & (df.benchmark_c != 0), :]\n mc = stats.kendalltau(df_c.loc[:, 'gt'], df_c.loc[:, 'model_c'])\n quant_list.append((region, 'model', 'c', mc.correlation, mc.pvalue))\n\n bc = stats.kendalltau(df_c.loc[:, 'gt'], df_c.loc[:, 'benchmark_c'])\n quant_list.append((region, 'benchmark', 'c', bc.correlation, bc.pvalue))\n\n df_v = df.loc[(df.gt != 0) & (df.model_v != 0) & (df.benchmark_v != 0), :]\n mv = stats.kendalltau(df_v.loc[:, 'gt'], df_v.loc[:, 'model_v'])\n quant_list.append((region, 'model', 'v', mv.correlation, mv.pvalue))\n\n bv = stats.kendalltau(df_v.loc[:, 'gt'], df_v.loc[:, 'benchmark_v'])\n quant_list.append((region, 'benchmark', 'v', bv.correlation, bv.pvalue))\ndf_stats = pd.DataFrame(quant_list, columns=['region', 'type', 'data', 'cor', 'p'])\ndf_stats",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_stats.groupby(['region', 'type'])['cor'].mean()\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe61dfbe55610d24c0d88d36213753b94b3fb0a
| 21,393 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
week1/ankitm/Q5 - Q/Attempt1_filesubmission_ankit_dashboard.ipynb
|
naveenmoto/lablet102
|
24de9daa4ae75cbde93567a3239ede43c735cf03
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-07-09T16:48:44.000Z
|
2021-07-09T16:48:44.000Z
|
week1/ankitm/Q5 - Q/Attempt1_filesubmission_ankit_dashboard.ipynb
|
naveenmoto/lablet102
|
24de9daa4ae75cbde93567a3239ede43c735cf03
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
week1/ankitm/Q5 - Q/Attempt1_filesubmission_ankit_dashboard.ipynb
|
naveenmoto/lablet102
|
24de9daa4ae75cbde93567a3239ede43c735cf03
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 55.27907 | 213 | 0.553966 |
[
[
[
"You now know the following\n\n1. Generate open-loop control from a given route\n\n2. Simulate vehicular robot motion using bicycle/ unicycle model\n\nImagine you want to make an utility for your co-workers to try and understand vehicle models. \nDashboards are common way to do this.\n\nThere are several options out there : Streamlit, Voila, Observable etc\n\nFollow this\n<a href=\"https://medium.com/plotly/introducing-jupyterdash-811f1f57c02e\">Medium post</a> on Jupyter Dash and see how to package what you learnt today in an interactive manner\n\nHere is a <a href=\"https://stackoverflow.com/questions/53622518/launch-a-dash-app-in-a-google-colab-notebook\">stackoverflow question </a> on how to run dash applications on Collab",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"What can you assume?\n+ Fix $v,\\omega$ or $v,\\delta$ depending on the model (users can still pick the actual value)\n+ fixed wheelbase for bicycle model\n\nUsers can choose \n+ unicycle and bicycle models\n+ A pre-configured route (\"S\", \"inverted-S\", \"figure-of-eight\" etc)\n+ 1 of 3 values for $v, \\omega$ (or $\\delta$) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pip install jupyter-dash",
"Collecting jupyter-dash\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/46/21/d3893ad0b7a7061115938d6c38f5862522d45c4199fb7e8fde0765781e13/jupyter_dash-0.4.0-py3-none-any.whl\nRequirement already satisfied: requests in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from jupyter-dash) (2.23.0)\nCollecting ansi2html\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/c6/85/3a46be84afbb16b392a138cd396117f438c7b2e91d8dc327621d1ae1b5dc/ansi2html-1.6.0-py3-none-any.whl\nCollecting dash\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/d4/50/e7c2830168db186f84b7de2988543e974433a6cdb0a0b23d51c781e2b2ab/dash-1.20.0.tar.gz (77kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 81kB 2.7MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: ipython in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from jupyter-dash) (5.5.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: retrying in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from jupyter-dash) (1.3.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: ipykernel in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from jupyter-dash) (4.10.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: flask in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from jupyter-dash) (1.1.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: certifi>=2017.4.17 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from requests->jupyter-dash) (2021.5.30)\nRequirement already satisfied: chardet<4,>=3.0.2 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from requests->jupyter-dash) (3.0.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: idna<3,>=2.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from requests->jupyter-dash) (2.10)\nRequirement already satisfied: urllib3!=1.25.0,!=1.25.1,<1.26,>=1.21.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from requests->jupyter-dash) (1.24.3)\nCollecting flask-compress\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/75/fa/a3c96f3f367ad1d6532fa8394c9a6f5879513868207096f6b41f4168b342/Flask_Compress-1.10.1-py3-none-any.whl\nRequirement already satisfied: plotly in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from dash->jupyter-dash) (4.4.1)\nCollecting dash_renderer==1.9.1\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/5f/d3/d661a68b4ce71498d5c0c79617bce3d5fc884d4448c698f77c2247cd1b46/dash_renderer-1.9.1.tar.gz (1.0MB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 1.0MB 16.3MB/s \n\u001b[?25hCollecting dash-core-components==1.16.0\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/f4/79/434e14d77dbf82b27f98df077936a424de254059d47152b0445b7116e97e/dash_core_components-1.16.0.tar.gz (3.5MB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 3.5MB 33.9MB/s \n\u001b[?25hCollecting dash-html-components==1.1.3\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/8f/ca/7eeca4cae4e15cc6f7d0bc41a46368dd3fcdddc72aaa5bac61a8b92d541c/dash_html_components-1.1.3.tar.gz (82kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 92kB 10.0MB/s \n\u001b[?25hCollecting dash-table==4.11.3\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/97/f7/f4969a926f20a55d3e5970d01b85ff9ad510dba32de189e72dd8f4992740/dash_table-4.11.3.tar.gz (1.8MB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 1.8MB 29.6MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: future in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from dash->jupyter-dash) (0.16.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: prompt-toolkit<2.0.0,>=1.0.4 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from ipython->jupyter-dash) (1.0.18)\nRequirement already satisfied: pexpect; sys_platform != \"win32\" in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from ipython->jupyter-dash) (4.8.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: simplegeneric>0.8 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from ipython->jupyter-dash) (0.8.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: traitlets>=4.2 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from ipython->jupyter-dash) (5.0.5)\nRequirement already satisfied: pygments in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from ipython->jupyter-dash) (2.6.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: setuptools>=18.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from ipython->jupyter-dash) (57.0.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: pickleshare in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from ipython->jupyter-dash) (0.7.5)\nRequirement already satisfied: decorator in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from ipython->jupyter-dash) (4.4.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: six>=1.7.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from retrying->jupyter-dash) (1.15.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: jupyter-client in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from ipykernel->jupyter-dash) (5.3.5)\nRequirement already satisfied: tornado>=4.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from ipykernel->jupyter-dash) (5.1.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: itsdangerous<2.0,>=0.24 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from flask->jupyter-dash) (1.1.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: Werkzeug<2.0,>=0.15 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from flask->jupyter-dash) (1.0.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: Jinja2<3.0,>=2.10.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from flask->jupyter-dash) (2.11.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: click<8.0,>=5.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from flask->jupyter-dash) (7.1.2)\nCollecting brotli\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/15/ea/5bd575511b37bbd1c794606a0a621e6feff8e96b7dd007a86a5d218b2d94/Brotli-1.0.9-cp37-cp37m-manylinux1_x86_64.whl (357kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 358kB 35.4MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: wcwidth in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from prompt-toolkit<2.0.0,>=1.0.4->ipython->jupyter-dash) (0.2.5)\nRequirement already satisfied: ptyprocess>=0.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from pexpect; sys_platform != \"win32\"->ipython->jupyter-dash) (0.7.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: ipython-genutils in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from traitlets>=4.2->ipython->jupyter-dash) (0.2.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: pyzmq>=13 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from jupyter-client->ipykernel->jupyter-dash) (22.1.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: jupyter-core>=4.6.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from jupyter-client->ipykernel->jupyter-dash) (4.7.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: python-dateutil>=2.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from jupyter-client->ipykernel->jupyter-dash) (2.8.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: MarkupSafe>=0.23 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from Jinja2<3.0,>=2.10.1->flask->jupyter-dash) (2.0.1)\nBuilding wheels for collected packages: dash, dash-renderer, dash-core-components, dash-html-components, dash-table\n Building wheel for dash (setup.py) ... \u001b[?25l\u001b[?25hdone\n Created wheel for dash: filename=dash-1.20.0-cp37-none-any.whl size=85845 sha256=a612111c426e04c777fa74da1fda59c9a1f9b72db25e55894205d6674500edc2\n Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/e6/33/41/ce361d0d1da277d2350f815b10f2ab1e331592d93ef2b07e29\n Building wheel for dash-renderer (setup.py) ... \u001b[?25l\u001b[?25hdone\n Created wheel for dash-renderer: filename=dash_renderer-1.9.1-cp37-none-any.whl size=1014873 sha256=78338f5112b46a91741f48035a1f7af422566570a9656d6eee0d818a1ccfdc9f\n Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/03/a9/c5/dd5815c601b0ede164c223ffd7bafebde716ca57de06ef8aec\n Building wheel for dash-core-components (setup.py) ... \u001b[?25l\u001b[?25hdone\n Created wheel for dash-core-components: filename=dash_core_components-1.16.0-cp37-none-any.whl size=3540992 sha256=ddbd059b293bd0308de45d5894544cbcec80180c9854844c89e10ee3d5ef8cb9\n Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/86/1e/8c/e87ebba30b73c20dcd641224274febc983af88ed0fd7712a07\n Building wheel for dash-html-components (setup.py) ... \u001b[?25l\u001b[?25hdone\n Created wheel for dash-html-components: filename=dash_html_components-1.1.3-cp37-none-any.whl size=319488 sha256=498f41de3688b589ad67f4cd6320fd5631a61c33a5debdb843d030ffd0d4f846\n Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/07/f9/6c/f9b73a6ae1b7f347a92dc240293cebc267b370ba2a80added2\n Building wheel for dash-table (setup.py) ... \u001b[?25l\u001b[?25hdone\n Created wheel for dash-table: filename=dash_table-4.11.3-cp37-none-any.whl size=1827623 sha256=7b519b744b4e01a190d2e56f3f9885414c1aa927474b6797fb00c97993184e9e\n Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/51/9b/89/374be1bc250e28a15edbd657cf364f163e392ba5257bfd0e87\nSuccessfully built dash dash-renderer dash-core-components dash-html-components dash-table\nInstalling collected packages: ansi2html, brotli, flask-compress, dash-renderer, dash-core-components, dash-html-components, dash-table, dash, jupyter-dash\nSuccessfully installed ansi2html-1.6.0 brotli-1.0.9 dash-1.20.0 dash-core-components-1.16.0 dash-html-components-1.1.3 dash-renderer-1.9.1 dash-table-4.11.3 flask-compress-1.10.1 jupyter-dash-0.4.0\n"
],
[
"import plotly.express as px\nfrom jupyter_dash import JupyterDash\nimport dash_core_components as dcc\nimport dash_html_components as html\nfrom dash.dependencies import Input, Output\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\n\n# Load Data\nvelocities = ['1','2','3']\nomegas = ['15','30','45']\nshapes = [\"S\", \"Inverted-S\", \"Figure of 8\"]\nmodels = [\"Unicycle\", \"Bicycle\"]\n\ndef unicycle_model(curr_pose, v, w, dt=1.0):\n '''\n >>> unicycle_model((0.0,0.0,0.0), 1.0, 0.0)\n (1.0, 0.0, 0.0)\n >>> unicycle_model((0.0,0.0,0.0), 0.0, 1.0)\n (0.0, 0.0, 1.0)\n >>> unicycle_model((0.0, 0.0, 0.0), 1.0, 1.0)\n (1.0, 0.0, 1.0)\n '''\n ## write code to calculate next_pose\n # refer to the kinematic equations of a unicycle model\n x, y, theta = curr_pose\n x += v*np.cos(theta)*dt\n y += v*np.sin(theta)*dt\n theta += w*dt\n \n # Keep theta bounded between [-pi, pi]\n theta = np.arctan2(np.sin(theta), np.cos(theta))\n\n # return calculated (x, y, theta)\n return x, y, theta\n \ndef bicycle_model(curr_pose, v, delta, dt=1.0):\n '''\n >>> bicycle_model((0.0,0.0,0.0), 1.0, 0.0)\n (1.0, 0.0, 0.0)\n >>> bicycle_model((0.0,0.0,0.0), 0.0, np.pi/4)\n (0.0, 0.0, 0.0) \n >>> bicycle_model((0.0, 0.0, 0.0), 1.0, np.pi/4)\n (1.0, 0.0, 1.11) \n '''\n # write code to calculate next_pose\n # refer to the kinematic equations of a bicycle model\n #x, y, theta = \n #x =\n #y =\n #theta =\n L = 0.9\n x, y, theta = curr_pose \n x += v*np.cos(theta)*dt \n y += v*np.sin(theta)*dt\n theta += (v/L)*np.tan(delta)*dt\n # Keep theta bounded between [-pi, pi]\n theta = np.arctan2(np.sin(theta), np.cos(theta))\n # return calculated (x, y, theta)\n return x, y, theta\n\ndef get_open_loop_commands(route, vc_fast=1, wc=np.pi/12, dt=1.0):\n all_w = []\n omegas = {'straight': 0, 'left': wc, 'right': -wc}\n for manoeuvre, command in route:\n u = np.ceil(command/vc_fast).astype('int')\n v = np.ceil(np.deg2rad(command)/wc).astype('int')\n t_cmd = u if manoeuvre == 'straight' else v\n all_w += [omegas[manoeuvre]]*t_cmd\n all_v = vc_fast * np.ones_like(all_w)\n return all_v, all_w\n\ndef get_commands(shape):\n if(shape == shapes[0]):\n return [(\"right\", 180),(\"left\", 180)]\n elif(shape == shapes[1]):\n return [(\"left\", 180),(\"right\", 180)]\n return [(\"right\", 180),(\"left\", 180),(\"left\", 180),(\"right\", 180)]\n\ndef get_angle(omega):\n if(omega == omegas[0]):\n return np.pi/12\n elif(omega == omegas[1]):\n return np.pi/6\n return np.pi/4\n\n\n# Build App\napp = JupyterDash(__name__)\napp.layout = html.Div([\n html.H1(\"Unicycle/Bicycle\"),\n html.Label([\n \"velocity\",\n dcc.Dropdown(\n id='velocity', clearable=False,\n value='1', options=[\n {'label': c, 'value': c}\n for c in velocities\n ])\n ]),\n html.Label([\n \"omega/delta\",\n dcc.Dropdown(\n id='omega', clearable=False,\n value='15', options=[\n {'label': c, 'value': c}\n for c in omegas\n ])\n ]),\n html.Label([\n \"shape\",\n dcc.Dropdown(\n id='shape', clearable=False,\n value='S', options=[\n {'label': c, 'value': c}\n for c in shapes\n ])\n ]),\n html.Label([\n \"model\",\n dcc.Dropdown(\n id='model', clearable=False,\n value='Unicycle', options=[\n {'label': c, 'value': c}\n for c in models\n ])\n ]),\n dcc.Graph(id='graph'),\n])\n# Define callback to update graph\[email protected](\n Output('graph', 'figure'),\n [Input(\"velocity\", \"value\"), Input(\"omega\", \"value\"), Input(\"shape\", \"value\"), Input(\"model\", \"value\")]\n)\ndef update_figure(velocity, omega, shape, model):\n robot_trajectory = []\n all_v, all_w = get_open_loop_commands(get_commands(shape), int(velocity), get_angle(omega))\n pose = (0, 0, np.pi/2)\n for v, w in zip(all_v, all_w):\n robot_trajectory.append(pose)\n if model == models[0]:\n pose = unicycle_model(pose, v, w)\n else:\n pose = bicycle_model(pose,v,w)\n robot_trajectory = np.array(robot_trajectory)\n dt = pd.DataFrame({'x-axis': robot_trajectory[:,0],'y-axis': robot_trajectory[:,1]})\n return px.line(dt, x=\"x-axis\", y=\"y-axis\", title='Simulate vehicular robot motion using unicycle/bicycle model')\n# Run app and display result inline in the notebook\napp.run_server(mode='inline')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe61f0f2a9ab584c239f75655aeea473770dea9
| 153,964 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/180227_wg_u_net_2.ipynb
|
williamgrimes/nuclei_segmentation
|
e4bd8787ed6586536ecc6d1cfdffa8699a73d900
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/180227_wg_u_net_2.ipynb
|
williamgrimes/nuclei_segmentation
|
e4bd8787ed6586536ecc6d1cfdffa8699a73d900
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/180227_wg_u_net_2.ipynb
|
williamgrimes/nuclei_segmentation
|
e4bd8787ed6586536ecc6d1cfdffa8699a73d900
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 181.561321 | 66,196 | 0.879803 |
[
[
[
"# U-Net: nuclei segmentation 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This is an implementation of a [Kaggle kernel](https://www.kaggle.com/c0conuts/unet-imagedatagenerator-lb-0-336/notebook) of a [U-net](https://arxiv.org/abs/1505.04597).\n\nChanges:\n* added model time elapsed with timeit\n* modelling:\n * batch_size=100\n * epochs=3\n* data augmentation:\n * shear_range=0.3\n * rotation_range=90\n * zoom_range=0.4\n * width_shift_range=0.3\n * height_shift_range=0.3\n * fill_mode='reflect'\n\nIdeas:\n* add watershed transform to mask image",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%pwd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import os\nimport sys\nimport random\nimport warnings\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport tensorflow as tf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from tqdm import tqdm\nfrom datetime import datetime \nfrom itertools import chain\n\nfrom skimage.io import imread, imsave, imshow, imread_collection, concatenate_images\nfrom skimage.transform import resize\nfrom skimage.morphology import label\n\nfrom keras.preprocessing import image\nfrom keras.models import Model, load_model\nfrom keras.layers import Input\nfrom keras.layers.core import Dropout, Lambda\nfrom keras.layers.convolutional import Conv2D, Conv2DTranspose\nfrom keras.layers.pooling import MaxPooling2D\nfrom keras.layers.merge import concatenate\nfrom keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ModelCheckpoint\nfrom keras import backend as K",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from utils.imaging import get_path, get_image_ids, label_mask, segmented_annotate\nfrom utils.evaluate import keras_mean_iou, submit_kaggle\nfrom utils import run_length_encoding",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%matplotlib inline\nwarnings.filterwarnings('ignore', category=UserWarning, module='skimage')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"get model name form notebook name using javascript",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%javascript\nIPython.notebook.kernel.execute('nb_name = ' + '\"' + IPython.notebook.notebook_name + '\"')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"notebook_name = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(nb_name))[0]\n\nmodel_name = notebook_name + '.h5'\nmodel_path = get_path('models') + model_name\n\nsubmission_name = notebook_name + '.csv'\nsubmission_path = get_path('submission') + submission_name",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 0. U-Net Parameters",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seed = 42\n\n# model parameters\nBATCH_SIZE = 100 # the higher the better\nIMG_WIDTH = 128 # for faster computing on kaggle\nIMG_HEIGHT = 128 # for faster computing on kaggle\nIMG_CHANNELS = 3\nTRAIN_PATH = get_path('data_train_1')\nTEST_PATH = get_path('data_test_1')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 1. Preprocess data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get train and test IDs\ntrain_ids = get_image_ids(TRAIN_PATH)\ntest_ids = get_image_ids(TEST_PATH)\nnp.random.seed(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Get and resize train images and masks\nX_train = np.zeros((len(train_ids), IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH, IMG_CHANNELS), dtype=np.uint8)\nY_train = np.zeros((len(train_ids), IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH, 1), dtype=np.bool)\n\nprint('Getting and resizing train images and masks ... ')\nsys.stdout.flush()\nfor n, id_ in tqdm(enumerate(train_ids), total=len(train_ids)):\n path = TRAIN_PATH + id_\n img = imread(path + '/images/' + id_ + '.png')[:,:,:IMG_CHANNELS]\n img = resize(img, (IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH), mode='constant', preserve_range=True)\n X_train[n] = img\n mask = np.zeros((IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH, 1), dtype=np.bool)\n for mask_file in next(os.walk(path + '/masks/'))[2]:\n mask_ = imread(path + '/masks/' + mask_file)\n mask_ = np.expand_dims(resize(mask_, (IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH), mode='constant', \n preserve_range=True), axis=-1)\n mask = np.maximum(mask, mask_)\n Y_train[n] = mask",
"Getting and resizing train images and masks ... \n"
],
[
"# Get and resize test images\nX_test = np.zeros((len(test_ids), IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH, IMG_CHANNELS), dtype=np.uint8)\n\nsizes_test = []\nprint('Getting and resizing test images ... ')\nsys.stdout.flush()\nfor n, id_ in tqdm(enumerate(test_ids), total=len(test_ids)):\n path = TEST_PATH + id_\n img = imread(path + '/images/' + id_ + '.png')[:,:,:IMG_CHANNELS]\n sizes_test.append([img.shape[0], img.shape[1]])\n img = resize(img, (IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH), mode='constant', preserve_range=True)\n X_test[n] = img",
"Getting and resizing test images ... \n"
]
],
[
[
"### 2. Data augmentation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Creating the training Image and Mask generator\nimage_datagen = image.ImageDataGenerator(shear_range=0.3, rotation_range=90, zoom_range=0.4, width_shift_range=0.3, height_shift_range=0.3, fill_mode='reflect')\nmask_datagen = image.ImageDataGenerator(shear_range=0.3, rotation_range=90, zoom_range=0.4, width_shift_range=0.3, height_shift_range=0.3, fill_mode='reflect')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Keep the same seed for image and mask generators so they fit together\nimage_datagen.fit(X_train[:int(X_train.shape[0]*0.9)], augment=True, seed=seed)\nmask_datagen.fit(Y_train[:int(Y_train.shape[0]*0.9)], augment=True, seed=seed)\n\nx=image_datagen.flow(X_train[:int(X_train.shape[0]*0.9)],batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,shuffle=True, seed=seed)\ny=mask_datagen.flow(Y_train[:int(Y_train.shape[0]*0.9)],batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,shuffle=True, seed=seed)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Creating the validation Image and Mask generator\nimage_datagen_val = image.ImageDataGenerator()\nmask_datagen_val = image.ImageDataGenerator()\n\nimage_datagen_val.fit(X_train[int(X_train.shape[0]*0.9):], augment=True, seed=seed)\nmask_datagen_val.fit(Y_train[int(Y_train.shape[0]*0.9):], augment=True, seed=seed)\n\nx_val=image_datagen_val.flow(X_train[int(X_train.shape[0]*0.9):],batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,shuffle=True, seed=seed)\ny_val=mask_datagen_val.flow(Y_train[int(Y_train.shape[0]*0.9):],batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,shuffle=True, seed=seed)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"f, axarr = plt.subplots(2,2,figsize=(12,12))\naxarr[0,0].imshow(x.next()[0].astype(np.uint8))\naxarr[0,1].imshow(np.squeeze(y.next()[0].astype(np.uint8)))\naxarr[1,0].imshow(x_val.next()[0].astype(np.uint8))\naxarr[1,1].imshow(np.squeeze(y_val.next()[0].astype(np.uint8)))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#creating a training and validation generator that generate masks and images\ntrain_generator = zip(x, y)\nval_generator = zip(x_val, y_val)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 3. Initialise U-Net model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Build U-Net model\ninputs = Input((IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH, IMG_CHANNELS))\ns = Lambda(lambda x: x / 255) (inputs)\n\nc1 = Conv2D(16, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (s)\nc1 = Dropout(0.1) (c1)\nc1 = Conv2D(16, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (c1)\np1 = MaxPooling2D((2, 2)) (c1)\n\nc2 = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (p1)\nc2 = Dropout(0.1) (c2)\nc2 = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (c2)\np2 = MaxPooling2D((2, 2)) (c2)\n\nc3 = Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (p2)\nc3 = Dropout(0.2) (c3)\nc3 = Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (c3)\np3 = MaxPooling2D((2, 2)) (c3)\n\nc4 = Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (p3)\nc4 = Dropout(0.2) (c4)\nc4 = Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (c4)\np4 = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)) (c4)\n\nc5 = Conv2D(256, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (p4)\nc5 = Dropout(0.3) (c5)\nc5 = Conv2D(256, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (c5)\n\nu6 = Conv2DTranspose(128, (2, 2), strides=(2, 2), padding='same') (c5)\nu6 = concatenate([u6, c4])\nc6 = Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (u6)\nc6 = Dropout(0.2) (c6)\nc6 = Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (c6)\n\nu7 = Conv2DTranspose(64, (2, 2), strides=(2, 2), padding='same') (c6)\nu7 = concatenate([u7, c3])\nc7 = Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (u7)\nc7 = Dropout(0.2) (c7)\nc7 = Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (c7)\n\nu8 = Conv2DTranspose(32, (2, 2), strides=(2, 2), padding='same') (c7)\nu8 = concatenate([u8, c2])\nc8 = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (u8)\nc8 = Dropout(0.1) (c8)\nc8 = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (c8)\n\nu9 = Conv2DTranspose(16, (2, 2), strides=(2, 2), padding='same') (c8)\nu9 = concatenate([u9, c1], axis=3)\nc9 = Conv2D(16, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (u9)\nc9 = Dropout(0.1) (c9)\nc9 = Conv2D(16, (3, 3), activation='elu', kernel_initializer='he_normal', padding='same') (c9)\n\noutputs = Conv2D(1, (1, 1), activation='sigmoid') (c9)\n\nmodel = Model(inputs=[inputs], outputs=[outputs])\nmodel.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=[keras_mean_iou])\nmodel.summary()",
"__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to \n==================================================================================================\ninput_4 (InputLayer) (None, 128, 128, 3) 0 \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nlambda_4 (Lambda) (None, 128, 128, 3) 0 input_4[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_58 (Conv2D) (None, 128, 128, 16) 448 lambda_4[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_28 (Dropout) (None, 128, 128, 16) 0 conv2d_58[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_59 (Conv2D) (None, 128, 128, 16) 2320 dropout_28[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nmax_pooling2d_13 (MaxPooling2D) (None, 64, 64, 16) 0 conv2d_59[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_60 (Conv2D) (None, 64, 64, 32) 4640 max_pooling2d_13[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_29 (Dropout) (None, 64, 64, 32) 0 conv2d_60[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_61 (Conv2D) (None, 64, 64, 32) 9248 dropout_29[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nmax_pooling2d_14 (MaxPooling2D) (None, 32, 32, 32) 0 conv2d_61[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_62 (Conv2D) (None, 32, 32, 64) 18496 max_pooling2d_14[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_30 (Dropout) (None, 32, 32, 64) 0 conv2d_62[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_63 (Conv2D) (None, 32, 32, 64) 36928 dropout_30[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nmax_pooling2d_15 (MaxPooling2D) (None, 16, 16, 64) 0 conv2d_63[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_64 (Conv2D) (None, 16, 16, 128) 73856 max_pooling2d_15[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_31 (Dropout) (None, 16, 16, 128) 0 conv2d_64[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_65 (Conv2D) (None, 16, 16, 128) 147584 dropout_31[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nmax_pooling2d_16 (MaxPooling2D) (None, 8, 8, 128) 0 conv2d_65[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_66 (Conv2D) (None, 8, 8, 256) 295168 max_pooling2d_16[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_32 (Dropout) (None, 8, 8, 256) 0 conv2d_66[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_67 (Conv2D) (None, 8, 8, 256) 590080 dropout_32[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_transpose_13 (Conv2DTran (None, 16, 16, 128) 131200 conv2d_67[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconcatenate_13 (Concatenate) (None, 16, 16, 256) 0 conv2d_transpose_13[0][0] \n conv2d_65[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_68 (Conv2D) (None, 16, 16, 128) 295040 concatenate_13[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_33 (Dropout) (None, 16, 16, 128) 0 conv2d_68[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_69 (Conv2D) (None, 16, 16, 128) 147584 dropout_33[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_transpose_14 (Conv2DTran (None, 32, 32, 64) 32832 conv2d_69[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconcatenate_14 (Concatenate) (None, 32, 32, 128) 0 conv2d_transpose_14[0][0] \n conv2d_63[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_70 (Conv2D) (None, 32, 32, 64) 73792 concatenate_14[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_34 (Dropout) (None, 32, 32, 64) 0 conv2d_70[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_71 (Conv2D) (None, 32, 32, 64) 36928 dropout_34[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_transpose_15 (Conv2DTran (None, 64, 64, 32) 8224 conv2d_71[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconcatenate_15 (Concatenate) (None, 64, 64, 64) 0 conv2d_transpose_15[0][0] \n conv2d_61[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_72 (Conv2D) (None, 64, 64, 32) 18464 concatenate_15[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_35 (Dropout) (None, 64, 64, 32) 0 conv2d_72[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_73 (Conv2D) (None, 64, 64, 32) 9248 dropout_35[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_transpose_16 (Conv2DTran (None, 128, 128, 16) 2064 conv2d_73[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconcatenate_16 (Concatenate) (None, 128, 128, 32) 0 conv2d_transpose_16[0][0] \n conv2d_59[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_74 (Conv2D) (None, 128, 128, 16) 4624 concatenate_16[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_36 (Dropout) (None, 128, 128, 16) 0 conv2d_74[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_75 (Conv2D) (None, 128, 128, 16) 2320 dropout_36[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_76 (Conv2D) (None, 128, 128, 1) 17 conv2d_75[0][0] \n==================================================================================================\nTotal params: 1,941,105\nTrainable params: 1,941,105\nNon-trainable params: 0\n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 4. Train U-Net model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Fit model\nstart_time = datetime.now() \n\nearlystopper = EarlyStopping(patience=3, verbose=1)\ncheckpointer = ModelCheckpoint(model_path, verbose=1, save_best_only=True)\nresults = model.fit_generator(train_generator,\n validation_data=val_generator, \n validation_steps=10, \n steps_per_epoch=250,\n epochs=5, \n callbacks=[earlystopper, checkpointer]\n )\n\ntime_elapsed = datetime.now() - start_time \nprint('\\n Model training time elapsed (hh:mm:ss.ms) {}'.format(time_elapsed))",
"Epoch 1/5\n249/250 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1759 - keras_mean_iou: 0.6000\nEpoch 00001: val_loss improved from inf to 0.10701, saving model to /home/ubuntu/nuclei_segmentation/models/180227_wg_u_net_2.h5\n250/250 [==============================] - 157s 629ms/step - loss: 0.1756 - keras_mean_iou: 0.6005 - val_loss: 0.1070 - val_keras_mean_iou: 0.7067\nEpoch 2/5\n249/250 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.0989 - keras_mean_iou: 0.7399\nEpoch 00002: val_loss improved from 0.10701 to 0.08703, saving model to /home/ubuntu/nuclei_segmentation/models/180227_wg_u_net_2.h5\n250/250 [==============================] - 150s 600ms/step - loss: 0.0988 - keras_mean_iou: 0.7400 - val_loss: 0.0870 - val_keras_mean_iou: 0.7655\nEpoch 3/5\n249/250 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.0859 - keras_mean_iou: 0.7799\nEpoch 00003: val_loss improved from 0.08703 to 0.07610, saving model to /home/ubuntu/nuclei_segmentation/models/180227_wg_u_net_2.h5\n250/250 [==============================] - 150s 601ms/step - loss: 0.0858 - keras_mean_iou: 0.7799 - val_loss: 0.0761 - val_keras_mean_iou: 0.7917\nEpoch 4/5\n249/250 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.0830 - keras_mean_iou: 0.7993\nEpoch 00004: val_loss improved from 0.07610 to 0.07014, saving model to /home/ubuntu/nuclei_segmentation/models/180227_wg_u_net_2.h5\n250/250 [==============================] - 150s 601ms/step - loss: 0.0828 - keras_mean_iou: 0.7994 - val_loss: 0.0701 - val_keras_mean_iou: 0.8063\nEpoch 5/5\n249/250 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.0820 - keras_mean_iou: 0.8105\nEpoch 00005: val_loss improved from 0.07014 to 0.06738, saving model to /home/ubuntu/nuclei_segmentation/models/180227_wg_u_net_2.h5\n250/250 [==============================] - 151s 604ms/step - loss: 0.0819 - keras_mean_iou: 0.8105 - val_loss: 0.0674 - val_keras_mean_iou: 0.8156\n\n Model training time elapsed (hh:mm:ss.ms) 0:12:40.003556\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 5. Predict with U-Net model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Predict on train, val and test\nmodel = load_model(model_path, custom_objects={'keras_mean_iou': keras_mean_iou})\npreds_train = model.predict(X_train[:int(X_train.shape[0]*0.9)], verbose=1)\npreds_val = model.predict(X_train[int(X_train.shape[0]*0.9):], verbose=1)\npreds_test = model.predict(X_test, verbose=1)\n\n# Threshold predictions\npreds_train_t = (preds_train > 0.5).astype(np.uint8)\npreds_val_t = (preds_val > 0.5).astype(np.uint8)\npreds_test_t = (preds_test > 0.5).astype(np.uint8)",
"603/603 [==============================] - 2s 4ms/step\n67/67 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step\n65/65 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step\n"
],
[
"# Create list of upsampled test masks\npreds_test_upsampled = []\nfor i in range(len(preds_test)):\n preds_test_upsampled.append(resize(np.squeeze(preds_test[i]), \n (sizes_test[i][0], sizes_test[i][1]), \n mode='constant', preserve_range=True))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sanity check on some training examples",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"f, axarr = plt.subplots(2,3,figsize=(12,12))\nix1 = random.randint(0, len(preds_train_t))\nix2 = random.randint(0, len(preds_train_t))\naxarr[0,0].imshow(X_train[ix1])\naxarr[0,1].imshow(np.squeeze(Y_train[ix1]))\naxarr[0,2].imshow(np.squeeze(preds_train_t[ix1]))\naxarr[1,0].imshow(X_train[ix2])\naxarr[1,1].imshow(np.squeeze(Y_train[ix2]))\naxarr[1,2].imshow(np.squeeze(preds_train_t[ix2]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 7. Output image labels",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Saving test labelled images",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for idx, image_id in tqdm(enumerate(test_ids), total=len(test_ids)):\n mask = preds_test_upsampled[idx] > 0.5\n labels = label_mask(mask)\n imsave(get_path('output_test_1_lab_seg') + image_id + '.png', labels)",
"100%|██████████| 65/65 [00:00<00:00, 145.16it/s]\n"
]
],
[
[
"Saving test annotated images",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"segmented_annotate(image_type = 'test', stage_num = 1)",
"100%|██████████| 65/65 [00:27<00:00, 2.33it/s]\n"
],
[
"df = run_length_encoding.rle_images_in_dir(image_type = 'test', stage_num = 1)\ndf.to_csv(submission_path, index=False)",
"100%|██████████| 65/65 [00:07<00:00, 8.31it/s]\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 8. Kaggle submit",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"message = \"batch size of 100 and 5 epochs\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"submit_string = submit_kaggle(notebook_name, submission_path, message)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!$submit_string",
"0.294\r\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe62f35a116bf68ee018d1a237faf35f2d450ce
| 87,426 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
pyfund/Cap01/JupyterNotebook-ManualUsuario.ipynb
|
guimaraesalves/Data-Science-Academy
|
c24247cbf643a5a7c037013e4a122389aa523ac3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
pyfund/Cap01/JupyterNotebook-ManualUsuario.ipynb
|
guimaraesalves/Data-Science-Academy
|
c24247cbf643a5a7c037013e4a122389aa523ac3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
pyfund/Cap01/JupyterNotebook-ManualUsuario.ipynb
|
guimaraesalves/Data-Science-Academy
|
c24247cbf643a5a7c037013e4a122389aa523ac3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 36.171287 | 1,095 | 0.616865 |
[
[
[
"# Manual Jupyter Notebook:\n\nhttps://athena.brynmawr.edu/jupyter/hub/dblank/public/Jupyter%20Notebook%20Users%20Manual.ipynb",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Jupyter Notebook Users Manual\n\nThis page describes the functionality of the [Jupyter](http://jupyter.org) electronic document system. Jupyter documents are called \"notebooks\" and can be seen as many things at once. For example, notebooks allow:\n\n* creation in a **standard web browser**\n* direct **sharing**\n* using **text with styles** (such as italics and titles) to be explicitly marked using a [wikitext language](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wiki_markup)\n* easy creation and display of beautiful **equations**\n* creation and execution of interactive embedded **computer programs**\n* easy creation and display of **interactive visualizations**\n\nJupyter notebooks (previously called \"IPython notebooks\") are thus interesting and useful to different groups of people:\n\n* readers who want to view and execute computer programs\n* authors who want to create executable documents or documents with visualizations\n\n<hr size=\"5\"/>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"###Table of Contents\n* [1. Getting to Know your Jupyter Notebook's Toolbar](#1.-Getting-to-Know-your-Jupyter-Notebook's-Toolbar)\n* [2. Different Kinds of Cells](#2.-Different-Kinds-of-Cells)\n\t* [2.1 Code Cells](#2.1-Code-Cells)\n\t\t* [2.1.1 Code Cell Layout](#2.1.1-Code-Cell-Layout)\n\t\t\t* [2.1.1.1 Row Configuration (Default Setting)](#2.1.1.1-Row-Configuration-%28Default-Setting%29)\n\t\t\t* [2.1.1.2 Cell Tabbing](#2.1.1.2-Cell-Tabbing)\n\t\t\t* [2.1.1.3 Column Configuration](#2.1.1.3-Column-Configuration)\n\t* [2.2 Markdown Cells](#2.2-Markdown-Cells)\n\t* [2.3 Raw Cells](#2.3-Raw-Cells)\n\t* [2.4 Header Cells](#2.4-Header-Cells)\n\t\t* [2.4.1 Linking](#2.4.1-Linking)\n\t\t* [2.4.2 Automatic Section Numbering and Table of Contents Support](#2.4.2-Automatic-Section-Numbering-and-Table-of-Contents-Support)\n\t\t\t* [2.4.2.1 Automatic Section Numbering](#2.4.2.1-Automatic-Section-Numbering)\n\t\t\t* [2.4.2.2 Table of Contents Support](#2.4.2.2-Table-of-Contents-Support)\n\t\t\t* [2.4.2.3 Using Both Automatic Section Numbering and Table of Contents Support](#2.4.2.3-Using-Both-Automatic-Section-Numbering-and-Table-of-Contents-Support)\n* [3. Keyboard Shortcuts](#3.-Keyboard-Shortcuts)\n* [4. Using Markdown Cells for Writing](#4.-Using-Markdown-Cells-for-Writing)\n\t* [4.1 Block Elements](#4.1-Block-Elements)\n\t\t* [4.1.1 Paragraph Breaks](#4.1.1-Paragraph-Breaks)\n\t\t* [4.1.2 Line Breaks](#4.1.2-Line-Breaks)\n\t\t\t* [4.1.2.1 Hard-Wrapping and Soft-Wrapping](#4.1.2.1-Hard-Wrapping-and-Soft-Wrapping)\n\t\t\t* [4.1.2.2 Soft-Wrapping](#4.1.2.2-Soft-Wrapping)\n\t\t\t* [4.1.2.3 Hard-Wrapping](#4.1.2.3-Hard-Wrapping)\n\t\t* [4.1.3 Headers](#4.1.3-Headers)\n\t\t* [4.1.4 Block Quotes](#4.1.4-Block-Quotes)\n\t\t\t* [4.1.4.1 Standard Block Quoting](#4.1.4.1-Standard-Block-Quoting)\n\t\t\t* [4.1.4.2 Nested Block Quoting](#4.1.4.2-Nested-Block-Quoting)\n\t\t* [4.1.5 Lists](#4.1.5-Lists)\n\t\t\t* [4.1.5.1 Ordered Lists](#4.1.5.1-Ordered-Lists)\n\t\t\t* [4.1.5.2 Bulleted Lists](#4.1.5.2-Bulleted-Lists)\n\t\t* [4.1.6 Section Breaks](#4.1.6-Section-Breaks)\n\t* [4.2 Backslash Escape](#4.2-Backslash-Escape)\n\t* [4.3 Hyperlinks](#4.3-Hyperlinks)\n\t\t* [4.3.1 Automatic Links](#4.3.1-Automatic-Links)\n\t\t* [4.3.2 Standard Links](#4.3.2-Standard-Links)\n\t\t* [4.3.3 Standard Links With Mouse-Over Titles](#4.3.3-Standard-Links-With-Mouse-Over-Titles)\n\t\t* [4.3.4 Reference Links](#4.3.4-Reference-Links)\n\t\t* [4.3.5 Notebook-Internal Links](#4.3.5-Notebook-Internal-Links)\n\t\t\t* [4.3.5.1 Standard Notebook-Internal Links Without Mouse-Over Titles](#4.3.5.1-Standard-Notebook-Internal-Links-Without-Mouse-Over-Titles)\n\t\t\t* [4.3.5.2 Standard Notebook-Internal Links With Mouse-Over Titles](#4.3.5.2-Standard-Notebook-Internal-Links-With-Mouse-Over-Titles)\n\t\t\t* [4.3.5.3 Reference-Style Notebook-Internal Links](#4.3.5.3-Reference-Style-Notebook-Internal-Links)\n\t* [4.4 Tables](#4.4-Tables)\n\t\t* [4.4.1 Cell Justification](#4.4.1-Cell-Justification)\n\t* [4.5 Style and Emphasis](#4.5-Style-and-Emphasis)\n\t* [4.6 Other Characters](#4.6-Other-Characters)\n\t* [4.7 Including Code Examples](#4.7-Including-Code-Examples)\n\t* [4.8 Images](#4.8-Images)\n\t\t* [4.8.1 Images from the Internet](#4.8.1-Images-from-the-Internet)\n\t\t\t* [4.8.1.1 Reference-Style Images from the Internet](#4.8.1.1-Reference-Style-Images-from-the-Internet)\n\t* [4.9 LaTeX Math](#4.9-LaTeX-Math)\n* [5. Bibliographic Support](#5.-Bibliographic-Support)\n\t* [5.1 Creating a Bibtex Database](#5.1-Creating-a-Bibtex-Database)\n\t\t* [5.1.1 External Bibliographic Databases](#5.1.1-External-Bibliographic-Databases)\n\t\t* [5.1.2 Internal Bibliographic Databases](#5.1.2-Internal-Bibliographic-Databases)\n\t\t\t* [5.1.2.1 Hiding Your Internal Database](#5.1.2.1-Hiding-Your-Internal-Database)\n\t\t* [5.1.3 Formatting Bibtex Entries](#5.1.3-Formatting-Bibtex-Entries)\n\t* [5.2 Cite Commands and Citation IDs](#5.2-Cite-Commands-and-Citation-IDs)\n* [6. Turning Your Jupyter Notebook into a Slideshow](#6.-Turning-Your-Jupyter-Notebook-into-a-Slideshow)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 1. Getting to Know your Jupyter Notebook's Toolbar",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"At the top of your Jupyter Notebook window there is a toolbar. It looks like this:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Below is a table which helpfully pairs a picture of each of the items in your toolbar with a corresponding explanation of its function. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Button|Function\n-|-\n|This is your save button. You can click this button to save your notebook at any time, though keep in mind that Jupyter Notebooks automatically save your progress very frequently. \n|This is the new cell button. You can click this button any time you want a new cell in your Jupyter Notebook. \n|This is the cut cell button. If you click this button, the cell you currently have selected will be deleted from your Notebook. \n|This is the copy cell button. If you click this button, the currently selected cell will be duplicated and stored in your clipboard. \n|This is the past button. It allows you to paste the duplicated cell from your clipboard into your notebook. \n|These buttons allow you to move the location of a selected cell within a Notebook. Simply select the cell you wish to move and click either the up or down button until the cell is in the location you want it to be.\n|This button will \"run\" your cell, meaning that it will interpret your input and render the output in a way that depends on [what kind of cell] [cell kind] you're using. \n|This is the stop button. Clicking this button will stop your cell from continuing to run. This tool can be useful if you are trying to execute more complicated code, which can sometimes take a while, and you want to edit the cell before waiting for it to finish rendering. \n|This is the restart kernel button. See your kernel documentation for more information.\n|This is a drop down menu which allows you to tell your Notebook how you want it to interpret any given cell. You can read more about the [different kinds of cells] [cell kind] in the following section. \n|Individual cells can have their own toolbars. This is a drop down menu from which you can select the type of toolbar that you'd like to use with the cells in your Notebook. Some of the options in the cell toolbar menu will only work in [certain kinds of cells][cell kind]. \"None,\" which is how you specify that you do not want any cell toolbars, is the default setting. If you select \"Edit Metadata,\" a toolbar that allows you to edit data about [Code Cells][code cells] directly will appear in the corner of all the Code cells in your notebook. If you select \"Raw Cell Format,\" a tool bar that gives you several formatting options will appear in the corner of all your [Raw Cells][raw cells]. If you want to view and present your notebook as a slideshow, you can select \"Slideshow\" and a toolbar that enables you to organize your cells in to slides, sub-slides, and slide fragments will appear in the corner of every cell. Go to [this section][slideshow] for more information on how to create a slideshow out of your Jupyter Notebook. \n|These buttons allow you to move the location of an entire section within a Notebook. Simply select the Header Cell for the section or subsection you wish to move and click either the up or down button until the section is in the location you want it to be. If your have used [Automatic Section Numbering][section numbering] or [Table of Contents Support][table of contents] remember to rerun those tools so that your section numbers or table of contents reflects your Notebook's new organization. \n|Clicking this button will automatically number your Notebook's sections. For more information, check out the Reference Guide's [section on Automatic Section Numbering][section numbering].\n|Clicking this button will generate a table of contents using the titles you've given your Notebook's sections. For more information, check out the Reference Guide's [section on Table of Contents Support][table of contents].\n|Clicking this button will search your document for [cite commands][] and automatically generate intext citations as well as a references cell at the end of your Notebook. For more information, you can read the Reference Guide's [section on Bibliographic Support][bib support].\n|Clicking this button will toggle [cell tabbing][], which you can learn more about in the Reference Guides' [section on the layout options for Code Cells][cell layout].\n|Clicking this button will toggle the [collumn configuration][] for Code Cells, which you can learn more about in the Reference Guides' [section on the layout options for Code Cells][cell layout].\n|Clicking this button will toggle spell checking. Spell checking only works in unrendered [Markdown Cells][] and [Header Cells][]. When spell checking is on all incorrectly spelled words will be underlined with a red squiggle. Keep in mind that the dictionary cannot tell what are [Markdown][md writing] commands and what aren't, so it will occasionally underline a correctly spelled word surrounded by asterisks, brackets, or other symbols that have specific meaning in Markdown. \n\n\n[cell kind]: #2.-Different-Kinds-of-Cells \"Different Kinds of Cells\"\n[code cells]: #2.1-Code-Cells \"Code Cells\"\n[raw cells]: #2.3-Raw-Cells \"Raw Cells\"\n[slideshow]: #6.-Turning-Your-Jupyter-Notebook-into-a-Slideshow \"Turning Your Jupyter Notebook Into a Slideshow\"\n[section numbering]: #2.4.2.1-Automatic-Section-Numbering\n[table of contents]: #2.4.2.2-Table-of-Contents-Support\n[cell tabbing]: #2.1.1.2-Cell-Tabbing\n[cell layout]: #2.1.1-Code-Cell-Layout\n[bib support]: #5.-Bibliographic-Support\n[cite commands]: #5.2-Cite-Commands-and-Citation-IDs\n[md writing]: #4.-Using-Markdown-Cells-for-Writing\n[collumn configuration]: #2.1.1.3-Column-Configuration\n[Markdown Cells]: #2.2-Markdown-Cells\n[Header Cells]: #2.4-Header-Cells\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 2. Different Kinds of Cells",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"There are essentially four kinds of cells in your Jupyter notebook: Code Cells, Markdown Cells, Raw Cells, and Header Cells, though there are six levels of Header Cells. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 2.1 Code Cells",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"By default, Jupyter Notebooks' Code Cells will execute Python. Jupyter Notebooks generally also support JavaScript, Python, HTML, and Bash commands. For a more comprehensive list, see your Kernel's documentation. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 2.1.1 Code Cell Layout",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Code cells have both an input and an output component. You can view these components in three different ways. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 2.1.1.1 Row Configuration (Default Setting)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Unless you specific otherwise, your Code Cells will always be configured this way, with both the input and output components appearing as horizontal rows and with the input above the output. Below is an example of a Code Cell in this default setting:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"2 + 3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### 2.1.1.2 Cell Tabbing",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Cell tabbing allows you to look at the input and output components of a cell separately. It also allows you to hide either component behind the other, which can be usefull when creating visualizations of data. Below is an example of a tabbed Code Cell:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"2+3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### 2.1.1.3 Column Configuration",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Like the row configuration, the column layout option allows you to look at both the input and the output components at once. In the column layout, however, the two components appear beside one another, with the input on the left and the output on the right. Below is an example of a Code Cell in the column configuration:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"2+3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 2.2 Markdown Cells",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In Jupyter Notebooks, Markdown Cells are the easiest way to write and format text. For a more thorough explanation of how to write in Markdown cells, refer to [this section of the guide][writing markdown].\n\n[writing markdown]: #4.-Using-Markdown-Cells-for-Writing \"Using Markdown Cells for Writing\"\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 2.3 Raw Cells",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Raw Cells, unlike all other Jupyter Notebook cells, have no input-output distinction. This means that Raw Cells cannot be rendered into anything other than what they already are. If you click the run button in your tool bar with a Raw Cell selected, the cell will remain exactly as is and your Jupyter Notebook will automatically select the cell directly below it. Raw cells have no style options, just the same monospace font that you use in all other unrendered Notebook cells. You cannot bold, italicize, or enlarge any text or characters in a Raw Cell. \n\nBecause they have no rendered form, Raw Cells are mainly used to create examples. If you save and close your Notebook and then reopen it, all of the Code, Markdown, and Header Cells will automatically render in whatever form you left them when you first closed the document. This means that if you wanted to preserve the unrendered version of a cell, say if you were writing a computer science paper and needed code examples, or if you were writing [documentation on how to use Markdown] [writing markdown] and needed to demonstrate what input would yield which output, then you might want to use a Raw Cell to make sure your examples stayed in their most useful form. \n\n[writing markdown]: #4.-Using-Markdown-Cells-for-Writing \"Using Markdown Cells for Writing\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 2.4 Header Cells",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"While it is possible to organize your document using [Markdown headers][], Header Cells provide a more deeply structural organization for your Notebook and thus there are several advantages to using them. \n\n[Markdown headers]: #4.1.3-Headers \"Headers\" ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 2.4.1 Linking",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Header Cells have specific locations inside your Notebook. This means you can use them to [create Notebook-internal links](#4.3.5-Notebook-Internal-Links \"Notebook-Internal Links\").",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 2.4.2 Automatic Section Numbering and Table of Contents Support",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Your Jupyter Notebook has two helpful tools that utilize the structural organization that Header Cells give your document: automatic section numbering and table of contents generation. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 2.4.2.1 Automatic Section Numbering",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Suppose you are writing a paper and, as is prone to happening when you have a lot of complicate thoughts buzzing around your brain, you've reorganized your ideas several times. Automatic section numbering will go through your Notebook and number your sections and subsection as designated by your Header Cells. This means that if you've moved one or more big sections around several times, you won't have to go through your paper and renumber it, as well as all its subsections, yourself.\n\n\n\n**Notes:** Automatic Section Numbering tri-toggling tool, so when you click the Number Sections button one of three actions will occur: Automatic Section Numbering will number your sections, correct inconsistent numbering, or unnumber your sections (if all of your sections are already consistently and correctly numbered). \n\nSo, even if you have previously numbered your sections, Automatic Section Numbering will go through your document, delete the current section numbers, and replace them the correct number in a linear sequence. This means that if your third section was once your second, Automatic Section Numbering will delete the \"2\" in front of your section's name and replace it with a \"3.\" \n\nWhile this function saves you a lot of time, it creates one limitation. Maybe you're writing a paper about children's books and one of the books you're discussing is called **`2 Cats`**. You've unsurprisingly titled the section where you summarize and analyze this book **`2 Cats`**. Automatic Section Numbering will assume the number 2 is section information and delete it, leaving just the title **`Cats`** behind. If you bold, italicize, or place the title of the section inside quotes, however, the entire section title will be be preserved without any trouble. It should also be noted that even if you must title a section with a number occurring before any letters and you do not want to bold it, italicize it, or place it inside quotes, then you can always run Automatic Section Numbering and then go to that section and retype its name by hand. \n\nBecause Automatic Section Numbering uses your header cells, its performance relies somewhat on the clarity of your organization. If you have two sections that begin with Header 1 Cells in your paper, and each of the sections has two subsections that begin with Header 2 Cells, Automatic Section Numbering will number them 1, 1.1, 1.2, 2, 2.1, and 2.2 respectively. If, however, you have used a Header 3 Cell to indicate the beginning of what would have been section 2.1, Automatic Section Numbering will number that section 2.0.1 and an error message will appear telling you that \"You placed a Header 3 cell under a Header 2 Cell in section 2\". Similarly, if you begin your paper with any Header Cell smaller than a Header 1, say a Header 3 Cell, then Automatic Section Numbering will number your first section 0.0.3 and an error message will appear telling you that \"Notebook begins with a Header 3 Cell.\"\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 2.4.2.2 Table of Contents Support",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The Table of Contents tool will automatically generate a table of contents for your paper by taking all your Header Cell titles and ordering them in a list, which it will place in a new cell at the very beginning of you Notebook. Because your Notebook does note utilize formal page breaks or numbers, each listed section will be hyperlinked to the actual section within your document.\n\n**Notes: **Because Table of Contents Support uses your header cells, its performance relies somewhat on the clarity of your organization. If you have two sections that begin with Header 1 Cells in your paper, and each of the sections has two subsections that begin with Header 2 Cells, Table of Contents will order them in the following way:\n\n* 1.\n * 1.1\n * 1.2\n* 2.\n * 2.1\n * 2.2\n \n\nIf, however, you have used a Header 3 Cell to indicate the beginning of what would have been section 2.1, Table of Contents Support will insert a dummy line so that your table of contents looks like this:\n\n\n* 1.\n * 1.1\n * 1.2\n* 2.\n * \n * 2.0.1\n * 2.2\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 2.4.2.3 Using Both Automatic Section Numbering and Table of Contents Support",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Automatic Section Numbering will always update every aspect of your notebook that is dependent on the title of one or more of your sections. This means that it will automatically correct an existing table of contents and all of your Notebook-internal links to reflect the new numbered section titles.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 3. Keyboard Shortcuts",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Jupyter Notebooks support many helpful Keyboard shortcuts, including ones for most of the buttons in [your toolbar][]. To view these shortcuts, you can click the help menu and then select Keyboard Shortcuts, as pictured below. \n\n[your toolbar]: #1.-Getting-to-Know-your-Jupyter-Notebook's-Toolbar \"Getting to know Your Jupyter Notebook's Toolbar\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 4. Using Markdown Cells for Writing",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Why aren't there font and font size selection drop down menus, buttons I can press to bold and italicize my text, or other advanced style options in my Notebook?**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"When you use Microsoft Word, Google Docs, Apple Pages, Open Office, or any other word processing software, you generally use your mouse to select various style options, like line spacing, font size, font color, paragraph format etc. This kind of system is often describes as a WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) interface. This means that the input (what you tell the computer) exactly matches the output (what the computer gives back to you). If you type the letter **`G`**, highlight it, select the color green and up the font size to 64 pt, your word processor will show you a fairly large green colored letter **`G`**. And if you print out that document you will print out a fairly large green colored letter **`G`**. \n\nThis Notebook, however, does not use a WYSIWYG interface. Instead it uses something called a \"[markup Language][]\". When you use a a markup language, your input does not necessarily exactly equal your output.\n\n\n[markup language]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Markup_language \"Wikipedia Article on Markup\"\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"For example, if I type \"#Header 1\" at the beginning of a cell, but then press Shift-Enter (or click the play button at the top of the window), this notebook will turn my input into a somewhat different output in the following way:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n#Header 1\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Header 1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"And if I type \"##Header 2\" (at the beginning of a cell), this notebook will turn that input into another output:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n##Header 2\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##Header 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In these examples, the hashtags are markers which tell the Notebook how to typeset the text. There are many markup languages, but one family, or perhaps guiding philosophy, of markup languages is called \"Markdown,\" named somewhat jokingly for its simplicity. Your Notebook uses \"marked,\" a Markdown library of typeset and other formatting instructions, like the hashtags in the examples above.\n\nMarkdown is a markup language that generates HTML, which the cell can interpret and render. This means that Markdown Cells can also render plain HTML code. If you're interested in learning HTML, check out this [helpful online tutorial][html tutorial].\n\n[html tutorial]: http://www.w3schools.com/html/ \"w3schools.com HTML Tutorial\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Why Use Markdown (and not a WYSIWYG)?**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Why is Markdown better? Well, it’s worth saying that maybe it isn't. Mainly, it’s not actually a question of better or worse, but of what’s in front of you and of who you are. A definitive answer depends on the user and on that user’s goals and experience. These Notebooks don't use Markdown because it's definitely better, but rather because it's different and thus encourages users to think about their work differently. \n\nIt is very important for computer science students to learn how to conceptualize input and output as dependent, but also distinct. One good reason to use Markdown is that it encourages this kind of thinking. Relatedly, it might also promote focus on substance over surface aesthetic. Markdown is somewhat limited in its style options, which means that there are inherently fewer non-subject-specific concerns to agonize over while working. It is the conceit of this philosophy that you would, by using Markdown and this Notebook, begin to think of the specific stylistic rendering of your cells as distinct from what you type into those same cells, and thus also think of the content of your writing as necessarily separate from its formating and appearance. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 4.1 Block Elements",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.1.1 Paragraph Breaks",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Paragraphs consist of one or more consecutive lines of text and they are separated by one or more blank lines. If a line contains only spaces, it is a blank line.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.1.2 Line Breaks",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 4.1.2.1 Hard-Wrapping and Soft-Wrapping",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"If you're used to word processing software, you've been writing with automatically hard-wrapped lines and paragraphs. In a hard-wrapped paragraph the line breaks are not dependent on the size of the viewing window. If you click and drag your mouse to expand a word processing document, for example, the shape of the paragraphs and the length of the lines will not change. In other words, the length of a hard-wrapped line is determined either by the number of words in the line (in the case of word processing software where this number is predetermined and the program wraps for the user automatically), or individual intention (when a user manually presses an Enter or Return key to control exactly how long a line is).\n\nSoft-wrapped paragraphs and lines, however, *do* depend on the size of their viewing window. If you increase the size of a window where soft-wrapped paragraphs are displayed, they too will expand into longer lines, becoming shorter and wider to fill the increased window space horizontally. Unsurprising, then, if you *narrow* a window, soft-wrapped lines will shrink and the paragraphs will become longer vertically. \n\nMarkdown, unlike most word processing software, does not automatically hard-wrap. If you want your paragraphs to have a particular or deliberate shape and size, you must insert your own break by ending the line with two spaces and then typing Return.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 4.1.2.2 Soft-Wrapping",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<tt>\nblah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah\n</tt>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 4.1.2.3 Hard-Wrapping",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<tt>\nblah blah blah blah blah \nblah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah \nblah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah \nblah blah blah blah blah \nblah blah blah blah blah \nblah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah \n</tt>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"blah blah blah blah blah \nblah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah \nblah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah \nblah blah blah blah blah \nblah blah blah blah blah \nblah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.1.3 Headers",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n#Header 1\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Header 1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n##Header 2\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##Header 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n###Header 3\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"###Header 3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n####Header 4\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"####Header 4",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n#####Header 5\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#####Header 5",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n######Header 6\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"######Header 6",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.1.4 Block Quotes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 4.1.4.1 Standard Block Quoting",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<tt>\n>blah blah block quote blah blah block quote blah blah block \nquote blah blah block quote blah blah block \nquote blah blah block quote blah blah block quote blah blah block quote\n</tt>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
">blah blah block quote blah blah block quote blah blah block \nquote blah blah block quote blah blah block \nquote blah blah block quote blah blah block quote blah blah block quote",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Note**: Block quotes work best if you intentionally hard-wrap the lines.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 4.1.4.2 Nested Block Quoting",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n>blah blah block quote blah blah block quote blah blah block \nblock quote blah blah block block quote blah blah block \n>>quote blah blah block quote blah blah \nblock block quote blah blah block \n>>>quote blah blah block quote blah blah block quote blah blah block quote\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
">blah blah block quote blah blah block quote blah blah block \nblock quote blah blah block block quote blah blah block \n>>quote blah blah block quote blah blah \nblock block quote blah blah block \n>>>quote blah blah block quote blah blah block quote blah blah block quote",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.1.5 Lists",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 4.1.5.1 Ordered Lists",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In Markdown, you can list items using numbers, a **`+`**, a **` - `**, or a **`*`**. However, if the first item in a list or sublist is numbered, Markdown will interpret the entire list as ordered and will automatically number the items linearly, no matter what character you use to denote any given separate item.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n####Groceries:\n\n0. Fruit:\n 6. Pears\n 0. Peaches\n 3. Plums\n 4. Apples \n 2. Granny Smith \n 7. Gala\n * Oranges\n - Berries \n 8. Strawberries \n + Blueberries\n * Raspberries\n - Bananas\n9. Bread:\n 9. Whole Wheat\n 0. With oats on crust\n 0. Without oats on crust\n 0. Rye \n 0. White\n0. Dairy:\n 0. Milk\n 0. Whole\n 0. Skim\n 0. Cheese\n 0. Wisconsin Cheddar\n 0. Pepper Jack\n</pre> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"####Groceries:\n\n0. Fruit:\n 6. Pears\n 0. Peaches\n 3. Plums\n 4. Apples \n 2. Granny Smith \n 7. Gala\n * Oranges\n - Berries \n 8. Strawberries \n + Blueberries\n * Raspberries\n - Bananas\n9. Bread:\n 9. Whole Wheat\n 0. With oats on crust\n 0. Without oats on crust\n 0. Rye \n 0. White\n0. Dairy:\n 0. Milk\n 0. Whole\n 0. Skim\n 0. Cheese\n 0. Wisconsin Cheddar\n 0. Pepper Jack",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 4.1.5.2 Bulleted Lists",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"If you begin your list or sublist with a **`+`**, a **` - `**, or a **`*`**, then Markdown will interpret the whole list as unordered and will use bullets regardless of the characters you type before any individual list item.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n####Groceries:\n\n* Fruit:\n * Pears\n 0. Peaches\n 3. Plums\n 4. Apples \n - Granny Smith \n 7. Gala\n * Oranges\n - Berries \n - Strawberries \n + Blueberries\n * Raspberries\n - Bananas\n9. Bread:\n * Whole Wheat\n * With oats on crust\n 0. Without oats on crust\n + Rye \n 0. White\n0. Dairy:\n * Milk\n + Whole\n 0. Skim\n - Cheese\n - Wisconsin Cheddar\n 0. Pepper Jack\n </pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"####Groceries:\n\n* Fruit:\n * Pears\n 0. Peaches\n 3. Plums\n 4. Apples \n - Granny Smith \n 7. Gala\n * Oranges\n - Berries \n - Strawberries \n + Blueberries\n * Raspberries\n - Bananas\n9. Bread:\n * Whole Wheat\n * With oats on crust\n 0. Without oats on crust\n + Rye \n 0. White\n0. Dairy:\n * Milk\n + Whole\n 0. Skim\n - Cheese\n - Wisconsin Cheddar\n 0. Pepper Jack",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.1.6 Section Breaks",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n___\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"___ ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n***\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>------</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"------",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n* * *\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* * *",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n_ _ _\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"_ _ _",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre> \n- - -\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"- - -",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 4.2 Backslash Escape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"What happens if you want to include a literal character, like a **`#`**, that usually has a specific function in Markdown? Backslash Escape is a function that prevents Markdown from interpreting a character as an instruction, rather than as the character itself. It works like this:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n\\# Wow, this isn't a header. \n# This is definitely a header.\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\\# Wow, this isn't a header. \n# This is definitely a header.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Markdown allows you to use a backslash to escape from the functions of the following characters:\n* \\ backslash\n* ` backtick\n* \\* asterisk\n* _ underscore\n* {} curly braces\n* [] square brackets\n* () parentheses\n* \\# hashtag\n* \\+ plus sign|\n* \\- minus sign (hyphen)\n* . dot\n* ! exclamation mark",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 4.3 Hyperlinks",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.3.1 Automatic Links",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\nhttp://en.wikipedia.org\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"http://en.wikipedia.org",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.3.2 Standard Links",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n[click this link](http://en.wikipedia.org)\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"[click this link](http://en.wikipedia.org)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.3.3 Standard Links With Mouse-Over Titles",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre> \n[click this link](http://en.wikipedia.org \"Wikipedia\")\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"[click this link](http://en.wikipedia.org \"Wikipedia\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.3.4 Reference Links",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Suppose you are writing a document in which you intend to include many links. The format above is a little arduous and if you have to do it repeatedly *while* you're trying to focus on the content of what you're writing, it's going to be a really big pain. \n\nFortunately, there is an alternative way to insert hyperlinks into your text, one where you indicate that there is a link, name that link, and then use the name to provide the actually URL later on when you're less in the writing zone. This method can be thought of as a \"reference-style\" link because it is similar to using in-text citations and then defining those citations later in a more detailed reference section or bibliography. \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\nThis is [a reference] [identification tag for link]\n\n[identification tag for link]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chile \"Wikipedia Article About Chile\"\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This is [a reference] [identification tag for link]\n\n[identification tag for link]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chile \"Wikipedia Article About Chile\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Note:** The \"identification tag for link\" can be anything. For example:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\nThis is [a reference] [lfskdhflhslgfh333676]\n\n[lfskdhflhslgfh333676]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chile \"Wikipedia Article About Chile\"\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This is [a reference] [lfskdhflhslgfh333676]\n\n[lfskdhflhslgfh333676]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chile \"Wikipedia Article About Chile\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This means you can give your link an intuitive, easy to remember, and relevant ID:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\nThis is [a reference][Chile]\n\n[chile]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chile \"Wikipedia Article About Chile\"\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This is [a reference][Chile]\n\n[chile]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chile \"Wikipedia Article About Chile\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Note**: Link IDs are not case-sensitive.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"If you don't want to give your link an ID, you don't have to. As a short cut, Markdown will understand if you just use the words in the first set of brackets to define the link later on. This works in the following way:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\nThis is [a reference][]\n\n[a reference]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chile \"Wikipedia Article About Chile\"\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This is [a reference][]\n\n[a reference]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chile \"Wikipedia Article About Chile\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Another really helpful feature of a reference-style link is that you can define the link anywhere in the cell. (must be in the cell) For example:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<tt>\nThis is [a reference] [ref] blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah\nblah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah <br/><br/>\n\n[ref]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chile \"Wikipedia Article About Chile\"\n</tt>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This is [a reference] [ref] blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah\nblah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah blah\n\n[ref]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chile \"Wikipedia Article About Chile\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Note:** Providing a mouse-over title for any link, regardless of whether it is a standard or reference-stlye type, is optional. With reference-style links, you can include the mouse-over title by placing it in quotes, single quotes, or parentheses. For standard links, you can only define a mouse-over title in quotes.\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.3.5 Notebook-Internal Links",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"When you create a Header you also create a discrete location within your Notebook. This means that, just like you can link to a specific location on the web, you can also link to a Header Cell inside your Notebook. Internal links have very similar Markdown formatting to regular links. The only difference is that the name of the link, which is the URL in the case of external links, is just a hashtag plus the name of the Header Cell you are linking to (case-sensitive) with dashes in between every word. If you hover your mouse over a Header Cell, a blue Greek pi letter will appear next to your title. If you click on it, the URL at the top of your window will change and the internal link to that section will appear last in the address. You can copy and paste it in order to make an internal link inside a Markdown Cell. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 4.3.5.1 Standard Notebook-Internal Links Without Mouse-Over Titles",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n[Here's a link to the section of Automatic Section Numbering](#Automatic-Section-Numbering)\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"[Here's a link to the section of Automatic Section Numbering](#2.4.2.1-Automatic-Section-Numbering)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 4.3.5.2 Standard Notebook-Internal Links With Mouse-Over Titles",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n[Here's a link to the section on lists](#Lists \"Lists\")\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"[Here's a link to the section of Automatic Section Numbering](#2.4.2.1-Automatic-Section-Numbering)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 4.3.5.3 Reference-Style Notebook-Internal Links",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n[Here's a link to the section on Table of Contents Support][TOC]\n\n[TOC]: #Table-of-Contents-Support\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"[Here's a link to the section on Table of Contents Support][TOC]\n\n[TOC]: #2.4.2.2-Table-of-Contents-Support",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 4.4 Tables",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In Markdown, you can make a table by using vertical bars and dashes to define the cell and header borders:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n|Header|Header|Header|Header|\n|------|------|------|------|\n|Cell |Cell |Cell | Cell |\n|Cell |Cell |Cell | Cell |\n|Cell |Cell |Cell | Cell |\n|Cell |Cell |Cell | Cell |\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"|Header|Header|Header|Header|\n|------|------|------|------|\n|Cell |Cell |Cell | Cell |\n|Cell |Cell |Cell | Cell |\n|Cell |Cell |Cell | Cell |\n|Cell |Cell |Cell | Cell |\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Making a table this way might be especially useful if you want your document to be legible both rendered and unrendered. However, you don't *need* to include all of those dashes, vertical bars, and spaces for Markdown to understand that you're making a table. Here's the bare minimum you would need to create the table above: ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\nHeader|Header|Header|Header\n-|-|-|-\nCell|Cell|Cell|Cell\nCell|Cell|Cell|Cell\nCell|Cell|Cell|Cell\nCell|Cell|Cell|Cell\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Header|Header|Header|Header\n-|-|-|-\nCell|Cell|Cell|Cell\nCell|Cell|Cell|Cell\nCell|Cell|Cell|Cell\nCell|Cell|Cell|Cell\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"It's important to note that the second line of dashes and vertical bars is essential. If you have just the line of headers and the second line of dashes and vertical bars, that's enough for Markdown to make a table. \n\nAnother important formatting issue has to do with the vertical bars that define the left and right edges of the table. If you include all the vertical bars on the far left and right of the table, like in the first example above, Markdown will ignore them completely. *But*, if you leave out some and include others, Markdown will interpret any extra vertical bar as an additional cell on the side that the bar appears in the unrendered version of the text. This also means that if you include the far left or right vertical bar in the second line of bars and dashes, you must include all of the otherwise optional vertical bars (like in the first example above).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.4.1 Cell Justification",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"If not otherwise specified the text in each header and cell of a table will justify to the left. If, however, you wish to specify either right justification or centering, you may do so like this: ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<tt>\n**Centered, Right-Justified, and Regular Cells and Headers**:\n\ncentered header | regular header | right-justified header | centered header | regular header \n:-:|-|-:|:-:|-\ncentered cell|regular cell|right-justified cell|centered cell|regular cell\ncentered cell|regular cell|right-justified cell|centered cell|regular cell\n</tt>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Centered, Right-Justified, and Regular Cells and Headers**:\n\ncentered header | regular header | right-justified header | centered header | regular header \n:-:|-|-:|:-:|-\ncentered cell|regular cell|right-justified cell|centered cell|regular cell\ncentered cell|regular cell|right-justified cell|centered cell|regular cell\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"While it is difficult to see that the headers are differently justified from one another, this is just because the longest line of characters in any column defines the width of the headers and cells in that column. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Note:** You cannot make tables directly beneath a line of text. You must put a blank line between the end of a paragraph and the beginning of a table. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 4.5 Style and Emphasis",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n*Italics*\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"*Italics*",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n_Italics_\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"_Italics_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n**Bold**\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Bold**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n__Bold__\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"__Bold__",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Note:** If you want actual asterisks or underscores to appear in your text, you can use the [backslash escape function] [backslash] like this:\n\n[backslash]: #4.2-Backslash-Escape \"Backslash Escape\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n\\*awesome asterisks\\* and \\_incredible under scores\\_\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\\*awesome asterisks\\* and \\_incredible under scores\\_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 4.6 Other Characters",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre> \nAmpersand &amp; Ampersand\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Ampersand & Ampersand",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n&lt; angle brackets &gt;\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"< angle brackets >",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n&quot; quotes &quot; ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"" quotes " ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 4.7 Including Code Examples",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"If you want to signify that a particular section of text is actually an example of code, you can use backquotes to surround the code example. These will switch the font to monospace, which creates a clear visual formatting difference between the text that is meant to be code and the text that isn't. \n\nCode can either in the middle of a paragraph, or as a block. Use a single backquote to start and stop code in the middle of a paragraph. Here's an example:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\nThe word `monospace` will appear in a code-like form.\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The word `monospace` will appear in a code-like form.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Note:** If you want to include a literal backquote in your code example you must suround the whole text block in double backquotes like this: ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n`` Look at this literal backquote ` ``\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"`` Look at this literal backquote ` ``",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To include a complete code-block inside a Markdown cell, use triple backquotes. Optionally, you can put the name of the language that you are quoting after the starting triple backquotes, like this:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n```python\ndef function(n):\n return n + 1\n```\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"That will format the code-block (sometimes called \"fenced code\") with syntax coloring. The above code block will be rendered like this:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"```python\ndef function(n):\n return n + 1\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The language formatting names that you can currently use after the triple backquote are:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\napl django go jinja2 ntriples q smalltalk toml\nasterisk dtd groovy julia octave r smarty turtle\nclike dylan haml less pascal rpm smartymixed vb\nclojure ecl haskell livescript pegjs rst solr vbscript\ncobol eiffel haxe lua perl ruby sparql velocity\ncoffeescript erlang htmlembedded markdown php rust sql verilog\ncommonlisp fortran htmlmixed pig sass stex xml\ncss gas http mirc properties scheme tcl xquery\nd gfm jade mllike puppet shell tiddlywiki yaml\ndiff gherkin javascript nginx python sieve tiki z80\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 4.8 Images",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.8.1 Images from the Internet",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Inserting an image from the internet is almost identical to inserting a link. You just also type a **`!`** before the first set of brackets:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Note:** Unlike with a link, the words that you type in the first set of brackets do not appear when they are rendered into html by Markdown. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 4.8.1.1 Reference-Style Images from the Internet",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Just like with links, you can also use a reference-style format when inserting images from the internet. This involves indicating where you want to place a picture, giving that picture an ID tag, and then later defining that ID tag. The process is nearly identical to using the reference-style format to insert a link:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n![][giraffe]\n\n[giraffe]:http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b7/South_African_Giraffe,_head.jpg/877px-South_African_Giraffe,_head.jpg \"Picture of a Giraffe\"\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"![][giraffe]\n\n[giraffe]: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b7/South_African_Giraffe,_head.jpg/877px-South_African_Giraffe,_head.jpg \"Picture of a Giraffe\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 4.9 LaTeX Math",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Jupyter Notebooks' Markdown cells support LateX for formatting mathematical equations. To tell Markdown to interpret your text as LaTex, surround your input with dollar signs like this:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n$z=\\dfrac{2x}{3y}$\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$z=\\dfrac{2x}{3y}$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"An equation can be very complex:\n\n<pre>\n$F(k) = \\int_{-\\infty}^{\\infty} f(x) e^{2\\pi i k} dx$\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$F(k) = \\int_{-\\infty}^{\\infty} f(x) e^{2\\pi i k} dx$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"If you want your LaTex equations to be indented towards the center of the cell, surround your input with two dollar signs on each side like this: ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n$$2x+3y=z$$\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$2x+3y=z$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"For a comprehensive guide to the mathematical symbols and notations supported by Jupyter Notebooks' Markdown cells, check out [Martin Keefe's helpful reference materials on the subject][mkeefe].\n\n[mkeefe]: http://martinkeefe.com/math/mathjax1 \"Martin Keefe's MathJax Guide\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 5. Bibliographic Support",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Bibliographic Support makes managing references and citations in your Notebook much easier, by automating some of the bibliographic process every person goes through when doing research or writing in an academic context. There are essentially three steps to this process for which your Notebook's Bibliographic support can assist: gathering and organizing sources you intend to use, citing those sources within the text you are writing, and compiling all of the material you referenced in an organized, correctly formatted list, the kind which usually appears at the end of a paper in a section titled \"References,\" \"Bibliography,\" or \"Works Cited. \n\nIn order to benefit from this functionality, you need to do two things while writing your paper: first, you need to create a [Bibtex database][bibdb] of information about your sources and second, you must use the the [cite command][cc] in your Markdown writing cells to indicate where you want in-text citations to appear.\n\nIf you do both these things, the \"Generate References\" button will be able to do its job by replacing all of your cite commands with validly formatted in-text citations and creating a References section at the end of your document, which will only ever include the works you specifically cited within in your Notebook. \n\n**Note:** References are generated without a header cell, just a [markdown header][]. This means that if you want a References section to appear in your table of contents, you will have to unrender the References cell, delete the \"References\" header, make a Header Cell of the appropriate level and title it \"References\" yourself, and then generate a table of contents using [Table of Contents Support][table of contents]. This way, you can also title your References section \"Bibliography\" or \"Works Cited,\" if you want.\n\n[markdown header]: #4.1.3-Headers\n[table of contents]: #2.4.2.2-Table-of-Contents-Support\n[bibdb]: #5.1-Creating-a-Bibtex-Database\n[cc]:#5.2-Cite-Commands-and-Citation-IDs\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 5.1 Creating a Bibtex Database",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Bibtex is reference management software for formatting lists of references ([from Wikipedia](BibTeX is reference management software for formatting lists of references \"Wikipedia Article On Bibtex\")). While your Notebook does not use the Bibtex software, it does use [Bibtex formatting](#5.1.3-Formatting-Bibtex-Entries) for creating references within your Bibliographic database.\n\nIn order for the Generate References button to work, you need a bibliographic database for it to search and match up with the sources you've indicated you want to credit using [cite commands and citation IDs](#5.2-Cite-Commands-and-Citation-IDs).\n\nWhen creating a bibliographic database for your Notebook, you have two options: you can make an external database, which will exist in a separate Notebook from the one you are writing in, or you can make an internal database which will exist in a single cell inside the Notebook in which you are writing. Below are explanations of how to use these database creation strategies, as well as a discussion of the pros and cons for each. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 5.1.1 External Bibliographic Databases",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To create an external bibliographic database, you will need to create a new Notebook and title it **`Bibliography`** in the toplevel folder of your current Jupyter session. As long as you do not also have an internal bibliographic database, when you click the Generate References button your Notebook's Bibliographic Support will search this other **`Bibliography`** Notebook for Bibtex entries. Bibtex entries can be in any cell and in any kind of cell in your **`Bibliography`** Notebook as long as the cell begins with **`<!--bibtex`** and ends with **`-->`**. Go to [this section][bibfor] for examples of valid BibTex formatting.\n\nNot every cell has to contain BibTex entries for the external bibliographic database to work as intended with your Notebook's bibliographic support. This means you can use the same helpful organization features that you use in other Notebooks, like [Automatic Section Numbering][asn] and [Table of Contents Support][toc], to structure your own little library of references. The best part of this is that any Notebook containing validly formatted [cite commands][cc] can check your external database and find only the items that you have indicated you want to cite. So you only ever have to make the entry once and your external database can grow large and comprehensive over the course of your accademic writing career. \n\nThere are several advantages to using an external database over [an internal one][internal database]. The biggest one, which has already been described, is that you will only ever need to create one and you can organize it into sections by using headers and generating [automatic section numbers][asn] and a [table of contents][toc]. These tools will help you to easily find the right [citation ID][cc] for a given source you want to cite. The other major advantage is that an external database is not visible when viewing the Notebook in which you are citing sources and generating a References list. Bibtex databases are not very attractive or readable and you probably won't want one to show up in your finished document. There are [ways to hide internal databases][hiding bibtex cell], but it's convenient not to have to worry about that. \n\n\n[asn]: #2.4.2.1-Automatic-Section-Numbering\n[toc]: #2.4.2.2-Table-of-Contents-Support\n[cc]: #5.2-Cite-Commands-and-Citation-IDs\n[hiding bibtex cell]: #5.1.2.1-Hiding-Your-Internal-Database\n[bibfor]:#5.1.3-Formatting-Bibtex-Entries",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 5.1.2 Internal Bibliographic Databases",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Unlike [external bibliographic databases][exd], which are comprised from an entire separate notebook, internal bibliographic databases consist of only one cell within in the Notebook in which you are citing sources and compiling a References list. The single cell, like all of the many BibTex cells that can make up an external database, must begin with **`<!--bibtex`** and end with **`-->`** in order to be validly formatted and correctly interpreted by your Notebook's Bibliographic Support. It's probably best to keep this cell at the very end or the very beginning of your Notebook so you always know where it is. This is because when you use an intenral bibliographic databse it can only consist of one cell. This means that if you want to cite multiple sources you will need to keep track of the single cell that comprises your entire internal bibliographic database during every step of the research and writing process. \n\nInternal bibliographic databases make more sense when your project is a small one and the list of total sources is short. This is especially convenient if you don't already have a built-up external database. With an internal database you don't have to create and organize a whole separate Notebook, a task that's only useful when you have to keep track of a lot of different material. Additionally, if you want to share your finished Notebook with others in a form that retains its structural validity, you only have to send one Notebook, as oppose to both the project itself and the Notebook that comprises your external bibliographic database. This is especially useful for a group project, where you want to give another reader the ability to edit, not simply read, your References section. \n\n[exd]:#5.1.1-External-Bibliographic-Databases\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 5.1.2.1 Hiding Your Internal Database",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Even though they have some advantages, especially for smaller projects, internal databases have on major draw back. They are not very attractive or polished looking and you probably won't want one to appear in your final product. Fortunately, there are two methods for hiding your internal biblioraphic database.\n\nWhile your Notebook's bibliographic support will be able to interpret [correctly formatted BibTex entries][bibfor] in any [kind of cell][cell kind], if you use a [Markdown Cell][md cell] to store your internal bibliographic database, then when you run the cell all of the ugly BibTex formatting will disappear. This is handy, but it also makes the cell very difficult to find, so remember to keep careful track of where your hidden BibTex databse is if you're planning to edit it later. If you want your final product to be viewed stably as HTML, then you can make your internal BibTex database inside a [Raw Cell][RC], use the [cell toolbar][] to select \"Raw Cell Format\", and then select \"None\" in the toolbar that appears in the corner of your Raw Cell BibTex database. This way, you will still be able to easily find and edit the database when you are working on your Notebook, but others won't be able to see the database when viewing your project in its final form. \n\n\n[cell toolbar]: #1.-Getting-to-Know-your-Jupyter-Notebook's-Toolbar\n[bibfor]:#5.1.3-Formatting-Bibtex-Entries\n[RC]:#2.3-Raw-Cells\n[md cell]: #2.2-Markdown-Cells\n[cell kind]: #2.-Different-Kinds-of-Cells",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 5.1.3 Formatting Bibtex Entries",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"BibTex entries consist of three crucial components: one, the type of source you are citing (a book, article, website, etc.); two, the unique [citation ID][cc] you wish to remember the source by; and three, the fields of information about that source (author, title of work, date of publication, etc.). Below is an example entry, with each of these three components designated clearly\n\n<pre>\n\n<!--bibtex\n\n@ENTRY TYPE{CITATION ID,\n FIELD 1 = {source specific information},\n FIELD 2 = {source specific informatio},\n FIEL 3 = {source specific informatio},\n FIELD 4 = {source specific informatio}\n}\n\n-->\n\n</pre>\n\nMore comprehensive documentation of what entry types and corresponding sets of required and optional fields BibTex supports can be found in the [Wikipedia article on BibTex][wikibibt].\n\nBelow is a section of the external bibliographic database for a fake history paper about the fictional island nation of Calico. (None of the entries contain information about real books or articles):\n\n[cc]: #5.2-Cite-Commands-and-Citation-IDs\n[wikibibt]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Markdown\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<pre>\n\n<!--bibtex\n\n@book{wellfarecut,\n title = {Our Greatest Threat: The Rise of Anti-Wellfare Politics in Calico in the 21st Century},\n author = {Jacob, Bernadette},\n year = {2010},\n publisher = {Jupyter University Press}\n}\n \n@article{militaryex2,\n title = {Rethinking Calican Military Expansion for the New Century},\n author = {Collier, Brian F.},\n journal = {Modern Politics},\n volume = {60},\n issue = {25},\n pages = {35 - 70},\n year = {2012} \n}\n\n@article{militaryex1,\n title = {Conservative Majority Passes Budget to Grow Military},\n author = {Lane, Lois},\n journal = {The Daily Calican},\n month = {October 19th, 2011},\n pages = {15 - 17},\n year = {2011}\n}\n\n@article{oildrill,\n title = {Oil Drilling Off the Coast of Jupyter Approved for Early Next Year},\n author = {Marks, Meghan L.},\n journal = {The Python Gazette},\n month = {December 5th, 2012},\n pages = {8 - 9},\n year = {2012}\n}\n\n@article{rieseinterview,\n title = {Interview with Up and Coming Freshman Senator, Alec Riese of Python},\n author = {Wilmington, Oliver},\n journal = {The Jupyter Times},\n month = {November 24th, 2012},\n pages = {4 - 7},\n year = {2012}\n}\n\n@book{calicoww2:1,\n title = {Calico and WWII: Untold History},\n author = {French, Viola},\n year = {1997},\n publisher = {Calicia City Free Press}\n}\n\n@book{calicoww2:2,\n title = {Rebuilding Calico After Japanese Occupation},\n author = {Kepps, Milo },\n year = {2002},\n publisher = {Python Books}\n}\n-->\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 5.2 Cite Commands and Citation IDs",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"When you want to cite a bibliographic entry from a database (either internal or external), you must know the citation ID, sometimes called the \"key\", for that entry. Citation IDs are strings of letters, numbers, and symbols that *you* make up, so they can be any word or combination of words you find easy to remember. Once, you've given an entry a citation ID, however, you do need to use that same ID every time you cite that source, so it may behoove you to keep your database organized. This way it will be much easier to locate any given source's entry and its potentially forgotten citation ID. \n\nOnce you know the citation ID for a given entry, use the following format to indicate to your Notebook's bibliographic support that you'd like to insert an in-text citation:\n\n<pre>\n[](#cite-CITATION ID)\n</pre>\n\nThis format is the cite command. For example, if you wanted to cite *Rebuilding Calico After Japanese Occupation* listed above, you would use the cite command and the specific citation ID for that source:\n\n<pre>\n[](#cite-calicoww2:2)\n</pre>\n\nBefore clicking the \"Generate References\" button, your unrendered text might look like this:\n\n\n<pre>\nRebuilding Calico took many years [](#cite-calicoww2:2).\n</pre>\n\n\nAfter clicking the \"Generate References\" button, your unrendered text might look like this:\n\n\n<pre>\nRebuilding Calico took many years <a name=\"ref-1\"/>[(Kepps, 2002)](#cite-calicoww2:2).\n</pre>\n\n\nand then the text would render as:\n\n\n>Rebuilding Calico took many years <a name=\"ref-1\"/>[(Kepps, 2002)](#cite-calicoww2:2).\n\n\nIn addition, a cell would be added at the bottom with the following contents:\n\n\n>#References\n\n><a name=\"cite-calicoww2:2\"/><sup>[^](#ref-1) [^](#ref-2) </sup>Kepps, Milo . 2002. _Rebuilding Calico After Japanese Occupation_.\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 6. Turning Your Jupyter Notebook into a Slideshow",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To install slideshow support for your Notebook, go [here](http://nbviewer.ipython.org/github/fperez/nb-slideshow-template/blob/master/install-support.ipynb).\n\nTo see a tutorial and example slideshow, go [here](http://www.damian.oquanta.info/posts/make-your-slides-with-ipython.html).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe63c3ec0348943cf49ccc8d57e11c24fafab96
| 324,231 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
xgboost/BikeSharingRegression/bikerental_data_preparation_rev1.ipynb
|
thiago1080/sagemaker
|
0e59c8052f5a3ae7067e9ee5afe1aa3ac023407e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
xgboost/BikeSharingRegression/bikerental_data_preparation_rev1.ipynb
|
thiago1080/sagemaker
|
0e59c8052f5a3ae7067e9ee5afe1aa3ac023407e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
xgboost/BikeSharingRegression/bikerental_data_preparation_rev1.ipynb
|
thiago1080/sagemaker
|
0e59c8052f5a3ae7067e9ee5afe1aa3ac023407e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 306.167139 | 47,600 | 0.918614 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nfrom pandas.plotting import register_matplotlib_converters\nregister_matplotlib_converters()\n# https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.plotting.register_matplotlib_converters.html\n# Register converters for handling timestamp values in plots ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<h2>Kaggle Bike Sharing Demand Dataset</h2>\n<h4>To download dataset, sign-in and download from this link: https://www.kaggle.com/c/bike-sharing-demand/data</h4>\n<br>\n\nInput Features:<br>\n['season', 'holiday', 'workingday', 'weather', 'temp', 'atemp', 'humidity', 'windspeed', 'year', 'month', 'day', 'dayofweek','hour']<br>\n \nTarget:<br>\n['count']<br>\n\nObjective:\n\nYou are provided hourly rental data spanning two years. \n \nFor this competition, the training set is comprised of the first 19 days of each month, while the test set is the 20th to the end of the month. \n\nYou must predict the total count of bikes rented during each hour covered by the test set, using only information available prior to the rental period\n\nReference: https://www.kaggle.com/c/bike-sharing-demand/data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"columns = ['count', 'season', 'holiday', 'workingday', 'weather', 'temp',\n 'atemp', 'humidity', 'windspeed', 'year', 'month', 'day', 'dayofweek','hour']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.read_csv('train.csv', parse_dates=['datetime'],index_col=0)\ndf_test = pd.read_csv('test.csv', parse_dates=['datetime'],index_col=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# We need to convert datetime to numeric for training.\n# Let's extract key features into separate numeric columns\ndef add_features(df):\n df['year'] = df.index.year\n df['month'] = df.index.month\n df['day'] = df.index.day\n df['dayofweek'] = df.index.dayofweek\n df['hour'] = df.index.hour",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Add New Features\nadd_features(df)\nadd_features(df_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Need to predict the missing data\nplt.title('Rental Count - Gaps')\ndf['2011-01':'2011-02']['count'].plot()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Rentals change hourly!\nplt.plot(df['2011-01-01']['count'])\nplt.xticks(fontsize=14, rotation=45)\nplt.xlabel('Date')\nplt.ylabel('Rental Count')\nplt.title('Hourly Rentals for Jan 01, 2011')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Seasonal\nplt.plot(df['2011-01']['count'])\nplt.xticks(fontsize=14, rotation=45)\nplt.xlabel('Date')\nplt.ylabel('Rental Count')\nplt.title('Jan 2011 Rentals (1 month)')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"group_hour = df.groupby(['hour'])\naverage_by_hour = group_hour['count'].mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(average_by_hour.index,average_by_hour)\nplt.xlabel('Hour')\nplt.ylabel('Rental Count')\nplt.xticks(np.arange(24))\nplt.grid(True)\nplt.title('Average Hourly Rental Count')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Year to year trend\nplt.plot(df['2011']['count'],label='2011')\nplt.plot(df['2012']['count'],label='2012')\nplt.xticks(fontsize=14, rotation=45)\nplt.xlabel('Date')\nplt.ylabel('Rental Count')\nplt.title('2011 and 2012 Rentals (Year to Year)')\nplt.legend()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"group_year_month = df.groupby(['year','month'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"average_year_month = group_year_month['count'].mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"average_year_month",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for year in average_year_month.index.levels[0]:\n plt.plot(average_year_month[year].index,average_year_month[year],label=year)\n \nplt.legend() \nplt.xlabel('Month')\nplt.ylabel('Count')\nplt.grid(True)\nplt.title('Average Monthly Rental Count for 2011, 2012')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"group_year_hour = df.groupby(['year','hour'])\naverage_year_hour = group_year_hour['count'].mean()\nfor year in average_year_hour.index.levels[0]:\n #print (year)\n #print(average_year_month[year])\n plt.plot(average_year_hour[year].index,average_year_hour[year],label=year)\n \nplt.legend() \nplt.xlabel('Hour')\nplt.ylabel('Count')\nplt.xticks(np.arange(24))\nplt.grid(True)\nplt.title('Average Hourly Rental Count - 2011, 2012')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"group_workingday_hour = df.groupby(['workingday','hour'])\naverage_workingday_hour = group_workingday_hour['count'].mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for workingday in average_workingday_hour.index.levels[0]:\n #print (year)\n #print(average_year_month[year])\n plt.plot(average_workingday_hour[workingday].index,average_workingday_hour[workingday],\n label=workingday)\n \nplt.legend() \nplt.xlabel('Hour')\nplt.ylabel('Count')\nplt.xticks(np.arange(24))\nplt.grid(True)\nplt.title('Average Hourly Rental Count by Working Day')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Let's look at correlation beween features and target\ndf.corr()['count']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Any relation between temperature and rental count?\nplt.scatter(x=df.temp,y=df[\"count\"])\nplt.grid(True)\nplt.xlabel('Temperature')\nplt.ylabel('Count')\nplt.title('Temperature vs Count')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Any relation between humidity and rental count?\nplt.scatter(x=df.humidity,y=df[\"count\"],label='Humidity')\nplt.grid(True)\nplt.xlabel('Humidity')\nplt.ylabel('Count')\nplt.title('Humidity vs Count')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Save all data\ndf.to_csv('bike_all.csv',index=True,index_label='datetime',columns=columns)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Training and Validation Set\n### Target Variable as first column followed by input features\n### Training, Validation files do not have a column header",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Training = 70% of the data\n# Validation = 30% of the data\n# Randomize the datset\nnp.random.seed(5)\nl = list(df.index)\nnp.random.shuffle(l)\ndf = df.loc[l]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"rows = df.shape[0]\ntrain = int(.7 * rows)\ntest = rows-train",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"rows, train, test",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Write Training Set\ndf.iloc[:train].to_csv('bike_train.csv'\n ,index=False,header=False\n ,columns=columns)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Write Validation Set\ndf.iloc[train:].to_csv('bike_validation.csv'\n ,index=False,header=False\n ,columns=columns)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Test Data has only input features\ndf_test.to_csv('bike_test.csv',index=True,index_label='datetime')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(','.join(columns))",
"count,season,holiday,workingday,weather,temp,atemp,humidity,windspeed,year,month,day,dayofweek,hour\n"
],
[
"# Write Column List\nwith open('bike_train_column_list.txt','w') as f:\n f.write(','.join(columns))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe6468baec73cfd6081f32f28beed9c87e5deb4
| 24,848 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
analytics notebook/Detect Spam Emails.ipynb
|
miniatureengineer/mini-projects
|
52fdcb3240795e272565747b28749be40f9f05eb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
analytics notebook/Detect Spam Emails.ipynb
|
miniatureengineer/mini-projects
|
52fdcb3240795e272565747b28749be40f9f05eb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
analytics notebook/Detect Spam Emails.ipynb
|
miniatureengineer/mini-projects
|
52fdcb3240795e272565747b28749be40f9f05eb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 28.300683 | 167 | 0.39645 |
[
[
[
"#### Naive bayes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#import library\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#read data\ndf = pd.read_csv(\"spam.csv\")\n#display all data \ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#print full summary\ndf.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 5572 entries, 0 to 5571\nData columns (total 2 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 Category 5572 non-null object\n 1 Message 5572 non-null object\ndtypes: object(2)\nmemory usage: 87.2+ KB\n"
],
[
"#display data first five rows\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#display data last five rows\ndf.tail()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#groupby category and describe\ndf.groupby('Category').describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#describe non-spam emails \ndf[df.Category == 'ham'].describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#describe spam emails \ndf[df.Category == 'spam'].describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#check number of rows where particular columns of null values\n#check sum of null values\ndf.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"It can be obeserved that there are no NaN or None values in the data set.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Machine learning model understand numerical values\n\n- Need to convert Category and Message into numbers first.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#take category column and apply lambda function check if spam will return 1 else 0\n#create a new spam column\ndf['Spam'] = df['Category'].apply(lambda x: 1 if x=='spam' else 0)\n\n# display data first five rows\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"- Created a new column named as \"Spam\", grouping emails into 1 and 0.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#train model using sklearn and train test data\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#use X, y as input and test_size as ratio of spliting > will get 4 parameters back\n#25% test and 75% train\n#when run the cell, it will split samples into train and test data set\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(df.Message,df.Spam,test_size=0.25)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#convert a collection of text documents to a matrix of token counts\n#find unique words, treat as columns and build matrix\n#...represent unique words in huge data set\n\nfrom sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer\nv = CountVectorizer()\nX_train_count = v.fit_transform(X_train.values)\nX_train_count.toarray()[:3]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#use in discrete data and have certain frequency to represent\nfrom sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB\nmodel = MultinomialNB()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#fit method to train model\n#X_train_count text converted into emails numbers matrix\nmodel.fit(X_train_count,y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#predict data\n\nemails = [\n 'You have updated Instagram username.',\n 'Click on this link to change your account details.'\n]\n\nemails_count = v.transform(emails)\nmodel.predict(emails_count)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Based on the emails above, first email is a normal email to update account user that username has been updated, while model detected that second email is a spam.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#model works only on numerical values not text\n#need to convert X_test model into count and fit into prediction\nX_test_count = v.transform(X_test)\n\n#check accuracy of model by calling score method\n#score will use X_test to predict model.predict(X_test) and compare with y_test value to find accuracy\nmodel.score(X_test_count, y_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"98% result shows that naive bayes spam filtering method is able to detect spam emails with high accuracy.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe6548e1cc75be97328c102ce7e01ce80c1c58b
| 32,713 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
docs/intro_sql_basic.ipynb
|
bakera81/siuba
|
568729989333193ff38c26ac68604aa8ba9b490b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
docs/intro_sql_basic.ipynb
|
bakera81/siuba
|
568729989333193ff38c26ac68604aa8ba9b490b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
docs/intro_sql_basic.ipynb
|
bakera81/siuba
|
568729989333193ff38c26ac68604aa8ba9b490b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 29.234138 | 323 | 0.348791 |
[
[
[
"import matplotlib.cbook\n\nimport warnings\nimport plotnine\nwarnings.filterwarnings(module='plotnine*', action='ignore')\nwarnings.filterwarnings(module='matplotlib*', action='ignore')\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Querying SQL (intro)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Reading in data\n\nIn this tutorial, we'll use the mtcars data ([source](https://stat.ethz.ch/R-manual/R-devel/library/datasets/html/mtcars.html)) that comes packaged with siuba. This data contains information about 32 cars, like their miles per gallon (`mpg`), and number of cylinders (`cyl`). This data in siuba is a pandas DataFrame.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from siuba.data import mtcars\n\nmtcars.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"First, we'll use sqlalchemy, and the pandas method `create_engine` to copy the data into a sqlite table.\nOnce we have that, `siuba` can use a class called `LazyTbl` to connect to the table.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sqlalchemy import create_engine\nfrom siuba.sql import LazyTbl\n\n# copy in to sqlite\nengine = create_engine(\"sqlite:///:memory:\")\nmtcars.to_sql(\"mtcars\", engine, if_exists = \"replace\")\n\n# connect with siuba\ntbl_mtcars = LazyTbl(engine, \"mtcars\")\n\ntbl_mtcars",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Notice that `siuba` by default prints a glimpse into the current data, along with some extra information about the database we're connected to. However, in this case, there are more than 5 rows of data. In order to get all of it back as a pandas DataFrame we need to `collect()` it.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Connecting to existing database\n\nWhile we use `sqlalchemy.create_engine` to connect to a database in the previous section, `LazyTbl` also accepts a string as its first argument, followed by a table name.\n\nThis is shown below, with placeholder variables, like \"username\" and \"password\". See this [SqlAlchemy doc](https://docs.sqlalchemy.org/en/13/core/engines.html#database-urls) for more.\n\n```python\ntbl = LazyTbl(\n \"postgresql://username:password@localhost:5432/dbname\",\n \"tablename\"\n )\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Collecting data and previewing queries",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from siuba import head, collect, show_query\n\ntbl_mtcars >> head(2) >> collect()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tbl_mtcars >> head(2) >> show_query()",
"SELECT mtcars.\"index\", mtcars.mpg, mtcars.cyl, mtcars.disp, mtcars.hp, mtcars.drat, mtcars.wt, mtcars.qsec, mtcars.vs, mtcars.am, mtcars.gear, mtcars.carb \nFROM mtcars\n LIMIT 2 OFFSET 0\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Basic queries",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"A core goal of `siuba` is to make sure most column operations and methods that work on a pandas DataFrame, also work with a SQL table. As a result, the examples in these docs also work when applied to SQL.\n\nThis is shown below for `filter`, `summarize`, and `mutate`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from siuba import _, filter, select, group_by, summarize, mutate\n\ntbl_mtcars >> filter(_.cyl == 6)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"(tbl_mtcars\n >> group_by(_.cyl)\n >> summarize(avg_mpg = _.mpg.mean())\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tbl_mtcars >> select(_.mpg, _.cyl, _.endswith('t'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tbl_mtcars >> \\\n mutate(feetpg = _.mpg * 5290, inchpg = _.feetpg * 12)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Note that the two SQL implementations supported are postgresql, and sqlite. Support for window and aggregate functions is currently limited.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Diving deeper\n\n**TODO**\n\n* using raw SQL\n* how methods and function calls are translated\n* uses sqlalchemy column objects",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe6693b94d9151f7d5ea3ed87009f92bd42813a
| 13,791 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Cap14/expression-leanguage.ipynb
|
carlos-freitas-gitHub/python-analytics
|
4b55cb2acb3383ded700596c5a856b7e2124f2da
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2020-07-31T20:31:19.000Z
|
2020-07-31T20:31:19.000Z
|
Cap14/expression-leanguage.ipynb
|
carlos-freitas-gitHub/python-analytics
|
4b55cb2acb3383ded700596c5a856b7e2124f2da
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Cap14/expression-leanguage.ipynb
|
carlos-freitas-gitHub/python-analytics
|
4b55cb2acb3383ded700596c5a856b7e2124f2da
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 29.980435 | 639 | 0.50823 |
[
[
[
"## Expressões Regulares\nUma expressão regular é um método formal de se especificar um padrão de texto.\nMais detalhadamente, é uma composição de símbolos, caracteres com funções especiais, que agrupados entre si e com caracteres literais, formam uma sequência, uma expressão,Essa expressão é interpretada como uma regra que indicará sucesso se uma entrada de dados qualquer casar com essa regra ou seja obdecer exatamente a todas as suas condições.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# importando o módulo re(regular expression)\n# Esse módulo fornece operações com expressões regulares (ER)\nimport re",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# lista de termos para busca\nlista_pesquisa = ['informações', 'Negócios']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# texto para o parse\ntexto = 'Existem muitos desafios para o Big Data. O primerio deles é a coleta dos dados, pois fala-se aquie de'\\\n'enormes quantidades sendo geradas em uma taxa maior do que um servidor comum seria capaz de processar e armazenar.'\\\n'O segundo desafio é justamente o de processar essas informações. Com elas então distribuídas, a aplicação deve ser'\\\n'capaz de consumir partes das informações e gerar pequenas quantidades de dados processados, que serão calculados em'\\\n'conjunto depois para criar o resultado final. Outro desafio é a exibição dos resultados, de forma que as informações'\\\n'estejam disponíveis de forma clara para os tomadores de decisão.'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# exemplo básico de Data Mining\nfor item in lista_pesquisa:\n print('Buscando por \"%s\" em :\\n\\n\"%s\"'% (item, texto))\n \n # verificando o termo da pesquisa existe no texto\n if re.search(item, texto):\n print('\\n')\n print('Palavra encontrada. \\n')\n print('\\n')\n else:\n print('\\n')\n print('Palavra não encontrada. \\n')\n print('\\n')",
"Buscando por \"informações\" em :\n\n\"Existem muitos desafios para o Big Data. O primerio deles é a coleta dos dados, pois fala-se aquie deenormes quantidades sendo geradas em uma taxa maior do que um servidor comum seria capaz de processar e armazenar.O segundo desafio é justamente o de processar essas informações. Com elas então distribuídas, a aplicação deve sercapaz de consumir partes das informações e gerar pequenas quantidades de dados processados, que serão calculados emconjunto depois para criar o resultado final. Outro desafio é a exibição dos resultados, de forma que as informaçõesestejam disponíveis de forma clara para os tomadores de decisão.\"\n\n\nPalavra encontrada. \n\n\n\nBuscando por \"Negócios\" em :\n\n\"Existem muitos desafios para o Big Data. O primerio deles é a coleta dos dados, pois fala-se aquie deenormes quantidades sendo geradas em uma taxa maior do que um servidor comum seria capaz de processar e armazenar.O segundo desafio é justamente o de processar essas informações. Com elas então distribuídas, a aplicação deve sercapaz de consumir partes das informações e gerar pequenas quantidades de dados processados, que serão calculados emconjunto depois para criar o resultado final. Outro desafio é a exibição dos resultados, de forma que as informaçõesestejam disponíveis de forma clara para os tomadores de decisão.\"\n\n\nPalavra não encontrada. \n\n\n\n"
],
[
"# termo usado para dividir uma string\nsplit_term = '@'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"frase = 'Qual o domínio de alguém com o e-mail: [email protected]'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# dividindo a frase\nre.split(split_term, frase)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def encontrar_padrao(lista, frase):\n \n for item in lista:\n print('Pesquisa na f: %r'% item)\n print(re.findall(item, frase))\n print('\\n')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"frase_padrao = 'zLzL..zzzLLL...zLLLzLLL...LzLz..dzzzzz...zLLLLL'\n\nlista_padroes = [ 'zL*', # z seguido de zero ou mais L\n 'zL+', # z seguido por um ou mais L\n 'zL?', # z seguido por zero ou um L\n 'zL{3}', # z seguido por três L\n 'zL{2, 3}', # z seguido por dois a três L\n ]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"encontrar_padrao(lista_padroes, frase_padrao)",
"Pesquisa na f: 'zL*'\n['zL', 'zL', 'z', 'z', 'zLLL', 'zLLL', 'zLLL', 'zL', 'z', 'z', 'z', 'z', 'z', 'z', 'zLLLLL']\n\n\nPesquisa na f: 'zL+'\n['zL', 'zL', 'zLLL', 'zLLL', 'zLLL', 'zL', 'zLLLLL']\n\n\nPesquisa na f: 'zL?'\n['zL', 'zL', 'z', 'z', 'zL', 'zL', 'zL', 'zL', 'z', 'z', 'z', 'z', 'z', 'z', 'zL']\n\n\nPesquisa na f: 'zL{3}'\n['zLLL', 'zLLL', 'zLLL', 'zLLL']\n\n\nPesquisa na f: 'zL{2, 3}'\n[]\n\n\n"
],
[
"frase = 'Esta é uma string com pontuação. Isso pode ser um problema quando fazemos mineração de dados em busca'\\\n'de padrões! Não seria melhor retirar os sinais ao fim de cada frase?'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# A expressão [^!.?] verifica por valores que não sejam pontuação\n# (!, ., ?) e o sinal de adição (+) verifica se o item aparece pelo menos\n# uma vez. Traduzindo: esta expressão diz: traga apenas as palavras na \n# frase\nre.findall('[^!.? ]+', frase)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"frase = 'Está é uma frase do exemplo. Vamos verificar quais padrões serâo encontradas.'\nlista_padroes = ['[a-z]+', # sequência de letras minúsculas \n '[A-Z]+', # sequência de letras maiúsculas\n '[a-zA-Z]+', # sequência de letras minúculas e maiúsculas\n '[A-Z][a-z]+'] # uma letra maiúscula, seguida de uma letra minúscula",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"encontrar_padrao(lista_padroes, frase)",
"Pesquisa na f: '[a-z]+'\n['st', 'uma', 'frase', 'do', 'exemplo', 'amos', 'verificar', 'quais', 'padr', 'es', 'ser', 'o', 'encontradas']\n\n\nPesquisa na f: '[A-Z]+'\n['E', 'V']\n\n\nPesquisa na f: '[a-zA-Z]+'\n['Est', 'uma', 'frase', 'do', 'exemplo', 'Vamos', 'verificar', 'quais', 'padr', 'es', 'ser', 'o', 'encontradas']\n\n\nPesquisa na f: '[A-Z][a-z]+'\n['Est', 'Vamos']\n\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Escape code\nÉ possível usar códigos específicos para enocntrar padrões nos dados, tais como dígitos, não dígitos, espaços, etc..\n\n<table border=\"1\" class=\"docutils\">\n<colgroup>\n<col width=\"14%\" />\n<col width=\"86%\" />\n</colgroup>\n<thead valign=\"bottom\">\n<tr class=\"row-odd\"><th class=\"head\">Código</th>\n<th class=\"head\">Significado</th>\n</tr>\n</thead>\n<tbody valign=\"top\">\n<tr class=\"row-even\"><td><tt class=\"docutils literal\"><span class=\"pre\">\\d</span></tt></td>\n<td>um dígito</td>\n</tr>\n<tr class=\"row-odd\"><td><tt class=\"docutils literal\"><span class=\"pre\">\\D</span></tt></td>\n<td>um não-dígito</td>\n</tr>\n<tr class=\"row-even\"><td><tt class=\"docutils literal\"><span class=\"pre\">\\s</span></tt></td>\n<td>espaço (tab, espaço, nova linha, etc.)</td>\n</tr>\n<tr class=\"row-odd\"><td><tt class=\"docutils literal\"><span class=\"pre\">\\S</span></tt></td>\n<td>não-espaço</td>\n</tr>\n<tr class=\"row-even\"><td><tt class=\"docutils literal\"><span class=\"pre\">\\w</span></tt></td>\n<td>alfanumérico</td>\n</tr>\n<tr class=\"row-odd\"><td><tt class=\"docutils literal\"><span class=\"pre\">\\W</span></tt></td>\n<td>não-alfanumérico</td>\n</tr>\n</tbody>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# O prefixo r antes da expressão regular evita o pré-processamenta da ER\n# pela linguage. Colocamos o modificador r (do inglês 'raw', crú)\n# imediatamente antes das aspas\nr'\\b'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"'\\b'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"frase = 'Está é uma string com alguns números, como 1287 e um símbolo #hashtag'\n\nlista_padroes = [r'\\d+', # sequência de digitos\n r'\\D+', # sequência de não digitos\n r'\\s+', # sequência de espaços\n r'\\S+', # sequência de não espaços\n r'\\w+', # caracteres alganuméricos\n r'\\W+', # não-alfanúmerico\n ]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"encontrar_padrao(lista_padroes, frase)",
"Pesquisa na f: '\\\\d+'\n['1287']\n\n\nPesquisa na f: '\\\\D+'\n['Está é uma string com alguns números, como ', ' e um símbolo #hashtag']\n\n\nPesquisa na f: '\\\\s+'\n[' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ']\n\n\nPesquisa na f: '\\\\S+'\n['Está', 'é', 'uma', 'string', 'com', 'alguns', 'números,', 'como', '1287', 'e', 'um', 'símbolo', '#hashtag']\n\n\nPesquisa na f: '\\\\w+'\n['Está', 'é', 'uma', 'string', 'com', 'alguns', 'números', 'como', '1287', 'e', 'um', 'símbolo', 'hashtag']\n\n\nPesquisa na f: '\\\\W+'\n[' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ', ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' #']\n\n\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe6720eb06d09cdaf88b2cb3d9b4dd694d24c59
| 21,405 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Climate change LDA_Tourists.ipynb
|
Farshid123/Old-Win-7
|
74296e56fc5d89f908e58858fd1c0e8208a5cbf3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Climate change LDA_Tourists.ipynb
|
Farshid123/Old-Win-7
|
74296e56fc5d89f908e58858fd1c0e8208a5cbf3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Climate change LDA_Tourists.ipynb
|
Farshid123/Old-Win-7
|
74296e56fc5d89f908e58858fd1c0e8208a5cbf3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 37.486865 | 2,715 | 0.564307 |
[
[
[
"with open('Tourists_text2.txt','r') as myfile:\n Tourists_text2=myfile.read().replace('\\n','')\nprint(\"This string has\", len(Tourists_text2), \"characters.\")",
"This string has 183776 characters.\n"
],
[
"type(Tourists_text2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"doc_set = [Tourists_text2]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(doc_set)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(doc_set)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from nltk.tokenize import RegexpTokenizer\ntokenizer = RegexpTokenizer(r'\\w+')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"raw1 = Tourists_text2.lower()\ntokens1 = tokenizer.tokenize(raw1)\nprint(tokens1[:20])",
"['review', 'tweet', 'one', 'of', 'the', 'great', 'drivesthis', 'is', 'often', 'rated', 'one', 'of', 'the', 'most', 'scenic', 'drives', 'in', 'the', 'world', 'and']\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Stop words:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sys\n!{sys.executable} --version",
"Python 3.6.5 :: Anaconda, Inc.\n"
],
[
"!pip install gensim",
"Collecting gensim\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/52/d8/1a966940585bdd828d6ca8bca37d1be81e3e7e2fa1f51098117f15c32a1b/gensim-3.6.0-cp36-cp36m-win_amd64.whl (23.6MB)\nRequirement already satisfied: scipy>=0.18.1 in c:\\users\\papar\\appdata\\local\\continuum\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from gensim) (1.1.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: six>=1.5.0 in c:\\users\\papar\\appdata\\local\\continuum\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from gensim) (1.11.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy>=1.11.3 in c:\\users\\papar\\appdata\\local\\continuum\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from gensim) (1.14.3)\nCollecting smart-open>=1.2.1 (from gensim)\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/4b/1f/6f27e3682124de63ac97a0a5876da6186de6c19410feab66c1543afab055/smart_open-1.7.1.tar.gz\nRequirement already satisfied: boto>=2.32 in c:\\users\\papar\\appdata\\local\\continuum\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from smart-open>=1.2.1->gensim) (2.48.0)\nCollecting bz2file (from smart-open>=1.2.1->gensim)\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/61/39/122222b5e85cd41c391b68a99ee296584b2a2d1d233e7ee32b4532384f2d/bz2file-0.98.tar.gz\nRequirement already satisfied: requests in c:\\users\\papar\\appdata\\local\\continuum\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from smart-open>=1.2.1->gensim) (2.18.4)\nCollecting boto3 (from smart-open>=1.2.1->gensim)\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/7b/c8/9f4489d72515dfdcd798a71fbebb885820ec60491f92da25045d3b3b5d12/boto3-1.9.7-py2.py3-none-any.whl (128kB)\nRequirement already satisfied: chardet<3.1.0,>=3.0.2 in c:\\users\\papar\\appdata\\local\\continuum\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from requests->smart-open>=1.2.1->gensim) (3.0.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: idna<2.7,>=2.5 in c:\\users\\papar\\appdata\\local\\continuum\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from requests->smart-open>=1.2.1->gensim) (2.6)\nRequirement already satisfied: urllib3<1.23,>=1.21.1 in c:\\users\\papar\\appdata\\local\\continuum\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from requests->smart-open>=1.2.1->gensim) (1.22)\nRequirement already satisfied: certifi>=2017.4.17 in c:\\users\\papar\\appdata\\local\\continuum\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from requests->smart-open>=1.2.1->gensim) (2018.4.16)\nCollecting jmespath<1.0.0,>=0.7.1 (from boto3->smart-open>=1.2.1->gensim)\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/b7/31/05c8d001f7f87f0f07289a5fc0fc3832e9a57f2dbd4d3b0fee70e0d51365/jmespath-0.9.3-py2.py3-none-any.whl\nCollecting botocore<1.13.0,>=1.12.7 (from boto3->smart-open>=1.2.1->gensim)\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/a6/93/25b23c1b853d2a6d5e597eb7ff5b9760f8f7fe98fb4469a6cf1fa9da597d/botocore-1.12.7-py2.py3-none-any.whl (4.7MB)\nCollecting s3transfer<0.2.0,>=0.1.10 (from boto3->smart-open>=1.2.1->gensim)\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/d7/14/2a0004d487464d120c9fb85313a75cd3d71a7506955be458eebfe19a6b1d/s3transfer-0.1.13-py2.py3-none-any.whl (59kB)\nRequirement already satisfied: python-dateutil<3.0.0,>=2.1; python_version >= \"2.7\" in c:\\users\\papar\\appdata\\local\\continuum\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from botocore<1.13.0,>=1.12.7->boto3->smart-open>=1.2.1->gensim) (2.7.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: docutils>=0.10 in c:\\users\\papar\\appdata\\local\\continuum\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from botocore<1.13.0,>=1.12.7->boto3->smart-open>=1.2.1->gensim) (0.14)\nBuilding wheels for collected packages: smart-open, bz2file\n Running setup.py bdist_wheel for smart-open: started\n Running setup.py bdist_wheel for smart-open: finished with status 'done'\n Stored in directory: C:\\Users\\Papar\\AppData\\Local\\pip\\Cache\\wheels\\23\\00\\44\\e5b939f7a80c04e32297dbd6d96fa3065af89ecf57e2b5f89f\n Running setup.py bdist_wheel for bz2file: started\n Running setup.py bdist_wheel for bz2file: finished with status 'done'\n Stored in directory: C:\\Users\\Papar\\AppData\\Local\\pip\\Cache\\wheels\\81\\75\\d6\\e1317bf09bf1af5a30befc2a007869fa6e1f516b8f7c591cb9\nSuccessfully built smart-open bz2file\nInstalling collected packages: bz2file, jmespath, botocore, s3transfer, boto3, smart-open, gensim\nSuccessfully installed boto3-1.9.7 botocore-1.12.7 bz2file-0.98 gensim-3.6.0 jmespath-0.9.3 s3transfer-0.1.13 smart-open-1.7.1\n"
],
[
"!pip install lda",
"Collecting lda\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/fa/fe/98cec39e45411a83430978ea2ad21a47468875013e3c3512a9aef9afc46f/lda-1.1.0-cp36-cp36m-win_amd64.whl (334kB)\nCollecting pbr<4,>=0.6 (from lda)\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/0c/5d/b077dbf309993d52c1d71e6bf6fe443a8029ea215135ebbe0b1b10e7aefc/pbr-3.1.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl (99kB)\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy<2.0,>=1.13.0 in c:\\users\\papar\\appdata\\local\\continuum\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from lda) (1.14.3)\nInstalling collected packages: pbr, lda\nSuccessfully installed lda-1.1.0 pbr-3.1.1\n"
],
[
"!pip install nltk",
"Requirement already satisfied: nltk in c:\\users\\papar\\appdata\\local\\continuum\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (3.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: six in c:\\users\\papar\\appdata\\local\\continuum\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from nltk) (1.11.0)\n"
],
[
"!pip install stop_words",
"Collecting stop_words\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/1c/cb/d58290804b7a4c5daa42abbbe2a93c477ae53e45541b1825e86f0dfaaf63/stop-words-2018.7.23.tar.gz\nBuilding wheels for collected packages: stop-words\n Running setup.py bdist_wheel for stop-words: started\n Running setup.py bdist_wheel for stop-words: finished with status 'done'\n Stored in directory: C:\\Users\\Papar\\AppData\\Local\\pip\\Cache\\wheels\\75\\37\\6a\\2b295e03bd07290f0da95c3adb9a74ba95fbc333aa8b0c7c78\nSuccessfully built stop-words\nInstalling collected packages: stop-words\nSuccessfully installed stop-words-2018.7.23\n"
],
[
"import pip\nimport conda\nimport nltk\nimport lda\nimport lda.datasets\nimport gensim\nfrom nltk.corpus import stopwords",
"C:\\Users\\Papar\\AppData\\Local\\Continuum\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\gensim\\utils.py:1212: UserWarning: detected Windows; aliasing chunkize to chunkize_serial\n warnings.warn(\"detected Windows; aliasing chunkize to chunkize_serial\")\n"
],
[
"from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import stop_words\nfrom stop_words import get_stop_words",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"en_stop = get_stop_words('en')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# remove stop words from tokens\nstopped_tokens1 = [i for i in tokens1 if not i in en_stop]\n\nprint(stopped_tokens1[:20])",
"['review', 'tweet', 'one', 'great', 'drivesthis', 'often', 'rated', 'one', 'scenic', 'drives', 'world', 'certainly', 'one', 'scenic', 've', 'ever', 'taken', 'gorgeous', 'mountains', 'around']\n"
]
],
[
[
"# stemming:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from nltk.stem.porter import PorterStemmer\n\n# Create p_stemmer of class PorterStemmer\np_stemmer = PorterStemmer()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# stem token\nstemmed_stopped_token1= [p_stemmer.stem(i) for i in stopped_tokens1]\n\nprint(stemmed_stopped_token1[:20])",
"['review', 'tweet', 'one', 'great', 'drivesthi', 'often', 'rate', 'one', 'scenic', 'drive', 'world', 'certainli', 'one', 'scenic', 've', 'ever', 'taken', 'gorgeou', 'mountain', 'around']\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Cleaning:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"type(stemmed_stopped_token1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(en_stop)",
"['a', 'about', 'above', 'after', 'again', 'against', 'all', 'am', 'an', 'and', 'any', 'are', \"aren't\", 'as', 'at', 'be', 'because', 'been', 'before', 'being', 'below', 'between', 'both', 'but', 'by', \"can't\", 'cannot', 'could', \"couldn't\", 'did', \"didn't\", 'do', 'does', \"doesn't\", 'doing', \"don't\", 'down', 'during', 'each', 'few', 'for', 'from', 'further', 'had', \"hadn't\", 'has', \"hasn't\", 'have', \"haven't\", 'having', 'he', \"he'd\", \"he'll\", \"he's\", 'her', 'here', \"here's\", 'hers', 'herself', 'him', 'himself', 'his', 'how', \"how's\", 'i', \"i'd\", \"i'll\", \"i'm\", \"i've\", 'if', 'in', 'into', 'is', \"isn't\", 'it', \"it's\", 'its', 'itself', \"let's\", 'me', 'more', 'most', \"mustn't\", 'my', 'myself', 'no', 'nor', 'not', 'of', 'off', 'on', 'once', 'only', 'or', 'other', 'ought', 'our', 'ours', 'ourselves', 'out', 'over', 'own', 'same', \"shan't\", 'she', \"she'd\", \"she'll\", \"she's\", 'should', \"shouldn't\", 'so', 'some', 'such', 'than', 'that', \"that's\", 'the', 'their', 'theirs', 'them', 'themselves', 'then', 'there', \"there's\", 'these', 'they', \"they'd\", \"they'll\", \"they're\", \"they've\", 'this', 'those', 'through', 'to', 'too', 'under', 'until', 'up', 'very', 'was', \"wasn't\", 'we', \"we'd\", \"we'll\", \"we're\", \"we've\", 'were', \"weren't\", 'what', \"what's\", 'when', \"when's\", 'where', \"where's\", 'which', 'while', 'who', \"who's\", 'whom', 'why', \"why's\", 'with', \"won't\", 'would', \"wouldn't\", 'you', \"you'd\", \"you'll\", \"you're\", \"you've\", 'your', 'yours', 'yourself', 'yourselves']\n"
],
[
"import nltk\nfrom nltk.stem.porter import PorterStemmer\n\n# Create p_stemmer of class PorterStemmer\np_stemmer = PorterStemmer()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from gensim import corpora, models\n\ndictionary = corpora.Dictionary()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# LDA Topic Modeling:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Applying these steps on the whole text (stemmed_stopped_token1):",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"texts = []\n\n# loop through document list\nfor i in stemmed_stopped_token1:\n \n # clean and tokenize document string\n raw = i.lower()\n tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(raw)\n\n # remove stop words from tokens\n stopped_tokens = [i for i in tokens if not i in en_stop]\n \n # stem tokens\n stemmed_tokens = [p_stemmer.stem(i) for i in stopped_tokens]\n \n # add tokens to list\n texts.append(stemmed_tokens)\n\n# turn our tokenized documents into a id <-> term dictionary\ndictionary = corpora.Dictionary(texts)\n \n# convert tokenized documents into a document-term matrix\ncorpus = [dictionary.doc2bow(text) for text in texts]\n\n# generate LDA model\nldamodel = gensim.models.ldamodel.LdaModel(corpus, num_topics=10, id2word = dictionary, passes=20)\nprint(ldamodel.print_topics(num_topics=10, num_words=15))",
"[(0, '0.036*\"icefield\" + 0.032*\"trail\" + 0.032*\"inform\" + 0.028*\"place\" + 0.028*\"around\" + 0.025*\"back\" + 0.023*\"nation\" + 0.023*\"athabasca\" + 0.020*\"centr\" + 0.017*\"quit\" + 0.014*\"pretti\" + 0.014*\"short\" + 0.014*\"driver\" + 0.013*\"crowd\" + 0.013*\"vehicl\"'), (1, '0.069*\"warm\" + 0.049*\"wildfir\" + 0.029*\"make\" + 0.026*\"worth\" + 0.026*\"melt\" + 0.025*\"banff\" + 0.024*\"trip\" + 0.018*\"onto\" + 0.018*\"canyon\" + 0.017*\"mani\" + 0.013*\"smoke\" + 0.012*\"pass\" + 0.012*\"wonder\" + 0.012*\"attract\" + 0.012*\"thing\"'), (2, '0.072*\"year\" + 0.064*\"global\" + 0.063*\"get\" + 0.047*\"will\" + 0.028*\"amaz\" + 0.019*\"good\" + 0.017*\"now\" + 0.014*\"know\" + 0.014*\"ticket\" + 0.014*\"sign\" + 0.014*\"start\" + 0.013*\"opportun\" + 0.013*\"give\" + 0.013*\"far\" + 0.012*\"stun\"'), (3, '0.111*\"ice\" + 0.093*\"park\" + 0.081*\"walk\" + 0.051*\"time\" + 0.032*\"peopl\" + 0.031*\"day\" + 0.025*\"even\" + 0.024*\"drive\" + 0.022*\"still\" + 0.020*\"use\" + 0.018*\"sinc\" + 0.016*\"cold\" + 0.016*\"visitor\" + 0.015*\"didn\" + 0.014*\"ride\"'), (4, '0.235*\"glacier\" + 0.075*\"see\" + 0.044*\"climat\" + 0.037*\"tour\" + 0.034*\"go\" + 0.034*\"way\" + 0.026*\"us\" + 0.023*\"road\" + 0.016*\"columbia\" + 0.014*\"explor\" + 0.013*\"close\" + 0.011*\"seen\" + 0.010*\"snow\" + 0.009*\"gone\" + 0.009*\"say\"'), (5, '0.093*\"s\" + 0.027*\"stop\" + 0.025*\"retreat\" + 0.021*\"parkway\" + 0.020*\"ago\" + 0.019*\"last\" + 0.018*\"jasper\" + 0.015*\"took\" + 0.014*\"center\" + 0.014*\"need\" + 0.012*\"river\" + 0.011*\"fire\" + 0.010*\"skywalk\" + 0.010*\"later\" + 0.009*\"small\"'), (6, '0.057*\"visit\" + 0.056*\"bu\" + 0.050*\"one\" + 0.046*\"view\" + 0.043*\"beauti\" + 0.033*\"due\" + 0.023*\"canada\" + 0.021*\"fall\" + 0.021*\"easi\" + 0.020*\"part\" + 0.020*\"want\" + 0.017*\"enjoy\" + 0.017*\"along\" + 0.016*\"actual\" + 0.016*\"big\"'), (7, '0.053*\"hike\" + 0.043*\"area\" + 0.035*\"rece\" + 0.026*\"guid\" + 0.023*\"natur\" + 0.020*\"bit\" + 0.020*\"don\" + 0.019*\"sure\" + 0.017*\"sad\" + 0.014*\"huge\" + 0.013*\"recommend\" + 0.013*\"show\" + 0.012*\"effect\" + 0.012*\"highway\" + 0.012*\"larg\"'), (8, '0.072*\"lake\" + 0.061*\"chang\" + 0.041*\"much\" + 0.031*\"great\" + 0.027*\"water\" + 0.027*\"well\" + 0.026*\"also\" + 0.023*\"mountain\" + 0.023*\"like\" + 0.019*\"flood\" + 0.018*\"rocki\" + 0.017*\"must\" + 0.016*\"littl\" + 0.016*\"2\" + 0.016*\"first\"'), (9, '0.069*\"t\" + 0.068*\"field\" + 0.066*\"can\" + 0.055*\"take\" + 0.046*\"lot\" + 0.044*\"just\" + 0.036*\"experi\" + 0.026*\"realli\" + 0.018*\"tourist\" + 0.018*\"think\" + 0.016*\"love\" + 0.015*\"interest\" + 0.012*\"buse\" + 0.011*\"access\" + 0.011*\"edg\"')]\n"
]
],
[
[
"# End of coding",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe6784602584f2f3b1b9b60d470803f67f166f3
| 231,805 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Week 2/Time Series with Tensorflow/Course_4_Week_4_Lesson_1.ipynb
|
atharvagj-ai/ML-Deep-Learning-Journey
|
c336354ebef7e9a159ae03873fc1612b48aa9161
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Week 2/Time Series with Tensorflow/Course_4_Week_4_Lesson_1.ipynb
|
atharvagj-ai/ML-Deep-Learning-Journey
|
c336354ebef7e9a159ae03873fc1612b48aa9161
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Week 2/Time Series with Tensorflow/Course_4_Week_4_Lesson_1.ipynb
|
atharvagj-ai/ML-Deep-Learning-Journey
|
c336354ebef7e9a159ae03873fc1612b48aa9161
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 133.297872 | 67,138 | 0.705097 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/MoRebaie/Sequences-Time-Series-Prediction-in-Tensorflow/blob/master/Course_4_Week_4_Lesson_1.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pip install tf-nightly-2.0-preview\n",
"Collecting tf-nightly-2.0-preview\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/be/6b/2576cfd094d3aae3f60b115dbd30f201df7e5b51d97572597e9c1c1c7357/tf_nightly_2.0_preview-2.0.0.dev20190817-cp36-cp36m-manylinux2010_x86_64.whl (88.9MB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 88.9MB 51.9MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: grpcio>=1.8.6 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tf-nightly-2.0-preview) (1.15.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy<2.0,>=1.16.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tf-nightly-2.0-preview) (1.16.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: protobuf>=3.6.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tf-nightly-2.0-preview) (3.7.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: google-pasta>=0.1.6 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tf-nightly-2.0-preview) (0.1.7)\nCollecting tensorflow-estimator-2.0-preview (from tf-nightly-2.0-preview)\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/35/7b/1b26beebe6f1b800a043d22f85c74ef3861c915daa33c9ac2d8497f0fd3f/tensorflow_estimator_2.0_preview-1.14.0.dev2019081701-py2.py3-none-any.whl (450kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 450kB 47.6MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: keras-preprocessing>=1.0.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tf-nightly-2.0-preview) (1.1.0)\nCollecting tb-nightly<1.16.0a0,>=1.15.0a0 (from tf-nightly-2.0-preview)\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/98/62/499aa16d23a7a17b3786ecc5efe4a7ccadfc8337cd699f21cca71c8634e8/tb_nightly-1.15.0a20190817-py3-none-any.whl (4.1MB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 4.1MB 40.2MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: termcolor>=1.1.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tf-nightly-2.0-preview) (1.1.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: wrapt>=1.11.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tf-nightly-2.0-preview) (1.11.2)\nCollecting opt-einsum>=2.3.2 (from tf-nightly-2.0-preview)\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/c8/7b/8eeb7a6e0dcb23b49dfb38c33d6a640c7cb2375973ca2f0597725f024c01/opt_einsum-3.0.0.tar.gz (66kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 71kB 32.9MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: absl-py>=0.7.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tf-nightly-2.0-preview) (0.7.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: wheel>=0.26 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tf-nightly-2.0-preview) (0.33.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: six>=1.10.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tf-nightly-2.0-preview) (1.12.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: astor>=0.6.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tf-nightly-2.0-preview) (0.8.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: keras-applications>=1.0.8 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tf-nightly-2.0-preview) (1.0.8)\nRequirement already satisfied: gast>=0.2.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tf-nightly-2.0-preview) (0.2.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: setuptools in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from protobuf>=3.6.1->tf-nightly-2.0-preview) (41.0.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: markdown>=2.6.8 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tb-nightly<1.16.0a0,>=1.15.0a0->tf-nightly-2.0-preview) (3.1.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: werkzeug>=0.11.15 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from tb-nightly<1.16.0a0,>=1.15.0a0->tf-nightly-2.0-preview) (0.15.5)\nRequirement already satisfied: h5py in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from keras-applications>=1.0.8->tf-nightly-2.0-preview) (2.8.0)\nBuilding wheels for collected packages: opt-einsum\n Building wheel for opt-einsum (setup.py) ... \u001b[?25l\u001b[?25hdone\n Created wheel for opt-einsum: filename=opt_einsum-3.0.0-cp36-none-any.whl size=58490 sha256=4afd0b2e200783fefc95eb0c8ba12a6a0310b20c4eb24464fbf459823f895e1f\n Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/a1/82/aa/e6d68e36a66706a69f890a6072793d2b87730572499c626ed8\nSuccessfully built opt-einsum\nInstalling collected packages: tensorflow-estimator-2.0-preview, tb-nightly, opt-einsum, tf-nightly-2.0-preview\nSuccessfully installed opt-einsum-3.0.0 tb-nightly-1.15.0a20190817 tensorflow-estimator-2.0-preview-1.14.0.dev2019081701 tf-nightly-2.0-preview-2.0.0.dev20190817\n"
],
[
"import tensorflow as tf\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nprint(tf.__version__)",
"2.0.0-dev20190817\n"
],
[
