question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
largest-1-bordered-square
|
Solution Largest 1-Bordered Square
|
solution-largest-1-bordered-square-by-su-azww
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Suyono-Sukorame
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-17T20:51:55.489541+00:00
|
2024-03-17T20:51:55.489570+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n\n /**\n * @param Integer[][] $grid\n * @return Integer\n */\n function largest1BorderedSquare($grid) {\n $m = count($grid);\n $n = count($grid[0]);\n $maxSize = 0;\n \n $horizontal = array_fill(0, $m, array_fill(0, $n, 0));\n $vertical = array_fill(0, $m, array_fill(0, $n, 0));\n \n for ($i = 0; $i < $m; $i++) {\n for ($j = 0; $j < $n; $j++) {\n if ($grid[$i][$j] == 1) {\n $horizontal[$i][$j] = ($j == 0) ? 1 : $horizontal[$i][$j - 1] + 1;\n $vertical[$i][$j] = ($i == 0) ? 1 : $vertical[$i - 1][$j] + 1;\n }\n }\n }\n \n for ($i = 0; $i < $m; $i++) {\n for ($j = 0; $j < $n; $j++) {\n $size = min($horizontal[$i][$j], $vertical[$i][$j]);\n while ($size > $maxSize) {\n if ($horizontal[$i - $size + 1][$j] >= $size && $vertical[$i][$j - $size + 1] >= $size) {\n $maxSize = $size;\n }\n $size--;\n }\n }\n }\n \n return $maxSize * $maxSize;\n }\n}\n\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['PHP']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
Pre-Computation || Simple Solution || Commented
|
pre-computation-simple-solution-commente-l31i
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(mn) \n\n- Space complexity: O(mn) \n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int largest1BorderedSquare(vector<vector<int>>&
|
coder_rastogi_21
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-14T14:29:58.069706+00:00
|
2024-03-14T14:29:58.069739+00:00
| 201 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(m*n)$$ \n\n- Space complexity: $$O(m*n)$$ \n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int largest1BorderedSquare(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {\n int side = 0;\n vector<vector<int>> row = grid, col = grid;\n\n for(int i=0; i<grid.size(); i++) {\n for(int j=0; j<grid[0].size(); j++) {\n //compute row-wise and col-wise prefix sum\n if(grid[i][j] == 1) { \n row[i][j] = (j > 0) ? 1 + row[i][j-1] : 1;\n col[i][j] = (i > 0) ? 1 + col[i-1][j] : 1;\n }\n else { //if value in grid is 0, then its value in both row and col will be 0\n row[i][j] = 0;\n col[i][j] = 0;\n }\n }\n }\n for(int i=0; i<grid.size(); i++) {\n for(int j=0; j<grid[0].size(); j++) {\n int limit = min(row[i][j],col[i][j]);\n //check for all possibilities of making a square\n for(int mini=1; mini<=limit; mini++) {\n if(i-(mini-1) >= 0 && j-(mini-1) >= 0 && row[i-(mini-1)][j] >= mini && col[i][j-(mini-1)] >= mini) {\n side = max(side,mini); //update maximum possible side\n }\n }\n }\n }\n return side*side; //return it\'s area\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Prefix Sum', 'C++']
| 1 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
[Python3] Dynamic programming solution
|
python3-dynamic-programming-solution-by-3xpl9
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n> O(MN * min(M\N))\n- Space complexity:\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n)
|
pipilongstocking
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-27T00:12:47.648570+00:00
|
2024-02-27T00:12:47.648605+00:00
| 32 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n> O(M*N * min(M\\*N))\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n> O(M*N)\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def largest1BorderedSquare(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])\n Table = [[[0,0] for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(m)]\n ans = 0\n for i in range(m-1, -1, -1):\n for j in range(n-1, -1, -1):\n if grid[i][j]:\n Table[i][j][0] = 1 + (Table[i][j+1][0] if j+1<n and grid[i][j+1] else 0)\n Table[i][j][1] = 1 + (Table[i+1][j][1] if i+1<m and grid[i+1][j] else 0)\n for s in range(min(Table[i][j][0],Table[i][j][1]), -1 ,-1):\n if Table[i][j+s-1][1] >= s and Table[i+s-1][j][0] >= s:\n ans = max(ans, s)\n break\n return ans**2\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python3']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
solution using dp+tabulation
|
solution-using-dptabulation-by-shree_gov-7mic
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public int largest1BorderedSquare(int[][] grid) {\n if (grid == null || grid.length == 0)\n return 0;\n\n
|
Shree_Govind_Jee
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-23T05:54:24.187269+00:00
|
2024-01-23T05:54:24.187298+00:00
| 41 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int largest1BorderedSquare(int[][] grid) {\n if (grid == null || grid.length == 0)\n return 0;\n\n int[][][] dp = new int[grid.length + 1][grid[0].length + 1][2];\n int max = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {\n if (grid[i][j] == 1) {\n dp[i + 1][j + 1][0] = dp[i][j + 1][0] + 1;\n dp[i + 1][j + 1][1] = dp[i + 1][j][1] + 1;\n\n int l = Math.min(dp[i + 1][j + 1][0], dp[i + 1][j + 1][1]);\n for (int k = l; k > max; k--) {\n int len = Math.min(dp[i + 1 - k + 1][j + 1][1], dp[i + 1][j + 1 - k + 1][0]);\n if (len >= k) {\n max = Math.max(max, k);\n }\n }\n } else {\n dp[i + 1][j + 1][0] = 0;\n dp[i + 1][j + 1][1] = 0;\n }\n }\n }\n\n return max*max;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Matrix', 'Java']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
Java || Easy || loop through matrix
|
java-easy-loop-through-matrix-by-vsai512-337r
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(m * n)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity: O(m * n)\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n)
|
vsai5120
|
NORMAL
|
2023-12-31T13:08:22.592088+00:00
|
2023-12-31T13:08:22.592110+00:00
| 27 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(m * n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(m * n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int largest1BorderedSquare(int[][] grid) {\n int m = grid.length;\n int n = grid[0].length;\n int[][] ver = new int[m][n];\n int[][] hor = new int[m][n];\n int max = 0;\n\n\n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n if (grid[i][j] == 1) {\n hor[i][j] = j == 0 ? 1 : hor[i][j - 1] + 1;\n ver[i][j] = i == 0 ? 1 : ver[i - 1][j] + 1;\n }\n }\n }\n\n for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) {\n for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {\n int side = Math.min(hor[i][j], ver[i][j]);\n \n while (side > max) {\n if (ver[i][j - side + 1] >= side && hor[i - side + 1][j] >= side) {\n max = side;\n }\n side--;\n }\n }\n }\n\n return max * max;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Matrix', 'Java']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
Java || Easy || Traversal
|
java-easy-traversal-by-vsai5120-o7ae
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(m * n)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity: O(m * n)\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n)
|
vsai5120
|
NORMAL
|
2023-12-31T11:49:48.017707+00:00
|
2023-12-31T11:49:48.017736+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(m * n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(m * n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int largest1BorderedSquare(int[][] grid) {\n int m = grid.length;\n int n = grid[0].length;\n int[][] ver = new int[m][n];\n int[][] hor = new int[m][n];\n int max = 0;\n\n\n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n if (grid[i][j] == 1) {\n hor[i][j] = j == 0 ? 1 : hor[i][j - 1] + 1;\n ver[i][j] = i == 0 ? 1 : ver[i - 1][j] + 1;\n }\n }\n }\n\n for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) {\n for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {\n int side = Math.min(hor[i][j], ver[i][j]);\n \n while (side > max) {\n if (ver[i][j - side + 1] >= side && hor[i - side + 1][j] >= side) {\n max = side;\n }\n side--;\n }\n }\n }\n\n return max * max;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Matrix', 'Java']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
java simple solution commented step by step
|
java-simple-solution-commented-step-by-s-40su
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
trivedi_cs1
|
NORMAL
|
2023-12-29T14:38:45.302404+00:00
|
2023-12-29T14:38:45.302430+00:00
| 11 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public boolean check(int r,int c,int i,int j,int arr[][])\n {\n if(r>=arr.length||c>=arr[0].length)\n {\n return false;\n } \n // check col.. horizantal\n for(int k=j;k<=Math.min(c,arr[0].length-1);k++)\n {\n if(arr[i][k]==0)\n {\n return false;\n }\n }\n // check row vertical\n for(int k=i;k<=Math.min(r,arr.length-1);k++)\n {\n if(arr[k][j]==0)\n {\n return false;\n }\n }\n // check last row \n for(int k=j;k<=Math.min(c,arr[0].length-1);k++)\n {\n if(arr[r][k]==0)\n {\n return false;\n }\n }\n // check last col\n for(int k=i;k<=Math.min(r,arr.length-1);k++)\n {\n if(arr[k][c]==0)\n {\n return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n public int largest1BorderedSquare(int[][] grid) {\n int n=grid.length;\n int m=grid[0].length;\n int max=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++)\n {\n int curr_i=i;\n int curr_j=j;\n int ans=0;\n int next_i=curr_i;\n int next_j=curr_j;\n for(int k=0;k<grid.length;k++)\n {\n if(check(next_i,next_j,i,j,grid))\n {\n int area=k+1;\n max=Math.max(area*area,max);\n }\n next_i++;\n next_j++;\n } \n }\n } \n // System.out.println(max);\n return max; \n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
Largest 1-Bordered Square || JAVASCRIPT || Solution by Bharadwaj
|
largest-1-bordered-square-javascript-sol-r1t6
|
Approach\nDynamic Programming and Prefix Sum \n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(h^2 * w^2)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(h * w)\n\n# Code\n\nfunction largest1B
|
Manu-Bharadwaj-BN
|
NORMAL
|
2023-12-25T07:17:31.672641+00:00
|
2023-12-25T07:17:31.672659+00:00
| 94 | false |
# Approach\nDynamic Programming and Prefix Sum \n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(h^2 * w^2)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(h * w)\n\n# Code\n```\nfunction largest1BorderedSquare(grid) {\n // Initialize dimensions and result\n let h = grid.length, w = grid[0].length, res = 0;\n // Create DP arrays to store prefix sums of 1s in rows and columns\n let dp1 = new Array(h).fill(0).map(() => new Array(w).fill(0));\n let dp2 = new Array(h).fill(0).map(() => new Array(w).fill(0));\n // Calculate prefix sums for rows and columns\n for (let y = 0; y < h; y++) {\n for (let x = 0; x < w; x++) {\n dp1[y][x] = x > 0 ? (dp1[y][x - 1] + 1) * grid[y][x] : grid[y][0];\n dp2[y][x] = y > 0 ? (dp2[y - 1][x] + 1) * grid[y][x] : grid[0][x];\n }\n }\n // Iterate through potential square corners\n for (let y = 0; y < h; y++) {\n for (let x = 0; x < w; x++) {\n if (grid[y][x] === 1) {\n // Expand potential squares from the current corner\n let x2 = x, y2 = y;\n while (y2 < h && x2 < w) {\n // Check if current square is 1-bordered using prefix sums\n if (check(x, y, x2, y2)) {\n res = Math.max(res, (x2 - x + 1) * (y2 - y + 1));\n }\n x2++;\n y2++;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n return res;\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
O(n^3) tiny solution
|
on3-tiny-solution-by-yavinci-ymja
|
\nHow to avoid repetitive computations in 2d array? Usually, "prefix sum" and "dp". \n\nMaintain two 2d arrays for max "1-border" length ending in i and j respe
|
yavinci
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-05T00:49:00.461947+00:00
|
2023-11-05T00:50:26.888004+00:00
| 11 | false |
\nHow to avoid repetitive computations in 2d array? Usually, "prefix sum" and "dp". \n\nMaintain two 2d arrays for max "1-border" length ending in `i` and `j` respectively. At each `(i, j)`, try to form a "1-square-border". \n\nBased on the 2d arrays, we immediately form the lower border with length `row[i][j]` and right border with length `col[i][j]`. The square border length must be smaller than `len = min(row[i][j], col[i][j])`. To find the longest border length, for l = `len,..., 3, 2, 1`, see if the left and upper borders have length at least `l`.\n\nFinally return the longest border length. One for loop block is enough, as for each `i, j`, we have full informations for left and upper directions.\n\n```\n* row[][]: max len with 1 till i\n* col[][]: max len with 1 till j\n//\n// For l = 4, 3, 2, 1, see if the left and upper borders are valid.\n// 1 1 1 [1] (i, j - l + 1)\n//\n// 1 1\n// \n// 1 1\n//\n// [1] 1 1 [1] (i, j) \n//\uFF08i - l + 1, j) \n\n```\nCode is straightforward:\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int largest1BorderedSquare(int[][] grid) {\n int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;\n int[][] row = new int[m][n], col = new int[m][n];\n int res = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n if (grid[i][j] == 1) {\n row[i][j] = j >= 1 ? row[i][j - 1] + 1 : 1;\n col[i][j] = i >= 1 ? col[i - 1][j] + 1 : 1;\n }\n\n int len = Math.min(row[i][j], col[i][j]);\n for (int l = len; l >= 1; l--) {\n if (row[i - l + 1][j] >= l && col[i][j - l + 1] >= l) {\n res = Math.max(res, l * l);\n break;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
Java Solution DP
|
java-solution-dp-by-ndsjqwbbb-7p21
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
ndsjqwbbb
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-04T00:24:25.957358+00:00
|
2023-11-04T00:24:25.957376+00:00
| 19 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int largest1BorderedSquare(int[][] grid) {\n int m = grid.length;\n int n = grid[0].length;\n int[][] left_to_right = new int[m + 1][n + 1];\n int[][] top_to_bottom = new int[m + 1][n + 1];\n int result = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){\n if(grid[i][j] == 1){\n left_to_right[i + 1][j + 1] = left_to_right[i + 1][j] + 1;\n top_to_bottom[i + 1][j + 1] = top_to_bottom[i][j + 1] + 1;\n int length = Math.min(left_to_right[i + 1][j + 1], top_to_bottom[i + 1][j + 1]);\n for(; length >= 1; length--){\n if(left_to_right[i + 2 - length][j + 1] >= length && top_to_bottom[i + 1][j + 2 - length] >= length){\n result = Math.max(length, result);\n break;\n }\n } \n }\n }\n }\n return result * result;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
Java || DP || 5ms
|
java-dp-5ms-by-shuiyi-rx41
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nuse DP algorithm to solve the problem\n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving
|
shuiyi
|
NORMAL
|
2023-09-28T00:15:20.426258+00:00
|
2023-09-28T00:21:11.562969+00:00
| 22 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nuse DP algorithm to solve the problem\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. for the direction from right to left, create the 2D-array dp, dp1[r][i] represents that the number of continous 1s from right to the index i (must including [r][i]).\n2. for the direction from bottom to top, create the 2D-array dp, dp2[i][C] represents that the number of continous 1s from botoom to the index i (must including (i)[c])\n3. from above dp1 and dp2, it\'s easy to know the min number (minLen) of continous 1s from right to left and from bottom to top at index [r][c].\n4. check the index from (r + 0 to r + minLen - 1, and c + 0 to c + minLen -1), check at those index, if dp1 and dp2 equal or greaten than minLen, those if there exist square that all boards are 1s, count the elements of that square.\n5. compare the max and current elements, get max number of elements\n6. return the results\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(m*n*min(m,n)),\nmin(m,n) means the min number of coninuous 1s from every direction\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n*m)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int largest1BorderedSquare(int[][] grid) {\n boolean exist1s = false;\n for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i ++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j ++) {\n if (grid[i][j] == 1) {\n exist1s = true;\n break;\n }\n }\n }\n if (!exist1s) {\n return 0;\n }\n int row = grid.length;\n int col = grid[0].length;\n int max = 0;\n //check the continues 1s from right to left\n int[][] dp1 = new int[grid.length][grid[0].length];\n for (int i = 0; i < row; i ++) {\n dp1[i][col - 1] = grid[i][col - 1] == 1 ? 1 : 0; \n for(int j = col - 2; j >=0; j --) {\n if (grid[i][j] == 1) {\n dp1[i][j] = dp1[i][j + 1] + 1;\n } else {\n dp1[i][j] = 0;\n }\n }\n }\n //check the number of continue 1s from bottom to top\n int[][] dp2 = new int[row][col];\n for (int i = 0; i < col; i ++) {\n dp2[row -1][i] = grid[row - 1][i] == 1? 1: 0;\n for (int j = row - 2; j >=0; j --) {\n if(grid[j][i] == 1) {\n dp2[j][i] = dp2[j +1][i] + 1;\n } else {\n dp2[j][i] = 0;\n }\n }\n }\n\n for(int r = 0; r < row; r ++) {\n for (int c = 0; c < col; c ++) {\n if(grid[r][c] == 1) {\n int minLen = Math.min(dp1[r][c], dp2[r][c]);\n for (int k = minLen; k > 0; k --) {\n if(dp2[r][c + k -1] >= k && dp1[r + k - 1][c] >= k) {\n int count = k * k;\n max = Math.max(max,count);\n }\n }\n } \n }\n }\n return max;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
✅C++ O(n ^ 3)✅✅
|
c-on-3-by-jayesh_06-fber
|
AUTHOR: JAYESH BADGUJAR\n\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic: \n //dp_0[i][0]=horizontal\n //dp_0[i][1]=vertical\n bool isValid(int i,int j,int n,in
|
Jayesh_06
|
NORMAL
|
2023-09-01T07:28:17.219671+00:00
|
2023-09-01T07:28:17.219694+00:00
| 85 | false |
# AUTHOR: JAYESH BADGUJAR\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic: \n //dp_0[i][0]=horizontal\n //dp_0[i][1]=vertical\n bool isValid(int i,int j,int n,int m){\n if(i>=0 && i<n && j>=0 && j<m){\n return true;\n }\n return false;\n }\n int largest1BorderedSquare(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {\n int n=grid.size(),m=grid[0].size();\n vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(n,vector<vector<int>>(m,vector<int>(2,0)));\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n if(grid[i][0]==1){\n dp[i][0][0]=1;\n if(i>0){\n dp[i][0][1]=1+dp[i-1][0][1];\n }else{\n dp[i][0][1]=1;\n }\n }\n }\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n if(grid[0][i]==1){\n if(i>0){\n dp[0][i][0]=1+dp[0][i-1][0];\n }else{\n dp[0][i][0]=1;\n }\n dp[0][i][1]=1;\n }\n }\n \n for(int i=1;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=1;j<m;j++){\n if(grid[i][j]==1){\n dp[i][j][0]=1+dp[i][j-1][0];\n dp[i][j][1]=1+dp[i-1][j][1];\n \n }\n }\n }\n \n int maxi=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++){\n for(int k=0;k<min(n,m);k++){\n if(isValid(i-k,j,n,m) && isValid(i,j-k,n,m) && grid[i][j]==1){\n \n if(dp[i][j][0]>k && dp[i][j][1]>k && dp[i][j-k][1]>k && dp[i-k][j][0]>k){\n int size=(k+1)*(k+1);\n maxi=max(maxi,size);\n }\n }\n }\n }\n }\n return maxi;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
Ruby 100%
|
ruby-100-by-monkeeit-eha5
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
MonkeeIT
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-20T00:49:25.540780+00:00
|
2023-08-20T00:49:25.540808+00:00
| 22 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\ndef largest1_bordered_square(grid)\n rows, cols = grid.size, grid[0].size\n max_side = 0\n dp = Array.new(rows) { Array.new(cols) { [0, 0] } }\n\n (0...rows).each do |r|\n (0...cols).each do |c|\n next if grid[r][c].zero?\n dp[r][c] = [c > 0 ? dp[r][c - 1][0] + 1 : 1, r > 0 ? dp[r - 1][c][1] + 1 : 1]\n side = [dp[r][c][0], dp[r][c][1]].min\n\n while side > max_side\n max_side = side if dp[r - side + 1][c][0] >= side && dp[r][c - side + 1][1] >= side\n side -= 1\n end\n end\n end\n\n max_side * max_side\nend\n\ngrid = [[1, 1, 1], [1, 0, 1], [1, 1, 1]]\nputs largest1_bordered_square(grid)\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Ruby']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
C++ | Dynamic programming
|
c-dynamic-programming-by-shubhamdoke-l4kf
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int largest1BorderedSquare(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {\n int r = grid.size();\n int c = grid[0].size();\n
|
ShubhamDoke
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-15T05:55:45.455798+00:00
|
2023-07-15T05:56:04.145552+00:00
| 136 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int largest1BorderedSquare(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {\n int r = grid.size();\n int c = grid[0].size();\n vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> dp(r, vector<pair<int,int>>(c,{0,0}));\n \n int mx = 0;\n\n for(int i=0;i<r;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<c;j++){\n if(grid[i][j]!=0){\n \n dp[i][j].first = i == 0 ? 1 : dp[i-1][j].first+1;\n dp[i][j].second = j == 0 ? 1 : dp[i][j-1].second+1;\n \n int sz = min(dp[i][j].first, dp[i][j].second);\n while(sz>mx){\n int p = min(dp[i-sz+1][j].second,dp[i][j-sz+1].first);\n if(p>=sz)\n mx = max(mx,sz);\n sz--;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n \n return mx*mx;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
92% FASTER || BOTTOM-UP DP || count row, col
|
92-faster-bottom-up-dp-count-row-col-by-qevry
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
hail-cali
|
NORMAL
|
2023-06-26T11:06:56.707647+00:00
|
2023-06-26T11:06:56.707680+00:00
| 85 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def largest1BorderedSquare(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n\n m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])\n res = 0\n col = [[0]*(n+1) for _ in range(m+1)]\n row = [[0]*(n+1) for _ in range(m+1)]\n\n for i in range(1, m+1):\n for j in range(1, n+1):\n if grid[i-1][j-1] != 0:\n row[i][j] = row[i-1][j] + 1\n col[i][j] = col[i][j-1] + 1\n \n\n x = min(col[i][j], row[i][j])\n \n for k in range(x, res, -1):\n if k <= min(col[i-k+1][j], row[i][j-k+1]):\n res = max(1, res, k)\n \n \n \n \n return res**2\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
Brute Force: O(N*M*min(N, M)^2), O(1)
|
brute-force-onmminn-m2-o1-by-ivzap-98u4
|
Intuition\nJust write a brute force algorithm. Treat the start row and start col as the top left edge of the square, then search for 1ns on its sides until we h
|
ivzap
|
NORMAL
|
2023-06-04T17:07:39.071185+00:00
|
2023-06-04T17:10:43.152329+00:00
| 62 | false |
# Intuition\nJust write a brute force algorithm. Treat the start row and start col as the **top left edge** of the square, then search for 1ns on its sides until we have an invalid square. Kinda suprised this passed as this can be O(N^4)\n\n\n\n# Code\n### Time Complexity: $$O(N * M * min(N, M)^2)$$\n### Space Complexity: $$O(1)$$\n```\nclass Solution:\n def largest1BorderedSquare(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n N,M = len(grid), len(grid[0])\n largest_square = 0\n for start_r in range(N):\n for start_c in range(M):\n for i in range(0, min(M-start_c, N-start_r)):\n valid_square = True\n if not (grid[start_r][start_c+i] and grid[start_r+i][start_c]):\n valid_square = False\n break\n for j in range(0, i+1):\n if not (grid[start_r+i][start_c+i-j] and grid[start_r+i-j][start_c+i]):\n valid_square = False\n break\n if valid_square:\n largest_square = max(largest_square, (i+1)*(i+1))\n return largest_square\n\n\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
Square with dp
|
square-with-dp-by-jaiarora-97y0
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Jaiarora
|
NORMAL
|
2023-05-21T17:44:45.343637+00:00
|
2023-05-21T17:44:45.343667+00:00
| 49 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int largest1BorderedSquare(int[][] grid) {\n int m=grid.length;\n int n=grid[0].length;\n\t\t// rows[r][c] is the length of the line ended at [r,c] on row r\n int[][] rows=new int[m][n]; \n\t\t// the length of the line ended at [r,c] on colume c\n int[][] cols=new int[m][n];\n int res=0;\n for(int r=0;r<m;r++){\n for(int c=0;c<n;c++){\n if(grid[r][c]==0){\n rows[r][c]=0;\n cols[r][c]=0;\n }else{\n rows[r][c]=c==0?1:rows[r][c-1]+1;\n cols[r][c]=r==0?1:cols[r-1][c]+1;\n if(res>=rows[r][c]||res>=cols[r][c]){\n continue;\n }\n res=Math.max(res,getD(rows,cols,r,c));\n }\n }\n }\n return res*res;\n }\n \n\t// get the dimension of the largest square which bottom-right point is [row,col]\n private int getD(int[][] rows,int[][] cols,int row,int col){\n int len=Math.min(rows[row][col],cols[row][col]);\n for(int i=len-1;i>=0;i--){\n if(rows[row-i][col]>i && cols[row][col-i]>i){\n return i+1;\n }\n }\n return 1;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
Clear approach | Easy to undestand | C++
|
clear-approach-easy-to-undestand-c-by-it-uu5s
