question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
C++✅ || Beats 💯|| Hashing Logic🔥 || Simple & Fast Code 🚀
|
c-beats-hashing-logic-simple-fast-code-b-0u4j
|
Intuition 🤔We need to remove nodes from a linked list whose values exist in a given vector.Approach 🚀
Store the values from nums in an unordered_map for quick l
|
yashm01
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-23T08:10:15.270348+00:00
|
2025-03-23T08:10:15.270348+00:00
| 38 | false |
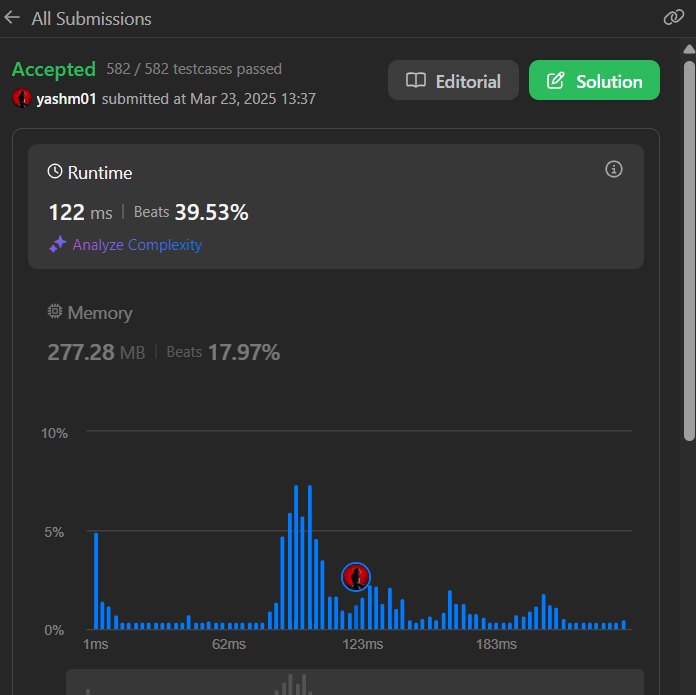
# Intuition 🤔
We need to remove nodes from a linked list whose values exist in a given vector.
# Approach 🚀
1. Store the values from `nums` in an **unordered_map** for quick lookup.
2. Adjust the `head` pointer if initial nodes need to be removed.
3. Traverse the list and remove nodes whose values exist in the map.
# Complexity ⏳
- **Time Complexity:** $$O(n)$$ (Traversing the list once, plus $$O(m)$$ for storing values in the map)
- **Space Complexity:** $$O(m)$$ (Using an unordered_map for storing values)
# Code 💻
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {
unordered_map<int, bool> umap;
for (int n : nums) umap[n] = true;
// Adjust head if its value is in nums
while (head && umap[head->val]) head = head->next;
ListNode* temp = head;
ListNode* curr = temp;
while (temp && temp->next) {
if (umap[temp->next->val]) {
temp->next = temp->next->next;
} else {
temp = temp->next;
}
}
return head;
}
};
```

| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'C++']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Solution in Java and C
|
solution-in-java-and-c-by-vickyy234-qrm9
|
Code
|
vickyy234
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-05T04:31:10.750138+00:00
|
2025-03-05T04:31:10.750138+00:00
| 108 | false |
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int val : nums){
set.add(val);
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0,head);
ListNode current = dummy;
while (current.next != null) {
if (set.contains(current.next.val)) {
current.next = current.next.next;
} else
current = current.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
```
```c []
struct ListNode* modifiedList(int* nums, int numsSize, struct ListNode* head) {
bool* hash = calloc(100001, sizeof(bool));
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) {
hash[nums[i]] = true;
}
struct ListNode dummy;
dummy.next = head;
struct ListNode* current = &dummy;
while (current->next) {
if (hash[current->next->val]) {
current->next = current->next->next;
} else
current = current->next;
}
free(hash);
return dummy.next;
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'C', 'Java']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
C#
|
c-by-adchoudhary-wv7a
|
Code
|
adchoudhary
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-26T04:08:33.104756+00:00
|
2025-02-26T04:08:33.104756+00:00
| 10 | false |
# Code
```csharp []
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode ModifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {
var set = new HashSet<int>(nums);
var dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
var cur = dummy;
while (cur.next != null)
{
if (set.Contains(cur.next.val))
{
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
else
{
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Exactly same as 203. Just added one set!!!!🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥
|
exactly-same-as-203-just-added-one-set-b-zr7s
|
Code
|
adityamah2002
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-09T14:35:48.811755+00:00
|
2025-02-09T14:35:48.811755+00:00
| 73 | false |
# Code
```java []
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int num : nums) {
set.add(num);
}
while (head != null && set.contains(head.val)) {
head = head.next;
}
ListNode prev = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
if (set.contains(curr.val)) {
prev.next = curr.next;
curr = curr.next;
} else {
prev = curr;
curr = curr.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Delete Nodes Using BS and sort algo
|
delete-nodes-using-bs-and-sort-algo-by-l-wxa4
|
IntuitionPrimarily, I wanted to go through LL and check the value using iterator and when I implementeded the code and submit it I did not consider the time com
|
letv1n
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-28T20:28:32.792152+00:00
|
2025-03-15T16:51:45.741311+00:00
| 57 | false |
# Intuition
Primarily, I wanted to go through LL and check the value using iterator and when I implementeded the code and submit it I did not consider the time complexity of iterator (O(N)), so I decided to use binary search.
# Approach
1. Iterate through the linked list and check if each value is in nums
2. If it is, I check all possible cases (head, nodes between the start and end, and the last node). For each case, I use different approaches.
3. Otherwise, I move to the next node.
For finding node->val I used bs to decrease overall time complexity.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(NlogN)
# Code
```cpp []
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool bs(vector<int>& nums, int target){
int low = 0, high = nums.size() - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int middle = (high + low) / 2;
if (nums[middle] == target) return true;
else if (nums[middle] < target) low = middle + 1;
else high = middle - 1;
}
return false;
}
ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
ListNode* curr = head;
ListNode* prev = nullptr;
while (curr != nullptr) {
if (bs(nums, curr->val)) {
if (prev == nullptr) {
head = curr->next;
curr = head;
}
else {
prev->next = curr->next;
curr = prev->next;
}
}
else {
prev = curr;
curr = curr->next;
}
}
return head;
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Binary Search', 'Sorting', 'C++']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Simple Hash table approach || 100% Beat
|
simple-hash-table-approach-100-beat-by-d-3nwp
|
\n### Solution Breakdown\n\n#### Approach\n\n1. Find the Maximum Value in nums:\n - Determine the largest value in nums. This ensures that the boolean array (
|
DS_Sijwali
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-04T08:34:18.612956+00:00
|
2024-12-04T08:34:18.613002+00:00
| 8 | false |
\n### **Solution Breakdown**\n\n#### **Approach**\n\n1. **Find the Maximum Value in `nums`**:\n - Determine the largest value in `nums`. This ensures that the boolean array (`check`) only needs to handle values up to this maximum, optimizing memory usage.\n\n2. **Create a Boolean Array**:\n - Use a boolean array (`check`) to mark the values present in `nums`. This provides constant-time lookups for whether a value should be removed.\n\n3. **Traverse the Linked List**:\n - Iterate through the linked list.\n - For each node, check if its value is:\n - **Within bounds** of the `check` array.\n - **Not marked** in the `check` array (indicating it should not be removed).\n - If the node should not be removed, append it to the result list.\n\n4. **Return the Modified List**:\n - Ensure the result list ends correctly by setting the `next` pointer of the last node to `null`.\n\n---\n\n### **Code Walkthrough**\n\n#### **Step 1: Initialize Dummy Node**\n```java []\nListNode ans = new ListNode(0, head);\n```\n- Use a dummy node (`ans`) pointing to the head of the list. This simplifies handling edge cases, such as removing the head node.\n\n#### **Step 2: Determine the Maximum Value in `nums`**\n```java []\nint max = -1;\nfor (int i : nums) {\n max = max > i ? max : i;\n}\n```\n- Traverse the `nums` array to find the largest value. This ensures the boolean array (`check`) can accommodate all possible values in `nums`.\n\n#### **Step 3: Populate the Boolean Array**\n```java []\nboolean[] check = new boolean[max + 1];\nfor (int i : nums) {\n check[i] = true;\n}\n```\n- Create a boolean array of size `max + 1` to map each value in `nums` to `true`.\n\n#### **Step 4: Traverse and Modify the List**\n```java []\nListNode tail = ans;\nwhile (head != null) {\n if (head.val >= check.length || !check[head.val]) {\n tail.next = head; // Append the current node to the result list\n tail = tail.next; // Move the tail pointer\n }\n head = head.next; // Move to the next node\n}\n```\n- Iterate through the linked list:\n - If the node\u2019s value is greater than `max` (out of bounds for the `check` array) or is not marked in `check`, append the node to the result list.\n - Otherwise, skip the node.\n\n#### **Step 5: Terminate the Result List**\n```java []\ntail.next = null;\n```\n- Ensure the `next` pointer of the last node is `null` to properly terminate the result list.\n\n#### **Step 6: Return the Modified List**\n```java []\nreturn ans.next;\n```\n- Return the new list starting from the node after the dummy node.\n\n---\n\n### **Example Walkthrough**\n\n#### **Example 1**\n**Input**:\n- `nums = [2, 3]`\n- `head = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]`\n\n**Execution**:\n1. Find `max = 3`.\n2. Create `check = [false, false, true, true]` (values `2` and `3` are marked `true`).\n3. Traverse the list:\n - Node `1`: Not in `check` \u2192 Append to result: `tail = [1]`.\n - Node `2`: In `check` \u2192 Skip.\n - Node `3`: In `check` \u2192 Skip.\n - Node `4`: Not in `check` \u2192 Append to result: `tail = [1 \u2192 4]`.\n - Node `5`: Not in `check` \u2192 Append to result: `tail = [1 \u2192 4 \u2192 5]`.\n\n**Output**: `[1 \u2192 4 \u2192 5]`.\n\n---\n\n#### **Example 2**\n**Input**:\n- `nums = [1, 4, 5]`\n- `head = [1, 4, 2, 5, 3]`\n\n**Execution**:\n1. Find `max = 5`.\n2. Create `check = [false, true, false, false, true, true]` (values `1`, `4`, and `5` are marked `true`).\n3. Traverse the list:\n - Node `1`: In `check` \u2192 Skip.\n - Node `4`: In `check` \u2192 Skip.\n - Node `2`: Not in `check` \u2192 Append to result: `tail = [2]`.\n - Node `5`: In `check` \u2192 Skip.\n - Node `3`: Not in `check` \u2192 Append to result: `tail = [2 \u2192 3]`.\n\n**Output**: `[2 \u2192 3]`.\n\n---\n\n### **Time and Space Complexity**\n\n#### **Time Complexity**\n1. **Finding `max`**: \\( O(M) \\), where \\( M \\) is the size of `nums`.\n2. **Populating `check`**: \\( O(M) \\), iterating through `nums` to mark values.\n3. **Traversing the List**: \\( O(N) \\), where \\( N \\) is the number of nodes in the linked list.\n\n**Total**: O(M + N) .\n\n#### **Space Complexity**\n1. **Boolean Array**: \\( O(\\text{max}) \\), where `max` is the largest value in `nums`.\n2. **Result List**: Uses the existing linked list nodes (in-place modification).\n\n**Total**: O(max) .\n\n---\n\n### **Key Points**\n- **Efficiency**: The boolean array enables \\( O(1) \\) lookups, improving performance for large lists.\n- **Edge Case Handling**: The code handles values outside the range of `nums` by checking `head.val >= check.length`.\n- **Space Optimization**: The boolean array is only as large as the maximum value in `nums`.
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'Java']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Easy solution using HashSet
|
easy-solution-using-hashset-by-chandrans-agv6
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Chandranshu31
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-14T07:28:08.657532+00:00
|
2024-11-14T07:28:08.657566+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n int n=nums.length;\n if(head==null){\n return head;\n }\n\n HashSet<Integer> hset= new HashSet<>(); // so that we can easily search array elements in O(1)\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n hset.add(nums[i]); // add all elements of array into hset\n }\n\n\n ListNode dummy= new ListNode(-1);\n dummy.next=head;\n ListNode temp=head;\n ListNode prev=dummy;\n\n while(temp!=null){\n boolean remove=false; // to check wether we want to remove ths node or not\n if(hset.contains(temp.val)){\n remove=true; // if conditions meets then we want to remove this elemtn as it is in array\n \n }\n if(remove){\n prev.next=temp.next;\n }else{\n prev=prev.next;\n }\n temp=temp.next;\n \n }\n return dummy.next;\n\n \n\n }\n}\n\n/**\nAnother method without using hashset using loop but it will give TLE in large array cases \n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n \nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n int n=nums.length;\n if(head==null){\n return head;\n }\n ListNode dummy= new ListNode(-1);\n dummy.next=head;\n ListNode temp=head;\n ListNode prev=dummy;\n\n while(temp!=null){\n boolean remove=false; // to check wether we want to remove ths node or not\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n if(nums[i]==temp.val){\n remove=true; // if conditions meets then we want to remove it\n break;\n }\n }\n if(remove){\n prev.next=temp.next;\n }else{\n prev=prev.next;\n }\n temp=temp.next;\n \n }\n return dummy.next;\n\n \n\n }\n} */\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'Two Pointers', 'Java']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
BEATS 100% || A VERY EASY APPROACH ||BEGINNER FRIENDLY
|
beats-100-a-very-easy-approach-beginner-ybj0t
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
K_L_Sri_Harsha
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-24T14:50:38.752455+00:00
|
2024-10-24T14:50:38.752499+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python []\n# Definition for singly-linked list.\n# class ListNode(object):\n# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.next = next\nclass Solution(object):\n def modifiedList(self, nums, head):\n """\n :type nums: List[int]\n :type head: Optional[ListNode]\n :rtype: Optional[ListNode]\n """\n s=set(nums)\n prev=None\n t=head\n while(t!=None):\n if(t.val in s):\n if(prev==None):\n head=head.next\n t=head\n \n else:\n prev.next=t.next\n t=prev.next\n else:\n prev=t\n t=t.next\n return head\n \n \n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Easy Python Program For Beginners||Beats 100%||O(n) Approach
|
easy-python-program-for-beginnersbeats-1-xem4
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
RaghavaYagnesh_Kola
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-24T14:49:46.613857+00:00
|
2024-10-24T14:49:46.613888+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python []\n# Definition for singly-linked list.\n# class ListNode(object):\n# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):\n# self.val = val\n# self.next = next\nclass Solution(object):\n def modifiedList(self, nums, head):\n b=set(nums)\n c=[]\n temp=head\n while(temp!=None):\n if(temp.val not in b):\n c.append(temp.val)\n temp=temp.next\n new=None\n i=0\n while(i<len(c)):\n t=ListNode(c[i])\n if(new==None):\n new=t\n newhead=new\n else:\n newhead.next=t\n newhead=t\n i+=1\n return new\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Very easy approach:- Java
|
very-easy-approach-java-by-swati112-ktvl
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
swati112
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-17T17:32:20.581208+00:00
|
2024-10-17T17:32:20.581246+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n Set<Integer> numSet = new HashSet<>();\n for (int num : nums) {\n numSet.add(num);\n }\n while(head!=null && numSet.contains(head.val)){\n head=head.next;\n }\n ListNode temp=head;\n while(temp!=null && temp.next!=null){\n if(numSet.contains(temp.next.val)){\n temp.next=temp.next.next;\n }else{\n temp=temp.next;\n }\n }\n return head;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Easy Video Solution 🔥 || How to 🤔 in Interview || Using Temp Node ✅
|
easy-video-solution-how-to-in-interview-bm9y9
|
\n\n# Code\njava []\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();\n L
|
Ankit1317
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-08T23:47:42.470308+00:00
|
2024-09-08T23:47:42.470326+00:00
| 7 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();\n ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);\n ListNode newnode = dummy;\n for (int x : nums) {\n set.add(x);\n }\n while (head != null) {\n if (!set.contains(head.val)) {\n newnode.next = head;\n newnode = newnode.next;\n }\n head = head.next;\n }\n newnode.next = null;\n return dummy.next;\n }\n}\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'Java']
| 1 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Java Solution using Set
|
java-solution-using-set-by-amargupta721-n5t2
|
Intuition\n1. Add all the items of nums into set.\n2. now iterate over the linked list.\n3. if the current node\'s value is present in the set then skip that no
|
amargupta721
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-07T19:07:26.511883+00:00
|
2024-09-07T19:07:26.511908+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n1. Add all the items of nums into set.\n2. now iterate over the linked list.\n3. if the current node\'s value is present in the set then skip that node else adjust the prev pointer as used in the code and move the pointer on next node.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: size of linked list(n)\n\n- Space complexity: length of nums array(m)\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);\n dummy.next = head;\n ListNode prev = dummy;\n ListNode temp = head;\n Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++){\n set.add(nums[i]);\n }\n while(temp!=null){\n if(!set.contains(temp.val)){\n prev.next = temp;\n prev = temp;\n }\n temp = temp.next;\n }\n if(prev.next!=null)prev.next = null;\n return dummy.next;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Simple and Easy C++ Solution | 💻 With Explanation
|
simple-and-easy-c-solution-with-explanat-7n36
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nSince we will nedd to go node by node and check if this is the one to be removed or not
|
gpranchal2003
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-07T18:35:08.111537+00:00
|
2024-09-07T18:35:08.111563+00:00
| 12 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nSince we will nedd to go node by node and check if this is the one to be removed or not, I took unordered_set to store all the elements of array in set , so that i can perform st.find(node->val), that is, if it exists in the set or not.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1) Connecting nodes that do not exist in the set, and maintaining head correctly. If head is found in the set, then move it forward, and delete the previous head you just remove using delete(), so that node is not left hanging.\n\n\n2) Once we have settled with head, now you can move on to other nodes, by keeping curr to the present node you are standing on, checking before hand if it\'s front position exists or not? If not, then connect curr to node that comes after it\'s next.\n1->2->3\nSuppose 2 exists in the set, so then remove 1\'s connection from 2 and joint it with 3.\n\n3) if curr and curr->next both are not in the set, then you can just move curr forwad.\n\n4) Hope ,it helps.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N+M)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n unordered_set<int>st(begin(nums), end(nums)); // inserted\n\n while(head!=NULL && st.find(head->val)!=st.end())\n {\n //we should delete this hanging node also\n ListNode* temp = head;\n head = head->next;\n delete(temp);\n }\n\n ListNode* curr = head;\n while(curr!=NULL && curr->next!=NULL)\n {\n if(st.find(curr->next->val)!=st.end()) // pehle hi dekh lenge ki agar iska aage wala exist ni karta toh hata denge isko , or uske aage wale ke join kar denge curr ko \n {\n ListNode* temp = curr->next;\n curr->next = curr->next->next;\n delete(temp);\n }\n else\n {\n curr = curr->next;\n }\n }\n return head;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'C++']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
EASY UNDERSTANDABLE || BEGINAR FRENDLY || JAVA SOLUTION
|
easy-understandable-beginar-frendly-java-8cy3
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nUSING HASH SET\n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n\n# C
|
Piyush_7488
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-07T18:28:15.402979+00:00
|
2024-09-07T18:28:15.403005+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nUSING HASH SET\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(N)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n HashSet<Integer>st=new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){\n st.add(nums[i]);\n\n }\n ListNode dummy=new ListNode();\n ListNode current=head;\n ListNode prev=dummy;\n while(current!=null){\n if(st.contains(current.val)){\n prev.next=current.next;\n }else{\n prev.next=current;\n prev=prev.next;\n }\n current=current.next;\n \n }\n return dummy.next;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Best C++ Code (beats 80% in both complexity)
|
best-c-code-beats-80-in-both-complexity-2l9sx
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
souravsinghal2004
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-07T11:31:08.907269+00:00
|
2024-09-07T11:31:08.907299+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n\n/***struct ListNode {\n int val;\n ListNode *next;\n ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n};\n***/\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n // Create a set for quick lookup\n unordered_set<int> valuesToRemove(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n \n // Create a dummy node to handle edge cases easily\n ListNode dummy(0);\n dummy.next = head;\n ListNode* prev = &dummy;\n ListNode* curr = head;\n \n // Traverse the list\n while (curr != nullptr) {\n if (valuesToRemove.find(curr->val) != valuesToRemove.end()) {\n // If the current node\'s value is in the set, remove the node\n prev->next = curr->next;\n } else {\n // Move the previous pointer forward\n prev = curr;\n }\n // Move the current pointer forward\n curr = curr->next;\n }\n \n return dummy.next;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Just 7 Liner solution (Even in Java) | O(n+m)
|
just-7-liner-solution-even-in-java-onm-b-y7sd
|
Took just 3 min\'s to write down the code,\nhas 7 line\'s within java\nO(m + n)\n\nhttps://youtu.be/hVIVXDjXB3g
|
obrutus
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T23:01:34.923622+00:00
|
2024-09-06T23:01:34.923650+00:00
| 12 | false |
Took just 3 min\'s to write down the code,\nhas 7 line\'s within java\nO(m + n)\n\nhttps://youtu.be/hVIVXDjXB3g
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Simple to understand!
|
simple-to-understand-by-nehasinghal03241-dyyx
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n)->(here n is size of linked list)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity:O(nums.length)\n Add your
|
NehaSinghal032415
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T19:29:01.779775+00:00
|
2024-09-06T19:29:01.779807+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n)->(here n is size of linked list)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(nums.length)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n HashSet<Integer> set =new HashSet<>();\n for(int num :nums){\n set.add(num);\n }\n ListNode previous=null;\n ListNode current=head;\n while(current!=null){\n if(set.contains(current.val)){\n if(previous==null){\n current=current.next;\n head=current;\n }else{\n current=current.next;\n previous.next=current; \n }\n } \n else{\n previous=current;\n current=current.next;\n }\n }\n return head;\n }\n} \n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'Java']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Easy and simple solution in c++ using map
|
easy-and-simple-solution-in-c-using-map-nlsy9
|
Intuition\nEasy and simple solution in c++ using map\n\n# Approach\nAt first, i put all the numbers that l have to delete from the linked list (head) into the m
|
Mo7amed_3bdelghany
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T19:09:08.002773+00:00
|
2024-09-06T19:09:08.002809+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Intuition\nEasy and simple solution in c++ using map\n\n# Approach\n*At first, i put all the numbers that l have to delete from the linked list (head) into the map and loop along the linked list(head) if the number is\'nt in the map, l add it to the linked list(ans).*\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n map<int,int>mp;\n for(auto it:nums) mp[it]++;\n ListNode * ans = new ListNode(0,NULL);\n ListNode * t = ans;\n while(head!=NULL){\n if(!mp[head->val]) {\n ans->next=new ListNode(head->val);\n ans=ans->next;\n }\n head=head->next;\n }\n return t->next;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'C++']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
BEATS 98.49% 💯✅ || BEST AND EASY APPROACH 🔥🚀|| JAVA
|
beats-9849-best-and-easy-approach-java-b-m2o2
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe function removes nodes from a linked list if their values are present in a given ar
|
surajdivekarsd27
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T18:39:00.005770+00:00
|
2024-09-06T18:39:00.005801+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe function removes nodes from a linked list if their values are present in a given array. It first marks the values to be removed using a boolean array for quick lookup. Then, as it traverses the linked list, it adjusts pointers to exclude the nodes with marked values, effectively removing them from the list.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. Array Marking: We create a boolean array arr of size 100001, assuming the maximum possible value for nums is 100000. This array is used to mark the elements that need to be removed.\n\n2. Traversing the Linked List: We iterate through the linked list:\n\n- For each node, check if its value exists in the arr array (i.e., if it needs to be removed).\n- If it does, we adjust the pointers to remove the node from the list.\n- If it\'s the head node, we update the head of the list.\n3. Edge Case: If the head node needs to be removed, special handling is required to update the head pointer correctly.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n+m) \nn - number of elements in the array\nm - number of nodes in the linked list\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n boolean[] arr= new boolean[(int)1e5+1];\n for(int num:nums){\n arr[num] = true;\n }\n\n ListNode prev = null;\n ListNode curr = head;\n while(curr!=null){\n if(arr[curr.val]==true){\n if(prev==null){ //delition at head vala\n head= curr.next;\n curr.next = null;\n curr= head;\n }else{\n prev.next = curr.next;\n curr.next = null;\n curr = prev.next;\n }\n }else{\n prev= curr;\n curr = curr.next;\n }\n }\n return head;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Best optimal approach 100%
|
best-optimal-approach-100-by-aminreneesm-8x2c
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
AminReneesMV
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T18:17:35.707249+00:00
|
2024-09-06T18:17:35.707287+00:00
| 11 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n if(head==NULL){\n return 0;\n }\n int n = nums.size();\n // for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){\n // if(nums[i]==head->val){\n // ListNode* temp = head;\n // head = head->next;\n // delete(temp);\n // }\n // }\n // return head;\n unordered_set<int> st(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n while(head!=NULL && st.find(head->val)!=st.end()){\n ListNode* temp = head;\n head = head->next;\n delete(temp);\n }\n ListNode* curr = head;\n while(curr!=NULL && curr->next!=NULL){\n if(st.find(curr->next->val)!=st.end()){\n ListNode* temp = curr->next;\n curr->next = curr->next->next;\n delete(temp);\n } else {\n curr = curr->next;\n }\n }\n return head;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Optimized Java Solution using HashSet for O(1)
|
optimized-java-solution-using-hashset-fo-o6ls
|
Approach:\n\n- Convert the nums array into a HashSet to enable O(1) lookup for checking whether a value exists in nums.\n- Traverse the linked list and only add
|
RahulSharma21110
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T18:10:15.544642+00:00
|
2024-09-06T18:10:15.544682+00:00
| 10 | false |
# **Approach:**\n\n- Convert the nums array into a HashSet to enable O(1) lookup for checking whether a value exists in nums.\n- Traverse the linked list and only add nodes to the result list if their value is not in the nums set.\n- Use a dummy node to simplify list manipulation, ensuring that the head of the new list is easily accessible.\n- At the end of traversal, terminate the list properly to avoid any dangling references.\n\n# ****Time complexity:****\n- **O(n + m)** where n is the number of nodes in the linked list and m is the length of the nums array:\n- **O(m)** to create the **HashSet** from nums.\n- **O(n)** to traverse the **linked list** and build the new list.\n\n# **Space complexity:**\n- O(m) for the HashSet storing nums.\n- O(1) additional space for the list traversal.\n\n# Code\n```java []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * public class ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode next;\n * ListNode() {}\n * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }\n * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }\n * }\n */\nclass Solution {\n public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {\n\n // Convert nums array to a HashSet for O(1) lookup time\n Set<Integer> numSet = new HashSet<>();\n for (int num : nums) {\n numSet.add(num);\n }\n\n // Dummy node to start the filtered list\n ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);\n ListNode temp = dummy; // Temporary pointer to form the new list\n\n // Traverse the linked list directly\n while (head != null) {\n // If the value is NOT in nums, add the node to the result list\n if (!numSet.contains(head.val)) {\n temp.next = head; // Link the node to the new list\n temp = temp.next; // Move temp to the next node\n }\n head = head.next; // Move to the next node in the original list\n }\n\n // Terminate the list properly\n temp.next = null;\n\n // Return the head of the new list (skipping the dummy node)\n return dummy.next;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'Java']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Beats: 93.99% || C++
|
beats-9399-c-by-pramaywankhade7-72y3
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
pramaywankhade7
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T17:15:16.577072+00:00
|
2024-09-06T17:15:16.577107+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(m+n)\nwhere \uD835\uDC5A is the number of elements in nums, and \uD835\uDC5B is the number of nodes in the linked list.\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(m)\nwhere \uD835\uDC5A is the number of elements in nums\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n unordered_set<int> st(nums.begin(),nums.end());\n ListNode *temp=new ListNode(0,head);\n for(ListNode *prev=temp;prev->next;){\n if(st.count(prev->next->val))\n prev->next=prev->next->next;\n else prev=prev->next;\n }\n return temp->next;\n \n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'C++']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Beats 95% people|| Very Beginner Friendly
|
beats-95-people-very-beginner-friendly-b-h07w
|
Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nFor Easy accessing of data firstly convert the nums array into a hashset. Then start traversing the
|
sdeepu2003
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T16:50:29.600066+00:00
|
2024-09-06T16:50:29.600099+00:00
| 93 | false |
# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nFor Easy accessing of data firstly convert the nums array into a hashset. Then start traversing the linkedlist from starting by maintaining current pointer and previous pointer. \n1. If you encounter a node whose value is present in the hashset then assign previous->next to cuurent node next value. If incase your previous is NULL it means you have to remove your head node so place you head to cuurent->next.\n2. Else the Node value is not in hashset so, assign cuurent to previous.\n3. Now regardless of above operations move your current pointer to next node.\n4. After successfull traversal return the head.\n**I Think if you explain this approach to interviewer he will be satisfied with your approach.**\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:$$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n/**\n * Definition for singly-linked list.\n * struct ListNode {\n * int val;\n * ListNode *next;\n * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n * };\n */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n unordered_set<int>s;\n for(auto it:nums)\n s.insert(it);\n ListNode*t=head,*prev=NULL;\n while(t!=NULL)\n {\n if(s.find(t->val)!=s.end())\n {\n if(prev==NULL)\n head=t->next;\n else\n prev->next=t->next;\n }\n else\n {\n prev=t;\n }\n t=t->next;\n }\n return head;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Linked List', 'C++']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
C++ Solution || Beats 92% || Easy For Beginners
|
c-solution-beats-92-easy-for-beginners-b-ulq5
|
Intuition\nWe know that we can traverse the linked list by having 2 pointers, prev and current, and continuining until the current pointer is pointing to NULL.