"def plot_series(time, series, format=\"-\", start=0, end=None):\n plt.plot(time[start:end], series[start:end], format)\n plt.xlabel(\"Time\")\n plt.ylabel(\"Value\")\n plt.grid(True)\n\ndef trend(time, slope=0):\n return slope * time\n\ndef seasonal_pattern(season_time):\n \"\"\"Just an arbitrary pattern, you can change it if you wish\"\"\"\n return np.where(season_time < 0.4,\n np.cos(season_time * 2 * np.pi),\n 1 / np.exp(3 * season_time))\n\ndef seasonality(time, period, amplitude=1, phase=0):\n \"\"\"Repeats the same pattern at each period\"\"\"\n season_time = ((time + phase) % period) / period\n return amplitude * seasonal_pattern(season_time)\n\ndef noise(time, noise_level=1, seed=None):\n rnd = np.random.RandomState(seed)\n return rnd.randn(len(time)) * noise_level\n\ntime = np.arange(4 * 365 + 1, dtype=\"float32\")\nbaseline = 10\nseries = trend(time, 0.1) \nbaseline = 10\namplitude = 40\nslope = 0.05\nnoise_level = 5\n\n# Create the series\nseries = baseline + trend(time, slope) + seasonality(time, period=365, amplitude=amplitude)\n# Update with noise\nseries += noise(time, noise_level, seed=42)\n\nsplit_time = 1000\ntime_train = time[:split_time]\nx_train = series[:split_time]\ntime_valid = time[split_time:]\nx_valid = series[split_time:]\n\nwindow_size = 20\nbatch_size = 32\nshuffle_buffer_size = 1000",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def windowed_dataset(series, window_size, batch_size, shuffle_buffer):\n series = tf.expand_dims(series, axis=-1)\n ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(series)\n ds = ds.window(window_size + 1, shift=1, drop_remainder=True)\n ds = ds.flat_map(lambda w: w.batch(window_size + 1))\n ds = ds.shuffle(shuffle_buffer)\n ds = ds.map(lambda w: (w[:-1], w[1:]))\n return ds.batch(batch_size).prefetch(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def model_forecast(model, series, window_size):\n ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(series)\n ds = ds.window(window_size, shift=1, drop_remainder=True)\n ds = ds.flat_map(lambda w: w.batch(window_size))\n ds = ds.batch(32).prefetch(1)\n forecast = model.predict(ds)\n return forecast",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tf.keras.backend.clear_session()\ntf.random.set_seed(51)\nnp.random.seed(51)\n\nwindow_size = 30\ntrain_set = windowed_dataset(x_train, window_size, batch_size=128, shuffle_buffer=shuffle_buffer_size)\n\nmodel = tf.keras.models.Sequential([\n tf.keras.layers.Conv1D(filters=32, kernel_size=5,\n strides=1, padding=\"causal\",\n activation=\"relu\",\n input_shape=[None, 1]),\n tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(32, return_sequences=True)),\n tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(32, return_sequences=True)),\n tf.keras.layers.Dense(1),\n tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: x * 200)\n])\nlr_schedule = tf.keras.callbacks.LearningRateScheduler(\n lambda epoch: 1e-8 * 10**(epoch / 20))\noptimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=1e-8, momentum=0.9)\nmodel.compile(loss=tf.keras.losses.Huber(),\n optimizer=optimizer,\n metrics=[\"mae\"])\nhistory = model.fit(train_set, epochs=100, callbacks=[lr_schedule])",
"WARNING: Logging before flag parsing goes to stderr.\nW0817 14:43:49.112814 140651683645312 deprecation.py:323] From /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/tensorflow_core/python/data/util/random_seed.py:58: where (from tensorflow.python.ops.array_ops) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\nInstructions for updating:\nUse tf.where in 2.0, which has the same broadcast rule as np.where\n"
],
[
"plt.semilogx(history.history[\"lr\"], history.history[\"loss\"])\nplt.axis([1e-8, 1e-4, 0, 30])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tf.keras.backend.clear_session()\ntf.random.set_seed(51)\nnp.random.seed(51)\n#batch_size = 16\ndataset = windowed_dataset(x_train, window_size, batch_size, shuffle_buffer_size)\n\nmodel = tf.keras.models.Sequential([\n tf.keras.layers.Conv1D(filters=32, kernel_size=3,\n strides=1, padding=\"causal\",\n activation=\"relu\",\n input_shape=[None, 1]),\n tf.keras.layers.LSTM(32, return_sequences=True),\n tf.keras.layers.LSTM(32, return_sequences=True),\n tf.keras.layers.Dense(1),\n tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: x * 200)\n])\n\noptimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=1e-5, momentum=0.9)\nmodel.compile(loss=tf.keras.losses.Huber(),\n optimizer=optimizer,\n metrics=[\"mae\"])\nhistory = model.fit(dataset,epochs=500)",
"Epoch 1/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 3s 97ms/step - loss: 21.5713 - mae: 22.3311\nEpoch 2/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 8.2302 - mae: 8.7146\nEpoch 3/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 6.6533 - mae: 7.1294\nEpoch 4/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 6.5045 - mae: 6.9897\nEpoch 5/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 5.9441 - mae: 6.4212\nEpoch 6/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 5.5678 - mae: 6.0458\nEpoch 7/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 5.3540 - mae: 5.8331\nEpoch 8/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 5.2692 - mae: 5.7491\nEpoch 9/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 5.2261 - mae: 5.6994\nEpoch 10/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 5.2973 - mae: 5.7732\nEpoch 11/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 5.1711 - mae: 5.6467\nEpoch 12/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 5.0422 - mae: 5.5175\nEpoch 13/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 5.0738 - mae: 5.5545\nEpoch 14/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 5.0245 - mae: 5.5123\nEpoch 15/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 5.0019 - mae: 5.4793\nEpoch 16/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.9367 - mae: 5.4086\nEpoch 17/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.9490 - mae: 5.4333\nEpoch 18/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.8578 - mae: 5.3355\nEpoch 19/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.8529 - mae: 5.3292\nEpoch 20/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.9044 - mae: 5.3778\nEpoch 21/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.7779 - mae: 5.2692\nEpoch 22/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.7478 - mae: 5.2271\nEpoch 23/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.7348 - mae: 5.2154\nEpoch 24/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 27ms/step - loss: 4.6953 - mae: 5.1724\nEpoch 25/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.6803 - mae: 5.1599\nEpoch 26/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.7415 - mae: 5.2134\nEpoch 27/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.6411 - mae: 5.1252\nEpoch 28/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.6818 - mae: 5.1668\nEpoch 29/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.6203 - mae: 5.1008\nEpoch 30/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.6079 - mae: 5.0834\nEpoch 31/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.5816 - mae: 5.0553\nEpoch 32/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.5894 - mae: 5.0634\nEpoch 33/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.5870 - mae: 5.0679\nEpoch 34/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.5519 - mae: 5.0339\nEpoch 35/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.5214 - mae: 4.9959\nEpoch 36/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.5761 - mae: 5.0539\nEpoch 37/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.4975 - mae: 4.9763\nEpoch 38/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.5065 - mae: 4.9893\nEpoch 39/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.4992 - mae: 4.9766\nEpoch 40/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.4990 - mae: 4.9748\nEpoch 41/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.4483 - mae: 4.9287\nEpoch 42/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.5112 - mae: 4.9825\nEpoch 43/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.4474 - mae: 4.9204\nEpoch 44/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.4363 - mae: 4.9159\nEpoch 45/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.5550 - mae: 5.0352\nEpoch 46/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.5455 - mae: 5.0240\nEpoch 47/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.4906 - mae: 4.9639\nEpoch 48/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 27ms/step - loss: 4.3940 - mae: 4.8732\nEpoch 49/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.4096 - mae: 4.8861\nEpoch 50/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.3915 - mae: 4.8717\nEpoch 51/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.3922 - mae: 4.8666\nEpoch 52/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.3620 - mae: 4.8414\nEpoch 53/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.5551 - mae: 5.0258\nEpoch 54/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.3905 - mae: 4.8654\nEpoch 55/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.4021 - mae: 4.8710\nEpoch 56/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.4715 - mae: 4.9460\nEpoch 57/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.3345 - mae: 4.8086\nEpoch 58/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.3924 - mae: 4.8629\nEpoch 59/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.3354 - mae: 4.8124\nEpoch 60/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.3225 - mae: 4.7954\nEpoch 61/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.4221 - mae: 4.8996\nEpoch 62/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.4090 - mae: 4.8842\nEpoch 63/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.3204 - mae: 4.7937\nEpoch 64/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.3316 - mae: 4.8134\nEpoch 65/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.3084 - mae: 4.7846\nEpoch 66/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.3694 - mae: 4.8546\nEpoch 67/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.3277 - mae: 4.8007\nEpoch 68/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.5148 - mae: 4.9905\nEpoch 69/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.4992 - mae: 4.9711\nEpoch 70/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2972 - mae: 4.7700\nEpoch 71/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2938 - mae: 4.7642\nEpoch 72/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.2939 - mae: 4.7700\nEpoch 73/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.3659 - mae: 4.8399\nEpoch 74/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.3751 - mae: 4.8467\nEpoch 75/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.3101 - mae: 4.7824\nEpoch 76/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.2532 - mae: 4.7299\nEpoch 77/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2634 - mae: 4.7371\nEpoch 78/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2616 - mae: 4.7326\nEpoch 79/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.3301 - mae: 4.8043\nEpoch 80/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.2949 - mae: 4.7787\nEpoch 81/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2871 - mae: 4.7619\nEpoch 82/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.2602 - mae: 4.7352\nEpoch 83/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.3676 - mae: 4.8403\nEpoch 84/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.3269 - mae: 4.8035\nEpoch 85/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.4834 - mae: 4.9580\nEpoch 86/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.3806 - mae: 4.8550\nEpoch 87/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.2654 - mae: 4.7399\nEpoch 88/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 27ms/step - loss: 4.3047 - mae: 4.7805\nEpoch 89/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.2364 - mae: 4.7050\nEpoch 90/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.2205 - mae: 4.6976\nEpoch 91/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2344 - mae: 4.7091\nEpoch 92/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2536 - mae: 4.7257\nEpoch 93/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2256 - mae: 4.7021\nEpoch 94/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.2132 - mae: 4.6915\nEpoch 95/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2993 - mae: 4.7733\nEpoch 96/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2388 - mae: 4.7141\nEpoch 97/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2173 - mae: 4.6962\nEpoch 98/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2500 - mae: 4.7213\nEpoch 99/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.3691 - mae: 4.8457\nEpoch 100/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.2805 - mae: 4.7501\nEpoch 101/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.2017 - mae: 4.6726\nEpoch 102/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.2132 - mae: 4.6855\nEpoch 103/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.2168 - mae: 4.6880\nEpoch 104/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.2021 - mae: 4.6775\nEpoch 105/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1984 - mae: 4.6708\nEpoch 106/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.2519 - mae: 4.7263\nEpoch 107/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2615 - mae: 4.7436\nEpoch 108/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.3020 - mae: 4.7743\nEpoch 109/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1901 - mae: 4.6636\nEpoch 110/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.1908 - mae: 4.6678\nEpoch 111/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2039 - mae: 4.6780\nEpoch 112/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.2211 - mae: 4.6967\nEpoch 113/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.2030 - mae: 4.6791\nEpoch 114/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1789 - mae: 4.6531\nEpoch 115/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2250 - mae: 4.7071\nEpoch 116/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.2317 - mae: 4.7054\nEpoch 117/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.1537 - mae: 4.6310\nEpoch 118/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.2181 - mae: 4.6894\nEpoch 119/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1804 - mae: 4.6546\nEpoch 120/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2192 - mae: 4.6939\nEpoch 121/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1953 - mae: 4.6676\nEpoch 122/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1449 - mae: 4.6210\nEpoch 123/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.2087 - mae: 4.6805\nEpoch 124/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.1675 - mae: 4.6423\nEpoch 125/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.1597 - mae: 4.6353\nEpoch 126/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1863 - mae: 4.6614\nEpoch 127/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1782 - mae: 4.6507\nEpoch 128/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1542 - mae: 4.6287\nEpoch 129/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.3117 - mae: 4.7823\nEpoch 130/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.2353 - mae: 4.7060\nEpoch 131/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2768 - mae: 4.7491\nEpoch 132/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.3227 - mae: 4.7983\nEpoch 133/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.3878 - mae: 4.8646\nEpoch 134/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.3604 - mae: 4.8402\nEpoch 135/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1775 - mae: 4.6464\nEpoch 136/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.1568 - mae: 4.6287\nEpoch 137/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1433 - mae: 4.6161\nEpoch 138/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1505 - mae: 4.6301\nEpoch 139/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1916 - mae: 4.6688\nEpoch 140/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2313 - mae: 4.7071\nEpoch 141/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.1763 - mae: 4.6485\nEpoch 142/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1256 - mae: 4.5981\nEpoch 143/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.1266 - mae: 4.5994\nEpoch 144/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1584 - mae: 4.6326\nEpoch 145/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2122 - mae: 4.6892\nEpoch 146/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.1264 - mae: 4.5999\nEpoch 147/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.1322 - mae: 4.6040\nEpoch 148/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1567 - mae: 4.6288\nEpoch 149/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1881 - mae: 4.6592\nEpoch 150/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1555 - mae: 4.6315\nEpoch 151/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.1089 - mae: 4.5843\nEpoch 152/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1346 - mae: 4.6064\nEpoch 153/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.3769 - mae: 4.8562\nEpoch 154/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1794 - mae: 4.6516\nEpoch 155/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2178 - mae: 4.6901\nEpoch 156/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2761 - mae: 4.7481\nEpoch 157/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2064 - mae: 4.6787\nEpoch 158/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1305 - mae: 4.6049\nEpoch 159/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.2047 - mae: 4.6773\nEpoch 160/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1076 - mae: 4.5808\nEpoch 161/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.1691 - mae: 4.6415\nEpoch 162/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1271 - mae: 4.6015\nEpoch 163/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1193 - mae: 4.5932\nEpoch 164/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.0990 - mae: 4.5775\nEpoch 165/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.1944 - mae: 4.6726\nEpoch 166/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.1590 - mae: 4.6349\nEpoch 167/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.0937 - mae: 4.5747\nEpoch 168/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1050 - mae: 4.5758\nEpoch 169/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1271 - mae: 4.5973\nEpoch 170/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1149 - mae: 4.5872\nEpoch 171/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2336 - mae: 4.7127\nEpoch 172/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1305 - mae: 4.6008\nEpoch 173/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1600 - mae: 4.6358\nEpoch 174/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1040 - mae: 4.5783\nEpoch 175/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1085 - mae: 4.5812\nEpoch 176/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1159 - mae: 4.5923\nEpoch 177/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.1316 - mae: 4.6060\nEpoch 178/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1155 - mae: 4.5927\nEpoch 179/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1024 - mae: 4.5782\nEpoch 180/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.3091 - mae: 4.7812\nEpoch 181/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0951 - mae: 4.5665\nEpoch 182/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1088 - mae: 4.5827\nEpoch 183/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 28ms/step - loss: 4.1259 - mae: 4.6018\nEpoch 184/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.2386 - mae: 4.7163\nEpoch 185/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.1245 - mae: 4.5985\nEpoch 186/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0833 - mae: 4.5576\nEpoch 187/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1111 - mae: 4.5845\nEpoch 188/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2368 - mae: 4.7074\nEpoch 189/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1196 - mae: 4.5935\nEpoch 190/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1966 - mae: 4.6668\nEpoch 191/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1399 - mae: 4.6171\nEpoch 192/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.1063 - mae: 4.5787\nEpoch 193/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.1331 - mae: 4.6039\nEpoch 194/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0612 - mae: 4.5393\nEpoch 195/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1710 - mae: 4.6487\nEpoch 196/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1448 - mae: 4.6217\nEpoch 197/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1795 - mae: 4.6543\nEpoch 198/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0882 - mae: 4.5615\nEpoch 199/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0766 - mae: 4.5515\nEpoch 200/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0953 - mae: 4.5684\nEpoch 201/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1192 - mae: 4.5876\nEpoch 202/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.0934 - mae: 4.5674\nEpoch 203/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0621 - mae: 4.5359\nEpoch 204/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1642 - mae: 4.6402\nEpoch 205/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1649 - mae: 4.6362\nEpoch 206/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.1160 - mae: 4.5832\nEpoch 207/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1035 - mae: 4.5770\nEpoch 208/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0679 - mae: 4.5423\nEpoch 209/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1373 - mae: 4.6088\nEpoch 210/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0702 - mae: 4.5429\nEpoch 211/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0804 - mae: 4.5564\nEpoch 212/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0994 - mae: 4.5725\nEpoch 213/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.0494 - mae: 4.5207\nEpoch 214/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0770 - mae: 4.5505\nEpoch 215/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0525 - mae: 4.5250\nEpoch 216/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0686 - mae: 4.5427\nEpoch 217/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.0969 - mae: 4.5738\nEpoch 218/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1102 - mae: 4.5838\nEpoch 219/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0496 - mae: 4.5196\nEpoch 220/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0488 - mae: 4.5194\nEpoch 221/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0642 - mae: 4.5401\nEpoch 222/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0407 - mae: 4.5091\nEpoch 223/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1386 - mae: 4.6058\nEpoch 224/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.2665 - mae: 4.7401\nEpoch 225/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0727 - mae: 4.5455\nEpoch 226/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0868 - mae: 4.5617\nEpoch 227/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1176 - mae: 4.5890\nEpoch 228/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0379 - mae: 4.5100\nEpoch 229/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1014 - mae: 4.5751\nEpoch 230/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0961 - mae: 4.5675\nEpoch 231/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0455 - mae: 4.5169\nEpoch 232/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1084 - mae: 4.5808\nEpoch 233/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0831 - mae: 4.5542\nEpoch 234/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0599 - mae: 4.5300\nEpoch 235/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1663 - mae: 4.6417\nEpoch 236/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1669 - mae: 4.6366\nEpoch 237/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0309 - mae: 4.5077\nEpoch 238/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0439 - mae: 4.5151\nEpoch 239/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1732 - mae: 4.6517\nEpoch 240/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1237 - mae: 4.5991\nEpoch 241/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1104 - mae: 4.5825\nEpoch 242/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.2450 - mae: 4.7184\nEpoch 243/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.0272 - mae: 4.5004\nEpoch 244/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1094 - mae: 4.5807\nEpoch 245/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0535 - mae: 4.5261\nEpoch 246/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.0402 - mae: 4.5110\nEpoch 247/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0479 - mae: 4.5208\nEpoch 248/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0545 - mae: 4.5233\nEpoch 249/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0233 - mae: 4.4970\nEpoch 250/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.0451 - mae: 4.5175\nEpoch 251/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.1133 - mae: 4.5854\nEpoch 252/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0996 - mae: 4.5745\nEpoch 253/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0456 - mae: 4.5196\nEpoch 254/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.0423 - mae: 4.5160\nEpoch 255/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0376 - mae: 4.5094\nEpoch 256/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1218 - mae: 4.5940\nEpoch 257/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1012 - mae: 4.5715\nEpoch 258/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0882 - mae: 4.5635\nEpoch 259/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0529 - mae: 4.5282\nEpoch 260/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0623 - mae: 4.5340\nEpoch 261/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1166 - mae: 4.5952\nEpoch 262/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 27ms/step - loss: 4.1738 - mae: 4.6442\nEpoch 263/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0982 - mae: 4.5741\nEpoch 264/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0744 - mae: 4.5477\nEpoch 265/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.0750 - mae: 4.5469\nEpoch 266/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0795 - mae: 4.5557\nEpoch 267/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0743 - mae: 4.5468\nEpoch 268/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1313 - mae: 4.6060\nEpoch 269/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0621 - mae: 4.5341\nEpoch 270/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0152 - mae: 4.4909\nEpoch 271/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.0364 - mae: 4.5080\nEpoch 272/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0189 - mae: 4.4911\nEpoch 273/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0221 - mae: 4.4914\nEpoch 274/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0385 - mae: 4.5122\nEpoch 275/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0268 - mae: 4.4953\nEpoch 276/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0205 - mae: 4.4922\nEpoch 277/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1437 - mae: 4.6189\nEpoch 278/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.2104 - mae: 4.6858\nEpoch 279/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0518 - mae: 4.5317\nEpoch 280/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0240 - mae: 4.4992\nEpoch 281/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0610 - mae: 4.5352\nEpoch 282/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0289 - mae: 4.5015\nEpoch 283/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0464 - mae: 4.5217\nEpoch 284/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1144 - mae: 4.5863\nEpoch 285/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0361 - mae: 4.5067\nEpoch 286/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.0686 - mae: 4.5402\nEpoch 287/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0429 - mae: 4.5161\nEpoch 288/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0104 - mae: 4.4860\nEpoch 289/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.0193 - mae: 4.4932\nEpoch 290/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.0839 - mae: 4.5564\nEpoch 291/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0939 - mae: 4.5665\nEpoch 292/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1534 - mae: 4.6255\nEpoch 293/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0654 - mae: 4.5369\nEpoch 294/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0524 - mae: 4.5223\nEpoch 295/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.0516 - mae: 4.5271\nEpoch 296/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0298 - mae: 4.5065\nEpoch 297/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1342 - mae: 4.6073\nEpoch 298/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1305 - mae: 4.6046\nEpoch 299/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0830 - mae: 4.5596\nEpoch 300/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1576 - mae: 4.6366\nEpoch 301/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1046 - mae: 4.5792\nEpoch 302/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0253 - mae: 4.4992\nEpoch 303/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0452 - mae: 4.5183\nEpoch 304/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0051 - mae: 4.4789\nEpoch 305/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9927 - mae: 4.4645\nEpoch 306/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0159 - mae: 4.4896\nEpoch 307/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9942 - mae: 4.4693\nEpoch 308/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0167 - mae: 4.4869\nEpoch 309/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9966 - mae: 4.4703\nEpoch 310/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9949 - mae: 4.4665\nEpoch 311/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9952 - mae: 4.4669\nEpoch 312/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.1365 - mae: 4.6121\nEpoch 313/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0959 - mae: 4.5661\nEpoch 314/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0331 - mae: 4.5052\nEpoch 315/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.0052 - mae: 4.4812\nEpoch 316/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0109 - mae: 4.4819\nEpoch 317/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9897 - mae: 4.4612\nEpoch 318/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0269 - mae: 4.5005\nEpoch 319/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0430 - mae: 4.5117\nEpoch 320/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9861 - mae: 4.4570\nEpoch 321/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0172 - mae: 4.4917\nEpoch 322/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0535 - mae: 4.5262\nEpoch 323/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0053 - mae: 4.4762\nEpoch 324/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0417 - mae: 4.5162\nEpoch 325/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.0128 - mae: 4.4847\nEpoch 326/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.0090 - mae: 4.4818\nEpoch 327/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9788 - mae: 4.4523\nEpoch 328/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0096 - mae: 4.4832\nEpoch 329/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.0192 - mae: 4.4999\nEpoch 330/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.1078 - mae: 4.5801\nEpoch 331/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 3.9986 - mae: 4.4720\nEpoch 332/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 3.9671 - mae: 4.4422\nEpoch 333/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9818 - mae: 4.4550\nEpoch 334/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 3.9662 - mae: 4.4416\nEpoch 335/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 27ms/step - loss: 3.9834 - mae: 4.4538\nEpoch 336/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.0790 - mae: 4.5575\nEpoch 337/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 27ms/step - loss: 4.0027 - mae: 4.4765\nEpoch 338/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0174 - mae: 4.4918\nEpoch 339/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9963 - mae: 4.4680\nEpoch 340/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9753 - mae: 4.4477\nEpoch 341/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0478 - mae: 4.5254\nEpoch 342/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.1193 - mae: 4.5888\nEpoch 343/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0111 - mae: 4.4849\nEpoch 344/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0136 - mae: 4.4880\nEpoch 345/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.0467 - mae: 4.5179\nEpoch 346/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.0255 - mae: 4.4997\nEpoch 347/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9754 - mae: 4.4479\nEpoch 348/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9866 - mae: 4.4577\nEpoch 349/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0341 - mae: 4.5050\nEpoch 350/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0599 - mae: 4.5312\nEpoch 351/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9777 - mae: 4.4488\nEpoch 352/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9705 - mae: 4.4446\nEpoch 353/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0149 - mae: 4.4861\nEpoch 354/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9972 - mae: 4.4749\nEpoch 355/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9676 - mae: 4.4397\nEpoch 356/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9931 - mae: 4.4693\nEpoch 357/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9834 - mae: 4.4544\nEpoch 358/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 26ms/step - loss: 4.0412 - mae: 4.5165\nEpoch 359/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0556 - mae: 4.5275\nEpoch 360/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9618 - mae: 4.4327\nEpoch 361/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9568 - mae: 4.4287\nEpoch 362/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9924 - mae: 4.4660\nEpoch 363/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0945 - mae: 4.5656\nEpoch 364/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0828 - mae: 4.5542\nEpoch 365/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0402 - mae: 4.5136\nEpoch 366/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9880 - mae: 4.4640\nEpoch 367/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9760 - mae: 4.4551\nEpoch 368/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0362 - mae: 4.5089\nEpoch 369/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9966 - mae: 4.4665\nEpoch 370/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0161 - mae: 4.4907\nEpoch 371/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9586 - mae: 4.4298\nEpoch 372/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0294 - mae: 4.5031\nEpoch 373/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0043 - mae: 4.4771\nEpoch 374/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9662 - mae: 4.4376\nEpoch 375/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9674 - mae: 4.4423\nEpoch 376/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9468 - mae: 4.4212\nEpoch 377/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9551 - mae: 4.4271\nEpoch 378/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9825 - mae: 4.4545\nEpoch 379/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9662 - mae: 4.4366\nEpoch 380/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9888 - mae: 4.4639\nEpoch 381/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9734 - mae: 4.4476\nEpoch 382/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9713 - mae: 4.4454\nEpoch 383/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9935 - mae: 4.4646\nEpoch 384/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0087 - mae: 4.4808\nEpoch 385/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9686 - mae: 4.4410\nEpoch 386/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9702 - mae: 4.4410\nEpoch 387/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9638 - mae: 4.4354\nEpoch 388/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9989 - mae: 4.4716\nEpoch 389/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0018 - mae: 4.4734\nEpoch 390/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9858 - mae: 4.4602\nEpoch 391/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0451 - mae: 4.5150\nEpoch 392/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9821 - mae: 4.4559\nEpoch 393/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9702 - mae: 4.4433\nEpoch 394/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9948 - mae: 4.4679\nEpoch 395/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9910 - mae: 4.4643\nEpoch 396/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9483 - mae: 4.4216\nEpoch 397/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9599 - mae: 4.4329\nEpoch 398/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9545 - mae: 4.4284\nEpoch 399/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9648 - mae: 4.4386\nEpoch 400/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9712 - mae: 4.4445\nEpoch 401/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0273 - mae: 4.5028\nEpoch 402/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0611 - mae: 4.5379\nEpoch 403/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.0587 - mae: 4.5295\nEpoch 404/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0226 - mae: 4.4977\nEpoch 405/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9926 - mae: 4.4651\nEpoch 406/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0823 - mae: 4.5564\nEpoch 407/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0077 - mae: 4.4809\nEpoch 408/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9590 - mae: 4.4300\nEpoch 409/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9692 - mae: 4.4429\nEpoch 410/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9608 - mae: 4.4322\nEpoch 411/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0644 - mae: 4.5408\nEpoch 412/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9311 - mae: 4.4063\nEpoch 413/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9428 - mae: 4.4134\nEpoch 414/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9437 - mae: 4.4163\nEpoch 415/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9476 - mae: 4.4186\nEpoch 416/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9493 - mae: 4.4222\nEpoch 417/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9524 - mae: 4.4240\nEpoch 418/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 4.0238 - mae: 4.4991\nEpoch 419/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0021 - mae: 4.4715\nEpoch 420/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9564 - mae: 4.4292\nEpoch 421/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9678 - mae: 4.4378\nEpoch 422/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9271 - mae: 4.4005\nEpoch 423/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9455 - mae: 4.4191\nEpoch 424/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9487 - mae: 4.4242\nEpoch 425/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9474 - mae: 4.4225\nEpoch 426/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9697 - mae: 4.4400\nEpoch 427/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9567 - mae: 4.4268\nEpoch 428/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9855 - mae: 4.4539\nEpoch 429/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9258 - mae: 4.3951\nEpoch 430/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9313 - mae: 4.4044\nEpoch 431/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9965 - mae: 4.4667\nEpoch 432/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9672 - mae: 4.4386\nEpoch 433/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9392 - mae: 4.4112\nEpoch 434/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9246 - mae: 4.3989\nEpoch 435/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9593 - mae: 4.4326\nEpoch 436/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0861 - mae: 4.5595\nEpoch 437/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9372 - mae: 4.4085\nEpoch 438/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0859 - mae: 4.5614\nEpoch 439/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0033 - mae: 4.4734\nEpoch 440/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9951 - mae: 4.4665\nEpoch 441/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0209 - mae: 4.4907\nEpoch 442/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9835 - mae: 4.4552\nEpoch 443/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9777 - mae: 4.4528\nEpoch 444/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9446 - mae: 4.4164\nEpoch 445/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0076 - mae: 4.4829\nEpoch 446/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9201 - mae: 4.3926\nEpoch 447/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9385 - mae: 4.4082\nEpoch 448/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9293 - mae: 4.4025\nEpoch 449/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9915 - mae: 4.4654\nEpoch 450/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 4.0349 - mae: 4.5045\nEpoch 451/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9769 - mae: 4.4494\nEpoch 452/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9349 - mae: 4.4063\nEpoch 453/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9161 - mae: 4.3901\nEpoch 454/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9246 - mae: 4.3998\nEpoch 455/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0616 - mae: 4.5353\nEpoch 456/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9410 - mae: 4.4148\nEpoch 457/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9188 - mae: 4.3892\nEpoch 458/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9162 - mae: 4.3907\nEpoch 459/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9250 - mae: 4.3980\nEpoch 460/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9503 - mae: 4.4226\nEpoch 461/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 22ms/step - loss: 3.9646 - mae: 4.4349\nEpoch 462/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9841 - mae: 4.4565\nEpoch 463/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9184 - mae: 4.3902\nEpoch 464/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9632 - mae: 4.4372\nEpoch 465/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9412 - mae: 4.4110\nEpoch 466/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9501 - mae: 4.4230\nEpoch 467/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9507 - mae: 4.4245\nEpoch 468/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9540 - mae: 4.4252\nEpoch 469/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9194 - mae: 4.3904\nEpoch 470/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9007 - mae: 4.3746\nEpoch 471/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9774 - mae: 4.4499\nEpoch 472/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9955 - mae: 4.4646\nEpoch 473/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9398 - mae: 4.4094\nEpoch 474/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9176 - mae: 4.3899\nEpoch 475/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9392 - mae: 4.4107\nEpoch 476/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9428 - mae: 4.4137\nEpoch 477/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9576 - mae: 4.4294\nEpoch 478/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9811 - mae: 4.4550\nEpoch 479/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 25ms/step - loss: 3.9513 - mae: 4.4222\nEpoch 480/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0087 - mae: 4.4794\nEpoch 481/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9649 - mae: 4.4411\nEpoch 482/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 4.0385 - mae: 4.5070\nEpoch 483/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9460 - mae: 4.4192\nEpoch 484/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9466 - mae: 4.4196\nEpoch 485/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9439 - mae: 4.4125\nEpoch 486/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9526 - mae: 4.4235\nEpoch 487/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9969 - mae: 4.4710\nEpoch 488/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9530 - mae: 4.4267\nEpoch 489/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9271 - mae: 4.3982\nEpoch 490/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9526 - mae: 4.4266\nEpoch 491/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9411 - mae: 4.4146\nEpoch 492/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9223 - mae: 4.3961\nEpoch 493/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9315 - mae: 4.4021\nEpoch 494/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9126 - mae: 4.3847\nEpoch 495/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9413 - mae: 4.4152\nEpoch 496/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9581 - mae: 4.4310\nEpoch 497/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9280 - mae: 4.4021\nEpoch 498/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 3.9122 - mae: 4.3884\nEpoch 499/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9338 - mae: 4.4042\nEpoch 500/500\n31/31 [==============================] - 1s 24ms/step - loss: 3.9186 - mae: 4.3922\n"
],
[
"rnn_forecast = model_forecast(model, series[..., np.newaxis], window_size)\nrnn_forecast = rnn_forecast[split_time - window_size:-1, -1, 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))\nplot_series(time_valid, x_valid)\nplot_series(time_valid, rnn_forecast)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tf.keras.metrics.mean_absolute_error(x_valid, rnn_forecast).numpy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import matplotlib.image as mpimg\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\n#-----------------------------------------------------------\n# Retrieve a list of list results on training and test data\n# sets for each training epoch\n#-----------------------------------------------------------\nmae=history.history['mae']\nloss=history.history['loss']\n\nepochs=range(len(loss)) # Get number of epochs\n\n#------------------------------------------------\n# Plot MAE and Loss\n#------------------------------------------------\nplt.plot(epochs, mae, 'r')\nplt.plot(epochs, loss, 'b')\nplt.title('MAE and Loss')\nplt.xlabel(\"Epochs\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Accuracy\")\nplt.legend([\"MAE\", \"Loss\"])\n\nplt.figure()\n\nepochs_zoom = epochs[200:]\nmae_zoom = mae[200:]\nloss_zoom = loss[200:]\n\n#------------------------------------------------\n# Plot Zoomed MAE and Loss\n#------------------------------------------------\nplt.plot(epochs_zoom, mae_zoom, 'r')\nplt.plot(epochs_zoom, loss_zoom, 'b')\nplt.title('MAE and Loss')\nplt.xlabel(\"Epochs\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Accuracy\")\nplt.legend([\"MAE\", \"Loss\"])\n\nplt.figure()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe6795e4a49e99fc8f0764d66652a93d3490fe5
| 4,679 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
demo/FSB-IC.ipynb
|
andreamad8/FSB
|
a81593590189fa5ad1cc37c5857f974effd9750a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 53 |
2021-10-11T03:24:14.000Z
|
2022-03-30T15:17:23.000Z
|
demo/FSB-IC.ipynb
|
andreamad8/FSB
|
a81593590189fa5ad1cc37c5857f974effd9750a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-12-26T22:48:38.000Z
|
2022-01-15T18:05:32.000Z
|
demo/FSB-IC.ipynb
|
andreamad8/FSB
|
a81593590189fa5ad1cc37c5857f974effd9750a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2022-01-27T09:07:39.000Z
|
2022-03-04T08:58:23.000Z
| 55.702381 | 1,748 | 0.662107 |
[
[
[
"from utils.utils import load_model\nfrom prompts.generic_prompt import load_prefix, generate_response_interactive, select_prompt_interactive\nfrom prompts.generic_prompt_parser import load_prefix as load_prefix_parse\nfrom prompts.image_chat import convert_sample_to_shot_IC_prefix, convert_sample_to_shot_IC_inference\nfrom IPython.display import Image\nimport random\nimport torch\nimport pprint\npp = pprint.PrettyPrinter(indent=4)\nargs = type('', (), {})()\nargs.multigpu = False\ndevice = 4\n\n## To use GPT-Jumbo (178B) set this to true and input your api-key\n## Visit https://studio.ai21.com/account for more info\n## AI21 provides 10K tokens per day, so you can try only for few turns\napi = False\napi_key = ''",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Image(filename='https://hips.hearstapps.com/hmg-prod.s3.amazonaws.com/images/dog-puppy-on-garden-royalty-free-image-1586966191.jpg?crop=1.00xw:0.669xh;0,0.190xh&resize=980:*') ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe68161454d305b1726a106781ee97ea18970a1
| 10,462 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
practical_examples/03_bokeh/03 - Data Sources and Transformations.ipynb
|
teije01/course-material
|
a7336ac5bbbe7040abc5e3d18622b44b5b3f92b1
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2018-11-30T21:16:31.000Z
|
2022-03-28T14:47:19.000Z
|
practical_examples/03_bokeh/03 - Data Sources and Transformations.ipynb
|
teije01/course-material
|
a7336ac5bbbe7040abc5e3d18622b44b5b3f92b1
|
[
"MIT"
] | 6 |
2019-11-20T15:29:59.000Z
|
2021-05-04T11:31:27.000Z
|
practical_examples/03_bokeh/03 - Data Sources and Transformations.ipynb
|
MAMBA-python/course-material
|
8bbfcee7076878d83007d2e628cdd08c20e153b3
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2019-11-26T06:48:39.000Z
|
2020-05-25T16:31:27.000Z
| 30.324638 | 508 | 0.577423 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
cbe68f76c5555caf2d61d0446b58970d2dc62c43
| 1,372 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
my_notebook.ipynb
|
khosseini1130/MyProject.jl
|
4883e2d8f738a06bcee9e87330282ec35554a59e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
my_notebook.ipynb
|
khosseini1130/MyProject.jl
|
4883e2d8f738a06bcee9e87330282ec35554a59e
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2022-03-14T02:36:49.000Z
|
2022-03-14T02:36:49.000Z
|
my_notebook.ipynb
|
khosseini1130/MyProject.jl
|
4883e2d8f738a06bcee9e87330282ec35554a59e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 18.052632 | 80 | 0.502187 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
cbe6a3e80cd26810b216fa7c0f78dd54f84218e1
| 76,539 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
biobb_wf_amber_md_setup/notebooks/mdsetup_lig/biobb_amber_complex_setup_notebook.ipynb
|
bioexcel/biobb_wf_amber_md_setup
|
8bcda75405183a84476acd7ba733e4cb666ce397
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
biobb_wf_amber_md_setup/notebooks/mdsetup_lig/biobb_amber_complex_setup_notebook.ipynb
|
bioexcel/biobb_wf_amber_md_setup
|
8bcda75405183a84476acd7ba733e4cb666ce397
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2021-06-30T08:33:41.000Z
|
2021-06-30T08:33:41.000Z
|
biobb_wf_amber_md_setup/notebooks/mdsetup_lig/biobb_amber_complex_setup_notebook.ipynb
|
bioexcel/biobb_wf_amber_md_setup
|
8bcda75405183a84476acd7ba733e4cb666ce397
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 40.220179 | 1,261 | 0.588406 |
[
[
[
"# Protein-ligand complex MD Setup tutorial using BioExcel Building Blocks (biobb) \n### --***AmberTools package version***--\n**Based on the [MDWeb](http://mmb.irbbarcelona.org/MDWeb2/) [Amber FULL MD Setup tutorial](https://mmb.irbbarcelona.org/MDWeb2/help.php?id=workflows#AmberWorkflowFULL)**\n\n***\nThis tutorial aims to illustrate the process of **setting up a simulation system** containing a **protein in complex with a ligand**, step by step, using the **BioExcel Building Blocks library (biobb)** wrapping the **AmberTools** utility from the **AMBER package**. The particular example used is the **T4 lysozyme** protein (PDB code [3HTB](https://www.rcsb.org/structure/3HTB)) with two residue modifications ***L99A/M102Q*** complexed with the small ligand **2-propylphenol** (3-letter code [JZ4](https://www.rcsb.org/ligand/JZ4)). \n***\n\n## Settings\n\n### Biobb modules used\n\n - [biobb_io](https://github.com/bioexcel/biobb_io): Tools to fetch biomolecular data from public databases.\n - [biobb_amber](https://github.com/bioexcel/biobb_amber): Tools to setup and run Molecular Dynamics simulations with AmberTools.\n - [biobb_structure_utils](https://github.com/bioexcel/biobb_structure_utils): Tools to modify or extract information from a PDB structure file.\n - [biobb_analysis](https://github.com/bioexcel/biobb_analysis): Tools to analyse Molecular Dynamics trajectories.\n - [biobb_chemistry](https://github.com/bioexcel/biobb_chemistry): Tools to to perform chemical conversions.\n \n### Auxiliar libraries used\n\n - [nb_conda_kernels](https://github.com/Anaconda-Platform/nb_conda_kernels): Enables a Jupyter Notebook or JupyterLab application in one conda environment to access kernels for Python, R, and other languages found in other environments.\n - [nglview](http://nglviewer.org/#nglview): Jupyter/IPython widget to interactively view molecular structures and trajectories in notebooks.\n - [ipywidgets](https://github.com/jupyter-widgets/ipywidgets): Interactive HTML widgets for Jupyter notebooks and the IPython kernel.\n - [plotly](https://plot.ly/python/offline/): Python interactive graphing library integrated in Jupyter notebooks.\n - [simpletraj](https://github.com/arose/simpletraj): Lightweight coordinate-only trajectory reader based on code from GROMACS, MDAnalysis and VMD.\n\n### Conda Installation and Launch\n\n```console\ngit clone https://github.com/bioexcel/biobb_wf_amber_md_setup.git\ncd biobb_wf_amber_md_setup\nconda env create -f conda_env/environment.yml\nconda activate biobb_AMBER_MDsetup_tutorials\njupyter-nbextension enable --py --user widgetsnbextension\njupyter-nbextension enable --py --user nglview\njupyter-notebook biobb_wf_amber_md_setup/notebooks/mdsetup_lig/biobb_amber_complex_setup_notebook.ipynb\n``` \n\n***\n## Pipeline steps\n 1. [Input Parameters](#input)\n 2. [Fetching PDB Structure](#fetch)\n 3. [Preparing PDB file for AMBER](#pdb4amber)\n 4. [Create ligand system topology](#ligtop)\n 5. [Create Protein-Ligand Complex System Topology](#top)\n 6. [Energetically Minimize the Structure](#minv)\n 7. [Create Solvent Box and Solvating the System](#box)\n 8. [Adding Ions](#ions)\n 9. [Energetically Minimize the System](#min)\n 10. [Heating the System](#heating)\n 11. [Equilibrate the System (NVT)](#nvt)\n 12. [Equilibrate the System (NPT)](#npt)\n 13. [Free Molecular Dynamics Simulation](#free)\n 14. [Post-processing and Visualizing Resulting 3D Trajectory](#post)\n 15. [Output Files](#output)\n 16. [Questions & Comments](#questions)\n \n***\n<img src=\"https://bioexcel.eu/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Bioexcell_logo_1080px_transp.png\" alt=\"Bioexcel2 logo\"\n\ttitle=\"Bioexcel2 logo\" width=\"400\" />\n***\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id=\"input\"></a>\n## Input parameters\n**Input parameters** needed:\n - **pdbCode**: PDB code of the protein structure (e.g. 3HTB)\n - **ligandCode**: 3-letter code of the ligand (e.g. JZ4)\n - **mol_charge**: Charge of the ligand (e.g. 0)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import nglview\nimport ipywidgets\nimport plotly\nfrom plotly import subplots\nimport plotly.graph_objs as go\n\npdbCode = \"3htb\"\nligandCode = \"JZ4\"\nmol_charge = 0",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"fetch\"></a>\n***\n## Fetching PDB structure\nDownloading **PDB structure** with the **protein molecule** from the RCSB PDB database.<br>\nAlternatively, a **PDB file** can be used as starting structure. <br>\nStripping from the **downloaded structure** any **crystallographic water** molecule or **heteroatom**. <br>\n***\n**Building Blocks** used:\n - [pdb](https://biobb-io.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api.html#module-api.pdb) from **biobb_io.api.pdb**\n - [remove_pdb_water](https://biobb-structure-utils.readthedocs.io/en/latest/utils.html#module-utils.remove_pdb_water) from **biobb_structure_utils.utils.remove_pdb_water**\n - [remove_ligand](https://biobb-structure-utils.readthedocs.io/en/latest/utils.html#module-utils.remove_ligand) from **biobb_structure_utils.utils.remove_ligand**\n***",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_io.api.pdb import pdb\n\n# Create properties dict and inputs/outputs\ndownloaded_pdb = pdbCode+'.pdb'\n\nprop = {\n 'pdb_code': pdbCode,\n 'filter': False\n}\n\n#Create and launch bb\npdb(output_pdb_path=downloaded_pdb,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Show protein\nview = nglview.show_structure_file(downloaded_pdb)\nview.clear_representations()\nview.add_representation(repr_type='cartoon', selection='protein', color='sstruc')\nview.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick', radius='0.1', selection='water')\nview.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick', radius='0.5', selection='ligand')\nview.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick', radius='0.5', selection='ion')\nview._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['','600px'])\nview",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_structure_utils.utils.remove_pdb_water import remove_pdb_water\n\n# Create properties dict and inputs/outputs\nnowat_pdb = pdbCode+'.nowat.pdb'\n\n#Create and launch bb\nremove_pdb_water(input_pdb_path=downloaded_pdb,\n output_pdb_path=nowat_pdb)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_structure_utils.utils.remove_ligand import remove_ligand\n\n# Removing PO4 ligands:\n\n# Create properties dict and inputs/outputs\nnopo4_pdb = pdbCode+'.noPO4.pdb'\n\nprop = {\n 'ligand' : 'PO4'\n}\n\n#Create and launch bb\nremove_ligand(input_structure_path=nowat_pdb,\n output_structure_path=nopo4_pdb,\n properties=prop)\n\n# Removing BME ligand:\n\n# Create properties dict and inputs/outputs\nnobme_pdb = pdbCode+'.noBME.pdb'\n\nprop = {\n 'ligand' : 'BME'\n}\n\n#Create and launch bb\nremove_ligand(input_structure_path=nopo4_pdb,\n output_structure_path=nobme_pdb,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Visualizing 3D structure",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Show protein\nview = nglview.show_structure_file(nobme_pdb)\nview.clear_representations()\nview.add_representation(repr_type='cartoon', selection='protein', color='sstruc')\nview.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick', radius='0.5', selection='hetero')\nview._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['','600px'])\nview",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"pdb4amber\"></a>\n***\n## Preparing PDB file for AMBER\nBefore starting a **protein MD setup**, it is always strongly recommended to take a look at the initial structure and try to identify important **properties** and also possible **issues**. These properties and issues can be serious, as for example the definition of **disulfide bridges**, the presence of a **non-standard aminoacids** or **ligands**, or **missing residues**. Other **properties** and **issues** might not be so serious, but they still need to be addressed before starting the **MD setup process**. **Missing hydrogen atoms**, presence of **alternate atomic location indicators** or **inserted residue codes** (see [PDB file format specification](https://www.wwpdb.org/documentation/file-format-content/format33/sect9.html#ATOM)) are examples of these not so crucial characteristics. Please visit the [AMBER tutorial: Building Protein Systems in Explicit Solvent](http://ambermd.org/tutorials/basic/tutorial7/index.php) for more examples. **AmberTools** utilities from **AMBER MD package** contain a tool able to analyse **PDB files** and clean them for further usage, especially with the **AmberTools LEaP program**: the **pdb4amber tool**. The next step of the workflow is running this tool to analyse our **input PDB structure**.<br>\n\nFor the particular **T4 Lysosyme** example, the most important property that is identified by the **pdb4amber** utility is the presence of **disulfide bridges** in the structure. Those are marked changing the residue names **from CYS to CYX**, which is the code that **AMBER force fields** use to distinguish between cysteines forming or not forming **disulfide bridges**. This will be used in the following step to correctly form a **bond** between these cysteine residues. \n\nWe invite you to check what the tool does with different, more complex structures (e.g. PDB code [6N3V](https://www.rcsb.org/structure/6N3V)). \n\n***\n**Building Blocks** used:\n - [pdb4amber_run](https://biobb-amber.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pdb4amber.html#pdb4amber-pdb4amber-run-module) from **biobb_amber.pdb4amber.pdb4amber_run**\n***",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.pdb4amber.pdb4amber_run import pdb4amber_run\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_pdb4amber_path = 'structure.pdb4amber.pdb'\n\n# Create and launch bb\npdb4amber_run(input_pdb_path=nobme_pdb,\n output_pdb_path=output_pdb4amber_path,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"ligtop\"></a>\n***\n## Create ligand system topology\n**Building AMBER topology** corresponding to the ligand structure.<br>\nForce field used in this tutorial step is **amberGAFF**: [General AMBER Force Field](http://ambermd.org/antechamber/gaff.html), designed for rational drug design.<br>\n- [Step 1](#ligandTopologyStep1): Extract **ligand structure**.\n- [Step 2](#ligandTopologyStep2): Add **hydrogen atoms** if missing.\n- [Step 3](#ligandTopologyStep3): **Energetically minimize the system** with the new hydrogen atoms. \n- [Step 4](#ligandTopologyStep4): Generate **ligand topology** (parameters). \n***\n**Building Blocks** used:\n - [ExtractHeteroAtoms](https://biobb-structure-utils.readthedocs.io/en/latest/utils.html#module-utils.extract_heteroatoms) from **biobb_structure_utils.utils.extract_heteroatoms**\n - [ReduceAddHydrogens](https://biobb-chemistry.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ambertools.html#module-ambertools.reduce_add_hydrogens) from **biobb_chemistry.ambertools.reduce_add_hydrogens**\n - [BabelMinimize](https://biobb-chemistry.readthedocs.io/en/latest/babelm.html#module-babelm.babel_minimize) from **biobb_chemistry.babelm.babel_minimize** \n - [AcpypeParamsAC](https://biobb-chemistry.readthedocs.io/en/latest/acpype.html#module-acpype.acpype_params_ac) from **biobb_chemistry.acpype.acpype_params_ac** \n***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id=\"ligandTopologyStep1\"></a>\n### Step 1: Extract **Ligand structure**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create Ligand system topology, STEP 1\n# Extracting Ligand JZ4\n# Import module\nfrom biobb_structure_utils.utils.extract_heteroatoms import extract_heteroatoms\n\n# Create properties dict and inputs/outputs\nligandFile = ligandCode+'.pdb'\n\nprop = {\n 'heteroatoms' : [{\"name\": \"JZ4\"}]\n}\n\nextract_heteroatoms(input_structure_path=output_pdb4amber_path,\n output_heteroatom_path=ligandFile,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"ligandTopologyStep2\"></a>\n### Step 2: Add **hydrogen atoms**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create Ligand system topology, STEP 2\n# Reduce_add_hydrogens: add Hydrogen atoms to a small molecule (using Reduce tool from Ambertools package)\n# Import module\nfrom biobb_chemistry.ambertools.reduce_add_hydrogens import reduce_add_hydrogens\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_reduce_h = ligandCode+'.reduce.H.pdb' \n\nprop = {\n 'nuclear' : 'true'\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nreduce_add_hydrogens(input_path=ligandFile,\n output_path=output_reduce_h,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"ligandTopologyStep3\"></a>\n### Step 3: **Energetically minimize the system** with the new hydrogen atoms. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create Ligand system topology, STEP 3\n# Babel_minimize: Structure energy minimization of a small molecule after being modified adding hydrogen atoms\n# Import module\nfrom biobb_chemistry.babelm.babel_minimize import babel_minimize\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_babel_min = ligandCode+'.H.min.mol2' \n\nprop = {\n 'method' : 'sd',\n 'criteria' : '1e-10',\n 'force_field' : 'GAFF'\n}\n\n\n# Create and launch bb\nbabel_minimize(input_path=output_reduce_h,\n output_path=output_babel_min,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Visualizing 3D structures\nVisualizing the small molecule generated **PDB structures** using **NGL**: \n- **Original Ligand Structure** (Left)\n- **Ligand Structure with hydrogen atoms added** (with Reduce program) (Center)\n- **Ligand Structure with hydrogen atoms added** (with Reduce program), **energy minimized** (with Open Babel) (Right) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Show different structures generated (for comparison)\n\nview1 = nglview.show_structure_file(ligandFile)\nview1.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick')\nview1._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['350px','400px'])\nview1.camera='orthographic'\nview1\nview2 = nglview.show_structure_file(output_reduce_h)\nview2.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick')\nview2._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['350px','400px'])\nview2.camera='orthographic'\nview2\nview3 = nglview.show_structure_file(output_babel_min)\nview3.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick')\nview3._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['350px','400px'])\nview3.camera='orthographic'\nview3\nipywidgets.HBox([view1, view2, view3])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"ligandTopologyStep4\"></a>\n### Step 4: Generate **ligand topology** (parameters).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create Ligand system topology, STEP 4\n# Acpype_params_gmx: Generation of topologies for AMBER with ACPype\n# Import module\nfrom biobb_chemistry.acpype.acpype_params_ac import acpype_params_ac\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_acpype_inpcrd = ligandCode+'params.inpcrd'\noutput_acpype_frcmod = ligandCode+'params.frcmod'\noutput_acpype_lib = ligandCode+'params.lib'\noutput_acpype_prmtop = ligandCode+'params.prmtop'\noutput_acpype = ligandCode+'params'\n\nprop = {\n 'basename' : output_acpype,\n 'charge' : mol_charge\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nacpype_params_ac(input_path=output_babel_min, \n output_path_inpcrd=output_acpype_inpcrd,\n output_path_frcmod=output_acpype_frcmod,\n output_path_lib=output_acpype_lib,\n output_path_prmtop=output_acpype_prmtop,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"top\"></a>\n***\n## Create protein-ligand complex system topology\n**Building AMBER topology** corresponding to the protein-ligand complex structure.<br>\n\n*IMPORTANT: the previous pdb4amber building block is changing the proper cysteines residue naming in the PDB file from CYS to CYX so that this step can automatically identify and add the disulfide bonds to the system topology.*<br>\n\nThe **force field** used in this tutorial is [**ff14SB**](https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00255) for the **protein**, an evolution of the **ff99SB** force field with improved accuracy of protein side chains and backbone parameters; and the [**gaff**](https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20035) force field for the small molecule. **Water** molecules type used in this tutorial is [**tip3p**](https://doi.org/10.1021/jp003020w).<br>\nAdding **side chain atoms** and **hydrogen atoms** if missing. Forming **disulfide bridges** according to the info added in the previous step. <br>\n\n*NOTE: From this point on, the **protein-ligand complex structure and topology** generated can be used in a regular MD setup.*\n\nGenerating three output files: \n- **AMBER structure** (PDB file)\n- **AMBER topology** (AMBER [Parmtop](https://ambermd.org/FileFormats.php#topology) file)\n- **AMBER coordinates** (AMBER [Coordinate/Restart](https://ambermd.org/FileFormats.php#restart) file) \n***\n**Building Blocks** used:\n - [leap_gen_top](https://biobb-amber.readthedocs.io/en/latest/leap.html#module-leap.leap_gen_top) from **biobb_amber.leap.leap_gen_top**\n***",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.leap.leap_gen_top import leap_gen_top\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_pdb_path = 'structure.leap.pdb'\noutput_top_path = 'structure.leap.top'\noutput_crd_path = 'structure.leap.crd'\n\nprop = {\n \"forcefield\" : [\"protein.ff14SB\",\"gaff\"]\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nleap_gen_top(input_pdb_path=output_pdb4amber_path,\n input_lib_path=output_acpype_lib,\n input_frcmod_path=output_acpype_frcmod,\n output_pdb_path=output_pdb_path,\n output_top_path=output_top_path,\n output_crd_path=output_crd_path,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Visualizing 3D structure\nVisualizing the **PDB structure** using **NGL**. <br>\nTry to identify the differences between the structure generated for the **system topology** and the **original one** (e.g. hydrogen atoms). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import nglview\nimport ipywidgets\n\n# Show protein\nview = nglview.show_structure_file(output_pdb_path)\nview.clear_representations()\nview.add_representation(repr_type='cartoon', selection='protein', opacity='0.4')\nview.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick', selection='protein')\nview.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick', radius='0.5', selection='JZ4')\nview._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['','600px'])\nview",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"minv\"></a>\n## Energetically minimize the structure\n\n**Energetically minimize** the **protein-ligand complex structure** (in vacuo) using the **sander tool** from the **AMBER MD package**. This step is **relaxing the structure**, usually **constrained**, especially when coming from an X-ray **crystal structure**. <br/>\n\nThe **miminization process** is done in two steps:\n- [Step 1](#minv_1): **Hydrogen** minimization, applying **position restraints** (50 Kcal/mol.$Å^{2}$) to the **protein heavy atoms**.\n- [Step 2](#minv_2): **System** minimization, with **no restraints**.\n***\n**Building Blocks** used:\n - [sander_mdrun](https://biobb-amber.readthedocs.io/en/latest/sander.html#module-sander.sander_mdrun) from **biobb_amber.sander.sander_mdrun**\n - [process_minout](https://biobb-amber.readthedocs.io/en/latest/process.html#module-process.process_minout) from **biobb_amber.process.process_minout**\n***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id=\"minv_1\"></a>\n### Step 1: Minimize Hydrogens\n**Hydrogen** minimization, applying **position restraints** (50 Kcal/mol.$Å^{2}$) to the **protein heavy atoms**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.sander.sander_mdrun import sander_mdrun\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_h_min_traj_path = 'sander.h_min.x'\noutput_h_min_rst_path = 'sander.h_min.rst'\noutput_h_min_log_path = 'sander.h_min.log'\n\nprop = {\n 'simulation_type' : \"min_vacuo\",\n \"mdin\" : { \n 'maxcyc' : 500,\n 'ntpr' : 5,\n 'ntr' : 1,\n 'restraintmask' : '\\\":*&!@H=\\\"',\n 'restraint_wt' : 50.0\n }\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nsander_mdrun(input_top_path=output_top_path,\n input_crd_path=output_crd_path,\n input_ref_path=output_crd_path,\n output_traj_path=output_h_min_traj_path,\n output_rst_path=output_h_min_rst_path,\n output_log_path=output_h_min_log_path,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Checking Energy Minimization results\nChecking **energy minimization** results. Plotting **potential energy** along time during the **minimization process**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.process.process_minout import process_minout\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_h_min_dat_path = 'sander.h_min.energy.dat'\n\nprop = {\n \"terms\" : ['ENERGY']\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nprocess_minout(input_log_path=output_h_min_log_path,\n output_dat_path=output_h_min_dat_path,\n properties=prop) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Read data from file and filter energy values higher than 1000 Kj/mol^-1\nwith open(output_h_min_dat_path,'r') as energy_file:\n x,y = map(\n list,\n zip(*[\n (float(line.split()[0]),float(line.split()[1]))\n for line in energy_file \n if not line.startswith((\"#\",\"@\")) \n if float(line.split()[1]) < 1000 \n ])\n )\n\nplotly.offline.init_notebook_mode(connected=True)\n\nfig = {\n \"data\": [go.Scatter(x=x, y=y)],\n \"layout\": go.Layout(title=\"Energy Minimization\",\n xaxis=dict(title = \"Energy Minimization Step\"),\n yaxis=dict(title = \"Potential Energy kcal/mol\")\n )\n}\n\nplotly.offline.iplot(fig)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"minv_2\"></a>\n### Step 2: Minimize the system\n**System** minimization, with **restraints** only on the **small molecule**, to avoid a possible change in position due to **protein repulsion**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.sander.sander_mdrun import sander_mdrun\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_n_min_traj_path = 'sander.n_min.x'\noutput_n_min_rst_path = 'sander.n_min.rst'\noutput_n_min_log_path = 'sander.n_min.log'\n\nprop = {\n 'simulation_type' : \"min_vacuo\",\n \"mdin\" : { \n 'maxcyc' : 500,\n 'ntpr' : 5,\n 'restraintmask' : '\\\":' + ligandCode + '\\\"',\n 'restraint_wt' : 500.0\n }\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nsander_mdrun(input_top_path=output_top_path,\n input_crd_path=output_h_min_rst_path,\n output_traj_path=output_n_min_traj_path,\n output_rst_path=output_n_min_rst_path,\n output_log_path=output_n_min_log_path,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Checking Energy Minimization results\nChecking **energy minimization** results. Plotting **potential energy** by time during the **minimization process**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.process.process_minout import process_minout\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_n_min_dat_path = 'sander.n_min.energy.dat'\n\nprop = {\n \"terms\" : ['ENERGY']\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nprocess_minout(input_log_path=output_n_min_log_path,\n output_dat_path=output_n_min_dat_path,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Read data from file and filter energy values higher than 1000 Kj/mol^-1\nwith open(output_n_min_dat_path,'r') as energy_file:\n x,y = map(\n list,\n zip(*[\n (float(line.split()[0]),float(line.split()[1]))\n for line in energy_file \n if not line.startswith((\"#\",\"@\")) \n if float(line.split()[1]) < 1000 \n ])\n )\n\nplotly.offline.init_notebook_mode(connected=True)\n\nfig = {\n \"data\": [go.Scatter(x=x, y=y)],\n \"layout\": go.Layout(title=\"Energy Minimization\",\n xaxis=dict(title = \"Energy Minimization Step\"),\n yaxis=dict(title = \"Potential Energy kcal/mol\")\n )\n}\n\nplotly.offline.iplot(fig)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"box\"></a>\n***\n## Create solvent box and solvating the system\nDefine the unit cell for the **protein structure MD system** to fill it with water molecules.<br>\nA **truncated octahedron box** is used to define the unit cell, with a **distance from the protein to the box edge of 9.0 Angstroms**. <br>\nThe solvent type used is the default **TIP3P** water model, a generic 3-point solvent model.\n***\n**Building Blocks** used:\n - [amber_to_pdb](https://biobb-amber.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ambpdb.html#module-ambpdb.amber_to_pdb) from **biobb_amber.ambpdb.amber_to_pdb**\n - [leap_solvate](https://biobb-amber.readthedocs.io/en/latest/leap.html#module-leap.leap_solvate) from **biobb_amber.leap.leap_solvate** \n***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Getting minimized structure\nGetting the result of the **energetic minimization** and converting it to **PDB format** to be then used as input for the **water box generation**. <br/>This is achieved by converting from **AMBER topology + coordinates** files to a **PDB file** using the **ambpdb** tool from the **AMBER MD package**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.ambpdb.amber_to_pdb import amber_to_pdb\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_ambpdb_path = 'structure.ambpdb.pdb'\n\n# Create and launch bb\namber_to_pdb(input_top_path=output_top_path,\n input_crd_path=output_h_min_rst_path,\n output_pdb_path=output_ambpdb_path)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create water box\nDefine the **unit cell** for the **protein-ligand complex structure MD system** and fill it with **water molecules**.<br/>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.leap.leap_solvate import leap_solvate\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_solv_pdb_path = 'structure.solv.pdb'\noutput_solv_top_path = 'structure.solv.parmtop'\noutput_solv_crd_path = 'structure.solv.crd'\n\nprop = {\n \"forcefield\" : [\"protein.ff14SB\",\"gaff\"],\n \"water_type\": \"TIP3PBOX\",\n \"distance_to_molecule\": \"9.0\", \n \"box_type\": \"truncated_octahedron\"\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nleap_solvate(input_pdb_path=output_ambpdb_path,\n input_lib_path=output_acpype_lib,\n input_frcmod_path=output_acpype_frcmod,\n output_pdb_path=output_solv_pdb_path,\n output_top_path=output_solv_top_path,\n output_crd_path=output_solv_crd_path,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"ions\"></a>\n## Adding ions\n\n**Neutralizing** the system and adding an additional **ionic concentration** using the **leap tool** from the **AMBER MD package**. <br/>\nUsing **Sodium (Na+)** and **Chloride (Cl-)** counterions and an **additional ionic concentration** of 150mM.\n***\n**Building Blocks** used:\n - [leap_add_ions](https://biobb-amber.readthedocs.io/en/latest/leap.html#module-leap.leap_add_ions) from **biobb_amber.leap.leap_add_ions**\n***",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.leap.leap_add_ions import leap_add_ions\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_ions_pdb_path = 'structure.ions.pdb'\noutput_ions_top_path = 'structure.ions.parmtop'\noutput_ions_crd_path = 'structure.ions.crd'\n\nprop = {\n \"forcefield\" : [\"protein.ff14SB\",\"gaff\"],\n \"neutralise\" : True,\n \"positive_ions_type\": \"Na+\",\n \"negative_ions_type\": \"Cl-\",\n \"ionic_concentration\" : 150, # 150mM\n \"box_type\": \"truncated_octahedron\"\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nleap_add_ions(input_pdb_path=output_solv_pdb_path,\n input_lib_path=output_acpype_lib,\n input_frcmod_path=output_acpype_frcmod,\n output_pdb_path=output_ions_pdb_path,\n output_top_path=output_ions_top_path,\n output_crd_path=output_ions_crd_path,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Visualizing 3D structure\nVisualizing the **protein-ligand complex system** with the newly added **solvent box** and **counterions** using **NGL**.<br> Note the **truncated octahedron box** filled with **water molecules** surrounding the **protein structure**, as well as the randomly placed **positive** (Na+, blue) and **negative** (Cl-, gray) **counterions**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Show protein\nview = nglview.show_structure_file(output_ions_pdb_path)\nview.clear_representations()\nview.add_representation(repr_type='cartoon', selection='protein')\nview.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick', selection='solvent')\nview.add_representation(repr_type='spacefill', selection='Cl- Na+')\nview._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['','600px'])\nview",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"min\"></a>\n## Energetically minimize the system\n\n**Energetically minimize** the **system** (protein structure + ligand + solvent + ions) using the **sander tool** from the **AMBER MD package**. **Restraining heavy atoms** with a force constant of 15 15 Kcal/mol.$Å^{2}$ to their initial positions.\n\n- [Step 1](#emStep1): Energetically minimize the **system** through 500 minimization cycles.\n- [Step 2](#emStep2): Checking **energy minimization** results. Plotting energy by time during the **minimization** process. \n***\n**Building Blocks** used:\n - [sander_mdrun](https://biobb-amber.readthedocs.io/en/latest/sander.html#module-sander.sander_mdrun) from **biobb_amber.sander.sander_mdrun**\n - [process_minout](https://biobb-amber.readthedocs.io/en/latest/process.html#module-process.process_minout) from **biobb_amber.process.process_minout**\n***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id=\"emStep1\"></a>\n### Step 1: Running Energy Minimization\nThe **minimization** type of the **simulation_type property** contains the main default parameters to run an **energy minimization**:\n\n- imin = 1 ; Minimization flag, perform an energy minimization.\n- maxcyc = 500; The maximum number of cycles of minimization.\n- ntb = 1; Periodic boundaries: constant volume.\n- ntmin = 2; Minimization method: steepest descent.\n\n\nIn this particular example, the method used to run the **energy minimization** is the default **steepest descent**, with a **maximum number of 500 cycles** and **periodic conditions**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.sander.sander_mdrun import sander_mdrun\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_min_traj_path = 'sander.min.x'\noutput_min_rst_path = 'sander.min.rst'\noutput_min_log_path = 'sander.min.log'\n\nprop = {\n \"simulation_type\" : \"minimization\",\n \"mdin\" : { \n 'maxcyc' : 300, # Reducing the number of minimization steps for the sake of time\n 'ntr' : 1, # Overwritting restrain parameter\n 'restraintmask' : '\\\"!:WAT,Cl-,Na+\\\"', # Restraining solute\n 'restraint_wt' : 15.0 # With a force constant of 50 Kcal/mol*A2\n }\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nsander_mdrun(input_top_path=output_ions_top_path,\n input_crd_path=output_ions_crd_path,\n input_ref_path=output_ions_crd_path,\n output_traj_path=output_min_traj_path,\n output_rst_path=output_min_rst_path,\n output_log_path=output_min_log_path,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"emStep2\"></a>\n### Step 2: Checking Energy Minimization results\nChecking **energy minimization** results. Plotting **potential energy** along time during the **minimization process**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.process.process_minout import process_minout\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_dat_path = 'sander.min.energy.dat'\n\nprop = {\n \"terms\" : ['ENERGY']\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nprocess_minout(input_log_path=output_min_log_path,\n output_dat_path=output_dat_path,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Read data from file and filter energy values higher than 1000 Kj/mol^-1\nwith open(output_dat_path,'r') as energy_file:\n x,y = map(\n list,\n zip(*[\n (float(line.split()[0]),float(line.split()[1]))\n for line in energy_file \n if not line.startswith((\"#\",\"@\")) \n if float(line.split()[1]) < 1000 \n ])\n )\n\nplotly.offline.init_notebook_mode(connected=True)\n\nfig = {\n \"data\": [go.Scatter(x=x, y=y)],\n \"layout\": go.Layout(title=\"Energy Minimization\",\n xaxis=dict(title = \"Energy Minimization Step\"),\n yaxis=dict(title = \"Potential Energy kcal/mol\")\n )\n}\n\nplotly.offline.iplot(fig)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"heating\"></a>\n## Heating the system\n\n**Warming up** the **prepared system** using the **sander tool** from the **AMBER MD package**. Going from 0 to the desired **temperature**, in this particular example, 300K. **Solute atoms restrained** (force constant of 10 Kcal/mol). Length 5ps.\n***\n- [Step 1](#heatStep1): Warming up the **system** through 500 MD steps.\n- [Step 2](#heatStep2): Checking results for the **system warming up**. Plotting **temperature** along time during the **heating** process. \n***\n**Building Blocks** used:\n - [sander_mdrun](https://biobb-amber.readthedocs.io/en/latest/sander.html#module-sander.sander_mdrun) from **biobb_amber.sander.sander_mdrun**\n - [process_mdout](https://biobb-amber.readthedocs.io/en/latest/process.html#module-process.process_mdout) from **biobb_amber.process.process_mdout**\n***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id=\"heatStep1\"></a>\n### Step 1: Warming up the system\nThe **heat** type of the **simulation_type property** contains the main default parameters to run a **system warming up**:\n\n- imin = 0; Run MD (no minimization)\n- ntx = 5; Read initial coords and vels from restart file\n- cut = 10.0; Cutoff for non bonded interactions in Angstroms\n- ntr = 0; No restrained atoms\n- ntc = 2; SHAKE for constraining length of bonds involving Hydrogen atoms\n- ntf = 2; Bond interactions involving H omitted\n- ntt = 3; Constant temperature using Langevin dynamics\n- ig = -1; Seed for pseudo-random number generator\n- ioutfm = 1; Write trajectory in netcdf format\n- iwrap = 1; Wrap coords into primary box\n- nstlim = 5000; Number of MD steps \n- dt = 0.002; Time step (in ps)\n- tempi = 0.0; Initial temperature (0 K)\n- temp0 = 300.0; Final temperature (300 K)\n- irest = 0; No restart from previous simulation\n- ntb = 1; Periodic boundary conditions at constant volume\n- gamma_ln = 1.0; Collision frequency for Langevin dynamics (in 1/ps)\n\nIn this particular example, the **heating** of the system is done in **2500 steps** (5ps) and is going **from 0K to 300K** (note that the number of steps has been reduced in this tutorial, for the sake of time). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.sander.sander_mdrun import sander_mdrun\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_heat_traj_path = 'sander.heat.netcdf'\noutput_heat_rst_path = 'sander.heat.rst'\noutput_heat_log_path = 'sander.heat.log'\n\nprop = {\n \"simulation_type\" : \"heat\",\n \"mdin\" : { \n 'nstlim' : 2500, # Reducing the number of steps for the sake of time (5ps)\n 'ntr' : 1, # Overwritting restrain parameter\n 'restraintmask' : '\\\"!:WAT,Cl-,Na+\\\"', # Restraining solute\n 'restraint_wt' : 10.0 # With a force constant of 10 Kcal/mol*A2\n }\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nsander_mdrun(input_top_path=output_ions_top_path,\n input_crd_path=output_min_rst_path,\n input_ref_path=output_min_rst_path,\n output_traj_path=output_heat_traj_path,\n output_rst_path=output_heat_rst_path,\n output_log_path=output_heat_log_path,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"heatStep2\"></a>\n### Step 2: Checking results from the system warming up\nChecking **system warming up** output. Plotting **temperature** along time during the **heating process**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.process.process_mdout import process_mdout\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_dat_heat_path = 'sander.md.temp.dat'\n\nprop = {\n \"terms\" : ['TEMP']\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nprocess_mdout(input_log_path=output_heat_log_path,\n output_dat_path=output_dat_heat_path,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Read data from file and filter energy values higher than 1000 Kj/mol^-1\nwith open(output_dat_heat_path,'r') as energy_file:\n x,y = map(\n list,\n zip(*[\n (float(line.split()[0]),float(line.split()[1]))\n for line in energy_file \n if not line.startswith((\"#\",\"@\")) \n if float(line.split()[1]) < 1000 \n ])\n )\n\nplotly.offline.init_notebook_mode(connected=True)\n\nfig = {\n \"data\": [go.Scatter(x=x, y=y)],\n \"layout\": go.Layout(title=\"Heating process\",\n xaxis=dict(title = \"Heating Step (ps)\"),\n yaxis=dict(title = \"Temperature (K)\")\n )\n}\n\nplotly.offline.iplot(fig)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"nvt\"></a>\n***\n## Equilibrate the system (NVT)\nEquilibrate the **protein-ligand complex system** in **NVT ensemble** (constant Number of particles, Volume and Temperature). Protein **heavy atoms** will be restrained using position restraining forces: movement is permitted, but only after overcoming a substantial energy penalty. The utility of position restraints is that they allow us to equilibrate our solvent around our protein, without the added variable of structural changes in the protein.\n\n- [Step 1](#eqNVTStep1): Equilibrate the **protein system** with **NVT** ensemble.\n- [Step 2](#eqNVTStep2): Checking **NVT Equilibration** results. Plotting **system temperature** by time during the **NVT equilibration** process. \n***\n**Building Blocks** used:\n - [sander_mdrun](https://biobb-amber.readthedocs.io/en/latest/sander.html#module-sander.sander_mdrun) from **biobb_amber.sander.sander_mdrun**\n - [process_mdout](https://biobb-amber.readthedocs.io/en/latest/process.html#module-process.process_mdout) from **biobb_amber.process.process_mdout** \n***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id=\"eqNVTStep1\"></a>\n### Step 1: Equilibrating the system (NVT)\nThe **nvt** type of the **simulation_type property** contains the main default parameters to run a **system equilibration in NVT ensemble**:\n\n- imin = 0; Run MD (no minimization)\n- ntx = 5; Read initial coords and vels from restart file\n- cut = 10.0; Cutoff for non bonded interactions in Angstroms\n- ntr = 0; No restrained atoms\n- ntc = 2; SHAKE for constraining length of bonds involving Hydrogen atoms\n- ntf = 2; Bond interactions involving H omitted\n- ntt = 3; Constant temperature using Langevin dynamics\n- ig = -1; Seed for pseudo-random number generator\n- ioutfm = 1; Write trajectory in netcdf format\n- iwrap = 1; Wrap coords into primary box\n- nstlim = 5000; Number of MD steps \n- dt = 0.002; Time step (in ps)\n- irest = 1; Restart previous simulation\n- ntb = 1; Periodic boundary conditions at constant volume\n- gamma_ln = 5.0; Collision frequency for Langevin dynamics (in 1/ps)\n\nIn this particular example, the **NVT equilibration** of the system is done in **500 steps** (note that the number of steps has been reduced in this tutorial, for the sake of time). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.sander.sander_mdrun import sander_mdrun\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_nvt_traj_path = 'sander.nvt.netcdf'\noutput_nvt_rst_path = 'sander.nvt.rst'\noutput_nvt_log_path = 'sander.nvt.log'\n\nprop = {\n \"simulation_type\" : 'nvt',\n \"mdin\" : { \n 'nstlim' : 500, # Reducing the number of steps for the sake of time (1ps)\n 'ntr' : 1, # Overwritting restrain parameter\n 'restraintmask' : '\\\"!:WAT,Cl-,Na+ & !@H=\\\"', # Restraining solute heavy atoms\n 'restraint_wt' : 5.0 # With a force constant of 5 Kcal/mol*A2\n }\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nsander_mdrun(input_top_path=output_ions_top_path,\n input_crd_path=output_heat_rst_path,\n input_ref_path=output_heat_rst_path,\n output_traj_path=output_nvt_traj_path,\n output_rst_path=output_nvt_rst_path,\n output_log_path=output_nvt_log_path,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"eqNVTStep2\"></a>\n### Step 2: Checking NVT Equilibration results\nChecking **NVT Equilibration** results. Plotting **system temperature** by time during the NVT equilibration process. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.process.process_mdout import process_mdout\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_dat_nvt_path = 'sander.md.nvt.temp.dat'\n\nprop = {\n \"terms\" : ['TEMP']\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nprocess_mdout(input_log_path=output_nvt_log_path,\n output_dat_path=output_dat_nvt_path,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Read data from file and filter energy values higher than 1000 Kj/mol^-1\nwith open(output_dat_nvt_path,'r') as energy_file:\n x,y = map(\n list,\n zip(*[\n (float(line.split()[0]),float(line.split()[1]))\n for line in energy_file \n if not line.startswith((\"#\",\"@\")) \n if float(line.split()[1]) < 1000 \n ])\n )\n\nplotly.offline.init_notebook_mode(connected=True)\n\nfig = {\n \"data\": [go.Scatter(x=x, y=y)],\n \"layout\": go.Layout(title=\"NVT equilibration\",\n xaxis=dict(title = \"Equilibration Step (ps)\"),\n yaxis=dict(title = \"Temperature (K)\")\n )\n}\n\nplotly.offline.iplot(fig)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"npt\"></a>\n***\n## Equilibrate the system (NPT)\nEquilibrate the **protein-ligand complex system** in **NPT ensemble** (constant Number of particles, Pressure and Temperature). Protein **heavy atoms** will be restrained using position restraining forces: movement is permitted, but only after overcoming a substantial energy penalty. The utility of position restraints is that they allow us to equilibrate our solvent around our protein, without the added variable of structural changes in the protein.\n\n- [Step 1](#eqNPTStep1): Equilibrate the **protein system** with **NPT** ensemble.\n- [Step 2](#eqNPTStep2): Checking **NPT Equilibration** results. Plotting **system pressure and density** by time during the **NVT equilibration** process. \n***\n**Building Blocks** used:\n - [sander_mdrun](https://biobb-amber.readthedocs.io/en/latest/sander.html#module-sander.sander_mdrun) from **biobb_amber.sander.sander_mdrun**\n - [process_mdout](https://biobb-amber.readthedocs.io/en/latest/process.html#module-process.process_mdout) from **biobb_amber.process.process_mdout** \n***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id=\"eqNPTStep1\"></a>\n### Step 1: Equilibrating the system (NPT)\nThe **npt** type of the **simulation_type property** contains the main default parameters to run a **system equilibration in NPT ensemble**:\n\n- imin = 0; Run MD (no minimization)\n- ntx = 5; Read initial coords and vels from restart file\n- cut = 10.0; Cutoff for non bonded interactions in Angstroms\n- ntr = 0; No restrained atoms\n- ntc = 2; SHAKE for constraining length of bonds involving Hydrogen atoms\n- ntf = 2; Bond interactions involving H omitted\n- ntt = 3; Constant temperature using Langevin dynamics\n- ig = -1; Seed for pseudo-random number generator\n- ioutfm = 1; Write trajectory in netcdf format\n- iwrap = 1; Wrap coords into primary box\n- nstlim = 5000; Number of MD steps \n- dt = 0.002; Time step (in ps)\n- irest = 1; Restart previous simulation\n- gamma_ln = 5.0; Collision frequency for Langevin dynamics (in 1/ps)\n- pres0 = 1.0; Reference pressure\n- ntp = 1; Constant pressure dynamics: md with isotropic position scaling\n- taup = 2.0; Pressure relaxation time (in ps)\n\nIn this particular example, the **NPT equilibration** of the system is done in **500 steps** (note that the number of steps has been reduced in this tutorial, for the sake of time). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.sander.sander_mdrun import sander_mdrun\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_npt_traj_path = 'sander.npt.netcdf'\noutput_npt_rst_path = 'sander.npt.rst'\noutput_npt_log_path = 'sander.npt.log'\n\nprop = {\n \"simulation_type\" : 'npt',\n \"mdin\" : { \n 'nstlim' : 500, # Reducing the number of steps for the sake of time (1ps)\n 'ntr' : 1, # Overwritting restrain parameter\n 'restraintmask' : '\\\"!:WAT,Cl-,Na+ & !@H=\\\"', # Restraining solute heavy atoms\n 'restraint_wt' : 2.5 # With a force constant of 2.5 Kcal/mol*A2\n }\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nsander_mdrun(input_top_path=output_ions_top_path,\n input_crd_path=output_nvt_rst_path,\n input_ref_path=output_nvt_rst_path,\n output_traj_path=output_npt_traj_path,\n output_rst_path=output_npt_rst_path,\n output_log_path=output_npt_log_path,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"eqNPTStep2\"></a>\n### Step 2: Checking NPT Equilibration results\nChecking **NPT Equilibration** results. Plotting **system pressure and density** by time during the **NPT equilibration** process. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.process.process_mdout import process_mdout\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_dat_npt_path = 'sander.md.npt.dat'\n\nprop = {\n \"terms\" : ['PRES','DENSITY']\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nprocess_mdout(input_log_path=output_npt_log_path,\n output_dat_path=output_dat_npt_path,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Read pressure and density data from file \nwith open(output_dat_npt_path,'r') as pd_file:\n x,y,z = map(\n list,\n zip(*[\n (float(line.split()[0]),float(line.split()[1]),float(line.split()[2]))\n for line in pd_file \n if not line.startswith((\"#\",\"@\")) \n ])\n )\n\nplotly.offline.init_notebook_mode(connected=True)\n\ntrace1 = go.Scatter(\n x=x,y=y\n)\ntrace2 = go.Scatter(\n x=x,y=z\n)\n\nfig = subplots.make_subplots(rows=1, cols=2, print_grid=False)\n\nfig.append_trace(trace1, 1, 1)\nfig.append_trace(trace2, 1, 2)\n\nfig['layout']['xaxis1'].update(title='Time (ps)')\nfig['layout']['xaxis2'].update(title='Time (ps)')\nfig['layout']['yaxis1'].update(title='Pressure (bar)')\nfig['layout']['yaxis2'].update(title='Density (Kg*m^-3)')\n\nfig['layout'].update(title='Pressure and Density during NPT Equilibration')\nfig['layout'].update(showlegend=False)\n\nplotly.offline.iplot(fig)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"free\"></a>\n***\n## Free Molecular Dynamics Simulation\nUpon completion of the **two equilibration phases (NVT and NPT)**, the system is now well-equilibrated at the desired temperature and pressure. The **position restraints** can now be released. The last step of the **protein** MD setup is a short, **free MD simulation**, to ensure the robustness of the system. \n- [Step 1](#mdStep1): Run short MD simulation of the **protein system**.\n- [Step 2](#mdStep2): Checking results for the final step of the setup process, the **free MD run**. Plotting **Root Mean Square deviation (RMSd)** and **Radius of Gyration (Rgyr)** by time during the **free MD run** step.\n***\n**Building Blocks** used:\n - [sander_mdrun](https://biobb-amber.readthedocs.io/en/latest/sander.html#module-sander.sander_mdrun) from **biobb_amber.sander.sander_mdrun**\n - [process_mdout](https://biobb-amber.readthedocs.io/en/latest/process.html#module-process.process_mdout) from **biobb_amber.process.process_mdout** \n - [cpptraj_rms](https://biobb-analysis.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ambertools.html#module-ambertools.cpptraj_rms) from **biobb_analysis.cpptraj.cpptraj_rms**\n - [cpptraj_rgyr](https://biobb-analysis.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ambertools.html#module-ambertools.cpptraj_rgyr) from **biobb_analysis.cpptraj.cpptraj_rgyr**\n***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id=\"mdStep1\"></a>\n### Step 1: Creating portable binary run file to run a free MD simulation\n\nThe **free** type of the **simulation_type property** contains the main default parameters to run an **unrestrained MD simulation**:\n\n- imin = 0; Run MD (no minimization)\n- ntx = 5; Read initial coords and vels from restart file\n- cut = 10.0; Cutoff for non bonded interactions in Angstroms\n- ntr = 0; No restrained atoms\n- ntc = 2; SHAKE for constraining length of bonds involving Hydrogen atoms\n- ntf = 2; Bond interactions involving H omitted\n- ntt = 3; Constant temperature using Langevin dynamics\n- ig = -1; Seed for pseudo-random number generator\n- ioutfm = 1; Write trajectory in netcdf format\n- iwrap = 1; Wrap coords into primary box\n- nstlim = 5000; Number of MD steps \n- dt = 0.002; Time step (in ps)\n\nIn this particular example, a short, **5ps-length** simulation (2500 steps) is run, for the sake of time. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import module\nfrom biobb_amber.sander.sander_mdrun import sander_mdrun\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_free_traj_path = 'sander.free.netcdf'\noutput_free_rst_path = 'sander.free.rst'\noutput_free_log_path = 'sander.free.log'\n\nprop = {\n \"simulation_type\" : 'free',\n \"mdin\" : { \n 'nstlim' : 2500, # Reducing the number of steps for the sake of time (5ps)\n 'ntwx' : 500 # Print coords to trajectory every 500 steps (1 ps)\n }\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\nsander_mdrun(input_top_path=output_ions_top_path,\n input_crd_path=output_npt_rst_path,\n output_traj_path=output_free_traj_path,\n output_rst_path=output_free_rst_path,\n output_log_path=output_free_log_path,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"mdStep2\"></a>\n### Step 2: Checking free MD simulation results\n\nChecking results for the final step of the setup process, the **free MD run**. Plotting **Root Mean Square deviation (RMSd)** and **Radius of Gyration (Rgyr)** by time during the **free MD run** step. **RMSd** against the **experimental structure** (input structure of the pipeline) and against the **minimized and equilibrated structure** (output structure of the NPT equilibration step).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# cpptraj_rms: Computing Root Mean Square deviation to analyse structural stability \n# RMSd against minimized and equilibrated snapshot (backbone atoms) \n\n# Import module\nfrom biobb_analysis.ambertools.cpptraj_rms import cpptraj_rms\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_rms_first = pdbCode+'_rms_first.dat'\n\nprop = {\n 'mask': 'backbone',\n 'reference': 'first'\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\ncpptraj_rms(input_top_path=output_ions_top_path,\n input_traj_path=output_free_traj_path,\n output_cpptraj_path=output_rms_first,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# cpptraj_rms: Computing Root Mean Square deviation to analyse structural stability \n# RMSd against experimental structure (backbone atoms) \n\n# Import module\nfrom biobb_analysis.ambertools.cpptraj_rms import cpptraj_rms\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_rms_exp = pdbCode+'_rms_exp.dat'\n\nprop = {\n 'mask': 'backbone',\n 'reference': 'experimental'\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\ncpptraj_rms(input_top_path=output_ions_top_path,\n input_traj_path=output_free_traj_path,\n output_cpptraj_path=output_rms_exp,\n input_exp_path=output_pdb_path, \n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Read RMS vs first snapshot data from file \nwith open(output_rms_first,'r') as rms_first_file:\n x,y = map(\n list,\n zip(*[\n (float(line.split()[0]),float(line.split()[1]))\n for line in rms_first_file \n if not line.startswith((\"#\",\"@\")) \n ])\n )\n\n# Read RMS vs experimental structure data from file \nwith open(output_rms_exp,'r') as rms_exp_file:\n x2,y2 = map(\n list,\n zip(*[\n (float(line.split()[0]),float(line.split()[1]))\n for line in rms_exp_file\n if not line.startswith((\"#\",\"@\")) \n ])\n )\n \ntrace1 = go.Scatter(\n x = x,\n y = y,\n name = 'RMSd vs first'\n)\n\ntrace2 = go.Scatter(\n x = x,\n y = y2,\n name = 'RMSd vs exp'\n)\n\ndata = [trace1, trace2]\n\nplotly.offline.init_notebook_mode(connected=True)\n\nfig = {\n \"data\": data,\n \"layout\": go.Layout(title=\"RMSd during free MD Simulation\",\n xaxis=dict(title = \"Time (ps)\"),\n yaxis=dict(title = \"RMSd (Angstrom)\")\n )\n}\n\nplotly.offline.iplot(fig)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# cpptraj_rgyr: Computing Radius of Gyration to measure the protein compactness during the free MD simulation \n\n# Import module\nfrom biobb_analysis.ambertools.cpptraj_rgyr import cpptraj_rgyr\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_rgyr = pdbCode+'_rgyr.dat'\n\nprop = {\n 'mask': 'backbone'\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\ncpptraj_rgyr(input_top_path=output_ions_top_path,\n input_traj_path=output_free_traj_path,\n output_cpptraj_path=output_rgyr,\n properties=prop)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Read Rgyr data from file \nwith open(output_rgyr,'r') as rgyr_file:\n x,y = map(\n list,\n zip(*[\n (float(line.split()[0]),float(line.split()[1]))\n for line in rgyr_file \n if not line.startswith((\"#\",\"@\")) \n ])\n )\n\nplotly.offline.init_notebook_mode(connected=True)\n\nfig = {\n \"data\": [go.Scatter(x=x, y=y)],\n \"layout\": go.Layout(title=\"Radius of Gyration\",\n xaxis=dict(title = \"Time (ps)\"),\n yaxis=dict(title = \"Rgyr (Angstrom)\")\n )\n}\n\nplotly.offline.iplot(fig)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"post\"></a>\n***\n## Post-processing and Visualizing resulting 3D trajectory\nPost-processing and Visualizing the **protein system** MD setup **resulting trajectory** using **NGL**\n- [Step 1](#ppStep1): *Imaging* the resulting trajectory, **stripping out water molecules and ions** and **correcting periodicity issues**.\n- [Step 2](#ppStep3): Visualizing the *imaged* trajectory using the *dry* structure as a **topology**. \n***\n**Building Blocks** used:\n - [cpptraj_image](https://biobb-analysis.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ambertools.html#module-ambertools.cpptraj_image) from **biobb_analysis.cpptraj.cpptraj_image** \n***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id=\"ppStep1\"></a>\n### Step 1: *Imaging* the resulting trajectory.\nStripping out **water molecules and ions** and **correcting periodicity issues** ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# cpptraj_image: \"Imaging\" the resulting trajectory\n# Removing water molecules and ions from the resulting structure\n\n# Import module\nfrom biobb_analysis.ambertools.cpptraj_image import cpptraj_image\n\n# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs\noutput_imaged_traj = pdbCode+'_imaged_traj.trr'\n\nprop = {\n 'mask': 'solute',\n 'format': 'trr'\n}\n\n# Create and launch bb\ncpptraj_image(input_top_path=output_ions_top_path,\n input_traj_path=output_free_traj_path,\n output_cpptraj_path=output_imaged_traj,\n properties=prop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"ppStep2\"></a>\n### Step 2: Visualizing the generated dehydrated trajectory.\nUsing the **imaged trajectory** (output of the [Post-processing step 1](#ppStep1)) with the **dry structure** (output of",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Show trajectory\nview = nglview.show_simpletraj(nglview.SimpletrajTrajectory(output_imaged_traj, output_ambpdb_path), gui=True)\nview.clear_representations()\nview.add_representation('cartoon', color='sstruc')\nview.add_representation('licorice', selection='JZ4', color='element', radius=1)\nview",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"output\"></a>\n## Output files\n\nImportant **Output files** generated:\n - {{output_ions_pdb_path}}: **System structure** of the MD setup protocol. Structure generated during the MD setup and used in the MD simulation. With hydrogen atoms, solvent box and counterions. \n - {{output_free_traj_path}}: **Final trajectory** of the MD setup protocol.\n - {{output_free_rst_path}}: **Final checkpoint file**, with information about the state of the simulation. It can be used to **restart** or **continue** a MD simulation.\n - {{output_ions_top_path}}: **Final topology** of the MD system in AMBER Parm7 format.\n\n**Analysis** (MD setup check) output files generated:\n - {{output_rms_first}}: **Root Mean Square deviation (RMSd)** against **minimized and equilibrated structure** of the final **free MD run step**.\n - {{output_rms_exp}}: **Root Mean Square deviation (RMSd)** against **experimental structure** of the final **free MD run step**.\n - {{output_rgyr}}: **Radius of Gyration** of the final **free MD run step** of the **setup pipeline**.\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"***\n<a id=\"questions\"></a>\n\n## Questions & Comments\n\nQuestions, issues, suggestions and comments are really welcome!\n\n* GitHub issues:\n * [https://github.com/bioexcel/biobb](https://github.com/bioexcel/biobb)\n\n* BioExcel forum:\n * [https://ask.bioexcel.eu/c/BioExcel-Building-Blocks-library](https://ask.bioexcel.eu/c/BioExcel-Building-Blocks-library)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe6aaad786acbeb312e444bd2eaede2f707cea0
| 293,784 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
license_recognition.ipynb
|
chayandeokar/SUMMER_TASK_task-8
|
0d6df84a4e217b555f250b923c48118331372dd6
|
[
"OLDAP-2.3"
] | null | null | null |
license_recognition.ipynb
|
chayandeokar/SUMMER_TASK_task-8
|
0d6df84a4e217b555f250b923c48118331372dd6
|
[
"OLDAP-2.3"
] | null | null | null |
license_recognition.ipynb
|
chayandeokar/SUMMER_TASK_task-8
|
0d6df84a4e217b555f250b923c48118331372dd6
|
[
"OLDAP-2.3"
] | 2 |
2021-07-05T16:58:55.000Z
|
2021-07-05T18:13:22.000Z
| 475.378641 | 199,432 | 0.927351 |
[
[
[
"# Object Recognition using CNN model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport cv2\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#detecting license plate on the vehicle\nplateCascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier('indian_license_plate.xml')\n#detect the plate and return car + plate image\ndef plate_detect(img):\n plateImg = img.copy()\n roi = img.copy()\n plateRect = plateCascade.detectMultiScale(plateImg,scaleFactor = 1.2, minNeighbors = 7)\n for (x,y,w,h) in plateRect:\n roi_ = roi[y:y+h, x:x+w, :]\n plate_part = roi[y:y+h, x:x+w, :]\n cv2.rectangle(plateImg,(x+2,y),(x+w-3, y+h-5),(0,255,0),3)\n return plateImg, plate_part",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#normal function to display \ndef display_img(img):\n img_ = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)\n plt.imshow(img_)\n plt.show()\n#test image is used for detecting plate\ninputImg = cv2.imread('car.jpg')\ninpImg, plate = plate_detect(inputImg)\ndisplay_img(inpImg)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"display_img(plate)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Now we are taking every letter of it",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def find_contours(dimensions, img) :\n\n #finding all contours in the image using \n #retrieval mode: RETR_TREE\n #contour approximation method: CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE\n cntrs, _ = cv2.findContours(img.copy(), cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)\n\n #Approx dimensions of the contours\n lower_width = dimensions[0]\n upper_width = dimensions[1]\n lower_height = dimensions[2]\n upper_height = dimensions[3]\n \n #Check largest 15 contours for license plate character respectively\n cntrs = sorted(cntrs, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)[:15]\n \n ci = cv2.imread('contour.jpg')\n \n x_cntr_list = []\n target_contours = []\n img_res = []\n for cntr in cntrs :\n #detecting contour in binary image and returns the coordinates of rectangle enclosing it\n intX, intY, intWidth, intHeight = cv2.boundingRect(cntr)\n \n #checking the dimensions of the contour to filter out the characters by contour's size\n if intWidth > lower_width and intWidth < upper_width and intHeight > lower_height and intHeight < upper_height :\n x_cntr_list.append(intX) \n char_copy = np.zeros((44,24))\n #extracting each character using the enclosing rectangle's coordinates.\n char = img[intY:intY+intHeight, intX:intX+intWidth]\n char = cv2.resize(char, (20, 40))\n cv2.rectangle(ci, (intX,intY), (intWidth+intX, intY+intHeight), (50,21,200), 2)\n plt.imshow(ci, cmap='gray')\n char = cv2.subtract(255, char)\n char_copy[2:42, 2:22] = char\n char_copy[0:2, :] = 0\n char_copy[:, 0:2] = 0\n char_copy[42:44, :] = 0\n char_copy[:, 22:24] = 0\n img_res.append(char_copy) # List that stores the character's binary image (unsorted)\n \n #return characters on ascending order with respect to the x-coordinate\n \n plt.show()\n #arbitrary function that stores sorted list of character indeces\n indices = sorted(range(len(x_cntr_list)), key=lambda k: x_cntr_list[k])\n img_res_copy = []\n for idx in indices:\n img_res_copy.append(img_res[idx])# stores character images according to their index\n img_res = np.array(img_res_copy)\n\n return img_res",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def segment_characters(image) :\n\n #pre-processing cropped image of plate\n #threshold: convert to pure b&w with sharpe edges\n #erod: increasing the backgroung black\n #dilate: increasing the char white\n img_lp = cv2.resize(image, (333, 75))\n img_gray_lp = cv2.cvtColor(img_lp, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)\n _, img_binary_lp = cv2.threshold(img_gray_lp, 200, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)\n img_binary_lp = cv2.erode(img_binary_lp, (3,3))\n img_binary_lp = cv2.dilate(img_binary_lp, (3,3))\n\n LP_WIDTH = img_binary_lp.shape[0]\n LP_HEIGHT = img_binary_lp.shape[1]\n img_binary_lp[0:3,:] = 255\n img_binary_lp[:,0:3] = 255\n img_binary_lp[72:75,:] = 255\n img_binary_lp[:,330:333] = 255\n\n #estimations of character contours sizes of cropped license plates\n dimensions = [LP_WIDTH/6,\n LP_WIDTH/2,\n LP_HEIGHT/10,\n 2*LP_HEIGHT/3]\n plt.imshow(img_binary_lp, cmap='gray')\n plt.show()\n cv2.imwrite('contour.jpg',img_binary_lp)\n\n #getting contours\n char_list = find_contours(dimensions, img_binary_lp)\n\n return char_list",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"char = segment_characters(plate)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for i in range(10):\n plt.subplot(1, 10, i+1)\n plt.imshow(char[i], cmap='gray')\n plt.axis('off')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import keras.backend as K\nimport tensorflow as tf\nfrom sklearn.metrics import f1_score \nfrom keras import optimizers\nfrom keras.models import Sequential\nfrom keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator\nfrom keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, MaxPooling2D, Dropout, Conv2D\ntrain_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255, width_shift_range=0.1, height_shift_range=0.1)\npath = 'data/data/'\ntrain_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(\n path+'/train', \n target_size=(28,28), \n batch_size=1,\n class_mode='sparse')\n\nvalidation_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(\n path+'/val', \n target_size=(28,28), \n class_mode='sparse')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#It is the harmonic mean of precision and recall\n#Output range is [0, 1]\n#Works for both multi-class and multi-label classification\ndef f1score(y, y_pred):\n return f1_score(y, tf.math.argmax(y_pred, axis=1), average='micro') \n\ndef custom_f1score(y, y_pred):\n return tf.py_function(f1score, (y, y_pred), tf.double)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"K.clear_session()\nmodel = Sequential()\nmodel.add(Conv2D(16, (22,22), input_shape=(28, 28, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'))\nmodel.add(Conv2D(32, (16,16), input_shape=(28, 28, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'))\nmodel.add(Conv2D(64, (8,8), input_shape=(28, 28, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'))\nmodel.add(Conv2D(64, (4,4), input_shape=(28, 28, 3), activation='relu', padding='same'))\nmodel.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(4, 4)))\nmodel.add(Dropout(0.4))\nmodel.add(Flatten())\nmodel.add(Dense(128, activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(Dense(36, activation='softmax'))\n\nmodel.compile(loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=optimizers.Adam(lr=0.0001), metrics=[custom_f1score])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class stop_training_callback(tf.keras.callbacks.Callback):\n def on_epoch_end(self, epoch, logs={}):\n if(logs.get('val_custom_f1score') > 0.99):\n self.model.stop_training = True",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"batch_size = 1\ncallbacks = [stop_training_callback()]\nmodel.fit_generator(\n train_generator,\n steps_per_epoch = train_generator.samples // batch_size,\n validation_data = validation_generator, \n epochs = 80, verbose=1, callbacks=callbacks)",
"Epoch 1/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 64ms/step - loss: 3.0620 - custom_f1score: 0.1458 - val_loss: 1.7536 - val_custom_f1score: 0.3839\nEpoch 2/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 64ms/step - loss: 1.3608 - custom_f1score: 0.5984 - val_loss: 0.5923 - val_custom_f1score: 0.8036\nEpoch 3/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 63ms/step - loss: 0.6554 - custom_f1score: 0.8009 - val_loss: 0.5468 - val_custom_f1score: 0.8363\nEpoch 4/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 63ms/step - loss: 0.4089 - custom_f1score: 0.8553 - val_loss: 0.5638 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9271\nEpoch 5/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 64ms/step - loss: 0.3245 - custom_f1score: 0.8889 - val_loss: 0.1515 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9345\nEpoch 6/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 64ms/step - loss: 0.2489 - custom_f1score: 0.9225 - val_loss: 0.2837 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9003\nEpoch 7/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 64ms/step - loss: 0.2235 - custom_f1score: 0.9294 - val_loss: 0.2711 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9658\nEpoch 8/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 63ms/step - loss: 0.1664 - custom_f1score: 0.9410 - val_loss: 0.1404 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9449\nEpoch 9/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 64ms/step - loss: 0.1948 - custom_f1score: 0.9410 - val_loss: 0.0715 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9494\nEpoch 10/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 63ms/step - loss: 0.1086 - custom_f1score: 0.9618 - val_loss: 0.0611 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9866\nEpoch 11/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 63ms/step - loss: 0.1234 - custom_f1score: 0.9572 - val_loss: 0.0417 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9420\nEpoch 12/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 63ms/step - loss: 0.1146 - custom_f1score: 0.9606 - val_loss: 0.0669 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9539\nEpoch 13/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 63ms/step - loss: 0.1200 - custom_f1score: 0.9537 - val_loss: 0.0045 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9821\nEpoch 14/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 63ms/step - loss: 0.1442 - custom_f1score: 0.9514 - val_loss: 0.0479 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9688\nEpoch 15/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 54s 63ms/step - loss: 0.0737 - custom_f1score: 0.9711 - val_loss: 0.0037 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9688\nEpoch 16/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 63ms/step - loss: 0.0829 - custom_f1score: 0.9734 - val_loss: 0.0297 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9688\nEpoch 17/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 63ms/step - loss: 0.1086 - custom_f1score: 0.9583 - val_loss: 0.0016 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9732\nEpoch 18/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 63ms/step - loss: 0.0450 - custom_f1score: 0.9850 - val_loss: 6.5763e-04 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9866\nEpoch 19/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 54s 63ms/step - loss: 0.1628 - custom_f1score: 0.9525 - val_loss: 0.0144 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9732\nEpoch 20/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 55s 63ms/step - loss: 0.0704 - custom_f1score: 0.9734 - val_loss: 0.0678 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9851\nEpoch 21/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 54s 63ms/step - loss: 0.0705 - custom_f1score: 0.9734 - val_loss: 0.0427 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9539\nEpoch 22/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 54s 63ms/step - loss: 0.0562 - custom_f1score: 0.9780 - val_loss: 1.2299 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9613\nEpoch 23/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 54s 63ms/step - loss: 0.0827 - custom_f1score: 0.9722 - val_loss: 0.0628 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9762\nEpoch 24/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 54s 63ms/step - loss: 0.0764 - custom_f1score: 0.9688 - val_loss: 0.0886 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9449\nEpoch 25/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 54s 63ms/step - loss: 0.0924 - custom_f1score: 0.9676 - val_loss: 0.0016 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9777\nEpoch 26/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 54s 63ms/step - loss: 0.0452 - custom_f1score: 0.9826 - val_loss: 0.0233 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9777\nEpoch 27/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 54s 63ms/step - loss: 0.1004 - custom_f1score: 0.9676 - val_loss: 0.1289 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9717\nEpoch 28/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 54s 63ms/step - loss: 0.0333 - custom_f1score: 0.9815 - val_loss: 0.0555 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9851\nEpoch 29/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 54s 63ms/step - loss: 0.1074 - custom_f1score: 0.9676 - val_loss: 0.4019 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9449\nEpoch 30/80\n864/864 [==============================] - 54s 63ms/step - loss: 0.0462 - custom_f1score: 0.9780 - val_loss: 0.0076 - val_custom_f1score: 0.9911\n"
],
[
"def fix_dimension(img):\n new_img = np.zeros((28,28,3))\n for i in range(3):\n new_img[:,:,i] = img\n return new_img\n \ndef show_results():\n dic = {}\n characters = '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'\n for i,c in enumerate(characters):\n dic[i] = c\n\n output = []\n for i,ch in enumerate(char): \n img_ = cv2.resize(ch, (28,28), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)\n img = fix_dimension(img_)\n img = img.reshape(1,28,28,3)\n y_ = model.predict_classes(img)[0]\n character = dic[y_] #\n output.append(character) \n \n plate_number = ''.join(output)\n \n return plate_number\n\nfinal_plate = show_results()\nprint(final_plate)",
"DL8CAF5030\n"
],
[
"import requests\nimport xmltodict\nimport json",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_vehicle_info(plate_number):\n r = requests.get(\"http://www.regcheck.org.uk/api/reg.asmx/CheckIndia?RegistrationNumber={0}&username=geerling\".format(str(plate_number)))\n data = xmltodict.parse(r.content)\n jdata = json.dumps(data)\n df = json.loads(jdata)\n df1 = json.loads(df['Vehicle']['vehicleJson'])\n return df1\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"get_vehicle_info(final_plate)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.save('license_plate_character.pkl')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"get_vehicle_info('WB06F5977')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe6b0d2ae4b6b64d45976182b461b31487fd1c6
| 128,317 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
docs/notebook/iraf_specreduce_tutorial.ipynb
|
crawfordsm/specidentify
|
7e108c05d2dd110d0d4a90f977d26389de6ca7b4
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause-No-Nuclear-License-2014",
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 5 |
2019-08-16T13:47:10.000Z
|
2021-05-13T17:40:42.000Z
|
docs/notebook/iraf_specreduce_tutorial.ipynb
|
crawfordsm/specidentify
|
7e108c05d2dd110d0d4a90f977d26389de6ca7b4
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause-No-Nuclear-License-2014",
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 6 |
2018-05-03T17:51:54.000Z
|
2021-03-17T07:03:57.000Z
|
docs/notebook/iraf_specreduce_tutorial.ipynb
|
crawfordsm/specidentify
|
7e108c05d2dd110d0d4a90f977d26389de6ca7b4
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause-No-Nuclear-License-2014",
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 4 |
2019-02-20T15:11:44.000Z
|
2021-01-15T20:46:11.000Z
| 202.074016 | 71,130 | 0.843801 |
[
[
[
"# Optical Data Reduction using Python \n\nby Steve Crawford (South African Astronomical Observatory)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\n%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2",
"The autoreload extension is already loaded. To reload it, use:\n %reload_ext autoreload\n"
]
],
[
[
"In addition to instrument specific python pipelines, there now exists a suite of tools available for general reduction of optical observations. This includes *ccdproc*, an astropy affiliated package for basic CCD reductions. The package is useful from student tutorials for learning CCD reductions to building science-quality reduction pipelines for observatories. In addition, we also present specreduce, a python package for reducing optical spectroscopy. The package includes an interactive graphical users interface for line identification as well as tools for extracting spectra. With this set of tools, pipelines can be built for instruments in relatively short times. While nearly complete, further improvements and enhancements are still needed and contributions are welcome.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Introduction\n\nFor our purposes, we will use the [same data](http://iraf.noao.edu/iraf/ftp/iraf/misc/) in the [IRAF tutorials](http://iraf.noao.edu/tutorials/). However, we will show how to reduce the data in the same way only using current general purpose python tools. \n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nfrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt\n\nfrom astropy import units as u\nfrom astropy.io import fits\nfrom astropy import modeling as mod",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## CCD Reduction",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import ccdproc \nfrom ccdproc import CCDData, ImageFileCollection",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"[*ccdproc*](https://github.com/astropy/ccdproc) is an astropy affiliated package for handling CCD data reductions. The code contains all the necessary content to produce pipelines for basic CCD reductions. Here we use *ccdproc* to reduce a spectroscopic data set.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The *ImageFileCollection* class in *ccdproc* is useful for reading and sorting of the FITS files in a directory. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from ccdproc import ImageFileCollection\nimage_dir = 'exercises/spec/'\nic = ImageFileCollection('exercises/spec/') #read in all FITS files in the directory",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ic.summary",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from ginga.web.pgw import ipg\nuse_opencv = False\n\nserver = ipg.make_server(host='localhost', port=9914, use_opencv=use_opencv)\nserver.start(no_ioloop=True)\nv1 = server.get_viewer('v1')\nv1.open()\nv1.load('exercises/spec/sp0020.fits')\nv1.embed(height=650)\nv1.show()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# create the master biasframe\n\n# function used for fitting bias frames\ncheb_1 = mod.models.Chebyshev1D(1)\n#create a list of bias frames\nbias_list = []\nfor hdu, fname in ic.hdus(return_fname=True, object='biases 1st afternoon'):\n ccd = CCDData.read(image_dir+fname, unit='adu')\n ccd = ccdproc.subtract_overscan(ccd, fits_section='[105:130,1:1024]')\n ccd = ccdproc.trim_image(ccd, fits_section=\"[34:74,1:1022]\")\n bias_list.append(ccd)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#combine into master bias frame\nmaster_bias = ccdproc.combine(bias_list, method='average', clip_extrema=True, \n nlow = 1, nhigh = 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#process flat data\n# In this case we use ccdproc.ccd_process instead of each individual step\n\n#create a list of flat frames\nflat_list = []\nfor hdu, fname in ic.hdus(return_fname=True, object='flats-6707'):\n ccd = CCDData.read(image_dir+fname, unit='adu')\n ccd = ccdproc.ccd_process(ccd, oscan='[105:130,1:1024]', oscan_model=cheb_1, \n trim=\"[34:74,1:1022]\", master_bias=master_bias)\n flat_list.append(ccd)\n \n#combine into a single master flat\nmaster_flat = ccdproc.combine(flat_list, method='average', sigma_clip=True, \n low_thresh=3, high_thresh=3)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#process the sky flat data\n\n#create a list of sky flat frames\nskyflat_list = []\nexp_list = []\nfor fname in ['sp0011.fits','sp0012.fits','sp0013.fits']:\n ccd = CCDData.read(image_dir+fname, unit='adu')\n exp_list.append(ccd.header['EXPTIME'])\n ccd = ccdproc.ccd_process(ccd, oscan='[105:130,1:1024]', oscan_model=cheb_1, \n trim=\"[34:74,1:1022]\", master_bias=master_bias)\n skyflat_list.append(ccd)\n \n#combine into a single master flat\n\nmaster_sky = ccdproc.combine(skyflat_list, method='average', scale=np.median, \n weights=np.array(exp_list), sigma_clip=True, \n slow_thresh=3, high_thresh=3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# correct for the response function\ncheb_5 = mod.models.Chebyshev1D(5)\nfitter = mod.fitting.LinearLSQFitter()\n\nfy = master_flat.data.sum(axis=1)/master_flat.shape[1]\nyarr = np.arange(len(fy))\nresp_func = fitter(cheb_5, yarr, fy)\nresponse = master_flat.divide(resp_func(yarr).reshape((len(yarr),1))*u.dimensionless_unscaled)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# correct for the illumination correction\nsky = master_sky.divide(resp_func(yarr).reshape((len(yarr),1))*u.dimensionless_unscaled)\n\ncheb_22 = mod.models.Chebyshev2D(2,2)\nyarr, xarr = np.indices(sky.data.shape)\nillum = fitter(cheb_22, xarr, yarr, sky.data)\n# add fitting with rejection\n# todo update to fit set regions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sky.data = illum(xarr, yarr)\nsky.data = sky.divide(sky.data.mean())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"super_flat = sky.multiply(response)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"img_list = []\nfor fname in ['sp0018.fits', 'sp0020.fits','sp0021.fits','sp0022.fits', 'sp0023.fits'\n ,'sp0024.fits','sp0025.fits', 'sp0027.fits']:\n ccd = CCDData.read(image_dir+fname, unit='adu')\n hdr = ccd.header\n ccd = ccdproc.ccd_process(ccd, oscan='[105:130,1:1024]', oscan_model=cheb_1, \n trim=\"[34:74,1:1022]\", master_bias=master_bias, \n master_flat=super_flat)\n # add comsic ray cleaning\n ccd = ccdproc.cosmicray_lacosmic(ccd, sigclip=3., sigfrac=0.3, \n gain=hdr['GAIN'], readnoise=hdr['RDNOISE']) \n img_list.append(ccd)\n ccd.write('p'+fname, clobber=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Spectroscopic Reductions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from specreduce.interidentify import InterIdentify\nfrom specreduce import spectools as st\nfrom specreduce import WavelengthSolution\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"[*specreduce*](https://github.com/crawfordsm/specreduce) is a package for handling the wavelength calibration of spectroscopic data. The code contains all the necessary content to identify arc lines and to rectify spectra. It can be used for longslit, multi-object, or echelle spectrographs. \n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# read in the line lists -- if line ratios are availabe, it is easier to find\n# an automatic solution\nslines = np.loadtxt('thorium.dat')\nsfluxes = np.ones_like(slines)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# setup the data and correct for the orientation of the data\n# so that it is \narc1 = img_list[0]\ndata = arc1.data.T\ndata = data[:,::-1]\nxarr = np.arange(data.shape[1])\nistart = int(data.shape[0]/2.0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# initial guess for the wavelength solution\nws_init = mod.models.Chebyshev1D(3)\nws_init.domain = [xarr.min(), xarr.max()]\nws = WavelengthSolution.WavelengthSolution(xarr, xarr, ws_init)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"iws = InterIdentify(xarr, data, slines, sfluxes, ws, mdiff=20, rstep=5,\n function='poly', order=3, sigma=3, niter=5, wdiff=0.5,\n res=0.2, dres=0.05, dc=3, ndstep=50, istart=istart,\n method='Zeropoint', smooth=0, filename=None,\n subback=0, textcolor='black', log=None, verbose=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# correct for curvature in the arc\nws_init = mod.models.Chebyshev1D(2)\nws_init.domain = [xarr.min(), xarr.max()]\nws = WavelengthSolution.WavelengthSolution(xarr, xarr, ws_init)\naws = st.arc_straighten(data, istart, ws, rstep=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# create wavelength map and apply wavelength solution to all data\nwave_map = st.wave_map(data, aws)\nk = 20.5\nws = iws[k]\nfor i in range(data.shape[0]):\n wave_map[i,:] = iws[k](wave_map[i,:])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# extra the data\nobj_data = img_list[3].data\nobj_data = obj_data.T\nobj_data = obj_data[:,::-1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.imshow(obj_data, aspect='auto')\nax = plt.gca()\nxt = ax.get_xticks()\nax.set_xticklabels([int(x) for x in ws(xt)])\nplt.xlabel('Wavelength ($\\AA$)', size='x-large')\nax.set_yticklabels([])\nplt.savefig('spec2d.pdf')\nplt.show()\n#ax.set_yticklabels([])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# sum the spectra between two steps \n# The spectra could be traced for better results\n# or it could extracted using more optimum methods\n\nwarr = ws(xarr)\nflux = np.zeros_like(warr)\nfor i in range(18,25):\n f = np.interp(warr, wave_map[i], obj_data[i])\n flux += f\n\nsky = np.zeros_like(warr)\nfor i in range(25,32):\n f = np.interp(warr, wave_map[i], obj_data[i])\n sky += f\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(warr, flux - sky)\nplt.xlabel('Wavelength ($\\AA$)', size='x-large')\nplt.ylabel('counts')\nplt.savefig('spec1d.pdf')\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#import pickle\n#pickle.dump(iws, open('iws.db', 'wb'))\n#iws = pickle.load(open('iws.db', 'rb'))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"raw",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"raw"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe6bd491a1d46c7a45bc4d704aa4a853615451e
| 255,738 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
docs/source/Tutorials/archive/Tutorial 2 - Organization of annotated data.ipynb
|
Packer-Lab/packerlabimaging
|
95b4eb6285b045b0821f9835881000321a5972b7
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
docs/source/Tutorials/archive/Tutorial 2 - Organization of annotated data.ipynb
|
Packer-Lab/packerlabimaging
|
95b4eb6285b045b0821f9835881000321a5972b7
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2022-03-09T18:50:08.000Z
|
2022-03-09T21:42:48.000Z
|
docs/source/Tutorials/archive/Tutorial 2 - Organization of annotated data.ipynb
|
Packer-Lab/packerlabimaging
|
95b4eb6285b045b0821f9835881000321a5972b7
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 533.899791 | 229,637 | 0.924931 |
[
[
[
"from IPython import display",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import packerlabimaging as pkg",
"Warning: cellpose did not import\nNo module named 'cellpose'\ncannot use anatomical mode, but otherwise suite2p will run normally\nimport packerlabimaging\n\tversion: under...alpha...development\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"### In this notebook, we demonstrate the basics of how data is organized inside of a trial object. \n\n\nFirst, an already existing trial object is loaded:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# import trial object to use as example\n\ntrialobj = pkg.import_obj(pkl_path='/home/pshah/Documents/code/packerlabimaging/tests/2020-12-19_t-013.pkl')",
"|- Loaded (RL109 t-013) TwoPhotonImagingTrial.alloptical experimental trial object, last saved: Sat Jan 22 04:01:26 2022\n"
]
],
[
[
"The AnnData library is used to store data in an efficient, multi-functional format. This is stored under: `trialobject.data` . \n\nThe AnnData object is built around the raw Flu matrix of each `trialobject` . In keeping with AnnData conventions, the data structure is organized in *n* observations (obs) x *m* variables (var), where observations are suite2p ROIs and variables are imaging frame timepoints. \n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"display.Image(\"/home/pshah/Documents/code/packerlabimaging/files/packerlabimaging-anndata-integration-01.jpg\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"trialobj.data # this is the anndata object for this trial",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## storage of Flu data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The raw data is stored in `.X`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(trialobj.data.X)\n\nprint('shape: ', trialobj.data.X.shape)",
"[[184.1814 317.08673 290.3114 ... 226.17331 381.18915\n 148.0913 ]\n [385.88657 137.67667 143.93521 ... -6.068924 134.3343\n 297.7108 ]\n [ 60.864273 261.0147 104.70546 ... 129.49275 312.83362\n 94.42384 ]\n ...\n [154.93796 5.2811584 299.87506 ... 57.443832 185.83585\n 91.68779 ]\n [ 39.04761 72.97851 47.687088 ... 52.206535 107.23722\n 78.30358 ]\n [ 68.78638 149.34642 123.59329 ... 129.84854 101.720566\n 116.995895 ]]\nshape: (640, 16368)\n"
]
],
[
[
"Processed data is added to `trialobj.data` as a unique `layers` key. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"trialobj.data.layers",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(trialobj.data.layers['dFF'])\n\nprint('shape: ', trialobj.data.layers['dFF'].shape)\n",
"[[ 2.49849148e+01 1.15174057e+02 9.70044022e+01 ... 5.34804955e+01\n 1.58673752e+02 4.94285583e-01]\n [ 4.89079651e+02 1.10171936e+02 1.19725990e+02 ... -1.09264587e+02\n 1.05069611e+02 3.54473907e+02]\n [ 4.28867249e+02 2.16803198e+03 8.09815979e+02 ... 1.02519995e+03\n 2.61830151e+03 7.20476013e+02]\n ...\n [ 1.07392031e+04 2.69461121e+02 2.08787637e+04 ... 3.91867554e+03\n 1.29007676e+04 6.31432617e+03]\n [ 6.17029190e+01 2.02216629e+02 9.74804840e+01 ... 1.16196297e+02\n 3.44087921e+02 2.24268677e+02]\n [ 3.56949688e+04 7.73824844e+04 6.40559766e+04 ... 6.72928906e+04\n 5.27374688e+04 6.06420117e+04]]\nshape: (640, 16368)\n"
]
],
[
[
"The rest of the AnnData data object is built according to the dimensions of the original Flu data input.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## observations (Suite2p ROIs metadata and associated processing info)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"For instance, the metadata for each suite2p ROI stored in Suite2p’s stat.npy output is added to `trialobject.data` under `obs` and `obsm` (1D and >1-D observations annotations, respectively).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"trialobj.data.obs",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"trialobj.data.obsm",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The `.obsm` includes the ypix and xpix outputs for each suite2p ROI which represent the pixel locations of the ROI mask.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print('ypix:', trialobj.data.obsm['ypix'][:5], '\\n\\nxpix: \\t', trialobj.data.obsm['xpix'][:5])",
"ypix: [array([102, 102, 102, 102, 102, 103, 103, 103, 103, 103, 103, 103, 104,\n 104, 104, 104, 104, 104, 104, 104, 105, 105, 105, 105, 105, 105,\n 105, 105, 106, 106, 106, 106, 106, 106, 106, 106, 107, 107, 107,\n 107, 107, 107, 107, 108, 108, 108, 108, 108])\n array([46, 46, 46, 46, 46, 46, 47, 47, 47, 47, 47, 47, 47, 47, 47, 48, 48,\n 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 49, 49, 49, 49, 49, 49, 49, 49, 50, 50, 50,\n 50, 50, 50, 50, 51, 51, 51, 51, 51, 52, 52, 52])\n array([18, 18, 18, 18, 19, 19, 19, 19, 19, 19, 19, 19, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20,\n 20, 20, 20, 20, 21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 21, 22, 22, 22,\n 22, 22, 22, 22, 22, 22, 22, 23, 23, 23, 23, 23, 23, 23, 23, 24, 24,\n 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 24, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 25, 26, 26, 26, 26])\n array([43, 44, 45, 46, 46, 47, 47, 47, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 49, 49, 49, 49,\n 49, 49, 50, 50, 50, 50, 50, 50, 50, 51, 51, 51, 51, 51, 51, 51, 52,\n 52, 52, 52, 52, 52, 52, 52, 52, 52, 52, 52, 53, 53, 53, 53, 53, 53,\n 53, 53, 53, 53, 53, 53, 54, 54, 54, 54, 54, 54, 54, 54, 54, 54, 55,\n 55, 55, 55, 55, 55, 55, 55, 55, 56, 56, 56, 56, 56, 56, 56, 56, 57,\n 57, 57, 57, 57, 57, 57, 58, 58, 58, 58, 58, 59, 59])\n array([156, 156, 156, 156, 156, 157, 157, 157, 157, 157, 157, 157, 157,\n 158, 158, 158, 158, 158, 158, 158, 158, 159, 159, 159, 159, 159,\n 159, 159, 159, 160, 160, 160, 160, 160, 160, 160, 161, 161, 161,\n 161, 161]) ] \n\nxpix: \t [array([457, 458, 459, 460, 461, 456, 457, 458, 459, 460, 461, 462, 455,\n 456, 457, 458, 459, 460, 461, 462, 455, 456, 457, 458, 459, 460,\n 461, 462, 455, 456, 457, 458, 459, 460, 461, 462, 456, 457, 458,\n 459, 460, 461, 462, 457, 458, 459, 460, 461])\n array([116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120,\n 121, 122, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 115, 116, 117,\n 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 117,\n 118, 119, 120, 121, 118, 119, 120])\n array([202, 203, 204, 205, 200, 201, 202, 203, 204, 205, 206, 207, 200,\n 201, 202, 203, 204, 205, 206, 207, 208, 200, 201, 202, 203, 204,\n 205, 206, 207, 208, 209, 199, 200, 201, 202, 203, 204, 205, 206,\n 207, 208, 200, 201, 202, 203, 204, 205, 206, 207, 200, 201, 202,\n 203, 204, 205, 206, 207, 201, 202, 203, 204, 205, 206, 207, 202,\n 203, 204, 205])\n array([352, 352, 352, 352, 353, 352, 353, 354, 351, 352, 353, 354, 355,\n 350, 351, 352, 353, 354, 355, 350, 351, 352, 353, 354, 355, 356,\n 349, 350, 351, 352, 353, 354, 355, 349, 350, 351, 352, 353, 354,\n 355, 357, 358, 359, 360, 361, 350, 351, 352, 353, 354, 355, 356,\n 357, 358, 359, 360, 361, 352, 353, 354, 355, 356, 357, 358, 359,\n 360, 361, 354, 355, 356, 357, 358, 359, 360, 361, 362, 354, 355,\n 356, 357, 358, 359, 360, 361, 355, 356, 357, 358, 359, 360, 361,\n 357, 358, 359, 360, 361, 358, 359])\n array([382, 383, 384, 385, 386, 380, 381, 382, 383, 384, 385, 386, 387,\n 380, 381, 382, 383, 384, 385, 386, 387, 380, 381, 382, 383, 384,\n 385, 386, 387, 380, 381, 382, 383, 384, 385, 386, 381, 382, 383,\n 384, 385]) ]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## variables (temporal synchronization of paq channels and imaging)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"And the temporal synchronization data of the experiment collected in .paq output is added to the variables annotations under `var`. These variables are timed to the imaging frame clock timings. The total # of variables is the number of imaging frames in the original Flu data input.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\npd.options.display.max_rows = 999",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"trialobj.data.var",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe6bf28692a900a0b428e34df973d75ad11e5b9
| 29,948 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/02-enrich-vancouver.ipynb
|
knu2xs/canada-modeling
|
d65222de2025da2e19f73272d128113dfbfd19ba
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/02-enrich-vancouver.ipynb
|
knu2xs/canada-modeling
|
d65222de2025da2e19f73272d128113dfbfd19ba
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/02-enrich-vancouver.ipynb
|
knu2xs/canada-modeling
|
d65222de2025da2e19f73272d128113dfbfd19ba
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 31.825717 | 143 | 0.409376 |
[
[
[
"import importlib\nimport os\nfrom pathlib import Path\nimport sys\n\nfrom arcgis.features import GeoAccessor, GeoSeriesAccessor\nfrom arcgis.gis import GIS\nfrom dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv\nimport pandas as pd\n\nfrom dm import Country, DemographicModeling\nfrom dm.utils import get_countries, add_enrich_aliases\n\n# import arcpy if available\nif importlib.util.find_spec(\"arcpy\") is not None:\n import arcpy",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# paths to common data locations - NOTE: to convert any path to a raw string, simply use str(path_instance)\ndir_prj = Path.cwd().parent\n\ndir_data = dir_prj/'data'\ndir_raw = dir_data/'raw'\ndir_int = dir_data/'interim'\n\ngdb_raw = dir_raw/'raw.gdb'\ngdb_int = dir_int/'interim.gdb'\n\n# import the project package from the project package path - only necessary if you are not using a unique environemnt for this project\nsys.path.append(str(dir_prj/'src'))\nimport canada_modeling\n\n# load the \"autoreload\" extension so that code can change, & always reload modules so that as you change code in src, it gets loaded\n%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2\n\n# load environment variables from .env\nload_dotenv(find_dotenv())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"get_countries('local')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"can = Country('CAN')\n\ncan",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"can.geographies",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"van_df = can.cmacas.get('vancouver')\n\nvan_df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"van_df.spatial.plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lvl0_df = van_df.dm.level(0).get()\n\nlvl0_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lvl0_df.spatial.plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"evars = can.enrich_variables\n\nkeyvars = evars[(evars.data_collection.str.startswith('Key')) & (evars.vintage == '2022')].copy().reset_index(drop=True)\n\nkeyvars",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"enrich_df = lvl0_df.dm.enrich(keyvars)\n\nenrich_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"enrich_fc = enrich_df.spatial.to_featureclass(gdb_int/'van_lvl0_keyvars')\n\nenrich_fc",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"add_enrich_aliases(enrich_fc, can)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe6c085e9fababed1fa0c76a3fb06f2e64143cf
| 15,412 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
TITANIC2.ipynb
|
BALBOARC/Titanic_Kaggle
|
749818b54d03252942473be76d81aad83e2c1bfd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
TITANIC2.ipynb
|
BALBOARC/Titanic_Kaggle
|
749818b54d03252942473be76d81aad83e2c1bfd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
TITANIC2.ipynb
|
BALBOARC/Titanic_Kaggle
|
749818b54d03252942473be76d81aad83e2c1bfd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 29.581574 | 133 | 0.401311 |
[
[
[
"# Machine Learning using Titanic Data - Kaggle Competition 2\n\n Curso elaborado por Mario Filho - www.mariofilho.com/\n\n- O que é treino, validação e teste\n- Porque precisamos de validação\n- Como dividir seus dados em treino e validação (e teste).\n- O que é e como usar a \"random seed\" (semente de números aleatórios)\n- Como remover o máximo de aleatoriedade para poder comparar resultado\n- Como calcular a acurácia\n- Como interpretar e usar o resultado da validação\n- Princípios básicos para saber se a validação está correta\n\ngithub: /BALBOARC\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Carregando os dados de treino e de teste:\nlocal_train = '~/Documentos/KAGGLE/TITANIC/train.csv'\nlocal_test = '~/Documentos/KAGGLE/TITANIC/test.csv'\ntrain_data = pd.read_csv(local_train) \ntest_data = pd.read_csv(local_test) \ntrain_data.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Para utilizar as variáveis \"Male\" e \"Female\" transformamos elas em um binário:\ndef transformar_sexo(valor):\n if valor == 'female':\n return 1\n else:\n return 0\n\ntrain_data['Sex_binario'] = train_data['Sex'].map(transformar_sexo)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"variaveis = ['Sex_binario', 'Age']\n\nX = train_data[variaveis].fillna(-1)\nY = train_data['Survived']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_data.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Criação de instância do modelo (conjunto de modelos de árvore de decisão)\n# Para usar o método de divisão mais simples de validação importamos o train_test_split\n# Definiremos assim de maneira aleatória quem vai para o treino e quem vai para o test\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Utilizamos o np.random.seed(0) para manter a escolha aleatória definida em 0 assim como no random_state:\nnp.random.seed(0)\nX_treino, X_valid, y_treino, y_valid = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.5) # 50% pois os dados são pequenos",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_treino.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_treino.shape, X_valid.shape, y_treino.shape, y_valid.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"modelo = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, n_jobs=-1, random_state=0)\nmodelo.fit(X_treino, y_treino)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"p = modelo.predict(X_valid)\np",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Calculando o quanto estamos certos na validação:\n# Comparamos o y_valid (respostas para esse conjunto de dados) com o p, \n# e então realizamos a acurácia (média dessa comparação)\ny_valid == p\nnp.mean(y_valid == p)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"p = (X_valid['Sex_binario'] == 1).astype(np.int64)\nnp.mean(y_valid == p)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Conclusão:\nPercebemos que o resultado do modelo é pior que o anterior no qual consideramos que apenas as mulheres sobrevivem (Notebook 01)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe6f687299517953a5dc8471ee3740360929e4d
| 613,954 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
dementia_optima/models/misc/data_kernel_sl_nr_ft_newfeaturevariable_maya_notAskedandnull.ipynb
|
SDM-TIB/dementia_mmse
|
bf22947aa06350edd454794eb2b926f082d2dcf2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
dementia_optima/models/misc/data_kernel_sl_nr_ft_newfeaturevariable_maya_notAskedandnull.ipynb
|
SDM-TIB/dementia_mmse
|
bf22947aa06350edd454794eb2b926f082d2dcf2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
dementia_optima/models/misc/data_kernel_sl_nr_ft_newfeaturevariable_maya_notAskedandnull.ipynb
|
SDM-TIB/dementia_mmse
|
bf22947aa06350edd454794eb2b926f082d2dcf2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 48.499408 | 5,624 | 0.358677 |
[
[
[