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int largest1BorderedSquare(vector<vector<int>>& A) {\n int m = A.size(); //Num of columns\n int n = A[0].si
|
iteshgavel
|
NORMAL
|
2023-05-07T03:23:47.893499+00:00
|
2023-05-07T03:23:47.893529+00:00
| 199 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int largest1BorderedSquare(vector<vector<int>>& A) {\n int m = A.size(); //Num of columns\n int n = A[0].size(); //Num of rows\n vector<vector<int>> left(m, vector<int>(n)), top(m, vector<int>(n));\n for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {\n for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {\n left[i][j] = A[i][j] + (j && A[i][j] ? left[i][j - 1] : 0);\n top[i][j] = A[i][j] + (i && A[i][j] ? top[i - 1][j] : 0);\n }\n }\n for (int l = min(m, n); l > 0; --l) {\n for (int i = 0; i < m - l + 1; ++i) {\n for (int j = 0; j < n - l + 1; ++j) {\n if (min({\n top[i + l - 1][j], \n top[i + l - 1][j + l - 1], \n left[i][j + l - 1], \n left[i + l - 1][j + l - 1]\n }) >= l)\n return l * l;\n }\n }\n }\n return 0;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
[golang] prefix sum by row and col
|
golang-prefix-sum-by-row-and-col-by-vl4d-nige
|
\nfunc largest1BorderedSquare(grid [][]int) int {\n pl:=make([][]int, len(grid))\n for i := range pl {\n pl[i]=make([]int, len(grid[0]))\n p
|
vl4deee11
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-14T03:11:40.879095+00:00
|
2023-04-14T03:11:40.879126+00:00
| 37 | false |
```\nfunc largest1BorderedSquare(grid [][]int) int {\n pl:=make([][]int, len(grid))\n for i := range pl {\n pl[i]=make([]int, len(grid[0]))\n pl[i][0]=grid[i][0]\n for j := 1; j <len(grid[0]);j++{\n if grid[i][j]==0{\n pl[i][j]=0\n continue\n }\n pl[i][j]+=grid[i][j]+pl[i][j-1]\n }\n }\n pc:=make([][]int, len(grid))\n for i := range pc {\n pc[i]=make([]int, len(grid[0]))\n \n }\n for j := range pc[0] {\n pc[0][j]=grid[0][j]\n for i := 1; i <len(grid);i++ {\n if grid[i][j]==0 {\n pc[i][j]=0\n continue\n }\n pc[i][j]+=grid[i][j]+pc[i-1][j]\n }\n } \n r:=0\n for i := 0;i < len(grid);i++{\n for j := 0;j < len(grid[0]);j++{\n m:=min(pc[i][j],pl[i][j])\n for sz:=1;sz<=m;sz++{\n d:=sz-1\n if i-d<0 || j-d<0{continue}\n rsz:=min(pl[i-d][j],pc[i][j-d])\n if rsz>=sz{ r=max(r,sz*sz) }\n }\n }\n }\n return r\n}\nfunc min(x, y int) int {\n\tif x < y { return x }\n\treturn y\n}\nfunc max(x, y int) int {\n\tif x > y { return x }\n\treturn y\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
Python, dp solution with explanation
|
python-dp-solution-with-explanation-by-s-lfzt
|
python\n\'\'\'\ni+1 -> next row, j+1 -> next column\ndp[i][j][0] means that there are number of continous 1 which forms a horizontal edge end at position (i, j)
|
shun6096tw
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-27T11:30:52.275001+00:00
|
2023-03-27T11:30:52.275048+00:00
| 71 | false |
```python\n\'\'\'\ni+1 -> next row, j+1 -> next column\ndp[i][j][0] means that there are number of continous 1 which forms a horizontal edge end at position (i, j).\ndp[i][j][1] means that there are number of continous 1 which forms a vertical edge end at position (i, j).\nif the number at the position (i, j) is 1, calculate length of the vertical and horizontal edges first, and we start to enumerate squares formed with both edges.\nFind the minimum length of two edge, and enumerate the edge length from 0(ans) to minimum length:\n\tcheck length of the vertical edge at position (i, j-minimum length+1) and the horizontal edge at position (i-minimum length+1, j) can form a square\n\ntc is O(n^3), sc is O(n^2)\n\'\'\'\nclass Solution:\n def largest1BorderedSquare(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n rowNum, colNum = len(grid), len(grid[0])\n dp = [[[0] * 2 for _ in range(colNum)] for _ in range(rowNum)]\n ans = 0\n for r, row in enumerate(grid):\n for c, n in enumerate(row):\n if n == 1:\n dp[r][c][0] = dp[r][c-1][0] + 1 if c - 1 >= 0 else 1\n dp[r][c][1] = dp[r-1][c][1] + 1 if r - 1 >= 0 else 1\n lenOfEdge = dp[r][c][0] if dp[r][c][0] < dp[r][c][1] else dp[r][c][1]\n for e in range(ans+1, lenOfEdge+1):\n if dp[r][c-e+1][1] >= e and dp[r-e+1][c][0] >= e and e > ans:\n ans = e\n return ans * ans\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
C++ DP solution
|
c-dp-solution-by-user7685x-3evs
|
\n int largest1BorderedSquare(vector>& grid) {\n int n=grid.size();\n int m=grid[0].size();\n vector>> dp (n, vector> (m, vector (2, 0))
|
user7685x
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-06T12:40:03.193628+00:00
|
2023-03-06T12:50:26.774142+00:00
| 102 | false |
\n int largest1BorderedSquare(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {\n int n=grid.size();\n int m=grid[0].size();\n vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp (n, vector<vector<int>> (m, vector<int> (2, 0)));\n for(int i=0;i<dp.size();i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<dp[0].size();j++)\n {\n if(grid[i][j]==1)\n {\n if(i==0 && j==0)\n {\n dp[i][j][0]=1;\n dp[i][j][1]=1;\n \n }\n else if(i==0)\n {\n dp[i][j][0]=1;\n dp[i][j][1]=dp[i][j-1][1]+1;\n \n }\n else if(j==0)\n {\n dp[i][j][0]=dp[i-1][j][0]+1;\n dp[i][j][1]=1;\n }\n else\n {\n dp[i][j][0]=dp[i-1][j][0]+1;\n dp[i][j][1]=dp[i][j-1][1]+1;\n \n }\n \n\n \n }\n }\n }\n \n int ans=0;\n for(int i=dp.size()-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n for(int j=dp[0].size()-1;j>=0;j--)\n {\n int mini=min(dp[i][j][0],dp[i][j][1]);\n int k=mini;\n \n for(k=mini;k>=1;k--)\n {\n if(dp[i][j-k+1][0]>=k && dp[i-k+1][j][1]>=k)\n {\n break;\n \n }\n }\n ans=max(ans,k); \n }\n }\n \n return ans*ans;\n \n \n }\n
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
[Python3] Prefix Sum Solution
|
python3-prefix-sum-solution-by-samuel3sh-kyvx
|
Code\n\nclass Solution:\n def largest1BorderedSquare(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n m = len(grid)\n n = len(grid[0])\n\n horiPre
|
Samuel3Shin
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-21T17:20:56.434841+00:00
|
2023-02-21T17:20:56.434890+00:00
| 105 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def largest1BorderedSquare(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n m = len(grid)\n n = len(grid[0])\n\n horiPrefix = [[0 for j in range(n)] for i in range(m)]\n vertiPrefix = [[0 for j in range(n)] for i in range(m)]\n\n for i in range(m):\n for j in range(n):\n if grid[i][j]==1:\n horiPrefix[i][j] = (horiPrefix[i][j-1] if j-1>=0 else 0) + grid[i][j]\n\n for j in range(n):\n for i in range(m):\n if grid[i][j]==1:\n vertiPrefix[i][j] = (vertiPrefix[i-1][j] if i-1>=0 else 0) + grid[i][j]\n \n ans = 0\n for i in range(m):\n for j in range(n):\n possibleLen = min(i,j)+1\n for l in range(1, possibleLen+1):\n if horiPrefix[i][j]>=l and vertiPrefix[i][j]>=l and horiPrefix[i-l+1][j]>=l and vertiPrefix[i][j-l+1]>=l:\n ans = max(ans, l*l)\n \n return ans\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
Clean Python | High Speed | O(n) time, O(1) space | Beats 98.9%
|
clean-python-high-speed-on-time-o1-space-2gts
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution:\n def largest1BorderedSquare(self, A):\n m, n = len(A), len(A[0])\n res = 0\n top, left = [a[:] for a in A
|
avs-abhishek123
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-17T06:02:22.363205+00:00
|
2023-02-17T06:02:22.363250+00:00
| 102 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def largest1BorderedSquare(self, A):\n m, n = len(A), len(A[0])\n res = 0\n top, left = [a[:] for a in A], [a[:] for a in A]\n for i in range(m):\n for j in range(n):\n if A[i][j]:\n if i: top[i][j] = top[i - 1][j] + 1\n if j: left[i][j] = left[i][j - 1] + 1\n for r in range(min(m, n), 0, -1):\n for i in range(m - r + 1):\n for j in range(n - r + 1):\n if min(top[i + r - 1][j], top[i + r - 1][j + r - 1], left[i]\n [j + r - 1], left[i + r - 1][j + r - 1]) >= r:\n return r * r\n return 0\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
Java, DP with explanation. Beats 100%
|
java-dp-with-explanation-beats-100-by-sm-jkk5
|
Intuition\nA square border comprises of 4 parts, 2 vertical lines and 2 horizontal lines. The length of side of square formed from these 4 lines of varying leng
|
smbody
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-14T16:45:18.039190+00:00
|
2023-02-14T16:45:18.039233+00:00
| 125 | false |
# Intuition\nA square border comprises of 4 parts, 2 vertical lines and 2 horizontal lines. The length of side of square formed from these 4 lines of varying length will be the minimum of the four lines.\n\n# Approach\nIf we could find the length of these four lines mentioned above and then find the minimum of the four and then square it, we would get the required answer.\n\nTo do so, I kept a count of number of consecutive ones occuring vertically and the number of consecutive ones appearing horizontally with the help of two 2D arrays, namely `horizontal_count` and `vertica_count`.\n\nAfter which it is a simple nested for-loop to check for squares by checking if length of all the four sides is greater than our current answer\n\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int largest1BorderedSquare(int[][] grid) {\n int horizontal_count[][]=new int [grid.length][grid[0].length];\n int vertical_count[][]=new int [grid.length][grid[0].length];\n int ans=1,flag=0;\n for(int i=0;i<grid.length;i++)\n {\n int c=0;\n for(int j=grid[0].length-1;j>=0;j--)\n {\n if(grid[i][j]==1)\n {\n flag=1;\n c++;\n horizontal_count[i][j]=c;\n }\n else\n c=0;\n }\n }\n if(flag==0)\n return 0;\n for(int i=0;i<grid[0].length;i++)\n {\n int c=0;\n for(int j=grid.length-1;j>=0;j--)\n {\n if(grid[j][i]==1)\n {\n c++;\n vertical_count[j][i]=c;\n }\n else\n c=0;\n }\n }\n for(int i=0;i<grid.length;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<grid[0].length;j++)\n {\n if(vertical_count[i][j]>ans)\n {\n int temp=vertical_count[i][j]>=horizontal_count[i][j]?horizontal_count[i][j]:vertical_count[i][j];\n if(j-1+temp>=grid[0].length)\n temp=grid[0].length-j-1;\n if(i-1+temp>=grid.length)\n temp=grid.length-i-1;\n if(temp<ans)\n continue;\n while(temp>ans)\n {\n if(temp<=vertical_count[i][j-1+temp]&&temp<=horizontal_count[i-1+temp][j])\n {\n ans=temp;\n break;\n }\n else\n temp--;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n return ans*ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
Easy C++ Solution
|
easy-c-solution-by-clary_shadowhunters-jowv
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int largest1BorderedSquare(vector<vector<int>>& grid) \n {\n int n=grid.size();\n int m=grid[0].si
|
Clary_ShadowHunters
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-30T13:23:48.469804+00:00
|
2023-01-30T13:23:48.469860+00:00
| 210 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int largest1BorderedSquare(vector<vector<int>>& grid) \n {\n int n=grid.size();\n int m=grid[0].size();\n vector<vector<int>>hor(n,vector<int>(m,0));\n vector<vector<int>>ver(n,vector<int>(m,0));\n for (int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n int cnt=0;\n for (int j=0;j<m;j++)\n {\n if (grid[i][j]==1)\n {\n cnt++;\n hor[i][j]=cnt;\n }\n else cnt=0;\n }\n }\n for (int j=0;j<m;j++)\n {\n int cnt=0;\n for (int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n if (grid[i][j]==1)\n {\n cnt++;\n ver[i][j]=cnt;\n }\n else cnt=0;\n }\n }\n \n int ans=0;\n for (int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for (int j=0;j<m;j++)\n {\n int sz=min(hor[i][j],ver[i][j]);\n if (sz==0) continue;\n for (int k=sz;k>ans;k--)\n {\n if (hor[i-k+1][j]>=k && ver[i][j-k+1]>=k)\n {\n ans=max(ans,k);\n }\n }\n }\n }\n return ans*ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
largest-1-bordered-square
|
Python3 || Beats 100% || Easy Solution
|
python3-beats-100-easy-solution-by-glock-8nnr
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
glock17
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-30T07:15:24.247414+00:00
|
2023-01-30T07:15:24.247465+00:00
| 129 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def largest1BorderedSquare(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n maxi = 0\n rows = len(grid)\n cols = len(grid[0])\n\n hor = [[0]*cols for _ in range(rows)]\n ver = [[0]*cols for _ in range(rows)]\n\n # Auxilliary Horizontal and Vertical DP\n\n for i in range(rows):\n for j in range(cols):\n\n if grid[i][j] == 1:\n if j == 0:\n hor[i][j] = hor[i][j] = 1\n else:\n hor[i][j] = hor[i][j-1] + 1\n \n if i == 0:\n ver[i][j] = 1\n else:\n ver[i][j] = ver[i-1][j] + 1\n \n # for i in range(rows):\n # for j in range(cols):\n # print(hor[i][j],sep=\' \',end=\'\')\n # print() \n \n # print()\n\n # for i in range(rows):\n # for j in range(cols):\n # print(ver[i][j],sep=\' \',end=\'\')\n # print()\n\n\n for i in range(rows-1,-1,-1):\n for j in range(cols-1,-1,-1):\n small = min(ver[i][j], hor[i][j])\n\n while(small > maxi):\n if ver[i][j - small + 1] >= small and hor[i - small + 1][j] >= small:\n maxi = small\n # If above conition is not true then decrement small\n small-=1\n\n return (maxi*maxi)\n \n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Linked List+bitset without Memory leaks||343 ms Beats 99.05%
|
linked-listbitset-without-memory-leaks34-w8jv
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nRemove the nodes with values seen in nums.\nUse a bitset to record the nums; then trans
|
anwendeng
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T00:49:22.937725+00:00
|
2024-09-06T01:29:31.465470+00:00
| 12,270 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nRemove the nodes with values seen in `nums`.\nUse a bitset to record the nums; then transverse the linked list `head` to proceed.\n\nFor comparison, an unordered_set version is also implemented.\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. Use `bitset<100001> hasN=0` to set `x in nums` to be `hasN[x]=1` instead of using `unordered_set`.\n2. Declare a dummy node `ListNode dummy(0, head)`.\n3. Initialize `prev=&dummy, *tmp=NULL`\n4. Use a loop to proceed `for(ListNode* curr=head; curr; curr=curr->next, delete tmp){....}` which deletes the node removed to avoid of memory leakage.\n5. The iteration in the loop is:\n```\nif (hasN[curr->val]){ \n prev->next = curr->next;\n tmp=curr;\n}\nelse{\n prev = prev->next;\n tmp=NULL;\n}\n```\n6. ` dummy.next` is the answer.\n7. 2nd C++ using unordered_set is also made.\n\n|Method|Elapsed time|Record|Memory|\n|---|---|---|---|\n|bitset w/o Memory leaks|343ms|99.05%|227.92MB|\n|bitset with Memory leaks|346ms|98.94%|223.56MB|\n|unordered_set w/o Memory leaks|454ms|47.11%|262.89MB|\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(|nums|+|head|)$$\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$O(10^5)$\n# Code||343 ms Beats 99.05%\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n bitset<100001> hasN=0;\n for(int x: nums) hasN[x]=1;\n ListNode dummy(0, head);\n ListNode* prev=&dummy, *tmp=NULL;\n for(ListNode* curr=head; curr; curr=curr->next, delete tmp){\n if (hasN[curr->val]){ \n prev->next = curr->next;\n tmp=curr;\n }\n else{\n prev = prev->next;\n tmp=NULL;\n }\n }\n return dummy.next;\n }\n};\n```\n# C++ with unordered_set||454ms Beats 47.11%\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n unordered_set<int> hasN(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n ListNode dummy(0, head);\n ListNode* prev=&dummy, *tmp=NULL;\n for(ListNode* curr=head; curr; curr=curr->next, delete tmp){\n if (hasN.count(curr->val)){ \n prev->next = curr->next;\n tmp=curr;\n }\n else{\n prev = prev->next;\n tmp=NULL;\n }\n }\n return dummy.next;\n }\n};\n```\nClassical Leetcode question [19. Remove Nth Node From End of List](https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/solutions/4813267/fast-slow-pointers-care-with-memory-leaks-0ms-beats-100/)\n[Please turn on English subtitles if necessary]\n[https://youtu.be/OqLR3ShDALY?si=SDv3JLDQxgsfJGNf](https://youtu.be/OqLR3ShDALY?si=SDv3JLDQxgsfJGNf)
| 66 | 5 |
['Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'Bit Manipulation', 'C++']
| 16 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
😎 Best Solution || 💯 % on Runtime 🚀 || 💻 With Explanation
|
best-solution-on-runtime-with-explanatio-jmky
|
\n\n\n### Intuition \nImagine you\'re running a party, but only some guests are invited (based on a list of numbers). If a guest shows up and isn\'t on the lis
|
IamHazra
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T07:52:22.411544+00:00
|
2024-09-06T07:52:22.411571+00:00
| 15,273 | false |
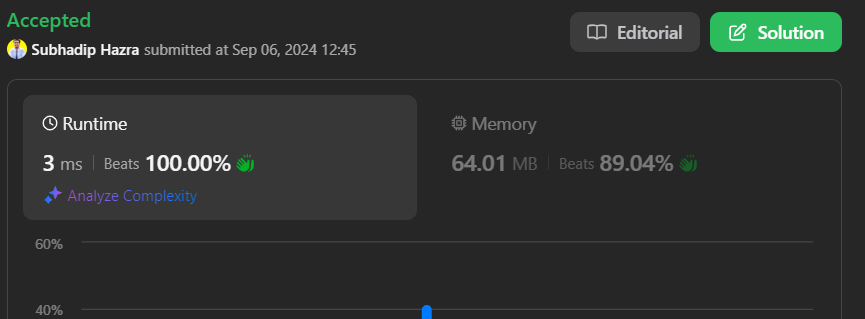\n\n\n### Intuition \nImagine you\'re running a party, but only some guests are invited (based on a list of numbers). If a guest shows up and isn\'t on the list, you need to remove them. That\'s what we\'re doing here with linked lists. We want to keep only the nodes whose values match the numbers from the array.\n\n### Approach \n1. First, we find the largest number in the list to know how big our frequency array needs to be.\n2. We create a frequency array (like a guest list) where `True` means the number is invited, and `False` means they aren\'t.\n3. Then we walk through the linked list. If a node\u2019s value is on the guest list (i.e., the frequency array says `True`), we skip it. If not, we add it to our new, modified linked list.\n4. Finally, we return the new linked list that only contains the uninvited guests (nodes with values not in the array).\n\n### Time Complexity \n- Time complexity: \n We first loop through the array to find the max value and then build a frequency array based on that. After that, we loop through both the `nums` array and the linked list. So, overall it\'s $$O(n + m)$$ where `n` is the length of `nums` and `m` is the length of the linked list.\n\n### Space Complexity \n- Space complexity: \n We need extra space for the frequency array, which depends on the largest number in the input array. Therefore, the space complexity is $$O(k)$$, where `k` is the largest number in `nums`.\n\n---\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n int max = -1;\n for(int num : nums ){\n max = num > max ? num : max;\n }\n boolean[] freq = new boolean[max+1];\n\n for(int num : nums) freq[num] = true;\n\n ListNode temp = new ListNode();\n ListNode current = temp;\n\n while(head != null){\n if( head.val >= freq.length || freq[head.val] == false){\n current.next = head;\n current = current.next;\n }\n head = head.next;\n }\n\n current.next = null;\n return temp.next;\n }\n}\n```\n``` C++ []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n int max = -1;\n for (int num : nums) {\n max = num > max ? num : max;\n }\n\n vector<bool> freq(max + 1, false);\n\n for (int num : nums) {\n freq[num] = true;\n }\n\n ListNode* temp = new ListNode();\n ListNode* current = temp;\n\n while (head != nullptr) {\n if (head->val >= freq.size() || !freq[head->val]) {\n current->next = head;\n current = current->next;\n }\n head = head->next;\n }\n\n current->next = nullptr;\n\n return temp->next;\n }\n};\n```\n\n``` Javascript []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * function ListNode(val, next) {\n * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)\n * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)\n * }\n */\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @param {ListNode} head\n * @return {ListNode}\n */\nvar modifiedList = function(nums, head) {\n let max = -1;\n for( let num of nums ){\n max = num > max ? num : max;\n }\n\n let freq = new Array(max+1).fill(false);\n\n for(let num of nums)freq[num] = true;\n\n let temp = new ListNode();\n let current = temp;\n\n while(head != null ){\n if( head.val >= freq.length || freq[head.val] == false){\n current.next = head;\n current = current.next;\n }\n head = head.next;\n }\n\n current.next = null;\n return temp.next;\n};\n\n\n```\n\n``` Python []\n# Definition for singly-linked list.\n# class ListNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.next = next\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:\n max_val = -1\n for num in nums:\n max_val = max(num, max_val)\n\n freq = [False] * (max_val + 1)\n\n for num in nums:\n freq[num] = True\n\n temp = ListNode()\n current = temp\n\n while head:\n if head.val >= len(freq) or not freq[head.val]:\n current.next = head\n current = current.next\n head = head.next\n\n current.next = None\n\n return temp.next\n\n \n```\n\nHappy Coding \uD83D\uDCBB\n\n\n
| 65 | 1 |
['Array', 'Linked List', 'Counting', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'JavaScript']
| 9 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Temp Node
|
temp-node-by-votrubac-n12s
|
A standard linked list removal problem where we use a temp node.\n\nWe also need to use a hashset to check for values efficiently.\n\n> Note that contains was i
|
votrubac
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T04:01:14.739529+00:00
|
2024-07-14T04:03:50.572291+00:00
| 3,543 | false |
A standard linked list removal problem where we use a temp node.\n\nWe also need to use a hashset to check for values efficiently.\n\n> Note that `contains` was introduced in C++20.\n\n**C++**\n```cpp \nListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n ListNode tmp(0, head);\n unordered_set<int> s(begin(nums), end(nums));\n for (auto *p = &tmp; p->next != nullptr; )\n if (s.contains(p->next->val))\n p->next = p->next->next;\n else\n p = p->next;\n return tmp.next;\n}\n```
| 33 | 0 |
[]
| 10 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Straightforward Approach || C++
|
straightforward-approach-c-by-fahad06-t0tl
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(nlogn + mlogn) where n is the size of nums and m is the number of nodes in the linked list.\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n\n# Co
|
fahad_Mubeen
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T03:49:50.935195+00:00
|
2024-09-06T04:58:28.415399+00:00
| 6,439 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(nlogn + mlogn)$$ where n is the size of nums and m is the number of nodes in the linked list.\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n // Convert the array `nums` into a set for fast lookup of values to be removed.\n set<int> st(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n\n // Initialize a pointer `curr` to traverse the linked list.\n ListNode* curr = head;\n \n // Traverse the list to find the first node whose value is NOT in the set.\n // This node will be the new head of the modified linked list.\n while(curr) {\n if(st.count(curr->val)) { \n // If the current node\'s value is in the set, skip this node.\n curr = curr->next;\n }\n else break; // Stop when we find a node whose value is NOT in the set.\n }\n\n // The first valid node becomes the new head of the modified list.\n ListNode* newHead = curr;\n\n // Traverse the rest of the linked list and remove nodes whose values exist in the set.\n while(curr && curr->next) { \n if(st.count(curr->next->val)) {\n // If the next node\'s value is in the set, skip the next node by adjusting pointers.\n curr->next = curr->next->next;\n } \n else {\n // Move to the next node if it\'s not in the set.\n curr = curr->next;\n }\n }\n\n // Return the new head of the modified linked list.\n return newHead;\n }\n};\n\n```\n# Same idea, but implemented in a single pass with memory deallocation\n```cpp []\nListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n set<int> st(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n ListNode* temp = new ListNode(0);\n temp->next = head;\n ListNode* newHead = temp;\n\n while(temp->next){\n if(st.count(temp->next->val)){\n ListNode* d = temp->next;\n temp->next = temp->next->next;\n delete(d);\n }\n else{\n temp = temp->next;\n }\n }\n return newHead->next;\n}\n```\n# Recursive Method\n```cpp []\nListNode* f(ListNode* head, set<int> &st){\n if(! head) return NULL;\n head->next = f(head->next, st);\n if(st.count(head->val)){\n ListNode* next = head->next;\n delete(head);\n return next;\n }\n return head;\n}\n\nListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n set<int> st(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n return f(head, st);\n}\n```
| 25 | 13 |
['C++']
| 14 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Easy Video Solution 🔥 || How to 🤔 in Interview || Using Temp Node ✅
|
easy-video-solution-how-to-in-interview-kflkw
|
If you like the solution Please Upvote and subscribe to my youtube channel\n\n\n\nEasy Video Explanation\n\nhttps://youtu.be/LHe2bHokebc\n\n \n\n# Code\n\n\n
|
ayushnemmaniwar12
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T04:29:06.327606+00:00
|
2024-07-14T07:20:51.911560+00:00
| 3,786 | false |
