question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
largest-plus-sign
|
C ++ || DP SOLUTION || Intuition Explained ||
|
c-dp-solution-intuition-explained-by-i_q-kkqy
|
Intution and Thought Process :\n\n Idea is to store the length of longest consecutive 1\'s in all four directions. \n For this we need to have 4 seperate matrix
|
i_quasar
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-10T03:52:58.981019+00:00
|
2021-09-10T03:52:58.981053+00:00
| 391 | false |
**Intution and Thought Process :**\n\n* Idea is to store the length of longest consecutive 1\'s in all four directions. \n* For this we need to have 4 seperate matrix that stores the length for **left, right, up, down.**\n* And then for every 1\'s in the grid, we need to find the minimum of left, right, up, and down. That will be the order of plus. \n# Code : \n```\nint orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n \n\tvector<vector<int>> grid(n, vector<int>(n, 1));\n\tint orderOfPlus = 0;\n\tfor(auto& mine : mines)\n\t{\n\t\tgrid[mine[0]][mine[1]] = 0;\n\t}\n\n\t// UP and LEFT\n\tvector<vector<int>> up(n, vector<int>(n, 0));\n\tvector<vector<int>> left(n, vector<int>(n, 0));\n\tfor(int i=0; i<n; i++)\n\t{\n\t\tfor(int j=0; j<n; j++)\n\t\t{\n\t\t\tif(grid[i][j])\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tup[i][j] = 1;\n\t\t\t\tleft[i][j] = 1;\n\t\t\t\tif(i > 0) up[i][j] = 1 + up[i-1][j];\n\t\t\t\tif(j > 0) left[i][j] = 1 + left[i][j-1];\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\n\t// DOWN and RIGHT\n\tvector<vector<int>> down(n, vector<int>(n, 0));\n\tvector<vector<int>> right(n, vector<int>(n, 0));\n\tfor(int i=n-1; i>=0; i--)\n\t{\n\t\tfor(int j=n-1; j>=0; j--)\n\t\t{\n\t\t\tif(grid[i][j])\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tdown[i][j] = 1;\n\t\t\t\tright[i][j] = 1;\n\t\t\t\tif(i<n-1) down[i][j] = 1 + down[i+1][j];\n\t\t\t\tif(j<n-1) right[i][j] = 1 + right[i][j+1];\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\n\t// Find min in all 4 directions\n\tfor(int i=0; i<n; i++)\n\t{\n\t\tfor(int j=0; j<n; j++)\n\t\t{\n\t\t\tif(grid[i][j])\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tint order = min({up[i][j], left[i][j], down[i][j], right[i][j]});\n\t\t\t\torderOfPlus = max(orderOfPlus, order);\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\treturn (orderOfPlus);\n}\n```\n**Time : O(N^2)**\n**Space : O(N^2) **\n\n**Follow UP :**\n* Here, we can do some more optimizations. Like, instead of taking 4 different matrix for each direction, we can take a single DP matrix. \n* Also, instead of computing separately for *UP, LEFT* and *DOWN, RIGHT*, we can put them into one nested loop.\n\n*If you liked the solution do give it an upvote :)*
| 7 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Python TLE DP straighforward approach O(N^2)
|
python-tle-dp-straighforward-approach-on-r341
|
Not sure, if there is a better way, but Python was giving TLE, for the straighforward DP approach\n\n\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, N, mines):\n
|
Cubicon
|
NORMAL
|
2018-01-14T04:05:39.603000+00:00
|
2018-01-14T04:05:39.603000+00:00
| 1,587 | false |
Not sure, if there is a better way, but Python was giving TLE, for the straighforward DP approach\n\n```\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, N, mines):\n if N == 1: return 0 if mines else 1\n info = [[[0] * 4 for _ in range(N)] for _ in range(N)]\n res = 0\n s = {(mine[0], mine[1]) for mine in mines}\n \n for x in range(N):\n for y in range(N):\n if (x,y) not in s:\n info[x][y][0], info[x][y][1] = 1, 1\n if x-1 >= 0: info[x][y][0] = info[x-1][y][0] + 1 # UP\n if y-1 >= 0: info[x][y][1] = info[x][y-1][1] + 1 # LEFT\n\n for x in range(N-1, -1, -1):\n for y in range(N-1, -1, -1):\n if (x, y) not in s:\n info[x][y][2], info[x][y][3] = 1, 1\n if x+1 < N: info[x][y][2] = info[x+1][y][2] + 1 # DOWN\n if y+1 < N: info[x][y][3] = info[x][y+1][3] + 1 # RIGHT\n\n temp = []\n temp.append(info[x - 1][y][0] if x - 1 >= 0 else 0)\n temp.append(info[x][y - 1][1] if y - 1 >= 0 else 0)\n temp.append(info[x + 1][y][2] if x + 1 < N else 0)\n temp.append(info[x][y + 1][3] if y + 1 < N else 0)\n\n res = max([min(temp) + 1, res])\n return res\n```
| 7 | 4 |
[]
| 4 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ (4 approaches - Just like how an interview goes)
|
c-4-approaches-just-like-how-an-intervie-ivt1
|
See the HINGLISH explanation on my LinkedIn page : https://www.linkedin.com/groups/12559380/\n\n\n//Approach-0 (Brute Force - Naive approach which comes to our
|
mazhar_mik
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-10T05:54:38.227375+00:00
|
2021-09-14T17:26:22.814958+00:00
| 286 | false |
See the HINGLISH explanation on my LinkedIn page : https://www.linkedin.com/groups/12559380/\n\n```\n//Approach-0 (Brute Force - Naive approach which comes to our mind instantly) O(n^3)\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> t(n, vector<int>(n, 1));\n \n for(vector<int>& vec : mines) {\n t[vec[0]][vec[1]] = 0;\n }\n \n int maxC = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i<n; i++) {\n for(int j = 0; j<n; j++) {\n\t\t\t\t//As soon as you see one, find 1 to its left, right, top and bottom\n if(t[i][j] == 1) {\n int k = j+1;\n int right = 0, left = 0, up = 0, down = 0;\n while(k < n && t[i][k] == 1) {\n k++;\n right++;\n }\n \n k = j-1;\n while(k >= 0 && t[i][k] == 1) {\n k--;\n left++;\n }\n \n k = i-1;\n while(k >= 0 && t[k][j] == 1) {\n k--;\n up++;\n }\n \n k = i+1;\n while(k < n && t[k][j] == 1) {\n k++;\n down++;\n }\n \n int minL = min({left, right, up, down});\n maxC = max(maxC, minL+1);\n }\n }\n }\n return maxC;\n }\n};\n```\n\n```\n//Approach-1 (Improving your brute force) O(n^3)\n/Approach-1 (Brute Force : O(n^3))\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n if(n*n == mines.size())\n return 0;\n \n int t[n][n];\n for(int i = 0; i<n; i++) {\n for(int j = 0; j<n; j++) {\n t[i][j] = 1;\n }\n }\n \n for(vector<int>& vec : mines)\n t[vec[0]][vec[1]] = 0;\n \n int ans = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i<n; i++) {\n for(int j = 0; j<n; j++) {\n if(t[i][j] == 0) continue;\n \n //Taking [i][j] as center try to expand it (up, down, left, right)\n\t\t\t\t/*\n\t\t\t\t\tup = i-expand\n\t\t\t\t\tdown = i + expand\n\t\t\t\t\tleft = j - expand\n\t\t\t\t\tright = j + expand\n\t\t\t\t*/\n int expand = 0;\n while(true) {\n expand++;\n if(i - expand < 0 || j - expand < 0 || i + expand >= n || j + expand >= n)\n break;\n \n if(t[i-expand][j] == 0 || t[i][j-expand] == 0 || t[i+expand][j] == 0 || t[i][j+expand] == 0)\n break;\n }\n \n ans = max(ans, expand);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n```\n//Approach-2 (Dynamic Programming, Time : O(n^2), Space : O(n^2))\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> t(n, vector<int>(n, 1));\n for(vector<int>& vec : mines) {\n t[vec[0]][vec[1]] = 0;\n }\n \n int ans = 0;\n vector<vector<int>> left, right, top, bottom;\n /*\n left[i][j] = count of 1s in the left direction of t[i][j]\n right[i][j] = count of 1s in the right direction of t[i][j]\n so on..\n */\n left = right = top = bottom = t;\n \n for(int i = 0; i<n; i++) {\n for(int j = 0; j<n; j++) {\n if(i > 0 && top[i][j]) top[i][j] += top[i-1][j];\n if(j > 0 && left[i][j]) left[i][j] += left[i][j-1];\n \n /*\n You can write a seperate loop for filling right and bottom\n Because in right and bottom you will have to traverse from\n bottom right to top\n BUT, you can manipulate the index here only to achieve that\n */\n \n /*\n As i moves from top to down, j moves from left to right\n \n n-i-1 will move from bottom to up\n n-j-1 will move from right to left\n */\n int x = n-i-1;\n int y = n-j-1;\n if(x < n-1 && bottom[x][y]) bottom[x][y] += bottom[x+1][y];\n if(y < n-1 && right[x][y]) right[x][y] += right[x][y+1];\n }\n }\n \n /*\n Now, for any i and j, we need to find the minimum of its (left, right, bottom and up)\n And among all those minimum, we need to find the maximum\n */\n \n for(int i = 0; i<n; i++) {\n for(int j = 0; j<n; j++) {\n int minL = min({left[i][j], right[i][j], top[i][j], bottom[i][j]});\n ans = max(ans, minL);\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n```\n//Approach-3 (Dynamic Programming, Time : O(n^2), Space : O(n^2)\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n if(n*n == mines.size())\n return 0;\n \n int t[n][n];\n for(int i = 0; i<n; i++) {\n for(int j = 0; j<n; j++) {\n t[i][j] = n;\n }\n }\n \n for(vector<int>& vec : mines)\n t[vec[0]][vec[1]] = 0;\n \n int ans = 0;\n \n for(int i = 0; i<n; i++) {\n //t[][] will be updated to minimum of its left, right, up and down (count of 1s)\n \n //Look for longest streak of 1 at its left\n int left = 0;\n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n left = t[i][j] == 0 ? 0 : left+1;\n t[i][j] = min(t[i][j], left);\n }\n \n //Look for longest streak of 1 at its right\n int right = 0;\n for(int j = n-1; j>=0; j--) {\n right = t[i][j] == 0 ? 0 : right+1;\n t[i][j] = min(t[i][j], right);\n }\n \n //Look for longest streak of 1 at its up\n int up = 0;\n for(int k = 0; k < n; k++) {\n up = t[k][i] == 0 ? 0 : up+1;\n t[k][i] = min(t[k][i], up);\n }\n \n //Look for longest streak of 1 at its down\n int down = 0;\n for(int k = n-1; k >= 0; k--) {\n down = t[k][i] == 0 ? 0 : down+1;\n t[k][i] = min(t[k][i], down);\n }\n }\n \n //Finally, find the max one\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n ans = max(ans, t[i][j]);\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 6 | 3 |
[]
| 1 |
largest-plus-sign
|
[C++] Easy Solution (DP/DFS)
|
c-easy-solution-dpdfs-by-jontystanley21-v6ye
|
In this particular post at first we look at the raw code which is essentially the same as the shorter version. This will help us understand the code better. \n\
|
jontystanley21
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-09T14:05:10.145009+00:00
|
2021-09-09T19:23:47.758637+00:00
| 285 | false |
In this particular post at first we look at the raw code which is essentially the same as the shorter version. This will help us understand the code better. \n\n**Algorithm**\n\nFor each (cardinal) direction, and for each coordinate (r, c) let\'s compute the count of that coordinate: the longest line of \'1\'s starting from (r, c) and going in that direction. With dynamic programming, it is either 0 if **grid[r][c]** is zero, else it is 1 plus the count of the coordinate in the same direction. For example, if the direction is left and we have a row like 01110110, the corresponding count values are 01230120, and the integers are either 1 more than their successor, or 0. For each square, we want **grid[r][c]** to end up being the minimum of the 4 possible counts. At the end, we take the maximum value in dp.\n\n\nTime Complexity: *O(N^2)*, as the work we do under two nested for loops is O(1)O(1).\nSpace Complexity: *O(N^2)*, the size of grid.\n\n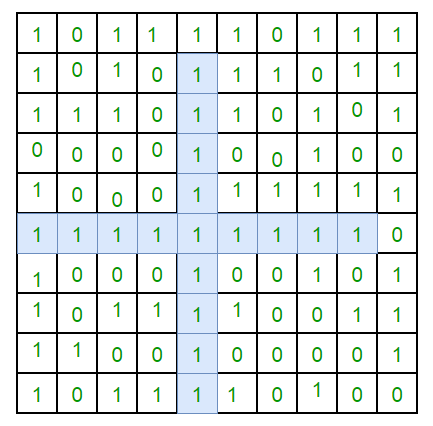\n\n\n**C++ DP Raw Version**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>>grid(n,vector<int>(n,n));\n \n for(auto m:mines){\n grid[m[0]][m[1]]=0;\n }\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n \n \n for(int j=0,left=0;j<n;j++){\n if(grid[i][j]==0)left=0;\n else left+=1;\n grid[i][j]=min(grid[i][j],left);\n }\n \n \n for(int k=n-1,right=0;k>=0;k--){\n if(grid[i][k]==0)right=0;\n else right+=1;\n grid[i][k]=min(grid[i][k],right);\n }\n \n \n for(int j=0,top=0;j<n;j++){\n if(grid[j][i]==0)top=0;\n else top+=1;\n grid[j][i]=min(grid[j][i],top);\n }\n \n for(int k=n-1,bottom=0;k>=0;k--){\n if(grid[k][i]==0)bottom=0;\n else bottom+=1;\n grid[k][i]=min(grid[k][i],bottom);\n }\n \n }\n \n int mxorder=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n mxorder=max(mxorder,grid[i][j]);\n }\n }\n \n return mxorder;\n }\n };\n```\n\n\n**C++ DP Shortened Version**\n```\nint orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> grid(n, vector<int>(n, n));\n \n for (auto& m : mines) {\n grid[m[0]][m[1]] = 0;\n }\n \n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for (int j = 0, k = n - 1, left = 0, right= 0, top = 0, bottom = 0; j < n; j++, k--) {\n grid[i][j] = min(grid[i][j], left = (grid[i][j] == 0 ? 0 : left + 1));\n grid[i][k] = min(grid[i][k], right = (grid[i][k] == 0 ? 0 : right + 1));\n grid[j][i] = min(grid[j][i], top = (grid[j][i] == 0 ? 0 : top + 1));\n grid[k][i] = min(grid[k][i], bottom = (grid[k][i] == 0 ? 0 : bottom + 1));\n }\n }\n \n int mxorder = 0;\n \n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n mxorder = max(mxorder, grid[i][j]);\n }\n }\n \n return mxorder;\n}\n```\n\n**C++ DFS Version (TLE on some cases)**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> grid(N, vector<int>(N, 1));\n for(auto &p: mines){\n grid[p[0]][p[1]] = 0;\n }\n \n auto all_ones = [&](int i, int j, int k){\n if(i - k < 0 || i + k >= N || j - k < 0 || j + k >= N)\n return false;\n return grid[i - k][j] && grid[i + k][j] && grid[i][j - k] && grid[i][j + k];\n };\n int K = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i){\n for(int j = 0; j < N; ++j){\n if(grid[i][j] == 1){\n int k = 1;\n while(all_ones(i, j, k))\n ++k;\n K = max(k, K);\n }\n }\n }\n return K;\n }\n};\n```
| 6 | 1 |
[]
| 1 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Python || DP
|
python-dp-by-in_sidious-0krl
|
Just keep a check of nos of consecutive 1s in left and top in first loop\nRight and down in second loop,and take min of all 4 directions,thats it !!!!\n\nclass
|
iN_siDious
|
NORMAL
|
2021-08-25T19:04:30.047298+00:00
|
2021-08-25T19:04:30.047342+00:00
| 513 | false |
Just keep a check of nos of consecutive 1s in left and top in first loop\nRight and down in second loop,and take min of all 4 directions,thats it !!!!\n```\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, n: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n m=len(mines)\n if m==n*n: return 0\n seen=set()\n for i,j in mines:\n seen.add((i,j))\n ans=1\n #(left,up,right,down)\n dp=[[[0,0,0,0] for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(n)]\n for i in range(n):\n for j in range(n):\n if (i,j) not in seen:\n dp[i][j][0]=(dp[i][j-1][0]+1) if j-1>=0 else 1\n dp[i][j][1]=(dp[i-1][j][1]+1) if i-1>=0 else 1\n for i in range(n-1,-1,-1):\n for j in range(n-1,-1,-1):\n if (i,j) not in seen:\n dp[i][j][2]=(dp[i][j+1][2]+1) if j+1<n else 1\n dp[i][j][3]=(dp[i+1][j][3]+1) if i+1<n else 1\n ans=max(ans,min(dp[i][j]))\n return ans\n \n\n\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python']
| 1 |
largest-plus-sign
|
764: Memory Beats 91.40%, Solution with step by step explanation
|
764-memory-beats-9140-solution-with-step-p8pv
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n\ngrid = [[n] * n for _ in range(n)]\n\nWe initialize a grid with all val
|
Marlen09
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-24T18:14:40.844660+00:00
|
2023-10-24T18:14:40.844685+00:00
| 439 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n```\ngrid = [[n] * n for _ in range(n)]\n```\nWe initialize a grid with all values set to n. Why? Because in the best case, if a cell isn\'t blocked (by a mine), its maximum potential reach in any direction is n (from one edge to another).\n\n```\nfor x, y in mines:\n grid[x][y] = 0\n```\n\nWe then loop through the mines and set those cells to 0 in the grid, as they can\'t be a part of any plus sign.\n\nWe need to determine how far each cell can reach in every direction. This will let us determine the size of the plus sign for which the cell can be a center.\n\n```\nfor i in range(n):\n l, r, u, d = 0, 0, 0, 0 \n```\n\nWe begin by iterating through each row and column of the matrix using i. For each row and column, we initialize counters for all four directions (left, right, up, down).\n\n```\n for j in range(n):\n l = l + 1 if grid[i][j] != 0 else 0\n r = r + 1 if grid[i][n-j-1] != 0 else 0\n u = u + 1 if grid[j][i] != 0 else 0\n d = d + 1 if grid[n-j-1][i] != 0 else 0\n \n grid[i][j] = min(grid[i][j], l)\n grid[i][n-j-1] = min(grid[i][n-j-1], r)\n grid[j][i] = min(grid[j][i], u)\n grid[n-j-1][i] = min(grid[n-j-1][i], d)\n```\nWe use another loop with j to traverse through each cell in the row or column. For each cell:\n\nIf the cell isn\'t blocked (i.e., it\'s not a mine), we increment the corresponding counter.\nIf the cell is blocked (i.e., it\'s a mine), we reset the counter to 0 because we can\'t pass through mines.\nWe then update the cell\'s value in the grid to be the minimum of its current value and the counter. This is because the cell\'s value represents the maximum size of the plus sign for which it can be a center, so we\'re continuously refining this estimate.\n\n```\nreturn max(map(max, grid))\n```\n\nFinally, after populating the entire grid with each cell\'s potential as a center of a plus sign, we determine the largest possible plus sign in the grid. This is done by finding the maximum value in the grid.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n^2)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n^2)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, n: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n grid = [[n] * n for _ in range(n)]\n \n for x, y in mines:\n grid[x][y] = 0\n\n for i in range(n):\n l, r, u, d = 0, 0, 0, 0\n for j in range(n):\n l = l + 1 if grid[i][j] != 0 else 0\n r = r + 1 if grid[i][n-j-1] != 0 else 0\n u = u + 1 if grid[j][i] != 0 else 0\n d = d + 1 if grid[n-j-1][i] != 0 else 0\n \n grid[i][j] = min(grid[i][j], l)\n grid[i][n-j-1] = min(grid[i][n-j-1], r)\n grid[j][i] = min(grid[j][i], u)\n grid[n-j-1][i] = min(grid[n-j-1][i], d)\n \n return max(map(max, grid))\n\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 1 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ || SIMPLE || TIME O(n^2)
|
c-simple-time-on2-by-abhay_12345-bh8r
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> grid(n,vector<int>(n,1));\n
|
abhay_12345
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-29T11:06:01.407182+00:00
|
2022-09-29T11:06:01.407235+00:00
| 1,013 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> grid(n,vector<int>(n,1));\n for(auto &i: mines){\n grid[i[0]][i[1]] = 0;\n }\n vector<vector<int>> left,right,top,bottom;\n left = vector<vector<int>>(n,vector<int>(n,0));\n right = vector<vector<int>>(n,vector<int>(n,0));\n top = vector<vector<int>>(n,vector<int>(n,0));\n bottom = vector<vector<int>>(n,vector<int>(n,0));\n int i,j;\n // for(auto &i: grid){\n // for(auto &j: i)cout<<j<<" ";\n // cout<<endl;\n // }\n for(i = 0; i < n; i++){\n for(j = 0; j < n; j++){\n if(j==0){\n left[i][j] = (grid[i][j]);\n }else if(grid[i][j]){\n left[i][j] = left[i][j-1]+1;\n }\n // cout<<left[i][j]<<" ";\n }\n // cout<<endl;\n }\n //cout<<endl;\n for(i = 0; i < n; i++){\n for(j = n-1; j >= 0; j--){\n if(j==n-1){\n right[i][j] = (grid[i][j]);\n }else if(grid[i][j]){\n right[i][j] =1+ right[i][j+1];\n }\n \n // cout<<right[i][j]<<" ";\n }\n // cout<<endl;\n }//cout<<endl;\n for(i = 0; i < n; i++){\n for(j = 0; j < n; j++){\n if(i==0){\n top[i][j] = (grid[i][j]);\n }else if(grid[i][j]){\n top[i][j] +=1+ top[i-1][j];\n }\n // cout<<top[i][j]<<" ";\n }\n // cout<<endl;\n }//cout<<endl;\n for(i = n-1; i >= 0; i--){\n for(j = 0; j < n; j++){\n if(i==n-1){\n bottom[i][j] = (grid[i][j]);\n }else if(grid[i][j]){\n bottom[i][j] +=1+ bottom[i+1][j];\n }\n // cout<<bottom[i][j]<<" ";\n }\n // cout<<endl;\n }\n int ans = 0;\n for(i = 0; i < n; i++){\n for(j = 0; j < n; j++){\n ans = max(ans,min(min(left[i][j],right[i][j]),min(top[i][j],bottom[i][j])));\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ Easy & Understandable code with Comments || O(n^2)
|
c-easy-understandable-code-with-comments-3evi
|
Brute Force approach\n- In the brute approach we can try each cell(r,c) as potential plus center then expand left, right, bottom, top and among then compute mi
|
akashdb101
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-05T03:34:36.307053+00:00
|
2022-03-05T03:34:36.307085+00:00
| 380 | false |
**Brute Force approach**\n- In the brute approach we can try each cell(r,c) as potential plus center then expand left, right, bottom, top and among then compute minimum distance. \n- Brute force approach will be inefficient having T.C. O(n^3)\n\n**Dynamic Programming**\n- In this approach we take a dp matrix.\n- here we count continuos 1s in four directions and store minimum in dp\n\n<hr>\n\n**Please Upvote. Thanks:)**\n\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n void computeOrderOfPlus(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<int>>& dp, int n){\n \n int leftToRight = 0, topToBottom = 0, rightToBottom = 0, bottomToTop = 0;\n \n for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){\n leftToRight = 0, topToBottom = 0; // reset value becuase we restarting counting for each row\n for(int j=0; j<n; ++j){\n // calcualte continuous 1s present left to current cell until zero\n leftToRight = grid[i][j] ? leftToRight+1 : 0;\n dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], leftToRight);\n \n // calcualte continuous 1s present top till current cell until zero\n topToBottom = grid[j][i] ? topToBottom+1 : 0; // here cell ( j, i ) because we compute top to bottom.\n dp[j][i] = min(dp[j][i], topToBottom);\n }\n }\n \n for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){\n rightToBottom = 0, bottomToTop = 0;\n for(int j=n-1; j>=0; --j){\n // calcualte continuous 1s present right to current cell\n rightToBottom = grid[i][j] ? rightToBottom+1 : 0;\n dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], rightToBottom);\n \n // calcualte continuous 1s present bottom till current cell\n bottomToTop = grid[j][i] ? bottomToTop+1 : 0; // here cell ( j, i ) because we compute bottom to top\n dp[j][i] = min(dp[j][i], bottomToTop); \n }\n }\n }\n \n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> grid(n, vector<int>(n, 1));//prefill with 1s\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int>(n, INT_MAX));// initialize with max value so later will update with minimum left, right, top, bottom distance\n \n for(auto mine: mines){\n grid[mine.at(0)][mine.at(1)] = 0; // fill grid with zero\n }\n \n computeOrderOfPlus(grid, dp, n);\n // fillDP(dp, grid, n);\n \n int res = 0;\n // get the maximum value from dp matrix\n for(auto row: dp){\n for(auto ele : row){\n res = max(res, ele);\n }\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n};
| 4 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Nice O(n^2) solution
|
nice-on2-solution-by-trishanku_sarma-w5km
|
class Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector>& mines) {\n \n vector< vector< int >>DP( n, vector< int >( n, 1));\n
|
TRISHANKU_SARMA
|
NORMAL
|
2021-12-17T18:51:31.812973+00:00
|
2021-12-17T18:51:31.813016+00:00
| 167 | false |
class Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n \n vector< vector< int >>DP( n, vector< int >( n, 1));\n \n for( auto x:mines )\n DP[ x[0] ][ x[1] ] = 0;\n \n vector< vector< int >>left = DP, top = DP, right = DP, bottom =DP; \n \n for( int i=0 ; i<n ; i++ ){\n \n for( int j=0 ; j<n ; j++ ){\n \n if( DP[ i ][ j ] ){\n \n if( j>0 )\n left[ i ][ j ] = 1 + left[ i ][ j-1 ];\n else\n left[ i ][ j ] = 1;\n \n if( i>0 )\n top[ i ][ j ] = 1 + top[ i-1 ][ j ];\n else\n top[ i ][ j ] = 1;\n }\n }\n }\n \n int maxm = 0;\n \n for( int i=n-1 ; i>=0 ; i-- ){\n \n for( int j=n-1 ; j>=0 ; j-- ){\n \n if( DP[ i ][ j ] ){\n \n if( j<(n-1) )\n right[ i ][ j ] = 1 + right[ i ][ j+1 ];\n else\n right[ i ][ j ] = 1;\n \n if( i<(n-1) )\n bottom[ i ][ j ] = 1 + bottom[ i+1 ][ j ];\n else\n bottom[ i ][ j ] = 1;\n }\n \n int k = min({ left[i][j] , right[i][j] , top[i][j] , bottom[i][j] });\n \n maxm = max( k, maxm );\n }\n }\n \n return maxm;\n }\n};
| 4 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
JAVA SOLUTION USING DFS
|
java-solution-using-dfs-by-subhankar752-0m28
|
The idea is very similar to doing a DFS only a slight variation that the distace keeps on increasing if a certain condition is satisfied. Once left, right, top,
|
Subhankar752
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-10T03:41:23.629127+00:00
|
2021-09-10T03:41:23.629160+00:00
| 472 | false |
The idea is very similar to doing a DFS only a slight variation that the distace keeps on increasing if a certain condition is satisfied. Once left, right, top, and bottom are met then we have to increase the distance by 1 and see if it satisfies the plus sign. If the condition is not met we simply break from the loop ans maximise our answer. Refer to the code for implementation. Do upvote id it was helpful!!!\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, int[][] mines) {\n int[][] arr = new int[n][n];\n for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){\n for(int j = 0 ; j < n ; j++){\n arr[i][j] = 1;\n }\n }\n for(int[] i : mines){\n int x = i[0];\n int y = i[1];\n arr[x][y] = 0;\n }\n // for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){\n // for(int j = 0 ; j < n ; j++){\n // System.out.print(arr[i][j] +" ");\n // }\n // System.out.println();\n // }\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){\n for(int j = 0 ; j < n ; j++){\n if(arr[i][j] == 1)\n {\n int order = 1;\n while(true){\n // System.out.println(order);\n if(!isValid(i - order , j , n , arr))\n break;\n if(!isValid(i + order , j , n , arr))\n break;\n if(!isValid(i , j - order , n , arr))\n break;\n if(!isValid(i , j + order , n , arr))\n break;\n \n order++;\n \n }\n ans = Math.max(ans , order);\n } \n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n public boolean isValid(int i , int j , int n , int[][] arr){\n if(i < 0 || j < 0 || i > n - 1 || j > n - 1)\n return false;\n if(arr[i][j] != 1)\n return false;\n return true;\n }\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Java']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Question about Largest Plus Sign
|
question-about-largest-plus-sign-by-ssjl-cfx2
|
Hi, I am trying to solve the problem. \nOne of my submission says I have a wrong expected answer. \n\nThe input is \n\n2\n[[0,0],[0,1],[1,0]]\n\nThe expected an
|
ssjlee93
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-09T15:47:01.623476+00:00
|
2021-09-09T19:38:08.393251+00:00
| 215 | false |
Hi, I am trying to solve the problem. \nOne of my submission says I have a wrong expected answer. \n\nThe input is \n```\n2\n[[0,0],[0,1],[1,0]]\n```\nThe expected answer is `1` \n\nI don\'t understand how this is possible. \nHow can you have a plus sign with lengths and widths 2? \n\nSomeone please explain this to me.\n\n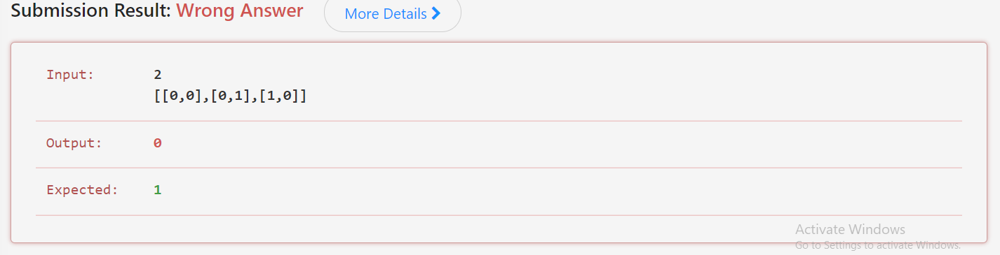\n\nAnswer: \n\nAfter testing and trying for a while, my understanding is that: \n` 1 <= mines <= 5000` \nSo when `n = 1` `mines = 1` , meaning max order = `0` \nBut when `n = 2` the order can be `1`, which leaves with the center and nothing else. \n\nBut how is this a plus sign though... \nIt\'s just one dot. \nI argue that `n >=3` in order for a plus sign to exist. \nCorrect me if I\'m wrong.
