question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Python (Simple Binary Search)
|
python-simple-binary-search-by-rnotappl-nnbl
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
rnotappl
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-01T16:47:36.100455+00:00
|
2024-11-01T16:47:36.100493+00:00
| 86 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def kthSmallestProduct(self, nums1, nums2, k):\n def function(x):\n total = 0 \n\n for num in nums1:\n if num > 0: total += bisect.bisect_right(nums2,x//num)\n if num < 0: total += len(nums2) - bisect.bisect_left(nums2,math.ceil(x/num))\n if num == 0 and x >= 0: total += len(nums2)\n\n return total \n\n low, high = -10**11, 10**11\n\n while low <= high:\n mid = (low+high)//2 \n\n if function(mid) >= k:\n high = mid - 1 \n else:\n low = mid + 1 \n\n return low \n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
2040. Kth Smallest Product of Two Sorted Arrays.cpp
|
2040-kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-zlh62
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) {\n \n auto fn = [&](doub
|
202021ganesh
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T08:59:56.991522+00:00
|
2024-10-28T08:59:56.991554+00:00
| 1 | false |
**Code**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) {\n \n auto fn = [&](double val) {\n long long ans = 0; \n for (auto& x : nums1) {\n if (x < 0) ans += nums2.end() - lower_bound(nums2.begin(), nums2.end(), ceil(val/x)); \n else if (x == 0) {\n if (0 <= val) ans += nums2.size(); \n } else ans += upper_bound(nums2.begin(), nums2.end(), floor(val/x)) - nums2.begin(); \n }\n return ans; \n }; \n \n long long lo = -pow(10ll, 10), hi = pow(10ll, 10)+1;\n while (lo < hi) {\n long long mid = lo + (hi - lo)/2; \n if (fn(mid) < k) lo = mid + 1; \n else hi = mid; \n }\n return lo; \n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Binary Search | Commented
|
binary-search-commented-by-anonymous_k-5s7k
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
anonymous_k
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-05T12:58:10.188305+00:00
|
2024-10-05T12:58:10.188332+00:00
| 77 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\n\nclass Solution:\n def kthSmallestProduct(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n # Naive - O(N^2 * logN)\n # BS over answer - O(log2(10 ^ 10) * n * log2(n))\n nums1.sort()\n nums2.sort()\n \n def findRank(product: int) -> int:\n ans = 0\n \n for num1 in nums1:\n if num1 == 0:\n if product >= 0: ans += len(nums2)\n continue\n # simple maths\n # n1 * n2 <= prod\n # if n1 > 0, n2 <= prod / n1\n # else, n2 >= prod / n1\n if num1 < 0:\n # greater than or equal to\n ans += len(nums2) - bisect_left(nums2, ceil(product / num1))\n else:\n # everything less than or equal to \n ans += bisect_right(nums2, product // num1)\n return ans\n\n l, r = -int(1e10), int(1e10)\n while l < r:\n mid = l + (r - l) // 2\n if findRank(mid) >= k:\n r = mid\n else:\n l = mid + 1\n return r\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
binary search w/ case analysis by signs
|
binary-search-w-case-analysis-by-signs-b-dz2g
|
Intuition & Approach\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\nThe question constraint specifies that each element in both input arrays i
|
jyscao
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-21T04:30:16.783306+00:00
|
2024-09-21T04:30:16.783336+00:00
| 63 | false |
# Intuition & Approach\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\nThe question constraint specifies that each element in both input arrays is in the range of $[-10^5, 10^5]$. This implies that the entirety of the possible numerical search space is in the range of $[-10^{10}, 10^{10}]$, therefore binary search is an appropriate method for solving this problem.\n\nThe predicate function we want to construct will return `True` if there are at least `k` products that can be generated from pairwise elements of `nums1` & `nums2` that are less than or equal to some candidate product, and `False` otherwise.\n\nThe tricky part of this problem is handling all the cases for when the candidate is either negative (-ve) or positive (+ve), and when the pairwise factors are (-ve, -ve), (-ve, +ve), (+ve, -ve) & (+ve, +ve), and counting the number of viable products efficiently. See the comments in the code below for explanations of each case.\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def kthSmallestProduct(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n m, n = len(nums1), len(nums2)\n if m > n: nums1, nums2 = nums2, nums1 # swap num arrays, if latter is shorter than former\n\n idx_0 = bisect.bisect_left(nums2, 0)\n nums2_neg, nums2_pos = nums2[:idx_0], nums2[idx_0:] # split `nums2` into -ve & +ve (non-negative more accurately) halves\n N, P = len(nums2_neg), len(nums2_pos) # sizes of the negative & positive splits above\n def has_at_least_k_prods_le_(candidate):\n le_cnt = 0 # tracks the count of all pairwise products that are less than or equal (<=) to the candidate\n if candidate < 0:\n for x in nums1:\n if x < 0: # prods <= a -ve candidate can be made from a -ve x and +ve nums w/ sufficiently large abs-vals\n le_cnt += P - bisect.bisect_left(nums2_pos, candidate/x)\n elif x > 0: # prods <= a -ve candidate can be made from a +ve x and -ve nums w/ sufficiently large abs-vals\n le_cnt += bisect.bisect_right(nums2_neg, candidate/x)\n else: # candidate >= 0\n for x in nums1:\n if x == 0: # prods <= a +ve candidate can be made from 0 and all numbers, since 0 * n = 0\n le_cnt += N + P\n elif x < 0: # prods <= a +ve candidate can be made from a -ve x, and all +ve nums & -ve