"------\n# **Dementia Patients -- Analysis and Prediction**\n### ***Author : Akhilesh Vyas***\n### ****Date : August, 2019****\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# ***Result Plots***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"- <a href='#00'>0. Setup </a>\n - <a href='#00.1'>0.1. Load libraries </a>\n - <a href='#00.2'>0.2. Define paths </a>\n\n- <a href='#01'>1. Data Preparation </a> \n - <a href='#01.1'>1.1. Read Data </a> \n - <a href='#01.2'>1.2. Prepare data </a>\n - <a href='#01.3'>1.3. Prepare target </a>\n - <a href='#01.4'>1.4. Removing Unwanted Features </a>\n \n- <a href='#02'>2. Data Analysis</a> \n - <a href='#02.1'>2.1. Feature </a> \n - <a href='#02.2'>2.2. Target </a> \n \n- <a href='#03'>3. Data Preparation and Vector Transformation</a>\n\n- <a href='#04'>4. Analysis and Imputing Missing Values </a>\n\n- <a href='#05'>5. Feature Analysis</a> \n - <a href='#05.1'>5.1. Correlation Matrix</a>\n - <a href='#05.2'>5.2. Feature and target </a>\n - <a href='#05.3'>5.3. Feature Selection Models </a>\n \n- <a href='#06'>6.Machine Learning -Classification Model</a> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# <a id='00'>0. Setup </a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# <a id='00.1'>0.1 Load libraries </a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Loading Libraries",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sys\nsys.path.insert(1, '../preprocessing/')\nimport numpy as np\nimport pickle\nimport scipy.stats as spstats\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport pandas_profiling\nfrom sklearn.datasets.base import Bunch\n#from data_transformation_cls import FeatureTransform\nfrom ast import literal_eval\nimport plotly.figure_factory as ff\nimport plotly.offline as py\nimport plotly.graph_objects as go\n\nimport pandas as pd\npd.set_option('display.max_columns', None) \npd.set_option('display.max_rows', None)\npd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', -1)\n\nfrom ordered_set import OrderedSet\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# <a id='00.2'>0.2 Define paths </a>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# data_path\ndata_path = '../../../datalcdem/data/optima/dementia_18July/data_notasked/'\nresult_path = '../../../datalcdem/data/optima/dementia_18July/data_notasked/results/'\noptima_path = '../../../datalcdem/data/optima/optima_excel/'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# <a id='1'>1. Data Preparation </a> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## <a id='01.1'>1.1. Read Data</a>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Preparation Features from Raw data\n\n# Patient Comorbidities data\n'''patient_com_raw_df = pd.read_csv(data_path + 'optima_patients_comorbidities.csv').groupby(by=['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE'], as_index=False).agg(lambda x: x.tolist())[['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE', 'Comorbidity_cui']]\ndisplay(patient_com_raw_df.head(5))\npatient_com_raw_df['EPISODE_DATE'] = pd.to_datetime(patient_com_raw_df['EPISODE_DATE'])\n\n\n# Patient Treatment data\npatient_treat_raw_df = pd.read_csv(data_path + 'optima_patients_treatments.csv').groupby(by=['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE'], as_index=False).agg(lambda x: x.tolist())[['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE', 'Medication_cui']]\ndisplay(patient_treat_raw_df.head(5))\npatient_treat_raw_df['EPISODE_DATE'] = pd.to_datetime(patient_treat_raw_df['EPISODE_DATE'])\n\n# Join Patient Treatment and Comorbidities data\npatient_com_treat_raw_df = pd.merge(patient_com_raw_df, patient_treat_raw_df,on=['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE'], how='outer')\npatient_com_treat_raw_df.sort_values(by=['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE'],axis=0, inplace=True, ascending=True)\npatient_com_treat_raw_df.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True)\npatient_com_treat_raw_df.head(5)\n\n\n#Saving data\npatient_com_treat_raw_df.to_csv(data_path + 'patient_com_treat_episode_df.csv', index=False)'''\n\n# Extracting selected features from Raw data\ndef rename_columns(col_list):\n d = {}\n for i in col_list:\n if i=='GLOBAL_PATIENT_DB_ID':\n d[i]='patient_id'\n elif 'CAMDEX SCORES: ' in i:\n d[i]=i.replace('CAMDEX SCORES: ', '').replace(' ', '_')\n elif 'CAMDEX ADMINISTRATION 1-12: ' in i:\n d[i]=i.replace('CAMDEX ADMINISTRATION 1-12: ', '').replace(' ', '_')\n elif 'DIAGNOSIS 334-351: ' in i:\n d[i]=i.replace('DIAGNOSIS 334-351: ', '').replace(' ', '_')\n elif 'OPTIMA DIAGNOSES V 2010: ' in i:\n d[i]=i.replace('OPTIMA DIAGNOSES V 2010: ', '').replace(' ', '_')\n elif 'PM INFORMATION: ' in i:\n d[i]=i.replace('PM INFORMATION: ', '').replace(' ', '_')\n else:\n d[i]=i.replace(' ', '_')\n return d\n\nsel_col_df = pd.read_excel(data_path+'Variable_Guide_Highlighted_Fields_.xlsx')\ndisplay(sel_col_df.head(5))\nsel_cols = [i+j.replace('+', ':')for i,j in zip(sel_col_df['Sub Category '].tolist(), sel_col_df['Variable Label'].tolist())]\nrem_cols= ['OPTIMA DIAGNOSES V 2010: OTHER SYSTEMIC ILLNESS: COMMENT'] # Missing column in the dataset\nsel_cols = sorted(list(set(sel_cols)-set(rem_cols)))\nprint (sel_cols)\n\ncolumns_selected = list(OrderedSet(['GLOBAL_PATIENT_DB_ID', 'EPISODE_DATE'] + sel_cols))\n\ndf_datarequest = pd.read_excel(optima_path+'Data_Request_Jan_2019_final.xlsx')\ndisplay(df_datarequest.head(1))\ndf_datarequest_features = df_datarequest[columns_selected]\ndisplay(df_datarequest_features.columns)\n\ncolumns_renamed = rename_columns(df_datarequest_features.columns.tolist())\ndf_datarequest_features.rename(columns=columns_renamed, inplace=True)\n\ndisplay(df_datarequest_features.head(5))\n# df_datarequest_features.drop(columns=['Age_At_Episode', 'PETERSEN_MCI_TYPE'], inplace=True)\ndisplay(df_datarequest_features.head(5))\n\n# drop columns having out of range MMSE value\n#df_datarequest_features = df_datarequest_features[(df_datarequest_features['MINI_MENTAL_SCORE']<=30) & (df_datarequest_features['MINI_MENTAL_SCORE']>=0)]\n\n# Merging Join Patient Treatment, Comorbidities and selected features from raw data\n#patient_com_treat_raw_df['EPISODE_DATE'] = pd.to_datetime(patient_com_treat_raw_df['EPISODE_DATE'])\n#patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df = pd.merge(patient_com_treat_raw_df,df_datarequest_features,on=['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE'], how='left')\n#patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.sort_values(by=['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE'],axis=0, inplace=True, ascending=True)\n#patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.reset_index(inplace=True, drop=True)\n#display(patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.head(5))\npatient_com_treat_fea_raw_df = df_datarequest_features # Need to be changed ------------------------\n\n# Filling misssing MMSE value with patient group Average\n\n#patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df['MINI_MENTAL_SCORE']\\\n# = patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.groupby(by=['patient_id'])['MINI_MENTAL_SCORE'].transform(lambda x: x.fillna(x.mean()))\ndisplay(patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.head(5))\n\n# 19<=Mild<=24 , 14<=Moderate<=18 , Severe<=13 \n#patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df['MINI_MENTAL_SCORE_CATEGORY']=np.nan\n\ndef change_minimentalscore_to_category(df):\n df.loc[(df['MINI_MENTAL_SCORE']<=30) & (df['MINI_MENTAL_SCORE']>24),'MINI_MENTAL_SCORE_CATEGORY'] = 'Normal'\n df.loc[(df['MINI_MENTAL_SCORE']<=24) & (df['MINI_MENTAL_SCORE']>=19),\n 'MINI_MENTAL_SCORE_CATEGORY'] = 'Mild'\n df.loc[(df['MINI_MENTAL_SCORE']<=18) & (df['MINI_MENTAL_SCORE']>=14),\n 'MINI_MENTAL_SCORE_CATEGORY'] = 'Moderate'\n df.loc[(df['MINI_MENTAL_SCORE']<=13) & (df['MINI_MENTAL_SCORE']>=0),'MINI_MENTAL_SCORE_CATEGORY'] = 'Severe'\n \n return df\n\n#patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df = change_minimentalscore_to_category(patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df)\n\n# saving file\npatient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.to_csv(data_path + 'patient_com_treat_fea_episode_raw_without_expand_df.csv', index=False)\n\n# Set line number for treatment line\ndef setLineNumber(lst):\n lst_dict = {ide:0 for ide in lst}\n lineNumber_list = []\n \n for idx in lst:\n if idx in lst_dict:\n lst_dict[idx] = lst_dict[idx] + 1 \n lineNumber_list.append(lst_dict[idx])\n \n return lineNumber_list\n\npatient_com_treat_fea_raw_df['lineNumber'] = setLineNumber(patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df['patient_id'].tolist())\ndisplay(patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.head(5))\n\n# Extend episode data into columns\ndef extend_episode_data(df):\n id_dict = {i:0 for i in df['patient_id'].tolist()}\n for x in df['patient_id'].tolist():\n if x in id_dict:\n id_dict[x]=id_dict[x]+1\n \n line_updated = [int(j) for i in id_dict.values() for j in range(1,i+1)]\n # print (line_updated[0:10])\n df.update(pd.Series(line_updated, name='lineNumber'),errors='ignore')\n print ('\\n----------------After creating line-number for each patients------------------')\n display(df.head(20))\n \n # merging episodes based on id and creating new columns for each episode\n r = df['lineNumber'].max()\n print ('Max line:',r)\n l = [df[df['lineNumber']==i] for i in range(1, int(r+1))]\n print('Number of Dfs to merge: ',len(l))\n df_new = pd.DataFrame()\n tmp_id = []\n for i, df_l in enumerate(l):\n df_l = df_l[~df_l['patient_id'].isin(tmp_id)]\n for j, df_ll in enumerate(l[i+1:]):\n #df_l = df_l.merge(df_ll, on='id', how='left', suffix=(str(j), str(j+1))) #suffixe is not working\n #print (j)\n df_l = df_l.join(df_ll.set_index('patient_id'), on='patient_id', rsuffix='_'+str(j+1))\n tmp_id = tmp_id + df_l['patient_id'].tolist()\n #display(df_l)\n df_new = df_new.append(df_l, ignore_index=True, sort=False)\n return df_new\n \n\n\npatient_com_treat_fea_raw_df['lineNumber'] = setLineNumber(patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df['patient_id'].tolist())\n# drop rows with duplicated episode for a patient\npatient_com_treat_fea_raw_df = patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.drop_duplicates(subset=['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE'])\npatient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.sort_values(by=['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE'], inplace=True)\ncolumns = patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.columns.tolist()\npatient_com_treat_fea_raw_df = patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df[columns[0:2]+columns[-1:]\n +columns[2:4]+columns[-2:-1]\n +columns[4:-2]]\n# Expand patient \n#patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df = extend_episode_data(patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df)\ndisplay(patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.head(2))\n\n\n#Saving extended episode of each patients\n#patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.to_csv(data_path + 'patient_com_treat_fea_episode_raw_df.csv', index=False)\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"display(patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.describe(include='all'))\ndisplay(patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.info())\n\ntmp_l = []\nfor i in range(len(patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.index)) :\n # print(\"Nan in row \", i , \" : \" , patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.iloc[i].isnull().sum())\n tmp_l.append(patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.iloc[i].isnull().sum())\n \nplt.hist(tmp_l)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# find NAN and Notasked after filled value\ndef findnotasked(v):\n #print(v)\n c = 0.0\n flag = False\n try:\n for i in v:\n if float(i)<9.0 and float(i)>=0.0 and flag==False: #float(i)<9.0 and float(i)>=0.0:\n flag = True\n elif (float(i)==9.0 and flag==True):\n c = c+1\n except:\n pass\n '''try:\n for i in v:\n if i!=9.0 or i!=i: #float(i)<9.0 and float(i)>=0.0:\n flag = True\n elif (float(i)==9.0 and flag==True):\n c = c+1\n except:\n pass'''\n return c\n\ndef findnan(v):\n #print(v)\n c = 0.0\n flag = False\n try:\n for i in v:\n if float(i)<9.0 and float(i)>=0.0 and flag==False: #float(i)<9.0 and float(i)>=0.0:\n flag = True\n elif (float(i)!=float(i) and flag==True):\n c = c+1\n except:\n pass\n '''try:\n for i in v:\n if i!=9.0 or i!=i: #float(i)<9.0 and float(i)>=0.0:\n flag = True\n elif (float(i)!=float(i) and flag==True):\n c = c+1\n except:\n pass'''\n return c\n \ndf = patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df[list(\n set([col for col in patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.columns.tolist()])\n -set(['EPISODE_DATE']))]\ntmpdf = pd.DataFrame(data=df['patient_id'].unique(), columns=['patient_id'])\ndisplay(tmpdf.head(5))\nfor col in df.columns.tolist():\n #print (col)\n tmp_df1 = df.groupby(by=['patient_id'])[col].apply(lambda x : findnotasked(x) \n ).reset_index(name='Count(notAsked)_'+col )\n tmp_df2 = df.groupby(by=['patient_id'])[col].apply(lambda x : findnan(x) \n ).reset_index(name='Count(nan)_'+col )\n #print (tmp_df1.isnull().sum().sum(), tmp_df2.isnull().sum().sum())\n tmpdf = tmpdf.merge(tmp_df1, on=['patient_id'], how='inner')\n tmpdf = tmpdf.merge(tmp_df2, on=['patient_id'], how='inner')\n #print (tmpdf.columns.tolist()[-2])\n \n#display(tmpdf)\n#display(tmpdf.agg(lambda x: x.sum(), axis=1))\ncol_notasked = [col for col in tmpdf.columns if 'Count(notAsked)_' in col]\ncol_nan = [col for col in tmpdf.columns.tolist() if 'Count(nan)_' in col]\ntmpdf['count_Total(notasked)']=tmpdf[col_notasked].agg(lambda x: x.sum(),axis=1)\ntmpdf['count_Total(nan)']=tmpdf[col_nan].agg(lambda x: x.sum(),axis=1)\ndisplay(tmpdf.head(5))\n\nprofile = tmpdf.profile_report(title='Dementia Profiling Report')\nprofile.to_file(output_file= result_path + \"dementia_data_profiling_report_output_all_patients_notasked_nan.html\")\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# find NAN and Notasked after filled value\ndef findnotasked_full(v):\n #print(v)\n c = 0.0\n try:\n for i in v:\n if float(i)==9.0:\n c = c+1\n except:\n pass\n return c\n\ndef findnan_full(v):\n c = 0.0\n try:\n for i in v:\n if float(i)!=i:\n c = c+1\n except:\n pass\n return c\n\n \ndf = patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df[list(\n set([col for col in patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.columns.tolist()])\n -set(['EPISODE_DATE']))]\ntmpdf_full = pd.DataFrame(data=df['patient_id'].unique(), columns=['patient_id'])\ndisplay(tmpdf_full.head(5))\nfor col in df.columns.tolist():\n #print (col)\n tmp_df1_full = df.groupby(by=['patient_id'])[col].apply(lambda x : findnotasked_full(x) \n ).reset_index(name='Count(notAsked)_'+col )\n tmp_df2_full = df.groupby(by=['patient_id'])[col].apply(lambda x : findnan_full(x) \n ).reset_index(name='Count(nan)_'+col )\n #print (tmp_df1.isnull().sum().sum(), tmp_df2.isnull().sum().sum())\n tmpdf_full = tmpdf_full.merge(tmp_df1_full, on=['patient_id'], how='inner')\n tmpdf_full = tmpdf_full.merge(tmp_df2_full, on=['patient_id'], how='inner')\n #print (tmpdf.columns.tolist()[-2])\n \n#display(tmpdf)\n#display(tmpdf.agg(lambda x: x.sum(), axis=1))\ncol_notasked_full = [col for col in tmpdf_full.columns if 'Count(notAsked)_' in col]\ncol_nan_full = [col for col in tmpdf_full.columns.tolist() if 'Count(nan)_' in col]\ntmpdf_full['count_Total(notasked)']=tmpdf_full[col_notasked].agg(lambda x: x.sum(),axis=1)\ntmpdf_full['count_Total(nan)']=tmpdf_full[col_nan].agg(lambda x: x.sum(),axis=1)\ndisplay(tmpdf_full.head(5))\n\nprofile = tmpdf_full.profile_report(title='Dementia Profiling Report')\nprofile.to_file(output_file= result_path + \"dementia_data_profiling_report_output_all_patients_notasked_nan_full.html\")\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# profile = patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.profile_report(title='Dementia Profiling Report', style={'full_width':True})\nprofile = patient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.profile_report(title='Dementia Profiling Report')\nprofile.to_file(output_file= result_path + \"dementia_data_profiling_report_output_all_patients_notasked.html\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#columnswise sum\ntotal_notasked_nan = tmpdf.sum(axis = 0, skipna = True)\ntotal_notasked_nan.to_csv(data_path+'total_notasked_nan.csv', index=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"total_notasked_nan_com = tmpdf_full.sum(axis = 0, skipna = True)\ntotal_notasked_nan_com.to_csv(data_path+'total_notasked_nan_com.csv', index=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\npatient_com_treat_fea_raw_df.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe708636a5f798c341fca91290051c2f4d7a72b
| 228,545 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
hmms.ipynb
|
denklewer/HMMs
|
25045b061a65a1ea56c84407b4d30d709cb589e2
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | 87 |
2017-05-28T20:06:23.000Z
|
2022-03-18T09:52:44.000Z
|
hmms.ipynb
|
denklewer/HMMs
|
25045b061a65a1ea56c84407b4d30d709cb589e2
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | 15 |
2017-04-03T11:08:56.000Z
|
2021-08-16T22:41:14.000Z
|
hmms.ipynb
|
denklewer/HMMs
|
25045b061a65a1ea56c84407b4d30d709cb589e2
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | 52 |
2017-07-18T23:49:02.000Z
|
2022-02-12T18:42:05.000Z
| 54.793814 | 49,002 | 0.756998 |
[
[
[
"HMMs Library \n============================\n#### (Discrete & Continuous hidden markov models )\n\nThe document contain the tutorial ( usage explained by example ) for the hidden markov models library [link to pip].\n* [The **first** part](#dthmm) will cover disrete-time hidden markov model (**DtHMM**)\n* [The **second** part](#cthmm) will be dedicated to continuous-time hidden markov model (**CtHMM**)\n* [The **third** part](#conv) will compare the convergences of **both** models\n* [The **fourth** part](#dataset) will explain how to use more complex **datasets** and run **multiple trains** by one function call\n\nThe all of the part are independent, so you do not need to run all notebook, if you are interested only in one of them. \n\n\nIf you are not familiar with the hidden markov model theory, We recommend ...\n%todo: refer to DP theory, (simple guide to cthmm?), github, sources\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id='dthmm'></a>\nPart 1: Discrete Time Hidden Markov Model\n---------------------------------------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport hmms\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Construct DtHMM \nYou can directly initialize the DtHMM by passing the **model parameters**. \n\nWe will create simple DtHMM of two hidden states and three output variables.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# A is the matrix of transition probabilities from state [row] to state [column].\nA = np.array([[0.9,0.1],[0.4,0.6]])\n# B is the matrix of probabilities that the state [row] will emmit output variable [column].\nB = np.array([[0.9,0.08,0.02],[0.2,0.5,0.3]])\n# Pi is the vector of initial state probabilities. \nPi = np.array( [0.8,0.2] )\n\n# Create DtHMM by given parameters.\ndhmm = hmms.DtHMM(A,B,Pi)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Or you can initialize it by **random parameters**. Passing the number of hidden states and output variables. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dhmm_random = hmms.DtHMM.random(2,3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Save & Read from File\nOnce you have created the model you can **save** its parameters in file simply by calling *save_params* method. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dhmm.save_params(\"hello_dthmm\") ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The method stored the parameters in *.npz* format. \n\nThe saved file can be later used to **read** parametrs for model initialization.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dhmm_from_file = hmms.DtHMM.from_file( \"hello_dthmm.npz\" )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Set & Get Parameters\nLater you can always **set** parameters with triple of methods corresponding to the constructors.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dhmm.set_params(A,B,Pi)\ndhmm.set_params_random(2,3)\ndhmm.set_params_from_file( \"hello_dthmm.npz\" )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can **get** parameters by calling them separately,",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dhmm.a, dhmm.b, dhmm.pi",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"or **get** them **all** together as the triple.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"(A,B,Pi) = dhmm.params",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Generate Random State and Emission Sequence\n Now we can use our model to generate state and emission sequence. \n The model will randomly choose which transition or emission will happen, taking into consideration the parameters we have previously defined.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seq_len = 20\ns_seq, e_seq = dhmm.generate( seq_len )\n\n#resize plot\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [20,20]\n\nhmms.plot_hmm( s_seq, e_seq )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Find Most Likely State Sequence\nIf we have the model parameters and emission sequence, we can find the most probable state sequence that would generate it. Notice, that it can be different, than the actual sequence that has generated the emissions. \nWe will use Viterbi algorithm for the calculation.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"( log_prob, s_seq ) = dhmm.viterbi( e_seq )\n# Let's print the most likely state sequence, it can be same or differ from the sequence above.\nhmms.plot_hmm( s_seq, e_seq )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The *log_prob* parameter store the probability of the sequence. \nAll the probabilities in the library are stored in the logarithm of their actual value. As the number of possible sequences grows exponentialy by it length, it could easily lead to float underflow. \nYou can easily transform it to the normal scale value applying *exp* function. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.exp( log_prob )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### State Confidence ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We may want to know what is the probability that the emission was generated by some concrete state. You can get the result for every state in every time by calling the method *states_confidence*. **Notice** that the viterbi most probable sequence, presented above, doesn't neccessery contain the most probable states from this method as here is not important the consecutive states transition probability. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"log_prob_table = dhmm.states_confidence( e_seq )\nnp.exp( log_prob_table )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='dtest'></a>\n### The Probability of the Emission Sequence",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We can compute the probability, that the model will generate the emission sequence.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.exp( dhmm.emission_estimate( e_seq ) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### The Probability of the State and Emission Sequences ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Similary we can compute the probabilty of the state and emission sequences given the model parameters.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.exp( dhmm.estimate( s_seq, e_seq ) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Notice!** - You can simply count the probability estimations for whole dataset by one command, watch [The chapter 4](#dsest).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Generate Artificial Dataset\n\nYou can easily generate many sequences in once by using the generate_data function.\nThe generated emission sequences are in the form that is suitable for training of parameters. You can switch times=True, if you want to generate also the corresponding equidistant time sequences.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seq_num= 3 #number of data sequences\nseq_len= 10 #length of each sequence\n\ndhmm.generate_data( (seq_num,seq_len) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Parameters Estimation - Baum Welch Algorithm\nWe usually do not know the real parameters of the model. But, if we have sufficient data, we can estimate them by EM algorithm. \nHere we will have several output variables (emissions) sequences and we will show, how to use them to train the model parameters\n\nLet's start by creating some artifficial data. We will use the previously defined *dhmm* model for it.\n\n**Notice!** - For more detail information about possible datasets watch [The chapter 4](#datasets).\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seq_num = 5\nseq_len = 50\n\n_ , data = dhmm.generate_data( (seq_num,seq_len) )\n\ndata",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, we will create the model with random parameters, that will be eventually trained to match the data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dhmm_r = hmms.DtHMM.random( 2,3 )\n# We can print all the parameters.\nhmms.print_parameters( dhmm_r )",
"Initial probabilities (π) :\n"
]
],
[
[
"Let's compare the dataset likelihood estimation of model used for generating the data and the random parameters model. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print( \"Generator model:\" , np.exp( dhmm.data_estimate(data) ) )\nprint( \"Random model: \" ,np.exp( dhmm_r.data_estimate(data) ) )",
"Generator model: 7.99358091973e-65\nRandom model: 5.74532109077e-162\n"
]
],
[
[
"Most likely the probability that the data was generated by random model is extremly low.\n\nNow we can take the random model and reestimate it to fit the data better.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dhmm_r.baum_welch( data, 10 )\nprint( \"Reestimated model after 10 iterations: \" ,np.exp( dhmm_r.data_estimate(data) ) )",
"iteration 4351609 / 10\niteration 2 / 10\niteration 2 / 10\niteration 2 / 10\niteration 2 / 10\niteration 2 / 10\niteration 2 / 10\niteration 2 / 10\niteration 2 / 10\niteration 2 / 10\nReestimated model after 10 iterations: 8.42721211172e-67\n"
]
],
[
[
"The probability of the reestimated model should now be similiar (possibly even higher) that the generator's model. If it is not, you can try to run the estimation procedure more time at different randomly generated models. It could happen that the estimation fall in the local optima.\n\nIf you are satisfied with the results, you can run some more iteration to fine-tune it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dhmm_r.baum_welch( data, 100 )\nprint( \"Reestimated model after 110 iterations: \" ,np.exp( dhmm_r.data_estimate(data) ) )",
"iteration 4351609 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\niteration 2 / 100\nReestimated model after 110 iterations: 1.56505367922e-66\n"
]
],
[
[
"We can compare the parameters of the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"hmms.print_parameters( dhmm_r )\nhmms.print_parameters( dhmm )",
"Initial probabilities (π) :\n"
]
],
[
[
"Alternatively, we can run *baum_welch_graph* method to get learning curve of estimated probabilities.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dhmm_r = hmms.DtHMM.random(2,3) \nout = dhmm_r.baum_welch( data, 50, est=True )\n\nnp.exp(out)",
"iteration -965849439 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\niteration 2 / 50\n"
]
],
[
[
"Let's plot it in the graph, comparing the results in ratio with *real* data-generator model. ( Notice, it is the ratio of logaritmic probability values. )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"real = dhmm.data_estimate(data)\n#For better visibility of the graph, we cut first two values.\nplt.plot( out[2:] / real )\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Maximum Likelihood Estimation",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Sometimes, we can have a dataset of full observations (i.e. both emission and hidden states sequences). We can use method *maximum_likelihood estimation* to estimate most likely parameters. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seq_num = 5\nseq_len = 50\n\n#generate artificial dataset of both hidden states and emissions sequences\ns_seqs , e_seqs = dhmm.generate_data( (seq_num,seq_len) )\n\ndhmm_r = hmms.DtHMM.random(2,3) \ndhmm_r.maximum_likelihood_estimation(s_seqs,e_seqs)\n\nlog_est = dhmm.full_data_estimate ( s_seqs, e_seqs )\nlog_est_mle = dhmm_r.full_data_estimate( s_seqs, e_seqs )\n\nprint(\"The probability of the dataset being generated by the original model is:\", \\\nnp.exp(log_est), \".\" )\nprint(\"The probability of the dataset being generated by the MLE model is:\", \\\nnp.exp(log_est_mle), \".\" )",
"The probability of the dataset being generated by the original model is: 9.59995696965e-97 .\nThe probability of the dataset being generated by the MLE model is: 6.54309210608e-95 .\n"
]
],
[
[
"For the discrete-time model will be the probability of dataset estimated by parameters from *maximum_likelihood_estimation* always higher equal to probability of being generated by original model. It is the consequence of statistical inaccuracy of dataset. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id='cthmm'></a>\nPart 2: Continuous Time Hidden Markov Model\n-----------------------------------------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport hmms\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Construct CtHMM \nConstruction of CtHMM is similar to the discrete model. \n\nYou can directly initialize the CtHMM by passing the **model parameters**. \nWe will create simple CtHMM of three hidden states and three output variables.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Q is the matrix of transition rates from state [row] to state [column].\nQ = np.array( [[-0.375,0.125,0.25],[0.25,-0.5,0.25],[0.25,0.125,-0.375]] )\n# B is the matrix of probabilities that the state [row] will emmit output variable [column].\nB = np.array( [[0.8,0.05,0.15],[0.05,0.9,0.05],[0.2,0.05,0.75]] )\n# Pi is the vector of initial state probabilities. \nPi = np.array( [0.6,0,0.4] )\n\n# Create CtHMM by given parameters.\nchmm = hmms.CtHMM(Q,B,Pi)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Or you can initialize it by **random parameters**. Passing the number of hidden states and output variables. \nBy default are the parameters generated by exponential distribution and than normalized to sum to one.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"chmm_random = hmms.CtHMM.random(3,3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can choose generating by uniform distribution passing the parameter *method*. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"chmm_random = hmms.CtHMM.random(3,3,method=\"unif\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Save & Read from File\n\nOnce you have created the model you can save its parameters in file simply by calling save_params method.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"chmm.save_params(\"hello_cthmm\") ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The method stored the parameters in .npz format.\nThe saved file can be later used to read parametrs for model initialization.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"chmm_from_file = hmms.CtHMM.from_file( \"hello_cthmm.npz\" )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Set & Get Parameters\nLater you can always set parameters with triple of methods corresponding to the constructors.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"chmm.set_params(Q,B,Pi)\nchmm.set_params_random(3,3)\nchmm.set_params_from_file( \"hello_cthmm.npz\" )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can **get** parameters by calling them separately,",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"chmm.q, chmm.b, chmm.pi",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"or get them all together as the triple.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"(A,B,Pi) = chmm.params",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Generate Random Sequence\nNow we can use our model to **generate** time, state and emission sequence.\nThe model will **randomly** choose which transition or emission will happen, taking into consideration the parameters we have previously defined.\n\nThe times are generated with **exponencial** waiting times, you can define the parameter of exponencial distribution as second optional parameter. \n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seq_len = 10\nt_seq, s_seq, e_seq = chmm.generate( seq_len, 0.5)\n\n#resize plot\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [20,20]\n\nhmms.plot_hmm( s_seq, e_seq, time=t_seq )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Optionally, you can generate the sequences by putting your own time sequence (as list or numpy array ) with wished observation times.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"t_seq, s_seq, e_seq = chmm.generate( 7, time=[0,3,5,7,8,11,14])\n\n#resize plot\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [20,20]\n\nhmms.plot_hmm( s_seq, e_seq, time=t_seq )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Find Most Likely State Sequence\nIf we have corresponding time and emission sequence, we can find the most probable state sequence that would generate it given the current model parameters. Notice, that it can be different, than the actual sequence that has generated the emissions. \nWe will use Viterbi algorithm for the calculation.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"( log_prob, s_seq ) = chmm.viterbi( t_seq, e_seq )\n# Let's print the most likely state sequence, it can be same or differ from the sequence above.\nhmms.plot_hmm( s_seq, e_seq, time = t_seq )\nprint( \"Probability of being generated by the found state sequence:\", np.exp( log_prob ) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### State Confidence",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We may want to know what is the probability that the emission was generated by some concrete state. You can get the result for every state in every time by calling the method *states_confidence*. **Notice** that the viterbi most probable sequence, presented above, doesn't neccessery contain the most probable states from this method as here is not important the consecutive states transition probability.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"log_prob_table = chmm.states_confidence( t_seq, e_seq )\nnp.exp( log_prob_table )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### The Probability of the Time and Emission Sequences",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We can compute the probability, of the emission sequence given model and its time sequence.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.exp( chmm.emission_estimate( t_seq, e_seq ) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### The Probability of the State, Time and Emission Sequences",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Similary we can compute the probabilty of the state, time and emission sequences given the model parameters.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.exp( chmm.estimate( s_seq, t_seq, e_seq ) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Notice!** - You can simply count the probability estimations for whole dataset by one command, watch [The chapter 4](#dsest).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Generate Artificial Dataset\nYou can easily generate many sequences in once by using the *generate_data* function. \nThe generated data are in the form that is suitable for training of parameters. \nYou can switch *states=True*, if you want to generate also the corresponding state sequences.\n\nThe times are generated with **exponencial** waiting times, you can define the parameter of exponencial distribution as second optional parameter. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seq_num= 5 #number of data sequences\nseq_len= 30 #length of each sequence\n\nt,e = chmm.generate_data( (seq_num,seq_len) )\nt,e",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Parameters Estimation - Continuous Version of Baum Welch Algorithm\n\nWe will use the previously generated data for the training of randomly generated model.\n\n**Notice!** - Always use the integers in your time points dataset. Floats times are also supported, but it can make the computation significantly slower and you should know, why you are using them. For more detail information watch [The chapter 4](#dataset).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"chmm_r = hmms.CtHMM.random( 3,3 )\n# We can print all the parameters.\nhmms.print_parameters( chmm_r )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we can compare the probabilities, that the data was generated by the given model. Its ratio is most probably not so big as in the disrete model. It is because the intervals between the observations are the source of many unknown, so it is pushing the probability of real model down. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print( \"Generator model:\" , np.exp( chmm.data_estimate(t,e) ) )\nprint( \"Random model: \" ,np.exp( chmm_r.data_estimate(t,e) ) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's run the EM algorithm for couple of iterations.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"out = chmm_r.baum_welch( t,e, 100, est=True )\n\nnp.exp(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We will plot its probabilities estimations in ratio with generator model. (Notice, it is the ratio of logarithms of probabilities)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"real = chmm.data_estimate( t, e )\n#For better visibility of the graph, we cut first two values.\nplt.plot( out[2:] / real )\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Maximum Likelihood Estimation",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Sometimes, we can have a dataset of full observations (i.e. both emission and hidden states sequences). We can use method *maximum_likelihood_estimation* to estimate most likely parameters. The usage and parameters of the methods are similiar to the *baum_welch method*.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seq_num = 5\nseq_len = 50\n\n#generate artificial dataset of times, hidden states and emissions sequences\nt_seqs, s_seqs, e_seqs = chmm.generate_data( (seq_num,seq_len), states=True )\n\nchmm_r = hmms.CtHMM.random(3,3) \ngraph = chmm_r.maximum_likelihood_estimation(s_seqs,t_seqs,e_seqs,100,est=True )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#print the convergence graph\nlog_est = chmm.full_data_estimate ( s_seqs,t_seqs,e_seqs )\n\nplt.plot( graph / log_est )\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='conv'></a>\nPart 3: Comparison of Models Convergences\n-----------------------------------------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this chapter we will compare the convergence rate of discrete and continuous models. It will show some functions usefull for convergence among model parameters. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport hmms\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We will start by defining the continuous time model. For that, who have read the previous section, it will be the familiar.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Q = np.array( [[-0.375,0.125,0.25],[0.25,-0.5,0.25],[0.25,0.125,-0.375]] )\nB = np.array( [[0.8,0.05,0.15],[0.05,0.9,0.05],[0.2,0.05,0.75]] )\nPi = np.array( [0.6,0,0.4] )\n\nchmm = hmms.CtHMM( Q,B,Pi )\nhmms.print_parameters( chmm )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can simply create discrete model with equivalent parameters, using function *get_dthmm_params*. \nBy default, it will create the model with transition probabilities equal to one time unit probability transition in continuous model. You can pass the optional parameter for different time steps.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dhmm = hmms.DtHMM( *chmm.get_dthmm_params() )\nhmms.print_parameters( dhmm )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can let the disrete model to generate the data sufficient for both models by passing the *times* parameter as *True*.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"t,_,e = dhmm.generate_data( (50,50), times=True ) \n# The free space in the return triple is for the state sequences, \n# we do not need them for the training ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can compare the estimation of the data, using both of the model. (They should be the same.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"creal = chmm.data_estimate(t,e)\ndreal = dhmm.data_estimate(e)\nprint(\"Data estimation by continuous model:\", creal)\nprint(\"Data estimation by discrete model: \", dreal)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we will create two equivalent random models. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ct = hmms.CtHMM.random(3,3)\ndt = hmms.DtHMM( *ct.get_dthmm_params() )\n \nhmms.print_parameters( ct )\nhmms.print_parameters( dt )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We will train them at our dataset. (It can take a while.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"iter_num = 50\noutd = dt.baum_welch( e, iter_num, est=True )\noutc = ct.baum_welch( t,e, iter_num, est=True )\noutd,outc",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can plot and compare both convergence rates. From the essence of models, the continuous model will probably converge a bit slower, but finally will reach the similar value.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.plot( outd[1:] / dreal )\nplt.plot( outc[1:] / dreal, color=\"red\" )\n#plt.savefig('my_plot.svg') #Optional save the figure\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='dataset'></a>\n## Part 4: Advance Work with Datasets",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport hmms\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Various Length of Training Vectors",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"There are two supported data-structures, that you can pass toward training:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 1. The Numpy Matrix\nThe two dimensional array, where the rows consist of training sequences. \nThough, this way is restricted in the way that all the vectors need to have the same size. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_n = np.array( [[0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],\n [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0],\n [2, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]] )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dhmm_r = hmms.DtHMM.random( 2,3 )\ngraph_n = dhmm_r.baum_welch( data_n, 10, est=True )\nnp.exp( dhmm_r.data_estimate(data_n) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### 2. The List of Numpy Vectors\nThe standard Python list, consisting of Numpy vectors.\nEvery vector can have different length.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_l = [ np.array( [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1] ) ,\n np.array( [0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1 ] ),\n np.array( [2, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] ) ]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dhmm_r = hmms.DtHMM.random( 2,3 )\ngraph_l = dhmm_r.baum_welch( data_l, 10, est=True )\nnp.exp( dhmm_r.data_estimate(data_l) )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# you can plot the graphs, just for fun.\nplt.plot( graph_n, color='red' )\nplt.plot( graph_l )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Continuous-Time HMM\nThe work with datasets in CtHMM is analogous.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_n = np.array( [[0, 0, 0, 1],\n [0, 2, 0, 0],\n [2, 0, 1, 0] ] )\ntime_n = np.array( [[0, 1, 3, 4],\n [0, 2, 3, 5],\n [0, 2, 4, 6] ] )\n\nchmm_r = hmms.CtHMM.random( 2,3 )\ngraph_n = chmm_r.baum_welch( time_n, data_n, 10, est=True ) \nnp.exp( chmm_r.data_estimate(time_n, data_n) )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_l = [ np.array( [0, 0, 2, 0 ] ) ,\n np.array( [0, 1, 0, 0, 1 ] ),\n np.array( [2, 0, 1 ] ) ]\ntime_l = [ np.array( [0, 1, 2, 4 ] ) ,\n np.array( [0, 1, 3, 5, 6 ] ),\n np.array( [0, 2, 3 ] ) ]\n\nchmm_r = hmms.CtHMM.random( 2,3 )\ngraph_n = chmm_r.baum_welch( time_l, data_l, 10, est=True ) \nnp.exp( chmm_r.data_estimate(time_l, data_l) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Time Sequences in Floats",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The time sequences datatypes can be **integers** or **floats**.\nHowever both datatypes are allowed, it is strongly *adviced* to *use* integers or floats with *integral distance*\n(be carefull about float operation unprecision here.) \nThe *non-integral* time intervals among two neigbouring observation are *computationaly costly*, as it doesn't allow to compute matrix power and more complex operations are needed. \nLater are showed two examples with the float data and possible *tricks* how to make computation *faster*.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Example one: Change intervals length to integer",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data = np.array( [[0, 0, 0, 1],\n [0, 2, 0, 0],\n [2, 0, 1, 0] ] )\ntime = np.array( [[0, 1.5, 3.4, 4.7],\n [0, 2.6, 5.7, 8.9],\n [0, 2.2, 4.1, 9.8] ] )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Use data as float",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"chmm_r = hmms.CtHMM.random( 2,3 )\ngraph_f = chmm_r.baum_welch( time, data, 10, est=True ) \nnp.exp( chmm_r.data_estimate(time, data) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"or use the **trick** so the intervals were integral.\nHere it is enough to **multiply** it times 10. \n**Notice**: Here we are working with randomly generated jump rates matrix, otherwise you would need to reevaluate its values, when multiplying times. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"chmm_r = hmms.CtHMM.random( 2,3 )\ngraph = chmm_r.baum_welch( time*10, data, 10, est=True ) \nnp.exp( chmm_r.data_estimate( time*10, data ) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Example 2: Approximate the time values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Sometimes, depending upon the data, the exact observation time may not be important, so the small approximation can be helpful to get better computational time.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data = np.array( [[0, 0, 0, 1],\n [0, 2, 0, 0],\n [2, 0, 1, 0] ] )\ntime = np.array( [[0, 1.54587435, 3.4435434, 4.74535345],\n [0, 2.64353245, 5.7435435, 8.94353454],\n [0, 2.24353455, 4.1345435, 9.83454354] ] )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Use data as float",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"chmm_r = hmms.CtHMM.random( 2,3 )\ngraph_f = chmm_r.baum_welch( time, data, 10, est=True ) \nnp.exp( chmm_r.data_estimate(time, data) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"or perform the **trick**. Here multiply by 100 and round to the integers.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"time = np.round( time * 100 )\n\nchmm_r = hmms.CtHMM.random( 2,3 )\ngraph = chmm_r.baum_welch( time, data, 10, est=True ) \nnp.exp( chmm_r.data_estimate(time, data) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='dsest'></a>\n### Datasets Probability Estimations ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We have showed previously how to compute sequence probability estimations in [The discrete](#dtest) and [continuous](#ctest) model. \nHere it is showed, how to make it for whole dataset by using just one command. \n(We will show it at continuous time model, the discrete one is analogous, just omit the time sequences.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seq_num= 10 #number of data sequences\nseq_len= 10 #length of each sequence\n\n# Create data and generate model\n\nchmm = hmms.CtHMM.random(3,3)\nt,s,e = chmm.generate_data( (seq_num,seq_len), states=True )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### The Probability of the Time and Emission Sequences\nWe can compute the probability, of the emissions sequence given model and its time sequences.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.exp( chmm.data_estimate( t, e ) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### The Probability of the State, Time and Emission Sequences\nSimilary we can compute the probabilty of the state, time and emission sequences given the model parameters.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.exp( chmm.full_data_estimate( s, t, e ) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Multi Training",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nFor more convenient train from various random begnings, you can use *multi_train* function. \nIt has parameters \nmethod: \n- 'exp' - [default] Use exponential distribution for random initialization\n- 'unif' - Use uniform distribution for random initialization \n\nand ret: \n- 'all' - Return all trained models, sorted by their probability estimation\n- 'best' - [default] Return only the model with the best probability estimation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"t,e = chmm.generate_data( (5,10) )\nhidden_states = 3\nruns = 10\niterations = 50\nout = hmms.multi_train_ct( hidden_states , t, e, runs, iterations, ret='all', method='exp')\nout",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<hr/>\nYou can play with the models as you like and feel free to share your result with me, if you have made some interesting experiment!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Contact: ([email protected])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Experimental features\n#### Fast Convergence ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#The experiment is frozen\n\n\nseq_num= 1 #number of data sequences\nseq_len= 4 #length of each sequence\n\nt,e = chmm.generate_data( (seq_num,seq_len) )\nt,e\n\n\nt = np.array([[ 0,1,3,5,6,7,9,11,12]])\ne = np.array([[ 0,0,0,1,2,1,0,0,1]])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ct1 = hmms.CtHMM.random(3,3)\nct2 = hmms.CtHMM( *ct1.params )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"iter_num = 50\nout1 = ct1.baum_welch( t,e, iter_num, est=True )\n#out2 = ct2.baum_welch( t,e, iter_num )\nout1,out2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot( out1[1:] / dreal , color = \"red\" )\nplt.plot( out2[1:] / dreal )\n#plt.savefig('graph.svg') #Optional save the figure\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hmms.print_parameters(ct1)\nhmms.print_parameters(ct2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Exponential random generation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport hmms\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Q is the matrix of transition rates from state [row] to state [column].\nQ = np.array( [[-0.375,0.125,0.25],[0.25,-0.5,0.25],[0.25,0.125,-0.375]] )\n# B is the matrix of probabilities that the state [row] will emmit output variable [column].\nB = np.array( [[0.8,0.05,0.15],[0.05,0.9,0.05],[0.2,0.05,0.75]] )\n# Pi is the vector of initial state probabilities. \nPi = np.array( [0.6,0,0.4] )\n\n# Create CtHMM by given parameters.\nchmm = hmms.CtHMM(Q,B,Pi)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"seq_num= 5 #number of data sequences\nseq_len= 30 #length of each sequence\n\nt,e = chmm.generate_data( (seq_num,seq_len) )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chmm_r = hmms.CtHMM.random( 3,3, method='unif' )\nchmm_re = hmms.CtHMM.random( 3,3, method='exp' )\n\nout = chmm_r.baum_welch( t,e, 10 )\noute = chmm_re.baum_welch( t,e, 10 )\n\n\n#aout = np.average(out, axis=0)\n#aoute = np.average(oute, axis=0)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"out = hmms.multi_train(3, t, e, 10, 200, ret='all', method='exp')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"aout = np.average(out, axis=0)\naoute = np.average(oute, axis=0)\n\nmout = np.min(out, axis=0)\nmoute = np.min(oute, axis=0)\n\n\nreal = chmm.data_estimate( t, e )\n#For better visibility of the graph, we cut first two values.\n\noffset = 3\n\n#plt.plot( aout[offset:] / real , color = \"red\" )\n#plt.plot( aoute[offset:] / real , color = \"blue\" )\n\n#plt.plot( mout[offset:] / real , color = \"orange\" )\n#plt.plot( moute[offset:] / real , color = \"green\")\n\nfor line in out:\n print( line/real )\n plt.plot( line[offset:] / real )\n\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"real = chmm.data_estimate( t, e )\n\noffset = 3\n\nprint(out)\n\nfor line in out:\n #graph= line[1]\n #print( type(line) )\n #print( line[1]/real )\n plt.plot( line[1][offset:] / real )\n\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"oute",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Test different length of vectors",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport hmms\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_l = [ np.array( [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1] ) ,\n np.array( [0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1 ] ),\n np.array( [2, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] ) ]\n\ndata_n = np.array( [[0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],\n [0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 2, 1, 0, 1, 0],\n [2, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]] )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Test Numpy matrix",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dhmm_r = hmms.DtHMM.random( 2,3 )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"graph_n = dhmm_r.baum_welch( data_n, 10, est=True ) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dhmm_r.maximum_likelihood_estimation(data_n, data_n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.exp( dhmm_r.data_estimate(data_n) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Test List of numpy arrays",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dhmm_r = hmms.DtHMM.random( 2,3 )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"graph_l = dhmm_r.baum_welch( data_l, 10, est=True )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.exp( dhmm_r.data_estimate(data_l) )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot( graph_n, color='red' )\nplt.plot( graph_l )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Make the similar for the continuous model ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_l = [ np.array( [0, 0, 2, 0 ] ) ,\n np.array( [0, 1, 0, 0, 1 ] ),\n np.array( [2, 0, 1 ] ) ]\n\ndata_n = np.array( [[0, 0, 0, 1],\n [0, 2, 0, 0],\n [2, 0, 1, 0] ] )\n\ntime_l = [ np.array( [0, 1, 2, 4 ] ) ,\n np.array( [0, 1, 3, 5, 6 ] ),\n np.array( [0, 2, 3 ] ) ]\n\ntime_n = np.array( [[0, 1, 3, 4],\n [0, 2, 3, 5],\n [0, 2, 4, 6] ] )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chmm_r = hmms.CtHMM.random( 2,3 )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"graph_n = chmm_r.baum_welch( time_n, data_n, 10, est=True ) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.exp( chmm_r.data_estimate(time_n, data_n) )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chmm_r = hmms.CtHMM.random( 2,3 )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"graph_n = chmm_r.baum_welch( time_l, data_l, 10, est=True ) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.exp( chmm_r.data_estimate(time_l, data_l) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Test double times",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport hmms\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data = [ np.array( [0, 0, 2, 0 ] ) ,\n np.array( [0, 1, 0, 0, 1 ] ),\n np.array( [2, 0, 1 ] ) ]\n\ntime_i = [ np.array( [0, 1, 2, 4 ] ) ,\n np.array( [0, 1, 3, 5, 6 ] ),\n np.array( [0, 2, 3 ] ) ]\n\ntime_f = [ np.array( [0, 1.1, 2.1, 4.1 ] ) ,\n np.array( [0, 1.1, 3.1, 5.1, 6.1 ] ),\n np.array( [0, 2.1, 3.1 ] ) ]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chmm_r = hmms.CtHMM.random( 2,3 )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"graph_i = chmm_r.baum_welch( time_i, data, 10, est=True ) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.exp( chmm_r.data_estimate(time_i, data) )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"double",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"chmm_r = hmms.CtHMM.random( 2,3 )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"graph_f = chmm_r.baum_welch( time_f, data, 10, est=True ) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.exp( chmm_r.data_estimate(time_f, data) )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot( graph_i, color='red' )\nplt.plot( graph_f )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Soft & Hard",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport hmms\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Q = np.array( [[-0.375,0.125,0.25],[0.25,-0.5,0.25],[0.25,0.125,-0.375]] )\nB = np.array( [[0.8,0.05,0.15],[0.05,0.9,0.05],[0.2,0.05,0.75]] )\nPi = np.array( [0.6,0,0.4] )\n\nchmm = hmms.CtHMM( Q,B,Pi )\n#chmm = hmms.CtHMM.random(15,15)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"t,e = chmm.generate_data( (50,10) )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chmm_s = hmms.CtHMM.random( 3,3 )\nchmm_h = hmms.CtHMM( * chmm_s.params )\nchmm_c = hmms.CtHMM( * chmm_s.params )\n\nprint(\"comb\")\n#graph_comb = chmm_c.baum_welch( t, e, 5, est=True, method=\"hard\" ) \n#graph_comb = np.append( graph_comb, chmm_c.baum_welch( t, e, 95, est=True, method=\"soft\" ) )\nprint(\"hard\")\ngraph_hard = chmm_h.baum_welch( t, e, 100, est=True, method=\"hard\" )\nprint(\"soft\")\ngraph_soft = chmm_s.baum_welch( t, e, 100, est=True, method=\"soft\" ) \n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"real = chmm.data_estimate( t,e )\n#real = 0\n#for tt,ee in zip(t,e): \n# x,_ = chmm.viterbi( tt, ee )\n# real += x\n\n#For better visibility of the graph, we cut first two values.\nplt.plot( graph_soft[1:] / real, color=\"red\" )\nplt.plot( graph_hard[1:] / real, color=\"blue\" )\n##plt.plot( graph_comb[1:-1] / real, color=\"purple\")\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [20,20]\nplt.savefig('graph.png')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print( chmm_h.data_estimate( t,e ) )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hmms.print_parameters( chmm )\nhmms.print_parameters( chmm_s )\nhmms.print_parameters( chmm_h )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chmm_h.check_params() ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Int-intervals vs Double-intervals",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport hmms\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Q = np.array( [[-0.375,0.125,0.25],[0.25,-0.5,0.25],[0.25,0.125,-0.375]] )\nB = np.array( [[0.8,0.05,0.15],[0.05,0.9,0.05],[0.2,0.05,0.75]] )\nPi = np.array( [0.6,0,0.4] )\n\nchmm = hmms.CtHMM( Q,B,Pi )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"t,e = chmm.generate_data( (50,50) )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chmm_i = hmms.CtHMM.random( 3,3 )\nchmm_d = hmms.CtHMM( * chmm_i.params )\n\nimport time\n\ntime0 = time.time()\ngraph_i = chmm_i.baum_welch( t, e, 100, est=True, method=\"soft\", fast=True )\ntime1 = time.time()\ngraph_d = chmm_d.baum_welch( t, e, 100, est=True, method=\"soft\", fast=False ) \ntime2 = time.time()\nprint(time2-time1)\nprint(time1-time0)\nchmm_i.print_ts()\nchmm_d.print_ts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"real = chmm.data_estimate( t,e )\nplt.plot( graph_i[1:] / real, color=\"red\" )\nplt.plot( graph_d[1:] / real, color=\"blue\" )\n\nhmms.print_parameters( chmm_i )\nhmms.print_parameters( chmm_d )\n\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [25,25]\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chmm_i.q[0,0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chmm_d.q[0,0]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### zeros",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport hmms\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n\n# Q is the matrix of transition rates from state [row] to state [column].\nQ = np.array( [[-0.375,0.125,0.25],[0.25,-0.5,0.25],[0.25,0.125,-0.375]] )\n# B is the matrix of probabilities that the state [row] will emmit output variable [column].\nB = np.array( [[0.8,0.05,0.15],[0.05,0.9,0.05],[0.2,0.05,0.75]] )\n# Pi is the vector of initial state probabilities. \nPi = np.array( [0.6,0,0.4] )\n\n# Create CtHMM by given parameters.\nchmm = hmms.CtHMM(Q,B,Pi)\n\n\nt,e = chmm.generate_data( (10,50) )\n\n\n\n# Q is the matrix of transition rates from state [row] to state [column].\nQ = np.array( [[-0.125,0.125,0.0],[0.45,-0.45,0.0],[0.25,0.125,-0.375]] )\n# B is the matrix of probabilities that the state [row] will emmit output variable [column].\nB = np.array( [[0.8,0.05,0.15],[0.05,0.9,0.05],[0.2,0.05,0.75]] )\n# Pi is the vector of initial state probabilities. \nPi = np.array( [0.6,0.4,0.0] )\n\n# Create CtHMM by given parameters.\nchmm_i = hmms.CtHMM(Q,B,Pi)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"graph_i = chmm_i.baum_welch( t, e, 100, est=True, method=\"soft\", fast=True )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hmms.print_parameters( chmm_i )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### random tests",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport hmms\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Q = np.array( [[-0.375,0.125,0.25],[0.25,-0.5,0.25],[0.25,0.125,-0.375]] )\nB = np.array( [[0.8,0.05,0.15],[0.05,0.9,0.05],[0.2,0.05,0.75]] )\nPi = np.array( [0.6,0,0.4] )\n\nchmm = hmms.CtHMM( Q,B,Pi )\nt,e = chmm.generate_data( (50,50) )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chmm_i = hmms.CtHMM.random( 3,3 )\nchmm_d = hmms.CtHMM( * chmm_i.params )\n\ngraph_i = chmm_i.baum_welch( t, e, 100, est=True, method=\"soft\", fast=True )\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"real = chmm.data_estimate( t,e )\nplt.plot( graph_i[1:]/real , color=\"red\" )\n\n#hmms.print_parameters( chmm_i )\n\n#plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [25,25]\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"real = chmm.data_estimate( t,e )\nplt.plot( real-graph_i[1:] , color=\"red\" )\n\n#hmms.print_parameters( chmm_i )\n\n#plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [25,25]\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"real = chmm.data_estimate( t,e )\nplt.plot( np.exp(graph_i[1:] - real) , color=\"red\" )\nprint(np.exp(graph_i[1:] - real))\n#hmms.print_parameters( chmm_i )\n\n#plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [25,25]\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"real = chmm.data_estimate( t,e )\n\n\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_subplot(111)\nax.set_yscale(\"log\", nonposx='clip')\n\nplt.plot( np.exp(graph_i[1:] - real) , color=\"red\" )\n\n#plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [25,25]\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe70de08f52de91f048c329a709e64f61163324
| 178,126 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
jupyter_notebooks/notebooks/NB13_CIX-DNN_susy_Pytorch.ipynb
|
pluflou/MLreviewNotebooks
|
60ac3a0cbe286c5477340db252625bfad569e111
|
[
"MIT"
] | 115 |
2019-02-05T16:49:03.000Z
|
2022-03-26T13:58:44.000Z
|
jupyter_notebooks/notebooks/NB13_CIX-DNN_susy_Pytorch.ipynb
|
pluflou/MLreviewNotebooks
|
60ac3a0cbe286c5477340db252625bfad569e111
|
[
"MIT"
] | 65 |
2021-03-09T20:36:00.000Z
|
2021-05-14T19:48:15.000Z
|
jupyter_notebooks/notebooks/NB13_CIX-DNN_susy_Pytorch.ipynb
|
pluflou/MLreviewNotebooks
|
60ac3a0cbe286c5477340db252625bfad569e111
|
[
"MIT"
] | 73 |
2019-02-16T03:40:53.000Z
|
2022-03-29T04:48:40.000Z
| 60.035726 | 30,680 | 0.628156 |
[
[
[
"# Notebook 13: Using Deep Learning to Study SUSY with Pytorch",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Learning Goals\nThe goal of this notebook is to introduce the powerful PyTorch framework for building neural networks and use it to analyze the SUSY dataset. After this notebook, the reader should understand the mechanics of PyTorch and how to construct DNNs using this package. In addition, the reader is encouraged to explore the GPU backend available in Pytorch on this dataset.\n\n## Overview\nIn this notebook, we use Deep Neural Networks to classify the supersymmetry dataset, first introduced by Baldi et al. in [Nature Communication (2015)](https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms5308). The SUSY data set consists of 5,000,000 Monte-Carlo samples of supersymmetric and non-supersymmetric collisions with $18$ features. The signal process is the production of electrically-charged supersymmetric particles which decay to $W$ bosons and an electrically-neutral supersymmetric particle that is invisible to the detector.\n\nThe first $8$ features are \"raw\" kinematic features that can be directly measured from collisions. The final $10$ features are \"hand constructed\" features that have been chosen using physical knowledge and are known to be important in distinguishing supersymmetric and non-supersymmetric collision events. More specifically, they are given by the column names below.\n\nIn this notebook, we study this dataset using Pytorch.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from __future__ import print_function, division\nimport os,sys\nimport numpy as np\nimport torch # pytorch package, allows using GPUs\n# fix seed\nseed=17\nnp.random.seed(seed)\ntorch.manual_seed(seed)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Structure of the Procedure\n\nConstructing a Deep Neural Network to solve ML problems is a multiple-stage process. Quite generally, one can identify the key steps as follows:\n\n* ***step 1:*** Load and process the data\n* ***step 2:*** Define the model and its architecture\n* ***step 3:*** Choose the optimizer and the cost function\n* ***step 4:*** Train the model \n* ***step 5:*** Evaluate the model performance on the *unseen* test data\n* ***step 6:*** Modify the hyperparameters to optimize performance for the specific data set\n\nBelow, we sometimes combine some of these steps together for convenience.\n\nNotice that we take a rather different approach, compared to the simpler MNIST Keras notebook. We first define a set of classes and functions and run the actual computation only in the very end.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Step 1: Load and Process the SUSY Dataset\n\nThe supersymmetry dataset can be downloaded from the UCI Machine Learning repository on [https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/00279/SUSY.csv.gz](https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/00279/SUSY.csv.gz). The dataset is quite large. Download the dataset and unzip it in a directory.\n\nLoading data in Pytroch is done by creating a user-defined a class, which we name `SUSY_Dataset`, and is a child of the `torch.utils.data.Dataset` class. This ensures that all necessary attributes required for the processing of the data during the training and test stages are easily inherited. The `__init__` method of our custom data class should contain the usual code for loading the data, which is problem-specific, and has been discussed for the SUSY data set in Notebook 5. More importantly, the user-defined data class must override the `__len__` and `__getitem__` methods of the parent `DataSet` class. The former returns the size of the data set, while the latter allows the user to access a particular data point from the set by specifying its index.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from torchvision import datasets # load data\n\nclass SUSY_Dataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):\n \"\"\"SUSY pytorch dataset.\"\"\"\n\n def __init__(self, data_file, root_dir, dataset_size, train=True, transform=None, high_level_feats=None):\n \"\"\"\n Args:\n csv_file (string): Path to the csv file with annotations.\n root_dir (string): Directory with all the images.\n train (bool, optional): If set to `True` load training data.\n transform (callable, optional): Optional transform to be applied on a sample.\n high_level_festures (bool, optional): If set to `True`, working with high-level features only. \n If set to `False`, working with low-level features only.\n Default is `None`: working with all features\n \"\"\"\n\n import pandas as pd\n\n features=['SUSY','lepton 1 pT', 'lepton 1 eta', 'lepton 1 phi', 'lepton 2 pT', 'lepton 2 eta', 'lepton 2 phi', \n 'missing energy magnitude', 'missing energy phi', 'MET_rel', 'axial MET', 'M_R', 'M_TR_2', 'R', 'MT2', \n 'S_R', 'M_Delta_R', 'dPhi_r_b', 'cos(theta_r1)']\n\n low_features=['lepton 1 pT', 'lepton 1 eta', 'lepton 1 phi', 'lepton 2 pT', 'lepton 2 eta', 'lepton 2 phi', \n 'missing energy magnitude', 'missing energy phi']\n\n high_features=['MET_rel', 'axial MET', 'M_R', 'M_TR_2', 'R', 'MT2','S_R', 'M_Delta_R', 'dPhi_r_b', 'cos(theta_r1)']\n\n\n #Number of datapoints to work with\n df = pd.read_csv(root_dir+data_file, header=None,nrows=dataset_size,engine='python')\n df.columns=features\n Y = df['SUSY']\n X = df[[col for col in df.columns if col!=\"SUSY\"]]\n\n # set training and test data size\n train_size=int(0.8*dataset_size)\n self.train=train\n\n if self.train:\n X=X[:train_size]\n Y=Y[:train_size]\n print(\"Training on {} examples\".format(train_size))\n else:\n X=X[train_size:]\n Y=Y[train_size:]\n print(\"Testing on {} examples\".format(dataset_size-train_size))\n\n\n self.root_dir = root_dir\n self.transform = transform\n\n # make datasets using only the 8 low-level features and 10 high-level features\n if high_level_feats is None:\n self.data=(X.values.astype(np.float32),Y.values.astype(int))\n print(\"Using both high and low level features\")\n elif high_level_feats is True:\n self.data=(X[high_features].values.astype(np.float32),Y.values.astype(int))\n print(\"Using both high-level features only.\")\n elif high_level_feats is False:\n self.data=(X[low_features].values.astype(np.float32),Y.values.astype(int))\n print(\"Using both low-level features only.\")\n\n\n # override __len__ and __getitem__ of the Dataset() class\n\n def __len__(self):\n return len(self.data[1])\n\n def __getitem__(self, idx):\n\n sample=(self.data[0][idx,...],self.data[1][idx])\n\n if self.transform:\n sample=self.transform(sample)\n\n return sample",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Last, we define a helper function `load_data()` that accepts as a required argument the set of parameters `args`, and returns two generators: `test_loader` and `train_loader` which readily return mini-batches.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def load_data(args):\n\n data_file='SUSY.csv'\n root_dir=os.path.expanduser('~')+'/ML_review/SUSY_data/'\n\n kwargs = {} # CUDA arguments, if enabled\n # load and noralise train and test data\n train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(\n SUSY_Dataset(data_file,root_dir,args.dataset_size,train=True,high_level_feats=args.high_level_feats),\n batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs)\n\n test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(\n SUSY_Dataset(data_file,root_dir,args.dataset_size,train=False,high_level_feats=args.high_level_feats),\n batch_size=args.test_batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs)\n\n return train_loader, test_loader",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 2: Define the Neural Net and its Architecture\n\nTo construct neural networks with Pytorch, we make another class called `model` as a child of Pytorch's `nn.Module` class. The `model` class initializes the types of layers needed for the deep neural net in its `__init__` method, while the DNN is assembled in a function method called `forward`, which accepts an `autograd.Variable` object and returns the output layer. Using this convention Pytorch will automatically recognize the structure of the DNN, and the `autograd` module will pull the gradients forward and backward using backprop.\n\nOur code below is constructed in such a way that one can choose whether to use the high-level and low-level features separately and altogether. This choice determines the size of the fully-connected input layer `fc1`. Therefore the `__init__` method accepts the optional argument `high_level_feats`. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import torch.nn as nn # construct NN\n\nclass model(nn.Module):\n def __init__(self,high_level_feats=None):\n # inherit attributes and methods of nn.Module\n super(model, self).__init__()\n\n # an affine operation: y = Wx + b\n if high_level_feats is None:\n self.fc1 = nn.Linear(18, 200) # all features\n elif high_level_feats:\n self.fc1 = nn.Linear(10, 200) # low-level only\n else:\n self.fc1 = nn.Linear(8, 200) # high-level only\n\n\n self.batchnorm1=nn.BatchNorm1d(200, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1)\n self.batchnorm2=nn.BatchNorm1d(100, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1)\n\n self.fc2 = nn.Linear(200, 100) # see forward function for dimensions\n self.fc3 = nn.Linear(100, 2)\n\n def forward(self, x):\n '''Defines the feed-forward function for the NN.\n\n A backward function is automatically defined using `torch.autograd`\n\n Parameters\n ----------\n x : autograd.Tensor\n input data\n\n Returns\n -------\n autograd.Tensor\n output layer of NN\n\n '''\n\n # apply rectified linear unit\n x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))\n # apply dropout\n #x=self.batchnorm1(x)\n x = F.dropout(x, training=self.training)\n\n\n # apply rectified linear unit\n x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))\n # apply dropout\n #x=self.batchnorm2(x)\n x = F.dropout(x, training=self.training)\n\n\n # apply affine operation fc2\n x = self.fc3(x)\n # soft-max layer\n x = F.log_softmax(x,dim=1)\n\n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Steps 3+4+5: Choose the Optimizer and the Cost Function. Train and Evaluate the Model\n\nNext, we define the function `evaluate_model`. The first argument, `args`, contains all hyperparameters needed for the DNN (see below). The second and third arguments are the `train_loader` and the `test_loader` objects, returned by the function `load_data()` we defined in Step 1 above. The `evaluate_model` function returns the final `test_loss` and `test_accuracy` of the model.\n\nFirst, we initialize a `model` and call the object `DNN`. In order to define the loss function and the optimizer, we use modules `torch.nn.functional` (imported here as `F`) and `torch.optim`. As a loss function we choose the negative log-likelihood, and stored is under the variable `criterion`. As usual, we can choose any from a variety of different SGD-based optimizers, but we focus on the traditional SGD.\n\nNext, we define two functions: `train()` and `test()`. They are called at the end of `evaluate_model` where we loop over the training epochs to train and test our model. \n\nThe `train` function accepts an integer called `epoch`, which is only used to print the training data. We first set the `DNN` in a train mode using the `train()` method inherited from `nn.Module`. Then we loop over the mini-batches in `train_loader`. We cast the data as pytorch `Variable`, re-set the `optimizer`, perform the forward step by calling the `DNN` model on the `data` and computing the `loss`. The backprop algorithm is then easily done using the `backward()` method of the loss function `criterion`. We use `optimizer.step` to update the weights of the `DNN`. Last print the performance for every minibatch. `train` returns the loss on the data.\n\nThe `test` function is similar to `train` but its purpose is to test the performance of a trained model. Once we set the `DNN` model in `eval()` mode, the following steps are similar to those in `train`. We then compute the `test_loss` and the number of `correct` predictions, print the results and return them. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import torch.nn.functional as F # implements forward and backward definitions of an autograd operation\nimport torch.optim as optim # different update rules such as SGD, Nesterov-SGD, Adam, RMSProp, etc\n\ndef evaluate_model(args,train_loader,test_loader):\n\n # create model\n DNN = model(high_level_feats=args.high_level_feats)\n # negative log-likelihood (nll) loss for training: takes class labels NOT one-hot vectors!\n criterion = F.nll_loss\n # define SGD optimizer\n optimizer = optim.SGD(DNN.parameters(), lr=args.lr, momentum=args.momentum)\n #optimizer = optim.Adam(DNN.parameters(), lr=0.001, betas=(0.9, 0.999))\n\n\n ################################################\n\n def train(epoch):\n '''Trains a NN using minibatches.\n\n Parameters\n ----------\n epoch : int\n Training epoch number.\n\n '''\n\n # set model to training mode (affects Dropout and BatchNorm)\n DNN.train()\n # loop over training data\n for batch_idx, (data, label) in enumerate(train_loader):\n # zero gradient buffers\n optimizer.zero_grad()\n # compute output of final layer: forward step\n output = DNN(data)\n # compute loss\n loss = criterion(output, label)\n # run backprop: backward step\n loss.backward()\n # update weigths of NN\n optimizer.step()\n \n # print loss at current epoch\n if batch_idx % args.log_interval == 0:\n print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(\n epoch, batch_idx * len(data), len(train_loader.dataset),\n 100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.item() ))\n \n\n return loss.item()\n\n ################################################\n\n def test():\n '''Tests NN performance.\n\n '''\n\n # evaluate model\n DNN.eval()\n\n test_loss = 0 # loss function on test data\n correct = 0 # number of correct predictions\n # loop over test data\n for data, label in test_loader:\n # compute model prediction softmax probability\n output = DNN(data)\n # compute test loss\n test_loss += criterion(output, label, size_average=False).item() # sum up batch loss\n # find most likely prediction\n pred = output.data.max(1, keepdim=True)[1] # get the index of the max log-probability\n # update number of correct predictions\n correct += pred.eq(label.data.view_as(pred)).cpu().sum().item()\n\n # print test loss\n test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset)\n \n print('\\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.3f}%)\\n'.format(\n test_loss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset),\n 100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset)))\n \n\n return test_loss, correct / len(test_loader.dataset)\n\n\n ################################################\n\n\n train_loss=np.zeros((args.epochs,))\n test_loss=np.zeros_like(train_loss)\n test_accuracy=np.zeros_like(train_loss)\n\n epochs=range(1, args.epochs + 1)\n for epoch in epochs:\n\n train_loss[epoch-1] = train(epoch)\n test_loss[epoch-1], test_accuracy[epoch-1] = test()\n\n\n\n return test_loss[-1], test_accuracy[-1]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 6: Modify the Hyperparameters to Optimize Performance of the Model\n\nTo study the performance of the model for a variety of different `data_set_sizes` and `learning_rates`, we do a grid search. \n\nLet us define a function `grid_search`, which accepts the `args` variable containing all hyper-parameters needed for the problem. After choosing logarithmically-spaced `data_set_sizes` and `learning_rates`, we first loop over all `data_set_sizes`, update the `args` variable, and call the `load_data` function. We then loop once again over all `learning_rates`, update `args` and call `evaluate_model`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def grid_search(args):\n\n\n # perform grid search over learnign rate and number of hidden neurons\n dataset_sizes=[1000, 10000, 100000, 200000] #np.logspace(2,5,4).astype('int')\n learning_rates=np.logspace(-5,-1,5)\n\n # pre-alocate data\n test_loss=np.zeros((len(dataset_sizes),len(learning_rates)),dtype=np.float64)\n test_accuracy=np.zeros_like(test_loss)\n\n # do grid search\n for i, dataset_size in enumerate(dataset_sizes):\n # upate data set size parameters\n args.dataset_size=dataset_size\n args.batch_size=int(0.01*dataset_size)\n\n # load data\n train_loader, test_loader = load_data(args)\n\n for j, lr in enumerate(learning_rates):\n # update learning rate\n args.lr=lr\n\n print(\"\\n training DNN with %5d data points and SGD lr=%0.6f. \\n\" %(dataset_size,lr) )\n\n test_loss[i,j],test_accuracy[i,j] = evaluate_model(args,train_loader,test_loader)\n\n\n plot_data(learning_rates,dataset_sizes,test_accuracy)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Last, we use the function `plot_data`, defined below, to plot the results. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\ndef plot_data(x,y,data):\n\n # plot results\n fontsize=16\n\n\n fig = plt.figure()\n ax = fig.add_subplot(111)\n cax = ax.matshow(data, interpolation='nearest', vmin=0, vmax=1)\n \n cbar=fig.colorbar(cax)\n cbar.ax.set_ylabel('accuracy (%)',rotation=90,fontsize=fontsize)\n cbar.set_ticks([0,.2,.4,0.6,0.8,1.0])\n cbar.set_ticklabels(['0%','20%','40%','60%','80%','100%'])\n\n # put text on matrix elements\n for i, x_val in enumerate(np.arange(len(x))):\n for j, y_val in enumerate(np.arange(len(y))):\n c = \"${0:.1f}\\\\%$\".format( 100*data[j,i]) \n ax.text(x_val, y_val, c, va='center', ha='center')\n\n # convert axis vaues to to string labels\n x=[str(i) for i in x]\n y=[str(i) for i in y]\n\n\n ax.set_xticklabels(['']+x)\n ax.set_yticklabels(['']+y)\n\n ax.set_xlabel('$\\\\mathrm{learning\\\\ rate}$',fontsize=fontsize)\n ax.set_ylabel('$\\\\mathrm{hidden\\\\ neurons}$',fontsize=fontsize)\n\n plt.tight_layout()\n\n plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Run Code\n\nAs we mentioned in the beginning of the notebook, all functions and classes discussed above only specify the procedure but do not actually perform any computations. This allows us to re-use them for different problems. \n\nActually running the training and testing for every point in the grid search is done below. The `argparse` class allows us to conveniently keep track of all hyperparameters, stored in the variable `args` which enters most of the functions we defined above. \n\nTo run the simulation, we call the function `grid_search`. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Exercises\n\n* One of the advantages of Pytorch is that it allows to automatically use the CUDA library for fast performance on GPU's. For the sake of clarity, we have omitted this in the above notebook. Go online to check how to put the CUDA commands back into the code above. _Hint:_ study the [Pytorch MNIST tutorial](https://github.com/pytorch/examples/blob/master/mnist/main.py) to see how this works in practice.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import argparse # handles arguments\nimport sys; sys.argv=['']; del sys # required to use parser in jupyter notebooks\n\n# Training settings\nparser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch SUSY Example')\nparser.add_argument('--dataset_size', type=int, default=100000, metavar='DS',\n help='size of data set (default: 100000)')\nparser.add_argument('--high_level_feats', type=bool, default=None, metavar='HLF',\n help='toggles high level features (default: None)')\nparser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=100, metavar='N',\n help='input batch size for training (default: 64)')\nparser.add_argument('--test-batch-size', type=int, default=1000, metavar='N',\n help='input batch size for testing (default: 1000)')\nparser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=10, metavar='N',\n help='number of epochs to train (default: 10)')\nparser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=0.05, metavar='LR',\n help='learning rate (default: 0.02)')\nparser.add_argument('--momentum', type=float, default=0.8, metavar='M',\n help='SGD momentum (default: 0.5)')\nparser.add_argument('--no-cuda', action='store_true', default=False,\n help='disables CUDA training')\nparser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=2, metavar='S',\n help='random seed (default: 1)')\nparser.add_argument('--log-interval', type=int, default=10, metavar='N',\n help='how many batches to wait before logging training status')\nargs = parser.parse_args()\n\n# set seed of random number generator\ntorch.manual_seed(args.seed)\n\ngrid_search(args)\n",
"Training on 800 examples\nUsing both high and low level features\nTesting on 200 examples\nUsing both high and low level features\n\n training DNN with 1000 data points and SGD lr=0.000010. \n\nTrain Epoch: 1 [0/800 (0%)]\tLoss: 0.561476\nTrain Epoch: 1 [100/800 (12%)]\tLoss: 0.823435\nTrain Epoch: 1 [200/800 (25%)]\tLoss: 0.647225\nTrain Epoch: 1 [300/800 (38%)]\tLoss: 0.612186\nTrain Epoch: 1 [400/800 (50%)]\tLoss: 0.962393\nTrain Epoch: 1 [500/800 (62%)]\tLoss: 0.835941\nTrain Epoch: 1 [600/800 (75%)]\tLoss: 0.808794\nTrain Epoch: 1 [700/800 (88%)]\tLoss: 0.766973\n\nTest set: Average loss: 0.7115, Accuracy: 109/200 (54.500%)\n\nTrain Epoch: 2 [0/800 (0%)]\tLoss: 0.861468\nTrain Epoch: 2 [100/800 (12%)]\tLoss: 0.653841\nTrain Epoch: 2 [200/800 (25%)]\tLoss: 0.823339\nTrain Epoch: 2 [300/800 (38%)]\tLoss: 0.745887\nTrain Epoch: 2 [400/800 (50%)]\tLoss: 0.694589\nTrain Epoch: 2 [500/800 (62%)]\tLoss: 0.693052\nTrain Epoch: 2 [600/800 (75%)]\tLoss: 0.719047\nTrain Epoch: 2 [700/800 (88%)]\tLoss: 0.591686\n\nTest set: Average loss: 0.7107, Accuracy: 109/200 (54.500%)\n\nTrain Epoch: 3 [0/800 (0%)]\tLoss: 0.728128\nTrain Epoch: 3 [100/800 (12%)]\tLoss: 0.698269\nTrain Epoch: 3 [200/800 (25%)]\tLoss: 0.705191\nTrain Epoch: 3 [300/800 (38%)]\tLoss: 0.683300\nTrain Epoch: 3 [400/800 (50%)]\tLoss: 0.732665\nTrain Epoch: 3 [500/800 (62%)]\tLoss: 0.849138\nTrain Epoch: 3 [600/800 (75%)]\tLoss: 0.728277\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
cbe72624a076210fd98a1b79a3d18e4457525104
| 377,479 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Tutorial-Start_to_Finish-BSSNCurvilinear-Setting_up_Exact_Initial_Data.ipynb
|
philchang/nrpytutorial
|
a69d90777b2519192e3c53a129fe42827224faa3
|
[
"BSD-2-Clause"
] | 2 |
2021-07-16T02:35:40.000Z
|
2021-08-02T15:08:20.000Z
|
Tutorial-Start_to_Finish-BSSNCurvilinear-Setting_up_Exact_Initial_Data.ipynb
|
philchang/nrpytutorial
|
a69d90777b2519192e3c53a129fe42827224faa3
|
[
"BSD-2-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
Tutorial-Start_to_Finish-BSSNCurvilinear-Setting_up_Exact_Initial_Data.ipynb
|
philchang/nrpytutorial
|
a69d90777b2519192e3c53a129fe42827224faa3
|
[
"BSD-2-Clause"
] | null | null | null | 305.403722 | 191,120 | 0.912965 |
[
[
[
"<script async src=\"https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtag/js?id=UA-59152712-8\"></script>\n<script>\n window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || [];\n function gtag(){dataLayer.push(arguments);}\n gtag('js', new Date());\n\n gtag('config', 'UA-59152712-8');\n</script>\n\n# Start-to-Finish Example: Setting up Exact Initial Data for Einstein's Equations, in Curvilinear Coordinates\n## Authors: Brandon Clark, George Vopal, and Zach Etienne\n\n## This module sets up initial data for a specified exact solution written in terms of ADM variables, using the [*Exact* ADM Spherical to BSSN Curvilinear initial data module](../edit/BSSN/ADM_Exact_Spherical_or_Cartesian_to_BSSNCurvilinear.py).\n\n**Notebook Status:** <font color='green'><b> Validated </b></font>\n\n**Validation Notes:** This module has been validated, confirming that all initial data sets exhibit convergence to zero of the Hamiltonian and momentum constraints at the expected rate or better.\n\n### NRPy+ Source Code for this module:\n* [BSSN/ADM_Exact_Spherical_or_Cartesian_to_BSSNCurvilinear.py](../edit/BSSN/ADM_Exact_Spherical_or_Cartesian_to_BSSNCurvilinear.py); [\\[**tutorial**\\]](Tutorial-ADM_Initial_Data-Converting_Exact_ADM_Spherical_or_Cartesian_to_BSSNCurvilinear.ipynb): *Exact* Spherical ADM$\\to$Curvilinear BSSN converter function\n* [BSSN/BSSN_constraints.py](../edit/BSSN/BSSN_constraints.py); [\\[**tutorial**\\]](Tutorial-BSSN_constraints.ipynb): Hamiltonian & momentum constraints in BSSN curvilinear basis/coordinates\n\n## Introduction:\nHere we use NRPy+ to generate a C code confirming that specified *exact* initial data satisfy Einstein's equations of general relativity. The following exact initial data types are supported:\n\n* Shifted Kerr-Schild spinning black hole initial data\n* \"Static\" Trumpet black hole initial data\n* Brill-Lindquist two black hole initial data\n* UIUC black hole initial data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id='toc'></a>\n\n# Table of Contents\n$$\\label{toc}$$\n\nThis notebook is organized as follows\n\n0. [Preliminaries](#prelim): The Choices for Initial Data\n 1. [Choice 1](#sks): Shifted Kerr-Schild spinning black hole initial data\n 1. [Choice 2](#st): \"Static\" Trumpet black hole initial data\n 1. [Choice 3](#bl): Brill-Lindquist two black hole initial data\n 1. [Choice 4](#uiuc): UIUC black hole initial data\n1. [Step 2](#initializenrpy): Set core NRPy+ parameters for numerical grids and reference metric\n1. [Step 3](#adm_id): Import Black Hole ADM initial data C function from NRPy+ module\n1. [Step 4](#validate): Validating that the black hole initial data satisfy the Hamiltonian constraint\n 1. [Step 4.a](#ham_const_output): Output C code for evaluating the Hamiltonian and Momentum constraint violation\n 1. [Step 4.b](#apply_bcs): Apply singular, curvilinear coordinate boundary conditions\n 1. [Step 4.c](#enforce3metric): Enforce conformal 3-metric $\\det{\\bar{\\gamma}_{ij}}=\\det{\\hat{\\gamma}_{ij}}$ constraint\n1. [Step 5](#mainc): `Initial_Data.c`: The Main C Code\n1. [Step 6](#plot): Plotting the initial data\n1. [Step 7](#convergence): Validation: Convergence of numerical errors (Hamiltonian constraint violation) to zero\n1. [Step 8](#latex_pdf_output): Output this notebook to $\\LaTeX$-formatted PDF file",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id='prelim'></a>\n\n# Preliminaries: The Choices for Initial Data\n$$\\label{prelim}$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id='sks'></a>\n\n## Shifted Kerr-Schild spinning black hole initial data \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{sks}$$\n\nHere we use NRPy+ to generate initial data for a spinning black hole.\n\nShifted Kerr-Schild spinning black hole initial data has been <font color='green'><b> validated </b></font> to exhibit convergence to zero of both the Hamiltonian and momentum constraint violations at the expected order to the exact solution.\n\n**NRPy+ Source Code:**\n* [BSSN/ShiftedKerrSchild.py](../edit/BSSN/ShiftedKerrSchild.py); [\\[**tutorial**\\]](Tutorial-ADM_Initial_Data-ShiftedKerrSchild.ipynb)\n\nThe [BSSN.ShiftedKerrSchild](../edit/BSSN/ShiftedKerrSchild.py) NRPy+ module does the following:\n\n1. Set up shifted Kerr-Schild initial data, represented by [ADM](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ADM_formalism) quantities in the **Spherical basis**, as [documented here](Tutorial-ADM_Initial_Data-ShiftedKerrSchild.ipynb). \n1. Convert the exact ADM **Spherical quantities** to **BSSN quantities in the desired Curvilinear basis** (set by `reference_metric::CoordSystem`), as [documented here](Tutorial-ADM_Initial_Data-Converting_Numerical_ADM_Spherical_or_Cartesian_to_BSSNCurvilinear.ipynb).\n1. Sets up the standardized C function for setting all BSSN Curvilinear gridfunctions in a pointwise fashion, as [written here](../edit/BSSN/BSSN_ID_function_string.py), and returns the C function as a Python string.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id='st'></a>\n\n## \"Static\" Trumpet black hole initial data \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{st}$$\n\nHere we use NRPy+ to generate initial data for a single trumpet black hole ([Dennison & Baumgarte, PRD ???](https://arxiv.org/abs/??)).\n\n\"Static\" Trumpet black hole initial data has been <font color='green'><b> validated </b></font> to exhibit convergence to zero of the Hamiltonian constraint violation at the expected order to the exact solution. It was carefully ported from the [original NRPy+ code](https://bitbucket.org/zach_etienne/nrpy).\n\n**NRPy+ Source Code:**\n* [BSSN/StaticTrumpet.py](../edit/BSSN/StaticTrumpet.py); [\\[**tutorial**\\]](Tutorial-ADM_Initial_Data-StaticTrumpet.ipynb)\n\nThe [BSSN.StaticTrumpet](../edit/BSSN/StaticTrumpet.py) NRPy+ module does the following:\n\n1. Set up static trumpet black hole initial data, represented by [ADM](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ADM_formalism) quantities in the **Spherical basis**, as [documented here](Tutorial-ADM_Initial_Data-StaticTrumpetBlackHole.ipynb). \n1. Convert the exact ADM **Spherical quantities** to **BSSN quantities in the desired Curvilinear basis** (set by `reference_metric::CoordSystem`), as [documented here](Tutorial-ADM_Initial_Data-Converting_Numerical_ADM_Spherical_or_Cartesian_to_BSSNCurvilinear.ipynb).\n1. Sets up the standardized C function for setting all BSSN Curvilinear gridfunctions in a pointwise fashion, as [written here](../edit/BSSN/BSSN_ID_function_string.py), and returns the C function as a Python string.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id='bl'></a>\n\n## Brill-Lindquist initial data \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{bl}$$\n\nHere we use NRPy+ to generate initial data for two black holes (Brill-Lindquist, [Brill & Lindquist, Phys. Rev. 131, 471, 1963](https://journals.aps.org/pr/abstract/10.1103/PhysRev.131.471); see also Eq. 1 of [Brandt & Brügmann, arXiv:gr-qc/9711015v1](https://arxiv.org/pdf/gr-qc/9711015v1.pdf)).\n\n[//]: # \" and then we use it to generate the RHS expressions for [Method of Lines](https://reference.wolfram.com/language/tutorial/NDSolveMethodOfLines.html) time integration based on the [explicit Runge-Kutta fourth-order scheme](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Runge%E2%80%93Kutta_methods) (RK4).\"\n\nBrill-Lindquist initial data has been <font color='green'><b> validated </b></font> to exhibit convergence to zero of the Hamiltonian constraint violation at the expected order to the exact solution, and all quantities have been validated against the [original SENR code](https://bitbucket.org/zach_etienne/nrpy).\n\n**NRPy+ Source Code:**\n* [BSSN/BrillLindquist.py](../edit/BSSN/BrillLindquist.py); [\\[**tutorial**\\]](Tutorial-ADM_Initial_Data-Brill-Lindquist.ipynb)\n* [BSSN/BSSN_ID_function_string.py](../edit/BSSN/BSSN_ID_function_string.py)\n\nThe [BSSN.BrillLindquist](../edit/BSSN/BrillLindquist.py) NRPy+ module does the following:\n\n1. Set up Brill-Lindquist initial data [ADM](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ADM_formalism) quantities in the **Cartesian basis**, as [documented here](Tutorial-ADM_Initial_Data-Brill-Lindquist.ipynb). \n1. Convert the ADM **Cartesian quantities** to **BSSN quantities in the desired Curvilinear basis** (set by `reference_metric::CoordSystem`), as [documented here](Tutorial-ADM_Initial_Data-Converting_ADMCartesian_to_BSSNCurvilinear.ipynb).\n1. Sets up the standardized C function for setting all BSSN Curvilinear gridfunctions in a pointwise fashion, as [written here](../edit/BSSN/BSSN_ID_function_string.py), and returns the C function as a Python string.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id='uiuc'></a>\n\n## UIUC black hole initial data \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{uiuc}$$ \n\nUIUC black hole initial data has been <font color='green'><b> validated </b></font> to exhibit convergence to zero of the Hamiltonian constraint violation at the expected order to the exact solution, and all quantities have been validated against the [original SENR code](https://bitbucket.org/zach_etienne/nrpy).\n\n**NRPy+ Source Code:**\n* [BSSN/UIUCBlackHole.py](../edit/BSSN/UIUCBlackHole.py); [\\[**tutorial**\\]](Tutorial-ADM_Initial_Data-UIUCBlackHole.ipynb)\n\nThe [BSSN.UIUCBlackHole](../edit/BSSN/UIUCBlackHole.py) NRPy+ module does the following:\n\n1. Set up UIUC black hole initial data, represented by [ADM](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ADM_formalism) quantities in the **Spherical basis**, as [documented here](Tutorial-ADM_Initial_Data-UIUCBlackHole.ipynb). \n1. Convert the numerical ADM **Spherical quantities** to **BSSN quantities in the desired Curvilinear basis** (set by `reference_metric::CoordSystem`), as [documented here](Tutorial-ADM_Initial_Data-Converting_Numerical_ADM_Spherical_or_Cartesian_to_BSSNCurvilinear.ipynb).\n1. Sets up the standardized C function for setting all BSSN Curvilinear gridfunctions in a pointwise fashion, as [written here](../edit/BSSN/BSSN_ID_function_string.py), and returns the C function as a Python string.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id='-pickid'></a>\n\n# Step 1: Specify the Initial Data to Test \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{pickid}$$\n\nHere you have a choice for which initial data you would like to import and test for convergence. The following is a list of the currently compatible `initial_data_string` options for you to choose from.\n\n* `\"Shifted KerrSchild\"`\n* `\"Static Trumpet\"`\n* `\"Brill-Lindquist\"`\n* `\"UIUC\"`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import collections\n\n#################\n# For the User: Choose initial data, default is Shifted KerrSchild.\n# You are also encouraged to adjust any of the\n# DestGridCoordSystem, freeparams, or EnableMomentum parameters!\n# NOTE: Only DestGridCoordSystem == Spherical or SinhSpherical\n# currently work out of the box; additional modifications\n# will likely be necessary for other CoordSystems.\n#################\ninitial_data_string = \"Shifted KerrSchild\" # \"UIUC\"\n\n\ndictID = {}\nIDmod_retfunc = collections.namedtuple('IDmod_retfunc', 'modulename functionname DestGridCoordSystem freeparams EnableMomentum')\n\ndictID['Shifted KerrSchild'] = IDmod_retfunc(\n modulename = \"BSSN.ShiftedKerrSchild\", functionname = \"ShiftedKerrSchild\",\n DestGridCoordSystem = \"Spherical\",\n freeparams = [\"const REAL M = 1.0;\", \"const REAL a = 0.9;\", \"const REAL r0 = 1.0;\"],\n EnableMomentum = True)\n\ndictID['Static Trumpet'] = IDmod_retfunc(\n modulename = \"BSSN.StaticTrumpet\", functionname = \"StaticTrumpet\",\n DestGridCoordSystem = \"Spherical\",\n freeparams = [\"const REAL M = 1.0;\"],\n EnableMomentum = False)\n\ndictID['Brill-Lindquist'] = IDmod_retfunc(\n modulename = \"BSSN.BrillLindquist\", functionname = \"BrillLindquist\",\n DestGridCoordSystem = \"Spherical\",\n freeparams = [\"const REAL BH1_posn_x =-1.0,BH1_posn_y = 0.0,BH1_posn_z = 0.0;\",\n \"const REAL BH2_posn_x = 1.0,BH2_posn_y = 0.0,BH2_posn_z = 0.0;\", \"const REAL BH1_mass = 0.5,BH2_mass = 0.5;\"],\n EnableMomentum = False)\n\ndictID['UIUC'] = IDmod_retfunc(modulename = \"BSSN.UIUCBlackHole\", functionname = \"UIUCBlackHole\",\n DestGridCoordSystem = \"SinhSpherical\",\n freeparams = [\"const REAL M = 1.0;\", \"const REAL chi = 0.99;\"],\n EnableMomentum = True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='initializenrpy'></a>\n\n# Step 2: Set up the needed NRPy+ infrastructure and declare core gridfunctions \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{initializenrpy}$$\n\nWe will import the core modules of NRPy that we will need and specify the main gridfunctions we will need.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Step P1: Import needed NRPy+ core modules:\nfrom outputC import lhrh,outC_function_dict,outCfunction # NRPy+: Core C code output module\nimport finite_difference as fin # NRPy+: Finite difference C code generation module\nimport NRPy_param_funcs as par # NRPy+: Parameter interface\nimport grid as gri # NRPy+: Functions having to do with numerical grids\nimport indexedexp as ixp # NRPy+: Symbolic indexed expression (e.g., tensors, vectors, etc.) support\nimport reference_metric as rfm # NRPy+: Reference metric support\nimport cmdline_helper as cmd # NRPy+: Multi-platform Python command-line interface\nimport shutil, os, sys, time # Standard Python modules for multiplatform OS-level functions, benchmarking\nimport importlib # Standard Python module for interactive module imports\n\n# Step P2: Create C code output directory:\nCcodesdir = os.path.join(\"BlackHoleID_Ccodes/\")\n# First remove C code output directory if it exists\n# Courtesy https://stackoverflow.com/questions/303200/how-do-i-remove-delete-a-folder-that-is-not-empty\n# !rm -r ScalarWaveCurvilinear_Playground_Ccodes\nshutil.rmtree(Ccodesdir, ignore_errors=True)\n# Then create a fresh directory\ncmd.mkdir(Ccodesdir)\n\n# Step P3: Create executable output directory:\noutdir = os.path.join(Ccodesdir,\"output/\")\ncmd.mkdir(outdir)\n\n# Step 1: Set the spatial dimension parameter\n# to three this time, and then read\n# the parameter as DIM.\npar.set_parval_from_str(\"grid::DIM\",3)\nDIM = par.parval_from_str(\"grid::DIM\")\n\n# Step 2: Set some core parameters, including CoordSystem MoL timestepping algorithm,\n# FD order, floating point precision, and CFL factor:\n# Choices are: Spherical, SinhSpherical, SinhSphericalv2, Cylindrical, SinhCylindrical,\n# SymTP, SinhSymTP\nCoordSystem = \"Spherical\"\n\n# Step 2.a: Set defaults for Coordinate system parameters.\n# These are perhaps the most commonly adjusted parameters,\n# so we enable modifications at this high level.\n\n# domain_size sets the default value for:\n# * Spherical's params.RMAX\n# * SinhSpherical*'s params.AMAX\n# * Cartesians*'s -params.{x,y,z}min & .{x,y,z}max\n# * Cylindrical's -params.ZMIN & .{Z,RHO}MAX\n# * SinhCylindrical's params.AMPL{RHO,Z}\n# * *SymTP's params.AMAX\ndomain_size = 3.0\n\n# sinh_width sets the default value for:\n# * SinhSpherical's params.SINHW\n# * SinhCylindrical's params.SINHW{RHO,Z}\n# * SinhSymTP's params.SINHWAA\nsinh_width = 0.4 # If Sinh* coordinates chosen\n\n# sinhv2_const_dr sets the default value for:\n# * SinhSphericalv2's params.const_dr\n# * SinhCylindricalv2's params.const_d{rho,z}\nsinhv2_const_dr = 0.05# If Sinh*v2 coordinates chosen\n\n# SymTP_bScale sets the default value for:\n# * SinhSymTP's params.bScale\nSymTP_bScale = 0.5 # If SymTP chosen\n\nFD_order = 4 # Finite difference order: even numbers only, starting with 2. 12 is generally unstable\nREAL = \"double\" # Best to use double here.\n\n# Step 3: Set the coordinate system for the numerical grid\npar.set_parval_from_str(\"reference_metric::CoordSystem\",CoordSystem)\nrfm.reference_metric() # Create ReU, ReDD needed for rescaling B-L initial data, generating BSSN RHSs, etc.\n\n# Step 4: Set the finite differencing order to FD_order (set above).\npar.set_parval_from_str(\"finite_difference::FD_CENTDERIVS_ORDER\", FD_order)\n\n# Step 5: Set the direction=2 (phi) axis to be the symmetry axis; i.e.,\n# axis \"2\", corresponding to the i2 direction.\n# This sets all spatial derivatives in the phi direction to zero.\npar.set_parval_from_str(\"indexedexp::symmetry_axes\",\"2\")\n\n# Step 6: The MoLtimestepping interface is only used for memory allocation/deallocation\nimport MoLtimestepping.C_Code_Generation as MoL\nfrom MoLtimestepping.RK_Butcher_Table_Dictionary import Butcher_dict\nRK_method = \"Euler\" # DOES NOT MATTER; Again MoL interface is only used for memory alloc/dealloc.\nRK_order = Butcher_dict[RK_method][1]\ncmd.mkdir(os.path.join(Ccodesdir,\"MoLtimestepping/\"))\nMoL.MoL_C_Code_Generation(RK_method, RHS_string = \"\", post_RHS_string = \"\",\n outdir = os.path.join(Ccodesdir,\"MoLtimestepping/\"))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='adm_id'></a>\n\n# Step 3: Import Black Hole ADM initial data C function from NRPy+ module \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{adm_id}$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import Black Hole initial data\n\nIDmodule = importlib.import_module(dictID[initial_data_string].modulename)\nIDfunc = getattr(IDmodule, dictID[initial_data_string].functionname)\nIDfunc() # Registers ID C function in dictionary, used below to output to file.\nwith open(os.path.join(Ccodesdir,\"initial_data.h\"),\"w\") as file:\n file.write(outC_function_dict[\"initial_data\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='cparams_rfm_and_domainsize'></a>\n\n## Step 3.a: Output C codes needed for declaring and setting Cparameters; also set `free_parameters.h` \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{cparams_rfm_and_domainsize}$$\n\nBased on declared NRPy+ Cparameters, first we generate `declare_Cparameters_struct.h`, `set_Cparameters_default.h`, and `set_Cparameters[-SIMD].h`.\n\nThen we output `free_parameters.h`, which sets initial data parameters, as well as grid domain & reference metric parameters, applying `domain_size` and `sinh_width`/`SymTP_bScale` (if applicable) as set above",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Step 3.a.i: Set free_parameters.h\n# Output to $Ccodesdir/free_parameters.h reference metric parameters based on generic\n# domain_size,sinh_width,sinhv2_const_dr,SymTP_bScale,\n# parameters set above.\nrfm.out_default_free_parameters_for_rfm(os.path.join(Ccodesdir,\"free_parameters.h\"),\n domain_size,sinh_width,sinhv2_const_dr,SymTP_bScale)\n\n# Step 3.a.ii: Generate set_Nxx_dxx_invdx_params__and__xx.h:\nrfm.set_Nxx_dxx_invdx_params__and__xx_h(Ccodesdir)\n\n# Step 3.a.iii: Generate xx_to_Cart.h, which contains xx_to_Cart() for\n# (the mapping from xx->Cartesian) for the chosen\n# CoordSystem:\nrfm.xx_to_Cart_h(\"xx_to_Cart\",\"./set_Cparameters.h\",os.path.join(Ccodesdir,\"xx_to_Cart.h\"))\n\n# Step 3.a.iv: Generate declare_Cparameters_struct.h, set_Cparameters_default.h, and set_Cparameters[-SIMD].h\npar.generate_Cparameters_Ccodes(os.path.join(Ccodesdir))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='validate'></a>\n\n# Step 4: Validating that the black hole initial data satisfy the Hamiltonian constraint \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{validate}$$\n\nWe will validate that the black hole initial data satisfy the Hamiltonian constraint, modulo numerical finite differencing error.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id='ham_const_output'></a>\n\n## Step 4.a: Output C code for evaluating the Hamiltonian and Momentum constraint violation \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{ham_const_output}$$\n\nFirst output C code for evaluating the Hamiltonian constraint violation. For the initial data where `EnableMomentum = True` we must also output C code for evaluating the Momentum constraint violation.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import BSSN.BSSN_constraints as bssncon\n# Now register the Hamiltonian & momentum constraints as gridfunctions.\nH = gri.register_gridfunctions(\"AUX\",\"H\")\nMU = ixp.register_gridfunctions_for_single_rank1(\"AUX\", \"MU\")\n\n# Generate symbolic expressions for Hamiltonian & momentum constraints\nimport BSSN.BSSN_constraints as bssncon\nbssncon.BSSN_constraints(add_T4UUmunu_source_terms=False)\n\n# Generate optimized C code for Hamiltonian constraint\ndesc=\"Evaluate the Hamiltonian constraint\"\nname=\"Hamiltonian_constraint\"\noutCfunction(\n outfile = os.path.join(Ccodesdir,name+\".h\"), desc=desc, name=name,\n params = \"\"\"const paramstruct *restrict params, REAL *restrict xx[3],\n REAL *restrict in_gfs, REAL *restrict aux_gfs\"\"\",\n body = fin.FD_outputC(\"returnstring\",lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"aux_gfs\", \"H\"), rhs=bssncon.H),\n params=\"outCverbose=False\"),\n loopopts = \"InteriorPoints,Read_xxs\")\n\n# Generate optimized C code for momentum constraint\ndesc=\"Evaluate the momentum constraint\"\nname=\"momentum_constraint\"\noutCfunction(\n outfile = os.path.join(Ccodesdir,name+\".h\"), desc=desc, name=name,\n params = \"\"\"const paramstruct *restrict params, REAL *restrict xx[3],\n REAL *restrict in_gfs, REAL *restrict aux_gfs\"\"\",\n body = fin.FD_outputC(\"returnstring\",\n [lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"aux_gfs\", \"MU0\"), rhs=bssncon.MU[0]),\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"aux_gfs\", \"MU1\"), rhs=bssncon.MU[1]),\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"aux_gfs\", \"MU2\"), rhs=bssncon.MU[2])],\n params=\"outCverbose=False\"),\n loopopts = \"InteriorPoints,Read_xxs\")",
"Output C function Hamiltonian_constraint() to file BlackHoleID_Ccodes/Hamiltonian_constraint.h\nOutput C function momentum_constraint() to file BlackHoleID_Ccodes/momentum_constraint.h\n"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='enforce3metric'></a>\n\n## Step 4.b: Enforce conformal 3-metric $\\det{\\bar{\\gamma}_{ij}}=\\det{\\hat{\\gamma}_{ij}}$ constraint \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{enforce3metric}$$\n\nThen enforce conformal 3-metric $\\det{\\bar{\\gamma}_{ij}}=\\det{\\hat{\\gamma}_{ij}}$ constraint (Eq. 53 of [Ruchlin, Etienne, and Baumgarte (2018)](https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.07658)), as [documented in the corresponding NRPy+ tutorial notebook](Tutorial-BSSN_enforcing_determinant_gammabar_equals_gammahat_constraint.ipynb)\n\nApplying curvilinear boundary conditions should affect the initial data at the outer boundary, and will in general cause the $\\det{\\bar{\\gamma}_{ij}}=\\det{\\hat{\\gamma}_{ij}}$ constraint to be violated there. Thus after we apply these boundary conditions, we must always call the routine for enforcing the $\\det{\\bar{\\gamma}_{ij}}=\\det{\\hat{\\gamma}_{ij}}$ constraint:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Set up the C function for the det(gammahat) = det(gammabar)\nimport BSSN.Enforce_Detgammahat_Constraint as EGC\nenforce_detg_constraint_symb_expressions = EGC.Enforce_Detgammahat_Constraint_symb_expressions()\n\nEGC.output_Enforce_Detgammahat_Constraint_Ccode(Ccodesdir,exprs=enforce_detg_constraint_symb_expressions,\n Read_xxs=True)",
"Output C function enforce_detgammahat_constraint() to file BlackHoleID_Ccodes/enforce_detgammahat_constraint.h\n"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='bc_functs'></a>\n\n## Step 4.c: Set up boundary condition functions for chosen singular, curvilinear coordinate system \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{bc_functs}$$\n\nNext apply singular, curvilinear coordinate boundary conditions [as documented in the corresponding NRPy+ tutorial notebook](Tutorial-Start_to_Finish-Curvilinear_BCs.ipynb)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import CurviBoundaryConditions.CurviBoundaryConditions as cbcs\ncbcs.Set_up_CurviBoundaryConditions(os.path.join(Ccodesdir,\"boundary_conditions/\"),Cparamspath=os.path.join(\"../\"))",
"Wrote to file \"BlackHoleID_Ccodes/boundary_conditions/parity_conditions_symbolic_dot_products.h\"\nEvolved parity: ( aDD00:4, aDD01:5, aDD02:6, aDD11:7, aDD12:8, aDD22:9,\n alpha:0, betU0:1, betU1:2, betU2:3, cf:0, hDD00:4, hDD01:5, hDD02:6,\n hDD11:7, hDD12:8, hDD22:9, lambdaU0:1, lambdaU1:2, lambdaU2:3, trK:0,\n vetU0:1, vetU1:2, vetU2:3 )\nAuxiliary parity: ( H:0, MU0:1, MU1:2, MU2:3 )\n\nWrote to file \"BlackHoleID_Ccodes/boundary_conditions/EigenCoord_Cart_to_xx.h\"\n"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='mainc'></a>\n\n# Step 5: `Initial_Data_Playground.c`: The Main C Code \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{mainc}$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Part P0: Set the number of ghost cells, from NRPy+'s FD_CENTDERIVS_ORDER\n# set REAL=double, so that all floating point numbers are stored to at least ~16 significant digits.\n\nwith open(os.path.join(Ccodesdir,\"Initial_Data_Playground_REAL__NGHOSTS.h\"), \"w\") as file:\n file.write(\"\"\"\n// Part P0.a: Set the number of ghost cells, from NRPy+'s FD_CENTDERIVS_ORDER\n#define NGHOSTS \"\"\"+str(int(par.parval_from_str(\"finite_difference::FD_CENTDERIVS_ORDER\")/2)+1)+\"\"\"\\n\n// Part P0.b: Set the numerical precision (REAL) to double, ensuring all floating point\n// numbers are stored to at least ~16 significant digits\n#define REAL double\\n\"\"\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%writefile $Ccodesdir/Initial_Data_Playground.c\n\n// Step P0: Define REAL and NGHOSTS. This header is generated by NRPy+.\n#include \"Initial_Data_Playground_REAL__NGHOSTS.h\"\n\n#include \"declare_Cparameters_struct.h\"\n\n// Step P1: Import needed header files\n#include \"stdio.h\"\n#include \"stdlib.h\"\n#include \"math.h\"\n#ifndef M_PI\n#define M_PI 3.141592653589793238462643383279502884L\n#endif\n#ifndef M_SQRT1_2\n#define M_SQRT1_2 0.707106781186547524400844362104849039L\n#endif\n\n// Step P2: Declare the IDX4S(gf,i,j,k) macro, which enables us to store 4-dimensions of\n// data in a 1D array. In this case, consecutive values of \"i\"\n// (all other indices held to a fixed value) are consecutive in memory, where\n// consecutive values of \"j\" (fixing all other indices) are separated by\n// Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0 elements in memory. Similarly, consecutive values of\n// \"k\" are separated by Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS1 in memory, etc.\n#define IDX4S(g,i,j,k) \\\n( (i) + Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0 * ( (j) + Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS1 * ( (k) + Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS2 * (g) ) ) )\n#define IDX4ptS(g,idx) ( (idx) + (Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS1*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS2) * (g) )\n#define IDX3S(i,j,k) ( (i) + Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0 * ( (j) + Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS1 * ( (k) ) ) )\n#define LOOP_REGION(i0min,i0max, i1min,i1max, i2min,i2max) \\\n for(int i2=i2min;i2<i2max;i2++) for(int i1=i1min;i1<i1max;i1++) for(int i0=i0min;i0<i0max;i0++)\n#define LOOP_ALL_GFS_GPS(ii) _Pragma(\"omp parallel for\") \\\n for(int (ii)=0;(ii)<Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS_tot*NUM_EVOL_GFS;(ii)++)\n\n// Step P3: Set UUGF and VVGF macros, as well as xx_to_Cart()\n#include \"boundary_conditions/gridfunction_defines.h\"\n\n// Step P4: Set xx_to_Cart(const paramstruct *restrict params,\n// REAL *restrict xx[3],\n// const int i0,const int i1,const int i2,\n// REAL xCart[3]),\n// which maps xx->Cartesian via\n// {xx[0][i0],xx[1][i1],xx[2][i2]}->{xCart[0],xCart[1],xCart[2]}\n#include \"xx_to_Cart.h\"\n\n// Step P5: Defines set_Nxx_dxx_invdx_params__and__xx(const int EigenCoord, const int Nxx[3],\n// paramstruct *restrict params, REAL *restrict xx[3]),\n// which sets params Nxx,Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS,dxx,invdx, and xx[] for\n// the chosen Eigen-CoordSystem if EigenCoord==1, or\n// CoordSystem if EigenCoord==0.\n#include \"set_Nxx_dxx_invdx_params__and__xx.h\"\n\n// Step P6: Include basic functions needed to impose curvilinear\n// parity and boundary conditions.\n#include \"boundary_conditions/CurviBC_include_Cfunctions.h\"\n\n// Step P8: Include function for enforcing detgammabar constraint.\n#include \"enforce_detgammahat_constraint.h\"\n\n// Step P10: Declare function necessary for setting up the initial data.\n// Step P10.a: Define BSSN_ID() for BrillLindquist initial data\n\n// Step P10.b: Set the generic driver function for setting up BSSN initial data\n#include \"initial_data.h\"\n\n// Step P11: Declare function for evaluating Hamiltonian constraint (diagnostic)\n#include \"Hamiltonian_constraint.h\"\n#include \"momentum_constraint.h\"\n\n// main() function:\n// Step 0: Read command-line input, set up grid structure, allocate memory for gridfunctions, set up coordinates\n// Step 1: Set up initial data to an exact solution\n// Step 2: Start the timer, for keeping track of how fast the simulation is progressing.\n// Step 3: Integrate the initial data forward in time using the chosen RK-like Method of\n// Lines timestepping algorithm, and output periodic simulation diagnostics\n// Step 3.a: Output 2D data file periodically, for visualization\n// Step 3.b: Step forward one timestep (t -> t+dt) in time using\n// chosen RK-like MoL timestepping algorithm\n// Step 3.c: If t=t_final, output conformal factor & Hamiltonian\n// constraint violation to 2D data file\n// Step 3.d: Progress indicator printing to stderr\n// Step 4: Free all allocated memory\nint main(int argc, const char *argv[]) {\n paramstruct params;\n#include \"set_Cparameters_default.h\"\n\n // Step 0a: Read command-line input, error out if nonconformant\n if((argc != 4) || atoi(argv[1]) < NGHOSTS || atoi(argv[2]) < NGHOSTS || atoi(argv[3]) < 2 /* FIXME; allow for axisymmetric sims */) {\n fprintf(stderr,\"Error: Expected three command-line arguments: ./BrillLindquist_Playground Nx0 Nx1 Nx2,\\n\");\n fprintf(stderr,\"where Nx[0,1,2] is the number of grid points in the 0, 1, and 2 directions.\\n\");\n fprintf(stderr,\"Nx[] MUST BE larger than NGHOSTS (= %d)\\n\",NGHOSTS);\n exit(1);\n }\n // Step 0b: Set up numerical grid structure, first in space...\n const int Nxx[3] = { atoi(argv[1]), atoi(argv[2]), atoi(argv[3]) };\n if(Nxx[0]%2 != 0 || Nxx[1]%2 != 0 || Nxx[2]%2 != 0) {\n fprintf(stderr,\"Error: Cannot guarantee a proper cell-centered grid if number of grid cells not set to even number.\\n\");\n fprintf(stderr,\" For example, in case of angular directions, proper symmetry zones will not exist.\\n\");\n exit(1);\n }\n\n // Step 0c: Set free parameters, overwriting Cparameters defaults\n // by hand or with command-line input, as desired.\n#include \"free_parameters.h\"\n\n // Step 0d: Uniform coordinate grids are stored to *xx[3]\n REAL *xx[3];\n // Step 0d.i: Set bcstruct\n bc_struct bcstruct;\n {\n int EigenCoord = 1;\n // Step 0d.ii: Call set_Nxx_dxx_invdx_params__and__xx(), which sets\n // params Nxx,Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS,dxx,invdx, and xx[] for the\n // chosen Eigen-CoordSystem.\n set_Nxx_dxx_invdx_params__and__xx(EigenCoord, Nxx, ¶ms, xx);\n // Step 0d.iii: Set Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS_tot\n#include \"set_Cparameters-nopointer.h\"\n const int Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS_tot = Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS1*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS2;\n // Step 0e: Find ghostzone mappings; set up bcstruct\n#include \"boundary_conditions/driver_bcstruct.h\"\n // Step 0e.i: Free allocated space for xx[][] array\n for(int i=0;i<3;i++) free(xx[i]);\n }\n\n // Step 0f: Call set_Nxx_dxx_invdx_params__and__xx(), which sets\n // params Nxx,Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS,dxx,invdx, and xx[] for the\n // chosen (non-Eigen) CoordSystem.\n int EigenCoord = 0;\n set_Nxx_dxx_invdx_params__and__xx(EigenCoord, Nxx, ¶ms, xx);\n\n // Step 0g: Set all C parameters \"blah\" for params.blah, including\n // Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0 = params.Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0, etc.\n#include \"set_Cparameters-nopointer.h\"\n const int Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS_tot = Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS1*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS2;\n\n // Step 0j: Error out if the number of auxiliary gridfunctions outnumber evolved gridfunctions.\n // This is a limitation of the RK method. You are always welcome to declare & allocate\n // additional gridfunctions by hand.\n if(NUM_AUX_GFS > NUM_EVOL_GFS) {\n fprintf(stderr,\"Error: NUM_AUX_GFS > NUM_EVOL_GFS. Either reduce the number of auxiliary gridfunctions,\\n\");\n fprintf(stderr,\" or allocate (malloc) by hand storage for *diagnostic_output_gfs. \\n\");\n exit(1);\n }\n\n // Step 0k: Allocate memory for gridfunctions\n#include \"MoLtimestepping/RK_Allocate_Memory.h\"\n REAL *restrict auxevol_gfs = (REAL *)malloc(sizeof(REAL) * NUM_AUXEVOL_GFS * Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS_tot);\n\n // Step 1: Set up initial data to an exact solution\n initial_data(¶ms, xx, y_n_gfs);\n\n // Step 1b: Apply boundary conditions, as initial data\n // are sometimes ill-defined in ghost zones.\n // E.g., spherical initial data might not be\n // properly defined at points where r=-1.\n apply_bcs_curvilinear(¶ms, &bcstruct, NUM_EVOL_GFS,evol_gf_parity, y_n_gfs);\n enforce_detgammahat_constraint(¶ms, xx, y_n_gfs);\n\n // Evaluate Hamiltonian & momentum constraint violations\n Hamiltonian_constraint(¶ms, xx, y_n_gfs, diagnostic_output_gfs);\n momentum_constraint( ¶ms, xx, y_n_gfs, diagnostic_output_gfs);\n\n /* Step 2: 2D output: Output conformal factor (CFGF) and constraint violations (HGF, MU0GF, MU1GF, MU2GF). */\n const int i0MIN=NGHOSTS; // In spherical, r=Delta r/2.\n const int i1mid=Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS1/2;\n const int i2mid=Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS2/2;\n LOOP_REGION(NGHOSTS,Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0-NGHOSTS, i1mid,i1mid+1, NGHOSTS,Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS2-NGHOSTS) {\n REAL xCart[3];\n xx_to_Cart(¶ms, xx, i0,i1,i2, xCart);\n int idx = IDX3S(i0,i1,i2);\n printf(\"%e %e %e %e %e %e %e\\n\",xCart[0],xCart[1], y_n_gfs[IDX4ptS(CFGF,idx)],\n log10(fabs(diagnostic_output_gfs[IDX4ptS(HGF,idx)])),\n log10(fabs(diagnostic_output_gfs[IDX4ptS(MU0GF,idx)])+1e-200),\n log10(fabs(diagnostic_output_gfs[IDX4ptS(MU1GF,idx)])+1e-200),\n log10(fabs(diagnostic_output_gfs[IDX4ptS(MU2GF,idx)])+1e-200));\n }\n // Step 4: Free all allocated memory\n#include \"boundary_conditions/bcstruct_freemem.h\"\n#include \"MoLtimestepping/RK_Free_Memory.h\"\n free(auxevol_gfs);\n for(int i=0;i<3;i++) free(xx[i]);\n\n return 0;\n}",
"Writing BlackHoleID_Ccodes//Initial_Data_Playground.c\n"
],
[
"import cmdline_helper as cmd\n\ncmd.C_compile(os.path.join(Ccodesdir,\"Initial_Data_Playground.c\"), \"Initial_Data_Playground\")\ncmd.delete_existing_files(\"out*.txt\")\ncmd.delete_existing_files(\"out*.png\")\nargs_output_list = [[\"96 96 96\", \"out96.txt\"], [\"48 48 48\", \"out48.txt\"]]\nfor args_output in args_output_list:\n cmd.Execute(\"Initial_Data_Playground\", args_output[0], args_output[1])",
"Compiling executable...\n(EXEC): Executing `gcc -std=gnu99 -Ofast -fopenmp -march=native -funroll-loops BlackHoleID_Ccodes/Initial_Data_Playground.c -o Initial_Data_Playground -lm`...\n(BENCH): Finished executing in 1.8086323738098145 seconds.\nFinished compilation.\n(EXEC): Executing `taskset -c 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15 ./Initial_Data_Playground 96 96 96`...\n(BENCH): Finished executing in 0.4055624008178711 seconds.\n(EXEC): Executing `taskset -c 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15 ./Initial_Data_Playground 48 48 48`...\n(BENCH): Finished executing in 0.20548486709594727 seconds.\n"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='plot'></a>\n\n# Step 6: Plotting the initial data \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{plot}$$\n\nHere we plot the evolved conformal factor of these initial data on a 2D grid, such that darker colors imply stronger gravitational fields. Hence, we see the black hole(s) centered at $x/M=\\pm 1$, where $M$ is an arbitrary mass scale (conventionally the [ADM mass](https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=ADM_formalism&oldid=846335453) is chosen), and our formulation of Einstein's equations adopt $G=c=1$ [geometrized units](https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Geometrized_unit_system&oldid=861682626).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# First install scipy if it's not yet installed. This will have no effect if it's already installed.\n!pip install scipy",
"Requirement already satisfied: scipy in /home/zetienne/jup310/lib/python3.10/site-packages (1.8.0.dev0+1731.9629282)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy>=1.17.3 in /home/zetienne/jup310/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from scipy) (1.21.2)\r\n"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nfrom scipy.interpolate import griddata\nfrom pylab import savefig\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport matplotlib.cm as cm\nfrom IPython.display import Image\n\nx96,y96,valuesCF96,valuesHam96,valuesmomr96,valuesmomtheta96,valuesmomphi96 = np.loadtxt('out96.txt').T #Transposed for easier unpacking\n\n\npl_xmin = -3.\npl_xmax = +3.\npl_ymin = -3.\npl_ymax = +3.\n\ngrid_x, grid_y = np.mgrid[pl_xmin:pl_xmax:100j, pl_ymin:pl_ymax:100j]\npoints96 = np.zeros((len(x96), 2))\nfor i in range(len(x96)):\n points96[i][0] = x96[i]\n points96[i][1] = y96[i]\n\ngrid96 = griddata(points96, valuesCF96, (grid_x, grid_y), method='nearest')\ngrid96cub = griddata(points96, valuesCF96, (grid_x, grid_y), method='cubic')\n\nplt.clf()\nplt.title(\"Initial Data\")\nplt.xlabel(\"x/M\")\nplt.ylabel(\"y/M\")\n\n# fig, ax = plt.subplots()\n#ax.plot(grid96cub.T, extent=(pl_xmin,pl_xmax, pl_ymin,pl_ymax))\nplt.imshow(grid96.T, extent=(pl_xmin,pl_xmax, pl_ymin,pl_ymax))\nsavefig(\"ID.png\")\nplt.close()\nImage(\"ID.png\")\n# # interpolation='nearest', cmap=cm.gist_rainbow)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='convergence'></a>\n\n# Step 7: Validation: Convergence of numerical errors (Hamiltonian & momentum constraint violations) to zero \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{convergence}$$\n\n**Special thanks to George Vopal for creating the following plotting script.**\n\nThe equations behind these initial data solve Einstein's equations exactly, at a single instant in time. One reflection of this solution is that the Hamiltonian constraint violation should be exactly zero in the initial data. \n\nHowever, when evaluated on numerical grids, the Hamiltonian constraint violation will *not* generally evaluate to zero due to the associated numerical derivatives not being exact. However, these numerical derivatives (finite difference derivatives in this case) should *converge* to the exact derivatives as the density of numerical sampling points approaches infinity.\n\nIn this case, all of our finite difference derivatives agree with the exact solution, with an error term that drops with the uniform gridspacing to the fourth power: $\\left(\\Delta x^i\\right)^4$. \n\nHere, as in the [Start-to-Finish Scalar Wave (Cartesian grids) NRPy+ tutorial](Tutorial-Start_to_Finish-ScalarWave.ipynb) and the [Start-to-Finish Scalar Wave (curvilinear grids) NRPy+ tutorial](Tutorial-Start_to_Finish-ScalarWaveCurvilinear.ipynb) we confirm this convergence.\n\nFirst, let's take a look at what the numerical error looks like on the x-y plane at a given numerical resolution, plotting $\\log_{10}|H|$, where $H$ is the Hamiltonian constraint violation:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"RefData=[valuesHam96,valuesmomr96,valuesmomtheta96,valuesmomphi96]\nSubTitles=[\"\\mathcal{H}\",'\\mathcal{M}^r',r\"\\mathcal{M}^{\\theta}\",\"\\mathcal{M}^{\\phi}\"]\naxN = [] #this will let us automate the subplots in the loop that follows\ngrid96N = [] #we need to calculate the grid96 data for each constraint for use later\nplt.clf()\n\n# We want to create four plots. One for the Hamiltonian, and three for the momentum\n# constraints (r,th,ph)\n# Define the size of the overall figure\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,12)) # 8 in x 8 in\n\nnum_plots = 4\n\nif dictID[initial_data_string].EnableMomentum == False:\n num_plots = 1\n\n\nfor p in range(num_plots):\n grid96 = griddata(points96, RefData[p], (grid_x, grid_y), method='nearest')\n grid96N.append(grid96)\n grid96cub = griddata(points96, RefData[p], (grid_x, grid_y), method='cubic')\n\n #fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, sharex=True, sharey=True)\n\n\n #Generate the subplot for the each constraint\n ax = fig.add_subplot(221+p)\n axN.append(ax) # Grid of 2x2\n\n axN[p].set_xlabel('x/M')\n axN[p].set_ylabel('y/M')\n axN[p].set_title('$96^3$ Numerical Err.: $log_{10}|'+SubTitles[p]+'|$')\n\n fig96cub = plt.imshow(grid96cub.T, extent=(pl_xmin,pl_xmax, pl_ymin,pl_ymax))\n cb = plt.colorbar(fig96cub)\n\n# Adjust the spacing between plots\nplt.tight_layout(pad=4)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next, we set up the same initial data but on a lower-resolution, $48^3$ grid. Since the constraint violation (numerical error associated with the fourth-order-accurate, finite-difference derivatives) should converge to zero with the uniform gridspacing to the fourth power: $\\left(\\Delta x^i\\right)^4$, we expect the constraint violation will increase (relative to the $96^3$ grid) by a factor of $\\left(96/48\\right)^4$. Here we demonstrate that indeed this order of convergence is observed as expected. I.e., at all points *except* at the points immediately surrounding the coordinate center of the black hole (due to the spatial slice excising the physical singularity at this point through [the puncture method](http://gr.physics.ncsu.edu/UMD_June09.pdf)) exhibit numerical errors that drop as $\\left(\\Delta x^i\\right)^4$.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x48,y48,valuesCF48,valuesHam48,valuesmomr48,valuesmomtheta48,valuesmomphi48 = np.loadtxt('out48.txt').T #Transposed for easier unpacking\npoints48 = np.zeros((len(x48), 2))\nfor i in range(len(x48)):\n points48[i][0] = x48[i]\n points48[i][1] = y48[i]\n\nRefData=[valuesHam48,valuesmomr48,valuesmomtheta48,valuesmomphi48]\nSubTitles=[\"\\mathcal{H}\",'\\mathcal{M}^r',r\"\\mathcal{M}^{\\theta}\",\"\\mathcal{M}^{\\phi}\"]\naxN = []\nplt.clf()\n\n# We want to create four plots. One for the Hamiltonian, and three for the momentum\n# constrains (r,th,ph)\n# Define the size of the overall figure\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,12)) # 8 in x 8 in\n\nfor p in range(num_plots): #loop to cycle through our constraints and plot the data\n grid48 = griddata(points48, RefData[p], (grid_x, grid_y), method='nearest')\n griddiff_48_minus_96 = np.zeros((100,100))\n griddiff_48_minus_96_1darray = np.zeros(100*100)\n gridx_1darray_yeq0 = np.zeros(100)\n grid48_1darray_yeq0 = np.zeros(100)\n grid96_1darray_yeq0 = np.zeros(100)\n count = 0\n for i in range(100):\n for j in range(100):\n griddiff_48_minus_96[i][j] = grid48[i][j] - grid96N[p][i][j]\n griddiff_48_minus_96_1darray[count] = griddiff_48_minus_96[i][j]\n if j==49:\n gridx_1darray_yeq0[i] = grid_x[i][j]\n grid48_1darray_yeq0[i] = grid48[i][j] + np.log10((48./96.)**4)\n grid96_1darray_yeq0[i] = grid96N[p][i][j]\n count = count + 1\n\n #Generate the subplot for the each constraint\n ax = fig.add_subplot(221+p)\n axN.append(ax) # Grid of 2x2\n axN[p].set_title('Plot Demonstrating $4^{th}$-Order Convergence of $'+SubTitles[p]+'$')\n axN[p].set_xlabel(\"x/M\")\n axN[p].set_ylabel(\"$log_{10}$(Relative Error)\")\n\n ax.plot(gridx_1darray_yeq0, grid96_1darray_yeq0, 'k-', label='Nr=96')\n ax.plot(gridx_1darray_yeq0, grid48_1darray_yeq0, 'k--', label='Nr=48, mult by (48/96)^4')\n ax.set_ylim([-14,4.])\n\n legend = ax.legend(loc='lower right', shadow=True, fontsize='x-large')\n legend.get_frame().set_facecolor('C1')\n\n# Adjust the spacing between plots\nplt.tight_layout(pad=4)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='latex_pdf_output'></a>\n\n# Step 7: Output this notebook to $\\LaTeX$-formatted PDF file \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{latex_pdf_output}$$\n\nThe following code cell converts this Jupyter notebook into a proper, clickable $\\LaTeX$-formatted PDF file. After the cell is successfully run, the generated PDF may be found in the root NRPy+ tutorial directory, with filename\n[Tutorial-Start_to_Finish-BSSNCurvilinear-Setting_up_Exact_Initial_Data.pdf](Tutorial-Start_to_Finish-BSSNCurvilinear-Setting_up_Exact_Initial_Data.pdf) (Note that clicking on this link may not work; you may need to open the PDF file through another means.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import cmdline_helper as cmd # NRPy+: Multi-platform Python command-line interface\ncmd.output_Jupyter_notebook_to_LaTeXed_PDF(\"Tutorial-Start_to_Finish-BSSNCurvilinear-Setting_up_Exact_Initial_Data\")",
"Created Tutorial-Start_to_Finish-BSSNCurvilinear-\n Setting_up_Exact_Initial_Data.tex, and compiled LaTeX file to PDF file\n Tutorial-Start_to_Finish-BSSNCurvilinear-\n Setting_up_Exact_Initial_Data.pdf\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
cbe72cf11ed154ba7e18823bc7575c5939964635
| 126,403 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
fastinference/02_FI_and_Dendrogram.ipynb
|
ANGELLOPARR/Practical-Deep-Learning-for-Coders-2.0
|
554078890162a155fbfc8fec8d3a4cb5c5bc089a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
fastinference/02_FI_and_Dendrogram.ipynb
|
ANGELLOPARR/Practical-Deep-Learning-for-Coders-2.0
|
554078890162a155fbfc8fec8d3a4cb5c5bc089a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
fastinference/02_FI_and_Dendrogram.ipynb
|
ANGELLOPARR/Practical-Deep-Learning-for-Coders-2.0
|
554078890162a155fbfc8fec8d3a4cb5c5bc089a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 133.477297 | 20,298 | 0.836491 |
[
[
[
"# 02: Feature Importance and Dendrograms:\n\n> Dendrograms were originally by Pak on the forums",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pip install fastinference --quiet",
"\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 21.9MB 61.4MB/s \n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 194kB 56.8MB/s \n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 276kB 57.7MB/s \n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 7.4MB 23.8MB/s \n\u001b[?25h Building wheel for shap (setup.py) ... \u001b[?25l\u001b[?25hdone\n"
],
[
"from fastinference.tabular import *\nfrom fastai.tabular.all import *",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Initial Training",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"First let's start with tabular. Let's train a model real quick:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"path = untar_data(URLs.ADULT_SAMPLE)\ndf = pd.read_csv(path/'adult.csv')\nsplits = RandomSplitter()(range_of(df))\ncat_names = ['workclass', 'education', 'marital-status', 'occupation', 'relationship', 'race']\ncont_names = ['age', 'fnlwgt', 'education-num']\nprocs = [Categorify, FillMissing, Normalize]\ny_names = 'salary'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"to = TabularPandas(df, procs=procs, cat_names=cat_names, cont_names=cont_names,\n y_names=y_names, splits=splits)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dls = to.dataloaders()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"learn = tabular_learner(dls, layers=[200,100], metrics=accuracy)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"learn.fit(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we can get into looking at the results! \n\nSo what's new?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Feature Importance\n\n* Permutation-based approach\n\nTake one column, shuffle it's innards, then measure the amount of change from your baseline:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pip install nbdev --quiet",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"doc(learn.feature_importance)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fi = learn.feature_importance()",
"Calculating Permutation Importance\n"
],
[
"fi",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If nothing is passed in, it will only work on the validation set:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fi = learn.feature_importance(metric=CrossEntropyLossFlat())",
"Calculating Permutation Importance\n"
],
[
"fi",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"So we can see based on what we want on our *metric* to be, our attention changes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"test_dl = learn.dls.test_dl(df.iloc[:100])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fi = learn.feature_importance(metric=RocAuc(), dl=test_dl)",
"Calculating Permutation Importance\n"
],
[
"fi = learn.feature_importance(metric=RocAuc())",
"Calculating Permutation Importance\n"
],
[
"fi",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Dendrogram Plots and Correlation:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We can calculate how similar two variables are to each other by calculating what is known as the \"correlation matrix\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"doc(learn.get_top_corr_dict)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"corr_dict = learn.get_top_corr_dict(df, thresh=0.3); corr_dict",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"While this gives us a window, we can also plot the entire dendrogram and see the family:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"doc(learn.plot_dendrogram)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"learn.plot_dendrogram(df)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe73d77d4d17f270610d5180e9af8e6a8b83cfb
| 350,760 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/PhysTuning/SurfaceSilicon.ipynb
|
SalishSeaCast/analysis-susan
|
52633f4fe82af6d7c69dff58f69f0da4f7933f48
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/PhysTuning/SurfaceSilicon.ipynb
|
SalishSeaCast/analysis-susan
|
52633f4fe82af6d7c69dff58f69f0da4f7933f48
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/PhysTuning/SurfaceSilicon.ipynb
|
SalishSeaCast/analysis-susan
|
52633f4fe82af6d7c69dff58f69f0da4f7933f48
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 254.358231 | 29,980 | 0.894187 |
[
[
[
"## Silicon above 15 m",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import datetime as dt\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom matplotlib.colors import LogNorm\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport statsmodels.api as sm\nimport xarray as xr",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"foramt = \"{:.2}\"\nmyformat = {'bias': foramt, 'rmse': foramt, 'swillmott': foramt, 'slopedev': foramt, 'const': foramt,\n 'systematic': foramt, 'nonsystematic':foramt, \n 'spread': foramt}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"with xr.open_dataset('/home/sallen/MEOPAR/grid/mesh_mask201702.nc') as mesh:\n deptht = mesh.gdept_1d[0].values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def bias(df, obs, mod):\n diffy = df[mod] - df[obs]\n return diffy.count(), diffy.mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def rmse(df, obs, mod):\n return (np.sqrt(((df[mod] - df[obs])**2).mean()))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def swillmott(df, obs, mod):\n meanobs = df[obs].mean()\n return (((df[mod] - df[obs])**2).sum()\n /(( (df[mod] - meanobs).abs() + (df[obs] - meanobs).abs() )**2).sum())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def slope_inter(df, obs, mod):\n X = df[obs]\n X2 = X**2\n y = df[mod]\n X = np.column_stack((X, X2))\n X = sm.add_constant(X)\n\n # Fit and make the predictions by the model\n model = sm.OLS(y, X, missing='drop').fit()\n predictions = model.predict(X)\n \n nonsyst = np.sqrt(((y - predictions)**2).mean())\n systematic = np.sqrt(((predictions - df[obs])**2).mean())\n \n return predictions, model.params['x2'], model.params['x1'], model.params['const'], systematic, nonsyst",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def spread(df, obs, mod):\n return 1 - ((df[mod] - df[mod].mean())**2).mean() / ((df[obs] - df[obs].mean())**2).mean() ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def read_pieces(pieces):\n temp1 = pd.read_csv(pieces[0])\n for piece in pieces[1:]:\n nextpiece = pd.read_csv(piece)\n temp1 = pd.concat([temp1, nextpiece], ignore_index=True)\n return temp1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def plot_and_stats(temp1, name, idepth, jdepth):\n fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(6, 5))\n vmax = 90\n vmin = 0\n condition = (temp1.k >= idepth) & (temp1.k <= jdepth)\n print (deptht[idepth], deptht[jdepth])\n counts, xedges, yedges, color = ax.hist2d(temp1.Si[(temp1.k >= idepth) & (temp1.k <= jdepth)], \n temp1.mod_silicon[(temp1.k >= idepth) & (temp1.k <= jdepth)], \n bins=np.arange(vmin, vmax, 1), norm=LogNorm());\n fig.colorbar(color)\n number, tbias = bias(temp1[(temp1.k >= idepth) & (temp1.k <= jdepth)], 'Si', 'mod_silicon')\n trmse = rmse(temp1[(temp1.k >= idepth) & (temp1.k <= jdepth)], 'Si', 'mod_silicon')\n tswillmott = swillmott(temp1[temp1.k >=idepth], 'Si', 'mod_silicon')\n predictions, m2, m, c, syst, nonsyst = slope_inter(temp1[(temp1.k >= idepth) & (temp1.k <= jdepth)], 'Si', 'mod_silicon')\n tspread = spread(temp1[temp1.k >= idepth], 'Si', 'mod_silicon')\n ax.plot([vmin, vmax], [vmin, vmax], 'w-');\n xr = np.arange(vmin, vmax, 0.5)\n ax.plot(temp1.Si[condition], predictions, 'r.');\n sc = 5\n sh = 2*sc-1\n bot = 65\n top = bot + 2*sh \n ax.arrow(5, bot, 0, sh-np.abs(tbias)/2, head_width=0.5*sc, head_length=0.2*sc, length_includes_head=True)\n ax.arrow(5, top, 0, -sh+np.abs(tbias)/2, head_width=0.5*sc, head_length=0.2*sc, length_includes_head=True)\n ax.arrow(9, bot, 0, sh-syst/2, head_width=0.5*sc, head_length=0.2*sc, length_includes_head=True)\n ax.arrow(9, top, 0, -sh+syst/2, head_width=0.5*sc, head_length=0.2*sc, length_includes_head=True)\n ax.arrow(13, bot, 0, sh-nonsyst/2, head_width=0.5*sc, head_length=0.2*sc, length_includes_head=True)\n ax.arrow(13, top, 0, -sh+nonsyst/2, head_width=0.5*sc, head_length=0.2*sc, length_includes_head=True);\n Cp2 = {'number': number,\n 'bias': tbias,\n 'rmse': trmse,\n 'swillmott': tswillmott,\n 'slopedev': 1-m,\n 'const': c,\n 'systematic': syst,\n 'nonsystematic': nonsyst,\n 'spread': tspread}\n ax.text(5-1.2, 48, 'bias', rotation=90)\n ax.text(9-1.2, 48, 'systematic', rotation=90)\n ax.text(13-1.2, 42, 'non-systematic', rotation=90)\n ax.set_title(f'{name}, Silicon between 0 and 15 m');\n dCp2 = pd.DataFrame(data=Cp2, index=[name])\n return dCp2\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pieces = ('/home/sallen/202007/H201812/ObsModel_201812_Bio_20150101-20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201812/ObsModel_201812_Bio_20160101-20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201812/ObsModel_201812_Bio_20170101-20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201812/ObsModel_201812_PSF_20150101-20151231.csv',\n # '/home/sallen/202007/H201905/ObsModel_201812_PSF_20160101-20161231.csv',\n # '/home/sallen/202007/H201905/ObsModel_201812_PSF_20170101-20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201812/ObsModel_H201812_pug_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201812/ObsModel_H201812_pug_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201812/ObsModel_H201812_pug_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201812/ObsModel_H201812_hplc_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201812/ObsModel_H201812_hplc_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201812/ObsModel_H201812_hplc_20170101_20171231.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp1 = read_pieces(pieces)\ntemp1['Si'] = temp1.Si.fillna(value=temp1['Silicate [umol/L]'])\nidepth = 0\njdepth = 14\nd201812 = plot_and_stats(temp1, 'H201812', idepth, jdepth)\nd201812.style.format(myformat)",
"0.5000002726327963 14.568982157803276\n"
],
[
"pieces = ('/home/sallen/202007/H201905/ObsModel_201905_Bio_20150101-20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201905/ObsModel_201905_Bio_20160101-20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201905/ObsModel_201905_Bio_20170101-20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201905/ObsModel_201905_PSF_20150101-20151231.csv',\n # '/home/sallen/202007/H201905/ObsModel_201905_PSF_20160101-20161231.csv',\n # '/home/sallen/202007/H201905/ObsModel_201905_PSF_20170101-20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201905/ObsModel_H201905_pug_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201905/ObsModel_H201905_pug_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201905/ObsModel_H201905_pug_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201905/ObsModel_H201905_hplc_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201905/ObsModel_H201905_hplc_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/H201905/ObsModel_H201905_hplc_20170101_20171231.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp1 = read_pieces(pieces)\ntemp1['Si'] = temp1.Si.fillna(value=temp1['Silicate [umol/L]'])\n\nd201905 = plot_and_stats(temp1, 'H201905', idepth, jdepth)\nd201905.style.format(myformat)",
"0.5000002726327963 14.568982157803276\n"
],
[
"pieces = ('/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p2/ObsModel_202007Cp2_Bio_20150101-20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p2/ObsModel_202007Cp2_Bio_20160101-20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p2/ObsModel_202007Cp2_Bio_20170101-20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p2/ObsModel_202007Cp2_PSF_20150101-20151231.csv',\n # '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p2/ObsModel_202007Cp2_PSF_20160101-20161231.csv',\n # '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p2/ObsModel_202007Cp2_PSF_20170101-20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p2/ObsModel_202007Cp2_PUG_20150101-20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p2/ObsModel_202007Cp2_PUG_20160101-20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p2/ObsModel_202007Cp2_PUG_20170101-20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p2/ObsModel_202007Cp2_hplc_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p2/ObsModel_202007Cp2_hplc_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p2/ObsModel_202007Cp2_hplc_20170101_20171231.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp1 = read_pieces(pieces)\ntemp1['Si'] = temp1.Si.fillna(value=temp1['Silicate [umol/L]'])\ndCp2 = plot_and_stats(temp1, 'Cp2', idepth, jdepth)\ndCp2.style.format(myformat)",
"0.5000002726327963 14.568982157803276\n"
],
[
"pieces = ('/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_bot_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_bot_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_bot_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_psf_20150101_20150331.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_psf_20150401_20150630.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_PSF_20150701-20151231.csv',\n# '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_psf_20160101_20161231.csv',\n# '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_psf_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_pug_20150101_20150331.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_pug_20150401_20150630.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_PUG_20150701-20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_pug_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_pug_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_hplc_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_hplc_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_hplc_20170101_20171231.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp1 = read_pieces(pieces)\ntemp1['Si'] = temp1.Si.fillna(value=temp1['Silicate [umol/L]'])\ndCp3 = plot_and_stats(temp1, 'Cp3', idepth, jdepth)\ndCp3.style.format(myformat)",
"0.5000002726327963 14.568982157803276\n"
],
[
"pieces = ('/home/sallen/202007/202007D-again/ObsModel_202007D-again_Bio_20150101-20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-again/ObsModel_202007D-again_Bio_20160101-20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-again/ObsModel_202007D-again_Bio_20170101-20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-again/ObsModel_202007D-again_PSF_20150101-20151231.csv',\n # '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-again/ObsModel_202007D-again_PSF_20160101-20161231.csv',\n # '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-again/ObsModel_202007D-again_PSF_20170101-20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-again/ObsModel_202007D-again_pug_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-again/ObsModel_202007D-again_pug_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-again/ObsModel_202007D-again_pug_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-again/ObsModel_202007D-again_hplc_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-again/ObsModel_202007D-again_hplc_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-again/ObsModel_202007D-again_hplc_20170101_20171231.csv'\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp1 = read_pieces(pieces)\ntemp1['Si'] = temp1.Si.fillna(value=temp1['Silicate [umol/L]'])\nDagain = plot_and_stats(temp1, 'Dagain', idepth, jdepth)\nDagain.style.format(myformat)",
"0.5000002726327963 14.568982157803276\n"
],
[
"pieces = ('/home/sallen/202007/202007D-lowR/ObsModel_202007D-lowR_Bio_20150101-20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-lowR/ObsModel_202007D-lowR_bot_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-lowR/ObsModel_202007D-lowR_bot_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-lowR/ObsModel_202007D-lowR_PSF_20150101-20151231.csv',\n # '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-lowR/ObsModel_202007D-lowR_psf_20160101_20161231.csv',\n # '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-lowR/ObsModel_202007D-lowR_psf_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-lowR/ObsModel_202007D-lowR_pug_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-lowR/ObsModel_202007D-lowR_pug_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-lowR/ObsModel_202007D-lowR_pug_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-lowR/ObsModel_202007D-lowR_hplc_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-lowR/ObsModel_202007D-lowR_hplc_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007D-lowR/ObsModel_202007D-lowR_hplc_20170101_20171231.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp1 = read_pieces(pieces)\ntemp1['Si'] = temp1.Si.fillna(value=temp1['Silicate [umol/L]'])\nDlowR = plot_and_stats(temp1, 'D-lowR', idepth, jdepth)\nDlowR.style.format(myformat)",
"0.5000002726327963 14.568982157803276\n"
],
[
"pieces = ('/home/sallen/202007/202007F/ObsModel_202007F_bot_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007F/ObsModel_202007F_bot_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007F/ObsModel_202007F_bot_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007F/ObsModel_202007F_psf_20150101_20151231.csv',\n# '/home/sallen/202007/202007F/ObsModel_202007F_psf_20160101_20161231.csv',\n# '/home/sallen/202007/202007F/ObsModel_202007F_psf_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007F/ObsModel_202007F_pug_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007F/ObsModel_202007F_pug_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007F/ObsModel_202007F_pug_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007F/ObsModel_202007F_hplc_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007F/ObsModel_202007F_hplc_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007F/ObsModel_202007F_hplc_20170101_20171231.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp1 = read_pieces(pieces)\ntemp1['Si'] = temp1.Si.fillna(value=temp1['Silicate [umol/L]'])\nmodF = plot_and_stats(temp1, 'F', idepth, jdepth)\nmodF.style.format(myformat)",
"0.5000002726327963 14.568982157803276\n"
],
[
"pieces = ('/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p1/ObsModel_202007Gp1_bot_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p1/ObsModel_202007Gp1_bot_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p1/ObsModel_202007Gp1_bot_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p1/ObsModel_202007Gp1_psf_20150101_20151231.csv',\n#bd '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p1/ObsModel_202007Gp1_psf_20160101_20161231.csv',\n# bd '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p1/ObsModel_202007Gp1_psf_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p1/ObsModel_202007Gp1_pug_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p1/ObsModel_202007Gp1_pug_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p1/ObsModel_202007Gp1_pug_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p1/ObsModel_202007Gp1_hplc_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p1/ObsModel_202007Gp1_hplc_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p1/ObsModel_202007Gp1_hplc_20170101_20171231.csv'\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp1 = read_pieces(pieces)\ntemp1['Si'] = temp1.Si.fillna(value=temp1['Silicate [umol/L]'])\nmodGp1 = plot_and_stats(temp1, 'Gp1', idepth, jdepth)\nmodGp1.style.format(myformat)",
"0.5000002726327963 14.568982157803276\n"
],
[
"pieces = ('/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p2/ObsModel_202007Gp2_bot_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p2/ObsModel_202007Gp2f0_bot_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p2/ObsModel_202007Gp2f0_bot_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p2/ObsModel_202007Gp2_psf_20150101_20151231.csv',\n# '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_psf_20160101_20161231.csv',\n# '/home/sallen/202007/202007C-p3/ObsModel_202007Cp3_psf_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p2/ObsModel_202007Gp2_pug_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p2/ObsModel_202007Gp2f0_pug_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p2/ObsModel_202007Gp2f0_pug_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p2/ObsModel_202007Gp2_hplc_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p2/ObsModel_202007Gp2f0_hplc_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007G-p2/ObsModel_202007Gp2f0_hplc_20170101_20171231.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp1 = read_pieces(pieces)\ntemp1['Si'] = temp1.Si.fillna(value=temp1['Silicate [umol/L]'])\nmodGp2 = plot_and_stats(temp1, 'Gp2', idepth, jdepth)\nmodGp2.style.format(myformat)",
"0.5000002726327963 14.568982157803276\n"
],
[
"pieces = ('/home/sallen/202007/202007H/ObsModel_202007H_bot_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007H/ObsModel_202007H_bot_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007H/ObsModel_202007H_bot_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007H/ObsModel_202007H_hplc_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007H/ObsModel_202007H_hplc_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007H/ObsModel_202007H_hplc_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007H/ObsModel_202007H_pug_20150101_20151231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007H/ObsModel_202007H_pug_20160101_20161231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007H/ObsModel_202007H_pug_20170101_20171231.csv',\n '/home/sallen/202007/202007H/ObsModel_202007H_psf_20150101_20151231.csv',\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp1 = read_pieces(pieces)\ntemp1['Si'] = temp1.Si.fillna(value=temp1['Silicate [umol/L]'])\nmodH = plot_and_stats(temp1, 'H', idepth, jdepth)\nmodH.style.format(myformat)",
"0.5000002726327963 14.568982157803276\n"
],
[
"def highlight_max_min(s):\n '''\n highlight the maximum in a Series yellow.\n '''\n is_max = abs(s) == abs(s).max()\n is_min = abs(s) == abs(s).min()\n color = []\n for v, v2 in zip(is_max, is_min):\n if v:\n color.append('red')\n elif v2:\n color.append('darkgreen')\n else:\n color.append('black')\n return ['color: %s' % color[i] for i in range(len(is_max))]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"alltogether = pd.concat([d201812, d201905, dCp2, dCp3, Dagain, DlowR, modF, modGp1, modGp2, modH], axis=0)\nforamt = \"{:.2}\"\nalltogether.style.format(myformat).apply(highlight_max_min)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Conclusion** None of these look great. The best is Gp1 probably a little better than Gp2. BUT again Gp1 is better than Gp2 (consistent with everything except salinity)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe73d8eed59bddd32b51974ffea986497e6b7e5
| 4,314 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/archive.ipynb
|
deinal/aerosol-modeling
|
d778458619929cc52d3170640b71239d936b10bb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/archive.ipynb
|
deinal/aerosol-modeling
|
d778458619929cc52d3170640b71239d936b10bb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/archive.ipynb
|
deinal/aerosol-modeling
|
d778458619929cc52d3170640b71239d936b10bb
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-03-04T15:08:46.000Z
|
2021-03-04T15:08:46.000Z
| 32.43609 | 116 | 0.534771 |
[
[
[
"# Archived code\nThis notebook contains code for variables that I removed from the model.\n\n## Previous Week Averages\nNote: in add_pwa first pwa columns are removed twice when calculating pwa for t and co",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n# function for calculating the pwa of a column (excludes the day measured in the t and co columns)\ndef calc_pwa(data, col, pwa):\n pwa_data = pd.DataFrame()\n \n # shifting the data for the number of days and creating a new column for each day\n for i in range(1, pwa+1):\n pwa_data[col + '_' + str(i)] = data.shift(i)[col]\n \n # saving the row means as a new x_pwa column in the original dataframe\n data[col + '_pwa'] = pwa_data.aggregate(np.mean, axis=1)\n \n return data\n\n\n# interface that makes calls to add_pwa depending on whether only one or all cities are used\ndef add_pwa(data, col, pwa):\n if use_all_cities:\n # creating a unique id for every row\n data['id'] = data.city + data.index\n\n data_pwa = []\n names_pwa = []\n \n # iterating over all cities\n for city in unique_cities:\n subset = data.loc[data.city == city].copy() \n subset = calc_pwa(subset, col, pwa)\n \n # saving the pwa values and rows ids for the current city\n data_pwa.extend(subset[col+'_pwa'].iloc[pwa:])\n names_pwa.extend(subset.id[pwa:])\n \n # joining the data from each city with the original dataframe and removing the unique ids\n data_pwa = pd.Series(data_pwa, index=names_pwa, name=col+'_pwa')\n data = data.join(data_pwa, how='inner', on='id')\n data.drop(columns='id', inplace=True)\n else:\n data = calc_pwa(data, col, pwa)\n data = data[pwa:]\n \n return data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Temperature experiments",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"counts, values = np.histogram(df_comb.t, bins=100)\nvalues = values[:-1] + ((values[1:] - values[:-1])/2)\nvalues = values.astype('float64')\n\ny = np.array(pd.Series(counts).rolling(window=7).mean())\n \nmaxima = find_peaks(y)[0]\nminima = argrelmin(y)[0]\n\nplt.plot(values, counts)\nplt.plot(values, y, c='orange', alpha=0.75)\n\nfor maximum in maxima:\n plt.plot(np.repeat(values[maximum], 2), np.array([0, y[maximum]]))\n \nfor minimum in minima:\n plt.plot(np.repeat(values[minimum], 2), np.array([0, y[minimum]]))\n \nt_split = values[maxima][0]\nprint('Splitting on:', t_split)\n\nt_split_mask = df_comb.t > t_split\n\ndf_high_t = df.loc[t_split_mask]\ndf_comb_high_t = df_comb.loc[t_split_mask]\ndates_high_t = dates.loc[t_split_mask]\n\nprint('Using', df_comb_high_t.shape[0], 'out of', df_comb.shape[0], 'data points', '(',\n np.round(100*df_comb_high_t.shape[0]/df_comb.shape[0], 2), '% )\\n')\n\ny_train, y_test, log_y_test, X_train, X_test, dates_test = split_data(df_high_t, df_comb_high_t, dates_high_t)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
cbe769264aa540876bde2fb48d2a7314ab4f0dc2
| 5,480 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
pair_distances.ipynb
|
VikramNoibu/gretel-path-extrapolation
|
7219c4b3eff9ce25e78182105dcbacdacd5bd010
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