***If you like the solution Please Upvote and subscribe to my youtube channel***\n\n\n\n***Easy Video Explanation***\n\nhttps://youtu.be/LHe2bHokebc\n\n \n\n# Code\n\n\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& v, ListNode* head) {\n ListNode *d= new ListNode(-1);\n ListNode *t=d;\n set<int>s;\n for(auto i:v)\n s.insert(i);\n while(head!=NULL) {\n if(s.find(head->val)==s.end()) {\n t->next=head;\n t=t->next;\n }\n head=head->next;\n }\n t->next=NULL;\n return d->next;\n }\n};\n```\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, v, head):\n dummy = ListNode(-1)\n t = dummy\n s = set(v)\n \n while head:\n if head.val not in s:\n t.next = head\n t = t.next\n head = head.next\n \n t.next = None\n return dummy.next\n```\n```Java []\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(List<Integer> v, ListNode head) {\n ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);\n ListNode t = dummy;\n Set<Integer> s = new HashSet<>(v);\n \n while (head != null) {\n if (!s.contains(head.val)) {\n t.next = head;\n t = t.next;\n }\n head = head.next;\n }\n \n t.next = null;\n return dummy.next;\n }\n}\n\n```\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n O(N*log(N))\n \n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n O(1)\n\n# ***If you like the solution Please Upvote and subscribe to my youtube channel***\n***It Motivates me to record more videos***\n\n*Thank you* \uD83D\uDE00
| 19 | 5 |
['Linked List', 'Ordered Set', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 8 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Python | Runtime beats 98.34%, Memory beats 58.49%
|
python-runtime-beats-9834-memory-beats-5-kuee
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
r9n
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T19:53:47.681423+00:00
|
2024-09-06T19:53:47.681454+00:00
| 264 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass ListNode:\n def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):\n self.val = val\n self.next = next\n\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:\n # Convert nums to a set for O(1) lookups\n to_delete = set(nums)\n \n # Create a dummy node that points to the head of the list\n dummy = ListNode(0)\n dummy.next = head\n \n # Use two pointers: current to iterate and prev to manage the deletion\n prev = dummy\n current = head\n \n while current:\n if current.val in to_delete:\n # Skip the node to be deleted\n prev.next = current.next\n else:\n # Move prev to current\n prev = current\n \n # Move to the next node\n current = current.next\n \n # Return the modified list, which is next of dummy\n return dummy.next\n\n```
| 16 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Simple python Solution beats 90% of the python users
|
simple-python-solution-beats-90-of-the-p-fmfd
|
\n# Problem Description:\nWe are given a linked list and a list of integers nums. The goal is to modify the linked list such that all nodes containing values pr
|
user0197ub
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T02:07:21.739479+00:00
|
2024-09-06T02:07:21.739505+00:00
| 3,600 | false |
\n# Problem Description:\nWe are given a linked list and a list of integers nums. The goal is to modify the linked list such that all nodes containing values present in nums are removed from the list. The modified list should contain only nodes whose values are not in nums.\n\n# Hash Set for Fast Lookup:\n\nWe store the values from nums in a set to achieve O(1) lookup time. This helps in quickly determining whether a node\u2019s value is in nums or not.\n\n# Skipping Initial Invalid Nodes:\n\nWe start by handling edge cases where the initial nodes (including the head) are invalid. If the head node\u2019s value is in nums, we keep advancing the head to the next node until we find a valid node or reach the end of the list.\n# Iterating Through the List:\n\nOnce the head is positioned at a valid node, we traverse the list using two pointers:\nprev keeps track of the last valid node.\ncurr is used to traverse the rest of the list.\nIf a node\u2019s value is not in nums, we connect it to the prev node; otherwise, it is skipped.\n\n# Ensuring Proper Termination:\n\nAfter processing all nodes, the last valid node\u2019s next pointer is set to None to mark the end of the modified list, avoiding dangling references.\n# Example:\nLet\u2019s walk through an example:\n\nInput:\nhead = [1, 2, 6, 3, 4, 5, 6]\nnums = [6, 3]\nOutput:\nThe modified list after removing all nodes containing values from nums will be [1, 2, 4, 5].\n\n# Complexity\n- # Time Complexity:\n O(n): We traverse the list once, where n is the number of nodes in the linked list. This ensures efficient processing.\n\n- Space complexity:\n O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\n# Definition for singly-linked list.\n# class ListNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.next = next\n\n\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:\n s = set(nums)\n \n while head and head.val in s:\n head = head.next\n \n \n if not head:\n return None\n\n prev = head\n curr = head.next\n \n while curr:\n if curr.val not in s:\n prev.next = curr\n prev = curr\n curr = curr.next\n \n prev.next = None\n return head\n\n \n```
| 16 | 9 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'Python3']
| 12 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Python 3 || 10 lines, list traversal || T/S: 93% / 70%
|
python-3-10-lines-list-traversal-ts-93-7-3zee
|
Here\'s the plan:\n1. We traverse the linked list and reset head at the first node for which its value is not in nums.\n2. We record this node using ans and con
|
Spaulding_
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T18:45:24.387199+00:00
|
2024-07-20T22:06:45.908088+00:00
| 937 | false |
Here\'s the plan:\n1. We traverse the linked list and reset `head` at the first node for which its value is not in `nums`.\n2. We record this node using `ans` and continue to traverse the linked list. \n3. For each node in the traverse, we "leapfrog" over any number of consecutive, subsequent nodes with values in `nums`. \n4. When we encounter a node with a value not in the list, we move to that node and continue the traverse.\n5. We return `ans` as the head of the revised linked list.\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:\n \n nums = set(nums) \n \n while head.val in nums: # <-- 1)\n head = head.next\n\n ans = ListNode(head.val, head) # <-- 2)\n \n while head and head.next: # <-- 3)\n if head.next.val in nums:\n head.next = head.next.next\n\n else: # <-- 4)\n head = head.next\n\n return ans.next # <-- 5)\n\n```\n[https://leetcode.com/problems/delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array/submissions/1327797714/](https://leetcode.com/problems/delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array/submissions/1327797714/)\n\nI could be wrong, but I think that time complexity is *O*(*N* + *M*) and space complexity is *O*(*N*), in which *M* ~ the number of nodes in the linked list and *N* ~ `len(nums)`.
| 16 | 0 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 4 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
✅ Java Solution
|
java-solution-by-harsh__005-mq4y
|
CODE\nJava []\npublic ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n\tSet<Integer> dup = new HashSet();\n\tfor(int num : nums) dup.add(num);\n\n\tListNode
|
Harsh__005
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T04:11:00.199774+00:00
|
2024-07-14T04:11:00.199800+00:00
| 1,281 | false |
## **CODE**\n```Java []\npublic ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n\tSet<Integer> dup = new HashSet();\n\tfor(int num : nums) dup.add(num);\n\n\tListNode res = new ListNode(-1);\n\tListNode trv = res;\n\twhile(head != null) {\n\t\tif(!dup.contains(head.val)) {\n\t\t\ttrv.next = head;\n\t\t\ttrv = trv.next;\n\t\t}\n\t\thead = head.next;\n\t}\n\ttrv.next = null;\n\treturn res.next;\n}\n```
| 12 | 1 |
['Java']
| 4 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Beats 100% | C++ | Python | Java | Go | Rust | JavaScript
|
beats-100-c-python-java-go-rust-javascri-jmv1
|
\nEDIT1: Working on Optimization, removed the explanation\n\n# Code\n\n\nC++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& excludeValue
|
kartikdevsharma_
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T04:03:09.584879+00:00
|
2024-09-02T19:02:38.540607+00:00
| 1,357 | false |
\nEDIT1: Working on Optimization, removed the explanation\n\n# Code\n\n\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& excludeValues, ListNode* head) {\n bitset<100001> excludeSet; \n for (int val : excludeValues) {\n excludeSet.set(val);\n }\n \n ListNode dummy(0);\n dummy.next = head;\n ListNode* curr = &dummy;\n \n while (curr->next) {\n if (excludeSet[curr->next->val]) {\n curr->next = curr->next->next; \n } else {\n curr = curr->next; \n }\n }\n \n return dummy.next;\n }\n};\n\nstatic const int speedup = []() {\n ios::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(nullptr);\n cout.tie(nullptr);\n return 0;\n}();\n\n\n\n\n```\n\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, excludeValues: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:\n exclude_set = set(excludeValues)\n \n dummy = ListNode(0)\n dummy.next = head\n curr = dummy\n \n while curr.next:\n if curr.next.val in exclude_set:\n curr.next = curr.next.next \n else:\n curr = curr.next \n \n return dummy.next\n\ndef list_to_linked_list(arr):\n dummy = ListNode(0)\n curr = dummy\n for val in arr:\n curr.next = ListNode(val)\n curr = curr.next\n return dummy.next\n\ndef linked_list_to_list(head):\n result = []\n while head:\n result.append(head.val)\n head = head.next\n return result\n\ndef kdsmain():\n inputs = map(loads, sys.stdin)\n results = []\n\n for excludeValues in inputs:\n head_list = next(inputs)\n head = list_to_linked_list(head_list)\n \n filtered_head = Solution().modifiedList(excludeValues, head)\n results.append(linked_list_to_list(filtered_head))\n\n with open("user.out", "w") as f:\n for result in results:\n print(dumps(result).replace(", ", ","), file=f)\n\nif __name__ == "__main__":\n kdsmain()\n sys.exit(0)\n\n\n```\n```Java []\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] excludeValues, ListNode head) {\n\n java.util.BitSet excludeSet = new java.util.BitSet();\n for (int val : excludeValues) {\n excludeSet.set(val);\n }\n ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);\n dummy.next = head;\n ListNode curr = dummy;\n\n while (curr.next != null) {\n if (excludeSet.get(curr.next.val)) {\n curr.next = curr.next.next; \n } else {\n curr = curr.next; \n }\n }\n\n return dummy.next;\n }\n}\n\n```\n```Go []\nfunc modifiedList(excludeValues []int, head *ListNode) *ListNode {\n excludeSet := make(map[int]bool)\n for _, val := range excludeValues {\n excludeSet[val] = true\n }\n \n dummy := &ListNode{Val: 0, Next: head}\n curr := dummy\n \n for curr.Next != nil {\n if excludeSet[curr.Next.Val] {\n curr.Next = curr.Next.Next \n } else {\n curr = curr.Next \n }\n }\n \n return dummy.Next\n}\n\n```\n\n```Rust []\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn modified_list(exclude_values: Vec<i32>, head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {\n let mut exclude_set = std::collections::HashSet::new();\n for &val in &exclude_values {\n exclude_set.insert(val);\n }\n \n let mut dummy = Box::new(ListNode::new(0));\n dummy.next = head;\n let mut curr = &mut dummy;\n \n while let Some(next) = curr.next.take() {\n if exclude_set.contains(&next.val) {\n curr.next = next.next;\n } else {\n curr.next = Some(next);\n curr = curr.next.as_mut().unwrap();\n }\n }\n \n dummy.next\n }\n}\n\n```\n```JavaScript []\n/**\n * @param {number[]} excludeValues\n * @param {ListNode} head\n * @return {ListNode}\n */\nvar modifiedList = function(excludeValues, head) {\n const excludeSet = new Set(excludeValues);\n \n const dummy = new ListNode(0);\n dummy.next = head;\n let curr = dummy;\n \n while (curr.next) {\n if (excludeSet.has(curr.next.val)) {\n curr.next = curr.next.next;\n } else {\n curr = curr.next; \n }\n }\n \n return dummy.next;\n};\n\n```\n
| 11 | 0 |
['Array', 'Linked List', 'C++', 'Java', 'Go', 'Python3', 'Rust', 'JavaScript']
| 5 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Easy 5 Language || Beats Everyone || Set
|
easy-5-language-beats-everyone-set-by-ga-1ia4
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\nComplexityComplexit Describe y# Algorithm (Spoiler \uD83D\uDEA8)\n(You sh
|
Garv_Virmani
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T01:06:30.751388+00:00
|
2024-09-06T01:06:30.751417+00:00
| 3,831 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\nComplexityComplexit Describe y# Algorithm (Spoiler \uD83D\uDEA8)\n(You should first try yourself)\n1.Initialize a set valuesToRemove and populate it with the values of the nums array.\n2.While the head of the linked list is not null and the head\'s value is present in valuesToRemove:\n3.Move head to head.next.\n4.If the head is null, return null since all nodes have been removed.\n5.Start iterating from the head of the modified list:\n6.For each node current, check if the value of the next node (current.next) is in the valuesToRemove set.\n7.If it is, skip the next node by updating current.next to current.next.next\n8.If it is not, move the current pointer to the next node in the list.\nReturn the updated head of the list.our approach to solving the problem. \n\n# CoComplexitymplexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n unordered_set<int>s;\n for(auto x:nums) s.insert(x);\n ListNode* newHead= new ListNode(-1);\n ListNode* temp=newHead;\n while(head){\n if(s.count(head->val)==0){\n newHead->next=new ListNode(head->val);\n newHead=newHead->next;\n }\n head=head->next;\n }\n return temp->next;\n }\n};\n```
| 10 | 8 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 10 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
✅✅✅SIMPLE AND EASY SOLUTION✅✅WITH EXPLANATION USING PYTHON✅✅🔥🔥🔥
|
simple-and-easy-solutionwith-explanation-ri0u
|
PLEASE UPVOTE IF THIS HELPED YOU!!!!\n# Intuition\nTo solve this problem, the goal is to traverse the linked list and remove any nodes whose values are present
|
user0517qU
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T01:04:02.759035+00:00
|
2024-09-06T01:15:50.930747+00:00
| 1,151 | false |
# PLEASE UPVOTE IF THIS HELPED YOU!!!!\n# Intuition\nTo solve this problem, the goal is to traverse the linked list and remove any nodes whose values are present in the list nums. Using a set allows us to efficiently check whether a value exists in nums.\n\n# Approach\n- Convert the list nums into a set for fast O(1) lookups.\n- Create a dummy node to simplify edge cases (like removing the head node).\n- Traverse the linked list using two pointers: prev to track the previous node and curr to point to the current node.\n- If curr.val exists in the set, update prev.next to skip over curr, effectively removing it from the list.\n- Return the updated list starting from dummy.next.\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the linked list. Each node is visited once.\n- Space complexity: O(m), where m is the size of the set created from the list nums.\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:\n if not head:\n return None\n num_set = set(nums)\n dummy = ListNode(0)\n dummy.next = head\n prev, curr = dummy, head\n while curr:\n if curr.val in num_set:\n prev.next = curr.next\n else:\n prev = curr\n curr = curr.next\n return dummy.next\n\n\n```
| 9 | 6 |
['Python3']
| 8 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Deleting Nodes Using Link Updation And Fast Look Ups Using Set | Java | C++ | [Video Solution]
|
deleting-nodes-using-link-updation-and-f-yg34
|
Intuition, approach, and complexity discussed in video solution in detail.\nhttps://youtu.be/32-3yHQy4ek\n\n# Code\njava []\nclass Solution {\n public ListNo
|
Lazy_Potato_
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T04:33:25.325785+00:00
|
2024-09-06T04:33:25.325807+00:00
| 4,363 | false |
# Intuition, approach, and complexity discussed in video solution in detail.\nhttps://youtu.be/32-3yHQy4ek\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n Set<Integer> toBeDel = new HashSet<>();\n for(var num : nums)toBeDel.add(num);\n ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();\n dummyHead.next = head;\n ListNode curr = dummyHead, prev = dummyHead;\n while(curr != null){\n ListNode nextNode = curr.next;\n if(toBeDel.contains(curr.val)){\n prev.next = nextNode;\n }else{\n prev = curr;\n }\n curr = nextNode;\n }\n return dummyHead.next;\n }\n}\n```\n``` cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n unordered_set<int> toBeDel;\n for(auto & num : nums)toBeDel.insert(num);\n ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode();\n dummyHead->next = head;\n ListNode *curr = dummyHead, *prev = dummyHead;\n while(curr != NULL){\n ListNode *nextNode = curr->next;\n if(toBeDel.count(curr->val) != 0){\n prev->next = nextNode;\n }else{\n prev = curr;\n }\n curr = nextNode;\n }\n return dummyHead->next;\n }\n};\n```
| 8 | 1 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'C++', 'Java']
| 5 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
[Python3] Temp Node - Simple Solution
|
python3-temp-node-simple-solution-by-dol-efgu
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
dolong2110
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T05:59:29.267996+00:00
|
2024-09-06T09:28:17.414621+00:00
| 536 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(N)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(N)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n# Definition for singly-linked list.\n# class ListNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.next = next\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:\n s = set(nums)\n dummy = tmp = ListNode()\n dummy.next = head\n while tmp.next:\n if tmp.next.val in s: tmp.next = tmp.next.next\n else: tmp = tmp.next\n return dummy.next\n```
| 8 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'Python3']
| 6 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Easy Solution With Explanation in C++ using map
|
easy-solution-with-explanation-in-c-usin-eu6x
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n1. Map Creation: \n
|
Amarnath_garai
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T09:18:52.030270+00:00
|
2024-09-06T09:18:52.030304+00:00
| 364 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n1. **Map Creation**: \n - A `map<int, int>` is used to store the values from the `nums` vector. Each value in `nums` is mapped to `1` to mark it as "to be deleted" if found in the linked list.\n \n2. **Iterating the Linked List**:\n - A pointer `temp` is used to traverse the linked list, and `prev` is used to keep track of the previous node.\n - For each node, the value (`temp->val`) is checked in the map.\n \n3. **Node Deletion**:\n - If the current node\'s value exists in the map (`mpp[data] == 1`), the node is deleted.\n - If the node is the head, the head is moved to the next node.\n - Otherwise, the `prev->next` is updated to skip the current node.\n - After deletion, the memory is freed using `delete`.\n\n4. **Return the New Head**:\n - The function returns the potentially modified head of the linked list.\n\n# Complexity\n- **Time complexity:**\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n- **O(n + m)** where `n` is the length of the `nums` vector and `m` is the number of nodes in the linked list. We iterate over the vector and linked list once each.\n\n- **Space complexity:**\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n- **O(n)** because of the map used to store the values from the `nums` vector.\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n map<int , int> mpp;\n\n for(auto i : nums){\n mpp[i] = 1;\n }\n\n ListNode* prev = head;\n ListNode* temp = head;\n\n while(temp){\n int data = temp->val;\n if(mpp[data] == 1){\n if(temp == head){\n head = temp->next;\n ListNode *del = temp;\n temp = temp->next;\n delete del;\n }\n else{\n prev->next = temp->next;\n ListNode* del = temp;\n temp = temp->next;\n delete del;\n }\n }\n else{\n prev = temp;\n temp = temp->next;\n }\n \n }\n\n return head;\n }\n};\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'C++']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
simple and easy Python solution 😍❤️🔥
|
simple-and-easy-python-solution-by-shish-cqaj
|
\n# if it\'s help, please up \u2B06 vote! \u2764\uFE0F\n\n###### Let\'s Connect on LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/in/shishirrsiam\n###### Let\'s Connect on Facebook
|
shishirRsiam
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T00:45:17.861236+00:00
|
2024-09-06T00:45:17.861262+00:00
| 977 | false |
\n# if it\'s help, please up \u2B06 vote! \u2764\uFE0F\n\n###### Let\'s Connect on LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/in/shishirrsiam\n###### Let\'s Connect on Facebook: www.fb.com/shishirrsiam\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n+m)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python []\nclass Solution(object):\n def modifiedList(self, nums, head):\n nums = set(nums) \n ans = ListNode(0)\n tail = ans\n\n while head:\n val = head.val\n head = head.next\n if val not in nums:\n tail.next = ListNode(val)\n tail = tail.next\n return ans.next\n```\n\n\n# if it\'s help, please up \u2B06 vote! \u2764\uFE0F\n\n###### Let\'s Connect on LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/in/shishirrsiam\n###### Let\'s Connect on Facebook: www.fb.com/shishirrsiam
| 7 | 1 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 9 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Simple Java || C++ Code ☠️
|
simple-java-c-code-by-abhinandannaik1717-22jp
|
Code (Using sorting) :\n\njava []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNo
|
abhinandannaik1717
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-15T17:44:07.318274+00:00
|
2024-09-06T02:25:23.887650+00:00
| 496 | false |