nums w/ sufficiently small abs-vals\n le_cnt += P + int(candidate > 0) * (N - bisect.bisect_left(nums2_neg, candidate/x))\n else: # prods <= a +ve candidate can be made from a +ve x, and all -ve nums & +ve nums w/ sufficiently small abs-vals\n le_cnt += N + bisect.bisect_right(nums2_pos, candidate/x)\n return le_cnt >= k\n\n left, right = -10**10, 10**10\n while left < right:\n mid = left + (right - left) // 2\n if has_at_least_k_prods_le_(mid):\n right = mid\n else:\n left = mid + 1\n\n return left\n```\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(min(m,n)\u22C5log(max(m,n))\u22C5log(2\xD710^{10}))$$ - linear iteration on the smaller of `nums1` & `nums2`, where each iteration performs a binary search on the larger of `nums1` & `nums2`, with a constant factor of $log_2(2\xD710^{10})$ which is the size constraint of the numerical search space\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(max(m,n))$$ - as we\'re splitting the larger of `nums1` & `nums2` into 2 halves for more convenient counting\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
| 0 | 0 |
['Binary Search', 'Python3']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Python 3: TC O((M+N)*log(range), SC O(1): Guess-And-Check, Heinous 2-Pointer
|
python-3-tc-omnlogrange-sc-o1-guess-and-icz4i
|
Intuition\n\nUsually the answer to finding the kth highest value in these cases is to find the smallest p where there are at least k items smaller than p.\n\nTh
|
biggestchungus
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-23T00:15:02.299754+00:00
|
2024-08-23T00:15:02.299783+00:00
| 20 | false |
# Intuition\n\nUsually the answer to finding the `kth` highest value in these cases is to find the smallest `p` where there are at least `k` items smaller than `p`.\n\nThen you can use binary search and/or clever math to find that value of `p`.\n\n## Guess And Check\n\nHere we use binary search to find that smallest product `p` with at least `k` products `<= p`.\n\n## Counting Products Less than `p`\n\nThis is the tricky part.\n\nA brute force answer would to be enumerate over all the products of `x` from `nums1` and `y` from `nums2`.\n\n**But we can do better than brute force.**\n\n**For these examples let the product `p` be positive.**\n\nSuppose `x > 0`. We know that as values in `y` increase in `nums2`, the value of `x*y` is increasing. Therefore if we can find the last `y` where `x*y <= p`, then all prior values of `y` will work too. **This implies a binary search algorithm.**\n\nBinary search is fine and it will work, you\'ll probably get FT 30% or better.\n\n**But there\'s another pattern: as `x > 0` increases, our limit on `y` decreases.** This is the tricky part and why I called the 2-pointer heinous, because it depends on the sign of x, AND the sign of the product, ugh.\n\nIf we "flip things around" then the largest `x` means we have the lowest limit on `y`. When we find that lowest `y`, every prior value works too.\n\n**Then the next largest `x` allows for a slightly higher `y`. Therefore as we iterate backwards in `nums1` with `x > 0`, we iterate forwards in `nums2`. We have a 2-pointer algorithm!**\n\n## `p >= 0`\n\nFor `x > 0`, as x decreases, the max `y` we can use increases. So iterate over `x > 0` descending, and increment a pointer `j` in `nums2`.\n\nFor `x < 0`, as `x < 0` increases toward zero, the more negative the `y` values we can use get. Any `y > 0` also works. So start with `j = N-1` and decrement for each `x`.\n\n## `p < 0`\n\nSame general idea as `p >= 0`, but the details are different.\n\nFor `x > 0` we require negative `y`. As `x` increases the required `y` is less negative. Therefore we iterate over `x` ascending and increment the `j` pointer into `nums2`.\n\nFor `x < 0` we need positive `y`. As `x` decreases toward `-inf` we need less negative `y` values. So we can start with the least negative `x` and iterate descending, then decrement `j`.\n\n**I got to the answer after a lot of wrangling with the orders and edge cases so the code may not match this exactly... but the ideas are the same.**\n\n# Final Binary Search\n\nOnce we can compute the number of pairs, then we do binary search over the range `[smallestProduct, greatestProduct]`.\n\nThe smallest and greatest products involve the endpoints of the arrays. Intead of having complicated logic for what to do if the endpoints are positive versus negative, I just brute-force iterated over all 4 combinations and took the min and max.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: `O((M+N)*log(range))`, we do binary search over the range of products, `log(range)` steps, and the 2-pointer lets us count products in `O(M+N)`\n\n- Space complexity: constant, just iteration and pointers and such\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def kthSmallestProduct(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n # nums1 and nums2 are sorted, can have negatives\n # return 1-based kth smallest product\n\n\n # if nums1[i] < 0 then products grow in reverse order for nums2\n # if nums1[i] > 0 then products grow in forward order for nums2\n\n # for a guess-and-check solution we can ask how many products are below P\n # using this (binary search)\n\n # cost would be O(log(range) * m * log(n))\n # binsearch foreach binsearch, index math\n\n # that\'s acceptable time\n\n # or we can brute-force iterate, e.g. for each next product in O(range) time\n # update all O(m) pointers in O(m*n) time\n # ouch, not good\n\n # so m-pointer doesn\'t seem to be a good plan at all\n\n if len(nums1) > len(nums2): nums1, nums2 = nums2, nums1\n M = len(nums1)\n N = len(nums2)\n\n lastNegative = bisect_right(nums1, -1) - 1\n firstPositive = bisect_left(nums1, 1)\n z1 = firstPositive - lastNegative - 1\n\n def atLeastK(p: int) -> bool:\n # TODO: skip over positive/negative y values in O(1)\n\n total = 0\n\n if p >= 0:\n total += z1*N\n \n # x*y <= p\n # as x gets smaller (toward zero) y can get farther from zero\n j = N-1\n for i in range(0, lastNegative+1):\n while j >= 0 and nums1[i]*nums2[j] <= p: j -= 1\n total += N-j-1\n if total >= k: return True\n\n j = 0\n for i in range(M-1, firstPositive-1, -1):\n while j < N and nums1[i]*nums2[j] <= p: j += 1\n total += j\n if total >= k: return True\n else:\n\n # for small x < 0 we need a large positive y to get under the threshold\n # as x decreases away from zero then the y threshold gets smaller, so for descending x we have j descending too from N-1\n j = N-1\n for i in range(lastNegative, -1, -1):\n while j >= 0 and nums1[i]*nums2[j] <= p: j -= 1\n total += N-j-1\n if total >= k: return True\n\n # for small x > 0 we need large negative y to get under p < 0\n # as x increases we can use less negative y\n # so increasing x --> increasing j\n j = 0\n for i in range(firstPositive, M):\n while j < N and nums1[i]*nums2[j] <= p: j += 1\n total += j\n if total >= k: return True\n\n return False\n\n # max values come from the ends (?)\n lo = math.inf\n hi = -math.inf\n for e1 in [0, -1]:\n for e2 in [0, -1]:\n p = nums1[e1]*nums2[e2]\n lo = min(lo, p)\n hi = max(hi, p)\n\n while lo < hi:\n p = (hi-lo)//2 + lo # not (hi+lo)//2 to avoid round-down for negative numbers -> inf loop shennanigans\n if atLeastK(p):\n hi = p\n else:\n lo = p+1\n\n return lo\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Waaaaaggggghhhhhhh
|
waaaaaggggghhhhhhh-by-kotomord-v5bl
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nLet we have some pairs of collections of numbers (A_i, B_i), for any i any number from
|
kotomord
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-06T12:13:29.099546+00:00
|
2024-08-06T12:13:29.099575+00:00
| 143 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nLet we have some pairs of collections of numbers (A_i, B_i), for any i any number from A_i less or equals to any number from B_i\nLet sum of sizes of A_i is T, and we need find the Kth number of union (A_i) and (B_i) (K starts from 1)\n\nSo:\nif T >= K, we can drop B_i with the maximal floor\nif T < K, we can drop A_i with the minimal ceil and decrease K to the size of this A_i\n\nSo, simultion of this process with drop and resplit pair of the dropped se \n\n\n# Complexity\n n = max(nums1.length, nums2.length)\n m = min(nums1.length, nums2.length)\n- - Time complexity:\n- O(m*log(m)*log(n))\n \n- Space complexity:\nO(n + m)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n long lowerCount;\n long wantedPos;\n\n public class SmallSplittedLongs {\n long[] smalls;\n long[] bigs;\n int bigCount;\n int smallCount;\n long smallUp;\n long bigDown;\n boolean empty;\n\n\n SmallSplittedLongs(int size) {\n smalls = new long[size];\n bigs = new long[size];\n empty = true;\n }\n\n public void dropBigs() {\n bigCount = 0;\n if (smallCount == 1) {\n smallCount = 0;\n --lowerCount;\n empty = true;\n handleSingleValue(smalls[0]);\n return;\n }\n int nt = smallCount / 2;\n quickSelectInSmall(nt - 1);\n bigCount = 0;\n bigDown = smalls[nt];\n for (int i = nt; i < smallCount; ++i) {\n bigs[bigCount++] = smalls[i];\n if (smalls[i] < bigDown) bigDown = smalls[i];\n }\n lowerCount += nt - smallCount;\n smallCount = nt;\n smallUp = smalls[nt - 1];\n }\n\n\n public void dropSmalls() {\n lowerCount -= smallCount;\n wantedPos -= smallCount;\n smallCount = 0;\n\n if (bigCount == 1) {\n bigCount = 0;\n empty = true;\n handleSingleValue(bigs[0]);\n return;\n }\n\n smallCount = bigCount;\n long[] t = smalls;\n smalls = bigs;\n bigs = t;\n\n int nt = smallCount / 2;\n quickSelectInSmall(nt - 1);\n bigCount = 0;\n bigDown = smalls[nt];\n for (int i = nt; i < smallCount; ++i) {\n bigs[bigCount++] = smalls[i];\n if (smalls[i] < bigDown) bigDown = smalls[i];\n }\n lowerCount += nt;\n smallCount = nt;\n smallUp = smalls[nt - 1];\n }\n\n public long getWanted() {\n int wanted = (int) wantedPos;\n if (smallCount >= wanted) {\n quickSelectInSmall(wanted - 1);\n return smalls[wanted - 1];\n }\n wanted -= smallCount;\n smalls = bigs;\n smallCount = bigCount;\n quickSelectInSmall(wanted - 1);\n return smalls[wanted - 1];\n }\n\n\n public void addForce(long l) {\n if (empty) {\n smalls[smallCount++] = l;\n ++lowerCount;\n smallUp = l;\n empty = false;\n return;\n }\n addOne(l);\n }\n\n public void addPair(long a, long b) {\n if (empty) {\n addFirstPair(Math.min(a, b), Math.max(a, b));\n return;\n }\n addOne(a);\n addOne(b);\n }\n\n\n private Random rnd = new Random(1442);\n\n private void quickSelectInSmall(int t) {\n int down = 0;\n int up = smallCount;\n while (up - down > 1) {\n long pivotVal = smalls[down + rnd.nextInt(up - down)];\n int store1 = down;\n for (int i = down; i < up; ++i) {\n if (smalls[i] < pivotVal) {\n swap(i, store1++);\n }\n }\n if (store1 > t) {\n up = store1;\n continue;\n }\n int store2 = store1;\n for (int i = store1; i < up; ++i) {\n if (smalls[i] == pivotVal) {\n swap(i, store2++);\n }\n }\n if (store2 > t) return;\n down = store2;\n\n }\n }\n\n private void swap(int a, int b) {\n if (a == b) return;\n long l = smalls[a];\n smalls[a] = smalls[b];\n smalls[b] = l;\n }\n\n private void addFirstPair(long min, long max) {\n empty = false;\n smalls[smallCount++] = min;\n ++lowerCount;\n smallUp = min;\n bigs[bigCount++] = max;\n bigDown = max;\n }\n\n\n private void addOne(long l) {\n if (l < smallUp) {\n