pair_distances.ipynb
|
VikramNoibu/gretel-path-extrapolation
|
7219c4b3eff9ce25e78182105dcbacdacd5bd010
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
pair_distances.ipynb
|
VikramNoibu/gretel-path-extrapolation
|
7219c4b3eff9ce25e78182105dcbacdacd5bd010
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 34.037267 | 100 | 0.470985 |
[
[
[
"from main import *",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"domain = 'pollini'\nconfig_path = \"config/\" + domain\nconfig = Config()\nconfig.load_from_file(config_path)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"graph, trajectories, pairwise_node_features, _ = load_data(config)",
"number of trajectories: 33181\nnumber of valid trajectories (length in [11, 50]): 17013\ntrajectories length: min 11 | max 50 | mean 21.55\nsplit train/(valid)?/test 0.8/0.2\n"
],
[
"graph._distances",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"graph.nodes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe769ffcc2eb4b228ea468a19fbccc1b4e5f675
| 71,915 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Section 7/7-Demo.ipynb
|
PacktPublishing/Pandas-and-NumPy-Tips-Trick-and-Techniques
|
d9073b7353ad49c0a9ecf5759e50291c22b5d3dd
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2020-09-29T02:31:09.000Z
|
2021-08-09T07:19:05.000Z
|
Section 7/7-Demo.ipynb
|
PacktPublishing/Pandas-and-NumPy-Tips-Trick-and-Techniques
|
d9073b7353ad49c0a9ecf5759e50291c22b5d3dd
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2019-11-06T20:55:11.000Z
|
2019-11-06T20:55:11.000Z
|
Section 7/7-Demo.ipynb
|
PacktPublishing/Pandas-and-NumPy-Tips-Trick-and-Techniques
|
d9073b7353ad49c0a9ecf5759e50291c22b5d3dd
|
[
"MIT"
] | 7 |
2019-11-01T09:28:56.000Z
|
2022-01-28T18:33:13.000Z
| 129.810469 | 36,172 | 0.859084 |
[
[
[
"# Demo of Analyze class",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from finance import Analyze as fa",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 1. Get data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"amzn = fa.get_data(\"AMZN\")\namzn.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 2. Apply analytical methods",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"amzn = fa.calc_vol(amzn)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fa.high_low(amzn)\nfa.moving_avg(amzn)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"amzn.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nDatetimeIndex: 251 entries, 2018-10-04 to 2019-10-03\nData columns (total 15 columns):\nHigh 251 non-null float64\nLow 251 non-null float64\nOpen 251 non-null float64\nClose 251 non-null float64\nVolume 251 non-null int64\nAdj Close 251 non-null float64\nReturn 251 non-null float64\nVolatility 251 non-null float64\nChange 251 non-null float64\nExp_Change 251 non-null float64\nMagnitude 251 non-null float64\nAbs_Magnitude 251 non-null float64\nHigh_Low_Spread 251 non-null float64\n21_day 231 non-null float64\n63_day 189 non-null float64\ndtypes: float64(14), int64(1)\nmemory usage: 31.4 KB\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 3. Examine results",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"amzn['High_Low_Spread'].describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fa.mag_hist(amzn)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fa.plot_magnitude(amzn)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fa.plot_MA(amzn)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 4. Advanced Analyses",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"exp = fa.exp_friday(amzn)\nexp[['Return', 'Change', 'Abs_Magnitude']].describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"exp.Close - exp.Close // 10 * 10",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"low_vol = fa.low_vol_duration(amzn)\nlow_vol['Days<2sd']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"amzn['Days<2sd'].tail()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe78b257383aeb52f14772a0858ed4906a2f9cf
| 304,707 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Baseline_Model.ipynb
|
ysraell/creditcardfraud
|
9da8a2c8f25cb27c2cabd5c6a852f8085aabfbb2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Baseline_Model.ipynb
|
ysraell/creditcardfraud
|
9da8a2c8f25cb27c2cabd5c6a852f8085aabfbb2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Baseline_Model.ipynb
|
ysraell/creditcardfraud
|
9da8a2c8f25cb27c2cabd5c6a852f8085aabfbb2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 36.531231 | 216 | 0.328283 |
[
[
[
"# Baseline Model \n\n- Initial parameters search.\n\n- Search parameter for baseline model.\n\n#### Author: Israel Oliveira [\\[e-mail\\]](mailto:'Israel%20Oliveira%20'<[email protected]>)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%load_ext watermark",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\n\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, ParameterGrid\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nfrom sklearn.metrics import f1_score, roc_auc_score",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from tqdm import tqdm\n\nfrom glob import glob\n\n# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n# %matplotlib inline\n# from matplotlib import rcParams\n# from cycler import cycler\n\n# rcParams['figure.figsize'] = 12, 8 # 18, 5\n# rcParams['axes.spines.top'] = False\n# rcParams['axes.spines.right'] = False\n# rcParams['axes.grid'] = True\n# rcParams['axes.prop_cycle'] = cycler(color=['#365977'])\n# rcParams['lines.linewidth'] = 2.5\n\n# import seaborn as sns\n# sns.set_theme()\n\n# pd.set_option(\"max_columns\", None)\n# pd.set_option(\"max_rows\", None)\n# pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', None)\n\nfrom IPython.display import Markdown, display\ndef md(arg):\n display(Markdown(arg))\n\n# from pandas_profiling import ProfileReport\n# #report = ProfileReport(#DataFrame here#, minimal=True)\n# #report.to\n\n# import pyarrow.parquet as pq\n# #df = pq.ParquetDataset(path_to_folder_with_parquets, filesystem=None).read_pandas().to_pandas()\n\n# import json\n# def open_file_json(path,mode='r',var=None):\n# if mode == 'w':\n# with open(path,'w') as f:\n# json.dump(var, f)\n# if mode == 'r':\n# with open(path,'r') as f:\n# return json.load(f)\n\n# import functools\n# import operator\n# def flat(a):\n# return functools.reduce(operator.iconcat, a, [])\n\n# import json\n# from glob import glob\n# from typing import NewType\n\n\n# DictsPathType = NewType(\"DictsPath\", str)\n\n\n# def open_file_json(path):\n# with open(path, \"r\") as f:\n# return json.load(f)\n\n# class LoadDicts:\n# def __init__(self, dict_path: DictsPathType = \"./data\"):\n# Dicts_glob = glob(f\"{dict_path}/*.json\")\n# self.List = []\n# self.Dict = {}\n# for path_json in Dicts_glob:\n# name = path_json.split(\"/\")[-1].replace(\".json\", \"\")\n# self.List.append(name)\n# self.Dict[name] = open_file_json(path_json)\n# setattr(self, name, self.Dict[name])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Run this cell before close.\n%watermark -d --iversion -b -r -g -m -v\n!cat /proc/cpuinfo |grep 'model name'|head -n 1 |sed -e 's/model\\ name/CPU/'\n!free -h |cut -d'i' -f1 |grep -v total",
"Python implementation: CPython\nPython version : 3.9.6\nIPython version : 7.26.0\n\nCompiler : GCC 8.3.0\nOS : Linux\nRelease : 5.11.0-7620-generic\nMachine : x86_64\nProcessor : \nCPU cores : 8\nArchitecture: 64bit\n\nGit hash: 38749d73a7d8f2b4d7906687d79829b7ff7b69d3\n\nGit repo: https://github.com/ysraell/creditcardfraud.git\n\nGit branch: main\n\npandas: 1.3.1\nnumpy : 1.19.5\n\nCPU\t: Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E3-1241 v3 @ 3.50GHz\nMem: 31G\nSwap: 4.0G\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Initial search",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#\nn_jobs = 4\n\n#\nN_fraud_test = 200\nN_truth_test = int(2e4)\nN_truth_train = int(2e5)\n\n#\nsplit_seeds = [13, 17, 47, 53]\n\n# random_state used by RandomForestClassifier\nrandom_state = 42\n\n# Number of trees in random forest\nn_estimators = [200, 400, 800]\n\n# Number of features to consider at every split\nmax_features = ['auto', 'sqrt']\n\n# Minimum number of samples required to split a node\nmin_samples_split = [2, 8]\n\n# Minimum number of samples required at each leaf node\nmin_samples_leaf = [1, 4]\n\n# Method of selecting samples for training each tree\nbootstrap = [True]\n\n# Create the random grid\nsearch_grid = {'n_estimators': n_estimators,\n 'max_features': max_features,\n 'min_samples_split': min_samples_split,\n 'min_samples_leaf': min_samples_leaf,\n 'bootstrap': bootstrap}\n\nprint(search_grid)",
"{'n_estimators': [200, 400, 800], 'max_features': ['auto', 'sqrt'], 'min_samples_split': [2, 8], 'min_samples_leaf': [1, 4], 'bootstrap': [True]}\n"
],
[
"target_col = 'Class'\nds_cols = ['V1', 'V2', 'V3', 'V4', 'V5', 'V6', 'V7', 'V8', 'V9', 'V10', 'V11', 'V12', 'V13', 'V14', 'V15', 'V16', 'V17', 'V18', 'V19', 'V20', 'V21', 'V22', 'V23', 'V24', 'V25', 'V26', 'V27', 'V28', 'Amount']\nglob_paths = glob('/work/data/creditcard*.csv')\n\ntotal_exps = len(glob_paths)*len(split_seeds)*len(ParameterGrid(search_grid))\nprint(total_exps)",
"288\n"
],
[
"\nwith tqdm(total=total_exps) as progress_bar:\n\n def RunGrid(df_train, df_test, random_state):\n out = []\n for params in ParameterGrid(search_grid):\n params['random_state'] = random_state\n params['n_jobs'] = n_jobs\n rf = RandomForestClassifier(**params)\n rf.fit(df_train[ds_cols].to_numpy(), df_train[target_col].to_numpy())\n probs = rf.predict_proba(df_test[ds_cols].to_numpy())\n exp = {\n 'probs' : probs,\n 'rf_classes': rf.classes_,\n 'params': params\n }\n out.append(exp)\n progress_bar.update(1)\n return out\n\n\n Results = {}\n for ds_path in glob_paths:\n df = pd.read_csv(ds_path)\n df = df[ds_cols+[target_col]]\n df_fraud = df.query('Class == 1').reset_index(drop=True).copy()\n df_truth = df.query('Class == 0').reset_index(drop=True).copy()\n del df\n set_exp = {}\n for seed in split_seeds:\n df_fraud_train, df_fraud_test = train_test_split(df_fraud, test_size=N_fraud_test, random_state=seed)\n df_truth_train, df_truth_test = train_test_split(df_truth, train_size=N_truth_train, test_size=N_truth_test, random_state=seed)\n df_train = pd.concat([df_fraud_train, df_truth_train]).reset_index(drop=True)\n df_test = pd.concat([df_fraud_test, df_truth_test]).reset_index(drop=True)\n out = RunGrid(df_train, df_test, random_state)\n set_exp[seed] = {\n 'target_test': df_test[target_col].to_numpy(),\n 'exps': out\n }\n Results[ds_path] = set_exp",
"100%|██████████| 288/288 [15:42:06<00:00, 196.27s/it] \n"
],
[
"cols_results = ['ds_path', 'seed']\ncols_param = ['bootstrap', 'max_features', 'min_samples_leaf', 'min_samples_split', 'n_estimators', 'random_state']\ncols_metrics = ['Fraud_True_Sum','Truth_False_Sum', 'Fraud_False_Sum', 'F1_M', 'AUC_ROC_M', 'TP_0', 'TP_1']\ncols = cols_results+cols_param+cols_metrics",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"', '.join(cols_metrics)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"''.join([ f'param[\\'{col}\\'], ' for col in cols_param])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data = []\nfor ds_path,sets_exp in Results.items():\n for seed,set_exp in sets_exp.items():\n target_test = set_exp['target_test']\n for exp in set_exp['exps']:\n df_exp = pd.DataFrame(exp['probs'], columns=exp['rf_classes'])\n df_exp['pred'] = df_exp[[0, 1]].apply(lambda x: exp['rf_classes'][np.argmax(x)], axis=1)\n df_exp['target'] = target_test\n Fraud_True_Sum = df_exp.loc[(df_exp.pred == 1) & (df_exp.target == 1)][1].sum()/sum(df_exp.target == 1)\n Truth_False_Sum = df_exp.loc[(df_exp.pred == 0) & (df_exp.target == 1)][0].sum()/sum(df_exp.target == 1)\n Fraud_False_Sum = df_exp.loc[(df_exp.pred == 1) & (df_exp.target == 0)][1].sum()/sum(df_exp.target == 0)\n F1_M = f1_score(target_test, df_exp['pred'].to_numpy(), average='macro')\n AUC_ROC_M = roc_auc_score(target_test, df_exp['pred'].to_numpy(), average='macro')\n TP_0 = df_exp.loc[(df_exp.pred == 0) & (df_exp.target == 0)].shape[0]/sum(df_exp.target == 0)\n TP_1 = df_exp.loc[(df_exp.pred == 1) & (df_exp.target == 1)].shape[0]/sum(df_exp.target == 1)\n param = exp['params']\n data.append([\n ds_path, seed,\n param['bootstrap'], param['max_features'], param['min_samples_leaf'],\n param['min_samples_split'], param['n_estimators'], param['random_state'],\n Fraud_True_Sum, Truth_False_Sum, Fraud_False_Sum, F1_M, AUC_ROC_M, TP_0, TP_1\n ])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_Results = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=cols)\n#df_Results.to_csv('/work/data/Results_creditcard_Init.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_Results.to_csv('/work/data/Results_creditcard_Init.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_Results = pd.read_csv('/work/data/Results_creditcard_Init.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"map_ds_path = {\n '/work/data/creditcard_trans_float.csv': 'Float',\n '/work/data/creditcard.csv': 'Original',\n '/work/data/creditcard_trans_int.csv': 'Integer'\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_Results['DS'] = df_Results.ds_path.apply(lambda x: map_ds_path[x])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for metric in cols_metrics:\n md(f'# {metric}')\n display(df_Results.sort_values(metric, ascending=False).head(20)[['DS', 'seed']+cols_param[:-1]+cols_metrics])\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for col in cols_param[:-1]:\n md(f'# {col}')\n display(df_Results[['DS', col]+cols_metrics].groupby(['DS', col]).mean())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Baseline model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#\nN_fraud_test = 200\nN_truth_test = int(2e4)\nN_truth_train = int(2e5)\n\n#\nsplit_seeds = [13, 17, 19, 41]\n\n# random_state used by RandomForestClassifier\nrandom_state = 42\n\n# Number of trees in random forest\nn_estimators = [100, 200, 400, 800, 100]\n\n# Number of features to consider at every split\nmax_features = ['auto']\n\n# Minimum number of samples required to split a node\nmin_samples_split = [2]\n\n# Minimum number of samples required at each leaf node\nmin_samples_leaf = [1]\n\n# Method of selecting samples for training each tree\nbootstrap = [True]\n\n# Create the random grid\nsearch_grid = {'n_estimators': n_estimators,\n 'max_features': max_features,\n 'min_samples_split': min_samples_split,\n 'min_samples_leaf': min_samples_leaf,\n 'bootstrap': bootstrap}\n\nprint(search_grid)",
"{'n_estimators': [100, 200, 400, 800, 100], 'max_features': ['auto'], 'min_samples_split': [2], 'min_samples_leaf': [1], 'bootstrap': [True]}\n"
],
[
"glob_paths = ['/work/data/creditcard_trans_int.csv']\ntotal_exps = len(glob_paths)*len(split_seeds)*len(ParameterGrid(search_grid))\nprint(total_exps)",
"20\n"
],
[
"\nwith tqdm(total=total_exps) as progress_bar:\n\n def RunGrid(df_train, df_test, random_state):\n out = []\n for params in ParameterGrid(search_grid):\n params['random_state'] = random_state\n params['n_jobs'] = n_jobs\n rf = RandomForestClassifier(**params)\n rf.fit(df_train[ds_cols].to_numpy(), df_train[target_col].to_numpy())\n probs = rf.predict_proba(df_test[ds_cols].to_numpy())\n exp = {\n 'probs' : probs,\n 'rf_classes': rf.classes_,\n 'params': params\n }\n out.append(exp)\n progress_bar.update(1)\n return out\n\n\n Results = {}\n for ds_path in glob_paths:\n df = pd.read_csv(ds_path)\n df = df[ds_cols+[target_col]]\n df_fraud = df.query('Class == 1').reset_index(drop=True).copy()\n df_truth = df.query('Class == 0').reset_index(drop=True).copy()\n del df\n set_exp = {}\n for seed in split_seeds:\n df_fraud_train, df_fraud_test = train_test_split(df_fraud, test_size=N_fraud_test, random_state=seed)\n df_truth_train, df_truth_test = train_test_split(df_truth, train_size=N_truth_train, test_size=N_truth_test, random_state=seed)\n df_train = pd.concat([df_fraud_train, df_truth_train]).reset_index(drop=True)\n df_test = pd.concat([df_fraud_test, df_truth_test]).reset_index(drop=True)\n out = RunGrid(df_train, df_test, random_state)\n set_exp[seed] = {\n 'target_test': df_test[target_col].to_numpy(),\n 'exps': out\n }\n Results[ds_path] = set_exp",
"100%|██████████| 20/20 [44:34<00:00, 133.75s/it]\n"
],
[
"data = []\nfor ds_path,sets_exp in Results.items():\n for seed,set_exp in sets_exp.items():\n target_test = set_exp['target_test']\n for exp in set_exp['exps']:\n df_exp = pd.DataFrame(exp['probs'], columns=exp['rf_classes'])\n df_exp['pred'] = df_exp[[0, 1]].apply(lambda x: exp['rf_classes'][np.argmax(x)], axis=1)\n df_exp['target'] = target_test\n Fraud_True_Sum = df_exp.loc[(df_exp.pred == 1) & (df_exp.target == 1)][1].sum()/sum(df_exp.target == 1)\n Truth_False_Sum = df_exp.loc[(df_exp.pred == 0) & (df_exp.target == 1)][0].sum()/sum(df_exp.target == 1)\n Fraud_False_Sum = df_exp.loc[(df_exp.pred == 1) & (df_exp.target == 0)][1].sum()/sum(df_exp.target == 0)\n F1_M = f1_score(target_test, df_exp['pred'].to_numpy(), average='macro')\n AUC_ROC_M = roc_auc_score(target_test, df_exp['pred'].to_numpy(), average='macro')\n TP_0 = df_exp.loc[(df_exp.pred == 0) & (df_exp.target == 0)].shape[0]/sum(df_exp.target == 0)\n TP_1 = df_exp.loc[(df_exp.pred == 1) & (df_exp.target == 1)].shape[0]/sum(df_exp.target == 1)\n param = exp['params']\n data.append([\n ds_path, seed,\n param['bootstrap'], param['max_features'], param['min_samples_leaf'],\n param['min_samples_split'], param['n_estimators'], param['random_state'],\n Fraud_True_Sum, Truth_False_Sum, Fraud_False_Sum, F1_M, AUC_ROC_M, TP_0, TP_1\n ])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_Results = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=cols)\ndf_Results.to_csv('/work/data/Results_creditcard_Baseline.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_Results",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for metric in cols_metrics:\n md(f'# {metric}')\n display(df_Results.sort_values(metric, ascending=False).head(20)[cols_param[:-1]+cols_metrics])\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe7b3052551067f15935190ed3366969e53ca57
| 254,447 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
demos/node-classification/gat-node-classification.ipynb
|
vishalbelsare/stellargraph
|
3c2c8c18ab4c5c16660f350d8e23d7dc39e738de
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2,428 |
2018-09-14T01:47:25.000Z
|
2022-03-31T06:43:35.000Z
|
demos/node-classification/gat-node-classification.ipynb
|
vishalbelsare/stellargraph
|
3c2c8c18ab4c5c16660f350d8e23d7dc39e738de
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1,749 |
2018-09-14T01:31:19.000Z
|
2022-03-17T08:40:16.000Z
|
demos/node-classification/gat-node-classification.ipynb
|
vishalbelsare/stellargraph
|
3c2c8c18ab4c5c16660f350d8e23d7dc39e738de
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 390 |
2018-09-18T07:05:44.000Z
|
2022-03-24T00:40:23.000Z
| 220.109862 | 169,264 | 0.908217 |
[
[
[
"# Node classification with Graph ATtention Network (GAT)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<table><tr><td>Run the latest release of this notebook:</td><td><a href=\"https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/stellargraph/stellargraph/master?urlpath=lab/tree/demos/node-classification/gat-node-classification.ipynb\" alt=\"Open In Binder\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://mybinder.org/badge_logo.svg\"/></a></td><td><a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/stellargraph/stellargraph/blob/master/demos/node-classification/gat-node-classification.ipynb\" alt=\"Open In Colab\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\"/></a></td></tr></table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Import NetworkX and stellar:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# install StellarGraph if running on Google Colab\nimport sys\nif 'google.colab' in sys.modules:\n %pip install -q stellargraph[demos]==1.3.0b",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# verify that we're using the correct version of StellarGraph for this notebook\nimport stellargraph as sg\n\ntry:\n sg.utils.validate_notebook_version(\"1.3.0b\")\nexcept AttributeError:\n raise ValueError(\n f\"This notebook requires StellarGraph version 1.3.0b, but a different version {sg.__version__} is installed. Please see <https://github.com/stellargraph/stellargraph/issues/1172>.\"\n ) from None",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import networkx as nx\nimport pandas as pd\nimport os\n\nimport stellargraph as sg\nfrom stellargraph.mapper import FullBatchNodeGenerator\nfrom stellargraph.layer import GAT\n\nfrom tensorflow.keras import layers, optimizers, losses, metrics, Model\nfrom sklearn import preprocessing, feature_extraction, model_selection\nfrom stellargraph import datasets\nfrom IPython.display import display, HTML\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Loading the CORA network",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"(See [the \"Loading from Pandas\" demo](../basics/loading-pandas.ipynb) for details on how data can be loaded.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dataset = datasets.Cora()\ndisplay(HTML(dataset.description))\nG, node_subjects = dataset.load()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(G.info())",
"StellarGraph: Undirected multigraph\n Nodes: 2708, Edges: 5429\n\n Node types:\n paper: [2708]\n Edge types: paper-cites->paper\n\n Edge types:\n paper-cites->paper: [5429]\n"
]
],
[
[
"We aim to train a graph-ML model that will predict the \"subject\" attribute on the nodes. These subjects are one of 7 categories:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"set(node_subjects)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Splitting the data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"For machine learning we want to take a subset of the nodes for training, and use the rest for validation and testing. We'll use scikit-learn again to do this.\n\nHere we're taking 140 node labels for training, 500 for validation, and the rest for testing.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_subjects, test_subjects = model_selection.train_test_split(\n node_subjects, train_size=140, test_size=None, stratify=node_subjects\n)\nval_subjects, test_subjects = model_selection.train_test_split(\n test_subjects, train_size=500, test_size=None, stratify=test_subjects\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Note using stratified sampling gives the following counts:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from collections import Counter\n\nCounter(train_subjects)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The training set has class imbalance that might need to be compensated, e.g., via using a weighted cross-entropy loss in model training, with class weights inversely proportional to class support. However, we will ignore the class imbalance in this example, for simplicity.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Converting to numeric arrays",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"For our categorical target, we will use one-hot vectors that will be fed into a soft-max Keras layer during training. To do this conversion ...",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"target_encoding = preprocessing.LabelBinarizer()\n\ntrain_targets = target_encoding.fit_transform(train_subjects)\nval_targets = target_encoding.transform(val_subjects)\ntest_targets = target_encoding.transform(test_subjects)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We now do the same for the node attributes we want to use to predict the subject. These are the feature vectors that the Keras model will use as input. The CORA dataset contains attributes 'w_x' that correspond to words found in that publication. If a word occurs more than once in a publication the relevant attribute will be set to one, otherwise it will be zero.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Creating the GAT model in Keras",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To feed data from the graph to the Keras model we need a generator. Since GAT is a full-batch model, we use the `FullBatchNodeGenerator` class to feed node features and graph adjacency matrix to the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"generator = FullBatchNodeGenerator(G, method=\"gat\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For training we map only the training nodes returned from our splitter and the target values.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_gen = generator.flow(train_subjects.index, train_targets)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we can specify our machine learning model, we need a few more parameters for this:\n\n * the `layer_sizes` is a list of hidden feature sizes of each layer in the model. In this example we use two GAT layers with 8-dimensional hidden node features for the first layer and the 7 class classification output for the second layer.\n * `attn_heads` is the number of attention heads in all but the last GAT layer in the model\n * `activations` is a list of activations applied to each layer's output\n * Arguments such as `bias`, `in_dropout`, `attn_dropout` are internal parameters of the model, execute `?GAT` for details. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To follow the GAT model architecture used for Cora dataset in the original paper [Graph Attention Networks. P. Veličković et al. ICLR 2018 https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.10903], let's build a 2-layer GAT model, with the second layer being the classifier that predicts paper subject: it thus should have the output size of `train_targets.shape[1]` (7 subjects) and a softmax activation.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"gat = GAT(\n layer_sizes=[8, train_targets.shape[1]],\n activations=[\"elu\", \"softmax\"],\n attn_heads=8,\n generator=generator,\n in_dropout=0.5,\n attn_dropout=0.5,\n normalize=None,\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Expose the input and output tensors of the GAT model for node prediction, via GAT.in_out_tensors() method:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x_inp, predictions = gat.in_out_tensors()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Training the model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now let's create the actual Keras model with the input tensors `x_inp` and output tensors being the predictions `predictions` from the final dense layer",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = Model(inputs=x_inp, outputs=predictions)\nmodel.compile(\n optimizer=optimizers.Adam(lr=0.005),\n loss=losses.categorical_crossentropy,\n metrics=[\"acc\"],\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Train the model, keeping track of its loss and accuracy on the training set, and its generalisation performance on the validation set (we need to create another generator over the validation data for this)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"val_gen = generator.flow(val_subjects.index, val_targets)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Create callbacks for early stopping (if validation accuracy stops improving) and best model checkpoint saving:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ModelCheckpoint\n\nif not os.path.isdir(\"logs\"):\n os.makedirs(\"logs\")\nes_callback = EarlyStopping(\n monitor=\"val_acc\", patience=20\n) # patience is the number of epochs to wait before early stopping in case of no further improvement\nmc_callback = ModelCheckpoint(\n \"logs/best_model.h5\", monitor=\"val_acc\", save_best_only=True, save_weights_only=True\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Train the model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"history = model.fit(\n train_gen,\n epochs=50,\n validation_data=val_gen,\n verbose=2,\n shuffle=False, # this should be False, since shuffling data means shuffling the whole graph\n callbacks=[es_callback, mc_callback],\n)",
"Epoch 1/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 2.0089 - acc: 0.1286 - val_loss: 1.8361 - val_acc: 0.3440\nEpoch 2/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 1.8543 - acc: 0.2786 - val_loss: 1.7295 - val_acc: 0.3860\nEpoch 3/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 1.7033 - acc: 0.4143 - val_loss: 1.6395 - val_acc: 0.3880\nEpoch 4/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 1.5959 - acc: 0.4500 - val_loss: 1.5602 - val_acc: 0.3960\nEpoch 5/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 1.4899 - acc: 0.4786 - val_loss: 1.4882 - val_acc: 0.4360\nEpoch 6/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 1.4368 - acc: 0.5286 - val_loss: 1.4199 - val_acc: 0.5040\nEpoch 7/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 1.3643 - acc: 0.4786 - val_loss: 1.3548 - val_acc: 0.5840\nEpoch 8/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 1.1994 - acc: 0.6286 - val_loss: 1.2938 - val_acc: 0.6420\nEpoch 9/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 1.2092 - acc: 0.6357 - val_loss: 1.2381 - val_acc: 0.6880\nEpoch 10/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 1.1780 - acc: 0.6214 - val_loss: 1.1883 - val_acc: 0.7460\nEpoch 11/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 1.0629 - acc: 0.7571 - val_loss: 1.1438 - val_acc: 0.7540\nEpoch 12/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.9646 - acc: 0.7786 - val_loss: 1.1008 - val_acc: 0.7660\nEpoch 13/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.9697 - acc: 0.7357 - val_loss: 1.0610 - val_acc: 0.7660\nEpoch 14/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.9924 - acc: 0.7571 - val_loss: 1.0250 - val_acc: 0.7760\nEpoch 15/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.9264 - acc: 0.7929 - val_loss: 0.9903 - val_acc: 0.7820\nEpoch 16/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.9189 - acc: 0.7571 - val_loss: 0.9571 - val_acc: 0.7900\nEpoch 17/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.7993 - acc: 0.8429 - val_loss: 0.9268 - val_acc: 0.7960\nEpoch 18/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.7887 - acc: 0.8429 - val_loss: 0.8978 - val_acc: 0.8060\nEpoch 19/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.7488 - acc: 0.8714 - val_loss: 0.8694 - val_acc: 0.8120\nEpoch 20/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.8564 - acc: 0.7929 - val_loss: 0.8415 - val_acc: 0.8140\nEpoch 21/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.6635 - acc: 0.8643 - val_loss: 0.8154 - val_acc: 0.8120\nEpoch 22/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.7209 - acc: 0.8571 - val_loss: 0.7931 - val_acc: 0.8160\nEpoch 23/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.7705 - acc: 0.7714 - val_loss: 0.7732 - val_acc: 0.8240\nEpoch 24/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.7272 - acc: 0.7857 - val_loss: 0.7560 - val_acc: 0.8280\nEpoch 25/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.5554 - acc: 0.8643 - val_loss: 0.7410 - val_acc: 0.8320\nEpoch 26/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.6467 - acc: 0.7929 - val_loss: 0.7278 - val_acc: 0.8340\nEpoch 27/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.5838 - acc: 0.9000 - val_loss: 0.7157 - val_acc: 0.8340\nEpoch 28/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.5867 - acc: 0.8786 - val_loss: 0.7062 - val_acc: 0.8340\nEpoch 29/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.5223 - acc: 0.8500 - val_loss: 0.6971 - val_acc: 0.8360\nEpoch 30/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.6319 - acc: 0.8214 - val_loss: 0.6904 - val_acc: 0.8340\nEpoch 31/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.5651 - acc: 0.8429 - val_loss: 0.6837 - val_acc: 0.8340\nEpoch 32/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.5362 - acc: 0.8429 - val_loss: 0.6789 - val_acc: 0.8280\nEpoch 33/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.5855 - acc: 0.8357 - val_loss: 0.6736 - val_acc: 0.8260\nEpoch 34/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.5116 - acc: 0.8929 - val_loss: 0.6671 - val_acc: 0.8280\nEpoch 35/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.6374 - acc: 0.8000 - val_loss: 0.6612 - val_acc: 0.8280\nEpoch 36/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.4589 - acc: 0.8714 - val_loss: 0.6546 - val_acc: 0.8300\nEpoch 37/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.5649 - acc: 0.8286 - val_loss: 0.6479 - val_acc: 0.8300\nEpoch 38/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.4521 - acc: 0.8786 - val_loss: 0.6407 - val_acc: 0.8280\nEpoch 39/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.5769 - acc: 0.8429 - val_loss: 0.6335 - val_acc: 0.8320\nEpoch 40/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.6275 - acc: 0.8071 - val_loss: 0.6255 - val_acc: 0.8320\nEpoch 41/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.5329 - acc: 0.8286 - val_loss: 0.6178 - val_acc: 0.8300\nEpoch 42/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.5978 - acc: 0.8286 - val_loss: 0.6110 - val_acc: 0.8280\nEpoch 43/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.4852 - acc: 0.8857 - val_loss: 0.6047 - val_acc: 0.8280\nEpoch 44/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.5016 - acc: 0.8714 - val_loss: 0.5996 - val_acc: 0.8280\nEpoch 45/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.4713 - acc: 0.9000 - val_loss: 0.5963 - val_acc: 0.8320\nEpoch 46/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.4520 - acc: 0.8643 - val_loss: 0.5945 - val_acc: 0.8340\nEpoch 47/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.4885 - acc: 0.8786 - val_loss: 0.5934 - val_acc: 0.8340\nEpoch 48/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.4595 - acc: 0.8786 - val_loss: 0.5932 - val_acc: 0.8300\nEpoch 49/50\n1/1 - 0s - loss: 0.4557 - acc: 0.8571 - val_loss: 0.5929 - val_acc: 0.8300\n"
]
],
[
[
"Plot the training history:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sg.utils.plot_history(history)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Reload the saved weights of the best model found during the training (according to validation accuracy)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model.load_weights(\"logs/best_model.h5\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Evaluate the best model on the test set",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"test_gen = generator.flow(test_subjects.index, test_targets)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test_metrics = model.evaluate(test_gen)\nprint(\"\\nTest Set Metrics:\")\nfor name, val in zip(model.metrics_names, test_metrics):\n print(\"\\t{}: {:0.4f}\".format(name, val))",
"\nTest Set Metrics:\n\tloss: 0.7227\n\tacc: 0.8109\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Making predictions with the model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now let's get the predictions for all nodes:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"all_nodes = node_subjects.index\nall_gen = generator.flow(all_nodes)\nall_predictions = model.predict(all_gen)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"These predictions will be the output of the softmax layer, so to get final categories we'll use the `inverse_transform` method of our target attribute specification to turn these values back to the original categories",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Note that for full-batch methods the batch size is 1 and the predictions have shape $(1, N_{nodes}, N_{classes})$ so we we remove the batch dimension to obtain predictions of shape $(N_{nodes}, N_{classes})$.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"node_predictions = target_encoding.inverse_transform(all_predictions.squeeze())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's have a look at a few predictions after training the model:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = pd.DataFrame({\"Predicted\": node_predictions, \"True\": node_subjects})\ndf.head(20)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Node embeddings\nEvaluate node embeddings as activations of the output of the 1st GraphAttention layer in GAT layer stack (the one before the top classification layer predicting paper subjects), and visualise them, coloring nodes by their true subject label. We expect to see nice clusters of papers in the node embedding space, with papers of the same subject belonging to the same cluster.\n\nLet's create a new model with the same inputs as we used previously `x_inp` but now the output is the embeddings rather than the predicted class. We find the embedding layer by taking the first graph attention layer in the stack of Keras layers. Additionally note that the weights trained previously are kept in the new model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"emb_layer = next(l for l in model.layers if l.name.startswith(\"graph_attention\"))\nprint(\n \"Embedding layer: {}, output shape {}\".format(emb_layer.name, emb_layer.output_shape)\n)",
"Embedding layer: graph_attention_sparse, output shape (1, 2708, 64)\n"
],
[
"embedding_model = Model(inputs=x_inp, outputs=emb_layer.output)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The embeddings can now be calculated using the predict function. Note that the embeddings returned are 64 dimensional features (8 dimensions for each of the 8 attention heads) for all nodes.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"emb = embedding_model.predict(all_gen)\nemb.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Project the embeddings to 2d using either TSNE or PCA transform, and visualise, coloring nodes by their true subject label",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.decomposition import PCA\nfrom sklearn.manifold import TSNE\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Note that the embeddings from the GAT model have a batch dimension of 1 so we `squeeze` this to get a matrix of $N_{nodes} \\times N_{emb}$.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X = emb.squeeze()\ny = np.argmax(target_encoding.transform(node_subjects), axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"if X.shape[1] > 2:\n transform = TSNE # PCA\n\n trans = transform(n_components=2)\n emb_transformed = pd.DataFrame(trans.fit_transform(X), index=list(G.nodes()))\n emb_transformed[\"label\"] = y\nelse:\n emb_transformed = pd.DataFrame(X, index=list(G.nodes()))\n emb_transformed = emb_transformed.rename(columns={\"0\": 0, \"1\": 1})\n emb_transformed[\"label\"] = y",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"alpha = 0.7\n\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 7))\nax.scatter(\n emb_transformed[0],\n emb_transformed[1],\n c=emb_transformed[\"label\"].astype(\"category\"),\n cmap=\"jet\",\n alpha=alpha,\n)\nax.set(aspect=\"equal\", xlabel=\"$X_1$\", ylabel=\"$X_2$\")\nplt.title(\n \"{} visualization of GAT embeddings for cora dataset\".format(transform.__name__)\n)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<table><tr><td>Run the latest release of this notebook:</td><td><a href=\"https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/stellargraph/stellargraph/master?urlpath=lab/tree/demos/node-classification/gat-node-classification.ipynb\" alt=\"Open In Binder\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://mybinder.org/badge_logo.svg\"/></a></td><td><a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/stellargraph/stellargraph/blob/master/demos/node-classification/gat-node-classification.ipynb\" alt=\"Open In Colab\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\"/></a></td></tr></table>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe7cb6e85c9562a4172fbc286969ab22834b247
| 7,222 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
tutorials/advanced_features/State Preparation with the SLM Mask.ipynb
|
TripleRD/Pulser
|
7405d8cd7463782891cbbf40335f163dc8f284cc
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2022-02-18T02:48:24.000Z
|
2022-02-18T02:51:21.000Z
|
tutorials/advanced_features/State Preparation with the SLM Mask.ipynb
|
TripleRD/Pulser
|
7405d8cd7463782891cbbf40335f163dc8f284cc
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
tutorials/advanced_features/State Preparation with the SLM Mask.ipynb
|
TripleRD/Pulser
|
7405d8cd7463782891cbbf40335f163dc8f284cc
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 27.992248 | 629 | 0.596372 |
[
[
[
"# State preparation with the SLM mask",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Basics",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"When performing quantum computations with global pulses, it might be hard to prepare the system in an arbitrary initial state. This is especially true in the XY mode, where only a global $\\sigma^x$ pulse can produce excitations whose number is otherwise conserved during free evolution. A partial solution to this problem is to utilize an SLM mask. <br>\nAssume a system of three qubits in XY mode is initially in state $\\left| \\downarrow \\downarrow \\downarrow \\right\\rangle$, and that we are interested in preparing the state $\\left| \\uparrow \\downarrow \\downarrow \\right\\rangle$. Acting naively with a global $\\sigma^x$ pulse of area $\\pi$ would result in state $\\left| \\uparrow \\uparrow \\uparrow \\right\\rangle$. Using an SLM pattern, however, it is possible to detune the last two qubits away from resonance, and the same global $\\sigma^x$ pulse will produced instead the desired state $\\left| \\uparrow \\downarrow \\downarrow \\right\\rangle$. <br>\nLet's see how it works in practice. First create the register:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nfrom pulser import Pulse, Sequence, Register\nfrom pulser.devices import MockDevice\nfrom pulser.waveforms import BlackmanWaveform\nfrom pulser.simulation import Simulation\n\n# Qubit register\nqubits = {\"q0\": (-5,0), \"q1\": (0,0), \"q2\": (5,0)}\nreg = Register(qubits)\nreg.draw()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now create the sequence and add a global $\\sigma^x$ pulse of area $\\pi$ in XY mode:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create the sequence\nseq = Sequence(reg, MockDevice)\n\n# Declare a global XY channel and add the pi pulse\nseq.declare_channel('ch', 'mw_global')\npulse = Pulse.ConstantDetuning(BlackmanWaveform(200, np.pi), 0, 0)\nseq.add(pulse, 'ch')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Drawing the sequence will show the following:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seq.draw()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To set up the SLM mask all we need to do is to create a list that contains the name of the qubits that we want to mask, and pass it to the $\\verb:Sequence.config_slm_mask:$ method:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Mask the last two qubits\nmasked_qubits = [\"q1\", \"q2\"]\nseq.config_slm_mask(masked_qubits)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"At this point it is possible to visualize the mask by drawing the sequence. The masked pulse will appear with a shaded background, and the names of the masked qubits will be shown in the bottom left corner.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seq.draw()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The sequence drawing method also allows to visualize the register. If an SLM mask is defined, the masked qubits will appear with a shaded square halo around them:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seq.draw(draw_register=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now let's see how the system evolves under this masked pulse. Since the pulse only acts on the first qubit, we expect the final state to be $\\left| \\uparrow \\downarrow \\downarrow \\right\\rangle$, or, according to Pulser's conventions for XY basis states, $(1,0)^T \\otimes (0,1)^T \\otimes (0,1)^T$ in the Hilbert space $C^8$:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import qutip\n\nqutip.tensor(qutip.basis(2, 0), qutip.basis(2, 1), qutip.basis(2, 1))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now run the simulation and print the final state as given by Pulser:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sim = Simulation(seq)\nresults = sim.run()\n\nresults.get_final_state()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As expected, the two states agree up to numerical errors.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Notes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Since the SLM mask is mostly useful for state preparation, its use in Pulser is restricted to the first pulse in the sequence. This can be seen by adding an extra pulse in the previous example and drawing the sequence:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seq.add(pulse, 'ch')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"seq.draw()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This example also illustrates the fact that the SLM mask can be configured at any moment during the creation of a sequence (either before or after adding pulses) and it will automatically latch to the first pulse. <br>\nHowever, in order to reflect real hardware constraints, the mask can be configured only once. Trying to configure the mask a second time will raise an error:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"try:\n seq.config_slm_mask(masked_qubits)\nexcept ValueError as err:\n print(err)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Although the example shown here makes use of the XY mode, everything translates directly to the Ising mode as well with the same syntax and restrictions.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe7d171c2c7bef5f98e547153610af7fc1b6e14
| 237,033 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/DeepConvRFWithCNN_fashion_mnist_n_trees_2_layers.ipynb
|
NeuroDataDesign/deep-conv-rf
|
2a324c326aebc6949351a29ecc79c83035bbe4d0
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2020-06-08T21:15:33.000Z
|
2021-08-31T05:12:54.000Z
|
notebooks/DeepConvRFWithCNN_fashion_mnist_n_trees_2_layers.ipynb
|
NeuroDataDesign/deep-conv-rf
|
2a324c326aebc6949351a29ecc79c83035bbe4d0
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/DeepConvRFWithCNN_fashion_mnist_n_trees_2_layers.ipynb
|
NeuroDataDesign/deep-conv-rf
|
2a324c326aebc6949351a29ecc79c83035bbe4d0
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2019-09-09T15:40:33.000Z
|
2020-10-02T17:39:23.000Z
| 292.633333 | 102,888 | 0.914556 |
[
[
[
"# general imports\nimport random\nimport numpy as np\n\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score\nfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\n\nimport torch\nimport torch.nn as nn\nimport torch.utils.data as utils\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nplt.rcParams[\"legend.loc\"] = \"best\"\nplt.rcParams['figure.facecolor'] = 'white'\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# filter python warnings\nimport warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings(\"ignore\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# prepare Fashion MNIST data\nimport torchvision.datasets as datasets\n\n# train data\nmnist_trainset = datasets.FashionMNIST(root='./data/fashion', train=True, download=True, transform=None)\nmnist_train_images = mnist_trainset.train_data.numpy()[..., np.newaxis]\nmnist_train_labels = mnist_trainset.train_labels.numpy()\n\n# test data\nmnist_testset = datasets.FashionMNIST(root='./data/fashion', train=False, download=True, transform=None)\nmnist_test_images = mnist_testset.test_data.numpy()[..., np.newaxis]\nmnist_test_labels = mnist_testset.test_labels.numpy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# The Deep Convolution Random Forest class (for binary classification)\nclass ConvRF(object):\n def __init__(self, kernel_size=5, stride=2):\n self.kernel_size = kernel_size\n self.stride = stride\n self.kernel_forests = None\n\n def _convolve_chop(self, images, labels=None, flatten=False):\n\n batch_size, in_dim, _, num_channels = images.shape\n\n out_dim = int((in_dim - self.kernel_size) / self.stride) + 1 # calculate output dimensions\n\n # create matrix to hold the chopped images\n out_images = np.zeros((batch_size, out_dim, out_dim,\n self.kernel_size, self.kernel_size, num_channels))\n out_labels = None\n\n curr_y = out_y = 0\n # move kernel vertically across the image\n while curr_y + self.kernel_size <= in_dim:\n curr_x = out_x = 0\n # move kernel horizontally across the image\n while curr_x + self.kernel_size <= in_dim:\n # chop images\n out_images[:, out_x, out_y] = images[:, curr_x:curr_x +\n self.kernel_size, curr_y:curr_y+self.kernel_size, :]\n curr_x += self.stride\n out_x += 1\n curr_y += self.stride\n out_y += 1\n\n if flatten:\n out_images = out_images.reshape(batch_size, out_dim, out_dim, -1)\n\n if labels is not None:\n out_labels = np.zeros((batch_size, out_dim, out_dim))\n out_labels[:, ] = labels.reshape(-1, 1, 1)\n\n return out_images, out_labels\n\n def convolve_fit(self, images, labels):\n num_channels = images.shape[-1]\n sub_images, sub_labels = self._convolve_chop(images, labels=labels, flatten=True)\n\n batch_size, out_dim, _, _ = sub_images.shape\n self.kernel_forests = np.zeros((out_dim, out_dim), dtype=np.int).tolist()\n convolved_image = np.zeros((images.shape[0], out_dim, out_dim, 1))\n \n for i in range(out_dim):\n for j in range(out_dim):\n self.kernel_forests[i][j] = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=32)\n self.kernel_forests[i][j].fit(sub_images[:, i, j], sub_labels[:, i, j])\n convolved_image[:, i, j] = self.kernel_forests[i][j].predict_proba(sub_images[:, i, j])[..., 1][..., np.newaxis]\n return convolved_image\n\n def convolve_predict(self, images):\n if not self.kernel_forests:\n raise Exception(\"Should fit training data before predicting\")\n\n num_channels = images.shape[-1]\n sub_images, _ = self._convolve_chop(images, flatten=True)\n\n batch_size, out_dim, _, _ = sub_images.shape\n \n kernel_predictions = np.zeros((images.shape[0], out_dim, out_dim, 1))\n \n for i in range(out_dim):\n for j in range(out_dim):\n kernel_predictions[:, i, j] = self.kernel_forests[i][j].predict_proba(sub_images[:, i, j])[..., 1][..., np.newaxis]\n return kernel_predictions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# define a simple CNN arhcitecture\nfrom torch.autograd import Variable\nimport torch.nn.functional as F\n\nclass SimpleCNNOneFilter(torch.nn.Module):\n \n def __init__(self):\n super(SimpleCNNOneFilter, self).__init__() \n self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=10, stride=2)\n self.fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(100, 2)\n \n def forward(self, x):\n x = F.relu(self.conv1(x))\n x = x.view(-1, 100)\n x = self.fc1(x)\n return(x)\n\nclass SimpleCNN32Filter(torch.nn.Module):\n \n def __init__(self):\n super(SimpleCNN32Filter, self).__init__() \n self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel_size=10, stride=2) # try 64 too, if possible\n self.fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(100*32, 2)\n \n def forward(self, x):\n x = F.relu(self.conv1(x))\n x = x.view(-1, 100*32)\n x = self.fc1(x)\n return(x)\n\nclass SimpleCNN32Filter2Layers(torch.nn.Module):\n \n def __init__(self):\n super(SimpleCNN32Filter2Layers, self).__init__() \n self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel_size=10, stride=2)\n self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=7, stride=1)\n self.fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(16*32, 2)\n \n def forward(self, x):\n x = F.relu(self.conv1(x))\n x = F.relu(self.conv2(x))\n x = x.view(-1, 16*32)\n x = self.fc1(x)\n return(x)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def run_naive_rf(train_images, train_labels, test_images, test_labels, fraction_of_train_samples, class1=3, class2=8):\n num_train_samples_class_1 = int(np.sum(train_labels==class1) * fraction_of_train_samples)\n num_train_samples_class_2 = int(np.sum(train_labels==class2) * fraction_of_train_samples)\n \n # get only train images and labels for class 1 and class 2\n train_images = np.concatenate([train_images[train_labels==class1][:num_train_samples_class_1], train_images[train_labels==class2][:num_train_samples_class_2]])\n train_labels = np.concatenate([np.repeat(0, num_train_samples_class_1), np.repeat(1, num_train_samples_class_2)])\n\n # get only test images and labels for class 1 and class 2\n test_images = np.concatenate([test_images[test_labels==class1], test_images[test_labels==class2]])\n test_labels = np.concatenate([np.repeat(0, np.sum(test_labels==class1)), np.repeat(1, np.sum(test_labels==class2))])\n\n # Train\n clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)\n clf.fit(train_images.reshape(-1, 28*28*1), train_labels)\n # Test\n test_preds = clf.predict(test_images.reshape(-1, 28*28*1))\n return accuracy_score(test_labels, test_preds)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def run_one_layer_deep_conv_rf(train_images, train_labels, test_images, test_labels, fraction_of_train_samples, class1=3, class2=8):\n num_train_samples_class_1 = int(np.sum(train_labels==class1) * fraction_of_train_samples)\n num_train_samples_class_2 = int(np.sum(train_labels==class2) * fraction_of_train_samples)\n \n # get only train images and labels for class 1 and class 2\n train_images = np.concatenate([train_images[train_labels==class1][:num_train_samples_class_1], train_images[train_labels==class2][:num_train_samples_class_2]])\n train_labels = np.concatenate([np.repeat(0, num_train_samples_class_1), np.repeat(1, num_train_samples_class_2)])\n\n # get only test images and labels for class 1 and class 2\n test_images = np.concatenate([test_images[test_labels==class1], test_images[test_labels==class2]])\n test_labels = np.concatenate([np.repeat(0, np.sum(test_labels==class1)), np.repeat(1, np.sum(test_labels==class2))])\n \n ## Train\n # ConvRF (layer 1)\n conv1 = ConvRF(kernel_size=10, stride=2)\n conv1_map = conv1.convolve_fit(train_images, train_labels)\n\n # Full RF\n conv1_full_RF = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)\n conv1_full_RF.fit(conv1_map.reshape(len(train_images), -1), train_labels)\n\n ## Test (after ConvRF 1 and Full RF)\n conv1_map_test = conv1.convolve_predict(test_images)\n mnist_test_preds = conv1_full_RF.predict(conv1_map_test.reshape(len(test_images), -1))\n\n return accuracy_score(test_labels, mnist_test_preds)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def run_two_layer_deep_conv_rf(train_images, train_labels, test_images, test_labels, fraction_of_train_samples, class1=3, class2=8):\n num_train_samples_class_1 = int(np.sum(train_labels==class1) * fraction_of_train_samples)\n num_train_samples_class_2 = int(np.sum(train_labels==class2) * fraction_of_train_samples)\n \n # get only train images and labels for class 1 and class 2\n train_images = np.concatenate([train_images[train_labels==class1][:num_train_samples_class_1], train_images[train_labels==class2][:num_train_samples_class_2]])\n train_labels = np.concatenate([np.repeat(0, num_train_samples_class_1), np.repeat(1, num_train_samples_class_2)])\n\n # get only test images and labels for class 1 and class 2\n test_images = np.concatenate([test_images[test_labels==class1], test_images[test_labels==class2]])\n test_labels = np.concatenate([np.repeat(0, np.sum(test_labels==class1)), np.repeat(1, np.sum(test_labels==class2))])\n \n ## Train\n # ConvRF (layer 1)\n conv1 = ConvRF(kernel_size=10, stride=2)\n conv1_map = conv1.convolve_fit(train_images, train_labels)\n \n # ConvRF (layer 2)\n conv2 = ConvRF(kernel_size=7, stride=1)\n conv2_map = conv2.convolve_fit(conv1_map, train_labels)\n\n # Full RF\n conv1_full_RF = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)\n conv1_full_RF.fit(conv2_map.reshape(len(train_images), -1), train_labels)\n\n ## Test (after ConvRF 1 and Full RF)\n conv1_map_test = conv1.convolve_predict(test_images)\n conv2_map_test = conv2.convolve_predict(conv1_map_test)\n test_preds = conv1_full_RF.predict(conv2_map_test.reshape(len(test_images), -1))\n\n return accuracy_score(test_labels, test_preds)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def cnn_train_test(cnn_model, x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test):\n # set params\n num_epochs = 25\n learning_rate = 0.001\n\n # prepare data\n tensor_x = torch.stack([torch.Tensor(i.reshape(1, 28, 28)) for i in x_train]).float() # transform to torch tensors\n tensor_y = torch.stack([torch.Tensor([i]) for i in y_train]).long()\n\n my_dataset = utils.TensorDataset(tensor_x,tensor_y) # create your datset\n train_loader = utils.DataLoader(my_dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True) # create your dataloader\n\n tensor_x = torch.stack([torch.Tensor(i.reshape(1, 28, 28)) for i in x_test]).float() # transform to torch tensors\n tensor_y = torch.stack([torch.Tensor([i]) for i in y_test]).long()\n\n my_dataset = utils.TensorDataset(tensor_x,tensor_y) # create your datset\n test_loader = utils.DataLoader(my_dataset, batch_size=64) # create your dataloader\n\n # define model\n model = cnn_model()\n\n # loss and optimizer\n criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()\n optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)\n\n # train the model\n total_step = len(train_loader)\n for epoch in range(num_epochs):\n for i, (images, labels) in enumerate(train_loader):\n images = images\n labels = labels\n\n # Forward pass\n outputs = model(images)\n loss = criterion(outputs, labels.view(-1))\n\n # Backward and optimize\n optimizer.zero_grad()\n loss.backward()\n optimizer.step()\n\n\n # test the model\n accuracy = 0\n model.eval() # eval mode (batchnorm uses moving mean/variance instead of mini-batch mean/variance)\n with torch.no_grad():\n correct = 0\n total = 0\n for images, labels in test_loader:\n images = images\n labels = labels\n outputs = model(images)\n _, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)\n total += labels.size(0)\n correct += (predicted.view(-1) == labels.view(-1)).sum()\n accuracy = float(correct) / float(total)\n return accuracy",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def run_cnn(cnn_model, train_images, train_labels, test_images, test_labels, fraction_of_train_samples, class1=3, class2=8):\n num_train_samples_class_1 = int(np.sum(train_labels==class1) * fraction_of_train_samples)\n num_train_samples_class_2 = int(np.sum(train_labels==class2) * fraction_of_train_samples)\n \n # get only train images and labels for class 1 and class 2\n train_images = np.concatenate([train_images[train_labels==class1][:num_train_samples_class_1], train_images[train_labels==class2][:num_train_samples_class_2]])\n train_labels = np.concatenate([np.repeat(0, num_train_samples_class_1), np.repeat(1, num_train_samples_class_2)])\n\n # get only test images and labels for class 1 and class 2\n test_images = np.concatenate([test_images[test_labels==class1], test_images[test_labels==class2]])\n test_labels = np.concatenate([np.repeat(0, np.sum(test_labels==class1)), np.repeat(1, np.sum(test_labels==class2))])\n\n return cnn_train_test(cnn_model, train_images, train_labels, test_images, test_labels)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Sneaker(7) vs Ankel Boot(9) classification\n\n# get only train images and labels for two classes: 7 and 9\nmnist_train_images_7_9 = np.concatenate([mnist_train_images[mnist_train_labels==7], mnist_train_images[mnist_train_labels==9]])\nmnist_train_labels_7_9 = np.concatenate([np.repeat(0, np.sum(mnist_train_labels==7)), np.repeat(1, np.sum(mnist_train_labels==9))])\n\n# visualize data and labels\n\n# 7 (label 0)\nindex = 3000\nprint(\"Label:\", mnist_train_labels_7_9[index])\nplt.imshow(mnist_train_images_7_9[index].reshape(28, 28),cmap='gray')\nplt.show()\n\n# 9 (label 1)\nindex = 8000\nprint(\"Label:\", mnist_train_labels_7_9[index])\nplt.imshow(mnist_train_images_7_9[index].reshape(28, 28),cmap='gray')\nplt.show()",
"Label: 0\n"
],
[
"# accuracy vs num training samples (naive_rf)\nnaive_rf_acc_vs_n = list()\nfraction_of_train_samples_space = np.geomspace(0.01, 1.0, num=10)\nfor fraction_of_train_samples in fraction_of_train_samples_space:\n best_accuracy = np.mean([run_naive_rf(mnist_train_images, mnist_train_labels, mnist_test_images, mnist_test_labels, fraction_of_train_samples, 7, 9) for _ in range(3)])\n naive_rf_acc_vs_n.append(best_accuracy)\n print(\"Train Fraction:\", str(fraction_of_train_samples))\n print(\"Accuracy:\", str(best_accuracy))",
"Train Fraction: 0.01\nAccuracy: 0.9158333333333334\nTrain Fraction: 0.016681005372000592\nAccuracy: 0.9255\nTrain Fraction: 0.027825594022071243\nAccuracy: 0.9338333333333333\nTrain Fraction: 0.046415888336127774\nAccuracy: 0.9366666666666666\nTrain Fraction: 0.0774263682681127\nAccuracy: 0.9394999999999999\nTrain Fraction: 0.1291549665014884\nAccuracy: 0.9451666666666666\nTrain Fraction: 0.21544346900318834\nAccuracy: 0.9506666666666667\nTrain Fraction: 0.3593813663804626\nAccuracy: 0.9573333333333333\nTrain Fraction: 0.5994842503189409\nAccuracy: 0.9571666666666666\nTrain Fraction: 1.0\nAccuracy: 0.9618333333333333\n"
],
[
"# accuracy vs num training samples (one layer deep_conv_rf)\ndeep_conv_rf_acc_vs_n = list()\nfraction_of_train_samples_space = np.geomspace(0.01, 1.0, num=10)\nfor fraction_of_train_samples in fraction_of_train_samples_space:\n best_accuracy = np.mean([run_one_layer_deep_conv_rf(mnist_train_images, mnist_train_labels, mnist_test_images, mnist_test_labels, fraction_of_train_samples, 7, 9) for _ in range(3)])\n deep_conv_rf_acc_vs_n.append(best_accuracy)\n print(\"Train Fraction:\", str(fraction_of_train_samples))\n print(\"Accuracy:\", str(best_accuracy))",
"Train Fraction: 0.01\nAccuracy: 0.9153333333333333\nTrain Fraction: 0.016681005372000592\nAccuracy: 0.9223333333333334\nTrain Fraction: 0.027825594022071243\nAccuracy: 0.931\nTrain Fraction: 0.046415888336127774\nAccuracy: 0.9396666666666667\nTrain Fraction: 0.0774263682681127\nAccuracy: 0.9413333333333332\nTrain Fraction: 0.1291549665014884\nAccuracy: 0.9486666666666667\nTrain Fraction: 0.21544346900318834\nAccuracy: 0.9533333333333333\nTrain Fraction: 0.3593813663804626\nAccuracy: 0.9538333333333333\nTrain Fraction: 0.5994842503189409\nAccuracy: 0.9566666666666667\nTrain Fraction: 1.0\nAccuracy: 0.9598333333333334\n"
],
[
"# accuracy vs num training samples (one layer cnn)\ncnn_acc_vs_n = list()\nfraction_of_train_samples_space = np.geomspace(0.01, 1.0, num=10)\nfor fraction_of_train_samples in fraction_of_train_samples_space:\n best_accuracy = np.mean([run_cnn(SimpleCNNOneFilter, mnist_train_images, mnist_train_labels, mnist_test_images, mnist_test_labels, fraction_of_train_samples, 7, 9) for _ in range(3)])\n cnn_acc_vs_n.append(best_accuracy)\n print(\"Train Fraction:\", str(fraction_of_train_samples))\n print(\"Accuracy:\", str(best_accuracy))",
"Train Fraction: 0.01\nAccuracy: 0.8176666666666668\nTrain Fraction: 0.016681005372000592\nAccuracy: 0.8671666666666668\nTrain Fraction: 0.027825594022071243\nAccuracy: 0.8418333333333333\nTrain Fraction: 0.046415888336127774\nAccuracy: 0.8918333333333334\nTrain Fraction: 0.0774263682681127\nAccuracy: 0.8971666666666666\nTrain Fraction: 0.1291549665014884\nAccuracy: 0.93\nTrain Fraction: 0.21544346900318834\nAccuracy: 0.9293333333333335\nTrain Fraction: 0.3593813663804626\nAccuracy: 0.945\nTrain Fraction: 0.5994842503189409\nAccuracy: 0.949\nTrain Fraction: 1.0\nAccuracy: 0.9458333333333333\n"
],
[
"# accuracy vs num training samples (one layer cnn (32 filters))\ncnn32_acc_vs_n = list()\nfraction_of_train_samples_space = np.geomspace(0.01, 1.0, num=10)\nfor fraction_of_train_samples in fraction_of_train_samples_space:\n best_accuracy = np.mean([run_cnn(SimpleCNN32Filter, mnist_train_images, mnist_train_labels, mnist_test_images, mnist_test_labels, fraction_of_train_samples, 7, 9) for _ in range(3)])\n cnn32_acc_vs_n.append(best_accuracy)\n print(\"Train Fraction:\", str(fraction_of_train_samples))\n print(\"Accuracy:\", str(best_accuracy))",
"Train Fraction: 0.01\nAccuracy: 0.9036666666666666\nTrain Fraction: 0.016681005372000592\nAccuracy: 0.9286666666666666\nTrain Fraction: 0.027825594022071243\nAccuracy: 0.9406666666666667\nTrain Fraction: 0.046415888336127774\nAccuracy: 0.9453333333333332\nTrain Fraction: 0.0774263682681127\nAccuracy: 0.9441666666666667\nTrain Fraction: 0.1291549665014884\nAccuracy: 0.9550000000000001\nTrain Fraction: 0.21544346900318834\nAccuracy: 0.9593333333333334\nTrain Fraction: 0.3593813663804626\nAccuracy: 0.9558333333333332\nTrain Fraction: 0.5994842503189409\nAccuracy: 0.9620000000000001\nTrain Fraction: 1.0\nAccuracy: 0.9613333333333333\n"
],
[
"# accuracy vs num training samples (two layer deep_conv_rf)\ndeep_conv_rf_two_layer_acc_vs_n = list()\nfraction_of_train_samples_space = np.geomspace(0.01, 1.0, num=10)\nfor fraction_of_train_samples in fraction_of_train_samples_space:\n best_accuracy = np.mean([run_two_layer_deep_conv_rf(mnist_train_images, mnist_train_labels, mnist_test_images, mnist_test_labels, fraction_of_train_samples, 7, 9) for _ in range(3)])\n deep_conv_rf_two_layer_acc_vs_n.append(best_accuracy)\n print(\"Train Fraction:\", str(fraction_of_train_samples))\n print(\"Accuracy:\", str(best_accuracy))",
"Train Fraction: 0.01\nAccuracy: 0.9065\nTrain Fraction: 0.016681005372000592\nAccuracy: 0.9183333333333333\nTrain Fraction: 0.027825594022071243\nAccuracy: 0.9265\nTrain Fraction: 0.046415888336127774\nAccuracy: 0.9388333333333333\nTrain Fraction: 0.0774263682681127\nAccuracy: 0.9416666666666668\nTrain Fraction: 0.1291549665014884\nAccuracy: 0.9456666666666665\nTrain Fraction: 0.21544346900318834\nAccuracy: 0.9513333333333334\nTrain Fraction: 0.3593813663804626\nAccuracy: 0.9528333333333333\nTrain Fraction: 0.5994842503189409\nAccuracy: 0.9528333333333334\nTrain Fraction: 1.0\nAccuracy: 0.9546666666666667\n"
],
[
"# accuracy vs num training samples (two layer cnn (32 filters))\ncnn32_two_layer_acc_vs_n = list()\nfraction_of_train_samples_space = np.geomspace(0.01, 1.0, num=10)\nfor fraction_of_train_samples in fraction_of_train_samples_space:\n best_accuracy = np.mean([run_cnn(SimpleCNN32Filter2Layers, mnist_train_images, mnist_train_labels, mnist_test_images, mnist_test_labels, fraction_of_train_samples, 7, 9) for _ in range(3)])\n cnn32_two_layer_acc_vs_n.append(best_accuracy)\n print(\"Train Fraction:\", str(fraction_of_train_samples))\n print(\"Accuracy:\", str(best_accuracy))",
"Train Fraction: 0.01\nAccuracy: 0.9123333333333333\nTrain Fraction: 0.016681005372000592\nAccuracy: 0.93\nTrain Fraction: 0.027825594022071243\nAccuracy: 0.9406666666666667\nTrain Fraction: 0.046415888336127774\nAccuracy: 0.9491666666666666\nTrain Fraction: 0.0774263682681127\nAccuracy: 0.9493333333333333\nTrain Fraction: 0.1291549665014884\nAccuracy: 0.9571666666666667\nTrain Fraction: 0.21544346900318834\nAccuracy: 0.9636666666666667\nTrain Fraction: 0.3593813663804626\nAccuracy: 0.959\nTrain Fraction: 0.5994842503189409\nAccuracy: 0.9706666666666667\nTrain Fraction: 1.0\nAccuracy: 0.9653333333333333\n"
],
[
"plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = 10, 8\nplt.rcParams['font.size'] = 20\nplt.rcParams['legend.fontsize'] = 20\nplt.rcParams['figure.titlesize'] = 20\n\nfig, ax = plt.subplots() # create a new figure with a default 111 subplot\nax.plot(fraction_of_train_samples_space, naive_rf_acc_vs_n, marker='X', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10, color='orange', linewidth=4, label=\"Naive RF\")\nax.plot(fraction_of_train_samples_space, deep_conv_rf_acc_vs_n, marker='X', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10, color='green', linewidth=4, label=\"Deep Conv RF\")\nax.plot(fraction_of_train_samples_space, deep_conv_rf_two_layer_acc_vs_n, marker='X', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10, color='grey', linewidth=4, label=\"Deep Conv RF Two Layer\")\nax.plot(fraction_of_train_samples_space, cnn_acc_vs_n, marker='X', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10, color='red', linewidth=4, label=\"CNN\")\nax.plot(fraction_of_train_samples_space, cnn32_acc_vs_n, marker='X', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10, color='brown', linewidth=4, label=\"CNN (32 filters)\")\nax.plot(fraction_of_train_samples_space, cnn32_two_layer_acc_vs_n, marker='X', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10, color='black', linewidth=4, label=\"CNN Two Layer (32 filters)\")\n\nax.set_xlabel('Fraction of Train Samples')\nax.set_xlim(0, 1.0)\nax.set_ylabel('Accuracy')\nax.set_ylim(0.81, 1)\nax.set_title(\"Sneaker(7) vs Ankel Boot(9) Classification\")\nplt.legend()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = 10, 8\nplt.rcParams['font.size'] = 20\nplt.rcParams['legend.fontsize'] = 20\nplt.rcParams['figure.titlesize'] = 20\n\nfig, ax = plt.subplots() # create a new figure with a default 111 subplot\nax.plot(fraction_of_train_samples_space, naive_rf_acc_vs_n, marker='X', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10, color='orange', linewidth=4, label=\"Naive RF\")\nax.plot(fraction_of_train_samples_space, deep_conv_rf_acc_vs_n, marker='X', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10, color='green', linewidth=4, label=\"Deep Conv RF\")\nax.plot(fraction_of_train_samples_space, deep_conv_rf_two_layer_acc_vs_n, marker='X', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10, color='grey', linewidth=4, label=\"Deep Conv RF 2 Layer\")\nax.plot(fraction_of_train_samples_space, cnn_acc_vs_n, marker='X', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10, color='red', linewidth=4, label=\"CNN\")\nax.plot(fraction_of_train_samples_space, cnn32_acc_vs_n, marker='X', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10, color='brown', linewidth=4, label=\"CNN (32 filters)\")\nax.plot(fraction_of_train_samples_space, cnn32_two_layer_acc_vs_n, marker='X', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10, color='black', linewidth=4, label=\"CNN 2 Layer (32 filters)\")\n\nax.set_xlabel('Fraction of Train Samples')\nax.set_xlim(0, 1.0)\nax.set_ylabel('Accuracy')\nax.set_ylim(0.92, 0.98)\nax.set_title(\"Sneaker(7) vs Ankel Boot(9) Classification\")\nplt.legend()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe7e05de3ecf29a581affaabcff85093c1ce4ba
| 2,157 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
prisma/tests/test_pipelines.ipynb
|
eibfl-dtu/PRISMA
|
599a6635ace479c70b624c3ec538a04e36cfd35e
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 2 |
2022-02-06T08:42:33.000Z
|
2022-03-09T16:31:39.000Z
|
prisma/tests/test_pipelines.ipynb
|
BIG-MAP/PRISMA
|
599a6635ace479c70b624c3ec538a04e36cfd35e
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
prisma/tests/test_pipelines.ipynb
|
BIG-MAP/PRISMA
|
599a6635ace479c70b624c3ec538a04e36cfd35e
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null | 20.349057 | 120 | 0.534539 |
[
[
[
"# from pipelines.baseline import BaselineCorrection\n# subapp = BaselineCorrection()\n# subapp.interface",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# from pipelines.peakfit import PeakFitting\n# subapp = PeakFitting()\n# subapp.interface",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from pipelines.baseline_peakfit import BaselinePeakFitting\nsubapp = BaselinePeakFitting()\nsubapp.interface",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"'my {} string'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe7e1a405c9d75f829a06d49c48c0c5ce374070
| 3,274 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
work/problem021.ipynb
|
robireton/math-capstone
|
71f4217aef2e11a7e4e63cec38392a185c72598b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
work/problem021.ipynb
|
robireton/math-capstone
|
71f4217aef2e11a7e4e63cec38392a185c72598b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
work/problem021.ipynb
|
robireton/math-capstone
|
71f4217aef2e11a7e4e63cec38392a185c72598b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 30.314815 | 401 | 0.536042 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
cbe7e3bf9be2918a8ef960d32c36c05d3bbf8721
| 10,495 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
site/en-snapshot/addons/tutorials/losses_triplet.ipynb
|
rapsealk/docs-l10n
|
e549cdcd84620fe4ac8571cff38628cb5e4d745b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
site/en-snapshot/addons/tutorials/losses_triplet.ipynb
|
rapsealk/docs-l10n
|
e549cdcd84620fe4ac8571cff38628cb5e4d745b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
site/en-snapshot/addons/tutorials/losses_triplet.ipynb
|
rapsealk/docs-l10n
|
e549cdcd84620fe4ac8571cff38628cb5e4d745b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 32.094801 | 345 | 0.533969 |
[
[
[
"##### Copyright 2020 The TensorFlow Authors.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#@title Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n#\n# https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n#\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TensorFlow Addons Losses: TripletSemiHardLoss\n\n<table class=\"tfo-notebook-buttons\" align=\"left\">\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/addons/tutorials/losses_triplet\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/tf_logo_32px.png\" />View on TensorFlow.org</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/tensorflow/addons/blob/master/docs/tutorials/losses_triplet.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/colab_logo_32px.png\" />Run in Google Colab</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://github.com/tensorflow/addons/blob/master/docs/tutorials/losses_triplet.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/GitHub-Mark-32px.png\" />View source on GitHub</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a href=\"https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow_docs/addons/docs/tutorials/losses_triplet.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/download_logo_32px.png\" />Download notebook</a>\n </td>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Overview\nThis notebook will demonstrate how to use the TripletSemiHardLoss function in TensorFlow Addons.\n\n### Resources:\n* [FaceNet: A Unified Embedding for Face Recognition and Clustering](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1503.03832.pdf)\n* [Oliver Moindrot's blog does an excellent job of describing the algorithm in detail](https://omoindrot.github.io/triplet-loss)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## TripletLoss\n\nAs first introduced in the FaceNet paper, TripletLoss is a loss function that trains a neural network to closely embed features of the same class while maximizing the distance between embeddings of different classes. To do this an anchor is chosen along with one negative and one positive sample.\n\n\n**The loss function is described as a Euclidean distance function:**\n\n\n\nWhere A is our anchor input, P is the positive sample input, N is the negative sample input, and alpha is some margin we use to specify when a triplet has become too \"easy\" and we no longer want to adjust the weights from it.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## SemiHard Online Learning\nAs shown in the paper, the best results are from triplets known as \"Semi-Hard\". These are defined as triplets where the negative is farther from the anchor than the positive, but still produces a positive loss. To efficiently find these triplets we utilize online learning and only train from the Semi-Hard examples in each batch. \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Setup",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pip install -U tensorflow-addons",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import io\nimport numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import tensorflow as tf\nimport tensorflow_addons as tfa\nimport tensorflow_datasets as tfds",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Prepare the Data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def _normalize_img(img, label):\n img = tf.cast(img, tf.float32) / 255.\n return (img, label)\n\ntrain_dataset, test_dataset = tfds.load(name=\"mnist\", split=['train', 'test'], as_supervised=True)\n\n# Build your input pipelines\ntrain_dataset = train_dataset.shuffle(1024).batch(32)\ntrain_dataset = train_dataset.map(_normalize_img)\n\ntest_dataset = test_dataset.batch(32)\ntest_dataset = test_dataset.map(_normalize_img)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Build the Model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"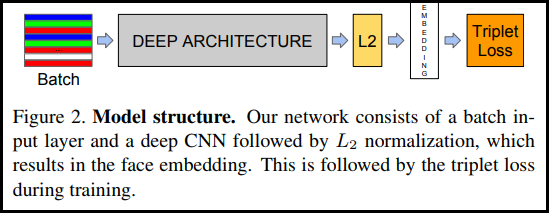",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = tf.keras.Sequential([\n tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=64, kernel_size=2, padding='same', activation='relu', input_shape=(28,28,1)),\n tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=2),\n tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.3),\n tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=32, kernel_size=2, padding='same', activation='relu'),\n tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=2),\n tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.3),\n tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),\n tf.keras.layers.Dense(256, activation=None), # No activation on final dense layer\n tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: tf.math.l2_normalize(x, axis=1)) # L2 normalize embeddings\n\n])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Train and Evaluate",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Compile the model\nmodel.compile(\n optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.001),\n loss=tfa.losses.TripletSemiHardLoss())\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Train the network\nhistory = model.fit(\n train_dataset,\n epochs=5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Evaluate the network\nresults = model.predict(test_dataset)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Save test embeddings for visualization in projector\nnp.savetxt(\"vecs.tsv\", results, delimiter='\\t')\n\nout_m = io.open('meta.tsv', 'w', encoding='utf-8')\nfor img, labels in tfds.as_numpy(test_dataset):\n [out_m.write(str(x) + \"\\n\") for x in labels]\nout_m.close()\n\n\ntry:\n from google.colab import files\n files.download('vecs.tsv')\n files.download('meta.tsv')\nexcept:\n pass",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Embedding Projector",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The vector and metadata files can be loaded and visualized here: https://projector.tensorflow.org/\n\nYou can see the results of our embedded test data when visualized with UMAP:\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe7e553c92a58579630dcef302f4b87369c732d
| 5,897 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Exploration.ipynb
|
jayhack/chainer-char-rnn-1.7.1
|
4319c86ec01afa14c8da164c82bc50b6f234ccd0
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2016-11-15T02:19:16.000Z
|
2016-11-15T02:19:16.000Z
|
Exploration.ipynb
|
jayhack/chainer-char-rnn-1.7.1
|
4319c86ec01afa14c8da164c82bc50b6f234ccd0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Exploration.ipynb
|
jayhack/chainer-char-rnn-1.7.1
|
4319c86ec01afa14c8da164c82bc50b6f234ccd0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 28.080952 | 119 | 0.512294 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\n%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Overview\n\nWhat does this thing look like?\n- Object that you can import\n- Can call train, load, featurize, import\n- Inherits from sklearn.transform? Multiple inheritance is hard...",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# I. Load Data\n\n- words: np.ndarray of all characters\n- dataset: np.ndarray of character indices",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import codecs \n\n#=====[ Load a whole corpus ]=====\ndef load_data(data_dir='./data/tinyshakespeare/'):\n vocab = {}\n print ('%s/input.txt'% data_dir)\n words = codecs.open('%s/input.txt' % data_dir, 'rb', 'utf-8').read()\n words = list(words)\n dataset = np.ndarray((len(words),), dtype=np.int32)\n for i, word in enumerate(words):\n if word not in vocab:\n vocab[word] = len(vocab)\n dataset[i] = vocab[word]\n print 'corpus length (in characters):', len(words)\n print 'vocab size:', len(vocab)\n return dataset, words, vocab\n#print 'corpus length (in characters):', len(words)\n#dataset, words, vocab = load_data()\n\n#=====[ Load only the vocabulary ]=====\nvocab = pickle.load(open('./data/audit_data/vocab.bin', 'rb'))\nivocab = {i:c for c, i in vocab.items()}\nprint 'vocab size:', len(vocab)",
"vocab size: 125\n"
]
],
[
[
"# II. Load Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pickle\nfrom CharRNN import CharRNN, make_initial_state\nfrom chainer import cuda\n\n#####[ PARAMS ]#####\nn_units = 128\nseq_length = 50\nbatchsize = 50\nseed = 123\nlength = 50\n####################\n\nnp.random.seed(seed)\nmodel = pickle.load(open('./data/audit_data/audit_model.chainermodel', 'rb'))\nn_units = model.embed.W.data.shape[1]\ninitial_state = make_initial_state(n_units, batchsize=1, train=False)\nprint '# of units: ', n_units",
"# of units: 128\n"
]
],
[
[
"# III. Create TextFeaturizer",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class TextFeaturizer(object):\n \"\"\"Featurizes Text using a CharRNN\"\"\"\n def __init__(self, model, vocab):\n self.__dict__.update(locals())\n self.n_units = model.embed.W.data.shape[1]\n \n def preprocess(self, text):\n \"\"\"returns preprocessed version of text\"\"\"\n if not isinstance(text, str):\n raise NotImplementedError(\"Must pass in a string\")\n return np.array([vocab[c] for c in text]).astype(np.int32)\n \n def featurize(self, text):\n \"\"\"returns a list of feature vectors for the text\"\"\"\n #=====[ Step 1: Convert to an array ]=====\n dataset = self.preprocess(text)\n \n #=====[ Step 2: Create initial state ]=====\n initial_state = make_initial_state(n_units, batchsize=1, train=False)\n init_char = np.array([0]).astype(np.int32)\n state, prob = rnn.forward_one_step(init_char, init_char, initial_state, train=False)\n \n #=====[ Step 3: Find feature vectors ]=====\n states = []\n for i in range(len(dataset)):\n cur_char = np.array([dataset[i]]).astype(np.int32)\n state, prob = model.forward_one_step(cur_char, cur_char, state, train=False)\n states.append(state['h2'].data.copy())\n\n #=====[ Step 4: Sanity check ]=====\n if not all([s.shape == (1, self.n_units) for s in states]):\n raise Exception(\"For some reason, generated the wrong shape! {}\".format(np.array(states).shape))\n return states",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"featurizer = TextFeaturizer(model, vocab)\n\n#=====[ TEST ]=====\ntext = 'Conducted an investigation of WalMart and concluded air and fire safety were correct'\nstates = featurizer.featurize(text)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe7ffff189e3e5ca9c18c8f545475e89f272794
| 466,535 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
.ipynb_checkpoints/Untitled-checkpoint.ipynb
|
jianming93/incremental_learner
|
dd477bb65c2d1f56365b487cebc6357a70e8f460
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
.ipynb_checkpoints/Untitled-checkpoint.ipynb
|
jianming93/incremental_learner
|
dd477bb65c2d1f56365b487cebc6357a70e8f460
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
.ipynb_checkpoints/Untitled-checkpoint.ipynb
|
jianming93/incremental_learner
|
dd477bb65c2d1f56365b487cebc6357a70e8f460
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 80.367786 | 179,624 | 0.744574 |
[
[
[
"from PIL import Image\nfrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib notebook\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport os\nimport sys\nsys.path.append(\"..\")\n\nimport numpy as np\nfrom tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image_dataset_from_directory\nfrom tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image\nfrom tensorflow.keras.applications.resnet50 import preprocess_input\nimport tensorflow as tf\nfrom sklearn.decomposition import PCA\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\n\nimport utils\nimport shell",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# dataset_directory = \"data/people\"\n# dataset_directory = \"data/STL10/images\"\ndataset_directory = \"data/fruits\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# shell_family = shell.ShellFamily(\"resnet50\")\nshell_family = shell.ShellFamily()\nshell_family.create_preprocessor(\"resnet50\")\n# shell_family.load(\"test.pkl\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_class_folders_from_main_directory(directory):\n sub_folders = next(os.walk(directory))[1]\n classes = sub_folders.copy()\n for i in range(len(sub_folders)):\n sub_folders[i] = os.path.join(directory, sub_folders[i])\n return sorted(sub_folders), classes\n\ndef extract_classes_sub_folder(sub_folders):\n all_image_filepaths = np.array([])\n class_array = np.array([])\n for i in range(len(sub_folders)):\n image_files = os.listdir(sub_folders[i])\n image_filepaths = list(map(lambda x : os.path.join(sub_folders[i], x), image_files))\n new_image_filepaths = []\n for j in image_filepaths:\n try:\n Image.open(j)\n new_image_filepaths.append(j)\n except:\n continue\n all_image_filepaths = np.append(all_image_filepaths, new_image_filepaths)\n class_array = np.append(class_array, [i] * len(new_image_filepaths))\n# all_image_filepaths = np.append(all_image_filepaths, image_filepaths)\n# class_array = np.append(class_array, [i] * len(image_filepaths))\n return all_image_filepaths, class_array.astype(np.int32)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class ImageGenerator():\n def __init__(self, filepath_array, class_array, batch_size, target_size):\n self.filepath_array = filepath_array\n self.class_array = class_array\n self.batch_size = batch_size\n self.target_size = target_size\n self.steps = len(self.class_array) // self.batch_size\n self.index = 0\n print(\"Found {} images with {} classes!\".format(self.__len__(), len(np.unique(self.class_array))))\n \n def __iter__(self):\n return self\n \n def __len__(self):\n assert(len(self.class_array) == len(self.filepath_array))\n return len(self.class_array)\n \n def __next__(self):\n if self.index == self.__len__():\n raise StopIteration\n elif self.index + self.batch_size >= self.__len__():\n batch_filepaths = self.filepath_array[self.index : self.__len__()]\n batch_images = np.array([np.asarray(Image.open(i).convert(\"RGB\").resize(self.target_size))[..., :3] for i in batch_filepaths]).astype(np.float32)\n batch_images = preprocess_input(batch_images)\n batch_classes = self.class_array[self.index : self.__len__()]\n self.index = self.__len__()\n return (batch_images, batch_filepaths, batch_classes)\n else:\n batch_filepaths = self.filepath_array[self.index : self.index + self.batch_size]\n batch_images = np.array([np.asarray(Image.open(i).convert(\"RGB\").resize(self.target_size))[..., :3] for i in batch_filepaths]).astype(np.float32)\n batch_images = preprocess_input(batch_images)\n batch_classes = self.class_array[self.index : self.index + self.batch_size]\n self.index += self.batch_size\n return (batch_images, batch_filepaths, batch_classes)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sub_folders, classes = get_class_folders_from_main_directory(dataset_directory)\nfilepath_array, class_array = extract_classes_sub_folder(sub_folders)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(filepath_array,\n class_array,\n test_size=0.2,\n random_state=42,\n shuffle=True,\n stratify=class_array)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_image_generator = ImageGenerator(X_train, y_train, 2048, (224, 224))\ntest_image_generator = ImageGenerator(X_test, y_test, 1, (224, 224))",
"Found 13483 images with 33 classes!\nFound 3371 images with 33 classes!\n"
],
[
"shell_family.fit(train_image_generator, classes, \"test.pkl\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_predict = []\nfor processed_image_array, _, groundtruth in test_image_generator:\n sample_features = shell_family.preprocessor.predict(processed_image_array)\n class_index, class_name, score, full_results = shell_family.score(sample_features, 0.5, with_update=False, return_full_results=True)\n y_predict.append(class_index)\n print(\"predicted: {}, groundtruth: {}\".format(class_name, shell_family.mapping[groundtruth[0]]))\n",
"predicted: Cactus fruit, groundtruth: Cactus fruit\npredicted: Corn, groundtruth: Corn\npredicted: Limes, groundtruth: Limes\npredicted: Orange, groundtruth: Orange\npredicted: Banana, groundtruth: Banana\npredicted: Blueberry, groundtruth: Blueberry\npredicted: Strawberry, groundtruth: Strawberry\npredicted: Corn, groundtruth: Corn\npredicted: Onion White, groundtruth: Onion White\npredicted: Cherry, groundtruth: Cherry\npredicted: Apple Braeburn, groundtruth: Apple Braeburn\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Cactus fruit, groundtruth: Cactus fruit\npredicted: Raspberry, groundtruth: Raspberry\npredicted: Lemon, groundtruth: Lemon\npredicted: Cherry, groundtruth: Cherry\npredicted: Clementine, groundtruth: Clementine\npredicted: Apple Granny Smith, groundtruth: Apple Granny Smith\npredicted: Strawberry, groundtruth: Strawberry\npredicted: Cucumber Ripe, groundtruth: Cucumber Ripe\npredicted: Mango, groundtruth: Mango\npredicted: Raspberry, groundtruth: Raspberry\npredicted: Pomegranate, groundtruth: Pomegranate\npredicted: Cactus fruit, groundtruth: Cactus fruit\npredicted: Blueberry, groundtruth: Blueberry\npredicted: Cucumber Ripe, groundtruth: Cucumber Ripe\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Orange, groundtruth: Orange\npredicted: Orange, groundtruth: Orange\npredicted: Clementine, groundtruth: Clementine\npredicted: Blueberry, groundtruth: Blueberry\npredicted: Apple Granny Smith, groundtruth: Apple Granny Smith\npredicted: Pineapple, groundtruth: Pineapple\npredicted: Papaya, groundtruth: Papaya\npredicted: Peach, groundtruth: Peach\npredicted: Tomato, groundtruth: Tomato\npredicted: Pomegranate, groundtruth: Pomegranate\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Lemon, groundtruth: Lemon\npredicted: Mango, groundtruth: Mango\npredicted: Pepper Green, groundtruth: Pepper Green\npredicted: Strawberry, groundtruth: Strawberry\npredicted: Watermelon, groundtruth: Watermelon\npredicted: Mango, groundtruth: Mango\npredicted: Strawberry, groundtruth: Strawberry\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Apricot, groundtruth: Apricot\npredicted: Avocado, groundtruth: Avocado\npredicted: Passion Fruit, groundtruth: Passion Fruit\npredicted: Raspberry, groundtruth: Raspberry\npredicted: Onion White, groundtruth: Onion White\npredicted: Tomato, groundtruth: Tomato\npredicted: Apple Granny Smith, groundtruth: Apple Granny Smith\npredicted: Apricot, groundtruth: Apricot\npredicted: Blueberry, groundtruth: Blueberry\npredicted: Pepper Green, groundtruth: Pepper Green\npredicted: Apple Granny Smith, groundtruth: Apple Granny Smith\npredicted: Plum, groundtruth: Plum\npredicted: Pepper Red, groundtruth: Pepper Red\npredicted: Pepper Red, groundtruth: Pepper Red\npredicted: Pear, groundtruth: Pear\npredicted: Passion Fruit, groundtruth: Passion Fruit\npredicted: Pepper Green, groundtruth: Pepper Green\npredicted: Tomato, groundtruth: Tomato\npredicted: Peach, groundtruth: Peach\npredicted: Plum, groundtruth: Plum\npredicted: Passion Fruit, groundtruth: Passion Fruit\npredicted: Peach, groundtruth: Peach\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Mango, groundtruth: Mango\npredicted: Avocado, groundtruth: Avocado\npredicted: Apple Granny Smith, groundtruth: Apple Granny Smith\npredicted: Mango, groundtruth: Mango\npredicted: Watermelon, groundtruth: Watermelon\npredicted: Banana, groundtruth: Banana\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Tomato, groundtruth: Tomato\npredicted: Cactus fruit, groundtruth: Cactus fruit\npredicted: Lemon, groundtruth: Lemon\npredicted: Cherry, groundtruth: Cherry\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Apricot, groundtruth: Apricot\npredicted: Banana, groundtruth: Banana\npredicted: Onion White, groundtruth: Onion White\npredicted: Lemon, groundtruth: Lemon\npredicted: Pepper Green, groundtruth: Pepper Green\npredicted: Strawberry, groundtruth: Strawberry\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Cherry, groundtruth: Cherry\npredicted: Pear, groundtruth: Pear\npredicted: Raspberry, groundtruth: Raspberry\npredicted: Cherry, groundtruth: Cherry\npredicted: Raspberry, groundtruth: Raspberry\npredicted: Pineapple, groundtruth: Pineapple\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Limes, groundtruth: Limes\npredicted: Strawberry, groundtruth: Strawberry\npredicted: Passion Fruit, groundtruth: Passion Fruit\npredicted: Avocado, groundtruth: Avocado\npredicted: Lemon, groundtruth: Lemon\npredicted: Banana, groundtruth: Banana\npredicted: Limes, groundtruth: Limes\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Limes, groundtruth: Limes\npredicted: Avocado, groundtruth: Avocado\npredicted: Strawberry, groundtruth: Strawberry\npredicted: Kiwi, groundtruth: Kiwi\npredicted: Clementine, groundtruth: Clementine\npredicted: Onion White, groundtruth: Onion White\npredicted: Plum, groundtruth: Plum\npredicted: Tomato, groundtruth: Tomato\npredicted: Avocado, groundtruth: Avocado\npredicted: Apricot, groundtruth: Apricot\npredicted: Raspberry, groundtruth: Raspberry\npredicted: Cherry, groundtruth: Cherry\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Pepper Red, groundtruth: Pepper Red\npredicted: Cactus fruit, groundtruth: Cactus fruit\npredicted: Blueberry, groundtruth: Blueberry\npredicted: Lemon, groundtruth: Lemon\npredicted: Papaya, groundtruth: Papaya\npredicted: Apple Braeburn, groundtruth: Apple Braeburn\npredicted: Apple Granny Smith, groundtruth: Apple Granny Smith\npredicted: Avocado, groundtruth: Avocado\npredicted: Raspberry, groundtruth: Raspberry\npredicted: Strawberry, groundtruth: Strawberry\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Pepper Red, groundtruth: Pepper Red\npredicted: Apricot, groundtruth: Apricot\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Passion Fruit, groundtruth: Passion Fruit\npredicted: Corn, groundtruth: Corn\npredicted: Banana, groundtruth: Banana\npredicted: Pepper Red, groundtruth: Pepper Red\npredicted: Clementine, groundtruth: Clementine\npredicted: Tomato, groundtruth: Tomato\npredicted: Corn, groundtruth: Corn\npredicted: Apricot, groundtruth: Apricot\npredicted: Mango, groundtruth: Mango\npredicted: Limes, groundtruth: Limes\npredicted: Strawberry, groundtruth: Raspberry\npredicted: Limes, groundtruth: Limes\npredicted: Apple Braeburn, groundtruth: Apple Braeburn\npredicted: Clementine, groundtruth: Clementine\npredicted: Limes, groundtruth: Limes\npredicted: Pear, groundtruth: Pear\npredicted: Corn, groundtruth: Corn\npredicted: Raspberry, groundtruth: Raspberry\npredicted: Papaya, groundtruth: Papaya\npredicted: Strawberry, groundtruth: Cucumber Ripe\npredicted: Watermelon, groundtruth: Watermelon\npredicted: Pomegranate, groundtruth: Pomegranate\npredicted: Limes, groundtruth: Limes\npredicted: Potato Red, groundtruth: Potato Red\npredicted: Orange, groundtruth: Orange\npredicted: Onion White, groundtruth: Onion White\npredicted: Pepper Red, groundtruth: Pepper Red\npredicted: Peach, groundtruth: Peach\npredicted: Passion Fruit, groundtruth: Passion Fruit\npredicted: Cantaloupe, groundtruth: Cantaloupe\npredicted: Limes, groundtruth: Limes\npredicted: Papaya, groundtruth: Kiwi\npredicted: Strawberry, groundtruth: Strawberry\npredicted: Apricot, groundtruth: Apricot\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Strawberry, groundtruth: Cucumber Ripe\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Pineapple, groundtruth: Pineapple\npredicted: Tomato, groundtruth: Tomato\npredicted: Peach, groundtruth: Peach\npredicted: Pineapple, groundtruth: Pineapple\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Banana, groundtruth: Banana\npredicted: Pomegranate, groundtruth: Pomegranate\npredicted: Raspberry, groundtruth: Raspberry\npredicted: Mango, groundtruth: Mango\npredicted: Pear, groundtruth: Pear\npredicted: Cherry, groundtruth: Cherry\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Cantaloupe, groundtruth: Cantaloupe\npredicted: Orange, groundtruth: Orange\npredicted: Pear, groundtruth: Pear\npredicted: Limes, groundtruth: Limes\npredicted: Apple Braeburn, groundtruth: Apple Braeburn\npredicted: Passion Fruit, groundtruth: Passion Fruit\npredicted: Pear, groundtruth: Pear\npredicted: Grape Blue, groundtruth: Grape Blue\npredicted: Orange, groundtruth: Orange\npredicted: Cherry, groundtruth: Cherry\n"
],
[
"full_results",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_predict = np.array(y_predict)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"xtick_labels = [\"Predicted {}\".format(class_name) for class_name in shell_family.mapping]\nytick_labels = [\"Actual {}\".format(class_name) for class_name in shell_family.mapping]\nprint(\"Classification Report\\n\")\nprint(classification_report(y_test, y_predict))\nprint(\"\")\nprint(\"Confusion Matrix\\n\")\nplt.figure(figsize=(10,6))\nsns.heatmap(confusion_matrix(y_test, y_predict), cmap=\"viridis\", annot=True, fmt=\"d\", xticklabels=xtick_labels, yticklabels=ytick_labels)\nplt.title(\"Confusion Matrix\", fontsize=6)\nplt.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=4)\nplt.show()",
"Classification Report\n\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.96 0.98 0.97 98\n 1 1.00 0.99 0.99 98\n 2 1.00 0.99 0.99 99\n 3 1.00 0.98 0.99 85\n 4 1.00 0.99 0.99 98\n 5 0.98 1.00 0.99 92\n 6 0.71 1.00 0.83 98\n 7 1.00 1.00 1.00 98\n 8 1.00 1.00 1.00 99\n 9 1.00 1.00 1.00 98\n 10 1.00 0.97 0.98 90\n 11 1.00 0.94 0.97 78\n 12 1.00 0.99 0.99 197\n 13 1.00 0.89 0.94 93\n 14 1.00 1.00 1.00 98\n 15 1.00 0.95 0.97 98\n 16 1.00 1.00 1.00 98\n 17 1.00 0.95 0.98 88\n 18 1.00 1.00 1.00 96\n 19 0.87 0.88 0.87 99\n 20 1.00 1.00 1.00 98\n 21 0.98 0.94 0.96 99\n 22 1.00 0.98 0.99 139\n 23 1.00 1.00 1.00 89\n 24 1.00 1.00 1.00 133\n 25 1.00 1.00 1.00 98\n 26 1.00 0.99 0.99 89\n 27 1.00 1.00 1.00 98\n 28 1.00 1.00 1.00 90\n 29 1.00 0.97 0.98 98\n 30 0.92 0.97 0.95 99\n 31 1.00 0.99 0.99 148\n 32 1.00 0.96 0.98 95\n\n accuracy 0.98 3371\n macro avg 0.98 0.98 0.98 3371\nweighted avg 0.98 0.98 0.98 3371\n\n\nConfusion Matrix\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"2D PCA",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mean_array = []\nfor shell in shell_family.classifiers:\n mean_array.append(shell_family.classifiers[shell].shell_mean[0])\nscaler = StandardScaler()\nscaled_mean = scaler.fit_transform(mean_array)\npca = PCA(n_components=2, random_state=42)\ntransformed = pca.fit_transform(scaled_mean)\nfor i in range(len(transformed)):\n plt.scatter(transformed[i, 0], transformed[i, 1])\n plt.text(transformed[i, 0] + 0.5, transformed[i, 1] + 0.5, shell_family.mapping[i])\nplt.title(\"PCA shell mean\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"3D PCA",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mean_array = []\nfor shell in shell_family.classifiers:\n mean_array.append(shell_family.classifiers[shell].shell_mean[0])\nscaler = StandardScaler()\nscaled_mean = scaler.fit_transform(mean_array)\npca = PCA(n_components=3, random_state=42)\ntransformed = pca.fit_transform(scaled_mean)\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')\nfor i in range(len(transformed)):\n ax.scatter(transformed[i, 0], transformed[i, 1], transformed[i, 2])\n ax.text(transformed[i, 0] + 0.5, transformed[i, 1] + 0.5, transformed[i, 2], shell_family.mapping[i])\nplt.title(\"PCA shell mean\")\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
cbe8014fafc99a1d49b4c54dd26f7112959e79e0
| 1,473 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
00_core.ipynb
|
guilhermemt21/nbdev_test
|
d42d97e05e58bebd87945c62f1f81fa6a168fc3a
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
00_core.ipynb
|
guilhermemt21/nbdev_test
|
d42d97e05e58bebd87945c62f1f81fa6a168fc3a
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2021-09-28T05:37:09.000Z
|
2022-02-26T10:11:21.000Z
|
00_core.ipynb
|
guilhermemt21/nbdev_test
|
d42d97e05e58bebd87945c62f1f81fa6a168fc3a
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 16.366667 | 53 | 0.46979 |
[
[
[
"# default_exp core",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# module name here\n\n> API details.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#hide\nfrom nbdev.showdoc import *",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\ndef say_hello(to):\n \"Say hello to somebody\"\n return f'Hello {to}!'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"say_hello(\"Guilherme\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"assert say_hello(\"Jeremy\")==\"Hello Jeremy!\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe81371100b5c19eb4007d23e871c03fd2c2f30
| 102,315 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
01.Getting-Started.ipynb
|
juicedata/juicefs-deeplearning-tutorials
|
79e93bb3ddf2293aec7b278f1e1bd73fb48cd084
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2019-05-16T00:07:53.000Z
|
2022-02-15T03:39:45.000Z
|
01.Getting-Started.ipynb
|
juicedata/juicefs-deeplearning-tutorials
|
79e93bb3ddf2293aec7b278f1e1bd73fb48cd084
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
01.Getting-Started.ipynb
|
juicedata/juicefs-deeplearning-tutorials
|
79e93bb3ddf2293aec7b278f1e1bd73fb48cd084
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 135.15852 | 67,438 | 0.849494 |
[
[
[
"# Deep Learning on JuiceFS Tutorial - 01. Getting Started",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"JuiceFS is a shared POSIX file system for the cloud.\n\nYou may replace existing solutions with JuiceFS with zero cost, turns any object store into a shared POSIX file system.\n\nSign up for 1T free quota now at https://juicefs.com\n\nSource code of this tutorial can be found in https://github.com/juicedata/juicefs-dl-tutorial",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 0. Requirements",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"It's very easy to setup JuiceFS in your remote HPC machine or Google Colab or CoCalc by insert just one line of command into your Jupyter Notebook:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!curl -sL https://juicefs.com/static/juicefs -o juicefs && chmod +x juicefs",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here we go, let's try the magic of JuiceFS!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 1. Mounting your JuiceFS",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"After create your JuiceFS volumn followed by [documentation here](https://juicefs.com/docs/en/getting_started.html), you have two ways to mount your JuiceFS here:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 1.1 The security way",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Just run the mount command, and input your access key and secret key from the public cloud or storage provider. This scene is for people who want to collaborate with others and protecting credentials. It can also let your teammates using their JuiceFS volume or share notebook publicly.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!./juicefs mount {JFS_VOLUMN_NAME} /jfs",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 1.2 The convenient way",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"However, maybe you are working alone, no worries about leak credentials, and don't want to do annoying input credentials every time restart kernel. Surely, you can save your token and access secrets in your notebook, just change the corresponding fields in the following command to your own.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!./juicefs auth --token {JUICEFS_TOKEN} --accesskey {ACCESSKEY} --secretkey {SECRETKEY} JuiceFS\n!./juicefs mount -h",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 2. Preparing dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Okay, let's assume you have already mounted your JuiceFS volume. You can test by list your file here.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!ls /jfs",
"mnist.npz\n"
]
],
[
[
"You have many ways to get data into your JuiceFS volume, like mounting in your local machine and directly drag and drop, or mounting in cloud servers and write data or crawling data and save. Here we took the [MNIST dataset](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/) (with a training set of 60,000 images, and a test set of 10,000 images) as an example. If you have not to get the MNIST dataset ready, you can execute the following block:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!curl -sL https://s3.amazonaws.com/img-datasets/mnist.npz -o /jfs/mnist.npz",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 3. Training model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Once we have got our dataset ready in JuiceFS, we can begin the training process.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport keras\nfrom keras.models import Sequential\nfrom keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Flatten\nfrom keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D\n\nimport warnings\nwarnings.simplefilter(action='ignore')",
"Using TensorFlow backend.\n"
]
],
[
[
"Firstly, load our MNIST dataset from JuiceFS volume.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with np.load('/jfs/mnist.npz') as f:\n X_train, y_train = f['x_train'], f['y_train']\n X_test, y_test = f['x_test'], f['y_test']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Visualize some data to ensure we have successfully loaded data from JuiceFS.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sns.countplot(y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(6, 6, figsize = (12, 12))\nfig.suptitle('First 36 images in MNIST')\nfig.tight_layout(pad = 0.3, rect = [0, 0, 0.9, 0.9])\nfor x, y in [(i, j) for i in range(6) for j in range(6)]:\n ax[x, y].imshow(X_train[x + y * 6].reshape((28, 28)), cmap = 'gray')\n ax[x, y].set_title(y_train[x + y * 6])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Cool! We have successfully loaded the MNIST dataset from JuiceFS! Let's training a CNN model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"batch_size = 128\nnum_classes = 10\nepochs = 12",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"img_rows, img_cols = 28, 28\nX_train = X_train.reshape(X_train.shape[0], img_rows, img_cols, 1)\nX_test = X_test.reshape(X_test.shape[0], img_rows, img_cols, 1)\ninput_shape = (img_rows, img_cols, 1)\n\nX_train = X_train.astype('float32')\nX_test = X_test.astype('float32')\nX_train /= 255\nX_test /= 255\n\ny_train = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, num_classes)\ny_test = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test, num_classes)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model = Sequential()\nmodel.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=(3, 3),\n activation='relu',\n input_shape=input_shape))\nmodel.add(Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))\nmodel.add(Dropout(0.25))\nmodel.add(Flatten())\nmodel.add(Dense(128, activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(Dropout(0.5))\nmodel.add(Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax'))\n\nmodel.compile(loss=keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy,\n optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adadelta(),\n metrics=['accuracy'])\n\nmodel.fit(X_train, y_train,\n batch_size=batch_size,\n epochs=epochs,\n verbose=1,\n validation_data=(X_test, y_test))",
"Train on 60000 samples, validate on 10000 samples\nEpoch 1/12\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 11s 175us/step - loss: 0.2805 - acc: 0.9142 - val_loss: 0.0796 - val_acc: 0.9749\nEpoch 2/12\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 9s 156us/step - loss: 0.0915 - acc: 0.9723 - val_loss: 0.0405 - val_acc: 0.9855\nEpoch 3/12\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 10s 159us/step - loss: 0.0676 - acc: 0.9802 - val_loss: 0.0379 - val_acc: 0.9869\nEpoch 4/12\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 10s 162us/step - loss: 0.0559 - acc: 0.9832 - val_loss: 0.0344 - val_acc: 0.9879\nEpoch 5/12\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 10s 160us/step - loss: 0.0462 - acc: 0.9864 - val_loss: 0.0307 - val_acc: 0.9898\nEpoch 6/12\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 10s 163us/step - loss: 0.0403 - acc: 0.9879 - val_loss: 0.0297 - val_acc: 0.9907\nEpoch 7/12\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 10s 158us/step - loss: 0.0381 - acc: 0.9884 - val_loss: 0.0300 - val_acc: 0.9894\nEpoch 8/12\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 9s 158us/step - loss: 0.0348 - acc: 0.9896 - val_loss: 0.0285 - val_acc: 0.9902\nEpoch 9/12\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 10s 160us/step - loss: 0.0324 - acc: 0.9897 - val_loss: 0.0300 - val_acc: 0.9910\nEpoch 10/12\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 10s 160us/step - loss: 0.0298 - acc: 0.9904 - val_loss: 0.0260 - val_acc: 0.9918\nEpoch 11/12\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 10s 166us/step - loss: 0.0284 - acc: 0.9917 - val_loss: 0.0262 - val_acc: 0.9915\nEpoch 12/12\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 10s 159us/step - loss: 0.0271 - acc: 0.9915 - val_loss: 0.0291 - val_acc: 0.9914\n"
],
[
"score = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=0)\nprint('Test loss:', score[0])\nprint('Test accuracy:', score[1])",
"Test loss: 0.029089462164806172\nTest accuracy: 0.9914\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 4. Saving model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Awesome! We have trained a simple CNN model, now let's try to write back the model into JuiceFS. Thanks to the POSIX-compatible feature of JuiceFS, we can easily save the model as usual. No additional effort need.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model.save('/jfs/mnist_model.h5')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 5. Loading model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Assuming you want to debug the model in your local machine or want to sync with the production environment. You can load your model from JuiceFS in any machine in real time. JuiceFS's strong consistency feature will ensure all confirmed changes made to your data reflected in different machines immediately.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from keras.models import load_model\nmodel_from_jfs = load_model('/jfs/mnist_model.h5')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We have successfully load our previous model from JuiceFS here, let's randomly pick an image from test dataset and use loader model to make a prediction.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import random\npick_idx = random.randint(0, X_test.shape[0])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"What image have we picked?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.imshow(X_test[pick_idx].reshape((28, 28)), cmap = 'gray')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's do prediction using the model loaded from JuiceFS.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y_pred = np.argmax(model_from_jfs.predict(np.expand_dims(X_test[pick_idx], axis=0)))\nprint(f'Prediction: {y_pred}')",
"Prediction: 1\n"
]
],
[
[
"That's it. We will cover some advanced usages and public datasets in the next tutorials.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe82af125f0376c7e6fbc21d9b56370342be517
| 55,740 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
explore/Explore_Exploit.ipynb
|
jasonyum/math-puzzles
|
006b51d92a942efe469873735a204cf976f479fd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
explore/Explore_Exploit.ipynb
|
jasonyum/math-puzzles
|
006b51d92a942efe469873735a204cf976f479fd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
explore/Explore_Exploit.ipynb
|
jasonyum/math-puzzles
|
006b51d92a942efe469873735a204cf976f479fd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 249.955157 | 18,880 | 0.919125 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport matplotlib.pylab as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Draw u from Gaussian(0,1), i = 1,...,10 (unknown to agent) \n# arms = number of possible of actions (known to agent)\narms = 10\nu = np.random.randn(arms,1) \n\n# Rewards of action i at time t => x_i(t) ~ N(u_i,1)\n# x_i(t) is itself randomly drawn, so it's not deterministic\nrounds = 1000\nx = np.zeros((rounds,1))\n\n# Initialize Q: agent's record of rewards\n# Initialize estQ: agent's estimate of rewards\nQ = np.zeros((arms, rounds))\nestQ = np.zeros((arms,1))\n\n# Initialize the first column of Q with randomly drawn \"expectations\" \n# Set probability of exploring at whatever %. \nQ[:,0] = 0.01 # np.random.randn(arms) \nexploreProbability = 0.1\n\n# Initialize rolling_sum and average returns! \nrolling_sum = 0\navg_returns = []\n\nfor time in range(rounds): \n \n # Estimate return belief for each arm\n # Belief => Q_t(a) = sum of rewards / number of times action taken\n for i in range(arms): \n estQ[i] = sum(Q[i,:])/np.count_nonzero(Q[i,:])\n \n if np.random.uniform(0,1) > exploreProbability: \n \n # argmax(estQ) chooses the row (arm) with the highest value\n # np.random.normal(u[chosenLever],1) generates N(u_i,1) \n chosenLever = np.argmax(estQ) \n Q[chosenLever, time] = np.random.normal(u[chosenLever],1)\n rolling_sum += Q[chosenLever,time] \n avg_returns.append(rolling_sum/(time+1)) # because time starts at 0!\n \n else: # go exploring\n chosenLever = np.random.choice(arms)\n Q[chosenLever, time] = np.random.normal(u[chosenLever],1)\n rolling_sum += Q[chosenLever,time] \n avg_returns.append(rolling_sum/(time+1))\n \n# Determine average return\naverage_return = rolling_sum/(rounds)\n \n# Create the plot. \nax = sns.heatmap(Q, annot = False, cmap=\"YlGnBu\") #, linewidth=0)\nplt.ylabel('Arm')\nplt.xlabel('Round') \nplt.show()\n\nprint(\"The average return acheived is \", average_return)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Optimal Play!\n\n# Determine the \"ideal\" arm to pick, label ideal_pick\nideal_pick = np.argmax(u)\n\n# Initialize avg_perfect = list, records the average return achieved at time t\n# Initialize rolling_perfect = cumulative run you achieve\navg_perfect = []\nrolling_perfect = 0\n\nfor time in range(rounds):\n rolling_perfect += np.random.normal(u[ideal_pick],1)\n avg_perfect.append(rolling_perfect/(time+1))\n \nplt.plot(avg_returns[5:])\nplt.plot(avg_perfect[5:])\nplt.title(\"Perfect vs. Our Choice\")\nplt.ylabel('Avg Return Achieved') \nplt.xlabel('Round')\nplt.show()\n\nfinal_avg_perfect_return = rolling_perfect/rounds\nprint(final_avg_perfect_return) \nprint(\"The mean for optimal was \", u[ideal_pick])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Did we pick the right arm? \n\nnon_zero_elements = (Q != 0).sum(1) # this creates an array of the # of non-zero occurences\nmost_picked_arm = np.argmax(non_zero_elements)\n\nprint(\"we picked arm \", most_picked_arm)\nprint(\"the optimal arm was \", ideal_pick)\n\nplt.plot(u)\nplt.title(\"average means of arms\")\nplt.ylabel(\"mean\") \nplt.xlabel(\"arms\")\n\n# How many times did you pick the optimal arm? \n# (Q[most_picked_arm,:]).sum(1) # finds the # of non-zero occurrences in the most_picked_arm\nour_accuracy = (Q[ideal_pick,:] != 0).sum(0)/rounds *100\nprint(\"We picked the optimal arm with a probability of \", our_accuracy, \"%.\")",
"we picked arm 4\nthe optimal arm was 4\nWe picked the optimal arm with a probability of 87.7 %.\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe85098d9e0fc4abe1f836f5465d30910789064
| 14,513 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
REMARKs/CGMPortfolio/Related/Summaries/Matt/Zahn_CGMConsumpPortChoice.ipynb
|
MridulS/REMARK
|
65544dfca901d0ac2dad928cf08e3a8530422e41
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
REMARKs/CGMPortfolio/Related/Summaries/Matt/Zahn_CGMConsumpPortChoice.ipynb
|
MridulS/REMARK
|
65544dfca901d0ac2dad928cf08e3a8530422e41
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
REMARKs/CGMPortfolio/Related/Summaries/Matt/Zahn_CGMConsumpPortChoice.ipynb
|
MridulS/REMARK
|
65544dfca901d0ac2dad928cf08e3a8530422e41
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 74.045918 | 804 | 0.675877 |
[
[
[
"# Cocco, Gomes, and Maenhout (2005)\n\n# \"[Consumption and Portfolio Choice Over the Life Cycle](https://academic.oup.com/rfs/article-abstract/18/2/491/1599892)\"\n\n- Notebook created by Matt Zahn\n\n## Summary\n\nThis paper uses a realistically calibrated model of consumption and portfolio choice with non-tradable assets and borrowing constraints and finds that the optimal share invested in equities decreases over the agent's life span. The author's also examine the importance of human capital for investment behavior as well as the implications of introducing endogenous borrowing constraints. \n\nThe main findings are summarized below. \n- The shape of the income profile over the life span induces investors to reduce proportional stock holdings when aging, which rationalizes the advice from the popular finance literature. \n- Labor income that is uncorrelated with equity returns is perceived as a closer substitute for risk free asset holdings than equities. Thus, the presence of labor income increases the demand for stocks, particularly earlier in an investor's life. \n- Even small risks to employment income have a significant effect on investing behavior. Author's describe it has a \"crowding\" out effect that is particularly strong for younger households. \n- The lower bound of the income distribution is very relevant to understanding borrowing capacity and portfolio allocations.\n\nThis notebook summarizes the setup and calibration of the model. \n\n\n## Model\n\n\n### Setup\n\n__Time parameters and preferences__ \n\nAn investor’s age is denoted as $t$ and they live for a maximum of $T$ periods. The investor works for the first $K$ periods of their life, where $K$ is assumed to be exogenous and deterministic. The probability that an investor alive in period $t$ is alive in $t+1$ is $p_t$. \n\nInvestor $i$ has the following time separable utility function:\n\n\\begin{eqnarray*}\nE_1 \\sum^{T}_{t=1} \\delta^{t-1} \\left( \\prod^{t-2}_{j=0}p_j \\right) \\left[p_{t-1} \\frac{C_{it}^{1-\\gamma}}{1-\\gamma} + b(1-p_{t-1}) \\frac{D^{1-\\gamma}_{it}}{1-\\gamma}\\right]\n\\end{eqnarray*}\n\nWhere $\\delta<1$ is the discount factor, $C_{it}$ is the level of consumption in period $t$, $\\gamma>0$ is the coefficient of relative risk aversion and $D_{it}$ is the level of wealth that the investor bequeaths to descendants upon their death. Bequests are governed by the same the utility as the one from living consumption. The parameter $b$ controls the intensity of the bequest motive.\n\n\n__Labor income__\n\nBefore retiring, investor $i$ at age $t$ learns labor income $Y_{it}$, which is exogenously given by:\n\n\\begin{eqnarray*}\n\\log(Y_{it}) = f(t, Z_{it}) + v_{it} + \\epsilon_{it} \\text{ for } t \\leq K\n\\end{eqnarray*}\n\nWhere $f(t, Z_{it})$ is a deterministic function of the investor's age and individual characteristics. An idiosyncratic temporary shock is given by $\\epsilon_{it}$ and is distributed according to $N(0, \\sigma^2_\\epsilon)$ and $v_{it}$ is given by:\n\n\\begin{eqnarray*}\nv_{it} = v_{i, t-1} + u_{it}\n\\end{eqnarray*}\n\nwhere $u_{it}$ is distributed according to $N(0,\\sigma^2_u)$ and is independent of $\\epsilon_{it}$. Pre-retirement log income is the sum of a deterministic component calibrated to capture the hump-shaped profile observed in the data. The author's take $v_t$ as a random walk and assume that $\\epsilon_{it}$ is uncorrelated across households. The permanent component can be decomposed into an aggregate component $\\xi_t$ with the distribution $N(0,\\sigma^2_\\xi)$ and an idiosyncratic component $\\omega_{it}$ (distributed by $N(0,\\sigma^2_\\omega)$):\n\n\\begin{eqnarray*}\nu_{it} = \\xi_t + \\omega_{it}\n\\end{eqnarray*}\n\nThis construction allows the author's to model random component of labor income as a random walk. Additionally, they allow for correlation between innovations to excess stock return and labor income shocks through the aggregate component $\\xi_t$, which will be discussed later.\n\nRetirement income is a constant fraction $\\lambda$ of permanent labor income from the last year worked by the investor:\n\n\\begin{eqnarray*}\n\\log(Y_{it}) = \\log(\\lambda) + f(t, Z_{it}) + v_{it}\n\\end{eqnarray*}\n\n__Financial assets__\n\nRiskless assets are _Treasury bills_ that have a constant gross return of $\\bf{\\bar{R}}_f$. The dollar amount of the investor's Treasury bill holdings at time $t$ is given by $B_{it}$. The risky asset has a gross return of $R_t$ with an excess return given by:\n\n\\begin{eqnarray*}\nR_{t+1} - \\bf{\\bar{R}}_f = \\mu + \\eta_{t+1}\n\\end{eqnarray*}\n\nwhere $\\eta_{t+1}$ is the innovation to excess returns and is assumed to be $iid$ over time and distributed according to $N(0,\\sigma^2_\\eta)$. These innovations are allowed to be correlated with innovations to the aggregate component of aggregate income $\\xi_t$ with coefficient $\\rho$. Risky assets are called _stocks_ and the investor's dollar holding of them at time $t$ is denoted as $S_{it}$. \n\nThe investor has the following short run constraints:\n\n\\begin{eqnarray*}\nB_{it} &\\geq& 0 \\\\\nS_{it} &\\geq& 0\n\\end{eqnarray*}\n\nThese ensure that the agent cannot allocate negative dollars to either of these assets and borrowing against future labor income or retirement wealth. The author's define $\\alpha_{it}$ as the proportion of the investor's savings that are invested in stocks, the constraints imply that $\\alpha_{it} \\in [0,1]$ and wealth is non-negative.\n\n### Investor's problem\n\nIn each period $t$ the investor faces the following problem. They start off with wealth $W_{it}$ and then realize their labor income $Y_{it}$. Cash on hand is defined as $X_{it} = W_{it} + Y_{it}$. Then the investor must decide how much to consume $C_{it}$ and how to allocated their savings between stocks and Treasury bills. Next period's wealth is given by:\n\n\\begin{eqnarray*}\nW_{i,t+1} = R^p_{i,t+1}(W_{it} + Y_{it} - C_{it})\n\\end{eqnarray*}\n\nWhere $R^p_{i,t+1}$ is the return on the investor's total portfolio and is given by:\n\n\\begin{eqnarray*}\nR^p_{i,t+1} \\equiv \\alpha_{it}R_{t+1} + (1-\\alpha_{it})\\bf{\\bar{R}}_f\n\\end{eqnarray*}\n\nThe control variables in the problem are $\\{C_{it}, \\alpha_{it}\\}^T_{t=1}$ and the state variables are $\\{t, X_{it}, v_{it} \\}^T_{t=1}$. The agent solves for a policy rule as a function of the state variables $C_{it}(X_{it}, v_{it})$ and $\\alpha_{it}(X_{it}, v_{it})$. \n\nThe Bellman equation for the problem is:\n\n\\begin{eqnarray*}\nV_{it}(X_{it}) &=& \\max_{C_{it}\\geq 0, 0\\leq \\alpha_{it} \\leq 1} \\left[U(C_{it}) + \\delta p_t E_t V_{i,t+1}(X_{i,t+1})\\right] \\text{ for } t<T, \\\\\n\\text{where} \\\\\nX_{i,t+1} &=& Y_{i,t+1} + (X_{it}-C_{it})(\\alpha_{it}R_{t+1} + (1-\\alpha_{it}) \\bf{\\bar{R}}_f)\n\\end{eqnarray*}\n\nThis cannot be solved analytically and is done numerically via backward induction. \n\n## Calibration\n\n__Labor income process__\n\nThe PSID is used to estimate the labor income equation and its permanent component. This estimation controls for family specific fixed effects. In order to control for education, the sample was split into three groups: no high school, high school but no college degree, and college graduates. Across each of these groups, $f(t,Z_{it})$ is assumed to be additively separable across its arguments. The vector of personal characteristics $Z_{it}$ includes age, household fixed effects, marital status, household size/composition. The sample uses households that have a head between the age of 20 and 65. For the retirement stage, $\\lambda$ is calibrated as the ratio of the average of labor income in a given education group to the average labor income in the last year of work before retirement. \n\nThe error structure of the labor income process is estimated by following the variance decomposition method described in Carroll and Samwick (1997). A similar method is used to estimate the correlation parameter $\\rho$. Define $r_{id}$ as:\n\n\\begin{eqnarray*}\nr_{id} &\\equiv& \\log(Y^*_{i,t+d}) - \\log(Y^*_{it}), d\\in \\{1,2,...,22\\} \\\\\n\\text{where }& Y^*_t \\\\ \n\\log(Y^*_{it}) &\\equiv& \\log(Y_{it}) - f(t,Z_{it}), \\\\\n\\text{then}& \\\\\n\\text{VAR}(R_{id}) &=& d*\\sigma^2_u + 2*\\sigma^2_\\epsilon\n\\end{eqnarray*}\n\nThe variance estimates can be obtained by an OLS on the variance equation on $d$ and a constant term. These estimated values are assumed to be the same across all individuals. For the correlation parameter, start by writing the change in $\\log(Y_{it})$ as:\n\n\\begin{eqnarray*}\nr_{i1} = \\xi_t + \\omega_{it} + \\epsilon_{it} - \\epsilon_{i,t-1}\n\\end{eqnarray*}\n\nAveraging across individuals gives\n\n\\begin{eqnarray*}\n\\bar{r_1} = \\xi_t\n\\end{eqnarray*}\n\nThe correlation coefficient is also obtained via OLS by regressing $\\overline{\\Delta \\log(Y^*_t)}$ on demeaned excess returns:\n\n\\begin{eqnarray*}\n\\bar{r_1} = \\beta(R_{t+1} - \\bf{\\bar{R}}_f - \\mu) + \\psi_t\n\\end{eqnarray*}\n\n__Other parameters__\n\nAdults start at age 20 without a college degree and age 22 with a college degree. The retirement age is 65 for all households. The investor will die for sure if they reach age 100. Prior to this age, survival probabilities come from the mortality tables published by the National Center for Health Statistics. The discount factor $\\delta$ is calibrated to be $0.96$ and the coefficient of relative risk aversion ($\\gamma$) is set to $10$. The mean equity premium $\\mu$ is $4%$, the risk free rate is $2%$, and the standard deviation of innovations to the risky asset is set to the historical value of $0.157$.\n\n## Core Results\n\n__Baseline model__\n\nThe results from the baseline model contextualize the results in the popular finance literature. Early in life, agent's invest fully in stocks and hit their borrowing constraints. In midlife as retirement comes closer, agent's begin to save more and invests more in the risk-free asset. Finally, in retirement the portfolio rule shifts in and wealth runs down quickly. This leads to an increase in holdings of risky assets. \n\n__Heterogeneity and sensitivity analysis__\n\n- Labor income risk: Income risk may vary across employment sectors relative to the baseline model. The author's examine extreme cases for industries that have a standard deviation and temporary income shocks. While some differences appear across sectors, the results are generally in line with the baseline model.\n- Disastrous labor income shocks: The author's find that even a small probability of zero labor income lowers the optimal portfolio allocation in stocks, while the qualitative features of the baseline model are preserved.\n- Uncertain retirement income: The author's consider two types of uncertainty for retirement income; it is stochastic and correlated with current stock market performance and allowing for disastrous labor income draws before retirement. The first extension has results essentially the same as the baseline case. The second leads to more conservative portfolio allocations but is broadly consistent with the model.\n- Endogenous borrowing constraints: The author's add borrowing to their model by building on credit-market imperfections. The author's find that the average investor borrows about \\$5,000 and are in debt for most of their working life. They eventually pay off this debt and save for retirement. Relative to the benchmark model, the investor has put less of their money in their portfolio and arrive at retirement with substantially less wealth. These results are particularly pronounced at the lower end of the income distribution relative to the higher end. Additional details are available in the text.\n- Bequest motive: The author's introduce a bequest motive into the agent's utility function (i.e., $b>0$). Young investors are more impatient and tend to save less for bequests. As the agent ages, savings increases and is strongest once the agent is retired. This leads to effects on the agent's portfolio allocation. Taking a step-back however, these effects are not very large unless $b$ is large. \n- Educational attainment: The author's generally find that savings are consistent across education groups. They note that for a given age, the importance of future income is increasing with education level. This implies that riskless asset holdings are larger for these households. \n- Risk aversion and intertemporal substitution: Lowering the level of risk aversion in the model leads to changes in the optimal portfolio allocation and wealth accumulation. Less risk-averse investors accumulate less precautionary savings and invest more in risky assets.\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe86f57645512f03cb6c8cbd6904a2d6db159bf
| 12,053 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
doc/source/cd/methods/onlinemmddrift.ipynb
|
sugatoray/alibi-detect
|
66d7873c248c0be1a1d836e6fe1ef59351b802d9
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1,227 |
2019-11-19T15:38:40.000Z
|
2022-03-31T11:18:32.000Z
|
doc/source/cd/methods/onlinemmddrift.ipynb
|
maxpark/alibi-detect
|
84384297a85764c18537aa1c8699c4ad040cf7cd
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 323 |
2019-11-21T18:41:00.000Z
|
2022-03-31T21:08:56.000Z
|
doc/source/cd/methods/onlinemmddrift.ipynb
|
maxpark/alibi-detect
|
84384297a85764c18537aa1c8699c4ad040cf7cd
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 133 |
2019-11-19T14:23:23.000Z
|
2022-03-31T07:55:43.000Z
| 54.049327 | 809 | 0.676761 |
[
[
[
"[source](../../api/alibi_detect.cd.mmd_online.rst)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Online Maximum Mean Discrepancy\n\n## Overview\n\nThe online [Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD)](http://jmlr.csail.mit.edu/papers/v13/gretton12a.html) detector is a kernel-based method for online drift detection. The MMD is a distance-based measure between 2 distributions *p* and *q* based on the mean embeddings $\\mu_{p}$ and $\\mu_{q}$ in a reproducing kernel Hilbert space $F$:\n\n$$\nMMD(F, p, q) = || \\mu_{p} - \\mu_{q} ||^2_{F}\n$$\n\nGiven reference samples $\\{X_i\\}_{i=1}^{N}$ and test samples $\\{Y_i\\}_{i=t}^{t+W}$ we may compute an unbiased estimate $\\widehat{MMD}^2(F, \\{X_i\\}_{i=1}^N, \\{Y_i\\}_{i=t}^{t+W})$ of the squared MMD between the two underlying distributions. The estimate can be updated at low-cost as new data points enter into the test-window. We use by default a [radial basis function kernel](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radial_basis_function_kernel), but users are free to pass their own kernel of preference to the detector.\n\nOnline detectors assume the reference data is large and fixed and operate on single data points at a time (rather than batches). These data points are passed into the test-window and a two-sample test-statistic (in this case squared MMD) between the reference data and test-window is computed at each time-step. When the test-statistic exceeds a preconfigured threshold, drift is detected. Configuration of the thresholds requires specification of the expected run-time (ERT) which specifies how many time-steps that the detector, on average, should run for in the absence of drift before making a false detection. It also requires specification of a test-window size, with smaller windows allowing faster response to severe drift and larger windows allowing more power to detect slight drift.\n\nFor high-dimensional data, we typically want to reduce the dimensionality before passing it to the detector. Following suggestions in [Failing Loudly: An Empirical Study of Methods for Detecting Dataset Shift](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.11953), we incorporate Untrained AutoEncoders (UAE) and black-box shift detection using the classifier's softmax outputs ([BBSDs](https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.03916)) as out-of-the box preprocessing methods and note that [PCA](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Principal_component_analysis) can also be easily implemented using `scikit-learn`. Preprocessing methods which do not rely on the classifier will usually pick up drift in the input data, while BBSDs focuses on label shift.\n\nDetecting input data drift (covariate shift) $\\Delta p(x)$ for text data requires a custom preprocessing step. We can pick up changes in the semantics of the input by extracting (contextual) embeddings and detect drift on those. Strictly speaking we are not detecting $\\Delta p(x)$ anymore since the whole training procedure (objective function, training data etc) for the (pre)trained embeddings has an impact on the embeddings we extract. The library contains functionality to leverage pre-trained embeddings from [HuggingFace's transformer package](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers) but also allows you to easily use your own embeddings of choice. Both options are illustrated with examples in the [Text drift detection on IMDB movie reviews](../../examples/cd_text_imdb.ipynb) notebook.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Usage\n\n### Initialize\n\n\nArguments:\n\n* `x_ref`: Data used as reference distribution.\n* `ert`: The expected run-time in the absence of drift, starting from *t=0*.\n* `window_size`: The size of the sliding test-window used to compute the test-statistic. Smaller windows focus on responding quickly to severe drift, larger windows focus on ability to detect slight drift.\n\n\nKeyword arguments:\n\n* `backend`: Backend used for the MMD implementation and configuration.\n* `preprocess_fn`: Function to preprocess the data before computing the data drift metrics.\n* `kernel`: Kernel used for the MMD computation, defaults to Gaussian RBF kernel.\n* `sigma`: Optionally set the GaussianRBF kernel bandwidth. Can also pass multiple bandwidth values as an array. The kernel evaluation is then averaged over those bandwidths. If `sigma` is not specified, the 'median heuristic' is adopted whereby `sigma` is set as the median pairwise distance between reference samples.\n* `n_bootstraps`: The number of bootstrap simulations used to configure the thresholds. The larger this is the more accurately the desired ERT will be targeted. Should ideally be at least an order of magnitude larger than the ERT.\n* `verbose`: Whether or not to print progress during configuration.\n* `input_shape`: Shape of input data.\n* `data_type`: Optionally specify the data type (tabular, image or time-series). Added to metadata.\n\n\nAdditional PyTorch keyword arguments:\n\n* `device`: Device type used. The default None tries to use the GPU and falls back on CPU if needed. Can be specified by passing either 'cuda', 'gpu' or 'cpu'. Only relevant for 'pytorch' backend.\n\n\nInitialized drift detector example:\n\n\n```python\nfrom alibi_detect.cd import MMDDriftOnline\n\ncd = MMDDriftOnline(x_ref, ert, window_size, backend='tensorflow')\n```\n\nThe same detector in PyTorch:\n\n```python\ncd = MMDDriftOnline(x_ref, ert, window_size, backend='pytorch')\n```\n\nWe can also easily add preprocessing functions for both frameworks. The following example uses a randomly initialized image encoder in PyTorch:\n\n```python\nfrom functools import partial\nimport torch\nimport torch.nn as nn\nfrom alibi_detect.cd.pytorch import preprocess_drift\n\ndevice = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')\n\n# define encoder\nencoder_net = nn.Sequential(\n nn.Conv2d(3, 64, 4, stride=2, padding=0),\n nn.ReLU(),\n nn.Conv2d(64, 128, 4, stride=2, padding=0),\n nn.ReLU(),\n nn.Conv2d(128, 512, 4, stride=2, padding=0),\n nn.ReLU(),\n nn.Flatten(),\n nn.Linear(2048, 32)\n).to(device).eval()\n\n# define preprocessing function\npreprocess_fn = partial(preprocess_drift, model=encoder_net, device=device, batch_size=512)\n\ncd = MMDDriftOnline(x_ref, ert, window_size, backend='pytorch', preprocess_fn=preprocess_fn)\n```\nThe same functionality is supported in TensorFlow and the main difference is that you would import from `alibi_detect.cd.tensorflow import preprocess_drift`. Other preprocessing steps such as the output of hidden layers of a model or extracted text embeddings using transformer models can be used in a similar way in both frameworks. TensorFlow example for the hidden layer output:\n\n```python\nfrom alibi_detect.cd.tensorflow import HiddenOutput, preprocess_drift\n\nmodel = # TensorFlow model; tf.keras.Model or tf.keras.Sequential\npreprocess_fn = partial(preprocess_drift, model=HiddenOutput(model, layer=-1), batch_size=128)\n\ncd = MMDDriftOnline(x_ref, ert, window_size, backend='tensorflow', preprocess_fn=preprocess_fn)\n```\n\nCheck out the [Online Drift Detection on the Wine Quality Dataset](../../examples/cd_online_wine.ipynb) example for more details.\n\nAlibi Detect also includes custom text preprocessing steps in both TensorFlow and PyTorch based on Huggingface's [transformers](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers) package:\n\n```python\nimport torch\nimport torch.nn as nn\nfrom transformers import AutoTokenizer\nfrom alibi_detect.cd.pytorch import preprocess_drift\nfrom alibi_detect.models.pytorch import TransformerEmbedding\n\ndevice = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')\n\nmodel_name = 'bert-base-cased'\ntokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)\n\nembedding_type = 'hidden_state'\nlayers = [5, 6, 7]\nembed = TransformerEmbedding(model_name, embedding_type, layers)\nmodel = nn.Sequential(embed, nn.Linear(768, 256), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(256, enc_dim)).to(device).eval()\npreprocess_fn = partial(preprocess_drift, model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer, max_len=512, batch_size=32)\n\n# initialise drift detector\ncd = MMDDriftOnline(x_ref, ert, window_size, backend='pytorch', preprocess_fn=preprocess_fn)\n```\n\nAgain the same functionality is supported in TensorFlow but with `from alibi_detect.cd.tensorflow import preprocess_drift` and `from alibi_detect.models.tensorflow import TransformerEmbedding` imports.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Detect Drift\n\nWe detect data drift by sequentially calling `predict` on single instances `x_t` (no batch dimension) as they each arrive. We can return the test-statistic and the threshold by setting `return_test_stat` to *True*.\n\nThe prediction takes the form of a dictionary with `meta` and `data` keys. `meta` contains the detector's metadata while `data` is also a dictionary which contains the actual predictions stored in the following keys:\n\n* `is_drift`: 1 if the test-window (of the most recent `window_size` observations) has drifted from the reference data and 0 otherwise.\n\n* `time`: The number of observations that have been so far passed to the detector as test instances.\n\n* `ert`: The expected run-time the detector was configured to run at in the absence of drift.\n\n* `test_stat`: MMD^2 metric between the reference data and the test_window if `return_test_stat` equals *True*.\n\n* `threshold`: The value the test-statsitic is required to exceed for drift to be detected if `return_test_stat` equals *True*.\n\n\n```python\npreds = cd.predict(x_t, return_test_stat=True)\n```\n\nResetting the detector with the same reference data and thresholds but with a new and empty test-window is straight-forward:\n\n```python\ncd.reset()\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Examples\n\n[Online Drift Detection on the Wine Quality Dataset](../../examples/cd_online_wine.ipynb)\n\n[Online Drift Detection on the Camelyon medical imaging dataset](../../examples/cd_online_camelyon.ipynb)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe8830d7c3c5a7c059e2964a49b78f25aa042ad
| 3,323 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Logistic Regression.ipynb
|
manishgaurav84/ml-from-scratch
|
2af963d6e13889b6dcc8486ecaa0374577cee0c8
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Logistic Regression.ipynb
|
manishgaurav84/ml-from-scratch
|
2af963d6e13889b6dcc8486ecaa0374577cee0c8
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Logistic Regression.ipynb
|
manishgaurav84/ml-from-scratch
|
2af963d6e13889b6dcc8486ecaa0374577cee0c8
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 28.646552 | 100 | 0.518507 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\n\nclass LogisticRegression:\n\n def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.001, n_iters=1000):\n self.lr = learning_rate\n self.n_iters = n_iters\n self.weights = None\n self.bias = None\n\n def fit(self, X, y):\n n_samples, n_features = X.shape\n\n # init parameters\n self.weights = np.zeros(n_features)\n self.bias = 0\n\n # gradient descent\n for _ in range(self.n_iters):\n # approximate y with linear combination of weights and x, plus bias\n linear_model = np.dot(X, self.weights) + self.bias\n # apply sigmoid function\n y_predicted = self._sigmoid(linear_model)\n\n # compute gradients\n dw = (1 / n_samples) * np.dot(X.T, (y_predicted - y))\n db = (1 / n_samples) * np.sum(y_predicted - y)\n # update parameters\n self.weights -= self.lr * dw\n self.bias -= self.lr * db\n\n def predict(self, X):\n linear_model = np.dot(X, self.weights) + self.bias\n y_predicted = self._sigmoid(linear_model)\n y_predicted_cls = [1 if i > 0.5 else 0 for i in y_predicted]\n return np.array(y_predicted_cls)\n\n def _sigmoid(self, x):\n return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn import datasets\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\n\ndef accuracy(y_true, y_pred):\n accuracy = np.sum(y_true == y_pred) / len(y_true)\n return accuracy\n\nbc = datasets.load_breast_cancer()\nX, y = bc.data, bc.target\n\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=1234)\n\nregressor = LogisticRegression(learning_rate=0.0001, n_iters=1000)\nregressor.fit(X_train, y_train)\npredictions = regressor.predict(X_test)\n\nprint(\"LR classification accuracy:\", accuracy(y_test, predictions))",
"LR classification accuracy: 0.9298245614035088\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe889beb7ab46679d1d234707797ed4cf88b934
| 317,016 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
contributors/Giulia_Mazzotti/spatiotemporal_variability.ipynb
|
GiuliaMazzotti/hot-pow
|
6c964b5b2af8897e9b998f5c804b8d8cfd80a3ea
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
contributors/Giulia_Mazzotti/spatiotemporal_variability.ipynb
|
GiuliaMazzotti/hot-pow
|
6c964b5b2af8897e9b998f5c804b8d8cfd80a3ea
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
contributors/Giulia_Mazzotti/spatiotemporal_variability.ipynb
|
GiuliaMazzotti/hot-pow
|
6c964b5b2af8897e9b998f5c804b8d8cfd80a3ea
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 1 |
2021-08-22T09:14:53.000Z
|
2021-08-22T09:14:53.000Z
| 249.030636 | 94,072 | 0.892081 |
[
[
[
"# Thermal data exploration notebook\n\n*Author: Giulia Mazzotti - heavily relying on Steven Pestana's amazing Thermal IR tutorials!* \n\n### Main goal - scientific\n\nOn February 8th, airborne thermal IR data was acquired over the Grand Mesa domain during multiple overpasses. \n\nThe goal of this notebook isto kick off working with this dataset. Some initial explorative analysis is done, and ideas for further datamining are provided.\n\nWe consider two aspects: \n\n1. How do surface temperature compare to ground measurements over time?\n2. How do surface temperature vary in space and time in forested and open areas?\n\n### Personal goal\n\nFirst steps with Python and Jupyter, and get familiar with SnowEx thermal data!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 0. Preparatory steps\n\nSo... we need some data! \n\nWe're going to work with two datasets: \n\n1. A NetCDF file including all airborne acquisitions of that day\n2. Temperature data from a snow pit that had stationary sensors\n\n---\n\n**<<<The code below only needs to be ran once, to download the data file. You can comment it out afterwards>>>**\n\nDownload a sample airborne IR netcdf file that contains 17 image mosaics from the morning of Feb. 8th, 2020.\n(Start by downloading [driveanon](https://github.com/friedrichknuth/driveanon) to download sample file from google drive using \"pip install\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%capture\n!pip install git+https://github.com/friedrichknuth/driveanon.git",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# import driveanon\nimport driveanon as da",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# download and save the file\nfolder_blob_id = '1BYz63HsSilPcQpCWPNZOp62ZZU2OdeWO'\nfile_names, file_blob_ids = da.list_blobs(folder_blob_id,'.nc')\nprint(file_names, file_blob_ids)\nda.save(file_blob_ids[0])",
"['SNOWEX2020_IR_PLANE_2020Feb08_mosaicked_APLUW_v2.nc'] ['1Rgw7y7hmnefZyMQXosQvF0g_rJRkoMPx']\n"
]
],
[
[
"Download the pit data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# import the temp data in lack of a better approach\n!aws s3 sync --quiet s3://snowex-data/tutorial-data/thermal-ir/ /tmp/thermal-ir/",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**<<<The above code only needs to be ran once, to download the data file. You can comment it out afterwards>>>**\n\n-----",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Import packages we're going to need",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# import xarray and rioxarray packages to work with the airborne raster data\nimport xarray as xr\nimport rioxarray\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\n# Import some general-purpose packages for handling different data structures\nimport numpy as np # for working with n-D arrays\nimport pandas as pd # for reading our csv data file and working with tabular data\n\n# Import some packages for working with the SnowEx SQL database\nfrom snowexsql.db import get_db # Import the connection function from the snowexsql library\nfrom snowexsql.data import SiteData # Import the table classes from our data module which is where our ORM classes are defined \nfrom datetime import date # Import some tools to build dates \nfrom snowexsql.conversions import query_to_geopandas # Import a useful function for plotting and saving queries! See https://snowexsql.readthedocs.io/en/latest/snowexsql.html#module-snowexsql.conversions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 1. Comparing time series of airborne images to snowpit data\n\n### Open and inspect the NetCDF file containing airborne IR time series",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# open the NetCDF file as dataset\nds = xr.open_dataset('SNOWEX2020_IR_PLANE_2020Feb08_mosaicked_APLUW_v2.nc')\nds",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This command opens a NetCDF file and creates a dataset that contains all 17 airborne thermal IR acquisitions throughout the day on February 8th, as seen by printing the timestamps.\n\nSome data conversion tasks are now necessary: ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# To make rioxarray happy, we should rename our spatial coorinates \"x\" and \"y\" (it automatically looks for coordinates with these names)\n# We want to look at the variable \"STBmosaic\" (temperatures in degrees C), so we can drop everything else.\nda = ds.STBmosaic.rename({'easting':'x', 'northing':'y'}) # create a new data array of \"STBmosaic\" with the renamed coordinates\n\n# We also need to perform a coordinate transformation to ensure compatibility with the pit dataset \nda = da.rio.write_crs('EPSG:32613') # assign current crs\nda = da.rio.reproject('EPSG:26912') # overwrite with new reprojected data array",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create a pandas timestamp array, subtract 7 hours from UTC time to get local time (MST, UTC-7)\n# Ideally programmatically by reading out the entries in da.time\nair_timestamps = [pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,8,7,17), pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,8,16,44), pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,8,28,32), pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,8,43,2),\\\n pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,8,55,59), pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,9,7,54), pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,11,7,37), pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,11,19,15),\\\n pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,11,29,16), pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,11,40,56), pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,11,50,20), pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,12,1,9),\\\n pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,12,6,22), pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,12,18,49), pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,12,31,35), pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,12,44,28),\\\n pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,12,56,16)] ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*Additional plotting ideas for later: create interactive plot of the 17 acquisitions with time slider to get an idea of data coverage*",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Get the location for snow pit 2S10 from the SnowEx SQL database (query [SiteData](https://snowexsql.readthedocs.io/en/latest/database_structure.html#sites-table) using [filter_by](https://docs.sqlalchemy.org/en/14/orm/query.html#sqlalchemy.orm.Query.filter_by) to find the entry with the site ID that we want). Then preview the resulting geodataframe, and perform some necessary data wrangling steps as demonstrated by Steven in his tutorial",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Standard commands to access the database according to tutorials\ndb_name = 'snow:[email protected]/snowex'\nengine, session = get_db(db_name)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Form the query to receive site_id='2S10' from the sites table\nqry = session.query(SiteData).filter_by(site_id='2S10')\n\n# Convert the record received into a geopandas dataframe\nsiteData_df = query_to_geopandas(qry, engine)\n\n# Preview the resulting geopandas dataframe; this is just the site info, not the data! \n# siteData_df\n\n# Check that coordinate systems match indeed\n# siteData_df.crs",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# need to create column headers\ncolumn_headers = ['table', 'year', 'doy', 'time', # year, day of year, time of day (local time, UTC-7)\n 'rad_avg', 'rad_max', 'rad_min', 'rad_std', # radiometer surface temperature\n 'sb_avg', 'sb_max', 'sb_min', 'sb_std', # radiometer sensor body temperature (for calibration)\n 'temp1_avg', 'temp1_max', 'temp1_min', 'temp1_std', # temperature at 5 cm below snow surface\n 'temp2_avg', 'temp2_max', 'temp2_min', 'temp2_std', # 10 cm\n 'temp3_avg', 'temp3_max', 'temp3_min', 'temp3_std', # 15 cm\n 'temp4_avg', 'temp4_max', 'temp4_min', 'temp4_std', # 20 cm\n 'temp5_avg', 'temp5_max', 'temp5_min', 'temp5_std', # 30 cm\n 'batt_a','batt_b', # battery voltage data\n ]\n\n# read the actual data and do the necessary conversion step to include column headers \ndf = pd.read_csv('/tmp/thermal-ir/SNEX20_VPTS_Raw/Level-0/snow-temperature-timeseries/CR10X_GM1_final_storage_1.dat',\n header = None, names = column_headers) \n\n# After the filepath we specify header=None because the file doesn't contain column headers, \n# then we specify names=column_headers to give our own names for each column.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create a zero-padded time string (e.g. for 9:30 AM we are changing '930' into '0930')\ndf['time_str'] = [('0' * (4 - len(str(df.time[i])))) + str(df.time[i]) for i in range(df.shape[0])]\n# change midnight from '2400' to '0000' ... might introduce some funny things...\ndf.time_str.replace('2400', '0000', inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def compose_date(years, months=1, days=1, weeks=None, hours=None, minutes=None,\n seconds=None, milliseconds=None, microseconds=None, nanoseconds=None):\n '''Compose a datetime object from various datetime components. This clever solution is from:\n https://stackoverflow.com/questions/34258892/converting-year-and-day-of-year-into-datetime-index-in-pandas'''\n years = np.asarray(years) - 1970\n months = np.asarray(months) - 1\n days = np.asarray(days) - 1\n types = ('<M8[Y]', '<m8[M]', '<m8[D]', '<m8[W]', '<m8[h]',\n '<m8[m]', '<m8[s]', '<m8[ms]', '<m8[us]', '<m8[ns]')\n vals = (years, months, days, weeks, hours, minutes, seconds,\n milliseconds, microseconds, nanoseconds)\n return sum(np.asarray(v, dtype=t) for t, v in zip(types, vals)\n if v is not None)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create a datetime value from the date field and zero-padded time_str field, set this as our dataframe's index\ndf.index = compose_date(df['year'], \n days=df['doy'], \n hours=df['time_str'].str[:2],\n minutes=df['time_str'].str[2:])\n\n# Remove entries that are from table \"102\" (this contains datalogger battery information we're not interested in at the moment)\ndf = df[df.table != 102]\n\n# drop the columns we no longer need\ndf.drop(columns=['table','year','doy','time','time_str','batt_a','batt_b'], inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create a datetime value from the date field and zero-padded time_str field, set this as our dataframe's index\ndf.index = compose_date(df['year'], \n days=df['doy'], \n hours=df['time_str'].str[:2],\n minutes=df['time_str'].str[2:])\n\n# Remove entries that are from table \"102\" (this contains datalogger battery information we're not interested in at the moment)\ndf = df[df.table != 102]\n\n# drop the columns we no longer need\ndf.drop(columns=['table','year','doy','time','time_str','batt_a','batt_b'], inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Clip the airborne IR data around the pit and plot in time\nMake a simple plot of the data. We are interested in the variable `rad_avg` which is the average temperature measured by the radiometer over each 5 minute period.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# reminder of where our snow pit is at to create bounding box around it\nsiteData_df.geometry.bounds",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Let's first look at a 100m grid cell around the pit\nminx = 743026\nminy = 4322639\nmaxx = 743126\nmaxy = 4322739",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# clip\nda_clipped = da.rio.clip_box(minx,miny,maxx,maxy)\n\n# quick check to see where the bounding box and the pit data overlap by at least 80% (approx)\n# for da_clipped_step in da_clipped:\n# fig, ax = plt.subplots()\n \n# da_clipped_step.plot(ax=ax,cmap='magma')\n \n# save the corresponding indices for use in the next plot; skip index 1 because it's going to be plotted differently \nints = [3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 12, 14, 16]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(10,4))\n\n# plot radiometer average temperature\ndf.rad_avg.plot(linestyle='-', marker='', markersize=1, c='k', label='Ground-based $T_s$')\n\n# plot the mean airborne IR temperature from the area around the snow pit:\nplt.plot(air_timestamps[1], da_clipped.isel(time = 1).mean(),\n marker='o', c='r', linestyle='none',\n label='Airborne IR mean $T_s$ for 100 m bounding box area')\n\n# plot an error bar showing the maximum and minimum airborne IR temperature around the snow pit\nplt.errorbar(air_timestamps[1], da_clipped.isel(time = 1).mean(),\n yerr=[[da_clipped.isel(time = 1).mean()-da_clipped.isel(time = 1).min()], \n [da_clipped.isel(time = 1).max()-da_clipped.isel(time = 1).mean()]],\n capsize=3, fmt='none', ecolor='b',\n label='Airborne IR $T_s$ range for 100 m bounxing box area')\n \nfor i in ints:\n\n# plot the mean airborne IR temperature from the area around the snow pit:\n plt.plot(air_timestamps[i], da_clipped.isel(time = i).mean(),\n marker='o', c='r', linestyle='none') #,\n # label='Airborne IR mean $T_s$ for 100 m radius area')\n\n # plot an error bar showing the maximum and minimum airborne IR temperature around the snow pit\n plt.errorbar(air_timestamps[i], da_clipped.isel(time = i).mean(),\n yerr=[[da_clipped.isel(time = i).mean()-da_clipped.isel(time = i).min()], \n [da_clipped.isel(time = i).max()-da_clipped.isel(time = i).mean()]],\n capsize=3, fmt='none', ecolor='b')#,\n # label='Airborne IR $T_s$ range for 100 m radius area')\n\n \n# set axes limits\nplt.ylim((-15,0))\nplt.xlim((pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,6,0),pd.Timestamp(2020,2,8,20,0))) # zoom in to daytime hours on Feb. 8, 2020\n\n# add a legend to the plot\nplt.legend()\n\n# set axes labels\nplt.ylabel('Temperature [$C\\degree$]')\nplt.xlabel('Time')\n\n# add grid lines to the plot\nplt.grid('on')\n\n# set the plot title\nplt.title('Snow Surface Temperature at Snow Pit 2S10 compared to Airborne IR imagery (100 m box)');\n\nplt.savefig('timeseries.jpg')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Compare spatial patterns in open and forest",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# create new bounding boxes and quickly verify where they have overlapping data. now let's look at 500 m pixels just to make sure we see something",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# set up our box bounding coordinates - pit site (verified that it doesnt contain trees)\nminx = 742826\nminy = 4322439\nmaxx = 743326\nmaxy = 4322939\n\n# bounding box in forest for comparison\nminx_for = 743926\nminy_for = 4322839\nmaxx_for = 744426\nmaxy_for = 4323339",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# clip\nda_clipped = da.rio.clip_box(minx,miny,maxx,maxy)\nda_clipped_for = da.rio.clip_box(minx_for,miny_for,maxx_for,maxy_for)\n# both cases have cool datasets for i = 1 and i = 16",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# for da_clipped_step in da_clipped_for:\n # fig, ax = plt.subplots()\n \n # da_clipped_step.plot(ax=ax,cmap='magma')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(10,4), tight_layout=True)\n\nairborne_ir_area_temperature = da_clipped.isel(time = 1)\n# plot the portion of the airborne TIR image we selected within the buffer area geometry\nairborne_ir_area_temperature.plot(cmap='magma', vmin=-20, vmax=5, ax=ax[0], \n cbar_kwargs={'label': 'Temperature $\\degree C$'})\nax[0].set_title('Airborne TIR image within\\n500 m pixel - open area- 8AM\\n')\nax[0].set_aspect('equal')\nax[0].set_xlabel('Eastings UTM 12N (m)')\nax[0].set_ylabel('Northings UTM 12N (m)')\n# ax[0].set_xlim((xmin-150, xmax+150)) # x axis limits to +/- 150 m from our point's \"total bounds\"\n# ax[0].set_ylim((ymin-150, ymax+150)) # y axis limits to +/- 150 m from our point's \"total bounds\"\n\nairborne_ir_area_temperature = da_clipped_for.isel(time = 1)\n# plot the portion of the airborne TIR image we selected within the buffer area geometry\nairborne_ir_area_temperature.plot(cmap='magma', vmin=-20, vmax=5, ax=ax[1], \n cbar_kwargs={'label': 'Temperature $\\degree C$'})\nax[1].set_title('Airborne TIR image within\\n500 m pixel - forested area - 8AM\\n')\nax[1].set_aspect('equal')\nax[1].set_xlabel('Eastings UTM 12N (m)')\nax[1].set_ylabel('Northings UTM 12N (m)')\n\nplt.savefig('spatial_8am.jpg')\n\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(10,4), tight_layout=True)\n\nairborne_ir_area_temperature = da_clipped.isel(time = 16)\n# plot the portion of the airborne TIR image we selected within the buffer area geometry\nairborne_ir_area_temperature.plot(cmap='magma', vmin=-20, vmax=5, ax=ax[0], \n cbar_kwargs={'label': 'Temperature $\\degree C$'})\nax[0].set_title('Airborne TIR image within\\n500 m pixel - open area - 12PM\\n')\nax[0].set_aspect('equal')\nax[0].set_xlabel('Eastings UTM 12N (m)')\nax[0].set_ylabel('Northings UTM 12N (m)')\n# ax[0].set_xlim((xmin-150, xmax+150)) # x axis limits to +/- 150 m from our point's \"total bounds\"\n# ax[0].set_ylim((ymin-150, ymax+150)) # y axis limits to +/- 150 m from our point's \"total bounds\"\n\nairborne_ir_area_temperature = da_clipped_for.isel(time = 16)\n# plot the portion of the airborne TIR image we selected within the buffer area geometry\nairborne_ir_area_temperature.plot(cmap='magma', vmin=-20, vmax=5, ax=ax[1], \n cbar_kwargs={'label': 'Temperature $\\degree C$'})\nax[1].set_title('Airborne TIR image within\\n500 m pixel - forested area - 12PM\\n')\nax[1].set_aspect('equal')\nax[1].set_xlabel('Eastings UTM 12N (m)')\nax[1].set_ylabel('Northings UTM 12N (m)')\n\nplt.savefig('spatial_12pm.jpg')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=4, figsize=(16,4), tight_layout=True)\n\nairborne_ir_area_temperature = da_clipped.isel(time = 1)\n# plot a histogram of image temperature data within the buffer area geometry\nairborne_ir_area_temperature.plot.hist(ax=ax[0],\n color='grey', \n zorder=1, # use zorder to make sure this plots below the point\n label='zonal $T_S$ histogram') \n\n# plot a vertical line for the mean temperature within the buffer area geometry\nax[0].axvline(airborne_ir_area_temperature.mean(), \n color='b',linestyle='--', # set color and style\n zorder=2, # use zorder to make sure this plots on top of the histogram\n label='zonal mean $T_S$') \n\nax[0].legend(loc='upper left') # add a legend\nax[0].set_xlim((-22,-2)) # set xlim to same values as colorbar in image plot\nax[0].set_title('Open area - 8AM')\nax[0].set_ylabel('Number of pixels');\n\nairborne_ir_area_temperature = da_clipped_for.isel(time = 1)\n# plot a histogram of image temperature data within the buffer area geometry\nairborne_ir_area_temperature.plot.hist(ax=ax[1],\n color='grey', \n zorder=1, # use zorder to make sure this plots below the point\n label='zonal $T_S$ histogram') \n\n# plot a vertical line for the mean temperature within the buffer area geometry\nax[1].axvline(airborne_ir_area_temperature.mean(), \n color='g',linestyle='--', # set color and style\n zorder=2, # use zorder to make sure this plots on top of the histogram\n label='zonal mean $T_S$') \n\nax[1].legend(loc='upper left') # add a legend\nax[1].set_xlim((-22,-2)) # set xlim to same values as colorbar in image plot\nax[1].set_title('Forest area - 8AM')\nax[1].set_ylabel('Number of pixels');\n\nairborne_ir_area_temperature = da_clipped.isel(time = 16)\n# plot a histogram of image temperature data within the buffer area geometry\nairborne_ir_area_temperature.plot.hist(ax=ax[2],\n color='grey', \n zorder=1, # use zorder to make sure this plots below the point\n label='zonal $T_S$ histogram') \n\n# plot a vertical line for the mean temperature within the buffer area geometry\nax[2].axvline(airborne_ir_area_temperature.mean(), \n color='b',linestyle='--', # set color and style\n zorder=2, # use zorder to make sure this plots on top of the histogram\n label='zonal mean $T_S$') \n\nax[2].legend(loc='upper left') # add a legend\nax[2].set_xlim((-15,5)) # set xlim to same values as colorbar in image plot\n# ax[1].set_ylim((0,400)) # set ylim\nax[2].set_title('Open area - 12PM')\nax[2].set_ylabel('Number of pixels');\n\nairborne_ir_area_temperature = da_clipped_for.isel(time = 16)\n# plot a histogram of image temperature data within the buffer area geometry\nairborne_ir_area_temperature.plot.hist(ax=ax[3],\n color='grey', \n zorder=1, # use zorder to make sure this plots below the point\n label='zonal $T_S$ histogram') \n\n# plot a vertical line for the mean temperature within the buffer area geometry\nax[3].axvline(airborne_ir_area_temperature.mean(), \n color='g',linestyle='--', # set color and style\n zorder=2, # use zorder to make sure this plots on top of the histogram\n label='zonal mean $T_S$') \n\nax[3].legend(loc='upper left') # add a legend\nax[3].set_xlim((-15,5)) # set xlim to same values as colorbar in image plot\n# ax[1].set_ylim((0,400)) # set ylim\nax[3].set_title('Forest area - 12PM')\nax[3].set_ylabel('Number of pixels');\n\nplt.savefig('histograms.jpg')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe8933a2acc2104ad591f01f1ef9900aea274f9