|
SuperPowered-Cat
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T16:30:54.986654+00:00
|
2024-09-06T16:30:54.986686+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\nWe know that we can traverse the linked list by having 2 pointers, prev and current, and continuining until the current pointer is pointing to NULL. Now, we somehow have to traverse the list whilst also checking each element of the nums array. \n\nWe also need to delete and update the head pointer if the value is the same as that of the array nums. Note that we need to consider the edgecase where head is also to be deleted.\n\n# Approach\n1. **Use a Hash Set for Fast Lookups:**\nFirst, convert the nums array into a hash set. This allows for constant-time lookup (O(1)) when checking if a node\'s value needs to be removed, instead of looping through the array each time.\n\n2. **Create a Dummy Node:**\nTo handle edge cases like when the head node needs to be removed, we introduce a dummy node. This dummy node points to the original head of the list, simplifying the removal logic, especially for the head.\n\n3. **Traverse the Linked List:**\nUsing two pointers, prev and curr, we traverse the linked list:\n curr points to the current node being examined.\n prev points to the last node that wasn\'t removed.\n4. **Remove Matching Nodes:**\n For each node:\n - If curr->val exists in the set (i.e., the node\'s value is in nums), we remove it by updating prev->next to skip over curr.\n - If curr->val is not in the set, we simply move prev forward to curr.\n\n5. **Free Memory (Optional):**\nIf memory management is a concern, delete the removed nodes to free memory. Not required for this question.\n\n6. **Return the New Head:**\nAfter traversing and modifying the list, return dummy->next as the new head, which handles the case where the head might have been removed.\n\n# Complexity\n\n\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n\n// Definition for singly-linked list. (Given in question)\n\n// struct ListNode {\n// int val;\n// ListNode *next;\n// ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}\n// ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}\n// ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}\n// };\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {\n \n // Unordered set for the complexity of 1.\n // Will have to handle edge case where head is stored in num\n unordered_set<int> removables (nums.begin(), nums.end());\n ListNode *edgeCase = new ListNode(0); \n edgeCase->next = head;\n ListNode *prev = edgeCase;\n ListNode *curr = head; \n while (curr != NULL) {\n if (removables.count(curr->val)){\n prev->next = curr->next;\n // delete curr; \n \n }\n else prev = curr;\n curr = prev->next;\n }\n return edgeCase->next;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
delete-nodes-from-linked-list-present-in-array
|
Kotlin | O(max(n, nodes)) time, O(maxNum) space | count + iterator (974ms)
|
kotlin-omaxn-nodes-time-omaxnum-space-co-c0zw
|
Intuition\n\n- nums[i] from 1 to 10^5 - we can reduce the complexity of evaluation "should we remove this number" downto O(1)\n- just keep head and last pointer
|
tonycode88
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T16:14:06.405990+00:00
|
2024-09-06T16:14:06.406020+00:00
| 14 | false |
# Intuition\n\n- `nums[i]` from 1 to 10^5 - we can reduce the complexity of evaluation "should we remove this number" downto O(1)\n- just keep `head` and `last` pointers for a new list, and carefully iterate throught original building answer\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$ to iterate through `nums`, then throught list. Checking "should remove?" is O(1)\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(maxNum)$$ to keep array for O(1) checking\n\n# Code\n```kotlin []\nclass Solution {\n\n fun modifiedList(nums: IntArray, head: ListNode): ListNode {\n val shouldRemove = BooleanArray(MAX_NUM+1)\n for (num in nums) shouldRemove[num] = true\n\n var first: ListNode? = null\n var last: ListNode? = null\n\n var current: ListNode? = head\n while (current != null) {\n if (!shouldRemove[current.`val`]) {\n val newNode = ListNode(current.`val`)\n if (first == null) {\n first = newNode\n last = first\n } else {\n (last ?: error("last is null")).next = newNode\n last = last.next\n }\n }\n current = current.next\n }\n\n return first ?: error("All items were removed")\n }\n\n\n companion object {\n private const val MAX_NUM = 100_000 // 10^5\n }\n\n}\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Kotlin']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
[Java/Python] Sorting queries by their minSize - Clean & Concise
|
javapython-sorting-queries-by-their-mins-jkxp
|
Idea\n- We sort queries by the decreasing of its minSize order.\n- We sort rooms by the decreasing of its size order.\n- We initialize roomIdsSoFar TreeSet, thi
|
hiepit
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T16:01:28.569642+00:00
|
2021-05-02T06:53:41.925756+00:00
| 5,826 | false |
**Idea**\n- We sort `queries` by the decreasing of its `minSize` order.\n- We sort `rooms` by the decreasing of its `size` order.\n- We initialize `roomIdsSoFar` TreeSet, this includes all room ids which have `size` >=` minSize` of current query so far.\n- For each query `q` in `queries`:\n\t- Add all room ids which have `size` >=` minSize` of current query.\n\t- Query `floor` and `ceiling` of `q[0]` (preferredId) from `roomIdsSoFar` to pick the id which closest to our `preferredId`\n\n**Complexity**\n- Time: `O(NlogN + KlogK + K*logN)`\n- Space: `O(N + K)`\n\n**Java**\n- Using `TreeSet` structure which we can query `floor` and `ceiling` in `O(logN)`\n```java\nclass Solution {\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n int n = rooms.length, k = queries.length;\n Integer[] indexes = new Integer[k];\n for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) indexes[i] = i;\n Arrays.sort(rooms, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(b[1], a[1])); //Sort by decreasing order of room size\n Arrays.sort(indexes, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(queries[b][1], queries[a][1])); // Sort by decreasing order of query minSize\n TreeSet<Integer> roomIdsSoFar = new TreeSet<>();\n int[] ans = new int[k];\n int i = 0;\n for (int index : indexes) {\n while (i < n && rooms[i][1] >= queries[index][1]) { // Add id of the room which its size >= query minSize\n roomIdsSoFar.add(rooms[i++][0]);\n }\n ans[index] = searchClosetRoomId(roomIdsSoFar, queries[index][0]);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n int searchClosetRoomId(TreeSet<Integer> treeSet, int preferredId) {\n Integer floor = treeSet.floor(preferredId);\n Integer ceiling = treeSet.ceiling(preferredId);\n int ansAbs = Integer.MAX_VALUE, ans = -1;\n if (floor != null) {\n ans = floor;\n ansAbs = Math.abs(preferredId - floor);\n }\n if (ceiling != null && ansAbs > Math.abs(preferredId - ceiling)) {\n ans = ceiling;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```\n\n\n**Python 3 - Using SortedList from sortedcontainers library**\n- For Map/TreeMap structure, we can use [sortedcontainers](http://www.grantjenks.com/docs/sortedcontainers/) which is imported by Leetcode.\n```python\nfrom sortedcontainers import SortedList\n\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n rooms.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True) # Sort by decreasing order of room size\n qArr = [[i, q] for i, q in enumerate(queries)] # Zip queries with their index\n qArr.sort(key=lambda x: x[1][1], reverse=True) # Sort by decreasing order of query minSize\n\n def searchClosestRoomId(preferredId):\n if len(roomIdsSoFar) == 0: \n return -1\n cands = []\n i = roomIdsSoFar.bisect_right(preferredId)\n if i > 0: \n cands.append(roomIdsSoFar[i - 1])\n if i < len(roomIdsSoFar): \n cands.append(roomIdsSoFar[i])\n return min(cands, key=lambda x: abs(x - preferredId))\n\n roomIdsSoFar = SortedList()\n n, k = len(rooms), len(queries)\n i = 0\n ans = [-1] * k\n for index, (prefferedId, minSize) in qArr:\n while i < n and rooms[i][1] >= minSize:\n roomIdsSoFar.add(rooms[i][0]) # Add id of the room which its size >= query minSize\n i += 1\n ans[index] = searchClosestRoomId(prefferedId)\n return ans\n```\n\n\n**Python 3 - Using bisect.insort(arr, x)**\n- We can use `bisect.insort` which will insert an element into an array very fast, it has time complextity `O(N)` but it runs too fast, which we can treat it as `O(logN)`.\n```python\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n rooms.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True) # Sort by decreasing order of room size\n qArr = [[i, q] for i, q in enumerate(queries)] # Zip queries with their index\n qArr.sort(key=lambda x: x[1][1], reverse=True) # Sort by decreasing order of query minSize\n\n def searchClosestRoomId(preferredId):\n if len(roomIdsSoFar) == 0:\n return -1\n cands = []\n i = bisect_right(roomIdsSoFar, preferredId)\n if i > 0:\n cands.append(roomIdsSoFar[i - 1])\n if i < len(roomIdsSoFar):\n cands.append(roomIdsSoFar[i])\n return min(cands, key=lambda x: abs(x - preferredId))\n\n roomIdsSoFar = [] # Room id is sorted in increasing order\n n, k = len(rooms), len(queries)\n i = 0\n ans = [-1] * k\n for index, (prefferedId, minSize) in qArr:\n while i < n and rooms[i][1] >= minSize:\n bisect.insort(roomIdsSoFar, rooms[i][0]) # Add id of the room which its size >= query minSize\n i += 1\n ans[index] = searchClosestRoomId(prefferedId)\n return ans\n```
| 95 | 1 |
[]
| 18 |
closest-room
|
C++ solution. sort the query by room size.
|
c-solution-sort-the-query-by-room-size-b-xe17
|
\n#### Idea\n- Because we need the room which has minSize by the given query, so we can iterate from the largest minSize query and put all the valid room to an
|
chejianchao
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T16:00:34.403343+00:00
|
2021-05-03T18:52:04.816698+00:00
| 3,868 | false |
\n#### Idea\n- Because we need the room which has minSize by the given query, so we can iterate from the largest minSize query and put all the valid room to an ordered set, and then do binary search to get room id in the ordered set.\n\n#### Complexity\n- Time O(max(nLog(n), mLog(m))) n is rooms length, m is queries length.\n- Space O(n)\n\n#### Solution\n- C++\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n for(int i = 0; i < queries.size(); i++) queries[i].push_back(i);\n\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end(), [](auto &a, auto &b) {\n \n return a[1] > b[1];\n });\n sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), [](auto &a, auto &b){\n return a[1] > b[1];\n });\n int i = 0;\n set<int> st;\n vector<int> ans(queries.size());\n for(auto q : queries) {\n int prefer = q[0], minSize = q[1], idx = q[2];\n while(i < rooms.size() && rooms[i][1] >= minSize)\n st.insert(rooms[i++][0]);\n if(st.size()) {\n auto it = st.upper_bound(prefer);\n int res = it != st.end() ? abs(*it - prefer) : INT_MAX;\n int resRoomId = it != st.end() ? *it : INT_MAX;\n if(it != st.begin()) {\n --it;\n if(abs(*it - prefer) <= res)\n resRoomId = *it;\n }\n ans[idx] = resRoomId;\n }else\n ans[idx] = -1;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 65 | 4 |
[]
| 9 |
closest-room
|
[Python] Sorted List solution, explained
|
python-sorted-list-solution-explained-by-s55y
|
The idea of this problem is to sort our rooms and queries by time and start with biggest times and keep sorted list aval for avaliable rooms: such that we can c
|
dbabichev
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T16:02:00.393382+00:00
|
2021-05-02T11:56:29.812785+00:00
| 1,933 | false |
The idea of this problem is to sort our rooms and queries by time and start with biggest times and keep sorted list `aval` for avaliable rooms: such that we can choose from. Imagine, that we have rooms with sizes `[7, 6, 3, 2, 1]` and queries with sizes `[5, 3, 1]`. Then on the first step we see query with size `5` and avaliable rooms we have are `[7, 6]`. Then we look at query `3` and now we have avaliable rooms `[7, 6, 3]`. Finally, we look at query `1` and now avaliable rooms are `[7, 6, 3, 2, 1]`.\n\nHowever we need to return closest index among all avaliable rooms, so we need to keep our avaliable rooms sorted with `id`. If fact, we put tuple `(id, size)` into our sorted list. \n\nAlso we use two pointers approach: `p1` is responsible for rooms `R` and `p2` is responsible for queries `Q`. If `R[p1][0] >= Q[p2][0]`, it means that we can add one more room to `aval`, so we do it and update `p1`. If we can not do it, it means we already saturated `aval`, so we look at it. If it is empty, we must return `-1`, we do not have any candidates. If it is not empty, we use binary search: there can be at most `3` (in fact `2`) candidates for the nearest index: we chose the best of them.\n\n#### Complexity\nLet `n` be number of rooms and `q` is number of queries. Then we have time complexity `O(n log n + q log n)` to sort our data and then we have `n+q` iterations in our 2 pointers approach, where each time we use either `add` or `bisect` operation with complexity `O(log n)`. So, total time complexity is `O(n log n + q log q + q log n)`. Space complexity is `O(n + q)`.\n\n#### Code\n```python\nfrom sortedcontainers import SortedList\n\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms, queries):\n Q = sorted([(y, x, i) for i, (x,y) in enumerate(queries)])[::-1]\n R = sorted((y, x) for x, y in rooms)[::-1]\n n, q = len(R), len(Q)\n p1, p2, aval, ans = 0, 0, SortedList(), [-1]*q\n\n while p1 <= n and p2 < q:\n if p1 < n and R[p1][0] >= Q[p2][0]:\n aval.add(R[p1][1])\n p1 += 1\n else:\n if len(aval) != 0:\n preferred, ind = Q[p2][1], Q[p2][2]\n i = aval.bisect(preferred)\n \n cands = []\n if i > 0: cands.append(aval[i-1])\n if i < len(aval): cands.append(aval[i])\n ans[ind] = min(cands, key = lambda x: abs(x - preferred))\n\n p2 += 1\n\n return ans\n```\n\nIf you have any questions, feel free to ask. If you like solution and explanations, please **Upvote!**
| 50 | 0 |
[]
| 8 |
closest-room
|
C++/Java Sort Queries
|
cjava-sort-queries-by-votrubac-tboy
|
Our per-query time complexity should be better than O(n), so we will shoot for O(log n).\n\nTo do that, we need to binary search for our room in a list of rooms
|
votrubac
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T16:20:00.207906+00:00
|
2021-05-01T21:41:19.018187+00:00
| 2,636 | false |
Our per-query time complexity should be better than O(n), so we will shoot for O(log n).\n\nTo do that, we need to binary search for our room in a list of rooms sorted by `id`. However, all rooms in that list should have an acceptable size. If we process our queries based on the room size, from largest to smallest, we can efficiently track the list of acceptable rooms.\n\nWe first sort our rooms and queries by the room size in the decreasing order. Then, for each query, we add acceptable rooms into a set (`ids`). We only process each room once, as our iterator (`it`) points to the largest room that is not yet in a set.\n\nFinally, we binary-search for the closest id.\n\n**C++**\n```cpp\nvector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& qs) {\n auto by_size_desc = [](const auto& a, const auto& b) { return a[1] > b[1]; };\n vector<int> res(qs.size());\n for (int i = 0; i < qs.size(); ++i)\n qs[i].push_back(i);\n sort(begin(rooms), end(rooms), by_size_desc); \n sort(begin(qs), end(qs), by_size_desc);\n set<int> ids;\n for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < qs.size(); ++i) {\n for (; j < rooms.size() && rooms[j][1] >= qs[i][1]; ++j)\n ids.insert(rooms[j][0]);\n auto it = ids.lower_bound(qs[i][0]);\n int id1 = it == begin(ids) ? -1 : *(prev(it));\n int id2 = it == end(ids) ? -1 : *it;\n res[qs[i][2]] = min(id1, id2) == -1 ? max(id1, id2) : abs(qs[i][0] - id1) <= abs(qs[i][0] - id2) ? id1 : id2;\n }\n return res;\n}\n```\n**Java**\n```java\npublic int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n int[] res = new int[queries.length];\n int[][] qs = new int[queries.length][];\n for (var i = 0; i < queries.length; ++i) \n qs[i] = new int[] { queries[i][0], queries[i][1], i};\n Arrays.sort(rooms, (a, b) -> b[1] - a[1]); \n Arrays.sort(qs, (a, b) -> b[1] - a[1]); \n int id = 0;\n var ids = new TreeSet<Integer>();\n for (var q : qs) {\n for(; id < rooms.length && rooms[id][1] >= q[1]; ++id)\n ids.add(rooms[id][0]);\n Integer ans1 = ids.floor(q[0]), ans2 = ids.ceiling(q[0]); \n if (ans1 != null && ans2 != null)\n res[q[2]] = q[0] - ans1 <= ans2 - q[0] ? ans1 : ans2;\n else\n res[q[2]] = ans1 == null && ans2 == null ? -1 : ans1 == null ? ans2 : ans1;\n }\n return res;\n}\n```
| 43 | 1 |
[]
| 4 |
closest-room
|
C++ - O(nlogn) - Breakdown of the solution
|
c-onlogn-breakdown-of-the-solution-by-kr-f7ce
|
\nIf a question has queries the number one thing that comes to mind is asking myself: Is this problem easier if I process the queries in a different order?\nFor
|
kretash
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T16:00:38.966944+00:00
|
2021-05-01T16:03:01.407892+00:00
| 1,791 | false |
\nIf a question has queries the number one thing that comes to mind is asking myself: Is this problem easier if I process the queries in a different order?\nFor this problem if we process the queries starting with the ones that ask for the biggest rooms first the problem becomes easier.\nWe start with the query that asks for the biggest room, in a sorted array we remove all the rooms that are bigger or equal to this query and add them to our set.\nMoving forward we know that those rooms will be options to all other queries too, because the queries will need smaller or equal rooms.\n\nSo as we process queries we add to a set, every ID on the set is valid for the current query. Now the problem is to find the closest ID in the set.\nWe can use binary search to find the closest one. `lower_bound` will return the leftmost element that is equal or bigger. We might want the right most \nelement that is smaller too, so we need to look at the previous element returned by `lower_bound` too.\n\n```\nvector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries)\n{\n const int q = int(queries.size());\n vector<int> res(q, -1);\n\n // This vector will contain indices\'s from bigger to smaller, this way we process the queries in a different order\n // but maintain the order of the queries in the result as we need to return them in the original order.\n vector<int> qid(q, 0);\n iota(qid.begin(), qid.end(), 0);\n sort(qid.begin(), qid.end(), [&](const int& l, const int& r) { return queries[l][1] > queries[r][1]; });\n\n // bigger rooms at the back of the vector.\n sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), [](const auto& l, const auto& r){ return l[1] < r[1]; });\n\n set<int> room_ids = {};\n\n for (const int& i : qid)\n {\n // We can pop back of a vector in O(1), erasing the front element is O(n). That why it\'s backwards.\n // Add rooms that are bigger than the current query, this room will be bigger than all following queries.\n while (!rooms.empty() && rooms.back()[1] >= queries[i][1])\n {\n room_ids.insert(rooms.back()[0]);\n rooms.pop_back();\n }\n\n if (room_ids.empty())\n continue;\n\n // binary search on the room ids, lower_bound will return the next biggest element if the one searched is not there\n // eg: 7 9 15 17 19, lower_bound( 10 ) == 15\n auto ite = room_ids.lower_bound(queries[i][0]);\n if (ite == room_ids.end()) // if we asked for an id too big just use the last one.\n ite = prev(room_ids.end());\n int dist = abs(*ite - queries[i][0]);\n int id = *ite;\n\n // now we try the smaller ID, if it\'s closer or equal in distance we take this one as the ID will be smaller. \n ite = prev(ite);\n if (ite != room_ids.end())\n {\n const int d = abs(*ite - queries[i][0]);\n if (d <= dist) dist = d, id = *ite;\n }\n res[i] = id;\n }\n return res;\n}\n```
| 23 | 4 |
[]
| 2 |
closest-room
|
Java TreeSet
|
java-treeset-by-mayank12559-gfma
|
\npublic int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n Arrays.sort(rooms, (a,b) -> b[1] - a[1]);\n int m = queries.length;\n int n
|
mayank12559
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T16:00:43.221222+00:00
|
2021-05-01T16:00:43.221255+00:00
| 733 | false |
```\npublic int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n Arrays.sort(rooms, (a,b) -> b[1] - a[1]);\n int m = queries.length;\n int n = rooms.length;\n int [][]query = new int[m][3];\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n query[i][0] = queries[i][0];\n query[i][1] = queries[i][1];\n query[i][2] = i;\n }\n int []ans = new int[m];\n Arrays.sort(query, (a,b) -> b[1] - a[1]);\n TreeSet<Integer> ts = new TreeSet();\n int j = 0;\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n while(j < n && rooms[j][1] >= query[i][1]){\n ts.add(rooms[j++][0]);\n }\n Integer floor = ts.floor(query[i][0]);\n Integer ceil = ts.ceiling(query[i][0]);\n if(floor == null && ceil == null){\n ans[query[i][2]] = -1;\n }else if(floor == null){\n ans[query[i][2]] = ceil;\n }else if(ceil == null){\n ans[query[i][2]] = floor;\n }else{\n ans[query[i][2]] = ((ceil - query[i][0]) < (query[i][0] - floor) ? ceil : floor);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n```
| 16 | 1 |
[]
| 2 |
closest-room
|
Python3. Stacks. Without inserting to sorted lists.
|
python3-stacks-without-inserting-to-sort-vj8k
|
\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n queries = [tuple(q) for q in queries]\n
|
yaroslav-repeta
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T17:25:53.348067+00:00
|
2021-05-01T20:00:42.281464+00:00
| 656 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n queries = [tuple(q) for q in queries]\n queries_copy = list(queries)\n rooms.sort()\n queries.sort()\n\t\t# stack of rooms with increasing id and decreasing size\n stack = []\n i = 0\n res_cache = {}\n \n def binary_search(min_size):\n low = 0\n high = len(stack) - 1\n while low <= high:\n mid = (low + high + 1) // 2\n if stack[mid][1] < min_size:\n high = mid - 1\n elif low == mid:\n return low\n else:\n low = mid\n return -1\n \n\t\t# search the best to the left from prefered position\n for q in queries:\n\t\t # add all rooms to the left from query prefered postion (q[0]) to the stack\n while i < len(rooms) and q[0] >= rooms[i][0]:\n\t\t\t # discard all rooms that are farther than `rooms[i]` and have smaller size\n while stack and rooms[i][1] >= stack[-1][1]:\n stack.pop()\n stack.append(rooms[i])\n i += 1\n \n\t\t\t# best room fit to the left from `rooms[i]`\n room_index = binary_search(q[1])\n res_cache[q] = stack[room_index][0] if room_index != -1 else -1\n \n i = 0\n stack = []\n rooms.reverse()\n queries.reverse()\n\t\t# search the best to the right from prefered position\n for q in queries:\n\t\t # add all rooms to the right from query prefered postion `q[0]` to the stack\n while i < len(rooms) and q[0] <= rooms[i][0]:\n\t\t\t # discard all rooms that are farther than `rooms[i]` and have smaller size\n while stack and rooms[i][1] >= stack[-1][1]:\n stack.pop()\n stack.append(rooms[i])\n i += 1\n\n\t\t\t# best room fit to the right from `rooms[i]`\n room_index = binary_search(q[1])\n if room_index != -1 and (res_cache[q] == -1 or q[0] - res_cache[q] > stack[room_index][0] - q[0]):\n res_cache[q] = stack[room_index][0]\n \n return [res_cache[q] for q in queries_copy]\n```
| 10 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
closest-room
|
Sorting + BinarySearch + Simple Code in JAVA
|
sorting-binarysearch-simple-code-in-java-wfps
|
steps to follow:\n1. Sort the rooms array on the basis of capacity . So that we can do binary search and got the first room index which have size greater than m
|
himanshuchhikara
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T17:02:00.518360+00:00
|
2021-05-01T17:02:00.518404+00:00
| 922 | false |
**steps to follow:**\n1. Sort the rooms array on the basis of capacity . So that we can do binary search and got the first room index which have size greater than minsize for particular query. \n2. If we have found the start index . we know that array is sorted so all size in right are going to be greater than size So iterate and find the roomId where Math.abs(room_id-prefrence) is minimum.\n3. Have this point in mind if two rooms have value for Math.abs(room_id-preference) we have to select room with smaller id.\n4. Go through code you will understand rest things.\n\n**CODE:**\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n Arrays.sort(rooms,new Pair());\n int[] ans=new int[queries.length];\n \n for(int i=0;i<ans.length;i++){\n int size=queries[i][1];\n int p=queries[i][0];\n \n int start=binarySearch(rooms,size);\n if(start==-1){\n ans[i]=-1;\n continue;\n }\n \n int index=find(rooms,start,p);\n ans[i]=rooms[index][0];\n }\n return ans;\n }\n \n private int find(int[][] rooms,int start,int p){\n int ans=start;\n int min=Math.abs(rooms[start][0]-p);\n for(int i=start+1;i<rooms.length;i++){\n int diff=Math.abs(rooms[i][0]-p);\n if(diff<min){\n min=diff;\n ans=i;\n }else if(diff==min){\n if(rooms[i][0]<rooms[ans][0]){\n ans=i;\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n \n private int binarySearch(int[][] rooms,int size){\n int lo=0 , hi=rooms.length-1;\n int ans=-1;\n while(lo<=hi){\n int mid=lo + (hi-lo)/2;\n \n if(rooms[mid][1]<size){\n lo=mid+1;\n }else{\n ans=mid;\n hi=mid-1;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n \n public class Pair implements Comparator<int[]>{\n public int compare(int[] one,int[] two){\n return one[1]-two[1];\n }\n }\n}\n```\n\n**Complexity:**\n`Time:O(nlogn + m* (logn + n) ) where n:rooms.length , m=queries.length`\n`Space:O(1) if not considered answer array which we have to return)`\n\nPlease **UPVOTE** if found it helpful and feel free to comment down or reach out to me if you have any doubt.