smalls[smallCount++] = l;\n ++lowerCount;\n return;\n }\n if (l > bigDown) {\n bigs[bigCount++] = l;\n return;\n }\n if (bigCount > smallCount) {\n smalls[smallCount++] = l;\n ++lowerCount;\n smallUp = l;\n return;\n }\n bigs[bigCount++] = l;\n bigDown = l;\n }\n }\n\n\n public class HeapTree {\n /*\n * \u0445\u0440\u0430\u043D\u0438\u043C \u043F\u0430\u0440\u044B (key, value), key \\in [0, k), value - Long, \u043D\u0430 \u0441\u0442\u0430\u0440\u0442\u0435 \u0434\u043B\u044F \u0432\u0441\u0435\u0445 \u043A\u043B\u044E\u0447\u0435\u0439 \u0435\u0441\u0442\u044C \u0437\u043D\u0430\u0447\u0435\u043D\u0438\u044F\n * \u043E\u043F\u0435\u0440\u0430\u0446\u0438\u0438: \u0438\u0437\u043C\u0435\u043D\u0438\u0442\u044C \u0437\u043D\u0430\u0447\u0435\u043D\u0438\u0435 \u043F\u0440\u0438 \u043A\u043B\u044E\u0447\u0435, \u0443\u0434\u0430\u043B\u0438\u0442\u044C \u043A\u043B\u044E\u0447, \u043D\u0430\u0439\u0442\u0438 \u043A\u043B\u044E\u0447 \u0441 \u043C\u0438\u043D\u0438\u043C\u0430\u043B\u044C\u043D\u044B\u043C \u0437\u043D\u0430\u0447\u0435\u043D\u0438\u0435\u043C, \u043F\u043E\u043B\u0443\u0447\u0438\u0442\u044C \u0437\u043D\u0430\u0447\u0435\u043D\u0438\u0435 \u043F\u043E \u043A\u043B\u044E\u0447\u0443\n * \u0438\u0437\u043C\u0435\u043D\u0435\u043D\u0438\u0435 \u0438 \u0443\u0434\u0430\u043B\u0435\u043D\u0438\u0435 \u043B\u043E\u0433\u0430\u0440\u0438\u0444\u043C\u0438\u0447\u0435\u0441\u043A\u043E\u0439 \u0441\u043B\u043E\u0436\u043D\u043E\u0441\u0442\u0438, \u043F\u043E\u0438\u0441\u043A \u043A\u043E\u043D\u0441\u0442\u0430\u043D\u0442\u043D\u044B\u0439\n *\n * */\n private final int size;\n private final int[] poss;\n private final Long[] vals;\n\n\n HeapTree(Long[] vals) {\n this.vals = vals;\n this.size = vals.length;\n this.poss = new int[size];\n for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; --i)\n updateOne(i);\n }\n\n\n public int getMinValKey() {\n return poss[0];\n }\n\n public Long getMinVal() {\n return vals[poss[0]];\n }\n\n public void remove(int key) {\n vals[key] = null;\n update(key);\n }\n\n public void change(int key, long val) {\n if (vals[key].longValue() == val) return;\n vals[key] = val;\n update(key);\n }\n\n private void updateOne(int p) {\n poss[p] = (vals[p] == null) ? -1 : p;\n int t = 2 * p + 1;\n if (t < size) {\n poss[p] = updateOne(poss[p], poss[t]);\n }\n ++t;\n if (t < size) {\n poss[p] = updateOne(poss[p], poss[t]);\n }\n }\n\n private int updateOne(int p1, int p2) {\n if (p1 == -1) return p2;\n if (p2 == -1) return p1;\n return (vals[p1] < vals[p2]) ? p1 : p2;\n }\n\n\n private void update(int p) {\n while (true) {\n updateOne(p);\n if (p == 0) break;\n p -= 1;\n p /= 2;\n }\n }\n }\n\n\n HeapTree lowers;\n HeapTree uppers;\n SmallSplittedLongs ssp;\n\n void handleSingleValue(long l) {\n if (lowers.getMinValKey() != -1) {\n addToSegment(lowers.getMinValKey(), l);\n } else {\n ssp.addForce(l);\n }\n }\n\n private int[] sorted;\n\n private class Segment {\n final long multipier;\n final int from;\n final int to;\n Long addition;\n\n Segment(long multipier, int from, int to) {\n this.multipier = multipier;\n this.from = from;\n this.to = to;\n addition = null;\n }\n\n\n long minVal() {\n long mv = (multipier > 0) ? sorted[from] * multipier : sorted[to] * multipier;\n return addition == null ? mv : Math.min(addition, mv);\n }\n\n long maxVal() {\n\n long mv = (multipier > 0) ? sorted[to] * multipier : sorted[from] * multipier;\n return addition == null ? mv : Math.max(addition, mv);\n }\n\n int count() {\n return to - from + 1 + (addition == null ? 0 : 1);\n }\n\n public Segment[] split() {\n //count()>=3, from -to + 1 >= 2\n Segment[] ret = new Segment[2];\n int mid = (from + to) / 2;\n if (multipier >= 0) {\n ret[0] = new Segment(multipier, from, mid);\n ret[1] = new Segment(multipier, mid + 1, to);\n } else {\n ret[1] = new Segment(multipier, from, mid);\n ret[0] = new Segment(multipier, mid + 1, to);\n }\n if (addition != null) {\n if (ret[0].maxVal() >= addition) {\n ret[0].addSingle(addition);\n } else {\n ret[1].addSingle(addition);\n }\n }\n return ret;\n }\n\n public void addSingle(long v) {\n if (addition == null) {\n addition = v;\n } else {\n ssp.addPair(addition, v);\n addition = null;\n }\n }\n }\n\n\n private class SegmentPair {\n Segment lower;\n Segment upper;\n\n SegmentPair(long multipier, int from, int to) {\n Segment s = new Segment(multipier, from, to);\n Segment[] spl = s.split();\n lower = spl[0];\n upper = spl[1];\n }\n }\n\n\n List<SegmentPair> segmentPairs = new ArrayList<>();\n\n private void addToSegment(int segmentPairNum, long value) {\n SegmentPair p = segmentPairs.get(segmentPairNum);\n long smallUp = p.lower.maxVal();\n if (value < smallUp) {\n lowerCount -= p.lower.count();\n p.lower.addSingle(value);\n lowerCount += p.lower.count();\n\n } else {\n p.upper.addSingle(value);\n }\n lowers.change(segmentPairNum, p.lower.maxVal());\n uppers.change(segmentPairNum, -p.upper.minVal());\n }\n\n\n private void resplitSegment(int key, SegmentPair sp, Segment toSplit) {\n int cnt = toSplit.count();\n if (cnt == 1) {\n lowers.remove(key);\n uppers.remove(key);\n handleSingleValue(toSplit.maxVal());\n return;\n }\n\n if (cnt == 2) {\n lowers.remove(key);\n uppers.remove(key);\n ssp.addPair(toSplit.minVal(), toSplit.maxVal());\n return;\n }\n Segment[] spl = toSplit.split();\n sp.lower = spl[0];\n sp.upper = spl[1];\n lowerCount += sp.lower.count();\n lowers.change(key, sp.lower.maxVal());\n uppers.change(key, -sp.upper.minVal());\n\n }\n\n\n private void dropFromLower(int key) {\n SegmentPair sp = segmentPairs.get(key);\n lowerCount -= sp.lower.count();\n wantedPos -= sp.lower.count();\n