| 44,223 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Notebooks/Old/FITSImageViewer.ipynb
|
varuneagle555/VSPy
|
d4b27ef454d6a6258c1462920804abb54db2d39e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Notebooks/Old/FITSImageViewer.ipynb
|
varuneagle555/VSPy
|
d4b27ef454d6a6258c1462920804abb54db2d39e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Notebooks/Old/FITSImageViewer.ipynb
|
varuneagle555/VSPy
|
d4b27ef454d6a6258c1462920804abb54db2d39e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 221.115 | 34,508 | 0.840468 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nfrom astropy.io import fits",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"file_name = './varfind/varfind.fts'\n\nimage_file = fits.open(file_name)\nimage_data = image_file[0].data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"image_file[0].header",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.imshow(image_data, cmap='gray')\nplt.colorbar()\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"image_file.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe8a50993a9799dfaf93598f37e03626f6612a6
| 25,408 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
WEEKS/CD_Sata-Structures/_JUPYTER/Python-Lectures/07.ipynb
|
webdevhub42/Lambda
|
b04b84fb5b82fe7c8b12680149e25ae0d27a0960
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
WEEKS/CD_Sata-Structures/_JUPYTER/Python-Lectures/07.ipynb
|
webdevhub42/Lambda
|
b04b84fb5b82fe7c8b12680149e25ae0d27a0960
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
WEEKS/CD_Sata-Structures/_JUPYTER/Python-Lectures/07.ipynb
|
webdevhub42/Lambda
|
b04b84fb5b82fe7c8b12680149e25ae0d27a0960
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 21.351261 | 608 | 0.521293 |
[
[
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Classes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Variables, Lists, Dictionaries etc in python is a object. Without getting into the theory part of Object Oriented Programming, explanation of the concepts will be done along this tutorial.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"A class is declared as follows",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class class_name:\n\n Functions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class FirstClass:\n pass",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**pass** in python means do nothing. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Above, a class object named \"FirstClass\" is declared now consider a \"egclass\" which has all the characteristics of \"FirstClass\". So all you have to do is, equate the \"egclass\" to \"FirstClass\". In python jargon this is called as creating an instance. \"egclass\" is the instance of \"FirstClass\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"egclass = FirstClass()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(egclass)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(FirstClass)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now let us add some \"functionality\" to the class. So that our \"FirstClass\" is defined in a better way. A function inside a class is called as a \"Method\" of that class",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Most of the classes will have a function named \"\\_\\_init\\_\\_\". These are called as magic methods. In this method you basically initialize the variables of that class or any other initial algorithms which is applicable to all methods is specified in this method. A variable inside a class is called an attribute.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"These helps simplify the process of initializing a instance. For example,\n\nWithout the use of magic method or \\_\\_init\\_\\_ which is otherwise called as constructors. One had to define a **init( )** method and call the **init( )** function.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"eg0 = FirstClass()\neg0.init()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"But when the constructor is defined the \\_\\_init\\_\\_ is called thus intializing the instance created. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We will make our \"FirstClass\" to accept two variables name and symbol.\n\nI will be explaining about the \"self\" in a while.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class FirstClass:\n def __init__(self,name,symbol):\n self.name = name\n self.symbol = symbol",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now that we have defined a function and added the \\_\\_init\\_\\_ method. We can create a instance of FirstClass which now accepts two arguments. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"eg1 = FirstClass('one',1)\neg2 = FirstClass('two',2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print eg1.name, eg1.symbol\nprint eg2.name, eg2.symbol",
"one 1\ntwo 2\n"
]
],
[
[
"**dir( )** function comes very handy in looking into what the class contains and what all method it offers",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dir(FirstClass)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**dir( )** of an instance also shows it's defined attributes.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dir(eg1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Changing the FirstClass function a bit,",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class FirstClass:\n def __init__(self,name,symbol):\n self.n = name\n self.s = symbol",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Changing self.name and self.symbol to self.n and self.s respectively will yield,",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"eg1 = FirstClass('one',1)\neg2 = FirstClass('two',2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print eg1.name, eg1.symbol\nprint eg2.name, eg2.symbol",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"AttributeError, Remember variables are nothing but attributes inside a class? So this means we have not given the correct attribute for the instance.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dir(eg1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print eg1.n, eg1.s\nprint eg2.n, eg2.s",
"one 1\ntwo 2\n"
]
],
[
[
"So now we have solved the error. Now let us compare the two examples that we saw.\n\nWhen I declared self.name and self.symbol, there was no attribute error for eg1.name and eg1.symbol and when I declared self.n and self.s, there was no attribute error for eg1.n and eg1.s\n\nFrom the above we can conclude that self is nothing but the instance itself.\n\nRemember, self is not predefined it is userdefined. You can make use of anything you are comfortable with. But it has become a common practice to use self.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class FirstClass:\n def __init__(asdf1234,name,symbol):\n asdf1234.n = name\n asdf1234.s = symbol",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"eg1 = FirstClass('one',1)\neg2 = FirstClass('two',2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print eg1.n, eg1.s\nprint eg2.n, eg2.s",
"one 1\ntwo 2\n"
]
],
[
[
"Since eg1 and eg2 are instances of FirstClass it need not necessarily be limited to FirstClass itself. It might extend itself by declaring other attributes without having the attribute to be declared inside the FirstClass.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"eg1.cube = 1\neg2.cube = 8",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dir(eg1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Just like global and local variables as we saw earlier, even classes have it's own types of variables.\n\nClass Attribute : attributes defined outside the method and is applicable to all the instances.\n\nInstance Attribute : attributes defined inside a method and is applicable to only that method and is unique to each instance.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class FirstClass:\n test = 'test'\n def __init__(self,name,symbol):\n self.name = name\n self.symbol = symbol",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here test is a class attribute and name is a instance attribute.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"eg3 = FirstClass('Three',3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print eg3.test, eg3.name",
"test Three\n"
]
],
[
[
"Let us add some more methods to FirstClass.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class FirstClass:\n def __init__(self,name,symbol):\n self.name = name\n self.symbol = symbol\n def square(self):\n return self.symbol * self.symbol\n def cube(self):\n return self.symbol * self.symbol * self.symbol\n def multiply(self, x):\n return self.symbol * x",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"eg4 = FirstClass('Five',5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print eg4.square()\nprint eg4.cube()",
"25\n125\n"
],
[
"eg4.multiply(2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The above can also be written as,",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"FirstClass.multiply(eg4,2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##Inheritance",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"There might be cases where a new class would have all the previous characteristics of an already defined class. So the new class can \"inherit\" the previous class and add it's own methods to it. This is called as inheritance.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Consider class SoftwareEngineer which has a method salary.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class SoftwareEngineer:\n def __init__(self,name,age):\n self.name = name\n self.age = age\n def salary(self, value):\n self.money = value\n print self.name,\"earns\",self.money",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = SoftwareEngineer('Kartik',26)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a.salary(40000)",
"Kartik earns 40000\n"
],
[
"dir(SoftwareEngineer)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now consider another class Artist which tells us about the amount of money an artist earns and his artform.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class Artist:\n def __init__(self,name,age):\n self.name = name\n self.age = age\n def money(self,value):\n self.money = value\n print self.name,\"earns\",self.money\n def artform(self, job):\n self.job = job\n print self.name,\"is a\", self.job",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"b = Artist('Nitin',20)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"b.money(50000)\nb.artform('Musician')",
"Nitin earns 50000\nNitin is a Musician\n"
],
[
"dir(Artist)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"money method and salary method are the same. So we can generalize the method to salary and inherit the SoftwareEngineer class to Artist class. Now the artist class becomes,",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class Artist(SoftwareEngineer):\n def artform(self, job):\n self.job = job\n print self.name,\"is a\", self.job",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"c = Artist('Nishanth',21)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dir(Artist)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"c.salary(60000)\nc.artform('Dancer')",
"Nishanth earns 60000\nNishanth is a Dancer\n"
]
],
[
[
"Suppose say while inheriting a particular method is not suitable for the new class. One can override this method by defining again that method with the same name inside the new class.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class Artist(SoftwareEngineer):\n def artform(self, job):\n self.job = job\n print self.name,\"is a\", self.job\n def salary(self, value):\n self.money = value\n print self.name,\"earns\",self.money\n print \"I am overriding the SoftwareEngineer class's salary method\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"c = Artist('Nishanth',21)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"c.salary(60000)\nc.artform('Dancer')",
"Nishanth earns 60000\nI am overriding the SoftwareEngineer class's salary method\nNishanth is a Dancer\n"
]
],
[
[
"If not sure how many times methods will be called it will become difficult to declare so many variables to carry each result hence it is better to declare a list and append the result.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class emptylist:\n def __init__(self):\n self.data = []\n def one(self,x):\n self.data.append(x)\n def two(self, x ):\n self.data.append(x**2)\n def three(self, x):\n self.data.append(x**3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"xc = emptylist()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"xc.one(1)\nprint xc.data",
"[1]\n"
]
],
[
[
"Since xc.data is a list direct list operations can also be performed.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"xc.data.append(8)\nprint xc.data",
"[1, 8]\n"
],
[
"xc.two(3)\nprint xc.data",
"[1, 8, 9]\n"
]
],
[
[
"If the number of input arguments varies from instance to instance asterisk can be used as shown.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class NotSure:\n def __init__(self, *args):\n self.data = ''.join(list(args)) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"yz = NotSure('I', 'Do' , 'Not', 'Know', 'What', 'To','Type')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"yz.data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Where to go from here?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Practice alone can help you get the hang of python. Give your self problem statements and solve them. You can also sign up to any competitive coding platform for problem statements. The more you code the more you discover and the more you start appreciating the language.\n\n\nNow that you have been introduced to python, You can try out the different python libraries in the field of your interest. I highly recommend you to check out this curated list of Python frameworks, libraries and software http://awesome-python.com\n\n\nThe official python documentation : https://docs.python.org/2/\n\n\nYou can also check out Python practice programs written by my friend, Kartik Kannapur. Github Repo : https://github.com/rajathkumarmp/Python-Lectures \n\n\nEnjoy solving problem statements because life is short, you need python!\n\n\nPeace.\n\n\nRajath Kumar M.P ( rajathkumar dot exe at gmail dot com)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe8b69d87de341411e1277ed52cad9a72bdc307
| 19,350 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/vmd_backbone_stack_hb_1.ipynb
|
yizaochen/enmspring
|
84c9aabeb7f87eda43967d86c763b7d600986215
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/vmd_backbone_stack_hb_1.ipynb
|
yizaochen/enmspring
|
84c9aabeb7f87eda43967d86c763b7d600986215
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/vmd_backbone_stack_hb_1.ipynb
|
yizaochen/enmspring
|
84c9aabeb7f87eda43967d86c763b7d600986215
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 40.822785 | 161 | 0.681447 |
[
[
[
"from enmspring.vmddraw_bb_st_hb import DrawAgent\nimport numpy as np\nfrom enmspring.graphs_bigtraj import StackMeanModeAgent\nbig_traj_folder = '/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns'\ndrawzone_folder = '/home/yizaochen/Desktop/drawzone_temp'\ntcl_folder = '/home/yizaochen/Desktop/drawzone_temp/tcl_folder'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Part 1: Initailize Draw Agent",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"host = 'a_tract_21mer'\nd_agent = DrawAgent(host, big_traj_folder, tcl_folder)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Part 2: VMD show all-atom model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"d_agent.show_all_atom_model()\nprint('display resize 300 850')",
"vmd -gro /home/yizaochen/codes/dna_rna/all_systems/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/input/heavyatoms/bdna+bdna.perfect.noH.gro\ndisplay resize 300 850\n"
],
[
"print('mol color ColorID 16')\nprint('mol representation Licorice 0.200000 12.000000 12.000000')\nprint('mol selection resid 9')\nprint('mol material MetallicPastel')\nprint('mol addrep 0')\n\nprint('mol color ColorID 16')\nprint('mol representation Licorice 0.200000 12.000000 12.000000')\nprint('mol selection resid 34')\nprint('mol material MetallicPastel')\nprint('mol addrep 0')\n\nprint('mol delrep 3 0')\nprint('mol color ColorID 16')\nprint('mol representation CPK 0.100000 0.600000 12.000000 12.000000')\nprint('mol selection resid 33 34 35 8 9 10')\nprint('mol material Transparent')\nprint('mol addrep 0')\n\nprint('mol addrep 0')",
"mol color ColorID 16\nmol representation Licorice 0.200000 12.000000 12.000000\nmol selection resid 9\nmol material MetallicPastel\nmol addrep 0\nmol color ColorID 16\nmol representation Licorice 0.200000 12.000000 12.000000\nmol selection resid 34\nmol material MetallicPastel\nmol addrep 0\nmol delrep 3 0\nmol color ColorID 16\nmol representation CPK 0.100000 0.600000 12.000000 12.000000\nmol selection resid 33 34 35 8 9 10\nmol material Transparent\nmol addrep 0\nmol addrep 0\n"
],
[
"print('material change opacity Transparent 0.150000')",
"material change opacity Transparent 0.150000\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Part 3: Add backbone edges",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"d_agent.ini_b_agent()",
"/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/mean_mode_npy exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/0_500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/250_750/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/500_1000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/750_1250/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1000_1500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1250_1750/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1500_2000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1750_2250/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2000_2500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2250_2750/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2500_3000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2750_3250/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3000_3500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3250_3750/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3500_4000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3750_4250/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4000_4500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4250_4750/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4500_5000/pd_dfs exists\nThare are 855 nodes.\nInitialize adjacency, degree and Laplacian matrices... Done.\nFinish the setup for Laplaican matrix.\nTotal number of nodes: 855\nThere are 438 eigenvectors belonging to STRAND1.\nThere are 417 eigenvectors belonging to STRAND2.\nSum of two strands: 855\nLoad laplacian_mat from /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/mean_mode_npy/laplacian_backbone.npy\n"
],
[
"radius = 0.08\ncolorname = 'orange'\nk_criteria = 1.0\nd_agent.add_backbone_edges_trimer(radius, colorname, k_criteria)",
"source /home/yizaochen/Desktop/drawzone_temp/tcl_folder/add_backbone_edges_trimer.tcl\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Part 4: Add stack edges",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"d_agent.ini_s_agent()",
"/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/mean_mode_npy exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/0_500/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/250_750/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/500_1000/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/750_1250/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1000_1500/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1250_1750/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1500_2000/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1750_2250/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2000_2500/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2250_2750/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2500_3000/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2750_3250/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3000_3500/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3250_3750/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3500_4000/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3750_4250/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4000_4500/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4250_4750/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4500_5000/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nThare are 399 nodes.\nInitialize adjacency, degree and Laplacian matrices... Done.\nFinish the setup for Laplaican matrix.\nTotal number of nodes: 399\nThere are 210 eigenvectors belonging to STRAND1.\nThere are 189 eigenvectors belonging to STRAND2.\nSum of two strands: 399\nLoad laplacian_mat from /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/mean_mode_npy/laplacian.npy\n"
],
[
"radius = 0.05\ncolorname = 'red'\nk_criteria = 1.0\nd_agent.add_stack_edges_trimer(radius, colorname, k_criteria)",
"source /home/yizaochen/Desktop/drawzone_temp/tcl_folder/add_stack_edges_trimer.tcl\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Part 7: Add HB edges",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"d_agent.ini_h_agent()",
"/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/mean_mode_npy exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/0_500/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/0_500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/0_500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/250_750/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/250_750/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/250_750/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/500_1000/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/500_1000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/500_1000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/750_1250/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/750_1250/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/750_1250/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1000_1500/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1000_1500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1000_1500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1250_1750/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1250_1750/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1250_1750/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1500_2000/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1500_2000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1500_2000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1750_2250/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1750_2250/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1750_2250/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2000_2500/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2000_2500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2000_2500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2250_2750/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2250_2750/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2250_2750/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2500_3000/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2500_3000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2500_3000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2750_3250/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2750_3250/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2750_3250/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3000_3500/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3000_3500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3000_3500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3250_3750/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3250_3750/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3250_3750/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3500_4000/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3500_4000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3500_4000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3750_4250/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3750_4250/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3750_4250/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4000_4500/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4000_4500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4000_4500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4250_4750/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4250_4750/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4250_4750/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4500_5000/pd_dfs exists\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4500_5000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4500_5000/pd_dfs exists\nThare are 399 nodes.\nInitialize adjacency, degree and Laplacian matrices... Done.\nFinish the setup for Laplaican matrix.\nLoad laplacian_mat from /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/500ns/a_tract_21mer/mean_mode_npy/laplacian_hb.npy\n"
],
[
"radius = 0.1\ncolorname = 'blue'\nk_criteria = 0.5\nd_agent.add_hb_edges_trimer(radius, colorname, k_criteria)",
"source /home/yizaochen/Desktop/drawzone_temp/tcl_folder/add_hb_edges_trimer.tcl\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Part 8: Take Photo",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tga_name = 'bb_st_hb_trimer'\nd_agent.tachyon_take_photo_cmd(drawzone_folder, tga_name)",
"render Tachyon /home/yizaochen/Desktop/drawzone_temp/bb_st_hb_trimer \"/usr/local/lib/vmd/tachyon_LINUXAMD64\" -aasamples 12 %s -format TARGA -o %s.tga\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
cbe8bbfc436532f5ce4fccdab5cd443602ffddc0
| 123,890 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
module02/kevin/HW02_KevinEgedy.ipynb
|
kegedy/MLEARN520
|
d6f1f73a4985db217457ca53756e9828cf59d831
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
module02/kevin/HW02_KevinEgedy.ipynb
|
kegedy/MLEARN520
|
d6f1f73a4985db217457ca53756e9828cf59d831
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
module02/kevin/HW02_KevinEgedy.ipynb
|
kegedy/MLEARN520
|
d6f1f73a4985db217457ca53756e9828cf59d831
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 162.798949 | 80,152 | 0.879425 |
[
[
[
"# Decision Tree\n\nClassification And Regression Trees (CART for short) is a term introduced by [Leo Breiman](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leo_Breiman) to refer to Decision Tree algorithms that can be used for classification or regression predictive modeling problems.\n\nIn this lab assignment, you will implement various ways to calculate impurity which is used to split data in constructing the decision trees and apply the Decision Tree algorithm to solve two real-world problems: a classification one and a regression one. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# import packages\n%matplotlib inline\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom matplotlib.legend_handler import HandlerLine2D\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score\nfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\nfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error\nfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error\nfrom sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier\nfrom sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV\n\n# make this notebook's output stable across runs\nnp.random.seed(0)\n\nimport warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings(\"ignore\")\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Gini impurity and Entropy\n\n<span style=\"color:orange\">**Coding Part 1: Implement the functions to calculate Gini impurity and entropy.**</span> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Gini impurity\n\nThe CART algorithm recursively splits the training set into two subsets using a single feature k and a threshold $t_k$. The best feature and threshold are chosen to produce the purest subsets weighted by their size. **Gini impurity** measures the impurity of the data points in a set and is used to evaluate how good a split is when the CART algorithm searches for the best pair of feature and the threshold.\n\nTo compute Gini impurity for a set of items with J classes, suppose $i \\in \\{1, 2, \\dots, J\\}$ and let $p_i$ be the fraction of items labeled with class i in the set.\n\\begin{align}\nI(p) = 1 - \\sum_{i=1}^J p_i^2\n\\end{align}\n\nIn this exercise, you will implement the function to calculate gini impurity.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def gini_impurity(x):\n \"\"\"\n TODO: This function calculate the Gini impurity of an array.\n\n Args:\n x: a numpy ndarray\n \"\"\"\n classes,n_items_per_class = np.unique(x,return_counts=True)\n items = len(x)\n impurity = 1 - np.sum([\n np.square(i/items)\n for i in n_items_per_class])\n return impurity",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.testing.assert_equal(0, gini_impurity(np.array([1, 1, 1])))\nnp.testing.assert_equal(0.5, gini_impurity(np.array([1, 0, 1, 0])))\nnp.testing.assert_equal(3/4, gini_impurity(np.array(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])))\nnp.testing.assert_almost_equal(2.0/3, gini_impurity(np.array([1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3])))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Entropy\n\nAnother popular measure of impurity is called **entropy**, which measures the average information content of a message. Entropy is zero when all messages are identical. When it applied to CART, a set's entropy is zero when it contains instances of only one class. Entropy is calculated as follows:\n\\begin{align}\nI(p) = - \\sum_{i=1}^J p_i log_2{p_i}\n\\end{align}\n\nHere, you will implement entropy impurity function.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def entropy(x):\n \"\"\"\n TODO: This function calculate the entropy of an array.\n\n Args:\n x: a numpy ndarray\n \"\"\"\n classes,n_items_per_class = np.unique(x,return_counts=True)\n items = len(x)\n entropy = -1*np.sum([\n (i/items)*np.log2(i/items)\n for i in n_items_per_class])\n if entropy == -0.0 or entropy == +0.0:\n return 0\n else:\n return entropy",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.testing.assert_equal(0, entropy(np.array([1, 1, 1])))\nnp.testing.assert_equal(1.0, entropy(np.array([1, 0, 1, 0])))\nnp.testing.assert_equal(2.0, entropy(np.array(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])))\nnp.testing.assert_almost_equal(1.58496, entropy(np.array([1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3])), 4)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Decision Tree Classifier\n\n<span style=\"color:orange\">**Coding Part 2: In this exercise, we will apply the Decision Tree classifier to classify the Iris flower data.**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Iris dataset\n\nThe Iris data set contains the morphologic variation of Iris flowers of three related species (Iris setosa, Iris virginica and Iris versicolor). Four features were measured from each observation (see image below):\n- Sepal.Length: sepal length in centimeters.\n- Sepal.Width: sepal width in centimeters.\n- Petal.Length: petal length in centimeters.\n- Petal.Width: petal width in centimeters.\n\n<table>\n <tr>\n <td><img src=\"https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/56/Kosaciec_szczecinkowaty_Iris_setosa.jpg/180px-Kosaciec_szczecinkowaty_Iris_setosa.jpg\" style=\"width:250px\"></td>\n <td><img src=\"https://www.math.umd.edu/~petersd/666/html/iris_with_labels.jpg\" width=\"250px\"></td>\n <td><img src=\"https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/9f/Iris_virginica.jpg/295px-Iris_virginica.jpg\" width=\"250px\"></td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>Iris setosa</td>\n <td>Iris versicolor</td>\n <td>Iris virginica</td>\n </tr>\n</table>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# load the iris train and test data from CSV files\ntrain = pd.read_csv(\"../data/iris_train.csv\")\ntest = pd.read_csv(\"../data/iris_test.csv\")\n\ntrain_x = train.iloc[:,0:4]\ntrain_y = train.iloc[:,4]\n\ntest_x = test.iloc[:,0:4]\ntest_y = test.iloc[:,4]\n\n# print the number of instances in each class\nprint(train_y.value_counts().sort_index())\nprint(test_y.value_counts().sort_index())",
"Iris-setosa 34\nIris-versicolor 32\nIris-virginica 39\nName: species, dtype: int64\nIris-setosa 16\nIris-versicolor 18\nIris-virginica 11\nName: species, dtype: int64\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Train and visualize a simple Decision Tree",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TODO: read the scikit-learn doc on DecisionTreeClassifier and train a Decision Tree with max depth of 2\n#DecisionTreeClassifier?\ndtc = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2).fit(train_x,train_y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now let's visualize the decision tree we just trained on the iris dataset and see how it makes predictions.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from io import StringIO\nfrom IPython.display import Image \nfrom sklearn.tree import export_graphviz\nimport pydotplus\n\ndot_data = StringIO()\nfeature_names = train_x.columns\nclass_names = train_y.unique()\nclass_names.sort()\nexport_graphviz(dtc, out_file=dot_data, feature_names=feature_names, class_names=class_names, filled=True, rounded=True)\ngraph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data.getvalue()) \nImage(graph.create_png())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#from sklearn import tree\n#tree.plot_tree(dtc)\n#plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Decision trees are easy to inteprete and is often referred to as *whitebox* machine learning algorithm. Let's see how this decision tree represented above makes predictions. Suppose you find an iris flower and want to classify it into setosa, versicolor or virginica. You start at the root node (the very top node in the tree). In this node, we check if the flower's patel length is smaller than or equal to 2.35 cm. If it is, we move to the left child and predict setosa to be its class. Otherwise, we move to the right child node. Then similarly we check if the petal length is smaller than or equal to 4.95 cm. If it is, we move to its left child node and predict versicolor to be its class. Otherwise, we move to its right child and predict virginica to be its class. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Prediction with Decision tree\n\nWith this simple decision tree above, we can apply it to make predictions on the test dataset and evaluate its performance.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TODO: use the trained decision tree model to make predictions on the test data and evaluate the model performance\n# using evaluate(y, z) above.\ntest_z = dtc.predict(test_x)\nprint(\"model accuracy: {}\".format(accuracy_score(test_y, test_z)))\nprint(\"model confusion matrix:\\n {}\".format(confusion_matrix(test_y, test_z, labels=['Iris-setosa', 'Iris-versicolor', 'Iris-virginica'])))",
"model accuracy: 0.9111111111111111\nmodel confusion matrix:\n [[16 0 0]\n [ 0 17 1]\n [ 0 3 8]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Hyper-parameters\n\nHyper-parameter controls the complexity of the decision tree model. For example, the deeper the tree is, the more complex patterns the model will be able to capture. In this exercise, we train the decision trees with increasing number of maximum depth and plot its performance. We should see the accuracy of the training data increase as the tree grows deeper, but the accuracy on the test data might not as the model will eventually start to overfit and does not generalize well on the unseen test data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"max_depths = np.linspace(1, 8, 8, endpoint=True)\ntrain_results = []\ntest_results = []\n\nfor max_depth in max_depths:\n # TODO: train the decision tree model with various max_depth, make predictions and evaluate on both train and test data.\n dt = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=max_depth)\n dt.fit(train_x, train_y)\n \n train_z = dt.predict(train_x)\n train_accuracy = accuracy_score(train_y, train_z)\n train_results.append(train_accuracy)\n\n test_z = dt.predict(test_x)\n test_accuracy = accuracy_score(test_y, test_z)\n test_results.append(test_accuracy)\n\n# plot the accuracy on train and test data\nline1, = plt.plot(max_depths, train_results, 'b', label=\"Train Accuracy\")\nline2, = plt.plot(max_depths, test_results, 'r', label=\"Test Accuracy\")\nplt.legend(handler_map={line1: HandlerLine2D(numpoints=2)})\nplt.ylabel(\"Accuracy\")\nplt.xlabel(\"Max Depth\")\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Fine-tune the decision tree classifier\nDecision tree is a very powerful model with very few assumptions about the incoming training data (unlike linear models, which assume the data linear), however, it is more likely to overfit the data and won't generalize well to unseen data. To void overfitting, we need to restrict the decision tree's freedom during training via regularization (e.g. max_depth, min_sample_split, max_leaf_nodes and etc.).\n\nTo fine-tune the model and combat overfitting, use grid search with cross-validation (with the help of the GridSearchCV class) to find the best hyper-parameter settings for the DecisionTreeClassifier. In particular, we would like to fine-tune the following hyper-parameters:\n- **criteria**: this defines how we measure the quality of a split. we can choose either \"gini\" for the Gini impurity or \"entropy\" for the information gain.\n- **max_depth**: the maximum depth of the tree. This indicates how deep the tree can be. The deeper the tree, the more splits it has and it captures more information about the data. But meanwhile, deeper trees are more likely to overfit the data. For this practice, we will choose from {1, 2, 3} given there are only 4 features in the iris dataset.\n- **min_samples_split**: This value represents the minimum number of samples required to split an internal node. The smaller this value is, the deeper the tree will grow, thus more likely to overfit. On the other hand, if the value is really large (the size of the training data in the extreme case), the tree will be very shallow and could suffer from underfit. In this practice, we choose from {0.05, 0.1, 0.2}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TODO: fine-tune the model, use grid search with cross-validation.\n# cv: None, to use the default 5-fold cross validation,\nparameters = {\n 'criterion': ['gini', 'entropy'], \n 'max_depth': [1, 2, 4, 8], \n 'min_samples_split': [0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8]\n}\n\ndt = DecisionTreeClassifier()\ngrid = GridSearchCV(dt, parameters)\ngrid.fit(train_x, train_y)\n\n# summarize the results of the grid search\nprint(\"The best score is {}\".format(grid.best_score_))\nprint(\"The best hyper parameter setting is {}\".format(grid.best_params_))",
"The best score is 0.9619047619047618\nThe best hyper parameter setting is {'criterion': 'gini', 'max_depth': 4, 'min_samples_split': 0.05}\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Prediction and Evaluation\n\nNow we have a fine-tuned decision tree classifier based on the training data, let's apply this model to make predictions on the test data and evaluate its performance.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"test_z = grid.predict(test_x)\n\nprint(\"model accuracy: {}\".format(accuracy_score(test_y, test_z)))\nprint(\"model confusion matrix:\\n {}\".format(confusion_matrix(test_y, test_z, labels=['Iris-setosa', 'Iris-versicolor', 'Iris-virginica'])))",
"model accuracy: 0.9777777777777777\nmodel confusion matrix:\n [[16 0 0]\n [ 0 17 1]\n [ 0 0 11]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Decision Tree Regressor\n\n<span style=\"color:orange\">**Coding Part 3: In this exercise, we will apply the Decision Tree classifier to predict the California housing prices.**</span> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### California Housing Dataset\n\nThe California Housing dataset appeared in a 1997 paper titled Sparse Spatial Autoregressions by Pace, R. Kelley and Ronald Barry, published in the Statistics and Probability Letters journal. They built it using the 1990 California census data. It contains one row per census block group. A block group is the smallest geographical unit for which the U.S. Census Bureau publishes sample data (a block group typically has a population of 600 to 3,000 people). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load train and test data from CSV files.\ntrain = pd.read_csv(\"../data/housing_train.csv\")\ntest = pd.read_csv(\"../data/housing_test.csv\")\n\ntrain_x = train.iloc[:,0:8]\ntrain_y = train.iloc[:,8]\n\ntest_x = test.iloc[:,0:8]\ntest_y = test.iloc[:,8]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_x.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# TODO: fine-tune the model, use grid search with cross-validation.\n# cv: None, to use the default 5-fold cross validation,\nparameters = {\n 'max_depth': [4, 8, 16, 32], \n 'min_samples_split': [0.001, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2],\n 'max_features': [2, 4, 8]\n}\n\ndt = DecisionTreeClassifier()\ngrid = GridSearchCV(dt, parameters)\ngrid.fit(train_x, train_y)\n\n# summarize the results of the grid search\nprint(\"The best score is {}\".format(grid.best_score_))\nprint(\"The best hyper parameter setting is {}\".format(grid.best_params_))",
"The best score is 0.049211099014158224\nThe best hyper parameter setting is {'max_depth': 8, 'max_features': 2, 'min_samples_split': 0.1}\n"
],
[
"# Use the fine-tuned model to make predictions on the test data\ntest_z = grid.predict(test_x)\n\nprint(\"model Root Mean Squared Error: {}\".format(round(np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(test_y, test_z)))))\nprint(\"model Mean Absolute Error: {}\".format(round(mean_absolute_error(test_y, test_z))))",
"model Root Mean Squared Error: 206959\nmodel Mean Absolute Error: 157456\n"
],
[
"# Compare to classifier with default hyper paramters\ntest_z = dt.fit(train_x, train_y).predict(test_x)\n\nprint(\"model accuracy: {}\".format(accuracy_score(test_y, test_z)))\nprint(\"model Root Mean Squared Error: {}\".format(round(np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(test_y, test_z)))))\nprint(\"model Mean Absolute Error: {}\".format(round(mean_absolute_error(test_y, test_z))))",
"model accuracy: 0.025839793281653745\nmodel Root Mean Squared Error: 82463\nmodel Mean Absolute Error: 54655\n"
]
],
[
[
"### End of ML 310 Lab Assignment 2\n---\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<p><b>Conceptual Overview</b></p>\n<p>\nIn this lesson, I learned methods of measuring impurity that separate data into leaves. I also learned how to tune these models such that it doesn't overfit the training data and have large variance. Some of the most common hyper parameters to tune are max depth, min samples to split on, and max features.\n \nUsing grid search, model performance can improve drastically. In the first example the test score improved from %96.2 to 97.8%. It should also be noted, that training time for decision trees can be costly! Also, be cautious when using with a mostly numerical dataset.\n</p>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe8c1482d7de645a43e8f1c4d25b9e913b520fc
| 5,669 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
tsa/src/jupyter/python/foundations/probability-theory.ipynb
|
mikimaus78/ml_monorepo
|
b2c2627ff0e86e27f6829170d0dac168d8e5783b
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 51 |
2019-02-01T19:43:37.000Z
|
2022-03-16T09:07:03.000Z
|
tsa/src/jupyter/python/foundations/probability-theory.ipynb
|
mikimaus78/ml_monorepo
|
b2c2627ff0e86e27f6829170d0dac168d8e5783b
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 2 |
2019-02-23T18:54:22.000Z
|
2019-11-09T01:30:32.000Z
|
tsa/src/jupyter/python/foundations/probability-theory.ipynb
|
mikimaus78/ml_monorepo
|
b2c2627ff0e86e27f6829170d0dac168d8e5783b
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 35 |
2019-02-08T02:00:31.000Z
|
2022-03-01T23:17:00.000Z
| 28.20398 | 261 | 0.527959 |
[
[
[
"# Probability theory\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Random experiment\n\nWhen we toss an unbiased coin, we say that it lands heads up with probability $\\frac{1}{2}$ and tails up with probability $\\frac{1}{2}$.\n\nSuch a coin toss is an example of a **random experiment** and the set of **outcomes** of this random experiment is the **sample space** $\\Omega = \\{h, t\\}$, where $h$ stands for \"heads\" and $t$ stands for tails.\n\nWhat if we toss a coin twice? We could view the two coin tosses as a single random experiment with the sample space $\\Omega = \\{hh, ht, th, tt\\}$, where $ht$ (for example) denotes \"heads on the first toss\", \"tails on the second toss\".\n\nWhat if, instead of tossing a coin, we roll a die? The sample space for this random experiment is $\\Omega = \\{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6\\}$.\n\n## Events\n\nAn **event**, then, is a subset of the sample space. In our example of the two consecutive coin tosses, getting heads on all coin tosses is an event:\n$$A = \\text{\"getting heads on all coin tosses\"} = \\{hh\\} \\subseteq \\{hh, ht, th, tt\\} = \\Omega.$$\n\nGetting distinct results on the two coin tosses is also an event:\n$$D = \\{ht, th\\} \\subseteq \\{hh, ht, th, tt\\} = \\Omega.$$\n\nWe can simulate a coin toss in Python as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nnp.random.seed(42)\nnp.random.randint(0, 2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"(Let's say 0 is heads and 1 is tails.)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Similarly, in our roll-of-a-die example, the following are all events:\n$$S = \\text{\"six shows up\"} = \\{6\\} \\subseteq \\{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6\\} = \\Omega,$$\n$$E = \\text{\"even number shows up\"} = \\{2, 4, 6\\} \\subseteq \\{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6\\} = \\Omega,$$\n$$O = \\text{\"odd number shows up\"} = \\{1, 3, 5\\} \\subseteq \\{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6\\} = \\Omega.$$\nThe empty set, $\\emptyset = \\{\\}$, represents the **impossible event**, whereas the sample space $\\Omega$ itself represents the **certain event**: one of the numbers $1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6$ always occurs when a die is rolled, so $\\Omega$ always occurs.\n\nWe can simulate the roll of a die in Python as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.random.randint(1, 7)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If we get 4, say, $S$ has not occurred, since $4 \\notin S$; $E$ has occurred, since $4 \\in E$; $O$ has not occurred, since $4 \\notin O$.\n\nWhen all outcomes are equally likely, and the sample space is finite, the probability of an event $A$ is given by $$\\mathbb{P}(A) = \\frac{|A|}{|\\Omega|},$$ where $|\\cdot|$ denotes the number of elements in a given set.\n\nThus, the probability of the event $E$, \"even number shows up\" is equal to $$\\mathbb{P}(A) = \\frac{|E|}{|\\Omega|} = \\frac{3}{6} = \\frac{1}{2}.$$\n\nIf Python's random number generator is decent enough, we should get pretty close to this number by simulating die rolls:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"outcomes = np.random.randint(1, 7, 100)\nlen([x for x in outcomes if x % 2 == 0]) / len(outcomes)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here we have used 100 simulated \"rolls\". If we used, 1000000, say, we would get even closer to $\\frac{1}{2}$:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"outcomes = np.random.randint(1, 7, 1000000)\nlen([x for x in outcomes if x % 2 == 0]) / len(outcomes)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
cbe8c55cbaa0c9cc51bbc0c09f6268e6191afbed
| 29,528 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
data/word2vec/word2vec-local-train.ipynb
|
NikosKolitsas/twitter_sentiment_analysis
|
357ee270d911c62f978897ac606e6b39300fa815
|
[
"Apache-1.1"
] | null | null | null |
data/word2vec/word2vec-local-train.ipynb
|
NikosKolitsas/twitter_sentiment_analysis
|
357ee270d911c62f978897ac606e6b39300fa815
|
[
"Apache-1.1"
] | null | null | null |
data/word2vec/word2vec-local-train.ipynb
|
NikosKolitsas/twitter_sentiment_analysis
|
357ee270d911c62f978897ac606e6b39300fa815
|
[
"Apache-1.1"
] | null | null | null | 36.680745 | 176 | 0.617448 |
[
[
[
"# Train word2vec locally\n\nThis allows a smart initialization of our neural net's word embeddings.\nIt seems that initializing the embeddings by training them locally, as opposed to using pre-trained word2vec embeddings (available online) can lead to better performance.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\nimport sys\nprint(sys.executable)",
"/Users/andrei/anaconda3/envs/cil/bin/python\n"
],
[
"from gensim.models.word2vec import Word2Vec\n\nimport logging\nlogging.basicConfig(format='%(asctime)s : %(levelname)s : %(message)s', level=logging.INFO)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"TRAIN = os.path.join('..', 'train')\nTEST = os.path.join('..', 'test')\nPOS_TWEET_FILE = os.path.join(TRAIN, 'train_pos_full.txt')\nNEG_TWEET_FILE = os.path.join(TRAIN, 'train_neg_full.txt')\nTEST_TWEET_FILE = os.path.join(TEST, 'test_data.txt')\nEMBEDDING_SIZE = 300",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def read_tweets(fname):\n \"\"\"Read the tweets in the given file.\n \n Returns a 2d array where every row is a tweet, split into words.\n \"\"\"\n with open(fname, 'r') as f:\n return [l.split() for l in f.readlines()]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pos_tweets = read_tweets(POS_TWEET_FILE)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"neg_tweets = read_tweets(NEG_TWEET_FILE)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test_tweets = read_tweets(TEST_TWEET_FILE)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sentences = pos_tweets + neg_tweets + test_tweets\nprint(len(sentences))",
"2510000\n"
],
[
"tokens = [item.strip() for sentence in sentences for item in sentence]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Check for Nikos's 1st stage substitutions.\nassert '<num>' in tokens",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Another sanity check\nprint(len([t for t in tokens if 'bootstrap' == t]))",
"10\n"
],
[
"# Download this for testing: https://github.com/arfon/word2vec/blob/master/questions-words.txt\n# Highly recommended!\n\nquestion_file = \"questions-words.txt\"\n\ndef eval_embeddings(model):\n accuracy_results = model.accuracy(question_file)\n summary = accuracy_results[-1]\n assert summary['section'] == 'total'\n incorrect = summary['incorrect']\n correct = summary['correct']\n\n incorrect_n = len(incorrect)\n correct_n = len(correct)\n\n acc = correct_n / incorrect_n\n return acc, correct_n, incorrect_n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"WORKERS = 8\n# Note: Moises's team uses size=200 as of June 13.\n# See: https://groups.google.com/forum/#!msg/gensim/ggCHGncd5rU/Z_pQDD69AAAJ\n# for some parameter hints.\nmodel = Word2Vec(sentences, size=EMBEDDING_SIZE, window=10, min_count=5, workers=WORKERS)# , alpha=0.05, cbow_mean=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Yet another sanity check.\nmodel.vocab['bootstrap'].count",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Should be queen\nmodel.most_similar(positive=['woman', 'king'], negative=['man'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Should be germany\nmodel.most_similar(positive=['france', 'berlin'], negative=['paris'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.doesnt_match(\"breakfast cereal dinner lunch\".split())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.estimate_memory()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# A few more sanity checks\nprint(model.similarity('woman', 'man'))\nprint(model.similarity('woman', 'coffee'))\nprint(model.similarity('woman', 'penis'))\nprint(model.similarity('woman', 'football'))",
"0.52955911881\n0.114179236087\n0.268376207035\n0.0404427249823\n"
],
[
"print(model.similarity('car','man'))\nprint(model.similarity('car','truck'))",
"0.192689974775\n0.640076543279\n"
],
[
"acc, correct_n, incorrect_n = eval_embeddings(model)\nprint(\"{0:5.3f} accuracy; Analogies: {1} correct, {2} incorrect\".format(\n acc, correct_n, incorrect_n))",
"0.407 accuracy; Analogies: 3053 correct, 7493 incorrect\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Accuracies (full Twitter data)\n * Vanilla (size=225, window=5, min_count=5): 0.319 accuracy; Analogies: 2233 correct, 7004 incorrect\n * (size=300, window=5, min_count=5): 0.337 accuracy; Analogies: 2329 correct, 6908 incorrect\n * (size=500, window=5, min_count=5): 0.330 accuracy; Analogies: 2292 correct, 6945 incorrect\n * (size=300, window=10, min_count=5): 0.346 accuracy; Analogies: 2374 correct, 6863 incorrect\n * (size=300, window=15, min_count=5): 0.342 accuracy; Analogies: 2356 correct, 6881 incorrect\n * (size=400, window=10, min_count=5): 0.341 accuracy; Analogies: 2340 correct, 6870 incorrect\n\n### Accuracties (full Twitter data + Nikos 1st stage preprocessing)\n * (size=200, window=10, min_count=5): 0.327 accuracy; Analogies: 2316 correct, 7093 incorrect\n * (size=225, window=10, min_count=5): 0.331 accuracy; Analogies: 2342 correct, 7067 incorrect\n * (size=250, window=10, min_count=5): 0.330 accuracy; Analogies: 2336 correct, 7073 incorrect\n * (size=275, window=10, min_count=5): 0.337 accuracy; Analogies: 2374 correct, 7035 incorrect\n * (size=300, window=10, min_count=5): 0.334 accuracy; Analogies: 2355 correct, 7054 incorrect\n * (size=325, window=10, min_count=5): 0.334 accuracy; Analogies: 2356 correct, 7053 incorrect\n * (size=350, window=10, min_count=5): 0.330 accuracy; Analogies: 2334 correct, 7075 incorrect\n * (size=400, window=10, min_count=5): 0.321 accuracy; Analogies: 2289 correct, 7120 incorrect\n \n### After fixing Andrei's retarded bug\n * (size=300, window=10, min_count=5): 0.438 accuracy; Analogies: 3071 correct, 7019 incorrect\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\"Embedding dimensionality: {0}\".format(EMBEDDING_SIZE))",
"Embedding dimensionality: 300\n"
],
[
"fname = \"./word2vec-local-gensim-{0}.bin\".format(EMBEDDING_SIZE)\nprint(\"Writing embeddings to file {0}.\".format(fname))\nmodel.save(fname)\nprint(\"Done! Happy neural networking!\")",
"Writing embeddings to file ./word2vec-local-gensim-300.bin.\nDone! Happy neural networking!\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Some experimentation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"emb_sizes = [225, 250, 275, 300, 325, 350]\n\nfor w_size in [5, 8, 10, 12]:\n for emb_size in emb_sizes:\n print(\"Computing embeddings of size {0} and window {1}...\".format(emb_size, w_size))\n model = Word2Vec(sentences, size=emb_size, window=w_size, min_count=5, workers=4)\n print(\"Evaluating embeddings of size {0}...\".format(emb_size))\n acc, correct_n, incorrect_n = eval_embeddings(model)\n print(\"Size {3}; wsize {4}: {0:5.3f} accuracy; Analogies: {1} correct, {2} incorrect\".format(\n acc, correct_n, incorrect_n, emb_size, w_size))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"```\nComputing embeddings of size 225 and window 5...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 225...\nSize 225; wsize 5: 0.388 accuracy; Analogies: 2948 correct, 7598 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 250 and window 5...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 250...\nSize 250; wsize 5: 0.381 accuracy; Analogies: 2907 correct, 7639 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 275 and window 5...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 275...\nSize 275; wsize 5: 0.381 accuracy; Analogies: 2909 correct, 7637 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 300 and window 5...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 300...\nSize 300; wsize 5: 0.392 accuracy; Analogies: 2968 correct, 7578 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 325 and window 5...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 325...\nSize 325; wsize 5: 0.393 accuracy; Analogies: 2977 correct, 7569 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 350 and window 5...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 350...\nSize 350; wsize 5: 0.391 accuracy; Analogies: 2967 correct, 7579 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 225 and window 8...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 225...\nSize 225; wsize 8: 0.408 accuracy; Analogies: 3055 correct, 7491 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 250 and window 8...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 250...\nSize 250; wsize 8: 0.410 accuracy; Analogies: 3064 correct, 7482 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 275 and window 8...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 275...\nSize 275; wsize 8: 0.402 accuracy; Analogies: 3026 correct, 7520 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 300 and window 8...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 300...\nSize 300; wsize 8: 0.410 accuracy; Analogies: 3069 correct, 7477 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 325 and window 8...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 325...\nSize 325; wsize 8: 0.405 accuracy; Analogies: 3039 correct, 7507 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 350 and window 8...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 350...\nSize 350; wsize 8: 0.407 accuracy; Analogies: 3049 correct, 7497 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 225 and window 10...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 225...\nSize 225; wsize 10: 0.406 accuracy; Analogies: 3046 correct, 7500 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 250 and window 10...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 250...\nSize 250; wsize 10: 0.417 accuracy; Analogies: 3102 correct, 7444 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 275 and window 10...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 275...\nSize 275; wsize 10: 0.411 accuracy; Analogies: 3070 correct, 7476 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 300 and window 10...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 300...\nSize 300; wsize 10: 0.417 accuracy; Analogies: 3106 correct, 7440 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 325 and window 10...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 325...\nSize 325; wsize 10: 0.411 accuracy; Analogies: 3071 correct, 7475 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 350 and window 10...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 350...\nSize 350; wsize 10: 0.404 accuracy; Analogies: 3035 correct, 7511 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 225 and window 12...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 225...\nSize 225; wsize 12: 0.399 accuracy; Analogies: 3008 correct, 7538 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 250 and window 12...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 250...\nSize 250; wsize 12: 0.419 accuracy; Analogies: 3115 correct, 7431 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 275 and window 12...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 275...\nSize 275; wsize 12: 0.423 accuracy; Analogies: 3134 correct, 7412 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 300 and window 12...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 300...\nSize 300; wsize 12: 0.417 accuracy; Analogies: 3104 correct, 7442 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 325 and window 12...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 325...\nSize 325; wsize 12: 0.428 accuracy; Analogies: 3162 correct, 7384 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 350 and window 12...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 350...\nSize 350; wsize 12: 0.413 accuracy; Analogies: 3080 correct, 7466 incorrect\n\nComputing embeddings of size 225 and window 13...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 225...\nSize 225; wsize 13: 0.415 accuracy; Analogies: 3094 correct, 7452 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 250 and window 13...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 250...\nSize 250; wsize 13: 0.412 accuracy; Analogies: 3078 correct, 7468 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 275 and window 13...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 275...\nSize 275; wsize 13: 0.420 accuracy; Analogies: 3121 correct, 7425 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 300 and window 13...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 300...\nSize 300; wsize 13: 0.410 accuracy; Analogies: 3067 correct, 7479 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 325 and window 13...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 325...\nSize 325; wsize 13: 0.411 accuracy; Analogies: 3074 correct, 7472 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 350 and window 13...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 350...\nSize 350; wsize 13: 0.426 accuracy; Analogies: 3150 correct, 7396 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 225 and window 14...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 225...\nSize 225; wsize 14: 0.421 accuracy; Analogies: 3125 correct, 7421 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 250 and window 14...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 250...\nSize 250; wsize 14: 0.426 accuracy; Analogies: 3150 correct, 7396 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 275 and window 14...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 275...\nSize 275; wsize 14: 0.422 accuracy; Analogies: 3132 correct, 7414 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 300 and window 14...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 300...\nSize 300; wsize 14: 0.426 accuracy; Analogies: 3149 correct, 7397 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 325 and window 14...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 325...\nSize 325; wsize 14: 0.418 accuracy; Analogies: 3107 correct, 7439 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 350 and window 14...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 350...\nSize 350; wsize 14: 0.426 accuracy; Analogies: 3150 correct, 7396 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 225 and window 15...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 225...\nSize 225; wsize 15: 0.421 accuracy; Analogies: 3124 correct, 7422 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 250 and window 15...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 250...\nSize 250; wsize 15: 0.431 accuracy; Analogies: 3174 correct, 7372 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 275 and window 15...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 275...\nSize 275; wsize 15: 0.427 accuracy; Analogies: 3154 correct, 7392 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 300 and window 15...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 300...\nSize 300; wsize 15: 0.432 accuracy; Analogies: 3183 correct, 7363 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 325 and window 15...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 325...\nSize 325; wsize 15: 0.434 accuracy; Analogies: 3191 correct, 7355 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 350 and window 15...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 350...\nSize 350; wsize 15: 0.441 accuracy; Analogies: 3227 correct, 7319 incorrect\n\nComputing embeddings of size 225 and window 16...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 225...\nSize 225; wsize 16: 0.409 accuracy; Analogies: 3063 correct, 7483 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 250 and window 16...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 250...\nSize 250; wsize 16: 0.423 accuracy; Analogies: 3133 correct, 7413 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 275 and window 16...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 275...\nSize 275; wsize 16: 0.413 accuracy; Analogies: 3084 correct, 7462 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 300 and window 16...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 300...\nSize 300; wsize 16: 0.421 accuracy; Analogies: 3126 correct, 7420 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 325 and window 16...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 325...\nSize 325; wsize 16: 0.423 accuracy; Analogies: 3133 correct, 7413 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 350 and window 16...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 350...\nSize 350; wsize 16: 0.421 accuracy; Analogies: 3122 correct, 7424 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 225 and window 17...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 225...\nSize 225; wsize 17: 0.404 accuracy; Analogies: 3034 correct, 7512 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 250 and window 17...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 250...\nSize 250; wsize 17: 0.429 accuracy; Analogies: 3168 correct, 7378 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 275 and window 17...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 275...\nSize 275; wsize 17: 0.436 accuracy; Analogies: 3204 correct, 7342 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 300 and window 17...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 300...\nSize 300; wsize 17: 0.427 accuracy; Analogies: 3158 correct, 7388 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 325 and window 17...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 325...\nSize 325; wsize 17: 0.429 accuracy; Analogies: 3166 correct, 7380 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 350 and window 17...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 350...\nSize 350; wsize 17: 0.417 accuracy; Analogies: 3106 correct, 7440 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 225 and window 18...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 225...\nSize 225; wsize 18: 0.427 accuracy; Analogies: 3156 correct, 7390 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 250 and window 18...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 250...\nSize 250; wsize 18: 0.417 accuracy; Analogies: 3105 correct, 7441 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 275 and window 18...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 275...\nSize 275; wsize 18: 0.428 accuracy; Analogies: 3160 correct, 7386 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 300 and window 18...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 300...\nSize 300; wsize 18: 0.421 accuracy; Analogies: 3126 correct, 7420 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 325 and window 18...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 325...\nSize 325; wsize 18: 0.434 accuracy; Analogies: 3193 correct, 7353 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 350 and window 18...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 350...\nSize 350; wsize 18: 0.418 accuracy; Analogies: 3107 correct, 7439 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 225 and window 19...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 225...\nSize 225; wsize 19: 0.417 accuracy; Analogies: 3105 correct, 7441 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 250 and window 19...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 250...\nSize 250; wsize 19: 0.421 accuracy; Analogies: 3125 correct, 7421 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 275 and window 19...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 275...\nSize 275; wsize 19: 0.439 accuracy; Analogies: 3219 correct, 7327 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 300 and window 19...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 300...\nSize 300; wsize 19: 0.438 accuracy; Analogies: 3212 correct, 7334 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 325 and window 19...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 325...\nSize 325; wsize 19: 0.426 accuracy; Analogies: 3153 correct, 7393 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 350 and window 19...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 350...\nSize 350; wsize 19: 0.428 accuracy; Analogies: 3161 correct, 7385 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 225 and window 20...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 225...\nSize 225; wsize 20: 0.429 accuracy; Analogies: 3166 correct, 7380 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 250 and window 20...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 250...\nSize 250; wsize 20: 0.424 accuracy; Analogies: 3139 correct, 7407 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 275 and window 20...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 275...\nSize 275; wsize 20: 0.427 accuracy; Analogies: 3155 correct, 7391 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 300 and window 20...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 300...\nSize 300; wsize 20: 0.419 accuracy; Analogies: 3116 correct, 7430 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 325 and window 20...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 325...\nSize 325; wsize 20: 0.438 accuracy; Analogies: 3211 correct, 7335 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 350 and window 20...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 350...\nSize 350; wsize 20: 0.409 accuracy; Analogies: 3061 correct, 7485 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 225 and window 21...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 225...\nSize 225; wsize 21: 0.414 accuracy; Analogies: 3088 correct, 7458 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 250 and window 21...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 250...\nSize 250; wsize 21: 0.415 accuracy; Analogies: 3094 correct, 7452 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 275 and window 21...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 275...\nSize 275; wsize 21: 0.415 accuracy; Analogies: 3093 correct, 7453 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 300 and window 21...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 300...\nSize 300; wsize 21: 0.438 accuracy; Analogies: 3213 correct, 7333 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 325 and window 21...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 325...\nSize 325; wsize 21: 0.431 accuracy; Analogies: 3178 correct, 7368 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 350 and window 21...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 350...\nSize 350; wsize 21: 0.429 accuracy; Analogies: 3164 correct, 7382 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 225 and window 22...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 225...\nSize 225; wsize 22: 0.424 accuracy; Analogies: 3142 correct, 7404 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 250 and window 22...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 250...\nSize 250; wsize 22: 0.410 accuracy; Analogies: 3066 correct, 7480 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 275 and window 22...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 275...\nSize 275; wsize 22: 0.423 accuracy; Analogies: 3134 correct, 7412 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 300 and window 22...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 300...\nSize 300; wsize 22: 0.427 accuracy; Analogies: 3158 correct, 7388 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 325 and window 22...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 325...\nSize 325; wsize 22: 0.424 accuracy; Analogies: 3138 correct, 7408 incorrect\nComputing embeddings of size 350 and window 22...\nEvaluating embeddings of size 350...\nSize 350; wsize 22: 0.426 accuracy; Analogies: 3151 correct, 7395 incorrect\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe8d7830fb0df205902208024cfbb3f697af219
| 30,940 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
05-machine-learning-nao-tabular/02-texto/02_NLP_02/nlp_2.ipynb
|
abefukasawa/datascience_course
|
919c715598fa9529703ba340039ad82b23221a0e
|
[
"MIT"
] | 331 |
2019-01-26T21:11:45.000Z
|
2022-03-02T11:35:16.000Z
|
05-machine-learning-nao-tabular/02-texto/02_NLP_02/nlp_2.ipynb
|
abefukasawa/datascience_course
|
919c715598fa9529703ba340039ad82b23221a0e
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2019-11-02T22:32:13.000Z
|
2020-04-13T10:31:11.000Z
|
05-machine-learning-nao-tabular/02-texto/02_NLP_02/nlp_2.ipynb
|
sn3fru/datascience_course
|
ee0a505134383034e09020d9b1de18904d9b2665
|
[
"MIT"
] | 88 |
2019-01-25T16:53:47.000Z
|
2022-03-03T00:05:08.000Z
| 29.836066 | 432 | 0.567162 |
[
[
[
"# NLP 2 - Pré Processamento de Textos e Modelos Modernos\n\nFala galera! Na aula passada, tivemos uma introdução ao mundo de NLP: o modelo BoW (Bag of Words) e o algoritmo TF-iDF. Embora muito práticos, observamos alguns fenômenos de NLP e dessas técnicas:\n - NLP é naturalmente um problema de grandes dimensionalidades, o que nos leva a cair no caso de \"curse of dimensionality\"\n - O modelo BoW, mesmo com o conceito de N-Grams, tem dificuldades para carregar informação sequencial de palavras, uma vez que ele só pega sequências de termos, não de conceitos\n - Entender e implementar conceitos de linguística é importantíssimo para que o processamento-modelagem produza uma boa performance. Dessa forma, NLP é norteado pelo entendimento linguístico\n<br>\n\nDito isso, hoje no mundo de NLP temos ferramentas, approaches e tecnologias que implementam de formas mais eficientes conceitos linguísticos para que possamos realizar melhores modelagens. Nessa aula, veremos essa técnicas com as bibliotecas SpaCy, gensim e a arquitetura word2vec! Para quem não tem SpaCy ou gensim no computador, retire o comentário e rode as células abaixo:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# ! pip install spacy",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# ! pip install gensim",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## SpaCy Basics",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import spacy\n\n# Precisamos instanciar um objeto de NLP especificando qual linguagem ele utilizará.\n# No caso, vamos começar com português\nnlp = spacy.load('pt')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Opa, deu um erro no comando acima! O SpaCy precisa não somente ser instalado, mas seus pacotes linguísticos precisam ser baixados também. Retire os comentários e rode as células abaixo para fazer o download dos pacotes English e Português",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# ! python -m spacy download en",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# ! python -m spacy download pt",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Ok! Agora tudo certo para começarmos a mexer com o SpaCy. Vamos instanciar a ferramenta linguística para português",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"nlp = spacy.load('pt')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Vamos criar um documento para testes e demonstrações do SpaCy!\n# É muito importante que os textos passados estejam em encoding unicode,\n# por isso a presença do u antes da string\ndoc = nlp(u'Você encontrou o livro que eu te falei, Carla?')\ndoc.text.split()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Ok, temos um problema de pontuação aqui: o método split (ou REGEX em geral) não entende que a vírgula é uma entidade - vamos chamar essas entidades de tokens. Assim, não faz muito sentir quebrar o texto com esses métodos. Vamos utilizar uma compreensão de lista pra isso. O `nlp` consegue entender a diferença entre eles e, portanto, quando usamos os tokens dentro da estrutura do documento, temos uma divisão mais coerente:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tokens = [token for token in doc]\ntokens",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Para extrair as strings de cada token, utilizamos `orth_`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"[token.orth_ for token in doc]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Podemos ver que o SpaCy consegue entender a diferença de pontuações e palavras de fato:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"[token.orth_ for token in doc if not token.is_punct]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Um conceito muito importante de NLP é o de similaridade. Como medir se 2 palavras carregam informações similares? Isso pode ser interessante para, por exemplo, compactarmos nosso texto, ou ainda para descobrir o significado de palavras, termos e gírias desconhecidas. Para isso, utilizamos o método `.similarity()` de um token em relação ao outro:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(tokens[0].similarity(tokens[5]))\nprint(tokens[0].similarity(tokens[3]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Na célula abaixo, sinta-se livre para realizar os teste que quiser com similaridades em português!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Quando realizamos o load de um pacote linguístico, também estamos carregando noções da estrutura gramatical, sintática e sintagmática da língua. Podemos, por exemplo, utilizar o atributo `.pos_`, de Part of Speech (POS), para extrair a função de cada token na frase: ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"[(token.orth_, token.pos_) for token in doc]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Ok, mas como lidamos com o problema da dimensionalidade? Podemos utilizar 2 conceitos chamados **lemmatization** e **stemming**. A lemmatization em lingüística é o processo de agrupar as formas flexionadas de uma palavra para que elas possam ser analisadas como um único item, identificado pelo lema da palavra ou pela forma de dicionário. Já o stemming busca o radical da palavra:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
" [token.lemma_ for token in doc if token.pos_ == 'VERB'] # lemmatization",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Na célula abaixo, crie um novo doc e aplique uma lemmatization em seus verbos:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"doc = nlp(u'encontrei, encontraram, encontrarão, encontrariam')\n[token.lemma_ for token in doc if token.pos_ == 'VERB'] # lemmatization",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"doc = nlp(u'encontrar encontrei')\ntokens = [token for token in doc]\ntokens[0].is_ancestor(tokens[1]) #checagem de radicais",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Por fim, queremos extrair entidades de uma frase. Entenda entidades como personagens num doc. Podemos acessar as entidades de uma frase ao chamar `ents` de um doc:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"doc = nlp(u'Machado de Assis um dos melhores escritores do Brasil, foi o primeiro presidente da Academia Brasileira de Letras')\ndoc.ents",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Ao analisar as entidades de uma frase, podemos inclusive entender que tipo de entidade ela pertence:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"[(entity, entity.label_) for entity in doc.ents]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"wiki_obama = \"\"\"Barack Obama is an American politician who served as\n the 44th President of the United States from 2009 to 2017. He is the first\n African American to have served as president,\n as well as the first born outside the contiguous United States.\"\"\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"E isso funciona para cada pacote linguístico que você utilizar:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"nlp = spacy.load('en')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"nlp_obama = nlp(wiki_obama)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"[(i, i.label_) for i in nlp_obama.ents]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## SpaCy + Scikit Learn\n\nPara demonstrar como realizar o pré-processamento de um datasetv linguístico e como conectar SpaCy e sklearn, vamos fazer um reconhecedor de emoções simples:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# stopwords são tokens de uma língua que carregam pouca informação, como conectores e pontuações.\n# Fique atento ao utilizar isso! Por exemplo, @ e # são potnuações importantíssimas num case\n# utilizando dados do Twitter\nfrom sklearn.feature_extraction.stop_words import ENGLISH_STOP_WORDS as stopwords \n\n# Nosso modelo BoW\nfrom sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer \nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score \nfrom sklearn.base import TransformerMixin \nfrom sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline\nfrom sklearn.svm import LinearSVC\n\nimport string\npunctuations = string.punctuation\n\nfrom spacy.lang.en import English\nparser = English()\n\n# Custom transformer using spaCy \nclass predictors(TransformerMixin):\n def transform(self, X, **transform_params):\n return [clean_text(text) for text in X]\n def fit(self, X, y=None, **fit_params):\n return self\n def get_params(self, deep=True):\n return {}\n\n# Vamos limpar o texto jogando tudo para minúsculas\ndef clean_text(text): \n return text.strip().lower()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Vamos criar uma função que tokeniza nosso dataset já tratando-o com lemmatization e removendo stopwords:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def spacy_tokenizer(sentence):\n tokens = parser(sentence)\n tokens = [tok.lemma_.lower().strip() if tok.lemma_ != \"-PRON-\" else tok.lower_ for tok in tokens]\n tokens = [tok for tok in tokens if (tok not in stopwords and tok not in punctuations)] \n return tokens\n\n# create vectorizer object to generate feature vectors, we will use custom spacy’s tokenizer\nvectorizer = CountVectorizer(tokenizer = spacy_tokenizer, ngram_range=(1,2)) \nclassifier = LinearSVC()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create the pipeline to clean, tokenize, vectorize, and classify \npipe = Pipeline([(\"cleaner\", predictors()),\n ('vectorizer', vectorizer),\n ('classifier', classifier)])\n\n# Load sample data\ntrain = [('I love this sandwich.', 'pos'), \n ('this is an amazing place!', 'pos'),\n ('I feel very good about these beers.', 'pos'),\n ('this is my best work.', 'pos'),\n (\"what an awesome view\", 'pos'),\n ('I do not like this restaurant', 'neg'),\n ('I am tired of this stuff.', 'neg'),\n (\"I can't deal with this\", 'neg'),\n ('he is my sworn enemy!', 'neg'), \n ('my boss is horrible.', 'neg')] \ntest = [('the beer was good.', 'pos'), \n ('I do not enjoy my job', 'neg'),\n (\"I ain't feelin dandy today.\", 'neg'),\n (\"I feel amazing!\", 'pos'),\n ('Gary is a good friend of mine.', 'pos'),\n (\"I can't believe I'm doing this.\", 'neg')]\n\n# Create model and measure accuracy\npipe.fit([x[0] for x in train], [x[1] for x in train]) \npred_data = pipe.predict([x[0] for x in test]) \nfor (sample, pred) in zip(test, pred_data):\n print(sample, pred)\nprint(\"Accuracy:\", accuracy_score([x[1] for x in test], pred_data))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Nice! Conseguimos conectar SpaCy e sklearn para uma ferramenta de análise de sentimentos simples!. Agora vamos para um problema mais complexo:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<img src=\"imgs/simpsons.jpg\" align=\"left\" width=\"60%\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Simpsons Dataset\n\nEsse __[dataset](https://www.kaggle.com/wcukierski/the-simpsons-by-the-data/downloads/simpsons_script_lines.csv/1)__ é bem famoso em NLP, ele contém personagens, localizações, falas e outras infos de mais 600+ episódios de Simpsons! Vamos construir um classificador que consegue entender a linguagem de Simpsons e realizar operações linguísticas nela.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import re # For preprocessing\nimport pandas as pd \nfrom time import time \nfrom collections import defaultdict # For word frequency\n\nimport logging # Setting up the loggings to monitor gensim. DS SOBREVIVE DE LOGS\nlogging.basicConfig(format=\"%(levelname)s - %(asctime)s: %(message)s\", datefmt= '%H:%M:%S', level=logging.INFO)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.read_csv('./data/simpsons_script_lines.csv', error_bad_lines=False, usecols = ['raw_character_text', 'spoken_words'])\ndf.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Vamos fazer um exercício de sanidade e ver se temos valores nulos:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Ok, famoso `.dropna()` para limpar nosso dataset. Em casos de NLP, podemos fazer isso nessa escala",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = df.dropna().reset_index(drop=True)\ndf.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"nlp = spacy.load('en', disable=['ner', 'parser']) # disabling Named Entity Recognition for speed\n\ndef cleaning(doc):\n # Lemmatizes and removes stopwords\n # doc needs to be a spacy Doc object\n txt = [token.lemma_ for token in doc if not token.is_stop]\n # Word2Vec uses context words to learn the vector representation of a target word,\n # if a sentence is only one or two words long,\n # the benefit for the training is very small\n if len(txt) > 2:\n return ' '.join(txt)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Vamos retirar os caracteres não alfabéticos:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"brief_cleaning = (re.sub(\"[^A-Za-z']+\", ' ', str(row)).lower() for row in df['spoken_words']) #REGEX",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Ok, vamos executar nossa função de limpeza para todo o dataset! Observe como o shape vai mudar. O SpaCy nos permite criar pipelines para esse processo:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"t = time()\n\ntxt = [cleaning(doc) for doc in nlp.pipe(brief_cleaning, batch_size=5000, n_threads=-1)]\n\nprint('Time to clean up everything: {} mins'.format(round((time() - t) / 60, 2)))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_clean = pd.DataFrame({'clean': txt})\ndf_clean = df_clean.dropna().drop_duplicates()\ndf_clean.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Hora de utilizar a biblioteca Gensim. O Gensim é uma biblioteca de código aberto para modelagem de tópico não supervisionada e processamento de linguagem natural, usando o aprendizado de máquina estatístico moderno:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from gensim.models.phrases import Phrases, Phraser",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sent = [row.split() for row in df_clean['clean']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"phrases = Phrases(sent, min_count=30, progress_per=10000)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Vamos utilizar os __[bigrams](https://radimrehurek.com/gensim/models/phrases.html)__ do Gensim para detectar expressões comuns, como Bart Simpson e Mr Burns",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"bigram = Phraser(phrases)\nsentences = bigram[sent]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"word_freq = defaultdict(int)\nfor sent in sentences:\n for i in sent:\n word_freq[i] += 1\nlen(word_freq)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sorted(word_freq, key=word_freq.get, reverse=True)[:10]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Vamos construir o modelo __[word2vec](https://radimrehurek.com/gensim/models/word2vec.html)__ do Gensim. Antes disso, vamos entender o modelo:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<img src=\"imgs/word2vec.png\" align=\"left\" width=\"80%\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"O modelo word2vec foi implementado pelo time do Google Reaserch em 2013 com o objetivo de vetorizar tokens e entidades. Sua premissa é de que termos similares aparecem sob contextos similares, portanto, se 2 termos aparecem sob o mesmo contexto, eles têm uma chance grande de carregar informações próximas. Dessa forma, conseguimos construir um espaço n-dimensional de termos e realizar operações vetoriais sob essas palavras!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import multiprocessing\ncores = multiprocessing.cpu_count() # Count the number of cores in a computer\n\nfrom gensim.models import Word2Vec\n\nw2v_model = Word2Vec(min_count=20,\n window=2,\n size=300,\n sample=6e-5, \n alpha=0.03, \n min_alpha=0.0007, \n negative=20,\n workers=cores-1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Os hiperparâmetros utilizados são:\n - min_count = int - Ignores all words with total absolute frequency lower than this - (2, 100)\n - window = int - The maximum distance between the current and predicted word within a sentence. E.g. window words on the left and window words on the left of our target - (2, 10)\n - size = int - Dimensionality of the feature vectors. - (50, 300)\n - sample = float - The threshold for configuring which higher-frequency words are randomly downsampled. Highly influencial. - (0, 1e-5)\n - alpha = float - The initial learning rate - (0.01, 0.05)\n - min_alpha = float - Learning rate will linearly drop to min_alpha as training progresses. To set it: alpha - (min_alpha * epochs) ~ 0.00\n - negative = int - If > 0, negative sampling will be used, the int for negative specifies how many \"noise words\" should be drown. If set to 0, no - negative sampling is used. - (5, 20)\n - workers = int - Use these many worker threads to train the model (=faster training with multicore machines)\n<br>\n\nCom o modelo instanciado, precisamos construir nosso **corpus**, ou vocabulário. Vamos alimentar nosso modelo com os docs:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"t = time()\n\nw2v_model.build_vocab(sentences, progress_per=10000)\n\nprint('Time to build vocab: {} mins'.format(round((time() - t) / 60, 2)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Tudo pronto! Vamos treinar nosso modelo!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"t = time()\n\nw2v_model.train(sentences, total_examples=w2v_model.corpus_count, epochs=30, report_delay=1)\n\nprint('Time to train the model: {} mins'.format(round((time() - t) / 60, 2)))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w2v_model.init_sims(replace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w2v_model.wv.most_similar(positive=[\"homer\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w2v_model.wv.most_similar(positive=[\"marge\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w2v_model.wv.most_similar(positive=[\"bart\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w2v_model.wv.similarity('maggie', 'baby')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w2v_model.wv.similarity('bart', 'nelson')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w2v_model.wv.doesnt_match(['jimbo', 'milhouse', 'kearney'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w2v_model.wv.doesnt_match([\"nelson\", \"bart\", \"milhouse\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w2v_model.wv.most_similar(positive=[\"woman\", \"homer\"], negative=[\"marge\"], topn=3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w2v_model.wv.most_similar(positive=[\"woman\", \"bart\"], negative=[\"man\"], topn=3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline\n \nimport seaborn as sns\nsns.set_style(\"darkgrid\")\n\nfrom sklearn.decomposition import PCA\nfrom sklearn.manifold import TSNE\n\ndef tsnescatterplot(model, word, list_names):\n \"\"\" Plot in seaborn the results from the t-SNE dimensionality reduction algorithm of the vectors of a query word,\n its list of most similar words, and a list of words.\n \"\"\"\n arrays = np.empty((0, 300), dtype='f')\n word_labels = [word]\n color_list = ['red']\n\n # adds the vector of the query word\n arrays = np.append(arrays, model.wv.__getitem__([word]), axis=0)\n \n # gets list of most similar words\n close_words = model.wv.most_similar([word])\n \n # adds the vector for each of the closest words to the array\n for wrd_score in close_words:\n wrd_vector = model.wv.__getitem__([wrd_score[0]])\n word_labels.append(wrd_score[0])\n color_list.append('blue')\n arrays = np.append(arrays, wrd_vector, axis=0)\n \n # adds the vector for each of the words from list_names to the array\n for wrd in list_names:\n wrd_vector = model.wv.__getitem__([wrd])\n word_labels.append(wrd)\n color_list.append('green')\n arrays = np.append(arrays, wrd_vector, axis=0)\n \n # Reduces the dimensionality from 300 to 50 dimensions with PCA\n reduc = PCA(n_components=19).fit_transform(arrays)\n \n # Finds t-SNE coordinates for 2 dimensions\n np.set_printoptions(suppress=True)\n \n Y = TSNE(n_components=2, random_state=0, perplexity=15).fit_transform(reduc)\n \n # Sets everything up to plot\n df = pd.DataFrame({'x': [x for x in Y[:, 0]],\n 'y': [y for y in Y[:, 1]],\n 'words': word_labels,\n 'color': color_list})\n \n fig, _ = plt.subplots()\n fig.set_size_inches(9, 9)\n \n # Basic plot\n p1 = sns.regplot(data=df,\n x=\"x\",\n y=\"y\",\n fit_reg=False,\n marker=\"o\",\n scatter_kws={'s': 40,\n 'facecolors': df['color']\n }\n )\n \n # Adds annotations one by one with a loop\n for line in range(0, df.shape[0]):\n p1.text(df[\"x\"][line],\n df['y'][line],\n ' ' + df[\"words\"][line].title(),\n horizontalalignment='left',\n verticalalignment='bottom', size='medium',\n color=df['color'][line],\n weight='normal'\n ).set_size(15)\n\n \n plt.xlim(Y[:, 0].min()-50, Y[:, 0].max()+50)\n plt.ylim(Y[:, 1].min()-50, Y[:, 1].max()+50)\n \n plt.title('t-SNE visualization for {}'.format(word.title()))\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tsnescatterplot(w2v_model, 'homer', ['dog', 'bird', 'ah', 'maude', 'bob', 'mel', 'apu', 'duff'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tsnescatterplot(w2v_model, 'maggie', [i[0] for i in w2v_model.wv.most_similar(negative=[\"maggie\"])])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tsnescatterplot(w2v_model, \"mr_burn\", [t[0] for t in w2v_model.wv.most_similar(positive=[\"mr_burn\"], topn=20)][10:])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe8eae2f1ce694c8a80e7a770c50d9a6f7fed7c
| 18,218 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/developer_guide/DevelopingCustomModels.ipynb
|
andriyor/panel
|
e1d76f415df02ca90f54d42ebcaf42a1bcc65560
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 1,130 |
2019-11-23T09:53:37.000Z
|
2022-03-31T11:30:07.000Z
|
examples/developer_guide/DevelopingCustomModels.ipynb
|
andriyor/panel
|
e1d76f415df02ca90f54d42ebcaf42a1bcc65560
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 2,265 |
2019-11-20T17:09:09.000Z
|
2022-03-31T22:09:38.000Z
|
examples/developer_guide/DevelopingCustomModels.ipynb
|
datalayer-externals/holoviz-panel
|
5e25cb09447d8edf0b316f130ee1318a2aeb880f
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 215 |
2019-11-26T11:49:04.000Z
|
2022-03-30T10:23:11.000Z
| 39.518438 | 703 | 0.567461 |
[
[
[
"# Developing Custom Models\n\nPanel ships with a number of custom Bokeh models, which have both Python and Javascript components. When developing Panel these custom models have to be compiled. This happens automatically with `pip install -e .` or `python setup.py develop`, however when runnning actively developing you can rebuild the extension with `panel build panel`. The build command is just an alias for `bokeh build`; see the [Bokeh developer guide](https://docs.bokeh.org/en/latest/docs/dev_guide/setup.html) for more information about developing bokeh models or the [Awesome Panel - Bokeh Extensions Guide](https://awesome-panel.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guides/awesome-panel-extensions-guide/bokeh-extensions.html)\n\nJust like any other Javascript (or Typescript) library Panel defines a `package.json` and `package-lock.json` files. When adding, updating or removing a dependency in the `package.json` file ensure you commit the changes to the `package-lock.json` after running npm install.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Adding a new Custom Model\n\nThis example will guide you through adding a new model. \n\nWe will use the the `ChartJS` model as an example. But you should replace `ChartJS` and similar with the name of your model. \n\nHere we will add a simple Button model to start with. But we call it `ChartJS`. \n\nMy experience is that you should start small with a working example and the continue in small, incremental steps. For me it did not work trying to copy a large, complex example and refactoring it when I started out learning about Custom Models.\n\n1. Create a new branch `chartjs`.\n2. Add the files and code for a *minimum working model*. This includes\n - A Panel Python model\n - A Bokeh Python and TypeScript model\n\n#### Add the Panel Python Model\n\nAdd the file *panel/pane/chartjs.py* and the code\n \n```python\nimport param\n\nfrom panel.widgets.base import Widget\n\nfrom ..models import ChartJS as _BkChartJS\n\n\nclass ChartJS(Widget):\n # Set the Bokeh model to use\n _widget_type = _BkChartJS\n\n # Rename Panel Parameters -> Bokeh Model properties\n # Parameters like title that does not exist on the Bokeh model should be renamed to None\n _rename = {\n \"title\": None,\n }\n\n # Parameters to be mapped to Bokeh model properties\n object = param.String(default=\"Click Me!\")\n clicks = param.Integer(default=0)\n```\n\nAdd the Panel model to `panel/pane/__init__.py`\n\n```python\nfrom .chartjs import ChartJS\n```\n\n#### Add the Bokeh Python Model\n\nAdd the file *panel/models/chartjs.py* and the code\n\n```python\nfrom bokeh.core.properties import Int, String\nfrom bokeh.models import HTMLBox\n\nclass ChartJS(HTMLBox):\n \"\"\"Custom ChartJS Model\"\"\"\n\n object = String()\n clicks = Int()\n```\n\nAdd the Bokeh model to `panel/models/__init__.py` file\n\n```python\nfrom .chartjs import ChartJS\n```\n\n#### Add the Bokeh TypeScript Model\n\nAdd the file *panel/models/chartjs.ts* and the code\n\n```typescript\n// See https://docs.bokeh.org/en/latest/docs/reference/models/layouts.html\nimport { HTMLBox, HTMLBoxView } from \"@bokehjs/models/layouts/html_box\"\n\n// See https://docs.bokeh.org/en/latest/docs/reference/core/properties.html\nimport * as p from \"@bokehjs/core/properties\"\n\n// The view of the Bokeh extension/ HTML element\n// Here you can define how to render the model as well as react to model changes or View events.\nexport class ChartJSView extends HTMLBoxView {\n model: ChartJS\n objectElement: any // Element\n\n connect_signals(): void {\n super.connect_signals()\n\n this.connect(this.model.properties.object.change, () => {\n this.render();\n })\n }\n\n render(): void {\n super.render()\n this.el.innerHTML = `<button type=\"button\">${this.model.object}</button>`\n this.objectElement = this.el.firstElementChild\n\n this.objectElement.addEventListener(\"click\", () => {this.model.clicks+=1;}, false)\n }\n}\n\nexport namespace ChartJS {\n export type Attrs = p.AttrsOf<Props>\n export type Props = HTMLBox.Props & {\n object: p.Property<string>,\n clicks: p.Property<number>,\n }\n}\n\nexport interface ChartJS extends ChartJS.Attrs { }\n\n// The Bokeh .ts model corresponding to the Bokeh .py model\nexport class ChartJS extends HTMLBox {\n properties: ChartJS.Props\n\n constructor(attrs?: Partial<ChartJS.Attrs>) {\n super(attrs)\n }\n\n static __module__ = \"panel.models.chartjs\"\n\n static init_ChartJS(): void {\n this.prototype.default_view = ChartJSView;\n\n this.define<ChartJS.Props>(({Int, String}) => ({\n object: [String, \"Click Me!\"],\n clicks: [Int, 0],\n }))\n }\n}\n```\n\nAdd the `ChartJS` typescript model to *panel/models/index.ts*\n\n```typescript\nexport {ChartJS} from \"./chartjs\"\n```\n\n#### Build the Model\n\nYou can now build the model using `panel build panel`. It should look similar to\n\n```bash\n(base) root@475bb36209a9:/workspaces/panel# panel build panel\nWorking directory: /workspaces/panel/panel\nUsing /workspaces/panel/panel/tsconfig.json\nCompiling styles\nCompiling TypeScript (45 files)\nLinking modules\nOutput written to /workspaces/panel/panel/dist\nAll done.\n```\n\n#### Test the Model\n\nAdd the file *panel/tests/pane/test_chartjs.py* and the code\n\n```python\nimport panel as pn\n\n\ndef test_constructor():\n chartjs = pn.pane.ChartJS(object=\"Click Me Now!\")\n\ndef get_app():\n chartjs = pn.pane.ChartJS(object=\"Click Me Now!\")\n return pn.Column(\n chartjs, pn.Param(chartjs, parameters=[\"object\", \"clicks\"])\n )\n\nif __name__.startswith(\"bokeh\"):\n get_app().servable()\n```\n\nRun `pytest panel/tests/pane/test_chartjs.py` and make sure it passes.\n\nServe the app with `panel serve panel/tests/pane/test_chartjs.py --auto --show`\n\nYou have to *hard refresh* your browser to reload the new panel `.js` files with your `ChartJS` model. In Chrome I press `CTRL+F5`. See [How to hard refresh in Chrome, Firefox and IE](https://www.namecheap.com/support/knowledgebase/article.aspx/10078/2194/how-to-do-a-hard-refresh-in-chrome-firefox-and-ie/) for other browsers.\n\nNow you can manually test your model\n\n\n\n#### Save your new Model\n\nFinally you should save your changes via `git add .` and maybe even commit them `git commit -m \"First iteration on ChartJS model\"`",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Build a small HTML Example\n\nIn the beginning of your journey into Custom Models there will be things that break and difficulties figuring out why. When you combine several new things it can be really difficult to figure out why. Is the problem Panel, Bokeh, Python, Javascript, Node or ....? \n\nSo I suggest creating a small, working example in plain HTML/ JS before you start combining with Panel and Bokeh Models.\n\nPlease note the below example works out of the box. It is not always that easy importing javascript libraries in a Notebook. So it can be a good idea to work in a `.html` file first.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%HTML\n<script src=\"https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]\"></script>\n<div class=\"chart-container\" style=\"position: relative; height:400px; width:100%\">\n <canvas id=\"myChart\"></canvas>\n</div>\n<script>\nvar ctx = document.getElementById('myChart').getContext('2d');\nvar chart = new Chart(ctx, {\n // The type of chart we want to create\n type: 'line',\n\n // The data for our dataset\n data: {\n labels: ['January', 'February', 'March', 'April', 'May', 'June', 'July'],\n datasets: [{\n label: 'My First dataset',\n backgroundColor: 'rgb(255, 99, 132)',\n borderColor: 'rgb(255, 99, 132)',\n data: [0, 10, 5, 2, 20, 30, 45]\n }]\n },\n\n // Configuration options go here\n options: {\n responsive: true,\n maintainAspectRatio: false,\n }\n});\n</script>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Using the Javascript Model\n\nGetting something shown using the `ChartJS` `js` library would be the next step. It might require a bit of experimentation, looking at other examples, google or support from the community.\n\nHere I found that a good step where the following changes\n\n#### Import the Javascript Library\n\nUpdate *test_chartjs.py* tp\n\n```python\nimport panel as pn\n\n\ndef test_constructor():\n chartjs = pn.pane.ChartJS(object=\"Click Me Now!\")\n\ndef get_app():\n chartjs = pn.pane.ChartJS(object=\"Click Me Now!\")\n return pn.Column(\n chartjs, pn.Param(chartjs, parameters=[\"object\", \"clicks\"])\n )\n\nif __name__.startswith(\"bokeh\"):\n pn.config.js_files[\"chartjs\"]=\"https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]\"\n get_app().servable()\n```\n\n#### Render the Plot\n\nIn the *chartjs.ts* file add `import { canvas, div } from \"@bokehjs/core/dom\";` at the top and change the `render` function to \n\n```typescript\nrender(): void {\n super.render()\n var object = {\n type: 'line',\n data: {\n labels: ['January', 'February', 'March', 'April', 'May', 'June', 'July'],\n datasets: [{\n label: 'My First dataset',\n backgroundColor: 'rgb(255, 99, 132)',\n borderColor: 'rgb(255, 99, 132)',\n data: [0, 10, 5, 2, 20, 30, 45]\n }]\n },\n options: {\n responsive: true,\n maintainAspectRatio: false,\n }\n }\n\n var chartContainer = div({class: \"chartjs-container\", style: \"position: relative; height:400px; width:100%\"})\n var chartCanvas = canvas({class: \"chartjs\"})\n chartContainer.appendChild(chartCanvas)\n var ctx: any = chartCanvas.getContext('2d');\n new (window as any).Chart(ctx, object);\n\n this.el.appendChild(chartContainer)\n}\n```\n\n#### Build and Test\n\nRun `panel build panel` and hard refresh your browser. You should see\n\n\n\n#### Save Your Model\n\nRemember to stage and/ or commit your working changes.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Next Steps\n\n- Enable setting the Python `ChartJS.object` parameter to any ChartJS dictionary.\n- Checkout support for different sizing modes, responsiveness and window maximize.\n- Configure the javascript, css, .. dependencies in the Bokeh Python File.\n- .....",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Check List\n\nWhen you develop and test your model eventually you should consider implementing and testing\n\n- Dynamic updates to the `object` parameter and any other parameters added.\n- Resizing\n - Does it resize when `width` is changed dynamically?\n - Does it resize when `height` is changed dynamically?\n - Does it work with `sizing_mode=\"stretch_width\"` etc.\n- Themes (Light, Dark)\n- Window Resizing, Window Maximizing, Window Minimizing.\n- Streaming of Data. Is it efficient?\n- Events (Click, Hover etc.)\n- Consider supporting the Python Wrapper (ECharts -> PyECharts, ChartJS -> [PyChart.JS](https://pypi.org/project/pyChart.JS/))\n- Tests\n- Reference Notebook\n- Communication also to for example ChartJS community and developers.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Tips and Tricks\n\n- Work in small increments and stage your changes when they work\n- Remember to `panel build panel` and hard refresh before you test.\n- Add [console.log](https://www.w3schools.com/jsref/met_console_log.asp) statements to your `.ts` code for debugging.\n- Use the [*Developer Tools*](https://developers.google.com/web/tools/chrome-devtools) *console* to see the `console.log` output and identify errors. In my browsers I toggle the Developer Tools using `CTRL+SHIFT+I`.\n- Find inspiration for next steps in the [existing Panel Custom Models](https://github.com/holoviz/panel/tree/master/panel/models). For `ChartJS` one of the most relevant custom models would be `Echarts`. See Panel [echarts.py](https://github.com/holoviz/panel/blob/master/panel/pane/echarts.py), Bokeh [echarts.py](https://github.com/holoviz/panel/blob/master/panel/models/echarts.py) and [echarts.ts](https://github.com/holoviz/panel/blob/master/panel/models/echarts.ts).\n- Use the existing documentation\n - [Panel - Developer Guide](https://panel.holoviz.org/developer_guide/index.html)\n - [Bokeh - Extending Bokeh](https://docs.bokeh.org/en/latest/docs/user_guide/extensions.html)\n - [Awesome Panel - Bokeh Extensions Guide](https://awesome-panel.readthedocs.io/en/latest/guides/awesome-panel-extensions-guide/bokeh-extensions.html)\n- Use Google Search. You don't have to be an expert javascript or typescript developer. It's a very small subset of those languages that is used when developing Custom Models.\n- Ask for help in [PyViz Gitter](https://gitter.im/pyviz/pyviz), [HoloViz Discourse](https://discourse.holoviz.org/) and [Bokeh Discourse](https://discourse.bokeh.org/) forums.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe8eeb95e4310f752fb41c0612e1ec09dff74dd
| 31,962 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
07_training/07a_ingest.ipynb
|
bdwivedi/practical-ml-vision-book
|
056de3e127e05271eff711145b82e6e91a9296b2
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 201 |
2020-11-18T20:00:25.000Z
|
2022-03-27T00:41:11.000Z
|
07_training/07a_ingest.ipynb
|
saibaldas/practical-ml-vision-book
|
76f88ec370ecd32715a898b0c3439a1273ac839b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 6 |
2021-06-25T23:25:37.000Z
|
2021-12-05T04:29:40.000Z
|
07_training/07a_ingest.ipynb
|
saibaldas/practical-ml-vision-book
|
76f88ec370ecd32715a898b0c3439a1273ac839b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 91 |
2020-11-18T22:17:17.000Z
|
2022-03-29T15:07:20.000Z
| 33.893955 | 554 | 0.526563 |
[
[
[
"from IPython.display import Markdown as md\n\n### change to reflect your notebook\n_nb_loc = \"07_training/07a_ingest.ipynb\"\n_nb_title = \"Writing an efficient ingest Loop\"\n\n### no need to change any of this\n_nb_safeloc = _nb_loc.replace('/', '%2F')\nmd(\"\"\"\n<table class=\"tfo-notebook-buttons\" align=\"left\">\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://console.cloud.google.com/ai-platform/notebooks/deploy-notebook?name={1}&url=https%3A%2F%2Fgithub.com%2FGoogleCloudPlatform%2Fpractical-ml-vision-book%2Fblob%2Fmaster%2F{2}&download_url=https%3A%2F%2Fgithub.com%2FGoogleCloudPlatform%2Fpractical-ml-vision-book%2Fraw%2Fmaster%2F{2}\">\n <img src=\"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/practical-ml-vision-book/master/logo-cloud.png\"/> Run in AI Platform Notebook</a>\n </td>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/GoogleCloudPlatform/practical-ml-vision-book/blob/master/{0}\">\n <img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/colab_logo_32px.png\" />Run in Google Colab</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/practical-ml-vision-book/blob/master/{0}\">\n <img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/GitHub-Mark-32px.png\" />View source on GitHub</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a href=\"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/practical-ml-vision-book/master/{0}\">\n <img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/download_logo_32px.png\" />Download notebook</a>\n </td>\n</table>\n\"\"\".format(_nb_loc, _nb_title, _nb_safeloc))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Efficient Ingest\n\nIn this notebook, we speed the ingest of training/evaluation data into the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Enable GPU and set up helper functions\n\nThis notebook and pretty much every other notebook in this repository\nwill run faster if you are using a GPU.\nOn Colab:\n- Navigate to Edit→Notebook Settings\n- Select GPU from the Hardware Accelerator drop-down\n\nOn Cloud AI Platform Notebooks:\n- Navigate to https://console.cloud.google.com/ai-platform/notebooks\n- Create an instance with a GPU or select your instance and add a GPU\n\nNext, we'll confirm that we can connect to the GPU with tensorflow:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import tensorflow as tf\nprint('TensorFlow version' + tf.version.VERSION)\nprint('Built with GPU support? ' + ('Yes!' if tf.test.is_built_with_cuda() else 'Noooo!'))\nprint('There are {} GPUs'.format(len(tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices(\"GPU\"))))\ndevice_name = tf.test.gpu_device_name()\nif device_name != '/device:GPU:0':\n raise SystemError('GPU device not found')\nprint('Found GPU at: {}'.format(device_name))",
"TensorFlow version2.3.1\nBuilt with GPU support? Yes!\nThere are 2 GPUs\nFound GPU at: /device:GPU:0\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Original code\n\nThis is the original code, from [../06_preprocessing/06e_colordistortion.ipynb](../06_preprocessing/06e_colordistortion.ipynb)\n\nWe have a few variations of creating a preprocessed dataset.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.pylab as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport tensorflow as tf\nimport tensorflow_hub as hub\nimport os\n# Load compressed models from tensorflow_hub\nos.environ['TFHUB_MODEL_LOAD_FORMAT'] = 'COMPRESSED' \n\nfrom tensorflow.data.experimental import AUTOTUNE\n\nIMG_HEIGHT = 448 # note *twice* what we used to have\nIMG_WIDTH = 448\nIMG_CHANNELS = 3\nCLASS_NAMES = 'daisy dandelion roses sunflowers tulips'.split()\n\ndef training_plot(metrics, history):\n f, ax = plt.subplots(1, len(metrics), figsize=(5*len(metrics), 5))\n for idx, metric in enumerate(metrics):\n ax[idx].plot(history.history[metric], ls='dashed')\n ax[idx].set_xlabel(\"Epochs\")\n ax[idx].set_ylabel(metric)\n ax[idx].plot(history.history['val_' + metric]);\n ax[idx].legend([metric, 'val_' + metric])\n \nclass _Preprocessor: \n def __init__(self):\n # nothing to initialize\n pass\n \n def read_from_tfr(self, proto):\n feature_description = {\n 'image': tf.io.VarLenFeature(tf.float32),\n 'shape': tf.io.VarLenFeature(tf.int64),\n 'label': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string, default_value=''),\n 'label_int': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64, default_value=0),\n }\n rec = tf.io.parse_single_example(\n proto, feature_description\n )\n shape = tf.sparse.to_dense(rec['shape'])\n img = tf.reshape(tf.sparse.to_dense(rec['image']), shape)\n label_int = rec['label_int']\n return img, label_int\n \n def read_from_jpegfile(self, filename):\n # same code as in 05_create_dataset/jpeg_to_tfrecord.py\n img = tf.io.read_file(filename)\n img = tf.image.decode_jpeg(img, channels=IMG_CHANNELS)\n img = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(img, tf.float32)\n return img\n \n def preprocess(self, img):\n return tf.image.resize_with_pad(img, IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH)\n\ndef create_preproc_dataset_plain(pattern):\n preproc = _Preprocessor()\n trainds = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(\n [filename for filename in tf.io.gfile.glob(pattern)],\n compression_type='GZIP'\n ).map(preproc.read_from_tfr).map(\n lambda img, label: (preproc.preprocess(img), label)\n ) \n return trainds\n\n# note: addition of AUTOTUNE to the map() calls\ndef create_preproc_dataset_parallelmap(pattern):\n preproc = _Preprocessor()\n def _preproc_img_label(img, label):\n return (preproc.preprocess(img), label)\n trainds = (\n tf.data.TFRecordDataset(\n [filename for filename in tf.io.gfile.glob(pattern)],\n compression_type='GZIP'\n )\n .map(preproc.read_from_tfr, num_parallel_calls=AUTOTUNE)\n .map(_preproc_img_label, num_parallel_calls=AUTOTUNE)\n )\n return trainds\n\n# note: splits the files into two halves and interleaves datasets\ndef create_preproc_dataset_interleave(pattern, num_parallel=None):\n preproc = _Preprocessor()\n files = [filename for filename in tf.io.gfile.glob(pattern)]\n if len(files) > 1:\n print(\"Interleaving the reading of {} files.\".format(len(files)))\n def _create_half_ds(x):\n if x == 0:\n half = files[:(len(files)//2)]\n else:\n half = files[(len(files)//2):]\n return tf.data.TFRecordDataset(half,\n compression_type='GZIP')\n trainds = tf.data.Dataset.range(2).interleave(\n _create_half_ds, num_parallel_calls=AUTOTUNE)\n else:\n trainds = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(files,\n compression_type='GZIP')\n def _preproc_img_label(img, label):\n return (preproc.preprocess(img), label)\n \n trainds = (trainds\n .map(preproc.read_from_tfr, num_parallel_calls=num_parallel)\n .map(_preproc_img_label, num_parallel_calls=num_parallel)\n )\n return trainds\n\ndef create_preproc_image(filename):\n preproc = _Preprocessor()\n img = preproc.read_from_jpegfile(filename)\n return preproc.preprocess(img)\n\nclass RandomColorDistortion(tf.keras.layers.Layer):\n def __init__(self, contrast_range=[0.5, 1.5], \n brightness_delta=[-0.2, 0.2], **kwargs):\n super(RandomColorDistortion, self).__init__(**kwargs)\n self.contrast_range = contrast_range\n self.brightness_delta = brightness_delta\n \n def call(self, images, training=None):\n if not training:\n return images\n \n contrast = np.random.uniform(\n self.contrast_range[0], self.contrast_range[1])\n brightness = np.random.uniform(\n self.brightness_delta[0], self.brightness_delta[1])\n \n images = tf.image.adjust_contrast(images, contrast)\n images = tf.image.adjust_brightness(images, brightness)\n images = tf.clip_by_value(images, 0, 1)\n return images",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Speeding up the reading of data\n\nTo try it out, we'll simply read through the data several times and compute some quantity on the images.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def loop_through_dataset(ds, nepochs):\n lowest_mean = tf.constant(1.)\n for epoch in range(nepochs):\n thresh = np.random.uniform(0.3, 0.7) # random threshold\n count = 0\n sumsofar = tf.constant(0.)\n for (img, label) in ds:\n # mean of channel values > thresh\n mean = tf.reduce_mean(tf.where(img > thresh, img, 0))\n sumsofar = sumsofar + mean\n count = count + 1\n if count%100 == 0:\n print('.', end='')\n mean = sumsofar/count\n print(mean)\n if mean < lowest_mean:\n lowest_mean = mean\n return lowest_mean",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"PATTERN_SUFFIX, NUM_EPOCHS = '-0000[01]-*', 2 # 2 files, 2 epochs\n#PATTERN_SUFFIX, NUM_EPOCHS = '-*', 20 # 16 files, 20 epochs",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%time\nds = create_preproc_dataset_plain(\n 'gs://practical-ml-vision-book/flowers_tfr/train' + PATTERN_SUFFIX\n)\nloop_through_dataset(ds, NUM_EPOCHS)",
"...tf.Tensor(0.22762734, shape=(), dtype=float32)\n...tf.Tensor(0.21017572, shape=(), dtype=float32)\nCPU times: user 7.03 s, sys: 500 ms, total: 7.53 s\nWall time: 7.99 s\n"
],
[
"%%time\n# parallel map\nds = create_preproc_dataset_parallelmap(\n 'gs://practical-ml-vision-book/flowers_tfr/train' + PATTERN_SUFFIX\n)\nloop_through_dataset(ds, NUM_EPOCHS)",
"...tf.Tensor(0.14244522, shape=(), dtype=float32)\n...tf.Tensor(0.18533988, shape=(), dtype=float32)\nCPU times: user 7.93 s, sys: 375 ms, total: 8.3 s\nWall time: 5.94 s\n"
],
[
"%%time\n# with interleave\nds = create_preproc_dataset_interleave(\n 'gs://practical-ml-vision-book/flowers_tfr/train' + PATTERN_SUFFIX,\n num_parallel=None\n)\nloop_through_dataset(ds, NUM_EPOCHS)",
"Interleaving the reading of 2 files.\nfirst half\nsecond half\n...tf.Tensor(0.12316246, shape=(), dtype=float32)\n...tf.Tensor(0.15402032, shape=(), dtype=float32)\nCPU times: user 7.86 s, sys: 497 ms, total: 8.35 s\nWall time: 5.29 s\n"
],
[
"%%time\n# with interleave and parallel mpas\nds = create_preproc_dataset_interleave(\n 'gs://practical-ml-vision-book/flowers_tfr/train' + PATTERN_SUFFIX,\n num_parallel=AUTOTUNE\n)\nloop_through_dataset(ds, NUM_EPOCHS)",
"Interleaving the reading of 2 files.\n...tf.Tensor(0.18058446, shape=(), dtype=float32)\n...tf.Tensor(0.14600855, shape=(), dtype=float32)\nCPU times: user 7.99 s, sys: 443 ms, total: 8.44 s\nWall time: 5.23 s\n"
]
],
[
[
"When I did this, this is what I got:\n\n| Method | CPU time | Wall time |\n| ---------------------- | ----------- | ------------ |\n| Plain | 7.53s | 7.99s |\n| Parallel Map | 8.30s | 5.94s |\n| Interleave | 8.60s | 5.47s |\n| Interleave+Parallel Map| 8.44s | 5.23s |",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## ML model\n\nThe computation above was pretty cheap involving merely adding up all the pixel values.\nWhat happens if we need a bit more complexity (gradient calc, etc.)?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def train_simple_model(ds, nepochs):\n model = tf.keras.Sequential([\n tf.keras.layers.Flatten(\n input_shape=(IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH, IMG_CHANNELS)),\n #tf.keras.layers.Dense(32, activation='relu'),\n tf.keras.layers.Dense(len(CLASS_NAMES), activation='softmax')\n ])\n model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(),\n loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(\n from_logits=False),\n metrics=['accuracy'])\n model.fit(ds, epochs=nepochs)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%time\nds = create_preproc_dataset_plain(\n 'gs://practical-ml-vision-book/flowers_tfr/train' + PATTERN_SUFFIX\n).batch(1)\ntrain_simple_model(ds, NUM_EPOCHS)",
"Epoch 1/2\n359/359 [==============================] - 4s 11ms/step - loss: 384.5950 - accuracy: 0.2841\nEpoch 2/2\n359/359 [==============================] - 4s 11ms/step - loss: 260.8144 - accuracy: 0.3983\nCPU times: user 9.12 s, sys: 796 ms, total: 9.91 s\nWall time: 9.39 s\n"
],
[
"%%time\n# parallel map\nds = create_preproc_dataset_parallelmap(\n 'gs://practical-ml-vision-book/flowers_tfr/train' + PATTERN_SUFFIX\n).batch(1)\ntrain_simple_model(ds, NUM_EPOCHS)",
"Epoch 1/2\n359/359 [==============================] - 4s 10ms/step - loss: 378.1755 - accuracy: 0.2646\nEpoch 2/2\n359/359 [==============================] - 4s 10ms/step - loss: 277.4931 - accuracy: 0.4067\nCPU times: user 9.97 s, sys: 718 ms, total: 10.7 s\nWall time: 8.17 s\n"
],
[
"%%time\n# with interleave\nds = create_preproc_dataset_interleave(\n 'gs://practical-ml-vision-book/flowers_tfr/train' + PATTERN_SUFFIX,\n num_parallel=None\n).batch(1)\ntrain_simple_model(ds, NUM_EPOCHS)",
"Interleaving the reading of 2 files.\nEpoch 1/2\n359/359 [==============================] - 3s 9ms/step - loss: 359.4355 - accuracy: 0.3008\nEpoch 2/2\n359/359 [==============================] - 3s 9ms/step - loss: 296.0292 - accuracy: 0.3928\nCPU times: user 9.7 s, sys: 825 ms, total: 10.5 s\nWall time: 7.54 s\n"
],
[
"%%time\n# with interleave and parallel mpas\nds = create_preproc_dataset_interleave(\n 'gs://practical-ml-vision-book/flowers_tfr/train' + PATTERN_SUFFIX,\n num_parallel=AUTOTUNE\n).batch(1)\ntrain_simple_model(ds, NUM_EPOCHS)",
"Interleaving the reading of 2 files.\nEpoch 1/2\n359/359 [==============================] - 3s 9ms/step - loss: 403.3262 - accuracy: 0.2423\nEpoch 2/2\n359/359 [==============================] - 3s 8ms/step - loss: 260.8356 - accuracy: 0.4290\nCPU times: user 9.6 s, sys: 728 ms, total: 10.3 s\nWall time: 7.17 s\n"
]
],
[
[
"We note that the improvement remains:\n\n| Method | CPU time | Wall time |\n| -----------------------| ----------- | ------------ |\n| Plain | 9.91s | 9.39s |\n| Parallel Map | 10.7s | 8.17s |\n| Interleave | 10.5s | 7.54s |\n| Interleave+Parallel Map| 10.3s | 7.17s |",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Speeding up the handling of data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# alias to the more efficient one\ndef create_preproc_dataset(pattern):\n return create_preproc_dataset_interleave(pattern, num_parallel=AUTOTUNE)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%time\n# add prefetching\nds = create_preproc_dataset(\n 'gs://practical-ml-vision-book/flowers_tfr/train' + PATTERN_SUFFIX\n).prefetch(AUTOTUNE).batch(1)\ntrain_simple_model(ds, NUM_EPOCHS)",
"Interleaving the reading of 2 files.\nEpoch 1/2\n359/359 [==============================] - 3s 9ms/step - loss: 387.4389 - accuracy: 0.2813\nEpoch 2/2\n359/359 [==============================] - 3s 9ms/step - loss: 279.8046 - accuracy: 0.3760\nCPU times: user 10.5 s, sys: 899 ms, total: 11.4 s\nWall time: 8.09 s\n"
],
[
"%%time\n# Add batching of different sizes\nds = create_preproc_dataset(\n 'gs://practical-ml-vision-book/flowers_tfr/train' + PATTERN_SUFFIX\n).prefetch(AUTOTUNE).batch(8)\ntrain_simple_model(ds, NUM_EPOCHS)",
"Interleaving the reading of 2 files.\nEpoch 1/2\n45/45 [==============================] - 3s 60ms/step - loss: 113.6279 - accuracy: 0.2702\nEpoch 2/2\n45/45 [==============================] - 3s 56ms/step - loss: 120.0435 - accuracy: 0.2758\nCPU times: user 8.97 s, sys: 590 ms, total: 9.56 s\nWall time: 6.9 s\n"
],
[
"%%time\n# Add batching of different sizes\nds = create_preproc_dataset(\n 'gs://practical-ml-vision-book/flowers_tfr/train' + PATTERN_SUFFIX\n).prefetch(AUTOTUNE).batch(16)\ntrain_simple_model(ds, NUM_EPOCHS)",
"Interleaving the reading of 2 files.\nEpoch 1/2\n23/23 [==============================] - 3s 110ms/step - loss: 97.3240 - accuracy: 0.2507\nEpoch 2/2\n23/23 [==============================] - 2s 105ms/step - loss: 41.4950 - accuracy: 0.3900\nCPU times: user 8.97 s, sys: 939 ms, total: 9.9 s\nWall time: 6.7 s\n"
],
[
"%%time\n# Add batching of different sizes\nds = create_preproc_dataset(\n 'gs://practical-ml-vision-book/flowers_tfr/train' + PATTERN_SUFFIX\n).prefetch(AUTOTUNE).batch(32)\ntrain_simple_model(ds, NUM_EPOCHS)",
"Interleaving the reading of 2 files.\nEpoch 1/2\n12/12 [==============================] - 2s 187ms/step - loss: 121.8208 - accuracy: 0.2423\nEpoch 2/2\n12/12 [==============================] - 2s 185ms/step - loss: 51.0977 - accuracy: 0.3259\nCPU times: user 8.78 s, sys: 902 ms, total: 9.68 s\nWall time: 6.37 s\n"
],
[
"%%time\n# add caching: always do this optimization last.\nds = create_preproc_dataset(\n 'gs://practical-ml-vision-book/flowers_tfr/train' + PATTERN_SUFFIX\n).cache().batch(32)\ntrain_simple_model(ds, NUM_EPOCHS)",
"Interleaving the reading of 2 files.\nEpoch 1/2\n12/12 [==============================] - 3s 213ms/step - loss: 106.7971 - accuracy: 0.2423\nEpoch 2/2\n12/12 [==============================] - 1s 47ms/step - loss: 66.2376 - accuracy: 0.3203\nCPU times: user 5.16 s, sys: 1 s, total: 6.16 s\nWall time: 4.36 s\n"
],
[
"%%time\n# add caching: always do this optimization last.\nds = create_preproc_dataset(\n 'gs://practical-ml-vision-book/flowers_tfr/train' + PATTERN_SUFFIX\n).prefetch(AUTOTUNE).cache().batch(32)\ntrain_simple_model(ds, NUM_EPOCHS)",
"Interleaving the reading of 2 files.\nEpoch 1/2\n12/12 [==============================] - 2s 192ms/step - loss: 126.8334 - accuracy: 0.2340\nEpoch 2/2\n12/12 [==============================] - 1s 45ms/step - loss: 51.4512 - accuracy: 0.3287\nCPU times: user 5.01 s, sys: 756 ms, total: 5.76 s\nWall time: 4.04 s\n"
],
[
"%%time\n# add caching: always do this optimization last.\nds = create_preproc_dataset(\n 'gs://practical-ml-vision-book/flowers_tfr/train' + PATTERN_SUFFIX\n).cache().prefetch(AUTOTUNE).batch(32)\ntrain_simple_model(ds, NUM_EPOCHS)",
"Interleaving the reading of 2 files.\nEpoch 1/2\n12/12 [==============================] - 2s 208ms/step - loss: 148.2066 - accuracy: 0.2507\nEpoch 2/2\n12/12 [==============================] - 1s 44ms/step - loss: 71.6666 - accuracy: 0.3064\nCPU times: user 4.95 s, sys: 692 ms, total: 5.65 s\nWall time: 4.19 s\n"
]
],
[
[
"Adding to the previous table:\n\n| Method | CPU time | Wall time |\n| -----------------------| ----------- | ------------ |\n| Plain | 9.91s | 9.39s |\n| Parallel Map | 10.7s | 8.17s |\n| Interleave | 10.5s | 7.54s |\n| Interleave+Parallel Map| 10.3s | 7.17s |\n| Interleave + Parallel, and then adding: | - | - |\n| Prefetch | 11.4s | 8.09s |\n| Batch size 8 | 9.56s | 6.90s |\n| Batch size 16 | 9.90s | 6.70s |\n| Batch size 32 | 9.68s | 6.37s |\n| Interleave + Parallel + batchsize 32, and then adding: | - | - |\n| Cache | 6.16s | 4.36s |\n| Prefetch + Cache | 5.76s | 4.04s |\n| Cache + Prefetch | 5.65s | 4.19s |\n\nSo, the best option is:\n<pre>\nds = create_preproc_dataset_interleave(pattern, num_parallel=AUTOTUNE).prefetch(AUTOTUNE).cache().batch(32)\n</pre>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## License\nCopyright 2020 Google Inc. Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe8f1b1c7fdbe919ef0229cc8d036003dfef46c
| 553,146 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
C1/week3/Planar data classification with one hidden layer/Planar_data_classification_with_onehidden_layer_v6c.ipynb
|
atpavan/coursera-dl-specialization
|
0296d3e10882241f385eda0c4253462817372d37
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
C1/week3/Planar data classification with one hidden layer/Planar_data_classification_with_onehidden_layer_v6c.ipynb
|
atpavan/coursera-dl-specialization
|
0296d3e10882241f385eda0c4253462817372d37
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
C1/week3/Planar data classification with one hidden layer/Planar_data_classification_with_onehidden_layer_v6c.ipynb
|
atpavan/coursera-dl-specialization
|
0296d3e10882241f385eda0c4253462817372d37
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 333.019868 | 322,004 | 0.922621 |
[
[
[
"\n### <font color = \"darkblue\">Updates to Assignment</font>\n\n#### If you were working on the older version:\n* Please click on the \"Coursera\" icon in the top right to open up the folder directory. \n* Navigate to the folder: Week 3/ Planar data classification with one hidden layer. You can see your prior work in version 6b: \"Planar data classification with one hidden layer v6b.ipynb\"\n\n#### List of bug fixes and enhancements\n* Clarifies that the classifier will learn to classify regions as either red or blue.\n* compute_cost function fixes np.squeeze by casting it as a float.\n* compute_cost instructions clarify the purpose of np.squeeze.\n* compute_cost clarifies that \"parameters\" parameter is not needed, but is kept in the function definition until the auto-grader is also updated.\n* nn_model removes extraction of parameter values, as the entire parameter dictionary is passed to the invoked functions.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Planar data classification with one hidden layer\n\nWelcome to your week 3 programming assignment. It's time to build your first neural network, which will have a hidden layer. You will see a big difference between this model and the one you implemented using logistic regression. \n\n**You will learn how to:**\n- Implement a 2-class classification neural network with a single hidden layer\n- Use units with a non-linear activation function, such as tanh \n- Compute the cross entropy loss \n- Implement forward and backward propagation\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 1 - Packages ##\n\nLet's first import all the packages that you will need during this assignment.\n- [numpy](https://www.numpy.org/) is the fundamental package for scientific computing with Python.\n- [sklearn](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/) provides simple and efficient tools for data mining and data analysis. \n- [matplotlib](http://matplotlib.org) is a library for plotting graphs in Python.\n- testCases provides some test examples to assess the correctness of your functions\n- planar_utils provide various useful functions used in this assignment",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Package imports\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom testCases_v2 import *\nimport sklearn\nimport sklearn.datasets\nimport sklearn.linear_model\nfrom planar_utils import plot_decision_boundary, sigmoid, load_planar_dataset, load_extra_datasets\n\n%matplotlib inline\n\nnp.random.seed(1) # set a seed so that the results are consistent",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 2 - Dataset ##\n\nFirst, let's get the dataset you will work on. The following code will load a \"flower\" 2-class dataset into variables `X` and `Y`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X, Y = load_planar_dataset()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Visualize the dataset using matplotlib. The data looks like a \"flower\" with some red (label y=0) and some blue (y=1) points. Your goal is to build a model to fit this data. In other words, we want the classifier to define regions as either red or blue.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Y.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.squeeze(Y).shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Visualize the data:\nplt.scatter(X[0, :], X[1, :], c=np.squeeze(Y), s=40, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You have:\n - a numpy-array (matrix) X that contains your features (x1, x2)\n - a numpy-array (vector) Y that contains your labels (red:0, blue:1).\n\nLets first get a better sense of what our data is like. \n\n**Exercise**: How many training examples do you have? In addition, what is the `shape` of the variables `X` and `Y`? \n\n**Hint**: How do you get the shape of a numpy array? [(help)](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.ndarray.shape.html)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines of code)\nshape_X = X.shape\nshape_Y = Y.shape\nm = X.shape[1] # training set size\n### END CODE HERE ###\n\nprint ('The shape of X is: ' + str(shape_X))\nprint ('The shape of Y is: ' + str(shape_Y))\nprint ('I have m = %d training examples!' % (m))",
"The shape of X is: (2, 400)\nThe shape of Y is: (1, 400)\nI have m = 400 training examples!\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**:\n \n<table style=\"width:20%\">\n \n <tr>\n <td>**shape of X**</td>\n <td> (2, 400) </td> \n </tr>\n \n <tr>\n <td>**shape of Y**</td>\n <td>(1, 400) </td> \n </tr>\n \n <tr>\n <td>**m**</td>\n <td> 400 </td> \n </tr>\n \n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 3 - Simple Logistic Regression\n\nBefore building a full neural network, lets first see how logistic regression performs on this problem. You can use sklearn's built-in functions to do that. Run the code below to train a logistic regression classifier on the dataset.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Train the logistic regression classifier\nclf = sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegressionCV();\nclf.fit(X.T, Y.T);",
"/usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/sklearn/utils/validation.py:724: DataConversionWarning: A column-vector y was passed when a 1d array was expected. Please change the shape of y to (n_samples, ), for example using ravel().\n y = column_or_1d(y, warn=True)\n/usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/sklearn/model_selection/_split.py:1978: FutureWarning: The default value of cv will change from 3 to 5 in version 0.22. Specify it explicitly to silence this warning.\n warnings.warn(CV_WARNING, FutureWarning)\n"
]
],
[
[
"You can now plot the decision boundary of these models. Run the code below.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Plot the decision boundary for logistic regression\nplot_decision_boundary(lambda x: clf.predict(x), X, np.squeeze(Y))\nplt.title(\"Logistic Regression\")\n\n# Print accuracy\nLR_predictions = clf.predict(X.T)\nprint ('Accuracy of logistic regression: %d ' % float((np.dot(Y,LR_predictions) + np.dot(1-Y,1-LR_predictions))/float(Y.size)*100) +\n '% ' + \"(percentage of correctly labelled datapoints)\")",
"Accuracy of logistic regression: 47 % (percentage of correctly labelled datapoints)\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**:\n\n<table style=\"width:20%\">\n <tr>\n <td>**Accuracy**</td>\n <td> 47% </td> \n </tr>\n \n</table>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Interpretation**: The dataset is not linearly separable, so logistic regression doesn't perform well. Hopefully a neural network will do better. Let's try this now! ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 4 - Neural Network model\n\nLogistic regression did not work well on the \"flower dataset\". You are going to train a Neural Network with a single hidden layer.\n\n**Here is our model**:\n<img src=\"images/classification_kiank.png\" style=\"width:600px;height:300px;\">\n\n**Mathematically**:\n\nFor one example $x^{(i)}$:\n$$z^{[1] (i)} = W^{[1]} x^{(i)} + b^{[1]}\\tag{1}$$ \n$$a^{[1] (i)} = \\tanh(z^{[1] (i)})\\tag{2}$$\n$$z^{[2] (i)} = W^{[2]} a^{[1] (i)} + b^{[2]}\\tag{3}$$\n$$\\hat{y}^{(i)} = a^{[2] (i)} = \\sigma(z^{ [2] (i)})\\tag{4}$$\n$$y^{(i)}_{prediction} = \\begin{cases} 1 & \\mbox{if } a^{[2](i)} > 0.5 \\\\ 0 & \\mbox{otherwise } \\end{cases}\\tag{5}$$\n\nGiven the predictions on all the examples, you can also compute the cost $J$ as follows: \n$$J = - \\frac{1}{m} \\sum\\limits_{i = 0}^{m} \\large\\left(\\small y^{(i)}\\log\\left(a^{[2] (i)}\\right) + (1-y^{(i)})\\log\\left(1- a^{[2] (i)}\\right) \\large \\right) \\small \\tag{6}$$\n\n**Reminder**: The general methodology to build a Neural Network is to:\n 1. Define the neural network structure ( # of input units, # of hidden units, etc). \n 2. Initialize the model's parameters\n 3. Loop:\n - Implement forward propagation\n - Compute loss\n - Implement backward propagation to get the gradients\n - Update parameters (gradient descent)\n\nYou often build helper functions to compute steps 1-3 and then merge them into one function we call `nn_model()`. Once you've built `nn_model()` and learnt the right parameters, you can make predictions on new data.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.1 - Defining the neural network structure ####\n\n**Exercise**: Define three variables:\n - n_x: the size of the input layer\n - n_h: the size of the hidden layer (set this to 4) \n - n_y: the size of the output layer\n\n**Hint**: Use shapes of X and Y to find n_x and n_y. Also, hard code the hidden layer size to be 4.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# GRADED FUNCTION: layer_sizes\n\ndef layer_sizes(X, Y):\n \"\"\"\n Arguments:\n X -- input dataset of shape (input size, number of examples)\n Y -- labels of shape (output size, number of examples)\n \n Returns:\n n_x -- the size of the input layer\n n_h -- the size of the hidden layer\n n_y -- the size of the output layer\n \"\"\"\n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines of code)\n n_x = X.shape[0] # size of input layer\n n_h = 4\n n_y = Y.shape[0] # size of output layer\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n return (n_x, n_h, n_y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_assess, Y_assess = layer_sizes_test_case()\n(n_x, n_h, n_y) = layer_sizes(X_assess, Y_assess)\nprint(\"The size of the input layer is: n_x = \" + str(n_x))\nprint(\"The size of the hidden layer is: n_h = \" + str(n_h))\nprint(\"The size of the output layer is: n_y = \" + str(n_y))",
"The size of the input layer is: n_x = 5\nThe size of the hidden layer is: n_h = 4\nThe size of the output layer is: n_y = 2\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output** (these are not the sizes you will use for your network, they are just used to assess the function you've just coded).\n\n<table style=\"width:20%\">\n <tr>\n <td>**n_x**</td>\n <td> 5 </td> \n </tr>\n \n <tr>\n <td>**n_h**</td>\n <td> 4 </td> \n </tr>\n \n <tr>\n <td>**n_y**</td>\n <td> 2 </td> \n </tr>\n \n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.2 - Initialize the model's parameters ####\n\n**Exercise**: Implement the function `initialize_parameters()`.\n\n**Instructions**:\n- Make sure your parameters' sizes are right. Refer to the neural network figure above if needed.\n- You will initialize the weights matrices with random values. \n - Use: `np.random.randn(a,b) * 0.01` to randomly initialize a matrix of shape (a,b).\n- You will initialize the bias vectors as zeros. \n - Use: `np.zeros((a,b))` to initialize a matrix of shape (a,b) with zeros.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# GRADED FUNCTION: initialize_parameters\n\ndef initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y):\n \"\"\"\n Argument:\n n_x -- size of the input layer\n n_h -- size of the hidden layer\n n_y -- size of the output layer\n \n Returns:\n params -- python dictionary containing your parameters:\n W1 -- weight matrix of shape (n_h, n_x)\n b1 -- bias vector of shape (n_h, 1)\n W2 -- weight matrix of shape (n_y, n_h)\n b2 -- bias vector of shape (n_y, 1)\n \"\"\"\n \n np.random.seed(2) # we set up a seed so that your output matches ours although the initialization is random.\n \n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)\n W1 = np.random.randn(n_h,n_x) * 0.01\n b1 = np.zeros((n_h,1))\n W2 = np.random.randn(n_y,n_h) * 0.01\n b2 = np.zeros((n_y,1))\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n assert (W1.shape == (n_h, n_x))\n assert (b1.shape == (n_h, 1))\n assert (W2.shape == (n_y, n_h))\n assert (b2.shape == (n_y, 1))\n \n parameters = {\"W1\": W1,\n \"b1\": b1,\n \"W2\": W2,\n \"b2\": b2}\n \n return parameters",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"n_x, n_h, n_y = initialize_parameters_test_case()\n\nparameters = initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y)\nprint(\"W1 = \" + str(parameters[\"W1\"]))\nprint(\"b1 = \" + str(parameters[\"b1\"]))\nprint(\"W2 = \" + str(parameters[\"W2\"]))\nprint(\"b2 = \" + str(parameters[\"b2\"]))",
"W1 = [[-0.00416758 -0.00056267]\n [-0.02136196 0.01640271]\n [-0.01793436 -0.00841747]\n [ 0.00502881 -0.01245288]]\nb1 = [[0.]\n [0.]\n [0.]\n [0.]]\nW2 = [[-0.01057952 -0.00909008 0.00551454 0.02292208]]\nb2 = [[0.]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**:\n\n<table style=\"width:90%\">\n <tr>\n <td>**W1**</td>\n <td> [[-0.00416758 -0.00056267]\n [-0.02136196 0.01640271]\n [-0.01793436 -0.00841747]\n [ 0.00502881 -0.01245288]] </td> \n </tr>\n \n <tr>\n <td>**b1**</td>\n <td> [[ 0.]\n [ 0.]\n [ 0.]\n [ 0.]] </td> \n </tr>\n \n <tr>\n <td>**W2**</td>\n <td> [[-0.01057952 -0.00909008 0.00551454 0.02292208]]</td> \n </tr>\n \n\n <tr>\n <td>**b2**</td>\n <td> [[ 0.]] </td> \n </tr>\n \n</table>\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.3 - The Loop ####\n\n**Question**: Implement `forward_propagation()`.\n\n**Instructions**:\n- Look above at the mathematical representation of your classifier.\n- You can use the function `sigmoid()`. It is built-in (imported) in the notebook.\n- You can use the function `np.tanh()`. It is part of the numpy library.\n- The steps you have to implement are:\n 1. Retrieve each parameter from the dictionary \"parameters\" (which is the output of `initialize_parameters()`) by using `parameters[\"..\"]`.\n 2. Implement Forward Propagation. Compute $Z^{[1]}, A^{[1]}, Z^{[2]}$ and $A^{[2]}$ (the vector of all your predictions on all the examples in the training set).\n- Values needed in the backpropagation are stored in \"`cache`\". The `cache` will be given as an input to the backpropagation function.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# GRADED FUNCTION: forward_propagation\n\ndef forward_propagation(X, parameters):\n \"\"\"\n Argument:\n X -- input data of size (n_x, m)\n parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters (output of initialization function)\n \n Returns:\n A2 -- The sigmoid output of the second activation\n cache -- a dictionary containing \"Z1\", \"A1\", \"Z2\" and \"A2\"\n \"\"\"\n # Retrieve each parameter from the dictionary \"parameters\"\n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)\n W1 = parameters[\"W1\"]\n b1 = parameters[\"b1\"]\n W2 = parameters[\"W2\"]\n b2 = parameters[\"b2\"]\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n # Implement Forward Propagation to calculate A2 (probabilities)\n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)\n Z1 = (np.dot(W1,X) + b1)\n A1 = np.tanh(Z1)\n Z2 = np.dot(W2,A1) + b2\n A2 = sigmoid(Z2)\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n assert(A2.shape == (1, X.shape[1]))\n \n cache = {\"Z1\": Z1,\n \"A1\": A1,\n \"Z2\": Z2,\n \"A2\": A2}\n \n return A2, cache",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_assess, parameters = forward_propagation_test_case()\nA2, cache = forward_propagation(X_assess, parameters)\n\n# Note: we use the mean here just to make sure that your output matches ours. \nprint(np.mean(cache['Z1']) ,np.mean(cache['A1']),np.mean(cache['Z2']),np.mean(cache['A2']))",
"0.26281864019752443 0.09199904522700109 -1.3076660128732143 0.21287768171914198\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**:\n<table style=\"width:50%\">\n <tr>\n <td> 0.262818640198 0.091999045227 -1.30766601287 0.212877681719 </td> \n </tr>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now that you have computed $A^{[2]}$ (in the Python variable \"`A2`\"), which contains $a^{[2](i)}$ for every example, you can compute the cost function as follows:\n\n$$J = - \\frac{1}{m} \\sum\\limits_{i = 1}^{m} \\large{(} \\small y^{(i)}\\log\\left(a^{[2] (i)}\\right) + (1-y^{(i)})\\log\\left(1- a^{[2] (i)}\\right) \\large{)} \\small\\tag{13}$$\n\n**Exercise**: Implement `compute_cost()` to compute the value of the cost $J$.\n\n**Instructions**:\n- There are many ways to implement the cross-entropy loss. To help you, we give you how we would have implemented\n$- \\sum\\limits_{i=0}^{m} y^{(i)}\\log(a^{[2](i)})$:\n```python\nlogprobs = np.multiply(np.log(A2),Y)\ncost = - np.sum(logprobs) # no need to use a for loop!\n```\n\n(you can use either `np.multiply()` and then `np.sum()` or directly `np.dot()`). \nNote that if you use `np.multiply` followed by `np.sum` the end result will be a type `float`, whereas if you use `np.dot`, the result will be a 2D numpy array. We can use `np.squeeze()` to remove redundant dimensions (in the case of single float, this will be reduced to a zero-dimension array). We can cast the array as a type `float` using `float()`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# GRADED FUNCTION: compute_cost\n\ndef compute_cost(A2, Y, parameters):\n \"\"\"\n Computes the cross-entropy cost given in equation (13)\n \n Arguments:\n A2 -- The sigmoid output of the second activation, of shape (1, number of examples)\n Y -- \"true\" labels vector of shape (1, number of examples)\n parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters W1, b1, W2 and b2\n [Note that the parameters argument is not used in this function, \n but the auto-grader currently expects this parameter.\n Future version of this notebook will fix both the notebook \n and the auto-grader so that `parameters` is not needed.\n For now, please include `parameters` in the function signature,\n and also when invoking this function.]\n \n Returns:\n cost -- cross-entropy cost given equation (13)\n \n \"\"\"\n \n m = Y.shape[1] # number of example\n first_part = np.multiply(np.log(A2),Y)\n second_part = np.multiply(np.log(1-A2),(1-Y))\n # Compute the cross-entropy cost\n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)\n logprobs = -np.sum(first_part+second_part)\n cost = logprobs/m\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n cost = float(np.squeeze(cost)) # makes sure cost is the dimension we expect. \n # E.g., turns [[17]] into 17 \n assert(isinstance(cost, float))\n \n return cost",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"A2, Y_assess, parameters = compute_cost_test_case()\n\nprint(\"cost = \" + str(compute_cost(A2, Y_assess, parameters)))",