| 4 | 1 |
[]
| 2 |
largest-plus-sign
|
my solution - java - easy - accepted - time & space - O(N^2)
|
my-solution-java-easy-accepted-time-spac-2wpx
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, int[][] mines) {\n \n return method1(n,mines);\n \n }\n \n privat
|
dhilipkumar116
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-09T13:19:39.241033+00:00
|
2021-09-09T13:19:53.262998+00:00
| 250 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, int[][] mines) {\n \n return method1(n,mines);\n \n }\n \n private int method1(int n,int[][] mines){\n \n int[][] mat = new int[n][n];\n for(int[] arr:mat){\n Arrays.fill(arr,1);\n }\n for(int[] mine:mines){\n mat[mine[0]][mine[1]]=0;\n }\n \n int maxOrder=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n \n if(mat[i][j]==1){\n int order=1;\n \n while(true){\n int left = j-order;\n int right = j+order;\n int top = i-order;\n int down = i+order;\n \n if(left<0||right>=n||top<0||down>=n||\n mat[i][right]==0||mat[i][left]==0||mat[top][j]==0||mat[down][j]==0){\n break;\n }\n order++;\n \n }\n \n maxOrder = Math.max(maxOrder,order);\n }\n }\n }\n return maxOrder;\n \n \n }\n}\n```\n**do upvote, if you like my approach**
| 4 | 1 |
['Java']
| 1 |
largest-plus-sign
|
different take - sorting mines to eliminate searches beats 100% Java by a wide margin
|
different-take-sorting-mines-to-eliminat-p30p
|
Admittedly this version takes more storage than the solutions that cleverly use a single 2D array to store the minimum results of 4 simultaneous scans for the l
|
flarbear
|
NORMAL
|
2019-04-17T22:29:41.171136+00:00
|
2019-04-17T22:29:41.171176+00:00
| 410 | false |
Admittedly this version takes more storage than the solutions that cleverly use a single 2D array to store the minimum results of 4 simultaneous scans for the longest legs in each of 4 directions, but it represents a more direct way to compute the "longest legs" than a scan.\n\nMy concept was to store the longest horizontal and vertical cross-sections rather than separate up/down/left/right legs. This is done by first creating sorted lists of mines on each row and column. Then we can visit every pair of mines and fill the space between them concentrically from the mines towards the center between them with increasing values. This involves 3 steps:\n\n**Step 1 - sorting mines**\nI create 2 arrays of PriorityQueues to sort the mines. This is probably overkill for most mine setups as it will be fairly sparse, but it simplified the code.\n\n**Step 2 - filling in h/v crossbar sizes**\nIt would be more space efficient to do this in the same grid for each direction, but that would mean either initializing both grids to "N" and then doing a "min()" operation as we fill the grids first by row and then by col, or letting the first pass fill them using assignment and then the second pass needing to do the "min()" operation on every fill. It simplified the code somewhat to simply fill 2 separate grids from the 2 separate lists of sorted mines and then do a final pass finding the minimum intersections between the two. Note that the row grid is oriented as you would expect ```grid[r][c]```, but the columns grid is transposed, as in ```grid[c][r]```. This allows both grids to be constructed by the same shared code for simplicity.\n\nThe filling operations are done by reading out the sorted list of mines on every row (or column) and then filling concentrically between each pair of mines. The first mine is also filled from the left/top edge and the last mine also fills to the right/bottom edge using the same concentric fill.\n\nA concentric fill is starting at both ends and fillling a 1 first, then moving both ends towards each other and filling with higher and higher numbers until the ends meet in the middle. In this case, the endpoints are specified as exclusive indices so the "bumping the ends towards each other" happens before the increasing distance is stored.\n\n**Step 3 - min/maxing the cross sizes**\nThe last step simply involves iterating over the two grids, comparing the longest horizontal and vertical crossbars possible at any given position and returning the largest such cross.\n\n**Complexity**\nThis has a very similar O(N^2) complexity to most solutions with the only distinction being that inserting the mines into the PriorityQueues could potentially increase the work for very unfortunately constructed lists of mines. There is one pass over the mines to insert them into the 2 queue lists. Then there are N^2 passes over each of the ```byrows``` and ```bycols``` grids, and finally there is one last N^2 pass over the pair of grids looking for a min/max.\n\nThe total running time is much shorter than the shortest recorded Java solutions, though, and it\'s not clear why this is in general, but I can speculate how it might be this way due to the way the test cases might be constructed.\n\nFirst, the insertion of the mine coordinates into the PriorityQueues could perform poorly if there are a lot of mines and/or the mines come in out of order, but I\'m guessing the test cases are focused more on the scan for cross pieces than on the processing of the mines so there are probably a lot of examples with a large ```N``` value, but a small number or a sparse distribution of mines.\n\nSecond, many of the solutions scan in 4 directions for the shortest arm of the cross. That means there are 4 N^2 scans that happen in the end, but my solution only uses 3 of them (1 for constructing ```byrows```, 1 for constructing ```bycols```, and 1 for iterating and min/maxing). Also, many of those will do min() operations at each grid location because they are accumulating the minimum leg for each of 4 directions. That technique results in 4xN^2 calls to a ```min()``` function. My solution avoids nearly all of those mins by directly constructing the distance to the nearest mine in both left/right at the same time and both up/down at the same time with no need to call a ```min()``` function. It does use a single call to ```min()``` per grid element in the final scan, though. All in all, this solution reduces 4N^2 scans with 4N^2 calls to ```min()``` down to 3N^2 scans and N^2 calls to ```min()```.\n\n**Possible optimizations**\nOne optimization could be to use the same grid for the lengths of the longest horizontal and vertical crossbars. This could be done by either preinitializing the grid to all values of N and then to use ```min()``` operations as it is filled - increasing the compute time by requiring another pass of ```min()``` calls, but removing one of the grid storage spaces.\n\nA similar optimization would reduce the amount of shared code by having the first pass that fills the grid with the horizontal crossbar lengths do a direct assignment rather than a ```min()``` operation and then having a very similar piece of code handle the second pass for the vertical crossbar lengths, but do a ```min()``` operation as it fills in the values. This should not increase the time complexity because we eventually do that ```min()``` operation in the final pass anyway, but it would mean a bit of code duplication.\n\n```\n void insert(PriorityQueue<Integer> vals[], int r, int c) {\n PriorityQueue<Integer> row = vals[r];\n if (row == null) {\n vals[r] = row = new PriorityQueue<>();\n }\n row.add(c);\n }\n void fill(int row[], int c0, int c1) {\n int i = 0;\n while (++c0 <= --c1) {\n row[c0] = row[c1] = ++i;\n }\n }\n int[][] toGrid(PriorityQueue<Integer> list[]) {\n int N = list.length;\n int grid[][] = new int[N][N];\n for (int r = 0; r < N; r++) {\n int prev = -1;\n if (list[r] != null) {\n for (int c : list[r]) {\n fill(grid[r], prev, c);\n prev = c;\n }\n }\n fill(grid[r], prev, N);\n }\n return grid;\n }\n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, int[][] mines) {\n PriorityQueue<Integer> rows[] = new PriorityQueue[N];\n PriorityQueue<Integer> cols[] = new PriorityQueue[N];\n for (int mine[] : mines) {\n insert(rows, mine[0], mine[1]);\n insert(cols, mine[1], mine[0]);\n }\n int byrows[][] = toGrid(rows);\n int bycols[][] = toGrid(cols);\n int biggest = 0;\n for (int r = 0; r < N; r++) {\n for (int c = 0; c < N; c++) {\n int order = Math.min(byrows[r][c], bycols[c][r]);\n if (biggest < order) biggest = order;\n }\n }\n return biggest;\n }\n```
| 4 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
largest-plus-sign
|
SIMPLE CODE | DP | O(N^2) TIME SPACE | PYTHON
|
simple-code-dp-on2-time-space-python-by-dg2ed
|
Naive Approach will go to every index, run while loop to top,bottom,left,right and find count of one for each. Minimum of those count gives largest size of + fo
|
Harry_VIT
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-09T15:42:28.883977+00:00
|
2021-09-09T15:42:28.884028+00:00
| 187 | false |
Naive Approach will go to every index, run while loop to top,bottom,left,right and find count of one for each. Minimum of those count gives largest size of + for that index. Then , we need to maximize the answer. \n\nRead the comments above each for loop to know its functionality. This is Dp approach that runs in O(N^2) Time complexity and O(N^2) Space complexity.\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, n: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n \n #creating matrix\n mine=[[1]*n for i in range(n)]\n for i in mines:\n mine[i[0]][i[1]]=0\n mines=mine\n \n x=[[[0,0,0,0] for k in range(n)] for i in range(n)]\n #top,bottom,left,right\n \n # initializing top and left of (0,0)th element\n if(mines[0][0]==1):\n x[0][0]=[1,0,1,0]\n \n answer=0\n \n # initializing top and left of 1st row elements\n for i in range(1,n):\n if(mines[0][i]==1):\n x[0][i][2]=x[0][i-1][2]+1\n x[0][i][0]=1\n answer=1\n \n # initializing top and left of 1st column elements\n for i in range(1,n):\n if(mines[i][0]==1):\n x[i][0][0]=x[i-1][0][0]+1\n x[i][0][2]=1\n answer=1\n \n # initializing bottom and right of (-1,-1)th element\n # increment instead of [0,1,0,1] coz it may fail for matrix size n=1\n if(mines[-1][-1]==1):\n x[-1][-1][1]+=1\n x[-1][-1][3]+=1\n answer=1\n \n # initializing bottom and right of last row elements\n for i in range(n-2,-1,-1):\n if(mines[-1][i]==1):\n x[-1][i][3]=x[-1][i+1][3]+1\n x[-1][i][1]=1\n answer=1\n \n # initializing bottom and right of last column elements\n for i in range(n-2,-1,-1):\n if(mines[i][-1]==1):\n x[i][-1][1]=x[i+1][-1][1]+1\n x[i][-1][3]=1\n answer=1\n \n # updating top and left of last n-1 row elements in top-down approach\n for i in range(1,n):\n for j in range(1,n):\n if(mines[i][j]==1):\n x[i][j][0]=x[i-1][j][0]+1\n answer=1\n if(mines[i][j]==1):\n x[i][j][2]=x[i][j-1][2]+1\n answer=1\n \n # updating bottom and right of first n-1 row elements in bottom up approach\n for i in range(n-2,-1,-1):\n for j in range(n-2,-1,-1):\n if(mines[i][j]==1):\n x[i][j][1]=x[i+1][j][1]+1\n if(mines[i][j]==1):\n x[i][j][3]=x[i][j+1][3]+1\n answer=max(answer,min(x[i][j]))\n \n return answer\n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ DP solution
|
c-dp-solution-by-aparna_g-558k
|
Same implementation as given in solution. Just in C++\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n
|
aparna_g
|
NORMAL
|
2021-04-07T13:42:36.480257+00:00
|
2021-04-07T13:42:36.480298+00:00
| 430 | false |
Same implementation as given in solution. Just in C++\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n set<int> banned;\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n,vector<int>(n));\n for(int i=0;i<mines.size();i++) {\n banned.insert(mines[i][0]*n + mines[i][1]);\n }\n int ans=0,count=0;\n\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {\n count =0;\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++) {\n count = (banned.find(i*n+j)!=banned.end()) ? 0 : count+1;\n dp[i][j] = count;\n }\n count =0;\n for(int j=n-1;j>=0;j--) {\n count = (banned.find(i*n+j) != banned.end()) ? 0 : count+1;\n dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] , count);\n }\n }\n \n for(int j=0;j<n;j++) {\n count=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {\n count = (banned.find(i*n+j)!=banned.end()) ? 0 : count+1;\n dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j],count);\n }\n count=0;\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--) {\n count = (banned.find(i*n+j) != banned.end()) ? 0 : count+1;\n dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] , count);\n ans = max(ans , dp[i][j]) ; \n }\n }\n return ans; \n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'C++']
| 1 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Compact Solution in Python 3 (nine lines)
|
compact-solution-in-python-3-nine-lines-z8ssm
|
Compact Version:\n\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, N: int, M: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n \tDP, M, R, T, m = [[math.inf]*N for i in ran
|
junaidmansuri
|
NORMAL
|
2019-09-30T06:11:42.145464+00:00
|
2019-09-30T06:22:20.935283+00:00
| 612 | false |
_Compact Version:_\n```\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, N: int, M: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n \tDP, M, R, T, m = [[math.inf]*N for i in range(N)], {tuple(m) for m in M}, list(range(N)), (0,1), 0\n \tfor k,i in itertools.product(T,R):\n \t\tfor _ in T:\n \t\t\tc, I, _ = 0, i, R.reverse()\n \t\t\tfor j in R:\n \t\t\t\tif k: i,j = j,i\n \t\t\t\tc = 0 if (i,j) in M else c + 1\n \t\t\t\tDP[i][j], i = min(DP[i][j],c), I\n \treturn max(max(i) for i in DP)\n\t\t\n\n```\n_Long Version:_\n```\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, N: int, M: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n \tDP, M, m = [[0]*N for i in range(N)], {tuple(m) for m in M}, 0\n \tfor i in range(N):\n \t\tc = 0\n \t\tfor j in range(N):\n \t\t\tc = 0 if (i,j) in M else c + 1\n \t\t\tDP[i][j] = c\n \t\tc = 0\n \t\tfor j in range(N-1,-1,-1):\n \t\t\tc = 0 if (i,j) in M else c + 1\n \t\t\tDP[i][j] = min(DP[i][j],c) \t\t\t\n \tfor j in range(N):\n \t\tc = 0\n \t\tfor i in range(N):\n \t\t\tc = 0 if (i,j) in M else c + 1\n \t\t\tDP[i][j] = min(DP[i][j],c)\n \t\tc = 0\n \t\tfor i in range(N-1,-1,-1):\n \t\t\tc = 0 if (i,j) in M else c + 1\n \t\t\tm = max(m,min(DP[i][j],c))\n \treturn m\n\t\t\n\t\t\n\t\t\n- Junaid Mansuri\n(LeetCode ID)@hotmail.com
| 3 | 0 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ clean code using 4 matrices
|
c-clean-code-using-4-matrices-by-wxd_sjt-5em8
|
C++\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> grid(N,vector<int> (N,1));\n vecto
|
wxd_sjtu
|
NORMAL
|
2018-09-16T13:11:10.199626+00:00
|
2018-09-27T05:53:48.261039+00:00
| 592 | false |
```C++\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> grid(N,vector<int> (N,1));\n vector<vector<int>> left(N,vector<int> (N,1)), right(N,vector<int> (N,1)), up(N,vector<int> (N,1)), down(N,vector<int> (N,1));\n\n int ans = 0;\n for(auto& mine:mines) grid[mine.front()][mine.back()] = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < N; j++)\n if(j == 0) left[i][j] = grid[i][j];\n else left[i][j] = grid[i][j] == 0 ?0: left[i][j-1] + 1;\n for(int j = N - 1; j >= 0; j--)\n if(j == N -1) right[i][j] = grid[i][j];\n else right[i][j] = grid[i][j] == 0 ?0: right[i][j+1] + 1;\n }\n for(int j = 0; j < N; j++){\n for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)\n if( i == 0) up[i][j] = grid[i][j];\n else up[i][j] = grid[i][j] == 0? 0: up[i - 1][j] + 1;\n for(int i = N-1; i >=0; i--)\n if(i == N - 1) down[i][j] = grid[i][j];\n else down[i][j] = grid[i][j] == 0? 0: down[i+1][j] + 1;\n }\n for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)\n for(int j = 0; j < N; j++)\n grid[i][j] =min( min(up[i][j], down[i][j]), min(left[i][j],right[i][j]));\n\n\n for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)\n for(int j = 0; j < N; j++)\n ans = max(ans, grid[i][j]);\n return ans;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
JAVA DFS Easy To Understand
|
java-dfs-easy-to-understand-by-johnsysu-4rkq
|
\n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, int[][] mines) {\n boolean[][] matrix = new boolean[N][N];\n for (int i = 0; i < N; i++){\n
|
johnsysu
|
NORMAL
|
2018-01-14T15:00:30.315000+00:00
|
2018-01-14T15:00:30.315000+00:00
| 194 | false |
\n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, int[][] mines) {\n boolean[][] matrix = new boolean[N][N];\n for (int i = 0; i < N; i++){\n for (int j = 0; j < N; j++){\n matrix[i][j] = true;\n }\n }\n for (int[] mine: mines){\n matrix[mine[0]][mine[1]] = false;\n }\n int max = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < N; i++){\n for (int j = 0; j < N; j++){\n if (i < max || j < max || i > N-max-1 || j > N-max-1)\n continue;\n int tmp = explore(matrix, i, j, N);\n max = Math.max(tmp, max);\n }\n }\n return max;\n }\n private int explore(boolean[][] matrix, int i, int j, int N){\n if (!matrix[i][j])\n return 0;\n int order = 1;\n while ((i-order>=0) && (j-order>=0) && (i+order<N) && (j+order<N) && (matrix[i-order][j]) && (matrix[i+order][j]) && (matrix[i][j-order]) && (matrix[i][j+order])){\n order++;\n }\n return order;\n }
| 3 | 1 |
[]
| 1 |
largest-plus-sign
|
O(N^2) python solution TLE on 2 test cases?
|
on2-python-solution-tle-on-2-test-cases-dmxfm
|
I read the note about stricter C/C++ time limit, so I wrote an N^2 python solution. Why was this rejected?\n\nMinor optimizations won't change the order O(N^2).