### Code (Using sorting) :\n\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n int n = nums.length;\n Arrays.sort(nums);\n ListNode slow = head;\n ListNode fast = slow.next;\n while(fast!=null){\n if(fast.val>nums[n-1]){\n slow=fast;\n fast=fast.next;\n continue;\n }\n if(help(nums,fast.val)){\n slow.next=fast.next;\n fast=fast.next;\n }\n else{\n slow=fast;\n fast=fast.next;\n }\n }\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n if(head.val==nums[i]){\n head = head.next;\n }\n }\n return head;\n }\n public boolean help(int[] nums,int a){\n int l=0,h=nums.length-1,mid=0;\n while(l<=h){\n mid=(l+h)/2;\n if(nums[mid]==a){\n return true;\n }\n else if(nums[mid]>a){\n h=mid-1;\n }\n else{\n l=mid+1;\n }\n }\n return false;\n }\n}\n```\n```C++ []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n int n = nums.size();\n sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());\n ListNode* slow = head;\n ListNode* fast = slow->next;\n while(fast!=NULL){\n if(fast->val>nums[n-1]){\n slow=fast;\n fast=fast->next;\n continue;\n }\n if(help(nums,fast->val)){\n slow->next=fast->next;\n fast=fast->next;\n }\n else{\n slow=fast;\n fast=fast->next;\n }\n }\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n if(head->val==nums[i]){\n head = head->next;\n }\n }\n return head;\n }\n bool help(vector<int>& nums,int a){\n int l=0,h=nums.size()-1,mid=0;\n while(l<=h){\n mid=(l+h)/2;\n if(nums[mid]==a){\n return true;\n }\n else if(nums[mid]>a){\n h=mid-1;\n }\n else{\n l=mid+1;\n }\n }\n return false;\n }\n};\n```\n\n### Code (Using HashSet) :\n``` java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n int n = nums.length;\n HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n set.add(nums[i]);\n }\n while(set.contains(head.val)){\n head=head.next;\n }\n ListNode slow = head;\n ListNode fast = slow.next;\n while(fast!=null){\n if(set.contains(fast.val)){\n slow.next = fast.next;\n fast=fast.next;\n }\n else{\n slow=fast;\n fast=fast.next;\n }\n }\n return head;\n }\n}\n```\n\n\n### Explanation For First Code:\n\n\n\n\n1. **Initialization**:\n - The array `nums` is sorted to enable binary search.\n - Two pointers, `slow` and `fast`, are initialized to traverse the linked list.\n\n2. **Traversal and Removal**:\n - Traverse the linked list using `fast` pointer.\n - If `fast.val` is greater than the maximum value in `nums`, move both `slow` and `fast` pointers forward.\n - If `fast.val` is found in `nums` using the `help` method (binary search), remove the `fast` node by updating `slow.next`.\n - If `fast.val` is not in `nums`, move both pointers forward.\n\n3. **Handling the Head Node**:\n - After the main traversal, check if the head node\'s value is in `nums` and remove it if necessary.\n\n4. **Return the Modified List**:\n - Return the updated head of the linked list.\n\n### Helper Method (Binary Search)\n\nThe `help` method performs a binary search to check if a value `a` exists in the sorted array `nums`.\n\n\n\n\n### Example\n\nSuppose we have the following inputs:\n- `nums = [2, 3, 5]`\n- Linked list: `1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6`\n\n### Step-by-Step Execution\n\n1. **Initial Setup**:\n - Sort the `nums` array: `nums = [2, 3, 5]` (already sorted in this case).\n - Initialize `slow` to point to the head of the list (`1`).\n - Initialize `fast` to point to the second node (`2`).\n\n2. **First Iteration**:\n - `fast.val = 2`, which is in `nums`.\n - Remove the node with value `2` by setting `slow.next` to `fast.next`:\n - Linked list becomes: `1 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6`\n - Move `fast` to the next node (`3`).\n\n3. **Second Iteration**:\n - `fast.val = 3`, which is in `nums`.\n - Remove the node with value `3` by setting `slow.next` to `fast.next`:\n - Linked list becomes: `1 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6`\n - Move `fast` to the next node (`4`).\n\n4. **Third Iteration**:\n - `fast.val = 4`, which is not in `nums`.\n - Move both `slow` and `fast` pointers forward:\n - `slow` points to `4`, `fast` points to `5`.\n\n5. **Fourth Iteration**:\n - `fast.val = 5`, which is in `nums`.\n - Remove the node with value `5` by setting `slow.next` to `fast.next`:\n - Linked list becomes: `1 -> 4 -> 6`\n - Move `fast` to the next node (`6`).\n\n6. **Fifth Iteration**:\n - `fast.val = 6`, which is not in `nums`.\n - Move both `slow` and `fast` pointers forward:\n - `slow` points to `6`, `fast` is now `null`.\n\n7. **End of Main Traversal**:\n - The main traversal ends since `fast` is `null`.\n - Now, we need to check if the head node (`1`) is in `nums`:\n - It is not, so we keep the head as it is.\n\n### Final Result\nThe modified linked list is:\n- `1 -> 4 -> 6`\n\n### Detailed Code Execution\n\nLet\'s break down the code execution for this example:\n\n1. **Initialization**:\n ```java\n int n = nums.length; // n = 3\n Arrays.sort(nums); // nums = [2, 3, 5]\n ListNode slow = head; // slow points to node with value 1\n ListNode fast = slow.next; // fast points to node with value 2\n ```\n\n2. **First Iteration**:\n ```java\n if (help(nums, fast.val)) { // help(nums, 2) returns true\n slow.next = fast.next; // remove node with value 2\n fast = fast.next; // fast moves to node with value 3\n } else {\n slow = fast;\n fast = fast.next;\n }\n ```\n\n3. **Second Iteration**:\n ```java\n if (help(nums, fast.val)) { // help(nums, 3) returns true\n slow.next = fast.next; // remove node with value 3\n fast = fast.next; // fast moves to node with value 4\n } else {\n slow = fast;\n fast = fast.next;\n }\n ```\n\n4. **Third Iteration**:\n ```java\n if (help(nums, fast.val)) { // help(nums, 4) returns false\n slow = fast;\n fast = fast.next; // slow points to node with value 4, fast moves to node with value 5\n } else {\n slow = fast;\n fast = fast.next;\n }\n ```\n\n5. **Fourth Iteration**:\n ```java\n if (help(nums, fast.val)) { // help(nums, 5) returns true\n slow.next = fast.next; // remove node with value 5\n fast = fast.next; // fast moves to node with value 6\n } else {\n slow = fast;\n fast = fast.next;\n }\n ```\n\n6. **Fifth Iteration**:\n ```java\n if (help(nums, fast.val)) { // help(nums, 6) returns false\n slow = fast;\n fast = fast.next; // slow points to node with value 6, fast is now null\n } else {\n slow = fast;\n fast = fast.next;\n }\n ```\n\n7. **Final Check**:\n ```java\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n if (head.val == nums[i]) { // head.val = 1, nums does not contain 1\n head = head.next; // no change\n }\n }\n ```\n\nThe final linked list is `1 -> 4 -> 6`, which is returned.\n\n\n\n\n\n### Complexity Analysis\n\n- **Time Complexity**:\n - Sorting the `nums` array takes \\(O(n log n)\\).\n - Traversing the linked list and performing binary search for each node takes \\(O(m \\log n)\\), where \\(m\\) is the number of nodes in the linked list.\n - Overall time complexity: \\(O(n log n + m log n)\\).\n\n- **Space Complexity**:\n - The space complexity is \\(O(1)\\) if the space for the output and input is not counted. Otherwise, the space complexity is \\(O(n + m)\\) for storing the `nums` array and the linked list.\n\n### Explanation of second code:\n\n\n\n1. **Convert the array to a HashSet**: The code first converts the array `nums` into a `HashSet`. This allows for O(1) average time complexity when checking whether a value exists in the set.\n\n ```java\n HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n set.add(nums[i]);\n }\n ```\n\n2. **Remove nodes from the head**: If the value of the current head node is in the `set`, the code updates the head to the next node, effectively removing the current node.\n\n ```java\n while(set.contains(head.val)){\n head = head.next;\n }\n ```\n\n3. **Traverse the list and remove nodes**: After ensuring the new head has a value not in the set, the code uses two pointers, `slow` and `fast`. The `slow` pointer always points to the last node that shouldn\'t be removed, and the `fast` pointer checks the next nodes. When a node with a value in `set` is found, it is skipped by updating `slow.next`.\n\n ```java\n ListNode slow = head;\n ListNode fast = slow.next;\n while(fast != null){\n if(set.contains(fast.val)){\n slow.next = fast.next; // Skip the node\n fast = fast.next; // Move fast pointer ahead\n }\n else{\n slow = fast; // Move slow pointer ahead\n fast = fast.next; // Move fast pointer ahead\n }\n }\n ```\n\n4. **Return the modified list**: After removing all nodes whose values exist in `nums`, the modified linked list starting from `head` is returned.\n\n### Example:\n#### Input:\n- `nums = [1, 3, 5]`\n- `linked list: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5`\n\n#### Process:\n1. Convert `nums` into a set: `{1, 3, 5}`.\n2. Start at the head:\n - Remove node with value `1` (head becomes `2`).\n - Traverse to node `3` (remove it).\n - Traverse to node `5` (remove it).\n\n#### Output:\n- Modified linked list: `2 -> 4`\n\n### Time Complexity:\n- **O(n)** to create the `HashSet` from the array `nums`, where `n` is the length of the array.\n- **O(m)** to traverse the linked list and remove nodes, where `m` is the number of nodes in the list.\n\nSo, the overall time complexity is **O(n + m)**.\n\n
| 7 | 0 |
['Array', 'Linked List', 'Simulation', 'C++', 'Java']
| 2 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Easy Video Solution 🔥 || How to 🤔 in Interview || Using Temp Node ✅
|
easy-video-solution-how-to-in-interview-5fwph
|
If you like the solution Please Upvote and subscribe to my youtube channel\n\n\n\nEasy Video Explanation\n\nhttps://youtu.be/LHe2bHokebc\n\n \n\n# Code\n\n\n
|
ayushnemmaniwar12
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T04:23:41.101673+00:00
|
2024-09-06T04:23:41.101711+00:00
| 1,759 | false |
***If you like the solution Please Upvote and subscribe to my youtube channel***\n\n\n\n***Easy Video Explanation***\n\nhttps://youtu.be/LHe2bHokebc\n\n \n\n# Code\n\n\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& v, ListNode* head) {\n ListNode *d= new ListNode(-1);\n ListNode *t=d;\n set<int>s;\n for(auto i:v)\n s.insert(i);\n while(head!=NULL) {\n if(s.find(head->val)==s.end()) {\n t->next=head;\n t=t->next;\n }\n head=head->next;\n }\n t->next=NULL;\n return d->next;\n }\n};\n```\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, v, head):\n dummy = ListNode(-1)\n t = dummy\n s = set(v)\n \n while head:\n if head.val not in s:\n t.next = head\n t = t.next\n head = head.next\n \n t.next = None\n return dummy.next\n```\n```Java []\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(List<Integer> v, ListNode head) {\n ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);\n ListNode t = dummy;\n Set<Integer> s = new HashSet<>(v);\n \n while (head != null) {\n if (!s.contains(head.val)) {\n t.next = head;\n t = t.next;\n }\n head = head.next;\n }\n \n t.next = null;\n return dummy.next;\n }\n}\n\n```\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n O(N*log(N))\n \n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n O(N)\n\n# ***If you like the solution Please Upvote and subscribe to my youtube channel***\n***It Motivates me to record more videos***\n\n*Thank you* \uD83D\uDE00
| 6 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 5 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
🔥BEGINNER FRIENDLY👏 C++ CODE || O(n) 💯 || EASY EXPLANATION 😊👍
|
beginner-friendly-c-code-on-easy-explana-v5d5
|
Intuition & Approach :\n\nLets see how you can solve this problem:\n\n1. Frequency Map Construction:\n - You create an unordered map mp to store the frequency
|
DEvilBackInGame
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T03:21:25.180225+00:00
|
2024-09-06T03:21:25.180254+00:00
| 1,293 | false |
# Intuition & Approach :\n\nLets see how you can solve this problem:\n\n1. **Frequency Map Construction**:\n - You create an unordered map `mp` to store the frequency of each element in the input vector `nums`.\n - For each element in `nums`, you increment its count in the map (`mp[i]++`).\n - This allows you to quickly check if a value from the linked list exists in `nums`.\n\n2. **Pointer Initialization**:\n - You use two pointers, `curr` and `prev`, both initially set to the `head` of the linked list:\n - `curr` is used to traverse the list.\n - `prev` is used to keep track of the previous node, which is necessary for node deletion.\n\n3. **Traversal and Removal**:\n - You iterate through the linked list using the `curr` pointer until it becomes `nullptr` (reaching the end of the list).\n - For each node, you check if its value exists in the `mp` map (i.e., `mp[curr->val] != 0`).\n - **If the node\u2019s value exists in the map (i.e., should be removed)**:\n - If `prev == curr` (this occurs when the node to be removed is at the head of the list):\n - You move the `head` to the next node (`head = head->next`), effectively removing the current node from the list.\n - Move `curr` to the next node (`curr = curr->next`) and update `prev` to point to `curr` as well.\n - If `prev != curr` (i.e., the node to be removed is somewhere after the head):\n - You skip the current node by making `prev->next = curr->next`, bypassing the node to be removed.\n - Move `curr` to the next node (`curr = curr->next`), but `prev` remains pointing to the previous node (since it already bypassed the current node).\n - **If the node\u2019s value does not exist in the map (i.e., should be retained)**:\n - You simply move both `prev` and `curr` pointers to the next nodes in the list (`prev = curr; curr = curr->next`).\n\n4. **Return the Updated List**:\n - After traversing and modifying the list, the function returns the `head` pointer, which now points to the modified list with the unwanted nodes removed.\n\n\n\n\n# Complexity\n- **Time complexity** : **O(n + m)** , where **n**-> *size of nums*, **m**-> *number of nodes* in the linked list.\n\n- **Space complexity** : **O(n)**, where **n**-> elements from nums in the unordered map.\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n unordered_map<int,int>mp;\n for(auto i:nums) mp[i]++;\n ListNode* curr=head;\n ListNode* prev=head;\n\n while(curr!=nullptr){\n if(mp[curr->val]>0){\n\n if(prev==curr){\n if(head==curr) head=head->next;\n\n curr=curr->next;\n prev=curr;\n }else {\n curr=curr->next;\n prev->next=curr;\n }\n }\n else {\n prev=curr;\n curr=curr->next;\n\n }\n }\n\n return head;\n \n }\n};\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Ordered Map', 'C++']
| 7 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
✅ Easy C++ Solution
|
easy-c-solution-by-moheat-ojny
|
Code\n\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\
|
moheat
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T04:30:19.581189+00:00
|
2024-07-14T04:30:19.581218+00:00
| 2,083 | false |
# Code\n```\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n unordered_set<int> s(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n \n ListNode* newHead = new ListNode(0);\n newHead-> next = head;\n ListNode* prev = newHead;\n ListNode* current = head;\n \n while(current != NULL)\n {\n if(s.find(current-> val) != s.end())\n {\n prev-> next = current-> next;\n delete current;\n current = prev-> next;\n }\n else\n {\n prev = current;\n current = current-> next;\n }\n }\n ListNode* result = newHead-> next;\n delete newHead;\n return result;\n }\n};\n```
| 6 | 1 |
['C++']
| 5 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Simple Solution | 99.5 % Beats | Java
|
simple-solution-995-beats-java-by-eshwar-j3hi
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nUsing a count array to say weather an element from head is present in nums or not.\n\n\
|
eshwaraprasad
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T03:17:15.789461+00:00
|
2024-09-06T03:17:15.789484+00:00
| 659 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nUsing a count array to say weather an element from `head` is present in `nums` or not.\n\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n int max = 0;\n for(int ele : nums) {\n if(ele > max) max = ele;\n }\n int count[] = new int[max + 1];\n for(int ele : nums) count[ele] = 1;\n\n ListNode prev = new ListNode(0);\n prev.next = head;\n ListNode result = prev;\n while(head != null) {\n if(head.val <= max && count[head.val] == 1) {\n prev.next = head.next;\n head = head.next;\n }\n else {\n prev = head;\n head = head.next;\n }\n }\n return result.next;\n }\n}\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Java']
| 4 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
DELETE IN DISGUISE ✅✅69_BEATS_100%✅✅🔥Easy Solution🔥With Explanation🔥
|
delete-in-disguise-69_beats_100easy-solu-po2y
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nwe need to drop off all the nodes we dont want ie which are already in the nums array w
|
srinivas_bodduru
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T02:25:06.025966+00:00
|
2024-09-06T02:25:06.026000+00:00
| 2,522 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nwe need to drop off all the nodes we dont want ie which are already in the nums array we can use 2 pointers to do this lets see\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nfirst of all we will hash set the nums array for O(1) look up\nthen we will attach an empty node to our head and an anchor pointer to this empty node\n\nthen we will start travelling \nwhile there is a node next to our moving pointer,\nwe will check if this pointer is in the set or not \nif it is we have to drop it we will assign the next of our pointer to the next.next to skip this node \nif the node is not in the set we will simply move forward with the next node \n\nfinally since our anchor is pointing to an empty node \nwe will retrn anchor .next \nthats it \n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(N)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nvar modifiedList = function(nums, head) {\n const set = new Set(nums);\n let cur = new ListNode(null, head);\n let newHead = cur;\n\n while(cur.next) {\n if(set.has(cur.next.val)) {\n cur.next = cur.next.next;\n } else {\n cur = cur.next;\n }\n }\n\n return newHead.next;\n};\n```\n```python []\nclass ListNode:\n def __init__(self, x, next=None):\n self.val = x\n self.next = next\n\ndef modified_list(nums, head):\n num_set = set(nums)\n dummy = ListNode(None, head)\n current = dummy\n\n while current.next:\n if current.next.val in num_set:\n current.next = current.next.next\n else:\n current = current.next\n\n return dummy.next\n\n```\n```ruby []\nimport java.util.HashSet;\nimport java.util.Set;\n\nclass ListNode {\n int val;\n ListNode next;\n ListNode(int x) {\n val = x;\n next = null;\n }\n ListNode(int x, ListNode next) {\n val = x;\n this.next = next;\n }\n}\n\npublic class Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();\n for (int num : nums) {\n set.add(num);\n }\n\n ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);\n ListNode current = dummy;\n\n while (current.next != null) {\n if (set.contains(current.next.val)) {\n current.next = current.next.next;\n } else {\n current = current.next;\n }\n }\n\n return dummy.next;\n }\n}\n\n```\n```c []\n#include <stdlib.h>\n#include <stdbool.h>\n\ntypedef struct ListNode {\n int val;\n struct ListNode *next;\n} ListNode;\n\ntypedef struct HashSet {\n bool *data;\n int size;\n} HashSet;\n\nHashSet* createHashSet(int max_size) {\n HashSet *set = (HashSet *)malloc(sizeof(HashSet));\n set->data = (bool *)calloc(max_size, sizeof(bool));\n set->size = max_size;\n return set;\n}\n\nvoid addToHashSet(HashSet *set, int num) {\n if (num >= 0 && num < set->size) {\n set->data[num] = true;\n }\n}\n\nbool containsHashSet(HashSet *set, int num) {\n return num >= 0 && num < set->size && set->data[num];\n}\n\nvoid freeHashSet(HashSet *set) {\n free(set->data);\n free(set);\n}\n\nListNode* modifiedList(int* nums, int numsSize, ListNode* head) {\n HashSet *set = createHashSet(100000); // Assume a large enough size\n for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) {\n addToHashSet(set, nums[i]);\n }\n\n ListNode dummy = {0, head};\n ListNode *current = &dummy;\n\n while (current->next != NULL) {\n if (containsHashSet(set, current->next->val)) {\n ListNode *temp = current->next;\n current->next = temp->next;\n free(temp);\n } else {\n current = current->next;\n }\n }\n\n freeHashSet(set);\n return dummy.next;\n}\n```
| 5 | 1 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'C', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'JavaScript', 'C#']
| 6 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
3 ways to resolve problem: binary search, hashmap and optimized way
|
3-ways-to-resolve-problem-binary-search-47f77
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
lainhdev
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T01:48:09.154586+00:00
|
2024-09-06T01:48:09.154607+00:00
| 81 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code 1 - Binary Search\n```golang []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * type ListNode struct {\n * Val int\n * Next *ListNode\n * }\n */\nfunc binarySearch(nums []int, val int) bool {\n low, high := 0, len(nums)-1\n\tvar mid int\n\n\tfor high >= low {\n\t\tmid = low + (high-low)/2\n\n\t\tif nums[mid] == val {\n\t\t\treturn true\n\t\t}\n\n\t\tif nums[mid] > val {\n\t\t\thigh = mid - 1\n\t\t} else {\n\t\t\tlow = mid + 1\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\n\treturn false\n}\n\nfunc modifiedList(nums []int, head *ListNode) *ListNode {\n\tdumpHead := &ListNode{0, head}\n\tcurrent := dumpHead\n \n slices.Sort(nums)\n\tfor current.Next != nil {\n\t\tif binarySearch(nums, current.Next.Val) {\n\t\t\tcurrent.Next = current.Next.Next\n\t\t} else {\n\t\t\tcurrent = current.Next\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\n\treturn dumpHead.Next\n}\n```\n\n# Code 2 - Hashmap\n\n```golang []\n\nfunc modifiedList(nums []int, head *ListNode) *ListNode {\n m := make(map[int]bool)\n for _, num := range nums {\n m[num] = true\n }\n\n\tdumpHead := &ListNode{0, head}\n\tcurrent := dumpHead\n \n\tfor current.Next != nil {\n\t\tif m[current.Next.Val] {\n\t\t\tcurrent.Next = current.Next.Next\n\t\t} else {\n\t\t\tcurrent = current.Next\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\n\treturn dumpHead.Next\n}\n```\n\n# Code 3 - Runtime beat 100%, Memory beat 97,57%\n```golang []\nfunc modifiedList(nums []int, head *ListNode) *ListNode {\n m := [100001]bool{}\n for _, num := range nums {\n m[num] = true\n }\n\n\tdumpHead := &ListNode{0, head}\n\tcurrent := dumpHead\n \n\tfor current.Next != nil {\n\t\tif m[current.Next.Val] {\n\t\t\tcurrent.Next = current.Next.Next\n\t\t} else {\n\t\t\tcurrent = current.Next\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\n\treturn dumpHead.Next\n}\n```\n
| 5 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Binary Search', 'Go']
| 1 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Dcc-: 06/09/2024 || LinkedList || O(N)🔥
|
dcc-06092024-linkedlist-on-by-sajaltiwar-vq6i
|
Approach:\nThe problem seems to involve removing nodes from a linked list where the node\'s value is present in a given array nums. Here\'s the approach and int
|
sajaltiwari007
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T01:17:43.385080+00:00
|
2024-09-06T01:17:43.385110+00:00
| 1,532 | false |
### Approach:\nThe problem seems to involve removing nodes from a linked list where the node\'s value is present in a given array `nums`. Here\'s the approach and intuition behind the solution:\n\n1. **Use of a HashSet**: \n - The array `nums` is first converted into a `HashSet`. This is done because checking for membership in a `HashSet` is faster (constant time on average, O(1)) than checking in a list (O(n) in the worst case).\n \n2. **Removing Nodes from the Start**:\n - The solution first ensures that any nodes at the beginning of the linked list (`head`) that have values present in the `HashSet` are removed. This loop progresses until it finds the first node whose value is not in the `HashSet`.\n\n3. **Traversing the Remaining List**:\n - A `temp` pointer is used to traverse the list, and a `prev` pointer keeps track of the last node that remains in the list. For every node:\n - If the current node\'s value (`temp.val`) is in the `HashSet`, the node is removed by updating `prev.next` to `temp.next`.\n - If the current node\u2019s value is not in the `HashSet`, `prev` is updated to be the current node (`temp`).\n\n4. **Return the Modified List**: \n - After completing the traversal and removal of nodes, the modified list is returned.\n\n### Time and Space Complexity:\n\n#### Time Complexity:\n1. **HashSet Construction**: Constructing the `HashSet` from the array `nums` takes O(m) time, where `m` is the length of the array.\n2. **First While Loop (Removing from the start)**: The first while loop potentially runs through the first few nodes until it finds a node that isn\u2019t in the `HashSet`. In the worst case, this will iterate over all `n` nodes in the list.\n3. **Second While Loop (Removing from the rest)**: The second loop iterates through the remaining nodes, and for each node, checking membership in the `HashSet` takes O(1). Hence, this loop also takes O(n) in total.\n\nThus, the total time complexity is **O(m + n)**, where `m` is the size of the array `nums` and `n` is the number of nodes in the linked list.\n\n#### Space Complexity:\n1. The `HashSet` takes **O(m)** space, where `m` is the size of the input array `nums`.\n2. No additional space is required for the linked list itself, so the overall space complexity is **O(m)**.\n\n### Intuition:\nThe intuition behind this approach is to make use of the faster lookup times provided by a `HashSet` to efficiently remove nodes with values present in the `nums` array. By updating pointers in the linked list as needed, we avoid creating a new list, keeping the space usage optimal while maintaining a linear time traversal.\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n \n HashSet<Integer> list = new HashSet<>();\n \n for(int i:nums)\n list.add(i);\n \n while(head!=null && list.contains(head.val)){\n \n head = head.next;\n }\n \n ListNode temp = head;\n ListNode prev = head;\n \n while(temp!=null){\n \n if(list.contains(temp.val)){\n prev.next = temp.next;\n temp = temp.next;\n }\n else{\n \n prev = temp;\n temp = temp.next;\n \n }\n \n \n }\n return head;\n \n }\n}\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'Java']
| 4 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
✅💯🔥Simple Code📌🚀| 🔥✔️Easy to understand🎯 | 🎓🧠Beginner friendly🔥| O(n) Time Complexity💀💯
|
simple-code-easy-to-understand-beginner-4e7lu
|
Tuntun Mosi ko Pranam\nSolution tuntun mosi ki photo ke baad hai. Scroll Down\n\n# Code\njava []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class Li
|
atishayj4in
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-11T17:41:17.439270+00:00
|
2024-09-11T17:41:17.439309+00:00
| 125 | false |
# Tuntun Mosi ko Pranam\nSolution tuntun mosi ki photo ke baad hai. Scroll Down\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n Set<Integer> setz = new HashSet<>();\n for(int num : nums){\n setz.add(num);\n }\n ListNode curr = head;\n ListNode prev = head;\n while(curr!=null){\n ListNode next = curr.next;\n if(setz.contains(curr.val)){\n if(curr==head){\n head=next;\n }\n prev.next = next;\n }else{\n prev = curr;\n }\n curr = next;\n }\n return head;\n }\n}\n```\n
| 4 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'C', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Delete Nodes From Linked List Present In Array || DCC 06/09/24 || Beginner Friendly Solution🔥🔥