| 9 | 1 |
['Sorting', 'Binary Tree', 'Java']
| 1 |
closest-room
|
[c++] Fenwick tree - per query: O(log(roomSize) * log(roomsLength))
|
c-fenwick-tree-per-query-ologroomsize-lo-h0yf
|
Build a fenwick tree, the index of tree node represents it\'s min room size, and value is a set of possible room ids.\n\nSince the tree nodes are sparse, we ca
|
donaldong
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-02T00:09:11.160717+00:00
|
2021-05-02T23:33:22.826955+00:00
| 686 | false |
Build a [fenwick tree](https://cp-algorithms.com/data_structures/fenwick.html), the index of tree node represents it\'s min room size, and value is a set of possible room ids.\n\nSince the tree nodes are sparse, we can use a hash map instead of an array for better efficiency.\n\nWhen answering a query,\n- we go through all the parent tree nodes (segments including the rooms with at least minRoomSize)\n\t- Time: ` O(log(roomSize))`. roomSize <= 1e7\n- and find the minimal possible id difference in each set of ids (binary search).\n\t- Time: `O(log(rooms.length)`). rooms.length <= 1e5\n\nSpace: `O(rooms.length*log(rooms.length))`\n\nNote a fenwick tree node aggregates indices from `0 ... i`. So to use a tree node to represent the `minRoomSize `, we can flip the range\nfrom `roomSize ... MAX_ROOM_SIZE` to `0 ... (MAX_ROOM_SIZE - roomSize + 1)`\n\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\n int N;\n unordered_map<int, set<int>> tree;\npublic:\n void update(int n, int v) {\n n = N - n + 1;\n for (;n <= N; n += n & (-n)) tree[n].insert(v); \n }\n \n int query(int n, int v) {\n n = N - n + 1;\n int res = -1, min_diff = INT_MAX, diff;\n for (; n > 0; n -= n & (-n)) {\n if (tree[n].size() == 0) continue;\n auto itr = tree[n].lower_bound(v);\n if (itr != tree[n].end()) {\n diff = *itr - v;\n if (diff < min_diff) res = *itr, min_diff = diff;\n else if (diff == min_diff) res = min(res, *itr);\n }\n if (itr != tree[n].begin()) {\n --itr;\n diff = v - *itr;\n if (diff < min_diff) res = *itr, min_diff = diff;\n else if (diff == min_diff) res = min(res, *itr);\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n \n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n N = 1e7;\n for (auto &&r : rooms) update(r[1], r[0]);\n \n vector<int> res(queries.size());\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.size(); ++i) {\n res[i] = query(queries[i][1], queries[i][0]);\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 8 | 0 |
['Tree', 'C', 'Binary Tree']
| 3 |
closest-room
|
[C++] sort-based search
|
c-sort-based-search-by-codedayday-taxe
|
Approach 1: sort-based search [1]\nTime complexity: O(nlogn + mlogm); where n = |rooms|, m = |queries|\nSpace complexity: O(n + m)\n\nSort queries and rooms by
|
codedayday
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-23T01:30:18.310231+00:00
|
2021-05-23T01:30:58.213098+00:00
| 741 | false |
Approach 1: sort-based search [1]\nTime complexity: O(nlogn + mlogm); where n = |rooms|, m = |queries|\nSpace complexity: O(n + m)\n\nSort queries and rooms by size in descending order, only add valid rooms (size >= min_size) to the treeset for binary search.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n const int n = rooms.size(), m = queries.size();\n for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) queries[i].push_back(i);\n sort(begin(queries), end(queries), [](const auto& a, const auto& b){return a[1] > b[1];});\n sort(begin(rooms), end(rooms), [](const auto& a, const auto& b){return a[1] > b[1];});\n vector<int> ans(m, -1);\n set<int> ids;\n int j = 0; \n for(const auto& q: queries){\n while(j < n && rooms[j][1] >=q[1]) ids.insert(rooms[j++][0]);\n if(ids.empty()) continue;\n int id = q[0];\n auto it = ids.lower_bound(id);\n int id1 = (it != end(ids) )? *it : INT_MAX;\n int id2 = id1;\n if(it != begin(ids)) id2 = *prev(it);\n ans[q[2]] = abs(id1 - id) < abs(id2 - id) ? id1 : id2;\n }\n return ans; \n }\n};\n```\nReference:\n[1] https://zxi.mytechroad.com/blog/algorithms/binary-search/leetcode-1847-closest-room/
| 6 | 0 |
['C']
| 1 |
closest-room
|
C++ solution as per given hints
|
c-solution-as-per-given-hints-by-aparna_-f4f4
|
This solution is no longer accepted. \n\n/*\nsort the rooms according to increasing order of size \nFor each query, find the first room with size atleast query[
|
aparna_g
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-12T07:34:51.445235+00:00
|
2021-07-16T08:53:32.507441+00:00
| 367 | false |
**This solution is no longer accepted**. \n```\n/*\nsort the rooms according to increasing order of size \nFor each query, find the first room with size atleast query[1] --- index variable here\nNow for all the rooms from index till the end of rooms, take the room with minimum difference between query[0] and room_id.\n*/\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n static bool cmp(const vector<int>&a , const vector<int>&b) {\n return a[1]<b[1];\n }\n \n int search(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, int min_size) {\n int low = 0;\n int high = rooms.size()-1;\n int ans=-1;\n while(low<=high) {\n int mid = low+(high-low)/2; \n if(rooms[mid][1]<min_size) {\n low = mid+1;\n }\n else {\n ans = mid; //finds the first index with size atleast min_size\n high = mid-1;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n \n int find(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, int index , int pref_id) {\n int ans = index; \n int min_diff = abs(rooms[index][0]-pref_id);\n for(int i=index+1;i<rooms.size();i++) {\n int diff = abs(rooms[i][0]-pref_id);\n if(diff<min_diff) {\n min_diff = diff;\n ans = i;\n }\n else if(diff == min_diff) {\n if(rooms[i][0] < rooms[ans][0]) \n ans = i;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n \n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n sort(rooms.begin(),rooms.end(),cmp);\n vector<int> result(queries.size(),-1);\n \n for(int i=0;i<queries.size();i++) {\n int min_size = queries[i][1];\n int id_pref = queries[i][0];\n \n int index = search(rooms,min_size);\n if(index == -1)\n {\n result[i] = -1;\n continue;\n }\n \n int room_no_index = find(rooms,index,id_pref);\n result[i] = rooms[room_no_index][0];\n }\n return result;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 2 |
['C', 'Sorting', 'C++']
| 1 |
closest-room
|
sorting in C++ Vs sorting in JAVA || Speed Analysis
|
sorting-in-c-vs-sorting-in-java-speed-an-ray5
|
Can anyone please explain the time difference in Sort function in C++ and Java in this problem?\n\nI have implemented the same concept in Java and C++.\nIn Java
|
nithish_2001_
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-03T08:49:24.915627+00:00
|
2021-05-03T16:50:26.496415+00:00
| 386 | false |
Can anyone please explain the time difference in Sort function in C++ and Java in this problem?\n\nI have implemented the same concept in Java and C++.\nIn Java, the soln is Accepted.\nBut in C++, it is showing TLE.\n\n\n**JAVA: Accepted**\n```\n\nclass Solution {\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n int diff = 0, min = Integer.MAX_VALUE, min_id = 0;\n Arrays.sort(rooms, (a,b) -> Integer.compare(a[1],b[1]));\n int[] res = new int[queries.length];\n for(int i=0;i<queries.length;i++){\n for(int j=rooms.length-1;j>=0;j--){\n if(rooms[j][1]>=queries[i][1]){\n diff = Math.abs(rooms[j][0]-queries[i][0]);\n if(diff<min){\n min = diff;\n min_id = rooms[j][0];\n }\n else if(diff==min){\n min_id = (min_id < rooms[j][0]) ? min_id : rooms[j][0];\n }\n }\n else break;\n }\n if(min == Integer.MAX_VALUE) min_id = -1;\n res[i] = min_id;\n min_id = 0;\n min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```\n**C++: Time Limit Exceeded**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n static bool cmp(const vector<int>&a,const vector<int>&b){\n return a[1]>b[1]; \n }\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& arr, vector<vector<int>>& q) {\n int diff = 0, min = INT_MAX, min_id = 0;\n sort(arr.begin(),arr.end(),cmp);\n int n=arr.size(),m=q.size();\n \n vector<int>ans(m);\n \n for(int j=0;j<m;j++){\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n if(q[j][1]<=arr[i][1]){\n diff = abs(arr[i][0]-q[j][0]);\n if(diff<min){\n min = diff;\n min_id = arr[i][0];\n }\n else if(diff==min){\n min_id = (min_id < arr[i][0]) ? min_id : arr[i][0];\n }\n }\n else\n break;\n \n }\n if(min == INT_MAX) min_id = -1;\n ans[j] = min_id;\n min_id = 0;\n min =INT_MAX;\n }\n return ans;\n \n }\n\n \n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Sorting', 'C++']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
C++ | Sorting + Binary Search
|
c-sorting-binary-search-by-kena7-l20s
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool static cmp(vector<int>&a,vector<int>&b)\n {\n return a[1]>b[1];\n }\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vecto
|
kenA7
|
NORMAL
|
2021-06-07T09:57:36.515858+00:00
|
2021-06-07T09:57:36.515892+00:00
| 512 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool static cmp(vector<int>&a,vector<int>&b)\n {\n return a[1]>b[1];\n }\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms,vector<vector<int>>& queries)\n {\n int i=0;\n for(auto &q:queries)\n q.push_back(i++);\n vector<int>res(i,-1);\n sort(rooms.begin(),rooms.end(),cmp);\n sort(queries.begin(),queries.end(),cmp);\n i=0;\n set<int>s;\n for(auto &q:queries)\n {\n while(i<rooms.size() && q[1]<=rooms[i][1])\n {\n s.insert(rooms[i][0]);\n i++;\n }\n if(!s.empty())\n {\n auto it=s.lower_bound(q[0]);\n int p1=INT_MAX,p2=INT_MAX;\n if(it!=s.begin())\n p1=*prev(it);\n if(it!=s.end())\n p2=*it;\n res[q[2]]=abs(q[0]-p1)<=abs(q[0]-p2)?p1:p2;\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
closest-room
|
[Python] Sort the queries and the rooms by size in decreasing order. 2000ms
|
python-sort-the-queries-and-the-rooms-by-r5rb
|
Sort the queries and the rooms by size from the largest to the smallest size, then initialize an empty array that will keep the rooms big enough for the current
|
valerioio
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T20:27:47.013963+00:00
|
2021-05-01T20:30:34.479699+00:00
| 423 | false |
Sort the queries and the rooms by size from the largest to the smallest size, then initialize an empty array that will keep the rooms big enough for the current querie, and is sorted by index ("rms" in my code).\nTo answer to the i-th querie update the array "rms" keeping it in order, then binary search for the preferred room and choose between the room found by the binary search and the one before.\n```\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n ans = [None] * len(queries)\n queries = sorted([(s, p, i) for i, (p, s) in enumerate(queries)], reverse = True)\n rooms.sort(reverse = True, key = itemgetter(1, 0))\n rms = [-1] #the -1 helps handle the case when there are no rooms with the right size\n j = 0\n for s, p, i in queries:\n while j < len(rooms) and rooms[j][1] >= s:\n insort(rms, rooms[j][0])\n j += 1\n x = bisect_left(rms,p)\n ans[i] = rms[x - 1] if (x == len(rms) or x != 1 and abs( rms[x - 1] - p) <= abs(rms[x] - p)) else rms[x]\n return ans\n```\nRuntime: 2000 ms\nMemory Usage: 49.3 MB\nThis solution is based on the one by DBabichev. Check out his post too for further explaination.
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Sorting', 'Binary Tree', 'Python']
| 1 |
closest-room
|
[Python 3] Aggregate sorted list, detailed explanation (2080 ms)
|
python-3-aggregate-sorted-list-detailed-bnudi
|
```\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n ans = [0] * len(queries)\n \n
|
chestnut890123
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T17:29:19.641926+00:00
|
2021-05-02T21:58:28.996369+00:00
| 274 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n ans = [0] * len(queries)\n \n # sort queries to handle largest size queries first\n q = deque(sorted([(size, room, i) for i, (room, size) in enumerate(queries)], key=lambda a: (-a[0], a[1], a[2])))\n\n # sort rooms by descending size\n rooms = deque(sorted(rooms, key=lambda x: -x[1]))\n\n # current available room ids\n cands = []\n \n \n while q:\n size, room, i = q.popleft()\n # add room ids to candidates as long as top of room size meet the requirements\n while rooms and rooms[0][1] >= size:\n bisect.insort(cands, rooms.popleft()[0])\n \n # if no room size available, return -1\n if not cands: ans[i] = -1\n \n # else use bisect to find optimal room ids\n else:\n loc = bisect.bisect_left(cands, room)\n if loc == 0: ans[i] = cands[loc]\n elif loc == len(cands): ans[i] = cands[-1]\n else: ans[i] = cands[loc - 1] if room - cands[loc - 1] <= cands[loc] - room else cands[loc]\n \n return ans
| 3 | 0 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
C++ sorting and easy solutions
|
c-sorting-and-easy-solutions-by-keepmoti-b22l
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n static bool cmp(vector<int>&a , vector<int>&b)\n {\n return a[1] > b[1];\n }\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<v
|
KeepMotivated
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T16:08:15.904191+00:00
|
2021-05-01T16:09:32.007564+00:00
| 347 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n static bool cmp(vector<int>&a , vector<int>&b)\n {\n return a[1] > b[1];\n }\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n sort(rooms.begin(),rooms.end(),cmp);\n for(int i = 0;i<queries.size();i++)\n {\n queries[i].push_back(i);\n }\n sort(queries.begin(),queries.end(),cmp);\n int j = 0;\n set<int>s;\n int n = queries.size();\n vector<int>ans(n);\n for(int i = 0;i<queries.size();i++)\n {\n while(j<rooms.size() && queries[i][1] <= rooms[j][1])\n {\n s.insert(rooms[j][0]);\n j++;\n }\n if(s.size()==0)\n {\n ans[queries[i][2]] = -1;\n continue;\n }\n //cout<<j<<"\\n";\n auto it = s.upper_bound(queries[i][0]);\n // cout<<queries[i][0]<<"\\n";\n int val1 = INT_MAX;\n if(it != s.end())\n {\n val1 = *it;\n }\n \n int val2 = INT_MAX;\n if(it != s.begin())\n {\n it--;\n val2 = *it;\n }\n int diff = abs(queries[i][0]-val1);\n int id = val1;\n // cout<<val1<<" "<<val2<<" "<<id<<"\\n";\n if( (diff == abs(queries[i][0]-val2) && val2 < val1 ) || ( diff > abs(queries[i][0]-val2)) )\n {\n id = val2;\n }\n ans[queries[i][2]] = id;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n\n\n**explaination:**\n**Please try to think after this main logic \n\nMain logic**\n\n1 see if we are finding answer of query with minSize lets say x and after that we are finding query with minsize y\nif lets say x > y so the number of rooms that we can include is more in y \ni mean we only have to include just more rooms + rooms that we will look for y.\nso we can sort the queries in decresing order and at each time we will include all the rooms whose size is greater than or equal to queries \nwe just have to include just extra rooms and we will store ids in a set\nthe to find answer we will just find the closest one using set.\n\n**steps**\n1. sort the queries and rooms in decreasing order \n2. we will keep on adding rooms id in set till size is greater than for particular queries.\n3 the just we have to use upper_bound for solving the problem\n**Do Ask your doubts**\n
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
closest-room
|
JAVA | Sort + Greedy
|
java-sort-greedy-by-abideenzainuel-tr76
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n\n Arrays.sort(rooms, (room1, room2) -> room1[1] == room2[1] ? room1[0
|
abideenzainuel
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T16:03:29.544501+00:00
|
2021-05-01T16:07:26.194888+00:00
| 342 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n\n Arrays.sort(rooms, (room1, room2) -> room1[1] == room2[1] ? room1[0]-room2[0] : room2[1]-room1[1]);\n int res[] = new int[queries.length];\n \n for(int i=0; i<queries.length; i++){\n int tempRes = -1;\n for(int j=0; j<rooms.length; j++){\n\t\t\t\n if(rooms[j][1] >= queries[i][1]){\n if(tempRes == -1){\n tempRes = j;\n }else{\n\t\t\t\t\t\n if( Math.abs(rooms[tempRes][0] - queries[i][0]) > Math.abs(rooms[j][0] - queries[i][0]) ){\n tempRes = j;\n }else if (Math.abs(rooms[tempRes][0] - queries[i][0]) == Math.abs(rooms[j][0] - queries[i][0]) && \n rooms[tempRes][0] > rooms[j][0]){\n temp = j;\n }\n }\n }else{\n break;\n }\n }\n res[i] = tempRes == -1 ? -1 : rooms[tempRes][0];\n\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 1 |
[]
| 3 |
closest-room
|
[Python] O(n log n): Sort the rooms and queries first, commented
|
python-on-log-n-sort-the-rooms-and-queri-0x3x
|
Explanation:\nThe question requires making two crucial observations. A naive approach would sort the rooms by id first, and binary search each query\'s preferre
|
kcsquared
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T16:00:40.111702+00:00
|
2021-05-01T16:11:05.845327+00:00
| 359 | false |
**Explanation:**\nThe question requires making two crucial observations. A naive approach would sort the rooms by id first, and binary search each query\'s preferred id in the rooms, then iterate over rooms until we found one of the right size. \n\nUnfortunately, this leads to an O(n^2) algorithm if we have to walk the entire list. Let\'s make some observations and do better. Here are the most important steps.\n\n1. (**CRUCIAL**) If we sort both the rooms and queries by their size, we can **limit our query searches to only rooms of the right size**. If the filtered rooms are maintained in sorted order of ID, we can use an O(log n) binary search to find the closest or 2 closest rooms to our preferred ID.\n\n2. We need to add rooms of varying ID\'s to our list dynamically, maintaining sorted order. Using bisect.insort can cause up to O(n) insert time to the middle of our list. We need a data structure like a **balanced BST** or order statistic tree. While Python doesn\'t have this built-in, I\'m using the leetcode approved sortedcontainers library for an order statistic tree with O(log n) lookups and inserts. \n\n\nThat was the hard part. Now, we just need to track the original query ID\'s for our answers, as well as deal with the edge cases of whether to use the lower or higher ID, closest to the preferred value.\n\n\n**Python Code:**\n```python\nimport sortedcontainers\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n\n # Sort rooms and queries in decreasing order of size\n rooms.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)\n sorted_queries = sorted(((i, pref, min_size) for i, (pref, min_size) in enumerate(queries)),\n key=lambda x: x[2], reverse=True)\n\n ans = [-1] * len(queries)\n id_list = sortedcontainers.SortedList()\n room_index = 0\n\n # Iterate over queries in decreasing order of size\n for orig_query_ind, preferred, min_size in sorted_queries:\n\n # Update our room id list, adding all rooms with size >= min_size\n while room_index < len(rooms) and rooms[room_index][1] >= min_size:\n my_id = rooms[room_index][0]\n room_index += 1\n id_list.add(my_id)\n\n # Keep -1 as answer if (min_size is above all actual room sizes) i.e. id_list is empty\n if not id_list:\n continue\n\n # Find index of the largest id <= preferred\n rightmost_ind_less_or_equal = id_list.bisect_right(preferred) - 1\n\n # If preferred id is smaller than the smallest existing id\n if rightmost_ind_less_or_equal < 0:\n ans[orig_query_ind] = id_list[0]\n continue\n\n # If preferred id is >= largest existing id\n if rightmost_ind_less_or_equal == len(id_list) - 1:\n ans[orig_query_ind] = id_list[rightmost_ind_less_or_equal]\n continue\n\n # Get value of left and right candidate ids\n smaller_id_choice, larger_id_choice = id_list[rightmost_ind_less_or_equal:rightmost_ind_less_or_equal+2]\n\n # Take larger id only if closer to preferred id\n if abs(larger_id_choice - preferred) < abs(smaller_id_choice - preferred):\n ans[orig_query_ind] = larger_id_choice\n else:\n ans[orig_query_ind] = smaller_id_choice\n\n return ans\n```\n\n**Complexity Analysis:**\nTime complexity: **O(n log n)** for sorting, and the n inserts and lookups in our BST each cost log n.\nSpace complexity: O(n)\n\nFeel free to ask any questions. If you found this explanation helpful, upvotes are always appreciated :)
| 3 | 1 |
[]
| 2 |
closest-room
|
C++ Sort Set Solution O(NLogN) + O(KLogN)
|
c-sort-set-solution-onlogn-oklogn-by-ahs-vc9e
|
Runtime: 644 ms, faster than 81.25% of C++ online submissions for Closest Room.\nMemory Usage: 149.3 MB, less than 53.75% of C++ online submissions for Closest
|
ahsan83
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-08T16:25:02.161544+00:00
|
2022-04-08T16:25:02.161581+00:00
| 440 | false |
Runtime: 644 ms, faster than 81.25% of C++ online submissions for Closest Room.\nMemory Usage: 149.3 MB, less than 53.75% of C++ online submissions for Closest Room.\n\n\n**Solution taken from votrubac.**\n\n```\nWe have to find the room id which is in the minimum distance with the query id and\nroom size is greater or equal the query size. So we can sort the rooms and queries based\non the size in descending order and then search the queries. From larger to smaller\nroom size we can insert ids in the Set and then use binary search to find the min distance\nid for query id. As we will add ids to Set N time, so complexity NLogN and also for K\nqueries we do binary search K times with complexity KLogN.\n\nTotal Complexity : O(NLogN) + O(KLogN)\n```\n\n```\nbool comparator(const vector<int>&a,const vector<int>&b)\n{\n return a[1] > b[1];\n}\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n \n int qsize = queries.size();\n vector<int>res(qsize);\n \n // add indexes of the queries as extra value\n for(int i=0;i<qsize;i++)\n queries[i].push_back(i);\n \n // sort rooms and queries in descending order of room size\n sort(begin(rooms),end(rooms),comparator);\n sort(begin(queries),end(queries),comparator);\n \n // ascending order of room ids\n set<int>ids;\n \n for(int i=0,j=0;i<qsize;i++)\n {\n // insert all romm ids for rooms with size >= query size\n for(;j<rooms.size() && rooms[j][1]>=queries[i][1];j++)\n ids.insert(rooms[j][0]);\n \n // if ids empty then room size does not exist and so set -1\n if(ids.empty())\n {\n res[queries[i][2]] = -1;\n continue;\n }\n \n int id,find,prevVal,nextVal;\n \n // find the upper bound of the query room id\n find = queries[i][0];\n auto iter = ids.upper_bound(find);\n \n // if iter is in the begin then no previous possible and begin value is the closest\n if(iter==ids.begin()) id = *ids.begin();\n else\n {\n // min distance id will be either in upper bound iter or its previous iter\n \n nextVal = iter==ids.end() ? INT_MAX : *iter;\n prevVal = *prev(iter);\n \n id = abs(prevVal-find)<=abs(nextVal-find) ? prevVal : nextVal;\n }\n \n res[queries[i][2]] = id;\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n};\n```\n\n\n
| 2 | 0 |
['C', 'Sorting', 'Binary Tree', 'Ordered Set']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Java Simple and easy T O(n log n), S O(n) solution, clean code with comments
|
java-simple-and-easy-t-on-log-n-s-on-sol-kvt8
|
PLEASE UPVOTE IF YOU LIKE THIS SOLUTION\n\n\n\n\n\nclass Solution {\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n \n int numRo
|
satyaDcoder
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-12T15:39:55.879442+00:00
|
2021-05-15T16:50:46.386384+00:00
| 480 | false |
**PLEASE UPVOTE IF YOU LIKE THIS SOLUTION**\n\n\n\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n \n int numRoom = rooms.length;\n int numQuery = queries.length;\n \n \n for(int i = 0; i < numQuery; i++){\n\t\t\t//append index\n queries[i] = new int[]{queries[i][0], queries[i][1], i};\n }\n \n //sort the roos and queries in increasing order of room size\n Arrays.sort(rooms, (a, b) -> (a[1] != b[1] ? (a[1] - b[1]) : (a[0] - b[0])));\n Arrays.sort(queries, (a, b) -> (a[1] != b[1] ? (a[1] - b[1]) : (a[0] - b[0])));\n \n TreeSet<Integer> roomIds = new TreeSet();\n int[] result = new int[numQuery];\n \n int j = numRoom - 1;\n for(int i = numQuery - 1; i >= 0; i--){\n \n int currRoomId = queries[i][0];\n int currRoomSize = queries[i][1];\n int currQueryIndex = queries[i][2];\n \n //add all the which size is greater or equal than query room size\n while(j >= 0 && rooms[j][1] >= currRoomSize){\n roomIds.add(rooms[j--][0]);\n }\n \n //found room with sufficient size,\n if(roomIds.contains(currRoomId)){\n //directly add this room\n result[currQueryIndex] = currRoomId;\n continue;\n }\n \n //next room which is just greater that current roomId\n Integer nextRoomId = roomIds.higher(currRoomId);\n \n //previous roomId which is just smaller than current roomId\n Integer prevRoomId = roomIds.lower(currRoomId);\n \n if(nextRoomId == null && prevRoomId == null){\n //no nearest roomId \n result[currQueryIndex] = -1;\n \n }else if(nextRoomId == null){\n \n result[currQueryIndex] = prevRoomId;\n \n }else if(prevRoomId == null){\n \n result[currQueryIndex] = nextRoomId;\n \n }else if(nextRoomId != null && prevRoomId != null){\n //get the nearest roomId\n if((currRoomId - prevRoomId) <= (nextRoomId - currRoomId)){\n result[currQueryIndex] = prevRoomId;\n }else{\n result[currQueryIndex] = nextRoomId;\n }\n }\n \n }\n \n return result;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 1 |
['Java']
| 2 |
closest-room
|
C# | List | BinarySearch api | O(n log n ) solution
|
c-list-binarysearch-api-on-log-n-solutio-txwx
|
I could not crack this solution during contest, I did not think about sorting query set would solve this problem in log (n) search, though it\'s not a suitable