resplitSegment(key, sp, sp.upper);\n }\n\n private void dropFromLower() {\n if (ssp.empty) {\n dropFromLower(lowers.getMinValKey());\n } else {\n long v1 = lowers.getMinVal();\n long v2 = ssp.smallUp;\n if (v2 < v1) {\n ssp.dropSmalls();\n } else {\n dropFromLower(lowers.getMinValKey());\n }\n }\n }\n\n\n\n private void dropFromUpper(int key) {\n SegmentPair sp = segmentPairs.get(key);\n lowerCount -= sp.lower.count();\n resplitSegment(key,sp, sp.lower);\n }\n\n private void dropFromUpper(){\n if(ssp.empty) {\n dropFromUpper(uppers.getMinValKey());\n }else{\n long v1 = - uppers.getMinVal();\n long v2 = ssp.bigDown;\n if(v2>v1) {\n ssp.dropBigs();\n }else {\n dropFromUpper(uppers.getMinValKey());\n }\n }\n }\n\n void prepareStateProcess(int[] first, int[] second) {\n sorted = first;\n int k = second.length;\n ssp = new SmallSplittedLongs(2*k);\n Long[] l1 = new Long[k];\n Long[] l2 = new Long[k];\n\n for(int i = 0; i<k; ++i) {\n SegmentPair sp = new SegmentPair(second[i], 0, first.length-1);\n segmentPairs.add(sp);\n l1[i] = sp.lower.maxVal();\n l2[i] = -sp.upper.minVal();\n lowerCount += sp.lower.count();\n }\n lowers = new HeapTree(l1);\n uppers = new HeapTree(l2);\n }\n\n long stateProcess() {\n while(uppers.getMinValKey() != -1) {\n if(lowerCount<wantedPos){\n dropFromLower();\n }else{\n dropFromUpper();\n }\n }\n return ssp.getWanted();\n }\n\n\n\n public long kthSmallestProduct(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, long k) {\n if (nums1.length * 1L* nums2.length < 10) {\n return simpleBrute(nums1, nums2, k);\n }\n\n if (nums1.length > nums2.length) {\n prepareStateProcess(nums1, nums2);\n } else {\n prepareStateProcess(nums2, nums1);\n }\n wantedPos = k;\n return stateProcess();\n\n }\n\n private long simpleBrute(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, long k) {\n List<Long> finState = new ArrayList<>();\n for (int i : nums1)\n for (int j : nums2)\n finState.add(i * 1L * j);\n Collections.sort(finState);\n return finState.get((int) (k - 1));\n }\n\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Heap (Priority Queue)', 'Quickselect', 'Java']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Java solution using binarysearch
|
java-solution-using-binarysearch-by-vhar-6e1t
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
vharshal1994
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-05T01:19:41.604086+00:00
|
2024-07-05T01:19:41.604111+00:00
| 30 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n //https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LktWIgiNKMQ\n public long kthSmallestProduct(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, long k) {\n List<Integer> negativeNums1 = applyFilter(nums1, false);\n List<Integer> positiveNums1 = applyFilter(nums1, true);\n List<Integer> negativeNums2 = applyFilter(nums2, false);\n List<Integer> positiveNums2 = applyFilter(nums2, true);\n\n long totalNegativeNumCount = negativeNums1.size() * positiveNums2.size() \n + negativeNums2.size() * positiveNums1.size();\n\n if (k > totalNegativeNumCount) {\n k -= totalNegativeNumCount;\n // search space is positiveNums1 and positiveNums2\n reverse(negativeNums1);\n reverse(negativeNums2);\n\n long low = (long) -1e10;\n long high = (long) 1e10 + 1;\n long mid, ans =-1, count;\n while (low <= high) {\n mid = low + (high - low) / 2;\n count = count(positiveNums1, positiveNums2, mid) + \n count(negativeNums1, negativeNums2, mid);\n if (count >= k) {\n ans = mid;\n high = mid - 1;\n } else {\n low = mid + 1;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n } else {\n reverse(positiveNums1);\n reverse(positiveNums2);\n\n long low = (long) -1e10;\n long high = (long) 1e10 + 1;\n long mid, ans = -1, count;\n while (low <= high) {\n mid = low + (high - low) / 2;\n count = count(negativeNums1, positiveNums2, mid) + \n count(negativeNums2, positiveNums1, mid);\n if (count >= k) {\n ans = mid;\n high = mid - 1;\n } else {\n low = mid + 1;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\n }\n\n private long count(List<Integer> list1, List<Integer> list2, long val) {\n \n int j = list2.size() - 1;\n long count = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++) {\n while (j >= 0) {\n if ((long) list1.get(i) * (long) list2.get(j) <= val) {\n count += j + 1;\n break;\n } else {\n j -= 1;\n }\n }\n }\n System.out.println(count + " " + val);\n return count;\n }\n\n private void reverse(List<Integer> list) {\n int low = 0, high = list.size() - 1;\n while (low <= high) {\n int temp = list.get(low);\n list.set(low, list.get(high));\n list.set(high, temp);\n low += 1;\n high -= 1;\n }\n }\n private List<Integer> applyFilter(int[] nums, boolean isPositive) {\n List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();\n for (int num : nums) {\n if (isPositive) {\n if (num >= 0) {\n list.add(num);\n }\n } else {\n if (num < 0) {\n list.add(num);\n }\n }\n }\n return list;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
C++ | Binary Search | O(nlog(Ans)) | dangerous code
|
c-binary-search-onlogans-dangerous-code-b79zf
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\nYou can read this if you want: https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-number-in-m
|
shubhamchandra01
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-27T14:07:07.851424+00:00
|
2024-06-27T18:02:30.531663+00:00