"cost = 0.6930587610394646\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**:\n<table style=\"width:20%\">\n <tr>\n <td>**cost**</td>\n <td> 0.693058761... </td> \n </tr>\n \n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Using the cache computed during forward propagation, you can now implement backward propagation.\n\n**Question**: Implement the function `backward_propagation()`.\n\n**Instructions**:\nBackpropagation is usually the hardest (most mathematical) part in deep learning. To help you, here again is the slide from the lecture on backpropagation. You'll want to use the six equations on the right of this slide, since you are building a vectorized implementation. \n\n<img src=\"images/grad_summary.png\" style=\"width:600px;height:300px;\">\n\n<!--\n$\\frac{\\partial \\mathcal{J} }{ \\partial z_{2}^{(i)} } = \\frac{1}{m} (a^{[2](i)} - y^{(i)})$\n\n$\\frac{\\partial \\mathcal{J} }{ \\partial W_2 } = \\frac{\\partial \\mathcal{J} }{ \\partial z_{2}^{(i)} } a^{[1] (i) T} $\n\n$\\frac{\\partial \\mathcal{J} }{ \\partial b_2 } = \\sum_i{\\frac{\\partial \\mathcal{J} }{ \\partial z_{2}^{(i)}}}$\n\n$\\frac{\\partial \\mathcal{J} }{ \\partial z_{1}^{(i)} } = W_2^T \\frac{\\partial \\mathcal{J} }{ \\partial z_{2}^{(i)} } * ( 1 - a^{[1] (i) 2}) $\n\n$\\frac{\\partial \\mathcal{J} }{ \\partial W_1 } = \\frac{\\partial \\mathcal{J} }{ \\partial z_{1}^{(i)} } X^T $\n\n$\\frac{\\partial \\mathcal{J} _i }{ \\partial b_1 } = \\sum_i{\\frac{\\partial \\mathcal{J} }{ \\partial z_{1}^{(i)}}}$\n\n- Note that $*$ denotes elementwise multiplication.\n- The notation you will use is common in deep learning coding:\n - dW1 = $\\frac{\\partial \\mathcal{J} }{ \\partial W_1 }$\n - db1 = $\\frac{\\partial \\mathcal{J} }{ \\partial b_1 }$\n - dW2 = $\\frac{\\partial \\mathcal{J} }{ \\partial W_2 }$\n - db2 = $\\frac{\\partial \\mathcal{J} }{ \\partial b_2 }$\n \n!-->\n\n- Tips:\n - To compute dZ1 you'll need to compute $g^{[1]'}(Z^{[1]})$. Since $g^{[1]}(.)$ is the tanh activation function, if $a = g^{[1]}(z)$ then $g^{[1]'}(z) = 1-a^2$. So you can compute \n $g^{[1]'}(Z^{[1]})$ using `(1 - np.power(A1, 2))`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# GRADED FUNCTION: backward_propagation\n\ndef backward_propagation(parameters, cache, X, Y):\n \"\"\"\n Implement the backward propagation using the instructions above.\n \n Arguments:\n parameters -- python dictionary containing our parameters \n cache -- a dictionary containing \"Z1\", \"A1\", \"Z2\" and \"A2\".\n X -- input data of shape (2, number of examples)\n Y -- \"true\" labels vector of shape (1, number of examples)\n \n Returns:\n grads -- python dictionary containing your gradients with respect to different parameters\n \"\"\"\n m = X.shape[1]\n \n # First, retrieve W1 and W2 from the dictionary \"parameters\".\n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)\n W1 = parameters[\"W1\"]\n W2 = parameters[\"W2\"]\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n # Retrieve also A1 and A2 from dictionary \"cache\".\n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)\n A1 = cache[\"A1\"]\n A2 = cache[\"A2\"]\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n # Backward propagation: calculate dW1, db1, dW2, db2. \n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 6 lines of code, corresponding to 6 equations on slide above)\n dZ2 = A2-Y\n dW2 = np.dot(dZ2,A1.T)/m\n db2 = np.sum(dZ2,axis=1,keepdims=True)/m\n dZ1 = np.dot(W2.T,dZ2) * (1-np.power(A1,2))\n dW1 = np.dot(dZ1,X.T)/m\n db1 = np.sum(dZ1,axis=1,keepdims=True)/m\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n grads = {\"dW1\": dW1,\n \"db1\": db1,\n \"dW2\": dW2,\n \"db2\": db2}\n \n return grads",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"parameters, cache, X_assess, Y_assess = backward_propagation_test_case()\n\ngrads = backward_propagation(parameters, cache, X_assess, Y_assess)\nprint (\"dW1 = \"+ str(grads[\"dW1\"]))\nprint (\"db1 = \"+ str(grads[\"db1\"]))\nprint (\"dW2 = \"+ str(grads[\"dW2\"]))\nprint (\"db2 = \"+ str(grads[\"db2\"]))",
"dW1 = [[ 0.00301023 -0.00747267]\n [ 0.00257968 -0.00641288]\n [-0.00156892 0.003893 ]\n [-0.00652037 0.01618243]]\ndb1 = [[ 0.00176201]\n [ 0.00150995]\n [-0.00091736]\n [-0.00381422]]\ndW2 = [[ 0.00078841 0.01765429 -0.00084166 -0.01022527]]\ndb2 = [[-0.16655712]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected output**:\n\n\n\n<table style=\"width:80%\">\n <tr>\n <td>**dW1**</td>\n <td> [[ 0.00301023 -0.00747267]\n [ 0.00257968 -0.00641288]\n [-0.00156892 0.003893 ]\n [-0.00652037 0.01618243]] </td> \n </tr>\n \n <tr>\n <td>**db1**</td>\n <td> [[ 0.00176201]\n [ 0.00150995]\n [-0.00091736]\n [-0.00381422]] </td> \n </tr>\n \n <tr>\n <td>**dW2**</td>\n <td> [[ 0.00078841 0.01765429 -0.00084166 -0.01022527]] </td> \n </tr>\n \n\n <tr>\n <td>**db2**</td>\n <td> [[-0.16655712]] </td> \n </tr>\n \n</table> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Question**: Implement the update rule. Use gradient descent. You have to use (dW1, db1, dW2, db2) in order to update (W1, b1, W2, b2).\n\n**General gradient descent rule**: $ \\theta = \\theta - \\alpha \\frac{\\partial J }{ \\partial \\theta }$ where $\\alpha$ is the learning rate and $\\theta$ represents a parameter.\n\n**Illustration**: The gradient descent algorithm with a good learning rate (converging) and a bad learning rate (diverging). Images courtesy of Adam Harley.\n\n<img src=\"images/sgd.gif\" style=\"width:400;height:400;\"> <img src=\"images/sgd_bad.gif\" style=\"width:400;height:400;\">\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# GRADED FUNCTION: update_parameters\n\ndef update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate = 1.2):\n \"\"\"\n Updates parameters using the gradient descent update rule given above\n \n Arguments:\n parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters \n grads -- python dictionary containing your gradients \n \n Returns:\n parameters -- python dictionary containing your updated parameters \n \"\"\"\n # Retrieve each parameter from the dictionary \"parameters\"\n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)\n W1 = parameters[\"W1\"]\n b1 = parameters[\"b1\"]\n W2 = parameters[\"W2\"]\n b2 = parameters[\"b2\"]\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n # Retrieve each gradient from the dictionary \"grads\"\n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)\n dW1 = grads[\"dW1\"]\n db1 = grads[\"db1\"]\n dW2 = grads[\"dW2\"]\n db2 = grads[\"db2\"]\n ## END CODE HERE ###\n \n # Update rule for each parameter\n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)\n W1 = W1 - learning_rate * dW1\n b1 = b1 - learning_rate * db1\n W2 = W2 - learning_rate * dW2\n b2 = b2 - learning_rate * db2\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n parameters = {\"W1\": W1,\n \"b1\": b1,\n \"W2\": W2,\n \"b2\": b2}\n \n return parameters",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"parameters, grads = update_parameters_test_case()\nparameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads)\n\nprint(\"W1 = \" + str(parameters[\"W1\"]))\nprint(\"b1 = \" + str(parameters[\"b1\"]))\nprint(\"W2 = \" + str(parameters[\"W2\"]))\nprint(\"b2 = \" + str(parameters[\"b2\"]))",
"W1 = [[-0.00643025 0.01936718]\n [-0.02410458 0.03978052]\n [-0.01653973 -0.02096177]\n [ 0.01046864 -0.05990141]]\nb1 = [[-1.02420756e-06]\n [ 1.27373948e-05]\n [ 8.32996807e-07]\n [-3.20136836e-06]]\nW2 = [[-0.01041081 -0.04463285 0.01758031 0.04747113]]\nb2 = [[0.00010457]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**:\n\n\n<table style=\"width:80%\">\n <tr>\n <td>**W1**</td>\n <td> [[-0.00643025 0.01936718]\n [-0.02410458 0.03978052]\n [-0.01653973 -0.02096177]\n [ 0.01046864 -0.05990141]]</td> \n </tr>\n \n <tr>\n <td>**b1**</td>\n <td> [[ -1.02420756e-06]\n [ 1.27373948e-05]\n [ 8.32996807e-07]\n [ -3.20136836e-06]]</td> \n </tr>\n \n <tr>\n <td>**W2**</td>\n <td> [[-0.01041081 -0.04463285 0.01758031 0.04747113]] </td> \n </tr>\n \n\n <tr>\n <td>**b2**</td>\n <td> [[ 0.00010457]] </td> \n </tr>\n \n</table> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.4 - Integrate parts 4.1, 4.2 and 4.3 in nn_model() ####\n\n**Question**: Build your neural network model in `nn_model()`.\n\n**Instructions**: The neural network model has to use the previous functions in the right order.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# GRADED FUNCTION: nn_model\n\ndef nn_model(X, Y, n_h, num_iterations = 10000, print_cost=False):\n \"\"\"\n Arguments:\n X -- dataset of shape (2, number of examples)\n Y -- labels of shape (1, number of examples)\n n_h -- size of the hidden layer\n num_iterations -- Number of iterations in gradient descent loop\n print_cost -- if True, print the cost every 1000 iterations\n \n Returns:\n parameters -- parameters learnt by the model. They can then be used to predict.\n \"\"\"\n \n np.random.seed(3)\n n_x = layer_sizes(X, Y)[0]\n n_y = layer_sizes(X, Y)[2]\n \n # Initialize parameters\n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)\n parameters = initialize_parameters(n_x,n_h,n_y)\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n # Loop (gradient descent)\n\n for i in range(0, num_iterations):\n \n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)\n # Forward propagation. Inputs: \"X, parameters\". Outputs: \"A2, cache\".\n A2, cache = forward_propagation(X,parameters)\n \n # Cost function. Inputs: \"A2, Y, parameters\". Outputs: \"cost\".\n cost = compute_cost(A2,Y,parameters)\n \n # Backpropagation. Inputs: \"parameters, cache, X, Y\". Outputs: \"grads\".\n grads = backward_propagation(parameters,cache,X,Y)\n \n # Gradient descent parameter update. Inputs: \"parameters, grads\". Outputs: \"parameters\".\n parameters = update_parameters(parameters,grads)\n \n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n # Print the cost every 1000 iterations\n if print_cost and i % 1000 == 0:\n print (\"Cost after iteration %i: %f\" %(i, cost))\n\n return parameters",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_assess, Y_assess = nn_model_test_case()\nparameters = nn_model(X_assess, Y_assess, 4, num_iterations=10000, print_cost=True)\nprint(\"W1 = \" + str(parameters[\"W1\"]))\nprint(\"b1 = \" + str(parameters[\"b1\"]))\nprint(\"W2 = \" + str(parameters[\"W2\"]))\nprint(\"b2 = \" + str(parameters[\"b2\"]))",
"Cost after iteration 0: 0.692739\nCost after iteration 1000: 0.000218\nCost after iteration 2000: 0.000107\nCost after iteration 3000: 0.000071\nCost after iteration 4000: 0.000053\nCost after iteration 5000: 0.000042\nCost after iteration 6000: 0.000035\nCost after iteration 7000: 0.000030\nCost after iteration 8000: 0.000026\nCost after iteration 9000: 0.000023\nW1 = [[-0.65848169 1.21866811]\n [-0.76204273 1.39377573]\n [ 0.5792005 -1.10397703]\n [ 0.76773391 -1.41477129]]\nb1 = [[ 0.287592 ]\n [ 0.3511264 ]\n [-0.2431246 ]\n [-0.35772805]]\nW2 = [[-2.45566237 -3.27042274 2.00784958 3.36773273]]\nb2 = [[0.20459656]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**:\n\n<table style=\"width:90%\">\n\n<tr> \n <td> \n **cost after iteration 0**\n </td>\n <td> \n 0.692739\n </td>\n</tr>\n\n<tr> \n <td> \n <center> $\\vdots$ </center>\n </td>\n <td> \n <center> $\\vdots$ </center>\n </td>\n</tr>\n\n <tr>\n <td>**W1**</td>\n <td> [[-0.65848169 1.21866811]\n [-0.76204273 1.39377573]\n [ 0.5792005 -1.10397703]\n [ 0.76773391 -1.41477129]]</td> \n </tr>\n \n <tr>\n <td>**b1**</td>\n <td> [[ 0.287592 ]\n [ 0.3511264 ]\n [-0.2431246 ]\n [-0.35772805]] </td> \n </tr>\n \n <tr>\n <td>**W2**</td>\n <td> [[-2.45566237 -3.27042274 2.00784958 3.36773273]] </td> \n </tr>\n \n\n <tr>\n <td>**b2**</td>\n <td> [[ 0.20459656]] </td> \n </tr>\n \n</table> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.5 Predictions\n\n**Question**: Use your model to predict by building predict().\nUse forward propagation to predict results.\n\n**Reminder**: predictions = $y_{prediction} = \\mathbb 1 \\text{{activation > 0.5}} = \\begin{cases}\n 1 & \\text{if}\\ activation > 0.5 \\\\\n 0 & \\text{otherwise}\n \\end{cases}$ \n \nAs an example, if you would like to set the entries of a matrix X to 0 and 1 based on a threshold you would do: ```X_new = (X > threshold)```",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# GRADED FUNCTION: predict\n\ndef predict(parameters, X):\n \"\"\"\n Using the learned parameters, predicts a class for each example in X\n \n Arguments:\n parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters \n X -- input data of size (n_x, m)\n \n Returns\n predictions -- vector of predictions of our model (red: 0 / blue: 1)\n \"\"\"\n \n # Computes probabilities using forward propagation, and classifies to 0/1 using 0.5 as the threshold.\n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)\n A2, cache = forward_propagation(X,parameters)\n predictions = A2 > 0.5\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n return predictions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"parameters, X_assess = predict_test_case()\n\npredictions = predict(parameters, X_assess)\nprint(\"predictions mean = \" + str(np.mean(predictions)))",
"predictions mean = 0.6666666666666666\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**: \n\n\n<table style=\"width:40%\">\n <tr>\n <td>**predictions mean**</td>\n <td> 0.666666666667 </td> \n </tr>\n \n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"It is time to run the model and see how it performs on a planar dataset. Run the following code to test your model with a single hidden layer of $n_h$ hidden units.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Build a model with a n_h-dimensional hidden layer\nparameters = nn_model(X, Y, n_h = 4, num_iterations = 10000, print_cost=True)\n\n# Plot the decision boundary\nplot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict(parameters, x.T), X, np.squeeze(Y))\nplt.title(\"Decision Boundary for hidden layer size \" + str(4))",
"Cost after iteration 0: 0.693048\nCost after iteration 1000: 0.288083\nCost after iteration 2000: 0.254385\nCost after iteration 3000: 0.233864\nCost after iteration 4000: 0.226792\nCost after iteration 5000: 0.222644\nCost after iteration 6000: 0.219731\nCost after iteration 7000: 0.217504\nCost after iteration 8000: 0.219439\nCost after iteration 9000: 0.218553\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**:\n\n<table style=\"width:40%\">\n <tr>\n <td>**Cost after iteration 9000**</td>\n <td> 0.218607 </td> \n </tr>\n \n</table>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Print accuracy\npredictions = predict(parameters, X)\nprint ('Accuracy: %d' % float((np.dot(Y,predictions.T) + np.dot(1-Y,1-predictions.T))/float(Y.size)*100) + '%')",
"Accuracy: 90%\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**: \n\n<table style=\"width:15%\">\n <tr>\n <td>**Accuracy**</td>\n <td> 90% </td> \n </tr>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Accuracy is really high compared to Logistic Regression. The model has learnt the leaf patterns of the flower! Neural networks are able to learn even highly non-linear decision boundaries, unlike logistic regression. \n\nNow, let's try out several hidden layer sizes.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.6 - Tuning hidden layer size (optional/ungraded exercise) ###\n\nRun the following code. It may take 1-2 minutes. You will observe different behaviors of the model for various hidden layer sizes.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# This may take about 2 minutes to run\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(16, 32))\nhidden_layer_sizes = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 20, 50]\nfor i, n_h in enumerate(hidden_layer_sizes):\n plt.subplot(5, 2, i+1)\n plt.title('Hidden Layer of size %d' % n_h)\n parameters = nn_model(X, Y, n_h, num_iterations = 5000)\n plot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict(parameters, x.T), X, np.squeeze(Y))\n predictions = predict(parameters, X)\n accuracy = float((np.dot(Y,predictions.T) + np.dot(1-Y,1-predictions.T))/float(Y.size)*100)\n print (\"Accuracy for {} hidden units: {} %\".format(n_h, accuracy))",
"Accuracy for 1 hidden units: 67.5 %\nAccuracy for 2 hidden units: 67.25 %\nAccuracy for 3 hidden units: 90.75 %\nAccuracy for 4 hidden units: 90.5 %\nAccuracy for 5 hidden units: 91.25 %\nAccuracy for 20 hidden units: 90.5 %\nAccuracy for 50 hidden units: 90.25 %\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Interpretation**:\n- The larger models (with more hidden units) are able to fit the training set better, until eventually the largest models overfit the data. \n- The best hidden layer size seems to be around n_h = 5. Indeed, a value around here seems to fits the data well without also incurring noticeable overfitting.\n- You will also learn later about regularization, which lets you use very large models (such as n_h = 50) without much overfitting. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Optional questions**:\n\n**Note**: Remember to submit the assignment by clicking the blue \"Submit Assignment\" button at the upper-right. \n\nSome optional/ungraded questions that you can explore if you wish: \n- What happens when you change the tanh activation for a sigmoid activation or a ReLU activation?\n- Play with the learning_rate. What happens?\n- What if we change the dataset? (See part 5 below!)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<font color='blue'>\n**You've learnt to:**\n- Build a complete neural network with a hidden layer\n- Make a good use of a non-linear unit\n- Implemented forward propagation and backpropagation, and trained a neural network\n- See the impact of varying the hidden layer size, including overfitting.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Nice work! ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 5) Performance on other datasets",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"If you want, you can rerun the whole notebook (minus the dataset part) for each of the following datasets.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Datasets\nnoisy_circles, noisy_moons, blobs, gaussian_quantiles, no_structure = load_extra_datasets()\n\ndatasets = {\"noisy_circles\": noisy_circles,\n \"noisy_moons\": noisy_moons,\n \"blobs\": blobs,\n \"gaussian_quantiles\": gaussian_quantiles}\n\n### START CODE HERE ### (choose your dataset)\ndataset = \"noisy_moons\"\n### END CODE HERE ###\n\nX, Y = datasets[dataset]\nX, Y = X.T, Y.reshape(1, Y.shape[0])\n\n# make blobs binary\nif dataset == \"blobs\":\n Y = Y%2\n\n# Visualize the data\nplt.scatter(X[0, :], X[1, :], c=np.squeeze(Y), s=40, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Congrats on finishing this Programming Assignment!\n\nReference:\n- http://scs.ryerson.ca/~aharley/neural-networks/\n- http://cs231n.github.io/neural-networks-case-study/",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe8f2ac1acb09a9fbc238656088c7c8a67fed35
| 2,326 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
text_docs/text_generator.ipynb
|
ZiggerZZ/DB-TF-IDF
|
2de2f4bb1fdd02128ad1c9cf75184ea318cc68a9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
text_docs/text_generator.ipynb
|
ZiggerZZ/DB-TF-IDF
|
2de2f4bb1fdd02128ad1c9cf75184ea318cc68a9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
text_docs/text_generator.ipynb
|
ZiggerZZ/DB-TF-IDF
|
2de2f4bb1fdd02128ad1c9cf75184ea318cc68a9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 26.431818 | 127 | 0.521926 |
[
[
[
"from nltk.corpus import brown\nimport random \ncorpus_length = len(brown.words())\nhardcopy = brown.words()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def create_docs(number_of_words_per_doc = 200, num_doc = 10,startnr = 0):\n # control number of words per doc \n # and number of documents \n #we fix the line length at 20\n line_length = 20 \n number_of_lines = int(number_of_words_per_doc / line_length)\n\n for i in range(0,num_doc):\n #create new file with writing + permission\n new_file = open(\"getsize\"+str(number_of_words_per_doc) +\"words\" + str(i+startnr)+\".txt\",\"w+\")\n for line in range(0,number_of_lines):\n words = list(map(lambda x:hardcopy[x:x+line_length], random.sample(range(corpus_length), line_length ) ))\n sentences = list(map(lambda x: ' '.join(word for word in x) , words))\n text = ''.join(map(str, sentences))\n new_file.write(text + \"\\n\")\n new_file.close()\n if (i%10==0):\n print(\"You created \"+str(i)+\" files! \"+str(num_doc-i)+\" left\")\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"create_docs(number_of_words_per_doc = 300, num_doc = 1,startnr = 2)",
"You created 0 files! 1 left\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe8f2f79c09d3a11399bf797777fc6efd0164fa
| 15,622 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/tutorial/Drive_PDA_Ch12_Recording.ipynb
|
danielmartincraig/Jove
|
4642da25557f0baeb6b34a538d8c76fd2480ee7a
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/tutorial/Drive_PDA_Ch12_Recording.ipynb
|
danielmartincraig/Jove
|
4642da25557f0baeb6b34a538d8c76fd2480ee7a
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/tutorial/Drive_PDA_Ch12_Recording.ipynb
|
danielmartincraig/Jove
|
4642da25557f0baeb6b34a538d8c76fd2480ee7a
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null | 21.637119 | 94 | 0.415568 |
[
[
[
"# This Youtube video walks through this notebook\nfrom IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\nYouTubeVideo('cvVl1lQ4agU')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
" # Tests on PDA",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from jove.SystemImports import *\nfrom jove.DotBashers import *\nfrom jove.Def_md2mc import *\nfrom jove.Def_PDA import *",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pdaDyck = md2mc('''PDA\nIF : (, #; (# -> A\nA : (, (; (( -> A\nA : ), (; '' -> A\nA : '',#; # -> IF\n''')\nDOpdaDyck = dotObj_pda(pdaDyck, FuseEdges=True)\nDOpdaDyck",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"explore_pda(\"\", pdaDyck)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"explore_pda(\"()\", pdaDyck)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"explore_pda(\"()()(())\", pdaDyck)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"explore_pda(\"()()(()\", pdaDyck) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pda1 = md2mc('''PDA\nI : a, b; c -> F\n''')\nDOpda1 = dotObj_pda(pda1, FuseEdges=True)\nDOpda1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pda2 = md2mc('''PDA\nI : a, b ; c -> F\nI : '', ''; d -> A\nA : '', d ; '' -> F\n''')\nDOpda2 = dotObj_pda(pda2, FuseEdges=True)\nDOpda2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"DOpda2.source",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"explore_pda(\"a\", pda1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"explore_pda(\"a\", pda2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pda3 = md2mc('''PDA\nI : a, b ; c -> F\nI : '', ''; d -> A\nA : a, d ; '' -> F\n''')\nDOpda3 = dotObj_pda(pda3, FuseEdges=True)\nDOpda3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"DOpda3.source",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"explore_pda(\"a\", pda3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pda4 = md2mc('''PDA\nI : a, # ; c -> F\nI : '', ''; d -> A\nA : a, d ; '' -> F\n''')\nDOpda4 = dotObj_pda(pda4, FuseEdges=True)\nDOpda4",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"explore_pda(\"a\", pda4)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pda5 = md2mc('''PDA\nI : a, # ; c -> F\nI : '', ''; d -> A\nA : '', ''; '' -> A\nA : a, d ; '' -> F\n''')\nDOpda5 = dotObj_pda(pda5, FuseEdges=True)\nDOpda5",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"DOpda5.source",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"explore_pda(\"a\", pda5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pda6 = md2mc('''PDA\nI : a, # ; c -> F\nI : '', ''; d -> A\nA : '', ''; z -> A\nA : '', z ; '' -> B\nB : '', z ; '' -> C\nC : '', z ; '' -> C\nC : '', # ; '' | a, d; '' -> F\nA : a, d ; '' -> F\n''')\nDOpda6 = dotObj_pda(pda6, FuseEdges=True)\nDOpda6",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"DOpda6.source",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"explore_pda(\"a\", pda6)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"explore_pda(\"a\", pda6, chatty=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"explore_pda(\"a\", pda6, STKMAX = 6, chatty=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"f27sip = md2mc('''PDA \n!!---------------------------------------------------------------------------\n!! This is a PDA From Sipser's book\n!! This matches a's and b's ignoring c's\n!! or matches a's and c's, ignoring b's in the middle\n!! thus matching either a^m b^m c^n or a^m b^n c^m\n!!---------------------------------------------------------------------------\n\n!!---------------------------------------------------------------------------\n!! State: in , sin ; spush -> tostates !! comment\n!!---------------------------------------------------------------------------\niq1 : '' , '' ; $ -> q2 !! start in init state by pushing a $\n\nq2 : a , '' ; a -> q2 !! stack a's\nq2 : '' , '' ; '' -> q3,q5 !! split non-det for a^m b^m c^n (q3)\n !! or a^m b^n c^m (q5)\n\nq3 : b , a ; '' -> q3 !! match b's against a's\nq3 : '' , $ ; '' -> fq4 !! hope for acceptance when $ surfaces\n\nfq4 : c , '' ; '' -> fq4 !! be happy so long as c's come\n !! will choke and reject if anything\n !! other than c's come\n\nq5 : b , '' ; '' -> q5 !! here, we are going to punt over b's\nq5 : '' , '' ; '' -> q6 !! and non-det decide to honor c's matching\n !! against a's\n\nq6 : c , a ; '' -> q6 !! OK to match so long as c's keep coming\nq6 : '' , $ ; '' -> fq7 !! when $ surfaces, be ready to accept in\n !! state fq7. However, anything else coming in\n !! now will foil match and cause rejection.\n!!---------------------------------------------------------------------------\n!! You may use the line below as an empty shell to populate for your purposes\n!! Also serves as a syntax reminder for entering PDAs.\n!!\n!! State : i1 , si1 ; sp1 | i2 , si2 ; sp2 -> tos1, tos2 !! comment\n!!\n!! .. : .. , .. ; .. | .. , .. ; .. -> .. , .. !! ..\n!!---------------------------------------------------------------------------\n!!---------------------------------------------------------------------------\n!!\n!! Good commenting and software-engineering methods, good clean indentation,\n!! grouping of similar states, columnar alignment, etc etc. are HUGELY\n!! important in any programming endeavor -- especially while programming\n!! automata. Otherwise, you can easily make a mistake in your automaton\n!! code. Besides, you cannot rely upon others to find your mistakes, as\n!! they will find your automaton code impossible to read!\n!!\n!!---------------------------------------------------------------------------\n\n''')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Dof27sip = dotObj_pda(f27sip, FuseEdges=True)\nDof27sip",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"explore_pda(\"aaabbbccc\", f27sip)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Parsing an arithmetic expression\npdaEamb = md2mc('''PDA\n!!E -> E * E | E + E | ~E | ( E ) | 2 | 3\nI : '', # ; E# -> M\nM : '', E ; ~E -> M\nM : '', E ; E+E -> M\nM : '', E ; E*E -> M\nM : '', E ; (E) -> M\nM : '', E ; 2 -> M\nM : '', E ; 3 -> M\nM : ~, ~ ; '' -> M\nM : 2, 2 ; '' -> M\nM : 3, 3 ; '' -> M\nM : (, ( ; '' -> M\nM : ), ) ; '' -> M\nM : +, + ; '' -> M\nM : *, * ; '' -> M\nM : '', # ; # -> F\n'''\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"DOpdaEamb = dotObj_pda(pdaEamb, FuseEdges=True)\nDOpdaEamb",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"explore_pda(\"3+2*3+2*3\", pdaEamb, STKMAX=8)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Parsing an arithmetic expression\npdaE = md2mc('''PDA\n!!E -> E+T | T\n!!T -> T*F | F\n!!F -> 2 | 3 | ~F | (E)\nI : '', # ; E# -> M\nM : '', E ; E+T -> M\nM : '', E ; T -> M\nM : '', T ; T*F -> M\nM : '', T ; F -> M\nM : '', F ; 2 -> M\nM : '', F ; 3 -> M\nM : '', F ; ~F -> M\nM : '', F ; (E) -> M\nM : ~, ~ ; '' -> M\nM : 2, 2 ; '' -> M\nM : 3, 3 ; '' -> M\nM : (, ( ; '' -> M\nM : ), ) ; '' -> M\nM : +, + ; '' -> M\nM : *, * ; '' -> M\nM : '', # ; # -> F\n'''\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"DOpdaE = dotObj_pda(pdaE, FuseEdges=True)\nDOpdaE",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"explore_pda(\"3+3+2+2*3+2*3\", pdaE, STKMAX=5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"explore_pda(\"3*2*~3+~~3*~3\", pdaEamb, STKMAX=5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"explore_pda(\"3*~2*3+~2*3+3+~2+3*~2\", pdaE, STKMAX=13)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe8f6f235908c8d128416b4ad0d8b997533ec8c
| 187,868 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/16-17_UrbanRural-Land.ipynb
|
nicolepaul/30-day-map-challenge
|
919bb7ae967e4365eff3b7e07034f72f1059606f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 14 |
2021-11-02T00:41:56.000Z
|
2021-11-12T22:46:23.000Z
|
notebooks/16-17_UrbanRural-Land.ipynb
|
nicolepaul/30-day-map-challenge
|
919bb7ae967e4365eff3b7e07034f72f1059606f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/16-17_UrbanRural-Land.ipynb
|
nicolepaul/30-day-map-challenge
|
919bb7ae967e4365eff3b7e07034f72f1059606f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 73.015157 | 45,129 | 0.684874 |
[
[
[
"# Day 16-17: Urban/Rural - Land\n\nI need to catch up...\n\nThis won't be the most artistic day, but I would find it useful in my life to have code that downloads GHSL datasets and plots them.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Configuration",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\nimport rioxarray\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport matplotlib.colors as colors\n\n%matplotlib inline\n%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'svg'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## GHSL-POP\nPopulation dataset from [Global Human Settlement Layer, GHSL](https://ghsl.jrc.ec.europa.eu/)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Choose tile of interest\ntile = \"28_9\"\n\n# Arrange URL\nurl = (\"zip+https://cidportal.jrc.ec.europa.eu/\"\\\n \"ftp/jrc-opendata/GHSL/\"\\\n \"GHS_POP_MT_GLOBE_R2019A/\"\\\n \"GHS_POP_E2015_GLOBE_R2019A_54009_1K/\"\\\n \"V1-0/tiles/\"\\\n f\"GHS_POP_E2015_GLOBE_R2019A_54009_1K_V1_0_{tile}.zip\"\\\n f\"!GHS_POP_E2015_GLOBE_R2019A_54009_1K_V1_0_{tile}.tif\")\n\n# Read data\npop = rioxarray.open_rasterio(url, masked=True)\n\n# Preview\npop",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Construct plot\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,6))\nim = pop.squeeze().plot.imshow(\n ax=ax,\n vmin=0,\n vmax=1000,\n cmap='inferno',\n cbar_kwargs={\"label\": \"Population\"}\n )\nax.axis('off')\nax.set(title=\"GHSL-POP\")\n\n# Save\nout_file = f\"16-17_POP.png\"\nout_path = os.path.join(\"..\", \"contributions\", out_file)\nfig.savefig(out_path, dpi=300, facecolor=\"w\", bbox_inches=\"tight\")\n\n# Preview\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## GHSL-SMOD\nSettlement dataset from [Global Human Settlement Layer, GHSL](https://ghsl.jrc.ec.europa.eu/)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Arrange URL\nurl = (\"zip+https://cidportal.jrc.ec.europa.eu/\"\\\n \"ftp/jrc-opendata/GHSL/\"\\\n \"GHS_SMOD_POP_GLOBE_R2019A/\"\\\n \"GHS_SMOD_POP2015_GLOBE_R2019A_54009_1K/\"\\\n \"V2-0/tiles/\"\\\n f\"GHS_SMOD_POP2015_GLOBE_R2019A_54009_1K_V2_0_{tile}.zip\"\\\n f\"!GHS_SMOD_POP2015_GLOBE_R2019A_54009_1K_V2_0_{tile}.tif\")\n\n# Read data\nsmod = rioxarray.open_rasterio(url, masked=True)\n\n# Preview\nsmod",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Set colors\ncmap_discrete = colors.ListedColormap([\"#ffffff\",\"#7ab6f5\",\"#cdf57a\",\"#abcd66\",\"#375623\",\"#ffff00\",\"#a87000\",\"#732600\",\"#ff0000\"])\ncmap_labels = [\"n/a\",\"Water\",\"Very low density rural\",\"Low density rural\",\"Rural\",\"Suburban or peri-urban\",\"Semi-dense urban cluster\",\"Dense urban cluster\",\"Urban centre\"] \ncmap_vals = [-200,10,11,12,13,21,22,23,30.1]\n\n# Construct map\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,6))\nim = smod.squeeze().plot.imshow(ax=ax,\n cmap=cmap_discrete,\n levels=cmap_vals,\n add_colorbar=False,\n )\ncbar = ax.figure.colorbar(im, ax=ax, ticks=cmap_vals)\ncbar.set_ticklabels(cmap_labels)\nax.set(title=\"GHSL-SMOD\")\nax.axis('off')\n\n# Save\nout_file = f\"16-17_SMOD.png\"\nout_path = os.path.join(\"..\", \"contributions\", out_file)\nfig.savefig(out_path, dpi=300, facecolor=\"w\", bbox_inches=\"tight\")\n\n# Preview\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe8f82fcbb4c21ad19624e2977cceafe6963b91
| 1,576 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
venv/Lib/site-packages/nbdime/tests/files/multi_cell_nb--cellchange.ipynb
|
PeerHerholz/guideline_jupyter_book
|
ce445e4be0d53370b67708a22550565b90d71ac6
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 2 |
2021-02-16T16:17:07.000Z
|
2021-11-08T20:27:13.000Z
|
venv/Lib/site-packages/nbdime/tests/files/multi_cell_nb--cellchange.ipynb
|
PeerHerholz/guideline_jupyter_book
|
ce445e4be0d53370b67708a22550565b90d71ac6
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
venv/Lib/site-packages/nbdime/tests/files/multi_cell_nb--cellchange.ipynb
|
PeerHerholz/guideline_jupyter_book
|
ce445e4be0d53370b67708a22550565b90d71ac6
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 4 |
2020-11-14T17:05:36.000Z
|
2020-11-16T18:44:54.000Z
| 15.919192 | 37 | 0.458756 |
[
[
[
"from math import sqrt\n\ndef f(x, y):\n r2 = x**2 + y**2\n return sqrt(r2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l = f(3, 4)\nprint(l)",
"5.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"## from Inserted Markdown cell!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"f(6, -2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
cbe8fed6cdfb31dc488e58cc7184315d5f3c4afd
| 272,618 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
ERHS2.ipynb
|
jolterhs/ERHS
|
30f8ec243e8d936ba0e0a95f0dd9dd5f5383b00f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
ERHS2.ipynb
|
jolterhs/ERHS
|
30f8ec243e8d936ba0e0a95f0dd9dd5f5383b00f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
ERHS2.ipynb
|
jolterhs/ERHS
|
30f8ec243e8d936ba0e0a95f0dd9dd5f5383b00f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2018-12-03T09:03:10.000Z
|
2018-12-03T09:03:10.000Z
| 85.999369 | 55,316 | 0.735502 |
[
[
[
"import arff\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport os\nimport subprocess\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport re\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score\nfrom sklearn.decomposition import PCA\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df1 = pd.read_csv('/home/veerlosar/Desktop/df.csv', encoding='utf-8')\n#Unnamed column csv \ndf1.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(list(df1).index('name'))\nprint(list(df1).index('frameTime'))\nprint(list(df1).index('F0_sma_min'))\nprint(list(df1).index('F0env_sma_minPos'))\nprint(list(df1).index('class'))",
"1\n2\n460\n482\n991\n"
],
[
"y = df1['class']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = df1.drop(['class', 'Unnamed: 0', 'name', 'frameTime', 'F0_sma_min', 'F0env_sma_minPos'], axis=1)\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"'''\nfrom scipy.stats import zscore\n\ndf = df.astype('float64').apply(zscore)\ndf.head()\n'''\ndf1.drop(['Unnamed: 0', 'name', 'frameTime', 'F0_sma_min', 'F0env_sma_minPos'], axis=1, inplace=True)\ndf1.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(df, y, test_size=0.18, random_state=42)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_test.isnull().sum().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#feature selection\nfrom sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest, chi2, f_classif\n\nselector = SelectKBest(score_func=f_classif, k=10).fit(X_train, y_train)\nranking = np.argsort(selector.scores_)[::-1]\nprint('Top-10 features according to SelectKBest, f_classif: ')\nprint()\nprint('{}'.format(df.columns[ranking][0:11]))",
"Top-10 features according to SelectKBest, f_classif: \n\nIndex(['F0env_sma_quartile2', 'F0_sma_quartile3', 'F0_sma_stddev',\n 'F0env_sma_quartile3', 'F0env_sma_de_amean', 'F0env_sma_linregc1',\n 'F0_sma_linregerrA', 'mfcc_sma[1]_quartile3', 'mfcc_sma[12]_max',\n 'F0_sma_linregerrQ', 'mfcc_sma[12]_linregerrQ'],\n dtype='object')\n"
],
[
"#models\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score\n\n\nclf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=250, max_depth=10,\n random_state=0)\nclf.fit(X_train, y_train)\ny_pred_clf_test = clf.predict(X_test)\ny_pred_clf_train = clf.predict(X_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_clf_test)) #no pca for random forest",
"0.9313725490196079\n"
],
[
"from sklearn import svm\n\n\nsvm_ = svm.SVC(kernel='linear') \nsvm_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#v = dict()\nt = dict()\nfor i in range(10, 986, 5):\n std_pca_svm_ = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), PCA(n_components=i), svm_)\n std_pca_svm_.fit(X_train, y_train)\n t[i] = accuracy_score(y_train, std_pca_svm_.predict(X_train))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"svm_pipeline = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), PCA(n_components=230), svm_)\nsvm_pipeline.fit(X_train, y_train)\nprint(accuracy_score(y_test, svm_pipeline.predict(X_test)))",
"0.9240196078431373\n"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(12,6))\nplt.plot(v.keys(), v.values())\nplt.plot(t.keys(), t.values(), color='red')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"svm_.fit(X_train, y_train)\ny_pred_svm_test = svm_.predict(X_test)\ny_pred_svm_train = svm_.predict(X_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier\n\ndt = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='gini', max_depth=10)\ndt.fit(X_train, y_train)\ny_pred_dt_test = dt.predict(X_test)\ny_pred_dt_train = dt.predict(X_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"'''\ntoo slow\n\n\nada_dt = AdaBoostClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=10),\n n_estimators=250,\n learning_rate=1.0)\n\nada_dt.fit(X_train, y_train)\ny_pred_ada_dt_test = ada_dt.predict(X_test)\ny_pred_ada_dt_train = ada_dt.predict(X_train)\n'''",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC\n\nlin_svm = LinearSVC(loss='squared_hinge', penalty='l1', dual=False)\nlin_svm.fit(X_train, y_train)\ny_pred_lin_svm_test = lin_svm.predict(X_test)\ny_pred_lin_svm_train = lin_svm.predict(X_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#accuracy without scaling and pca\n\nprint('Random Forests: ', accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_clf_test), accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred_clf_train))\nprint('Kernel SVM: ', accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_svm_test), accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred_svm_train), \n svm_.score(X_test, y_test))\nprint('Decision Tree: ', accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_dt_test), accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred_dt_train))\n#print('Decision Tree with AdaBoost: ', accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_ada_dt_test), accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred_ada_dt_train))\nprint('Linear SVM: ', accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_lin_svm_test), accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred_lin_svm_train))",
"Random Forests: 0.9313725490196079 1.0\nKernel SVM: 0.8529411764705882 1.0 0.8529411764705882\nDecision Tree: 0.8333333333333334 0.9768568353067815\nLinear SVM: 0.8774509803921569 1.0\n"
],
[
"importances = clf.feature_importances_\n\nprint(list(importances).index(max(importances)), max(importances))",
"472 0.023543248445896607\n"
],
[
"indices = np.argsort(importances)[::-1]\ntop_10_features = df.columns[indices][0:11]\nprint(top_10_features)",
"Index(['F0_sma_iqr2-3', 'F0env_sma_quartile3', 'F0_sma_quartile3',\n 'F0env_sma_iqr1-2', 'F0env_sma_quartile2', 'voiceProb_sma_iqr2-3',\n 'F0env_sma_linregc1', 'F0_sma_iqr1-3', 'F0_sma_quartile2',\n 'F0env_sma_de_amean', 'F0env_sma_quartile1'],\n dtype='object')\n"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(25, 10))\nplt.bar(indices, importances[indices])\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def predict_new(filename, model):\n arff_file = arff.load(open('{}.arff'.format(filename[:-4]), 'r'))\n df = pd.DataFrame(np.array(arff_file['data']))\n df.drop([0, 1, 459, 481, 990], axis=1, inplace=True)\n print(model.predict(df))\n return df\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\n\npreds = [y_pred_lin_svm_test, y_pred_dt_test, svm_pipeline.predict(X_test), y_pred_clf_test]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import itertools\ndef plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes,\n normalize=False,\n title='Confusion matrix',\n cmap=plt.cm.Blues):\n if normalize:\n cm = cm.astype('float') / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]\n print(\"Normalized confusion matrix\")\n else:\n print('Confusion matrix, without normalization')\n\n print(cm)\n\n plt.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap)\n plt.title(title)\n plt.colorbar()\n tick_marks = np.arange(len(classes))\n plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, rotation=45)\n plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes)\n\n fmt = '.2f' if normalize else 'd'\n thresh = cm.max() / 2.\n for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])):\n plt.text(j, i, format(cm[i, j], fmt),\n horizontalalignment=\"center\",\n color=\"white\" if cm[i, j] > thresh else \"black\")\n\n plt.ylabel('True label')\n plt.xlabel('Predicted label')\n plt.tight_layout()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class_names = ['angry', 'fear', 'happy', 'neutral']\nfor i in preds:\n plt.figure()\n plot_confusion_matrix(confusion_matrix(y_test, i), classes=class_names)\n\n plt.show()\n ",
"Confusion matrix, without normalization\n[[100 7 7 1]\n [ 5 95 6 2]\n [ 7 4 91 3]\n [ 3 2 2 73]]\n"
],
[
"d.values[0][472]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#x = df1[df1['class'] == 2.].loc[1178:1180].drop(['class'], axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# :D \n\ncolors = ['red', 'green', 'yellow', 'blue']\nplt.figure(figsize=(12,6))\n\nfor i, color in enumerate(colors):\n plt.scatter(df1['F0_sma_iqr2-3'].loc[df1['class']==i], df1['F0env_sma_quartile3'].loc[df1['class']==i], color=color)\n\n\n\nplt.show()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"top_10_features",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df2 = df1.drop(df1.columns[:449], axis=1).drop(df1.columns[501:949], axis=1)\ndf3 = df1.drop(df1.columns[:449], axis=1).drop(df1.columns[501:], axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"list(df1).index('voiceProb_sma_kurtosis')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df2.head()\nX2_train, X2_test, y2_train, y2_test = train_test_split(df2, y, test_size=0.18, random_state=42)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(X2_train.shape)\nprint(y2_train.shape)\nX2_train.head()",
"(1858, 90)\n(1858,)\n449\n"
],
[
"clf.fit(X2_train, y2_train)\nprint(accuracy_score(y2_test, clf.predict(X2_test)))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X3_train, X3_test, y3_train, y3_test = train_test_split(df3, y, test_size=0.18, random_state=42)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(X2_train.columns)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df3.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"svm2_pipeline = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), PCA(n_components=70), svm_)\nsvm2_pipeline.fit(X_train, y_train)\nsvm2_pipeline.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(accuracy_score(y_test, svm2_pipeline.predict(X_test)))",
"0.9044117647058824\n"
],
[
"print(accuracy_score(y_test, svm3_pipeline.predict(X_test)))",
"0.9313725490196079\n"
],
[
"clf_pipeline = make_pipeline(PCA(n_components=50), clf)\nclf_pipeline.fit(X_train, y_train)\nprint(accuracy_score(y_test, clf_pipeline.predict(X_test)))",
"0.8627450980392157\n"
],
[
"predict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/neutral_maria2.wav', clf_pipeline)\npredict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/neutral_lalit.wav', clf_pipeline)\npredict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/happy_maria.wav', clf_pipeline)\npredict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/happy_lalit.wav', clf_pipeline)",
"[1.]\n[0.]\n[1.]\n[1.]\n"
],
[
"acc = dict()\ncs = np.arange(0.25, 2.0, 0.10)\nfor c in cs:\n for n in range(2, 50, 4):\n svm4_pipeline = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), PCA(n_components=n), svm.SVC(C=c, kernel='poly', degree=2))\n svm4_pipeline.fit(X3_train, y3_train)\n acc[(c, n)] = (accuracy_score(y3_test, svm4_pipeline.predict(X3_test)))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"svm4_pipeline = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), PCA(n_components=50), svm.SVC(C=1.0, kernel='poly', degree=2))\nsvm4_pipeline.fit(X_train, y_train)\nprint(accuracy_score(y_test, svm4_pipeline.predict(X_test)))",
"0.9313725490196079\n"
],
[
"predict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/angry_show.wav', svm4_pipeline)\npredict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/neutral_maria2.wav', svm4_pipeline)\npredict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/neutral_lalit.wav', svm4_pipeline)\npredict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/happy_lalit.wav', svm4_pipeline)",
"[1.]\n[1.]\n[3.]\n[2.]\n"
],
[
"predict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/angry_show.wav', svm_pipeline)\npredict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/neutral_maria2.wav', svm_pipeline)\npredict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/neutral_lalit.wav', svm_pipeline)\npredict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/happy_maria.wav', svm_pipeline)\npredict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/happy_lalit.wav', svm_pipeline)",
"[0.]\n[1.]\n[2.]\n[1.]\n[1.]\n"
],
[
"svmlin_pipeline = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), PCA(n_components=50), lin_svm)\nsvmlin_pipeline.fit(X_train, y_train)\nprint(accuracy_score(y_test, svmlin_pipeline.predict(X_test)))",
"0.8848039215686274\n"
],
[
"\npredict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/angry_show.wav', svm2_pipeline)\npredict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/neutral_maria2.wav', svm2_pipeline)\npredict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/neutral_lalit.wav', svm2_pipeline)\npredict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/happy_maria.wav', svm2_pipeline)\npredict_new('/home/veerlosar/Downloads/ERHS/happy_lalit.wav', svm2_pipeline)",
"[0.]\n[1.]\n[2.]\n[1.]\n[2.]\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe9018f9eee376653e1b089874a01a60eed64c8
| 22,895 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
week3 - Evaluation/Assignment 3.ipynb
|
zuhaalfaraj/Applied-Machine-Learning-In-Python
|
b5a293e26848f75ad4e594346dd8dccbd85563b0
|
[
"BSD-2-Clause"
] | 1 |
2021-02-27T21:58:37.000Z
|
2021-02-27T21:58:37.000Z
|
week3 - Evaluation/Assignment 3.ipynb
|
zuhaalfaraj/Applied-Machine-Learning-In-Python
|
b5a293e26848f75ad4e594346dd8dccbd85563b0
|
[
"BSD-2-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
week3 - Evaluation/Assignment 3.ipynb
|
zuhaalfaraj/Applied-Machine-Learning-In-Python
|
b5a293e26848f75ad4e594346dd8dccbd85563b0
|
[
"BSD-2-Clause"
] | null | null | null | 45.426587 | 457 | 0.478926 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
cbe90dba62dd820732c80c15fa106cda97260581
| 143,238 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/notebooks/san-jose-pd-firearm-report.ipynb
|
fristhon/pdfplumber
|
b904dd6a7c5164c5e051fa9b4121f8af6a105ae9
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2022-02-18T17:13:01.000Z
|
2022-02-18T17:13:01.000Z
|
examples/notebooks/san-jose-pd-firearm-report.ipynb
|
fristhon/pdfplumber
|
b904dd6a7c5164c5e051fa9b4121f8af6a105ae9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
examples/notebooks/san-jose-pd-firearm-report.ipynb
|
fristhon/pdfplumber
|
b904dd6a7c5164c5e051fa9b4121f8af6a105ae9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 216.045249 | 72,560 | 0.86972 |
[
[
[
"# Parsing San Jose PD's firearm search reports\n\nThis example uses `pdfplumber`'s visual debugging and text-extraction features to parse a fixed-width table embedded in a PDF. Thanks to [Ron Campbell](https://twitter.com/campbellronaldw) for the sample PDF.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pdfplumber\nimport re\nprint(pdfplumber.__version__)",
"0.6.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Load the PDF",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pdf = pdfplumber.open(\"../pdfs/san-jose-pd-firearm-sample.pdf\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Examine the first page",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"p0 = pdf.pages[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"im = p0.to_image()\nim",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## See where the characters are on the page\n\nBelow, we draw rectangles around each of the `char` objects that `pdfplumber` detected. By doing so, we can see that every line of the main part of the report is the same width, and that there are space (`\" \"`) characters padding out each field. That means we can parse those lines a lot like we'd parse a standard fixed-width data file.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"im.reset().draw_rects(p0.chars)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Extract the text from the PDF\n\nUsing the `Page.extract_text(...)` method, we grab every character on the page, line by line:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"text = p0.extract_text()\nprint(text)",
"For:1094N \nPage 1 SAN JOSE POLICE DEPT Date Report Run : Tue, May-24-16\n FIREARM SEARCH \nSEARCH CRITERIA: fi_property.item_status='B' and fi_property.entry_date between '07/01/2012' and '05/24/2016' and fi_p\n roperty.jurisdiction='SJ' \nNUMBER OF RECORDS RETURNED: 983\nTYPE ITEM MAKE MODEL CALIBRE STATUS FLAGS\n-------------------- -------------------- --------------------------------------------- --------------- ------- -------- -----\nSERIAL NUMBER REPORT/TAG NUMBER CASE/FILE NUMBER STORAGE LOCATION\n------------- ------------------- -------------------- ----------------------- \nPISTOL REVOLVER UNKWN/UNPUBLSHD MAKE UNKNOWN 38 FOUND _d__\n1721 Tag#:SJ3095-1 GO SJ 2012-122590518 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION \nSHOTGUN DOUBLE BARREL STEVEN/J STVNS ARMS 311 SERIES H 12GA FOUND _d__\nREMOVED Tag#:SJ3123-1 GO SJ 2012-122620320 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION \nPISTOL SEMI-AUTOMATIC TAURUS FORJAS PT40 PRO MIL'NU 40 FOUND _d__\nSZH77919 Tag#:SJ3360-1 GO SJ 2012-122670386 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION/G\nPISTOL SEMI-AUTOMATIC SMITH AND WESSON 39 9MM FOUND _d__\n85517 Tag#:SJ3686-1 GO SJ 2012-122741016 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION/G\nPISTOL SEMI-AUTOMATIC HIGH POINT JCP 40 FOUND ____\nREMOVED Tag#:SJ3724-1 GO SJ 2012-122750582 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION/G\nPISTOL REVOLVER COLT DETECTIVE SPEC 38 FOUND _d__\n982982 Tag#:SJ4077-2 GO SJ 2012-122840637 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION/Z\nSHOTGUN DOUBLE BARREL MISS.VALLEY ARMS CO. UNK 12GA FOUND _d__\n279861 Tag#:SJ4117-1 GO SJ 2012-122850220 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION \nRIFLE LEVER ACTION SEARS ROEBUCK & CO. 5 22 FOUND _d__\n63723 Tag#:SJ4172-1 GO SJ 2012-122860208 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION \nPISTOL SEMI-AUTOMATIC COLT MATCH TARGET .22 FOUND _d__\n142061S Tag#:SJ4324-1 GO SJ 2012-122890285 WA-GR/GD-SCCCL \nPISTOL REVOLVER SMITH AND WESSON UNKNOWN .22 FOUND _d__\nK22539 Tag#:SJ4324-2 GO SJ 2012-122890285 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION \nRIFLE LEVER ACTION STEVEN/J STVNS ARMS CRACK SHOT 26 .22 FOUND _d__\nUNKNOWN Tag#:SJ4324-3 GO SJ 2012-122890285 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION \nPISTOL SEMI-AUTOMATIC CARL WALTHER PPK 7.65 FOUND _d__\n832229 Tag#:SJ4664-1 GO SJ 2012-122960284 WA-GR/GD-SCCCL \n Flags = e (evidence) d (disposed) x (x-reference) n (entered on NCIC)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Stripping away the header and footer\n\nIn this step, we use a regular expression to focus on the core part of the page — the table.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"core_pat = re.compile(r\"LOCATION[\\-\\s]+(.*)\\n\\s+Flags = e\", re.DOTALL)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"core = re.search(core_pat, text).group(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(core)",
"PISTOL REVOLVER UNKWN/UNPUBLSHD MAKE UNKNOWN 38 FOUND _d__\n1721 Tag#:SJ3095-1 GO SJ 2012-122590518 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION \nSHOTGUN DOUBLE BARREL STEVEN/J STVNS ARMS 311 SERIES H 12GA FOUND _d__\nREMOVED Tag#:SJ3123-1 GO SJ 2012-122620320 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION \nPISTOL SEMI-AUTOMATIC TAURUS FORJAS PT40 PRO MIL'NU 40 FOUND _d__\nSZH77919 Tag#:SJ3360-1 GO SJ 2012-122670386 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION/G\nPISTOL SEMI-AUTOMATIC SMITH AND WESSON 39 9MM FOUND _d__\n85517 Tag#:SJ3686-1 GO SJ 2012-122741016 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION/G\nPISTOL SEMI-AUTOMATIC HIGH POINT JCP 40 FOUND ____\nREMOVED Tag#:SJ3724-1 GO SJ 2012-122750582 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION/G\nPISTOL REVOLVER COLT DETECTIVE SPEC 38 FOUND _d__\n982982 Tag#:SJ4077-2 GO SJ 2012-122840637 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION/Z\nSHOTGUN DOUBLE BARREL MISS.VALLEY ARMS CO. UNK 12GA FOUND _d__\n279861 Tag#:SJ4117-1 GO SJ 2012-122850220 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION \nRIFLE LEVER ACTION SEARS ROEBUCK & CO. 5 22 FOUND _d__\n63723 Tag#:SJ4172-1 GO SJ 2012-122860208 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION \nPISTOL SEMI-AUTOMATIC COLT MATCH TARGET .22 FOUND _d__\n142061S Tag#:SJ4324-1 GO SJ 2012-122890285 WA-GR/GD-SCCCL \nPISTOL REVOLVER SMITH AND WESSON UNKNOWN .22 FOUND _d__\nK22539 Tag#:SJ4324-2 GO SJ 2012-122890285 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION \nRIFLE LEVER ACTION STEVEN/J STVNS ARMS CRACK SHOT 26 .22 FOUND _d__\nUNKNOWN Tag#:SJ4324-3 GO SJ 2012-122890285 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION \nPISTOL SEMI-AUTOMATIC CARL WALTHER PPK 7.65 FOUND _d__\n832229 Tag#:SJ4664-1 GO SJ 2012-122960284 WA-GR/GD-SCCCL \n"
]
],
[
[
"## Parse each group of two lines\n\nIn the report, each firearm takes up two lines. The code below splits the core table into two-line groups, and then parses out the fields, based on the number of characters in each field:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"lines = core.split(\"\\n\")\nline_groups = list(zip(lines[::2], lines[1::2]))\nprint(line_groups[0])",
"('PISTOL REVOLVER UNKWN/UNPUBLSHD MAKE UNKNOWN 38 FOUND _d__', '1721 Tag#:SJ3095-1 GO SJ 2012-122590518 WA-GR/GUN DESTRUCTION ')\n"
],
[
"def parse_row(first_line, second_line):\n return {\n \"type\": first_line[:20].strip(),\n \"item\": first_line[21:41].strip(),\n \"make\": first_line[44:89].strip(),\n \"model\": first_line[90:105].strip(),\n \"calibre\": first_line[106:111].strip(),\n \"status\": first_line[112:120].strip(),\n \"flags\": first_line[124:129].strip(),\n \"serial_number\": second_line[0:13].strip(),\n \"report_tag_number\": second_line[21:41].strip(),\n \"case_file_number\": second_line[44:64].strip(),\n \"storage_location\": second_line[68:91].strip(),\n }",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"parsed = [ parse_row(first_line, second_line) \n for first_line, second_line in line_groups ]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Result\n\nBelow, you can see the parsed data for the first two firearms in the report:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"parsed[:2]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Preview via `pandas.DataFrame`\n\nTo make it a little easier to read, here's the full table, parsed and represented as a `pandas.DataFrame` (for ease of viewing):",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\ncolumns = list(parsed[0].keys())\npd.DataFrame(parsed)[columns]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\n\n---\n\n---",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe913ea6b30c14d39a15ae2f93be9db542ce77b
| 15,828 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
0 - OOP.ipynb
|
ada-k/MLClasses
|
ae7a09c4765742812c2dd50f5a564bf225af7c04
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-11-29T22:34:11.000Z
|
2020-11-29T22:34:11.000Z
|
0 - OOP.ipynb
|
ada-k/MLClasses
|
ae7a09c4765742812c2dd50f5a564bf225af7c04
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
0 - OOP.ipynb
|
ada-k/MLClasses
|
ae7a09c4765742812c2dd50f5a564bf225af7c04
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 27.010239 | 188 | 0.511562 |
[
[
[
"## OOP\nA programming paradigm that provides a means of structuring programs so that properties and behaviors are bundled into individual objects.\n\nPros:\n* code modularisation thus ease in troubleshooting.\n* reuse of code through inheritance.\n* flexibility through polymorphism (multiple usage).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 1. Class Definition\n\n> Classes define functions called methods, which identify the behaviors and actions that an object created from the class can perform with its data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# function definition\ndef fix_laptop(harddisk, money):\n # check if laptop is ok\n if 'not' in harddisk:\n print('Laptop has a problem')\n else:\n print('Laptop is OK')\n code modularisation thus ease in troubleshooting.\n # fix it kama iko na issue\n if money == 'yes':\n return 'DJ can get his laptop fixed'\n else:\n return 'DJ is fucked'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# class definition\nclass Kisauni():\n \n # attributes\n \n # class attributes\n security = 'mateja everywhere'\n ethnicity = 'waswahili'\n \n # instance attributes // dunder methods\n def __init__(self, mtaa, drainage_system, housing_style):\n self.mtaa = mtaa\n self.drainage_system = drainage_system\n self.housing_style = housing_style \n \n def __str__(self):\n return 'A class indicating conditions in Kisauni'\n \n # instance methods (customised functions)\n def students(self, status, name, age, campus):\n if 'yes' in status.lower():\n return f'{name} is a {age} year old at The {campus}'\n else:\n return f'{name} is a {age} year old non student'\n \n def relationships(self,status, name, sex):\n if 'YES'in status.upper():\n return f'{name} is a {sex}'\n else:\n return f'{name} is a bi'\n def rehabilitations(self,status,name,age):\n if 'yes' in status.lower():\n\n return f'{name}is a {age} must go to rehab.'\n else:\n\n return f'{name} is a {age} no rehab.'\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# inheritance ( - overriding; - extending)\nclass Birds():\n \n def flight(self):\n return 'ALmost all birds can fly'\n \n def edibility(self):\n return 'almost all birds are edible'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class Chicken(Birds):\n \n def flight(self):\n print('chicken cannot fly')\n \n def food(self):\n return 'chicken feed on mash'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class Student:\n \n # class attributes (uniform for all class objects)\n campus = 'Technical University of Munich'\n \n ## dunder methods\n ''' universal properties (instance attributes - not necessarily uniform for all objects) \n - arguments must be supplied when calling the class '''\n def __init__(self, name, age, level, academic_year):\n self.name = name\n self.age = age\n self.level = level\n self.academic_year = academic_year\n \n ''' Class descriptor'''\n def __str__(self):\n return f\" This is a Student class with methods: course, year and location.\"\n\n ## Instance Methods \n '''- begine with a self, and can only be called from an instance of the class '''\n # course\n def course(self, course_name):\n return f\"{self.name} is pursuing a {self.level} in {course_name} at the {self.campus}\"\n \n # year\n def year(self, year, gender):\n if 'f' in gender.lower():\n return f\" She is a {self.age} year old currently in her {year} year.\"\n else:\n return f\" He is a {self.age} year old currently in his {year} year.\"\n \n # location\n def location(self, location):\n return f\" Residing in {location}\"\n \n #race\n def race(self, race):\n pass",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ola = Student('ola', 25, 'PhD', 3)\nola.course('MAchine LEarning')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# creating a class object/instantiating the class\nstudent = Student('Ada', 21, 'B.Sc')\nprint('Object type/description:', student)\nstudent.course('Mathematics and Computer Science'), student.year(4, 'female'), student.location('Kisauni')",
"Object type/description: This is a Student class with methods: course, year and location.\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 2. Inheritance\n> A class takes on the attributes/methods of another. Newly formed classes are called child classes, and the classes that child classes are derived from are called parent classes.\n\n> **extending** - having additional attributes.\n> **overriding** - overwriting inherited attributes.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"''' Using the example of class Student, every time we pass a new student, we have to pass the gender\nargument which determines the way the year function is returned. We can create child classes of \ndifferent genders that inherit attributes of the Student Class and override the year method'''\n\nclass Female(Student):\n \n # overriding\n def year(self, year, gender = 'female'):\n return f\" She is a {self.age} year old currently in her {year} year.\"\n\n #extending\n def under_18(self):\n if self.age < 18:\n return True\n else:\n return False\n \nclass Male(Student):\n \n # overriding\n def year(self, year, gender = 'male'):\n return f\" He is a {self.age} year old currently in his {year} year.\"\n \n #extending\n def under_18(self):\n if self.age < 18:\n return True\n else:\n return False",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ada = Female('Ada', 21, 'B.Sc', 4)\nada.year(4)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"f = Female('Denise', 17, 'B.Sc', 4)\nf.course('Mathematics and Computer Science'), f.year(4), f.location('Berlin'), f.under_18()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"m = Male('Denis', 20, 'B.Sc', 4)\nm.course('Mathematics and Finance'), m.year(3), f.location('Munich'), m.under_18()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 3. Polymorphism\n> same function name (but different signatures) being uses for different types.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print('ada is a lady')\nprint(456)\nprint([5,6])",
"ada is a lady\n456\n[5, 6]\n"
],
[
"''' Polymorphism with uniform class methods'''\nclass Kenya(): \n def capital(self): \n print(\"Nairobi is the capital of Kenya.\") \n\n def president(self): \n print(\"Kenyatta is the president of Kenya\") \n\n\nclass USA(): \n def capital(self): \n print(\"Washington D.C. is the capital of USA.\") \n\n def president(self): \n print(\"Biden is their newly elected president.\") \n\nk = Kenya()\nu = USA()\n\n\nfor country in [k, u]: \n country.capital() \n country.president() ",
"Nairobi is the capital of Kenya.\nKenyatta is the president of Kenya\nWashington D.C. is the capital of USA.\nBiden is their newly elected president.\n"
],
[
"'''Polymorphism with a function and object'''\n\n# in the previous example. Instead of looping: creating a function. \n\ndef func(obj): \n obj.capital() \n obj.president() \n \nk = Kenya() \nu = USA() \n \nfunc(k) \nfunc(u)",
"Nairobi is the capital of Kenya.\nKenyatta is the president of Kenya\nWashington, D.C. is the capital of USA.\nBiden is their newly elected president.\n"
],
[
"'''Polymorphism with inheritance'''\n\n# This is equal to overriding in inheritance.\nclass Bird: \n def intro(self): \n print(\"There are many types of birds.\") \n \n def flight(self): \n print(\"Most of the birds can fly but some cannot.\") \n \nclass sparrow(Bird): \n def flight(self): \n print(\"Sparrows can fly.\") ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Procedural Programming\n> Structures a program like a recipe in that it provides a set of steps, in the form of functions and code blocks, that flow sequentially in order to complete a task.\n\n>relies on procedure calls to create modularized code. This approach simplifies your application code by breaking it into small pieces that a developer can view easily.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## summing elements of a list\ndef sum_elements(my_list):\n sum = 0\n for x in my_list:\n sum += x\n return sum\n\nprint(sum_elements([4,5,6,7]))",
"22\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Task:\nCreate a class Rectangle and define the following methods:\n* create_rectangle\n Input parameters: x, y, width, height\n Return value: instance of Rectangle\n Operation: create a new instance of Rectangle \n* area_of_rectangle\n* perimeter_of__rectangle\n* product_of_the diagonals\n\nCreate a class square that inherits from class rectangle with an additional function of:\n* angle_between_diagonals",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe915eb12e3cc7333643b069654fcf861060969
| 14,856 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Section 6/using_mc_application.ipynb
|
PacktPublishing/Hands-on-Python-for-Finance-V-
|
e387663505d225c613c7d575673d9b42e3b3c761
|
[
"MIT"
] | 31 |
2019-03-07T13:49:22.000Z
|
2022-01-18T20:31:37.000Z
|
Section 6/using_mc_application.ipynb
|
PacktPublishing/Hands-on-Python-for-Finance-V-
|
e387663505d225c613c7d575673d9b42e3b3c761
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Section 6/using_mc_application.ipynb
|
PacktPublishing/Hands-on-Python-for-Finance-V-
|
e387663505d225c613c7d575673d9b42e3b3c761
|
[
"MIT"
] | 23 |
2019-03-15T06:09:35.000Z
|
2021-10-04T03:26:17.000Z
| 34.230415 | 135 | 0.428581 |
[
[
[
"# Using the Application",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from montecarlo import MonteCarlo as mc",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"help(mc)",
"Help on class MonteCarlo in module montecarlo:\n\nclass MonteCarlo(builtins.object)\n | Will calculate:\n | Parametric VaR deterministically given current value, volatility, time horizon (1 = one year) & \n | confidence level - value between 0 and 1, typically .95 or higher\n | \n | expected return effect will be negligible for short time horizons\n | \n | Parametric VaR Monte Carlo estimation given current value, expected return, volatility, \n | time horizon (1 = one year), confidence level\n | \n | Expected portfolio ending value given present value, expected return, volatility, time horizon and number of iterations.\n | It is recommended that the result be stored in a variable for analysis\n | \n | Methods defined here:\n | \n | mc_VaR(pv, er, volatility, T)\n | \n | monte_carlo_sim(pv, er, volatility, horizon, iterations)\n | \n | quick_var(value, vol, T, CL)\n | \n | ----------------------------------------------------------------------\n | Data descriptors defined here:\n | \n | __dict__\n | dictionary for instance variables (if defined)\n | \n | __weakref__\n | list of weak references to the object (if defined)\n\n"
],
[
"sim = mc.monte_carlo_sim(10000,.095,.185,30,5000)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sim[list(range(5))]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe91d7022af0d3559bdde8c0c99db672801456b
| 9,651 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebook/NonStiffDDE/Mackey_Glass_wpd.ipynb
|
staticfloat/SciMLBenchmarks.jl
|
7e69f44acf0e32e98aeb3ddcdb1810febe41ffcb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebook/NonStiffDDE/Mackey_Glass_wpd.ipynb
|
staticfloat/SciMLBenchmarks.jl
|
7e69f44acf0e32e98aeb3ddcdb1810febe41ffcb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebook/NonStiffDDE/Mackey_Glass_wpd.ipynb
|
staticfloat/SciMLBenchmarks.jl
|
7e69f44acf0e32e98aeb3ddcdb1810febe41ffcb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 55.786127 | 669 | 0.565952 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
cbe91dce5a553188ffa832491dbd9ae9f6bac778
| 470,545 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/06_Denoise_Solution.ipynb
|
luckyvamshi/2013_fall_ASTR599
|
c717b6e122940f83c3c9a5b579901e886084501f
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 56 |
2015-03-09T04:49:28.000Z
|
2022-01-12T08:06:56.000Z
|
notebooks/06_Denoise_Solution.ipynb
|
dbw44/2013_fall_ASTR599
|
d053d8fea22ae9a022c92f5b2de027614d42d713
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/06_Denoise_Solution.ipynb
|
dbw44/2013_fall_ASTR599
|
d053d8fea22ae9a022c92f5b2de027614d42d713
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 42 |
2015-01-05T19:23:27.000Z
|
2021-08-29T04:59:20.000Z
| 2,262.235577 | 464,643 | 0.950483 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
cbe9296a36f87a55493ac7705bb827d4462ae65d
| 108,808 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
4/z4.ipynb
|
iCarrrot/Evol-algs
|
cb79440f0c5430b1d63a43acf2d64faed6db1b17
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2019-12-18T11:31:03.000Z
|
2019-12-18T11:31:03.000Z
|
4/z4.ipynb
|
iCarrrot/Evol-algs
|
cb79440f0c5430b1d63a43acf2d64faed6db1b17
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
4/z4.ipynb
|
iCarrrot/Evol-algs
|
cb79440f0c5430b1d63a43acf2d64faed6db1b17
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 243.418345 | 20,348 | 0.898904 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport math\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\n%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from kinematics import *\nfrom es import es",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"d = 20\nN = 800\nT = 800\ntarget = np.array([10,20])\nlengths = [1,3] * (d//2)\nranges = np.array([[-180, 180]]*d).T\nbest_objective_value, best_chromosome, history_objective_values, history_best_chromosome, history_best_sigmas, diag = es(\n objective_function, d, N, T, 2*N, 2, 50.0, 1/np.sqrt(2*d), 1/np.sqrt(2*np.sqrt(d)), 10, \n cut=True,\n target = target, lengths=lengths, ranges=ranges)\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(18, 4))\nplt.plot(history_objective_values[:, 0],)\nplt.plot(history_objective_values[:, 1],)\nplt.plot(history_objective_values[:, 2],)\nplt.xlabel('iteration')\nplt.ylabel('objective function value')\nplt.title('min/avg/max objective function values')\nplt.show()\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(18, 4))\nplt.plot(history_best_sigmas, 'r-')\nplt.xlabel('iteration')\nplt.ylabel('sigma value')\nplt.title('best sigmas')\nplt.show()",
"Iteration 0000 : best score = -1.47471989, mean score = -14.84602150.\nIteration 0010 : best score = -0.15588247, mean score = -3.23527162.\nIteration 0020 : best score = -0.03835286, mean score = -1.11108468.\nIteration 0030 : best score = -0.03835286, mean score = -0.73846931.\nIteration 0040 : best score = -0.03835286, mean score = -0.58137522.\nIteration 0050 : best score = -0.02400008, mean score = -0.48346984.\nIteration 0060 : best score = -0.01847182, mean score = -0.41668514.\nIteration 0070 : best score = -0.00886747, mean score = -0.36980685.\nIteration 0080 : best score = -0.00886747, mean score = -0.32363665.\nIteration 0090 : best score = -0.00886747, mean score = -0.29390072.\nIteration 0100 : best score = -0.00886747, mean score = -0.27092956.\nIteration 0110 : best score = -0.00886747, mean score = -0.24968632.\nIteration 0120 : best score = -0.00886747, mean score = -0.22792256.\nIteration 0130 : best score = -0.00886747, mean score = -0.21468929.\nIteration 0140 : best score = -0.00886747, mean score = -0.20254149.\nIteration 0150 : best score = -0.00886747, mean score = -0.18933642.\nIteration 0160 : best score = -0.00886747, mean score = -0.17915868.\nIteration 0170 : best score = -0.00886747, mean score = -0.16952736.\nIteration 0180 : best score = -0.00886747, mean score = -0.16039307.\nIteration 0190 : best score = -0.00719244, mean score = -0.15111910.\nIteration 0200 : best score = -0.00719244, mean score = -0.14197729.\nIteration 0210 : best score = -0.00719244, mean score = -0.13331474.\nIteration 0220 : best score = -0.00719244, mean score = -0.12814716.\nIteration 0230 : best score = -0.00719244, mean score = -0.12260786.\nIteration 0240 : best score = -0.00719244, mean score = -0.11553116.\nIteration 0250 : best score = -0.00719244, mean score = -0.10772885.\nIteration 0260 : best score = -0.00719244, mean score = -0.10064307.\nIteration 0270 : best score = -0.00719244, mean score = -0.09495530.\nIteration 0280 : best score = -0.00719244, mean score = -0.09009084.\nIteration 0290 : best score = -0.00719244, mean score = -0.08362804.\nIteration 0300 : best score = -0.00535253, mean score = -0.07910946.\nIteration 0310 : best score = -0.00535253, mean score = -0.07538790.\nIteration 0320 : best score = -0.00535253, mean score = -0.07010066.\nIteration 0330 : best score = -0.00535253, mean score = -0.06656498.\nIteration 0340 : best score = -0.00535253, mean score = -0.06274803.\nIteration 0350 : best score = -0.00535253, mean score = -0.05969738.\nIteration 0360 : best score = -0.00535253, mean score = -0.05605598.\nIteration 0370 : best score = -0.00456755, mean score = -0.05234829.\nIteration 0380 : best score = -0.00456755, mean score = -0.04938473.\nIteration 0390 : best score = -0.00456755, mean score = -0.04604114.\nIteration 0400 : best score = -0.00442365, mean score = -0.04299223.\nIteration 0410 : best score = -0.00316727, mean score = -0.04055341.\nIteration 0420 : best score = -0.00111133, mean score = -0.03776448.\nIteration 0430 : best score = -0.00053294, mean score = -0.03537677.\nIteration 0440 : best score = -0.00053294, mean score = -0.03212509.\nIteration 0450 : best score = -0.00053294, mean score = -0.02991304.\nIteration 0460 : best score = -0.00038593, mean score = -0.02741518.\nIteration 0470 : best score = -0.00038593, mean score = -0.02536852.\nIteration 0480 : best score = -0.00038593, mean score = -0.02324707.\nIteration 0490 : best score = -0.00038593, mean score = -0.02109320.\nIteration 0500 : best score = -0.00038593, mean score = -0.01900736.\nIteration 0510 : best score = -0.00038593, mean score = -0.01723095.\nIteration 0520 : best score = -0.00038593, mean score = -0.01556137.\nIteration 0530 : best score = -0.00038593, mean score = -0.01396034.\nIteration 0540 : best score = -0.00038593, mean score = -0.01221373.\nIteration 0550 : best score = -0.00038593, mean score = -0.01048166.\nIteration 0560 : best score = -0.00038593, mean score = -0.00906924.\nIteration 0570 : best score = -0.00038593, mean score = -0.00734556.\nIteration 0580 : best score = -0.00032724, mean score = -0.00609477.\nIteration 0590 : best score = -0.00018966, mean score = -0.00480012.\nIteration 0600 : best score = -0.00018068, mean score = -0.00376750.\nIteration 0610 : best score = -0.00018068, mean score = -0.00282135.\nIteration 0620 : best score = -0.00018068, mean score = -0.00212174.\nIteration 0630 : best score = -0.00015988, mean score = -0.00161843.\nIteration 0640 : best score = -0.00003286, mean score = -0.00122709.\nIteration 0650 : best score = -0.00003286, mean score = -0.00088713.\nIteration 0660 : best score = -0.00003286, mean score = -0.00062824.\nIteration 0670 : best score = -0.00002854, mean score = -0.00043119.\nIteration 0680 : best score = -0.00001607, mean score = -0.00028600.\nIteration 0690 : best score = -0.00001607, mean score = -0.00019575.\nIteration 0700 : best score = -0.00000108, mean score = -0.00013128.\nIteration 0710 : best score = -0.00000108, mean score = -0.00008965.\nIteration 0720 : best score = -0.00000108, mean score = -0.00006048.\nIteration 0730 : best score = -0.00000020, mean score = -0.00004063.\nIteration 0740 : best score = -0.00000020, mean score = -0.00002634.\nIteration 0750 : best score = -0.00000020, mean score = -0.00001861.\nIteration 0760 : best score = -0.00000020, mean score = -0.00001292.\nIteration 0770 : best score = -0.00000020, mean score = -0.00000948.\nIteration 0780 : best score = -0.00000020, mean score = -0.00000692.\nIteration 0790 : best score = -0.00000020, mean score = -0.00000514.\n"
],
[
"# for k in diag:\n# print(k, diag[k])\n\n# x, y = diag['min_x'], diag['min_y']\n# plt.plot(x, y)\n# plt.scatter([x[-1]], [y[-1]], c='r')\n# plt.scatter([target[0]], [target[1]], c='g')\n# plt.axis('equal')\n# plt.show()\n\nx, y = diag['max_x'], diag['max_y']\nplt.plot(x, y)\nplt.scatter([x[-1]], [y[-1]], c='r')\nplt.scatter([target[0]], [target[1]], c='g')\nplt.axis('equal')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"history_best_chromosome[-1,:]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"d = 20\nN = 200\nT = 800\ntarget = np.array([10,20])\nlengths = [1,3] * (d//2)\nranges = np.array([[120, 240]]*d).T\nbest_objective_value, best_chromosome, history_objective_values, history_best_chromosome, history_best_sigmas, diag = es(\n objective_function, d, N, T, 2*N, 2, 50.0, 1/np.sqrt(2*d), 1/np.sqrt(2*np.sqrt(d)), 10, \n cut=True,\n target = target, lengths=lengths, ranges=ranges)\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(18, 4))\nplt.plot(history_objective_values[:, 0],)\nplt.plot(history_objective_values[:, 1],)\nplt.plot(history_objective_values[:, 2],)\nplt.xlabel('iteration')\nplt.ylabel('objective function value')\nplt.title('min/avg/max objective function values')\nplt.show()\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(18, 4))\nplt.plot(history_best_sigmas, 'r-')\nplt.xlabel('iteration')\nplt.ylabel('sigma value')\nplt.title('best sigmas')\nplt.show()\nx, y = diag['max_x'], diag['max_y']\nplt.plot(x, y)\nplt.scatter([x[-1]], [y[-1]], c='r')\nplt.scatter([target[0]], [target[1]], c='g')\nplt.axis('equal')\nplt.show()\nhistory_best_chromosome[-1,:]",
"Iteration 0000 : best score = -5200000028.21212292, mean score = -6720000022.79447556.\nIteration 0010 : best score = -800000017.42581522, mean score = -1754000024.77647090.\nIteration 0020 : best score = -2.38606166, mean score = -4.52322359.\nIteration 0030 : best score = -1.59247650, mean score = -2.05621524.\nIteration 0040 : best score = -1.40850781, mean score = -1.60431341.\nIteration 0050 : best score = -1.25059344, mean score = -1.37616909.\nIteration 0060 : best score = -1.11614121, mean score = -1.21563609.\nIteration 0070 : best score = -1.03378599, mean score = -1.11275367.\nIteration 0080 : best score = -0.92840760, mean score = -1.01788434.\nIteration 0090 : best score = -0.78334386, mean score = -0.93853625.\nIteration 0100 : best score = -0.71979315, mean score = -0.83420936.\nIteration 0110 : best score = -0.65552690, mean score = -0.71805760.\nIteration 0120 : best score = -0.60324138, mean score = -0.64029063.\nIteration 0130 : best score = -0.56408399, mean score = -0.59149407.\nIteration 0140 : best score = -0.53076263, mean score = -0.54782632.\nIteration 0150 : best score = -0.45800462, mean score = -0.49102614.\nIteration 0160 : best score = -0.40238020, mean score = -0.44724455.\nIteration 0170 : best score = -0.37439192, mean score = -0.39631167.\nIteration 0180 : best score = -0.33270790, mean score = -0.35597862.\nIteration 0190 : best score = -0.27429456, mean score = -0.31098309.\nIteration 0200 : best score = -0.22834236, mean score = -0.26336990.\nIteration 0210 : best score = -0.16339918, mean score = -0.20681791.\nIteration 0220 : best score = -0.07355851, mean score = -0.12170101.\nIteration 0230 : best score = -0.01322934, mean score = -0.06062382.\nIteration 0240 : best score = -0.00355665, mean score = -0.01970716.\nIteration 0250 : best score = -0.00059904, mean score = -0.00781527.\nIteration 0260 : best score = -0.00043873, mean score = -0.00408436.\nIteration 0270 : best score = -0.00015303, mean score = -0.00245371.\nIteration 0280 : best score = -0.00010815, mean score = -0.00154272.\nIteration 0290 : best score = -0.00010815, mean score = -0.00104518.\nIteration 0300 : best score = -0.00010815, mean score = -0.00080006.\nIteration 0310 : best score = -0.00004849, mean score = -0.00060160.\nIteration 0320 : best score = -0.00003941, mean score = -0.00046213.\nIteration 0330 : best score = -0.00003941, mean score = -0.00035115.\nIteration 0340 : best score = -0.00003941, mean score = -0.00025780.\nIteration 0350 : best score = -0.00000908, mean score = -0.00017967.\nIteration 0360 : best score = -0.00000908, mean score = -0.00013790.\nIteration 0370 : best score = -0.00000908, mean score = -0.00009666.\nIteration 0380 : best score = -0.00000908, mean score = -0.00006368.\nIteration 0390 : best score = -0.00000575, mean score = -0.00004571.\nIteration 0400 : best score = -0.00000302, mean score = -0.00003386.\nIteration 0410 : best score = -0.00000302, mean score = -0.00002560.\nIteration 0420 : best score = -0.00000053, mean score = -0.00001977.\nIteration 0430 : best score = -0.00000053, mean score = -0.00001491.\nIteration 0440 : best score = -0.00000053, mean score = -0.00001167.\nIteration 0450 : best score = -0.00000053, mean score = -0.00000960.\nIteration 0460 : best score = -0.00000053, mean score = -0.00000756.\nIteration 0470 : best score = -0.00000034, mean score = -0.00000608.\nIteration 0480 : best score = -0.00000034, mean score = -0.00000481.\nIteration 0490 : best score = -0.00000034, mean score = -0.00000373.\nIteration 0500 : best score = -0.00000034, mean score = -0.00000303.\nIteration 0510 : best score = -0.00000034, mean score = -0.00000252.\nIteration 0520 : best score = -0.00000019, mean score = -0.00000211.\nIteration 0530 : best score = -0.00000019, mean score = -0.00000172.\nIteration 0540 : best score = -0.00000019, mean score = -0.00000148.\nIteration 0550 : best score = -0.00000019, mean score = -0.00000132.\nIteration 0560 : best score = -0.00000019, mean score = -0.00000120.\nIteration 0570 : best score = -0.00000019, mean score = -0.00000102.\nIteration 0580 : best score = -0.00000014, mean score = -0.00000090.\nIteration 0590 : best score = -0.00000014, mean score = -0.00000077.\nIteration 0600 : best score = -0.00000014, mean score = -0.00000068.\nIteration 0610 : best score = -0.00000003, mean score = -0.00000060.\nIteration 0620 : best score = -0.00000003, mean score = -0.00000054.\nIteration 0630 : best score = -0.00000002, mean score = -0.00000049.\nIteration 0640 : best score = -0.00000002, mean score = -0.00000042.\nIteration 0650 : best score = -0.00000002, mean score = -0.00000039.\nIteration 0660 : best score = -0.00000002, mean score = -0.00000034.\nIteration 0670 : best score = -0.00000002, mean score = -0.00000031.\nIteration 0680 : best score = -0.00000002, mean score = -0.00000029.\nIteration 0690 : best score = -0.00000002, mean score = -0.00000027.\nIteration 0700 : best score = -0.00000002, mean score = -0.00000024.\nIteration 0710 : best score = -0.00000001, mean score = -0.00000022.\nIteration 0720 : best score = -0.00000001, mean score = -0.00000020.\nIteration 0730 : best score = -0.00000001, mean score = -0.00000019.\nIteration 0740 : best score = -0.00000001, mean score = -0.00000017.\nIteration 0750 : best score = -0.00000000, mean score = -0.00000015.\nIteration 0760 : best score = -0.00000000, mean score = -0.00000013.\nIteration 0770 : best score = -0.00000000, mean score = -0.00000012.\nIteration 0780 : best score = -0.00000000, mean score = -0.00000011.\nIteration 0790 : best score = -0.00000000, mean score = -0.00000010.\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe935c297d6213aeb2f73aedf78c1d751d93a62
| 28,656 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
content/03_regression/03_regression_quality/colab.ipynb
|
skykykykykykykykykykykys/applied-machine-learning-intensive
|
7b988359ff627638d11c4d90c8005dfeda41c348
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 126 |
2020-09-10T21:58:56.000Z
|
2022-03-23T14:21:09.000Z
|
content/03_regression/03_regression_quality/colab.ipynb
|
skykykykykykykykykykykys/applied-machine-learning-intensive
|
7b988359ff627638d11c4d90c8005dfeda41c348
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2021-10-16T08:16:46.000Z
|
2021-10-16T08:16:46.000Z
|
content/03_regression/03_regression_quality/colab.ipynb
|
skykykykykykykykykykykys/applied-machine-learning-intensive
|
7b988359ff627638d11c4d90c8005dfeda41c348
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 58 |
2020-09-10T15:23:13.000Z
|
2022-01-20T02:24:05.000Z
| 26.41106 | 418 | 0.564733 |
[
[
[
"#### Copyright 2020 Google LLC.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n#\n# https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n#\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Regression Quality",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"So far in this course, we have spent some time building and testing regression models. But how can we measure how good these models are? In this Colab, we will examine a few of the ways that we can measure and graph the results of a regression model in order to better understand the quality of the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Building a Dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In order to discuss regression quality, we should probably start by building a regression model.\n\nWe will start by creating an artificial dataset to model.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Start by importing [NumPy](http://numpy.org) and setting a random seed so that we get reproducible results.\n \nRemember: **Do not set a random seed in production code!**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\n\nnp.random.seed(0xFACADE)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Recall that linear regression is about trying to fit a straight line through a set of data points. The equation for a straight line is:\n\n> $y = m*x + b$\n\nwhere:\n- $x$ is the feature\n- $y$ is the outcome\n- $m$ is the slope of the line\n- $b$ is the intercept of the line on the $y$-axis\n\nBut at this point we don't even have $x$-values!\n\nWe will use NumPy's [random.uniform](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.15.0/reference/generated/numpy.random.uniform.html) function to generate 50 random numbers between 0 and 200 as $x$-values.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X = np.random.uniform(low=0, high=200, size=50)\n\nprint(f'min: {np.min(X)}')\nprint(f'max: {np.max(X)}')\nprint(f'mean: {np.mean(X)}')\nprint(f'count: {np.size(X)}')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You should see a:\n\n * minimum value near, but not below 0\n * maximum value near, but not above 200\n * mean value somewhere near 100\n * count value of exactly 50",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's visualize the $x$-values, just to get some idea of the distribution of the values in the range of 0-200.\n \n*How do we plot a one-dimensional list of values in two-dimensional space?*\n \nWe can plot it against itself!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nplt.plot(X, X, 'g.')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As you can see, we have a straight line of $x$-values that span from roughly 0 to 200. Let's now create some $y$-values via the equation $y=4x+10$ (i.e. the slope is 4 and the intercept is 10).\n\nWe'll call the new variable `Y_PRED` since it is the predicted variable.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"SLOPE = 4\nINTERCEPT = 10\n\nY_PRED = (SLOPE * X) + INTERCEPT\n\nplt.plot(X, Y_PRED, 'b.')\nplt.plot(X, Y_PRED, 'r-')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This regression line fits amazingly well! If only we could have this perfect of a fit in the real world. Unfortunately, this is almost never the case. There is always some variability.\n \nLet's add some randomness into our $y$-values to get a more realistic dataset. We will keep our original $y$-values in order to remember our base regression line.\n \nWe'll recreate our original $y$-values and store them in `Y_PRED`. Then, we'll create `Y` with the same equation but with added randomness.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Y_PRED = (SLOPE * X) + INTERCEPT\n\nrandomness = np.random.uniform(low=-200, high=200, size=50)\nY = SLOPE * X + randomness + INTERCEPT\n\nplt.plot(X, Y, 'b.')\nplt.plot(X, Y_PRED, 'r-')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We now have the line that was used to generate the data plotted in red, and the randomly displaced data points in blue. The dots, though definitely not close to the line, at least follow the linear trend in general. This seems like a reasonable dataset for a linear regression.\n \nLet's remind ourselves of the key variables in the model:\n \n* `X`: the $x$-values that we used to \"train\" the model\n* `Y`: the $y$-values that represent the actual values that correlate to `X`\n* `Y_PRED`: the $y$-values that the model would predict for each $x$-value",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Coefficient of Determination\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The **coefficient of determination**, denoted $R^2$, is one of the most important metrics in regression. It tells us how much of the data is \"explained\" by the model.\n\nBefore we can define the metric itself, we need to define a few other key terms.\n \nA **residual** is the difference between the target value $y_i$ and the predicted value $\\hat{y_i}$. The **residual sum of squares** is the summation of the square of every residual in the prediction set.\n \n> $$ SS_{res} = \\sum_{i}(y_i - \\hat{y_i})^2$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ss_res = ((Y - Y_PRED) ** 2).sum(axis=0, dtype=np.float64)\nprint(ss_res)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The **total sum of squares** is the sum of the squares of the difference between each value $y_i$ and their mean.\n\n> $$\\bar{y} = \\frac{1}{n}\\sum_{i=1}^{n}y_{i}$$\n\n> $$SS_{tot} = \\sum_{i}(y_{i}-\\bar{y})^2$$\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y_mean = np.average(Y, axis=0)\nprint(y_mean)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ss_tot = ((Y - y_mean)**2).sum(axis=0, dtype=np.float64)\nprint(ss_tot)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Given the total sum of squares and the residual sum of squares, we can calculate the coefficient of determination $R^2$.\n\n> $$R^{2} = 1 - \\frac{SS_{res}}{SS_{tot}}$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"r2 = 1 - (ss_res/ss_tot)\nprint(r2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If you just ran the cells in this Colab from top to bottom you probably got a score of `0.846`.\n \nIs this good? Bad? Mediocre?\n \nThe $R^2$ score measures how well the actual variance from $x$-values to $y$-values is represented in the variance between the $x$-values and the predicted $y$-values.\n \nTypically, this score ranges from 0 to 1, where 0 is bad and 1 is a perfect mapping. However, the score can also be negative. Can you guess why?\n \nIf a line drawn horizontally through the data points performs better than your regression, then the $R^2$ score would be negative. If you see this, try again. Your model *really* isn't working.\n \nFor values in the range 0-1, interpreting the $R^2$ is more subjective. The closer to 0, the worse your model is at fitting the data. And generally, the closer to 1, the better (but you also don't want to overfit). This is where testing, observation, and experience come into play.\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"It turns out that scikit-learn can calculate $R^2$ for us:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.metrics import r2_score\n\nprint(r2_score(Y, Y_PRED))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Knowing that we don't have to manually do all of the math again, let's now see the perfect and a very imperfect case of a regression fitting a dataset.\n\nTo begin with, we'll show a perfect fit. What happens if our predictions and our actual values are identical?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(r2_score(Y, Y))\nprint(r2_score(Y_PRED, Y_PRED))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"1.0: just what we thought! A perfect fit.\n\nNow let's see if we can make a regression so poor that $R^2$ is negative.\n\nIn this case, we need to make our predicted data look different than our actuals. To do this, we'll negate our predictions and save them into a new variable called `Y_PRED_BAD`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Y_PRED_BAD = -Y_PRED\nplt.plot(X, Y, 'y.')\nplt.plot(X, Y_PRED_BAD, 'r-')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"That prediction line looks horrible! Indeed, a horizontal line would fit this data better.\n\nLet's check the $R^2$.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(r2_score(Y, Y_PRED_BAD))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A negative $R^2$ is rare in practice. But if you do ever see one, it means the model has gone quite wrong.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Predicted vs. Actual Plots",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We have now seen a quantitative way to measure the goodness-of-fit of our regressions: the coefficient of determination. We know that if we see negative numbers that our model is very broken and if we see numbers approaching 1, the model is decent (or overfitted). But what about the in-between?\n \nThis is where qualitative observations based on expert opinion needs to come into play.\n\nThere are numerous ways to visualize regression predictions, but one of the most basic is the \"predicted vs. actual\" plot.\n \nTo create this plot, we scatter-plot the actual $y$-values used to train our model against the predicted $y$-values generated from the training features. We then draw a line from the lowest prediction to the largest.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.plot(Y_PRED, Y, 'b.')\nplt.plot([Y_PRED.min(), Y_PRED.max()], [Y_PRED.min(), Y_PRED.max()], 'r-')\nplt.xlabel('Predicted')\nplt.ylabel('Actual')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In this case, the data points scatter pretty evenly around the prediction-to-actual line.\n\nSo what does a bad plot look like?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's first negate all of our predictions, making them exactly the opposite of what they should be. This creates the exact opposite of a good actual-vs-predicted line.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Y_BAD = -Y_PRED\n\nplt.plot(Y, Y_BAD, 'b.')\nplt.plot([Y_BAD.min(), Y_BAD.max()], [Y_BAD.min(), Y_BAD.max()], 'r-')\nplt.xlabel('Predicted')\nplt.ylabel('Actual')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In this case we made a very contrived example where the predictions are exact opposites of the actual values. When you see this case, you have a model predicting roughly the opposite of what it should be predicting.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's look at another case, where we add a large positive bias to every prediction.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Y_BAD = Y_PRED + 200\n\nplt.plot(Y, Y_BAD, 'b.')\nplt.plot([Y_BAD.min(), Y_BAD.max()], [Y_BAD.min(), Y_BAD.max()], 'r-')\nplt.xlabel('Predicted')\nplt.ylabel('Actual')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we have a situation where there is an obvious **bias**. All predictions are higher than the actual values, so the model needs to be adjusted to make smaller predictions.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Most cases aren't quite so obvious. In the chart below, you can see that the predictions are okay for low values, but tend to underpredict for larger target values.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Y_BAD = Y_PRED - Y_PRED / 4\n\nplt.plot(Y, Y_BAD, 'b.')\nplt.plot([Y_BAD.min(), Y_BAD.max()], [Y_BAD.min(), Y_BAD.max()], 'r-')\nplt.xlabel('Predicted')\nplt.ylabel('Actual')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Predicted vs. actual charts are a useful tool for giving you a visual indication of how your model is performing. While single measures like $R^2$ give you an aggregated metric, charts allow you to see if there is a trend or outlier where your model isn't performing well.\n\nIf you identify problem areas, you can work on retraining your model.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Residual Plots",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Another helpful visualization tool is to plot the regression residuals. As a reminder, residuals are the difference between the actual values and the predicted values.\n \nWe plot residuals on the $y$-axis against the predicted values on the $x$-axis, and draw a horizontal line through $y=0$.\n \nCases where our predictions were too low are above the line. Cases where our predictions were too high are below the line.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"RESIDUALS = Y - Y_PRED\nplt.plot(Y_PRED, RESIDUALS, 'b.')\nplt.plot([0, Y_PRED.max()], [0, 0], 'r-')\nplt.xlabel('Predicted')\nplt.ylabel('Residual')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In the \"Predicted vs. Actual\" section above, we plotted a case where there was a large positive bias in our predictions. Plotting the same biased data on a residual plot shows all of the residuals below the zero line.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"RESIDUALS = Y - (Y_PRED + 200)\n\nplt.plot(Y_PRED, RESIDUALS, 'b.')\nplt.plot([0, Y_PRED.max()], [0, 0], 'r-')\nplt.xlabel('Predicted')\nplt.ylabel('Residual')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The other example in the \"Predicted vs. Actual\" section reduced our predictions by an amount proportional to the scale of the predictions. Below is the residual plot for that scenario.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"RESIDUALS = Y - (Y_PRED - Y_PRED / 4)\n\nplt.plot(Y_PRED, RESIDUALS, 'b.')\nplt.plot([0, Y_PRED.max()], [0, 0], 'r-')\nplt.xlabel('Predicted')\nplt.ylabel('Residual')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Resources",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* [Coefficient of Determination](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coefficient_of_determination)\n* [Interpreting Residual Plots](http://docs.statwing.com/interpreting-residual-plots-to-improve-your-regression/#gallery)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Exercises",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The [Interpreting Residual Plots](http://docs.statwing.com/interpreting-residual-plots-to-improve-your-regression/#gallery) resource gives examples of patterns in different residual plots and what those patterns might mean for your model.\n \nEach exercise below contains code that generates an image. Run the code to view the image, and then find the corresponding pattern name in [Interpreting Residual Plots](http://docs.statwing.com/interpreting-residual-plots-to-improve-your-regression/#gallery). Note the name of the pattern in the answer cell, and provide a one or two sentence explanation of what this could signal about your model's predictions.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Exercise 1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Run the code below to generate an image. Identify the corresponding residual plot pattern, and write a sentence or two about what this could signal about the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nnp.random.seed(42)\n\nx = np.linspace(-10.0, 10.0, 100)\ny = np.linspace(-10.0, 10.0, 100)\nf = x**2 + y**2 + np.random.uniform(low=-14, high=14, size=100)\nplt.plot(x, f, 'b.')\nplt.plot([x.min(), x.max()], [0, 0], 'r-')\nplt.xlabel('Predicted')\nplt.ylabel('Residual')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### **Student Solution**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"*Which [plot pattern](http://docs.statwing.com/interpreting-residual-plots-to-improve-your-regression/#gallery) does this residual plot follow? And what might it mean about the model?*",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Exercise 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Run the code below to generate an image. Identify the corresponding residual plot pattern, and write a sentence or two about what this could signal about the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nnp.random.seed(42)\n\nx = np.linspace(0.0, 10.0, 100)\ny = np.concatenate([\n np.random.uniform(low=-5, high=5, size=90),\n np.random.uniform(low=50, high=55, size=10)\n])\nplt.plot(x, y, 'b.')\nplt.plot([x.min(), x.max()], [0, 0], 'r-')\nplt.xlabel('Predicted')\nplt.ylabel('Residual')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### **Student Solution**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"*Which [plot pattern](http://docs.statwing.com/interpreting-residual-plots-to-improve-your-regression/#gallery) does this residual plot follow? And what might it mean about the model?*",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Exercise 3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Run the code below to generate an image. Identify the corresponding residual plot pattern, and write a sentence or two about what this could signal about the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nnp.random.seed(42)\n\nx = np.concatenate([\n np.random.uniform(low=0, high=2, size=90),\n np.random.uniform(low=4, high=10, size=10)\n])\ny = np.random.uniform(low=-5, high=5, size=100)\nplt.plot(x, y, 'b.')\nplt.plot([x.min(), x.max()], [0, 0], 'r-')\nplt.xlabel('Predicted')\nplt.ylabel('Residual')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### **Student Solution**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"*Which [plot pattern](http://docs.statwing.com/interpreting-residual-plots-to-improve-your-regression/#gallery) does this residual plot follow? And what might it mean about the model?*",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"---",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe93e780f0be4345c64812276a853c8b43fe927
| 61,531 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/tools/run_openvino2tf.ipynb
|
fixstars/arachne
|
03c00fc5105991d0d706b935d77e6f9255bae9e7
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2022-03-29T03:02:20.000Z
|
2022-03-29T03:48:38.000Z
|
examples/tools/run_openvino2tf.ipynb
|
fixstars/arachne
|
03c00fc5105991d0d706b935d77e6f9255bae9e7
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
examples/tools/run_openvino2tf.ipynb
|
fixstars/arachne
|
03c00fc5105991d0d706b935d77e6f9255bae9e7
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2022-03-29T05:44:12.000Z
|
2022-03-29T05:44:12.000Z
| 46.720577 | 336 | 0.558206 |
[
[
[
"# openvino2tensorflow\n\nThis tutorial explains the use case of openvino2tensorflow while using arachne. \n\n`openvino2tensorflow` is developed in the following GitHub repository. \nhttps://github.com/PINTO0309/openvino2tensorflow\n\nWhen you convert onnx model to tensorflow model by `onnx-tf`, the converted model includes many unnecessary transpose layers. This is because onnx has NCHW layer format while tensorflow has NHWC. \nThe inclusion of many unnecessary transpose layers causes performance degradation in inference.\n\nBy using openvino2tensorflow, you can avoid the inclusion of unnecessary transpose layers when converting a model from to tensorflow. \nIn this tutorial, we compare two convert methods and their converted models: \n1. PyTorch -> (torch2onnx) -> ONNX -> (onnx-simplifier) -> ONNX -> (onnx-tf) -> Tensorflow -> (tflite_converter) -> TfLite\n2. PyTorch -> (torch2onnx) -> ONNX -> (onnx-simplifier) -> ONNX -> (openvino_mo) -> OpenVino -> (openvino2tensorflow) -> Tensorflow -> (tflite_converter) -> TfLite\n\nThe developers of openvino2tensorflow provides the detail article about the advantage using openvino2tensorflow: [Converting PyTorch, ONNX, Caffe, and OpenVINO (NCHW) models to Tensorflow / TensorflowLite (NHWC) in a snap](https://qiita.com/PINTO/items/ed06e03eb5c007c2e102)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Create Simple Model\nHere we create and save a very simple PyTorch model to be converted.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import torch\nfrom torch import nn\nimport torch.onnx\n\nmodel = nn.Sequential(\n nn.Conv2d(3, 16, 3, padding=1),\n nn.Conv2d(16, 16, 3, padding=1),\n)\ntorch.save(model.eval(), \"./sample.pth\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Save model input and output information as yaml format for `arachne`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"yml = \"\"\"\ninputs:\n - dtype: float32\n name: input\n shape:\n - 1\n - 3\n - 224\n - 224\noutputs:\n - dtype: float32\n name: output\n shape:\n - 1\n - 16\n - 224\n - 224\n\"\"\"\nopen(\"sample.yml\", \"w\").write(yml)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Convert using onnx-tf\nYou can apply multiple tools in sequence with `arachne.pipeline`. \nModels are converted in the following order: \nPyTorch -> (torch2onnx) -> ONNX -> (onnx-simplifier) -> ONNX -> (onnx-tf) -> Tensorflow -> (tflite_converter) -> TfLite",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!python -m arachne.driver.pipeline \\\n +pipeline=[torch2onnx,onnx_simplifier,onnx_tf,tflite_converter] \\\n model_file=./sample.pth \\\n output_path=./pipeline1.tar \\\n model_spec_file=./sample.yml",
"/workspaces/arachne/.venv/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow/python/autograph/impl/api.py:22: DeprecationWarning: the imp module is deprecated in favour of importlib; see the module's documentation for alternative uses\n import imp\n/workspaces/arachne/.venv/lib/python3.6/site-packages/kedro/io/data_catalog.py:194: DeprecationWarning: The transformer API will be deprecated in Kedro 0.18.0.Please use Dataset Hooks to customise the load and save methods.For more information, please visithttps://kedro.readthedocs.io/en/stable/07_extend_kedro/02_hooks.html\n DeprecationWarning,\nChecking 0/3...\nChecking 1/3...\nChecking 2/3...\n2022-03-17 13:15:47,879 - onnx-tf - INFO - Start converting onnx pb to tf pb:\n2022-03-17 13:15:48.122144: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:142] This TensorFlow binary is optimized with oneAPI Deep Neural Network Library (oneDNN) to use the following CPU instructions in performance-critical operations: SSE3 SSE4.1 SSE4.2 AVX AVX2 FMA\nTo enable them in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags.\n2022-03-17 13:15:50.663788: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1510] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0 with 30851 MB memory: -> device: 0, name: Tesla V100-DGXS-32GB, pci bus id: 0000:07:00.0, compute capability: 7.0\n2022-03-17 13:15:50.666064: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1510] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:1 with 30997 MB memory: -> device: 1, name: Tesla V100-DGXS-32GB, pci bus id: 0000:08:00.0, compute capability: 7.0\n2022-03-17 13:15:50.668276: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1510] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:2 with 30997 MB memory: -> device: 2, name: Tesla V100-DGXS-32GB, pci bus id: 0000:0e:00.0, compute capability: 7.0\n2022-03-17 13:15:50.670470: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1510] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:3 with 30997 MB memory: -> device: 3, name: Tesla V100-DGXS-32GB, pci bus id: 0000:0f:00.0, compute capability: 7.0\nWARNING:absl:Function `__call__` contains input name(s) input.1 with unsupported characters which will be renamed to input_1 in the SavedModel.\n2022-03-17 13:15:56.707619: W tensorflow/python/util/util.cc:348] Sets are not currently considered sequences, but this may change in the future, so consider avoiding using them.\nWARNING:absl:Found untraced functions such as gen_tensor_dict while saving (showing 1 of 1). These functions will not be directly callable after loading.\n2022-03-17 13:15:56,844 - onnx-tf - INFO - Converting completes successfully.\nINFO:onnx-tf:Converting completes successfully.\n2022-03-17 13:15:57.776819: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:142] This TensorFlow binary is optimized with oneAPI Deep Neural Network Library (oneDNN) to use the following CPU instructions in performance-critical operations: SSE3 SSE4.1 SSE4.2 AVX AVX2 FMA\nTo enable them in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags.\n2022-03-17 13:16:00.329354: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1510] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0 with 30852 MB memory: -> device: 0, name: Tesla V100-DGXS-32GB, pci bus id: 0000:07:00.0, compute capability: 7.0\n2022-03-17 13:16:00.331575: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1510] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:1 with 30997 MB memory: -> device: 1, name: Tesla V100-DGXS-32GB, pci bus id: 0000:08:00.0, compute capability: 7.0\n2022-03-17 13:16:00.333731: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1510] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:2 with 30997 MB memory: -> device: 2, name: Tesla V100-DGXS-32GB, pci bus id: 0000:0e:00.0, compute capability: 7.0\n2022-03-17 13:16:00.335900: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1510] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:3 with 30997 MB memory: -> device: 3, name: Tesla V100-DGXS-32GB, pci bus id: 0000:0f:00.0, compute capability: 7.0\n2022-03-17 13:16:00.994347: W tensorflow/compiler/mlir/lite/python/tf_tfl_flatbuffer_helpers.cc:351] Ignored output_format.\n2022-03-17 13:16:00.994375: W tensorflow/compiler/mlir/lite/python/tf_tfl_flatbuffer_helpers.cc:354] Ignored drop_control_dependency.\n2022-03-17 13:16:00.994385: W tensorflow/compiler/mlir/lite/python/tf_tfl_flatbuffer_helpers.cc:360] Ignored change_concat_input_ranges.\n2022-03-17 13:16:00.995334: I tensorflow/cc/saved_model/reader.cc:38] Reading SavedModel from: model_0-saved_model\n2022-03-17 13:16:00.995788: I tensorflow/cc/saved_model/reader.cc:90] Reading meta graph with tags { serve }\n2022-03-17 13:16:00.995813: I tensorflow/cc/saved_model/reader.cc:132] Reading SavedModel debug info (if present) from: model_0-saved_model\n2022-03-17 13:16:01.001992: I tensorflow/cc/saved_model/loader.cc:229] Restoring SavedModel bundle.\n2022-03-17 13:16:01.036068: I tensorflow/cc/saved_model/loader.cc:213] Running initialization op on SavedModel bundle at path: model_0-saved_model\n2022-03-17 13:16:01.040151: I tensorflow/cc/saved_model/loader.cc:301] SavedModel load for tags { serve }; Status: success: OK. Took 44820 microseconds.\n2022-03-17 13:16:01.049326: I tensorflow/compiler/mlir/tensorflow/utils/dump_mlir_util.cc:210] disabling MLIR crash reproducer, set env var `MLIR_CRASH_REPRODUCER_DIRECTORY` to enable.\n2022-03-17 13:16:01.079954: I tensorflow/compiler/mlir/lite/flatbuffer_export.cc:1899] Estimated count of arithmetic ops: 276.169 M ops, equivalently 138.084 M MACs\n"
]
],
[
[
"Extract tarfile and see network structure of the converted tflite model. \nYou can visualize model structure in netron: `netron ./pipeline1/model_0.tflite`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!mkdir -p pipeline1 && tar xvf pipeline1.tar -C ./pipeline1",
"model_0.tflite\nenv.yaml\n"
],
[
"import tensorflow as tf\n\ndef list_layers(model_path):\n interpreter = tf.lite.Interpreter(model_path)\n layer_details = interpreter.get_tensor_details()\n interpreter.allocate_tensors()\n\n for layer in layer_details:\n print(\"Layer Name: {}\".format(layer['name']))\n\nlist_layers(\"./pipeline1/model_0.tflite\")",
"Layer Name: serving_default_input.1:0\nLayer Name: transpose_2/perm\nLayer Name: transpose_1/perm\nLayer Name: Const\nLayer Name: convolution\nLayer Name: convolution_1\nLayer Name: Add;convolution_1;convolution;Const_1\nLayer Name: Add_1;convolution_1;Const_3\nLayer Name: Pad\nLayer Name: transpose_1\nLayer Name: Add;convolution_1;convolution;Const_11\nLayer Name: transpose_2\nLayer Name: Pad_1\nLayer Name: transpose_4\nLayer Name: Add_1;convolution_1;Const_31\nLayer Name: PartitionedCall:0\n"
]
],
[
[
"We have confirmed that the transpose layer is unexpectedly included.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Convert using openvino2tensorflow\nNext, try the second conversion method using openvino2tensorflow. \nModels are converted in the following order: \nPyTorch -> (torch2onnx) -> ONNX -> (onnx-simplifier) -> ONNX -> (openvino_mo) -> OpenVino -> (openvino2tensorflow) -> Tensorflow -> (tflite_converter) -> TfLite",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!python -m arachne.driver.pipeline \\\n +pipeline=[torch2onnx,onnx_simplifier,openvino_mo,openvino2tf,tflite_converter] \\\n model_file=./sample.pth \\\n output_path=./pipeline2.tar \\\n model_spec_file=./sample.yml",
"/workspaces/arachne/.venv/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow/python/autograph/impl/api.py:22: DeprecationWarning: the imp module is deprecated in favour of importlib; see the module's documentation for alternative uses\n import imp\n/workspaces/arachne/.venv/lib/python3.6/site-packages/kedro/io/data_catalog.py:194: DeprecationWarning: The transformer API will be deprecated in Kedro 0.18.0.Please use Dataset Hooks to customise the load and save methods.For more information, please visithttps://kedro.readthedocs.io/en/stable/07_extend_kedro/02_hooks.html\n DeprecationWarning,\nChecking 0/3...\nChecking 1/3...\nChecking 2/3...\nModel Optimizer arguments:\nCommon parameters:\n\t- Path to the Input Model: \t/workspaces/arachne/tutorial/outputs/2022-03-17/13-48-03/model_0_simplified.onnx\n\t- Path for generated IR: \t/workspaces/arachne/tutorial/outputs/2022-03-17/13-48-03/openvino_0\n\t- IR output name: \tmodel_0_simplified\n\t- Log level: \tERROR\n\t- Batch: \tNot specified, inherited from the model\n\t- Input layers: \tNot specified, inherited from the model\n\t- Output layers: \tNot specified, inherited from the model\n\t- Input shapes: \t[1, 3, 224, 224]\n\t- Mean values: \tNot specified\n\t- Scale values: \tNot specified\n\t- Scale factor: \tNot specified\n\t- Precision of IR: \tFP32\n\t- Enable fusing: \tTrue\n\t- Enable grouped convolutions fusing: \tTrue\n\t- Move mean values to preprocess section: \tNone\n\t- Reverse input channels: \tFalse\nONNX specific parameters:\n\t- Inference Engine found in: \t/workspaces/arachne/.venv/lib/python3.6/site-packages/openvino\nInference Engine version: \t2021.4.2-3976-0943ed67223-refs/pull/539/head\nModel Optimizer version: \t2021.4.2-3976-0943ed67223-refs/pull/539/head\n[ SUCCESS ] Generated IR version 10 model.\n[ SUCCESS ] XML file: /workspaces/arachne/tutorial/outputs/2022-03-17/13-48-03/openvino_0/model_0_simplified.xml\n[ SUCCESS ] BIN file: /workspaces/arachne/tutorial/outputs/2022-03-17/13-48-03/openvino_0/model_0_simplified.bin\n[ SUCCESS ] Total execution time: 2.28 seconds. \n[ SUCCESS ] Memory consumed: 86 MB. \nIt's been a while, check for a new version of Intel(R) Distribution of OpenVINO(TM) toolkit here https://software.intel.com/content/www/us/en/develop/tools/openvino-toolkit/download.html?cid=other&source=prod&campid=ww_2022_bu_IOTG_OpenVINO-2022-1&content=upg_all&medium=organic or on the GitHub*\n\u001b[07mTensorFlow/Keras model building process starts\u001b[0m ======================================\n\u001b[07mLayer structure\u001b[0m =====================================================================\n\u001b[32mlayer_type\u001b[0m: Input\n\u001b[32mlayer_id\u001b[0m: 0\n\u001b[32mtf_layers_dict\u001b[0m: KerasTensor(type_spec=TensorSpec(shape=(1, 224, 224, 3), dtype=tf.float32, name='input_1'), name='input_1', description=\"created by layer 'input_1'\")\n====================================================================================\n\u001b[32mlayer_type\u001b[0m: Const\n\u001b[32mlayer_id\u001b[0m: 1\n\u001b[32mtf_layers_dict_shape\u001b[0m: (16, 3, 3, 3)\n\u001b[32mtf_layers_dict_value\u001b[0m: [[[[-1.71311706e-01 1.61934465e-01 2.39328351e-02]\n [ 1.53671131e-01 6.08684160e-02 1.91059306e-01]\n [ 1.97988525e-02 -1.58006638e-01 1.33780673e-01]]\n\n [[-1.51626971e-02 1.01691745e-01 -6.85642287e-02]\n [ 2.98243890e-07 4.40349542e-02 5.26012555e-02]\n [ 1.04677029e-01 1.50355265e-01 -2.33971421e-02]]\n\n [[ 2.85385456e-02 1.00955129e-01 2.51905061e-02]\n [-1.77596897e-01 -1.48589075e-01 -1.62936524e-01]\n [-1.43519118e-01 -6.40965402e-02 9.33927372e-02]]]\n\n\n [[[ 4.44381796e-02 -1.15723729e-01 -1.57656308e-04]\n [ 4.77289371e-02 -1.23191826e-01 8.19096342e-02]\n [ 1.49217322e-01 5.77600002e-02 1.47024602e-01]]\n\n [[ 9.34414193e-03 -4.41334657e-02 -1.55262109e-02]\n [-7.14511871e-02 -6.73459992e-02 1.84997365e-01]\n [-1.58071473e-01 1.90485537e-01 5.47244996e-02]]\n\n [[ 7.43153617e-02 1.32899135e-01 -1.07004479e-01]\n [ 7.89263025e-02 1.10076502e-01 -2.12193429e-02]\n [ 1.27446026e-01 -1.06881440e-01 1.12039402e-01]]]\n\n\n [[[-8.77788439e-02 -9.03891698e-02 -4.44725715e-02]\n [-1.61485583e-01 8.65791515e-02 -1.74625322e-01]\n [-8.48901272e-02 9.99575932e-05 -1.77383527e-01]]\n\n [[ 1.23576857e-01 2.63852943e-02 -7.10472986e-02]\n [-1.37101829e-01 -1.27075210e-01 1.83900684e-01]\n [-1.90744892e-01 1.68083221e-01 -5.19266017e-02]]\n\n [[ 3.06450427e-02 -1.87265739e-01 6.28326237e-02]\n [-6.07392527e-02 7.99433365e-02 1.29460081e-01]\n [ 7.75680542e-02 -2.73236372e-02 -1.58224016e-01]]]\n\n\n [[[ 2.76795346e-02 1.15157820e-01 -8.55762437e-02]\n [-1.07718013e-01 -9.68503281e-02 8.19834396e-02]\n [-5.13624176e-02 -1.92527915e-03 4.52461019e-02]]\n\n [[-1.67537227e-01 -1.40648335e-01 -8.50251615e-02]\n [-1.36285052e-01 -2.97159664e-02 1.56828731e-01]\n [ 1.85627282e-01 -1.22866943e-01 -5.06778546e-02]]\n\n [[-7.13260397e-02 8.39068368e-02 -1.68737426e-01]\n [ 1.23552173e-01 -6.46400079e-03 -1.32841736e-01]\n [ 6.43096417e-02 9.91688482e-03 -1.76163822e-01]]]\n\n\n [[[-6.14270009e-02 1.84170883e-02 2.04257146e-02]\n [-8.31748992e-02 6.92123398e-02 -1.66968867e-01]\n [ 1.49244413e-01 1.00393899e-01 1.36650726e-01]]\n\n [[ 1.54569745e-01 1.26765430e-01 6.46200255e-02]\n [ 1.48961768e-01 -1.15316622e-01 -5.35309277e-02]\n [ 1.44369528e-01 -4.69643511e-02 1.49902731e-01]]\n\n [[ 1.68611184e-01 -1.58076033e-01 1.22993954e-01]\n [ 1.50980175e-01 -1.49744496e-01 -5.83870932e-02]\n [-4.15927507e-02 -1.00339822e-01 -1.75526842e-01]]]\n\n\n [[[ 1.87764063e-01 1.36669517e-01 1.70692995e-01]\n [-8.13047290e-02 -1.14642434e-01 -4.83423565e-03]\n [ 1.12476699e-01 -1.92008093e-01 -1.68378145e-01]]\n\n [[-1.60411417e-01 1.63037807e-01 1.68763950e-01]\n [-6.48775920e-02 -1.92095980e-01 7.20392764e-02]\n [-9.79196429e-02 1.96206868e-02 -1.63222000e-03]]\n\n [[ 9.94267836e-02 8.58506560e-03 -6.41057864e-02]\n [-8.41159299e-02 6.70917556e-02 5.99908456e-03]\n [ 1.24803647e-01 -1.33132204e-01 -1.78898513e-01]]]\n\n\n [[[ 5.31540625e-02 -1.10678837e-01 6.20576739e-03]\n [-5.97443320e-02 -1.07411027e-01 -9.05444846e-02]\n [ 8.72847065e-02 -8.99016783e-02 5.57488985e-02]]\n\n [[ 9.11436602e-02 8.29550698e-02 2.87676658e-02]\n [ 1.17006771e-01 1.18038259e-01 1.48495227e-01]\n [-8.56917128e-02 -1.60253599e-01 -8.55174214e-02]]\n\n [[-8.55481178e-02 1.26600772e-01 -8.48829895e-02]\n [ 8.75023082e-02 -4.44662832e-02 -7.51228211e-03]\n [-7.61978328e-02 -9.97853000e-03 1.26178235e-01]]]\n\n\n [[[-1.98460445e-02 -6.32467940e-02 1.77307904e-01]\n [ 5.54928891e-02 1.19402081e-01 -8.06201473e-02]\n [-5.70090227e-02 -1.65941790e-01 -2.24270467e-02]]\n\n [[ 1.90288484e-01 1.63549870e-01 -1.71809226e-01]\n [ 1.11255392e-01 5.33381216e-02 -5.65509424e-02]\n [-1.68550640e-01 -9.97736678e-02 1.70031756e-01]]\n\n [[ 1.08343266e-01 1.43813893e-01 3.81326377e-02]\n [-1.88587189e-01 1.08013965e-01 1.17833249e-01]\n [-9.45217982e-02 8.15466046e-02 -1.57763019e-01]]]\n\n\n [[[-1.92549247e-02 2.05763523e-02 5.13042584e-02]\n [-1.59563795e-01 2.88406434e-03 -8.72978047e-02]\n [-6.10057674e-02 -1.90732345e-01 1.53073911e-02]]\n\n [[ 2.25515291e-02 -4.50828932e-02 -1.71053037e-01]\n [ 1.86502069e-01 6.58960268e-02 7.32938051e-02]\n [-1.39477938e-01 -8.49830881e-02 -6.40988797e-02]]\n\n [[ 1.87667608e-01 -6.64252043e-02 -1.27751350e-01]\n [ 1.36388540e-02 1.86957166e-01 -1.72594432e-02]\n [-7.90607184e-02 -4.29161750e-02 -1.35246128e-01]]]\n\n\n [[[-4.85877842e-02 1.29052937e-01 -5.33773750e-02]\n [-6.89550936e-02 4.85443808e-02 -1.41382173e-01]\n [-1.89421386e-01 -7.61304284e-03 3.28135751e-02]]\n\n [[-9.12977383e-02 1.10734314e-01 1.47733971e-01]\n [-6.36214092e-02 1.82245374e-01 -9.84351262e-02]\n [-3.15092392e-02 1.77482173e-01 -1.20955318e-01]]\n\n [[-1.17245160e-01 -1.01958834e-01 8.17524642e-02]\n [-2.84025017e-02 -1.16190180e-01 2.23183483e-02]\n [-2.28002877e-03 -1.91770688e-01 2.51128469e-02]]]\n\n\n [[[-1.32496074e-01 -1.20089054e-02 2.77708210e-02]\n [ 2.88121738e-02 -1.51700452e-01 1.53997049e-01]\n [-5.81683889e-02 -1.30934808e-02 9.22084078e-02]]\n\n [[ 8.35119635e-02 4.98112962e-02 1.08126126e-01]\n [-1.74239233e-01 1.11410640e-01 1.24303699e-02]\n [ 3.68093066e-02 -8.01523849e-02 1.30268663e-01]]\n\n [[ 1.88189372e-01 -8.94299746e-02 3.23432200e-02]\n [-9.08765942e-02 -1.46379396e-01 1.71526998e-01]\n [ 9.86140221e-02 3.36217228e-03 -4.03004363e-02]]]\n\n\n [[[ 2.76747402e-02 -1.76990479e-01 -8.46886933e-02]\n [ 4.82123196e-02 -1.35846704e-01 -5.57315983e-02]\n [-1.68181255e-01 1.13369159e-01 1.04564108e-01]]\n\n [[-5.06453477e-02 1.26207396e-01 -1.71016268e-02]\n [ 1.75701723e-01 -1.85604841e-01 1.78065807e-01]\n [-1.31930694e-01 5.35749272e-03 1.61289334e-01]]\n\n [[-1.60110429e-01 6.23956509e-02 -7.94699565e-02]\n [-7.40859434e-02 -8.10715705e-02 7.84594845e-03]\n [-1.44227877e-01 -1.45148471e-01 8.38812813e-02]]]\n\n\n [[[ 6.84346557e-02 1.08379446e-01 1.32707506e-01]\n [-1.10960200e-01 9.85327885e-02 -6.65394962e-02]\n [-6.16172589e-02 -2.95490870e-04 -2.29622107e-02]]\n\n [[ 6.66402355e-02 -7.61233130e-03 1.19521700e-01]\n [-1.13630354e-01 5.97983152e-02 1.14855126e-01]\n [ 1.47352606e-01 -1.25038065e-02 -1.68588325e-01]]\n\n [[-1.65449664e-01 -1.66683540e-01 -5.83471283e-02]\n [ 1.08359076e-01 -1.97953661e-03 7.50912726e-02]\n [ 1.70841441e-02 9.44346413e-02 -5.83445616e-02]]]\n\n\n [[[-6.18175194e-02 4.64488938e-02 -3.34856324e-02]\n [-1.42252252e-01 -1.06620453e-01 -6.13780208e-02]\n [-7.72645995e-02 1.33631960e-01 1.70237735e-01]]\n\n [[-1.58798367e-01 -1.55270174e-01 1.75619707e-01]\n [ 1.03979684e-01 -7.18250722e-02 -1.25801593e-01]\n [ 5.74296154e-02 -1.48116738e-01 -5.96716292e-02]]\n\n [[-1.65451661e-01 -1.56647384e-01 7.34499004e-03]\n [-3.32402699e-02 1.41382620e-01 -5.22334725e-02]\n [ 5.66182546e-02 -1.91236004e-01 -5.82605712e-02]]]\n\n\n [[[-8.71978253e-02 -2.64835078e-02 -4.59118485e-02]\n [ 4.25694771e-02 -1.13823637e-03 -5.52890748e-02]\n [ 1.26217663e-01 -1.15318760e-01 -3.78732607e-02]]\n\n [[ 1.71099976e-01 -5.17369658e-02 1.25876337e-01]\n [-1.57409683e-02 -9.80366692e-02 6.00136034e-02]\n [ 1.57849938e-01 -2.78084911e-02 -5.96195981e-02]]\n\n [[ 1.78385049e-01 -8.86295959e-02 1.49683774e-01]\n [ 1.24489345e-01 6.52259886e-02 -5.44661731e-02]\n [ 2.71410905e-02 -1.19284257e-01 1.17246099e-02]]]\n\n\n [[[ 1.27315924e-01 9.51309055e-02 -2.30228230e-02]\n [-1.68779045e-01 7.66261294e-02 -1.30248163e-02]\n [-1.53555989e-01 5.60983010e-02 2.36142632e-02]]\n\n [[ 7.66395777e-02 1.18852004e-01 1.37284279e-01]\n [-4.11164314e-02 7.15852603e-02 2.63142884e-02]\n [-1.49213031e-01 1.54465154e-01 -8.43192860e-02]]\n\n [[-6.46437258e-02 -1.64770082e-01 -1.71033479e-02]\n [-1.87533408e-01 1.82079971e-02 -1.56474516e-01]\n [ 1.80026144e-01 -1.11832470e-01 1.29382193e-01]]]]\n====================================================================================\n\u001b[32mlayer_type\u001b[0m: Convolution\n\u001b[32mlayer_id\u001b[0m: 2\n\u001b[32minput_layer0\u001b[0m: layer_id=0: KerasTensor(type_spec=TensorSpec(shape=(1, 224, 224, 3), dtype=tf.float32, name='input_1'), name='input_1', description=\"created by layer 'input_1'\")\n\u001b[32minput_layer1_value\u001b[0m: layer_id=1: [[[[-1.71311706e-01 1.61934465e-01 2.39328351e-02]\n [ 1.53671131e-01 6.08684160e-02 1.91059306e-01]\n [ 1.97988525e-02 -1.58006638e-01 1.33780673e-01]]\n\n [[-1.51626971e-02 1.01691745e-01 -6.85642287e-02]\n [ 2.98243890e-07 4.40349542e-02 5.26012555e-02]\n [ 1.04677029e-01 1.50355265e-01 -2.33971421e-02]]\n\n [[ 2.85385456e-02 1.00955129e-01 2.51905061e-02]\n [-1.77596897e-01 -1.48589075e-01 -1.62936524e-01]\n [-1.43519118e-01 -6.40965402e-02 9.33927372e-02]]]\n\n\n [[[ 4.44381796e-02 -1.15723729e-01 -1.57656308e-04]\n [ 4.77289371e-02 -1.23191826e-01 8.19096342e-02]\n [ 1.49217322e-01 5.77600002e-02 1.47024602e-01]]\n\n [[ 9.34414193e-03 -4.41334657e-02 -1.55262109e-02]\n [-7.14511871e-02 -6.73459992e-02 1.84997365e-01]\n [-1.58071473e-01 1.90485537e-01 5.47244996e-02]]\n\n [[ 7.43153617e-02 1.32899135e-01 -1.07004479e-01]\n [ 7.89263025e-02 1.10076502e-01 -2.12193429e-02]\n [ 1.27446026e-01 -1.06881440e-01 1.12039402e-01]]]\n\n\n [[[-8.77788439e-02 -9.03891698e-02 -4.44725715e-02]\n [-1.61485583e-01 8.65791515e-02 -1.74625322e-01]\n [-8.48901272e-02 9.99575932e-05 -1.77383527e-01]]\n\n [[ 1.23576857e-01 2.63852943e-02 -7.10472986e-02]\n [-1.37101829e-01 -1.27075210e-01 1.83900684e-01]\n [-1.90744892e-01 1.68083221e-01 -5.19266017e-02]]\n\n [[ 3.06450427e-02 -1.87265739e-01 6.28326237e-02]\n [-6.07392527e-02 7.99433365e-02 1.29460081e-01]\n [ 7.75680542e-02 -2.73236372e-02 -1.58224016e-01]]]\n\n\n [[[ 2.76795346e-02 1.15157820e-01 -8.55762437e-02]\n [-1.07718013e-01 -9.68503281e-02 8.19834396e-02]\n [-5.13624176e-02 -1.92527915e-03 4.52461019e-02]]\n\n [[-1.67537227e-01 -1.40648335e-01 -8.50251615e-02]\n [-1.36285052e-01 -2.97159664e-02 1.56828731e-01]\n [ 1.85627282e-01 -1.22866943e-01 -5.06778546e-02]]\n\n [[-7.13260397e-02 8.39068368e-02 -1.68737426e-01]\n [ 1.23552173e-01 -6.46400079e-03 -1.32841736e-01]\n [ 6.43096417e-02 9.91688482e-03 -1.76163822e-01]]]\n\n\n [[[-6.14270009e-02 1.84170883e-02 2.04257146e-02]\n [-8.31748992e-02 6.92123398e-02 -1.66968867e-01]\n [ 1.49244413e-01 1.00393899e-01 1.36650726e-01]]\n\n [[ 1.54569745e-01 1.26765430e-01 6.46200255e-02]\n [ 1.48961768e-01 -1.15316622e-01 -5.35309277e-02]\n [ 1.44369528e-01 -4.69643511e-02 1.49902731e-01]]\n\n [[ 1.68611184e-01 -1.58076033e-01 1.22993954e-01]\n [ 1.50980175e-01 -1.49744496e-01 -5.83870932e-02]\n [-4.15927507e-02 -1.00339822e-01 -1.75526842e-01]]]\n\n\n [[[ 1.87764063e-01 1.36669517e-01 1.70692995e-01]\n [-8.13047290e-02 -1.14642434e-01 -4.83423565e-03]\n [ 1.12476699e-01 -1.92008093e-01 -1.68378145e-01]]\n\n [[-1.60411417e-01 1.63037807e-01 1.68763950e-01]\n [-6.48775920e-02 -1.92095980e-01 7.20392764e-02]\n [-9.79196429e-02 1.96206868e-02 -1.63222000e-03]]\n\n [[ 9.94267836e-02 8.58506560e-03 -6.41057864e-02]\n [-8.41159299e-02 6.70917556e-02 5.99908456e-03]\n [ 1.24803647e-01 -1.33132204e-01 -1.78898513e-01]]]\n\n\n [[[ 5.31540625e-02 -1.10678837e-01 6.20576739e-03]\n [-5.97443320e-02 -1.07411027e-01 -9.05444846e-02]\n [ 8.72847065e-02 -8.99016783e-02 5.57488985e-02]]\n\n [[ 9.11436602e-02 8.29550698e-02 2.87676658e-02]\n [ 1.17006771e-01 1.18038259e-01 1.48495227e-01]\n [-8.56917128e-02 -1.60253599e-01 -8.55174214e-02]]\n\n [[-8.55481178e-02 1.26600772e-01 -8.48829895e-02]\n [ 8.75023082e-02 -4.44662832e-02 -7.51228211e-03]\n [-7.61978328e-02 -9.97853000e-03 1.26178235e-01]]]\n\n\n [[[-1.98460445e-02 -6.32467940e-02 1.77307904e-01]\n [ 5.54928891e-02 1.19402081e-01 -8.06201473e-02]\n [-5.70090227e-02 -1.65941790e-01 -2.24270467e-02]]\n\n [[ 1.90288484e-01 1.63549870e-01 -1.71809226e-01]\n [ 1.11255392e-01 5.33381216e-02 -5.65509424e-02]\n [-1.68550640e-01 -9.97736678e-02 1.70031756e-01]]\n\n [[ 1.08343266e-01 1.43813893e-01 3.81326377e-02]\n [-1.88587189e-01 1.08013965e-01 1.17833249e-01]\n [-9.45217982e-02 8.15466046e-02 -1.57763019e-01]]]\n\n\n [[[-1.92549247e-02 2.05763523e-02 5.13042584e-02]\n [-1.59563795e-01 2.88406434e-03 -8.72978047e-02]\n [-6.10057674e-02 -1.90732345e-01 1.53073911e-02]]\n\n [[ 2.25515291e-02 -4.50828932e-02 -1.71053037e-01]\n [ 1.86502069e-01 6.58960268e-02 7.32938051e-02]\n [-1.39477938e-01 -8.49830881e-02 -6.40988797e-02]]\n\n [[ 1.87667608e-01 -6.64252043e-02 -1.27751350e-01]\n [ 1.36388540e-02 1.86957166e-01 -1.72594432e-02]\n [-7.90607184e-02 -4.29161750e-02 -1.35246128e-01]]]\n\n\n [[[-4.85877842e-02 1.29052937e-01 -5.33773750e-02]\n [-6.89550936e-02 4.85443808e-02 -1.41382173e-01]\n [-1.89421386e-01 -7.61304284e-03 3.28135751e-02]]\n\n [[-9.12977383e-02 1.10734314e-01 1.47733971e-01]\n [-6.36214092e-02 1.82245374e-01 -9.84351262e-02]\n [-3.15092392e-02 1.77482173e-01 -1.20955318e-01]]\n\n [[-1.17245160e-01 -1.01958834e-01 8.17524642e-02]\n [-2.84025017e-02 -1.16190180e-01 2.23183483e-02]\n [-2.28002877e-03 -1.91770688e-01 2.51128469e-02]]]\n\n\n [[[-1.32496074e-01 -1.20089054e-02 2.77708210e-02]\n [ 2.88121738e-02 -1.51700452e-01 1.53997049e-01]\n [-5.81683889e-02 -1.30934808e-02 9.22084078e-02]]\n\n [[ 8.35119635e-02 4.98112962e-02 1.08126126e-01]\n [-1.74239233e-01 1.11410640e-01 1.24303699e-02]\n [ 3.68093066e-02 -8.01523849e-02 1.30268663e-01]]\n\n [[ 1.88189372e-01 -8.94299746e-02 3.23432200e-02]\n [-9.08765942e-02 -1.46379396e-01 1.71526998e-01]\n [ 9.86140221e-02 3.36217228e-03 -4.03004363e-02]]]\n\n\n [[[ 2.76747402e-02 -1.76990479e-01 -8.46886933e-02]\n [ 4.82123196e-02 -1.35846704e-01 -5.57315983e-02]\n [-1.68181255e-01 1.13369159e-01 1.04564108e-01]]\n\n [[-5.06453477e-02 1.26207396e-01 -1.71016268e-02]\n [ 1.75701723e-01 -1.85604841e-01 1.78065807e-01]\n [-1.31930694e-01 5.35749272e-03 1.61289334e-01]]\n\n [[-1.60110429e-01 6.23956509e-02 -7.94699565e-02]\n [-7.40859434e-02 -8.10715705e-02 7.84594845e-03]\n [-1.44227877e-01 -1.45148471e-01 8.38812813e-02]]]\n\n\n [[[ 6.84346557e-02 1.08379446e-01 1.32707506e-01]\n [-1.10960200e-01 9.85327885e-02 -6.65394962e-02]\n [-6.16172589e-02 -2.95490870e-04 -2.29622107e-02]]\n\n [[ 6.66402355e-02 -7.61233130e-03 1.19521700e-01]\n [-1.13630354e-01 5.97983152e-02 1.14855126e-01]\n [ 1.47352606e-01 -1.25038065e-02 -1.68588325e-01]]\n\n [[-1.65449664e-01 -1.66683540e-01 -5.83471283e-02]\n [ 1.08359076e-01 -1.97953661e-03 7.50912726e-02]\n [ 1.70841441e-02 9.44346413e-02 -5.83445616e-02]]]\n\n\n [[[-6.18175194e-02 4.64488938e-02 -3.34856324e-02]\n [-1.42252252e-01 -1.06620453e-01 -6.13780208e-02]\n [-7.72645995e-02 1.33631960e-01 1.70237735e-01]]\n\n [[-1.58798367e-01 -1.55270174e-01 1.75619707e-01]\n [ 1.03979684e-01 -7.18250722e-02 -1.25801593e-01]\n [ 5.74296154e-02 -1.48116738e-01 -5.96716292e-02]]\n\n [[-1.65451661e-01 -1.56647384e-01 7.34499004e-03]\n [-3.32402699e-02 1.41382620e-01 -5.22334725e-02]\n [ 5.66182546e-02 -1.91236004e-01 -5.82605712e-02]]]\n\n\n [[[-8.71978253e-02 -2.64835078e-02 -4.59118485e-02]\n [ 4.25694771e-02 -1.13823637e-03 -5.52890748e-02]\n [ 1.26217663e-01 -1.15318760e-01 -3.78732607e-02]]\n\n [[ 1.71099976e-01 -5.17369658e-02 1.25876337e-01]\n [-1.57409683e-02 -9.80366692e-02 6.00136034e-02]\n [ 1.57849938e-01 -2.78084911e-02 -5.96195981e-02]]\n\n [[ 1.78385049e-01 -8.86295959e-02 1.49683774e-01]\n [ 1.24489345e-01 6.52259886e-02 -5.44661731e-02]\n [ 2.71410905e-02 -1.19284257e-01 1.17246099e-02]]]\n\n\n [[[ 1.27315924e-01 9.51309055e-02 -2.30228230e-02]\n [-1.68779045e-01 7.66261294e-02 -1.30248163e-02]\n [-1.53555989e-01 5.60983010e-02 2.36142632e-02]]\n\n [[ 7.66395777e-02 1.18852004e-01 1.37284279e-01]\n [-4.11164314e-02 7.15852603e-02 2.63142884e-02]\n [-1.49213031e-01 1.54465154e-01 -8.43192860e-02]]\n\n [[-6.46437258e-02 -1.64770082e-01 -1.71033479e-02]\n [-1.87533408e-01 1.82079971e-02 -1.56474516e-01]\n [ 1.80026144e-01 -1.11832470e-01 1.29382193e-01]]]]\n\u001b[32mtf_layers_dict\u001b[0m: KerasTensor(type_spec=TensorSpec(shape=(1, 224, 224, 16), dtype=tf.float32, name=None), name='conv2d/Conv2D:0', description=\"created by layer 'conv2d'\")\n====================================================================================\n\u001b[32mlayer_type\u001b[0m: Const\n\u001b[32mlayer_id\u001b[0m: 3\n\u001b[32mtf_layers_dict_shape\u001b[0m: (1, 16, 1, 1)\n\u001b[32mtf_layers_dict_value\u001b[0m: [[[[ 0.03323612]]\n\n [[ 0.08333737]]\n\n [[-0.13509323]]\n\n [[ 0.13706905]]\n\n [[ 0.01487588]]\n\n [[ 0.12402532]]\n\n [[ 0.1195535 ]]\n\n [[-0.05163256]]\n\n [[-0.16966012]]\n\n [[-0.03548199]]\n\n [[-0.1032829 ]]\n\n [[ 0.02757281]]\n\n [[-0.10497215]]\n\n [[ 0.17104572]]\n\n [[-0.04356596]]\n\n [[-0.18591069]]]]\n====================================================================================\n\u001b[32mlayer_type\u001b[0m: Add\n\u001b[32mlayer_id\u001b[0m: 4\n\u001b[32minput_layer0\u001b[0m: layer_id=2: KerasTensor(type_spec=TensorSpec(shape=(1, 224, 224, 16), dtype=tf.float32, name=None), name='conv2d/Conv2D:0', description=\"created by layer 'conv2d'\")\n\u001b[32minput_layer1_value\u001b[0m: layer_id=3: [[[[ 0.03323612]]\n\n [[ 0.08333737]]\n\n [[-0.13509323]]\n\n [[ 0.13706905]]\n\n [[ 0.01487588]]\n\n [[ 0.12402532]]\n\n [[ 0.1195535 ]]\n\n [[-0.05163256]]\n\n [[-0.16966012]]\n\n [[-0.03548199]]\n\n [[-0.1032829 ]]\n\n [[ 0.02757281]]\n\n [[-0.10497215]]\n\n [[ 0.17104572]]\n\n [[-0.04356596]]\n\n [[-0.18591069]]]]\n\u001b[32mtf_layers_dict\u001b[0m: KerasTensor(type_spec=TensorSpec(shape=(1, 224, 224, 16), dtype=tf.float32, name=None), name='tf.math.add/Add:0', description=\"created by layer 'tf.math.add'\")\n====================================================================================\n\u001b[32mlayer_type\u001b[0m: Const\n\u001b[32mlayer_id\u001b[0m: 5\n\u001b[32mtf_layers_dict_shape\u001b[0m: (16, 16, 3, 3)\n\u001b[32mtf_layers_dict_value\u001b[0m: [[[[-0.04554008 0.03405847 -0.05978046]\n [-0.0206782 0.04863977 -0.05752119]\n [ 0.00263422 0.06992459 -0.06148377]]\n\n [[ 0.00938749 0.04105077 -0.03750723]\n [ 0.06331294 0.01229482 0.07040121]\n [-0.01045592 0.03855949 -0.07092514]]\n\n [[-0.04920384 0.05055832 -0.05776767]\n [ 0.01755506 -0.05912948 0.03812676]\n [-0.07239984 0.06950794 0.0199159 ]]\n\n ...\n\n [[-0.05365616 0.0726436 0.07619664]\n [-0.00765817 -0.07721674 -0.06883624]\n [ 0.03520527 0.06432831 0.04421742]]\n\n [[ 0.04557684 -0.02905875 -0.01612459]\n [ 0.01318257 0.05284571 0.04038739]\n [-0.00694061 0.02711397 0.00811062]]\n\n [[-0.03867297 -0.00801169 0.06710045]\n [-0.02326947 0.06634027 -0.05397308]\n [ 0.07394291 0.06489883 0.07907358]]]\n\n\n [[[ 0.04150238 -0.05718799 -0.03697311]\n [ 0.0829966 0.00355754 -0.02040519]\n [-0.0479629 0.0185533 0.08122125]]\n\n [[-0.03753284 0.01092864 -0.0800599 ]\n [ 0.0132617 0.08139055 0.013601 ]\n [-0.04257392 0.01181991 0.06117281]]\n\n [[-0.02947944 0.0611901 -0.02983826]\n [-0.0337003 -0.01842883 -0.06378716]\n [ 0.00292347 0.05637808 -0.01525874]]\n\n ...\n\n [[ 0.08208473 -0.04386745 -0.00533164]\n [-0.05967146 -0.02750031 0.07774355]\n [ 0.02875881 0.03729598 0.07546579]]\n\n [[ 0.05029345 -0.07855542 0.01717234]\n [ 0.05001915 0.03836102 -0.07876974]\n [ 0.07200658 -0.00294731 -0.0167397 ]]\n\n [[-0.00170049 0.0252423 -0.08049878]\n [ 0.02644814 0.03956728 0.01185008]\n [-0.05714941 0.01150963 0.04589819]]]\n\n\n [[[ 0.00575653 -0.00709666 0.00062998]\n [ 0.03350981 -0.04265278 0.05387348]\n [ 0.00370242 0.00187287 0.00669087]]\n\n [[ 0.07921952 -0.03352079 0.04833972]\n [ 0.00945206 0.07038709 0.01152408]\n [-0.08289847 0.023498 -0.01392396]]\n\n [[-0.0090033 -0.06283124 0.00110769]\n [-0.02421757 0.0412808 -0.02920415]\n [ 0.0584807 0.04290699 -0.05502883]]\n\n ...\n\n [[-0.05770941 0.05543792 0.03413137]\n [-0.06079156 0.02858713 0.07184728]\n [ 0.00585254 0.07632646 -0.00890372]]\n\n [[ 0.00058064 0.00643565 -0.08152693]\n [-0.07007304 0.07701802 -0.01942143]\n [-0.04955973 -0.07984637 0.06901503]]\n\n [[-0.08266807 -0.0646802 -0.04363805]\n [ 0.07034796 0.02971098 0.0492152 ]\n [ 0.01338942 0.02990884 -0.06663744]]]\n\n\n ...\n\n\n [[[ 0.01642013 -0.00418418 0.02699106]\n [-0.07379287 0.05032152 0.0531795 ]\n [-0.08215757 -0.07845385 -0.00768019]]\n\n [[-0.00790617 0.04845622 -0.02912269]\n [ 0.07765295 0.03571576 0.03701432]\n [-0.05344477 0.05688569 -0.06774579]]\n\n [[-0.07644736 -0.07206601 -0.05407382]\n [-0.07391082 -0.01799798 -0.01644122]\n [-0.01910152 0.02630306 0.00598508]]\n\n ...\n\n [[-0.00746907 0.05843086 -0.07319659]\n [ 0.02472647 0.06701951 0.02337588]\n [ 0.00057464 0.06418519 0.0376908 ]]\n\n [[-0.01047559 -0.07329005 0.04827262]\n [-0.08095761 -0.0268888 0.04877032]\n [-0.03053458 -0.000241 0.07870142]]\n\n [[ 0.01233124 -0.08022712 -0.05059677]\n [-0.08037157 0.02316496 -0.08219822]\n [ 0.07473486 -0.03218263 -0.05480286]]]\n\n\n [[[-0.06331088 -0.04102306 0.0078905 ]\n [-0.07737079 0.0457179 -0.07452011]\n [-0.04351804 0.03924372 0.00564839]]\n\n [[-0.03541887 -0.07313958 -0.05897783]\n [ 0.05340473 -0.02280995 0.04984494]\n [ 0.06880671 -0.0830851 -0.03176143]]\n\n [[ 0.04625544 -0.0341247 0.02425129]\n [ 0.00492181 0.08115117 -0.08327141]\n [-0.05392737 0.06252136 0.01423981]]\n\n ...\n\n [[-0.06819822 -0.08159746 0.0141194 ]\n [ 0.00515398 -0.06892547 0.05386277]\n [ 0.07924652 0.05666913 -0.01004289]]\n\n [[ 0.04838124 -0.0020589 0.06075826]\n [-0.04519067 0.0317311 -0.00204079]\n [ 0.01692012 0.0594186 -0.07058903]]\n\n [[ 0.03313974 0.00377096 -0.07965592]\n [-0.06335251 0.01566322 0.0437586 ]\n [ 0.02051635 -0.00873957 -0.0740987 ]]]\n\n\n [[[-0.05764706 0.07961996 0.06914219]\n [ 0.01695805 -0.0241123 0.07499006]\n [-0.06975975 -0.07846274 -0.06141602]]\n\n [[-0.03651681 0.04824371 0.03226409]\n [-0.05729762 -0.05019119 0.0436328 ]\n [ 0.05890773 0.05057728 0.02552928]]\n\n [[-0.00589621 0.03480625 0.03979409]\n [ 0.0435187 0.0619397 0.05088714]\n [ 0.01545423 -0.06955349 -0.05791961]]\n\n ...\n\n [[ 0.02478183 0.07740764 0.02654485]\n [ 0.03728571 0.0145494 -0.00683229]\n [-0.03618502 -0.03455635 -0.07997437]]\n\n [[ 0.01790215 -0.0528954 0.05230452]\n [-0.0250854 0.03818825 -0.06504694]\n [-0.051098 -0.01963489 0.0609969 ]]\n\n [[-0.01983848 -0.00341778 0.02031407]\n [ 0.0323057 0.02270891 0.06432669]\n [-0.02389361 0.04847889 -0.01805076]]]]\n====================================================================================\n\u001b[32mlayer_type\u001b[0m: Convolution\n\u001b[32mlayer_id\u001b[0m: 6\n\u001b[32minput_layer0\u001b[0m: layer_id=4: KerasTensor(type_spec=TensorSpec(shape=(1, 224, 224, 16), dtype=tf.float32, name=None), name='tf.math.add/Add:0', description=\"created by layer 'tf.math.add'\")\n\u001b[32minput_layer1_value\u001b[0m: layer_id=5: [[[[-0.04554008 0.03405847 -0.05978046]\n [-0.0206782 0.04863977 -0.05752119]\n [ 0.00263422 0.06992459 -0.06148377]]\n\n [[ 0.00938749 0.04105077 -0.03750723]\n [ 0.06331294 0.01229482 0.07040121]\n [-0.01045592 0.03855949 -0.07092514]]\n\n [[-0.04920384 0.05055832 -0.05776767]\n [ 0.01755506 -0.05912948 0.03812676]\n [-0.07239984 0.06950794 0.0199159 ]]\n\n ...\n\n [[-0.05365616 0.0726436 0.07619664]\n [-0.00765817 -0.07721674 -0.06883624]\n [ 0.03520527 0.06432831 0.04421742]]\n\n [[ 0.04557684 -0.02905875 -0.01612459]\n [ 0.01318257 0.05284571 0.04038739]\n [-0.00694061 0.02711397 0.00811062]]\n\n [[-0.03867297 -0.00801169 0.06710045]\n [-0.02326947 0.06634027 -0.05397308]\n [ 0.07394291 0.06489883 0.07907358]]]\n\n\n [[[ 0.04150238 -0.05718799 -0.03697311]\n [ 0.0829966 0.00355754 -0.02040519]\n [-0.0479629 0.0185533 0.08122125]]\n\n [[-0.03753284 0.01092864 -0.0800599 ]\n [ 0.0132617 0.08139055 0.013601 ]\n [-0.04257392 0.01181991 0.06117281]]\n\n [[-0.02947944 0.0611901 -0.02983826]\n [-0.0337003 -0.01842883 -0.06378716]\n [ 0.00292347 0.05637808 -0.01525874]]\n\n ...\n\n [[ 0.08208473 -0.04386745 -0.00533164]\n [-0.05967146 -0.02750031 0.07774355]\n [ 0.02875881 0.03729598 0.07546579]]\n\n [[ 0.05029345 -0.07855542 0.01717234]\n [ 0.05001915 0.03836102 -0.07876974]\n [ 0.07200658 -0.00294731 -0.0167397 ]]\n\n [[-0.00170049 0.0252423 -0.08049878]\n [ 0.02644814 0.03956728 0.01185008]\n [-0.05714941 0.01150963 0.04589819]]]\n\n\n [[[ 0.00575653 -0.00709666 0.00062998]\n [ 0.03350981 -0.04265278 0.05387348]\n [ 0.00370242 0.00187287 0.00669087]]\n\n [[ 0.07921952 -0.03352079 0.04833972]\n [ 0.00945206 0.07038709 0.01152408]\n [-0.08289847 0.023498 -0.01392396]]\n\n [[-0.0090033 -0.06283124 0.00110769]\n [-0.02421757 0.0412808 -0.02920415]\n [ 0.0584807 0.04290699 -0.05502883]]\n\n ...\n\n [[-0.05770941 0.05543792 0.03413137]\n [-0.06079156 0.02858713 0.07184728]\n [ 0.00585254 0.07632646 -0.00890372]]\n\n [[ 0.00058064 0.00643565 -0.08152693]\n [-0.07007304 0.07701802 -0.01942143]\n [-0.04955973 -0.07984637 0.06901503]]\n\n [[-0.08266807 -0.0646802 -0.04363805]\n [ 0.07034796 0.02971098 0.0492152 ]\n [ 0.01338942 0.02990884 -0.06663744]]]\n\n\n ...\n\n\n [[[ 0.01642013 -0.00418418 0.02699106]\n [-0.07379287 0.05032152 0.0531795 ]\n [-0.08215757 -0.07845385 -0.00768019]]\n\n [[-0.00790617 0.04845622 -0.02912269]\n [ 0.07765295 0.03571576 0.03701432]\n [-0.05344477 0.05688569 -0.06774579]]\n\n [[-0.07644736 -0.07206601 -0.05407382]\n [-0.07391082 -0.01799798 -0.01644122]\n [-0.01910152 0.02630306 0.00598508]]\n\n ...\n\n [[-0.00746907 0.05843086 -0.07319659]\n [ 0.02472647 0.06701951 0.02337588]\n [ 0.00057464 0.06418519 0.0376908 ]]\n\n [[-0.01047559 -0.07329005 0.04827262]\n [-0.08095761 -0.0268888 0.04877032]\n [-0.03053458 -0.000241 0.07870142]]\n\n [[ 0.01233124 -0.08022712 -0.05059677]\n [-0.08037157 0.02316496 -0.08219822]\n [ 0.07473486 -0.03218263 -0.05480286]]]\n\n\n [[[-0.06331088 -0.04102306 0.0078905 ]\n [-0.07737079 0.0457179 -0.07452011]\n [-0.04351804 0.03924372 0.00564839]]\n\n [[-0.03541887 -0.07313958 -0.05897783]\n [ 0.05340473 -0.02280995 0.04984494]\n [ 0.06880671 -0.0830851 -0.03176143]]\n\n [[ 0.04625544 -0.0341247 0.02425129]\n [ 0.00492181 0.08115117 -0.08327141]\n [-0.05392737 0.06252136 0.01423981]]\n\n ...\n\n [[-0.06819822 -0.08159746 0.0141194 ]\n [ 0.00515398 -0.06892547 0.05386277]\n [ 0.07924652 0.05666913 -0.01004289]]\n\n [[ 0.04838124 -0.0020589 0.06075826]\n [-0.04519067 0.0317311 -0.00204079]\n [ 0.01692012 0.0594186 -0.07058903]]\n\n [[ 0.03313974 0.00377096 -0.07965592]\n [-0.06335251 0.01566322 0.0437586 ]\n [ 0.02051635 -0.00873957 -0.0740987 ]]]\n\n\n [[[-0.05764706 0.07961996 0.06914219]\n [ 0.01695805 -0.0241123 0.07499006]\n [-0.06975975 -0.07846274 -0.06141602]]\n\n [[-0.03651681 0.04824371 0.03226409]\n [-0.05729762 -0.05019119 0.0436328 ]\n [ 0.05890773 0.05057728 0.02552928]]\n\n [[-0.00589621 0.03480625 0.03979409]\n [ 0.0435187 0.0619397 0.05088714]\n [ 0.01545423 -0.06955349 -0.05791961]]\n\n ...\n\n [[ 0.02478183 0.07740764 0.02654485]\n [ 0.03728571 0.0145494 -0.00683229]\n [-0.03618502 -0.03455635 -0.07997437]]\n\n [[ 0.01790215 -0.0528954 0.05230452]\n [-0.0250854 0.03818825 -0.06504694]\n [-0.051098 -0.01963489 0.0609969 ]]\n\n [[-0.01983848 -0.00341778 0.02031407]\n [ 0.0323057 0.02270891 0.06432669]\n [-0.02389361 0.04847889 -0.01805076]]]]\n\u001b[32mtf_layers_dict\u001b[0m: KerasTensor(type_spec=TensorSpec(shape=(1, 224, 224, 16), dtype=tf.float32, name=None), name='conv2d_1/Conv2D:0', description=\"created by layer 'conv2d_1'\")\n====================================================================================\n\u001b[32mlayer_type\u001b[0m: Const\n\u001b[32mlayer_id\u001b[0m: 7\n\u001b[32mtf_layers_dict_shape\u001b[0m: (1, 16, 1, 1)\n\u001b[32mtf_layers_dict_value\u001b[0m: [[[[-0.02533897]]\n\n [[ 0.03452766]]\n\n [[-0.08192988]]\n\n [[-0.0762841 ]]\n\n [[ 0.01504902]]\n\n [[-0.07279493]]\n\n [[-0.04693854]]\n\n [[ 0.03523269]]\n\n [[-0.06643175]]\n\n [[ 0.04456952]]\n\n [[-0.01470435]]\n\n [[ 0.05575951]]\n\n [[-0.00457138]]\n\n [[ 0.04792096]]\n\n [[ 0.00842363]]\n\n [[-0.00854001]]]]\n====================================================================================\n\u001b[32mlayer_type\u001b[0m: Add\n\u001b[32mlayer_id\u001b[0m: 8\n\u001b[32minput_layer0\u001b[0m: layer_id=6: KerasTensor(type_spec=TensorSpec(shape=(1, 224, 224, 16), dtype=tf.float32, name=None), name='conv2d_1/Conv2D:0', description=\"created by layer 'conv2d_1'\")\n\u001b[32minput_layer1_value\u001b[0m: layer_id=7: [[[[-0.02533897]]\n\n [[ 0.03452766]]\n\n [[-0.08192988]]\n\n [[-0.0762841 ]]\n\n [[ 0.01504902]]\n\n [[-0.07279493]]\n\n [[-0.04693854]]\n\n [[ 0.03523269]]\n\n [[-0.06643175]]\n\n [[ 0.04456952]]\n\n [[-0.01470435]]\n\n [[ 0.05575951]]\n\n [[-0.00457138]]\n\n [[ 0.04792096]]\n\n [[ 0.00842363]]\n\n [[-0.00854001]]]]\n\u001b[32mtf_layers_dict\u001b[0m: KerasTensor(type_spec=TensorSpec(shape=(1, 224, 224, 16), dtype=tf.float32, name=None), name='tf.math.add_1/Add:0', description=\"created by layer 'tf.math.add_1'\")\n====================================================================================\n\u001b[32mlayer_type\u001b[0m: Result\n\u001b[32mlayer_id\u001b[0m: 9\n\u001b[32minput_layer0\u001b[0m: layer_id=8: KerasTensor(type_spec=TensorSpec(shape=(1, 224, 224, 16), dtype=tf.float32, name=None), name='tf.math.add_1/Add:0', description=\"created by layer 'tf.math.add_1'\")\n\u001b[32mtf_layers_dict\u001b[0m: KerasTensor(type_spec=TensorSpec(shape=(1, 224, 224, 16), dtype=tf.float32, name=None), name='tf.identity/Identity:0', description=\"created by layer 'tf.identity'\")\n====================================================================================\n\u001b[32mTensorFlow/Keras model building process complete!\u001b[0m\n\u001b[07msaved_model output started\u001b[0m ==========================================================\n\u001b[32msaved_model output complete!\u001b[0m\n\u001b[07mAll the conversion process is finished!\u001b[0m =============================================\n2022-03-17 13:48:16.706320: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:142] This TensorFlow binary is optimized with oneAPI Deep Neural Network Library (oneDNN) to use the following CPU instructions in performance-critical operations: SSE3 SSE4.1 SSE4.2 AVX AVX2 FMA\nTo enable them in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags.\n2022-03-17 13:48:19.320736: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1510] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0 with 30851 MB memory: -> device: 0, name: Tesla V100-DGXS-32GB, pci bus id: 0000:07:00.0, compute capability: 7.0\n2022-03-17 13:48:19.323005: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1510] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:1 with 30997 MB memory: -> device: 1, name: Tesla V100-DGXS-32GB, pci bus id: 0000:08:00.0, compute capability: 7.0\n2022-03-17 13:48:19.325188: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1510] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:2 with 30997 MB memory: -> device: 2, name: Tesla V100-DGXS-32GB, pci bus id: 0000:0e:00.0, compute capability: 7.0\n2022-03-17 13:48:19.327422: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1510] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:3 with 30997 MB memory: -> device: 3, name: Tesla V100-DGXS-32GB, pci bus id: 0000:0f:00.0, compute capability: 7.0\n2022-03-17 13:48:20.296690: W tensorflow/compiler/mlir/lite/python/tf_tfl_flatbuffer_helpers.cc:351] Ignored output_format.\n2022-03-17 13:48:20.296725: W tensorflow/compiler/mlir/lite/python/tf_tfl_flatbuffer_helpers.cc:354] Ignored drop_control_dependency.\n2022-03-17 13:48:20.296735: W tensorflow/compiler/mlir/lite/python/tf_tfl_flatbuffer_helpers.cc:360] Ignored change_concat_input_ranges.\n2022-03-17 13:48:20.297706: I tensorflow/cc/saved_model/reader.cc:38] Reading SavedModel from: openvino2tf-0-saved_model\n2022-03-17 13:48:20.299163: I tensorflow/cc/saved_model/reader.cc:90] Reading meta graph with tags { serve }\n2022-03-17 13:48:20.299189: I tensorflow/cc/saved_model/reader.cc:132] Reading SavedModel debug info (if present) from: openvino2tf-0-saved_model\n2022-03-17 13:48:20.311571: I tensorflow/cc/saved_model/loader.cc:229] Restoring SavedModel bundle.\n2022-03-17 13:48:20.358025: I tensorflow/cc/saved_model/loader.cc:213] Running initialization op on SavedModel bundle at path: openvino2tf-0-saved_model\n2022-03-17 13:48:20.364292: I tensorflow/cc/saved_model/loader.cc:301] SavedModel load for tags { serve }; Status: success: OK. Took 66589 microseconds.\n2022-03-17 13:48:20.377893: I tensorflow/compiler/mlir/tensorflow/utils/dump_mlir_util.cc:210] disabling MLIR crash reproducer, set env var `MLIR_CRASH_REPRODUCER_DIRECTORY` to enable.\n2022-03-17 13:48:20.410937: I tensorflow/compiler/mlir/lite/flatbuffer_export.cc:1899] Estimated count of arithmetic ops: 276.169 M ops, equivalently 138.084 M MACs\n"
]
],
[
[
"Extract tarfile and see network structure of the converted tflite model. \nYou can visualize model structure in netron: `netron ./pipeline2/model_0.tflite`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!mkdir -p pipeline2 && tar xvf pipeline2.tar -C ./pipeline2",
"model_0.tflite\nenv.yaml\n"
],
[
"list_layers(\"./pipeline2/model_0.tflite\")",
"Layer Name: serving_default_input_1:0\nLayer Name: model/zero_padding2d/Pad/paddings\nLayer Name: model/conv2d/Conv2D\nLayer Name: model/conv2d_1/Conv2D\nLayer Name: model/tf.math.add/Add;model/conv2d_1/Conv2D;model/conv2d/Conv2D;model/tf.math.add/Add/y\nLayer Name: model/tf.math.add_1/Add;model/conv2d_1/Conv2D;model/tf.math.add_1/Add/y\nLayer Name: model/zero_padding2d/Pad\nLayer Name: model/tf.math.add/Add;model/conv2d_1/Conv2D;model/conv2d/Conv2D;model/tf.math.add/Add/y1\nLayer Name: model/zero_padding2d_1/Pad\nLayer Name: StatefulPartitionedCall:0\n"
]
],
[
[
"We have confirmed that the transpose layer is NOT included.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe973091733735ee5acc34864e2a446a20a8458
| 30,979 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
4_Applied ML with Python/Course/Week-4/Checks-2.ipynb
|
syedmeesamali/CourseraPlus
|
0e729d10938ecb55fde69433c6b02cb02b8e6d10
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
4_Applied ML with Python/Course/Week-4/Checks-2.ipynb
|
syedmeesamali/CourseraPlus
|
0e729d10938ecb55fde69433c6b02cb02b8e6d10
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
4_Applied ML with Python/Course/Week-4/Checks-2.ipynb
|
syedmeesamali/CourseraPlus
|
0e729d10938ecb55fde69433c6b02cb02b8e6d10
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 43.817539 | 9,662 | 0.596662 |
[
[
[
"# Checks for model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.read_csv(f\"D:/Docs/train_1.csv\", encoding='mac_roman')\n#tickets = pd.read_csv(f\"D:/SYED/Docs/train.csv\", encoding='mac_roman')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['ticket_date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['ticket_date'], format=\"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S\", errors='coerce')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 1. Encoding of disposition column",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df['disposition'].replace(['Not Responsible', 'Responsible', 'PENDING'], [0, 1, 2], inplace=True)\ndf['disposition'].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Simple histogram\ndf['disposition'].hist()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Make paid in full also as compliant\ndf.loc[df['payment_status'] == 'PAID IN FULL', 'compliance'] = 1\ndf['payment_status'].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 2. Encode payment status",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Need to encode the text values as numbers as well\ndf['payment_status'].replace(['NO PAYMENT APPLIED', 'PAID IN FULL', 'PARTIAL PAYMENT APPLIED'], [0, 1, 2], inplace=True)\ndf['payment_status'].value_counts()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 3. Fill missing compliance with 0.5 (yes/no)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df['compliance'] = df['compliance'].fillna(0.5)\ndf['city'].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 4. Encode city values > 300",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = df.groupby('city').filter(lambda x : len(x) > 300)\n#df['city'].value_counts()\n#counts = df.city.value_counts()\n#counts.to_csv('city100plus.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['fine_amount'] = df['fine_amount'].fillna(0)\ndf.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import OrdinalEncoder\nord_enc = OrdinalEncoder()\ndf[\"city_code\"] = ord_enc.fit_transform(df[[\"city\"]])\ndf[[\"city\", \"city_code\"]].head(11)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 5. Target values should be clear categories ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 6. Build the actual model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n\n#Feature selection is very interesting phase here where by own intuition I have to select the features\n#which might give best fit for data at hand\n\nfeature_names_tickets = ['ticket_id', 'disposition', 'fine_amount', 'city_code']\nX_tickets = df[feature_names_tickets]\n#Our target variable is compliance i.e., ticket chances of getting PAID\ny_tickets = df['compliance']\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_tickets, y_tickets, random_state = 0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_tickets.isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"clf = LogisticRegression(C=100).fit(X_train, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe97655a8420d4c6dd6ec69525915493757556e
| 7,065 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Collecting Data Using Web Scraping Lab.ipynb
|
okaffo/Collecting-Data-Using-Web-Scraping
|
c3c444c5974c484c2f3e986a0889d1290485040f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Collecting Data Using Web Scraping Lab.ipynb
|
okaffo/Collecting-Data-Using-Web-Scraping
|
c3c444c5974c484c2f3e986a0889d1290485040f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Collecting Data Using Web Scraping Lab.ipynb
|