|
crackthebig
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-06T14:52:29.839804+00:00
|
2021-05-06T14:52:29.839838+00:00
| 255 | false |
I could not crack this solution during contest, I did not think about sorting query set would solve this problem in log (n) search, though it\'s not a suitable solution during the realtime practical problems as we will not have queries in-hand upfront. \n\nI feel implementation of this solution in C# is a worth giving time, took the idea from @votrubac [here](https://leetcode.com/problems/closest-room/discuss/1186023/C%2B%2BJava-Sort-Queries)\n\nidea summary:\n - Sort rooms and queries by size decending order - O(n logn + qlogq)\n - For each query maintain rooms qualified sofar into sorted list - (q times)\n - Binary search on the rooms sofar to find the minimum perferred room for that query. - (log r)\n \n time: `O(r log r + qlog q + q log r)`\n space: `O(r)`\n \n **Note: I maintained list in sorted order using BinerySearch api and then did a binary search to find out the minimized preferred room.**\n\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public int[] ClosestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n Array.Sort(rooms, (a, b) => b[1] - a[1]);\n var sortedQueries = queries\n .Select((x, indx) => new []{x[0] , x[1], indx})\n .OrderByDescending(x=> x[1])\n .ToArray();\n \n int i=0, n = rooms.Length, q = queries.Length;\n List<int> roomsSoFar = new List<int>();\n int[] result = new int[q];\n \n foreach(var query in sortedQueries){\n int perferredId = query[0], minSize = query[1], queryIndx = query[2];\n \n while(i < n && rooms[i][1] >= minSize){\n int index = roomsSoFar.BinarySearch(rooms[i][0]);\n\n if(index < 0)\n index = ~index;\n roomsSoFar.Insert(index, rooms[i][0]);\n i++;\n }\n \n int ans = GetPreferedRoom(roomsSoFar, perferredId);\n result[queryIndx] = ans;\n }\n return result;\n }\n \n private int GetPreferedRoom(List<int> rooms, int id)\n {\n if(rooms.Count == 0)\n return -1;\n \n int lowerbound = rooms.LowerBound(id);\n int upperbound = rooms.UpperBound(id);\n \n if(lowerbound >= 0 && upperbound >= 0)\n return id - rooms[lowerbound] <= rooms[upperbound] - id ? rooms[lowerbound] : rooms[upperbound];\n else if(lowerbound >= 0)\n return rooms[lowerbound];\n else \n return rooms[upperbound];\n }\n}\npublic static class ListExtentions\n{\n public static int LowerBound(this List<int> list, int id){\n int left = 0, right = list.Count - 1;\n int lowerbound = -1;\n\n while(left <= right){\n int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;\n if(list[mid] <= id){\n lowerbound = mid;\n left = mid + 1;\n }\n else\n right = mid - 1;\n }\n return lowerbound;\n }\n\n public static int UpperBound(this List<int> list, int id){\n int left = 0, right = list.Count - 1;\n int upperbound = -1;\n\n left = 0; right = list.Count -1;\n while(left <= right){\n int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;\n if(list[mid] >= id){\n upperbound = mid;\n right = mid - 1;\n }\n else\n left = mid + 1;\n }\n return upperbound;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
closest-room
|
Python, bisect
|
python-bisect-by-coracodil-yko2
|
\nimport bisect\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms, queries):\n rooms = sorted([(j,i) for i ,j in rooms])[::-1]\n queries = sorted(
|
CoraCodil
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-05T18:07:45.928640+00:00
|
2021-05-05T22:38:51.634675+00:00
| 315 | false |
```\nimport bisect\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms, queries):\n rooms = sorted([(j,i) for i ,j in rooms])[::-1]\n queries = sorted((k,j,i) for i,(j,k) in enumerate(queries))[::-1]\n\n R= 0\n Q = 0\n aval = []\n res = [-1] * len(queries)\n while R <= len(rooms) and Q < len(queries):\n \n if R< len(rooms) and rooms[R][0] >= queries[Q][0]:\n aval.append(rooms[R][1])\n R+=1\n \n else:\n if len(aval)!=0:\n aval.sort()\n f,s=float(\'inf\'),float(\'inf\')\n pref, qid = queries[Q][1] , queries[Q][2]\n i = bisect_left(aval,pref)\n if i>0:\n f=abs(pref-aval[i-1])\n if i < len(aval):\n s = abs(pref-aval[i])\n if f<=s:\n res[qid]=aval[i-1]\n else: \n res[qid]=aval[i]\n Q+=1\n return res\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
javascript treeset 444ms 100%
|
javascript-treeset-444ms-100-by-henryche-f79e
|
reference:\nhttps://github.com/python/cpython/blob/3.9/Lib/bisect.py\nhttps://github.com/fukatani/TreeSet/blob/master/treeset.py\n\nJava Version:\nhttps://leetc
|
henrychen222
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-04T02:20:17.641567+00:00
|
2021-05-04T02:27:22.578975+00:00
| 239 | false |
reference:\nhttps://github.com/python/cpython/blob/3.9/Lib/bisect.py\nhttps://github.com/fukatani/TreeSet/blob/master/treeset.py\n\nJava Version:\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/closest-room/discuss/1186546/java-TreeSet-81ms\n```\nfunction Bisect() {\n return { insort_right, insort_left, bisect_left, bisect_right }\n function insort_right(a, x, lo = 0, hi = null) {\n lo = bisect_right(a, x, lo, hi);\n a.splice(lo, 0, x);\n }\n function bisect_right(a, x, lo = 0, hi = null) {\n if (lo < 0) throw new Error(\'lo must be non-negative\');\n if (hi == null) hi = a.length;\n while (lo < hi) {\n let mid = lo + hi >> 1;\n x < a[mid] ? hi = mid : lo = mid + 1;\n }\n return lo;\n }\n function insort_left(a, x, lo = 0, hi = null) {\n lo = bisect_left(a, x, lo, hi);\n a.splice(lo, 0, x);\n }\n function bisect_left(a, x, lo = 0, hi = null) {\n if (lo < 0) throw new Error(\'lo must be non-negative\');\n if (hi == null) hi = a.length;\n while (lo < hi) {\n let mid = lo + hi >> 1;\n a[mid] < x ? lo = mid + 1 : hi = mid;\n }\n return lo;\n }\n}\n\nfunction TreeSet(elements) {\n let ts = [];\n let se = new Set();\n let bisect = new Bisect();\n if (elements) addAll(elements);\n return { add, floor, ceiling, remove, contains, size, clear, toArray };\n function addAll(elements) {\n for (const e of elements) {\n if (se.has(e)) continue;\n add(e);\n se.add(e);\n }\n }\n function add(e) {\n if (!se.has(e)) {\n bisect.insort_right(ts, e);\n se.add(e);\n }\n }\n function ceiling(e) {\n let idx = bisect.bisect_right(ts, e);\n if (ts[idx - 1] == e) return e;\n return ts[bisect.bisect_right(ts, e)];\n }\n function floor(e) {\n let idx = bisect.bisect_left(ts, e);\n if (ts[idx] == e) {\n return e;\n } else {\n return ts[bisect.bisect_left(ts, e) - 1];\n }\n }\n function remove(e) {\n ts = ts.filter(x => x != e);\n se.delete(e);\n }\n function contains(e) {\n return se.has(e);\n }\n function size() {\n return ts.length;\n }\n function clear() {\n ts = [];\n }\n function toArray() {\n return ts;\n }\n}\n\nconst closestRoom = (rooms, queries) => {\n rooms.sort((x, y) => y[1] - x[1]);\n let qn = queries.length;\n queries = queries.map((t, i) => [i, ...t]);\n queries.sort((x, y) => y[2] - x[2]);\n let res = Array(qn).fill(0);\n let ri = 0;\n let ts = new TreeSet();\n for (const e of queries) {\n let qi = e[0];\n let qid = e[1];\n let qmize = e[2];\n while (ri < rooms.length && rooms[ri][1] >= qmize) {\n ts.add(rooms[ri][0]);\n ri++;\n }\n if (ts.size() == 0) {\n res[qi] = -1;\n } else {\n let lower = ts.floor(qid) || -1000000000;\n let higher = ts.ceiling(qid) || 1000000000;\n if (qid - lower <= higher - qid) {\n res[qi] = lower;\n } else {\n res[qi] = higher;\n }\n }\n }\n return res;\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Tree', 'Binary Tree', 'Ordered Set', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
C++ Solution | Offline query solving | Set
|
c-solution-offline-query-solving-set-by-4qcys
|
\nclass cmp{\npublic:\n bool operator()(vector<int>& a,vector<int>& b){\n if(a[1]==b[1]) return a[0]<b[0];\n return a[1]<b[1];\n }\n};\nclas
|
nayakashutosh9
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-02T06:19:36.093112+00:00
|
2021-05-02T06:19:36.093141+00:00
| 146 | false |
```\nclass cmp{\npublic:\n bool operator()(vector<int>& a,vector<int>& b){\n if(a[1]==b[1]) return a[0]<b[0];\n return a[1]<b[1];\n }\n};\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& a, vector<vector<int>>& q) {\n int n=a.size(),m=q.size();\n vector<vector<int>> b(m);\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n b[i]={q[i][1],q[i][0],i};\n }\n vector<int> ans(m,-1);\n sort(b.begin(),b.end());\n sort(a.begin(),a.end(),cmp());\n int i=n-1;\n set<int> id;\n for(int j=m-1;j>=0;j--){\n while(i>=0 && b[j][0]<=a[i][1]){\n id.insert(a[i][0]);\n i--;\n }\n auto l=id.upper_bound(b[j][1]);\n auto r=id.upper_bound(b[j][1]);\n int lv=-1,rv=-1;\n if(l!=id.begin()){\n l=prev(l);\n lv=*l;\n }\n if(r!=id.end()){\n rv=*r;\n }\n if(lv!=-1 && rv!=-1){\n if(abs(b[j][1]-lv)==abs(b[j][1]-rv)) ans[b[j][2]]=lv;\n else if(abs(b[j][1]-lv)<abs(b[j][1]-rv)) ans[b[j][2]]=lv;\n else ans[b[j][2]]=rv;\n }\n else if(lv!=-1) ans[b[j][2]]=lv;\n else if(rv!=-1) ans[b[j][2]]=rv;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
closest-room
|
Java - O(n*k) - Sort by Room size
|
java-onk-sort-by-room-size-by-ryanrehman-swno
|
\nclass Solution {\n class NewRoom {\n int index, id, size;\n NewRoom(int id, int size) {\n this.id = id;\n this.size = s
|
ryanrehman99
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T16:03:28.021116+00:00
|
2021-05-01T16:07:48.599522+00:00
| 140 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n class NewRoom {\n int index, id, size;\n NewRoom(int id, int size) {\n this.id = id;\n this.size = size;\n }\n }\n \n public int binSearch(NewRoom[] newRooms, int[] query) {\n int preferred = query[0], minSize = query[1];\n int left = 0, right = newRooms.length;\n \n while (left < right) {\n int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;\n \n if (newRooms[mid].size >= minSize) {\n if (mid-1 >= 0 && newRooms[mid-1].size >= minSize) right = mid;\n else return mid;\n } else {\n left = mid + 1;\n }\n }\n return left;\n }\n\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n int n = rooms.length, k = queries.length;\n int[] soln = new int[k];\n \n NewRoom[] newRooms = new NewRoom[n];\n for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {\n newRooms[i] = new NewRoom(rooms[i][0], rooms[i][1]);\n }\n Arrays.sort(newRooms, (a, b) -> {\n if (a.size < b.size) return -1;\n else if (a.size == b.size) {\n if (a.id <= b.id) return -1;\n else return 1;\n }\n else return 1;\n });\n \n int ct = 0;\n for (int[] query : queries) {\n int startIndex = binSearch(newRooms, query);\n int minDiff = Integer.MAX_VALUE, minIndex = -1;\n \n for (int i=startIndex; i<n; i++) {\n int newDiff = Math.abs(newRooms[i].id - query[0]);\n if (newDiff < minDiff || (newDiff == minDiff && newRooms[i].id < newRooms[minIndex].id)) {\n minDiff = newDiff;\n minIndex = i;\n }\n }\n \n if (minIndex == -1) soln[ct++] = -1;\n else soln[ct++] = newRooms[minIndex].id;\n }\n \n \n return soln;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Segment Tree + Binary search || Simple & Easy C++
|
segment-tree-binary-search-simple-easy-c-hwz6
|
Intuition\nIt\'s simple binary search multiple times along with the use of segment tree to find maximum in ranges efficiently. \n\n# Approach\nSorted arrays acc
|
vaibhav2740
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-12T13:17:19.730960+00:00
|
2024-11-12T13:17:19.730985+00:00
| 27 | false |
# Intuition\nIt\'s simple binary search multiple times along with the use of segment tree to find maximum in ranges efficiently. \n\n# Approach\nSorted arrays according to the indices of rooms.\nI binary searched for each distance d from 0 to 1e8, and then i checked if\nthe maximum in range from i1 to i2 is >= desired size or not. I also calculated i1 and i2 using binary search. \nHere i1 = first index where **id >= desired id - d** and i2 = last index where **id <= desired id + d.** hence we get the range [i1,i2].\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nq.log(1e8).log(n).log(n) ~ O(Q*(logn)^3)\n\n- Space complexity:\n)(4*n + n + n) ~ O(n)\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int>sgt;\n void build(int l, int r, vector<vector<int>>& v,int node){\n if(l==r){\n sgt[node] = v[l][1]; return;\n }\n int m = l + (r-l)/2;\n build(l,m,v,2*node); build(m+1,r,v,2*node+1);\n sgt[node] = max(sgt[2*node],sgt[2*node+1]);\n }\n int find(int l, int r, int i, int j, int node){\n if(l>=i&&r<=j) return sgt[node];\n if(l>j||r<i) return -1;\n int m = l + (r-l)/2;\n return max(find(l,m,i,j,2*node),find(m+1,r,i,j,2*node+1));\n }\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& v, vector<vector<int>>& q) {\n ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);\n int n = v.size();\n sort(v.begin(),v.end());\n map<int,int>mp; // map just to format the output int the end\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++) mp[v[i][0]] = v[i][1];\n sgt.resize(4*n);\n build(0,n-1,v,1); // classic max segment tree\n vector<int>tmp(n); // extra temp array just to use inbuilt lb/ub\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++) tmp[i] = v[i][0]; \n vector<int>res(q.size(),-1); // result\n for(int i=0;i<q.size();i++){\n int j = q[i][0], sz = q[i][1]; int val = -1;\n int l = 0, r = 1e8;\n while(l<=r){\n int m = l + (r-l)/2;\n int i1 = lower_bound(tmp.begin(),tmp.end(),j-m) - tmp.begin();\n int i2 = upper_bound(tmp.begin(),tmp.end(),j+m) - tmp.begin(); i2--;\n if(i2<0||i1>i2){\n l=m+1; continue;\n }\n else if(i1==n){\n r=m-1; continue;\n }\n if(find(0,n-1,i1,i2,1)>=sz){\n val = m; r=m-1;\n }\n else l = m+1; \n }\n res[i] = val;\n }\n for(int i=0;i<q.size();i++){\n if(res[i]==-1) continue;\n int i1 = q[i][0] - res[i], i2 = q[i][0] + res[i];\n if(mp[i1]>=q[i][1]) res[i] = i1; \n else res[i] = i2;\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Binary Search', 'Segment Tree', 'C++']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Python 3: FT 90%, TC O(Q log(Q) + (N+Q) log(N)), SC O(N + Q): SortedList/SortedSet
|
python-3-ft-90-tc-oq-logq-nq-logn-sc-on-xbe9r
|
Intuition\n\nThis problem seems to basically require ordered collections.\n\n## The Pattern\n\nFor each query: among rooms with size >= minsize, we want the clo
|
biggestchungus
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-08T22:24:05.442159+00:00
|
2024-07-08T22:24:05.442243+00:00
| 61 | false |
# Intuition\n\nThis problem seems to basically require ordered collections.\n\n## The Pattern\n\nFor each query: among rooms with size `>= minsize`, we want the closest `id`.\n\nClosest `id` pretty much screams "binary search" because we need to support arbitrary `id` queries.\n\nThis is a kind of "closest item meeting a criterion" problem.\n\nThe pattern for these problems is\n* **sort by the value involving the criterion**\n* **sort queries by the criterion**\n* **as the criterion gets less strict, add elements to a sorted collection**\n* **answer each query by bisecting the sorted collection**\n\nUse this pattern when the criterion is "monotonic," such that once we start answering queries that are less strict, each option remains valid for all future queries.\n\nIn this case the criterion is size. By processing queries in order of `minsize` descending, once a room is at least as big as the current minsize, it remains at least as large for the rest of the problem. This way we never need to remove elements from the sorted collection. Otherwise it\'s a nightmare (and bad asymtptotic complexity) review all items in the collection and evaluate whether they still belong or not after each query.\n\n## Sorted Collections in Python\n\nYour only options, thanks to the de facto dictator of Python Guido van Rossum\'s insistence that Python have absolutely no sorted collections, are\n* the heapq module, not suitable here\n* the `sortedcontainers` 3rd party library: `SortedList` or `SortedSet` are excellent choices\n* some other third-party library\n* some nasty wrangling with segment trees\n * map all the room ids to contiguous integers 1..n that are monotonic with those room ids\n * then make min and max segment trees on these indices, the initial value is -1 meaning "room not seen yet"\n * when rooms are available, map the room id to its index, and set its value in the tree to the room id\n * now you can answer in `log(len(rooms))` time what the max id less than the preferred room is and min id at least the preferred room is\n\nEnjoy!\n\n# Complexity\n\nLet `N` be the number of rooms and `Q` be the number of queries.\n\n- Time complexity: `O(N log(N)) + Q log(Q) + Q*log(N))`\n - `N log(N)` and `Q log(Q)`: sorting rooms by size, queries by `minsize`\n - `Q log(N)`: for each query we bisect the `SortedList` to find the nearest room ids above and below, a `log(N)` operation\n\n- Space complexity: `O(N + Q)`\n - sorting takes `O(N)` for sorting rooms and `O(Q)` for the query indices and sorting them; Python\'s sort is based on mergesort\n - the ordered collection of rooms takes `O(N)` memory\n - so no matter what sorting algo we pick we have `O(N+Q)` anyway\n\n\n# Code\n```\nfrom sortedcontainers import SortedList\n\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n # rooms is [id, size] pairs\n # queries are [preferred, min] pairs\n\n # so we want the closest room size to preferred among those with size >= min\n # binary search!\n\n # AHHHH DIDN\'T READ THE PROBLEM CAREFULLY.\n\n # among rooms with size >= minsize we want the one with the closest ID NUMBER, not the closest size\n\n # as queries ask for higher sizes, we have more options for room ids\n \n # we want the max id among rooms with lower IDs and min id among rooms with >= id that are valid\n\n # so maybe we process queries in order by minsize\n # as minsize increases we gain more room options: add to a sorted collection of ids\n # then we can bisect the sorted collection\n\n # in stock Python we\'re extremely limited here, best we can do in iview time is conditional maxes with\n # range trees, ugh\n\n # with sortedcontainers we can have a SortedList for this\n\n rooms.sort(key=lambda room: room[1], reverse=True) # by size desc\n r = 0 # next room not yet added to the SortedList of ids\n\n avail = SortedList() # list of ids\n ans = [-1]*len(queries)\n qidxs = list(range(len(queries)))\n qidxs.sort(key=lambda i: queries[i][1], reverse=True) # proc in order of min size desc\n\n for qidx in qidxs:\n # each minsize is <= than the last, yielding new room opportunities\n pref, minsize = queries[qidx]\n while r < len(rooms) and rooms[r][1] >= minsize:\n avail.add(rooms[r][0])\n r += 1\n\n if not avail: continue # leave answer as -1\n\n # avail now has all rooms with suitable size\n i = avail.bisect_left(pref)\n if i == len(avail):\n ans[qidx] = avail[-1]\n else:\n id = avail[i] # first id >= pref\n if i:\n # there is a lesser id as well\n lower = avail[i-1]\n if pref-lower <= id-pref:\n # if lower is closer: take lower\n # if lower is same distane: take lower as tie-breaker\n # hence <= to cover both cases\n id = lower\n\n ans[qidx] = id\n\n return ans\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n # print(f"{rooms=}")\n # print(f"{queries=}")\n\n # def answer(pref, minsize) -> int:\n # """Returns room index with size at least minsize closest to pref"""\n\n # if minsize > M: return -1 # no such room has this size\n # if pref >= M: return M_idx # earliest room index with max size, the closest to pref >= M\n\n # # start of room range with suitable sizes\n # lo = bisect_left(rooms, minsize, key=lambda room: room[1])\n\n # # index of room with closest size >= pref\n # i = bisect_left(rooms, pref, key=lambda room: room[1], lo=lo)\n # nxt_size = rooms[i][1]\n # if i > lo:\n # prev_size = rooms[i-1][1]\n # if pref-prev_size < nxt_size-pref:\n # # answer is min room index with prior size\n # i = bisect_left(rooms, prev_size, key=lambda room: room[1], hi=i)\n # return rooms[i][0]\n # elif pref-prev_size == nxt_size-pref:\n # # prior size is tied, return minimum earliest number\n # j = bisect_left(rooms, prev_size, key=lambda room: room[1], hi=i)\n # return min(rooms[i][0], rooms[j][0])\n \n # # else: nxt_size is closer\n # return rooms[i][0]\n # else:\n # # no valid room with < pref\n # return rooms[i][0]\n\n # return list(answer(*query) for query in queries)\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
[Rust] Offline Queries
|
rust-offline-queries-by-mortonjack-wfqe
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nWhen approaching a problem of the form "Given this data, answer these queries", there a
|
mortonjack
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-16T03:54:20.342721+00:00
|
2024-04-16T03:54:20.342748+00:00
| 57 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nWhen approaching a problem of the form "Given this data, answer these queries", there are two natural ways to approach it. First, you could create a data structure (often a segment tree) which allows for efficient querying, amortising the cost of building the data structure across all of the queries. This works well in many cases, and its initially what I went with for this question, although sometimes the data structure can be complicated and error-prone, which is what I found here.\n\nAnother approach is **offline queries**. Rather than changing our representation of the data alone to answer arbitrary queries, we can recognise that *we already know all of the queries we will be performing*. By changing our representation of the queries, often as simple as sorting them, we can answer them in an ideal order, then re-order our answers back into the original order of the queries. \n\nOffline queries often leads to simpler and more efficient algorithms - a poorly built (aka self-implemented) data structure could maintain good time complexities, but struggle with real-world efficiency due to excessive heap allocations or cache misses. I find custom-data-structure based solutions more intuitive, but I think its worthwhile re-evaluating other alternatives when they come up. (Another common segtree alternative is a custom mergesort). \n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nThe first step is to sort the queries and rooms vectors by size. I\'ve also converted them into custom structs, which are easier easier to understand and reduce memory indirection. I also initialise an empty set of available rooms. Note that we keep track of each query\'s initial index.\n\nNow, the queries can be answered in order from the largest required size to the smallest. Every new query will accept all the rooms available to the previous query, plus some extra, so the first step is adding the newly available rooms to the set. Then, check the first room available before and after the preferred id, and check which one (if any) to take.\n\nAfterwards, re-order the answer vector by the query indices to re-create the original query order, and return the vector.\n\n# Complexity\nLet `r = rooms.len()` and `q = queries.len()`.\n- Time complexity: $$O(r \\log(r) + q\\log(q)+q*B\\log(r))$$\n - $$O(r \\log(r) + q\\log(q))$$ for sorting.\n - $$O(B\\log(r))$$ lookup time for each query.\n - Note that Rust\'s standard library uses a B Tree rather than a standard Binary Search Tree to represent an ordered set. This means lookups involve linear searching, more comparisons in exchange for better cache efficiency. Currently, `B = 6`.\n- Space complexity: $$O(r + q)$$\n\n# Code\n```\nuse std::collections::BTreeSet;\n\nstruct Query {\n ideal: i32,\n size: i32,\n index: usize,\n}\n\nstruct Room {\n id: i32,\n size: i32\n}\n\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn closest_room(rooms: Vec<Vec<i32>>, queries: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<i32> {\n let mut queries: Vec<Query> = queries\n .into_iter()\n .enumerate()\n .map(|(index, query)| Query { ideal: query[0], size: query[1], index })\n .collect();\n let mut rooms: Vec<Room> = rooms\n .into_iter()\n .map(|r| Room { id: r[0], size: r[1] })\n .collect();\n queries.sort_unstable_by_key(|query| query.size);\n rooms.sort_unstable_by_key(|room| room.size);\n let mut available_rooms = BTreeSet::new();\n\n let mut ans = queries.into_iter().rev().map(|query| {\n while let Some(room) = rooms.pop() {\n if room.size < query.size {\n rooms.push(room);\n break;\n } else {\n available_rooms.insert(room.id);\n }\n }\n let lower = available_rooms.range(..query.ideal).next_back().copied();\n let upper = available_rooms.range(query.ideal..).next().copied();\n let room = match (lower, upper) {\n (None, None) => -1,\n (Some(x), None) => x,\n (None, Some(y)) => y,\n (Some(x), Some(y)) => \n if query.ideal - x > y - query.ideal { y } else { x },\n };\n (room, query.index)\n }).collect::<Vec<_>>();\n ans.sort_unstable_by_key(|(_, id)| *id);\n ans.into_iter().map(|(a, _)| a).collect()\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Sorting', 'Iterator', 'Enumeration', 'Ordered Set', 'Rust']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
[Golang] using Binary Search Tree
|
golang-using-binary-search-tree-by-nithi-c5fm
|
Code\n\ntype Node struct {\n\tval int\n\tleft *Node\n\tright *Node\n}\n\ntype BST struct {\n\troot *Node\n}\n\nfunc NewBST() *BST {\n\treturn &BST{}\n}\n\nfu
|
nithingudla23
|
NORMAL
|
2023-09-27T10:59:07.414205+00:00
|
2023-09-27T10:59:07.414224+00:00
| 19 | false |