| 62 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\nYou can read this if you want: https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-number-in-multiplication-table/solutions/5379213/general-technique-kth-smallest-any-problem-binary-search-more-practice-problems/\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(nlog(Ans))$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) {\n vector<int> pos, neg, pos1, neg1;\n int zero = 0, zero1 = 0;\n for (int &x: nums1) {\n if (x == 0) {\n zero++;\n } else if (x > 0) {\n pos.push_back(x);\n } else {\n neg.push_back(x);\n }\n }\n for (int &x: nums2) {\n if (x == 0) {\n zero1++;\n } else if (x > 0) {\n pos1.push_back(x);\n } else {\n neg1.push_back(x);\n }\n }\n \n int psz = pos.size(), nsz = neg.size(), psz1 = pos1.size(), nsz1 = neg1.size();\n long long totalZero = 1LL * (psz + nsz) * zero1 + 1LL * (psz1 + nsz1) * zero + 1LL * zero * zero1;\n\n auto getPosPos = [&](long long p) -> long long {\n if (p <= 0) return 0;\n int i = 0, j = psz1 - 1;\n long long cnt = 0;\n\n while (i < psz && j >= 0) {\n while (j >= 0 && 1LL * pos[i] * pos1[j] > p) {\n j--;\n }\n cnt += j + 1;\n i++;\n }\n return cnt;\n };\n\n auto getPosNeg = [&](long long p) -> long long {\n if (p >= 0) return 1LL * psz * nsz1;\n long long cnt = 0;\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n while (i < nsz1 && j < psz) {\n while (j < psz && 1LL * neg1[i] * pos[j] > p) {\n j++;\n }\n cnt += psz - j;\n i++;\n }\n return cnt;\n };\n\n auto getNegPos = [&](long long p) -> long long {\n if (p >= 0) return 1LL * nsz * psz1;\n long long cnt = 0;\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n while (i < nsz && j < psz1) {\n while (j < psz1 && 1LL * neg[i] * pos1[j] > p) {\n j++;\n }\n cnt += psz1 - j;\n i++;\n }\n return cnt;\n };\n\n auto getNegNeg = [&](long long p) -> long long {\n if (p <= 0) return 0;\n int i = nsz - 1, j = 0;\n long long cnt = 0;\n while (i >= 0 && j < nsz1) {\n while (j < nsz1 && 1LL * neg[i] * neg1[j] > p) {\n j++;\n }\n cnt += nsz1 - j;\n i--;\n }\n return cnt;\n };\n\n auto getCount = [&](long long p) -> long long {\n long long cnt = getPosPos(p) + getPosNeg(p) + getNegPos(p) + getNegNeg(p);\n if (p >= 0) {\n cnt += totalZero;\n }\n return cnt;\n };\n \n long long lo = -1e11, hi = 1e10;\n // smallest product whose count is >= k, where count is number of products in num1 * nums2 that are less than equal to given product\n while (lo < hi) {\n long long mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; // hi is always valid / true. Extend the valid region to the left\n if (getCount(mid) >= k) {\n hi = mid;\n } else {\n lo = mid + 1;\n }\n }\n return lo;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
C++ | Binary Search | O(nlogn) | dangerous
|
c-binary-search-onlogn-dangerous-by-shub-lyk6
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
shubhamchandra01
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-27T14:01:20.624930+00:00
|
2024-06-27T14:01:20.624951+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(nlogn)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) {\n vector<int> pos, neg, pos1, neg1;\n int zero = 0, zero1 = 0;\n for (int &x: nums1) {\n if (x == 0) {\n zero++;\n } else if (x > 0) {\n pos.push_back(x);\n } else {\n neg.push_back(x);\n }\n }\n for (int &x: nums2) {\n if (x == 0) {\n zero1++;\n } else if (x > 0) {\n pos1.push_back(x);\n } else {\n neg1.push_back(x);\n }\n }\n \n int psz = pos.size(), nsz = neg.size(), psz1 = pos1.size(), nsz1 = neg1.size();\n long long totalZero = 1LL * (psz + nsz) * zero1 + 1LL * (psz1 + nsz1) * zero + 1LL * zero * zero1;\n\n auto getPosPos = [&](long long p) -> long long {\n if (p <= 0) return 0;\n int i = 0, j = psz1 - 1;\n long long cnt = 0;\n\n while (i < psz && j >= 0) {\n while (j >= 0 && 1LL * pos[i] * pos1[j] > p) {\n j--;\n }\n cnt += j + 1;\n i++;\n }\n return cnt;\n };\n\n auto getPosNeg = [&](long long p) -> long long {\n if (p >= 0) return 1LL * psz * nsz1;\n long long cnt = 0;\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n while (i < nsz1 && j < psz) {\n while (j < psz && 1LL * neg1[i] * pos[j] > p) {\n j++;\n }\n cnt += psz - j;\n i++;\n }\n return cnt;\n };\n\n auto getNegPos = [&](long long p) -> long long {\n if (p >= 0) return 1LL * nsz * psz1;\n long long cnt = 0;\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n while (i < nsz && j < psz1) {\n while (j < psz1 && 1LL * neg[i] * pos1[j] > p) {\n j++;\n }\n cnt += psz1 - j;\n i++;\n }\n return cnt;\n };\n\n auto getNegNeg = [&](long long p) -> long long {\n if (p <= 0) return 0;\n int i = nsz - 1, j = 0;\n long long cnt = 0;\n while (i >= 0 && j < nsz1) {\n while (j < nsz1 && 1LL * neg[i] * neg1[j] > p) {\n j++;\n }\n cnt += nsz1 - j;\n i--;\n }\n return cnt;\n };\n\n auto getCount = [&](long long p) -> long long {\n long long cnt = getPosPos(p) + getPosNeg(p) + getNegPos(p) + getNegNeg(p);\n if (p >= 0) {\n cnt += totalZero;\n }\n return cnt;\n };\n \n long long lo = -1e11, hi = 1e10;\n // smallest product whose count is >= k, where count is number of products in num1 * nums2 that are less than equal to given product\n while (lo < hi) {\n long long mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; // hi is always valid / true. Extend the valid region to the left\n if (getCount(mid) >= k) {\n hi = mid;\n } else {\n lo = mid + 1;\n }\n }\n return lo;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
java solution with detailed explaination
|
java-solution-with-detailed-explaination-88mi
|
class Solution {\n public int findMaxNegativeIndex(int[] nums)\n {\n var low = 0;//negtive no\n var high = nums.length -1;//not a negative n
|
sumanth_gonal
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-14T03:35:42.102919+00:00
|
2024-06-14T03:35:42.102952+00:00
| 5 | false |