|
erjoalgo
|
NORMAL
|
2018-01-14T04:04:03.123000+00:00
|
2018-01-14T04:04:03.123000+00:00
| 653 | false |
I read the note about stricter C/C++ time limit, so I wrote an N^2 python solution. Why was this rejected?\n\nMinor optimizations won't change the order O(N^2).\n\n\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, N, mines):\n """\n :type N: int\n :type mines: List[List[int]]\n :rtype: int\n """\n left=[[0]*N for __ in xrange(N)]\n right=[[0]*N for __ in xrange(N)]\n up=[[0]*N for __ in xrange(N)]\n down=[[0]*N for __ in xrange(N)]\n\n g=[[1]*N for __ in xrange(N)]\n\n for (r, c) in mines:\n g[r][c]=0\n\n for r in xrange(N):\n last=None\n for c in xrange(N):\n if g[r][c]:\n last=last or c\n left[r][c]=last\n else:\n last=None\n\n last=None\n for c in xrange(N-1, -1, -1):\n if g[r][c]:\n last=last or c\n right[r][c]=last\n else:\n last=None\n \n for c in xrange(N):\n last=None\n for r in xrange(N):\n if g[r][c]:\n last=last or c\n up[r][c]=last\n else:\n last=None\n\n last=None\n for r in xrange(N-1, -1, -1):\n if g[r][c]:\n last=last or c\n down[r][c]=last\n else:\n last=None\n\n mx=0\n for r in xrange(N):\n for c in xrange(N):\n if g[r][c]:\n horz=min(right[r][c]-c,c-left[r][c])+1\n vert=min(down[r][c]-r,r-up[r][c])+1\n val=min(horz, vert)\n mx=max(val, mx)\n \n return mx\n```
| 3 | 2 |
[]
| 7 |
largest-plus-sign
|
✅ Simple Approach to Understand and Code | BF | Beats 95% in Memory ✅
|
simple-approach-to-understand-and-code-b-kv85
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nSince mines positions are given, the intuition is to build the grid and then calculate
|
omkannav
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-27T04:22:31.140886+00:00
|
2023-11-06T22:39:49.255617+00:00
| 263 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nSince mines positions are given, the intuition is to build the grid and then calculate max order at each position.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. Create a grid matrix and fill it with 1 and then update the value to 0 wherever mines are present.\n2. Declare mgrid (grid with mines) and len for global access in the class\n3. For each position in mgrid, calculate order using countOrder().\n4. countOrder function has order by default 1 value and then news variables (north, east, west, south) for direction to check 1 is there in the respective direction and in all the direction. So if the sum of all surrounding NEWS position for (i, j) then increment the counter and keep countin till in either of the directions, the loop goes beyond or sum is not 4.\n\nI hope, this helps:\n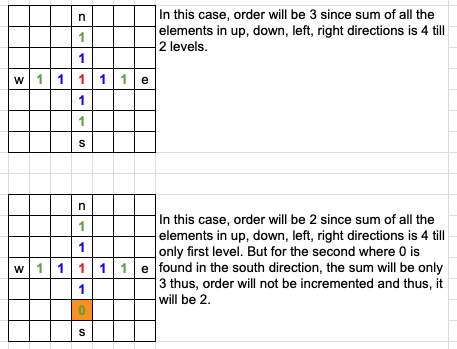\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n^3) because n^2 for each position in the grid and n to go till the boundry of the grid.\n\n- Space complexity: O(n^2)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n int len;\n int[][] mgrid;\n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, int[][] mines) {\n len = n;\n \n mgrid = new int[n][n];\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++)\n Arrays.fill(mgrid[i], 1);\n\n \n for(int i=0; i<mines.length; i++){\n int x = mines[i][0];\n int y = mines[i][1];\n mgrid[x][y] = 0;\n }\n\n int max = 0;\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++){\n for(int j=0; j<n; j++){\n if(mgrid[i][j] == 1)\n max = Math.max(max, countOrder(i, j));\n }\n }\n return max;\n }\n\n public int countOrder(int i, int j){\n int order=1;\n \n int n=i-1, e=j+1, w=j-1, s=i+1;\n \n while(n>=0 && w>=0 && s<len && e<len){\n if(mgrid[n][j] + mgrid[i][w] + mgrid[s][j] + mgrid[i][e] == 4)\n order++;\n else\n break; \n n--; w--; e++; s++;\n }\n \n return order;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Intersting solution, Worth your time
|
intersting-solution-worth-your-time-by-a-za40
|
you can check out my github repository where i am uploading famous interview questions topic wise with solutions.\nlink-- https://github.com/Abhaydutt2003/DataS
|
AbhayDutt
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-05T12:59:24.556239+00:00
|
2023-10-05T12:59:24.556262+00:00
| 174 | false |
you can check out my github repository where i am uploading famous interview questions topic wise with solutions.\nlink-- https://github.com/Abhaydutt2003/DataStructureAndAlgoPractice \nkindly upvote if you like my solution. you can ask doubts below.\xAF\n \n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, int[][] mines) {\n return util1(n,mines);\n }\n public int util1(int n, int mines[][]) {\n int matrix[][] = new int[n][n];\n // reverse the behaviour of 0 and 1\n for (int i = 0; i < mines.length; i++) {\n matrix[mines[i][0]][mines[i][1]] = 1;\n }\n int[][][] fuck = new int[n][n][4];\n // {up,left,bottom,right}\n // fill fuck for left and up\n for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == 1) {\n // do nothing\n continue;\n } else {\n if (i == 0 && j == 0) {\n fuck[i][j][0] = 1;\n fuck[i][j][1] = 1;\n } else if (i == 0) {\n fuck[i][j][0] = 1;\n fuck[i][j][1] = fuck[i][j - 1][1] + 1;\n } else if (j == 0) {\n fuck[i][j][1] = 1;\n fuck[i][j][0] = fuck[i - 1][j][0] + 1;\n } else {\n fuck[i][j][0] = fuck[i - 1][j][0] + 1;\n fuck[i][j][1] = fuck[i][j - 1][1] + 1;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n // fill fuck for bottom and right\n for (int i = matrix.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {\n for (int j = matrix[i].length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == 1) {\n // do nothing\n continue;\n } else {\n if (i == matrix.length - 1 && j == matrix.length - 1) {\n fuck[i][j][2] = 1;\n fuck[i][j][3] = 1;\n } else if (i == matrix.length - 1) {\n fuck[i][j][2] = 1;\n fuck[i][j][3] = fuck[i][j + 1][3] + 1;\n } else if (j == matrix.length - 1) {\n fuck[i][j][3] = 1;\n fuck[i][j][2] = fuck[i + 1][j][2] + 1;\n } else {\n fuck[i][j][2] = fuck[i + 1][j][2] + 1;\n fuck[i][j][3] = fuck[i][j + 1][3] + 1;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n // fuck is filled,now get the answer\n int ans = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < fuck.length; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < fuck[i].length; j++) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == 1) {\n // do nothing\n continue;\n } else {\n if (i == 0 || j == 0 || i == matrix.length - 1 || j == matrix[0].length - 1) {\n ans = Math.max(ans, 1);\n } else {\n int up = fuck[i][j][0];\n int left = fuck[i][j][1];\n int bottom = fuck[i][j][2];\n int right = fuck[i][j][3];\n int smallAns = Math.min(up, Math.min(left, Math.min(bottom, right)));\n ans = Math.max(smallAns, ans);\n }\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Matrix', 'Java']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Solution
|
solution-by-deleted_user-9w6g
|
C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n int ans=0,s,i,j,k;\n int dp[N+2][N+2][4],
|
deleted_user
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-26T21:38:05.890622+00:00
|
2023-04-26T22:07:23.938074+00:00
| 1,024 | false |
```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n int ans=0,s,i,j,k;\n int dp[N+2][N+2][4],v[N][N];\n for(i=0;i<N;i++)for(j=0;j<N;j++)v[i][j]=1;\n for(i=0;i<mines.size();i++)v[mines[i][0]][mines[i][1]]=0;\n memset(dp,0,sizeof dp);\n \n for(i=0;i<N;i++){\n for(j=0;j<N;j++){\n if(v[i][j]==1){\n dp[i+1][j+1][0]=dp[i][j+1][0]+1;\n dp[i+1][j+1][1]=dp[i+1][j][1]+1;\n }\n }\n }\n for(i=N-1;i>=0;i--){\n for(j=N-1;j>=0;j--){\n if(v[i][j]==1){\n dp[i+1][j+1][2]=dp[i+2][j+1][2]+1;\n dp[i+1][j+1][3]=dp[i+1][j+2][3]+1;\n }\n }\n }\n for(i=1;i<=N;i++){\n for(j=1;j<=N;j++){\n s=min(dp[i][j][0],min(dp[i][j][1],min(dp[i][j][2],dp[i][j][3])));\n ans=max(ans,s);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n```Python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, N: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n rows = [[-1, N] for _ in range(N)]\n cols = [[-1, N] for _ in range(N)]\n for r, c in mines:\n rows[r].append(c)\n cols[c].append(r)\n for i in range(N):\n rows[i].sort()\n cols[i].sort()\n mxp = 0\n for r in range(N):\n for i in range(len(rows[r]) - 1):\n left_b = rows[r][i]\n right_b = rows[r][i+1]\n for c in range(left_b + mxp + 1, right_b - mxp):\n idx = bisect_right(cols[c], r) - 1\n up_b = cols[c][idx]\n down_b = cols[c][idx + 1]\n mxp = max(mxp, min(c - left_b, right_b - c, r - up_b, down_b - r))\n return mxp\n```\n\n```Java []\nclass Solution {\n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, int[][] mines) {\n int[][] dp = new int[n][n];\n for(int[] mine : mines) {\n int row = mine[0], col = mine[1];\n dp[row][col] = -1;\n }\n for(int row = 0; row < n; row++) {\n int count = 0;\n for(int col = 0; col < n; col++) {\n if(dp[row][col] == -1) {\n count = 0;\n } else {\n count += 1;\n dp[row][col] = count;\n }\n }\n count = 0;\n for(int col = n - 1; col >= 0; col--) {\n if(dp[row][col] == -1) {\n count = 0;\n } else {\n count += 1;\n dp[row][col] = Math.min(dp[row][col], count);\n }\n }\n }\n int max = 0;\n for(int col = 0; col < n; col++) {\n int count = 0;\n for(int row = 0; row < n; row++) {\n if(dp[row][col] == -1) {\n count = 0;\n } else {\n count += 1;\n dp[row][col] = Math.min(dp[row][col], count);\n }\n }\n count = 0;\n for(int row = n - 1; row >= 0; row--) {\n if(dp[row][col] == -1) {\n count = 0;\n } else {\n count += 1;\n dp[row][col] = Math.min(dp[row][col], count);\n }\n max = Math.max(max, dp[row][col]);\n }\n }\n return max;\n }\n}\n```\n
| 2 | 0 |
['C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ || Simple and Concise || DP
|
c-simple-and-concise-dp-by-rohitraj13may-a58h
|
TC: O(3 * (N^2)) ---> ~= O(N^2)\nSC: O(4 * (N^2)) ---> ~= O(N^2)\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& arr) {
|
rohitraj13may1998
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-07T10:10:04.654463+00:00
|
2022-09-07T10:10:04.654502+00:00
| 397 | false |
TC: O(3 * (N^2)) ---> ~= O(N^2)\nSC: O(4 * (N^2)) ---> ~= O(N^2)\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& arr) {\n \n vector<vector<int>>nums(n,vector<int>(n,1));\n for(auto &it:arr){\n nums[it[0]][it[1]]=0;\n }\n vector<vector<int>>left=nums,right=nums,up=nums,down=nums;\n \n //up + left\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n if(nums[i][j]==1){\n up[i][j]+= (i-1<0 ? 0 : up[i-1][j]);\n left[i][j]+= (j-1<0 ? 0 :left[i][j-1]);\n } \n }\n }\n \n //right + down \n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){\n for(int j=n-1;j>=0;j--){\n if(nums[i][j]==1){\n right[i][j]+= (j+1>=n ? 0 : right[i][j+1]);\n down[i][j]+= (i+1>=n ? 0 : down[i+1][j]);\n }\n }\n } \n \n int maxi=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n int area= \n min({left[i][j],right[i][j],up[i][j],down[i][j]});\n maxi=max(maxi,area);\n }\n }\n return maxi;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ || Simple Approach || DP || TC: O(4 * (N^2))
|
c-simple-approach-dp-tc-o4-n2-by-rohitra-6jti
|
TC: O(5 * O(N^2)) ---> ~= O(N^2)\nSC: O(4 * (N^2)) ----> ~- O(N^2)\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& ar
|
rohitraj13may1998
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-07T10:01:31.718685+00:00
|
2022-09-07T10:01:31.718725+00:00
| 302 | false |
TC: O(5 * O(N^2)) ---> ~= O(N^2)\nSC: O(4 * (N^2)) ----> ~- O(N^2)\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& arr) {\n \n vector<vector<int>>nums(n,vector<int>(n,1));\n for(auto it:arr){\n nums[it[0]][it[1]]=0;\n }\n vector<vector<int>>left=nums,right=nums,up=nums,down=nums;\n \n //up\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n if(up[i][j]==1)\n up[i][j]+=up[i-1][j];\n }\n //left\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=1;j<n;j++){\n if(left[i][j]==1)\n left[i][j]+=left[i][j-1];\n }\n }\n //right\n //down\n for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n if(down[i][j]==1)\n down[i][j]+=down[i+1][j];\n }\n }\n //right\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=n-2;j>=0;j--){\n if(right[i][j]==1)\n right[i][j]+=right[i][j+1];\n }\n }\n \n int maxi=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n int area= \n min({left[i][j],right[i][j],up[i][j],down[i][j]});\n maxi=max(maxi,area);\n }\n }\n return maxi;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ | Recursion | Memoization | grid traversal
|
c-recursion-memoization-grid-traversal-b-fz14
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> dir={{0,-1},{0,1},{1,0},{-1,0}};\n int dp[501][501][4];\n int solve(int i,int j,int k,vector<vector<i
|
azadprajapat
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-02T01:07:48.122146+00:00
|
2022-09-02T01:07:48.122186+00:00
| 462 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> dir={{0,-1},{0,1},{1,0},{-1,0}};\n int dp[501][501][4];\n int solve(int i,int j,int k,vector<vector<int>> &grid){\n int n = grid.size();\n if(dp[i][j][k]!=-1) return dp[i][j][k];\n int ni=i+dir[k][0];\n int nj = j+dir[k][1];\n if(ni<0||nj<0||ni>=n||nj>=n||grid[ni][nj]==0)\n return 0;\n return dp[i][j][k]=1+solve(ni,nj,k,grid);\n }\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> grid(n,vector<int>(n,1));\n memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));\n for(int i=0;i<mines.size();i++)\n grid[mines[i][0]][mines[i][1]]=0;\n int ans =0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n if(grid[i][j]==1){\n ans=max(ans,1+min({solve(i,j,0,grid),solve(i,j,1,grid),solve(i,j,2,grid),solve(i,j,3,grid)})); \n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization']
| 1 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ | Dp | Easy | Faster | only O(n^2)
|
c-dp-easy-faster-only-on2-by-yashbansal2-r3wm
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n //jai shri ram\n int ans=0;\n vector<boo
|
yashbansal24
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-25T09:00:30.219502+00:00
|
2022-07-25T09:00:30.219552+00:00
| 355 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n //jai shri ram\n int ans=0;\n vector<bool>block(25*int(1e4)+1,0);\n vector<vector<int>>dp(n,vector<int>(n,0));\n for(auto x:mines){\n int a=x[0],b=x[1];\n block[a*n+b]=true;\n }\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int sum=0;\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n if(block[i*n+j]){\n sum=0;\n }else {\n sum+=1;\n }\n dp[i][j]=sum;\n }\n }\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n int sum=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n if(block[i*n+j]){\n sum=0;\n }else sum+=1;\n dp[i][j]=min(dp[i][j],sum);\n }\n }\n for(int j=n-1;j>=0;j--){\n int sum=0;\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){\n if(block[i*n+j]){\n sum=0;\n }else sum+=1;\n dp[i][j]=min(dp[i][j],sum);\n }\n }\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){\n int sum=0;\n for(int j=n-1;j>=0;j--){\n if(block[i*n+j]){\n sum=0;\n }else sum+=1;\n dp[i][j]=min(dp[i][j],sum);\n ans=max(ans,dp[i][j]);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
most easy to understand solution
|
most-easy-to-understand-solution-by-karn-6xyg
|
int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector>& mines) {\n \n \n vector> a(n,vector(n,1));\n int i;\n \n for(auto& x:mines
|
karna001
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-18T10:29:28.940690+00:00
|
2022-02-18T10:29:28.940729+00:00
| 132 | false |
int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n \n \n vector<vector<int>> a(n,vector<int>(n,1));\n int i;\n \n for(auto& x:mines)\n {\n a[x[0]][x[1]]=0;\n \n }\n \n vector<vector<int>> left=a;\n vector<vector<int>> right=a;\n vector<vector<int>> up=a;\n vector<vector<int>> down=a;\n int m=n;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=1;j<n;j++)\n {\n if(left[i][j]==1)\n {\n left[i][j] = left[i][j-1]+1;\n }\n \n }\n }\n \n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=m-2;j>=0;j--)\n {\n if(right[i][j]==1)\n {\n right[i][j]= right[i][j+1]+1;\n }\n \n }\n }\n \n \n for(int i=1;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++)\n {\n if(up[i][j]==1)\n {\n up[i][j] = up[i-1][j]+1;\n }\n \n }\n }\n \n \n for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++)\n {\n if(down[i][j]==1)\n {\n down[i][j] = down[i+1][j]+1;\n }\n \n }\n }\n \n \n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++)\n {\n ans=max(ans,min({left[i][j],right[i][j],down[i][j],up[i][j]}));\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Java Easy DP
|
java-easy-dp-by-gautamsw5-84th
|
\n// For each cell, store number of consecutive 1\'s in each direction: up, down, left and right\nclass Cell {\n int val, up, down, left, right;\n Cell(in
|
gautamsw5
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-12T09:23:33.517699+00:00
|
2021-09-12T09:23:33.517740+00:00
| 137 | false |
```\n// For each cell, store number of consecutive 1\'s in each direction: up, down, left and right\nclass Cell {\n int val, up, down, left, right;\n Cell(int val) {\n this.up = this.down = this.left = this.right = this.val = val;\n }\n int getPlusSize() {\n return Math.min(up, Math.min(down, Math.min(left, right)));\n }\n}\nclass Solution {\n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, int[][] mines) {\n Cell[][] mat = new Cell[n][n];\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) mat[i][j] = new Cell(1);\n for(int[] mine: mines) mat[mine[0]][mine[1]] = new Cell(0);\n \n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n if(mat[i][j].val == 1) {\n if(i > 0) mat[i][j].left += mat[i-1][j].left;\n if(j > 0) mat[i][j].up += mat[i][j-1].up;\n }\n }\n }\n \n for(int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {\n for(int j = n-1; j >= 0; j--) {\n if(mat[i][j].val == 1) {\n if(i+1 < n) mat[i][j].right += mat[i+1][j].right;\n if(j+1 < n) mat[i][j].down += mat[i][j+1].down;\n }\n }\n }\n \n int ans = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)\n ans = Math.max(ans, mat[i][j].getPlusSize());\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ Solution
|
c-solution-by-saurabhvikastekam-lgb7
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int>(n, 1));\n
|
SaurabhVikasTekam
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-10T08:20:04.024232+00:00
|
2021-09-10T08:20:04.024259+00:00
| 112 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int>(n, 1));\n unordered_set<int> mineSet;\n for(auto& e: mines) mineSet.insert(e[0]*n + e[1]);\n int ans = 0;\n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){ \n for(int i = 0, cnt = 0; i < n; i++){ \n cnt = mineSet.count(i*n+j) ? 0 : cnt + 1;\n dp[i][j] = cnt;\n }\n \n for(int i = n - 1, cnt = 0; i >= 0; i--){ \n cnt = mineSet.count(i*n+j) ? 0 : cnt + 1;\n dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], cnt);\n } \n }\n \n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ \n for(int j = 0, cnt = 0; j < n; j++){ \n cnt = mineSet.count(i*n+j) ? 0 : cnt + 1;\n dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], cnt);\n }\n \n for(int j = n - 1, cnt = 0; j >= 0; j--){ \n cnt = mineSet.count(i*n+j) ? 0 : cnt + 1;\n dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], cnt);\n ans = max(ans, dp[i][j]);\n } \n } \n \n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 1 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
[Java] - Pure Brute Approach
|
java-pure-brute-approach-by-pgthebigshot-m682
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, int[][] mines) {\n \n \tif(n*n==mines.length)\n \t\treturn 0;\n \n \tif(
|
pgthebigshot
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-10T05:55:57.922185+00:00
|
2021-09-10T06:04:55.188786+00:00
| 237 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, int[][] mines) {\n \n \tif(n*n==mines.length)\n \t\treturn 0;\n \n \tif(n<3)\n return 1;\n \t\n \tint arr[][]=new int[n][n];\n \t\n \tint i,j,k;\n \t\n \tfor(i=0;i<n;i++)\n \t\tArrays.fill(arr[i], 1);\n \t\n \tfor(i=0;i<mines.length;i++)\n \t\tarr[mines[i][0]][mines[i][1]]=0;\n \t\n int tm=n;\n if(tm%2==0)\n tm--;\n \t\t\n \tfor(i=tm;i>=3;i-=2)\n \t{\n \t\tfor(j=0;j<=n-i;j++)\n \t\t{\n \t\t\tfor(k=i/2;k<n-i/2;k++)\n \t\t\t{\n \t\t\t\t int l,m;\n \t\t\t\t //checking the vertical 1\'s of plus sign\n \t\t\t\t for(l=0;l<i;l++)\n \t\t\t\t {\n \t\t\t\t\t if(arr[l+j][k]!=1)\n \t\t\t\t\t\t break;\n \t\t\t\t }\n \t\t\t\t if(l<i)\n continue;\n \t\t\t\t //checking the horizontal 1\'s of plus sign\n \t\t\t\t for(m=0;m<i;m++)\n \t\t\t\t {\n \t\t\t\t\t if(arr[j+i/2][k-i/2+m]!=1)\n \t\t\t\t\t\t break;\n \t\t\t\t }\n \t\t\t\t if(m==i)\n return i/2+1;\n \t\t\t}\n \t\t}\n \t}\n \t\n\t return 1;\n }\n}\n```\nAny Questions?\nPlease do upvote:))
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Largest_Plus_Sign
|
largest_plus_sign-by-amit279-ywz2
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n int left[n][n];\n int right[n][n];\n int
|
amit279
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-09T09:59:36.962858+00:00
|
2021-09-09T09:59:36.962892+00:00
| 178 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n int left[n][n];\n int right[n][n];\n int up[n][n];\n int down[n][n];\n int ans = 0;\n int dp[n][n];\n for(int i = 0 ;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n {\n dp[i][j] = 1;\n up[i][j] = 1;\n down[i][j] = 1;\n left[i][j] = 1;\n right[i][j] = 1;\n }\n }\n for(int i=0;i<mines.size();i++)\n {\n dp[mines[i][0]][mines[i][1]] = 0;\n up[mines[i][0]][mines[i][1]] = 0;\n down[mines[i][0]][mines[i][1]] = 0;\n left[mines[i][0]][mines[i][1]] = 0;\n right[mines[i][0]][mines[i][1]] = 0;\n }\n int i = 0;\n for(int i = 1;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j =1;j<n;j++)\n {\n if(up[i][j]!=0)\n {\n up[i][j]+=up[i-1][j];\n }\n if(left[i][j]!=0)\n {\n left[i][j]+=left[i][j-1];\n }\n }\n }\n for(int i = n-2;i>=0;i--)\n {\n for(int j =n-2;j>=0;j--)\n {\n if(down[i][j]!=0)\n {\n down[i][j]+=down[i+1][j];\n }\n if(right[i][j]!=0)\n {\n right[i][j]+=right[i][j+1];\n }\n }\n }\n \n for(int i = 1; i<n-1;i++)\n {\n for(int j = 1;j<n-1;j++)\n {\n ans = max(ans,min(min(left[i][j],right[i][j]),min(up[i][j],down[i][j])));\n }\n }\n if(ans==0)\n {\n if(n*n!=mines.size())\n {\n return 1;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 2 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
[Python] Intuitive DP Solution
|
python-intuitive-dp-solution-by-vasu6-lu49
|
Intuition :- The main idea is to find the length of four wingspans at each point. We can do that using the wingspans of the adjacent elements, so we can utilize
|
vasu6
|
NORMAL
|
2020-11-30T19:10:00.046597+00:00
|
2020-11-30T19:10:13.594938+00:00
| 272 | false |