# Code\n```\ntype Node struct {\n\tval int\n\tleft *Node\n\tright *Node\n}\n\ntype BST struct {\n\troot *Node\n}\n\nfunc NewBST() *BST {\n\treturn &BST{}\n}\n\nfunc (bst *BST) insert(v int) {\n\tn := &Node{\n\t\tval: v,\n\t}\n\tif bst.root == nil {\n\t\tbst.root = n\n\t\treturn\n\t}\n\n\ttemp := bst.root\n\tfor {\n\t\tif v < temp.val {\n\t\t\tif temp.left == nil {\n\t\t\t\ttemp.left = n\n\t\t\t\treturn\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\ttemp = temp.left\n\t\t} else {\n\t\t\tif temp.right == nil {\n\t\t\t\ttemp.right = n\n\t\t\t\treturn\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\ttemp = temp.right\n\t\t}\n\t}\n}\n\nfunc (bst *BST) search(v int) int {\n\tif bst.root == nil {\n\t\treturn -1\n\t}\n\n\ttemp := bst.root\n\tcloseResult := temp.val\n\n\tfor {\n\t\tif temp.val == v {\n\t\t\treturn v\n\t\t}\n\n\t\tif abs(v, temp.val) < abs(closeResult, v) {\n\t\t\tcloseResult = temp.val\n\t\t}\n\n\t\tif v < temp.val {\n\t\t\tif temp.left == nil {\n\t\t\t\treturn closeResult\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\ttemp = temp.left\n\t\t} else {\n\t\t\tif temp.right == nil {\n\t\t\t\treturn closeResult\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\ttemp = temp.right\n\t\t}\n\t}\n}\n\nfunc abs(a, b int) int {\n\tif a > b {\n\t\treturn a - b\n\t}\n\treturn b - a\n}\n\nfunc min(a, b int) int {\n\tif a < b {\n\t\treturn a\n\t}\n\treturn b\n}\n\ntype Query struct {\n\troomID int\n\tsize int\n\tindex int\n}\n\nfunc closestRoom(rooms [][]int, queries [][]int) []int {\n\n\tmyQueries := make([]Query, 0)\n\tfor i, query := range queries {\n\t\tmyQueries = append(myQueries, Query{\n\t\t\tsize: query[1],\n\t\t\troomID: query[0],\n\t\t\tindex: i,\n\t\t})\n\t}\n\n\t// sort queries in descending order based on required size\n\tsort.Slice(myQueries, func(i, j int) bool {\n\t\tif myQueries[i].size > myQueries[j].size {\n\t\t\treturn true\n\t\t}\n\t\treturn false\n\t})\n\n\t// sort rooms in descending order based on size\n\tsort.Slice(rooms, func(i, j int) bool {\n\t\tif rooms[i][1] > rooms[j][1] {\n\t\t\treturn true\n\t\t}\n\t\treturn false\n\t})\n\n\troomsIndex := 0\n\tbst := NewBST()\n\n\tresult := make([]int, len(myQueries))\n\tfor _, query := range myQueries {\n\t\trequiredSize := query.size\n\t\tfor ; roomsIndex < len(rooms) && rooms[roomsIndex][1] >= requiredSize; roomsIndex++ {\n\t\t\tbst.insert(rooms[roomsIndex][0])\n\t\t}\n\t\tres := bst.search(query.roomID)\n\t\tif res > query.roomID {\n\t\t\t// If we are searching for 5, and res=7, then we can check if 3 (i.e 5 - (7-5)) exists in bst as priority is given to small number\n\t\t\trequiredSize2 := query.roomID - (res - query.roomID)\n\t\t\tif res2 := bst.search(requiredSize2); res2 == requiredSize2 {\n\t\t\t\tres = res2\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t}\n\n\t\tresult[query.index] = res\n\t}\n\n\treturn result\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Go']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
C++ solution
|
c-solution-by-pejmantheory-vrvu
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
pejmantheory
|
NORMAL
|
2023-09-18T04:34:55.507478+00:00
|
2023-09-18T04:34:55.507497+00:00
| 48 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms,\n vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n vector<int> ans(queries.size());\n set<int> roomIds;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.size(); ++i)\n queries[i].push_back(i);\n\n auto descSize = [](const auto& a, const auto& b) { return a[1] > b[1]; };\n sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), descSize);\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end(), descSize);\n\n int i = 0; // rooms\' pointer\n for (const vector<int>& query : queries) {\n while (i < rooms.size() && rooms[i][1] >= query[1])\n roomIds.insert(rooms[i++][0]);\n ans[query[2]] = searchClosestRoomId(roomIds, query[0]);\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n\n private:\n int searchClosestRoomId(set<int>& roomIds, int preferred) {\n const auto it = roomIds.lower_bound(preferred);\n const int id1 = it == roomIds.cbegin() ? -1 : *(prev(it));\n const int id2 = it == roomIds.cend() ? -1 : *it;\n if (id1 == -1)\n return id2;\n if (id2 == -1)\n return id1;\n if (abs(preferred - id1) <= abs(preferred - id2))\n return id1;\n return id2;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
2-D Binary Search
|
2-d-binary-search-by-user6192i-2tv8
|
Approach: \n1. Since room has to have a size of atleast minSize from query -> Sort the queries in decreasing order of room-size {3,2,1} => This will ensure that
|
user6192i
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-17T07:07:20.078222+00:00
|
2022-06-17T07:08:13.543851+00:00
| 247 | false |
Approach: \n1. Since room has to have a size of atleast minSize from query -> Sort the queries in decreasing order of room-size {3,2,1} => This will ensure that if **x rooms have size atleast 3**, then `rooms having size atleast 2= x + (rooms with size2)` OR rooms with size 1= x + (rooms>1) after it in the loop. \n2. Now, we will also need the rooms size to be sorted in decreasing order to make-1 work. \nFor eg: \nLet\'s maintain a counter for where we are at in Rooms, say ptr:\n*For, QuerySize=7*\nRoomSizes: [4,3,2]\nQuerySizes:[7,3,1]\nat the start. \n\n=>When we look for rooms with size atleast 7, we will get no element\n\n*For, QuerySize=3*\n\n=>When we look for rooms with size atleast 3, we will get {4, 3} [ptr moves to idx=2]\n\n*For, QuerySize=1*\n=>When we look for rooms with size atleast 1, we will get *{4,3,2} OR {} + {4,3} + {2}* [ptr moves to end]\n\n\t3. Rest, we just need to efficiently store the possibleRoomIDs in a set and then perform binary search to get the minimum difference. \n\t4. **Case of a Tie:** We don\'t need to run a loop for this, as Tie can only be between two elements not more as RoomIDs are unique!\n\n**Time-Complexity: O(K*log(N)+N*log(N))**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n static bool mysort(vector<int>&a, vector<int>&b){\n \n if(a[1]==b[1])\n {\n return a[0]>b[0];\n }\n return a[1]>b[1];\n }\n \n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n \n int k= queries.size();\n for(int i=0;i<k;i++)\n {\n queries[i].push_back(i);\n }\n \n sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), mysort);\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end(), mysort);\n \n set<int> PossibleIDs;\n int n = rooms.size();\n int prev=0;\n vector<int> ans(k, -1);\n \n for(int i=0;i<k;i++)\n {\n int size_query= queries[i][1];\n int pref_query= queries[i][0];\n \n while(prev<n && rooms[prev][1]>=size_query)\n {\n PossibleIDs.insert(rooms[prev][0]);\n prev++;\n \n }\n \n if(PossibleIDs.size()>0)\n {\n auto it= PossibleIDs.lower_bound(pref_query);\n \n int curr_ans= (it==PossibleIDs.end())?(int)1e8:(abs(pref_query-*it));\n int ans_push= (it==PossibleIDs.end())?(int)1e8:(*it);\n \n if(it!=PossibleIDs.begin())\n {\n it--; //Resolving Ties: If there is a Tie, then there can only be two cases (Upper Lower type), for eg: cur=4, arr[2,6]\n if(abs(pref_query-*it)<=curr_ans)\n {\n curr_ans= (pref_query-*it);\n ans_push= *it;\n }\n }\n ans[queries[i][2]]= (curr_ans==(int)1e8)?-1:ans_push;\n \n }\n \n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C', 'Binary Tree']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Binary Search
|
binary-search-by-diyora13-c0wm
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rm, vector<vector<int>>& q) \n {\n for(int i=0;i<rm.size();i++)\n
|
diyora13
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-09T08:33:42.491266+00:00
|
2022-06-09T08:33:42.491300+00:00
| 507 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rm, vector<vector<int>>& q) \n {\n for(int i=0;i<rm.size();i++)\n swap(rm[i][0],rm[i][1]);\n sort(rm.begin(),rm.end(),greater<vector<int>>());\n for(int i=0;i<q.size();i++)\n q[i].push_back(i),swap(q[i][0],q[i][1]);\n sort(q.begin(),q.end(),greater<vector<int>>());\n vector<int> ans(q.size());\n set<int> s;\n for(int i=0,j=0;j<q.size();j++)\n {\n while(i<rm.size() && rm[i][0]>=q[j][0])\n s.insert(rm[i][1]),i++;\n \n auto it=s.lower_bound(q[j][1]);\n auto tp=it;\n int d1=1e9,d2=1e9;\n if(it!=s.end()) d2=(*it)-q[j][1];\n if(it!=s.begin()) --it,d1=q[j][1]-(*it);\n \n if(d1==1e9 && d2==1e9) ans[q[j][2]]=-1;\n else if(d1<=d2) ans[q[j][2]]=(*it);\n else ans[q[j][2]]=(*tp);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Binary Search', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Python | Sorted List | Sort the Query and Rooms According to Room Size
|
python-sorted-list-sort-the-query-and-ro-rqa7
|
First sort the rooms and queries according to room size in decreasing order\nThen process the query one by one after inserting all the rooms with sizes greater
|
aryonbe
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-23T07:03:21.958243+00:00
|
2022-04-22T22:41:59.750124+00:00
| 159 | false |
First sort the rooms and queries according to room size in decreasing order\nThen process the query one by one after inserting all the rooms with sizes greater than or equal to current query\'s room size\n```\nfrom sortedcontainers import SortedList\n\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n queries = [ (q[1],q[0],i)for i,q in enumerate(queries)]\n queries.sort(reverse = True)\n rooms.sort(key = lambda e: (e[1],e[0]), reverse = True)\n sl = SortedList()\n res = [0]*len(queries)\n ri = 0\n for q in queries:\n qsz, qid, qi = q\n while ri < len(rooms) and rooms[ri][1] >= qsz:\n sl.add(rooms[ri][0])\n ri += 1\n if not sl:\n res[qi] = -1\n continue\n idx = sl.bisect_left(qid)\n if idx == 0:\n res[qi] = sl[idx]\n elif idx == len(sl):\n res[qi] = sl[-1]\n else:\n if sl[idx] >= 2*qid - sl[idx-1]:\n res[qi] = sl[idx-1]\n else:\n res[qi] = sl[idx]\n return res\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
C++, Sorting queries and rooms by their sizes, and using ordered set for id
|
c-sorting-queries-and-rooms-by-their-siz-ta94
|
The code is self explanatory. Let me know if there are any doubts\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n static bool cmp(vector<int> &a , vector<int> & b){\n
|
aditya_trips
|
NORMAL
|
2021-12-06T10:20:55.481468+00:00
|
2021-12-06T10:20:55.481494+00:00
| 223 | false |
**The code is self explanatory. Let me know if there are any doubts**\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n static bool cmp(vector<int> &a , vector<int> & b){\n return a[1] < b[1]; \n }\n \n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& q) {\n vector<vector<int>> queries; \n for(int i=0; i<q.size(); i++) {\n queries.push_back({q[i][0], q[i][1], i}); \n }\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end(), cmp); \n sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), cmp); \n set<int> st; \n for(auto x:rooms) st.insert(x[0]); \n \n vector<int > res(queries.size(), -1); \n int i=0 , n = rooms.size(); \n for(auto query:queries){\n while(i<n && rooms[i][1] < query[1]) st.erase(rooms[i][0]), i++; \n auto idx = st.lower_bound(query[0]); \n if(st.size() == 0) break; \n int curr = INT_MAX, prev; \n if(idx != st.end()){\n curr = abs(query[0] - (*idx)), prev = *idx; \n }\n \n if(idx != st.begin()){\n idx --; \n if(curr > abs(query[0] -(*idx))) res[query[2]] = (*idx); \n else if(curr == abs(query[0]- (*idx))) res[query[2]] = min(prev, *idx); \n else res[query[2]] = (prev); \n }\n else res[query[2]] = (prev); \n }\n return res ; \n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C', 'Sorting']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
C++ beat 100%
|
c-beat-100-by-sanzenin_aria-6r16
|
```\n vector closestRoom(vector>& rooms, vector>& queries) {\n set ids;\n sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), {return a[1] > b[1];});\n pri
|
sanzenin_aria
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-05T22:36:38.271158+00:00
|
2021-11-05T22:36:38.271200+00:00
| 152 | false |
```\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n set<int> ids;\n sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), [](auto& a, auto& b){return a[1] > b[1];});\n priority_queue<tuple<int,int,int>> queryQ;\n const int n = queries.size();\n vector<int> res(n, -1);\n for(int i=0;i<queries.size();i++){\n int preferId = queries[i][0];\n int minSize = queries[i][1];\n queryQ.emplace(minSize, preferId, i);\n }\n \n auto it = rooms.begin();\n while(!queryQ.empty()){\n auto [minSize, preferId, i] = queryQ.top(); queryQ.pop();\n while(it != rooms.end() && it->at(1)>= minSize){\n ids.insert(it->at(0));\n it++;\n }\n \n auto it2 = ids.lower_bound(preferId);\n int ans = -1, minDis = 1e9;\n if(it2 != ids.end()){\n ans = *it2;\n minDis = abs(*it2 - preferId);\n }\n if(it2 != ids.begin()){\n auto pre = *prev(it2);\n if(preferId - pre <= minDis)\n ans = pre;\n }\n res[i] = ans;\n }\n return res;\n }
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
closest-room
|
binary search python code
|
binary-search-python-code-by-waydez-j5h4
|
```\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n def binary_search(arr, target):\n
|
WaydeZ
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-28T03:03:32.924199+00:00
|
2021-10-28T03:03:32.924235+00:00
| 93 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n def binary_search(arr, target):\n left, right = 0, len(arr) - 1\n while left < right:\n mid = right - (right - left) // 2\n if arr[mid] <= target:\n left = mid\n else:\n right = mid - 1\n return left\n \n # sort rooms and queries\n rooms.sort(key = lambda x : x[1], reverse= True)\n new_queries = []\n for i in range(len(queries)):\n new_queries.append((queries[i][0], queries[i][1], i))\n new_queries.sort(key = lambda x : x[1], reverse= True)\n \n ans = [-1 for _ in range(len(new_queries))]\n # find candidates\n cur_search = 0\n candidates = []\n for query in new_queries:\n queryPrefered, querySize, queryIdx = query\n #print(query)\n while cur_search < len(rooms):\n if rooms[cur_search][1] >= querySize:\n room_id = rooms[cur_search][0]\n insert_idx = binary_search(candidates, room_id)\n if len(candidates) > 0 and candidates[insert_idx] < room_id:\n candidates.insert(insert_idx + 1, room_id)\n else:\n candidates.insert(insert_idx, room_id)\n cur_search += 1\n else:\n break\n #print(candidates)\n if len(candidates) > 0:\n # search queryPrefered\n found_id = binary_search(candidates, queryPrefered)\n ans[queryIdx] = candidates[found_id]\n if candidates[found_id] < queryPrefered and found_id < len(candidates) - 1: \n if abs(queryPrefered - candidates[found_id]) > abs(queryPrefered - candidates[found_id + 1]):\n ans[queryIdx] = candidates[found_id + 1]\n return ans
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
closest-room
|
C++,set,Explained
|
csetexplained-by-next_pointer-38es
|
idea is we will answer queries from largest to smalllest so when we encounter a query we ids of element whoose size is more than this query and for queries foll
|
next_pointer
|
NORMAL
|
2021-06-23T05:59:09.819873+00:00
|
2021-06-23T05:59:09.819933+00:00
| 263 | false |
idea is we will answer queries from largest to smalllest so when we encounter a query we ids of element whoose size is more than this query and for queries following this will also have size smaller than this id added.\nNow we have ids which has size larger than our query roomsize using lower_bound check closest.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n static bool compare(vector<int>&a,vector<int>&b){\n return a[1]>b[1];\n }\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n int n=rooms.size();\n int m=queries.size();\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++)\n {\n queries[i].push_back(i);\n }\n sort(rooms.begin(),rooms.end(),compare);\n sort(queries.begin(),queries.end(),compare);\n vector<int>ans(m,-1);\n int j=0;\n set<int>s;\n // for(auto &q:queries)\n // cout<<q[0]<<" "<<q[1]<<" "<<q[2]<<endl;\n \n for(auto &q:queries){\n while(j<n && q[1]<=rooms[j][1]){\n s.insert(rooms[j][0]);\n j++;\n }\n if(s.empty())\n continue;\n // cout<<q[1]<<" "<<s.size()<<endl;\n auto it=s.lower_bound(q[0]);\n if(it==s.end()){\n ans[q[2]]=*prev(it);\n }\n else if(it==s.begin()){\n ans[q[2]]=*it;\n }\n else{\n int h=*it;\n int g=*prev(it);\n if(abs(g-q[0])<=abs(h-q[0]))\n ans[q[2]]=g;\n else\n ans[q[2]]=h;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
closest-room
|
[C++] beats 96.97% using KMP algorithm
|
c-beats-9697-using-kmp-algorithm-by-josi-ez3r
|
This solution would be probably the best performing if we didn\'t know the queries beforehand, which we can sort beforehand by size and add only valid solutions
|
JosipDev
|
NORMAL
|
2021-06-14T08:13:32.917547+00:00
|
2021-06-14T08:13:32.917579+00:00
| 319 | false |
This solution would be probably the best performing if we didn\'t know the queries beforehand, which we can sort beforehand by size and add only valid solutions (by room size) in a set and search the closest ID in logN. Still it beats 96.97% of C++ online submissions. Why it is still good to know it? In an interview you could be asked the question slightly differently - you don\'t get the list of queries and you can\'t sort them beforehand. And the described alternative solution will quickly be unacceptable.\n\nIn this solution here, we sort the rooms by ID and search for the closest ID using binary search.\nIn order to get a room, which is big enough, we would need to search for the closest one to this ID from both sides. We can do this only in linear time, since we can\'t sort the rooms by size and ID at the same time...\nBut what we can do is utilize the principle used in the KPM algorithm (string search in O(N) - take a look on it for the interviews).\nHow does it work, we go through the rooms from left to right and for each room we save the index of the next room (on the left side), which has a greater size. The same we do for the opposite direction.\nIn this way, we can speed up our search process by skipping all the rooms in between, which have a smaller size. \nIn the concrete example, we will have to search on the left and on the right side and pick the closest room ID. Note that, if we didn\'t match the room ID initially with the binary search, we need to do the same for the idx on the left, since it is an alternative, which could result in a closer room ID.\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n int closer(int target, int alt1, int alt2) {\n if (alt1 == -1) return alt2;\n if (alt2 == -1) return alt1;\n if (abs(alt1 - target) < abs(alt2 - target)) return alt1;\n if (abs(alt1 - target) == abs(alt2 - target) && alt1 < alt2) return alt1;\n return alt2;\n } \npublic:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) { \n sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), [](const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b){\n return (a[0] == b[0])? a[1] < b[1] : a[0] < b[0]; // sort by room ID, size if same\n });\n \n // vector of indices with closest element by ID, which has a room\n // size greater than this; if non-existing: -1 (from left and right) \n int n = rooms.size();\n vector<int> left(n, -1), right(n, -1);\n\n for (int i = 1; i < rooms.size(); ++i) { // look only at the left side\n int idx = i - 1;\n while (idx >= 0 && rooms[i][1] >= rooms[idx][1]) {\n idx = left[idx];\n }\n left[i] = idx;\n }\n\n for (int i = rooms.size() - 2; i >= 0; --i) { // look only at the right side\n int idx = i + 1;\n while (idx >= 0 && idx < rooms.size() && \n rooms[i][1] >= rooms[idx][1]) {\n idx = right[idx];\n }\n right[i] = idx;\n }\n \n vector<int> ans;\n for (auto& q: queries) {\n auto it = lower_bound(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), q[0], // compare by ID\n [](const vector<int>& v, int value){\n return v[0] < value;\n });\n \n int idx = (it == rooms.end())? rooms.size() - 1 : distance(rooms.begin(), it);\n int id = -1, i = idx;\n\n for (i = idx; i >= 0 && rooms[i][1] < q[1]; i = left[i]);\n if (i >= 0) id = closer(q[0], rooms[i][0], id);\n \n for (i = idx; i >= 0 && rooms[i][1] < q[1]; i = right[i]);\n if (i >= 0) id = closer(q[0], rooms[i][0], id);\n\n if (rooms[idx][0] > q[0]) {\n for (i = idx - 1; i >= 0 && rooms[i][1] < q[1]; i = left[i]);\n if (i >= 0) id = closer(q[0], rooms[i][0], id);\n\n for (i = idx - 1; i >= 0 && rooms[i][1] < q[1]; i = right[i]);\n if (i >= 0) id = closer(q[0], rooms[i][0], id);\n }\n \n ans.push_back(id);\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Binary Tree', 'C++']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
[C++] Offline query solution with explanation | Priority Queue | O(nlogn)
|
c-offline-query-solution-with-explanatio-obyj
|
class Solution {\npublic:\n vector closestRoom(vector>& rooms, vector>& queries) {\n priority_queue > room;\n vector, int> > query;\n in
|
tarun_199734
|
NORMAL
|
2021-06-06T07:05:29.358051+00:00
|
2021-06-06T07:05:29.358094+00:00
| 207 | false |
class Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n priority_queue<pair<int, int> > room;\n vector<pair<pair<int, int>, int> > query;\n int n = queries.size();\n \n //Sort the rooms based on room size in descending order\n for (auto it : rooms) {\n room.push({it[1], it[0]});\n }\n \n //setting up data-structure which contains the original query index\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n query.push_back({{queries[i][1], queries[i][0]}, i});\n }\n \n //Sort the queries based on query min-size in descending order\n sort(query.begin(), query.end(), greater<pair<pair<int, int>, int> > ());\n set<int> s;\n \n vector<int> ans(n, 0);\n \n for (int i = 0; i < query.size(); i++) {\n //We will insert room-id of all rooms that have space more than min space required for current query in the set\n while (!room.empty()) {\n if (room.top().first >= query[i].first.first) {\n s.insert(room.top().second);\n \n room.pop();\n } else break;\n }\n \n //Now set contains all rooms that satisfy the min size condition\n //find out the nearest room id that exists, could be at lower_bound or --lower_bound\n auto it = s.lower_bound(query[i].first.second);\n if (s.empty()) {\n ans[query[i].second] = -1;\n } else if (it == s.begin()) {\n ans[query[i].second] = *it;\n } else if (it == s.end()){\n ans[query[i].second] = *(--it);\n } else {\n //prevIt points to element before lower_bound\n auto prevIt = it;\n prevIt --;\n \n if (abs(*it - query[i].first.second) < abs(*prevIt - query[i].first.second)) {\n ans[query[i].second] = *(it);\n } else {\n ans[query[i].second] = *(prevIt);\n }\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n};
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Treeset solution
|
treeset-solution-by-miseryangel1990-x770
|
sort queries and rooms by size, then put all viable options into treeset, compare dis of preferred location to floor and to ceiling.\n\nclass Solution {\n p
|
miseryangel1990
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-07T03:40:37.719441+00:00
|
2021-05-07T03:40:37.719477+00:00
| 98 | false |
sort queries and rooms by size, then put all viable options into treeset, compare dis of preferred location to floor and to ceiling.\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n Arrays.sort(rooms,(a,b) -> b[1] - a[1]);\n int n = queries.length, m = rooms.length, qs[][] = new int[n][3], res[] = new int[n];\n TreeSet<Integer> pq = new TreeSet<>();\n \n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n qs[i][0] = queries[i][0];\n qs[i][1] = queries[i][1];\n qs[i][2] = i;\n }\n \n Arrays.sort(qs,(a,b)->b[1] - a[1]);\n \n for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; i++){\n int size = qs[i][1], idx = qs[i][2], pre = qs[i][0];\n \n while (j < m && rooms[j][1] >= size){\n pq.add(rooms[j++][0]);\n }\n \n Integer floor = pq.floor(pre), ceiling = pq.ceiling(pre);\n if (floor == null && ceiling == null){\n res[idx] = -1;\n }else if (floor == null){\n res[idx] = ceiling;\n }else if (ceiling == null){\n res[idx] = floor;\n }else{\n res[idx] = ceiling - pre < pre - floor?ceiling:floor;\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 1 |
[]
| 0 |
closest-room
|
C++, binary search
|
c-binary-search-by-xuekaiwen94-brew
|
\n//TC: O(nlogn + 2 * mlogm + nlogm)\nvector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& room, vector<vector<int>>& query) {\n int n = query.size();\n v
|
xuekaiwen94
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-05T12:23:07.050992+00:00
|
2021-05-05T12:23:07.051034+00:00
| 294 | false |
```\n//TC: O(nlogn + 2 * mlogm + nlogm)\nvector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& room, vector<vector<int>>& query) {\n int n = query.size();\n vector<vector<int>> tquery;\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) tquery.push_back({query[i][0], query[i][1], i});\n auto cmp = [](const auto& a, const auto& b){return a[1] > b[1];};\n sort(begin(room), end(room), cmp); //O(mlogm)\n sort(begin(tquery), end(tquery), cmp); //O(nlogn)\n vector<int>res(n);\n int j = 0;\n int m = room.size();\n set<int> ts;\n\t\t////O(mlogm + nlogm)\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n while(j < m && room[j][1] >= tquery[i][1]) ts.insert(room[j++][0]);\n if(ts.empty()) res[tquery[i][2]] = -1;\n else{\n auto it = ts.lower_bound(tquery[i][0]);\n if(it != begin(ts)){\n auto bit = it;\n it--;\n res[tquery[i][2]] = abs(*bit - tquery[i][0]) < abs(*it - tquery[i][0]) ? *bit : *it;\n }\n else res[tquery[i][2]] = *it;\n }\n }\n return res;\n\n }\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
closest-room
|