class Solution {\n public int findMaxNegativeIndex(int[] nums)\n {\n var low = 0;//negtive no\n var high = nums.length -1;//not a negative no\n if(nums[low] > 0) return -1;//don\'t not have any negative value\n if(nums[high] < 0) return high;//all numbers are negative\n while(low < high)\n {\n var m = (low + high + 1)/2;\n if(nums[m] < 0)\n {\n low = m;\n }else{\n if(high == m) break;\n high = m;\n }\n }\n return low;\n }\n public long kthSmallestProduct(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, long k) {\n long low = Long.MIN_VALUE/2;//have less than k no product than this\n long high = Long.MAX_VALUE/2;//have atleast k no product less than this\n var negInd1 = findMaxNegativeIndex(nums1);\n var negInd2 = findMaxNegativeIndex(nums2);\n while(low < high)\n {\n long m = low + (high-low)/2;\n var val = getNoOfProductLessThan(m, nums1, nums2, negInd1, negInd2);\n if(k <= val){\n high = m;\n }else{\n if(low == m) break;\n low = m;\n }\n }\n\n return high;\n }\n public long getNoOfProductLessThan(long m, int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int f, int s)\n {\n var l1 = nums1.length;\n var l2 = nums2.length;\n \n long ans = 0;\n\n //when nums1 pos and nums2 is pos\n var j = l2-1;\n for(int i = f+1; i < l1; i++)\n {\n //special case when nums1[i] == 0\n if(nums1[i] == 0)\n {\n if(m >= 0) ans+= l2;\n continue;\n }\n while(j > s && ( (long)nums1[i] * (long)nums2[j] > m) )\n {\n j--;\n }\n if(j > s) ans+= j-s;\n }\n\n //when nums1 pos and nums2 is neg\n j = s;\n for(int i = l1-1; i > f; i--)\n {\n if(nums1[i] == 0) break;\n while(j >= 0 && ( (long)nums1[i] * (long)nums2[j] > m) )\n {\n j--;\n }\n if(j >= 0) ans += (j+1);\n }\n\n //when nums1 neg and nums2 is neg\n j = 0;\n for(int i = f; i >= 0; i--)\n {\n while(j <= s && ( (long)nums1[i] * (long)nums2[j] > m) )\n {\n j++;\n }\n if(j <= s) ans+= (s-j+1);\n }\n\n //when nums1 neg and nums2 is pos\n j = s+1;\n for(int i = 0; i <= f; i++)\n {\n while(j < l2 && ( (long)nums1[i] * (long)nums2[j] > m) )\n {\n j++;\n }\n if(j < l2) ans += (l2 - j);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
JS | Binary Search
|
js-binary-search-by-nanlyn-yryz
|
Code\n\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums1\n * @param {number[]} nums2\n * @param {number} k\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar kthSmallestProduct = function (nums1, n
|
nanlyn
|
NORMAL
|
2024-05-09T22:00:56.020104+00:00
|
2024-05-09T22:00:56.020180+00:00
| 17 | false |
# Code\n```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums1\n * @param {number[]} nums2\n * @param {number} k\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar kthSmallestProduct = function (nums1, nums2, k) {\n let nums1Neg = findMaxIndexLessThanNum(nums1, 0);\n let nums1NonPos = findMaxIndexLessThanNum(nums1, 1);\n let nums1Length = nums1.length;\n let nums2Length = nums2.length;\n\n var totalNums = function (mid) {\n let count = nums1Neg * nums2.length;\n\n let i = 0;\n while (i < nums1Neg) {\n count -= findMaxIndexLessThanNum(nums2, Math.ceil(mid / nums1[i++]));\n }\n \n count += (mid < 0) ? 0 : (nums1NonPos - nums1Neg) * nums2.length;\n\n i = nums1NonPos;\n while (i >= nums1NonPos && i < nums1Length) {\n count += findMaxIndexLessThanNum(nums2, Math.floor(mid / nums1[i++]) + 1);\n }\n return count;\n }\n\n let min = -1e10;\n let max = 1e10;\n while (min < max) {\n let mid = min + Math.floor((max - min) / 2);\n if (totalNums(mid) >= k) {\n max = mid;\n } else {\n min = mid + 1;\n }\n }\n\n return min;\n};\n\n\nvar findMaxIndexLessThanNum = function (arr, num) {\n let left = 0;\n let right = arr.length;\n while (left < right) {\n let mid = left + Math.floor((right - left) / 2);\n if (arr[mid] < num) {\n left = mid + 1;\n } else {\n right = mid;\n }\n }\n return left;\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
C# Solution - Binary Search with Counting
|
c-solution-binary-search-with-counting-b-dikk
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
taangels
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-12T10:25:37.158306+00:00
|
2024-02-12T10:25:37.158328+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\npublic class Solution {\n private void Parition(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, out int posLen1, out int negLen1, out int posLen2, out int negLen2, \n out int[] pos1, out int[] neg1, out int[] pos2, out int[] neg2, out bool isResultPositive, ref long k)\n {\n posLen1 = 0; negLen1 = 0; posLen2 = 0; negLen2 = 0;\n\n foreach (int num in nums1)\n {\n if (num < 0) negLen1++;\n else posLen1++;\n }\n\n foreach (int num in nums2)\n {\n if (num < 0) negLen2++;\n else posLen2++;\n }\n\n int numNegatives = posLen1 * negLen2 + posLen2 * negLen1;\n isResultPositive = k > numNegatives;\n\n pos1 = new int[posLen1]; neg1 = new int[negLen1];\n pos2 = new int[posLen2]; neg2 = new int[negLen2];\n\n int iPos = 0, iNeg = 0;\n foreach (int num in nums1)\n {\n if (num < 0)\n neg1[iNeg++] = num;\n else \n pos1[iPos++] = num;\n }\n\n iPos = 0; iNeg = 0;\n foreach (int num in nums2)\n {\n if (num < 0)\n neg2[iNeg++] = num;\n else \n pos2[iPos++] = num;\n }\n \n // if result is positive, we want negative numbers is descending order.\n // if result is positive, we want negative numbers is ascending order.