**Intuition** :- The main idea is to find the length of four wingspans at each point. We can do that using the wingspans of the adjacent elements, so we can utilize something like a dp for this. The wingspan for that point would be the mininum span value of all 4 direction spans and the final answer would be the maximum of all wingspan values(at each point). \n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, n: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n mines_dict = {(mine[0], mine[1]): True for mine in mines}\n dp = {}\n ans = 0\n\t\t\n\t\t# left and right wingspan calculation\n for row in range(n):\n cnt = 0\n for col in range(n):\n cnt = self.update_dp(dp, mines_dict, row, col, cnt)\n cnt = 0\n for col in range(n-1, -1, -1):\n cnt = self.update_dp(dp, mines_dict, row, col, cnt)\n \n \n\t\t# top and down wingspan calculation\n for col in range(n):\n cnt = 0\n for row in range(n):\n cnt = self.update_dp(dp, mines_dict, row, col, cnt)\n cnt = 0\n for row in range(n-1, -1, -1):\n cnt = self.update_dp(dp, mines_dict, row, col, cnt)\n\t\t\t\t\n\t\t\t\t# final answer would be the maximum wingspan at any point.\n ans = max(ans, dp[row, col])\n return ans\n \n \n def update_dp(self, dp, mines_dict, row, col, cnt):\n if (row, col) not in mines_dict:\n cnt += 1\n dp[row, col] = min(cnt, dp[row, col]) if (row, col) in dp else cnt\n else:\n cnt = 0\n dp[row, col] = 0\n return cnt\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python3']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
[Python] Nothing Fancy - 3 Steps
|
python-nothing-fancy-3-steps-by-rowe1227-aobn
|
html5\n<b>Time Complexity: O(N<sup>2</sup>)\nSpace Complexity: O(N<sup>2</sup>)</b>\n\n\n1. Make a binary grid where 1s represent spaces that can be used to mak
|
rowe1227
|
NORMAL
|
2020-10-30T04:22:00.207574+00:00
|
2020-10-30T04:22:00.207620+00:00
| 127 | false |
```html5\n<b>Time Complexity: O(N<sup>2</sup>)\nSpace Complexity: O(N<sup>2</sup>)</b>\n```\n\n1. Make a binary **grid** where 1s represent spaces that can be used to make a plus sign and 0s are mines. \n\n2. Make 4 helper grids **left, right, up,** and **down**. \nleft[i][j] says how many 1s there are to the **left** of location (i, j)\nLikewise right[i][j] says how many 1s there are to the **right** of location (i, j). \nSame for **up** and **down**. \n\n3. The largest plus sign you can make at location (i, j) is the mininum of **left[i][j], right[i][j], up[i][j],** and **down[i][j]**. \nIterate over all the locations on the grid and return the size of the maximum plus sign you can make. \n\n<br>\n\n```python\ndef orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, N: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n\n\tgrid = [[1 for _ in range(N)] for _ in range(N)]\n\tfor i, j in mines:\n\t\tgrid[i][j] = 0\n\n\tleft = [[0 for _ in range(N)] for _ in range(N)]\n\tright = [[0 for _ in range(N)] for _ in range(N)]\n\tup = [[0 for _ in range(N)] for _ in range(N)]\n\tdown = [[0 for _ in range(N)] for _ in range(N)]\n\n\t# Construct left and right\n\tfor i in range(N):\n\t\tcount = 0\n\t\tfor j in range(N):\n\t\t\tleft[i][j] = count\n\t\t\tcount = count + 1 if grid[i][j] else 0\n\n\t\tcount = 0\n\t\tfor j in range(N-1, -1, -1):\n\t\t\tright[i][j] = count\n\t\t\tcount = count + 1 if grid[i][j] else 0\n\n\t# Construct up and down\n\tfor j in range(N):\n\t\tcount = 0\n\t\tfor i in range(N):\n\t\t\tdown[i][j] = count\n\t\t\tcount = count + 1 if grid[i][j] else 0\n\n\t\tcount = 0\n\t\tfor i in range(N-1, -1, -1):\n\t\t\tup[i][j] = count\n\t\t\tcount = count + 1 if grid[i][j] else 0\n\n\t# Find the largest Plus Sign\n\tres = 0\n\tfor i in range(N):\n\t\tfor j in range(N):\n\t\t\tif grid[i][j]:\n\t\t\t\tsize = min(left[i][j], right[i][j], down[i][j], up[i][j])\n\t\t\t\tres = max(res, size + 1)\n\n\treturn res\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ Easy to Understand 95% Space 95% Time
|
c-easy-to-understand-95-space-95-time-by-iasv
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n int temp[N][N];\n for(int i=0;i<N;i++)\n
|
pjdope
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-13T18:28:02.011445+00:00
|
2020-08-13T18:28:02.011500+00:00
| 356 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n int temp[N][N];\n for(int i=0;i<N;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<N;j++)\n temp[i][j]=N;\n }\n for(auto i:mines)temp[i[0]][i[1]]=0;\n \n for(int i=0;i<N;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0,k=N-1,u=0,d=0,l=0,r=0;j<N;j++,k--)\n {\n temp[i][j]=min(temp[i][j],u=(temp[i][j]==0?0:u+1));\n temp[i][k]=min(temp[i][k],d=(temp[i][k]==0?0:d+1));\n temp[j][i]=min(temp[j][i],l=(temp[j][i]==0?0:l+1));\n temp[k][i]=min(temp[k][i],r=(temp[k][i]==0?0:r+1));\n }\n }\n int res=0;\n for(int i=0;i<N;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<N;j++)\n res=max(res,temp[i][j]);\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
largest-plus-sign
|
(66ms) Easy to understand Java Solution(O(N^2) Two Pass)
|
66ms-easy-to-understand-java-solutionon2-f7p4
|
In the solution we just need one 2d array grid[N][N].\n\nThe basic idea is to record the min length of 4 directions, for example:\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\n 1\n
|
aoooo
|
NORMAL
|
2018-08-24T16:57:32.588324+00:00
|
2018-09-29T06:30:34.892706+00:00
| 259 | false |
In the solution we just need one 2d array **grid[N][N]**.\n\nThe basic idea is to record the min length of 4 directions, for example:\n```\t\t\t\t\t\t\n 1\n 1\n 1 grid[i][j] 1 1 1 1\n 1\n```\nThe value of grid[i][j] should be 2 (because **grid[i][j]** it self is also considered 1).\n\nThen we iterator the grid twice.\nThe first pass is from left to right, top to bottom so that we can get the the min(left, top) for each element;\nThe second pass is from right to left , bottom to top so that we can get the min(right, bottom) for each element;\n\nThen we can get the min value of 4 direction and find the max.\n\nJava Code:\n```java\npublic int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, int[][] mines) {\n int[][] grid = new int[N][N];\n for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n Arrays.fill(grid[i], 1);\n }\n for (int[] mine: mines) {\n grid[mine[0]][mine[1]] = 0;\n }\n int[] pre = new int[N];\n for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n int count = 0;\n for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {\n if (grid[i][j] != 0) {\n grid[i][j] = Math.min(++count, ++pre[j]);\n } else {\n count = 0;\n pre[j] = 0;\n }\n }\n }\n Arrays.fill(pre, 0);\n int max = 0;\n for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--) {\n int count = 0;\n for (int j = N - 1; j >= 0; j--) {\n if (grid[i][j] != 0) {\n grid[i][j] = Math.min(grid[i][j], Math.min(++count, ++pre[j]));\n } else {\n count = 0;\n pre[j] = 0;\n }\n max = Math.max(max, grid[i][j]);\n }\n }\n return max;\n }\n```\n
| 2 | 1 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
[Python]: DP - code optimized - explanation in detail - ACCEPTED
|
python-dp-code-optimized-explanation-in-fpiww
|
The straightforward approach. The following code did some optimization, and it was accepted.\n\nTwo keys:\n1. convert mines from list to dictionary\n2. use try/
|
poweric
|
NORMAL
|
2018-02-09T21:23:59.499000+00:00
|
2018-02-09T21:23:59.499000+00:00
| 478 | false |
The straightforward approach. The following code did some optimization, and it was accepted.\n\nTwo keys:\n1. convert mines from list to dictionary\n2. use try/except instead of if/else to deal with matrix boundary issue. \n\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, N, mines):\n """\n :type N: int\n :type mines: List[List[int]]\n :rtype: int\n """\n # Methods to reduce computational time:\n # 1. convert mines from list to dictionary. O(n^3) to O(n^2)\n # 2. use try/except instead of if else to deal with matrix boundary\n \n L = [[0 for x in range(N)] for y in range(N)] #L[i][j]: number of continuous 1 from L[i][j] towards its left, L[i][j] included. \n R = [[0 for x in range(N)] for y in range(N)] #Right\n U = [[0 for x in range(N)] for y in range(N)] #Up\n D = [[0 for x in range(N)] for y in range(N)] #Down\n \n dicMines = {(mine[0], mine[1]) for mine in mines} # convert mines from list to dictionary\n \n # calcuate L and D in O(n^2) time\n for i in range(N):\n for j in range(N):\n if (i,j) not in dicMines:\n # use try/except instead of if/else to reduce time, if/else method is presented below as well\n try: L[i][j] = L[i][j-1] + 1\n except Exception: L[i][j] = 1\n try: D[i][j] = D[i-1][j] + 1\n except Exception: D[i][j] = 1\n \n #if/else method presented for reference\n #L[i][j] = L[i][j-1] + 1 if j > 0 else 1\n #D[i][j] = D[i-1][j] + 1 if i > 0 else 1\n \n # calcuate R and U in O(n^2) time\n for i in range (N-1, -1, -1):\n for j in range(N-1, -1, -1):\n if (i,j) not in dicMines:\n try: R[i][j] = R[i][j+1] + 1\n except Exception: R[i][j] = 1\n try: U[i][j] = U[i+1][j] + 1\n except Exception: U[i][j] = 1\n\n #R[i][j] = R[i][j+1] + 1 if j < N-1 else 1\n #U[i][j] = U[i+1][j] + 1 if i < N-1 else 1\n MaxK = 0\n MaxK = max(min(L[i][j], R[i][j], U[i][j], D[i][j]) for i in range(N) for j in range(N))\n return (MaxK)\n```
| 2 | 1 |
[]
| 3 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Python AC and the TRICK to avoid TLE
|
python-ac-and-the-trick-to-avoid-tle-by-xoo8y
|
I guess many python people also suffered from the TLE.\n\nHere is my code that just passed. It is not the best. But I just want to jump out to let those python
|
licaiuu
|
NORMAL
|
2018-01-14T05:33:41.373000+00:00
|
2018-01-14T05:33:41.373000+00:00
| 250 | false |
I guess many python people also suffered from the TLE.\n\nHere is my code that just passed. It is not the best. But I just want to jump out to let those python guys know this may be what the judge is expecting: avoid looking at those points that can not be better than known best "plus length".\n\nPlease pay attention to this two lines in my code below. This makes my solution from TLE to AC:\n```\nif N-j<=maxmin or N-i<=maxmin:\n continue\n```\n\nThe main thing that makes it from TLE to AC is that: when we move to area where the max plus length(which is my ```maxmin``` below) is already larger than the distance it can reach the boundary(```N-j``` or ```N-i```), either right boundary or lower boundary, we need to drop those to reduce unnecessary work, because there is no point to keep moving right or keep moving down.\n\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, N, mines):\n if not N: return 0\n if len(mines)==N*N: return 0\n self.mmset = []\n for i in range(N):\n self.mmset.append([True for j in range(N)])\n for p in mines:\n self.mmset[p[0]][p[1]] = False\n \n maxmin = 0\n # using rolling arrays to achieve DP.\n # the 4 elements tuple means length of 1s for [North, West, South, East].\n oldline = [[0,0,0,0] for _ in range(N)]\n for i in range(N):\n newline = [[0,0,0,0] for _ in range(N)]\n for j in range(0, N):\n if not self.mmset[i][j]:\n continue\n if N-j<=maxmin or N-i<=maxmin:\n continue\n newline[j][0] = oldline[j][0] + 1\n \n if j==0:\n newline[j][1] = 1\n else:\n newline[j][1] = newline[j-1][1]+1\n \n if oldline[j][2]==0:\n for newi in xrange(i,N):\n if self.mmset[newi][j]:\n newline[j][2]+=1\n else:\n break\n else:\n newline[j][2] = oldline[j][2]-1\n \n if j==0 or newline[j-1][3]==0:\n for newj in xrange(j, N):\n if self.mmset[i][newj]:\n newline[j][3] += 1\n else:\n break\n else:\n newline[j][3] = newline[j-1][3]-1\n \n maxmin = max(min(newline[j]), maxmin)\n \n oldline = newline\n return maxmin\n \n```
| 2 | 1 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ O(N^2 * LogN) Binary Search Solution
|
c-on2-logn-binary-search-solution-by-r_w-aels
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n int len = 0;\n vector<set<int>> row(N), col(N);
|
r_w
|
NORMAL
|
2018-01-14T06:30:54.606000+00:00
|
2018-08-30T02:32:01.811477+00:00
| 326 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n int len = 0;\n vector<set<int>> row(N), col(N);\n for (auto &v : mines) {\n row[v[0]].emplace(v[1]);\n col[v[1]].emplace(v[0]);\n }\n\n for (int r = 0; r < N; r++) {\n for (int c = 0; c < N; c++) {\n int row_len = maxlen(row[r], c, N); // max length of row\n int col_len = maxlen(col[c], r, N); // max length of col\n len = max(len, min(row_len, col_len));\n }\n }\n return (len + 1) / 2;\n }\n\n int maxlen(set<int>& s, int mid, int N) {\n auto it = s.lower_bound(mid);\n if (it != s.end() && *it == mid) return 0; // (i, j) is 0\n int end = it == s.end() ? N - 1 : *it - 1;\n int begin = it == s.begin() ? 0 : *(--it) + 1;\n int len = 2 * min(mid - begin, end - mid) + 1;\n return len;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Python straightforward 900ms
|
python-straightforward-900ms-by-likethef-64c6
|
Got AC by checking occurrence of '0' of the string. \nGeneral idea:\n1. check whether both row and col of location(i,j) can achieve a target order by finding th
|
liketheflower
|
NORMAL
|
2018-01-14T18:24:20.729000+00:00
|
2018-01-14T18:24:20.729000+00:00
| 396 | false |
Got AC by checking occurrence of '0' of the string. \nGeneral idea:\n1. check whether both row and col of location(i,j) can achieve a target order by finding the existence of '0'. If '0', false. Else increase the looking scope by one and recheck.\n2. checking whether we can satisfy the requirement based on the current maximum available order directly(which is k+1 to N where k is the already available maximum order) instead of checking from 1 to N. \n\nKey steps:\n1. get the strings for each row and get the string for each column\n2. for row i and col j, check whether the occurrence of '1' from both row and column can achieve order X. X is the current maximum order +1. \n 1) If it works, a) updated the available maximum order \n b) keep on checking a bigger X to see whether success and do the right thing based on the result: increase the available maximum order or quit when fail\n 2) if it doesn't work, check the next one.\n \n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, N, mines):\n if len(mines)==N**2: return 0\n grid = [['1']*N for _ in range(N)]\n for i,j in mines: grid[i][j]='0'\n grid_row = [''.join(row) for row in grid]\n grid_col = [''.join(col) for col in map(list, zip(*grid))]\n res = 1\n for i in xrange(N):\n for j in xrange(N):\n if grid[i][j]=='1':\n while True:\n if (j-res>=0 and j+res<N and i-res>=0 and i+res<N and\n '0' not in grid_row[i][j-res:j+res+1] and\n '0' not in grid_col[j][i-res:i+res+1]):\n res+=1 \n else: \n break\n return res\n```
| 2 | 2 |
[]
| 2 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Python Top Down + Memoization -> Bottom Up DP Solution
|
python-top-down-memoization-bottom-up-dp-a600
|
Top Down\n\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, n: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n \n memo = {}\n \n def re
|
tony353
|
NORMAL
|
2023-12-24T18:50:52.355759+00:00
|
2023-12-24T18:50:52.355787+00:00
| 228 | false |
Top Down\n```\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, n: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n \n memo = {}\n \n def recurse(r, c, direction):\n \n if (r, c, direction) in memo:\n return memo[(r, c, direction)]\n \n if not 0 <= r < n or not 0 <= c < n:\n return 0\n \n if (r, c) in mines_set:\n return 0\n \n if direction == "L":\n res = 1 + recurse(r, c - 1, "L")\n elif direction == "R":\n res = 1 + recurse(r, c + 1, "R")\n elif direction == "U":\n res = 1 + recurse(r - 1, c, "U")\n elif direction == "D":\n res = 1 + recurse(r + 1, c, "D")\n \n memo[(r, c, direction)] = res\n \n return res\n \n mines_set = set()\n \n for x, y in mines:\n mines_set.add((x, y))\n \n max_res = 0\n \n for i in range(n):\n for j in range(n):\n curr_res = min(\n recurse(i, j, "L"),\n recurse(i, j, "R"),\n recurse(i, j, "U"),\n recurse(i, j, "D")\n )\n \n max_res = max(max_res, curr_res)\n\n return max_res\n \n```\n\nBottom Up\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, n: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n\n mines_set = set()\n \n for x, y in mines:\n mines_set.add((x, y))\n \n dp = [[[0] * 4 for _ in range(n + 1)] for _ in range(n + 1)]\n \n max_res = 0\n\n for r in range(n - 1, -1, -1):\n for c in range(n - 1, -1, -1):\n \n for direction in [1, 3]:\n\n if (r, c) in mines_set:\n continue\n \n if direction == 1:\n dp[r][c][direction] = 1 + dp[r][c + 1][1]\n elif direction == 3:\n dp[r][c][direction] = 1 + dp[r + 1][c][3]\n\n\n for r in range(n):\n for c in range(n):\n \n for direction in [0, 2]:\n\n if (r, c) in mines_set:\n continue\n \n if direction == 0:\n dp[r][c][direction] = 1 + dp[r][c - 1][0]\n elif direction == 2:\n dp[r][c][direction] = 1 + dp[r - 1][c][2]\n\n max_res = max(max_res, min(dp[r][c]))\n \n\n return max_res\n \n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'Python3']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ Easy Solution
|
c-easy-solution-by-md_aziz_ali-1l76
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int directionArray[5] = {0,1,0,-1,0};\n int dp[500][500][4];\n int n;\n int solve(int x,int y,vector<vector<int>
|
Md_Aziz_Ali
|
NORMAL
|
2023-09-28T13:47:18.941901+00:00
|
2023-09-28T13:47:18.941925+00:00
| 95 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int directionArray[5] = {0,1,0,-1,0};\n int dp[500][500][4];\n int n;\n int solve(int x,int y,vector<vector<int>>& arr,int direction){\n if(x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= n || y >= n || arr[x][y] == 0)\n return 0;\n if(dp[x][y][direction] != -1)\n return dp[x][y][direction];\n return dp[x][y][direction] = 1 + solve(x+directionArray[direction],y+directionArray[direction+1],arr,direction);\n }\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n this->n = n;\n vector<vector<int>>arr(n,vector<int>(n,1));\n memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));\n for(int i = 0;i<mines.size();i++){\n arr[mines[i][0]][mines[i][1]] = 0;\n }\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){\n for(int j = 0;j < n;j++){\n int mini = INT_MAX;\n for(int k = 0;k < 4;k++)\n mini = min(mini,solve(i,j,arr,k));\n ans = max(mini,ans);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ | Easy To Understand | Prefix - Sum Approach
|
c-easy-to-understand-prefix-sum-approach-l40g
|
\nThis is not the fastest solution but it is very easy to understand and come up during an actual interview. Pls feel free to optimise this solution!\n# Code\n\
|
whitesaladchips
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-29T09:40:48.972459+00:00
|
2023-08-29T09:40:48.972492+00:00
| 847 | false |
\nThis is not the fastest solution but it is very easy to understand and come up during an actual interview. Pls feel free to optimise this solution!\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> up(n, vector<int>(n, 0)), down(n, vector<int>(n, 0)), left(n, vector<int>(n, 0)), right(n, vector<int>(n, 0));\n\n unordered_map<int, unordered_map<int,int>> mp;\n for(auto &p : mines)\n mp[p[0]][p[1]]++;\n\n//below code that includes 4 double loops are used for storing prefix sum of 1\'s in left, right,up and down direction.\n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n if(mp[i].find(j) != mp[i].end())\n up[i][j] = 0;\n else if(i == 0)\n up[i][j] = 1;\n else\n up[i][j] = 1 + up[i - 1][j];\n }\n }\n\n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){\n for(int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--){\n if(mp[i].find(j) != mp[i].end())\n down[i][j] = 0;\n else if(i == n - 1)\n down[i][j] = 1;\n else\n down[i][j] = 1 + down[i + 1][j];\n }\n }\n\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){\n if(mp[i].find(j) != mp[i].end())\n left[i][j] = 0;\n else if(j == 0)\n left[i][j] = 1;\n else\n left[i][j] = 1 + left[i][j - 1];\n }\n }\n\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n for(int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--){\n if(mp[i].find(j) != mp[i].end())\n right[i][j] = 0;\n else if(j == n - 1)\n right[i][j] = 1;\n else\n right[i][j] = 1 + right[i][j + 1];\n }\n }\n\n\n int res = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){\n // cout<<left[i][j]<<" "<<right[i][j]<<" "<<up[i][j]<<" "<<down[i][j]<<endl;\n res = max(res, min(left[i][j], min(right[i][j], min(up[i][j], down[i][j]))));\n //the \'order\' of plus sign will be the minimum of prefix sums from the four sides.\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Prefix Sum', 'C++']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Just a runnable solution
|
just-a-runnable-solution-by-ssrlive-8lxb
|
Code\n\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn order_of_largest_plus_sign(n: i32, mines: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {\n let n = n as usize;\n let mut grid = vec![
|
ssrlive
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-15T02:38:03.014491+00:00
|
2022-12-15T02:38:03.014539+00:00
| 29 | false |
# Code\n```\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn order_of_largest_plus_sign(n: i32, mines: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {\n let n = n as usize;\n let mut grid = vec![vec![1; n]; n];\n for mine in mines {\n grid[mine[0] as usize][mine[1] as usize] = 0;\n }\n\n let mut left = vec![vec![0; n]; n];\n let mut right = vec![vec![0; n]; n];\n let mut up = vec![vec![0; n]; n];\n let mut down = vec![vec![0; n]; n];\n\n for i in 0..n {\n for j in 0..n {\n if grid[i][j] == 1 {\n left[i][j] = if j == 0 { 1 } else { left[i][j - 1] + 1 };\n up[i][j] = if i == 0 { 1 } else { up[i - 1][j] + 1 };\n }\n }\n }\n\n for i in (0..n).rev() {\n for j in (0..n).rev() {\n if grid[i][j] == 1 {\n right[i][j] = if j == n - 1 { 1 } else { right[i][j + 1] + 1 };\n down[i][j] = if i == n - 1 { 1 } else { down[i + 1][j] + 1 };\n }\n }\n }\n\n let mut ans = 0;\n for i in 0..n {\n for j in 0..n {\n let len = std::cmp::min(left[i][j], std::cmp::min(right[i][j], std::cmp::min(up[i][j], down[i][j])));\n ans = std::cmp::max(ans, len);\n }\n }\n\n ans as i32\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Rust']
| 1 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++||DP+Memoization||Recursion||Easy to Understand
|
cdpmemoizationrecursioneasy-to-understan-o3ui
|
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dp[500][500][4];\n int dir[5]={0,1,0,-1,0};\n int solve(vector> &grid,int n,int r,int c,int d)\n {\n if(
|
return_7
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-01T13:39:58.677114+00:00
|
2022-12-01T13:39:58.677155+00:00
| 172 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dp[500][500][4];\n int dir[5]={0,1,0,-1,0};\n int solve(vector<vector<int>> &grid,int n,int r,int c,int d)\n {\n if(r<0||c<0||r>=n||c>=n||grid[r][c]==0)\n return 0;\n if(dp[r][c][d]!=-1)\n return dp[r][c][d];\n return dp[r][c][d]=1+solve(grid,n,r+dir[d],c+dir[d+1],d);\n \n }\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) \n {\n memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));\n vector<vector<int>> grid(n,vector<int>(n,1));\n for(auto &v:mines)\n {\n grid[v[0]][v[1]]=0;\n }\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n {\n int plus=solve(grid,n,i,j,0);\n for(int d=1;d<4;d++)\n {\n plus=min(plus,solve(grid,n,i,j,d));\n \n }\n ans=max(plus,ans);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n \n }\n};\n//if you like the solution plz upvote.