Sorting queries, and rooms and using TreeSet in JAVA
|
sorting-queries-and-rooms-and-using-tree-7y3x
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n Arrays.sort(rooms, (a, b) -> -1*(a[1] - b[1]));\n HashMap<Stri
|
blue_bubble
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-05T09:35:43.968961+00:00
|
2021-05-05T09:35:43.969004+00:00
| 60 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n Arrays.sort(rooms, (a, b) -> -1*(a[1] - b[1]));\n HashMap<String, Integer> hash = new HashMap<>();\n int[][] pro = new int[queries.length][2];\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++){pro[i] = new int[]{queries[i][0], queries[i][1]};}\n Arrays.sort(pro, (a, b) -> -1*(a[1]- b[1]));\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++){\n System.out.print(Arrays.toString(queries[i]) + " ");\n }\n System.out.println("");\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++){\n System.out.print(Arrays.toString(pro[i]) + " ");\n }\n TreeSet<Integer> set = new TreeSet<>();\n int counter = 0; \n for (int[] tt: pro){\n while (counter < rooms.length && rooms[counter][1] >= tt[1]){\n set.add(rooms[counter][0]);\n counter += 1;\n } \n Integer k1 = set.floor(tt[0]); Integer k2 = set.higher(tt[0]);\n \n if (k1 == null && k2 == null){\n hash.put(tt[0] + "_" + tt[1], -1);\n }\n else if (k1== null){\n hash.put(tt[0] + "_" + tt[1], k2);\n }\n else if (k2 == null) {\n hash.put(tt[0] + "_" + tt[1], k1);\n }\n \n else if (tt[0] - k1 > k2 - tt[0]){\n hash.put(tt[0] + "_" + tt[1], k2);\n }\n \n else {\n hash.put(tt[0] + "_" + tt[1], k1);\n }\n }\n System.out.println(hash);\n int[] ans = new int[queries.length];\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++){\n String uu = queries[i][0] + "_" + queries[i][1];\n ans[i] = hash.get(uu);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
closest-room
|
[Python3] greedy
|
python3-greedy-by-ye15-fsyy
|
\n\nfrom sortedcontainers import SortedList\n\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n
|
ye15
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-04T16:25:09.036687+00:00
|
2021-05-04T16:25:09.036723+00:00
| 191 | false |
\n```\nfrom sortedcontainers import SortedList\n\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n rooms.sort(key=lambda x: (-x[1], x[0])) # descending order \n \n ans = [-1] * len(queries)\n sl = SortedList()\n k = 0 \n \n for (preferred, msz), i in sorted(zip(queries, range(len(queries))), key=lambda x: (-x[0][1], x[0][0])): # descending order \n while k < len(rooms) and rooms[k][1] >= msz: \n sl.add(rooms[k][0])\n k += 1\n v = sl.bisect_left(preferred)\n if sl: \n if v == len(sl) or v > 0 and preferred - sl[v-1] <= sl[v] - preferred: ans[i] = sl[v-1]\n else: ans[i] = sl[v]\n return ans \n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 1 |
closest-room
|
[Javascript] AVL Tree(Set)- Self Balancing BST solution
|
javascript-avl-treeset-self-balancing-bs-qt1f
|
Yea so if you wanna do this in js with the optimal time complexity you\'re in a bit of a pickle because you probably have to create your own AVL/ RedBlack tree
|
George_Chrysochoou
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-03T23:17:52.569226+00:00
|
2021-05-03T23:31:51.444279+00:00
| 305 | false |
Yea so if you wanna do this in js with the optimal time complexity you\'re in a bit of a pickle because you probably have to create your own AVL/ RedBlack tree class. What these trees offer is simple. These are containers of unique elements that are always sorted and balance themselves after each operation. Insertion,deletion and traversal all take O(logN) as a result.\nIn our problem, the first observation that needs to be made is that, since the queries are given a priori, we can process them in any order we desire. This is important, because if we process them by descending size and in parallel with the available rooms (also in the same order), we essentially remove the first constraint that, for any query [id,minsize] the only rooms that are considered have bigger sizes. \nWhat\'s now left is to pick the room with the closest id to the query\'s id. This is where the AVL tree will come in handy. Given that all the ids inside the tree are already sorted, we can traverse them exploiting the BST nature of the tree. As a result, finding the next bigger and next smaller element inside the tree is simply a walk down the tree starting from the root. Both of these functionalities are abstracted inside the class AVL for ease of use.\n\n```\nclass Node{\n constructor(val,left=null,right=null,parent=null,bf=0,height=0){\n this.val=val\n this.left=left,this.right=right,this.parent=parent\n this.bf=bf,this.height=height\n }\n}\n\n// CAN ONLY STORE UNIQUE VALUES\nclass AVL{\n constructor(){\n this.nodeCount=0\n this.root=null\n }\n//===M O D I F Y FOR COMPLEX NODES==\\\\\n NODIFY(val){ //should return a new node based on the stats given\n return new Node(val)\n }\n comparator=(node1,node2)=>{// basic comparator that returns <0,0,>0 if node1>node2,node1==node2,node1<node2\n return node1.val-node2.val\n }\n//-------------U S A B L E------------------\\\\\n //returns true if the value was inserted successfully\n //returns false if the value already exists\n insert(NODE){ //O(logn) \n if(NODE===null)\n return false\n NODE=this.NODIFY(NODE)\n if(!this.contains(this.root,NODE)){\n this.root=this.ins(this.root,NODE)\n this.nodeCount++\n return true\n }\n return false\n }\n remove(NODE){ \n if(NODE===null)\n return false\n NODE=this.NODIFY(NODE)\n // console.log(this.contains(this.root,new Node(7)))\n if(this.contains(this.root,NODE)){\n this.root=this.rem(this.root,NODE)\n this.nodeCount--\n return true\n }\n return false\n //rebalance the tree\n }\n has(NODE){\n NODE=this.NODIFY(NODE)\n return this.contains(this.root,NODE)\n }\n traversalASC(){ //O(n)\n let result=[]\n let dfs=(node)=>{\n if(!node)\n return\n dfs(node.left)\n result.push(node)\n dfs(node.right)\n }\n dfs(this.root)\n return result\n }\n findNextSmaller(NODE){\n NODE=this.NODIFY(NODE)\n let cur=this.root,result=null\n while(cur!==null){\n if(this.comparator(cur,NODE)<0)\n result=cur,\n cur=cur.right\n else\n cur=cur.left\n }\n if(result===null)\n return false // no such element\n return result\n }\n findNextBigger(NODE){\n NODE=this.NODIFY(NODE)\n let cur=this.root,result=null\n while(cur!==null){\n if(this.comparator(cur,NODE)<=0)\n cur=cur.right\n else\n result=cur,\n cur=cur.left\n }\n if(result===null)\n return false // no such element\n return result\n }\n//--------- I N T E R N A L S -----------------\\\\\n contains(node,val){\n if(node===null)\n return false\n let compare=this.comparator(node,val)\n if(compare<0) //node<val\n return this.contains(node.right,val)\n if(compare>0)\n return this.contains(node.left,val)\n return true\n }\n //inserts newNode to target node\n ins(tree,value){\n if(tree===null)\n return value\n //(target is bigger? insert it to the left): else to the right\n if(this.comparator(tree,value)>0)\n tree.left=this.ins(tree.left,value)\n else\n tree.right=this.ins(tree.right,value)\n //update balance factor of the target\n this.update(tree) \n return this.rebalance(tree) //balance the target if it needs rebalancing\n }\n rem(node,elem){\n if(node===null)\n return null\n //search an existing node with the given value\n let compare=this.comparator(elem,node)//-----\n if(compare<0)\n node.left=this.rem(node.left,elem)\n else if(compare>0)\n node.right=this.rem(node.right,elem)\n else{ //node found\n //remove the node and replace it with its sucessor\n if(node.left===null)\n return node.right\n else if(node.right===null)\n return node.left\n else{ //still has both subtrees? \n if(node.left.height>node.right.height){\n let successor=this.findMax(node.left)/////\n node.left=this.rem(node.left,successor)\n } \n else{\n let successor=this.findMin(node.right)\n node.right=this.rem(node.right,successor)\n }\n }\n }\n this.update(node)\n return this.rebalance(node)\n }\n //find the min and max node of the subtree rooted at (node)\n findMin=(node)=>node.left?this.findMin(node.left):node\n findMax=(node)=>node.right?this.findMax(node.right):node\n //balances the subtree rooted at node if it is imbalanced (has balancefactor=+-2)\n //and returns the now balanced node\n rebalance(node){ //4 cases, 4 rotations\n if(node.bf==-2){\n if(node.left.bf<=0)\n return this.LL(node)\n else\n return this.LR(node)\n }\n else if(node.bf==2){\n if(node.right.bf>=0)\n return this.RR(node)\n else\n return this.RL(node)\n }\n return node\n }\n //update the balance factor and the height of the current node\n update(node){ \n let leftHeight=node.left!==null?node.left.height:-1,rightHeight=node.right!==null?node.right.height:-1\n node.height=Math.max(leftHeight,rightHeight)+1\n node.bf=rightHeight-leftHeight\n }\n\n //4 cases of unbalanced trees\n LL=(node)=>this.rightRotation(node)\n RR=(node)=>this.leftRotation(node)\n LR(node){\n node.left=this.leftRotation(node.left)\n return this.LL(node)\n }\n RL(node){\n node.right=this.rightRotation(node.right)\n return this.RR(node)\n }\n //2 total rotations that work on RR and LL cases\n leftRotation(node){\n let newParent=node.right\n node.right=newParent.left\n newParent.left=node\n this.update(node)\n this.update(newParent)\n return newParent\n }\n rightRotation(node){\n let newParent=node.left\n node.left=newParent.right\n newParent.right=node\n this.update(node)\n this.update(newParent)\n return newParent\n }\n\n}\n\n\nvar closestRoom = function(R, Q) {\n let A=new AVL(),result=[...Array(Q.length)]\n Q=Q.map((d,i)=>d.concat([i])) // save the original index in each query\n R.sort((a,b)=>a[1]-b[1]) //sort everything in ascending Size\n Q.sort((a,b)=>a[1]-b[1])\n while(Q.length){\n\t let [id,size,index]=Q.pop() //we re about to answer the biggest size query\n while(R.length>0 && size<=R[R.length-1][1]) //so make anything with bigger size available\n A.insert(R.pop()[0])\n let nextsmaller=A.findNextSmaller(id),nextbigger=A.findNextBigger(id)\n if(A.has(id))// the element exists inside the tree\n result[index]=id\n else if(nextsmaller!==false||nextbigger!==false ){\n if(nextsmaller===false)\n result[index]=nextbigger.val\n else if(nextbigger===false)\n result[index]=nextsmaller.val\n else{//always pick the smallest abs distance\n let d1=Math.abs(id-nextsmaller.val),d2=Math.abs(id-nextbigger.val)\n if(d1<=d2)\n result[index]=nextsmaller.val\n else\n result[index]=nextbigger.val\n }\n }\n else\n result[index]=-1\n }\n return result\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
closest-room
|
JavaScript Binary Search Tree
|
javascript-binary-search-tree-by-ektegje-dr7g
|
This is not optimal since some inputs could result in O(room length * query length), but it\'s less complex than implementing a self-balancing binary search tre
|
ektegjetost
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-02T19:16:31.796429+00:00
|
2021-05-02T19:16:31.796467+00:00
| 178 | false |
This is not optimal since some inputs could result in O(room length * query length), but it\'s less complex than implementing a self-balancing binary search tree.\n\nThe general gameplan:\n- Sort both rooms and queries in decreasing order by size. This will allow us to search the minimum number of rooms for each query.\n- Since our output needs to be in the same order as the queries, map a new array to the queries\' indices and sort that array instead.\n- Create an output array, set default to -1\n- For each query\n - If the requested size is greater than the largest room size, continue\n - While the next room we need to add to the BST is >= the current requested size, add the room number to the BST.\n - Then search the BST for the closest room id\n\n```\nvar closestRoom = function (rooms, queries) {\n rooms.sort((a, b) => b[1] - a[1]);\n const byRoomSize = queries\n .map((_, i) => i)\n .sort((a, b) => queries[b][1] - queries[a][1]);\n\n const closest = new Array(queries.length).fill(-1);\n const binarySearchTree = new BinarySearchTree();\n let currentRoom = 0;\n \n byRoomSize.forEach((query) => {\n const [preferredRoom, minimumSize] = queries[query];\n if (rooms[0][1] < minimumSize) {\n return;\n }\n\n while (currentRoom < rooms.length && rooms[currentRoom][1] >= minimumSize) {\n binarySearchTree.add(rooms[currentRoom][0]);\n currentRoom += 1;\n }\n\n closest[query] = binarySearchTree.search(preferredRoom);\n });\n\n return closest;\n};\n\nclass BinarySearchTree {\n constructor() {\n this.root = null;\n }\n\n add(room) {\n this.root = this.insert(this.root, room);\n }\n\n insert(node = this.root, room) {\n if (!node) return new TreeNode(room);\n\n if (node.room < room) {\n node.right = this.insert(node.right, room);\n } else {\n node.left = this.insert(node.left, room);\n }\n\n return node;\n }\n\n search(room, node = this.root) {\n if (node.room === room) return room;\n\n const currentDistance = Math.abs(node.room - room);\n const nextChild = node.room < room ? node.right : node.left;\n\n if (!nextChild) return node.room;\n\n const closestChild = this.search(room, nextChild);\n const childDistance = Math.abs(closestChild - room);\n\n if (childDistance < currentDistance) return closestChild;\n if (childDistance === currentDistance) return Math.min(closestChild, node.room);\n return node.room;\n }\n}\n\nclass TreeNode {\n constructor(room) {\n this.room = room;\n this.left = null;\n this.right = null;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Binary Search Tree', 'JavaScript']
| 1 |
closest-room
|
[ JAVA ] without sorting queries using segment tree
|
java-without-sorting-queries-using-segme-d4v9
|
I sorted rooms according to increasing order of their id and kept the indexes of these ids in a treeset to lookup their index in log(n) time\nCreated a segment
|
mubtasim91
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T19:06:28.133922+00:00
|
2021-05-01T20:13:52.873000+00:00
| 84 | false |
I sorted rooms according to increasing order of their id and kept the indexes of these ids in a treeset to lookup their index in log(n) time\nCreated a segment tree on rooms\' sizes which can give a range max query for room sizes on a specific range.\nFor every query, I got the closest room\'s index with id closest to the prefered id by using treeset. Then binary search on left and right of that index for prefered size. On every step on binary search I had to query the segment tree for that range\'s maxsize.\nAfter both binary search I took the best of the right and left.\n\n# **Complexity**\nAssume number of rooms is n\nand number of queries is q\n\n**Preprocessing complexity:** n*log*(n)\n**Query Complexity:** q*log*<sup>2</sup>(n) -> (*log*<sup>2</sup>(n) for each query)\n<br>\n**Total Complexity:** <h4>n*log*(n) + q*log*<sup>2</sup>(n)</h4>\n\n# **Code**\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n int n = rooms.length;\n int[] ids = new int[n];\n Arrays.sort(rooms, new Comparator<int[]>() {\n public int compare(int[] a, int[] b) {\n return Integer.compare(a[0],b[0]);\n }\n });\n int[] sizes = new int[n];\n TreeMap<Integer,Integer> map = new TreeMap();\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n int id = rooms[i][0];\n int size = rooms[i][1];\n ids[i] = id;\n sizes[i] = size;\n }\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n map.put(ids[i],i);\n }\n int[] ans = new int[queries.length];\n SegMax segmax = new SegMax(0,n-1,sizes);\n for(int qq = 0; qq < queries.length; qq++) {\n int pid = queries[qq][0];\n Integer up = map.ceilingKey(pid);\n Integer down = map.floorKey(pid);\n int ppid = pid;\n if(up==null) pid =down;\n if(down==null) pid =up;\n if(up!=null && down!=null) {\n int upDiff = Math.abs(up-pid);\n int downDiff = Math.abs(down-pid);\n if(upDiff<downDiff) pid = up;\n else pid = down;\n }\n int psize = queries[qq][1];\n int right = map.get(pid);\n int left = right;\n int at = left;\n int l = 0;\n int r = right;\n int leftIdx = -1;\n int rightIdx = -1;\n while(l<=r) {\n int mid = (l+r)>>1;\n int nowMax = segmax.query(mid,right);\n if(nowMax>=psize) {\n leftIdx = mid;\n l = mid+1;\n } else {\n r = mid-1;\n }\n }\n l = left;\n r = n-1;\n while(l<=r) {\n int mid = (l+r)>>1;\n int nowMax = segmax.query(left,mid);\n if(nowMax>=psize) {\n rightIdx = mid;\n r = mid-1;\n } else {\n l = mid+1;\n }\n }\n pid = ppid;\n if(leftIdx!=-1 && rightIdx!=-1) {\n int leftAns = ids[leftIdx];\n int rightAns = ids[rightIdx];\n int leftAbs = Math.abs(pid-leftAns);\n int rightAbs = Math.abs(pid-rightAns);\n if(leftAbs==rightAbs) ans[qq] = leftAns;\n else if(leftAbs<rightAbs) ans[qq] = leftAns;\n else ans[qq] = rightAns;\n } else if(leftIdx!=-1) {\n ans[qq] = ids[leftIdx];\n } else if(rightIdx!=-1) {\n ans[qq] = ids[rightIdx];\n } else {\n ans[qq] = -1;\n }\n \n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n\nclass SegMax {\n int leftMost, rightMost, mid;\n boolean leaf;\n int max;\n SegMax lchild, rchild;\n \n SegMax(int l, int r, int[] arr) {\n leftMost = l;\n rightMost = r;\n mid = (l+r)>>1;\n leaf = l==r;\n if(leaf) max =arr[l];\n else {\n lchild = new SegMax(l,mid,arr);\n rchild = new SegMax(mid+1,r,arr);\n max = Math.max(lchild.max,rchild.max);\n }\n }\n \n int query(int l, int r) {\n if(l>rightMost || r<leftMost) return Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n if(l<=leftMost && rightMost<=r) return max;\n return Math.max(lchild.query(l,r),rchild.query(l,r));\n }\n}\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
closest-room
|
C++ | Binary search
|
c-binary-search-by-tanishbothra22-0at8
|
\nvector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n \n int i=0;\n int n=rooms.size();\n int m=queries.
|
tanishbothra22
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T18:49:33.037539+00:00
|
2021-05-01T18:49:33.037579+00:00
| 185 | false |
```\nvector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n \n int i=0;\n int n=rooms.size();\n int m=queries.size();\n for(auto &x:queries){\n x.push_back(i);\n i++;\n }\n \n sort(begin(rooms),end(rooms),[](const vector<int>&v1,const vector<int>&v2){\n return v1[1]>v2[1]; \n });\n \n sort(begin(queries),end(queries),[](const vector<int>&v3,const vector<int>&v4){\n return v3[1]>v4[1]; \n });\n \n i=0;\n vector<int>res(m,-1);\n set<int>s;\n for(auto &y : queries){\n while(i<n&& rooms[i][1]>= y[1]){\n s.insert(rooms[i][0]);\n i++;\n }\n auto it = s.lower_bound(y[0]);\n if(it!=s.end()){ \n res[y[2]] =*it;\n }\n\t\t//if no lower bound and set size>0 take the last set element \n if(it==s.end() && s.size()>0){\n it--;\n res[y[2]]=*it;\n continue; \n }\n //suppose searching for 5 and set currently has elements 4,7,8 lower bound will point at 7 but abs(4-5)<(7-5) so we need to check 1 element before also\n int diff= abs(*it-y[0]);\n if(it!=begin(s)){\n it--;\n if(abs(*it-y[0])<=diff){\n res[y[2]]=*it;\n }\n \n }\n \n }\n \n \n return res;\n \n \n \n }\n\n```
| 1 | 1 |
['C', 'Binary Tree']
| 1 |
closest-room
|
Javascript - finally got it fast enough
|
javascript-finally-got-it-fast-enough-by-9b9m
|
\n/**\n * @param {number[][]} rooms\n * @param {number[][]} queries\n * @return {number[]}\n */\nvar closestRoom = function(rooms, queries) {\n let minId = 1
|
MarkFarmiloe
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T17:38:02.032677+00:00
|
2021-05-01T17:38:02.032728+00:00
| 88 | false |
```\n/**\n * @param {number[][]} rooms\n * @param {number[][]} queries\n * @return {number[]}\n */\nvar closestRoom = function(rooms, queries) {\n let minId = 10000001, maxId = 0;\n let maxSize = 0;\n rooms.forEach(r => {\n minId = minId < r[0] ? minId : r[0];\n maxId = maxId > r[0] ? maxId : r[0];\n maxSize = maxSize > r[1] ? maxSize : r[1];\n });\n const sizes = new Int32Array(maxId - minId + 1);\n rooms.forEach(r => {\n sizes[r[0] - minId] = r[1];\n });\n const answers = queries.map(([id, size]) => {\n if (size > maxSize) return -1;\n if (id > maxId) id = maxId;\n if (sizes[id - minId] >= size) return id;\n let idd = id - minId - 1, idu = id - minId + 1, sizeLen = sizes.length;\n while (true) {\n if (idd >= 0) {\n if (sizes[idd] >= size) return idd + minId;\n }\n if (idu <= sizeLen) {\n if (sizes[idu] >= size) return idu + minId;\n }\n idd--;\n idu++;\n }\n });\n return answers;\n};\n```\n
| 1 | 1 |
[]
| 2 |
closest-room
|
[Python 3] Tree Solution (100% time 100% space)
|
python-3-tree-solution-100-time-100-spac-ig3u
|
When you first look at this problem, you already know that you have to use binary search when searching for the ideal room for each query because linear search
|
triplewy
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T17:20:10.733304+00:00
|
2021-05-01T17:21:16.199311+00:00
| 248 | false |
When you first look at this problem, you already know that you have to use binary search when searching for the ideal room for each query because linear search is trivial to implement.\n\nThe difficult part is figuring out how to perform binary search on the subset of rooms where room_size >= preferred_size and where that subset is sorted by room_id.\n\nThe key to solving the above statement requires the following steps:\n\n1. Sort the rooms and queries by room size in descending order. This allows us to grow our subset of rooms to search without having to remove any rooms. (Example: a query with preferred size 1 will always include all the rooms for a query with preferred size 2)\n2. When iterating through each query, you will add the new rooms into your search data structure. It is necessary for this data structure to have O(logn) insert and O(logn) search. That is a binary tree. If you want to get fancy, you can say AVL tree.\n3. Search the binary tree for the best room_id and add it to your result array \n\n\n```\nclass Node:\n def __init__(self, val):\n self.val = val\n self.left = None\n self.right = None\n \nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n\t\t# sort by room size\n\t\trooms.sort(key=lambda x: -x[1])\n queries = sorted([[q[0], q[1], i] for i, q in enumerate(queries)], key=lambda x: -x[1])\n \n\t\t# pointer for iterating through your rooms in one pass\n r = 0\n \n root = None\n res = [-1] * len(queries)\n\n # pref size is going to be in descending order\n for pref_id, pref_size, index in queries:\n \n\t\t\t# add room_ids to your tree data structure\n while r < len(rooms) and rooms[r][1] >= pref_size:\n room_id = rooms[r][0]\n if root is None:\n root = Node(room_id)\n else:\n insert(root, room_id)\n \n r += 1\n\n\t\t\t# search your tree data structure for best room_id\n if root is not None:\n res[index] = search(root, pref_id, math.inf)\n \n return res\n \ndef insert(root, val):\n # each val is guaranteed to be unique\n if val < root.val:\n if root.left is None:\n root.left = Node(val)\n return\n else:\n return insert(root.left, val)\n else:\n if root.right is None:\n root.right = Node(val)\n return\n else:\n return insert(root.right, val)\n\ndef search(root, val, res):\n if abs(val - root.val) < abs(val - res):\n res = root.val\n \n elif abs(val - root.val) == abs(val - res):\n res = min(res, root.val)\n \n if val < root.val:\n if root.left is None:\n return res\n else:\n return search(root.left, val, res)\n else:\n if root.right is None:\n return res\n else:\n return search(root.right, val, res)\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Tree', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 1 |
closest-room
|
C# solution - all test cases passed but took too long to execute?! Java version gets accepted
|
c-solution-all-test-cases-passed-but-too-c73l
|
I can\'t figure out what\'s wrong with my solution so I would appreacite if anyone can look into it. It passes all test casses but I get "41 / 41 test cases pas
|
milosk
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T16:59:44.163856+00:00
|
2021-05-01T22:23:20.793051+00:00
| 329 | false |
I can\'t figure out what\'s wrong with my solution so I would appreacite if anyone can look into it. It passes all test casses but I get **"41 / 41 test cases passed, but took too long."** Thanks.\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public int[] ClosestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n Array.Sort(rooms, (item1, item2) => item1[1].CompareTo(item2[1]));\n var result = new int[queries.Length];\n var resultIndex = 0;\n \n foreach(var query in queries)\n {\n var minDifference = int.MaxValue;\n var minId = int.MaxValue;\n \n var roomSizeStartIndex = GetStartIndexForRoomSize(query[1], rooms);\n \n if(roomSizeStartIndex != -1)\n {\n for(int i = roomSizeStartIndex; i < rooms.Length; i++)\n {\n var room = rooms[i];\n\n if(room[1] >= query[1])\n {\n var roomIdDifference = Math.Abs(query[0] - room[0]);\n\n if(roomIdDifference < minDifference || (roomIdDifference == minDifference && room[0] < minId))\n {\n minDifference = roomIdDifference;\n minId = room[0];\n }\n }\n }\n }\n \n if(minDifference == int.MaxValue)\n minId = -1;\n \n result[resultIndex++] = minId;\n }\n \n return result;\n }\n \n private int GetStartIndexForRoomSize(int targetSize, int[][] rooms)\n {\n var left = 0;\n var right = rooms.Length - 1;\n var startIndex = -1;\n \n while(left <= right)\n {\n var mid = left + (right - left) / 2;\n \n if(rooms[mid][1] >= targetSize)\n {\n right = mid - 1;\n startIndex = mid;\n }\n else\n left = mid + 1;\n }\n \n return startIndex;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 3 |
closest-room
|
Easy C++ solution using set.