okaffo/Collecting-Data-Using-Web-Scraping
|
c3c444c5974c484c2f3e986a0889d1290485040f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 24.53125 | 349 | 0.536447 |
[
[
[
"<center>\n <img src=\"https://gitlab.com/ibm/skills-network/courses/placeholder101/-/raw/master/labs/module%201/images/IDSNlogo.png\" width=\"300\" alt=\"cognitiveclass.ai logo\" />\n</center>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# **Hands-on Lab : Web Scraping**\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Estimated time needed: **30 to 45** minutes\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Objectives\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this lab you will perform the following:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Extract information from a given web site\n* Write the scraped data into a csv file.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Extract information from the given web site\n\nYou will extract the data from the below web site: <br>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#this url contains the data you need to scrape\nurl = \"https://cf-courses-data.s3.us.cloud-object-storage.appdomain.cloud/IBM-DA0321EN-SkillsNetwork/labs/datasets/Programming_Languages.html\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The data you need to scrape is the **name of the programming language** and **average annual salary**.<br> It is a good idea to open the url in your web broswer and study the contents of the web page before you start to scrape.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Import the required libraries\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Your code here\nfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoup\nimport requests\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Download the webpage at the url\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#your code goes here\nurl = \"https://cf-courses-data.s3.us.cloud-object-storage.appdomain.cloud/IBM-DA0321EN-SkillsNetwork/labs/datasets/Programming_Languages.html\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Create a soup object\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#your code goes here\ndata = requests.get(url).text\nsoup = BeautifulSoup(data, \"html5lib\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Scrape the `Language name` and `annual average salary`.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#your code goes here\ntable = soup.find('table')\nfor row in table.find_all('tr'):\n cols = row.find_all('td')\n language_name = cols[1].getText()\n annual_average_salary = cols[3].getText()\n print(\"{}--->{}\".format(language_name,annual_average_salary))",
"Language--->Average Annual Salary\nPython--->$114,383\nJava--->$101,013\nR--->$92,037\nJavascript--->$110,981\nSwift--->$130,801\nC++--->$113,865\nC#--->$88,726\nPHP--->$84,727\nSQL--->$84,793\nGo--->$94,082\n"
]
],
[
[
"Save the scrapped data into a file named *popular-languages.csv*\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# your code goes here\nimport csv\nimport pandas as pd\ntable_rows = table.find_all('tr')\nl = []\nfor tr in table_rows:\n td = tr.find_all('td')\n row = [tr.text for tr in td]\n l.append(row)\ndf=pd.DataFrame(l, columns=[\"Column1\",\"column2\",...])\ndf\ndf.to_csv(\"filename.csv\") #this could be used to save data into csv \n\ncsv.save('popular-languages.csv')\nimport os\nos.getcwd()\nfrom IPython.display import HTML\nimport base64,io\n\n\ndef create_download_link( df, title = \"Download CSV file\", filename = \"/home/wsuser/work/popular-languages.csv\"):\n csv = df.to_csv()\n b64 = base64.b64encode(csv.encode())\n payload = b64.decode()\n html = '<a download=\"{filename}\" href=\"data:text/csv;base64,{payload}\" target=\"_blank\">{title}</a>'\n html = html.format(payload=payload,title=title,filename=filename)\n return HTML(html)\n\n\n\ncreate_download_link(df) #this could be used to save data into csv",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Authors\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Ramesh Sannareddy\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Other Contributors\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Rav Ahuja\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Change Log\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"| Date (YYYY-MM-DD) | Version | Changed By | Change Description |\n| ----------------- | ------- | ----------------- | ---------------------------------- |\n| 2020-10-17 | 0.1 | Ramesh Sannareddy | Created initial version of the lab |\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Copyright © 2020 IBM Corporation. This notebook and its source code are released under the terms of the [MIT License](https://cognitiveclass.ai/mit-license/?utm_medium=Exinfluencer&utm_source=Exinfluencer&utm_content=000026UJ&utm_term=10006555&utm_id=NA-SkillsNetwork-Channel-SkillsNetworkCoursesIBMDA0321ENSkillsNetwork21426264-2021-01-01).\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe97c14c81d53e9375371702a70e47d3a50af49
| 2,389 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
00-Index.ipynb
|
vmezzano21/neubias_academy_biapy
|
b6f21462bcd4202749efaf69e45724196ba712c0
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 50 |
2020-05-07T13:43:35.000Z
|
2021-12-10T13:05:02.000Z
|
00-Index.ipynb
|
vmezzano21/neubias_academy_biapy
|
b6f21462bcd4202749efaf69e45724196ba712c0
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
00-Index.ipynb
|
vmezzano21/neubias_academy_biapy
|
b6f21462bcd4202749efaf69e45724196ba712c0
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 30 |
2020-05-07T13:44:52.000Z
|
2021-11-29T11:48:59.000Z
| 26.544444 | 100 | 0.580159 |
[
[
[
"# Interactive Bioimage Analysis with Python and Jupyter\n#### **Guillaume Witz**, Science IT Support, Microscopy Imaging Center, Bern University",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Table of contents\n\n### [1. Python Bacics](01-Python_bare_minimum.ipynb)\n\n### [2. Numpy intro with focus on images](02-Numpy_images.ipynb)\n\n### [3. Matplotlib intro with focus on images](03-Matplotlib_images.ipynb)\n\n### [4. Importing images](04-Image_import.ipynb)\n\n### [5. Image filtering and thresholding](05-Filtering_thresholding.ipynb)\n\n### [6. Masks and region measurements](06-Binary_operations.ipynb)\n\n### [7. Writing re-usable code](07-Packaging_code.ipynb)\n\n### [8. Cell Tracking](08-Time_lapse_tracking.ipynb)\n\n### [9. Object detection by pattern matching](09-Pattern_matching.ipynb)\n\n### [10. Watershed segmentation](10-Watershed.ipynb)\n\n### [11. 3D image processing and visualization](11-3D_image_processing.ipynb)\n\n### [12. Image registration](12-Registration.ipynb)\n\n### [13. Machine Learning segmentation (Stardist/Cellpose)](13-ML_based_segmentation.ipynb)\n\n### [14. Mixing Python and Fiji](14-PyImageJ.ipynb)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe9831ddbb0adb7d08b8b9433edf3a477ed6d65
| 21,033 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
06 - Work with Data.ipynb
|
MicrosoftLearning/mslearn-dp100.zh-cn
|
4f391a85ab962709656a1b81ef6c512a228a6dde
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2021-09-26T09:02:05.000Z
|
2021-11-27T20:20:11.000Z
|
06 - Work with Data.ipynb
|
MicrosoftLearning/mslearn-dp100.zh-cn
|
4f391a85ab962709656a1b81ef6c512a228a6dde
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
06 - Work with Data.ipynb
|
MicrosoftLearning/mslearn-dp100.zh-cn
|
4f391a85ab962709656a1b81ef6c512a228a6dde
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2021-05-01T02:26:44.000Z
|
2022-02-03T17:53:16.000Z
| 35.172241 | 254 | 0.579708 |
[
[
[
"# 处理数据\r\n\r\n数据是构建机器学习模型的基础。在云中集中管理数据,并使在多个工作站上运行试验和训练模型的数据科学家团队能够访问这些数据以及计算目标,这是任何专业数据科学解决方案的重要组成部分。\r\n\r\n在该笔记本中,你将探索两个用于数据处理的 Azure 机器学习对象:数据存储和数据集。",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 连接到工作区\r\n\r\n首先,请连接到你的工作区。\r\n\r\n> **备注**:如果尚未与 Azure 订阅建立经过身份验证的会话,则系统将提示你通过执行以下操作进行身份验证:单击链接,输入验证码,然后登录到 Azure。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import azureml.core\nfrom azureml.core import Workspace\n\n# Load the workspace from the saved config file\nws = Workspace.from_config()\nprint('Ready to use Azure ML {} to work with {}'.format(azureml.core.VERSION, ws.name))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 使用数据存储\r\n\r\n在 Azure ML 中,数据存储是对存储位置(例如 Azure 存储 Blob 容器)的引用。每个工作区都有一个默认的数据存储,该存储通常是使用相应工作区创建的 Azure 存储 Blob 容器。如果需要使用存储在不同位置的数据,则可以将自定义数据存储添加到工作区中,并将其中任何一个设置为默认值。\r\n\r\n### 查看数据存储\r\n\r\n运行以下代码以确定工作区中的数据存储:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get the default datastore\ndefault_ds = ws.get_default_datastore()\n\n# Enumerate all datastores, indicating which is the default\nfor ds_name in ws.datastores:\n print(ds_name, \"- Default =\", ds_name == default_ds.name)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"你还可以在 [Azure 机器学习工作室](https://ml.azure.com)中工作区的“**数据集**”页面上查看和管理工作区中的数据存储。\r\n\r\n### 将数据上传到数据存储\r\n\r\n确定可用的数据存储后,可以将文件从本地文件系统上传到数据存储,这样无论试验脚本实际在何处运行,工作区中运行的试验都能访问相应文件。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"default_ds.upload_files(files=['./data/diabetes.csv', './data/diabetes2.csv'], # Upload the diabetes csv files in /data\n target_path='diabetes-data/', # Put it in a folder path in the datastore\n overwrite=True, # Replace existing files of the same name\n show_progress=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 使用数据集\r\n\r\nAzure 机器学习以数据集的形式提供数据的抽象。数据集是对可能要在试验中使用的一组特定数据的版本控制引用。数据集可以采用表格格式,也可以采用文件格式。\r\n\r\n### 创建表格数据集\r\n\r\n接下来根据上传到数据存储的糖尿病数据创建数据集,然后查看前 20 条记录。这种情况下,数据在 CSV 文件中采用结构化格式,因此我们将使用表格数据集。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from azureml.core import Dataset\n\n# Get the default datastore\ndefault_ds = ws.get_default_datastore()\n\n#Create a tabular dataset from the path on the datastore (this may take a short while)\ntab_data_set = Dataset.Tabular.from_delimited_files(path=(default_ds, 'diabetes-data/*.csv'))\n\n# Display the first 20 rows as a Pandas dataframe\ntab_data_set.take(20).to_pandas_dataframe()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"如上述代码中所见,可以轻松地将表格数据集转换为 Pandas 数据帧,从而使用常见的 python 技术处理数据。\r\n\r\n### 创建文件数据集\r\n\r\n你创建的数据集是表格数据集,可以在数据集定义所包含的结构化文件中作为包含所有数据的数据帧读取。这对于表格数据非常有效,但在某些机器学习场景中,可能需要使用非结构化数据;或者你可能只想通过自己的代码读取文件中的数据。为此,可以使用文件数据集,该数据集在虚拟装入点创建文件路径列表,用于读取文件中的数据。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Create a file dataset from the path on the datastore (this may take a short while)\nfile_data_set = Dataset.File.from_files(path=(default_ds, 'diabetes-data/*.csv'))\n\n# Get the files in the dataset\nfor file_path in file_data_set.to_path():\n print(file_path)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 注册数据集\r\n\r\n创建引用糖尿病数据的数据集后,可以将其注册,确保工作区中运行的所有试验可轻松对其进行访问。\r\n\r\n我们将表格数据集注册为“**糖尿病数据集**”,将文件数据集注册为“**糖尿病文件**”。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Register the tabular dataset\ntry:\n tab_data_set = tab_data_set.register(workspace=ws, \n name='diabetes dataset',\n description='diabetes data',\n tags = {'format':'CSV'},\n create_new_version=True)\nexcept Exception as ex:\n print(ex)\n\n# Register the file dataset\ntry:\n file_data_set = file_data_set.register(workspace=ws,\n name='diabetes file dataset',\n description='diabetes files',\n tags = {'format':'CSV'},\n create_new_version=True)\nexcept Exception as ex:\n print(ex)\n\nprint('Datasets registered')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"你可以在 [Azure 机器学习工作室](https://ml.azure.com)中工作区的“**数据集**”页面上查看和管理数据集。你还可以从工作区对象获取数据集列表:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\"Datasets:\")\nfor dataset_name in list(ws.datasets.keys()):\n dataset = Dataset.get_by_name(ws, dataset_name)\n print(\"\\t\", dataset.name, 'version', dataset.version)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"通过对数据集进行版本控制,可以重新定义数据集,从而无需破坏依赖先前定义的现有试验或管道。默认返回最新版本的已命名数据集,但可以通过指定版本号检索特定版本的数据集,如下所示:\r\n\r\n```python\r\ndataset_v1 = Dataset.get_by_name(ws, 'diabetes dataset', version = 1)\r\n```\r\n\r\n\r\n### 从表格数据集训练模型\r\n\r\n有数据集后,即可开始从中训练模型。可以在运行脚本的估算器中将数据集作为输入传递给脚本。\r\n\r\n运行以下两个代码单元格,创建以下内容:\r\n\r\n1. 名为 **diabetes_training_from_tab_dataset** 的文件夹\r\n2. 通过使用作为参数传递给分类模型的表格数据集来训练分类模型的脚本。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\n\n# Create a folder for the experiment files\nexperiment_folder = 'diabetes_training_from_tab_dataset'\nos.makedirs(experiment_folder, exist_ok=True)\nprint(experiment_folder, 'folder created')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%writefile $experiment_folder/diabetes_training.py\n# Import libraries\nimport os\nimport argparse\nfrom azureml.core import Run, Dataset\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport joblib\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score\nfrom sklearn.metrics import roc_curve\n\n# Get the script arguments (regularization rate and training dataset ID)\nparser = argparse.ArgumentParser()\nparser.add_argument('--regularization', type=float, dest='reg_rate', default=0.01, help='regularization rate')\nparser.add_argument(\"--input-data\", type=str, dest='training_dataset_id', help='training dataset')\nargs = parser.parse_args()\n\n# Set regularization hyperparameter (passed as an argument to the script)\nreg = args.reg_rate\n\n# Get the experiment run context\nrun = Run.get_context()\n\n# Get the training dataset\nprint(\"Loading Data...\")\ndiabetes = run.input_datasets['training_data'].to_pandas_dataframe()\n\n# Separate features and labels\nX, y = diabetes[['Pregnancies','PlasmaGlucose','DiastolicBloodPressure','TricepsThickness','SerumInsulin','BMI','DiabetesPedigree','Age']].values, diabetes['Diabetic'].values\n\n# Split data into training set and test set\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.30, random_state=0)\n\n# Train a logistic regression model\nprint('Training a logistic regression model with regularization rate of', reg)\nrun.log('Regularization Rate', np.float(reg))\nmodel = LogisticRegression(C=1/reg, solver=\"liblinear\").fit(X_train, y_train)\n\n# calculate accuracy\ny_hat = model.predict(X_test)\nacc = np.average(y_hat == y_test)\nprint('Accuracy:', acc)\nrun.log('Accuracy', np.float(acc))\n\n# calculate AUC\ny_scores = model.predict_proba(X_test)\nauc = roc_auc_score(y_test,y_scores[:,1])\nprint('AUC: ' + str(auc))\nrun.log('AUC', np.float(auc))\n\nos.makedirs('outputs', exist_ok=True)\n# note file saved in the outputs folder is automatically uploaded into experiment record\njoblib.dump(value=model, filename='outputs/diabetes_model.pkl')\n\nrun.complete()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"> **备注**:在脚本中,数据集作为形参(或实参)传递。对于表格数据集,此参数将包含已注册数据集的 ID,因此,你可以在脚本中编写代码以从运行上下文中获取试验的工作区,然后使用其 ID 获取数据集,如下所示:\r\n>\r\n> ```\r\n> run = Run.get_context()\r\n> ws = run.experiment.workspace\r\n> dataset = Dataset.get_by_id(ws, id=args.training_dataset_id)\r\n> diabetes = dataset.to_pandas_dataframe()\r\n> ```\r\n>\r\n> 但是,Azure 机器学习运行时会自动识别引用命名数据集的参数并将其添加到运行的 **input_datasets** 集合中,因此你还可以通过指定其“易记名称”来从该集合检索数据集(稍后你将看到,它在试验的脚本运行配置中的参数定义中指定)。这是上面脚本中采用的方法。\r\n\r\n现在,可以试验方式运行脚本,为训练数据集定义一个由脚本读取的参数。\r\n\r\n> **备注**:“数据集”类依赖于 **azureml-dataprep** 包中的一些组件,因此需要将此包包含在将运行训练试验的环境中。**azureml-dataprep** 包包含在 **azure-defaults** 包中。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from azureml.core import Experiment, ScriptRunConfig, Environment\nfrom azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n\n\n# Create a Python environment for the experiment (from a .yml file)\nenv = Environment.from_conda_specification(\"experiment_env\", \"environment.yml\")\n\n# Get the training dataset\ndiabetes_ds = ws.datasets.get(\"diabetes dataset\")\n\n# Create a script config\nscript_config = ScriptRunConfig(source_directory=experiment_folder,\n script='diabetes_training.py',\n arguments = ['--regularization', 0.1, # Regularizaton rate parameter\n '--input-data', diabetes_ds.as_named_input('training_data')], # Reference to dataset\n environment=env) \n\n# submit the experiment\nexperiment_name = 'mslearn-train-diabetes'\nexperiment = Experiment(workspace=ws, name=experiment_name)\nrun = experiment.submit(config=script_config)\nRunDetails(run).show()\nrun.wait_for_completion()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"> **备注**: **--input-data** 参数将数据集作为指定输入传递,其中包括该数据集的易记名称,脚本在试验运行中使用该名称从 **input_datasets** 集合读取它。**--input-data** 参数中的字符串值实际上是已注册数据集的 ID。作为一种替代方法,可以只传递 `diabetes_ds.id`,在这种情况下,脚本可以从脚本参数访问数据集 ID,并使用该 ID 从工作区(而不是从 **input_datasets** 集合)获取数据集。\r\n\r\n首次运行试验时,可能需要一些时间来设置 Python 环境 - 后续运行会更快。\r\n\r\n试验完成后,在小组件中查看 **azureml-logs/70_driver_log.txt** 输出日志和运行所生成的指标。\r\n\r\n### 注册训练后的模型\r\n\r\n与任何训练试验一样,可以检索训练后的模型并在 Azure 机器学习工作区中注册它。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from azureml.core import Model\n\nrun.register_model(model_path='outputs/diabetes_model.pkl', model_name='diabetes_model',\n tags={'Training context':'Tabular dataset'}, properties={'AUC': run.get_metrics()['AUC'], 'Accuracy': run.get_metrics()['Accuracy']})\n\nfor model in Model.list(ws):\n print(model.name, 'version:', model.version)\n for tag_name in model.tags:\n tag = model.tags[tag_name]\n print ('\\t',tag_name, ':', tag)\n for prop_name in model.properties:\n prop = model.properties[prop_name]\n print ('\\t',prop_name, ':', prop)\n print('\\n')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 从文件数据集训练模型\r\n\r\n你已了解了如何使用表格数据集中的训练数据来训练模型。但文件数据集呢?\r\n\r\n使用文件数据集时,传递给脚本的数据集参数表示包含文件路径的装入点。从这些文件中读取数据的方式取决于文件中的数据类型及其预期用途。对于糖尿病 CSV 文件,可以使用 Python **glob** 模块在数据集定义的虚拟装入点中创建文件列表,并将其全部读入可联结为单个数据帧的 Pandas 数据帧中。\r\n\r\n运行以下两个代码单元格,创建以下内容:\r\n\r\n1. 名为 **diabetes_training_from_file_dataset** 的文件夹\r\n2. 使用文件数据集(作为输入传递给脚本)训练分类模型的脚本。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\n\n# Create a folder for the experiment files\nexperiment_folder = 'diabetes_training_from_file_dataset'\nos.makedirs(experiment_folder, exist_ok=True)\nprint(experiment_folder, 'folder created')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%writefile $experiment_folder/diabetes_training.py\n# Import libraries\nimport os\nimport argparse\nfrom azureml.core import Dataset, Run\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport joblib\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score\nfrom sklearn.metrics import roc_curve\nimport glob\n\n# Get script arguments (rgularization rate and file dataset mount point)\nparser = argparse.ArgumentParser()\nparser.add_argument('--regularization', type=float, dest='reg_rate', default=0.01, help='regularization rate')\nparser.add_argument('--input-data', type=str, dest='dataset_folder', help='data mount point')\nargs = parser.parse_args()\n\n# Set regularization hyperparameter (passed as an argument to the script)\nreg = args.reg_rate\n\n# Get the experiment run context\nrun = Run.get_context()\n\n# load the diabetes dataset\nprint(\"Loading Data...\")\ndata_path = run.input_datasets['training_files'] # Get the training data path from the input\n# (You could also just use args.dataset_folder if you don't want to rely on a hard-coded friendly name)\n\n# Read the files\nall_files = glob.glob(data_path + \"/*.csv\")\ndiabetes = pd.concat((pd.read_csv(f) for f in all_files), sort=False)\n\n# Separate features and labels\nX, y = diabetes[['Pregnancies','PlasmaGlucose','DiastolicBloodPressure','TricepsThickness','SerumInsulin','BMI','DiabetesPedigree','Age']].values, diabetes['Diabetic'].values\n\n# Split data into training set and test set\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.30, random_state=0)\n\n# Train a logistic regression model\nprint('Training a logistic regression model with regularization rate of', reg)\nrun.log('Regularization Rate', np.float(reg))\nmodel = LogisticRegression(C=1/reg, solver=\"liblinear\").fit(X_train, y_train)\n\n# calculate accuracy\ny_hat = model.predict(X_test)\nacc = np.average(y_hat == y_test)\nprint('Accuracy:', acc)\nrun.log('Accuracy', np.float(acc))\n\n# calculate AUC\ny_scores = model.predict_proba(X_test)\nauc = roc_auc_score(y_test,y_scores[:,1])\nprint('AUC: ' + str(auc))\nrun.log('AUC', np.float(auc))\n\nos.makedirs('outputs', exist_ok=True)\n# note file saved in the outputs folder is automatically uploaded into experiment record\njoblib.dump(value=model, filename='outputs/diabetes_model.pkl')\n\nrun.complete()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"与表格数据集一样,你可以使用其易记名称从 **input_datasets** 集合中检索文件数据集。还可以从脚本参数检索它,对于文件数据集,脚本参数包含文件的安装路径(而不是传递给表格数据集的数据集 ID)。\r\n\r\n接下来需要更改将数据集传递到脚本的方式 - 这需要定义脚本可以从中读取文件的路径。可以使用 **as_download** 或 **as_mount** 方法来执行此操作。使用 **as_download** 会将文件数据集中的文件下载到计算机上运行脚本的临时位置,而 **as_mount** 会创建一个装入点,可以从该装入点直接从数据集传输文件。\r\n\r\n可以将访问方法与 **as_named_input** 方法结合使用,以在试验运行中将数据集包含在 **input_datasets** 集合中(如果不这样做,例如,通过将参数设置为 `diabetes_ds.as_mount()`,则脚本将能够从脚本参数(而不是从 **input_datasets** 集合)访问数据集装入点)。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from azureml.core import Experiment\nfrom azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n\n\n# Get the training dataset\ndiabetes_ds = ws.datasets.get(\"diabetes file dataset\")\n\n# Create a script config\nscript_config = ScriptRunConfig(source_directory=experiment_folder,\n script='diabetes_training.py',\n arguments = ['--regularization', 0.1, # Regularizaton rate parameter\n '--input-data', diabetes_ds.as_named_input('training_files').as_download()], # Reference to dataset location\n environment=env) # Use the environment created previously\n\n# submit the experiment\nexperiment_name = 'mslearn-train-diabetes'\nexperiment = Experiment(workspace=ws, name=experiment_name)\nrun = experiment.submit(config=script_config)\nRunDetails(run).show()\nrun.wait_for_completion()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"试验完成后,在小组件中查看 **azureml-logs/70_driver_log.txt** 输出日志,以验证文件数据集中的文件已下载到临时文件夹中,从而使脚本能够读取文件。\r\n\r\n### 注册训练后的模型\r\n\r\n同样,可以注册由试验训练的模型。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from azureml.core import Model\n\nrun.register_model(model_path='outputs/diabetes_model.pkl', model_name='diabetes_model',\n tags={'Training context':'File dataset'}, properties={'AUC': run.get_metrics()['AUC'], 'Accuracy': run.get_metrics()['Accuracy']})\n\nfor model in Model.list(ws):\n print(model.name, 'version:', model.version)\n for tag_name in model.tags:\n tag = model.tags[tag_name]\n print ('\\t',tag_name, ':', tag)\n for prop_name in model.properties:\n prop = model.properties[prop_name]\n print ('\\t',prop_name, ':', prop)\n print('\\n')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"> **详细信息**:有关使用数据集进行训练的详细信息,请参阅 Azure ML 文档中的[使用数据集进行训练](https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/machine-learning/how-to-train-with-datasets)。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe98db84cc443e3c0e20ce6553954cbfc107246
| 27,567 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
PY0101EN (IBM Course)/PY0101EN-Tuples.ipynb
|
vhaghani26/Learning-Python
|
b7b2df6558bfd6dc50bc404fc3265d41bb696c3d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
PY0101EN (IBM Course)/PY0101EN-Tuples.ipynb
|
vhaghani26/Learning-Python
|
b7b2df6558bfd6dc50bc404fc3265d41bb696c3d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
PY0101EN (IBM Course)/PY0101EN-Tuples.ipynb
|
vhaghani26/Learning-Python
|
b7b2df6558bfd6dc50bc404fc3265d41bb696c3d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 24.224077 | 716 | 0.523525 |
[
[
[
"<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-info\" style=\"margin-top: 20px\">\n <a href=\"https://cocl.us/PY0101EN_edx_add_top\">\n <img src=\"https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/PY0101EN/Ad/TopAd.png\" width=\"750\" align=\"center\">\n </a>\n</div>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a href=\"https://cognitiveclass.ai/\">\n <img src=\"https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/PY0101EN/Ad/CCLog.png\" width=\"200\" align=\"center\">\n</a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h1>Tuples in Python</h1>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<p><strong>Welcome!</strong> This notebook will teach you about the tuples in the Python Programming Language. By the end of this lab, you'll know the basics tuple operations in Python, including indexing, slicing and sorting.</p> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h2>Table of Contents</h2>\n<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-info\" style=\"margin-top: 20px\">\n <ul>\n <li>\n <a href=\"#dataset\">About the Dataset</a>\n </li>\n <li>\n <a href=\"#tuple\">Tuples</a>\n <ul>\n <li><a href=\"index\">Indexing</a></li>\n <li><a href=\"slice\">Slicing</a></li>\n <li><a href=\"sort\">Sorting</a></li>\n </ul>\n </li>\n <li>\n <a href=\"#escape\">Quiz on Tuples</a>\n </li>\n </ul>\n <p>\n Estimated time needed: <strong>15 min</strong>\n </p>\n</div>\n\n<hr>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h2 id=\"dataset\">About the Dataset</h2>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Imagine you received album recommendations from your friends and compiled all of the recommandations into a table, with specific information about each album.\n\nThe table has one row for each movie and several columns:\n\n- **artist** - Name of the artist\n- **album** - Name of the album\n- **released_year** - Year the album was released\n- **length_min_sec** - Length of the album (hours,minutes,seconds)\n- **genre** - Genre of the album\n- **music_recording_sales_millions** - Music recording sales (millions in USD) on [SONG://DATABASE](http://www.song-database.com/)\n- **claimed_sales_millions** - Album's claimed sales (millions in USD) on [SONG://DATABASE](http://www.song-database.com/)\n- **date_released** - Date on which the album was released\n- **soundtrack** - Indicates if the album is the movie soundtrack (Y) or (N)\n- **rating_of_friends** - Indicates the rating from your friends from 1 to 10\n<br>\n<br>\n\nThe dataset can be seen below:\n\n<font size=\"1\">\n<table font-size:xx-small style=\"width:100%\">\n <tr>\n <th>Artist</th>\n <th>Album</th> \n <th>Released</th>\n <th>Length</th>\n <th>Genre</th> \n <th>Music recording sales (millions)</th>\n <th>Claimed sales (millions)</th>\n <th>Released</th>\n <th>Soundtrack</th>\n <th>Rating (friends)</th>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>Michael Jackson</td>\n <td>Thriller</td> \n <td>1982</td>\n <td>00:42:19</td>\n <td>Pop, rock, R&B</td>\n <td>46</td>\n <td>65</td>\n <td>30-Nov-82</td>\n <td></td>\n <td>10.0</td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>AC/DC</td>\n <td>Back in Black</td> \n <td>1980</td>\n <td>00:42:11</td>\n <td>Hard rock</td>\n <td>26.1</td>\n <td>50</td>\n <td>25-Jul-80</td>\n <td></td>\n <td>8.5</td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>Pink Floyd</td>\n <td>The Dark Side of the Moon</td> \n <td>1973</td>\n <td>00:42:49</td>\n <td>Progressive rock</td>\n <td>24.2</td>\n <td>45</td>\n <td>01-Mar-73</td>\n <td></td>\n <td>9.5</td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>Whitney Houston</td>\n <td>The Bodyguard</td> \n <td>1992</td>\n <td>00:57:44</td>\n <td>Soundtrack/R&B, soul, pop</td>\n <td>26.1</td>\n <td>50</td>\n <td>25-Jul-80</td>\n <td>Y</td>\n <td>7.0</td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>Meat Loaf</td>\n <td>Bat Out of Hell</td> \n <td>1977</td>\n <td>00:46:33</td>\n <td>Hard rock, progressive rock</td>\n <td>20.6</td>\n <td>43</td>\n <td>21-Oct-77</td>\n <td></td>\n <td>7.0</td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>Eagles</td>\n <td>Their Greatest Hits (1971-1975)</td> \n <td>1976</td>\n <td>00:43:08</td>\n <td>Rock, soft rock, folk rock</td>\n <td>32.2</td>\n <td>42</td>\n <td>17-Feb-76</td>\n <td></td>\n <td>9.5</td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>Bee Gees</td>\n <td>Saturday Night Fever</td> \n <td>1977</td>\n <td>1:15:54</td>\n <td>Disco</td>\n <td>20.6</td>\n <td>40</td>\n <td>15-Nov-77</td>\n <td>Y</td>\n <td>9.0</td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>Fleetwood Mac</td>\n <td>Rumours</td> \n <td>1977</td>\n <td>00:40:01</td>\n <td>Soft rock</td>\n <td>27.9</td>\n <td>40</td>\n <td>04-Feb-77</td>\n <td></td>\n <td>9.5</td>\n </tr>\n</table></font>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<hr>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h2 id=\"tuple\">Tuples</h2>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In Python, there are different data types: string, integer and float. These data types can all be contained in a tuple as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<img src=\"https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/PY0101EN/Chapter%202/Images/TuplesType.png\" width=\"750\" align=\"center\" />",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now, let us create your first tuple with string, integer and float.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create your first tuple\n\ntuple1 = (\"disco\",10,1.2 )\ntuple1",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The type of variable is a **tuple**. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Print the type of the tuple you created\n\ntype(tuple1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<h3 id=\"index\">Indexing</h3>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
" Each element of a tuple can be accessed via an index. The following table represents the relationship between the index and the items in the tuple. Each element can be obtained by the name of the tuple followed by a square bracket with the index number:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<img src=\"https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/PY0101EN/Chapter%202/Images/TuplesIndex.gif\" width=\"750\" align=\"center\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We can print out each value in the tuple:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Print the variable on each index\n\nprint(tuple1[0])\nprint(tuple1[1])\nprint(tuple1[2])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can print out the **type** of each value in the tuple:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Print the type of value on each index\n\nprint(type(tuple1[0]))\nprint(type(tuple1[1]))\nprint(type(tuple1[2]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can also use negative indexing. We use the same table above with corresponding negative values:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<img src=\"https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/PY0101EN/Chapter%202/Images/TuplesNeg.png\" width=\"750\" align=\"center\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We can obtain the last element as follows (this time we will not use the print statement to display the values):",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Use negative index to get the value of the last element\n\ntuple1[-1]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can display the next two elements as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Use negative index to get the value of the second last element\n\ntuple1[-2]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Use negative index to get the value of the third last element\n\ntuple1[-3]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<h3 id=\"concate\">Concatenate Tuples</h3>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We can concatenate or combine tuples by using the **+** sign:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Concatenate two tuples\n\ntuple2 = tuple1 + (\"hard rock\", 10)\ntuple2",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can slice tuples obtaining multiple values as demonstrated by the figure below:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<img src=\"https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/PY0101EN/Chapter%202/Images/TuplesSlice.gif\" width=\"750\" align=\"center\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h3 id=\"slice\">Slicing</h3>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We can slice tuples, obtaining new tuples with the corresponding elements: ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Slice from index 0 to index 2\n\ntuple2[0:3]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can obtain the last two elements of the tuple:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Slice from index 3 to index 4\n\ntuple2[3:5]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can obtain the length of a tuple using the length command: ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get the length of tuple\n\nlen(tuple2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This figure shows the number of elements:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<img src=\"https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/PY0101EN/Chapter%202/Images/TuplesElement.png\" width=\"750\" align=\"center\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h3 id=\"sort\">Sorting</h3>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
" Consider the following tuple:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# A sample tuple\n\nRatings = (0, 9, 6, 5, 10, 8, 9, 6, 2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can sort the values in a tuple and save it to a new tuple: ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Sort the tuple\n\nRatingsSorted = sorted(Ratings)\nRatingsSorted",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<h3 id=\"nest\">Nested Tuple</h3>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"A tuple can contain another tuple as well as other more complex data types. This process is called 'nesting'. Consider the following tuple with several elements: ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a nest tuple\n\nNestedT =(1, 2, (\"pop\", \"rock\") ,(3,4),(\"disco\",(1,2)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Each element in the tuple including other tuples can be obtained via an index as shown in the figure:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<img src=\"https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/PY0101EN/Chapter%202/Images/TuplesNestOne.png\" width=\"750\" align=\"center\">",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Print element on each index\n\nprint(\"Element 0 of Tuple: \", NestedT[0])\nprint(\"Element 1 of Tuple: \", NestedT[1])\nprint(\"Element 2 of Tuple: \", NestedT[2])\nprint(\"Element 3 of Tuple: \", NestedT[3])\nprint(\"Element 4 of Tuple: \", NestedT[4])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can use the second index to access other tuples as demonstrated in the figure:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<img src=\"https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/PY0101EN/Chapter%202/Images/TuplesNestTwo.png\" width=\"750\" align=\"center\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
" We can access the nested tuples :",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Print element on each index, including nest indexes\n\nprint(\"Element 2, 0 of Tuple: \", NestedT[2][0])\nprint(\"Element 2, 1 of Tuple: \", NestedT[2][1])\nprint(\"Element 3, 0 of Tuple: \", NestedT[3][0])\nprint(\"Element 3, 1 of Tuple: \", NestedT[3][1])\nprint(\"Element 4, 0 of Tuple: \", NestedT[4][0])\nprint(\"Element 4, 1 of Tuple: \", NestedT[4][1])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can access strings in the second nested tuples using a third index:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Print the first element in the second nested tuples\n\nNestedT[2][1][0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Print the second element in the second nested tuples\n\nNestedT[2][1][1]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
" We can use a tree to visualise the process. Each new index corresponds to a deeper level in the tree:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<img src=\"https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/PY0101EN/Chapter%202/Images/TuplesNestThree.gif\" width=\"750\" align=\"center\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Similarly, we can access elements nested deeper in the tree with a fourth index:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Print the first element in the second nested tuples\n\nNestedT[4][1][0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Print the second element in the second nested tuples\n\nNestedT[4][1][1]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The following figure shows the relationship of the tree and the element <code>NestedT[4][1][1]</code>:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<img src=\"https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/PY0101EN/Chapter%202/Images/TuplesNestFour.gif\" width=\"750\" align=\"center\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h2 id=\"quiz\">Quiz on Tuples</h2>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Consider the following tuple:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# sample tuple\n\ngenres_tuple = (\"pop\", \"rock\", \"soul\", \"hard rock\", \"soft rock\", \\\n \"R&B\", \"progressive rock\", \"disco\") \ngenres_tuple",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Find the length of the tuple, <code>genres_tuple</code>:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Write your code below and press Shift+Enter to execute",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<img src=\"https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/PY0101EN/Chapter%202/Images/TuplesQuiz.png\" width=\"1100\" align=\"center\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Double-click __here__ for the solution.\n\n<!-- Your answer is below:\nlen(genres_tuple)\n-->",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Access the element, with respect to index 3: ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Write your code below and press Shift+Enter to execute",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Double-click __here__ for the solution.\n\n<!-- Your answer is below:\ngenres_tuple[3]\n-->",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Use slicing to obtain indexes 3, 4 and 5:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Write your code below and press Shift+Enter to execute",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Double-click __here__ for the solution.\n\n<!-- Your answer is below:\ngenres_tuple[3:6]\n-->",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Find the first two elements of the tuple <code>genres_tuple</code>:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Write your code below and press Shift+Enter to execute",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Double-click __here__ for the solution.\n\n<!-- Your answer is below:\ngenres_tuple[0:2]\n-->",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Find the first index of <code>\"disco\"</code>:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Write your code below and press Shift+Enter to execute",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Double-click __here__ for the solution.\n\n<!-- Your answer is below:\ngenres_tuple.index(\"disco\")\n-->",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Generate a sorted List from the Tuple <code>C_tuple=(-5, 1, -3)</code>:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Write your code below and press Shift+Enter to execute",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Double-click __here__ for the solution.\n\n<!-- Your answer is below:\nC_tuple = (-5, 1, -3)\nC_list = sorted(C_tuple)\nC_list\n-->",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<hr>\n<h2>The last exercise!</h2>\n<p>Congratulations, you have completed your first lesson and hands-on lab in Python. However, there is one more thing you need to do. The Data Science community encourages sharing work. The best way to share and showcase your work is to share it on GitHub. By sharing your notebook on GitHub you are not only building your reputation with fellow data scientists, but you can also show it off when applying for a job. Even though this was your first piece of work, it is never too early to start building good habits. So, please read and follow <a href=\"https://cognitiveclass.ai/blog/data-scientists-stand-out-by-sharing-your-notebooks/\" target=\"_blank\">this article</a> to learn how to share your work.\n<hr>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-info\" style=\"margin-top: 20px\">\n<h2>Get IBM Watson Studio free of charge!</h2>\n <p><a href=\"https://cocl.us/PY0101EN_edx_add_bbottom\"><img src=\"https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/PY0101EN/Ad/BottomAd.png\" width=\"750\" align=\"center\"></a></p>\n</div>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h3>About the Authors:</h3> \n<p><a href=\"https://www.linkedin.com/in/joseph-s-50398b136/\" target=\"_blank\">Joseph Santarcangelo</a> is a Data Scientist at IBM, and holds a PhD in Electrical Engineering. His research focused on using Machine Learning, Signal Processing, and Computer Vision to determine how videos impact human cognition. Joseph has been working for IBM since he completed his PhD.</p>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Other contributors: <a href=\"www.linkedin.com/in/jiahui-mavis-zhou-a4537814a\">Mavis Zhou</a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<hr>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<p>Copyright © 2018 IBM Developer Skills Network. This notebook and its source code are released under the terms of the <a href=\"https://cognitiveclass.ai/mit-license/\">MIT License</a>.</p>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe9a226c828148d35b55447ed0f1e8ed36df078
| 12,581 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
WebVisualizations/Data.ipynb
|
LeslySok/Web-Design-Challenge
|
b2934c94bf9c4b3cd8dceabcb545e383e39eb82b
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
WebVisualizations/Data.ipynb
|
LeslySok/Web-Design-Challenge
|
b2934c94bf9c4b3cd8dceabcb545e383e39eb82b
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
WebVisualizations/Data.ipynb
|
LeslySok/Web-Design-Challenge
|
b2934c94bf9c4b3cd8dceabcb545e383e39eb82b
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null | 30.987685 | 89 | 0.306812 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cities_df = pd.read_csv(\"Resources/cities.csv\")\ncities_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cities_df.set_index('City_ID')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cities_df.to_html(\"Resources/cities_html.html\", index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe9aee6927b57f2dcbb0c99ecdf19b8a51be6a2
| 3,217 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
17 Generic Trees/17.09 Print Levelwise.ipynb
|
suhassuhas/Coding-Ninjas---Data-Structures-and-Algorithms-in-Python
|
e660d5a83b80df9cb67b2d06f2b5ba182586f3da
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | 4 |
2021-09-09T06:52:31.000Z
|
2022-01-09T00:05:11.000Z
|
17 Generic Trees/17.09 Print Levelwise.ipynb
|
rishitbhojak/Coding-Ninjas---Data-Structures-and-Algorithms-in-Python
|
3b5625df60f7ac554fae58dc8ea9fd42012cbfae
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null |
17 Generic Trees/17.09 Print Levelwise.ipynb
|
rishitbhojak/Coding-Ninjas---Data-Structures-and-Algorithms-in-Python
|
3b5625df60f7ac554fae58dc8ea9fd42012cbfae
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | 5 |
2021-09-15T13:49:32.000Z
|
2022-01-20T20:37:46.000Z
| 26.154472 | 77 | 0.434877 |
[
[
[
"class treeNode:\n def __init__(self, data):\n self.data = data\n self.children = []\n def __str__(self):\n return str(self.data)\n\nimport queue \ndef printLevelWiseTree(tree):\n q = queue.Queue()\n if tree == None:\n return\n q.put(tree)\n \n while (not(q.empty())):\n current_node = q.get()\n print(current_node, \":\", end = \"\")\n for child in current_node.children:\n q.put(child)\n print(child.data, end = \",\")\n print()\n \n \n \ndef takeTreeInputLevelWise():\n q = queue.Queue()\n print(\"Enter root\")\n rootData = int(input())\n if rootData == -1:\n return None\n \n root = TreeNode(rootData)\n q.put(root)\n \n while (not(q.empty())):\n current_node = q.get()\n print(\"Enter number of childrens for \", current_node.data)\n numChildren = int(input())\n for i in range(numChildren):\n print(\"Enter next child for \", current_node.data)\n childData = int(input())\n child = TreeNode(childData)\n current_node.children.append(child)\n q.put(child)\n \n return root\n \n \ndef createLevelWiseTree(arr):\n root = treeNode(int(arr[0]))\n q = [root]\n size = len(arr)\n i = 1\n while i<size:\n parent = q.pop(0)\n childCount = int(arr[i])\n i += 1\n for j in range(0,childCount):\n temp = treeNode(int(arr[i+j]))\n parent.children.append(temp)\n q.append(temp)\n i += childCount\n return root\n\n# Main\narr = list(int(x) for x in input().strip().split(' '))\ntree = createLevelWiseTree(arr)\nprintLevelWiseTree(tree)\n",
"10 3 20 30 40 2 40 50 0 0 0 0 \n10 :20,30,40,\n20 :40,50,\n30 :\n40 :\n40 :\n50 :\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
]
] |
cbe9b354f6c775a5c3a21d6032f4c5e4baf1b5f6
| 2,046 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Notebook.ipynb
|
eo1989/VectorBTanalysis
|
bea3deaf2ee3fc114b308146f2af3e4f35f70197
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Notebook.ipynb
|
eo1989/VectorBTanalysis
|
bea3deaf2ee3fc114b308146f2af3e4f35f70197
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Notebook.ipynb
|
eo1989/VectorBTanalysis
|
bea3deaf2ee3fc114b308146f2af3e4f35f70197
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 21.092784 | 381 | 0.512219 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\n\ndata = pd.read_excel(\"./NASDAQ-100-Stock-Tickers-List.xlsx\", usecols=)\ndata",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.sheet_names",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = data.parse().head(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cols1 = list(df)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.dropna(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe9b78c58044ccea9c1063cabcbbce457644d4b
| 147,918 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Analyses/Jointure des tables/construction_emploi_pop.ipynb
|
verycourt/Elections
|
b954c2bb23422e85d10074d41f7d2adc537a1766
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Analyses/Jointure des tables/construction_emploi_pop.ipynb
|
verycourt/Elections
|
b954c2bb23422e85d10074d41f7d2adc537a1766
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Analyses/Jointure des tables/construction_emploi_pop.ipynb
|
verycourt/Elections
|
b954c2bb23422e85d10074d41f7d2adc537a1766
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 36.042398 | 190 | 0.434342 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\nfrom xml.etree import cElementTree as ET\nfrom dbfread import DBF\nimport time\nimport sqlite3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"os.getcwd()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"os.chdir(\"/Users/ninarethaller/Downloads/\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Les année d'élection :\n1965\t1969\t1974\t1981\t1988\t1995\t2002\t2007\t2012\t2017\n\nPour 2017, on utilise la date la plus proche",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Creation de la table de taux de chomage",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"file = \"TXCHO-DEP.xml\"\ntree_emploi = ET.parse(file)\nroot_emploi = tree_emploi.getroot()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"columns_name = ['time_period', 'dept_lib','dept_nb', 'rate']\ndata_emploi = pd.DataFrame(columns=columns_name)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for dept in root_emploi:\n\n dept_lib = dept.attrib[\"TITLE\"].split(\" - \")[1].replace(\" \",\"\")\n dept_nb = dept.attrib[\"DEPARTEMENT\"]\n \n for serie in dept:\n value = serie.attrib[\"OBS_VALUE\"]\n date = serie.attrib[\"TIME_PERIOD\"]\n \n it_dict = {'time_period':date, 'dept_lib':dept_lib, \"dept_nb\":dept_nb, 'rate':value} \n data_emploi = data_emploi.append(it_dict, ignore_index=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.unique(data_emploi[\"dept_nb\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_emploi.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Conserver seulements les années d'élections, et faire un taux de variation ante/post election\npour mesurer l'impact du quinquénat sur l'élection\nOn fait aussi un taux glissant de un an sur le chomage un an avant élection pour mesurer un impact local sur le chomage sur la dernière année",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def retry_quarter(q, value):\n q1 = np.nan\n q2 = np.nan\n q3 = np.nan\n q4 = np.nan\n if q == \"Q1\":\n q1 = float(value)\n elif q == \"Q2\":\n q2 = float(value)\n elif q == \"Q3\":\n q3 = float(value)\n else :\n q4 = float(value)\n return q1, q2, q3, q4",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Reorganisation de la table en ligne par année\ncolumns_name = ['time_period', 'dept_lib','dept_nb', 'Q1_rate','Q2_rate','Q3_rate','Q4_rate']\ndata_emploi_2 = pd.DataFrame(columns=columns_name)\n\nfor i in range(data_emploi.shape[0]):\n\n time_an = data_emploi.iloc[i, 0].split(\"-\")[0]\n time_q = data_emploi.iloc[i, 0].split(\"-\")[1]\n dept_lib = data_emploi.iloc[i, 1]\n dept_nb = data_emploi.iloc[i, 2]\n rate = data_emploi.iloc[i, 3]\n\n list_index = data_emploi_2[(data_emploi_2[\"time_period\"]==time_an) & (data_emploi_2[\"dept_nb\"]==dept_nb)].index\n \n q1, q2, q3, q4 = retry_quarter(time_q, rate) \n if len(list_index) == 0 :\n \n data_emploi_2 = data_emploi_2.append({\"time_period\":time_an,\"dept_lib\":dept_lib,\n \"dept_nb\":dept_nb, \"Q1_rate\":q1, \"Q2_rate\":q2,\n \"Q3_rate\":q3, \"Q4_rate\":q4}, ignore_index=True)\n elif len(list_index) == 1: \n \n if not np.isnan(q1):\n data_emploi_2.iloc[list_index.values, 3] = rate\n if not np.isnan(q2):\n data_emploi_2.iloc[list_index.values, 4] = rate\n if not np.isnan(q3):\n data_emploi_2.iloc[list_index.values, 5] = rate\n if not np.isnan(q4): \n data_emploi_2.iloc[list_index.values, 6] = rate\n \n else :\n print(\"Erreur longueur de liste\")\n print(\"Longueur de la liste %s\" % len(list_index))\n print(\"Index du dataframe %s\" %i)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_emploi_2.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(np.unique(data_emploi_2[\"dept_lib\"]))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(np.unique(data_emploi_2[\"time_period\"]))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.unique(data_emploi_2[\"time_period\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"96*35",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_emploi_2.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_emploi_2.to_csv(\"data_emploi.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Pour les variations ne devront t-on pas utiliser plutot moyenne annuelle?? \nPb pour les variations on commence en 82, on va encore perdre une année d'historique \nEssayer avec des chiffres national? ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Creation des varitions de taux et conservation des années electorales\n# 1981\t1988\t1995\t2002\t2007\t2012\t2017",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Etat Civil",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"file2 = \"ETAT-CIVIL-DEP.xml\"\ntree_civil = ET.parse(file2)\nroot_civil = tree_civil.getroot()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def each_serie(root, list_serie) :\n \n iteration = 0\n for name_serie in list_serie:\n columns_name = ['time_period', 'dept_lib','dept_nb'] + [name_serie]\n data_serie = pd.DataFrame(columns=columns_name)\n \n for dept in root:\n\n dept_lib = dept.attrib[\"TITLE\"].split(\" - \")[1].strip(\" \")\n dept_nb = dept.attrib[\"DEPARTEMENT\"]\n serie_lib = dept.attrib[\"TITLE\"].split(\" - \")[0].strip(\" \")\n\n if serie_lib == name_serie :\n for serie in dept:\n \n serie_value = serie.attrib[\"OBS_VALUE\"]\n serie_date = serie.attrib[\"TIME_PERIOD\"]\n it_dict = {'time_period': serie_date, 'dept_lib':dept_lib, \"dept_nb\":dept_nb, str(name_serie): serie_value} \n\n data_serie = data_serie.append(it_dict, ignore_index=True)\n \n iteration +=1\n data_serie.sort_values(by=[\"dept_nb\",\"time_period\"])\n \n if iteration==1:\n data = data_serie\n else :\n data = pd.merge(data, data_serie, how='left', \n on=['time_period', 'dept_lib','dept_nb'])\n \n print(data.shape)\n print(data.head())\n \n return data.sort_values(by=[\"dept_nb\",\"time_period\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"serie_a_garder = [\"Naissances domiciliées par département\", \n \"Nombre total de mariages domiciliés\", \"Décès domiciliés par département\"]\n\ndata_etat_civil = each_serie(root_civil, serie_a_garder)",
"(4022, 6)\n time_period dept_lib dept_nb Naissances domiciliées par département \\\n0 2015 Paris 75 28267 \n1 2014 Paris 75 29134 \n2 2013 Paris 75 28945 \n3 2012 Paris 75 29291 \n4 2011 Paris 75 30094 \n\n Nombre total de mariages domiciliés Décès domiciliés par département \n0 NaN 13997 \n1 12201 13487 \n2 11864 13939 \n3 11445 14114 \n4 11183 13771 \n"
],
[
"np.unique(data_etat_civil[\"dept_nb\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(np.unique(data_etat_civil[\"time_period\"]))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"41*101",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_etat_civil.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_etat_civil[data_etat_civil[\"dept_nb\"]==\"971\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_etat_civil.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Population",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def load_pop(start_year, end_year):\n iteration = 0\n for year in range(start_year, end_year, 1):\n \n if year in [2015, 2016, 2014, 1990]:\n data_pop = pd.read_excel(\"estim-pop-dep-sexe-gca-1975-2016.xls\", sheetname=str(year), \n skiprows=4, skip_footer=10, parse_cols=7,\n names=[\"dept_nb\", \"dept_lib\",\"0-19ans\",\"20-39ans\",\"40-59ans\",\n \"60-74ans\",\"75+ans\",\"Total\"])\n \n elif year > 1989 : \n data_pop = pd.read_excel(\"estim-pop-dep-sexe-gca-1975-2016.xls\", sheetname=str(year), \n skiprows=4, skip_footer=9, parse_cols=7,\n names=[\"dept_nb\", \"dept_lib\",\"0-19ans\",\"20-39ans\",\"40-59ans\",\n \"60-74ans\",\"75+ans\",\"Total\"])\n else : \n data_pop = pd.read_excel(\"estim-pop-dep-sexe-gca-1975-2016.xls\", sheetname=str(year), \n skiprows=4, skip_footer=4, parse_cols=7,\n names=[\"dept_nb\", \"dept_lib\",\"0-19ans\",\"20-39ans\",\"40-59ans\",\n \"60-74ans\",\"75+ans\",\"Total\"])\n iteration += 1\n data_pop[\"time_period\"]=str(year)\n print(data_pop.iloc[-1,:])\n \n if iteration == 1:\n data = data_pop\n else :\n data = pd.concat([data, data_pop])\n \n print(data.head())\n print(data.shape)\n \n return data.sort_values(by=[\"dept_nb\",\"time_period\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_pop = load_pop(1975, 2017)",
"dept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 293014\n20-39ans 262872\n40-59ans 181391\n60-74ans 72473\n75+ans 28545\nTotal 838295\ntime_period 1975\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 294883\n20-39ans 267373\n40-59ans 186497\n60-74ans 70684\n75+ans 29597\nTotal 849034\ntime_period 1976\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 296326\n20-39ans 272059\n40-59ans 192269\n60-74ans 68280\n75+ans 30757\nTotal 859691\ntime_period 1977\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 297971\n20-39ans 277552\n40-59ans 197784\n60-74ans 65995\n75+ans 32223\nTotal 871525\ntime_period 1978\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 298925\n20-39ans 283181\n40-59ans 202347\n60-74ans 64682\n75+ans 33230\nTotal 882365\ntime_period 1979\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 299724\n20-39ans 289460\n40-59ans 206447\n60-74ans 63717\n75+ans 34412\nTotal 893760\ntime_period 1980\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 302302\n20-39ans 295852\n40-59ans 207285\n60-74ans 65746\n75+ans 35392\nTotal 906577\ntime_period 1981\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 304335\n20-39ans 303686\n40-59ans 207911\n60-74ans 67477\n75+ans 36195\nTotal 919604\ntime_period 1982\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 306796\n20-39ans 314880\n40-59ans 205174\n60-74ans 69294\n75+ans 35645\nTotal 931789\ntime_period 1983\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 308657\n20-39ans 321067\n40-59ans 207092\n60-74ans 70761\n75+ans 36236\nTotal 943813\ntime_period 1984\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 311429\n20-39ans 327523\n40-59ans 209797\n60-74ans 72272\n75+ans 37009\nTotal 958030\ntime_period 1985\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 315046\n20-39ans 334780\n40-59ans 212876\n60-74ans 74118\n75+ans 37796\nTotal 974616\ntime_period 1986\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 320273\n20-39ans 338152\n40-59ans 220071\n60-74ans 76419\n75+ans 38513\nTotal 993428\ntime_period 1987\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 325514\n20-39ans 340820\n40-59ans 228056\n60-74ans 78574\n75+ans 39679\nTotal 1012643\ntime_period 1988\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 330061\n20-39ans 342520\n40-59ans 235743\n60-74ans 80785\n75+ans 40616\nTotal 1029725\ntime_period 1989\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 334679\n20-39ans 344988\n40-59ans 243448\n60-74ans 82908\n75+ans 41530\nTotal 1047553\ntime_period 1990\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 335561\n20-39ans 343914\n40-59ans 249832\n60-74ans 87014\n75+ans 41029\nTotal 1057350\ntime_period 1991\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 335977\n20-39ans 344710\n40-59ans 255535\n60-74ans 91291\n75+ans 40186\nTotal 1067699\ntime_period 1992\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 335527\n20-39ans 345204\n40-59ans 260856\n60-74ans 95349\n75+ans 39564\nTotal 1076500\ntime_period 1993\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 334581\n20-39ans 344806\n40-59ans 265753\n60-74ans 98428\n75+ans 39280\nTotal 1082848\ntime_period 1994\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 335172\n20-39ans 343377\n40-59ans 271489\n60-74ans 101343\n75+ans 39535\nTotal 1090916\ntime_period 1995\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 336255\n20-39ans 341086\n40-59ans 276898\n60-74ans 102178\n75+ans 41392\nTotal 1097809\ntime_period 1996\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 336031\n20-39ans 337011\n40-59ans 281395\n60-74ans 102666\n75+ans 42947\nTotal 1100050\ntime_period 1997\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 334550\n20-39ans 333218\n40-59ans 285747\n60-74ans 102990\n75+ans 44277\nTotal 1100782\ntime_period 1998\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 334367\n20-39ans 330363\n40-59ans 290677\n60-74ans 103461\n75+ans 45665\nTotal 1104533\ntime_period 1999\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 334840\n20-39ans 328494\n40-59ans 296499\n60-74ans 104032\n75+ans 47207\nTotal 1111072\ntime_period 2000\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 335087\n20-39ans 327873\n40-59ans 302169\n60-74ans 104362\n75+ans 48810\nTotal 1118301\ntime_period 2001\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 335267\n20-39ans 327875\n40-59ans 307772\n60-74ans 104379\n75+ans 50447\nTotal 1125740\ntime_period 2002\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 335448\n20-39ans 327771\n40-59ans 312731\n60-74ans 104858\n75+ans 52206\nTotal 1133014\ntime_period 2003\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 336520\n20-39ans 327161\n40-59ans 317238\n60-74ans 105609\n75+ans 53800\nTotal 1140328\ntime_period 2004\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 337951\n20-39ans 326727\n40-59ans 321227\n60-74ans 107093\n75+ans 55766\nTotal 1148764\ntime_period 2005\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 337810\n20-39ans 328244\n40-59ans 323885\n60-74ans 108429\n75+ans 58684\nTotal 1157052\ntime_period 2006\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 336059\n20-39ans 328308\n40-59ans 323309\n60-74ans 112904\n75+ans 60141\nTotal 1160721\ntime_period 2007\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 336768\n20-39ans 327003\n40-59ans 322559\n60-74ans 117025\n75+ans 62042\nTotal 1165397\ntime_period 2008\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 335383\n20-39ans 327597\n40-59ans 321264\n60-74ans 121064\n75+ans 63584\nTotal 1168892\ntime_period 2009\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 334258\n20-39ans 327414\n40-59ans 319910\n60-74ans 124587\n75+ans 64992\nTotal 1171161\ntime_period 2010\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 337058\n20-39ans 327104\n40-59ans 320176\n60-74ans 129561\n75+ans 66466\nTotal 1180365\ntime_period 2011\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 338164\n20-39ans 328591\n40-59ans 319658\n60-74ans 133024\n75+ans 67644\nTotal 1187081\ntime_period 2012\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 340649\n20-39ans 328403\n40-59ans 319829\n60-74ans 136976\n75+ans 68824\nTotal 1194681\ntime_period 2013\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 343825\n20-39ans 328219\n40-59ans 321898\n60-74ans 141849\n75+ans 69748\nTotal 1205539\ntime_period 2014\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 347010\n20-39ans 328045\n40-59ans 321979\n60-74ans 146326\n75+ans 70765\nTotal 1214125\ntime_period 2015\nName: 95, dtype: object\ndept_nb 95\ndept_lib Val-d'Oise\n0-19ans 349825\n20-39ans 328381\n40-59ans 322013\n60-74ans 150681\n75+ans 71463\nTotal 1222363\ntime_period 2016\nName: 95, dtype: object\n dept_nb dept_lib 0-19ans 20-39ans 40-59ans 60-74ans \\\n0 01 Ain 121326 105393 80174 50440 \n1 02 Aisne 189403 138789 111665 67810 \n2 03 Allier 110715 88944 87630 65152 \n3 04 Alpes-de-Haute-Provence 33382 28024 25479 18096 \n4 05 Hautes-Alpes 29358 25633 22261 14607 \n\n 75+ans Total time_period \n0 18944 376277 1975 \n1 26772 534439 1975 \n2 26731 379172 1975 \n3 7187 112168 1975 \n4 5548 97407 1975 \n(4032, 9)\n"
],
[
"data_pop.iloc[-1,:]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"42*96",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Etat Civil + population",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(data_pop.shape)\nprint(min(data_pop[\"time_period\"]))\nprint(max(data_pop[\"time_period\"]))\nprint(len(np.unique(data_pop[\"dept_nb\"])))\nprint(len(np.unique(data_pop[\"time_period\"])))",
"(4032, 9)\n1975\n2016\n96\n42\n"
],
[
"41*96",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(data_etat_civil.shape)\nprint(min(data_etat_civil[\"time_period\"]))\nprint(max(data_etat_civil[\"time_period\"]))\nprint(len(np.unique(data_etat_civil[\"dept_nb\"])))\nprint(len(np.unique(data_etat_civil[\"time_period\"])))",
"(4022, 6)\n1975\n2015\n101\n41\n"
],
[
"data_civil_pop = pd.merge(data_pop, data_etat_civil, how='left', \n on=['time_period', 'dept_lib','dept_nb'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_civil_pop.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(data_civil_pop.shape[0])\nprint(len(np.unique(data_civil_pop[\"dept_nb\"])))",
"4032\n96\n"
],
[
"print(data_emploi_2.shape[0])\nprint(len(np.unique(data_emploi_2[\"dept_nb\"])))",
"3360\n96\n"
],
[
"data_civil_pop.to_csv(\"data_civil_pop.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Données harmonisée 1968-2013",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"table1 = DBF('rp19682013_individus_dbase/rp19682013.dbf')\ntable2 = DBF('rp19682013_individus_dbase/rp19682013_varlist.dbf',encoding='latin-1')\ntable3 = DBF('rp19682013_individus_dbase/rp19682013_varmod.dbf',encoding='latin-1')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(table)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for re in table2 :\n print(re)\n print(\"\\n\")",
"OrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'AGE_REV'), ('LIBELLE', 'Age r\\x82volu'), ('TYPE', 'Caract\\x8are'), ('LONGUEUR', '3')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'AN_RECENS'), ('LIBELLE', 'Ann\\x82e du recensement de population'), ('TYPE', 'Caract\\x8are'), ('LONGUEUR', '4')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'CSP'), ('LIBELLE', 'Cat\\x82gorie socioprofessionnelle (en 8 postes)'), ('TYPE', 'Caract\\x8are'), ('LONGUEUR', '2')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('LIBELLE', 'D\\x82partement de naissance'), ('TYPE', 'Caract\\x8are'), ('LONGUEUR', '3')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('LIBELLE', 'D\\x82partement de r\\x82sidence ant\\x82rieure (en g\\x82ographie 2015)'), ('TYPE', 'Caract\\x8are'), ('LONGUEUR', '3')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('LIBELLE', 'D\\x82partement de r\\x82sidence (en g\\x82ographie 2015)'), ('TYPE', 'Caract\\x8are'), ('LONGUEUR', '3')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('LIBELLE', 'D\\x82partement de travail (en g\\x82ographie 2015)'), ('TYPE', 'Caract\\x8are'), ('LONGUEUR', '3')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DIPL'), ('LIBELLE', 'Dipl\\x93me regroup\\x82'), ('TYPE', 'Caract\\x8are'), ('LONGUEUR', '1')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NATIO'), ('LIBELLE', 'Nationalit\\x82 regroup\\x82e'), ('TYPE', 'Caract\\x8are'), ('LONGUEUR', '3')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NES4'), ('LIBELLE', \"Secteur d'activit\\x82(en 4 postes)\"), ('TYPE', 'Caract\\x8are'), ('LONGUEUR', '1')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'POND'), ('LIBELLE', 'Pond\\x82ration'), ('TYPE', 'Num\\x82rique'), ('LONGUEUR', '20.14')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('LIBELLE', 'R\\x82gion de naissance'), ('TYPE', 'Caract\\x8are'), ('LONGUEUR', '2')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('LIBELLE', 'R\\x82gion de r\\x82sidence ant\\x82rieure (en g\\x82ographie 2015)'), ('TYPE', 'Caract\\x8are'), ('LONGUEUR', '2')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('LIBELLE', 'R\\x82gion de r\\x82sidence (en g\\x82ographie 2015)'), ('TYPE', 'Caract\\x8are'), ('LONGUEUR', '2')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('LIBELLE', 'R\\x82gion de travail (en g\\x82ographie 2015)'), ('TYPE', 'Caract\\x8are'), ('LONGUEUR', '2')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'SEXE'), ('LIBELLE', 'Sexe'), ('TYPE', 'Caract\\x8are'), ('LONGUEUR', '1')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'STAT_CONJ'), ('LIBELLE', 'Statut conjugal'), ('TYPE', 'Caract\\x8are'), ('LONGUEUR', '1')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'TYP_ACT'), ('LIBELLE', \"Type d'activit\\x82 (en 6 postes)\"), ('TYPE', 'Caract\\x8are'), ('LONGUEUR', '1')])\n\n\n"
],
[
"for re in table3 :\n print(re)\n print(\"\\n\")\n ",
"OrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'AGE_REV'), ('MODALITE', '000 \\x85 120'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'de 0 \\x85 120 ans')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'AN_RECENS'), ('MODALITE', '1968'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Recensement de 1968')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'AN_RECENS'), ('MODALITE', '1975'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Recensement de 1975')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'AN_RECENS'), ('MODALITE', '1982'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Recensement de 1982')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'AN_RECENS'), ('MODALITE', '1990'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Recensement de 1990')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'AN_RECENS'), ('MODALITE', '1999'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Recensement de 1999')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'AN_RECENS'), ('MODALITE', '2008'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Recensement de 2008')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'AN_RECENS'), ('MODALITE', '2013'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Recensement de 2013')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'CSP'), ('MODALITE', '1'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Agriculteurs')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'CSP'), ('MODALITE', '2'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"Artisans-commer\\x87ants-chefs d'entreprises\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'CSP'), ('MODALITE', '3'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Cadres et professions intellectuelles sup\\x82rieures')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'CSP'), ('MODALITE', '4'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Professions interm\\x82diaires')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'CSP'), ('MODALITE', '5'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Employ\\x82s')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'CSP'), ('MODALITE', '6'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ouvriers')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'CSP'), ('MODALITE', '8'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Anciens actifs')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'CSP'), ('MODALITE', '9'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"Inactifs et ch\\x93meurs n'ayant jamais travaill\\x82\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '1'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ain')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '2'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aisne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '3'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Allier')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '4'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Alpes-de-Haute-Provence')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '5'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Hautes-Alpes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '6'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Alpes-Maritimes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '7'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ard\\x8ache')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '8'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ardennes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '9'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ari\\x8age')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '10'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aube')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '11'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aude')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '12'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aveyron')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '13'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Bouches-du-Rh\\x93ne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '14'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Calvados')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '15'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Cantal')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '16'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Charente')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '17'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Charente-Maritime')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '18'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Cher')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '19'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Corr\\x8aze')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '2A'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Corse-du-Sud')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '2B'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Corse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '20'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Corse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '21'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"C\\x93te d'or\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '22'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"C\\x93tes-d'Armor\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '23'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Creuse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '24'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Dordogne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '25'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Doubs')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '26'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Dr\\x93me')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '27'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Eure')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '28'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Eure-et-Loir')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '29'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Finist\\x8are')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '30'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Gard')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '31'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Garonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '32'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Gers')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '33'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Gironde')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '34'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'H\\x82rault')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '35'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ille-et-Vilaine')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '36'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Indre')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '37'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Indre-et-Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '38'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Is\\x8are')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '39'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Jura')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '40'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Landes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '41'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loir-et-Cher')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '42'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '43'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '44'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loire-Atlantique')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '45'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loiret')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '46'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Lot')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '47'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Lot-et-Garonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '48'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loz\\x8are')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '49'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Maine-et-Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '50'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Manche')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '51'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Marne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '52'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Marne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '53'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Mayenne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '54'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Meurthe-et-Moselle')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '55'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Meuse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '56'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Morbihan')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '57'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Moselle')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '58'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ni\\x8avre')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '59'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Nord')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '60'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Oise')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '61'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Orne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '62'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pas-de-Calais')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '63'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Puy-de-D\\x93me')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '64'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pyr\\x82n\\x82es-Atlantiques')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '65'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Hautes-Pyr\\x82n\\x82es')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '66'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pyr\\x82n\\x82es-Orientales')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '67'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Bas-Rhin')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '68'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haut-Rhin')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '69'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Rh\\x93ne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '70'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Sa\\x93ne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '71'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Sa\\x93ne-et-Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '72'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Sarthe')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '73'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Savoie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '74'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Savoie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '75'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Paris')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '76'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Seine-Maritime')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '77'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Seine-et-Marne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '78'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Yvelines')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '79'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Deux-S\\x8avres')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '80'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Somme')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '81'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Tarn')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '82'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Tarn-et-Garonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '83'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Var')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '84'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Vaucluse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '85'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Vend\\x82e')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '86'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Vienne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '87'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Vienne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '88'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Vosges')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '89'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Yonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '90'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Territoire de Belfort')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '91'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Essonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '92'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Hauts-de-Seine')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '93'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Seine-Saint-Denis')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '94'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Val-de-Marne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '95'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"Val-d'Oise\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '971'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Guadeloupe')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '972'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Martinique')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '973'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Guyane')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '974'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'R\\x82union')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '975'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '976'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Mayotte, Comores et Terres australes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '9Y'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pacifique (Polyn\\x82sie Fran\\x87aise, Nouvelle-Cal\\x82donie, Wallis-et-Futuna, Ile de Clipperton)')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '99'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Etranger et autre COM')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '1'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ain')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '2'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aisne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '3'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Allier')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '4'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Alpes-de-Haute-Provence')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '5'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Hautes-Alpes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '6'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Alpes-Maritimes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '7'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ard\\x8ache')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '8'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ardennes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '9'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ari\\x8age')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '10'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aube')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '11'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aude')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '12'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aveyron')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '13'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Bouches-du-Rh\\x93ne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '14'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Calvados')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '15'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Cantal')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '16'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Charente')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '17'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Charente-Maritime')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '18'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Cher')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '19'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Corr\\x8aze')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '2A'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Corse-du-Sud')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '2B'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Corse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '21'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"C\\x93te d'or\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '22'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"C\\x93tes-d'Armor\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '23'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Creuse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '24'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Dordogne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '25'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Doubs')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '26'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Dr\\x93me')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '27'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Eure')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '28'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Eure-et-Loir')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '29'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Finist\\x8are')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '30'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Gard')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '31'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Garonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '32'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Gers')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '33'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Gironde')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '34'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'H\\x82rault')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '35'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ille-et-Vilaine')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '36'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Indre')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '37'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Indre-et-Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '38'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Is\\x8are')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '39'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Jura')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '40'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Landes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '41'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loir-et-Cher')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '42'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '43'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '44'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loire-Atlantique')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '45'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loiret')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '46'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Lot')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '47'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Lot-et-Garonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '48'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loz\\x8are')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '49'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Maine-et-Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '50'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Manche')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '51'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Marne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '52'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Marne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '53'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Mayenne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '54'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Meurthe-et-Moselle')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '55'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Meuse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '56'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Morbihan')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '57'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Moselle')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '58'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ni\\x8avre')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '59'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Nord')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '60'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Oise')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '61'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Orne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '62'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pas-de-Calais')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '63'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Puy-de-D\\x93me')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '64'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pyr\\x82n\\x82es-Atlantiques')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '65'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Hautes-Pyr\\x82n\\x82es')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '66'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pyr\\x82n\\x82es-Orientales')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '67'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Bas-Rhin')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '68'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haut-Rhin')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '69'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Rh\\x93ne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '70'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Sa\\x93ne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '71'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Sa\\x93ne-et-Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '72'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Sarthe')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '73'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Savoie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '74'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Savoie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '75'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Paris')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '76'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Seine-Maritime')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '77'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Seine-et-Marne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '78'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Yvelines')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '79'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Deux-S\\x8avres')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '80'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Somme')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '81'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Tarn')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '82'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Tarn-et-Garonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '83'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Var')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '84'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Vaucluse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '85'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Vend\\x82e')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '86'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Vienne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '87'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Vienne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '88'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Vosges')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '89'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Yonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '90'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Territoire de Belfort')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '91'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Essonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '92'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Hauts-de-Seine')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '93'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Seine-Saint-Denis')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '94'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Val-de-Marne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '95'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"Val-d'Oise\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '971'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Guadeloupe')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '972'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Martinique')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '973'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Guyane')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '974'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'R\\x82union')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '975'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Saint-Pierre et Miquelon-Langlade')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '976'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Mayotte')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '977'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Saint-Barth\\x82lemy')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '978'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Saint-Martin')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '9Y'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pacifique')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '99'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Etranger')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', 'ZZ'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Individu n\\x82 apr\\x8as la p\\x82riode r\\x82f\\x82renc\\x82e')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '1'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ain')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '2'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aisne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '3'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Allier')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '4'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Alpes-de-Haute-Provence')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '5'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Hautes-Alpes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '6'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Alpes-Maritimes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '7'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ard\\x8ache')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '8'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ardennes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '9'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ari\\x8age')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '10'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aube')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '11'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aude')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '12'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aveyron')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '13'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Bouches-du-Rh\\x93ne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '14'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Calvados')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '15'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Cantal')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '16'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Charente')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '17'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Charente-Maritime')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '18'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Cher')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '19'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Corr\\x8aze')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '2A'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Corse-du-Sud')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '2B'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Corse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '21'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"C\\x93te d'or\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '22'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"C\\x93tes-d'Armor\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '23'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Creuse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '24'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Dordogne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '25'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Doubs')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '26'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Dr\\x93me')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '27'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Eure')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '28'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Eure-et-Loir')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '29'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Finist\\x8are')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '30'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Gard')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '31'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Garonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '32'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Gers')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '33'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Gironde')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '34'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'H\\x82rault')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '35'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ille-et-Vilaine')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '36'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Indre')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '37'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Indre-et-Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '38'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Is\\x8are')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '39'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Jura')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '40'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Landes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '41'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loir-et-Cher')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '42'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '43'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '44'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loire-Atlantique')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '45'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loiret')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '46'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Lot')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '47'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Lot-et-Garonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '48'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loz\\x8are')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '49'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Maine-et-Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '50'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Manche')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '51'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Marne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '52'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Marne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '53'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Mayenne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '54'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Meurthe-et-Moselle')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '55'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Meuse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '56'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Morbihan')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '57'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Moselle')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '58'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ni\\x8avre')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '59'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Nord')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '60'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Oise')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '61'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Orne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '62'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pas-de-Calais')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '63'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Puy-de-D\\x93me')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '64'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pyr\\x82n\\x82es-Atlantiques')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '65'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Hautes-Pyr\\x82n\\x82es')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '66'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pyr\\x82n\\x82es-Orientales')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '67'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Bas-Rhin')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '68'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haut-Rhin')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '69'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Rh\\x93ne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '70'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Sa\\x93ne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '71'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Sa\\x93ne-et-Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '72'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Sarthe')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '73'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Savoie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '74'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Savoie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '75'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Paris')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '76'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Seine-Maritime')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '77'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Seine-et-Marne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '78'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Yvelines')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '79'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Deux-S\\x8avres')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '80'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Somme')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '81'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Tarn')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '82'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Tarn-et-Garonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '83'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Var')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '84'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Vaucluse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '85'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Vend\\x82e')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '86'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Vienne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '87'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Vienne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '88'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Vosges')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '89'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Yonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '90'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Territoire de Belfort')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '91'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Essonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '92'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Hauts-de-Seine')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '93'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Seine-Saint-Denis')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '94'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Val-de-Marne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '95'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"Val-d'Oise\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '971'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Guadeloupe')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '972'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Martinique')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '973'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Guyane')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '974'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'R\\x82union')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '1'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ain')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '2'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aisne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '3'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Allier')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '4'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Alpes-de-Haute-Provence')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '5'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Hautes-Alpes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '6'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Alpes-Maritimes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '7'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ard\\x8ache')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '8'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ardennes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '9'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ari\\x8age')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '10'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aube')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '11'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aude')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '12'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aveyron')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '13'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Bouches-du-Rh\\x93ne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '14'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Calvados')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '15'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Cantal')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '16'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Charente')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '17'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Charente-Maritime')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '18'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Cher')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '19'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Corr\\x8aze')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '2A'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Corse-du-Sud')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '2B'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Corse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '21'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"C\\x93te d'or\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '22'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"C\\x93tes-d'Armor\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '23'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Creuse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '24'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Dordogne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '25'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Doubs')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '26'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Dr\\x93me')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '27'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Eure')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '28'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Eure-et-Loir')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '29'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Finist\\x8are')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '30'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Gard')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '31'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Garonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '32'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Gers')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '33'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Gironde')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '34'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'H\\x82rault')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '35'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ille-et-Vilaine')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '36'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Indre')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '37'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Indre-et-Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '38'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Is\\x8are')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '39'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Jura')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '40'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Landes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '41'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loir-et-Cher')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '42'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '43'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '44'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loire-Atlantique')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '45'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loiret')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '46'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Lot')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '47'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Lot-et-Garonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '48'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Loz\\x8are')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '49'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Maine-et-Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '50'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Manche')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '51'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Marne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '52'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Marne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '53'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Mayenne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '54'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Meurthe-et-Moselle')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '55'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Meuse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '56'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Morbihan')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '57'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Moselle')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '58'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ni\\x8avre')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '59'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Nord')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '60'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Oise')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '61'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Orne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '62'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pas-de-Calais')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '63'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Puy-de-D\\x93me')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '64'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pyr\\x82n\\x82es-Atlantiques')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '65'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Hautes-Pyr\\x82n\\x82es')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '66'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pyr\\x82n\\x82es-Orientales')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '67'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Bas-Rhin')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '68'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haut-Rhin')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '69'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Rh\\x93ne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '70'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Sa\\x93ne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '71'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Sa\\x93ne-et-Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '72'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Sarthe')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '73'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Savoie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '74'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Savoie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '75'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Paris')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '76'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Seine-Maritime')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '77'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Seine-et-Marne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '78'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Yvelines')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '79'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Deux-S\\x8avres')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '80'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Somme')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '81'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Tarn')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '82'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Tarn-et-Garonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '83'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Var')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '84'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Vaucluse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '85'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Vend\\x82e')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '86'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Vienne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '87'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Vienne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '88'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Vosges')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '89'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Yonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '90'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Territoire de Belfort')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '91'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Essonne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '92'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Hauts-de-Seine')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '93'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Seine-Saint-Denis')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '94'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Val-de-Marne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '95'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"Val-d'Oise\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '971'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Guadeloupe')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '972'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Martinique')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '973'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Guyane')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '974'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'R\\x82union')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '975'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '977'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Saint-Barth\\x82lemy')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '978'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Saint-Martin')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', 'AL'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Allemagne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', 'BE'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Belgique')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', 'ES'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Espagne et Andorre')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', 'GB'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Royaume Uni')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', 'IT'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Italie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', 'LU'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Luxembourg')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', 'MO'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Monaco')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', 'CH'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Suisse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DEP_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '99'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Autres cas')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DIPL'), ('MODALITE', 'A'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'aucun dipl\\x93me ou au mieux BEPC, brevet des coll\\x8ages, DNB')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DIPL'), ('MODALITE', 'B'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'CAP, BEP')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DIPL'), ('MODALITE', 'C'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Baccalaur\\x82at (g\\x82n\\x82ral, techno, pro)')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DIPL'), ('MODALITE', 'D'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"Dipl\\x93me d'\\x82tudes sup\\x82rieures\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'DIPL'), ('MODALITE', '*'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Personnes de moins de 15 ans (17 ans pour le RP 1975) ou \\x82tudiants, \\x82l\\x8aves')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NATIO'), ('MODALITE', '0'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Fran\\x87ais de naissance')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NATIO'), ('MODALITE', '1'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Fran\\x87ais par acquisition')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NATIO'), ('MODALITE', '1IT'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Italiens')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NATIO'), ('MODALITE', '1ES'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Espagnols')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NATIO'), ('MODALITE', '1PT'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Portugais')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NATIO'), ('MODALITE', '2**'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"Autres nationalit\\x82s d'Europe\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NATIO'), ('MODALITE', '3DZ'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Alg\\x82riens')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NATIO'), ('MODALITE', '3MA'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Marocains')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NATIO'), ('MODALITE', '3TN'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Tunisiens')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NATIO'), ('MODALITE', '3**'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"Autres nationalit\\x82s d'Afrique\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NATIO'), ('MODALITE', '4TR'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Turcs')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NATIO'), ('MODALITE', '***'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Autres nationalit\\x82s')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NES4'), ('MODALITE', '1'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Agriculture')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NES4'), ('MODALITE', '2'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Industrie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NES4'), ('MODALITE', '3'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'BTP')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NES4'), ('MODALITE', '4'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Tertiaire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'NES4'), ('MODALITE', '9'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Inactifs ou ch\\x93meurs')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '1'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Guadeloupe')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '2'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Martinique')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '3'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Guyane')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '4'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'R\\x82union')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '5'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '6'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Mayotte, Comores et Terres australes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '11'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ile-de-France')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '21'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Champagne-Ardenne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '22'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Picardie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '23'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Normandie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '24'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Centre')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '25'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Basse-Normandie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '26'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Bourgogne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '31'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Nord-Pas-de-Calais')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '41'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Lorraine')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '42'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Alsace')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '43'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Franche-Comt\\x82')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '52'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pays de la Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '53'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Bretagne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '54'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Poitou-Charentes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '72'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aquitaine')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '73'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Midi-Pyr\\x82n\\x82es')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '74'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Limousin')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '82'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Rh\\x93ne-Alpes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '83'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Auvergne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '91'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Languedoc-Roussillon')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '93'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"Provence-Alpes-C\\x93te d'Azur\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '94'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Corse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '9Y'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pacifique (Polyn\\x82sie Fran\\x87aise, Nouvelle-Cal\\x82donie, Wallis-et-Futuna, Ile de Clipperton)')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_NAIS'), ('MODALITE', '99'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Etranger et autre COM')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '1'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Guadeloupe')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '2'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Martinique')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '3'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Guyane')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '4'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'R\\x82union')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '5'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '6'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Mayotte')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '1A'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Saint-Barth\\x82lemy')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '1B'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Saint-Martin')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '11'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ile-de-France')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '21'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Champagne-Ardenne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '22'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Picardie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '23'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Normandie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '24'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Centre')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '25'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Basse-Normandie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '26'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Bourgogne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '31'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Nord-Pas-de-Calais')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '41'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Lorraine')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '42'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Alsace')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '43'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Franche-Comt\\x82')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '52'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pays de la Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '53'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Bretagne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '54'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Poitou-Charentes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '72'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aquitaine')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '73'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Midi-Pyr\\x82n\\x82es')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '74'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Limousin')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '82'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Rh\\x93ne-Alpes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '83'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Auvergne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '91'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Languedoc-Roussillon')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '93'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"Provence-Alpes-C\\x93te d'Azur\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '94'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Corse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '99'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Etranger')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', '9Y'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pacifique')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RAN_15'), ('MODALITE', 'ZZ'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Individu n\\x82 apr\\x8as la p\\x82riode r\\x82f\\x82renc\\x82e')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '1'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Guadeloupe')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '2'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Martinique')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '3'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Guyane')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '4'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'R\\x82union')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '11'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ile-de-France')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '21'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Champagne-Ardenne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '22'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Picardie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '23'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Normandie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '24'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Centre')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '25'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Basse-Normandie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '26'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Bourgogne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '31'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Nord-Pas-de-Calais')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '41'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Lorraine')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '42'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Alsace')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '43'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Franche-Comt\\x82')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '52'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pays de la Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '53'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Bretagne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '54'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Poitou-Charentes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '72'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aquitaine')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '73'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Midi-Pyr\\x82n\\x82es')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '74'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Limousin')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '82'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Rh\\x93ne-Alpes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '83'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Auvergne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '91'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Languedoc-Roussillon')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '93'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"Provence-Alpes-C\\x93te d'Azur\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_RES_15'), ('MODALITE', '94'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Corse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '1'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Guadeloupe')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '2'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Martinique')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '3'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Guyane')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '4'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'R\\x82union')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '5'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '1A'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Saint-Barth\\x82lemy')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '1B'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Saint-Martin')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '11'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ile-de-France')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '21'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Champagne-Ardenne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '22'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Picardie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '23'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Haute-Normandie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '24'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Centre')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '25'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Basse-Normandie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '26'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Bourgogne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '31'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Nord-Pas-de-Calais')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '41'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Lorraine')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '42'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Alsace')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '43'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Franche-Comt\\x82')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '52'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Pays de la Loire')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '53'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Bretagne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '54'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Poitou-Charentes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '72'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Aquitaine')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '73'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Midi-Pyr\\x82n\\x82es')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '74'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Limousin')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '82'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Rh\\x93ne-Alpes')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '83'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Auvergne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '91'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Languedoc-Roussillon')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '93'), ('MODLIBELLE', \"Provence-Alpes-C\\x93te d'Azur\")])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '94'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Corse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', 'AL'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Allemagne')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', 'BE'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Belgique')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', 'ES'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Espagne et Andorre')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', 'GB'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Royaume-Uni')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', 'IT'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Italie')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', 'LU'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Luxembourg')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', 'MO'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Monaco')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', 'CH'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Suisse')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'REG_TRA_15'), ('MODALITE', '99'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Autres cas')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'SEXE'), ('MODALITE', '1'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Homme')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'SEXE'), ('MODALITE', '2'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Femme')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'STAT_CONJ'), ('MODALITE', 'A'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Mari\\x82')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'STAT_CONJ'), ('MODALITE', 'B'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Non mari\\x82')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'TYP_ACT'), ('MODALITE', '1'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Actifs ayant un emploi')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'TYP_ACT'), ('MODALITE', '2'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Ch\\x93meurs')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'TYP_ACT'), ('MODALITE', '3'), ('MODLIBELLE', '\\x90tudiants, \\x82l\\x8aves')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'TYP_ACT'), ('MODALITE', '5'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Anciens actifs')])\n\n\nOrderedDict([('VARIABLE', 'TYP_ACT'), ('MODALITE', '6'), ('MODLIBELLE', 'Autres inactifs')])\n\n\n"
],
[
"conn = sqlite3.connect('rp19682013_individus_dbase/example.sqlite')\nc = conn.cursor()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for row in c.execute('SELECT AN_RECENS,COUNT(AN_RECENS) FROM rp19682013 GROUP BY AN_RECENS'):\n print (row)",
"('1968', 3725151)\n('1975', 3660591)\n('1982', 4704215)\n('1990', 5449400)\n('1999', 6660423)\n('2008', 7412933)\n('2013', 7063287)\n"
],
[
"for row in c.execute('SELECT AN_RECENS,NES4,COUNT(NES4) FROM rp19682013 GROUP BY NES4, AN_RECENS'):\n print (row)",
"('1968', '1', 171510)\n('1975', '1', 120761)\n('1982', '1', 128678)\n('1990', '1', 125746)\n('1999', '1', 139231)\n('2008', '1', 124055)\n('2013', '1', 118417)\n('1968', '2', 631622)\n('1975', '2', 599112)\n('1982', '2', 668216)\n('1990', '2', 687533)\n('1999', '2', 677028)\n('2008', '2', 687500)\n('2013', '2', 621147)\n('1968', '3', 247232)\n('1975', '3', 205829)\n('1982', '3', 233376)\n('1990', '3', 246949)\n('1999', '3', 234302)\n('2008', '3', 345660)\n('2013', '3', 344872)\n('1968', '4', 1181577)\n('1975', '4', 1223288)\n('1982', '4', 1650510)\n('1990', '4', 2023168)\n('1999', '4', 2599480)\n('2008', '4', 3263416)\n('2013', '4', 3101949)\n('1968', '9', 1493210)\n('1975', '9', 1511601)\n('1982', '9', 2023435)\n('1990', '9', 2366004)\n('1999', '9', 3010382)\n('2008', '9', 2992302)\n('2013', '9', 2876902)\n"
],
[
"for row in c.execute('SELECT TYP_ACT,SUM(POND) FROM rp19682013 WHERE AN_RECENS=\"2013\" GROUP BY TYP_ACT, AN_RECENS'):\n print (row)",
"('1', 26733241.530168764)\n('2', 4175157.586438414)\n('3', 5062741.779365853)\n('5', 14240929.046412589)\n('6', 15352801.949536229)\n"
],
[
"26733241.530168764+4175157.586438414+14240929.046412589",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"(4175157.586438414/45149328.16301977)*100",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for i in range(dataframe.shape):\n \n if data.loc(i,annee)==2016:\n data.loc(i,new_variable) = Nan\n else :\n data.loc(i,new_variable) = data.loc(i,Q4) - data.loc(i-1,Q4)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe9ca7a1f1801e7ab0cfae2ca33eef3755e5c35
| 224,094 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
code/report-specific/multi_agent_grouped_sellers/multiagent_grouped_sellers.ipynb
|
ekarais/RLFM
|
479679e39b4fdd230b5a67c2005dd2fb001e7169
|
[
"MIT"
] | 7 |
2020-06-17T14:09:57.000Z
|
2022-03-15T05:20:42.000Z
|
code/report-specific/multi_agent_grouped_sellers/multiagent_grouped_sellers.ipynb
|
ekarais/RLFM
|
479679e39b4fdd230b5a67c2005dd2fb001e7169
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
code/report-specific/multi_agent_grouped_sellers/multiagent_grouped_sellers.ipynb
|
ekarais/RLFM
|
479679e39b4fdd230b5a67c2005dd2fb001e7169
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-06-17T14:09:58.000Z
|
2020-06-17T14:09:58.000Z
| 583.578125 | 45,916 | 0.93882 |
[
[
[
"!pip install git+https://github.com/zhy0/dmarket_rl\n!pip install ray[rllib]",
"Collecting git+https://github.com/zhy0/dmarket_rl\r\n Cloning https://github.com/zhy0/dmarket_rl to /tmp/pip-req-build-p5b09xbr\r\n Running command git clone -q https://github.com/zhy0/dmarket_rl /tmp/pip-req-build-p5b09xbr\r\nRequirement already satisfied: gym in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from dmarket==0+untagged.29.g8fdcb89) (0.15.3)\r\nCollecting numpy>=1.17\r\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/d2/ab/43e678759326f728de861edbef34b8e2ad1b1490505f20e0d1f0716c3bf4/numpy-1.17.4-cp36-cp36m-manylinux1_x86_64.whl (20.0MB)\r\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 20.0MB 2.8MB/s \r\n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: scipy in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from gym->dmarket==0+untagged.29.g8fdcb89) (1.2.1)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: pyglet<=1.3.2,>=1.2.0 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from gym->dmarket==0+untagged.29.g8fdcb89) (1.3.2)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: six in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from gym->dmarket==0+untagged.29.g8fdcb89) (1.12.0)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: cloudpickle~=1.2.0 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from gym->dmarket==0+untagged.29.g8fdcb89) (1.2.2)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: future in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from pyglet<=1.3.2,>=1.2.0->gym->dmarket==0+untagged.29.g8fdcb89) (0.17.1)\r\nBuilding wheels for collected packages: dmarket\r\n Building wheel for dmarket (setup.py) ... \u001b[?25l-\b \b\\\b \bdone\r\n\u001b[?25h Created wheel for dmarket: filename=dmarket-0+untagged.29.g8fdcb89-cp36-none-any.whl size=11625 sha256=cfa21ad31b50663a9e32a7e6a8a6d94470f8cd80860f815b71620d855fbbd9a7\r\n Stored in directory: /tmp/pip-ephem-wheel-cache-golu0zda/wheels/10/ff/93/9ad42a43b72f3601e0af83027a619401a29561fe0423318dd2\r\nSuccessfully built dmarket\r\n\u001b[31mERROR: allennlp 0.9.0 requires flaky, which is not installed.\u001b[0m\r\n\u001b[31mERROR: allennlp 0.9.0 requires responses>=0.7, which is not installed.\u001b[0m\r\n\u001b[31mERROR: tsfresh 0.12.0 has requirement pandas<=0.23.4,>=0.20.3, but you'll have pandas 0.25.2 which is incompatible.\u001b[0m\r\n\u001b[31mERROR: tensorflow-probability 0.8.0 has requirement cloudpickle==1.1.1, but you'll have cloudpickle 1.2.2 which is incompatible.\u001b[0m\r\n\u001b[31mERROR: mizani 0.6.0 has requirement matplotlib>=3.1.1, but you'll have matplotlib 3.0.3 which is incompatible.\u001b[0m\r\n\u001b[31mERROR: kmeans-smote 0.1.2 has requirement imbalanced-learn<0.5,>=0.4.0, but you'll have imbalanced-learn 0.5.0 which is incompatible.\u001b[0m\r\n\u001b[31mERROR: kmeans-smote 0.1.2 has requirement numpy<1.16,>=1.13, but you'll have numpy 1.17.4 which is incompatible.\u001b[0m\r\n\u001b[31mERROR: kmeans-smote 0.1.2 has requirement scikit-learn<0.21,>=0.19.0, but you'll have scikit-learn 0.21.3 which is incompatible.\u001b[0m\r\n\u001b[31mERROR: hyperopt 0.2.1 has requirement networkx==2.2, but you'll have networkx 2.4 which is incompatible.\u001b[0m\r\n\u001b[31mERROR: allennlp 0.9.0 has requirement spacy<2.2,>=2.1.0, but you'll have spacy 2.2.1 which is incompatible.\u001b[0m\r\n\u001b[31mERROR: allennlp 0.9.0 has requirement torch>=1.2.0, but you'll have torch 1.1.0 which is incompatible.\u001b[0m\r\nInstalling collected packages: numpy, dmarket\r\n Found existing installation: numpy 1.16.4\r\n Uninstalling numpy-1.16.4:\r\n Successfully uninstalled numpy-1.16.4\r\nSuccessfully installed dmarket-0+untagged.29.g8fdcb89 numpy-1.17.4\r\nRequirement already satisfied: ray[rllib] in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (0.7.6)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: protobuf>=3.8.0 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from ray[rllib]) (3.10.0)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: jsonschema in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from ray[rllib]) (3.1.1)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: funcsigs in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from ray[rllib]) (1.0.2)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy>=1.14 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from ray[rllib]) (1.17.4)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: six>=1.0.0 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from ray[rllib]) (1.12.0)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: redis>=3.3.2 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from ray[rllib]) (3.3.11)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: pyyaml in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from ray[rllib]) (5.1.2)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: filelock in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from ray[rllib]) (3.0.12)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: click in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from ray[rllib]) (7.0)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: pytest in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from ray[rllib]) (5.0.1)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: colorama in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from ray[rllib]) (0.4.1)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: gym[atari]; extra == \"rllib\" in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from ray[rllib]) (0.15.3)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: opencv-python-headless; extra == \"rllib\" in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from ray[rllib]) (4.1.1.26)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: lz4; extra == \"rllib\" in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from ray[rllib]) (2.1.2)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: scipy; extra == \"rllib\" in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from ray[rllib]) (1.2.1)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: setuptools in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from protobuf>=3.8.0->ray[rllib]) (41.4.0)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: pyrsistent>=0.14.0 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from jsonschema->ray[rllib]) (0.15.4)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: importlib-metadata in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from jsonschema->ray[rllib]) (0.23)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: attrs>=17.4.0 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from jsonschema->ray[rllib]) (19.3.0)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: py>=1.5.0 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from pytest->ray[rllib]) (1.8.0)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: packaging in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from pytest->ray[rllib]) (19.2)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: more-itertools>=4.0.0 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from pytest->ray[rllib]) (7.2.0)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: atomicwrites>=1.0 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from pytest->ray[rllib]) (1.3.0)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: pluggy<1.0,>=0.12 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from pytest->ray[rllib]) (0.13.0)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: wcwidth in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from pytest->ray[rllib]) (0.1.7)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: pyglet<=1.3.2,>=1.2.0 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from gym[atari]; extra == \"rllib\"->ray[rllib]) (1.3.2)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: cloudpickle~=1.2.0 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from gym[atari]; extra == \"rllib\"->ray[rllib]) (1.2.2)\r\nCollecting atari-py~=0.2.0; extra == \"atari\"\r\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/58/45/c2f6523aed89db6672b241fa1aafcfa54126c564be769c1360d298f03852/atari_py-0.2.6-cp36-cp36m-manylinux1_x86_64.whl (2.8MB)\r\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 2.8MB 2.8MB/s \r\n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: opencv-python; extra == \"atari\" in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from gym[atari]; extra == \"rllib\"->ray[rllib]) (4.1.1.26)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: Pillow; extra == \"atari\" in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from gym[atari]; extra == \"rllib\"->ray[rllib]) (5.4.1)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: zipp>=0.5 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from importlib-metadata->jsonschema->ray[rllib]) (0.6.0)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: pyparsing>=2.0.2 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from packaging->pytest->ray[rllib]) (2.4.2)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: future in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from pyglet<=1.3.2,>=1.2.0->gym[atari]; extra == \"rllib\"->ray[rllib]) (0.17.1)\r\nInstalling collected packages: atari-py\r\nSuccessfully installed atari-py-0.2.6\r\n"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from dmarket.environments import MultiAgentTrainingEnv\nfrom dmarket.info_settings import OfferInformationSetting, BlackBoxSetting\nfrom dmarket.agents import GymRLAgent\n\nfrom ray.rllib.env.multi_agent_env import MultiAgentEnv\nfrom ray.rllib.agents import pg\nfrom ray.tune import register_env\n\nfrom gym.spaces import Box, Discrete, Tuple",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class MultiWrapper(MultiAgentTrainingEnv, MultiAgentEnv):\n def __init__(self, env_config):\n super().__init__(**env_config)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"rl_agents = [\n GymRLAgent('seller', 90, 'S1', max_factor=0.25, discretization=20),\n GymRLAgent('seller', 90, 'S2', max_factor=0.25, discretization=20),\n GymRLAgent('seller', 90, 'S3', max_factor=0.25, discretization=20),\n GymRLAgent('buyer', 110, 'B1', max_factor=0.25, discretization=20),\n GymRLAgent('buyer', 110, 'B2', max_factor=0.25, discretization=20),\n GymRLAgent('buyer', 110, 'B3', max_factor=0.25, discretization=20),\n]\n\nfixed_agents = []\nsetting = BlackBoxSetting()\nenv = MultiAgentTrainingEnv(rl_agents, fixed_agents, setting) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_policy = (None, env.observation_space, Discrete(20), {})\nmy_group = (\n None, \n Tuple([env.observation_space for i in range(3)]),\n Tuple([Discrete(20) for i in range(3)]),\n {},\n)\n\ndef select_policy(agent_id):\n \"\"\"This function maps the agent id to the policy id\"\"\"\n return agent_id\n\n# We name our policies the same as our RL agents\npolicies = {\n 'S1': my_policy,\n 'S2': my_policy,\n 'S3': my_policy,\n 'B1': my_policy,\n 'B2': my_policy,\n 'B3': my_policy,\n 'Sellers': my_group\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"EXP_NAME = \"multi_seller_group\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def run_experiment(iterations):\n grouped_sellers = lambda config: MultiWrapper(config).with_agent_groups(groups={\n \"Sellers\": ['S1', 'S2', 'S3']\n })\n register_env(\"grouped_sellers\", grouped_sellers)\n trainer = pg.PGTrainer(env=\"grouped_sellers\", config={\n \"env_config\": {\"rl_agents\": rl_agents, \"fixed_agents\": fixed_agents, \"setting\": setting},\n \"log_level\": \"ERROR\",\n \"timesteps_per_iteration\": 30,\n \"multiagent\": {\n \"policies\": policies,\n \"policy_mapping_fn\": select_policy\n }\n })\n rewards = []\n episodes = []\n episode_len = []\n for i in range(iterations):\n result = trainer.train()\n rewards.append(result['policy_reward_mean'])\n episodes.append(result['episodes_total'])\n episode_len.append(result['episode_len_mean'])\n \n df = pd.DataFrame(rewards, index=episodes)\n df.index.name = 'Episodes'\n df['episode_len'] = episode_len\n return df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%time\nN_iter = 500\nruns = 5\nfor i in range(runs):\n result = run_experiment(N_iter)\n plt.figure()\n result.plot()\n result.to_csv(f'{EXP_NAME}_iter{N_iter}_run{i}.csv')",