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
✅✅Faster || Easy To Understand || C++ Code
|
faster-easy-to-understand-c-code-by-__kr-4sls
|
Dynamic Programming\n\n Time Complexity :- O(N * N)\n\n Space Complexity :- O(N * N)\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vecto
|
__KR_SHANU_IITG
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-15T10:09:02.844931+00:00
|
2022-07-15T10:09:17.497837+00:00
| 348 | false |
* ***Dynamic Programming***\n\n* ***Time Complexity :- O(N * N)***\n\n* ***Space Complexity :- O(N * N)***\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n \n vector<vector<int>> grid(n, vector<int> (n, 1));\n \n for(auto v : mines)\n {\n int x = v[0];\n \n int y = v[1];\n \n grid[x][y] = 0;\n }\n \n // precalculate for left consecutive one\'s\n \n vector<vector<int>> left(n, vector<int> (n, 0));\n \n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)\n {\n if(j == 0)\n {\n if(grid[i][j])\n {\n left[i][j] = 1;\n }\n }\n else\n {\n if(grid[i][j])\n {\n left[i][j] = left[i][j - 1] + 1;\n }\n else\n {\n left[i][j] = 0;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n \n // precalculate for right consecutive one\'s\n \n vector<vector<int>> right(n, vector<int> (n, 0));\n \n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n for(int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--)\n {\n if(j == n - 1)\n {\n if(grid[i][j])\n {\n right[i][j] = 1;\n }\n }\n else\n {\n if(grid[i][j])\n {\n right[i][j] = right[i][j + 1] + 1;\n }\n else\n {\n right[i][j] = 0;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n \n // precalculate for top consecutive one\'s\n \n vector<vector<int>> top(n, vector<int> (n, 0));\n \n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)\n {\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n if(i == 0)\n {\n if(grid[i][j])\n {\n top[i][j] = 1;\n }\n }\n else\n {\n if(grid[i][j])\n {\n top[i][j] = top[i - 1][j] + 1;\n }\n else\n {\n top[i][j] = 0;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n \n // precalculate for bottom consecutive one\'s\n \n vector<vector<int>> bottom(n, vector<int> (n, 0));\n \n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)\n {\n for(int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)\n {\n if(i == n - 1)\n {\n if(grid[i][j])\n {\n bottom[i][j] = 1;\n }\n }\n else\n {\n if(grid[i][j])\n {\n bottom[i][j] = bottom[i + 1][j] + 1;\n }\n else\n {\n bottom[i][j] = 0;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n \n // calculate maxi\n \n int maxi = 0;\n \n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)\n {\n if(grid[i][j])\n {\n int left_co = left[i][j];\n \n int right_co = right[i][j];\n \n int top_co = top[i][j];\n \n int bottom_co = bottom[i][j];\n \n int curr = min({top_co, bottom_co, left_co, right_co});\n \n maxi = max(maxi, curr);\n }\n }\n }\n \n return maxi;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
🔥 Javascript Solution - Detailed Annotated
|
javascript-solution-detailed-annotated-b-y29p
|
\n/**\n * @param {number} n\n * @param {number[][]} mines\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar orderOfLargestPlusSign = function(n, mines) {\n // create n * n as a
|
joenix
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-15T02:33:15.696917+00:00
|
2022-05-15T02:33:15.696954+00:00
| 177 | false |
```\n/**\n * @param {number} n\n * @param {number[][]} mines\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar orderOfLargestPlusSign = function(n, mines) {\n // create n * n as a table, and each grid fill the maximum number\n const t = new Array(n).fill(0).map(() => new Array(n).fill(n));\n\n // insert `0` to the grid in table according the position in mines\n mines.forEach(a => t[a[0]][a[1]] = 0);\n\n // loop each rows and cols\n // - for rows: calculate non-zero grid from left to right\n // - for cols: calculate non-zero grid from top to bottom\n // - when the loop is completed, all of non-zero values will be calculated by four directions\n // - and these grids value will be updated by comparing. then we can obtain the minimum value of the four directions caculation, which is the maximum of the grid\n for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n // save the maximum value of non-zeros with for directions\n let [l, r, u, d] = [0, 0, 0, 0];\n\n // l: left, loop row i from left to right\n // r: right, loop row i from right to left\n // u: up, loop col i from top to bottom\n // d: down, loop col i from bottom to top\n for (let j = 0, k = n - 1; j < n; j++, k--) {\n // if the value is `0`, then set variable to `0`, and indicates it\'s broken\n l = t[i][j] && l + 1;\n r = t[i][k] && r + 1;\n u = t[j][i] && u + 1;\n d = t[k][i] && d + 1;\n\n // if current value is less than origin value\n // one possibility: the origin value is default\n // another possibility: the length of non-zero in a centain direction is langer than in the current direction, which the minimum value we need\n if (l < t[i][j]) t[i][j] = l;\n if (r < t[i][k]) t[i][k] = r;\n if (u < t[j][i]) t[j][i] = u;\n if (d < t[k][i]) t[k][i] = d;\n }\n }\n\n // return maximum value be saved by all cells\n return Math.max(...t.map(v => Math.max(...v)));\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Java - O(n^2) time and space
|
java-on2-time-and-space-by-blue_bubble-51y8
|
\n\nclass Solution {\n int[][] hori; int[][] verti; \n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, int[][] mines) {\n hori = new int[n][n]; \n
|
blue_bubble
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-25T15:14:39.086559+00:00
|
2022-04-25T15:14:39.086608+00:00
| 72 | false |
```\n\nclass Solution {\n int[][] hori; int[][] verti; \n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, int[][] mines) {\n hori = new int[n][n]; \n verti = new int[n][n]; \n int[][] grid = new int[n][n]; \n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){Arrays.fill(grid[i], 1); }\n for (int i = 0; i < mines.length; i++){\n grid[mines[i][0]][mines[i][1]] = 0; \n }\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n hori[i][0] = grid[i][0]; \n }\n \n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n verti[0][i] = grid[0][i]; \n }\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n for (int j = 1; j < n; j++){\n if (grid[i][j] == 1)\n hori[i][j] = hori[i][j- 1] + grid[i][j]; \n else hori[i][j] = 0; \n\n }\n }\n \n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++){\n for (int i = 1; i < n; i++){\n if (grid[i][j] == 1)\n verti[i][j] = verti[i - 1][j] + grid[i][j];\n else verti[i][j] = 0; \n }\n }\n \n for (int k = n ; k > 0; k--){\n boolean holdstrue = false;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++){\n if (hori[i][j] >= 2*k - 1){\n int center = j - (k) + 1; \n if (i + k - 1 < n && center >= 0 && verti[i + k - 1][center] >= 2*k - 1 && verti[i][center] >= k - 1){\n holdstrue = true; \n System.out.println(i + " " + j); \n System.out.println(i + " " + center);\n return k; \n \n }\n }\n }\n if (holdstrue) break;\n }\n if (holdstrue) return k; \n }\n if (mines.length < n*n)return 1; \n return 0; \n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ || EASY TO UNDERSTAND || Simple solution Prefix Sum
|
c-easy-to-understand-simple-solution-pre-gek0
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int> > v(n,vector<int>(n,1));\n for(aut
|
aarindey
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-25T07:35:24.137334+00:00
|
2022-03-25T07:35:24.137366+00:00
| 125 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int> > v(n,vector<int>(n,1));\n for(auto &it:mines)\n {\n v[it[0]][it[1]]=0;\n }\n vector<vector<int> > top,bottom,left,right;\n top=left=right=bottom=v;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n {\n int x,y;\n x=n-1-i;\n y=n-1-j;\n if(j>0&&left[i][j])\n left[i][j]=left[i][j]+left[i][j-1];\n if(i>0&&top[i][j])\n top[i][j]+=top[i-1][j];\n if(x<n-1&&bottom[x][y])\n bottom[x][y]+=bottom[x+1][y];\n if(y<n-1&&right[x][y])\n right[x][y]+=right[x][y+1];\n }\n }\n int ans=INT_MIN;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n {\n ans=max(ans,min(top[i][j],min(bottom[i][j],min(left[i][j],right[i][j]))));\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n**Please upvote to motivate me in my quest of documenting all leetcode solutions(to help the community). HAPPY CODING:)\nAny suggestions and improvements are always welcome**
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
APPROACH 1- PAIR TYPE 2D VECTOR | APPROACH 2- SIMPLE 2D DP
|
approach-1-pair-type-2d-vector-approach-4w040
|
\nstruct Cell{\n int ver;\n int hori;\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n int r
|
Decode_Apocalypse
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-22T07:09:43.141763+00:00
|
2022-01-22T07:09:43.141806+00:00
| 83 | false |
```\nstruct Cell{\n int ver;\n int hori;\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n int res=0;\n vector<vector<int>> arr(N,vector<int>(N,1));\n for(auto pair: mines){\n int x=pair[0];\n int y=pair[1];\n arr[x][y]=0;\n }\n vector<vector<Cell>> dp(N,vector<Cell>(N,{0,0}));\n for(int i=0;i<N;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<N;j++){\n if(arr[i][j]==1){\n res=1;\n if(i==0 && j==0){\n dp[i][j].hori=1;\n dp[i][j].ver=1;\n }\n else if(i==0){\n dp[i][j].hori=dp[i][j-1].hori+1;\n dp[i][j].ver=1;\n }\n else if(j==0){\n dp[i][j].ver=dp[i-1][j].ver+1;\n dp[i][j].hori=1;\n }\n else{\n dp[i][j].hori=dp[i][j-1].hori+1;\n dp[i][j].ver=dp[i-1][j].ver+1;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n for(int i=N-2;i>0;i--){\n for(int j=N-2;j>0;j--){\n if(dp[i][j].ver==0 || dp[i][j].hori==0 || dp[i][j].hori==1 || dp[i][j].ver==1){\n continue;\n }\n int mn=min(dp[i][j].ver,dp[i][j].hori);\n int side=mn;\n while(side>0){\n if(side+i-1>=N || side+j-1>=N){\n side--;\n continue;\n }\n if(dp[i][j+side-1].hori>=side && dp[i+side-1][j].ver>=side){\n break;\n }\n side--;\n }\n res=max(res,side);\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```\n\n\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n,vector<int>(n,INT_MAX));\n vector<vector<int>> mat(n,vector<int>(n,1));\n for(auto pair: mines){\n int x=pair[0];\n int y=pair[1];\n mat[x][y]=0;\n } \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int count=0;\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){ //moving left->right\n mat[i][j]==1 ? count++ : count=0;\n dp[i][j]=min(dp[i][j],count);\n }\n count=0;\n for(int j=n-1;j>=0;j--){ //moving right->left\n mat[i][j]==1 ? count++ : count=0;\n dp[i][j]=min(dp[i][j],count);\n }\n }\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int count=0;\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){ //moving top->bottom\n mat[j][i]==1 ? count++ : count=0;\n dp[j][i]=min(dp[j][i],count);\n }\n count=0;\n for(int j=n-1;j>=0;j--){ //moving bottom->top\n mat[j][i]==1 ? count++ : count=0;\n dp[j][i]=min(dp[j][i],count);\n }\n }\n int res=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n res=max(res,*max_element(dp[i].begin(),dp[i].end()));\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Easy C++ Solution
|
easy-c-solution-by-shreya1393-tuxy
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n int minimum (int a, int b, int c, int d) {\n // cout << a << " " << b << " " << c << " " << d << endl;\n int
|
shreya1393
|
NORMAL
|
2021-12-05T02:19:19.471944+00:00
|
2021-12-05T02:19:19.471971+00:00
| 126 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n int minimum (int a, int b, int c, int d) {\n // cout << a << " " << b << " " << c << " " << d << endl;\n int ans = min(a,b);\n ans = min(ans, c);\n ans = min(ans, d);\n return ans;\n }\n \n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> grid(n, vector<int> (n, 1));\n vector<vector<int>> left(n, vector<int> (n, 0));\n vector<vector<int>> right(n, vector<int> (n, 0));\n vector<vector<int>> up(n, vector<int> (n, 0));\n vector<vector<int>> down(n, vector<int> (n, 0));\n bool seen = false;\n \n for (auto m : mines) {\n int x = m[0];\n int y = m[1];\n grid[x][y] = 0;\n }\n \n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n if (grid[i][j]) {\n seen = true;\n if (i == 0) up[i][j] = 1;\n else up[i][j] = 1+up[i-1][j];\n }\n }\n }\n \n for (int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n if (grid[i][j]) {\n seen = true;\n if (i == n-1) down[i][j] = 1;\n else down[i][j] = 1+down[i+1][j];\n }\n }\n }\n \n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n if (grid[i][j]) {\n if (j == 0) left[i][j] = 1;\n else left[i][j] = 1+left[i][j-1];\n }\n }\n }\n \n for (int j = n-1; j >= 0; j--) {\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n if (grid[i][j]) {\n seen = true;\n if (j == n-1) right[i][j] = 1;\n else right[i][j] = 1+right[i][j+1];\n }\n }\n }\n \n int ans = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n //if (grid[i][j]) {\n ans = max(ans, minimum(up[i][j], left[i][j], right[i][j], down[i][j]));\n //}\n }\n }\n \n if (ans == 0 && seen) ans = 1;\n \n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming']
| 1 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Python3 most simple implementation
|
python3-most-simple-implementation-by-ad-zhnr
|
\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, n: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n grid = [[1 for j in range(n)] for i in range(n)]\n
|
aditya04848
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-13T13:28:21.687775+00:00
|
2021-09-13T13:28:21.687858+00:00
| 170 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, n: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n grid = [[1 for j in range(n)] for i in range(n)]\n for r,c in mines: grid[r][c] = 0\n \n left = [[0 for j in range(n)] for i in range(n)]\n for i in range(n):\n count = 0\n for j in range(n):\n if grid[i][j] == 1:\n count += 1\n else: \n count = 0\n left[i][j] = count\n \n \n right = [[0 for j in range(n)] for i in range(n)]\n for i in range(n):\n count = 0\n for j in range(n-1,-1,-1):\n if grid[i][j] == 1:\n count += 1\n else: \n count = 0\n right[i][j] = count\n \n \n \n up = [[0 for j in range(n)] for i in range(n)]\n for j in range(n):\n count = 0\n for i in range(n):\n if grid[i][j] == 1:\n count += 1\n else: \n count = 0\n up[i][j] = count\n \n \n down = [[0 for j in range(n)] for i in range(n)]\n for j in range(n):\n count = 0\n for i in range(n-1,-1,-1):\n if grid[i][j] == 1:\n count += 1\n else: \n count = 0\n down[i][j] = count\n \n \n max_plus = 0\n for i in range(n):\n for j in range(n):\n if grid[i][j] == 1:\n curr_plus = min(left[i][j],right[i][j],up[i][j],down[i][j])\n max_plus = max(max_plus, curr_plus)\n \n return max_plus\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ || Prefix Sum Concept || Dynamic programming || With Explanations
|
c-prefix-sum-concept-dynamic-programming-876a
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n // very good ques\n // dp approach\n // TIME
|
Ranjanatul73
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-10T16:46:40.599572+00:00
|
2021-09-10T16:46:40.599641+00:00
| 135 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n // very good ques\n // dp approach\n // TIME COMPLEXITY= O(N^2)\n //Space COMPLEXITY = O(N^2)\n vector<vector<int>>matrix(n,vector<int>(n,1)); // forming the matrix\n vector<vector<int>>left(n,vector<int>(n,1)); // will do prefix sum up to left[i][j]\n vector<vector<int>>up(n,vector<int>(n,1)); // will do prefix sum up to up[i][j]\n vector<vector<int>>right(n,vector<int>(n,1)); // will do prefix sum up to right[i][j]\n vector<vector<int>>down(n,vector<int>(n,1)); // will do prefix sum up to down[i][j]\n for(auto x:mines) {matrix[x[0]][x[1]]=0; left[x[0]][x[1]]=0 ; up[x[0]][x[1]]=0; right[x[0]][x[1]]=0; down[x[0]][x[1]]=0;}\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=1;j<n;j++){\n left[i][j]=matrix[i][j]?1+left[i][j-1]:0;\n }\n }\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n up[i][j]=matrix[i][j]?1+up[i-1][j]:0;\n }\n }\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=n-2;j>=0;j--){\n right[i][j]=matrix[i][j]?1+right[i][j+1]:0;\n }\n }\n for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n down[i][j]=matrix[i][j]?1+down[i+1][j]:0;\n }\n }\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n if(matrix[i][j]){\n ans=max(ans,min(min(left[i][j],right[i][j]),min(up[i][j],down[i][j])));\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 1 |
['C']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Python - Dynamic Programming - Explained
|
python-dynamic-programming-explained-by-4rn8d
|
Intuition:\nWe can convert this to 4 pieces of one dimensional array problem\nLet\'s say we have A = [1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1]\nWe will solve the left side 1s
|
ajith6198
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-10T07:43:26.501929+00:00
|
2021-09-10T07:51:45.307587+00:00
| 271 | false |
**Intuition:**\nWe can convert this to 4 pieces of one dimensional array problem\nLet\'s say we have ```A = [1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1]```\nWe will solve the left side 1st.\nFor each index ```i (0 <= i < len(A))```, we need to find how many consecutive ones are present in the left side from the current index.\n\n```\ni = 0\nA = [1]\n```\nThere\'s no left side, hence ```dp[0] = 1```\n\n\n```\ni = 1\nA = [1, 1]\n\t\t^\n```\nThere is a "1" to the left of current index, hence ```dp[1] = dp[0] + 1 = 1+1 = 2```\n\n\n```\ni = 2\nA = [1, 1, 1]\n\t\t ^\n```\nThere is a "1" to the left of current index, hence ```dp[2] = dp[1] + 1 = 2+1 = 3```\n\n\n```\ni = 3\nA = [1, 1, 1, 0]\n ^\n```\t\t\t\t\nSince current index has value as 0, it cannot be extended to left (or any direction), hence dp[3] = 0\n\n\n\nAnd so on.. So the dp formula for left side is ```dp[i] = dp[i-1] + 1 if d[i] == 1```\n\nSimilary, we can formulate for right, up and down\n\nAs the problem is a matrix (2-D), we will have to add another loop to find the dp values for each row\nand dp array has to be 2-D.\n\nFor up and down, we will consider columns as rows and the column values should be in i loop and rows in j loop.\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, n: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n\n grid = [ [1]*n for _ in range(n) ]\n left_dp = [ [1]*n for _ in range(n) ]\n right_dp = [ [1]*n for _ in range(n) ]\n down_dp = [ [1]*n for _ in range(n) ]\n up_dp = [ [1]*n for _ in range(n) ]\n \n for i, j in mines:\n grid[i][j] = left_dp[i][j] = right_dp[i][j] = down_dp[i][j] = up_dp[i][j] = 0\n \n for i in range(n):\n \n for j in range(1, n):\n if left_dp[i][j] and left_dp[i][j-1] > 0:\n left_dp[i][j] = left_dp[i][j-1] + 1\n \n for j in range(n-2, -1, -1):\n if right_dp[i][j] and right_dp[i][j+1] > 0:\n right_dp[i][j] = right_dp[i][j+1] + 1\n \n\n for j in range(n):\n \n for i in range(1, n):\n if up_dp[i][j] and up_dp[i-1][j] > 0:\n up_dp[i][j] = up_dp[i-1][j] + 1\n \n for i in range(n-2, -1, -1):\n if down_dp[i][j] and down_dp[i+1][j] > 0:\n down_dp[i][j] = down_dp[i+1][j] + 1\n \n res = 0\n for i in range(n):\n for j in range(n):\n if grid[i][j]:\n res = max(res, min(left_dp[i][j], right_dp[i][j], up_dp[i][j], down_dp[i][j]))\n return res\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python']
| 1 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C# DP solution
|
c-dp-solution-by-newbiecoder1-71py
|
time: O(N^2)\n- space: O(N^2)\n\npublic class Solution {\n public int OrderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, int[][] mines) {\n \n // build the grid\n
|
newbiecoder1
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-10T07:35:32.862916+00:00
|
2021-09-10T07:35:32.862946+00:00
| 46 | false |
- time: O(N^2)\n- space: O(N^2)\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public int OrderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, int[][] mines) {\n \n // build the grid\n int[,] grid = new int[n,n];\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)\n {\n grid[i,j] = 1;\n }\n }\n \n foreach(var mine in mines)\n {\n grid[mine[0],mine[1]] = 0;\n }\n \n // build the dp array. dp[i,j]: minimal length of the four arms starting from (i,j)\n int[,] dp = new int[n,n];\n for(int row = 0; row < n; row++)\n {\n // left -> right\n int maxLength = 0;\n for(int col = 0; col < n; col++)\n {\n maxLength = grid[row,col] == 0? 0 : maxLength + 1;\n dp[row,col] = maxLength;\n }\n \n // right -> left\n maxLength = 0;\n {\n for(int col = n - 1; col >= 0; col--)\n {\n maxLength = grid[row,col] == 0? 0 : maxLength + 1;\n dp[row,col] = Math.Min(dp[row,col], maxLength);\n }\n }\n }\n \n for(int col = 0; col < n; col++)\n {\n // up -> down\n int maxLength = 0;\n for(int row = 0; row < n; row++)\n {\n maxLength = grid[row,col] == 0? 0 : maxLength + 1;\n dp[row,col] = Math.Min(dp[row,col], maxLength);\n }\n \n // down -> up\n maxLength = 0;\n for(int row = n - 1; row >= 0; row--)\n {\n maxLength = grid[row,col] == 0? 0 : maxLength + 1;\n dp[row,col] = Math.Min(dp[row,col], maxLength);\n }\n }\n \n int res = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)\n {\n res = Math.Max(res, dp[i,j]);\n }\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Easy Solution in cpp
|
easy-solution-in-cpp-by-arin1-t8on
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>>matrix (n,vector<int>(n,n));\n
|
arin1
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-10T04:05:46.696081+00:00
|
2021-09-10T04:05:46.696130+00:00
| 51 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>>matrix (n,vector<int>(n,n));\n \n for(int i=0 ; i<n ; i++) {\n for(int j=0 ; j<n ; j++) {\n matrix[i][j] = 1 ;\n }\n }\n for(auto mine : mines) {\n matrix[mine[0]][mine[1]] = 0 ;\n }\n \n vector<vector<int>>left (n,vector<int>(n,n));\n vector<vector<int>>right (n,vector<int>(n,n));\n vector<vector<int>>top (n,vector<int>(n,n));\n vector<vector<int>>bottom (n,vector<int>(n,n));\n \n for(int i=0 ; i<n ; i++) {\n for(int j=0 ; j<n ; j++) {\n if(matrix[i][j] == 0) {\n left[i][j] = 0 ;\n top[i][j] = 0 ;\n } else {\n if(i==0) {\n top[i][j] = 1 ;\n } else {\n top[i][j] = top[i-1][j] + 1 ;\n }\n if(j==0) {\n left[i][j] = 1 ;\n } else {\n left[i][j] = left[i][j-1] + 1 ;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n \n for(int i=n-1 ; i>=0 ; i--) {\n for(int j=n-1 ; j>=0 ; j--) {\n if(matrix[i][j] == 0) {\n right[i][j] = 0 ;\n bottom[i][j] = 0 ;\n } else {\n if(i==n-1) {\n right[i][j] = 1 ;\n } else {\n right[i][j] = right[i+1][j] + 1 ;\n }\n if(j==n-1) {\n bottom[i][j] = 1 ;\n } else {\n bottom[i][j] = bottom[i][j+1] + 1 ;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n int ans = INT_MIN ;\n for(int i=0 ; i<n ; i++) {\n for(int j=0 ; j<n ; j++) {\n ans = max(ans, min(min(left[i][j],bottom[i][j]),min(right[i][j],top[i][j]))) ;\n }\n }\n return ans ;\n \n \n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
CPP | EASY-TO-GRASP
|
cpp-easy-to-grasp-by-sanchitraina1999-osim
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> a(n, vector<int> (n,1));\n
|
sanchitraina1999
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-09T20:05:32.080506+00:00
|
2021-09-09T20:05:32.080558+00:00
| 53 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> a(n, vector<int> (n,1));\n int m=n;\n for(auto i: mines){\n a[i[0]][i[1]]=0;\n }\n int dp[n][m][4];\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++){\n for(int k=0;k<4;k++){\n dp[i][j][k]=0;\n if(i==0 or j==0 or i==n-1 or j==m-1)\n dp[i][j][k]=a[i][j];\n }\n }\n }\n // [0]-top\n // [1]-bottom\n // [2]-right\n // [3]-left\n int maxx=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++){\n if(j!=0){\n dp[i][j][0]=(a[i][j]?1+dp[i][j-1][0]:0);\n }\n if(i!=0){\n dp[i][j][3]=(a[i][j]?1+dp[i-1][j][3]:0);\n }\n }\n }\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){\n for(int j=m-1;j>=0;j--){\n if(j!=m-1){\n dp[i][j][2]=(a[i][j]?1+dp[i][j+1][2]:0);\n }\n if(i!=n-1){\n dp[i][j][1]=(a[i][j]?1+dp[i+1][j][1]:0);\n }\n }\n }\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++){\n if(a[i][j])maxx=max(maxx,1);\n maxx=max(maxx,min({dp[i][j][0],dp[i][j][1],dp[i][j][2],dp[i][j][3]}));\n }\n }\n return maxx;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 1 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Python | Simple Solution
|
python-simple-solution-by-akash3anup-1c2w
|
\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, n: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n lookup = [[0 for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(n)]\n\n
|
akash3anup
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-09T19:08:15.702636+00:00
|
2021-09-09T19:08:15.702683+00:00
| 113 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, n: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n lookup = [[0 for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(n)]\n\n grid = [[1 for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(n)]\n for x, y in mines:\n grid[x][y] = 0\n\n largestPlusSignOrder = 0\n\n # Iterate forward then backward\n for x in range(n):\n plusSign = 0\n for y in range(n):\n if grid[x][y] == 1:\n plusSign += 1\n else:\n plusSign = 0\n lookup[x][y] = plusSign\n plusSign = 0\n for y in range(n - 1, -1, -1):\n if grid[x][y] == 1:\n plusSign += 1\n else:\n plusSign = 0\n lookup[x][y] = min(lookup[x][y], plusSign)\n\n # Iterate downward then upward\n for y in range(n):\n plusSign = 0\n for x in range(n):\n if grid[x][y] == 1:\n plusSign += 1\n else:\n plusSign = 0\n lookup[x][y] = min(lookup[x][y], plusSign)\n plusSign = 0\n for x in range(n - 1, -1, -1):\n if grid[x][y] == 1:\n plusSign += 1\n else:\n plusSign = 0\n lookup[x][y] = min(lookup[x][y], plusSign)\n largestPlusSignOrder = max(largestPlusSignOrder, lookup[x][y])\n\n return largestPlusSignOrder\n```\n\n***If you liked the above solution then please upvote!***
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Run Code and Submit giving different verdicts
|
run-code-and-submit-giving-different-ver-3bpc
|
This solution is getting accepted.\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int grid[500][500];\n int ans[500][500][4];\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vecto
|
hazy_007
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-09T16:55:46.076796+00:00
|
2021-09-09T16:55:46.076845+00:00
| 54 | false |
This solution is getting accepted.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int grid[500][500];\n int ans[500][500][4];\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n for(int i= 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n for(int j= 0; j < n; j++)\n {\n grid[i][j]= 1;\n }\n }\n for(auto e: mines)\n {\n grid[e[0]][e[1]]= 0;\n }\n if(mines.size() == n*n)\n {\n return 0;\n }\n vector<pair<int, int>> moves= {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};\n for(int i= 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n for(int j= 0; j < n; j++)\n {\n if(grid[i][j])\n {\n for(int ind= 2; ind < 4; ind++)\n {\n ans[i][j][ind]= 0;\n int x1= moves[ind].first;\n int y1= moves[ind].second;\n if((i+x1 < 0) || (i+x1 >= n) || (j+y1 < 0) || (j+y1 >= n))\n {\n continue;\n }\n if(grid[i+x1][j+y1])\n {\n ans[i][j][ind]= ans[i+x1][j+y1][ind]+1;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n }\n for(int i= n-1; i >= 0; i--)\n {\n for(int j= n-1; j >= 0; j--)\n {\n if(grid[i][j])\n {\n for(int ind= 0; ind < 2; ind++)\n {\n ans[i][j][ind]= 0;\n int x1= moves[ind].first;\n int y1= moves[ind].second;\n if((i+x1 < 0) || (i+x1 >= n) || (j+y1 < 0) || (j+y1 >= n))\n {\n continue;\n }\n if(grid[i+x1][j+y1])\n {\n ans[i][j][ind]= ans[i+x1][j+y1][ind]+1;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n }\n int ret= 0;\n for(int i= 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n for(int j= 0; j < n; j++)\n {\n int temp= 1e9;\n for(int ind= 0; ind < 4; ind++)\n {\n temp= min(temp, ans[i][j][ind]);\n }\n ret= max(ret, temp);\n }\n }\n return (ret+1);\n }\n};\n```\nBut this is giving wrong answer.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n int grid[500][500];\n int ans[500][500][4];\n for(int i= 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n for(int j= 0; j < n; j++)\n {\n grid[i][j]= 1;\n }\n }\n for(auto e: mines)\n {\n grid[e[0]][e[1]]= 0;\n }\n if(mines.size() == n*n)\n {\n return 0;\n }\n vector<pair<int, int>> moves= {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};\n for(int i= 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n for(int j= 0; j < n; j++)\n {\n if(grid[i][j])\n {\n for(int ind= 2; ind < 4; ind++)\n {\n ans[i][j][ind]= 0;\n int x1= moves[ind].first;\n int y1= moves[ind].second;\n if((i+x1 < 0) || (i+x1 >= n) || (j+y1 < 0) || (j+y1 >= n))\n {\n continue;\n }\n if(grid[i+x1][j+y1])\n {\n ans[i][j][ind]= ans[i+x1][j+y1][ind]+1;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n }\n for(int i= n-1; i >= 0; i--)\n {\n for(int j= n-1; j >= 0; j--)\n {\n if(grid[i][j])\n {\n for(int ind= 0; ind < 2; ind++)\n {\n ans[i][j][ind]= 0;\n int x1= moves[ind].first;\n int y1= moves[ind].second;\n if((i+x1 < 0) || (i+x1 >= n) || (j+y1 < 0) || (j+y1 >= n))\n {\n continue;\n }\n if(grid[i+x1][j+y1])\n {\n ans[i][j][ind]= ans[i+x1][j+y1][ind]+1;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n }\n int ret= 0;\n for(int i= 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n for(int j= 0; j < n; j++)\n {\n int temp= 1e9;\n for(int ind= 0; ind < 4; ind++)\n {\n temp= min(temp, ans[i][j][ind]);\n }\n ret= max(ret, temp);\n }\n }\n return (ret+1);\n }\n};\n```\nThe only difference between the two codes is that the two arrays(grid, ans) have been moved inside the function in the second code.\nI get wrong answer when I submit but running the code for that failing case gives correct answer. This does not have any global values which might not be updated, so I am not able to understand why the first one works but the second one doesn\'t. Can someone please explain what is happening.