|
easy-c-solution-using-set-by-f1re-8hl9
|
Sort queries and rooms by room size, largest first.\nFor the largest query, insert all rooms <= largest query into a set.\nThese rooms will be common for this q
|
f1re
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T16:41:38.414813+00:00
|
2021-05-01T16:41:38.414850+00:00
| 139 | false |
Sort queries and rooms by room size, largest first.\nFor the largest query, insert all rooms <= largest query into a set.\nThese rooms will be common for this query as well as all the queries later in the array with smaller room size.\n\n```\nvector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n int idx = 0;\n for (auto& q : queries) q.push_back(idx++);\n\n auto f = [&](const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b) { return a[1] > b[1]; };\n sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), f);\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end(), f);\n \n set<int> cans;\n vector<int> result(queries.size());\n idx = 0; // for rooms now\n for (auto& q : queries) {\n while (idx < rooms.size() && q[1] <= rooms[idx][1]) cans.insert(rooms[idx++][0]);\n if (cans.size() == 0) result[q[2]] = -1;\n else {\n auto it = cans.upper_bound(q[0]);\n int r = 20000001;\n if (it != cans.end()) r = *it;\n if (it != cans.begin()) {\n --it;\n if (q[0] - *it <= r - q[0]) r = *it;\n }\n result[q[2]] = r;\n }\n }\n return result;\n }\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Java | Sort and Loop through arrays| Explained with Comments
|
java-sort-and-loop-through-arrays-explai-ges5
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n //If you do not sort then we will have to scan all romes. Best is to
|
ravikrishnap
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T16:07:50.052177+00:00
|
2021-05-01T16:07:50.052202+00:00
| 77 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n //If you do not sort then we will have to scan all romes. Best is to sort. so we can break loop early when we hit values that wont satisfy the min space.\n //If did not do this at first place and hit TLE\n Arrays.sort(rooms, (r1,r2) -> Integer.compare(r2[1], r1[1]));\n \n int[] result = new int[queries.length];\n \n int resultIndex = 0;\n //For each query\n for(int[] query : queries) {\n int minId = -1;\n int minIdDiff = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n //Loop through all rooms\n for(int roomIndex = 0; roomIndex < rooms.length; roomIndex++) {\n //if the space satisfies\n if(query[1] <= rooms[roomIndex][1]) {\n //Find the difference in id\n int iDdiff = Math.abs(query[0] - rooms[roomIndex][0]);\n if(iDdiff < minIdDiff) {\n //If this diff is less than previus then use it\n minIdDiff = iDdiff;\n minId = rooms[roomIndex][0];\n } else if(iDdiff == minIdDiff) {\n //If this diff is equal than find if this is less than previous id. THis is the tie problem was talking about.\n //NOTE: You can merge some if-else conditions as you need. Seperated for readability.\n if(minId > rooms[roomIndex][0]) {\n minId = rooms[roomIndex][0];\n }\n }\n } else { //if space does not satisfy then none to right satisfies and we can break the loop\n break;\n }\n }\n //Assign the so far min id found. if not found it will be -1\n result[resultIndex++] = minId;\n }\n //return the result array\n return result;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
closest-room
|
[C++] Sorted the Queries and Rooms . Still Getting TLE , plz review the code
|
c-sorted-the-queries-and-rooms-still-get-ny1q
|
\nset<int>st;\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n sort(rooms.begin(),ro
|
lakh
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-01T16:06:35.775273+00:00
|
2021-05-01T16:06:35.775311+00:00
| 116 | false |
```\nset<int>st;\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n sort(rooms.begin(),rooms.end(),[&](vector<int>p,vector<int>q){\n return p[1]>q[1];\n });\n int n=queries.size();\n vector<int>ans(n);\n int ix=0;\n for(vector<int>&v:queries) {\n v.push_back(ix++);\n }\n sort(queries.begin(),queries.end(),[&](vector<int>p,vector<int>q){\n return p[1]>q[1];\n });\n ix=0;\n st.clear();\n for(vector<int>v:queries) {\n while(ix<rooms.size() && rooms[ix][1]>=v[1]) {\n st.insert(rooms[ix][0]);\n ix+=1;\n }\n int cid=v[0];\n if(st.size()==0) ans[v[2]]=-1;\n else {\n auto it = st.lower_bound(cid);\n int re=INT_MAX,rix=-1;\n if(it==st.end()) {\n ans[v[2]]=*st.rbegin();\n }\n else {\n int diff = *it-cid;\n if(re>diff){\n re=diff;\n rix=*it;\n }\n if(it!=st.begin()) {\n it--;\n diff=cid-*it;\n if(re>=diff) re=diff, rix=*it;\n \n \n }\n ans[v[2]]=rix;\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Using SortedList
|
using-sortedlist-by-pranavkapparad30-ojnp
|
Code
|
pranavkapparad30
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-06T05:44:34.858544+00:00
|
2025-02-06T05:44:34.858544+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Code
```python3 []
from sortedcontainers import SortedList
class Solution:
def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
rooms.sort(key=lambda x: -x[1])
queries = sorted(enumerate(queries), key=lambda x: -x[1][1])
res = [-1] * len(queries)
valid_rooms = SortedList()
i = 0
for idx, (room_id, min_size) in queries:
while i < len(rooms) and rooms[i][1] >= min_size:
valid_rooms.add(rooms[i][0])
i += 1
if not valid_rooms:
continue
pos = valid_rooms.bisect_left(room_id)
candidates = []
if pos < len(valid_rooms):
candidates.append(valid_rooms[pos])
if pos > 0:
candidates.append(valid_rooms[pos - 1])
res[idx] = min(candidates, key=lambda x: (abs(x - room_id), x))
return res
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Binary Search | Sorting | Without Set
|
binary-search-sorting-without-set-by-vis-n6o4
|
Complexity
Time complexity:
O(nlogn + m* (logn + n) ) where n:rooms.length , m=queries.length
Space complexity:
O(1) if not considered answer array which we hav
|
Vishnoi04
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-29T13:58:28.110542+00:00
|
2025-01-29T13:58:28.110542+00:00
| 11 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(nlogn + m* (logn + n) ) where n:rooms.length , m=queries.length
- Space complexity:
O(1) if not considered answer array which we have to return
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int findIndex(int num,vector<vector<int>>&rooms){
int n=rooms.size();
int l=0,r=n-1;
int index=-1;
while(l<=r){
int mid=(l+r)/2;
if(rooms[mid][1]<num){
l=mid+1;
}
else{
index=mid;
r=mid-1;
}
}
return index;
}
int findIndex_(int ind,vector<vector<int>>&rooms,int id){
int ans=ind;
int mini=abs(rooms[ind][0]-id);
for(int i=ind+1;i<rooms.size();i++){
int diff=abs(rooms[i][0]-id);
if(diff<mini){
mini=diff;
ans=i;
}else if(diff==mini){
if(rooms[i][0]<rooms[ans][0]){
ans=i;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
//sort rooms according to size
sort(rooms.begin(),rooms.end(),[](vector<int>&a,vector<int>&b){
if(a[1]<b[1] || (a[1]==b[1] && a[0]<b[0])){
return true;
}
return false;
});
for(auto i : rooms){
cout<<i[0]<<" "<<i[1]<<endl;
}
int maxSize=rooms[rooms.size()-1][1];
vector<int>res;
for(auto i : queries){
int id=i[0],minSize=i[1];
if(maxSize<minSize){
res.push_back(-1);
continue;
}
int index1=findIndex(minSize,rooms);
// cout<<index1<<endl;
int index2=findIndex_(index1,rooms,id);
res.push_back(rooms[index2][0]);
}
return res;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Binary Search', 'Sorting', 'C++']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Sort the rooms and queries by roomSize
|
sort-the-rooms-and-queries-by-roomsize-b-xi2k
|
Code
|
siic
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-02T08:25:34.556035+00:00
|
2025-01-02T08:25:34.556035+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
int n = rooms.size(), k = queries.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
reverse(rooms[i].begin(), rooms[i].end());
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
reverse(queries[i].begin(), queries[i].end());
queries[i].push_back(i);
}
sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end());
sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());
vector<int> res(k, -1);
set<int> inds;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
inds.insert(rooms[i][1]);
}
int i = 0;
for (auto& qu : queries) {
int minSz = qu[0], id = qu[1], j = qu[2];
while (i < n && rooms[i][0] < minSz) {
inds.erase(rooms[i++][1]);
}
if (inds.empty()) break;
if (id <= *inds.begin()) {
res[j] = *inds.begin();
} else if (id >= *inds.rbegin()) {
res[j] = *inds.rbegin();
} else {
auto it1 = inds.lower_bound(id);
auto it2 = it1;
if (it2 != inds.begin()) {
--it2;
}
res[j] = (abs(id - *it1) < abs(id - *it2) ? *it1 : *it2);
}
}
return res;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Java simple binary search beats 100%
|
java-simple-binary-search-beats-100-by-i-6ehb
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
siyang_yin
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-26T03:22:14.984275+00:00
|
2024-11-26T03:22:14.984312+00:00
| 11 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n*log(n))\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n*log(n))\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] a, int[][] q) {\n int n = q.length;\n int[] res = new int[n];\n int min = Arrays.stream(q).mapToInt(i -> i[1]).min().getAsInt();\n List<int[]> a1 = new ArrayList<>();\n Arrays.stream(a).filter(i -> i[1] >= min).forEach(i -> a1.add(i));\n int m = a1.size();\n a1.sort((i1, i2) -> i1[0] - i2[0]);\n int[] b = a1.stream().mapToInt(i -> i[0]).toArray();\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n int j = Arrays.binarySearch(b, q[i][0]);\n if (j < 0) j = - (j + 1);\n if (j == m) j--;\n int l = j - 1, r = j;\n while (l >= 0 && a1.get(l)[1] < q[i][1]) l--;\n while (r >= 0 && r < m && a1.get(r)[1] < q[i][1]) r++;\n if (l >= 0 && a1.get(l)[1] >= q[i][1] && (r == m || q[i][0] - b[l] <= b[r] - q[i][0])) {\n res[i] = b[l];\n }\n else if (r >= 0 && r < m && a1.get(r)[1] >= q[i][1] && (l < 0 || q[i][0] - b[l] > b[r] - q[i][0])) {\n res[i] = b[r];\n }\n else res[i] = -1;\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Binary Search', 'Sorting', 'Java']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
1847. Closest Room.cpp
|
1847-closest-roomcpp-by-202021ganesh-aef1
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.
|
202021ganesh
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-17T10:09:34.507121+00:00
|
2024-10-17T10:09:34.507152+00:00
| 6 | false |
**Code**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.size(); ++i) queries[i].push_back(i); \n sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), [](auto& lhs, auto& rhs){ return lhs[1] > rhs[1]; }); \n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end(), [](auto& lhs, auto& rhs){ return lhs[1] > rhs[1]; }); \n set<int> st; \n vector<int> ans(queries.size(), -1); \n for (int i = 0, k = 0; i < queries.size(); ++i) {\n while (k < rooms.size() && rooms[k][1] >= queries[i][1]) \n st.insert(rooms[k++][0]); \n if (st.size()) {\n auto it = st.upper_bound(queries[i][0]); \n int diff = INT_MAX; \n if (it != st.end()) diff = *it - queries[i][0]; \n if (it != st.begin() && queries[i][0] - *prev(it) <= diff) --it; \n ans[queries[i][2]] = *it; \n } \n }\n return ans; \n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Easy C++ Binary Search Solution || No Set Used
|
easy-c-binary-search-solution-no-set-use-q6sq
|
\n\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n static bool cmp(vector<int>&a,vector<int>&b)\n {\n if(a[1]==b[1])\n {\n return a[
|
NehaGupta_09
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-20T13:30:09.453205+00:00
|
2024-09-20T13:30:09.453230+00:00
| 8 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n static bool cmp(vector<int>&a,vector<int>&b)\n {\n if(a[1]==b[1])\n {\n return a[0]<b[0];\n }\n return a[1]<b[1];\n }\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& q) {\n //sort on the basis of rooms\n sort(rooms.begin(),rooms.end(),cmp);\n vector<int>ans;\n for(int i=0;i<q.size();i++)\n {\n int pref_id=q[i][0];\n int min_size=q[i][1];\n ans.push_back(fun(rooms,min_size,pref_id));\n }\n return ans;\n }\n int fun(vector<vector<int>>&rooms,int &ms,int &pId)\n {\n int start=0;\n int end=rooms.size()-1;\n int idx=-1;\n int mid;\n while(start<=end)\n {\n mid=(start+end)/2;\n if(rooms[mid][1]>=ms)\n {\n idx=mid;\n end=mid-1;\n }\n else\n {\n start=mid+1;\n }\n }\n if(idx==-1)\n return -1;\n return fun2(rooms,idx,pId);\n }\n int fun2(vector<vector<int>>&rooms,int &idx,int &pId)\n {\n //we have to find the number closest to pId\n //number having least distance from pId\n int diff=abs(pId-rooms[idx][0]);\n int ans=rooms[idx][0];\n for(int i=idx+1;i<rooms.size();i++)\n {\n int temp=abs(pId-rooms[i][0]);\n if(temp<diff)\n {\n diff=temp;\n ans=rooms[i][0];\n }\n else if(temp==diff)\n {\n ans=min(ans,rooms[i][0]);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Binary Search', 'Sorting', 'C++']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
My Solution
|
my-solution-by-hope_ma-cwb7
|
\n/**\n * Time Complexity: O(n_rooms * log(n_rooms) + n_queries * (log(n_rooms) + log(n_queries)))\n * Space Complexity: O(n_rooms + n_queries)\n * where `n_roo
|
hope_ma
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-11T03:09:07.937607+00:00
|
2024-09-11T03:09:16.358325+00:00
| 0 | false |
```\n/**\n * Time Complexity: O(n_rooms * log(n_rooms) + n_queries * (log(n_rooms) + log(n_queries)))\n * Space Complexity: O(n_rooms + n_queries)\n * where `n_rooms` is the length of the vector `rooms`\n * `n_queries` is the length of the vector `queries`\n */\nclass Solution {\n public:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>> &rooms, const vector<vector<int>> &queries) {\n constexpr int invalid_room_id = -1;\n sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), [](const vector<int> &lhs, const vector<int> &rhs) -> bool {\n return lhs.back() > rhs.back();\n });\n \n const int n = static_cast<int>(rooms.size());\n const int n_queries = static_cast<int>(queries.size());\n int indices[n_queries];\n iota(indices, indices + n_queries, 0);\n sort(indices, indices + n_queries, [&queries](const int lhs, const int rhs) -> bool {\n return queries[lhs].back() > queries[rhs].back();\n });\n \n vector<int> ret(n_queries);\n set<int> available_rooms;\n for (int i_room = 0, i_query = 0; i_query < n_queries; ++i_query) {\n const int index = indices[i_query];\n const int preferred_room_id = queries[index].front();\n const int min_room_size = queries[index].back();\n for (; i_room < n && rooms[i_room].back() >= min_room_size; ++i_room) {\n available_rooms.emplace(rooms[i_room].front());\n }\n \n if (available_rooms.empty()) {\n ret[index] = invalid_room_id;\n continue;\n }\n \n ret[index] = numeric_limits<int>::max();\n auto ub = available_rooms.upper_bound(preferred_room_id);\n if (ub != available_rooms.end()) {\n ret[index] = *ub;\n }\n if (ub != available_rooms.begin() && preferred_room_id - *prev(ub) <= ret[index] - preferred_room_id) {\n ret[index] = *prev(ub);\n }\n }\n return ret;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Python, sort queries and rooms and maintain sorted array of possible ids.
|
python-sort-queries-and-rooms-and-mainta-63q9
|
Intuition\n\nFor every query of (preferred_id, size) you need to find the most suitable id which has at least size. To do this, sort all the values of rooms bas
|
salvadordali
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-08T02:48:51.484728+00:00
|
2024-07-08T02:48:51.484757+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Intuition\n\nFor every query of `(preferred_id, size)` you need to find the most suitable `id` which has at least `size`. To do this, sort all the values of rooms based on `size` (I sort in decreasing order, but it does not matter).\n\nNow if you sort all the queries (same order by `size` and remember the position) you can iterate over queries and get all the ids which suit `size >= size_q`. Now when you do this you maintain a sorted list of the possible ids (you can do this with sorted containers).\n\nNow when you added everything, you do a binary search to find which id is the closest.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $O(n \\log n)$\n- Space complexity: $O(n)$\n\n# Code\n```\nfrom sortedcontainers import SortedList\n\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n rooms.sort(key=lambda x: -x[1])\n queries = [(queries[i][0], queries[i][1], i) for i in range(len(queries))]\n queries.sort(key=lambda x: -x[1])\n\n list_ids, pos, res = SortedList([]), 0, [-1] * len(queries)\n for pid, size, i in queries:\n while pos < len(rooms) and rooms[pos][1] >= size:\n list_ids.add(rooms[pos][0])\n pos += 1\n\n if not list_ids:\n res[i] = -1\n else:\n p = list_ids.bisect_left(pid)\n if p == 0:\n res[i] = list_ids[0]\n elif p == len(list_ids):\n res[i] = list_ids[-1]\n else:\n if abs(list_ids[p - 1] - pid) <= abs(list_ids[p] - pid):\n res[i] = list_ids[p - 1]\n else:\n res[i] = list_ids[p]\n \n return res\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Easy To Understand Beginner Friendly and Self Explanatory Solution In JAVA
|
easy-to-understand-beginner-friendly-and-viyt
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n Arrays.sort(rooms, new Comparator<int[]>(){\n
|
ArchitVohra
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-17T19:01:06.559470+00:00
|
2024-06-17T19:01:06.559535+00:00
| 30 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n Arrays.sort(rooms, new Comparator<int[]>(){\n @Override\n public int compare(int[] a, int[] b){\n return a[1]-b[1];\n }\n });\n int[] ans = new int[queries.length];\n int ptr = 0;\n for(int[] q:queries){\n int prefId = q[0];\n int minSize = q[1];\n int left = 0, right = rooms.length-1;\n while(left<=right){\n int mid = left+(right-left)/2;\n if(rooms[mid][1]>=minSize) right = mid - 1;\n else left = mid + 1;\n }\n if(left==rooms.length){\n ans[ptr++] = -1;\n continue;\n }\n int nearestId = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n int minDiff = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n while(left<rooms.length){\n if(Math.abs(rooms[left][0]-prefId)<minDiff){\n minDiff = Math.abs(rooms[left][0]-prefId);\n nearestId = rooms[left][0];\n }else if(Math.abs(rooms[left][0]-prefId)==minDiff){\n nearestId = Math.min(nearestId, rooms[left][0]);\n }\n left++;\n }\n ans[ptr++] = nearestId;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Binary Search', 'Sorting', 'Java']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Better Way | 2 TreeMaps | Java | Binary Search | O(N*logM + M*logN)
|
better-way-2-treemaps-java-binary-search-pwr2
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Anas10005
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-12T08:04:08.670466+00:00
|
2024-06-12T11:42:11.707332+00:00
| 20 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(N*logM + M*logN)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(N)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nimport java.util.*;\n\nclass Solution {\n\n // Nested class to represent a room\n class Room {\n private int id;\n private int size;\n private int index; \n\n // Constructor to initialize room attributes\n public Room(int id, int size, int index) {\n this.id = id;\n this.size = size;\n this.index = index;\n }\n\n // Getter method for room ID\n public int getId() {\n return id;\n }\n\n // Getter method for room size\n public int getSize() {\n return size;\n }\n\n // Getter method for room index in the original array\n public int getIndex() {\n return index;\n }\n\n // Override toString() method for better representation of Room object\n @Override\n public String toString() {\n return "Room{" +\n "id=" + id +\n ", size=" + size + ", index=" + index +\n \'}\';\n }\n }\n\n // Method to find the closest room to each query\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n // Comparator based on size and index\n Comparator<Room> roomComparator = Comparator\n .comparingInt(Room::getSize) // Compare rooms by size\n .thenComparingInt(Room::getIndex); // If sizes are equal, compare by index\n\n // TreeMap sorted by room size and index\n TreeMap<Room, List<Integer>> sortedSize = new TreeMap<>(roomComparator);\n // TreeMap to store room IDs mapped to their indices in the original array\n TreeMap<Integer, Integer> sortedID = new TreeMap<>();\n\n // Populate sortedSize and sortedID maps\n for (int i = 0; i < rooms.length; i++) {\n // Create a Room object for the current room with its attributes\n Room room = new Room(rooms[i][0], rooms[i][1], i);\n // Add room to sortedSize with an empty list for query indices\n sortedSize.put(room, new ArrayList<>());\n // Add room ID to sortedID mapped to its index in the original array\n sortedID.put(rooms[i][0], i);\n }\n\n // Processing queries and populating sortedSize\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {\n int[] query = queries[i];\n int minRoomSize = query[1];\n // Find the smallest room greater than or equal to the query\'s minimum size\n Room foundRoom = sortedSize.ceilingKey(new Room(-1, minRoomSize, 0)); // Initialize index with 0\n if (foundRoom != null) {\n // Add query index to the list corresponding to the found room in sortedSize\n sortedSize.get(foundRoom).add(i);\n }\n }\n\n // Initialize the result array\n int[] res = new int[queries.length];\n Arrays.fill(res, -1);\n \n // Processing queries and populating result array\n for (Room room : sortedSize.keySet()) {\n for (int qIndex : sortedSize.get(room)) {\n int desiredRoomID = queries[qIndex][0];\n // Find the room ID just greater or equal to the desired room ID\n Integer justGreater = sortedID.ceilingKey(desiredRoomID);\n // Find the room ID just smaller or equal to the desired room ID\n Integer justSmaller = sortedID.floorKey(desiredRoomID);\n // Choose the closest room ID based on absolute difference\n if (justGreater == null) {\n res[qIndex] = justSmaller;\n } else if (justSmaller == null) {\n res[qIndex] = justGreater;\n } else {\n if (Math.abs(desiredRoomID - justGreater) < Math.abs(desiredRoomID - justSmaller)) {\n res[qIndex] = justGreater;\n } else {\n res[qIndex] = justSmaller;\n }\n }\n }\n // Remove the processed room ID from sortedID\n sortedID.remove(room.getId());\n }\n\n return res;\n }\n}\n\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Python, sort solution with explanation
|
python-sort-solution-with-explanation-by-k6lj
|
For each query, size of the candidate rooms >= size_q, we can find the candidate room from the bigger to smaller size.\n2. we can sort query by its size, and st
|
shun6096tw
|
NORMAL
|
2024-05-15T07:12:24.597953+00:00
|
2024-05-15T07:12:24.597987+00:00
| 7 | false |
1. For each query, size of the candidate rooms >= size_q, we can find the candidate room from the bigger to smaller size.\n2. we can sort query by its size, and start with the query with the biggest size_q\n3. put ID of all the candidate room into BST, and use binary seach to find the room with smallest abs(room id - id_q).\ntc is O(mlogm + nlogn + nlogm), sc is O(m+n).\n\n\n```python\nINF = int(1e9)\nfrom sortedcontainers import SortedList\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n m, n = len(rooms), len(queries)\n arr_room = sorted(range(m), key=lambda x: rooms[x][1], reverse=True)\n arr_q = sorted(range(n), key=lambda x: queries[x][1], reverse=True)\n ans = [-1] * n\n bst = SortedList()\n i = 0\n for x in arr_q:\n pref, size = queries[x]\n while i < m and rooms[arr_room[i]][1] >= size:\n bst.add(rooms[arr_room[i]][0])\n i += 1\n if bst:\n pos = bst.bisect_left(pref)\n cand1, cand2 = bst[pos] if pos < len(bst) else INF, bst[pos-1] if pos > 0 else INF\n ans[x] = cand1 if abs(cand1 - pref) < abs(cand2 - pref) else cand2\n return ans\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Binary Search Tree', 'Sorting', 'Python']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
C++ | Binary Search | O(N*(K+LogN)) Solution
|
c-binary-search-onklogn-solution-by-thec-1dj6
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n int n = rooms.size();\n sor
|
theCuriousCoder
|
NORMAL
|
2024-05-10T08:31:03.205092+00:00
|
2024-05-10T08:31:17.933623+00:00
| 6 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n int n = rooms.size();\n sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), [] (const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b) {\n return a[1] < b[1];\n });\n int k = queries.size();\n vector<int> output;\n for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) {\n int pref = queries[i][0];\n int minSize = queries[i][1];\n int lo = -1, hi = n-1;\n while(hi - lo > 1) {\n int mid = lo + (hi-lo)/2;\n if (rooms[mid][1] >= minSize) {\n hi = mid;\n } else {\n lo = mid;\n }\n }\n int idx = lo+1;\n if (rooms[idx][1] < minSize) {\n output.push_back(-1);\n continue;\n }\n int diff = abs(rooms[idx][0] - pref);\n int val = idx;\n for(int j = idx; j<n; j++) {\n int currDiff = abs(rooms[j][0]- pref);\n if(currDiff < diff) {\n val = j;\n diff = currDiff;\n } else if (currDiff == diff && rooms[j][0] < rooms[val][0]) {\n val = j;\n diff = currDiff;\n } \n }\n \n output.push_back(rooms[val][0]);\n }\n return output;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Easy C++ , Set and Sorting
|
easy-c-set-and-sorting-by-udaysinghp95-labj
|
Intuition\nSort by weight and put in set\n\n# Approach\nIf current is current then room weight then push rooom weight\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n L
|
udaysinghp95
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-27T09:58:08.692857+00:00
|
2024-03-27T09:58:08.692902+00:00
| 49 | false |
# Intuition\nSort by weight and put in set\n\n# Approach\nIf current is current then room weight then push rooom weight\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n Log (n))$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n static bool compare(vector<int> &a,vector<int> &b)\n {\n return a[1]>b[1];\n }\n\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& room, vector<vector<int>>& query) \n {\n int n=query.size();\n\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n query[i].push_back(i);\n\n sort(room.begin(),room.end(),compare);\n sort(query.begin(),query.end(),compare);\n\n set<int> st;\n int j=0;\n\n room.push_back({INT_MIN,INT_MIN});\n vector<int> res(n,-1);\n\n for(auto &q:query)\n {\n while(q[1]<=room[j][1])\n {\n st.insert(room[j][0]);\n j++;\n }\n\n int l = -1;\n int r = -1;\n\n auto it=(st.lower_bound(q[0]));\n it = it == st.end() && st.size() ? prev(it) : it;\n\n if(it!=st.end())\n {\n l = r =*it;\n\n if(q[0]<*it)\n {\n it=prev(it);\n l=it ==st.end()?l:*it;\n }else if(next(it)!=st.end())\n r=*next(it);\n \n }\n\n res[q[2]] = abs(l-q[0])<=abs(r-q[0])?l:r;\n }\n\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Simple python3 solution | 1636 ms - faster than 86.84% solutions
|
simple-python3-solution-1636-ms-faster-t-gn4z
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n \cdot \log(n) + k \cdot \log(k) + (k + n) \cdot \log(n)) = \n= O(n\cdot\log(n) + k\cdot\log(max(k, n)))\n Add your time compl
|
tigprog
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-16T17:49:40.855160+00:00
|
2024-02-16T17:49:40.855191+00:00