"2019-12-05 11:57:38,435\tINFO trainer.py:345 -- Tip: set 'eager': true or the --eager flag to enable TensorFlow eager execution\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe9cd31a7fa365ca4fd4dce5038c90dd14138e6
| 36,925 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
data_ingestion/012_Ingest_text_data_v2.ipynb
|
ZhangHan/amazon-sagemaker-examples
|
e92b8bf109905a1a49ca1f24903c2369e3409c2c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2020-11-03T00:53:17.000Z
|
2020-11-12T07:10:14.000Z
|
data_ingestion/012_Ingest_text_data_v2.ipynb
|
muhyun/amazon-sagemaker-examples
|
b855dab101a87246949888f2f2ae569b5cd1e986
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
data_ingestion/012_Ingest_text_data_v2.ipynb
|
muhyun/amazon-sagemaker-examples
|
b855dab101a87246949888f2f2ae569b5cd1e986
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 35.710832 | 763 | 0.53067 |
[
[
[
"# Ingest Text Data\nLabeled text data can be in a structured data format, such as reviews for sentiment analysis, news headlines for topic modeling, or documents for text classification. In these cases, you may have one column for the label, one column for the text, and sometimes other columns for attributes. You can treat this structured data like tabular data, and ingest it in one of the ways discussed in the previous notebook [011_Ingest_tabular_data.ipynb](011_Ingest_tabular_data_v1.ipynb). Sometimes text data, especially raw text data comes as unstructured data and is often in .json or .txt format, and we will discuss how to ingest these types of data files into a SageMaker Notebook in this section.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Set Up Notebook",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%pip install -qU 'sagemaker>=2.15.0' 's3fs==0.4.2'",
"\u001b[33mWARNING: You are using pip version 20.0.2; however, version 20.2.4 is available.\nYou should consider upgrading via the '/home/ec2-user/anaconda3/envs/python3/bin/python -m pip install --upgrade pip' command.\u001b[0m\nNote: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.\n"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport json\nimport glob\nimport s3fs\nimport sagemaker",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Get SageMaker session & default S3 bucket\nsagemaker_session = sagemaker.Session()\nbucket = sagemaker_session.default_bucket() # replace with your own bucket if you have one \ns3 = sagemaker_session.boto_session.resource('s3')\n\nprefix = 'text_spam/spam'\nprefix_json = 'json_jeo'\nfilename = 'SMSSpamCollection.txt'\nfilename_json = 'JEOPARDY_QUESTIONS1.json'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Downloading data from Online Sources\n\n### Text data (in structured .csv format): Twitter -- sentiment140\n **Sentiment140** This is the sentiment140 dataset. It contains 1.6M tweets extracted using the twitter API. The tweets have been annotated with sentiment (0 = negative, 4 = positive) and topics (hashtags used to retrieve tweets). The dataset contains the following columns:\n* `target`: the polarity of the tweet (0 = negative, 4 = positive)\n* `ids`: The id of the tweet ( 2087)\n* `date`: the date of the tweet (Sat May 16 23:58:44 UTC 2009)\n* `flag`: The query (lyx). If there is no query, then this value is NO_QUERY.\n* `user`: the user that tweeted (robotickilldozr)\n* `text`: the text of the tweet (Lyx is cool\n\n[Second Twitter data](https://github.com/guyz/twitter-sentiment-dataset) is a Twitter data set collected as an extension to Sanders Analytics Twitter sentiment corpus, originally designed for training and testing Twitter sentiment analysis algorithms. We will use this data to showcase how to aggregate two data sets if you want to enhance your current data set by adding more data to it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#helper functions to upload data to s3\ndef write_to_s3(filename, bucket, prefix):\n #put one file in a separate folder. This is helpful if you read and prepare data with Athena\n filename_key = filename.split('.')[0]\n key = \"{}/{}/{}\".format(prefix,filename_key,filename)\n return s3.Bucket(bucket).upload_file(filename,key)\n\ndef upload_to_s3(bucket, prefix, filename):\n url = 's3://{}/{}/{}'.format(bucket, prefix, filename)\n print('Writing to {}'.format(url))\n write_to_s3(filename, bucket, prefix)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#run this cell if you are in SageMaker Studio notebook\n#!apt-get install unzip",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#download first twitter dataset\n!wget http://cs.stanford.edu/people/alecmgo/trainingandtestdata.zip -O sentimen140.zip\n# Uncompressing\n!unzip -o sentimen140.zip -d sentiment140",
"URL transformed to HTTPS due to an HSTS policy\n--2020-11-02 21:16:07-- https://cs.stanford.edu/people/alecmgo/trainingandtestdata.zip\nResolving cs.stanford.edu (cs.stanford.edu)... 171.64.64.64\nConnecting to cs.stanford.edu (cs.stanford.edu)|171.64.64.64|:443... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK\nLength: 81363704 (78M) [application/zip]\nSaving to: ‘sentimen140.zip’\n\nsentimen140.zip 100%[===================>] 77.59M 18.9MB/s in 6.4s \n\n2020-11-02 21:16:14 (12.1 MB/s) - ‘sentimen140.zip’ saved [81363704/81363704]\n\nArchive: sentimen140.zip\n inflating: sentiment140/testdata.manual.2009.06.14.csv \n inflating: sentiment140/training.1600000.processed.noemoticon.csv \n"
],
[
"#upload the files to the S3 bucket\ncsv_files = glob.glob(\"sentiment140/*.csv\")\nfor filename in csv_files:\n upload_to_s3(bucket, 'text_sentiment140', filename)",
"Writing to s3://sagemaker-us-east-2-060356833389/text_sentiment140/sentiment140/training.1600000.processed.noemoticon.csv\nWriting to s3://sagemaker-us-east-2-060356833389/text_sentiment140/sentiment140/testdata.manual.2009.06.14.csv\n"
],
[
"#download second twitter dataset\n!wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zfz/twitter_corpus/master/full-corpus.csv",
"--2020-11-02 21:16:18-- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zfz/twitter_corpus/master/full-corpus.csv\nResolving raw.githubusercontent.com (raw.githubusercontent.com)... 151.101.200.133\nConnecting to raw.githubusercontent.com (raw.githubusercontent.com)|151.101.200.133|:443... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK\nLength: 910195 (889K) [text/plain]\nSaving to: ‘full-corpus.csv.2’\n\nfull-corpus.csv.2 100%[===================>] 888.86K --.-KB/s in 0.08s \n\n2020-11-02 21:16:19 (10.2 MB/s) - ‘full-corpus.csv.2’ saved [910195/910195]\n\n"
],
[
"filename = 'full-corpus.csv'\nupload_to_s3(bucket, 'text_twitter_sentiment_2', filename)",
"Writing to s3://sagemaker-us-east-2-060356833389/text_twitter_sentiment_2/full-corpus.csv\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Text data (in .txt format): SMS Spam data \n[SMS Spam Data](https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/sms+spam+collection) was manually extracted from the Grumbletext Web site. This is a UK forum in which cell phone users make public claims about SMS spam messages, most of them without reporting the very spam message received. Each line in the text file has the correct class followed by the raw message. We will use this data to showcase how to ingest text data in .txt format.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"txt_files = glob.glob(\"spam/*.txt\")\nfor filename in txt_files:\n upload_to_s3(bucket, 'text_spam', filename)",
"Writing to s3://sagemaker-us-east-2-060356833389/text_spam/spam/SMSSpamCollection.txt\n"
],
[
"!wget http://www.dt.fee.unicamp.br/~tiago/smsspamcollection/smsspamcollection.zip -O spam.zip\n!unzip -o spam.zip -d spam",
"--2020-11-02 21:16:19-- http://www.dt.fee.unicamp.br/~tiago/smsspamcollection/smsspamcollection.zip\nResolving www.dt.fee.unicamp.br (www.dt.fee.unicamp.br)... 143.106.12.20\nConnecting to www.dt.fee.unicamp.br (www.dt.fee.unicamp.br)|143.106.12.20|:80... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK\nLength: 210521 (206K) [application/zip]\nSaving to: ‘spam.zip’\n\nspam.zip 100%[===================>] 205.59K 112KB/s in 1.8s \n\n2020-11-02 21:16:21 (112 KB/s) - ‘spam.zip’ saved [210521/210521]\n\nArchive: spam.zip\n inflating: spam/readme \n inflating: spam/SMSSpamCollection.txt \n"
]
],
[
[
"### Text Data (in .json format): Jeopardy Question data\n[Jeopardy Question](https://j-archive.com/) was obtained by crawling the Jeopardy question archive website. It is an unordered list of questions where each question has the following key-value pairs:\n\n* `category` : the question category, e.g. \"HISTORY\"\n* `value`: dollar value of the question as string, e.g. \"\\$200\"\n* `question`: text of question\n* `answer` : text of answer\n* `round`: one of \"Jeopardy!\",\"Double Jeopardy!\",\"Final Jeopardy!\" or \"Tiebreaker\"\n* `show_number` : string of show number, e.g '4680'\n* `air_date` : the show air date in format YYYY-MM-DD",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#json file format\n!wget http://skeeto.s3.amazonaws.com/share/JEOPARDY_QUESTIONS1.json.gz\n# Uncompressing\n!gunzip -f JEOPARDY_QUESTIONS1.json.gz\nfilename = 'JEOPARDY_QUESTIONS1.json'\nupload_to_s3(bucket, 'json_jeo', filename)",
"--2020-11-02 21:16:22-- http://skeeto.s3.amazonaws.com/share/JEOPARDY_QUESTIONS1.json.gz\nResolving skeeto.s3.amazonaws.com (skeeto.s3.amazonaws.com)... 52.216.241.76\nConnecting to skeeto.s3.amazonaws.com (skeeto.s3.amazonaws.com)|52.216.241.76|:80... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK\nLength: 12721082 (12M) [application/json]\nSaving to: ‘JEOPARDY_QUESTIONS1.json.gz’\n\nJEOPARDY_QUESTIONS1 100%[===================>] 12.13M 15.0MB/s in 0.8s \n\n2020-11-02 21:16:23 (15.0 MB/s) - ‘JEOPARDY_QUESTIONS1.json.gz’ saved [12721082/12721082]\n\nWriting to s3://sagemaker-us-east-2-060356833389/json_jeo/JEOPARDY_QUESTIONS1.json\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Ingest Data into Sagemaker Notebook\n## Method 1: Copying data to the Instance\nYou can use the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) to copy your data from s3 to your SageMaker instance. This is a quick and easy approach when you are dealing with medium sized data files, or you are experimenting and doing exploratory analysis. The documentation can be found [here](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/reference/s3/cp.html).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Specify file names\nprefix = 'text_spam/spam'\nprefix_json = 'json_jeo'\nfilename = 'SMSSpamCollection.txt'\nfilename_json = 'JEOPARDY_QUESTIONS1.json'\nprefix_spam_2 = 'text_spam/spam_2'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#copy data to your sagemaker instance using AWS CLI\n!aws s3 cp s3://$bucket/$prefix_json/ text/$prefix_json/ --recursive",
"download failed: s3://sagemaker-us-east-2-060356833389/json_jeo/JEOPARDY_QUESTIONS1.json to text/json_jeo/JEOPARDY_QUESTIONS1.json [Errno 28] No space left on device\ndownload failed: s3://sagemaker-us-east-2-060356833389/json_jeo/JEOPARDY_QUESTIONS1/JEOPARDY_QUESTIONS1.json to text/json_jeo/JEOPARDY_QUESTIONS1/JEOPARDY_QUESTIONS1.json [Errno 28] No space left on device\n"
],
[
"data_location = \"text/{}/{}\".format(prefix_json, filename_json)\nwith open(data_location) as f:\n data = json.load(f)\n print(data[0])",
"{'category': 'HISTORY', 'air_date': '2004-12-31', 'question': \"'For the last 8 years of his life, Galileo was under house arrest for espousing this man's theory'\", 'value': '$200', 'answer': 'Copernicus', 'round': 'Jeopardy!', 'show_number': '4680'}\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Method 2: Use AWS compatible Python Packages\nWhen you are dealing with large data sets, or do not want to lose any data when you delete your Sagemaker Notebook Instance, you can use pre-built packages to access your files in S3 without copying files into your instance. These packages, such as `Pandas`, have implemented options to access data with a specified path string: while you will use `file://` on your local file system, you will use `s3://` instead to access the data through the AWS boto library. For `pandas`, any valid string path is acceptable. The string could be a URL. Valid URL schemes include http, ftp, s3, and file. For file URLs, a host is expected. You can find additional documentation [here](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.read_csv.html). \n\nFor text data, most of the time you can read it as line-by-line files or use Pandas to read it as a DataFrame by specifying a delimiter.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_s3_location = \"s3://{}/{}/{}\".format(bucket, prefix, filename) # S3 URL\ns3_tabular_data = pd.read_csv(data_s3_location, sep=\"\\t\", header=None)\ns3_tabular_data.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For JSON files, depending on the structure, you can also use `Pandas` `read_json` function to read it if it's a flat json file.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_json_location = \"s3://{}/{}/{}\".format(bucket, prefix_json, filename_json)\ns3_tabular_data_json = pd.read_json(data_json_location, orient='records')\ns3_tabular_data_json.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Method 3: Use AWS Native methods\n#### s3fs\n[S3Fs](https://s3fs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) is a Pythonic file interface to S3. It builds on top of botocore. The top-level class S3FileSystem holds connection information and allows typical file-system style operations like cp, mv, ls, du, glob, etc., as well as put/get of local files to/from S3. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fs = s3fs.S3FileSystem()\ndata_s3fs_location = \"s3://{}/{}/\".format(bucket, prefix)\n# To List all files in your accessible bucket\nfs.ls(data_s3fs_location)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# open it directly with s3fs\ndata_s3fs_location = \"s3://{}/{}/{}\".format(bucket, prefix, filename) # S3 URL\nwith fs.open(data_s3fs_location) as f:\n print(pd.read_csv(f, sep = '\\t', nrows = 2))",
" ham \\\n0 ham \n1 spam \n\n Go until jurong point, crazy.. Available only in bugis n great world la e buffet... Cine there got amore wat... \n0 Ok lar... Joking wif u oni... \n1 Free entry in 2 a wkly comp to win FA Cup fina... \n"
]
],
[
[
"# Aggregating Data Set\nIf you would like to enhance your data with more data collected for your use cases, you can always aggregate your newly-collected data with your current data set. We will use the two data set -- Sentiment140 and Sanders Twitter Sentiment to show how to aggregate data together.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prefix_tw1 = 'text_sentiment140/sentiment140'\nfilename_tw1 = 'training.1600000.processed.noemoticon.csv'\nprefix_added = 'text_twitter_sentiment_2'\nfilename_added = 'full-corpus.csv'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's read in our original data and take a look at its format and schema:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_s3_location_base = \"s3://{}/{}/{}\".format(bucket, prefix_tw1, filename_tw1) # S3 URL\n# we will showcase with a smaller subset of data for demonstration purpose\ntext_data = pd.read_csv(data_s3_location_base, header = None,\n encoding = \"ISO-8859-1\", low_memory=False,\n nrows = 10000)\ntext_data.columns = ['target', 'tw_id', 'date', 'flag', 'user', 'text']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We have 6 columns, `date`, `text`, `flag` (which is the topic the twitter was queried), `tw_id` (tweet's id), `user` (user account name), and `target` (0 = neg, 4 = pos).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"text_data.head(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's read in and take a look at the data we want to add to our original data. \n\nWe will start by checking for columns for both data sets. The new data set has 5 columns, `TweetDate` which maps to `date`, `TweetText` which maps to `text`, `Topic` which maps to `flag`, `TweetId` which maps to `tw_id`, and `Sentiment` mapped to `target`. In this new data set, we don't have `user account name` column, so when we aggregate two data sets we can add this column to the data set to be added and fill it with `NULL` values. You can also remove this column from the original data if it does not provide much valuable information based on your use cases. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_s3_location_added = \"s3://{}/{}/{}\".format(bucket, prefix_added, filename_added) # S3 URL\n# we will showcase with a smaller subset of data for demonstration purpose\ntext_data_added = pd.read_csv(data_s3_location_added,\n encoding = \"ISO-8859-1\", low_memory=False,\n nrows = 10000)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"text_data_added.head(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Add the missing column to the new data set and fill it with `NULL`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"text_data_added['user'] = \"\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Renaming the new data set columns to combine two data sets",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"text_data_added.columns = ['flag', 'target', 'tw_id', 'date', 'text', 'user']\ntext_data_added.head(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Change the `target` column to the same format as the `target` in the original data set\nNote that the `target` column in the new data set is marked as \"positive\", \"negative\", \"neutral\", and \"irrelevant\", whereas the `target` in the original data set is marked as \"0\" and \"4\". So let's map \"positive\" to 4, \"neutral\" to 2, and \"negative\" to 0 in our new data set so that they are consistent. For \"irrelevant\", which are either not English or Spam, you can either remove these if it is not valuable for your use case (In our use case of sentiment analysis, we will remove those since these text does not provide any value in terms of predicting sentiment) or map them to -1. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#remove tweets labeled as irelevant\ntext_data_added = text_data_added[text_data_added['target'] != 'irelevant']\n# convert strings to number targets\ntarget_map = {'positive': 4, 'negative': 0, 'neutral': 2}\ntext_data_added['target'] = text_data_added['target'].map(target_map)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Combine the two data sets and save as one new file",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"text_data_new = pd.concat([text_data, text_data_added])\nfilename = 'sentiment_full.csv'\ntext_data_new.to_csv(filename, index = False)\nupload_to_s3(bucket, 'text_twitter_sentiment_full', filename)",
"Writing to s3://sagemaker-us-east-2-060356833389/text_twitter_sentiment_full/sentiment_full.csv\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Citation\nTwitter140 Data, Go, A., Bhayani, R. and Huang, L., 2009. Twitter sentiment classification using distant supervision. CS224N Project Report, Stanford, 1(2009), p.12.\n\nSMS Spaming data, Almeida, T.A., Gómez Hidalgo, J.M., Yamakami, A. Contributions to the Study of SMS Spam Filtering: New Collection and Results. Proceedings of the 2011 ACM Symposium on Document Engineering (DOCENG'11), Mountain View, CA, USA, 2011.\n\nJ! Archive, J! Archive is created by fans, for fans. The Jeopardy! game show and all elements thereof, including but not limited to copyright and trademark thereto, are the property of Jeopardy Productions, Inc. and are protected under law. This website is not affiliated with, sponsored by, or operated by Jeopardy Productions, Inc.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe9cec4fb291c33783dd3a5951a0f567e7191ea
| 31,716 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
working_notebook/.ipynb_checkpoints/VQE_001-checkpoint.ipynb
|
VoicuTomut/Qountry
|
841467eca5704fd24c49000668f739cae8155b59
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
working_notebook/.ipynb_checkpoints/VQE_001-checkpoint.ipynb
|
VoicuTomut/Qountry
|
841467eca5704fd24c49000668f739cae8155b59
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
working_notebook/.ipynb_checkpoints/VQE_001-checkpoint.ipynb
|
VoicuTomut/Qountry
|
841467eca5704fd24c49000668f739cae8155b59
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 43.327869 | 12,997 | 0.499054 |
[
[
[
"## VQE ansatz: 001",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\nimport numpy\n\n\nimport pennylane as qml\nfrom pennylane import numpy as np\nfrom pennylane.optimize import AdamOptimizer, GradientDescentOptimizer\n\n\nimport sys\nsys.path.append(\"..\")\nfrom wordsToNumbers import Corpus\nfrom wordsToNumbers import fibonacci_vocabulary\n\nfrom wordsToQubits import put_word_on_sphere\n\nfrom utils import get_corpus_from_directory, working_window, get_word_from_sphere",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.random.seed(73)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Corpus",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"corpus_path='/Users/voicutu/Desktop/Qountry/CountryMixt'\n\ncorpus_tex = get_corpus_from_directory(corpus_path, limit=1)\n\ncorpus= Corpus(corpus_tex)\nprint(corpus.prop())",
"nr. words:1648 \nnr. distinct words: 499 \nlen.text/len.vocab:3.302605210420842\n"
],
[
"parameterize_vovabulary = fibonacci_vocabulary(corpus.vocabulary)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(\"corpus:\",corpus.split_text)",
"corpus: ['same', 'old', 'dive', 'same', 'old', 'end', 'of', 'the', 'work', 'week', 'drink', 'bartender', 'knows', 'my', 'name', 'but', 'i', 'dont', 'mind', 'she', 'kicks', 'em', 'up', 'strong', 'serves', 'me', 'up', 'right', 'and', 'here', 'i', 'go', 'again', 'im', 'drinkin', 'one', 'im', 'drinkin', 'two', 'i', 'got', 'my', 'heartache', 'medication', 'a', 'strong', 'dedication', 'to', 'gettin', 'over', 'you', 'turnin', 'me', 'loose', 'on', 'that', 'hardwood', 'jukebox', 'lost', 'in', 'neon', 'time', 'my', 'heartache', 'medication', 'well', 'it', 'suits', 'me', 'fine', 'and', 'im', 'drinkin', 'enough', 'to', 'take', 'you', 'off', 'my', 'mind', 'i', 'got', 'my', 'heartache', 'medication', 'well', 'in', 'my', 'time', 'of', 'dying', 'dont', 'want', 'nobody', 'to', 'mourn', 'all', 'i', 'want', 'for', 'you', 'to', 'do', 'is', 'take', 'my', 'body', 'home', 'well', 'well', 'well', 'so', 'i', 'can', 'die', 'easy', 'well', 'well', 'well', 'well', 'well', 'well', 'so', 'i', 'can', 'die', 'easy', 'jesus', 'gonna', 'make', 'up', 'jesus', 'gonna', 'make', 'up', 'jesus', 'gonna', 'make', 'up', 'my', 'dying', 'bed', 'well', 'meet', 'me', 'jesus', 'meet', 'me', 'meet', 'me', 'in', 'the', 'middle', 'of', 'the', 'air', 'if', 'these', 'wings', 'should', 'fail', 'to', 'me', 'lord', 'wont', 'you', 'meet', 'me', 'with', 'another', 'pair', 'well', 'well', 'well', 'so', 'i', 'can', 'die', 'easy', 'well', 'well', 'well', 'well', 'well', 'well', 'so', 'i', 'can', 'die', 'easy', 'jesus', 'gonna', 'make', 'up', 'jesus', 'gonna', 'make', 'up', 'jesus', 'gonna', 'make', 'up', 'my', 'dying', 'bed', 'lord', 'in', 'my', 'time', 'of', 'dying', 'dont', 'want', 'nobody', 'to', 'cry', 'all', 'i', 'want', 'you', 'to', 'do', 'is', 'take', 'me', 'when', 'i', 'die', 'well', 'well', 'well', 'so', 'i', 'can', 'die', 'easy', 'well', 'well', 'well', 'well', 'well', 'well', 'so', 'i', 'can', 'die', 'easy', 'jesus', 'gonna', 'make', 'up', 'jesus', 'gonna', 'make', 'up', 'jesus', 'gonna', 'make', 'up', 'my', 'dying', 'bed', 'put', 'on', 'my', 'jeans', 'my', 'favorite', 'shirt', 'pull', 'up', 'my', 'boots', 'and', 'hit', 'the', 'dirt', 'finally', 'doin', 'somethin', 'ive', 'dreamed', 'of', 'for', 'years', 'dont', 'know', 'quite', 'what', 'to', 'expect', 'a', 'little', 'scared', 'but', 'what', 'the', 'heck', 'my', 'desire', 'is', 'always', 'greater', 'than', 'my', 'fear', 'big', 'dreams', 'and', 'faded', 'jeans', 'fit', 'together', 'like', 'a', 'team', 'always', 'busting', 'at', 'the', 'seams', 'big', 'dreams', 'and', 'faded', 'jeans', 'just', 'my', 'ole', 'guitar', 'and', 'me', 'out', 'to', 'find', 'my', 'destiny', 'nashville', 'is', 'the', 'place', 'to', 'be', 'for', 'big', 'dreams', 'and', 'faded', 'jeans', 'put', 'out', 'my', 'thumb', 'and', 'wish', 'for', 'luck', 'to', 'hitch', 'a', 'car', 'a', 'semitruck', 'sooner', 'or', 'later', 'one', 'will', 'catch', 'me', 'in', 'their', 'beams', 'then', 'ill', 'be', 'on', 'my', 'way', 'at', 'last', 'find', 'a', 'future', 'lose', 'a', 'past', 'waiting', 'silent', 'as', 'the', 'passion', 'in', 'me', 'screams', 'big', 'dreams', 'and', 'faded', 'jeans', 'fit', 'together', 'like', 'a', 'team', 'always', 'busting', 'at', 'the', 'seams', 'big', 'dreams', 'and', 'faded', 'jeans', 'may', 'the', 'stars', 'that', 'fill', 'my', 'eyes', 'guide', 'my', 'path', 'and', 'be', 'my', 'light', 'and', 'may', 'god', 'provide', 'the', 'means', 'to', 'accomplish', 'my', 'big', 'dreams', 'my', 'big', 'dreams', 'big', 'dreams', 'and', 'faded', 'jeans', 'fit', 'together', 'like', 'a', 'team', 'always', 'busting', 'at', 'the', 'seams', 'big', 'dreams', 'and', 'faded', 'jeans', 'like', 'the', 'song', 'bobby', 'mcgee', 'freedoms', 'just', 'another', 'word', 'im', 'just', 'longin', 'to', 'be', 'free', 'to', 'be', 'free', 'take', 'me', 'where', 'i', 'want', 'to', 'be', 'big', 'dreams', 'and', 'faded', 'jeans', 'and', 'there', 'are', 'many', 'just', 'like', 'me', 'with', 'big', 'dreams', 'and', 'faded', 'jeans', 'mmhmmmmmm', 'mmhmmmmmm', 'big', 'dreams', 'big', 'dreams', 'and', 'faded', 'jeans', 'ohohohoh', 'ohohohoh', 'im', 'just', 'longing', 'to', 'be', 'free', 'take', 'me', 'where', 'i', 'want', 'to', 'be', 'big', 'dreams', 'and', 'faded', 'jeans', 'well', 'i', 'dont', 'know', 'why', 'i', 'love', 'you', 'like', 'i', 'do', 'nobody', 'in', 'the', 'world', 'can', 'get', 'along', 'with', 'you', 'you', 'got', 'the', 'ways', 'of', 'a', 'devil', 'sleeping', 'in', 'a', 'lions', 'den', 'i', 'come', 'home', 'last', 'night', 'you', 'wouldnt', 'even', 'let', 'me', 'in', 'well', 'sometimes', 'youre', 'as', 'sweet', 'as', 'anybody', 'want', 'to', 'be', 'when', 'you', 'get', 'a', 'crazy', 'notion', 'of', 'jumpin', 'all', 'over', 'me', 'well', 'you', 'give', 'me', 'the', 'blues', 'i', 'guess', 'youre', 'satisfied', 'an', 'you', 'give', 'me', 'the', 'blues', 'i', 'wanna', 'lay', 'down', 'and', 'die', 'i', 'helped', 'you', 'when', 'you', 'had', 'no', 'shoes', 'on', 'your', 'feet', 'pretty', 'mama', 'i', 'helped', 'you', 'when', 'you', 'had', 'no', 'food', 'to', 'eat', 'youre', 'the', 'kind', 'of', 'woman', 'i', 'just', 'dont', 'understand', 'youre', 'takin', 'all', 'my', 'money', 'and', 'give', 'it', 'to', 'another', 'man', 'well', 'youre', 'the', 'kinda', 'woman', 'makes', 'a', 'man', 'lose', 'his', 'brain', 'youre', 'the', 'kinda', 'woman', 'drives', 'a', 'man', 'insane', 'you', 'give', 'me', 'the', 'blues', 'i', 'guess', 'youre', 'satisfied', 'you', 'give', 'me', 'the', 'blues', 'i', 'wanna', 'lay', 'down', 'and', 'die', 'well', 'you', 'give', 'me', 'the', 'blues', 'i', 'wanna', 'lay', 'down', 'and', 'die', 'i', 'am', 'a', 'man', 'of', 'constant', 'sorrow', 'ive', 'seen', 'trouble', 'all', 'my', 'days', 'ill', 'say', 'goodbye', 'to', 'colorado', 'where', 'i', 'was', 'born', 'and', 'partly', 'raised', 'your', 'mother', 'says', 'that', 'im', 'a', 'stranger', 'a', 'face', 'youll', 'never', 'see', 'no', 'more', 'but', 'heres', 'one', 'promise', 'to', 'ya', 'ill', 'see', 'you', 'on', 'gods', 'golden', 'shore', 'through', 'this', 'open', 'world', 'im', 'abound', 'to', 'ramble', 'through', 'ice', 'and', 'snow', 'sleet', 'and', 'rain', 'im', 'abound', 'to', 'ride', 'that', 'mornin', 'railroad', 'perhaps', 'ill', 'die', 'upon', 'that', 'train', 'im', 'agoin', 'back', 'to', 'colorado', 'the', 'place', 'that', 'ive', 'started', 'from', 'if', 'id', 'knowed', 'how', 'bad', 'youd', 'treat', 'me', 'babe', 'i', 'never', 'would', 'have', 'come', 'ive', 'been', 'around', 'this', 'whole', 'country', 'but', 'i', 'never', 'yet', 'found', 'fenneario', 'well', 'as', 'we', 'marched', 'down', 'as', 'we', 'marched', 'down', 'well', 'as', 'we', 'marched', 'down', 'to', 'fennerio', 'well', 'our', 'captain', 'fell', 'in', 'love', 'with', 'a', 'lady', 'like', 'a', 'dove', 'her', 'name', 'that', 'she', 'had', 'was', 'pretty', 'peggyo', 'well', 'what', 'will', 'your', 'mother', 'say', 'what', 'will', 'your', 'mother', 'say', 'what', 'will', 'your', 'mother', 'say', 'pretty', 'peggyo', 'what', 'will', 'your', 'mother', 'say', 'to', 'know', 'youre', 'going', 'away', 'youre', 'never', 'never', 'never', 'coming', 'backio', 'come', 'arunning', 'down', 'your', 'stairs', 'come', 'arunning', 'down', 'your', 'stairs', 'come', 'arunning', 'down', 'your', 'stairs', 'pretty', 'peggyo', 'come', 'arunning', 'down', 'your', 'stairs', 'combing', 'back', 'your', 'yellow', 'hair', 'youre', 'the', 'prettiest', 'darned', 'girl', 'i', 'ever', 'seenio', 'the', 'lieutenant', 'he', 'has', 'gone', 'the', 'lieutenant', 'he', 'has', 'gone', 'the', 'lieutenant', 'he', 'has', 'gone', 'pretty', 'peggyo', 'the', 'lieutenant', 'he', 'has', 'gone', 'long', 'gone', 'hes', 'ariding', 'down', 'in', 'texas', 'with', 'the', 'rodeo', 'well', 'our', 'captain', 'he', 'is', 'dead', 'our', 'captain', 'he', 'is', 'dead', 'our', 'captain', 'he', 'is', 'dead', 'pretty', 'peggyo', 'well', 'our', 'captain', 'he', 'is', 'dead', 'died', 'for', 'a', 'maid', 'hes', 'buried', 'somewhere', 'in', 'louisianao', 'feeling', 'funny', 'in', 'my', 'mind', 'lord', 'i', 'believe', 'im', 'fixing', 'to', 'die', 'fixing', 'to', 'die', 'feeling', 'funny', 'in', 'my', 'mind', 'lord', 'i', 'believe', 'im', 'fixing', 'to', 'die', 'well', 'i', 'dont', 'mind', 'dying', 'but', 'i', 'hate', 'to', 'leave', 'my', 'children', 'crying', 'well', 'i', 'look', 'over', 'yonder', 'to', 'that', 'burying', 'ground', 'look', 'over', 'yonder', 'to', 'that', 'burying', 'ground', 'sure', 'seems', 'lonesome', 'lord', 'when', 'the', 'sun', 'goes', 'down', 'feeling', 'funny', 'in', 'my', 'eyes', 'lord', 'i', 'believe', 'im', 'fixing', 'to', 'die', 'fixing', 'to', 'die', 'feeling', 'funny', 'in', 'my', 'eyes', 'lord', 'i', 'believe', 'im', 'fixing', 'to', 'die', 'well', 'i', 'dont', 'mind', 'dying', 'but', 'i', 'hate', 'to', 'leave', 'my', 'children', 'crying', 'theres', 'a', 'black', 'smoke', 'rising', 'lord', 'its', 'rising', 'up', 'above', 'my', 'head', 'up', 'above', 'my', 'head', 'its', 'rising', 'up', 'above', 'my', 'head', 'up', 'above', 'my', 'head', 'and', 'tell', 'jesus', 'make', 'up', 'my', 'dying', 'bed', 'im', 'walking', 'kind', 'of', 'funny', 'lord', 'i', 'believe', 'im', 'fixing', 'to', 'die', 'fixing', 'to', 'die', 'yes', 'im', 'walking', 'kind', 'of', 'funny', 'lord', 'i', 'believe', 'im', 'fixing', 'to', 'die', 'fixing', 'to', 'die', 'fixing', 'to', 'die', 'well', 'i', 'dont', 'mind', 'dying', 'but', 'i', 'hate', 'to', 'leave', 'my', 'children', 'crying', 'ramblin', 'outa', 'the', 'wild', 'west', 'leavin', 'the', 'towns', 'i', 'love', 'the', 'best', 'thought', 'id', 'seen', 'some', 'ups', 'and', 'downs', 'til', 'i', 'come', 'into', 'new', 'york', 'town', 'people', 'goin', 'down', 'to', 'the', 'ground', 'buildings', 'goin', 'up', 'to', 'the', 'sky', 'wintertime', 'in', 'new', 'york', 'town', 'the', 'wind', 'blowin', 'snow', 'around', 'walk', 'around', 'with', 'nowhere', 'to', 'go', 'somebody', 'could', 'freeze', 'right', 'to', 'the', 'bone', 'i', 'froze', 'right', 'to', 'the', 'bone', 'new', 'york', 'times', 'said', 'it', 'was', 'the', 'coldest', 'winter', 'in', 'seventeen', 'years', 'i', 'didnt', 'feel', 'so', 'cold', 'then', 'i', 'swung', 'onto', 'my', 'old', 'guitar', 'grabbed', 'hold', 'of', 'a', 'subway', 'car', 'and', 'after', 'a', 'rocking', 'reeling', 'rolling', 'ride', 'i', 'landed', 'up', 'on', 'the', 'downtown', 'side', 'greenwich', 'village', 'i', 'walked', 'down', 'there', 'and', 'ended', 'up', 'in', 'one', 'of', 'them', 'coffeehouses', 'on', 'the', 'block', 'got', 'on', 'the', 'stage', 'to', 'sing', 'and', 'play', 'man', 'there', 'said', 'come', 'back', 'some', 'other', 'day', 'you', 'sound', 'like', 'a', 'hillbilly', 'we', 'want', 'folk', 'singers', 'here', 'well', 'i', 'got', 'a', 'harmonica', 'job', 'begun', 'to', 'play', 'blowin', 'my', 'lungs', 'out', 'for', 'a', 'dollar', 'a', 'day', 'i', 'blowed', 'inside', 'out', 'and', 'upside', 'down', 'the', 'man', 'there', 'said', 'he', 'loved', 'm', 'sound', 'he', 'was', 'ravin', 'about', 'how', 'he', 'loved', 'm', 'sound', 'dollar', 'a', 'days', 'worth', 'and', 'after', 'weeks', 'and', 'weeks', 'of', 'hangin', 'around', 'i', 'finally', 'got', 'a', 'job', 'in', 'new', 'york', 'town', 'in', 'a', 'bigger', 'place', 'bigger', 'money', 'too', 'even', 'joined', 'the', 'union', 'and', 'paid', 'm', 'dues', 'now', 'a', 'very', 'great', 'man', 'once', 'said', 'that', 'some', 'people', 'rob', 'you', 'with', 'a', 'fountain', 'pen', 'it', 'didnt', 'take', 'too', 'long', 'to', 'find', 'out', 'just', 'what', 'he', 'was', 'talkin', 'about', 'a', 'lot', 'of', 'people', 'dont', 'have', 'much', 'food', 'on', 'their', 'table', 'but', 'they', 'got', 'a', 'lot', 'of', 'forks', 'n', 'knives', 'and', 'they', 'gotta', 'cut', 'somethin', 'so', 'one', 'mornin', 'when', 'the', 'sun', 'was', 'warm', 'i', 'rambled', 'out', 'of', 'new', 'york', 'town', 'pulled', 'my', 'cap', 'down', 'over', 'my', 'eyes', 'and', 'headed', 'out', 'for', 'the', 'western', 'skies', 'so', 'long', 'new', 'york', 'howdy', 'east', 'orange', 'i', 'first', 'heard', 'this', 'from', 'ric', 'von', 'schmidt', 'he', 'lives', 'in', 'cambridge', 'ric', 'is', 'a', 'blues', 'guitar', 'player', 'i', 'met', 'him', 'one', 'day', 'on', 'the', 'green', 'pastures', 'of', 'the', 'harvard', 'university', 'baby', 'let', 'me', 'follow', 'you', 'down', 'baby', 'let', 'me', 'follow', 'you', 'down', 'well', 'ill', 'do', 'anything', 'in', 'this', 'god', 'almighty', 'world', 'if', 'you', 'just', 'let', 'me', 'follow', 'you', 'down', 'can', 'i', 'come', 'home', 'with', 'you', 'baby', 'can', 'i', 'come', 'home', 'with', 'you', 'yes', 'ill', 'do', 'anything', 'in', 'this', 'god', 'almighty', 'world', 'if', 'you', 'just', 'let', 'me', 'come', 'home', 'with', 'you', 'baby', 'let', 'me', 'follow', 'you', 'down', 'baby', 'let', 'me', 'follow', 'you', 'down', 'well', 'ill', 'do', 'anything', 'in', 'this', 'god', 'almighty', 'world', 'if', 'you', 'just', 'let', 'me', 'follow', 'you', 'down', 'yes', 'ill', 'do', 'anything', 'in', 'this', 'god', 'almighty', 'world', 'if', 'you', 'just', 'let', 'me', 'follow', 'you', 'down']\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Training set ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"history_lenghth = 3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x,y = working_window(history_lenghth, splited_text=corpus.split_text)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(\"len training set:\", len(x))",
"len training set: 1644\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Circuit",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dev = qml.device(\"default.qubit\", wires=history_lenghth+1)\n\n# circuit initializer\ndef circuit_initializer(words):\n for i in range(len(words)):\n put_word_on_sphere(words[i], qubit=i)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def layer_type1(param, wires=[0,1,2]):\n\n qml.CRZ( param[0], wires=[0,1])\n qml.CRX( param[1], wires=[0,1])\n qml.CRY( param[2], wires=[0,1])\n\n qml.CRZ( param[3], wires=[1,2])\n qml.CRX( param[4], wires=[1,2])\n qml.CRY( param[5], wires=[1,2])\n\n qml.CRZ( param[6], wires=[2,3])\n qml.CRX( param[7], wires=[2,3])\n qml.CRY( param[8], wires=[2,3])\n\n qml.RX( param[9], wires=0)\n qml.RY( param[10], wires=0)\n\n qml.RX( param[11], wires=1)\n qml.RY( param[12], wires=1)\n\n qml.RX( param[13], wires=2)\n qml.RY( param[14], wires=2)\n\n qml.RX( param[15], wires=3)\n qml.RY( param[16], wires=3)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"@qml.qnode(dev)\ndef next_gen(params, x, obs='z'):\n \"\"\"\n obs:'z', 'x' or 'y'\n \"\"\"\n\n # initialize the circuit \n circuit_initializer(x)\n\n # \n for param in params:\n layer_type1(param, wires=[0,1,2])\n #circuit_initializer(x) # just for a test \n\n\n # measure \n if obs=='z':\n return qml.expval(qml.PauliZ(3))\n if obs=='x':\n return qml.expval(qml.PauliX(3))\n if obs=='y':\n return qml.expval(qml.PauliY(3))\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_vec=[ parameterize_vovabulary[w] for w in x[0]]\nprint(\"x:\",x[0])\nprint(\"x_vec:\",x_vec)",
"x: ['same', 'old', 'dive']\nx_vec: [[-0.5174781860030842, -0.6546184738955823, 0.5510816460793957], [-0.19127602086694068, 0.26104417670682734, 0.9461867794726179], [-0.3628495838337743, 0.9317269076305221, 0.015004969474187188]]\n"
],
[
"x_vec=[ parameterize_vovabulary[w] for w in x[0]]\nprint(\"x:\",x[0])\nprint(\"x_vec:\",x_vec)\n\nparams= np.random.uniform(size=(1, 17), requires_grad=True)\n\nprint(\"example tensor:\", x_vec )\nprint(\"\\n\\n\")\nprint(qml.draw(next_gen)(params,x_vec,obs='z'))",
"x: ['same', 'old', 'dive']\nx_vec: [[-0.5174781860030842, -0.6546184738955823, 0.5510816460793957], [-0.19127602086694068, 0.26104417670682734, 0.9461867794726179], [-0.3628495838337743, 0.9317269076305221, 0.015004969474187188]]\nexample tensor: [[-0.5174781860030842, -0.6546184738955823, 0.5510816460793957], [-0.19127602086694068, 0.26104417670682734, 0.9461867794726179], [-0.3628495838337743, 0.9317269076305221, 0.015004969474187188]]\n\n\n\n 0: ──RY(5.3)───RZ(0.902)───╭C──────────╭C──────────╭C───────────RX(0.311)───RY(0.404)────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤ \n 1: ──RY(5.95)──RZ(-0.938)──╰RZ(0.643)──╰RX(0.539)──╰RY(0.512)──╭C──────────╭C──────────╭C───────────RX(0.597)───RY(0.241)────────────────────────────────────┤ \n 2: ──RY(4.73)──RZ(-1.2)────────────────────────────────────────╰RZ(0.61)───╰RX(0.493)──╰RY(0.214)──╭C──────────╭C──────────╭C──────────RX(0.906)──RY(0.159)──┤ \n 3: ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╰RZ(0.244)──╰RX(0.572)──╰RY(0.773)──RX(0.589)──RY(0.262)──┤ ⟨Z⟩ \n\n"
],
[
"pred_vector=[ next_gen(params,x_vec, obs=o) for o in ['x', 'y', 'z']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Learning",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def pred_target_distance(pred_vector, target):\n\n distance= np.linalg.norm(pred_vector-target)\n\n #np.sqrt((pred_vector[0]-target[0])*(pred_vector[0]-target[0])+\n # (pred_vector[1]-target[1])*(pred_vector[1]-target[1])+\n # (pred_vector[2]-target[2])*(pred_vector[2]-target[2]))\n\n return distance",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(\"target word:\",y[0])\nprint(\"target vector:\",parameterize_vovabulary[y[0]] )\nprint(\"prediction:\",pred_vector)\npred_word= get_word_from_sphere(pred_vector, parameterize_vovabulary)\nprint(\"prediction word:\",pred_word)\ndistance= pred_target_distance(np.array(pred_vector), np.array(parameterize_vovabulary[y[0]]))\nprint(\"distance:\", distance)",
"target word: same\ntarget vector: [-0.5174781860030842, -0.6546184738955823, 0.5510816460793957]\nprediction: [tensor(0.41123432, requires_grad=True), tensor(-0.66660704, requires_grad=True), tensor(0.43325996, requires_grad=True)]\nprediction word: then\ndistance: 0.9362331935842173\n"
],
[
"distance= pred_target_distance( np.array(parameterize_vovabulary[y[1]]), np.array(parameterize_vovabulary[y[1]]))\nprint(\"distance check\",distance)",
"distance check 0.0\n"
],
[
"def cost( par , x, y):\n\n predictions = [[next_gen(par, w_input,obs='x') ,next_gen(par,w_input,obs='y') ,next_gen(par,w_input,obs='z') ] for w_input in x ]\n\n c=0.0\n for i in range(len(predictions)):\n c = c+ pred_target_distance(np.array(predictions[i]), y)\n\n c=c/len(predictions)\n\n return np.array(c)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def accuracy(predictions, y):\n pred_words=[ get_word_from_sphere(p_v, parameterize_vovabulary) for p_v in predictions]\n target_words=[ get_word_from_sphere(p_v, parameterize_vovabulary) for p_v in y]\n ac=0\n for i in range(len(pred_words)):\n if pred_words[i]==target_words[i]:\n ac=ac+1\n return ac/len(pred_words)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Training:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## shuffling data \nindex = np.array([ i for i in range(len(x))])\nprint(index)",
"[ 0 1 2 ... 1641 1642 1643]\n"
],
[
"X_train= []\nY_train= []\nY_train_w= []\n\nfor i in range(len(x)):\n vec = [parameterize_vovabulary[w] for w in x[i]]\n X_train.append(vec)\n Y_train.append(parameterize_vovabulary[y[i]])\n Y_train_w.append(y[i])\n \nX_train= np.array(X_train)\nY_train= np.array(Y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def iterate_batches(X,Y, batch_size):\n X1 = [torch.reshape(x[0], (1, 2 ** (len(spec.latent_qubits) + len(spec.trash_qubits)))) for x in X]\n X2 = []\n for i in range(len(X1)):\n X2.append([X1[1], X[i][1]])\n X = X2\n random.shuffle(X)\n\n batch_list = []\n batch = []\n for x in X:\n if len(batch) < batch_size:\n batch.append(x)\n\n else:\n batch_list.append(batch)\n batch = []\n if len(batch) != 0:\n batch_list.append(batch)\n return batch_list",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Model parameters \n\nnum_layers= 1\nlayer_param= 17\nparams = np.random.uniform(size=(2, layer_param), requires_grad=True)\n\nlearning_rate= 0.6\nopt = AdamOptimizer(learning_rate, beta1=0.9, beta2=0.999)\n\nnr_epochs= 300",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ls_progres=[]\nac_progres=[]\nfor e in range(nr_epochs):\n params, ls = opt.step_and_cost(lambda p: cost( par=p, x=X_train, y=Y_train),params)\n\n print(\"Iter:{} | train_cost:{}\".format(e, ls))\n ls_progres.append(ls)\n\n\n if e%10==0:\n predictions = [[next_gen(params, w_input,obs='x') ,next_gen(params,w_input,obs='y') ,next_gen(params,w_input,obs='z') ] for w_input in X_train ]\n ac=accuracy(predictions, y=Y_train)\n\n print(\"ac:\",ac)\n ac_progres.append(ac)\n ",
"Iter:0 | train_cost:53.60082886916693\nac: 0.0036496350364963502\nIter:1 | train_cost:51.22300344453689\nIter:2 | train_cost:43.94168400175275\nIter:3 | train_cost:43.02241166220944\nIter:4 | train_cost:42.20706998707202\nIter:5 | train_cost:42.22409169057897\nIter:6 | train_cost:41.569128379960745\nIter:7 | train_cost:41.62247286223286\nIter:8 | train_cost:41.42697478304665\nIter:9 | train_cost:41.5571161180561\nIter:10 | train_cost:41.756217205647744\nac: 0.0006082725060827251\nIter:11 | train_cost:41.81138947351213\nIter:12 | train_cost:41.50899039197157\nIter:13 | train_cost:41.284097932138984\nIter:14 | train_cost:41.23511784896323\nIter:15 | train_cost:41.445282858198446\nIter:16 | train_cost:41.17631706803689\nIter:17 | train_cost:41.183101421089425\nIter:18 | train_cost:41.23648509725077\nIter:19 | train_cost:41.10445623032547\nIter:20 | train_cost:41.017359535920136\nac: 0.0024330900243309003\nIter:21 | train_cost:41.03232950789743\nIter:22 | train_cost:40.9921434744548\nIter:23 | train_cost:40.91168859941484\nIter:24 | train_cost:40.90038964487262\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Results",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure()\nplt.plot([x for x in range(0,len(ls_progres))],np.array(ls_progres),label=\"train loss\")\n\n\nplt.legend()\nplt.title(\"loss_VQE_001_C1\",)\nplt.xlabel(\"epoch\")\nplt.ylabel(\"loss\")\n\nprint(\"last loss:\",ls_progres[-1])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure()\nplt.plot([x for x in range(0,len(ac_progres)*10,10)],np.array(ac_progres),label=\"train accuracy\")\n\n\nplt.legend()\nplt.title(\"accuracy_VQE_001_C1\",)\nplt.xlabel(\"epoch\")\nplt.ylabel(\"accyracy\")\n\nprint(\"accuracy loss:\",ac_progres[-1])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for i in range(len(x)):\n \n words_vec = [parameterize_vovabulary[w] for w in x[i]]\n pred_vector=[ next_gen(params,words_vec, obs=o) for o in ['x', 'y', 'z']]\n pred_word= get_word_from_sphere(pred_vector, parameterize_vovabulary)\n \n text=\"\"\n for w in x[i];\n text=text+w+\" \"\n \n print(\"{} {}|{}\".format(text, pred_word,y[i]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbe9d01fc72fdb6aaf4797b5a53b4946bec5e62e
| 1,806,532 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
boards/Pynq-Z2/base/notebooks/video/hdmi_introduction.ipynb
|
jackrosenthal/PYNQ
|
788bf18529bc7a0564af4033ef3e246c03fc5b10
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 1,537 |
2016-09-26T22:51:50.000Z
|
2022-03-31T13:33:54.000Z
|
boards/Pynq-Z2/base/notebooks/video/hdmi_introduction.ipynb
|
MakarenaLabs/PYNQ
|
6f3113278e62b23315cf4e000df8f57fb53c4f6d
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 414 |
2016-10-03T21:12:10.000Z
|
2022-03-21T14:55:02.000Z
|
boards/Pynq-Z2/base/notebooks/video/hdmi_introduction.ipynb
|
MakarenaLabs/PYNQ
|
6f3113278e62b23315cf4e000df8f57fb53c4f6d
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 826 |
2016-09-23T22:29:43.000Z
|
2022-03-29T11:02:09.000Z
| 3,284.603636 | 901,592 | 0.960538 |
[
[
[
"# New Style HDMI input and Pixel Formatting\n\nThis notebook introduces the new features of PYNQ 2.0 for interacting with the video pipeline. The API has been completely\nredesigned with high performance image processing applications in mind.\n\nTo start, download the base overlay and instantiate the HDMI input and output.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from pynq.overlays.base import BaseOverlay\nfrom pynq.lib.video import *\n\nbase = BaseOverlay(\"base.bit\")\nhdmi_in = base.video.hdmi_in\nhdmi_out = base.video.hdmi_out",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Getting started\n\nFirst we'll use the default pixel format which is 24 bit-per-pixel BGR formatted data for ease of use with OpenCV. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"hdmi_in.configure()\nhdmi_out.configure(hdmi_in.mode)\n\nhdmi_in.start()\nhdmi_out.start()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The monitor should turn on and show a blank screen. To pass the image data through we can tie the output to the input. The tie will last until we send something else to be displayed.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"hdmi_in.tie(hdmi_out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"While this provides for a fast way of passing video data through the pipeline there is no way to access or modify the frames. For that we a loop calling `readframe` and `writeframe`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import time\n\nnumframes = 600\nstart = time.time()\n\nfor _ in range(numframes):\n f = hdmi_in.readframe()\n hdmi_out.writeframe(f)\n \nend = time.time()\nprint(\"Frames per second: \" + str(numframes / (end - start)))",
"Frames per second: 34.12674016266714\n"
]
],
[
[
"Next we can start adding some OpenCV processing into the mix. For all of these examples we are going to use a Laplacian gradient filter. The first loop is going to perform the grayscale conversion in software.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import cv2\nimport numpy as np\n\nnumframes = 10\ngrayscale = np.ndarray(shape=(hdmi_in.mode.height, hdmi_in.mode.width),\n dtype=np.uint8)\nresult = np.ndarray(shape=(hdmi_in.mode.height, hdmi_in.mode.width),\n dtype=np.uint8)\n\nstart = time.time()\n\nfor _ in range(numframes):\n inframe = hdmi_in.readframe()\n cv2.cvtColor(inframe,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY,dst=grayscale)\n inframe.freebuffer()\n cv2.Laplacian(grayscale, cv2.CV_8U, dst=result)\n\n outframe = hdmi_out.newframe()\n cv2.cvtColor(result, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR,dst=outframe)\n hdmi_out.writeframe(outframe)\n \nend = time.time()\nprint(\"Frames per second: \" + str(numframes / (end - start)))",
"Frames per second: 3.5044367097311837\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Cleaning up\n\nFinally you must always stop the interfaces when you are done with them. Otherwise bad things can happen when the bitstream is reprogrammed. You can also use the HDMI interfaces in a context manager to ensure that the cleanup is always performed.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"hdmi_out.close()\nhdmi_in.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Cacheable and non-cacheable frames\n\nBy default frames used by the HDMI subsystem are marked as cacheable meaning that the CPU cache is available for speeding up software operation at the expense of needing to flush frames prior to handing them off to the video system. This flushing is handled by PYNQ but can still impose a significant perfomance penalty particularly on 32-bit ARM architectures. To mitigate this the `cacheable_frames` property can be set to `False` on the `hdmi_in` and `hdmi_out` subsystems. This will improve the performance of passing frames between accelerators at the expense of software libraries operating more slowly or in some cases not working at all.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"base.download()\n\nhdmi_in.configure()\nhdmi_out.configure(hdmi_in.mode)\nhdmi_out.cacheable_frames = False\nhdmi_in.cacheable_frames = False\nhdmi_out.start()\nhdmi_in.start()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Re-running the plain read-write loop now shows 60 FPS",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"numframes = 600\nstart = time.time()\n\nfor _ in range(numframes):\n f = hdmi_in.readframe()\n hdmi_out.writeframe(f)\n \nend = time.time()\nprint(\"Frames per second: \" + str(numframes / (end - start)))",
"Frames per second: 59.71590161628438\n"
]
],
[
[
"At the expense of much slower OpenCV performance",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"numframes = 10\nstart = time.time()\n\nfor _ in range(numframes):\n inframe = hdmi_in.readframe()\n cv2.cvtColor(inframe,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY,dst=grayscale)\n inframe.freebuffer()\n cv2.Laplacian(grayscale, cv2.CV_8U, dst=result)\n\n outframe = hdmi_out.newframe()\n cv2.cvtColor(result, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR,dst=outframe)\n hdmi_out.writeframe(outframe)\n \nend = time.time()\nprint(\"Frames per second: \" + str(numframes / (end - start)))",
"Frames per second: 1.0362505509777689\n"
],
[
"hdmi_out.close()\nhdmi_in.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Gray-scale\nUsing the new infrastructure we can delegate the color conversion to the hardware as well as only passing a single grayscale pixel to and from the processor.\n\nFirst reconfigure the pipelines in grayscale mode and tie the two together to make sure everything is working correctly.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"base.download()\n\nhdmi_in.configure(PIXEL_GRAY)\nhdmi_out.configure(hdmi_in.mode)\nhdmi_in.cacheable_frames = True\nhdmi_out.cacheable_frames = True\nhdmi_in.start()\nhdmi_out.start()\n\nhdmi_in.tie(hdmi_out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we can rewrite the loop without the software colour conversion.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"start = time.time()\n\nnumframes = 30\n\nfor _ in range(numframes):\n inframe = hdmi_in.readframe()\n outframe = hdmi_out.newframe()\n cv2.Laplacian(inframe, cv2.CV_8U, dst=outframe)\n inframe.freebuffer()\n hdmi_out.writeframe(outframe)\n \nend = time.time()\nprint(\"Frames per second: \" + str(numframes / (end - start)))",
"Frames per second: 5.684202166751887\n"
],
[
"hdmi_out.close()\nhdmi_in.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Other modes\n\nThere are two other 24 bit modes that are useful for interacting with PIL. The first is regular RGB mode.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"base.download()\n\nhdmi_in.configure(PIXEL_RGB)\nhdmi_out.configure(hdmi_in.mode, PIXEL_RGB)\n\nhdmi_in.start()\nhdmi_out.start()\n\nhdmi_in.tie(hdmi_out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This is useful for easily creating and displaying frames with Pillow.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import PIL.Image\n\nframe = hdmi_in.readframe()\nimage = PIL.Image.fromarray(frame)\nimage",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"An alternative mode is YCbCr which is useful for some image processing algorithms or exporting JPEG files. Because we are not changing the number of bits per pixel we can update the colorspace of the input dynamically.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"hdmi_in.colorspace = COLOR_IN_YCBCR",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"It's probably worth updating the output colorspace as well to avoid the psychedelic effects",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"hdmi_out.colorspace = COLOR_OUT_YCBCR",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we can use PIL to read in the frame and perform the conversion back for us.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import PIL.Image\n\nframe = hdmi_in.readframe()\nimage = PIL.Image.fromarray(frame, \"YCbCr\")\nframe.freebuffer()\nimage.convert(\"RGB\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hdmi_out.close()\nhdmi_in.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Next Steps\n\nThis notebook has only provided an overview of base overlay pipeline. One of the reasons for the changes was to make it easier to add hardware accelerated functions by supporting a wider range of pixel formats without software conversion and separating out the HDMI front end from the video DMA. Explore the code in pynq/lib/video.py for more details.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe9d3d1b1375c1d10ee9dcf555a25c730e8ccde
| 35,074 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
AI_Experiments/deep_learning_regularization.ipynb
|
hanhanwu/Hanhan_Data_Science_Practice
|
ac48401121062d03f9983f6a8c7f7adb0ab9b616
|
[
"MIT"
] | 24 |
2016-05-20T00:50:57.000Z
|
2020-10-01T15:42:16.000Z
|
AI_Experiments/deep_learning_regularization.ipynb
|
hanhanwu/Hanhan_Data_Science_Practice
|
ac48401121062d03f9983f6a8c7f7adb0ab9b616
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
AI_Experiments/deep_learning_regularization.ipynb
|
hanhanwu/Hanhan_Data_Science_Practice
|
ac48401121062d03f9983f6a8c7f7adb0ab9b616
|
[
"MIT"
] | 14 |
2018-01-29T06:08:59.000Z
|
2020-10-03T08:08:31.000Z
| 42.982843 | 2,372 | 0.595512 |
[
[
[
"## Deep Learning Regularization\n\n😓Be well prepared that when the code worked for me, may not work for you any more. It took me so much time tonight to debug, upgrade/install packages, change deprecated functions or just ignore warnings.... All because of the frequent changes in these open source packages. So, when it's your turn to try the code, who knows whether it still works...\n\n💝However, when you are seeing my code, you are lucky! At least I took the note on those things need to care about, including the solutions.\n\n❣️Also note, the model evaluation here I didn't evauate all the testing data, because of the labeling time for all those testing image can be huge and I'm really busy. <b>However</b>, you can pay attention to those val_acc and val_loss, lower the better\n\nReference: https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2018/04/fundamentals-deep-learning-regularization-techniques/?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+AnalyticsVidhya+%28Analytics+Vidhya%29\n\n<b>Get data from here</b>: https://datahack.analyticsvidhya.com/contest/practice-problem-identify-the-digits/",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport os\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom imageio import imread\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score\nimport pylab\n\nimport tensorflow as tf\nimport keras",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### NOTE\n\nYou may got an error saying cannot import module \"weakref\". This problem was not exist before but just appeared...\nHere's my solution:\n1. Find your tensorflow path by typing `pip show tensorflow`\n2. Find tensorflow/python/util/tf_should_use.py, open it\n3. Change `from backports import weakref` to `import weakref`\n4. Then comment the line that contains `finalize()` function, this is for garbage collection, but finalize function does not exist in weakref in my case.... 😓\n5. Restart your ipython",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seed = 10\nrng = np.random.RandomState(seed)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train = pd.read_csv('digit_recognition/train.csv')\ntest = pd.read_csv('digit_recognition/test.csv')\n\ntrain.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"img_name = rng.choice(train.filename)\ntraining_image_path = 'digit_recognition/Images/train/' + img_name\n\ntraining_img = imread(training_image_path, as_gray=True)\n\npylab.imshow(training_img, cmap='gray')\npylab.axis('off')\npylab.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"training_img[7:9]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# store all images as numpy arrays, to make data manipulation easier\n\ntemp = []\nfor img_name in train.filename:\n training_image_path = 'digit_recognition/Images/train/' + img_name\n training_img = imread(training_image_path, as_gray=True)\n img = training_img.astype('float32')\n temp.append(img)\n \ntrain_x = np.stack(temp)\n\ntrain_x /= 255.0\ntrain_x = train_x.reshape(-1, 784).astype('float32')\n\ntemp = []\nfor img_name in test.filename:\n testing_image_path = 'digit_recognition/Images/test/' + img_name\n testing_img = imread(testing_image_path, as_gray=True)\n img = testing_img.astype('float32')\n temp.append(img)\n \ntest_x = np.stack(temp)\n\ntest_x /= 255.0\ntest_x = test_x.reshape(-1, 784).astype('float32')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_x",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_y = keras.utils.np_utils.to_categorical(train.label.values)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# split into training and validation sets, 7:3\n\nsplit_size = int(train_x.shape[0]*0.7)\n\ntrain_x, val_x = train_x[:split_size], train_x[split_size:]\ntrain_y, val_y = train_y[:split_size], train_y[split_size:]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train.label.iloc[split_size:split_size+2]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from keras.models import Sequential\nfrom keras.layers import Dense\n\n# define variables\ninput_num_units = 784\nhidden1_num_units = 500\nhidden2_num_units = 500\nhidden3_num_units = 500\nhidden4_num_units = 500\nhidden5_num_units = 500\noutput_num_units = 10\n\nepochs = 10\nbatch_size = 128",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### NOTE\n\nKeras updated to 2.0\nWithout updating keras, the way you used `Dense()` function may keep giving warnings\n\n* Here's Keras 2.0 documentation: https://keras.io/\n* To update keras, type `sudo pip install --upgrade keras==2.1.3`. Has to be keras 2.1.3, if it's higher, softmax may get an error below.... (this is why I hate deep learning when you have to use open source!)\n* Holy s**t, even after the updating, you will get many warnings again, just ignore them..",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Method 1 - Without Regularization\nimport warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings('ignore')\n\nmodel = Sequential()\nmodel.add(Dense(output_dim=hidden1_num_units, input_dim=input_num_units, activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(Dense(output_dim=hidden1_num_units, input_dim=input_num_units, activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(Dense(output_dim=hidden2_num_units, input_dim=hidden1_num_units, activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(Dense(output_dim=hidden3_num_units, input_dim=hidden2_num_units, activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(Dense(output_dim=hidden4_num_units, input_dim=hidden3_num_units, activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(Dense(output_dim=hidden5_num_units, input_dim=hidden4_num_units, activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(Dense(output_dim=output_num_units, input_dim=hidden5_num_units, activation='softmax'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])\ntrained_model_5d = model.fit(train_x, train_y, nb_epoch=epochs, batch_size=batch_size, validation_data=(val_x, val_y)) ",
"Train on 34300 samples, validate on 14700 samples\nEpoch 1/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 20s 595us/step - loss: 0.3075 - acc: 0.9044 - val_loss: 0.1898 - val_acc: 0.9454\nEpoch 2/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 19s 562us/step - loss: 0.1248 - acc: 0.9633 - val_loss: 0.1333 - val_acc: 0.9607\nEpoch 3/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 20s 572us/step - loss: 0.0876 - acc: 0.9734 - val_loss: 0.1119 - val_acc: 0.9705\nEpoch 4/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 20s 586us/step - loss: 0.0627 - acc: 0.9806 - val_loss: 0.1204 - val_acc: 0.9681\nEpoch 5/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 20s 586us/step - loss: 0.0545 - acc: 0.9838 - val_loss: 0.1187 - val_acc: 0.9711\nEpoch 6/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 20s 588us/step - loss: 0.0470 - acc: 0.9858 - val_loss: 0.1165 - val_acc: 0.9731\nEpoch 7/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 20s 593us/step - loss: 0.0437 - acc: 0.9873 - val_loss: 0.1081 - val_acc: 0.9744\nEpoch 8/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 20s 583us/step - loss: 0.0345 - acc: 0.9899 - val_loss: 0.1444 - val_acc: 0.9670\nEpoch 9/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 20s 587us/step - loss: 0.0342 - acc: 0.9901 - val_loss: 0.1263 - val_acc: 0.9726\nEpoch 10/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 20s 592us/step - loss: 0.0273 - acc: 0.9928 - val_loss: 0.1238 - val_acc: 0.9718\n"
],
[
"# one sample evaluation\n\npred = model.predict_classes(test_x)\n\nimg_name = rng.choice(test.filename)\ntesting_image_path = 'digit_recognition/Images/test/' + img_name\ntesting_img = imread(testing_image_path, as_gray=True)\n\ntest_index = int(img_name.split('.')[0]) - train.shape[0]\n\nprint \"Prediction is: \", pred[test_index]\n\npylab.imshow(testing_img, cmap='gray')\npylab.axis('off')\npylab.show()",
"Prediction is: 9\n"
],
[
"from keras import regularizers",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Method 2 - With L2 regularizer\n\nmodel = Sequential([\n Dense(output_dim=hidden1_num_units, input_dim=input_num_units, activation='relu',\n kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.0001)), # lambda = 0.0001\n Dense(output_dim=hidden2_num_units, input_dim=hidden1_num_units, activation='relu',\n kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.0001)),\n Dense(output_dim=hidden3_num_units, input_dim=hidden2_num_units, activation='relu',\n kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.0001)),\n Dense(output_dim=hidden4_num_units, input_dim=hidden3_num_units, activation='relu',\n kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.0001)),\n Dense(output_dim=hidden5_num_units, input_dim=hidden4_num_units, activation='relu',\n kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.0001)),\n Dense(output_dim=output_num_units, input_dim=hidden5_num_units, activation='softmax'),\n ])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])\ntrained_model_5d = model.fit(train_x, train_y, nb_epoch=epochs, batch_size=batch_size, validation_data=(val_x, val_y))",
"Train on 34300 samples, validate on 14700 samples\nEpoch 1/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 44s 1ms/step - loss: 0.4895 - acc: 0.9100 - val_loss: 0.3137 - val_acc: 0.9559\nEpoch 2/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 72s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2882 - acc: 0.9628 - val_loss: 0.2913 - val_acc: 0.9612\nEpoch 3/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 41s 1ms/step - loss: 0.2332 - acc: 0.9743 - val_loss: 0.2642 - val_acc: 0.9664\nEpoch 4/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 43s 1ms/step - loss: 0.2073 - acc: 0.9789 - val_loss: 0.2475 - val_acc: 0.9665\nEpoch 5/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 31s 918us/step - loss: 0.1816 - acc: 0.9837 - val_loss: 0.2258 - val_acc: 0.9705\nEpoch 6/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 27s 802us/step - loss: 0.1630 - acc: 0.9857 - val_loss: 0.2180 - val_acc: 0.9710\nEpoch 7/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 29s 855us/step - loss: 0.1530 - acc: 0.9862 - val_loss: 0.2126 - val_acc: 0.9726\nEpoch 8/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 35s 1ms/step - loss: 0.1393 - acc: 0.9882 - val_loss: 0.2115 - val_acc: 0.9712\nEpoch 9/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 33s 958us/step - loss: 0.1339 - acc: 0.9883 - val_loss: 0.2196 - val_acc: 0.9661\nEpoch 10/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 33s 965us/step - loss: 0.1197 - acc: 0.9911 - val_loss: 0.2042 - val_acc: 0.9701\n"
],
[
"# Method 3 - L1 Regularizer\n\nmodel = Sequential([\n Dense(output_dim=hidden1_num_units, input_dim=input_num_units, activation='relu',\n kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l1(0.0001)),\n Dense(output_dim=hidden2_num_units, input_dim=hidden1_num_units, activation='relu',\n kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l1(0.0001)),\n Dense(output_dim=hidden3_num_units, input_dim=hidden2_num_units, activation='relu',\n kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l1(0.0001)),\n Dense(output_dim=hidden4_num_units, input_dim=hidden3_num_units, activation='relu',\n kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l1(0.0001)),\n Dense(output_dim=hidden5_num_units, input_dim=hidden4_num_units, activation='relu',\n kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l1(0.0001)),\n Dense(output_dim=output_num_units, input_dim=hidden5_num_units, activation='softmax'),\n ])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])\ntrained_model_5d = model.fit(train_x, train_y, nb_epoch=epochs, batch_size=batch_size, validation_data=(val_x, val_y))",
"Train on 34300 samples, validate on 14700 samples\nEpoch 1/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 27s 799us/step - loss: 2.8674 - acc: 0.9038 - val_loss: 1.7857 - val_acc: 0.9503\nEpoch 2/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 28s 804us/step - loss: 1.3601 - acc: 0.9543 - val_loss: 1.0440 - val_acc: 0.9523\nEpoch 3/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 28s 806us/step - loss: 0.8408 - acc: 0.9619 - val_loss: 0.7174 - val_acc: 0.9544\nEpoch 4/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 28s 805us/step - loss: 0.5903 - acc: 0.9688 - val_loss: 0.5198 - val_acc: 0.9683\nEpoch 5/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 29s 843us/step - loss: 0.4596 - acc: 0.9717 - val_loss: 0.4388 - val_acc: 0.9662\nEpoch 6/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 28s 805us/step - loss: 0.3848 - acc: 0.9737 - val_loss: 0.4031 - val_acc: 0.9627\nEpoch 7/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 30s 883us/step - loss: 0.3303 - acc: 0.9776 - val_loss: 0.3565 - val_acc: 0.9633\nEpoch 8/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 28s 813us/step - loss: 0.2965 - acc: 0.9786 - val_loss: 0.3257 - val_acc: 0.9686\nEpoch 9/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 30s 867us/step - loss: 0.2711 - acc: 0.9808 - val_loss: 0.2952 - val_acc: 0.9712\nEpoch 10/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 36s 1ms/step - loss: 0.2525 - acc: 0.9815 - val_loss: 0.2895 - val_acc: 0.9699\n"
],
[
"# method 4 - Dropout\nfrom keras.layers.core import Dropout\n\nmodel = Sequential([\n Dense(output_dim=hidden1_num_units, input_dim=input_num_units, activation='relu'),\n Dropout(0.25), # the drop probability is 0.25\n Dense(output_dim=hidden2_num_units, input_dim=hidden1_num_units, activation='relu'),\n Dropout(0.25),\n Dense(output_dim=hidden3_num_units, input_dim=hidden2_num_units, activation='relu'),\n Dropout(0.25),\n Dense(output_dim=hidden4_num_units, input_dim=hidden3_num_units, activation='relu'),\n Dropout(0.25),\n Dense(output_dim=hidden5_num_units, input_dim=hidden4_num_units, activation='relu'),\n Dropout(0.25),\n Dense(output_dim=output_num_units, input_dim=hidden5_num_units, activation='softmax'),\n ])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])\ntrained_model_5d = model.fit(train_x, train_y, nb_epoch=epochs, batch_size=batch_size, validation_data=(val_x, val_y))",
"Train on 34300 samples, validate on 14700 samples\nEpoch 1/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 27s 787us/step - loss: 0.4204 - acc: 0.8669 - val_loss: 0.1686 - val_acc: 0.9507\nEpoch 2/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 26s 771us/step - loss: 0.1715 - acc: 0.9497 - val_loss: 0.1343 - val_acc: 0.9601\nEpoch 3/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 26s 763us/step - loss: 0.1356 - acc: 0.9606 - val_loss: 0.1173 - val_acc: 0.9668\nEpoch 4/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 27s 776us/step - loss: 0.1038 - acc: 0.9692 - val_loss: 0.1060 - val_acc: 0.9705\nEpoch 5/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 30s 881us/step - loss: 0.0897 - acc: 0.9738 - val_loss: 0.1223 - val_acc: 0.9676\nEpoch 6/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 29s 841us/step - loss: 0.0785 - acc: 0.9774 - val_loss: 0.1158 - val_acc: 0.9703\nEpoch 7/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 27s 793us/step - loss: 0.0673 - acc: 0.9806 - val_loss: 0.1186 - val_acc: 0.9717\nEpoch 8/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 27s 790us/step - loss: 0.0645 - acc: 0.9809 - val_loss: 0.1080 - val_acc: 0.9731\nEpoch 9/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 26s 758us/step - loss: 0.0586 - acc: 0.9827 - val_loss: 0.1012 - val_acc: 0.9741\nEpoch 10/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 27s 778us/step - loss: 0.0560 - acc: 0.9836 - val_loss: 0.1046 - val_acc: 0.9748\n"
],
[
"# method 5 - early stopping\nfrom keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping\nfrom keras.layers.core import Dropout\nimport warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings('ignore')\n\nmodel = Sequential([\n Dense(output_dim=hidden1_num_units, input_dim=input_num_units, activation='relu'),\n Dropout(0.25), # the drop probability is 0.25\n Dense(output_dim=hidden2_num_units, input_dim=hidden1_num_units, activation='relu'),\n Dropout(0.25),\n Dense(output_dim=hidden3_num_units, input_dim=hidden2_num_units, activation='relu'),\n Dropout(0.25),\n Dense(output_dim=hidden4_num_units, input_dim=hidden3_num_units, activation='relu'),\n Dropout(0.25),\n Dense(output_dim=hidden5_num_units, input_dim=hidden4_num_units, activation='relu'),\n Dropout(0.25),\n Dense(output_dim=output_num_units, input_dim=hidden5_num_units, activation='softmax'),\n ])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])\ntrained_model_5d = model.fit(train_x, train_y, nb_epoch=epochs, batch_size=batch_size, validation_data=(val_x, val_y),\n callbacks = [EarlyStopping(monitor='val_acc', patience=2)])",
"Train on 34300 samples, validate on 14700 samples\nEpoch 1/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 20s 582us/step - loss: 0.4231 - acc: 0.8689 - val_loss: 0.2190 - val_acc: 0.9376\nEpoch 2/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 18s 516us/step - loss: 0.1737 - acc: 0.9499 - val_loss: 0.1651 - val_acc: 0.9529\nEpoch 3/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 15s 450us/step - loss: 0.1371 - acc: 0.9607 - val_loss: 0.1119 - val_acc: 0.9675\nEpoch 4/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 16s 469us/step - loss: 0.1083 - acc: 0.9681 - val_loss: 0.1044 - val_acc: 0.9703\nEpoch 5/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 18s 529us/step - loss: 0.0880 - acc: 0.9736 - val_loss: 0.1034 - val_acc: 0.9720\nEpoch 6/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 16s 455us/step - loss: 0.0793 - acc: 0.9769 - val_loss: 0.1121 - val_acc: 0.9707\nEpoch 7/10\n34300/34300 [==============================] - 15s 446us/step - loss: 0.0708 - acc: 0.9793 - val_loss: 0.1167 - val_acc: 0.9713\n"
],
[
"# method 6 - Data Augmentation\nfrom keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator\n\ndatagen = ImageDataGenerator(zca_whitening=True) \n# zca_whitening as the argument, will highlight the outline of each digit",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train = pd.read_csv('digit_recognition/train.csv')\n\ntemp = []\nfor img_name in train.filename:\n training_image_path = 'digit_recognition/Images/train/' + img_name\n training_img = imread(training_image_path, as_gray=True)\n img = training_img.astype('float32')\n temp.append(img)\n \ntrain_x = np.stack(temp)\n\n# The difference with above starts from here:\ntrain_x = train_x.reshape(train_x.shape[0], 1, 28, 28)\ntrain_x = train_x.astype('float32')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# fit parameters from data\n## fit the training data in order to augment\ndatagen.fit(train_x) # This will often cause the kernel to die on my machine\n\n# data spliting\nsplit_size = int(train_x.shape[0]*0.7)\ntrain_x, val_x = train_x[:split_size], train_x[split_size:]\ntrain_y, val_y = train_y[:split_size], train_y[split_size:]\n\n# train the model with drop out\nmodel = Sequential([\n Dense(output_dim=hidden1_num_units, input_dim=input_num_units, activation='relu'),\n Dropout(0.25), # the drop probability is 0.25\n Dense(output_dim=hidden2_num_units, input_dim=hidden1_num_units, activation='relu'),\n Dropout(0.25),\n Dense(output_dim=hidden3_num_units, input_dim=hidden2_num_units, activation='relu'),\n Dropout(0.25),\n Dense(output_dim=hidden4_num_units, input_dim=hidden3_num_units, activation='relu'),\n Dropout(0.25),\n Dense(output_dim=hidden5_num_units, input_dim=hidden4_num_units, activation='relu'),\n Dropout(0.25),\n Dense(output_dim=output_num_units, input_dim=hidden5_num_units, activation='softmax'),\n ])\n\nmodel.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])\ntrained_model_5d = model.fit(train_x, train_y, nb_epoch=epochs, batch_size=batch_size, validation_data=(val_x, val_y))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Observations\n\n1. Comparing the val_loss and vall_acc between each regularizer and the first method, we can see dropout works best and it is thr only one that has lower val_loss and higher val_acc. \n2. In the experiments here, after we applied early stopping on dropout it didn't give better results, maybe it needs more `patience`, because if we observe each epoch, the val_loss is not simply dropping along the way, it could increase in the middle and then drop again. This is why we need to be careful towards the number of epoch/patience\n3. L1, L2 tend to give higher val_loss, especially L1\n4. In my machine, with limited memory now, data augmentation failed, it will simply kill the kernel all the time. No wonder dropout is the most frequently used regularizer.....",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
cbe9eba7a0cb28bf41232cb3a2941b23ca4015c5
| 19,757 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/mac_season_6_data_cleaning.ipynb
|
genophenoenvo/terraref-datasets
|
84ef14cb368ebe3e3de86ee009bab66fff96ea91
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2019-10-22T23:41:54.000Z
|
2020-12-23T21:41:39.000Z
|
notebooks/mac_season_6_data_cleaning.ipynb
|
genophenoenvo/terraref-datasets
|
84ef14cb368ebe3e3de86ee009bab66fff96ea91
|
[
"MIT"
] | 132 |
2019-08-22T20:36:58.000Z
|
2021-09-27T20:51:04.000Z
|
notebooks/mac_season_6_data_cleaning.ipynb
|
genophenoenvo/terraref-datasets
|
84ef14cb368ebe3e3de86ee009bab66fff96ea91
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2019-12-09T20:45:49.000Z
|
2021-01-06T17:47:15.000Z
| 24.758145 | 210 | 0.510098 |
[
[
[
"### Maricopa Agricultural Center Season 6",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Citation for Input Trait Data\n\nLeBauer, David et al. (2020), Data From: TERRA-REF, An open reference data set from high resolution genomics, phenomics, and imaging sensors, v6, Dryad, Dataset, https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.4b8gtht99\n\n##### Environmental weather data can be downloaded from the MAC weather station [website](https://cals.arizona.edu/azmet/06.htm)\n\nPlease email [email protected] or [email protected] with any questions or comments, or create an issue in this [repository](https://github.com/genophenoenvo/terraref-datasets) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import datetime\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\nimport pandas as pd\nimport requests",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def download_csv(url, folder_name, file_name):\n response = requests.get(url)\n with open(os.path.join(folder_name, file_name), 'wb') as f:\n f.write(response.content)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def read_in_csv(folder_name, file_name):\n df = pd.read_csv(folder_name + '/' + file_name, low_memory=False)\n return df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def plot_hist(df, value_column, trait_column):\n \n trait_name = df[trait_column].unique()[0]\n return df[value_column].hist(color='navy').set_xlabel(trait_name);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def check_for_nulls_duplicates(df):\n \n print(\n f'Sum of null values:\\n{df.isnull().sum()}\\n-----\\n'\n f'Value counts for duplicates:\\n{df.duplicated().value_counts()}'\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def check_unique_values(df):\n\n for col in df.columns:\n \n if df[col].nunique() < 5:\n print(f'{df[col].nunique()} unique value(s) for {col} column: {df[col].unique()}')\n \n else:\n print(f'{df[col].nunique()} values for {col} column')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def extract_range_column_values(working_df, plot_column):\n \n new_df = working_df.copy()\n\n new_df['range'] = new_df[plot_column].str.extract(\"Range (\\d+)\").astype(int)\n new_df['column'] = new_df[plot_column].str.extract(\"Column (\\d+)\").astype(int)\n \n return new_df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def convert_datetime_column(working_df, date_column):\n \n new_datetimes = pd.to_datetime(working_df[date_column])\n \n new_df_0 = working_df.drop(labels=date_column, axis=1)\n new_df_1 = new_df_0.copy()\n new_df_1['date'] = new_datetimes\n \n return new_df_1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def rename_value_column(working_df, value_column, trait_column):\n \n trait = working_df[trait_column].unique()[0]\n \n new_df_0 = working_df.rename({value_column: trait}, axis=1)\n new_df_1 = new_df_0.drop(labels=trait_column, axis=1)\n \n return new_df_1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def reorder_columns(working_df, new_col_order_list):\n \n working_df_1 = pd.DataFrame(data=working_df, columns=new_col_order_list)\n return working_df_1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def save_to_csv_with_timestamp(df, name_of_dataset):\n \n timestamp = datetime.datetime.now().replace(microsecond=0).isoformat()\n output_filename = ('data/processed/' + f'{name_of_dataset}_' + f'{timestamp}.csv').replace(':', '')\n\n df.to_csv(output_filename, index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def save_to_csv_without_timestamp(list_of_dfs, list_of_output_filenames):\n\n for i,j in zip(list_of_dfs, list_of_output_filenames):\n i.to_csv(j, index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### A. Aboveground Dry Biomass",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"folder_name = 'data'\nif not os.path.exists(folder_name):\n os.makedirs(folder_name)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"aboveground_dry_biomass_s6_url = 'https://de.cyverse.org/dl/d/1333BF0F-9462-4F0A-8D35-2B446F0CC989/season_6_aboveground_dry_biomass_manual.csv'\naboveground_dry_biomass_s6_input_filename = 'aboveground_dry_biomass_s6.csv'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"download_csv(aboveground_dry_biomass_s6_url, folder_name=folder_name, file_name=aboveground_dry_biomass_s6_input_filename)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"adb_0 = read_in_csv(folder_name=folder_name, file_name=aboveground_dry_biomass_s6_input_filename)\n# print(adb_0.shape)\n# adb_0.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot_hist(adb_0, 'mean', 'trait')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check_for_nulls_duplicates(adb_0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"adb_1 = extract_range_column_values(adb_0, 'plot')\n# print(adb_1.shape)\n# adb_1.sample(n=3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Add Blocking Heights",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"bh_s6_url = 'https://de.cyverse.org/dl/d/73900334-1A0F-4C56-8F96-FAC303671431/s6_blocks.csv.txt'\nbh_s6_input_filename = 'blocking_heights_s6.csv'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"download_csv(bh_s6_url, folder_name=folder_name, file_name=bh_s6_input_filename)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bh_df = read_in_csv(folder_name=folder_name, file_name=bh_s6_input_filename)\n# print(bh_df.shape)\n# bh_df.head()",
"(999, 2)\n"
],
[
"# bh_df.height_block.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check_for_nulls_duplicates(bh_df)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bh_df_1 = bh_df.dropna(axis=0, how='all')\n# bh_df_1.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Merge blocking heights with aboveground dry biomass dataframe",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"adb_2 = adb_1.merge(bh_df_1, how='left', left_on='plot', right_on='plot')\n# print(adb_2.shape)\n# adb_2.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"adb_3 = convert_datetime_column(adb_2, 'date')\n# print(adb_3.shape)\n# adb_3.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"adb_4 = rename_value_column(adb_3, 'mean', 'trait')\n# print(adb_4.shape)\n# adb_4.tail(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cols_to_drop = ['checked', 'author', 'season', 'treatment']\n\nadb_5 = adb_4.drop(labels=cols_to_drop, axis=1)\n# print(adb_5.shape)\n# adb_5.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Add units (kg/ha) column to aboveground dry biomass dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"adb_6 = adb_5.copy()\nadb_6['units'] = 'kg/ha'\n\n# print(adb_6.shape)\n# adb_6.tail(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"new_col_order = ['date', 'plot', 'range', 'column', 'scientificname', 'genotype', 'height_block', 'method', \n 'aboveground_dry_biomass', 'units', 'method_type']\n\nadb_7 = reorder_columns(adb_6, new_col_order)\n# print(adb_7.shape)\n# adb_7.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### B. Canopy Height - Sensor",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"canopy_height_s6_url = 'https://de.cyverse.org/dl/d/D069737A-76F3-4B69-A213-4B8811A357C0/season_6_canopy_height_sensor.csv'\ncanopy_height_s6_input_filename = 'canopy_height_s6.csv'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"download_csv(canopy_height_s6_url, folder_name=folder_name, file_name=canopy_height_s6_input_filename)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ch_0 = read_in_csv(folder_name=folder_name, file_name=canopy_height_s6_input_filename)\n# print(ch_0.shape)\n# ch_0.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check_for_nulls_duplicates(ch_0)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Drop duplicates",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ch_1 = ch_0.drop_duplicates(ignore_index=True)\n# print(ch_1.shape)\n# check_for_nulls_duplicates(ch_1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ch_2 = extract_range_column_values(ch_1, 'plot')\n# print(ch_2.shape)\n# ch_2.sample(n=3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ch_3 = convert_datetime_column(ch_2, 'date')\n# print(ch_3.shape)\n# ch_3.dtypes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ch_4 = rename_value_column(ch_3, 'mean', 'trait')\n# print(ch_4.shape)\n# ch_4.tail(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# add units (cm) to column name\n\nch_5 = ch_4.rename({'canopy_height': 'canopy_height_cm'}, axis=1)\n# ch_5.sample(n=3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Add blocking heights",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# bh_df_1.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(bh_df_1['plot'].nunique())\nprint(ch_0['plot'].nunique())",
"714\n809\n"
]
],
[
[
"There is not a height block provided for every plot, so the final canopy height dataframe will contain some nulls.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ch_6 = ch_5.merge(bh_df_1, how='left', left_on='plot', right_on='plot')\n# print(ch_6.shape)\n# ch_6.tail(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ch_7 = ch_6.drop(labels=['checked', 'author', 'season', 'treatment'], axis=1)\n# print(ch_7.shape)\n# ch_7.tail(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# ch_7.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"new_col_order = ['date', 'plot', 'range', 'column', 'scientificname', 'genotype', 'method', 'canopy_height_cm', \n 'height_block', 'method_type']\n\nch_8 = reorder_columns(ch_7, new_col_order)\n# print(ch_8.shape)\n# ch_8.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### IV. Write derived data to csv files",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"list_of_dfs = [adb_7, ch_8]\nlist_of_file_output_names = ['mac_season_6_aboveground_dry_biomass.csv',\n 'mac_season_6_canopy_height_sensor.csv']\n\nsave_to_csv_without_timestamp(list_of_dfs, list_of_file_output_names)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
cbe9f9ae666fdab69053ef90193b6c9502bc8b81
| 414,614 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
TILDE/TILDE_endpoint02-data_DART.ipynb
|
megankortink/data-tutorials
|
19372969b27fe43c9ad73fb4acd8d624145cb97c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 11 |
2019-02-15T00:54:24.000Z
|
2022-02-10T05:46:09.000Z
|
TILDE/TILDE_endpoint02-data_DART.ipynb
|
megankortink/data-tutorials
|
19372969b27fe43c9ad73fb4acd8d624145cb97c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 9 |
2019-02-10T23:05:09.000Z
|
2022-03-22T20:19:18.000Z
|
TILDE/TILDE_endpoint02-data_DART.ipynb
|
megankortink/data-tutorials
|
19372969b27fe43c9ad73fb4acd8d624145cb97c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 16 |
2019-02-05T01:51:30.000Z
|
2022-01-12T10:58:12.000Z
| 285.94069 | 108,040 | 0.911785 |
[
[
[
"# Exploring Observation Data From TILDE, Application to DART Data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Table of contents\n### 1. Introduction\n### 2. Building a Query for a specific sensor code/stream\n### 3. Building a Query without sensor code/stream\n### 4. Building a Query for the latest data\n### 5. Building a Query for aggregated data\n### 6. Getting the data using ObsPy",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 1. Introduction",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this tutorial we will be learning how to use Python to access the TILDE API `data` endpoint. To highlight the different functionalities and the statistics available we will be using the DART (Deep-ocean Assessment and Reporting of Tsunamis) dataset. Tilde is the GeoNet API (Application Programming Interface) to access DART time series data. You do not need to know anything about APIs to use this tutorial. If you would like more info see https://tilde.geonet.org.nz/.\n\nThis tutorial assumes you have basic knowledge of Python.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"###### About GeoNet DART data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"GeoNet uses the 12 DART Tsunameters deployed offshore New Zealand and around the Southwestern Pacific Ocean to monitor ocean height. When a change has been detected of a certain magnitude, the buoy will \"trigger\" and go into a heightened detection mode. The DARTs have two operational reporting modes; standard and event. When in standard reporting mode, the BPR (bottom pressure recorder) and buoy system send four six-hour bundles of 15 minute water height values. When in event reporting mode, BPR data are sampled at 15 second intervals and are sent more regularly. The buoy surface location (latitude and longitude) will also be sent daily. <br>\nTILDE provides access to the 15 minutes and 15 second sampled data.\n\nFor more DART information see the GeoNet page: https://www.geonet.org.nz/tsunami/dart",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 2. Building a Query for a specific sensor code/stream",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"###### Import required modules and set the source URL",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import requests\nimport json\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom io import StringIO",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"source = 'https://tilde.geonet.org.nz'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Request data for a specific sensor/stream with date range, and then returning a CSV file\n\nThis query returns the observations of the specified data held in TILDE. <br>\nThe endpoint we are going to use is `https://tilde.geonet.org.nz/v1/data/`.\n\nThe minimum required parameters are:\n- domain = `dart`\n- key = `NZE/water-height/40/WTZ`, this is 15 minute sampled data for the station NZE\n- startdate = '2021-03-05'\n- enddate = '2021-03-05'\n\nWe will ask for data for 2021 March 05.\n\nWe begin by setting the URL with these new parameters.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"url = source+'/v1/data/dart/NZE/water-height/40/WTZ/2021-03-05/2021-03-05'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We will now query the URL and ask for a CSV format to be returned",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"r = requests.get(url, headers={'Accept':'text/csv'})\nprint (r)",
"<Response [200]>\n"
]
],
[
[
"We use `requests.get` to retrieve the data from the URL. The response status code says whether we were successful in getting the data requested and why not if we were unsuccessful:\n<ul>\n<li>200 -- everything went okay, and the result has been returned (if any)\n<li>301 -- the server is redirecting you to a different endpoint. This can happen when a company switches domain names, or an endpoint name is changed.\n<li>400 -- the server thinks you made a bad request. This can happen when you don't send along the right data, among other things.\n<li>404 -- the resource you tried to access wasn't found on the server.\n</ul>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To work with the observation data we will use python's pandas module (https://pandas.pydata.org/). We will now store the response of our request in a pandas dataframe (`df`), using `pd.read_csv`. By using `parse_dates=['time']` we can convert the 'time' to a datetime and with `index_col` we can set the time as the index of the dataframe. More information on `pd.read_csv` can be found here: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.read_csv.html. We need to use the `StringIO` function with the text returned from our query. By printing the beginning of the result (`df.head()`) we can also see the result of this new index column.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = pd.read_csv(StringIO(r.text),parse_dates=['time'], index_col='time')\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Data Summary\nBy using `df.describe` we can summarise the returned data as this features generates descriptive statistics from dataframes. From the result we can see that there are 59 values (and errors), and all of the qc values are currently undefined. By default, we also to get to see the mean, standard deviation, minimum, maximum, and some percentile values.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Basic Data Plot\nBy using the `value` column from our dataframe we are able to plot the data against time. For this plot we will use dots and a line so periods without data are obvious. As we are currently plotting low rate data (WTZ), when there is a gap of data it is likely we have high rate data (UTZ) for this period instead. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15,5))\ndf['value'].plot(ax=ax, color='#41b0f0', label='low rate (15 mins)')\ndf['value'].plot(ax=ax, color='blue', marker='.', linestyle='None')\n \n#stop exponential format for y-axis label\nax.ticklabel_format(axis='y', useOffset=False, style='plain')\n\nplt.legend(loc='best')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 3. Building a Query without sensor code/stream\n\nTILDE can also provide all of the available data for a date range without having to specify the sensor code and stream parameters.\n\nThe minimum required parameters are:\n- domain = `dart`\n- key = `NZE/water-height/-/-`\n- startdate = '2021-03-05'\n- enddate = '2021-03-05'\n\nUsing the above parameters will return data from all sensor codes (for NZE there is only sensor code 40 for this date) and all data types (WTZ and UTZ). These will be returned in CSV format. \nThe available location codes for each station are available in GeoNet's github repository (https://github.com/GeoNet/delta/blob/main/network/sites.csv). Sensor codes will be provided in the `Location` column (and for DART those will be either 40 or 41). <br>\n\nWe will begin by following similar steps to Section 2 and changing the URL with the new parameters, quering the URL and asking for the CSV format to be returned.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"url = source+'/v1/data/dart/NZE/water-height/-/-/2021-03-05/2021-03-05'\n\nr = requests.get(url, headers={'Accept':'text/csv'})\n\ndf = pd.read_csv(StringIO(r.text),parse_dates=['time'], index_col='time')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Sorted by type not date\nBy printing the top 2 rows of the dataframe (`df.head(2)`) and the bottom 2 rows (`df.tail(2)`), we can see that the data returned is sorted by type (UTZ/WTZ) and not by date. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.head(2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.tail(2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Separate UTZ and WTZ data into different dataframes\n<br>\nBy separating into two distinct dataframes using the `type` column we can then separate out the UTZ and the WTZ values.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dfw = df[df['type']=='WTZ']\ndfu = df[df['type']=='UTZ']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Basic visualization\n<br>\nAs the two datatypes (UTZ and WTZ) have now been separated, we can plot them with different colours. This is similar to the plot above, but now it is possible to see the low rate and the high rate data and how they fit together.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15,5))\nax.plot(dfw['value'], color='#41b0f0', label='low rate (15 mins)')\nax.plot(dfw['value'], color='blue', marker='.', linestyle='None', label='low rate (15 mins)')\nax.plot(dfu['value'], color='#f07b41', marker='.', linestyle='None', label='high rate (15 secs)')\n \n#stop exponential format for y-axis label\nax.ticklabel_format(axis='y', useOffset=False, style='plain')\n\nplt.legend(loc='best')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 4. Building a Query for the latest data\n\nThis query returns the observations of the specified data held in TILDE. The query is `https://tilde.geonet.org.nz/v1/data/`.\n\nThe minimum required parameters are:\n- domain = `dart`\n- key = `NZE/water-height/40/WTZ`, this is 15 minute sampled data\n- startdate = 'latest'\n- enddate = '30d'\n\nWe will begin by following similar steps that we have followed previously by, changing the URL with the new parameters, quering the URL and asking for the CSV format to be returned. This request will return data in a CSV format for the last 30 days.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"url = source+'/v1/data/dart/NZE/water-height/40/WTZ/latest/30d'\n\nr = requests.get(url, headers={'Accept':'text/csv'})\n\ndf = pd.read_csv(StringIO(r.text),parse_dates=['time'], index_col='time')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can see in the tail of the dataframe that we have the `latest` or most recent data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.tail()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Data volume\n<br>\nBy using `len(df.index)` we can easily generate a row count of the dataframe. This could be useful to see how many values we received in a certain period of time for a station. As we are looking at the low rate data, this is likely to be quite predictable, as this is the data that we regularly receive, however, for the high rate (triggered) data we would likely expect much fewer values, unless there has been a lot of recent activity. In this case, for the last 30 days we have received nearly 3000 observations of low rate data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"len(df.index)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Basic visualization of the data \n<br>\nPlotting the low rate data over the 30 day period allows us to visualise the different tidal periods. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15,5))\ndf['value'].plot(ax=ax, color='#41b0f0', label='low rate (15 mins)')\n \n#stop exponential format for y-axis label\nax.ticklabel_format(axis='y', useOffset=False, style='plain')\n\nplt.legend(loc='best')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 5. Building a query for aggregated data\n<br>\nWhen requesting a large amount of data over a long time period, the query can be optimized for quick visualisation using the optional `aggregationPeriod`and `aggregationFunction` parameters. We will use the same example as above, but for a 8 month range (2021-01-01 to 2021-08-31) and use an aggregation period of 1 day to return a daily average of the values. Notice that, due to the aggregation, our dataframe's index column has time values 00:00:00.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"url = source+'/v1/data/dart/NZE/water-height/-/-/2021-01-01/2021-08-31?aggregationPeriod=1d&aggregationFunction=avg'\n\nr = requests.get(url, headers={'Accept':'text/csv'})\ndf = pd.read_csv(StringIO(r.text),parse_dates=['time'], index_col='time')\ndf.tail(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15,5))\ndf['value'].plot(ax=ax, color='#41b0f0', label='low rate (15 mins)')\n \nax.ticklabel_format(axis='y', useOffset=False, style='plain')\n\nplt.legend(loc='best')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 6. Getting the data using ObsPy\n\nObsPy (https://github.com/obspy/obspy/wiki) is a python module used for analysis of seismological data.\n\nBy getting the data into ObsPy we can use all of the functionality that comes with it. To enable us to do this, we will use the TSPAIR format. More information on this can be found here: https://docs.obspy.org/packages/autogen/obspy.io.ascii.core._write_tspair.html\n\nTo begin, we will create a dataframe column that is formatted as needed. A change of formatting is required for the time series file as obspy modules can't read it as it is, so we will change the format to be like this: YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS ('%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S'). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#importing the obspy read module\nfrom obspy import read\n\nurl = source+'/v1/data/dart/NZE/water-height/40/WTZ/latest/30d'\nr = requests.get(url, headers={'Accept':'text/csv'})\ndf = pd.read_csv(StringIO(r.text),parse_dates=['time'], index_col='time')\n\ndf['tseries'] = df.index.strftime('%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S')\n#print(df['tseries'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next we need to generate a header for the time-series file, where we specify a few parameters. This is required so that ObsPy can read the file, and has important data such as the sampling rate.\n\nTSPAIR is a simple ASCII time series format. Each continuous time series segment (no gaps or overlaps) is represented with a header line followed by data samples in time-sample pairs. There are no restrictions on how the segments are organized into files, a file might contain a single segment or many, concatenated segments either for the same channel or many different channels.\n\nHeader lines have the general form: TIMESERIES SourceName, # samples, # sps, Time, Format, Type, Units.\nThe sourcename should be of the format `Net_Sta_Loc_Chan_Qual`, so for NZE this is `NZ_NZE_40_WTZ_R`. For the number of samples, we can use `len(df.index)` as we used above. For number of samples per second, as we are using low rate data (WTZ) this would be 15 minutes or 0.0011111 samples per second. For time, we are using the time dataframe column that we generated above. The format is TSPAIR, the datatype is a float and the units are in `mm`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sourcename = 'NZ_NZE_40_WTZ_R'\nsamples = len(df.index)\nsps = 0.0011111111111111111\ntime = df['tseries'][0]\ndformat = 'TSPAIR'\ndtype = 'FLOAT'\nunits = 'mm'\n\nheaderstr = 'TIMESERIES '+sourcename+', '+str(samples)+' samples, '+str(sps)+' sps, '+time+', TSPAIR, FLOAT, mm\\n'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"First we open a new file called tspair.dat, then we write the appropriate header string and then using `df.to_csv` we can write the time-series data to the same file. Finally, we close the file.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"f = open('tspair.dat', 'w')\nf.write(headerstr)\ndf.to_csv(f, columns=['tseries', 'value'], sep=' ', index=False, header=False, mode='a')\nf.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can now read the file `tspair.dat`as an Obspy stream using `read()`, where the file format is TSPAIR as specified when we generated the header string.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"st = read('tspair.dat', format='TSPAIR')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"From this string we can then pull out the first trace (`tr`) of the stream and print it's statistics. These statistics are generated from the header string that we made beforehand and is why it is important that those details are correct.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tr=st[0]\ntr.stats",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As a final step, we can also plot this trace and see how it compares to the waveform that we generated at the end of Section 4.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tr.plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
cbe9fc7b4e02d1bc5106365e95aaa04cc2ab43dd
| 24,985 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
community/aqua/artificial_intelligence/qsvm_variational.ipynb
|
Chibikuri/qiskit-tutorials
|
15c121b95249de17e311c869fbc455210b2fcf5e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2017-11-09T16:33:14.000Z
|
2018-02-26T00:42:17.000Z
|
community/aqua/artificial_intelligence/qsvm_variational.ipynb
|
Chibikuri/qiskit-tutorials
|
15c121b95249de17e311c869fbc455210b2fcf5e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2019-04-12T07:43:25.000Z
|
2020-02-07T13:32:18.000Z
|
community/aqua/artificial_intelligence/qsvm_variational.ipynb
|
Chibikuri/qiskit-tutorials
|
15c121b95249de17e311c869fbc455210b2fcf5e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2019-03-24T21:00:25.000Z
|
2019-03-24T21:57:10.000Z
| 90.198556 | 8,372 | 0.839384 |
[
[
[
"## _*Quantum SVM (variational method)*_\n\nThe QSVMKernel notebook here demonstrates a kernel based approach. This notebook shows a variational method.\n\nFor further information please see: [https://arxiv.org/pdf/1804.11326.pdf](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1804.11326.pdf)\n\n\n**This notebook shows the SVM implementation based on the variational method.**\n\nIn this file, we show two ways for using the quantum variational method: (1) the non-programming way and (2) the programming way. \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Part I: non-programming way.\nIn the non-programming way, we config a json-like configuration, which defines how the svm instance is internally constructed. After the execution, it returns the json-like output, which carries the important information (e.g., the details of the svm instance) and the processed results. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from datasets import *\nfrom qiskit_aqua.utils import split_dataset_to_data_and_labels, map_label_to_class_name\nfrom qiskit import Aer\nfrom qiskit_aqua.input import SVMInput\nfrom qiskit_aqua import run_algorithm, QuantumInstance\nfrom qiskit_aqua.algorithms import QSVMVariational\nfrom qiskit_aqua.components.optimizers import SPSA\nfrom qiskit_aqua.components.feature_maps import SecondOrderExpansion\nfrom qiskit_aqua.components.variational_forms import RYRZ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"First we prepare the dataset, which is used for training, testing and the finally prediction.\n\n*Note: You can easily switch to a different dataset, such as the Breast Cancer dataset, by replacing 'ad_hoc_data' to 'Breast_cancer' below.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"feature_dim = 2 # dimension of each data point\ntraining_dataset_size = 20\ntesting_dataset_size = 10\nrandom_seed = 10598\nshots = 1024\n\nsample_Total, training_input, test_input, class_labels = ad_hoc_data(training_size=training_dataset_size, \n test_size=testing_dataset_size, \n n=feature_dim, gap=0.3, PLOT_DATA=True)\n\ndatapoints, class_to_label = split_dataset_to_data_and_labels(test_input)\nprint(class_to_label)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we create the svm in the non-programming way.\nIn the following json, we config:\n- the algorithm name \n- the variational form\n- the feature map \n- the optimizer",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"params = {\n 'problem': {'name': 'svm_classification', 'random_seed': 10598},\n 'algorithm': {'name': 'QSVM.Variational', 'override_SPSA_params': True},\n 'backend': {'shots': 1024},\n 'optimizer': {'name': 'SPSA', 'max_trials': 200, 'save_steps': 1},\n 'variational_form': {'name': 'RYRZ', 'depth': 3},\n 'feature_map': {'name': 'SecondOrderExpansion', 'depth': 2}\n}\n\nsvm_input = SVMInput(training_input, test_input, datapoints[0])\nbackend = Aer.get_backend('qasm_simulator')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"With everything setup, we can now run the algorithm.\n\nFor the testing, the result includes the details and the success ratio.\n\nFor the prediction, the result includes the predicted labels. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"result = run_algorithm(params, svm_input, backend=backend)\nprint(\"testing success ratio: \", result['testing_accuracy'])\nprint(\"predicted classes:\", result['predicted_classes'])",
"testing success ratio: 1.0\npredicted classes: ['A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B']\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Part II: programming way.\nWe construct the svm instance directly from the classes. The programming way offers the users better accessibility, e.g., the users can access the internal state of svm instance or invoke the methods of the instance. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now we create the svm in the programming way.\n- we build the optimizer instance (required by the svm instance) by instantiating the class SPSA.\n- We build the feature map instance (required by the svm instance) by instantiating the class SecondOrderExpansion.\n- We build the varitional form instance (required by the svm instance) by instantiating the class RYRZ.\n- We build the svm instance by instantiating the class QSVMVariational. \n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"backend = Aer.get_backend('qasm_simulator')\noptimizer = SPSA(max_trials=100, c0=4.0, skip_calibration=True)\noptimizer.set_options(save_steps=1)\nfeature_map = SecondOrderExpansion(num_qubits=feature_dim, depth=2)\nvar_form = RYRZ(num_qubits=feature_dim, depth=3)\nsvm = QSVMVariational(optimizer, feature_map, var_form, training_input, test_input)\nquantum_instance = QuantumInstance(backend, shots=shots, seed=random_seed, seed_mapper=random_seed)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we run it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"result = svm.run(quantum_instance)\nprint(\"testing success ratio: \", result['testing_accuracy'])",
"testing success ratio: 1.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"Different from the non-programming way, the programming way allows the users to invoke APIs upon the svm instance directly. In the following, we invoke the API \"predict\" upon the trained svm instance to predict the labels for the newly provided data input.\n\nUse the trained model to evaluate data directly, and we store a label_to_class and class_to_label for helping converting between label and class name",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"predicted_probs, predicted_labels = svm.predict(datapoints[0])\npredicted_classes = map_label_to_class_name(predicted_labels, svm.label_to_class)\nprint(\"prediction: {}\".format(predicted_labels))",
"prediction: [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1]\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
cbea0e721d7cd12132c669ea5c9c5c88ee5697c9
| 806,867 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
25_03_22_BERT.ipynb
|
LanglangFan979/Text_Summarisation_SNLP
|
d4ad84addc73d9b6ccb3926cf550f1f0d4bfb530
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
25_03_22_BERT.ipynb
|
LanglangFan979/Text_Summarisation_SNLP
|
d4ad84addc73d9b6ccb3926cf550f1f0d4bfb530
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
25_03_22_BERT.ipynb
|
LanglangFan979/Text_Summarisation_SNLP
|
d4ad84addc73d9b6ccb3926cf550f1f0d4bfb530
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 55.046186 | 509 | 0.579599 |
[
[
[
"from google.colab import drive\ndrive.mount('/content/gdrive', force_remount=True)",
"Mounted at /content/gdrive\n"
],
[
"# !pip install torch==1.6.0+cpu torchvision==0.7.0+cpu -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html\n# !pip install transformers==2.2.0\n# !pip install bert-extractive-summarizer\n# !pip install spacy==2.0.12",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!pip install -q bert-extractive-summarizer\n!pip install -q spacy==2.1.3\n!pip install -q transformers==2.2.2\n!pip install -q neuralcoref",
"\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 3.8 MB 5.4 MB/s \n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 6.5 MB 33.6 MB/s \n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 596 kB 49.8 MB/s \n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 895 kB 47.9 MB/s \n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 67 kB 5.0 MB/s \n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 27.7 MB 1.3 MB/s \n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 82 kB 389 kB/s \n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 3.2 MB 34.4 MB/s \n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 2.1 MB 33.8 MB/s \n\u001b[31mERROR: pip's dependency resolver does not currently take into account all the packages that are installed. This behaviour is the source of the following dependency conflicts.\nnbclient 0.5.13 requires jupyter-client>=6.1.5, but you have jupyter-client 5.3.5 which is incompatible.\nen-core-web-sm 2.2.5 requires spacy>=2.2.2, but you have spacy 2.1.3 which is incompatible.\naltair 4.2.0 requires jsonschema>=3.0, but you have jsonschema 2.6.0 which is incompatible.\u001b[0m\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 387 kB 4.3 MB/s \n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 1.2 MB 47.1 MB/s \n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 132 kB 47.8 MB/s \n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 79 kB 8.3 MB/s \n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 8.6 MB 34.6 MB/s \n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 138 kB 53.9 MB/s \n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 127 kB 44.9 MB/s \n\u001b[31mERROR: pip's dependency resolver does not currently take into account all the packages that are installed. This behaviour is the source of the following dependency conflicts.\ndatascience 0.10.6 requires folium==0.2.1, but you have folium 0.8.3 which is incompatible.\u001b[0m\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 286 kB 4.3 MB/s \n\u001b[?25h"
],
[
"!pip install torch==1.6.0+cpu torchvision==0.7.0+cpu -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html\n!pip install bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0\nimport torch\nfrom summarizer import Summarizer",
"Looking in links: https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html\nCollecting torch==1.6.0+cpu\n Downloading https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu/torch-1.6.0%2Bcpu-cp37-cp37m-linux_x86_64.whl (154.6 MB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 154.6 MB 38 kB/s \n\u001b[?25hCollecting torchvision==0.7.0+cpu\n Downloading https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu/torchvision-0.7.0%2Bcpu-cp37-cp37m-linux_x86_64.whl (5.1 MB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 5.1 MB 806 kB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: future in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from torch==1.6.0+cpu) (0.16.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from torch==1.6.0+cpu) (1.21.5)\nRequirement already satisfied: pillow>=4.1.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from torchvision==0.7.0+cpu) (7.1.2)\nInstalling collected packages: torch, torchvision\n Attempting uninstall: torch\n Found existing installation: torch 1.10.0+cu111\n Uninstalling torch-1.10.0+cu111:\n Successfully uninstalled torch-1.10.0+cu111\n Attempting uninstall: torchvision\n Found existing installation: torchvision 0.11.1+cu111\n Uninstalling torchvision-0.11.1+cu111:\n Successfully uninstalled torchvision-0.11.1+cu111\n\u001b[31mERROR: pip's dependency resolver does not currently take into account all the packages that are installed. This behaviour is the source of the following dependency conflicts.\ntorchtext 0.11.0 requires torch==1.10.0, but you have torch 1.6.0+cpu which is incompatible.\ntorchaudio 0.10.0+cu111 requires torch==1.10.0, but you have torch 1.6.0+cpu which is incompatible.\u001b[0m\nSuccessfully installed torch-1.6.0+cpu torchvision-0.7.0+cpu\nCollecting bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0\n Downloading bert-extractive-summarizer-0.5.0.tar.gz (11 kB)\nRequirement already satisfied: transformers in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (2.2.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: scikit-learn in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (1.0.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: spacy in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (2.1.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: threadpoolctl>=2.0.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from scikit-learn->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (3.1.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: joblib>=0.11 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from scikit-learn->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (1.1.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: scipy>=1.1.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from scikit-learn->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (1.4.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy>=1.14.6 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from scikit-learn->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (1.21.5)\nRequirement already satisfied: murmurhash<1.1.0,>=0.28.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from spacy->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (1.0.6)\nRequirement already satisfied: cymem<2.1.0,>=2.0.2 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from spacy->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (2.0.6)\nRequirement already satisfied: blis<0.3.0,>=0.2.2 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from spacy->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (0.2.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: jsonschema<3.0.0,>=2.6.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from spacy->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (2.6.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: wasabi<1.1.0,>=0.2.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from spacy->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (0.9.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: srsly<1.1.0,>=0.0.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from spacy->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (1.0.5)\nRequirement already satisfied: thinc<7.1.0,>=7.0.2 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from spacy->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (7.0.8)\nRequirement already satisfied: preshed<2.1.0,>=2.0.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from spacy->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (2.0.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: plac<1.0.0,>=0.9.6 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from spacy->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (0.9.6)\nRequirement already satisfied: requests<3.0.0,>=2.13.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from spacy->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (2.23.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: idna<3,>=2.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from requests<3.0.0,>=2.13.0->spacy->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (2.10)\nRequirement already satisfied: chardet<4,>=3.0.2 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from requests<3.0.0,>=2.13.0->spacy->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (3.0.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: urllib3!=1.25.0,!=1.25.1,<1.26,>=1.21.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from requests<3.0.0,>=2.13.0->spacy->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (1.25.11)\nRequirement already satisfied: certifi>=2017.4.17 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from requests<3.0.0,>=2.13.0->spacy->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (2021.10.8)\nRequirement already satisfied: tqdm<5.0.0,>=4.10.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from thinc<7.1.0,>=7.0.2->spacy->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (4.63.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: regex in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from transformers->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (2019.12.20)\nRequirement already satisfied: sentencepiece in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from transformers->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (0.1.96)\nRequirement already satisfied: sacremoses in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from transformers->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (0.0.49)\nRequirement already satisfied: boto3 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from transformers->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (1.21.29)\nRequirement already satisfied: s3transfer<0.6.0,>=0.5.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from boto3->transformers->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (0.5.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: botocore<1.25.0,>=1.24.29 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from boto3->transformers->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (1.24.29)\nRequirement already satisfied: jmespath<2.0.0,>=0.7.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from boto3->transformers->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (1.0.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: python-dateutil<3.0.0,>=2.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from botocore<1.25.0,>=1.24.29->boto3->transformers->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (2.8.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: six>=1.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from python-dateutil<3.0.0,>=2.1->botocore<1.25.0,>=1.24.29->boto3->transformers->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (1.15.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: click in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from sacremoses->transformers->bert-extractive-summarizer==0.5.0) (7.1.2)\nBuilding wheels for collected packages: bert-extractive-summarizer\n Building wheel for bert-extractive-summarizer (setup.py) ... \u001b[?25l\u001b[?25hdone\n Created wheel for bert-extractive-summarizer: filename=bert_extractive_summarizer-0.5.0-py3-none-any.whl size=16417 sha256=9ae948a4371e4e997f84b92dfc951811649444099eed14e678933107a7f9f77b\n Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/84/46/04/7fc092936deb2b62c6eb14c1b92d79059ca697be3d423232e1\nSuccessfully built bert-extractive-summarizer\nInstalling collected packages: bert-extractive-summarizer\n Attempting uninstall: bert-extractive-summarizer\n Found existing installation: bert-extractive-summarizer 0.10.1\n Uninstalling bert-extractive-summarizer-0.10.1:\n Successfully uninstalled bert-extractive-summarizer-0.10.1\nSuccessfully installed bert-extractive-summarizer-0.5.0\n"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\n# !pip install Summarizer\n# !pip install TransformerSummarizer\n# from summarizer import Summarizer\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!pip install torch",
"Requirement already satisfied: torch in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (1.6.0+cpu)\nRequirement already satisfied: future in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from torch) (0.16.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from torch) (1.21.5)\n"
],
[
"# load in WikiHow dataset \ndf = pd.read_csv('gdrive/MyDrive/SNLP_Coursework/WikiHow_sample_leq512.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from copy import copy \n\ndf[:2]\nmyText = df['text'][:]\n\ndf_results = copy(df)\ndf_results.head()\n# df_results.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# myText[:5]\nallText = []\n\nfor i, text in enumerate(myText):\n allText.append(text)\n\nprint(len(allText))",
"70473\n"
],
[
"df_results['train_length'] = 'empty'\ndf_results['summary'] = 'empty'\ndf_results['summary_length'] = 'empty'\ndf_results.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# print(allText[0])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\ndef preprocess(text):\n preprocess_text = text.strip().replace(\"\\n\",\"\")\n return len(preprocess_text.split())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model = Summarizer()\n# model = model.to('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else \"cpu\")\n# device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else \"cpu\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"allSummaries = []\n\nfor i, text in enumerate(allText):\n train_length = preprocess(text)\n # model(text)\n m = round(0.33 * train_length)\n summary = ''.join(model(text, max_length=m))\n allSummaries.append(summary)\n df_results['train_length'][i] = train_length\n df_results['summary'][i] = summary\n df_results['summary_length'][i] = len(summary.split())\n df_results.to_csv('gdrive/MyDrive/SNLP_Coursework/WikiHow_sample_leq512_results_BERT.csv')\n print('Processing', i, 'out of', len(allText))\n df_results.head()\n \n\n\n\n\n\n# model(allText[0])\n# bert_summary = ''.join(model(allText[0], min_length=60))\n# print(bert_summary)",
"/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:9: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n if __name__ == '__main__':\n/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:10: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n # Remove the CWD from sys.path while we load stuff.\n/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:11: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n # This is added back by InteractiveShellApp.init_path()\n"
],
[
"# print(len(bert_summary))\n# distilModel = Summarizer('distilbert-base-uncased')\n# distilModel(myText)\n# bert_distil_summary = ''.join(model(myText, min_length=60))\n# print(bert_distil_summary)\n# words = bert_summary.split()\n# print(words)\n\n# words2 = bert_distil_summary.split()\n# print(len(words2))\n# bert_distil_summary[:-1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_results.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbea1bf5540327a672b292c65fa6a79bc376fda4
| 10,512 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Python/lecture1_build_blockchain.ipynb
|
LaGauffre/BLOCKASTICS
|
4087304a4fb6fe55b5e8746315f524eddedc72e8
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null |
Python/lecture1_build_blockchain.ipynb
|
LaGauffre/BLOCKASTICS
|
4087304a4fb6fe55b5e8746315f524eddedc72e8
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null |
Python/lecture1_build_blockchain.ipynb
|
LaGauffre/BLOCKASTICS
|
4087304a4fb6fe55b5e8746315f524eddedc72e8
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | 1 |
2021-09-21T08:20:38.000Z
|
2021-09-21T08:20:38.000Z
| 31.00885 | 269 | 0.522736 |
[
[
[
"# Building a blockchain in python\n\nInspired from [Python Tutorial: Build A Blockchain In < 60 Lines of Code](https://medium.com/coinmonks/python-tutorial-build-a-blockchain-713c706f6531) and [Learn Blockchains by Building One](https://hackernoon.com/learn-blockchains-by-building-one-117428612f46).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import datetime\nimport hashlib\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## The SHA-256 function",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"hashlib.sha256(b\"Moritz Voss is the man\").hexdigest()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## The block class",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class Block:\n hash = None # Hash of the block info\n index = 0 # Index of the block inside the chain\n timestamp = datetime.datetime.now() # Time of creation of the block\n nonce = 0 # Solution to the cryptopuzzle\n transactions = [] # Transaction data\n mined = False # Boolean set to True whenever the problem has been solved\n previous_hash = 0x0 # Hash of the previous block\n \n\n def __init__(self, transactions):\n self.transactions = transactions\n self.timestamp = datetime.datetime.now()\n\n def hash(self):# Compute the hash of the blockdata\n h = hashlib.sha256()\n h.update(\n str(self.nonce).encode('utf-8') +\n str(self.transactions).encode('utf-8') +\n str(self.previous_hash).encode('utf-8') \n )\n return h.hexdigest()\n \n # Add a new transaction to a block\n def new_transaction(self, sender, recipient, amount, fee):\n transaction = {\n 'sender': sender,\n 'recipient': recipient,\n 'amount': amount,\n 'fee' : fee\n }\n self.transactions.append(transaction)\n \n # Print the block info\n def __str__(self):\n return \"Block Height: \" + str(self.index) + \\\n \"\\nBlock Hash: \" + str(self.hash()) + \\\n \"\\nTime:\" + str(self.timestamp) + \\\n \"\\nBlock data: \" + str(self.transactions) + \\\n \"\\nMined: \" + str(self.mined) + \\\n \"\\nPrevious block hash: \" + str(self.previous_hash) +\"\\n--------------\"\n \n # Solve the cryptopuzzle of the block\n \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"B1 = Block([])\nB1.new_transaction(\"Coinbase\", \"Satoshi\", 100, 0)\nB1.new_transaction(\"Satoshi\", \"Pierre-O\", 5, 2)\nprint(B1)\n",
"Block Height: 0\nBlock Hash: 99f27c54043f4464a1f7a2ef0960a68c4ad07f3f0b863c57023b5a19efdf9a7c\nTime:2022-03-29 12:54:45.349994\nBlock data: [{'sender': 'Coinbase', 'recipient': 'Satoshi', 'amount': 100, 'fee': 0}, {'sender': 'Satoshi', 'recipient': 'Pierre-O', 'amount': 5, 'fee': 2}]\nMined: False\nPrevious block hash: 0\n--------------\n"
]
],
[
[
"## The blockchain class",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class Blockchain:\n diff = 0\n maxNonce = 2**32\n target = 2 ** (256-diff)\n reward = 50\n miner = \"Miner\"\n\n def __init__(self, genesis_block):\n self.chain = [genesis_block]\n self.pending_transactions = []\n \n def new_transaction(self, sender, recipient, amount, fee):\n transaction = {\n 'sender': sender,\n 'recipient': recipient,\n 'amount': amount,\n 'fee' : fee\n }\n self.pending_transactions.append(transaction) \n \n def add_block(self):\n# blockchain.pending_transactions\n current_block = blockchain.chain[-1]\n new_block = Block(blockchain.pending_transactions)\n new_block.index = current_block.index + 1\n new_block.previous_hash = current_block.hash()\n blockchain.chain.append(new_block)\n blockchain.pending_transactions = []\n \n def adjust_difficulty(self, new_diff):\n self.diff = new_diff\n self.target = 2 ** (256-new_diff)\n \n def halve_reward(self):\n self.reward = self.reward / 2\n \n def mine(self):\n block = self.chain[-1]\n target = self.target\n\n if block.transactions:\n fee = pd.DataFrame.from_records(block.transactions).fee.sum()\n else:\n fee = 0\n\n block.new_transaction(\"Coinbase\", self.miner, self.reward + fee, 0)\n while int(block.hash(), 16) > target:\n block.nonce = int(np.random.uniform(low = 0, high = 2**32 + 1))\n block.mined = True\n block.timestamp = datetime.datetime.now() \n \n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"genesis_block = Block([])\nblockchain = Blockchain(genesis_block)\nprint(blockchain.chain[-1])\nblockchain.adjust_difficulty(4)\nblockchain.halve_reward()\nblockchain.mine()\nprint(blockchain.chain[-1])",
"Block Height: 0\nBlock Hash: 32369d15916932bd1ade51c0cae9f32f5ded2cccd29d81d7eec27066c813e39d\nTime:2022-03-29 12:55:11.282139\nBlock data: []\nMined: False\nPrevious block hash: 0\n--------------\nBlock Height: 0\nBlock Hash: 0b03580f3162787757b84eeabde2b84624ab17ce0f2f8808a05e76877c359d07\nTime:2022-03-29 12:55:11.293743\nBlock data: [{'sender': 'Coinbase', 'recipient': 'Miner', 'amount': 25.0, 'fee': 0}]\nMined: True\nPrevious block hash: 0\n--------------\n"
],
[
"blockchain.new_transaction(\"miner\", \"Pierre-O\", 5, 0.1)\nblockchain.new_transaction(\"miner\", \"Satoshi\", 10, 0.2)\n# print(blockchain.pending_transactions)\nblockchain.add_block()\nfor block in blockchain.chain: \n print(block)",
"Block Height: 0\nBlock Hash: 000001fd671de3565b24871ed04da99b9b96a3bcd606df4d81c7d9e132e66677\nTime:2021-10-01 10:52:33.373224\nBlock data: [{'sender': 'Coinbase', 'recipient': 'Miner', 'amount': 25.0, 'fee': 0}]\nMined: True\nPrevious block hash: 0\n--------------\nBlock Height: 1\nBlock Hash: 7e12cf61f2d25499ad65610b9a713f922e8ec0a4704819acc7acf713094cd488\nTime:2021-10-01 10:53:01.662940\nBlock data: [{'sender': 'miner', 'recipient': 'Pierre-O', 'amount': 5, 'fee': 0.1}, {'sender': 'miner', 'recipient': 'Satoshi', 'amount': 10, 'fee': 0.2}]\nMined: False\nPrevious block hash: 000001fd671de3565b24871ed04da99b9b96a3bcd606df4d81c7d9e132e66677\n--------------\n"
],
[
"blockchain.mine()\nfor block in blockchain.chain: \n print(block)",
"Block Height: 0\nBlock Hash: 000001fd671de3565b24871ed04da99b9b96a3bcd606df4d81c7d9e132e66677\nTime:2021-10-01 10:52:33.373224\nBlock data: [{'sender': 'Coinbase', 'recipient': 'Miner', 'amount': 25.0, 'fee': 0}]\nMined: True\nPrevious block hash: 0\n--------------\nBlock Height: 1\nBlock Hash: 00000e607b0174d7e7222790db52817e09a147fdb875b12fb45ba454881ae8d2\nTime:2021-10-01 10:53:30.162343\nBlock data: [{'sender': 'miner', 'recipient': 'Pierre-O', 'amount': 5, 'fee': 0.1}, {'sender': 'miner', 'recipient': 'Satoshi', 'amount': 10, 'fee': 0.2}, {'sender': 'Coinbase', 'recipient': 'Miner', 'amount': 25.3, 'fee': 0}]\nMined: True\nPrevious block hash: 000001fd671de3565b24871ed04da99b9b96a3bcd606df4d81c7d9e132e66677\n--------------\n"
],
[
"\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
cbea31f76c54a54fdbec782c96c36c7d18cb6205
| 768,495 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
.ipynb_checkpoints/COVID-19 Risk Estimation using AutomaticAI-checkpoint.ipynb
|
CzakoZoltan08/COVID-19-patient-filtering-using-AutomaticAI
|
87c4cb1d2848a0258b0b6d652316cb69de382ff0
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-07-26T19:42:50.000Z
|
2021-07-26T19:42:50.000Z
|
COVID-19 Risk Estimation using AutomaticAI.ipynb
|
CzakoZoltan08/COVID-19-patient-filtering-using-AutomaticAI
|
87c4cb1d2848a0258b0b6d652316cb69de382ff0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
COVID-19 Risk Estimation using AutomaticAI.ipynb
|
CzakoZoltan08/COVID-19-patient-filtering-using-AutomaticAI
|
87c4cb1d2848a0258b0b6d652316cb69de382ff0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 64.611989 | 75,668 | 0.631986 |
[
[
[
"import xai\n\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sn\n\nfrom sklearn import preprocessing\nfrom sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.metrics import f1_score, confusion_matrix, precision_score, recall_score, roc_curve, auc, accuracy_score\n\nfrom AutoAIAlgorithm.ParticleSwarmOptimization import PSO",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.read_csv(\"data/covid-19.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"columns_to_delete = ['Patient ID', 'Patient addmited to semi-intensive unit (1=yes, 0=no)',\n 'Patient addmited to intensive care unit (1=yes, 0=no)',\n 'Patient addmited to regular ward (1=yes, 0=no)', \n 'Metapneumovirus', 'Respiratory Syncytial Virus', 'Influenza A', \n 'Influenza B', 'Parainfluenza 1', 'CoronavirusNL63', 'Rhinovirus/Enterovirus', \n 'Mycoplasma pneumoniae', 'Coronavirus HKU1', 'Parainfluenza 3', 'Chlamydophila pneumoniae', \n 'Adenovirus', 'Parainfluenza 4', 'Coronavirus229E', 'CoronavirusOC43', 'Inf A H1N1 2009',\n 'Bordetella pertussis', 'Metapneumovirus', 'Parainfluenza 2', 'Influenza B, rapid test',\n 'Influenza A, rapid test', 'Strepto A']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = df.drop(columns_to_delete, axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_no_nan = df.dropna(subset=['Hematocrit'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_clean = df_no_nan.loc[:, df_no_nan.isnull().mean() < 0.7]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_clean",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ims = xai.imbalance_plot(df_clean, \"SARS-Cov-2 exam result\")",
"WARNING:root:No categorical_cols passed so inferred using np.object, np.int8 and np.bool: Index(['SARS-Cov-2 exam result'], dtype='object'). If you see an error these are not correct, please provide them as a string array as: categorical_cols=['col1', 'col2', ...]\n"
],
[
"bal_df = xai.balance(df_clean, \"SARS-Cov-2 exam result\", upsample=0.4)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y = np.asarray(bal_df['SARS-Cov-2 exam result'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y = [1 if x == 'positive' else 0 for x in y]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X = bal_df.drop(['SARS-Cov-2 exam result'], axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"imputer = SimpleImputer(missing_values=np.nan, strategy='mean')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"idf = pd.DataFrame(imputer.fit_transform(X))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"idf.columns=X.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"idf.index=X.index",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X = idf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"num_particles=10\nnum_iterations=10\n\npso = PSO(particle_count=num_particles, distance_between_initial_particles=1.0, evaluation_metric=f1_score)\n\nbest_metric, best_model = pso.fit(X_train=x_train,\n X_test=x_test,\n Y_train=y_train,\n Y_test=y_test,\n maxiter=num_iterations,\n verbose=True,\n max_distance=0.05)",
"--- START EPOCH 0 ---\n* Parameter=C Value=0.18396975452910314 *\n* Parameter=tol Value=1.7382526766676483 *\n* Parameter=intercept_scaling Value=0.8953615999445083 *\n* Parameter=solver Value=sag *\n* Particle 0 Algorithm Type LOGISTIC_REGRESSION: personal best metric=0.6428571428571428 *\n* Parameter=C Value=1.2066142091485794 *\n* Parameter=tol Value=0.22429065510927776 *\n* Parameter=intercept_scaling Value=0.10245159567092944 *\n* Parameter=solver Value=sag *\n* Particle 1 Algorithm Type LOGISTIC_REGRESSION: personal best metric=0.6370370370370371 *\n* Parameter=C Value=1.0236071241837184 *\n* Parameter=tol Value=0.43893454007444516 *\n* Parameter=intercept_scaling Value=0.03881821535676816 *\n* Parameter=solver Value=newton-cg *\n* Particle 2 Algorithm Type LOGISTIC_REGRESSION: personal best metric=0.7346938775510204 *\n* Parameter=C Value=2.3023509081526674 *\n* Parameter=tol Value=0.5798743526153126 *\n* Parameter=intercept_scaling Value=0.5959082521208039 *\n* Parameter=solver Value=sag *\n* Particle 3 Algorithm Type LOGISTIC_REGRESSION: personal best metric=0.6582278481012658 *\n* Parameter=C Value=0.6964182642810155 *\n* Parameter=tol Value=0.60961781862508 *\n* Parameter=intercept_scaling Value=0.3189723589027618 *\n* Parameter=solver Value=lbfgs *\n* Particle 4 Algorithm Type LOGISTIC_REGRESSION: personal best metric=0.7346938775510204 *\n* Parameter=C Value=1.8870311662209376 *\n* Parameter=tol Value=1.1803311275996105 *\n* Parameter=intercept_scaling Value=0.5778914630667819 *\n* Parameter=solver Value=newton-cg *\n* Particle 5 Algorithm Type LOGISTIC_REGRESSION: personal best metric=0.7397260273972602 *\n* Parameter=C Value=2.531797621735333 *\n* Parameter=tol Value=0.4742094712887376 *\n* Parameter=intercept_scaling Value=0.6037589227413289 *\n* Parameter=solver Value=liblinear *\n* Particle 6 Algorithm Type LOGISTIC_REGRESSION: personal best metric=0.7189542483660131 *\n* Parameter=C Value=2.9575481143728926 *\n* Parameter=tol Value=1.8066473500835567 *\n* Parameter=intercept_scaling Value=0.7167838104323273 *\n* Parameter=solver Value=sag *\n* Particle 7 Algorithm Type LOGISTIC_REGRESSION: personal best metric=0.47540983606557385 *\n* Parameter=C Value=2.8738581300905675 *\n* Parameter=tol Value=0.6927674632818527 *\n* Parameter=intercept_scaling Value=0.5375249566663517 *\n* Parameter=solver Value=newton-cg *\n* Particle 8 Algorithm Type LOGISTIC_REGRESSION: personal best metric=0.7397260273972602 *\n* Parameter=C Value=0.13751613040554408 *\n* Parameter=tol Value=0.591787177539217 *\n* Parameter=intercept_scaling Value=0.6371781386429877 *\n* Parameter=solver Value=liblinear *\n* Particle 9 Algorithm Type LOGISTIC_REGRESSION: personal best metric=0.6832298136645962 *\n* Parameter=p Value=2 *\n* Parameter=n_neighbors Value=2 *\n* Parameter=leaf_size Value=53 *\n* Parameter=algorithm Value=brute *\n* Particle 10 Algorithm Type KNN: personal best metric=0.7155963302752293 *\n* Parameter=p Value=4 *\n* Parameter=n_neighbors Value=32 *\n* Parameter=leaf_size Value=34 *\n* Parameter=algorithm Value=brute *\n* Particle 11 Algorithm Type KNN: personal best metric=0.5576923076923077 *\n* Parameter=p Value=5 *\n* Parameter=n_neighbors Value=48 *\n* Parameter=leaf_size Value=21 *\n* Parameter=algorithm Value=brute *\n* Particle 12 Algorithm Type KNN: personal best metric=0.4086021505376343 *\n* Parameter=p Value=4 *\n* Parameter=n_neighbors Value=57 *\n* Parameter=leaf_size Value=73 *\n* Parameter=algorithm Value=kd_tree *\n* Particle 13 Algorithm Type KNN: personal best metric=0.46153846153846156 *\n* Parameter=p Value=2 *\n* Parameter=n_neighbors Value=53 *\n* Parameter=leaf_size Value=43 *\n* Parameter=algorithm Value=kd_tree *\n* Particle 14 Algorithm Type KNN: personal best metric=0.44943820224719105 *\n* Parameter=p Value=4 *\n* Parameter=n_neighbors Value=68 *\n* Parameter=leaf_size Value=82 *\n* Parameter=algorithm Value=brute *\n* Particle 15 Algorithm Type KNN: personal best metric=0.3764705882352941 *\n* Parameter=p Value=3 *\n* Parameter=n_neighbors Value=2 *\n* Parameter=leaf_size Value=14 *\n* Parameter=algorithm Value=brute *\n* Particle 16 Algorithm Type KNN: personal best metric=0.7102803738317757 *\n* Parameter=p Value=2 *\n* Parameter=n_neighbors Value=59 *\n* Parameter=leaf_size Value=79 *\n* Parameter=algorithm Value=ball_tree *\n* Particle 17 Algorithm Type KNN: personal best metric=0.45454545454545453 *\n* Parameter=p Value=5 *\n* Parameter=n_neighbors Value=66 *\n* Parameter=leaf_size Value=63 *\n* Parameter=algorithm Value=ball_tree *\n* Particle 18 Algorithm Type KNN: personal best metric=0.3953488372093023 *\n* Parameter=p Value=4 *\n* Parameter=n_neighbors Value=32 *\n* Parameter=leaf_size Value=15 *\n* Parameter=algorithm Value=auto *\n* Particle 19 Algorithm Type KNN: personal best metric=0.5576923076923077 *\n* Parameter=max_depth Value=13 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=18 *\n* Parameter=n_estimators Value=196 *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=gini *\n* Particle 20 Algorithm Type RANDOM FOREST: personal best metric=0.903225806451613 *\n* Parameter=max_depth Value=45 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=40 *\n* Parameter=n_estimators Value=213 *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=entropy *\n* Particle 21 Algorithm Type RANDOM FOREST: personal best metric=0.8270676691729323 *\n* Parameter=max_depth Value=83 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=43 *\n* Parameter=n_estimators Value=273 *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=gini *\n* Particle 22 Algorithm Type RANDOM FOREST: personal best metric=0.8661417322834646 *\n* Parameter=max_depth Value=55 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=71 *\n* Parameter=n_estimators Value=261 *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=entropy *\n* Particle 23 Algorithm Type RANDOM FOREST: personal best metric=0.8029197080291971 *\n* Parameter=max_depth Value=60 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=50 *\n* Parameter=n_estimators Value=287 *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=gini *\n* Particle 24 Algorithm Type RANDOM FOREST: personal best metric=0.8527131782945736 *\n* Parameter=max_depth Value=42 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=46 *\n* Parameter=n_estimators Value=120 *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=entropy *\n* Particle 25 Algorithm Type RANDOM FOREST: personal best metric=0.8270676691729323 *\n* Parameter=max_depth Value=74 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=13 *\n* Parameter=n_estimators Value=104 *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=entropy *\n* Particle 26 Algorithm Type RANDOM FOREST: personal best metric=0.8818897637795277 *\n* Parameter=max_depth Value=20 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=36 *\n* Parameter=n_estimators Value=219 *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=entropy *\n* Particle 27 Algorithm Type RANDOM FOREST: personal best metric=0.8396946564885496 *\n* Parameter=max_depth Value=62 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=15 *\n* Parameter=n_estimators Value=288 *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=gini *\n* Particle 28 Algorithm Type RANDOM FOREST: personal best metric=0.903225806451613 *\n* Parameter=max_depth Value=76 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=48 *\n* Parameter=n_estimators Value=16 *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=gini *\n* Particle 29 Algorithm Type RANDOM FOREST: personal best metric=0.8346456692913385 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.38437580035141083 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=104 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=96 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=best *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=gini *\n* Particle 30 Algorithm Type EXTRA TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.0 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.26064605679515407 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=147 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=2 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=random *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=gini *\n* Particle 31 Algorithm Type EXTRA TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.0 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.4503639459969029 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=125 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=64 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=best *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=entropy *\n* Particle 32 Algorithm Type EXTRA TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.0 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.46927733076642664 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=96 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=160 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=best *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=gini *\n* Particle 33 Algorithm Type EXTRA TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.0 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.06270643736387438 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=153 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=48 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=random *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=entropy *\n* Particle 34 Algorithm Type EXTRA TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.0 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.1584948816621755 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=55 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=28 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=best *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=gini *\n* Particle 35 Algorithm Type EXTRA TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.5970149253731344 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.487455755435778 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=117 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=68 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=random *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=gini *\n* Particle 36 Algorithm Type EXTRA TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.0 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.20455141166722512 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=30 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=52 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=random *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=entropy *\n* Particle 37 Algorithm Type EXTRA TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.0 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.36595210816606816 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=73 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=159 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=random *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=entropy *\n* Particle 38 Algorithm Type EXTRA TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.0 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.0418433036993584 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=169 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=50 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=best *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=entropy *\n* Particle 39 Algorithm Type EXTRA TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.55 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.31595396225553113 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=44 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=148 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=random *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=gini *\n* Particle 40 Algorithm Type DECISION TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.0 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.31859432270690524 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=86 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=106 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=random *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=gini *\n* Particle 41 Algorithm Type DECISION TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.0 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.21105765783893254 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=109 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=9 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=random *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=gini *\n* Particle 42 Algorithm Type DECISION TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.0 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.3883821101775102 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=63 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=158 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=best *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=entropy *\n* Particle 43 Algorithm Type DECISION TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.5853658536585367 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.22555347717503665 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=81 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=187 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=random *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=gini *\n* Particle 44 Algorithm Type DECISION TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.0 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.17127447767110238 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=127 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=114 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=random *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=entropy *\n* Particle 45 Algorithm Type DECISION TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.0 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.31374515866295416 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=24 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=9 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=random *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=entropy *\n* Particle 46 Algorithm Type DECISION TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.0 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.28771101759142936 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=31 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=36 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=best *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=gini *\n* Particle 47 Algorithm Type DECISION TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.5853658536585367 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.20889811182225881 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=66 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=80 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=best *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=entropy *\n* Particle 48 Algorithm Type DECISION TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.6206896551724138 *\n* Parameter=min_weight_fraction_leaf Value=0.2421982870650391 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_split Value=64 *\n* Parameter=min_samples_leaf Value=114 *\n* Parameter=splitter Value=random *\n* Parameter=criterion Value=entropy *\n* Particle 49 Algorithm Type DECISION TREE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.4220183486238532 *\n* Parameter=alpha Value=82.57907490182255 *\n* Parameter=tol Value=55.48507425015517 *\n* Parameter=normalize Value=False *\n* Parameter=fit_intercept Value=True *\n* Parameter=solver Value=lsqr *\n* Particle 50 Algorithm Type RIDGE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.4578313253012048 *\n* Parameter=alpha Value=79.4933810439695 *\n* Parameter=tol Value=37.69147689313977 *\n* Parameter=normalize Value=False *\n* Parameter=fit_intercept Value=True *\n* Parameter=solver Value=svd *\n* Particle 51 Algorithm Type RIDGE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.7114093959731544 *\n* Parameter=alpha Value=71.07459899925608 *\n* Parameter=tol Value=31.804705017305302 *\n* Parameter=normalize Value=False *\n* Parameter=fit_intercept Value=True *\n* Parameter=solver Value=lsqr *\n* Particle 52 Algorithm Type RIDGE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.4578313253012048 *\n* Parameter=alpha Value=76.5341193618104 *\n* Parameter=tol Value=23.502600375467154 *\n* Parameter=normalize Value=False *\n* Parameter=fit_intercept Value=True *\n* Parameter=solver Value=svd *\n* Particle 53 Algorithm Type RIDGE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.7114093959731544 *\n* Parameter=alpha Value=34.51496309945007 *\n* Parameter=tol Value=59.78878300707219 *\n* Parameter=normalize Value=False *\n* Parameter=fit_intercept Value=True *\n* Parameter=solver Value=lsqr *\n* Particle 54 Algorithm Type RIDGE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.4578313253012048 *\n* Parameter=alpha Value=2.58521131143875 *\n* Parameter=tol Value=87.87832879878718 *\n* Parameter=normalize Value=True *\n* Parameter=fit_intercept Value=True *\n* Parameter=solver Value=svd *\n* Particle 55 Algorithm Type RIDGE CLASSIFIER: personal best metric=0.7123287671232876 *\n* Parameter=alpha Value=5.411338223108509 *\n* Parameter=tol Value=17.52278997821334 *\n* Parameter=normalize Value=True *\n* Parameter=fit_intercept Value=True *\n* Parameter=solver Value=auto *\n"
],
[
"best_model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"best_metric",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_pred = best_model.predict(x_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import seaborn as sn\n\ndf_cm = pd.DataFrame(confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred), [\"negative\", \"positive\"], [\"negative\", \"positive\"])\n# plt.figure(figsize=(10,7))\nsn.set(font_scale=1.4) # for label size\nsn.heatmap(df_cm, annot=True, annot_kws={\"size\": 16}, cmap=\"Blues\", fmt='d') # font size\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"precision_score(y_test, y_pred)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"recall_score(y_test, y_pred)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"f1_score(y_test, y_pred)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y_test, y_pred)\nauc(fpr, tpr)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_avg(x, y):\n return f1_score(y, best_model.predict(x))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"imp = xai.feature_importance(x_test, y_test, get_avg)",
"C:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\nC:\\Users\\Zoltan\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\xai\\__init__.py:1127: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n x[c] = tmp\n"
],
[
"imp.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.