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Largest Plus Sign || C++, short and simple
|
largest-plus-sign-c-short-and-simple-by-mvm49
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<set<int>> rows(n, {-1, n});\n vector<set
|
yakov_olkhovskiy
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-09T13:51:33.714675+00:00
|
2021-09-09T13:51:33.714713+00:00
| 201 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<set<int>> rows(n, {-1, n});\n vector<set<int>> cols(n, {-1, n});\n \n for(auto &p : mines) {\n rows[p[1]].insert(p[0]);\n cols[p[0]].insert(p[1]);\n }\n \n int max_p = 0;\n for(int r = 0; r < n; ++r) {\n for(int c = 0; c < n; ++c) {\n auto hl = rows[r].upper_bound(c);\n auto hr = hl--;\n int h = min(c - *hl, *hr - c);\n \n auto vl = cols[c].upper_bound(r);\n auto vr = vl--;\n int v = min(r - *vl, *vr - r);\n \n max_p = max(max_p, min(h, v));\n }\n }\n \n return max_p;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Kotlin O(n^2) solution
|
kotlin-on2-solution-by-awawa-h1gt
|
\nfun orderOfLargestPlusSign(n: Int, mines: Array<IntArray>): Int {\n \n // Setup initial state\n // This matrix stores minimum vertical an
|
awawa
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-09T13:17:19.316387+00:00
|
2021-09-09T13:17:19.316434+00:00
| 66 | false |
```\nfun orderOfLargestPlusSign(n: Int, mines: Array<IntArray>): Int {\n \n // Setup initial state\n // This matrix stores minimum vertical and horizontal pathes to zero\n val minPathes = Array<Array<IntArray>>(n) {\n Array<IntArray>(n) { intArrayOf(Int.MAX_VALUE - 2, Int.MAX_VALUE - 2) }\n }\n \n // Place zeroes to the matrix\n for (mine in mines) {\n minPathes[mine[0]][mine[1]][0] = 0\n minPathes[mine[0]][mine[1]][1] = 0\n }\n \n // Walk through the grid forward from left to right and from top to bottom.\n // For each cell set minimum left path and minimum top path.\n // So if we at cell (1, 2) we would look up at cell (0, 2) and left\n // at cell (1, 1) to find out minimum top and left pathes to zero\n for (i in 0 until n) {\n for (j in 0 until n) {\n // Find out top path to zero which is top path of the top cell + 1, \n // or 1 if there is no top cell\n val topPath = if (i > 0) minPathes[i - 1][j][0] + 1 else 1\n \n // Same for the left path\n val leftPath = if(j > 0) minPathes[i][j - 1][1] + 1 else 1\n \n // Now set minimum top and left pathes for current cell\n minPathes[i][j][0] = minOf(minPathes[i][j][0], topPath)\n minPathes[i][j][1] = minOf(minPathes[i][j][1], leftPath)\n }\n }\n \n var maxPath = 0\n \n // Now walk back through grid from right to left and from bottom to top.\n // Here we will find minimum right and bottom pathes to zeroes for each cell.\n // And as we already know left and top pathes, we can actually calculate maximum\n // vertical and horizontal pathes to zero and find out maximal plus sign order for\n // current cell. We track maximum plus sign order walking through the grid \n // and return this value after all\n for (i in n - 1 downTo 0) {\n for (j in n - 1 downTo 0) {\n val bottomPath = if (i < n - 1) minPathes[i + 1][j][0] + 1 else 1\n val rightPath = if (j < n - 1) minPathes[i][j + 1][1] + 1 else 1\n \n minPathes[i][j][0] = minOf(minPathes[i][j][0], bottomPath)\n minPathes[i][j][1] = minOf(minPathes[i][j][1], rightPath)\n maxPath = maxOf(minPathes[i][j].min() ?: 0, maxPath)\n }\n }\n\n return maxPath\n }\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ simple
|
c-simple-by-colinyoyo26-s9ro
|
O(n^2)\n\nCalculate the arm length (include center) for each position from 4 directions and the minimum one will be finally in the g[i][j]\ncnt[0]: from left to
|
colinyoyo26
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-09T07:30:27.332214+00:00
|
2021-09-10T10:06:25.570456+00:00
| 61 | false |
O(n^2)\n\nCalculate the arm length (include center) for each position from 4 directions and the minimum one will be finally in the `g[i][j]`\n`cnt[0]`: from left to right\n`cnt[1]`: from right to left\netc...\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n int g[n][n], ans = 0;\n memset(g, 0x7f, sizeof(g));\n for (auto &m : mines) g[m[0]][m[1]] = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n int cnt[4] = {1, 1, 1, 1}; // count of arm length (include center) from 4 direction\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n int *t[4] = {&g[i][j], &g[i][n - j - 1], &g[j][i], &g[n - j - 1][i]};\n for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {\n if (!*t[k]) cnt[k] = 0;\n *t[k] = min(*t[k], cnt[k]++);\n }\n }\n }\n for (auto &r : g) ans = max(ans, *max_element(r, r + n));\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\nO(n * mines.size()) (worst O(n^3))\n\ninitialize every position in `g` to maxiumu length it can have under the situation every point in the grid are 1 -> O(n^2)\n\nthen we check the indies in `mines` and set the corresbonding point in grid to zero and update the elements it affects.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n int g[n][n], ans = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) \n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)\n g[i][j] = min({1 + i, 1 + j, n - i, n - j});\n for (auto &m : mines) {\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n g[i][m[1]] = min(g[i][m[1]], abs(m[0] - i));\n g[m[0]][i] = min(g[m[0]][i], abs(m[1] - i));\n }\n }\n for (auto &r : g) ans = max(ans, *max_element(r, r + n));\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 1 |
[]
| 2 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ Fast Solution, Easy to understand
|
c-fast-solution-easy-to-understand-by-ar-ub0m
|
\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>>grid(n,vector<int>(n,1000));\n \n for(auto i
|
aryan2621
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-07T17:19:06.843705+00:00
|
2021-09-07T17:19:06.843734+00:00
| 93 | false |
```\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>>grid(n,vector<int>(n,1000));\n \n for(auto i:mines){\n grid[i[0]][i[1]]=0;\n \n }\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int l=0;\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n {\n int temp=grid[i][j];\n \n if(temp!=0)\n l++;\n else\n l=0;\n grid[i][j]=min(grid[i][j],l);\n }\n int r=0;\n for(int j=n-1;j>=0;j--){\n int temp=grid[i][j];\n \n if(temp!=0)\n r++;\n else\n r=0;\n grid[i][j]=min(grid[i][j],r);\n }\n int d=0;\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n {\n int temp=grid[j][i];\n \n if(temp!=0)\n d++;\n else\n d=0;\n grid[j][i]=min(grid[j][i],d);\n }\n int t=0;\n for(int j=n-1;j>=0;j--){\n int temp=grid[j][i];\n \n if(temp!=0)\n t++;\n else\n t=0;\n grid[j][i]=min(grid[j][i],t);\n }\n }\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n {\n \n ans=max(ans,grid[i][j]);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n```
| 1 | 1 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Normal Approach (not dp)
|
normal-approach-not-dp-by-manishp0591-oi37
|
\n/**\n * @param {number} n\n * @param {number[][]} mines\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar orderOfLargestPlusSign = function(n, mines) {\n const row = n; colum
|
manishp0591
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-06T06:57:13.881670+00:00
|
2021-09-06T06:57:29.365245+00:00
| 128 | false |
```\n/**\n * @param {number} n\n * @param {number[][]} mines\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar orderOfLargestPlusSign = function(n, mines) {\n const row = n; column = n\n const matrix = Array.from(Array(n), () => Array(n).fill(1))\n for(let [x,y] of mines) {\n // console.log(x, y)\n matrix[x][y] = 0\n }\n let max = 1, flag = false\n for(let i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for(let j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n if(matrix[i][j] === 1){\n max = callCheck(1, max, matrix, i, j)\n flag = true\n }\n }\n }\n \n return flag ? max : 0\n};\n\nconst callCheck = (k, max, matrix, i, j) => {\n if(i-k < 0 || i+k >= matrix.length || j-k < 0 || j+k >= matrix.length || (matrix[i][j-k] === 0 || matrix[i][j+k] === 0 || matrix[i-k][j] === 0 || matrix[i+k][j] === 0))\n return max\n k++\n max = Math.max(max, k)\n return callCheck(k, max, matrix, i, j)\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
java fast solution , iterating matrix only ONCE
|
java-fast-solution-iterating-matrix-only-npn2
|
You can calculate all the left,right,top,bottom in one matrix iteration.\n\nFirst init the grid as -2 to know we havent visited it yet. \nand keep the mines as
|
technicalyogi
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-15T08:48:50.599648+00:00
|
2021-07-15T08:48:50.599680+00:00
| 134 | false |
You can calculate all the left,right,top,bottom in one matrix iteration.\n\nFirst init the grid as -2 to know we havent visited it yet. \nand keep the mines as -1 to make sure all the mines are marked ( eliminates the use of set and O(logn) factor for every iteration)\n\nif not visited then put the value as it is\nif visted then use the min of the left,right,top,bottom value or exisitng value\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, int[][] mines) {\n \n \n int dp[][] = new int[n][n];\n \n if(mines.length == dp.length*dp.length)\n return 0;\n \n for(int i=0;i<dp.length;i++)\n for(int j=0;j<dp.length;j++)\n dp[i][j] = -2;\n \n for(int i=0;i<mines.length;i++){\n dp[mines[i][0]][mines[i][1]] = -1;\n }\n \n \n \n int left = 0;\n int right =0;\n int top = 0;\n int bottom = 0;\n \n for(int i=0;i<dp.length;i++){\n \n for(int j=0;j<dp.length;j++) {\n \n if(dp[i][j] == -1) {\n left=0;\n }\n else {\n \n if(dp[i][j] == -2)\n dp[i][j] = left;\n else\n dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j],left);\n \n left++;\n }\n \n if(dp[i][dp.length-j-1] == -1)\n {\n right = 0;\n }else\n {\n if(dp[i][dp.length-j-1] == -2)\n dp[i][dp.length-j-1] = right;\n else\n dp[i][dp.length-j-1] = Math.min(dp[i][dp.length-j-1],right);\n \n right++;\n }\n \n \n if(dp[j][i] == -1)\n {\n top = 0;\n }else\n {\n if(dp[j][i] == -2)\n dp[j][i] = top;\n else\n dp[j][i] = Math.min(dp[j][i],top);\n \n top++;\n }\n \n \n if(dp[dp.length-j-1][i] == -1)\n {\n bottom = 0;\n }else\n {\n if(dp[dp.length-j-1][i] == -2)\n dp[dp.length-j-1][i] = bottom;\n else\n dp[dp.length-j-1][i] = Math.min(dp[dp.length-j-1][i],bottom);\n \n bottom++;\n }\n \n\n }\n \n left=0;\n right=0;\n bottom=0;\n top=0;\n }\n int max=0;\n for(int i=0;i<dp.length;i++) {\n \n for(int j=0;j<dp.length;j++) {\n \n if(max<dp[i][j])\n max = dp[i][j];\n \n }\n \n }\n \n \n return max+1;\n \n }\n}\n\t```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Ultra Simple Cpp Solution | Suggestions for optimization are welcomed |
|
ultra-simple-cpp-solution-suggestions-fo-wuu4
|
Runtime: 500 ms, faster than 13.71% of C++ online submissions for Largest Plus Sign.\nMemory Usage: 89.3 MB, less than 28.63% of C++ online submissions for Larg
|
angiras_rohit
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-09T07:39:20.024822+00:00
|
2021-07-09T07:39:20.024863+00:00
| 123 | false |
Runtime: 500 ms, faster than 13.71% of C++ online submissions for Largest Plus Sign.\nMemory Usage: 89.3 MB, less than 28.63% of C++ online submissions for Largest Plus Sign.\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n \n vector<vector<int>> grid(n,vector<int>(n,1));\n int prefix_sum=0;\n int sum = 0,maximum = 0;\n \n vector<vector<int>> left(n,vector<int>(n,0));\n vector<vector<int>> right(n,vector<int>(n,0));\n vector<vector<int>> top(n,vector<int>(n,0));\n vector<vector<int>> down(n,vector<int>(n,0));\n \n \n for(int i=0;i<mines.size();i++)\n grid[mines[i][0]][mines[i][1]]=0;\n \n \n //Going left\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n prefix_sum=grid[i][0];\n for(int j=1;j<n;j++){\n if(!grid[i][j]){\n prefix_sum=0;\n left[i][j]=prefix_sum;\n }\n else{\n left[i][j]=prefix_sum;\n prefix_sum+=grid[i][j];\n }\n }\n }\n \n // cout<<"Left Prefix"<<endl;\n // for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n // for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n // cout<<left[i][j]<<" ";\n // cout<<endl;\n // }\n \n \n //Going right\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n prefix_sum=grid[i][n-1];\n for(int j=n-2;j>=0;j--){\n if(!grid[i][j]){\n prefix_sum=0;\n right[i][j]=prefix_sum;\n }\n else{\n right[i][j]=prefix_sum;\n prefix_sum+=grid[i][j];\n }\n }\n }\n \n // cout<<"Right Prefix"<<endl;\n // for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n // for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n // cout<<right[i][j]<<" ";\n // cout<<endl;\n // }\n \n \n //Going top\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n prefix_sum=grid[0][i];\n for(int j=1;j<n;j++){\n if(!grid[j][i]){\n prefix_sum=0;\n top[j][i]=prefix_sum;\n }\n else{\n top[j][i]=prefix_sum;\n prefix_sum+=grid[j][i];\n }\n }\n }\n \n// cout<<"Top Prefix"<<endl;\n// for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n// for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n// cout<<top[i][j]<<" ";\n// cout<<endl;\n// }\n \n \n //Going down\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n prefix_sum=grid[n-1][i];\n for(int j=n-2;j>=0;j--){\n if(!grid[j][i]){\n prefix_sum=0;\n down[j][i]=prefix_sum;\n }\n else{\n down[j][i]=prefix_sum;\n prefix_sum+=grid[j][i];\n }\n }\n }\n \n // cout<<"Down Prefix"<<endl;\n // for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n // for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n // cout<<down[i][j]<<" ";\n // cout<<endl;\n // }\n \n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n if(grid[i][j]){\n sum = min(min(top[i][j],down[i][j]),min(left[i][j],right[i][j]));\n //cout<<sum<<" ";\n if(sum>=maximum)\n maximum = 1+sum;\n }\n //cout<<endl;\n }\n }\n\n return maximum;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 1 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ - Binary Search + DP (170ms Solution)
|
c-binary-search-dp-170ms-solution-by-yow-8lfp
|
What we do here is check whether a plus sign of order k could be found or not.\nIf it is possible then we search in the right half of the binary search else in
|
Yowaimo
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-02T18:51:45.474888+00:00
|
2021-07-09T16:56:59.717873+00:00
| 110 | false |
What we do here is check whether a plus sign of order **k** could be found or not.\nIf it is possible then we search in the right half of the binary search else in the left half.\n\nNow, to check if a plus sign of order k could be found or not on every valid index check whether the range sum of length **k** from that index in every four directions is **k** or not.\n\nFor finding the range sum we can use prefix sums for both column\'s and row\'s.\n\nBiggest Plus sign could be of size **ceil(n / 2)** so the search space is between **1** and **ceil(n / 2)**\n\nTime Complexity: **O(n^2 * log(n))**\nSpace Complexity: **O(n^2)**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> mat, row, col;\n int n;\n bool good(int k) {\n for(int i = k - 1; i < n - k + 1; ++i) {\n for(int j = k - 1; j < n - k + 1; ++j) {\n bool flag = 1;\n\t\t\t //in the right direction\n flag &= row[i][j + k] - row[i][j] == k;\n\t\t\t\t//in the left direction\n flag &= row[i][j + 1] - row[i][j - k + 1] == k;\n\t\t\t\t// in downward direction\n flag &= col[j][i + k] - col[j][i] == k;\n\t\t\t\t// in the upward direction\n flag &= col[j][i + 1] - col[j][i - k + 1] == k;\n if(flag) return 1;\n }\n }\n return 0;\n }\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& a) {\n this->n = n;\n mat.resize(n, vector<int> (n, 1));\n row.resize(n, vector<int> (n + 1, 0));\n col.resize(n, vector<int> (n + 1, 0));\n \n for(auto x: a) mat[x[0]][x[1]] = 0;\n \n\t\t// Calculating the prefix sum\'s for both row\'s and column\'s\n for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) \n for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) \n row[i][j + 1] = row[i][j] + mat[i][j];\n col[j][i + 1] = col[j][i] + mat[i][j];\n \n int lo = 1, hi = n - n / 2, best = 0;\n while(lo <= hi) {\n int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;\n if(good(mid)) {\n\t\t\t\t//if plus sign of order mid is found\n\t\t\t\t// then set the ans to mid and search in the right half\n best = mid;\n lo = mid + 1;\n } else {\n\t\t\t\t//if the plus sign could not be found search in the left half\n hi = mid - 1;\n }\n }\n \n return best;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
C++ solution dp
|
c-solution-dp-by-navneetkchy-dkh2
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> a(N, vector<int> (N, 1));\n
|
navneetkchy
|
NORMAL
|
2021-04-29T13:51:53.165833+00:00
|
2021-04-29T13:51:53.165860+00:00
| 159 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> a(N, vector<int> (N, 1));\n for(vector<int>& p : mines) {\n a[p[0]][p[1]] = 0;\n }\n pair<int, int> dp[N][N];\n for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n for(int j = 0; j < N; j++) {\n if(a[i][j] == 1) {\n dp[i][j].first = (i == 0 ? 0 : dp[i- 1][j].first) + 1;\n dp[i][j].second = (j == 0 ? 0 : dp[i][j - 1].second) + 1;\n }\n else {\n dp[i][j] = {0, 0};\n }\n \n }\n }\n pair<int, int> dp1[N][N];\n for(int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--) {\n for(int j = N - 1; j >= 0; j--) {\n if(a[i][j] == 1) {\n dp1[i][j].first = (i == N - 1 ? 0 : dp1[i + 1][j].first) + 1;\n dp1[i][j].second = (j == N - 1 ? 0 : dp1[i][j + 1].second) + 1;\n }\n else {\n dp1[i][j] = {0, 0};\n }\n }\n }\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n for(int j = 0; j < N; j++) {\n if(a[i][j] == 1) {\n int m = min({(i == 0 ? 0 : dp[i - 1][j].first), (j == 0 ? 0 : dp[i][j - 1].second), (i == N - 1 ? 0 : dp1[i + 1][j].first), (j == N - 1 ? 0 : dp1[i][j + 1].second)});\n ans = max(ans, m + 1);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
c++ prefix and suffix sum with 3D-DP array
|
c-prefix-and-suffix-sum-with-3d-dp-array-m90v
|
This solution is inspired from :\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/largest-plus-sign/discuss/1091541/C%2B%2B-oror-Faster-than-100-oror-Time-O(N2)-oror-DP-oror\n\n\
|
ajai_cr_7
|
NORMAL
|
2021-04-08T12:29:21.801730+00:00
|
2021-04-08T12:32:23.125914+00:00
| 258 | false |
This solution is inspired from :\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/largest-plus-sign/discuss/1091541/C%2B%2B-oror-Faster-than-100-oror-Time-O(N2)-oror-DP-oror\n\n\n\n\n````\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n \n int dp[1000][1000][4] , arr[1000][1000] ;\n int n = N , ans = 0;\n memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;++i){ //prepare array of 1\'s\n for(int j=0;j<n;++j){\n arr[i][j] = 1;\n }\n }\n \n for(auto it : mines){ //mark given points as 0\'s\n arr[it[0]][it[1]] = 0;\n }\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;++i){\n for(int j=0;j<n;++j){\n if(arr[i][j]){\n dp[i+1][j+1][0] = dp[i+1][j][0] + 1; //left prefix sum\n dp[i+1][j+1][1] = dp[i][j+1][1] + 1; //top prefix sum\n }\n }\n }\n \n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;--i){\n for(int j=n-1;j>=0;--j){\n if(arr[i][j]){\n dp[i+1][j+1][2] = dp[i+2][j+1][2] + 1; //down suffix sum\n dp[i+1][j+1][3] = dp[i+1][j+2][3] + 1; //right suffix sum\n }\n }\n }\n \n for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){ //find the max ans\n for(int j=1;j<=n;++j){\n int mini = INT_MAX;\n for(int k=0;k<4;++k){\n mini = min(mini,dp[i][j][k]);\n }\n ans = max(ans,mini);\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n \n }\n};\n\n````\n\n
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
JAVA SIMPLE SOLUTION WITH EXPLANATION FASTER THAN 80% WITH TIME AND SPACE
|
java-simple-solution-with-explanation-fa-6nw7
|
Explanation:\n 1.for every index we will store all four value(left,right,up,down).\n 2.to improve time complexity we will calculate index(i,j) values usign
|
shivam_gupta_
|
NORMAL
|
2021-02-04T08:18:23.266049+00:00
|
2021-02-04T08:18:23.266106+00:00
| 113 | false |
Explanation:\n 1.for every index we will store all four value(left,right,up,down).\n 2.to improve time complexity we will calculate index(i,j) values usign stored value of other indexed.\n\nJAVA CODE IS:\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, int[][] mines) {\n int grid[][][]=new int[N][N][4];\n for(int k=0;k<=3;k++){\n for(int a[] : mines)\n grid[a[0]][a[1]][k]=-1;\n }\n for(int i=0;i<N;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<N;j++){\n grid[i][j][0]=grid[i][j][0]==-1 ? 0 : j-1<0 ? 1 : grid[i][j-1][0]+1; \n grid[i][j][1]=grid[i][j][1]==-1 ? 0 : i-1<0 ? 1 : 1+grid[i-1][j][1]; \n }\n }\n for(int i=N-1;i>=0;i--){\n for(int j=N-1;j>=0;j--){\n grid[i][j][2]=grid[i][j][2]==-1 ? 0 : j+1>=N ? 1 : 1+grid[i][j+1][2]; \n grid[i][j][3]=grid[i][j][3]==-1 ? 0 : i+1>=N ? 1 : 1+grid[i+1][j][3]; \n }\n }\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<N;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<N;j++)\n ans=Math.max(ans,Math.min(grid[i][j][0],Math.min(grid[i][j][1],Math.min(grid[i][j][2],grid[i][j][3]))));\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```\nTime: O(m*4)+O(n*n)+O(n*n)+O(n*n)=O(n^2) means quadratic.\nSpace: O(n*n*4)=O(n*n)\n***PLEASE,UPVOTE IF THIS IS REALLY HELPFUL FOR YOU ***
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Python O(N^2 log(M)) solution
|
python-on2-logm-solution-by-wonszrzeczny-10ex
|
Worse solution than the dynamic programming one, but passes the tests.\nI create 2 lists of y coordinates of bombs along x axis and x coordinates along y axis,
|
wonszrzeczny
|
NORMAL
|
2021-01-08T16:54:49.744204+00:00
|
2021-01-08T16:54:49.744251+00:00
| 153 | false |
Worse solution than the dynamic programming one, but passes the tests.\nI create 2 lists of y coordinates of bombs along x axis and x coordinates along y axis, sort them\nand find the nearest bombs coordinates using binary search, then take the minimum of the 4 distances. Thought that while it\'s clearly worse, it\'s an interesting alternative.\n\n```\n\n\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, N: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n self.N = N\n res = 0\n x, y = {}, {}\n xy = {}\n for i in range(N):\n x[i] = [-1,N]\n y[i] = [-1,N]\n for mine in mines:\n mine_x = mine[0]\n mine_y = mine[1]\n x[mine_x].append(mine_y)\n y[mine_y].append(mine_x)\n xy[(mine_x, mine_y)] = True\n \n for k in range(N):\n x[k] = sorted(x[k])\n y[k] = sorted(y[k])\n print(x)\n \n coords = (-1,-1)\n for i in range(N):\n for j in range(N):\n if (i,j) not in xy:\n r = min(search(x[i], j), search(y[j], i))\n if r>res:\n res = r\n coords = (i,j)\n print(coords)\n return res\n \n \ndef search(mines, val):\n l, r = 0, len(mines)-1\n while l<=r:\n m = (l+r)//2\n if mines[m] > val:\n v1 = mines[m]\n r = m - 1\n else:\n l = m + 1\n l, r = 0, len(mines)-1\n while l<=r:\n m = (l+r)//2\n if mines[m] < val:\n v2 = mines[m]\n l = m + 1\n else:\n r = m - 1\n return min(val-v2, v1-val)\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
javascript brute force and dp
|
javascript-brute-force-and-dp-by-henrych-m2sc
|
reference:\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/largest-plus-sign/discuss/113350/C%2B%2B-simple-brute-force-easy-to-understand-with-detailed-explanation\nhttps://leet
|
henrychen222
|
NORMAL
|
2020-11-23T06:11:32.565512+00:00
|
2020-11-23T06:14:07.637528+00:00
| 69 | false |
reference:\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/largest-plus-sign/discuss/113350/C%2B%2B-simple-brute-force-easy-to-understand-with-detailed-explanation\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/largest-plus-sign/discuss/113314/JavaC%2B%2BPython-O(N2)-solution-using-only-one-grid-matrix\n```\n////////////////////////////// Brute force 492ms --- 50% fast //////////////////////////////\nconst orderOfLargestPlusSign = (N, mines) => {\n let res = 0;\n let data = initialize2DArrayNew(N, N);\n for (const m of mines) {\n data[m[0]][m[1]] = 0;\n }\n for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n for (let j = 0; j < N; j++) {\n let step = 0;\n while (ok(data, N, i, j, step)) {\n step++;\n }\n res = Math.max(res, step);\n }\n }\n return res;\n};\n\nconst ok = (data, N, x, y, step) => {\n if (x - step < 0 || y - step < 0 || x + step >= N || y + step >= N) return false;\n return data[x - step][y] && data[x + step][y] && data[x][y - step] && data[x][y + step];\n};\n\nconst initialize2DArrayNew = (m, n) => {\n let data = [];\n for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n let tmp = new Array(n).fill(1);\n data.push(tmp);\n }\n return data;\n};\n\n////////////////////////////// DP 180ms --- 100% fast //////////////////////////////\nconst orderOfLargestPlusSign = (N, mines) => {\n let res = 0;\n let dp = [];\n for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n dp.push(new Array(N).fill(N));\n }\n for (const m of mines) {\n dp[m[0]][m[1]] = 0;\n }\n for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n let l = r = u = d = 0;\n for (let j = 0, k = N - 1; j < N; j++, k--) {\n dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], l = (dp[i][j] == 0 ? 0 : l + 1));\n dp[j][i] = Math.min(dp[j][i], u = (dp[j][i] == 0 ? 0 : u + 1));\n dp[i][k] = Math.min(dp[i][k], r = (dp[i][k] == 0 ? 0 : r + 1));\n dp[k][i] = Math.min(dp[k][i], d = (dp[k][i] == 0 ? 0 : d + 1));\n }\n }\n for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n for (let j = 0; j < N; j++) {\n res = Math.max(res, dp[i][j]);\n }\n }\n return res;\n};\n\n////////////////////////////// DP another version 188ms --- 100% fast //////////////////////////////\nconst orderOfLargestPlusSign = (N, mines) => {\n let res = 0;\n let dp = [];\n for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n dp.push(new Array(N).fill(N));\n }\n for (const m of mines) {\n dp[m[0]][m[1]] = 0;\n }\n for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n let l = r = u = d = 0;\n for (let j = 0, k = N - 1; j < N; j++, k--) {\n dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], l = (dp[i][j] == 0 ? 0 : l + 1));\n dp[j][i] = Math.min(dp[j][i], u = (dp[j][i] == 0 ? 0 : u + 1));\n dp[i][k] = Math.min(dp[i][k], r = (dp[i][k] == 0 ? 0 : r + 1));\n dp[k][i] = Math.min(dp[k][i], d = (dp[k][i] == 0 ? 0 : d + 1));\n }\n }\n for (let k = 0; k < N * N; ++k) res = Math.max(res, dp[Math.floor(k / N)][k % N]); // difference\n return res;\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
[Python3] dp
|
python3-dp-by-ye15-xysp
|
\n\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, N: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n mines = {(x, y) for x, y in mines} # O(1) lookup \n
|
ye15
|
NORMAL
|
2020-11-04T01:20:05.041644+00:00
|
2021-09-09T15:28:02.718968+00:00
| 177 | false |
\n```\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, N: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n mines = {(x, y) for x, y in mines} # O(1) lookup \n \n top = [[0]*N for _ in range(N)]\n left = [[0]*N for _ in range(N)]\n for i in range(N):\n for j in range(N): \n if (i, j) in mines: continue \n top[i][j] = 1 + top[i-1][j] if i > 0 else 1\n left[i][j] = 1 + left[i][j-1] if j > 0 else 1\n \n right = [[0]*N for _ in range(N)]\n bottom = [[0]*N for _ in range(N)]\n for i in reversed(range(N)):\n for j in reversed(range(N)): \n if (i, j) in mines: continue \n right[i][j] = 1 + right[i][j+1] if j+1 < N else 1\n bottom[i][j] = 1 + bottom[i+1][j] if i+1 < N else 1\n \n return max(min(top[i][j], left[i][j], right[i][j], bottom[i][j]) for i in range(N) for j in range(N))\n```\n\nA more concise but less comprehensive implementation is given below \n```\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, n: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n dp = [[n] * n for _ in range(n)]\n for i, j in mines: dp[i][j] = 0\n \n for i in range(n):\n ll = dd = rr = uu = 0 \n for j in range(n): \n dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], ll := ll+1 if dp[i][j] else 0)\n dp[j][i] = min(dp[j][i], dd := dd+1 if dp[j][i] else 0)\n dp[i][~j] = min(dp[i][~j], rr := rr+1 if dp[i][~j] else 0)\n dp[~j][i] = min(dp[~j][i], uu := uu+1 if dp[~j][i] else 0)\n \n return max(map(max, dp))\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Easy DFS solution using boolean grid and caching - with FULL explanation