|
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-5y0y
|
Intuition\nThe problem requires modifying a linked list by removing nodes whose values exist in a given array nums. The idea is to traverse through the linked l
|
Ayush_Singh2004
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T14:02:27.287264+00:00
|
2024-09-06T14:02:27.287290+00:00
| 70 | false |
# Intuition\nThe problem requires modifying a linked list by removing nodes whose values exist in a given array `nums`. The idea is to traverse through the linked list and remove any node whose value is present in the nums array.\n\n# Approach\n**Convert nums to a Set:**\n- You use a `set` to store all the values from the array `nums`. This allows for $$O(1)$$ average-time complexity checks when determining if a value should be removed from the linked list.\n\n**Traverse and Mark Nodes:**\n- You traverse the linked list and mark nodes for removal by setting their value to $$0$$. This is done to avoid altering the linked list structure during the initial traversal.\n\n**Remove Marked Nodes:**\n- You traverse the linked list again, this time removing nodes that were marked with the value 0. \n- You handle three cases:\n->If the node to be removed is the head, adjust the head pointer.\n->If the node to be removed is in the middle or end, adjust pointers to skip over the removed node.\n->Ensure that all nodes are correctly removed, and the list is properly updated.\n\n# Complexity\n**Time complexity:**\n- Conversion to Set: $$O(N)$$ where N is the number of elements in nums. This is because each insertion into the set takes $$O(1)$$ on average.\n- First Traversal of Linked List: $$O(L)$$ where L is the number of nodes in the linked list. Each node is checked once.\n- Second Traversal and Removal: $$O(L)$$ for traversing the list again and removing nodes.\n- Therefore, the total time complexity is $$O(N + L)$$, where N is the size of nums and L is the size of the linked list.\n\n**Space complexity:**\n- Space for Set: $$O(N)$$, where N is the number of unique values in nums.\n- Space for Linked List Nodes: $$O(L)$$, but this is part of the input and not extra space used.\n- Thus, the space complexity is $$O(N)$$ for the additional space used by the set.\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n int i=0;\n set<long long int> st;\n\n for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); i++){\n st.insert(nums[i]);\n }\n\n \n ListNode* temp=head;\n\n while(temp!=NULL){\n if(temp!=NULL && st.find(temp->val)!=st.end()){\n temp->val=0;\n }\n temp=temp->next;\n }\n \n \n \n\n ListNode* prevN= NULL;\n ListNode* currN= head;\n\n while(currN){\n\n while(currN!=NULL && currN->val!=0){\n prevN=currN;\n currN=currN->next;\n }\n if(prevN==NULL && currN->val==0){\n head= currN->next;\n currN->next= NULL;\n currN= head;\n }\n \n else if(prevN->next!=NULL && currN->val==0){\n ListNode* nextN= currN->next;\n prevN->next= nextN;\n currN->next= NULL;\n currN=nextN;\n }\n else{\n return head;\n }\n }\n return head;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Array', 'Linked List', 'Ordered Set', 'C++']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Easy Solution
|
easy-solution-by-viratkohli-c95q
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n)\n n is a length of linked list.\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity:O(m)\n m is a size of nums
|
viratkohli_
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T03:33:44.520951+00:00
|
2024-09-06T03:37:42.373842+00:00
| 200 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n)\n n is a length of linked list.\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(m)\n m is a size of nums array (because of set).\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n unordered_set<int> s;\n for(int i = 0; i<nums.size(); i++){\n s.insert(nums[i]);\n }\n\n ListNode dummy(0);\n dummy.next = head;\n ListNode* prev = &dummy;\n ListNode* cur = head;\n\n while(cur != NULL){\n if(s.find(cur->val) != s.end()){\n prev->next = cur->next;\n delete cur;\n }\n else{\n prev = cur;\n }\n cur = prev->next;\n }\n\n return dummy.next;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'C++']
| 3 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Easy C++ Solution ✅✅
|
easy-c-solution-by-abhi242-85d2
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n unordered_set<int> s;\n int n=nums.size();\n
|
Abhi242
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T04:08:58.929059+00:00
|
2024-07-14T11:57:36.663669+00:00
| 1,231 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n unordered_set<int> s;\n int n=nums.size();\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n s.insert(nums[i]);\n }\n ListNode * ans=head; \n while(ans!=NULL && s.find(ans->val)!=s.end()){\n ans=ans->next; //Check for the head node excusively\n }\n head=ans;\n while(head!=NULL && head->next!=NULL){\n if(s.find(head->next->val)!=s.end()){\n head->next=head->next->next;\n continue;\n }\n head=head->next;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'C++']
| 2 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
[Beats 100%🔥] Counting | Easy and Beginner Friendly Solution 🚀
|
beats-100-counting-easy-and-beginner-fri-vrgn
|
IntuitionWe need to remove nodes from a linked list based on the values present in an array. Using a direct lookup mechanism will make deletions efficient.Appro
|
PradhumanGupta
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-18T10:16:51.605857+00:00
|
2025-02-18T10:16:51.605857+00:00
| 231 | false |
# Intuition
We need to remove nodes from a linked list based on the values present in an array. Using a direct lookup mechanism will make deletions efficient.
# Approach
1. **Find the maximum value** in the `nums` array to create a boolean lookup table.
2. **Mark elements in a frequency array** for quick existence checks.
3. **Traverse the linked list and remove nodes**:
- If the node's value exists in the `nums` array, remove it.
- Adjust the head if necessary.
- Maintain proper links when skipping nodes.
# Complexity
- **Time complexity:** $$O(n + m)$$
- `O(m)` to process `nums`, where `m` is the array length.
- `O(n)` to traverse the linked list.
- **Space complexity:** $$O(max)$$
- A boolean array of size `max+1` for quick lookup.
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null, pres = head, next = head != null ? head.next : null;
// Find the max value in nums array
int max = -1;
for (int num : nums) {
max = Math.max(max, num);
}
// Create a boolean lookup table
boolean[] freq = new boolean[max + 1];
for (int num : nums) freq[num] = true;
// Traverse the linked list and remove nodes
while (pres != null) {
if (pres.val < freq.length && freq[pres.val]) { // If value exists in nums
if (pres == head) {
head = head.next; // Update head if first node is removed
} else {
prev.next = next; // Remove the node
}
//move to next node
pres = next;
if (next != null) next = next.next;
} else {
//move to next node
prev = pres;
pres = next;
if (next != null) next = next.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
```
**Please Upvote⬆️**

| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Linked List', 'Counting', 'Java']
| 1 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
2 approaches Explained | CPP 🔥 🔥
|
2-approaches-explained-cpp-by-abhinav_sh-pey1
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n1. Creating a Set fro
|
Abhinav_Shakya
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T19:16:56.774405+00:00
|
2024-09-06T19:18:11.598544+00:00
| 33 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n1. **Creating a Set from the Vector**:\n ```cpp\n unordered_set<int> s(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n ```\n The elements of `nums` are stored in an unordered set `s` for fast lookup. This allows checking if a node\'s value is in `nums` in constant time on average.\n\n2. **Dummy Node**:\n ```cpp\n ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);\n dummy->next = head;\n ```\n A dummy node is created with value `0` and its `next` pointer set to the head of the linked list. This dummy node helps to simplify handling the case when the head of the list itself needs to be removed.\n\n3. **Two Pointers: `prev` and `curr`**:\n ```cpp\n ListNode* prev = dummy;\n ListNode* curr = head;\n ```\n Two pointers, `prev` and `curr`, are initialized. `prev` is used to keep track of the last node that remains in the list, and `curr` is used to traverse the list.\n\n4. **Traversing the List and Removing Nodes**:\n ```cpp\n while (curr != nullptr) {\n if (s.find(curr->val) != s.end()) {\n prev->next = curr->next;\n } else {\n prev = curr;\n }\n curr = curr->next;\n }\n ```\n The list is traversed using `curr`. For each node:\n - If the value of `curr` is found in the set `s`, that node is removed by setting `prev->next` to `curr->next` (skipping the current node).\n - If the value is not in the set, both `prev` and `curr` move forward.\n - `curr` is always moved to the next node in each iteration.\n\n5. **Returning the Modified List**:\n ```cpp\n return dummy->next;\n ```\n After the loop, the modified list is returned starting from `dummy->next`, which points to the new head (or the original head if no nodes were removed).\n\n---\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n+m)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code 1\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n // Step 1: Store the elements from the vector in a set for fast lookup.\n unordered_set<int> s(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n\n ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);\n dummy->next = head;\n\n ListNode* prev = dummy;\n ListNode* curr = head;\n\n while (curr != nullptr) {\n if (s.find(curr->val) != s.end()) {\n prev->next = curr->next;\n } else {\n prev = curr;\n }\n curr = curr->next;\n }\n\n return dummy->next;\n }\n};\n\n```\n\n# Code 2 explanation \n\n\n1. **Creating an Unordered Set from the Vector**:\n ```cpp\n unordered_set<int>s;\n for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {\n s.insert(nums[i]);\n }\n ```\n A set `s` is created to store all the elements of `nums`. This helps to quickly check whether a value exists in `nums`, as lookups in an unordered set take average constant time (**O(1)**).\n\n2. **Traversing the Original Linked List**:\n ```cpp\n ListNode* temp = head;\n ListNode* curr = new ListNode(0);\n vector<int> ans;\n while(temp != NULL) {\n int val1 = temp->val;\n if(s.find(val1) == s.end()) {\n ans.push_back(val1);\n }\n temp = temp->next;\n }\n ```\n - The linked list is traversed using the `temp` pointer. For each node:\n - The value `val1` of the current node (`temp->val`) is checked against the set `s`.\n - If the value is **not** found in the set (`s.find(val1) == s.end()`), it is pushed into the vector `ans`.\n - After processing all nodes, `ans` contains the values from the original list that are **not** in the vector `nums`.\n\n3. **Creating a New Linked List**:\n ```cpp\n ListNode* anshead = new ListNode(0);\n ListNode* tail = anshead;\n for(int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++) {\n ListNode* temp = new ListNode(ans[i]);\n tail->next = temp;\n tail = temp;\n }\n return anshead->next;\n ```\n - A new linked list is constructed using the values stored in the `ans` vector. \n - A dummy node (`anshead`) is used to simplify building the new list.\n - The new nodes are created with values from `ans`, and linked using the `tail` pointer.\n - Finally, the function returns `anshead->next`, which points to the head of the new linked list (skipping the dummy node).\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n+m)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(n+m)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n\n# Code 2\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n unordered_set<int>s;\n for(int i =0;i<nums.size();i++)\n {\n s.insert(nums[i]);\n }\n\n ListNode* temp = head;\n ListNode* curr = new ListNode(0);\n vector<int>ans;\n while(temp!=NULL)\n {\n int val1 = temp->val;\n if(s.find(val1)==s.end())\n {\n ans.push_back(val1);\n \n }\n temp = temp->next;\n \n }\n\n ListNode* anshead = new ListNode(0);\n ListNode* tail = anshead;\n for(int i=0;i<ans.size();i++)\n {\n ListNode* temp = new ListNode(ans[i]);\n tail->next = temp;\n tail = temp;\n }\n return anshead->next;\n \n }\n};\n\n```\n\n\n
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Linked List', 'C++']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Python | Two Pointers & Dummy Node
|
python-two-pointers-dummy-node-by-khosiy-ubc0
|
see the Successfully Accepted Submission\n\n# Code\npython3 []\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Option
|
Khosiyat
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T06:38:56.506456+00:00
|
2024-09-06T06:38:56.506488+00:00
| 182 | false |
[see the Successfully Accepted Submission](https://leetcode.com/problems/delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array/submissions/1380783070/?envType=daily-question&envId=2024-09-06)\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:\n # Convert nums to a set for O(1) lookup\n num_set = set(nums)\n \n # Create a dummy node to handle edge cases where the head itself needs to be removed\n dummy = ListNode(0)\n dummy.next = head\n \n # Corrected: Two pointers - prev starts at dummy, and current starts at head\n prev, current = dummy, head\n \n while current:\n if current.val in num_set:\n # Skip the current node by linking prev to current.next\n prev.next = current.next\n else:\n # Move prev to current if current is not removed\n prev = current\n # Move to the next node in the list\n current = current.next\n \n # Return the new head (which is dummy.next)\n return dummy.next\n\n```\n\n## Approach:\n\n1. **Convert `nums` to a set**: \n Since checking for an element in a set is O(1) compared to O(n) in a list, we first convert the `nums` array into a set. This will allow us to efficiently check whether the value of a node in the linked list exists in `nums`.\n\n2. **Traverse the linked list**: \n We\'ll traverse through the linked list and skip the nodes that have a value found in the `nums` set.\n\n3. **Maintain a dummy node**: \n To simplify the edge cases (like when the head node itself needs to be removed), we\'ll use a dummy node that points to the head of the linked list. This will help in re-assigning the head if the first few nodes are removed.\n\n4. **Two-pointer approach**:\n - One pointer (`current`) will traverse through the list.\n - Another pointer (`prev`) will keep track of the last valid node (i.e., a node whose value is not in `nums`).\n - When we encounter a node whose value is in `nums`, we\'ll bypass that node by setting `prev.next = current.next`.\n\n5. **Return the modified list**: \n After traversing the list, we return the list starting from `dummy.next` which will skip any removed nodes at the beginning of the list.\n\n---\n\n## Explanation:\n\n1. **`num_set = set(nums)`**: \n We convert the `nums` list into a set to improve the lookup time.\n\n2. **`dummy = ListNode(0)`**: \n We create a dummy node that points to the head. This helps in simplifying the logic when the head needs to be removed, as we can always return `dummy.next`.\n\n3. **`prev, current = dummy, head`**:\n - `prev` keeps track of the last valid node (the one before the nodes that will be removed).\n - `current` is the node being checked.\n\n4. **`if current.val in num_set`**: \n If the value of the `current` node is in `nums`, we skip this node by setting `prev.next = current.next`.\n\n5. **`prev = current`**: \n If the node is not removed, we move `prev` to point to `current`.\n\n6. **`current = current.next`**: \n Move the `current` pointer to the next node in the list.\n\n7. **Return `dummy.next`**: \n The modified list is returned, skipping the nodes removed at the beginning.\n\n---\n\n## Time Complexity:\n\n- The time complexity is O(n), where `n` is the number of nodes in the linked list. This is because we traverse the linked list once.\n- Converting `nums` into a set is O(m), where `m` is the length of `nums`.\n\nThus, the overall time complexity is O(n + m).\n\n---\n\n## Example:\n\nFor `nums = [1, 2, 3]` and `head = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]`, the output will be `[4, 5]` because nodes with values 1, 2, and 3 will be removed.\n\n\n
| 3 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 3 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
simple java solution || beats 90%
|
simple-java-solution-beats-90-by-binoy_s-ggo8
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
binoy_saren
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T06:27:22.347131+00:00
|
2024-09-06T06:27:22.347163+00:00
| 81 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();\n for (int i : nums) {\n set.add(i);\n }\n while(head.next!=null && set.contains(head.val)){\n head=head.next;\n }\n ListNode current=head;\n while(current.next!=null){\n if(set.contains(current.next.val)){\n current.next=current.next.next;\n }\n else{\n current=current.next;\n }\n }\n return head;\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'Java']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Clean Code For Java Using HashSet
|
clean-code-for-java-using-hashset-by-sau-4pxj
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe task is to remove nodes from the linked list whose values appear in the given array
|
Saumo_05
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T05:08:09.490906+00:00
|
2024-09-06T05:08:09.490932+00:00
| 19 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe task is to remove nodes from the linked list whose values appear in the given array. By storing these values in a HashSet, we can efficiently check whether a node\u2019s value needs to be removed or not.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. First, add all elements of the nums array to a HashSet. This allows for O(1) average time complexity when checking if a value exists in the set.\n2. Initialize a dummy node that points to the head of the linked list to handle edge cases where the head node itself might need to be removed.\n3. Use two pointers: prev to track the node before the current one, and temp to iterate through the list.\n4. For each node, check if its value exists in the HashSet:\n5. If it exists, adjust prev.next to skip the current node.\n6. If it doesn\'t exist, move prev to the current node.\n7. Continue this process until the end of the list is reached.\n8. Return dummy.next, which points to the modified linked list.\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n + m)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(m)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n HashSet<Integer> hm= new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++)\n {\n hm.add(nums[i]);\n }\n ListNode dummy=new ListNode(-1);\n ListNode prev=dummy;\n ListNode temp=head;\n prev.next=temp;\n while(temp!=null)\n {\n if(hm.contains(temp.val))\n {\n prev.next=temp.next;\n }\n else\n {\n prev=temp;\n }\n temp=temp.next;\n }\n\n return dummy.next;\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'Java']
| 1 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Easy to understand Code || Beats 100% || C++ || Java|| Pyhton || JavaScript
|
easy-to-understand-code-beats-100-c-java-y7wa
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe goal is to modify a linked list by removing nodes whose values are present in a giv
|
_Rachi
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T04:48:14.984059+00:00
|
2024-09-06T04:48:14.984094+00:00
| 117 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe goal is to modify a linked list by removing nodes whose values are present in a given list (nums). The challenge lies in properly managing the linked list\'s structure when nodes need to be deleted, especially handling edge cases like deletions at the head and the last node.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. **Build a Hash Map:** Use an unordered map to store the frequency of elements in the nums list. This helps in quickly checking if a node\'s value is in nums.\n\n2. **Handle Head Deletions:** First, handle deletions at the start of the list by iteratively updating the head if its value exists in nums. This ensures the head points to the first node that does not need to be removed.\n\n3. **Traverse the List:** Use two pointers, temp (current node) and prev (previous node), to traverse the linked list:\n\n - If temp\'s value is in the hash map, adjust the pointers to remove the node and delete it.\n - If temp\'s value is not in the hash map, simply move the prev and temp pointers forward.\n4. **Delete Nodes:** During the traversal, when a node matches a value in nums, update the previous node\'s next pointer to skip the current node (temp) and delete it.\n\n5. **Handle the Last Node:** Ensure that when you reach the end of the list, the last node is also checked and handled properly, adjusting pointers as necessary.\n\n6. **Return the Modified Head:** After processing all nodes, return the updated head of the linked list.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$ O(m+n) $$\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$ O(m) $$\n\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n if (head == NULL) {\n return NULL;\n }\n\n unordered_map<int, int> mp;\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {\n mp[nums[i]]++;\n }\n\n ListNode* temp = head;\n ListNode* prev = NULL;\n\n // Handle the case where the first node itself needs to be removed\n while (temp != NULL && mp.find(temp->val) != mp.end()) {\n head = temp->next;\n delete(temp);\n temp = head;\n }\n\n // Traverse and handle other nodes\n while (temp != NULL) {\n if (mp.find(temp->val) != mp.end()) {\n prev->next = temp->next;\n delete(temp);\n temp = prev->next;\n } else {\n prev = temp;\n temp = temp->next;\n }\n }\n\n return head;\n }\n};\n```\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums, head):\n if not head:\n return None\n\n # Create a set for quick lookup of nums values\n num_set = set(nums)\n\n # Handle head deletions\n while head and head.val in num_set:\n head = head.next\n\n # If the entire list is deleted\n if not head:\n return None\n\n temp = head\n prev = None\n next_node = head.next\n\n # Traverse the list\n while temp:\n if temp.val in num_set:\n prev.next = next_node\n temp = next_node\n next_node = next_node.next if next_node else None\n else:\n prev = temp\n temp = next_node\n next_node = next_node.next if next_node else None\n\n return head\n```\n```Java []\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(List<Integer> nums, ListNode head) {\n if (head == null) {\n return null;\n }\n\n HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(nums);\n\n // Handle head deletions\n while (head != null && set.contains(head.val)) {\n head = head.next;\n }\n\n // If the entire list is deleted\n if (head == null) {\n return null;\n }\n\n ListNode temp = head;\n ListNode prev = null;\n ListNode next = head.next;\n\n // Traverse the list\n while (temp != null) {\n if (set.contains(temp.val)) {\n prev.next = next;\n temp = next;\n next = (next != null) ? next.next : null;\n } else {\n prev = temp;\n temp = next;\n next = (next != null) ? next.next : null;\n }\n }\n\n return head;\n }\n}\n```\n```JavaScript []\nfunction modifiedList(nums, head) {\n if (head === null) {\n return null;\n }\n\n const numSet = new Set(nums);\n\n // Handle head deletions\n while (head !== null && numSet.has(head.val)) {\n head = head.next;\n }\n\n // If the entire list is deleted\n if (head === null) {\n return null;\n }\n\n let temp = head;\n let prev = null;\n let next = head.next;\n\n // Traverse the list\n while (temp !== null) {\n if (numSet.has(temp.val)) {\n prev.next = next;\n temp = next;\n next = next ? next.next : null;\n } else {\n prev = temp;\n temp = next;\n next = next ? next.next : null;\n }\n }\n\n return head;\n}\n```\n\n
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
✅ Easy C++ Soln ✅
|
easy-c-soln-by-jr_murphy_05-ynwb
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Jr_Murphy_05
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T04:35:32.838551+00:00
|
2024-09-06T04:35:32.838595+00:00