| 40 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n \\cdot \\log(n) + k \\cdot \\log(k) + (k + n) \\cdot \\log(n)) = $$\n$$= O(n\\cdot\\log(n) + k\\cdot\\log(max(k, n)))$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n + k)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\nwhere `n == rooms.length <= 10^5` and `k == queries.length <= 10^4`\n\nLet $$m = max(n, k)$$, then:\n- Time complexity: $$O(m \\cdot \\log(m))$$\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(m)$$\n\n# Code\n``` python3 []\nfrom sortedcontainers import SortedList\n\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n rooms.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])\n\n sorted_queries = sorted(\n (min_size, pref, i)\n for i, (pref, min_size) in enumerate(queries)\n )\n\n def get_room_id(sl, preferred):\n if len(sl) == 0:\n return -1\n\n index = sl.bisect_left(pref)\n if index == len(sl):\n return sl[-1]\n \n right = sl[index]\n if index != 0:\n left = sl[index - 1]\n if abs(left - preferred) <= abs(right - preferred):\n return left\n return right\n\n sl = SortedList()\n j = len(rooms) - 1\n result = {}\n\n for min_size, pref, i in reversed(sorted_queries):\n while j >= 0 and rooms[j][1] >= min_size:\n sl.add(rooms[j][0])\n j -= 1\n \n result[i] = get_room_id(sl, pref)\n \n return [j for _, j in sorted(result.items())]\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Binary Search', 'Sorting', 'Python3']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
python3 sorted list template
|
python3-sorted-list-template-by-0icy-o44a
|
\n\nfrom bisect import bisect_left as lower_bound\nfrom bisect import bisect_right as upper_bound\n\n\nclass FenwickTree:\n def __init__(self, x):\n b
|
0icy
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-10T09:39:38.324837+00:00
|
2024-02-10T09:39:38.324866+00:00
| 20 | false |
\n```\nfrom bisect import bisect_left as lower_bound\nfrom bisect import bisect_right as upper_bound\n\n\nclass FenwickTree:\n def __init__(self, x):\n bit = self.bit = list(x)\n size = self.size = len(bit)\n for i in range(size):\n j = i | (i + 1)\n if j < size:\n bit[j] += bit[i]\n\n def update(self, idx, x):\n """updates bit[idx] += x"""\n while idx < self.size:\n self.bit[idx] += x\n idx |= idx + 1\n\n def __call__(self, end):\n """calc sum(bit[:end])"""\n x = 0\n while end:\n x += self.bit[end - 1]\n end &= end - 1\n return x\n\n def find_kth(self, k):\n """Find largest idx such that sum(bit[:idx]) <= k"""\n idx = -1\n for d in reversed(range(self.size.bit_length())):\n right_idx = idx + (1 << d)\n if right_idx < self.size and self.bit[right_idx] <= k:\n idx = right_idx\n k -= self.bit[idx]\n return idx + 1, k\n\n\nclass SortedList:\n block_size = 700\n\n def __init__(self, iterable=()):\n self.macro = []\n self.micros = [[]]\n self.micro_size = [0]\n self.fenwick = FenwickTree([0])\n self.size = 0\n for item in iterable:\n self.insert(item)\n\n def insert(self, x):\n i = lower_bound(self.macro, x)\n j = upper_bound(self.micros[i], x)\n self.micros[i].insert(j, x)\n self.size += 1\n self.micro_size[i] += 1\n self.fenwick.update(i, 1)\n if len(self.micros[i]) >= self.block_size:\n self.micros[i:i + 1] = self.micros[i][:self.block_size >> 1], self.micros[i][self.block_size >> 1:]\n self.micro_size[i:i + 1] = self.block_size >> 1, self.block_size >> 1\n self.fenwick = FenwickTree(self.micro_size)\n self.macro.insert(i, self.micros[i + 1][0])\n\n def pop(self, k=-1):\n i, j = self._find_kth(k)\n self.size -= 1\n self.micro_size[i] -= 1\n self.fenwick.update(i, -1)\n return self.micros[i].pop(j)\n\n def __getitem__(self, k):\n i, j = self._find_kth(k)\n return self.micros[i][j]\n\n def count(self, x):\n return self.upper_bound(x) - self.lower_bound(x)\n\n def __contains__(self, x):\n return self.count(x) > 0\n\n def lower_bound(self, x):\n i = lower_bound(self.macro, x)\n return self.fenwick(i) + lower_bound(self.micros[i], x)\n\n def upper_bound(self, x):\n i = upper_bound(self.macro, x)\n return self.fenwick(i) + upper_bound(self.micros[i], x)\n\n def _find_kth(self, k):\n return self.fenwick.find_kth(k + self.size if k < 0 else k)\n\n def __len__(self):\n return self.size\n\n def __iter__(self):\n return (x for micro in self.micros for x in micro)\n\n def __repr__(self):\n return str(list(self))\n\n\n\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n d = defaultdict(int)\n que = sorted(queries,key = lambda a : a[1] , reverse = True)\n rooms.sort(key = lambda a : a[1] , reverse = True)\n s = SortedList()\n i = 0\n for a,b in que:\n while i<len(rooms) and rooms[i][1] >= b:\n s.insert(rooms[i][0])\n i+=1\n if not len(s):\n d[(a,b)] = -1\n else:\n ans = inf\n r = -1\n id = s.lower_bound(a)\n if 0<=id-1<len(s):\n if abs(s[id-1]-a) < ans:\n ans = abs(s[id-1]-a)\n r = s[id-1]\n if 0<=id<len(s):\n if abs(s[id]-a) < ans:\n ans = abs(s[id]-a)\n r = s[id]\n d[(a,b)] = r\n res = []\n for a,b in queries:\n res.append(d[(a,b)])\n return res\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
full comented solution py3 ))
|
full-comented-solution-py3-by-borkiss-ydx8
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
borkiss
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-28T21:13:01.262809+00:00
|
2024-01-28T21:13:01.262852+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def closestRoom(self, rooms: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:\n ans = [0] * len(queries)\n \n # Sort queries to handle largest size queries first\n q = deque(sorted([(size, room, i) for i, (room, size) in enumerate(queries)], key=lambda a: (-a[0], a[1], a[2])))\n\n # Sort rooms by descending size\n rooms = deque(sorted(rooms, key=lambda x: -x[1]))\n\n # Current available room ids\n cands = []\n \n while q:\n size, room, i = q.popleft()\n # Add room ids to candidates as long as the top of room size meets the requirements\n while rooms and rooms[0][1] >= size:\n bisect.insort(cands, rooms.popleft()[0])\n \n # If no room size available, return -1\n if not cands:\n ans[i] = -1\n \n # Else use bisect to find optimal room ids\n else:\n loc = bisect.bisect_left(cands, room)\n if loc == 0:\n ans[i] = cands[loc]\n elif loc == len(cands):\n ans[i] = cands[-1]\n else:\n ans[i] = cands[loc - 1] if room - cands[loc - 1] <= cands[loc] - room else cands[loc]\n \n return ans\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Persistent Ordered Set | No Query Sort | O(n lg n + k lg n) time | O(n lg n) space
|
persistent-ordered-set-no-query-sort-on-pv6gw
|
Intuition\nWe want to find the closest room. An ordered set solves this problem in O(\textrm{lg } n) time. However, there is an additional constraint: the room
|
calvinhigginspersonal
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-19T21:51:45.435683+00:00
|
2024-01-19T21:52:32.503345+00:00
| 27 | false |
# Intuition\nWe want to find the closest room. An ordered set solves this problem in $$O(\\textrm{lg } n)$$ time. However, there is an additional constraint: the room must have size greater than or equal to some threshold. If we had access to the ordered set that contained only the rooms with size greater than or equal to the threshold, this would be simple. Assuming the rooms are inserted with decreasing size, for each threshold we will have the correct ordered set at some timestep $$t$$. In fact, we can simply sort the queries and process them as we build the ordered set. \n\nWhile this is enough to solve the problem, this approach might not work in the real world. Queries are often not all known ahead of time. How can we solve this problem without sorting the queries? \n\n# Approach\n\nWe can save the state of the ordered set at each timestep $$t$$ during construction. Naively, this will take $$O(n^2)$$ space which leads to TLE. However, instead of cloning the entire set, we can only clone the parts that change. With a balanced tree, like an AVL tree, this is only $$O(\\textrm{lg } n)$$ nodes. Hence, each insertion will take $$O(\\textrm{lg } n)$$ memory and $$O(\\textrm{lg } n)$$ time. We can find the correct version of the ordered set for a given query with binary search in $$O(\\textrm{lg } n)$$ time. Hence, we can solve the problem in $$O(n \\textrm{ lg } n + k \\textrm{ lg } n)$$ time and $$O(n \\textrm{ lg } n)$$ space.\n\n# Analysis\n\nIt\'s interesting that all prior versions of the ordered set can be maintained while only incurring a log factor in the space complexity. The basic idea is that each insertion operation on a balanced binary tree can only change $$O(\\textrm{lg } n)$$ nodes and so each insertion only costs $$O(\\textrm{lg } n)$$ space.\n\nThe $$i$$-th insertion into the AVL tree will modify $$c_i \\textrm{ lg } i$$ nodes for some $$c_i > 0$$ since the AVL tree is balanced. The total number of modified nodes over all insertions is $$\\sum\\limits_{i=1}^n c_i \\textrm{ lg } i$$. Let $$c_{\\textrm{min}}$$ and $$c_{\\textrm{max}}$$ denote the smallest and largest $$c_i$$ respectively. \n\nNote that $$\\int\\limits_{1}^{n} c_{min} \\textrm{ lg } x \\leq \\sum\\limits_{i=1}^n c_i \\textrm{ lg } i \\leq \\int\\limits_{1}^{n} c_{max} \\textrm{ lg } (x + 1)$$. Also $$\\int\\limits_{1}^{n} c_{min} \\textrm{ lg } x = c_{min} (n \\textrm{ lg } n - n + C) = \\Theta(n \\textrm{ lg } n)$$ and $$\\int\\limits_{1}^{n} c_{max} \\textrm{ lg } x = c_{max} (n \\textrm{ lg } n - n + C) = \\Theta(n \\textrm{ lg } n)$$. Hence $$\\sum\\limits_{i=1}^n c_i \\textrm{ lg } i = \\Theta(n \\textrm{ lg } n)$$. \n\n# Code\n\nHere is a quick and dirty implementation. The underlying data structure for the persistent ordered set is a persistent AVL tree. The code is not great but hopefully it illustrates the main idea.\n\n```\nclass PersistentOrderedSet {\n\nprivate:\n\tstruct Node {\n\t\tint key;\n\t\tint height;\n\t\tNode* left;\n\t\tNode* right;\n\n\t\tNode(int key) : key(key), height(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) { }\n\t\tNode(int key, int height, Node* left, Node* right)\n\t\t\t: key(key), height(height), left(left), right(right) { }\n\t};\n\n\tvector<Node*> m_roots;\n\n\tint height(Node* root) {\n\t\treturn root != nullptr ? root->height : 0;\n\t}\n\n\tbool balanced(Node* left, Node* right) {\n\t\treturn abs(height(left) - height(right)) < 2;\n\t}\n\n\tNode* balance(Node* root, Node* left, Node* right, int key) {\n\t\tNode *a, *b, *c, *d, *x, *y, *z;\n\n\t\tif (height(left) - height(right) == 2) {\n\t\t\tif (key > left->key) {\n\t\t\t\tz = root;\n\t\t\t\tx = left;\n\t\t\t\td = right;\n\t\t\t\ta = x->left;\n\t\t\t\ty = x->right;\n\t\t\t\tb = y->left;\n\t\t\t\tc = y->right;\n\t\t\t} else {\n\t\t\t\tz = root;\n\t\t\t\ty = left;\n\t\t\t\td = right;\n\t\t\t\tx = y->left;\n\t\t\t\tc = y->right;\n\t\t\t\ta = x->left;\n\t\t\t\tb = x->right;\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t} else {\n\t\t\tif (key < right->key) {\n x = root;\n a = left;\n z = right;\n y = z->left;\n d = z->right;\n b = y->left;\n c = y->right;\n\t\t\t} else {\n\t\t\t\tx = root;\n a = left;\n y = right;\n b = y->left;\n z = y->right;\n c = z->left;\n d = z->right;\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t}\n\n\t\tauto xh = 1 + max(height(a), height(b));\n\t\tauto zh = 1 + max(height(c), height(d));\n\t\tauto yh = 1 + max(xh, zh);\n\n\t\treturn new Node(\n\t\t\ty->key, \n\t\t\tyh, \n\t\t\tnew Node(x->key, xh, a, b),\n\t\t\tnew Node(z->key, zh, c, d)\n\t\t);\n\t}\n\n\tNode* insert(Node* root, int key) {\n\t\tif (root == nullptr) {\n\t\t\treturn new Node(key);\n\t\t}\n\n\t\tif (key == root->key) {\n\t\t\treturn root;\n\t\t}\n\n\t\tauto left = root->left;\n\t\tauto right = root->right;\n\n\t\tif (key < root->key) {\n\t\t\tleft = insert(root->left, key);\n\t\t} else {\n\t\t\tright = insert(root->right, key);\n\t\t}\n\n\t\tif (balanced(left, right)) {\n\t\t\tauto h = 1 + max(height(left), height(right));\n\t\t\treturn new Node(root->key, h, left, right); \n\t\t}\n\n\t\treturn balance(root, left, right, key);\n\t}\n\n\tNode* predecessor(Node* root, int key) {\n if (root == nullptr) {\n return nullptr;\n }\n\n if (key == root->key && root->left != nullptr) {\n auto pred = root->left;\n while (pred->right != nullptr) {\n pred = pred->right;\n }\n return pred;\n }\n\n if (key <= root->key) {\n return predecessor(root->left, key);\n }\n\n auto pred = predecessor(root->right, key);\n return pred == nullptr || root->key > pred->key ? root : pred;\n }\n\n\n Node* successor(Node* root, int key) {\n if (root == nullptr) {\n return nullptr;\n }\n\n if (key == root->key && root->right != nullptr) {\n auto succ = root->right;\n while (succ->left != nullptr) {\n succ = succ->left;\n }\n return succ;\n }\n\n if (key >= root->key) {\n return successor(root->right, key);\n }\n\n auto succ = successor(root->left, key);\n return succ == nullptr || root->key < succ->key ? root : succ;\n }\n\npublic:\n\tPersistentOrderedSet() : m_roots{nullptr} { }\n\n\tvoid insert(int key) {\n\t\tauto root = insert(m_roots.back(), key);\n\t\tm_roots.push_back(root);\n\t}\n\n\toptional<int> predecessor(int t, int key) {\n\t\tauto pred = predecessor(m_roots[t], key);\n\t\tif (pred == nullptr)\n\t\t\treturn nullopt;\n\t\treturn make_optional(pred->key);\n\t}\n\n\toptional<int> successor(int t, int key) {\n\t\tauto succ = successor(m_roots[t], key);\n\t\tif (succ == nullptr)\n\t\t\treturn nullopt;\n\t\treturn make_optional(succ->key);\n\t}\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n auto cmp = [](const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b) {\n return a[1] < b[1];\n };\n\n sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), cmp);\n\n PersistentOrderedSet s;\n for (int i = rooms.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {\n s.insert(rooms[i][0]);\n }\n\n vector<int> ans;\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.size(); ++i) {\n auto t = rooms.end() - lower_bound(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), queries[i], cmp);\n auto pred = s.predecessor(t, queries[i][0] + 1);\n auto succ = s.successor(t, queries[i][0] - 1);\n\n if (pred == nullopt && succ == nullopt) {\n ans.push_back(-1);\n } else if (pred == nullopt) {\n ans.push_back(succ.value());\n } else if (succ == nullopt) {\n ans.push_back(pred.value());\n } else if (queries[i][0] - pred.value() <= succ.value() - queries[i][0]) {\n ans.push_back(pred.value());\n } else {\n ans.push_back(succ.value());\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Binary Search', 'Ordered Set', 'C++']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Typescript with Clean Code! using Sort and Binary Search
|
typescript-with-clean-code-using-sort-an-qd27
|
Approach\n - Sort the rooms to be able to binary seach\n - Binary search to get the first room with size equals or greated then the min size\n - Then search for
|
matheus-foscarinid
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-12T20:21:48.877129+00:00
|
2024-01-12T20:21:48.877156+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Approach\n - Sort the rooms to be able to binary seach\n - Binary search to get the first room with size equals or greated then the min size\n - Then search for the one with the min abs, if none answer is -1\n - Repeat for every query\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(m * (log n + n))$$, where m is the number of queries, and n is the number of rooms.\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(1)$$ ignoring the space required to answer\n\n# Code\n```\nfunction closestRoom(rooms: number[][], queries: number[][]): number[] {\n const results: number[] = [];\n\n rooms.sort((r1, r2) => r1[1] - r2[1]);\n\n for (let i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {\n const [preferred, minSize] = queries[i];\n let response = -1;\n\n // Find the first room with size >= minSize\n let start = binarySearch(rooms, minSize);\n\n if (start !== -1) {\n // If there is a room with size >= minSize find the closest room to preferred\n let index = findClosestRoom(rooms, start, preferred);\n response = rooms[index][0];\n }\n\n results.push(response)\n }\n\n return results;\n};\n\nfunction binarySearch(rooms: number[][], size: number): number {\n let low = 0;\n let high = rooms.length - 1;\n let answer = -1;\n\n while (low <= high) {\n const mid = low + Math.floor((high - low) / 2);\n\n if (rooms[mid][1] < size) {\n low = mid + 1;\n } else {\n answer = mid;\n high = mid - 1;\n }\n }\n\n return answer;\n}\n\nfunction findClosestRoom(rooms: number[][], start: number, preferred: number): number {\n let answer = start;\n let minAbs = Math.abs(rooms[start][0] - preferred);\n\n for (let i = start; i < rooms.length; i++) {\n const abs = Math.abs(rooms[i][0] - preferred);\n\n if (abs < minAbs || (abs === minAbs && rooms[i][0] < rooms[answer][0])) {\n minAbs = abs;\n answer = i;\n }\n }\n\n return answer;\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Binary Search', 'Sorting', 'TypeScript']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
java, sorting(rooms, queries), binarySearch(make possible room list, find closest room)
|
java-sortingrooms-queries-binarysearchma-4603
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
mot882000
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-10T10:49:25.003405+00:00
|
2024-01-10T10:49:25.003432+00:00
| 14 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) {\n\n // 1. rooms \uB97C size\uAC00 \uD070 \uC21C\uC73C\uB85C \uC815\uB82C\uD55C\uB2E4. \n \n // 2. queries\uB97C origin idx\uB97C \uD3EC\uD568\uD55C queriesWithIdx \uB85C \uBCC0\uD615\uD558\uACE0 (queriesWithIdx[][2] \uC5D0 origin Idx \uC800\uC7A5)\n // minSize\uAC00 \uD070 \uC21C\uC73C\uB85C \uC815\uB82C\uD55C\uB2E4. \n \n // 3. \uC815\uB82C\uB41C queriesWithIdx \uB97C \uC21C\uD68C\uD558\uBA74\uC11C \n // rooms\uC758 size \uAC00 queriesWithIdx[i][1] ( minSize) \uBCF4\uB2E4 \uD06C\uAC70\uB098 \uAC19\uC740 \uAC83\uB4E4\uB9CC List<int[]> roomList \uC5D0 \uCD94\uAC00\uD55C\uB2E4.\n // \u203B List<int[]> roomList\uB294 roomId \uC21C\uC73C\uB85C \uC815\uB82C\uB418\uC5B4\uC57C\uD558\uACE0 \uC774\uC5D0 \uB9DE\uAC8C \n // binarySearchUpper\uB85C roomList\uC5D0\uC11C roomId\uC758 \uC704\uCE58\uB97C \uCC3E\uC740 \uD6C4 \uD574\uB2F9 \uC704\uCE58\uC5D0 \uC0BD\uC785\uD574\uC900\uB2E4. \n\n // 4. 3\uBC88\uC758 \uACFC\uC815\uC774 \uB05D\uB0AC\uC73C\uBA74 roomList \uC5D0\uB294 queriesWithIdx[i] \uAC00 \uAC08 \uC218 \uC788\uB294 room\uB4E4\uB9CC \uC800\uC7A5\uB418\uC5B4\uC788\uACE0 \n // binarySearchUpper\uB85C queriesWithIdx[i][0](preferrred) \uB97C \uCC3E\uC740 \uD6C4 \n // \uCC3E\uC740 index, \uCC3E\uC740index-1, \uCC3E\uC740index+1 \uC911 \uAC00\uC7A5 \uAC00\uAE4C\uC6B4 \uACF3\uC73C\uB85C \uBC30\uC815\uD574\uC8FC\uBA74\uB41C\uB2E4.\n // result[queriesWithIdx[i][2]] \uC5D0 \uC800\uC7A5 \n // \u203B 2. \uC5D0\uC11C queriesWithIdx \uAC00 minSize \uD070 \uC21C\uC73C\uB85C \uC815\uB82C \uB418\uC5C8\uAE30 \uB54C\uBB38\uC5D0 originIdx\uB97C \uC774\uC6A9\uD574 \uB123\uC5B4\uC918\uC57C\uD55C\uB2E4. \n\n // 5. result \uBC18\uD658\n\n\n int queriesWithIdx[][] = new int[queries.length][3];\n for(int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {\n queriesWithIdx[i][0] = queries[i][0];\n queriesWithIdx[i][1] = queries[i][1];\n queriesWithIdx[i][2] = i;\n }\n\n Arrays.sort(queriesWithIdx, new Comparator<int[]>() {\n\n @Override\n public int compare(int[] arg0, int[] arg1) {\n return arg1[1]-arg0[1];\n }\n \n });\n\n\n Arrays.sort(rooms, new Comparator<int[]>() {\n\n @Override\n public int compare(int[] arg0, int[] arg1) {\n return arg1[1] - arg0[1];\n }\n \n });\n\n // for(int i = 0; i < rooms.length; i++) System.out.print("[" + rooms[i][0] + " " + rooms[i][1] + "] "); System.out.println();\n \n int result[] = new int[queries.length];\n\n List<int[]> roomList = new ArrayList<int[]>();\n int roomIdx = 0;\n \n\n for(int i = 0; i < queriesWithIdx.length; i++) {\n int preferred = queriesWithIdx[i][0];\n int minSize = queriesWithIdx[i][1];\n\n while(roomIdx < rooms.length && rooms[roomIdx][1] >= minSize) {\n int idx = binarySearchUpper(roomList, rooms[roomIdx][0]) ;\n roomList.add(idx, new int[]{rooms[roomIdx][0], rooms[roomIdx][1]});\n roomIdx++;\n } \n\n if ( roomList.size() == 0) {\n result[queriesWithIdx[i][2]] = -1;\n continue;\n }\n \n int idx = binarySearchUpper(roomList, preferred);\n if ( idx == roomList.size()) idx--;\n\n if ( roomList.get(idx)[0] == preferred ) {\n if (roomList.get(idx)[1] >= minSize) {\n result[queriesWithIdx[i][2]] = preferred;\n continue;\n } \n }\n\n\n int left = idx-1;\n int right = idx+1;\n\n int leftDist = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n int leftRoomId = -1;\n int rightDist = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n int rightRoomId = -1;\n\n if ( left >= 0 ) {\n if ( roomList.get(left)[1] >= minSize ) {\n leftRoomId = roomList.get(left)[0];\n leftDist = preferred - leftRoomId;\n }\n }\n\n if(right < roomList.size()) {\n if ( roomList.get(right)[1] >= minSize ) {\n rightRoomId = roomList.get(right)[0] ;\n rightDist = rightRoomId - preferred;\n }\n }\n\n if ( leftDist <= rightDist ) {\n if ( leftDist > Math.abs(roomList.get(idx)[0]-preferred) && roomList.get(idx)[1] >= minSize ) {\n result[queriesWithIdx[i][2]] = roomList.get(idx)[0];\n } else{\n result[queriesWithIdx[i][2]] = leftRoomId;\n }\n \n } else{\n\n if ( rightDist >= Math.abs(roomList.get(idx)[0]-preferred) && roomList.get(idx)[1] >= minSize ) {\n result[queriesWithIdx[i][2]] = roomList.get(idx)[0];\n } else{\n result[queriesWithIdx[i][2]] = rightRoomId;\n }\n \n }\n \n \n }\n\n // for(int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) System.out.print(result[i] + " "); System.out.println();\n\n\n return result;\n\n }\n\n\n private int binarySearchUpper(List<int[]> list, int target) {\n int start = 0;\n int end = list.size();\n int mid;\n\n while( start < end) {\n mid = (start + end)/2;\n\n if ( list.get(mid)[0] >= target) {\n end = mid;\n } else{\n start = mid+1;\n }\n }\n\n return end;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Binary Search', 'Sorting', 'Java']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
In c# because there was none
|
in-c-because-there-was-none-by-user1731q-c3vj
|
Intuition\nBased on heipit\'s solution a contribution in c# because there was none.\n\n# Code\n\npublic class Solution {\n public int[] ClosestRoom(int[][] r
|
user1731Qh
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-16T21:40:18.875852+00:00
|
2023-11-16T21:40:18.875873+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Intuition\nBased on heipit\'s solution a contribution in c# because there was none.\n\n# Code\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public int[] ClosestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries)\n {\n var indexes = new int[queries.Length];\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.Length; i++) indexes[i] = i;\n\n Array.Sort(rooms, (x, y) => y[1].CompareTo(x[1]));\n Array.Sort(indexes, (x, y) => queries[y][1].CompareTo(queries[x][1]));\n\n var answers = new int[queries.Length];\n var roomIdsSoFar = new List<int>();\n int roomIndex = 0;\n foreach(int index in indexes)\n {\n while(roomIndex < rooms.Length && rooms[roomIndex][1] >= queries[index][1])\n {\n roomIdsSoFar.Add(rooms[roomIndex][0]);\n roomIndex++;\n }\n roomIdsSoFar.Sort();\n\n int floor = 0;\n int ceil = int.MaxValue;\n foreach (int id in roomIdsSoFar)\n {\n if (id <= queries[index][0] && id > floor) floor = id;\n if (id > queries[index][0] && id < ceil) ceil = id;\n }\n\n int ansAbs = int.MaxValue, ans = -1;\n if (floor > 0)\n {\n ans = floor;\n ansAbs = Math.Abs(queries[index][0] - floor);\n }\n if (ceil < int.MaxValue && ansAbs > Math.Abs(queries[index][0] - ceil))\n {\n ans = ceil;\n }\n\n answers[index] = ans;\n }\n return answers;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
Binary Search
|
binary-search-by-khangar_aniket-dyn2
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Khangar_Aniket
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-11T09:57:28.917405+00:00
|
2023-10-11T09:57:28.917425+00:00
| 13 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution \n{\n public int[] closestRoom(int[][] rooms, int[][] queries) \n {\n //let\'s first sort the rooms on the \n Arrays.sort(rooms,(a,b)->Integer.compare(a[1],b[1]));\n int k=queries.length;\n\n //let\'s Iterate over the each query..\'\n\n int[]ans=new int[k];\n for(int i=0;i<k;i++)\n {\n int prefId=queries[i][0];\n int minSize=queries[i][1];\n \n //we\'ll first find the the perticular index which does exists or not using binary searc..\'\n int res=bs(rooms,prefId,minSize);\n\n if(res==-1)\n {\n ans[i]=-1;\n continue;\n }\n\n //this function will return the index of the answer room... \n\n int idx=find(rooms,res,prefId);\n\n //room Id will be on oth position ..\n ans[i]=rooms[idx][0];\n\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\n public int bs(int[][]rooms,int prefId,int minSize)\n {\n //This functions main motive is to Find the Left most room have size greater that or equals to minSize.\n int ans=-1;\n int l=0,r=rooms.length-1;\n while(l<=r)\n {\n int mdi=l+(r-l)/2;\n if(rooms[mdi][1]<minSize)l=mdi+1;\n else{\n ans=mdi;\n r=mdi-1;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n \n }\n\n public int find(int[][]rooms,int res,int prefId)\n {\n //The main motive of this function si to find the room having size grater that equals to min size \n //and to fidn the closet room to prefred Id..\n int mn=Math.abs(rooms[res][0]-prefId);\n int ans=res;\n for(int i=res+1;i<rooms.length;i++)\n {\n //let\'s check the min diffrence for other too..\'\n int temp=Math.abs(prefId-rooms[i][0]);\n if(temp<mn)\n {\n ans=i;\n mn=temp;\n }\n else if(temp==mn)\n {\n if(rooms[i][0]<rooms[ans][0])ans=i;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n\n\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
closest-room
|
C++ code || Easy to understand and implement || Beats in Runtime and Memory
|
c-code-easy-to-understand-and-implement-q2uq5
|
\n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. Try out this way!\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(sort(n)+sort(q)+qlogn)\n Add your time c
|
error_420
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-21T06:30:07.283540+00:00
|
2023-08-21T06:30:07.283561+00:00
| 58 | false |
\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->Try out this way!\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(sort(n)+sort(q)+qlogn)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n+q)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public:\n vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms,\n vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n vector<int> ans(queries.size());\n set<int> roomIds;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < queries.size(); ++i)\n queries[i].push_back(i);\n\n auto descSize = [](const auto& a, const auto& b) { return a[1] > b[1]; };\n sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), descSize);\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end(), descSize);\n\n int i = 0; // rooms\' pointer\n for (const vector<int>& query : queries) {\n while (i < rooms.size() && rooms[i][1] >= query[1])\n roomIds.insert(rooms[i++][0]);\n ans[query[2]] = searchClosestRoomId(roomIds, query[0]);\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n\n private:\n int searchClosestRoomId(set<int>& roomIds, int preferred) {\n const auto it = roomIds.lower_bound(preferred);\n const int id1 = it == roomIds.cbegin() ? -1 : *(prev(it));\n const int id2 = it == roomIds.cend() ? -1 : *it;\n if (id1 == -1)\n return id2;\n if (id2 == -1)\n return id1;\n if (abs(preferred - id1) <= abs(preferred - id2))\n return id1;\n return id2;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.