|
easy-dfs-solution-using-boolean-grid-and-yhwq
|
Idea:\n Form a boolean matrix, indicating the positions of mines : matrix\n Form a Data class which has 4 integer values, representating number of consecutive 1
|
parin2
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-19T10:38:32.251505+00:00
|
2020-08-19T10:38:32.251546+00:00
| 207 | false |
**Idea:**\n* Form a boolean matrix, indicating the positions of mines : `matrix`\n* Form a Data class which has 4 integer values, representating number of consecutive 1s in up, left, down and right directions\n* Form a matrix of Data type which will maintain cached values of number of 1s in all four directions for that particular position: `cache`\n* Start doing DFS for every position and fill out 4 values if not already filled out.\n* While doing DFS, keep the `cache` updated, so that one value for one cell is not calculated again through recursion.\n* After DFS completes, iterate over `cache` matrix, where we have number of consecutive `1`s in all 4 directions from that position, determine the largest square possible to form with that cell in the center, and maintain the max size of largest square in these loops.\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n private enum Direction {\n UP, LEFT, DOWN, RIGHT;\n }\n \n private class Data {\n int left, right, up, down;\n Data(int left, int right, int up, int down) {\n this.left = left;\n this.right = right;\n this.up = up;\n this.down = down;\n }\n }\n \n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, int[][] mines) {\n boolean[][] matrix = new boolean[N][N];\n for (int[] mine : mines) {\n matrix[mine[0]][mine[1]] = true;\n }\n \n Data[][] cache = new Data[N][N];\n \n for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {\n if (!matrix[i][j]) {\n dfs(matrix, cache, i, j);\n }\n }\n }\n \n int ans = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {\n if (!matrix[i][j]) {\n Data cur = cache[i][j];\n ans = Math.max(ans,\n Math.min(cur.up, Math.min(cur.left, Math.min(cur.down, cur.right))));\n }\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n \n }\n \n private void dfs(boolean[][] mines, Data[][] cache, int x, int y) {\n if (cache[x][y] == null) {\n cache[x][y] = new Data(-1, -1, -1, -1);\n }\n Data cur = cache[x][y];\n cur.up = helper(mines, cache, x, y, Direction.UP);\n cur.left = helper(mines, cache, x, y, Direction.LEFT);\n cur.down = helper(mines, cache, x, y, Direction.DOWN);\n cur.right = helper(mines, cache, x, y, Direction.RIGHT);\n }\n \n private int helper(boolean[][] mines, Data[][] cache, int x, int y, Direction dir) {\n if (!isValid(mines, x, y) || mines[x][y]) {\n return 0;\n \n } \n \n if (cache[x][y] == null) {\n cache[x][y] = new Data(-1, -1, -1, -1);\n }\n Data cur = cache[x][y];\n \n if (dir == Direction.UP) {\n if (cur.up == -1) {\n cur.up = 1 + helper(mines, cache, x-1, y, dir);\n }\n return cur.up;\n \n } else if (dir == Direction.LEFT) {\n if (cur.left == -1) {\n cur.left = 1 + helper(mines, cache, x, y-1, dir);\n }\n return cur.left;\n \n } else if (dir == Direction.DOWN) {\n if (cur.down == -1) {\n cur.down = 1 + helper(mines, cache, x + 1, y, dir);\n }\n return cur.down;\n \n } else if (dir == Direction.RIGHT) {\n if (cur.right == -1) {\n cur.right = 1 + helper(mines, cache, x, y+1, dir);\n }\n return cur.right;\n }\n \n return -1; // should not reach here\n }\n \n private boolean isValid(boolean[][] mines, int x, int y) {\n return x >= 0 && x < mines.length && y >= 0 && y < mines[0].length;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Easy C++ Top Down DP Solution (Similar Problem)
|
easy-c-top-down-dp-solution-similar-prob-r161
|
Easy C++ Top Down DP Solution\n\nThis is very similar to the following problem:\n\nI. LC-1139\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int
|
abhisharma404
|
NORMAL
|
2020-07-01T18:15:06.671079+00:00
|
2020-07-01T18:16:25.085877+00:00
| 322 | false |
**Easy C++ Top Down DP Solution**\n\nThis is very similar to the following problem:\n\nI. [LC-1139](https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-1-bordered-square/)\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector <vector<int>> hor(N, vector<int>(N, 1));\n vector <vector<int>> ver(N, vector<int>(N, 0));\n \n for (auto mine : mines) {\n hor[mine[0]][mine[1]] = 0;\n }\n \n int maxAns = 0;\n for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {\n for (int j=0; j<N; j++) {\n if (hor[i][j] == 1) {\n hor[i][j] = (j - 1 >= 0) ? hor[i][j - 1] + 1: 1;\n ver[i][j] = (i - 1 >= 0) ? ver[i - 1][j] + 1: 1;\n }\n }\n }\n \n for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {\n for (int j=0; j<N; j++) {\n if (hor[i][j] > 0) {\n int val = min(hor[i][j], ver[i][j]);\n while (val > maxAns) {\n if ((j + val - 1 < N) && (i + val - 1 < N) && (hor[i][j + val - 1] >= val) && (ver[i + val - 1][j] >= val)) {\n maxAns = max(maxAns, val);\n }\n val--;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n \n return maxAns;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 1 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
[Python] DP
|
python-dp-by-stephen2020-b0ve
|
Python\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, N: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n mines = set(tuple(i) for i in mines)\n dp
|
stephen2020
|
NORMAL
|
2020-03-19T04:34:55.576621+00:00
|
2020-03-19T04:34:55.576674+00:00
| 128 | false |
```Python\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, N: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n mines = set(tuple(i) for i in mines)\n dp = [[[0,0,0,0] for i in range(N+2)] for j in range(N+2)]\n for i in range(1,N+1):\n for j in range(1,N+1):\n if (i-1, j-1) not in mines:\n dp[i][j][0] = dp[i][j-1][0] + 1\n dp[i][j][1] = dp[i-1][j][1] + 1\n for i in range(N,0,-1):\n for j in range(N,0,-1):\n if (i-1, j-1) not in mines:\n dp[i][j][2] = dp[i][j+1][2] + 1\n dp[i][j][3] = dp[i+1][j][3] + 1 \n return max(min(j) for i in dp for j in i)\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Had trouble understanding other solutions: here's mine. (c++)
|
had-trouble-understanding-other-solution-sqva
|
Traverse each value in the matrix from each direction. calculate the distance from each mine. return the maximum distance after the last traversal.\n\nclass Sol
|
polyomino
|
NORMAL
|
2020-01-27T07:15:54.737691+00:00
|
2020-01-27T07:15:54.737742+00:00
| 87 | false |
Traverse each value in the matrix from each direction. calculate the distance from each mine. return the maximum distance after the last traversal.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {\n vector<vector<int>> minefield(N, vector(N, 1));\n for( auto mine : mines){\n minefield[mine[0]][mine[1]] = 0;\n }\n \n for(int y = 0; y < N; ++y) {\n int count = 0;\n for(int x = 0; x < N; ++x) {\n if(minefield[x][y] !=0) {\n minefield[x][y] = ++count;\n } else {\n count = 0;\n }\n }\n count = 0;\n for(int x= N-1; x >=0; --x) {\n if(minefield[x][y] != 0) {\n minefield[x][y] = min(minefield[x][y], ++count);\n } else {\n count = 0;\n }\n }\n }\n \n int ans = 0;\n \n for(int x = 0; x < N; ++x){\n int count = 0;\n for(int y = 0; y < N; ++y){\n if(minefield[x][y] != 0){\n minefield[x][y] = min(minefield[x][y], ++count);\n } else {\n count = 0;\n }\n }\n count = 0;\n for(int y = N-1; y >= 0; --y){\n if(minefield[x][y] != 0){\n ans = max(min(minefield[x][y], ++count), ans);\n } else {\n count = 0;\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 1 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Easy Solution Using Dp Time-O(N*2) Space-O(N*2) In [C++/Java]
|
easy-solution-using-dp-time-on2-space-on-en6k
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& v) {\n vector<vector<int>>dp(n,vector<int>(n,1));\n for(in
|
sanjaygarg
|
NORMAL
|
2019-11-01T10:14:21.058886+00:00
|
2020-01-04T10:04:14.230152+00:00
| 178 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& v) {\n vector<vector<int>>dp(n,vector<int>(n,1));\n for(int i=0;i<v.size();i++)\n {\n dp[v[i][0]][v[i][1]]=0;\n }\n //Now we have our matrix of 0\'s and 1\'s\n //Now what we will do is create 4 vectors to keep track of each direction having continous ones.\n vector<vector<int>>left(n,vector<int>(n,0));\n vector<vector<int>>right(n,vector<int>(n,0));\n vector<vector<int>>top(n,vector<int>(n,0));\n vector<vector<int>>down(n,vector<int>(n,0));\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n {\n if(j==0)\n {\n left[i][j]=dp[i][j];\n }\n else if(dp[i][j]==1)\n left[i][j]=left[i][j-1]+1;\n else\n left[i][j]=0;\n }\n }\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=n-1;j>=0;j--)\n {\n if(j==n-1)\n {\n right[i][j]=dp[i][j];\n }\n else if(dp[i][j]==1)\n right[i][j]=right[i][j+1]+1;\n else\n right[i][j]=0;\n }\n }\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n {\n if(i==0)\n {\n top[i][j]=dp[i][j];\n }\n else if(dp[i][j]==1)\n top[i][j]=top[i-1][j]+1;\n else\n top[i][j]=0;\n }\n }\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n {\n if(i==n-1)\n {\n down[i][j]=dp[i][j];\n }\n else if(dp[i][j]==1)\n down[i][j]=down[i+1][j]+1;\n else\n down[i][j]=0;\n }\n }\n int order=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n {\n int curr=min(left[i][j],min(right[i][j],min(top[i][j],down[i][j])));\n order=max(order,curr);\n }\n }\n return order;\n }\n};\n```\nJava\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, int[][] v) {\n int[][] arr=new int[n][n];\n int[][] left=new int[n][n];\n int[][] right=new int[n][n];\n int[][] up=new int[n][n];\n int[][] down=new int[n][n];\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n {\n arr[i][j]=1;\n up[i][j]=0;\n left[i][j]=0;\n right[i][j]=0;\n down[i][j]=0;\n }\n }\n if(v.length>0)\n {\n for(int i=0;i<v.length;i++)\n {\n arr[v[i][0]][v[i][1]]=0;\n }\n }\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n {\n if(arr[i][j]==1)\n {\n if(j==0)\n {\n left[i][j]=arr[i][j]; \n }\n else \n {\n left[i][j]=left[i][j-1]+1;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=n-1;j>=0;j--)\n {\n if(arr[i][j]==1)\n {\n if(j==n-1)\n {\n right[i][j]=arr[i][j]; \n }\n else \n {\n right[i][j]=right[i][j+1]+1;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n {\n if(arr[i][j]==1)\n {\n if(i==0)\n {\n up[i][j]=arr[i][j]; \n }\n else \n {\n up[i][j]=up[i-1][j]+1;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n {\n if(arr[i][j]==1)\n {\n if(i==n-1)\n {\n down[i][j]=arr[i][j]; \n }\n else \n {\n down[i][j]=down[i+1][j]+1;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n {\n if(arr[i][j]==1)\n {\n ans=Math.max(ans,Math.min(left[i][j],Math.min(right[i][j],Math.min(up[i][j],down[i][j])))); \n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n \n }\n}```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
I hate my ugly code - idea is simple
|
i-hate-my-ugly-code-idea-is-simple-by-re-djvh
|
for each pos[i, j], for each four direction, count the longest increasing 1.\nloop to find the min arm\nresult is the max min arm\n\nclass Solution {\n publi
|
rebecca_
|
NORMAL
|
2019-09-05T17:54:37.832902+00:00
|
2019-09-05T17:54:37.832971+00:00
| 217 | false |
for each pos[i, j], for each four direction, count the longest increasing 1.\nloop to find the min arm\nresult is the max min arm\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, int[][] mines) {\n //Sanity check\n if (N <= 0) {\n return 0;\n }\n int[][] arr = new int[N][N];\n for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n Arrays.fill(arr[i], 1);\n }\n for (int i = 0; i < mines.length; i++) {\n arr[mines[i][0]][mines[i][1]] = 0;\n }\n int[][] left = new int[N][N];\n int[][] right = new int[N][N];\n int[][] top = new int[N][N];\n int[][] bottom = new int[N][N];\n \n for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {\n if (arr[i][j] == 0) {\n left[i][j] = 0;\n } else {\n if (i == 0) {\n left[i][j] = arr[i][j];\n } else{\n left[i][j] = left[i - 1][j] + 1;\n }\n \n }\n }\n }\n for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--) {\n for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {\n if (arr[i][j] == 0) {\n right[i][j] = 0;\n } else {\n if (i == N - 1) {\n right[i][j] = arr[i][j];\n } else {\n right[i][j] = right[i + 1][j] + 1;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {\n if (arr[i][j] == 0) {\n top[i][j] = 0;\n } else {\n if (j == 0) {\n top[i][j] = arr[i][j];\n } else {\n top[i][j] = top[i][j - 1] + 1;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n for (int j = N - 1; j >= 0; j--) {\n if (arr[i][j] == 0) {\n bottom[i][j] = 0;\n } else {\n if (j == N - 1) {\n bottom[i][j] = arr[i][j];\n } else {\n bottom[i][j] = bottom[i][j + 1] + 1;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n int min = 0;\n int max = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {\n min = Math.min(Math.min(Math.min(left[i][j], right[i][j]), top[i][j]), bottom[i][j]);\n max = Math.max(max, min);\n \n }\n }\n return max;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 1 |
[]
| 1 |
largest-plus-sign
|
Java DP
|
java-dp-by-feihong_qian-eay2
|
\npublic int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, int[][] mines) {\n int[][] grid = new int[N][N];\n for(int i = 0; i < mines.length; i++){\n
|
feihong_qian
|
NORMAL
|
2019-08-27T07:43:14.119323+00:00
|
2019-08-27T07:43:14.119360+00:00
| 207 | false |
```\npublic int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int N, int[][] mines) {\n int[][] grid = new int[N][N];\n for(int i = 0; i < mines.length; i++){\n grid[mines[i][0]][mines[i][1]] = 1; \n }\n int[][] left = new int[N][N];\n int[][] right = new int[N][N];\n int[][] up = new int[N][N];\n int[][] down = new int[N][N];\n for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < N; j++){\n if(j == 0){\n if(grid[i][j] == 0){\n left[i][j] = 1;\n }\n }else{\n if(grid[i][j] == 1){\n left[i][j] = 0;\n }else{\n left[i][j] = 1 + left[i][j - 1];\n }\n }\n \n if(i == 0){\n if(grid[i][j] == 0){\n up[i][j] = 1;\n }\n }else{\n if(grid[i][j] == 1){\n up[i][j] = 0;\n }else{\n up[i][j] = 1 + up[i - 1][j];\n }\n }\n }\n }\n for(int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--){\n for(int j = N - 1; j >= 0; j--){\n if(j == N - 1){\n if(grid[i][j] == 0){\n right[i][j] = 1;\n }\n }else{\n if(grid[i][j] == 1){\n right[i][j] = 0;\n }else{\n right[i][j] = 1 + right[i][j + 1];\n }\n }\n \n if(i == N - 1){\n if(grid[i][j] == 0){\n down[i][j] = 1;\n }\n }else{\n if(grid[i][j] == 1){\n down[i][j] = 0;\n }else{\n down[i][j] = 1 + down[i + 1][j];\n }\n }\n }\n }\n int max = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < N; j++){\n int min = Math.min(up[i][j], down[i][j]);\n min = Math.min(min, Math.min(left[i][j], right[i][j]));\n max = Math.max(min, max);\n }\n }\n return max;\n }\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
largest-plus-sign
|
[Python] 2d dp (n3) to (n2) & binary search
|
python-2d-dp-n3-to-n2-binary-search-by-z-4kbb
|
intuition of binary search\ntransfer the mines map into\nrow [[-1,N], [-1,2,N],[-1,3,7,N]...]\ncolomn\nwhich means that in row 2,we have 2 mines on [2,3] and [2
|
zeyuuuuuuu
|
NORMAL
|
2019-08-26T13:15:18.039197+00:00
|
2019-08-26T13:28:50.163150+00:00
| 185 | false |
intuition of binary search\ntransfer the mines map into\nrow [[-1,N], [-1,2,N],[-1,3,7,N]...]\ncolomn\nwhich means that in row 2,we have 2 mines on [2,3] and [2,7]\nso if we are considering the length of one arm of a plus sign at [2,5]\nit should be (7-3)/2 horizontally\n```\nclass Solution:\n def orderOfLargestPlusSign(self, N: int, mines: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n maxOrder = 0\n zeros = set((i,j) for i,j in mines)\n dp = [[0]*N for _ in range(N)]\n for i in range(N):\n # ->\n count = 0\n for j in range(N):\n count = 0 if (i,j) in zeros else count + 1\n dp[i][j] = count\n # <-\n count = 0\n for j in range(N-1,-1,-1):\n count = 0 if (i,j) in zeros else count + 1\n dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j],count)\n for j in range(N):\n # ^\n count = 0\n for i in range(N):\n count = 0 if (i,j) in zeros else count + 1\n dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j],count)\n # v\n count = 0\n for i in range(N-1,-1,-1):\n count = 0 if (i,j) in zeros else count + 1\n dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j],count)\n maxOrder = max(dp[i][j],maxOrder)\n if maxOrder == (N+1)//2:\n return maxOrder\n return maxOrder\n \n \n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
[Java/C++/Python] Loop Twice
|
javacpython-loop-twice-by-lee215-oayh
|
Explanation\nLoop once, we can get the Next Greater Number of a normal array.\nLoop twice, we can get the Next Greater Number of a circular array\n\n\n## Comple
|
lee215
|
NORMAL
|
2017-02-28T22:32:40.357000+00:00
|
2020-01-26T14:58:33.574492+00:00
| 100,246 | false |
## **Explanation**\nLoop once, we can get the Next Greater Number of a normal array.\nLoop twice, we can get the Next Greater Number of a circular array\n<br>\n\n## **Complexity**\nTime `O(N)` for one pass\nSpce `O(N)` in worst case\n<br>\n\n**Java**\n```java\n public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] A) {\n int n = A.length, res[] = new int[n];\n Arrays.fill(res, -1);\n Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();\n for (int i = 0; i < n * 2; i++) {\n while (!stack.isEmpty() && A[stack.peek()] < A[i % n])\n res[stack.pop()] = A[i % n];\n stack.push(i % n);\n }\n return res;\n }\n```\n**C++:**\n```cpp\n vector<int> nextGreaterElements(vector<int>& A) {\n int n = A.size();\n vector<int> stack, res(n, -1);\n for (int i = 0; i < n * 2; ++i) {\n while (stack.size() && A[stack.back()] < A[i % n]) {\n res[stack.back()] = A[i % n];\n stack.pop_back();\n }\n stack.push_back(i % n);\n }\n return res;\n }\n```\n\n**Python:**\n```py\n def nextGreaterElements(self, A):\n stack, res = [], [-1] * len(A)\n for i in range(len(A)) * 2:\n while stack and (A[stack[-1]] < A[i]):\n res[stack.pop()] = A[i]\n stack.append(i)\n return res\n```\n<br>\n\n# More Good Stack Problems\nHere are some problems that impressed me.\nGood luck and have fun.\n\n[1130. Minimum Cost Tree From Leaf Values](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-cost-tree-from-leaf-values/discuss/339959/One-Pass-O(N)-Time-and-Space)\n[907. Sum of Subarray Minimums](https://leetcode.com/problems/sum-of-subarray-minimums/discuss/170750/C++JavaPython-Stack-Solution)\n[901. Online Stock Span](https://leetcode.com/problems/online-stock-span/discuss/168311/C++JavaPython-O(1))\n[856. Score of Parentheses](https://leetcode.com/problems/score-of-parentheses/discuss/141777/C++JavaPython-O(1)-Space)\n[503. Next Greater Element II](https://leetcode.com/problems/next-greater-element-ii/discuss/98270/JavaC++Python-Loop-Twice)\n496. Next Greater Element I\n84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram\n42. Trapping Rain Water\n
| 809 | 12 |
[]
| 68 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
Java 10 lines and C++ 12 lines linear time complexity O(n) with explanation
|
java-10-lines-and-c-12-lines-linear-time-22z8
|
The approach is same as Next Greater Element I\nSee explanation in my solution to the previous problem\nThe only difference here is that we use stack to keep th
|
yuxiangmusic
|
NORMAL
|
2017-02-05T05:59:54.363000+00:00
|
2018-10-26T05:04:25.117216+00:00
| 49,281 | false |
The approach is same as *Next Greater Element I*\nSee explanation in [my solution to the previous problem](https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/77916/java-10-lines-linear-time-complexity-o-n-with-explanation)\nThe only difference here is that we use ```stack``` to keep the **indexes** of the **decreasing** subsequence\n\n**Java**\n```\n public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {\n int n = nums.length, next[] = new int[n];\n Arrays.fill(next, -1);\n Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); // index stack\n for (int i = 0; i < n * 2; i++) {\n int num = nums[i % n]; \n while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums[stack.peek()] < num)\n next[stack.pop()] = num;\n if (i < n) stack.push(i);\n } \n return next;\n }\n```\n**C++**\n```\n vector<int> nextGreaterElements(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<int> next(n, -1);\n stack<int> s; // index stack\n for (int i = 0; i < n * 2; i++) {\n int num = nums[i % n]; \n while (!s.empty() && nums[s.top()] < num) {\n next[s.top()] = num;\n s.pop();\n }\n if (i < n) s.push(i);\n } \n return next;\n }\n```
| 316 | 2 |
[]
| 35 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
Typical ways to solve circular array problems. Java solution.
|
typical-ways-to-solve-circular-array-pro-dcvv
|
The first typical way to solve circular array problems is to extend the original array to twice length, 2nd half has the same element as first half. Then everyt
|
shawngao
|
NORMAL
|
2017-02-05T04:15:00.549000+00:00
|
2018-10-20T05:19:14.582960+00:00
| 33,842 | false |
The first typical way to solve circular array problems is to extend the original array to twice length, 2nd half has the same element as first half. Then everything become simple.\nNaive by simple solution, just look for the next greater element directly. Time complexity: O(n^2).\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {\n int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n for (int num : nums) {\n max = Math.max(max, num);\n }\n \n int n = nums.length;\n int[] result = new int[n];\n int[] temp = new int[n * 2];\n \n for (int i = 0; i < n * 2; i++) {\n temp[i] = nums[i % n];\n }\n \n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n result[i] = -1;\n if (nums[i] == max) continue;\n \n for (int j = i + 1; j < n * 2; j++) {\n if (temp[j] > nums[i]) {\n result[i] = temp[j];\n break;\n }\n }\n }\n \n return result;\n }\n}\n```\n\nThe second way is to use a ```stack``` to facilitate the look up. First we put all indexes into the stack, ```smaller``` index on the ```top```. Then we start from ```end``` of the array look for the first element (index) in the stack which is greater than the current one. That one is guaranteed to be the ```Next Greater Element```. Then put the current element (index) into the stack.\nTime complexity: O(n).\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {\n int n = nums.length;\n int[] result = new int[n];\n \n Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();\n for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {\n stack.push(i);\n }\n \n for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {\n result[i] = -1;\n while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums[stack.peek()] <= nums[i]) {\n stack.pop();\n }\n if (!stack.isEmpty()){\n result[i] = nums[stack.peek()];\n }\n stack.add(i);\n }\n \n return result;\n }\n}\n```
| 222 | 0 |
[]
| 31 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
Optimized solution 🔥 Easy C++ 🔥 Stack implementation 🔥 st
|
optimized-solution-easy-c-stack-implemen-j2hd
|
PLEASE UPVOTE \uD83D\uDC4D\n# Approach \n### Simple implementation of stacks and because of circular array we take 2*n elements instead of n elements\n Describe
|
ribhav_32
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-07T14:54:35.544806+00:00
|
2023-04-07T14:54:35.544845+00:00
| 18,110 | false |
# **PLEASE UPVOTE \uD83D\uDC4D**\n# Approach \n### Simple implementation of stacks and because of circular array we take 2*n elements instead of n elements\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> nextGreaterElements(vector<int>& a) {\n int n = a.size();\n vector<int>v(n,-1);\n\n stack<int>st;\n for(int i = 2*n - 1; i >= 0; i--)\n {\n // we pop out all elements smaller than current element\n while(!st.empty() && (a[i%n] >= st.top()))\n {\n st.pop();\n }\n\n // if stack is empty means no greater element is there\n // if not empty we make answer at that index equal to top element\n if(!st.empty() && (i < n))\n {\n v[i] = st.top();\n }\n\n st.push(a[i%n]);\n }\n\n return v;\n }\n};\n```\n\n\n
| 195 | 0 |
['Stack', 'C++']
| 5 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
C++ | Stack | Explained | O(2*n)
|
c-stack-explained-o2n-by-ayzastark-mssn
|
Imagine the input array as a concatenation of the same array, twice. [1,2,1] -> [1,2,1,1,2,1]\n Similar to Next Greater Element, store the index in the stack in
|
ayzastark
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-05T08:46:34.159513+00:00
|
2020-06-05T08:58:47.735976+00:00
| 13,761 | false |
* Imagine the input array as a concatenation of the same array, *twice*. ```[1,2,1] -> [1,2,1,1,2,1]```\n* Similar to *Next Greater Element*, store the ***index*** in the stack instead of the actual value.\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> nextGreaterElements(vector<int>& nums) \n {\n int n = nums.size();\n nums.resize(2*n);\n \n for(int i=n; i<2*n; i++) //concatenate the same array\n {\n nums[i] = nums[i-n];\n }\n \n vector<int> res(n, -1); //to be returned, initialize it with -1\n stack<int> st;\n \n for(int i=0; i<2*n; i++)\n {\n int ele = nums[i];\n \n while(!st.empty() && ele > nums[st.top()])\n {\n\t\t\t\t//ele acts as NGE to the value at st.top()\n\t\t\t\t\n if(st.top() >= n) //index should not exceed n\n {\n st.top() = st.top() - n;\n }\n \n res[st.top()] = ele;\n st.pop();\n }\n \n st.push(i);\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n};\n\n```\n\n**Upvote if this helped**
| 78 | 2 |
['Stack', 'C', 'C++']
| 7 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
Java Damn Easy to Understand
|
java-damn-easy-to-understand-by-rohitkum-qg7v
|
Time Complexity : O(n)\nSpace Complexity : O(n)\n\nclass Solution {\n public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {\n \n Stack<Integer> stack=
|
rohitkumarsingh369
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-07T08:43:03.258881+00:00
|
2022-07-12T07:31:30.580497+00:00
| 7,122 | false |
**Time Complexity : O(n)**\n**Space Complexity : O(n)**\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {\n \n Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<>();\n for(int i=nums.length-1;i>=0;i--){\n stack.push(nums[i]);\n }\n \n for(int i=nums.length-1;i>=0;i--){\n int number=nums[i];\n while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek()<=nums[i]){\n stack.pop();\n }\n \n nums[i]=stack.empty()?-1:stack.peek();\n stack.push(number);\n }\n \n return nums;\n }\n}\n```\n\n**Time Complexity : O(n)**\n**Space Complexity : O(n)**\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {\n \n Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<>();\n for(int i=nums.length-1;i>=0;i--){\n stack.push(nums[i]);\n }\n \n int greater[]=new int[nums.length];\n for(int i=nums.length-1;i>=0;i--){\n while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek()<=nums[i]){\n stack.pop();\n }\n greater[i]=stack.empty()?-1:stack.peek();\n stack.push(nums[i]);\n }\n \n return greater;\n }\n}\n```
| 68 | 0 |
['Stack', 'Java']
| 14 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
JavaScript O(n): 'Think-How-Your-Brain-Thinks' Solution. With comments.