| 230 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n set<int> st(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n\n ListNode* curr = head;\n\n while(curr)\n {\n if(st.count(curr->val))\n {\n curr = curr->next;\n }\n else break;\n }\n\n ListNode* newHead = curr;\n\n while(curr && curr->next)\n {\n if(st.count(curr->next->val))\n {\n curr->next = curr->next->next;\n }\n else\n {\n curr = curr->next;\n }\n }\n\n return newHead;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'C++']
| 1 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Simple Explanation and easy solution
|
simple-explanation-and-easy-solution-by-9pqei
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\nThe problem involves modifying a linked list by removing nodes that contain values fo
|
g_rk
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T03:58:29.901201+00:00
|
2024-09-06T03:58:29.901228+00:00
| 223 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\nThe problem involves modifying a linked list by removing nodes that contain values found in a given vector nums. The goal is to traverse the linked list and eliminate any node whose value is present in nums, ultimately returning the modified list with those nodes removed.\n\nThe approach leverages a hash map (or unordered map) to efficiently track which values should be removed. This allows for quick lookups when traversing the linked list, ensuring that we can determine in constant time whether a node\'s value needs to be deleted. The algorithm works by maintaining two pointers, curr (for traversal) and prev (to adjust the links as we remove nodes). If the current node\'s value is found in nums, we unlink it from the list, making sure to handle the case where the node to be deleted is at the head. Finally, we return the modified list with all unwanted nodes removed.\n\nThis approach provides a linear-time solution by combining an efficient lookup structure (the hash map) with a single pass through the linked list, making it scalable for larger inputs.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nInput Description:\n\nnums: A vector of integers that contains the values to be removed from the linked list.\nhead: The head pointer to a singly linked list.\nStep-by-Step Explanation:\n\n**Step 1: Populate a Hash Map (st)**\n\nFirst, we iterate through the nums vector and store the count of each element in an unordered map st. This map helps us quickly check whether a value exists in the nums vector (which indicates that the corresponding node should be deleted from the linked list).\n\n**Step 2: Initialize Pointers**\n\nWe initialize two pointers, curr and prev, both starting at the head of the linked list:\ncurr: This pointer is used to traverse the linked list.\nprev: This pointer keeps track of the previous node as we move through the list, helping to unlink the current node if necessary.\n\n**Step 3: Traverse the Linked List**\n\nWe loop through the list while curr is not nullptr.\nFor each node, we check if the value of curr exists in the hash map (st):\nIf st[curr->val] > 0 (i.e., the current node\'s value is in nums), we delete the node:\nIf prev is equal to curr, it means we are at the head of the list. We update the head pointer to skip the current node (head = head->next) and advance both curr and prev.\nIf prev is not equal to curr, we skip the current node by linking prev->next to curr->next and advancing curr while keeping prev unchanged.\nIf curr->val is not in the hash map, we simply move both prev and curr forward.\n\n**Step 4: Return the Modified List**\n\nAfter completing the traversal, we return the modified head pointer, which now points to the updated linked list with the specified values removed.\n\n**Edge Cases**:\n\nIf nums is empty, the list remains unchanged.\nIf all elements of the list are in nums, the entire list will be deleted, and nullptr will be returned.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(N+M);\n\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(M);\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n unordered_map<int,int>st;\n for(auto it : nums){\n st[it]++;\n }\n ListNode* curr=head;\n ListNode* prev=head;\n while(curr!=nullptr){\n if(st[curr->val]>0){\n if(prev==curr){\n if(head==curr){\n head=head->next;\n }\n curr=curr->next;\n prev=curr;\n }\n else{\n curr=curr->next;\n prev->next=curr;\n }\n }\n else{\n prev=curr;\n curr=curr->next;\n }\n }\n return head;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Linked List', 'C++']
| 3 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
🌟| Efficient Solution || 229ms Beats 99.99% | O(n) | C++ Py3 Java |
|
efficient-solution-229ms-beats-9999-on-c-6af6
|
\n\n---\n\n\uD83C\uDF1F\n\n# Intuition & Approach\nWe need to remove all nodes from the linked list whose values are present in the given array nums. We can ach
|
user4612MW
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T03:36:49.769110+00:00
|
2024-09-06T03:36:49.769128+00:00
| 20 | false |
\n\n---\n\n\uD83C\uDF1F\n\n# Intuition & Approach\nWe need to remove all nodes from the linked list whose values are present in the given array **nums**. We can achieve this efficiently by using a **bitset** to track the values that need to be removed, ensuring constant time checks. We initialize a dummy node to simplify the list manipulation and iterate through the list, bypassing nodes that are in the **bitset**. This method is efficient and leverages the bitset for fast lookups.\n\n# Complexity\n- **Time Complexity** $$O(n)$$, where $$n$$ is the number of nodes in the linked list, as we traverse the list once.\n- **Space Complexity** $$O(m)$$, where $$m$$ is the number of elements in **nums**, due to the space required for the bitset.\n\n---\n\n```cpp []\n#include <vector>\n#include <bitset>\nusing namespace std;\n\nstruct ListNode {\n int val;\n ListNode *next;\n ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n bitset<100001> filter;\n for (int num : nums) filter[num] = 1;\n ListNode dummy(0); dummy.next = head;\n for (ListNode* node = &dummy; node->next;)\n filter[node->next->val] ? node->next = node->next->next : node = node->next;\n return dummy.next;\n }\n};\nstatic const int speedup = []() {\n ios::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(nullptr);\n return 0;\n}();\n```\n\n```python []\nclass ListNode:\n def __init__(self, x):\n self.val = x\n self.next = None\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums, head):\n to_remove = set(nums)\n dummy = ListNode(0)\n dummy.next = head\n current = dummy\n while current.next:\n if current.next.val in to_remove:\n current.next = current.next.next\n else:\n current = current.next\n return dummy.next\n```\n\n```java []\nimport java.util.HashSet;\nimport java.util.Set;\nclass ListNode {\n int val;\n ListNode next;\n ListNode(int x) { val = x; }\n}\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n Set<Integer> toRemove = new HashSet<>();\n for (int num : nums) toRemove.add(num);\n\n ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);\n dummy.next = head;\n ListNode current = dummy;\n while (current.next != null) {\n if (toRemove.contains(current.next.val)) {\n current.next = current.next.next;\n } else {\n current = current.next;\n }\n }\n return dummy.next;\n }\n}\n```\n\n- \n\n---\n
| 3 | 0 |
['C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
JAVA | 100% Beats ✅
|
java-100-beats-by-sudhikshaghanathe-o9lv
|
\n# Code\njava []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n *
|
SudhikshaGhanathe
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T03:36:03.253923+00:00
|
2024-09-06T03:36:03.253944+00:00
| 420 | false |
\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n int max = 0;\n for (int i : nums) \n max = Math.max(max, i);\n\n boolean [] visited = new boolean[max + 1];\n\n for (int i : nums) visited[i] = true;\n\n ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);\n dummy.next = head;\n ListNode curr = dummy;\n\n while (head != null) {\n if(head.val <= max && visited[head.val])\n dummy.next = head.next;\n else\n dummy = head;\n head = head.next;\n }\n\n return curr.next;\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 2 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Golang solution with explanation
|
golang-solution-with-explanation-by-alek-pu3h
|
Intuition\nThe problem requires removing nodes from a linked list where the node values match any of the values present in a given array. The primary challenge
|
alekseiapa
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T01:48:09.841544+00:00
|
2024-09-06T01:48:09.841564+00:00
| 115 | false |
# Intuition\nThe problem requires removing nodes from a linked list where the node values match any of the values present in a given array. The primary challenge is to efficiently remove these nodes while preserving the structure of the remaining linked list.\n\n# Approach\n1. **Convert Array to Set**: Convert the given array of values into a set (using a map) to allow for constant time complexity checks when determining if a node\'s value should be removed.\n\n2. **Initialize Dummy Node**: Use a dummy node to simplify edge case handling, such as removing the head node. This dummy node will point to the start of the modified list.\n\n3. **Traverse the List**: Iterate through the linked list:\n - If the current node\'s value is in the set of values to be removed, adjust the `Next` pointer of the previous node to skip the current node.\n - If the current node\'s value is not in the set, update the previous node to the current node.\n\n4. **Return the Modified List**: After traversal, the `Next` pointer of the dummy node will point to the head of the modified list with the specified nodes removed.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$ \n Where $$n$$ is the number of nodes in the linked list. This is because we traverse each node exactly once and perform constant-time operations for each node.\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(k)$$ \n Where $$k$$ is the number of distinct values in the `nums` array. This is due to the space used by the set to store these values for quick lookup.\n\n\n# Code\n```golang []\n// Function to remove nodes with values present in the nums array\nfunc modifiedList(nums []int, head *ListNode) *ListNode {\n if head == nil {\n return nil\n }\n \n valueSet := make(map[int]bool)\n for _, value := range nums {\n valueSet[value] = true\n }\n \n // Initialize a dummy node to handle edge cases\n dummy := &ListNode{}\n dummy.Next = head\n previousNode := dummy\n currentNode := head\n \n // Traverse the linked list\n for currentNode != nil {\n if valueSet[currentNode.Val] {\n // Skip the node if its value is in the valueSet\n previousNode.Next = currentNode.Next\n } else {\n // Move previousNode to the currentNode\n previousNode = currentNode\n }\n // Move to the next node\n currentNode = currentNode.Next\n }\n \n return dummy.Next\n}\n\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Go']
| 1 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
simple and easy C++ solution 😍❤️🔥
|
simple-and-easy-c-solution-by-shishirrsi-vrbf
|
\n# if it\'s help, please up \u2B06 vote! \u2764\uFE0F\n\n###### Let\'s Connect on LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/in/shishirrsiam\n###### Let\'s Connect on Facebook
|
shishirRsiam
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T00:27:31.306490+00:00
|
2024-09-06T00:27:31.306515+00:00
| 1,101 | false |
\n# if it\'s help, please up \u2B06 vote! \u2764\uFE0F\n\n###### Let\'s Connect on LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/in/shishirrsiam\n###### Let\'s Connect on Facebook: www.fb.com/shishirrsiam\n\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) \n {\n set<int>st;\n for(auto num:nums) st.insert(num);\n \n ListNode* ans = new ListNode(0);\n ListNode* tail = ans;\n while(head)\n {\n int val = head->val; head = head->next;\n if(not st.count(val))\n {\n tail->next = new ListNode(val);\n tail = tail->next;\n }\n }\n return ans->next;\n }\n};\n```\n\n\n# if it\'s help, please up \u2B06 vote! \u2764\uFE0F\n\n###### Let\'s Connect on LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/in/shishirrsiam\n###### Let\'s Connect on Facebook: www.fb.com/shishirrsiam\n\n
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'C++']
| 11 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Detailed Explanation, Using STACK and SET || JAVA C++ PYTHON JS
|
detailed-explanation-using-stack-and-set-54b5
|
Intuition\nStore nums in a HashSet: The nums array is stored in a HashSet to allow fast lookups (O(1) average time complexity).\n\nTraverse the Linked List: The
|
sharforaz_rahman
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-02T18:01:38.034359+00:00
|
2024-09-02T18:01:38.034389+00:00
| 636 | false |
# Intuition\nStore nums in a HashSet: The nums array is stored in a HashSet to allow fast lookups (O(1) average time complexity).\n\nTraverse the Linked List: The linked list is traversed, and nodes with values not in the HashSet are pushed onto a stack. This stack helps reverse the order of these nodes.\n\nRebuild the List: The stack is then used to pop nodes and rebuild a new linked list, effectively reversing the order of the retained nodes.\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n + m)\n\n- Space complexity: O(m + n)\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();\n Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();\n ListNode current = head;\n\n for (int i : nums) set.add(i);\n while (current != null) {\n if (!set.contains(current.val)) {\n stack.push(current);\n }\n current = current.next;\n }\n ListNode newHead = null;\n while (!stack.isEmpty()) {\n ListNode node = stack.pop();\n node.next = newHead;\n newHead = node;\n }\n return newHead;\n }\n}\n\n```\n```javascript []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * function ListNode(val, next) {\n * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)\n * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)\n * }\n */\nvar modifiedList = function(nums, head) {\n let set = new Set(nums);\n let stack = [];\n let current = head;\n\n while (current !== null) {\n if (!set.has(current.val)) {\n stack.push(current);\n }\n current = current.next;\n }\n\n let newHead = null;\n while (stack.length > 0) {\n let node = stack.pop();\n node.next = newHead;\n newHead = node;\n }\n\n return newHead;\n};\n\n```\n```python []\n# Definition for singly-linked list.\nclass ListNode:\n def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):\n self.val = val\n self.next = next\n\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums, head):\n set_nums = set(nums)\n stack = []\n current = head\n\n while current:\n if current.val not in set_nums:\n stack.append(current)\n current = current.next\n\n new_head = None\n while stack:\n node = stack.pop()\n node.next = new_head\n new_head = node\n\n return new_head\n\n```\n```c++ []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\n#include <unordered_set>\n#include <stack>\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n unordered_set<int> set(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n stack<ListNode*> stk;\n ListNode* current = head;\n\n while (current != nullptr) {\n if (set.find(current->val) == set.end()) {\n stk.push(current);\n }\n current = current->next;\n }\n\n ListNode* newHead = nullptr;\n while (!stk.empty()) {\n ListNode* node = stk.top();\n stk.pop();\n node->next = newHead;\n newHead = node;\n }\n\n return newHead;\n }\n};\n\n```\n\n# Code\n
| 3 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'Ordered Set', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'JavaScript']
| 2 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
💢☠💫Easiest👾Faster✅💯 Lesser🧠 🎯 C++✅Python3🐍✅Java✅C✅Python🐍✅C#✅💥🔥💫Explained☠💥🔥 Beats 💯
|
easiestfaster-lesser-cpython3javacpython-7exp
|
Intuition\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nJavaScript []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * function Li
|
Edwards310
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T07:33:12.525903+00:00
|
2024-09-06T07:13:40.355901+00:00
| 303 | false |
# Intuition\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n```JavaScript []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * function ListNode(val, next) {\n * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)\n * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)\n * }\n */\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @param {ListNode} head\n * @return {ListNode}\n */\nvar modifiedList = function(nums, head) {\n const set = new Set(nums), temp = new ListNode(0, head);\n let curr = head, prev = temp;\n while(curr !== null){\n if(set.has(curr.val)){\n prev.next = curr.next;\n }\n else \n prev = curr;\n curr = curr.next;\n }\n return temp.next;\n};\n```\n```C++ []\n#inclde<bits/stdc++.h>\nusing namespace std;\n#define ALL(v) v.begin(). v.end()\n#define usi unordered_set<int> \n#define REVERSE(v) reverse(ALL(v))\n#define pb push_back\n#define Rep(i, n) for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n usi system(ALL(nums));\n vector<ListNode*> helper;\n while(head){\n if(!system.contains(head->val))\n helper.pb(head);\n head = head->next;\n }\n ListNode* prev = nullptr;\n REVERSE(helper);\n Rep(i, helper.size()){\n head = new ListNode(helper[i]->val, prev);\n prev = head;\n }\n return head;\n }\n};\n```\n```python3 []\n# Definition for singly-linked list.\n# class ListNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.next = next\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:\n if not head:\n return None\n \n system = set(nums)\n newhead = ListNode(0)\n newhead.next = head\n \n prev = newhead\n curr = head\n \n while curr:\n if curr.val in system:\n # Remove current node\n prev.next = curr.next\n curr = curr.next # Move curr to the next node (don\'t move prev)\n else:\n # Move both pointers forward\n prev = curr\n curr = curr.next\n \n return newhead.next\n```\n```C# []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * public int val;\n * public ListNode next;\n * public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {\n * this.val = val;\n * this.next = next;\n * }\n * }\n */\npublic class Solution {\n public ListNode ModifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n HashSet<int> set = new(nums);\n List<ListNode> helper = new List<ListNode>();\n while(head != null){\n if(!set.Contains(head.val))\n helper.Add(head);\n head = head.next;\n }\n helper.Reverse();\n ListNode prev = null;\n for(int i = 0; i < helper.Count(); ++i){\n head = new ListNode(helper[i].val, prev);\n prev = head;\n }\n return head;\n }\n}\n```\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();\n for(int x : nums)\n set.add(x);\n List<ListNode> helper = new ArrayList<>();\n while(head != null){\n if(!set.contains(head.val))\n helper.add(head);\n head = head.next;\n }\n ListNode prev = null;\n Collections.reverse(helper);\n for(int i = 0; i < helper.size(); ++i){\n head = new ListNode(helper.get(i).val, prev);\n prev = head;\n }\n return head;\n }\n}\n```\n```python []\n# Definition for singly-linked list.\n# class ListNode(object):\n# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.next = next\nclass Solution(object):\n def modifiedList(self, nums, head):\n """\n :type nums: List[int]\n :type head: Optional[ListNode]\n :rtype: Optional[ListNode]\n """\n if not head:\n return None\n \n system = set(nums)\n newhead = ListNode(0)\n newhead.next = head\n \n prev = newhead\n curr = head\n \n while curr:\n if curr.val in system:\n # Remove current node\n prev.next = curr.next\n curr = curr.next # Move curr to the next node (don\'t move prev)\n else:\n # Move both pointers forward\n prev = curr\n curr = curr.next\n \n return newhead.next\n```\n```C []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * struct ListNode *next;\n * };\n */\nstruct ListNode* newListNode(int val, struct ListNode* prev){\n struct ListNode* temp = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));\n temp->val = val;\n temp->next = prev;\n return temp;\n}\nstruct ListNode* reverse(struct ListNode* head){\n struct ListNode* curr = head, *prev = NULL;\n while(curr){\n struct ListNode* temp = curr->next;\n curr->next = prev;\n prev = curr;\n curr = temp;\n }\n return prev;\n}\nstruct ListNode* modifiedList(int* nums, int numsSize, struct ListNode* head) {\n bool present[100001] = {false};\n for(int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++)\n present[nums[i]] = true;\n int *arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 100001);\n int x = 0;\n while(head){\n if(!present[head->val])\n arr[x++] = head->val;\n head = head->next;\n }\n struct ListNode* prev = NULL;\n for(int i = 0; i < x; ++i){\n head = newListNode(arr[i], prev);\n prev = head;\n }\n return reverse(prev);\n}\n```\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n O(n)\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n O(n)\n# Code\n\n\n
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Linked List', 'Stack', 'C', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'JavaScript', 'C#']
| 2 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Easiest C++ / Python3 Solution -- Please upvote if you find this helpful
|
easiest-c-python3-solution-please-upvote-r84p
|
Intuition\n\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Tim
|
papaji310
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T05:48:22.811077+00:00
|
2024-07-14T05:48:22.811099+00:00
| 165 | false |
# Intuition\n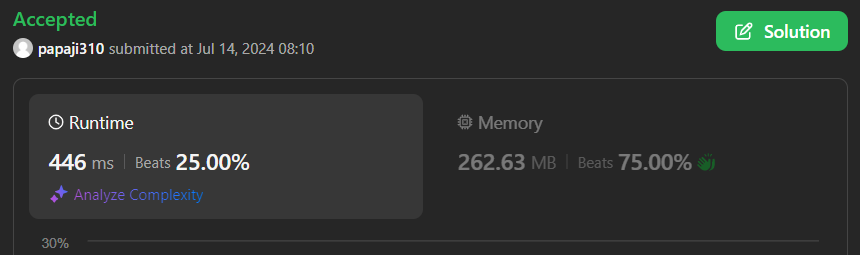\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n if (head == nullptr) \n return nullptr;\n \n unordered_set<int> apnaSet(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);\n dummy->next = head;\n \n ListNode* prev = dummy;\n ListNode* curr = head;\n \n while (curr != nullptr) {\n if (apnaSet.count(curr->val) > 0) {\n // Remove current node\n prev->next = curr->next;\n delete curr;\n curr = prev->next; // Move curr to the next node (don\'t move prev)\n } else {\n // Move both pointers forward\n prev = curr;\n curr = curr->next;\n }\n }\n \n ListNode* result = dummy->next;\n delete dummy;\n \n return result;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 2 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
✅ One Line Solution
|
one-line-solution-by-mikposp-59ri
|
(Disclaimer: this is not an example to follow in a real project - it is written for fun and training mostly)\n\n# Code #1.1 - One Line\nTime complexity: O(n). S
|
MikPosp
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T04:51:16.594676+00:00
|
2024-09-06T07:54:16.273859+00:00
| 639 | false |
(Disclaimer: this is not an example to follow in a real project - it is written for fun and training mostly)\n\n# Code #1.1 - One Line\nTime complexity: $$O(n)$$. Space complexity: $$O(n)$$.\n```python3\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, a: List[int], h: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:\n return (f:=lambda n,a={*a}:n and (f(n.next) if n.val in a else ListNode(n.val,f(n.next))))(h)\n```\n\n# Code #1.2 - Unwrapped\n```python3\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, a: List[int], h: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:\n def f(node, a={*a}):\n if node:\n if node.val in a:\n return f(node.next)\n \n return ListNode(node.val, f(node.next))\n \n return f(h)\n```\n\n# Code #2 - Shorter Version\nTime complexity: $$O(n)$$. Space complexity: $$O(n)$$.\n```python3\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, a: List[int], h: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:\n return (f:=lambda n,a={*a}:n and (ListNode(n.val,q:=f(n.next)),q)[n.val in a])(h)\n```\n\n(Disclaimer 2: code above is just a product of fantasy packed into one line, it is not claimed to be \'true\' oneliners - please, remind about drawbacks only if you know how to make it better)
| 3 | 1 |
['Linked List', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 1 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Solution By Dare2Solve | Detailed Explanation | Clean Code
|
solution-by-dare2solve-detailed-explanat-870u
|
Explanation []\nauthorslog.vercel.app/blog/p5FUHDtSrA\n\n\n# Code\n\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode*
|
Dare2Solve
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T04:07:13.713433+00:00
|
2024-07-14T04:12:55.136363+00:00
| 1,360 | false |