|
javascript-on-think-how-your-brain-think-pwzl
|
I looked at other solutions where they had a for loop going over double the size of the input array and doing \'%\' (modulo) and stuff like that. While that is
|
NobodyKnowsMan
|
NORMAL
|
2019-01-08T20:49:59.514160+00:00
|
2019-01-08T20:49:59.514224+00:00
| 4,885 | false |
I looked at other solutions where they had a for loop going over double the size of the input array and doing \'%\' (modulo) and stuff like that. While that is a smart way to do it, I think the following approach helped me think in a better/cleaner way.\n\nNOTE: We push the indexes of the elements in the stack and not the elements themselves. Just read the solution and try to go over this case (nums = [1,4,2,1,2]), you will get what it\'s doing.\n\n```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number[]}\n */\nvar nextGreaterElements = function(nums) {\n const ret = [];\n const stack = [];\n\n\t//paranoid base case.\n if (!nums || nums.length < 1) return ret;\n\t\n\t//normal case: while iterating over the array if we find an element which is bigger\n\t//than one in the stack, set ret[`smaller element from stack`] to the current\n\t//larger element found.\n for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {\n while (stack.length > 0 && nums[stack[stack.length - 1]] < nums[i]) {\n const smallerEleIndexFromStack = stack.pop();\n ret[smallerEleIndexFromStack] = nums[i];\n }\n stack.push(i);\n }\n\n\t//Now, we again begin from the start of nums and deal with elements\n\t//for which we couldn\'t find a \'next bigger element\' in the previous for loop\n\t//Example: nums = [1,4,2,1,2]. After the first loop, the stack would still hold the\n\t//indexes 1, 2 and 4 since we couldn\'t find next elements bigger than nums[1],\n\t//nums[2] and nums[4].\n for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {\n while (stack.length > 0 && nums[stack[stack.length - 1]] < nums[i]) {\n const smallerEleIndexFromStack = stack.pop();\n ret[smallerEleIndexFromStack] = nums[i];\n }\n }\n\n\t//Finally, still there would be some elements for which there was no \'next greater element\'\n\t//In the case of nums = [1,4,2,1,2], 4 would be such an element. So we just go over the\n\t//remaining elements in the stack and assign -1 to them in ret array.\n const remaining = stack.length;\n for (let i = 0; i < remaining; i++) {\n ret[stack.pop()] = -1;\n }\n\n return ret;\n};\n```\n\nPlease let me know if any part of the solution is unclear/confusing.
| 66 | 0 |
[]
| 12 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
C++ concise O(N) time solution using stack
|
c-concise-on-time-solution-using-stack-b-6nf1
|
\tclass Solution {\n\tpublic:\n\t\tvector nextGreaterElements(vector& nums) {\n\t\t\tstack st;\n\t\t\tvector ans;\n\t\t\tfor(int i=nums.size()-1;i>=0;i--)\n\t\t
|
jasperjoe
|
NORMAL
|
2020-04-21T13:49:06.755705+00:00
|
2020-04-21T13:49:06.755751+00:00
| 6,048 | false |
\tclass Solution {\n\tpublic:\n\t\tvector<int> nextGreaterElements(vector<int>& nums) {\n\t\t\tstack<int> st;\n\t\t\tvector<int> ans;\n\t\t\tfor(int i=nums.size()-1;i>=0;i--)\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tst.push(nums[i]);\n\n\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\tfor(int i=nums.size()-1;i>=0;i--)\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\twhile(!st.empty() && nums[i]>=st.top())\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\tst.pop();\n\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\tif(st.empty())\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\tans.push_back(-1);\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\telse\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\tans.push_back(st.top());\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\tst.push(nums[i]);\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\treverse(ans.begin(),ans.end());\n\t\t\treturn ans;\n\n\t\t}\n\t};
| 50 | 0 |
['Stack', 'C++']
| 10 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
C++/Python/Java/JavaScript |🚀✅ Using stack (With small modification in next-greater-element-1)
|
cpythonjavajavascript-using-stack-with-s-1r53
|
\n# Intuition:\nThe problem requires finding the next greater element for each element in the array, considering the array as a circular array. So, we need to c
|
devanshupatel
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-06T16:11:37.890864+00:00
|
2023-05-04T14:44:23.729259+00:00
| 5,951 | false |
\n# Intuition:\nThe problem requires finding the next greater element for each element in the array, considering the array as a circular array. So, we need to compare the elements in the array in a circular manner, and for each element, we need to find the next greater element. One way to do this is to use a stack.\n\n# Approach:\nWe start by initializing a stack and a vector to store the answer. We loop through the array from the end, twice the size of the array, to simulate a circular array. For each element, we compare it with the top element in the stack. If the top element in the stack is smaller than the current element, we pop it from the stack until the top element is greater than the current element or the stack becomes empty. If the stack is not empty, we store the top element as the next greater element for the current element, otherwise, we store -1. Finally, we push the current element into the stack.\n\n# Complexity:\n- Time complexity: The time complexity of the solution is O(n) because we are traversing the array twice, and for each element, we are performing a constant number of operations, which is popping elements from the stack and comparing them with the current element.\n\n- Space complexity: The space complexity of the solution is O(n) because we are using a stack and a vector, each of size n, to store the intermediate results.\n\n---\n# C++\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> nextGreaterElements(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n stack<int> st;\n vector<int> ans(n);\n for(int i=n*2-1;i>=0;i--){\n while(!st.empty() && st.top()<=nums[i%n]){\n st.pop();\n }\n if(i<n){\n if(!st.empty()){\n ans[i]=st.top();\n }\n else{\n ans[i]=-1;\n }\n }\n st.push(nums[i%n]);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n---\n# Java\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {\n int n = nums.length;\n Stack<Integer> st = new Stack<>();\n int[] ans = new int[n];\n Arrays.fill(ans, -1);\n for(int i = n * 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {\n while(!st.isEmpty() && st.peek() <= nums[i % n]) {\n st.pop();\n }\n if(i < n) {\n ans[i] = st.isEmpty() ? -1 : st.peek();\n }\n st.push(nums[i % n]);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n\n```\n---\n# Python\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def nextGreaterElements(self, nums):\n n = len(nums)\n st = []\n ans = [-1] * n\n for i in xrange(n * 2 - 1, -1, -1):\n while st and st[-1] <= nums[i % n]:\n st.pop()\n if i < n:\n ans[i] = st[-1] if st else -1\n st.append(nums[i % n])\n return ans\n\n```\n---\n# JavaScript\n```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number[]}\n */\nfunction nextGreaterElements(nums) {\n const n = nums.length;\n const st = [];\n const ans = new Array(n).fill(-1);\n for(let i = n * 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {\n while(st.length && st[st.length - 1] <= nums[i % n]) {\n st.pop();\n }\n if(i < n) {\n ans[i] = st.length ? st[st.length - 1] : -1;\n }\n st.push(nums[i % n]);\n }\n return ans; \n};\n```
| 39 | 0 |
['Monotonic Stack', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'JavaScript']
| 5 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
Python beats 100%
|
python-beats-100-by-ya-chen-wmzh
|
Use the stack to record the reversed array nums. Loop the array from last integer to the first one. If the last integer in stack is bigger than the current inte
|
ya-chen
|
NORMAL
|
2018-07-05T07:14:02.545825+00:00
|
2018-07-05T07:14:02.545825+00:00
| 5,162 | false |
Use the stack to record the reversed array **nums**. Loop the array from last integer to the first one. If the last integer in stack is bigger than the current interger in array, we have found the answer. Otherwise, we need to keep pop up the integer in stack. Besides, we need to push the current integer to the stack in each step.\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def nextGreaterElements(self, nums):\n n = len(nums)\n ret = [-1] * n\n stack = nums[::-1]\n for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):\n while stack and stack[-1] <= nums[i]:\n stack.pop()\n if stack:\n ret[i] = stack[-1]\n stack.append(nums[i])\n return ret\n```
| 37 | 1 |
[]
| 4 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
C++ solution | O(N) time complexity | with proper explaination
|
c-solution-on-time-complexity-with-prope-wogz
|
Time complexity - O(N)\nSpace complexity - O(N)\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> nextGreaterElements(vector<int>& nums) {\n //circular integer a
|
kritika_12
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-02T13:59:25.434099+00:00
|
2021-07-02T13:59:39.858576+00:00
| 3,758 | false |
**Time complexity - O(N)**\n**Space complexity - O(N)**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> nextGreaterElements(vector<int>& nums) {\n //circular integer array -> when we consider first element as the next of the last element hence it\'s circular \n \n vector<int> ans(nums.size(), -1); // to store the next greater element of every element and initialize it with -1 why ? because if there is no element in stack which is greater to the element we will return -1\n \n stack<int> s; //make a stack \n \n for(int i = 0; i < 2*nums.size()-1; i++) { //why ? 2*nums.size()-1 beacuse we assuming a joint imaginary array same as nums\n \n while(!s.empty() && nums[s.top()] < nums[i%nums.size()]) {\n //check if the stack is not empty and the check the top element of the stack if there is an element present which is smaller than i% nums.size\n ans[s.top()] = nums[i%nums.size()];\n s.pop();// pop the elements which are smaller \n }\n s.push(i%nums.size()); \n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n**Please upvote and comment if have doubt**
| 34 | 1 |
['C', 'C++']
| 7 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
Python solution with detailed explanation
|
python-solution-with-detailed-explanatio-oi0y
|
Solution with discussion https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/78268/python-solution-with-detailed-explanation\n\nNext Greater Element II https://leetcode.com/prob
|
gabbu
|
NORMAL
|
2017-02-07T14:45:53.418000+00:00
|
2018-09-06T01:21:47.020282+00:00
| 5,928 | false |
**Solution with discussion** https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/78268/python-solution-with-detailed-explanation\n\n**Next Greater Element II** https://leetcode.com/problems/next-greater-element-ii/\n\n**Algorithm**\n* **Stack for next greater element**: Suppose we have a decreasing sequence followed by a greater number. For example [5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 6] then the greater number 6 is the next greater element for all previous numbers in the sequence.\n* **Handling duplicates in input**: Push the index and value tuple on the stack instead of just the value. This makes sure duplicated elements are correctly handled. Example:[100,1,11,1,120,111,123,1,-1,-100] - we need to have the right answer for both 1s.\n* **Handling circular array**: Process it twice. Example: [5,4,3,2,1]. By processing it twice, you are essentially doing: [5,4,3,2,1]+[5,4,3,2,1]. Typical pattern to solve circular array problems is to extend the original array to twice length, 2nd half has the same element as first half. Then everything become simple.\nhttps://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/77881/typical-way-to-solve-circular-array-problems-java-solution\n\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def nextGreaterElements(self, nums):\n """\n :type nums: List[int]\n :rtype: List[int]\n """\n cache, st = {}, []\n for idx,x in enumerate(nums):\n while st and st[-1][1] < x:\n a,b = st.pop()\n cache[a] = x\n st.append((idx,x))\n for idx,x in enumerate(nums):\n while st and st[-1][1] < x:\n a,b = st.pop()\n cache[a] = x\n st.append((idx,x))\n result = [-1]*len(nums)\n for idx,x in enumerate(nums):\n if idx in cache:\n result[idx] = cache[idx]\n return result \n```
| 26 | 1 |
[]
| 3 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
simple cpp stack solution 95%similar to next greater element I
|
simple-cpp-stack-solution-95similar-to-n-xb9t
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> nextGreaterElements(vector<int>& nums) {\n stack<int>s;\n vector<int>ans;\n for(int i=nums.siz
|
bitrish
|
NORMAL
|
2020-09-01T06:32:04.980865+00:00
|
2021-07-13T23:40:29.818956+00:00
| 2,286 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> nextGreaterElements(vector<int>& nums) {\n stack<int>s;\n vector<int>ans;\n for(int i=nums.size()-1;i>=0;i--)\n\t\t s.push(nums[i]);\n for(int i=nums.size()-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n if(s.size()==0)\n ans.push_back(-1);\n else if(s.size()>0&&s.top()>nums[i])\n ans.push_back(s.top());\n else if(s.size()>0&&s.top()<=nums[i])\n {\n while(s.size()>0&&s.top()<=nums[i])\n s.pop();\n if(s.size()==0)\n ans.push_back(-1);\n else\n ans.push_back(s.top());\n }\n s.push(nums[i]);\n }\n reverse(ans.begin(),ans.end());\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 24 | 2 |
['Stack', 'C', 'C++']
| 3 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
✅💯🔥Simple Code📌🚀| 🔥✔️Easy to understand🎯 | 🎓🧠Beginner friendly🔥| O(n) Time Complexity💀💯
|
simple-code-easy-to-understand-beginner-x8rp2
|
Solution tuntun mosi ki photo ke baad hai. Scroll Down\n\n# Code\njava []\nclass Solution {\n public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {\n int n=n
|
atishayj4in
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-20T21:05:14.923118+00:00
|
2024-08-20T21:05:14.923141+00:00
| 2,822 | false |
Solution tuntun mosi ki photo ke baad hai. Scroll Down\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {\n int n=nums.length;\n Stack<Integer> stac=new Stack();\n int[] ans=new int[n];\n Arrays.fill(ans, -1); int k=n-1;\n for(int i=2*n-1; i>=0; i--){\n while(!stac.isEmpty() && nums[i%n]>=stac.peek()){\n stac.pop();\n }\n if(!stac.isEmpty() && i<n){\n ans[i]=stac.peek();\n }\n stac.push(nums[i%n]);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```\n
| 21 | 0 |
['Array', 'Stack', 'C', 'Monotonic Stack', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'JavaScript']
| 1 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
[Python] Monotonic Stack - One pass - Clean & Concise
|
python-monotonic-stack-one-pass-clean-co-76yh
|
Idea\n- Exactly the same idea with 496. Next Greater Element I.\n- Here, we iterate from [2n-1...0] instead of from [n-1..0], and to access value if nums[i] we
|
hiepit
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-25T14:47:13.932388+00:00
|
2021-10-25T14:50:39.028328+00:00
| 1,345 | false |
**Idea**\n- Exactly the same idea with **[496. Next Greater Element I](https://leetcode.com/problems/next-greater-element-i/discuss/1533016)**.\n- Here, we iterate from `[2n-1...0]` instead of from `[n-1..0]`, and to access value if `nums[i]` we access `nums[i % n]`.\n```python\nclass Solution:\n def nextGreaterElements(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n st = []\n n = len(nums)\n ans = [-1] * n\n for i in range(2*n-1, -1, -1):\n while st and st[-1] <= nums[i%n]:\n st.pop()\n if st and i < n:\n ans[i] = st[-1]\n st.append(nums[i%n])\n return ans\n```\nComplexity:\n- Time: `O(N)`, where `N <= 10^4` is length of `nums` array.\n- Space: `O(N)`
| 19 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
NO STACK: O(n) time complexity and O(1) space complexity using DP
|
no-stack-on-time-complexity-and-o1-space-1krz
|
The idea is to use the array to be returned to store information rather than an extra Stack. We use the array called result to store index of next larger elemen
|
random_leetcoder
|
NORMAL
|
2017-07-22T18:09:40.456000+00:00
|
2017-07-22T18:09:40.456000+00:00
| 5,446 | false |
The idea is to use the array to be returned to store information rather than an extra Stack. We use the array called result to store index of next larger element and replace with actual values before returning it. In first iteration, we move from right to left and find next greater element assuming array to be non-cyclical. Then we do another iteration from right to left. This time, we assume array is cyclical and find next larger element for the elements that do not have next larger element if array is not cyclical. \n```\npublic class Solution {\n public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {\n\n //Case when array is empty\n if(nums.length == 0) return nums;\n \n int[] result = new int[nums.length];\n\n //Assuming array to be non-cyclical, last element does not have next larger element\n result[nums.length - 1] = -1;\n\n //Case when only one element is there in array \n if(result.length == 1) return result;\n\n for (int i = nums.length - 2; i >= 0; i--){ \n //Starting from next element\n int k = i + 1;\n\n //Keep tracking next larger element until you find it or you find element with no next larger element\n while(nums[i] >= nums[k] && result[k] != -1){\n k = result[k];\n }\n \n //If next larger element is found, store index \n if(nums[k] > nums[i]) result[i] = k;\n //If not found, it doesn't have next larger element\n else result[i] = -1;\n }\n \n //Second iteration assuming cyclical array, last element can also have next larger element\n for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--){ \n\n //If next larger element assuming non-cyclical array already exists, continue\n if(result[i] != -1) continue;\n \n //Case when i + 1 is greater than length of array: when on last element\n int k = (i + 1) % nums.length;\n\n //Keep tracking next larger element until you find it or you find element with no next larger element\n while(nums[i] >= nums[k] && result[k] != -1){\n k = result[k];\n }\n\n //If next larger element is found, store it's index\n if(nums[k] > nums[i]) result[i] = k;\n //If not found, it doesn't have next larger element\n else result[i] = -1;\n }\n\n //Replace indices with actual values\n for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){\n if(result[i] != -1) result[i] = nums[result[i]];\n }\n\n return result;\n }\n}\n```
| 19 | 4 |
[]
| 6 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
[Python] Simple 2 pass solution using stack, 99% faster
|
python-simple-2-pass-solution-using-stac-yy6e
|
\nclass Solution:\n def nextGreaterElements(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n ## RC ##\n ## APPROACH : STACK ##\n ## Similar to lee
|
101leetcode
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-24T14:06:53.885588+00:00
|
2020-06-24T14:06:53.885636+00:00
| 3,904 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def nextGreaterElements(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n ## RC ##\n ## APPROACH : STACK ##\n ## Similar to leetcode 739. Daily Temperatures ##\n \n ## LOGIC ##\n ## 1. Monotone decreasing stack to find NGE (next greater element)\n ## 2. In the first loop, we fill NGE all possible.\n ## 3. In the second loop, there might be some elements left in the stack, so we iterate again (without appending to stack) and get NGE\n ## 4. The elements that are left in the stack even after second loop are max(nums).\n \n\t\t## TIME COMPLEXITY : O(N) ##\n\t\t## SPACE COMPLEXITY : O(N) ##\n\n stack, res = [], [-1] * len(nums)\n for i, num in enumerate(nums): # 2\n while stack and nums[stack[-1]] < num:\n res[stack.pop()] = num\n stack.append(i)\n for i, num in enumerate(nums): # 3\n while stack and nums[stack[-1]] < num:\n res[stack.pop()] = num\n return res\n```
| 17 | 0 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 3 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
Python solution explained
|
python-solution-explained-by-poorsolutio-q0uy
|
\n\'\'\'\nThe idea here is to store the indexes of the elements that we haven\'t seen a greater than value for them yet\nwe do this because if you stored the va
|
poorsolutions
|
NORMAL
|
2020-02-07T06:51:46.403789+00:00
|
2020-02-07T06:51:46.403845+00:00
| 1,196 | false |
```\n\'\'\'\nThe idea here is to store the indexes of the elements that we haven\'t seen a greater than value for them yet\nwe do this because if you stored the values you wouldn\'t be able to easily know where a value is at so you\ncan set it accordingly. This comes in handy in the second loop.\n\nThe values in the stack when we enter the second loop will always be decending, this is an important part of knowing that \nwe are setting the indexes to their correct value. Since we always will set the index\'s left in the stack to the smallest\nnumber when reiterating over the stack, ensuring a correct answer. \n\'\'\'\n\nclass Solution(object):\n def nextGreaterElements(self, nums):\n stack = []\n result = [-1] * len(nums)\n \n for i in range(len(nums)):\n while stack and nums[stack[-1]] < nums[i]:\n result[stack.pop()] = nums[i]\n stack.append(i)\n\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n while stack and nums[stack[-1]] < nums[i]:\n result[stack.pop()] = nums[i]\n \n return result\n \n\n```
| 16 | 1 |
[]
| 1 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
Optimized solution 🔥 Easy JAVA 🔥 Stack implementation 🔥
|
optimized-solution-easy-java-stack-imple-4yqf
|
Intuition<To solve the problem, we need to find the next greater element for each number in the circular array. A monotonic stack is ideal for this task, as it
|
Happy-Singh-Chauhan
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-14T14:18:34.011345+00:00
|
2025-02-14T14:18:34.011345+00:00
| 2,198 | false |
# Intuition
<To solve the problem, we need to find the next greater element for each number in the circular array. A monotonic stack is ideal for this task, as it allows us to efficiently track the next greater elements while iterating. By traversing the array twice (to simulate its circular nature), we can ensure all elements are covered.
# Approach
1. Simulate Circular Array:
* To handle the circular nature of the array, iterate over it twice using i % len(nums) to access elements.
2. Use a Monotonic Stack:
* Maintain a stack to store elements in decreasing order. This helps efficiently find the next greater element.
* As we traverse, pop elements from the stack that are smaller than or equal to the current element because they can’t be the next greater element.
3. Result Array:
* Initialize a result array res with -1 to represent elements with no next greater value.
* Update res[i] with the top of the stack when the next greater element is found.
4. Push to Stack:
* Add the current element to the stack for future comparisons.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(n)
- Space complexity:
O(n)
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<>();
int[] arr=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
arr[i]=-1;
}
for(int i=0;i<n*2;i++){
while(!stack.isEmpty() && nums[stack.peek()] < nums[i%n]){
arr[stack.pop()]=nums[i%n];
}
if(i<n){
stack.push(i);
}
}
return arr;
}
}
```
```c++ []
class Solution {
public:
std::vector<int> nextGreaterElements(std::vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
std::vector<int> result(n, -1); // Initialize result array with -1
std::stack<int> st;
// Traverse the array twice to handle circular nature
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * n; i++) {
while (!st.empty() && nums[st.top()] < nums[i % n]) {
result[st.top()] = nums[i % n];
st.pop();
}
if (i < n) {
st.push(i);
}
}
return result;
}
};
```
```python []
class Solution:
def nextGreaterElements(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
n = len(nums)
result = [-1] * n # Initialize result array with -1
stack = [] # Stack to store indices
# Traverse the array twice to handle circular nature
for i in range(2 * n):
while stack and nums[stack[-1]] < nums[i % n]:
result[stack.pop()] = nums[i % n]
if i < n:
stack.append(i)
return result
```

| 15 | 0 |
['Array', 'Stack', 'Monotonic Stack', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 0 |
next-greater-element-ii
|
Javascript Solution beats 84.78 %, TC - O(N) , SC - O(N)
|
javascript-solution-beats-8478-tc-on-sc-b99mu
|
// -------------------------------- APPROACH -------------------------------- \\\n \n Iterate from the last element :\n1. Check if there is any element l
|
payalpatra105
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-27T15:56:17.803028+00:00
|
2022-02-27T19:38:45.660163+00:00
| 1,828 | false |
// -------------------------------- APPROACH -------------------------------- \\\\\n \n Iterate from the last element :\n1. Check if there is any element lesser than current element in the satck \n a. If No lesser element found & the stack is empty, fill that index with -1.\n\t\t\t Then Insert the curr element into the stack.\n b. If No lesser element found & the stack has greater element than current, fill that index with the stack\'s top element. \n\t\t\t push the curr element into the stack.\n c. If there is less element keep removing from the top of the stack until you find the next greater element.\n\t\t\t Fill that index with stack\'s top element and insert the current element into the stack \n\n \n2. For traversing in circular fashion, Do i % n\n \n */\n \n TIME COMPLEXITY = O(2N) + O(2N) ~~ O(N)\n SPACE COMPLEXITY = O(N)\n \n \n // -------------------------------- STACK SOLUTION -------------------------------- \\\\\n \n var nextGreaterElements = function(nums) {\n let stack = [];\n let output = [];\n \n for(let i=2*(nums.length-1); i>=0; i--) {\n \n let Index = i % nums.length;\n while(stack.length > 0 && nums[Index] >= nums[stack[stack.length-1]]) {\n \n stack.pop();\n }\n \n if(stack.length === 0){\n output[Index] = -1;\n }else{\n output[Index] = nums[stack[stack.length-1]]\n }\n \n stack.push(Index);\n }\n \n return output;\n\t}
| 13 | 0 |
['Stack', 'JavaScript']
| 5 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.