```Explanation []\nauthorslog.vercel.app/blog/p5FUHDtSrA\n```\n\n# Code\n\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n ListNode* res = new ListNode();\n ListNode* resCur = res;\n ListNode* cur = head;\n unordered_set<int> set(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n \n while (cur) {\n if (set.find(cur->val) == set.end()) {\n resCur->next = new ListNode(cur->val);\n resCur = resCur->next;\n }\n cur = cur->next;\n }\n \n return res->next;\n }\n};\n```\n\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:\n res = ListNode()\n res_cur = res\n cur = head\n num_set = set(nums)\n \n while cur:\n if cur.val not in num_set:\n res_cur.next = ListNode(cur.val)\n res_cur = res_cur.next\n cur = cur.next\n \n return res.next\n```\n\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n ListNode res = new ListNode();\n ListNode resCur = res;\n ListNode cur = head;\n Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();\n for (int num : nums) {\n set.add(num);\n }\n \n while (cur != null) {\n if (!set.contains(cur.val)) {\n resCur.next = new ListNode(cur.val);\n resCur = resCur.next;\n }\n cur = cur.next;\n }\n \n return res.next;\n }\n}\n```\n\n```javascript []\nvar modifiedList = function (nums, head) {\n var res = new ListNode();\n var resCur = res;\n var cur = head;\n var set = new Set(nums);\n while (cur) {\n if (!set.has(cur.val)) {\n resCur.next = new ListNode(cur.val);\n resCur = resCur.next;\n }\n cur = cur.next;\n }\n return res.next;\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'JavaScript']
| 2 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
💯Faster✅💯Less Mem✅🧠Detailed Approach🎯Linked List 🔥C++😎
|
fasterless-memdetailed-approachlinked-li-7fqs
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
swarajkr
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T04:02:27.703955+00:00
|
2024-07-14T04:02:27.703978+00:00
| 601 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n // Create a set to store values from nums for quick lookup\n set<int> s;\n \n // Insert each element from nums into the set\n for (auto i : nums) {\n s.insert(i);\n }\n\n // Initialize pointers to traverse the linked list\n ListNode *curr = head;\n ListNode *prev = nullptr;\n\n // Traverse the linked list\n while (curr != nullptr) {\n // Check if the current node\'s value is in the set\n if (s.find(curr->val) != s.end()) {\n // If it is, we need to remove this node\n if (prev == nullptr) {\n // If prev is null, we are at the head of the list\n // Update the head to the next node\n head = curr->next;\n } else {\n // Otherwise, link the previous node to the next node\n prev->next = curr->next;\n }\n // Move to the next node\n curr = curr->next;\n } else {\n // If the current node\'s value is not in the set\n // Move both prev and curr forward\n prev = curr;\n curr = curr->next;\n }\n }\n // Return the modified head of the list\n return head;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 1 |
['C++']
| 2 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
✨🚀 Effortlessly 💯 Dominate 100% with Beginner C++ , Java and Python Solution! 🚀✨
|
effortlessly-dominate-100-with-beginner-qsj2s
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Ravi_Prakash_Maurya
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T04:02:12.546908+00:00
|
2024-07-14T04:02:12.546937+00:00
| 342 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```C++ []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n unordered_set<int> s;\n for(int i : nums) s.insert(i);\n ListNode* prev = nullptr;\n ListNode* curr = head;\n while(curr != nullptr) {\n if(s.find(curr->val) != s.end()) { // If the current node\'s value is in the set\n if (prev == nullptr) // If the node to be removed is the head\n head = curr->next; // Update the head to the next node\n else \n prev->next = curr->next; // Bypass the current node\n curr = curr->next; // Move to the next node\n } else {\n prev = curr; // Move the prev pointer to the current node\n curr = curr->next; // Move to the next node\n }\n }\n return head;\n }\n};\n\n```\n```Java []\npublic class Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();\n for (int num : nums) {\n set.add(num);\n }\n ListNode prev = null;\n ListNode curr = head;\n while (curr != null) { // Traverse the list until the end\n if (set.contains(curr.val)) { // If the current node\'s value is in the set\n if (prev == null) { // If the node to be removed is the head\n head = curr.next; // Update the head to the next node\n } else {\n prev.next = curr.next; // Bypass the current node\n }\n curr = curr.next; // Move to the next node\n } else {\n prev = curr; // Move the prev pointer to the current node\n curr = curr.next; // Move to the next node\n }\n }\n return head;\n }\n}\n```\n```Python []\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:\n s = set(nums) \n prev = None \n curr = head \n while curr is not None: # Traverse the list until the end\n if curr.val in s: # If the current node\'s value is in the set\n if prev is None: # If the node to be removed is the head\n head = curr.next # Update the head to the next node\n else:\n prev.next = curr.next # Bypass the current node\n curr = curr.next # Move to the next node\n else:\n prev = curr # Move the prev pointer to the current node\n curr = curr.next # Move to the next node\n \n return head # Return the modified list\n\n```\n\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 2 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Simple Solution in Java
|
simple-solution-in-java-by-sathurnithy-ilnp
|
Code
|
Sathurnithy
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-02T08:47:17.733691+00:00
|
2025-03-02T08:47:17.733691+00:00
| 162 | false |
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int val : nums)
set.add(val);
ListNode newDummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode curr = newDummy;
while (curr.next != null) {
if (set.contains(curr.next.val))
curr.next = curr.next.next;
else
curr = curr.next;
}
return newDummy.next;
}
}
```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'Java']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
🎯SUPER EASY FOR BEGINNERS 👏
|
super-easy-for-beginners-by-vigneshvaran-phwj
|
Code
|
vigneshvaran0101
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-31T16:13:35.813557+00:00
|
2025-01-31T16:13:35.813557+00:00
| 114 | false |
# Code
```python3 []
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def modifiedList(self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy = ListNode(-1)
temp = dummy
nums_set = set(nums) # If we use List it make O(N) time complexity
# Id we use Set() this makes O(1) time Complexity
curr = head
while curr:
if curr.val not in nums_set:
temp.next = ListNode(curr.val)
temp = temp.next
curr = curr.next
return dummy.next
```

| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Easy C++ Sol
|
easy-c-sol-by-sayak_jana-qua7
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
sayak_jana
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-25T20:56:04.047075+00:00
|
2025-01-25T20:56:04.047075+00:00
| 160 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {
if(nums.size() == 0 || !head) return head;
unordered_set<int> st(nums.begin(),nums.end());
ListNode* newHead = NULL;
ListNode* t = head;
ListNode* t2 = NULL;
while(t){
if(!st.contains(t->val)){
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(t->val);
if(newHead == NULL){
newHead = dummy;
t2 = dummy;
}else{
t2->next = dummy;
t2 = t2->next;
}
}
t = t->next;
}
return newHead;
}
};
```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Simple || Easy to Understand || Clear
|
simple-easy-to-understand-clear-by-kdhak-gfx8
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
kdhakal
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-25T23:52:18.822923+00:00
|
2024-09-25T23:52:18.822941+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n\n HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();\n\n for(int x : nums) set.add(x);\n\n ListNode temp = new ListNode();\n ListNode res = temp;\n\n while(head != null) {\n if(!set.contains(head.val)) {\n ListNode newNode = new ListNode(head.val);\n temp.next = newNode;\n temp = temp.next;\n }\n head = head.next;\n }\n\n return res.next;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
C++ || Easy Video Solution || Faster than 95%
|
c-easy-video-solution-faster-than-95-by-p2xob
|
The Video solution for the below code\nhttps://youtu.be/-1rhc_JtG-I\n\n# Code\ncpp []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n *
|
__SAI__NIVAS__
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T21:23:41.820412+00:00
|
2024-09-06T21:23:41.820447+00:00
| 22 | false |
The Video solution for the below code\nhttps://youtu.be/-1rhc_JtG-I\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(NULL);\n cout.tie(nullptr);\n // Note:\n // We need to remove every element from linked list if that is present in nums\n unordered_set<int> us;\n for(auto &num : nums) us.insert(num);\n ListNode *ans = new ListNode(-1);\n ListNode *tmpAns = ans;\n while(head){\n if(us.find(head->val) == us.end()){\n ans->next = new ListNode(head->val);\n ans = ans->next;\n }\n head = head->next;\n }\n return tmpAns->next;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Java || Easy and Simplest Approach
|
java-easy-and-simplest-approach-by-manoj-sls4
|
Code\njava []\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);\n dummy.next =
|
manojk67686
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T15:55:55.405480+00:00
|
2024-09-06T15:55:55.405504+00:00
| 31 | false |
# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);\n dummy.next = head;\n\n ListNode curr = dummy;\n HashSet<Integer> remNum = new HashSet<>();\n for(int num : nums){\n remNum.add(num);\n }\n while(curr.next!=null){\n if(remNum.contains(curr.next.val)){\n curr.next = curr.next.next;\n }\n else{\n curr = curr.next;\n }\n }\n return dummy.next;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Java | Python Solution
|
java-python-solution-by-pushkar91949-br9u
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe problem asks to modify a linked list by removing nodes that contain specific values
|
Pushkar91949
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T14:32:19.164975+00:00
|
2024-09-06T14:32:19.165006+00:00
| 106 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe problem asks to modify a linked list by removing nodes that contain specific values. The values to be removed are provided in an array. The goal is to efficiently remove nodes from the list while preserving the order of the remaining nodes.\n\nTo achieve this, we can use a set data structure to store the values to be removed. The set allows for **O(1)** lookups, which makes it efficient to check whether a node\'s value should be removed. We traverse the linked list, and for each node, if its value exists in the set, we remove the node by updating pointers. Otherwise, we move to the next node.\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. Create a dummy node: This is a common technique used when modifying linked lists. The dummy node is placed before the head to handle edge cases like removing the head node without additional checks.\n\n2. Populate the set: Convert the array nums to a set to allow constant-time lookups for values that need to be removed from the linked list.\n\n3. Iterate through the list:\n\n - Use a pointer **ptr** that starts at the dummy node.\n - For each node, check if its value exists in the set.\n - If the value is in the set, update ptr.next to skip the current node, effectively removing it from the list.\n - If the value is not in the set, move ptr to the next node.\n 4. Return the modified list: The dummy node\'s next pointer will now point to the modified list\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: **O(n + m)**\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: **O(n)**\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n ListNode dummy = new ListNode();\n dummy.next = head;\n ListNode ptr = dummy;\n Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();\n for (int num : nums){\n set.add(num);\n }\n while (ptr != null && ptr.next != null){\n if (set.contains(ptr.next.val)){\n ptr.next = ptr.next.next;\n } else {\n ptr = ptr.next;\n }\n }\n return dummy.next;\n }\n}\n```\n```Python []\n# Definition for singly-linked list.\n# class ListNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.next = next\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:\n dummy = ListNode()\n dummy.next = head\n ptr = dummy\n nums = set(nums)\n while ptr and ptr.next:\n if ptr.next.val in nums:\n ptr.next = ptr.next.next\n else:\n ptr = ptr.next\n return dummy.next\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Linked List', 'Python', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 2 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Explained Solution
|
explained-solution-by-nurliaidin-10fd
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n1. Create a hash that s
|
Nurliaidin
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T09:34:00.250996+00:00
|
2024-09-06T09:34:00.251025+00:00
| 145 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. Create a hash that stores all the values of the array for time efficiency\n\n - Create a hash (or a set) to store all the values in the array that need to be checked. This allows for efficient lookup in constant time, O(1), when determining whether a node\'s value exists in the array. This hash will help speed up comparisons as you iterate through the linked list.\n\n2. Create a previous node with a value of 0 and point it to the head, in case the head value exists in the array\n\n - Set up a "dummy" node before the head of the linked list, initializing it with a placeholder value (e.g., 0). This dummy node will point to the head. This is useful because if the head node\u2019s value needs to be discarded, you can still adjust the list starting from the dummy node without losing the reference to the modified head. The dummy node simplifies list manipulation, especially at the start.\n3. Iterate through the node list and if the current value is equal to a value that exists in the array, discard it by pointing the previous node to the current\'s next node\n\n - Traverse the linked list one node at a time. For each node, check if its value exists in the hash (i.e., it\'s a value that needs to be removed). If the current node\'s value is found in the hash, remove the node by making the previous node\u2019s next pointer skip the current node and point directly to the next node in the list. This effectively "deletes" the node by bypassing it. If the value is not found in the hash, simply move the previous node pointer to the current node and continue iterating.\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n)$$\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n)$$\n# Code\n```javascript []\nvar modifiedList = function(nums, head) {\n //create a hash that stores all the values of the array for time efficiency\n let hash = new Map();\n for(let i=0; i<nums.length; i++) {\n if(!hash.has(nums[i])) hash.set(nums[i], 1);\n }\n\n // create a previous node with a value 0 and point it to the head, in case head value exists in the array\n let prev = new ListNode(0);\n let list = head;\n prev.next = head;\n head = prev;\n\n //iterate the node list and if the current value is equal to the value that exists in the array, discard it by pointing the previous value to the currents next\n while(list) {\n if(hash.has(list.val)) {\n prev.next = list.next;\n list = prev.next;\n }\n else {\n prev = list;\n list = list.next;\n }\n }\n\n return head.next;\n};\n```\n``` cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n\n //create a hash that stores all the values of the array for time efficiency\n unordered_map<int, int> hash;\n for(auto i: nums) {\n hash[i] = 1;\n }\n\n // create a previous node with a value 0 and point it to the head, in case head value exists in the array\n ListNode* list = head;\n ListNode* prev = new ListNode(0);\n prev->next = head;\n head = prev;\n //iterate the node list\n while(list) {\n // if the current value is equal to the value that exists in the array\n if(hash.find(list->val) != hash.end()) {\n //discard it by pointing the previous value to the currents next\n prev->next = list->next;\n list = prev->next;\n } else {\n prev = list;\n list = list->next;\n }\n }\n return head->next;\n }\n};\n```\n``` python []\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:\n #create a hash that stores all the values of the array for time efficiency\n hash = {}\n for i in nums:\n if i not in hash:\n hash[i] = 1\n #create a previous node with a value 0 and point it to the head, in case head value exists in the array\n temp = head\n prev = ListNode(0)\n prev.next = head\n head = prev\n #iterate the node list\n while temp:\n #if the current value is equal to the value that exists in the array\n if temp.val in hash:\n #discard it by pointing the previous value to the currents next\n prev.next = temp.next\n temp = prev.next\n else:\n prev = temp\n temp = temp.next\n return head.next\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'C++', 'Python3', 'JavaScript']
| 1 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Delete Nodes From Linked List Present in Array - Java | Backtracking
|
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-c818
|
Intuition\nWe have to return head of ListNode, in this case if we iterate list node from head to tell it will be deffcult to get head after performing opertati
|
rahulsasamkar9028
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T09:18:07.413920+00:00
|
2024-09-06T09:18:07.413947+00:00
| 16 | false |
# Intuition\nWe have to return head of ListNode, in this case if we iterate list node from head to tell it will be deffcult to get head after performing opertation.\nso used backtracking to get new head after performing operation.\n\n# Approach\n1. Iterate ListNode till last node, where head becomes null and return head.\n2. For each time we will get previous node, head node(current node), lastNode(node after head).\n3. while backtracking applay condition to check does any val of array matches with node or not.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();\n\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n ListNode prv = new ListNode();\n prv.next = head;\n add(nums);\n ListNode temp = solve(head, prv);\n return temp;\n }\n\n public ListNode solve(ListNode head, ListNode prv) {\n if (head == null) {\n return head;\n } // prv -> head -> last\n ListNode last = solve(head.next, prv.next);\n\n if (map.containsKey(head.val)) {\n prv.next = last;\n return prv.next;\n } else {\n return head;\n }\n }\n\n public void add(int[] num) {\n for (int n : num) {\n map.put(n, 0);\n }\n return;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
C++ easy soultion
|
c-easy-soultion-by-_ashu1729-mlee
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
_Ashu1729
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T08:35:10.199353+00:00
|
2024-09-06T08:35:10.199374+00:00
| 62 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:o(N)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n unordered_set<int>s;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n s.insert(nums[i]);\n }\n ListNode* prev=new ListNode(0);;\n prev->next =head;\n ListNode* curr= prev; \n while(curr->next!=NULL) {\n if (s.find(curr->next->val)!=s.end()) {\n curr->next = curr->next->next; } \n else{\n curr = curr->next;} } \n return prev->next;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'C++']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Simple Approach || Easy Solution With Proper Explanation
|
simple-approach-easy-solution-with-prope-jns7
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe problem requires us to remove nodes from a linked list if their values are present
|
Yash_RajSingh
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T05:31:52.874854+00:00
|
2024-09-06T05:31:52.874889+00:00
| 47 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe problem requires us to remove nodes from a linked list if their values are present in a given list of numbers. The first thought is to traverse the linked list while maintaining pointers to the current and previous nodes. If the current node\'s value exists in the given list, we remove it by updating the previous node\'s next pointer.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. Use a set (or unordered set) to store all elements from the `nums` vector for fast lookup.\n2. Create a dummy node that points to the head of the list to handle edge cases, such as when the head node needs to be removed.\n3. Initialize two pointers, `prev` pointing to the dummy node and `curr` pointing to the head of the list.\n4. Traverse the linked list:\n - If the current node\'s value is in the set, adjust the `prev` node\'s `next` pointer to skip the current node.\n - Otherwise, move the `prev` pointer to the current node.\n - Move the `curr` pointer to the next node.\n5. Return the modified list starting from the node after the dummy node.\n\n# Complexity\n- **Time complexity:** \n The time complexity is $$O(n + m)$$, where `n` is the number of nodes in the linked list, and `m` is the size of the `nums` vector. The set lookup and insertion operations are on average $$O(1)$$, and traversing the list is $$O(n)$$.\n\n- **Space complexity:** \n The space complexity is $$O(m)$$, where `m` is the size of the `nums` vector, due to storing the values in the set.\n\n# Code\n```cpp\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n\n int n = nums.size();\n set<int> st;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n st.insert(nums[i]);\n }\n\n ListNode* dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);\n dummyNode->next = head;\n ListNode* prev = dummyNode;\n ListNode* temp = head;\n\n while (temp != nullptr) {\n if (st.find(temp->val) != st.end()) {\n\n prev->next = temp->next;// skip the current node\n temp = temp->next;\n } else {\n prev = temp;//update previous node when current node is not present in set\n temp = temp->next;\n }\n }\n return dummyNode->next;\n }\n};
| 2 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'C++']
| 1 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Beats 100% | Easy Code
|
beats-100-easy-code-by-b_i_t-sd7d
|
\n# Intuition\nThe task involves modifying a linked list by removing nodes that contain certain values. The list of values to be removed is provided in a vector
|
B_I_T
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T05:19:53.053376+00:00
|
2024-09-06T05:19:53.053399+00:00
| 101 | false |
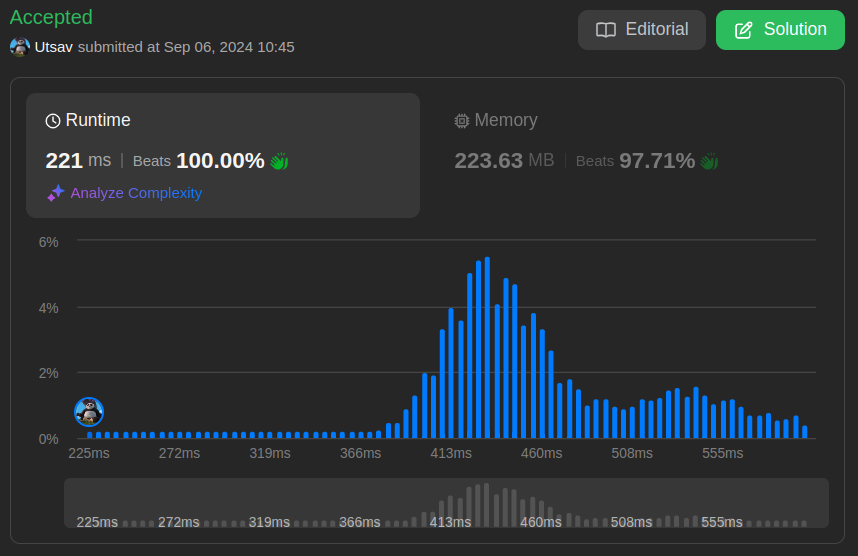\n# Intuition\nThe task involves modifying a linked list by removing nodes that contain certain values. The list of values to be removed is provided in a vector nums. The solution leverages a bitset to efficiently store and look up these values. The goal is to traverse the linked list and remove nodes whose values are present in the bitset, without affecting the structure of the remaining nodes.\n\n# Approach\n1. Using a bitset for Fast Lookup:\n\n - The idea is to use a bitset to store the values present in the nums array. This allows for fast constant-time lookups (O(1) complexity) when checking if a node\'s value should be removed from the linked list.\n2. Dummy Node:\n\n - A dummy node (ListNode(-1)) is added at the beginning of the list. This simplifies edge cases, such as removing the head of the list, by ensuring that every node has a previous node to reference.\n3. Linked List Traversal:\n\n - Start from the dummy node and traverse the list. For each node, check if its value is in the bitset. If it is, bypass the node by updating the next pointer of the previous node to skip the current node. Otherwise, move to the next node.\n4. Return the Modified List:\n\n - After the traversal, return the list starting from dummy->next, which points to the real head of the modified list.\n# Complexity\n- Time Complexity:\n - Constructing the bitset takes O(|nums|) where |nums| is the length of the nums vector.\n - Traversing the linked list takes O(|list|), where |list| is the length of the linked list.\n - Therefore, the overall time complexity is O(|nums| + |list|).\n- Space Complexity:\n - The bitset uses constant space (O(100001)), which is efficient given that it only holds boolean values for a fixed range.\n - The space complexity is O(1) apart from the input and output space (linked list and bitset).\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n ios::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(nullptr);\n\n bitset<100001> bs;\n for(const int & i : nums){\n bs.set(i);\n }\n \n head = new ListNode(-1,head);\n ListNode * prev = head;\n while(head->next){\n if(bs[head->next->val]){\n head->next = head->next->next;\n }else{\n head = head->next;\n }\n }\n return prev->next;\n }\n};\n```\n```Java []\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n BitSet bs = new BitSet(100001);\n for (int num : nums) {\n bs.set(num);\n }\n\n ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);\n ListNode prev = dummy;\n\n while (head != null) {\n if (bs.get(head.val)) {\n prev.next = head.next;\n } else {\n prev = head;\n }\n head = head.next;\n }\n \n return dummy.next;\n }\n}\n\n```\n```Python []\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums, head):\n bs = [False] * 100001\n for num in nums:\n bs[num] = True\n\n dummy = ListNode(-1, head)\n prev = dummy\n\n while head:\n if bs[head.val]:\n prev.next = head.next\n else:\n prev = head\n head = head.next\n\n return dummy.next\n\n```\n```Javascript []\nvar modifiedList = function(nums, head) {\n let bs = new Array(100001).fill(false);\n for (let num of nums) {\n bs[num] = true;\n }\n\n let dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);\n let prev = dummy;\n\n while (head) {\n if (bs[head.val]) {\n prev.next = head.next;\n } else {\n prev = head;\n }\n head = head.next;\n }\n\n return dummy.next;\n};\n\n```\n\n
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Binary Search Approach || C++ || O(nlog(n))
|
binary-search-approach-c-onlogn-by-hiro_-hj1v
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nBinary Search to search
|
RetryUntilAC
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T04:35:08.397934+00:00
|
2024-09-06T04:35:08.397978+00:00
| 17 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nBinary Search to search the element in array (nums)\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(nlog(n))\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n<!-- - Space complexity: -->\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool bs(vector<int> &nums, int k){\n int l =0;\n int h =nums.size()-1;\n while(l<=h){\n int m = h + (l-h)/2;\n if(nums[m]==k){\n return true;\n }\n else if(nums[m]<k){\n l=m+1;\n }\n else{\n h = m-1;\n }\n }\n return false;\n }\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());\n ListNode* temp = head;\n ListNode* curr = temp;\n while(temp->next!= nullptr){\n \n if(bs(nums,temp->next->val)){\n cout<<temp->val<<endl;\n ListNode* x = temp->next;\n temp->next = temp->next->next;\n delete x;\n }\n else{\n temp = temp -> next;\n }\n }\n //Below code for the 1st element of linked-list, the above \n // "while loop" skips the first element\n if(bs(nums,curr->val)){\n ListNode* y= curr;\n curr = curr->next;\n delete y;\n }\n return curr;\n }\n};\n\n```\n\n# \uD83D\uDC47Please Up-Vote
| 2 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'Binary Search', 'C++']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
🔥Simple Brute Force 🎓 ! 💯✔🔥
|
simple-brute-force-by-shivanshgoel1611-qvpd
|
\n\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n set<int> st;\n int n = nums.size(
|
ShivanshGoel1611
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T04:24:54.984215+00:00
|
2024-09-06T04:24:54.984252+00:00
| 96 | false |
\n\n***# Code***\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n set<int> st;\n int n = nums.size();\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n st.insert(nums[i]);\n }\n ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1);\n dummy->next = head;\n ListNode* newdummy = dummy;\n while (dummy->next != nullptr) {\n int t = dummy->next->val;\n if (st.find(t) != st.end()) {\n ListNode* newnode = dummy->next;\n dummy->next = newnode->next;\n continue;\n }\n dummy = dummy->next;\n }\n return newdummy->next;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'C++']
| 1 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Java Clean Simple Code
|
java-clean-simple-code-by-shree_govind_j-t78b
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity:O(n)\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n# Code
|
Shree_Govind_Jee
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T03:06:47.022124+00:00
|
2024-09-06T03:06:47.022154+00:00
| 213 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity:$$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:$$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();\n for (int num : nums) {\n set.add(num);\n }\n\n ListNode res = new ListNode(0);\n res.next = head;\n\n ListNode curr = res;\n while (curr.next != null) {\n if (set.contains(curr.next.val)) {\n curr.next = curr.next.next;\n } else {\n curr = curr.next;\n }\n }\n return res.next;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'Graph', 'Recursion', 'Java']
| 1 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Python Solution using Dummy Node
|
python-solution-using-dummy-node-by-adit-mgav
|
Intuition\nThe problem requires removing all nodes from the linked list whose values exist in a given list, nums. A direct traversal through the linked list is
|
aditya2802singh
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T02:09:26.514753+00:00
|
2024-09-06T02:09:26.514796+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition\nThe problem requires removing all nodes from the linked list whose values exist in a given list, nums. A direct traversal through the linked list is necessary to identify and remove the required nodes. Since the removal of nodes could affect the head of the list, using a dummy node simplifies the logic and ensures that edge cases, like deleting the head, are handled smoothly.\n\n\nHere\'s the breakdown of the dummy node solution with detailed explanations for each section:\n\n\n# Approach\n1. Dummy Node: Create a dummy node that points to the original head of the linked list. This dummy node will help in cases where the head itself needs to be removed.\n\n2. Set for Lookup: Convert the list nums into a set (nums_set) to allow O(1) lookup for checking whether a node\'s value is in nums.\n\n3. Traversal: Use a current pointer, initialized to the dummy node. Traverse the list from this pointer and check if the next node\'s value exists in nums_set.\n\n4. If it does, skip the node by adjusting the next pointer to bypass it.\nIf it doesn\'t, move the current pointer to the next node.\n5. Return Modified List: After the traversal, return dummy.next, which points to the head of the modified list (this handles cases where the original head was removed).\n\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n + m)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(m)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\n# Definition for singly-linked list.\n# class ListNode:\n# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.next = next\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:\n nums = set(nums)\n dummy = ListNode(0)\n dummy.next = head\n curr = dummy\n while curr.next:\n if curr.next.val in nums:\n curr.next = curr.next.next\n else:\n curr = curr.next\n return dummy.next\n\n \n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
C solution
|
c-solution-by-csld-arec
|
Code\nc []\n#define maxN 100005\n\nstruct ListNode *modifiedList(int *nums, int numsSize, struct ListNode *head) {\n int presented[maxN] = {0};\n for (int
|
csld
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T01:50:53.388762+00:00
|
2024-09-06T01:50:53.388778+00:00
| 323 | false |
# Code\n```c []\n#define maxN 100005\n\nstruct ListNode *modifiedList(int *nums, int numsSize, struct ListNode *head) {\n int presented[maxN] = {0};\n for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) {\n presented[nums[i]]++;\n }\n struct ListNode *dummy = (struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));\n dummy->next = head;\n struct ListNode *prev = dummy;\n struct ListNode *curr = head;\n while (curr != NULL) {\n if (presented[curr->val]) {\n prev->next = curr->next;\n free(curr);\n curr = prev->next;\n } else {\n prev = curr;\n curr = curr->next;\n }\n }\n struct ListNode *res = dummy->next;\n free(dummy);\n return res;\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C']
| 2 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
1 ms | Beates 100 %
|
1-ms-beates-100-by-ezsnippet_04-l69z
|
Intuition\nThe main idea behind this code is to modify a linked list by removing any node whose value appears in a given array nums. following solution efficien
|
ezsnippet_04
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T01:28:53.454071+00:00
|
2024-09-06T01:28:53.454090+00:00
| 344 | false |
# Intuition\nThe main idea behind this code is to modify a linked list by removing any node whose value appears in a given array nums. following solution efficiently eliminates unwanted nodes from the linked list by leveraging a set for quick lookups and adjusting the list\'s pointers accordingly\n\n# Approach\n# Approach for the code:\n\n1. **Convert `nums` to a Set**:\n - First, convert the given `nums` array into a **Set** (`numsSet`) to optimize lookup operations. Using a set allows you to check if an element exists in constant time (O(1)). This step ensures that when you traverse the linked list, you can quickly determine whether a node\u2019s value is present in the set.\n\n2. **Use a Dummy Node**:\n - A **dummy node** is initialized with a default value of `0` and its `next` pointer set to the head of the original list. This dummy node helps to manage edge cases, especially when the head node needs to be removed. It simplifies pointer manipulation and avoids the need for special handling of the first node.\n\n3. **Iterate over the Linked List**:\n - The iteration begins from the dummy node and proceeds through the list. For each node:\n - Check if the value of the next node (`curr.next.val`) exists in the `numsSet`.\n - If it does, remove the node by updating the `next` pointer to skip the current node (`curr.next = curr.next.next`).\n - If the value is not in `numsSet`, move to the next node (`curr = curr.next`).\n \n4. **Return the Modified List**:\n - Once the loop finishes, return the modified list starting from `dummy.next` (skipping the dummy node). This returns the modified version of the list with the desired elements removed.\n\nThis approach efficiently removes nodes by leveraging a set for fast lookups, and uses pointer manipulation to skip over nodes that need to be removed. The overall complexity is O(n + m), where n is the number of elements in `nums` and m is the number of nodes in the linked list.\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(\u2223nums\u2223+\u2223head\u2223)\n\n- Space complexity:\n- O(\u2223nums\u2223)\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);\n Set<Integer> numsSet = Arrays.stream(nums).boxed().collect(Collectors.toSet());\n\n for (ListNode curr = dummy; curr.next != null;)\n if (numsSet.contains(curr.next.val))\n curr.next = curr.next.next;\n else\n curr = curr.next;\n\n return dummy.next;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'Math', 'Java']
| 3 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Dart solution (using hash map, and with printout)
|
dart-solution-using-hash-map-and-with-pr-c7nf
|
Some care might be required to handle null nexts.\nOne can also sort the nums and perform binary search to save on space, but that will cause the performance to
|
mulliganaceous
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T01:14:17.870474+00:00
|
2024-09-06T01:16:38.465758+00:00
| 4 | false |
Some care might be required to handle null nexts.\nOne can also sort the nums and perform binary search to save on space, but that will cause the performance to go linearithmic.\n\n```\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode? next;\n * ListNode([this.val = 0, this.next]);\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n ListNode? modifiedList(List<int> nums, ListNode? head) {\n Set<int> numset = {};\n for (int k in nums) {\n numset.add(k);\n }\n while(head != null && numset.contains(head.val)) {\n head = head.next;\n }\n ListNode? cur = head;\n ListNode? next = head?.next;\n while (next != null) {\n print("${cur?.val} ${next.val}");\n while (next != null && numset.contains(next.val)) {\n next = next.next;\n }\n cur?.next = next;\n cur = cur?.next;\n next = next?.next;\n }\n\n return head;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
✅99% BEATS 🔥 RECURSION and BINARY SEARCH 🤠
|
99-beats-recursion-and-binary-search-by-atidq
|
Proof \uD83D\uDC68\u200D\uD83C\uDFEB\n\n\n\n---\n\n# Easy as fuck \uD83D\uDE14\uD83E\uDD1E\n\n# Code\ncpp []\n\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n std::vector<int>
|
xoy5
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T00:59:08.108348+00:00
|
2024-09-06T01:00:55.148803+00:00
| 80 | false |
# Proof \uD83D\uDC68\u200D\uD83C\uDFEB\n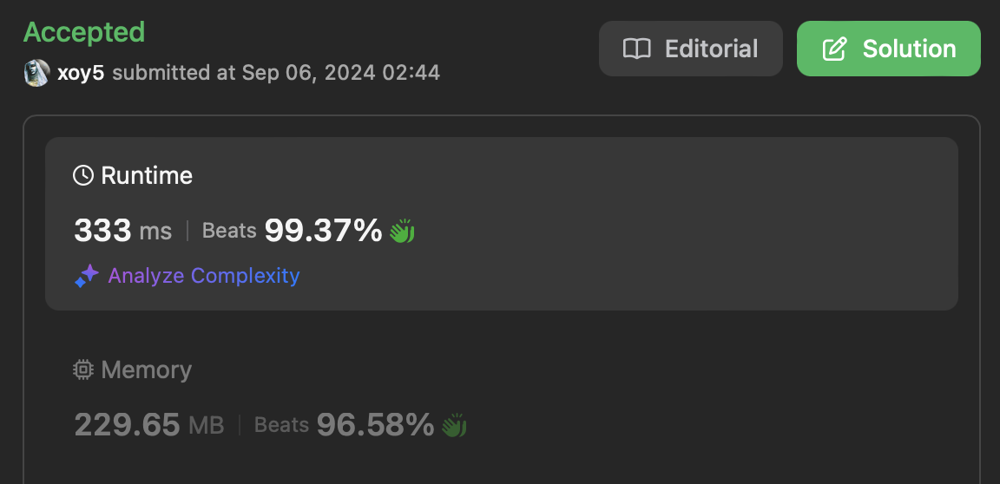\n\n\n---\n\n# Easy as fuck \uD83D\uDE14\uD83E\uDD1E\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n std::vector<int> sorted_nums;\n ListNode* DeleteNodes(ListNode* cur)\n {\n if(cur == nullptr) return cur; // this way is more READABLE fr\n cur->next = DeleteNodes(cur->next);\n if(std::binary_search(sorted_nums.begin(), sorted_nums.end(), cur->val)){\n return cur->next;\n }\n else{\n return cur;\n }\n }\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(std::vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n sorted_nums = nums;\n std::sort(sorted_nums.begin(), sorted_nums.end());\n return DeleteNodes(head);\n }\n};\n\nauto init = []() {\n std::ios::sync_with_stdio(0);\n std::cin.tie(0);\n std::cout.tie(0);\n return \'c\';\n}();\n```\n> If u need any help, just write in the comment section.\n\n\n\n\n
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 2 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
easy java,python,c++||clean code||easy to understand
|
easy-javapythoncclean-codeeasy-to-unders-1k4s
|
Intuition :Given that Nodes must be removed from a linked list where the node values should equal to nums list given Because the list of values \u200B\u200B(nu
|
MD__JAKIR1128__
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-20T13:42:27.141810+00:00
|
2024-08-20T13:42:27.141838+00:00
| 96 | false |
**Intuition** :Given that Nodes must be removed from a linked list where the node values should equal to nums list given Because the list of values \u200B\u200B(nums) is so large, it would be inefficient to check if the value of each node is in this list. To best deal with this, use the set.\n**Aprroach**:\napproach used by me is given below\n1. **Convert `nums` to a Set**: \n - Create a set from the `nums_set` from \'nums\' list. This makes it fast and easy to check if a node\u2019s value should be removed.\n2. **Create a Dummy Node**: \n - Add a dummy node at the beginning of the linked list. This dummy node helps handle cases where the first node might need to be removed.\n3. **Use Two Pointers**:\n - **`prev` Pointer**: Keeps track of the node right before the current node.\n - **`current` Pointer**: Moves through the linked list from start to end.\n4. **Iterate Through the List**:\n - For each node, check if its value is in the set of values to be removed.\n - If the node\u2019s value is in the set, remove it by making `prev` skip over this node.\n - If the node\u2019s value is not in the set, move the `prev` pointer to this node.\n5. **Return the Updated List**: \n - After processing all nodes, return the list starting from the node after the dummy node.\n\n\n\n```\nimport java.util.HashSet;\nimport java.util.Set;\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n Set<Integer> numsSet = new HashSet<>();\n for (int num : nums) {\n numsSet.add(num);\n }\n ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);\n dummy.next = head;\n ListNode prev = dummy;\n ListNode current = head;\n while (current != null) {\n if (numsSet.contains(current.val)) {\n prev.next = current.next;\n } else {\n prev = current;\n }\n current = current.next;\n }\n return dummy.next;\n }\n}\n```\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def modifiedList(self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:\n nums_set=set(nums)\n dummy=ListNode(-1)\n dummy.next=head\n prev=dummy\n current=head\n while current:\n if current.val in nums_set:\n prev.next=current.next\n else:\n prev=current\n current=current.next\n return dummy.next \n```\n\n```\n#include <unordered_set>\n#include <vector>\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(std::vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n std::unordered_set<int> nums_set(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n ListNode dummy(-1);\n dummy.next = head;\n ListNode* prev = &dummy;\n ListNode* current = head;\n while (current) {\n if (nums_set.find(current->val) != nums_set.end()) {\n prev->next = current->next;\n } else {\n prev = current;\n }\n current = current->next;\n }\n return dummy.next;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'C', 'Python', 'Java']
| 2 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
C++ | EASY TO UNDERSTAND | DETAILED SOLUTION
|
c-easy-to-understand-detailed-solution-b-qevh
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe problem requires modifying a linked list by removing all nodes that have values pre
|
nikhil_mane
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-31T21:43:58.438214+00:00
|
2024-07-31T21:43:58.438244+00:00
| 81 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe problem requires modifying a linked list by removing all nodes that have values present in a given vector. My first thought is to use a set for efficient lookup of values that need to be removed. By iterating through the linked list and checking each node\'s value against the set, we can determine whether to keep or remove each node.\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nInitialization:\n\nCreate a set from the given vector nums for quick lookups.\nUse a dummy node to simplify edge cases where the head of the list might be removed.\nIterate through the linked list:\n\nTraverse the list with a pointer curr, starting from the dummy node.\nFor each node, check if the value is in the set.\nIf the value is in the set, bypass the node by adjusting the next pointer of the previous node.\nIf the value is not in the set, move the pointer curr to the next node.\nReturn the modified list:\n\nReturn the list starting from dummy->next, which skips the dummy node.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\no(n)\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\no(n)\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n \n set<int> st;\n \n for(auto v:nums)\n {\n st.insert(v);\n }\n \n ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1,head);\n ListNode* newhead = dummy;\n ListNode* curr = newhead;\n \n while(curr->next!=NULL)\n {\n if(st.find(curr->next->val) != st.end())\n {\n curr->next = curr->next->next;\n \n }\n else{\n curr = curr->next;\n }\n }\n \n return dummy->next;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python', 'C++', 'Java']
| 1 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
|| How to 🤔 in Interview || Using Temp Node ✅
|
how-to-in-interview-using-temp-node-by-p-4wdt
|
Please Uovote\uD83D\uDE4C\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach \uD83E\uDD14\n- use Stream method to convert array to hash
|
patelmihir
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-15T04:10:00.705070+00:00
|
2024-07-15T04:10:00.705100+00:00
| 32 | false |
# Please Uovote\uD83D\uDE4C\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach \uD83E\uDD14\n- use Stream method to convert array to hashset.\n- for check node is exist or not use `.contains()` method.\n- after it deleting nodes using temp node. \n\n# Complexity \u23F2\n- Time complexity:\nO(n)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n)\n\n# Code \uD83D\uDCBB\n```\n\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n HashSet<Integer> list = IntStream.of(nums).boxed()\n .collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));\n while(list.contains(head.val) && head.next!=null)\n head = head.next;\n if(head.next==null || head == null)return head;\n ListNode h = head.next;\n ListNode prev = head;\n \n while(h!=null){\n if(list.contains(h.val)){\n prev.next = prev.next.next;\n h = prev.next;\n }\n else{\n h = h.next;\n prev = prev.next;\n }\n }\n return head;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++', 'Java']
| 1 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
100% beats java solution🔥👍 Easy Explain Basic !!!!
|
100-beats-java-solution-easy-explain-bas-m93b
|
Intuition\nThis Question is based on the problem delete a node from a linked list But the Actual Problem is there are a lot more nodes to be deleted.\n\n# Appro
|
ksv-1288
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T06:45:29.564813+00:00
|
2024-07-14T06:45:29.564837+00:00
| 168 | false |
# Intuition\nThis Question is based on the problem delete a node from a linked list But the Actual Problem is there are a lot more nodes to be deleted.\n\n# Approach\nSo, if we can acces the nodes that we what to delete, the time complexity wiol be reduced, i.e take a node from the array and check in the Linked list and then performing a delete operation will take O(n^2) so to reduce we use a HashSet \n\n* while trvering the LinkedList we are going to chech the next value is avialble in the nodes that we want to delete from our list\n* if we found then we are supposed to skip that node\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:$$O(n)$$ \n- Space complexity:$$O(n)$$ at worst case At an average<$$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n HashSet<Integer> st = new HashSet<>();\n for(int x:nums) st.add(x);\n // ListNode head=null;\n // ListNode tail=null;\n ListNode ptr=head;\n while(ptr!=null && st.contains(ptr.val))\n {\n ptr=ptr.next;\n }\n head=ptr;\n while(ptr!=null && ptr.next!=null)\n {\n while(ptr.next!=null && st.contains(ptr.next.val)){\n ptr.next=ptr.next.next;\n }\n ptr=ptr.next;\n }\n return head;\n\n\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 2 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Simple C++ Solution | Single Pass
|
simple-c-solution-single-pass-by-abhishe-cinj
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Abhishek_499
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T04:03:50.031732+00:00
|
2024-07-14T04:03:50.031774+00:00
| 46 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n unordered_set<int> st(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n \n ListNode* temp=new ListNode(-1);\n \n ListNode* curr=head;\n ListNode* t=temp;\n \n while(curr!=NULL){\n if(st.find(curr->val)!=st.end()){\n curr=curr->next;\n continue;\n }\n \n ListNode* t2=new ListNode(curr->val);\n curr=curr->next;\n t->next=t2;\n t=t->next;\n }\n \n return temp->next;\n \n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 1 |
['C++']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Java Clean Solution | Linear Traversal
|
java-clean-solution-linear-traversal-by-4ds8t
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity:O(n)\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n# Code
|
Shree_Govind_Jee
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-14T04:01:50.139820+00:00
|
2024-07-14T04:01:50.139855+00:00
| 374 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity:$$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:$$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();\n for(int num:nums){\n set.add(num);\n }\n \n ListNode res = new ListNode(0);\n res.next = head;\n \n ListNode curr = res;\n while(curr.next != null){\n if(set.contains(curr.next.val)){\n curr.next = curr.next.next;\n }else{\n curr = curr.next;\n }\n }\n return res.next;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'Doubly-Linked List', 'Java']
| 3 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
easy solution in c++.
|
easy-solution-in-c-by-xegl87zdze-mnil
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:O(n)
Space complexity:O(n)
Code
|
xegl87zdzE
|
NORMAL
|
2025-04-05T13:36:45.798005+00:00
|
2025-04-05T13:38:02.581163+00:00
| 29 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:O(n)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:O(n)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {
unordered_map<int,bool> m;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)
{
m[nums[i]]=true;
}
ListNode *prev=NULL;
ListNode *h=NULL;
while(head != NULL)
{
if(m.count(head->val) == 0)
{
ListNode *s=head->next;
head->next=NULL;
if(prev == NULL)
{
prev=head;
h=head;
}
else
{
prev->next=head;
prev=head;
}
head=s;
}
else
{
head=head->next;
}
}
return h;
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'C++']
| 0 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.