\n // Reason is - for two arrays, if we keep i at arr1[0] and j and arr2[n-1], by \n // comparing both values, we should be able to say that left side elements in arr2\n // are less than arr1[i] * arr2[j]\n if (isResultPositive)\n {\n k -= numNegatives; // find (k - numNeg)th positive number\n Array.Reverse(neg1);\n Array.Reverse(neg2);\n }\n else\n {\n Array.Reverse(pos1);\n Array.Reverse(pos2);\n }\n }\n\n private long GetValidNumberCount(int[] arr1, int[] arr2, long val)\n {\n int i = 0, j = arr2.Length-1;\n long count = 0L;\n\n while (i < arr1.Length && j >= 0)\n {\n // all numbers of left of j are less than val\n if (((long)arr1[i] * (long)arr2[j]) <= val)\n {\n count += (long)(j+1);\n i++;\n }\n else\n {\n j--;\n }\n }\n\n return count;\n }\n\n\n public long KthSmallestProduct(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, long k) \n {\n\n Parition(nums1, nums2, out int posLen1, out int negLen1, out int posLen2, out int negLen2, out int[] pos1, \n out int[] neg1, out int[] pos2, out int[] neg2, out bool isResultPositive, ref k);\n \n // high , low based on input constraints\n long low = -(long)Math.Pow(10, 10) - 1;\n long high = (long)Math.Pow(10, 10) + 1;\n\n while (low < high)\n {\n long mid = low + (high - low)/2;\n long count = isResultPositive ? GetValidNumberCount(pos1, pos2, mid) + GetValidNumberCount(neg1, neg2, mid)\n : GetValidNumberCount(pos1, neg2, mid) + GetValidNumberCount(pos2, neg1, mid);\n \n if (count >= k)\n {\n high = mid;\n }\n else\n {\n low = mid + 1;\n }\n }\n\n return high;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
C++ Not Best, But Simple Approach. BS
|
c-not-best-but-simple-approach-bs-by-its-d5up
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nApproach is Similar to
|
itsCapJohnPrice
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-26T07:28:57.621700+00:00
|
2024-01-26T07:38:13.811184+00:00
| 104 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nApproach is Similar to others but code is quite simple. Focus on below points :\n#1. Multiplication with negative reverses the order, so apply B.S carefully.\n#2. Dry run on some example to see where to apply lower_bound and upper_bound. Its better to write your own version of these for more clarity. (See the last code without stl\'s lb and ub)\n#3. Binary search on answer is the approach, where you have to check how many numbers(multiplications) are less than mid(of binary search). From this count you can compare it with k.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(nlogm)$$, where n is size of first array and m is size of second array. \n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(1)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n typedef long long ll;\n\n int counterFunc(const vector<int> &nums, ll mid, ll num){\n int n = nums.size(), counter=0;\n if(num == 0 && mid>=0)return n;\n if(num == 0) return 0;\n if(num > 0){\n counter += upper_bound(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 1.0*mid/num)-nums.begin();\n }\n else{\n counter += n - (lower_bound(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 1.0*mid/num) - nums.begin());\n }\n return counter;\n }\n \n bool isValid(const vector<int>& nums1, const vector<int>& nums2, ll k, ll mid){\n ll counter = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < nums1.size(); ++i){\n counter += counterFunc(nums2, mid, nums1[i]);\n }\n return counter>=k;\n }\n\n ll kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, ll k) {\n ll l = -10000000001LL, r = 10000000001LL;\n while(l < r){\n ll mid = l+(r-l)/2;\n if(isValid(nums1, nums2, k, mid)){\n r = mid;\n }else{\n l = mid+1;\n }\n }\n return l; \n }\n};\n```\nWithout using lower_bound and upper_bound, more practical and intutive(As we have more control over functions, which we write by our own).\n\n```\ntypedef long long ll;\n\n int counterFunc(const vector<int> &nums, ll mid, ll num){\n int n = nums.size(), counter=0, l = 0, r = n;\n if(num == 0 && mid>=0)return n;\n if(num == 0) return 0;\n if(num > 0){\n \n while(l < r){\n int _mid = l+(r-l)/2;\n if((ll)nums[_mid]*num > mid){\n r = _mid;\n }else{\n l = _mid+1;\n }\n }\n counter+=l;\n \n }\n else{\n \n while(l < r){\n int _mid = l+(r-l)/2;\n if((ll)nums[_mid]*num <= mid){\n r = _mid;\n }else{\n l = _mid+1;\n }\n }\n counter+=n-l;\n\n }\n\n return counter;\n }\n \n bool isValid(const vector<int>& nums1, const vector<int>& nums2, ll k, ll mid){\n ll counter = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < nums1.size(); ++i){\n counter += counterFunc(nums2, mid, nums1[i]);\n }\n return counter>=k;\n }\n\n ll kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, ll k) {\n ll l = -10000000001LL, r = 10000000001LL;\n while(l < r){\n ll mid = l+(r-l)/2;\n if(isValid(nums1, nums2, k, mid)){\n r = mid;\n }else{\n l = mid+1;\n }\n }\n return l; \n }\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
100% faster.
|
100-faster-by-si7845140-hkmx
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
si7845140
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-22T11:04:39.482806+00:00
|
2024-01-22T11:04:39.482835+00:00
| 52 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long getnum(vector<int>& arr1,vector<int>& arr2,vector<int>& arr3,vector<int>& arr4,long long num){\n int i = 0;\n int j = arr2.size()-1;\n long long cnt = 0;\n while(i<arr1.size() and j>=0 and arr2.size()>0){\n if(1l*arr1[i]*arr2[j]<=num){\n i++;\n cnt+=(j+1);\n }\n else j--;\n }\n i=0;j=arr4.size()-1;\n while(i<arr3.size() and j>=0 and arr4.size()>0){\n if(1l*arr3[i]*arr4[j]<=num){\n i++;\n cnt+=(j+1);\n }\n else j--;\n }\n \n return cnt;\n }\n \n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) {\n \n vector<int> pos1;\n vector<int> neg1;\n vector<int> pos2;\n vector<int> neg2;\n for(auto x:nums1){\n if(x<0){\n neg1.push_back(x);\n }\n else{\n pos1.push_back(x);\n }\n }\n for(auto x:nums2){\n if(x<0){\n neg2.push_back(x);\n }\n else{\n pos2.push_back(x);\n }\n }\n long long nofneg = neg1.size() * pos2.size() + neg2.size()*pos1.size();\n bool iskneg = k>nofneg?false:true;\n k = !iskneg?k-nofneg:k;\n if(!iskneg){\n reverse(neg1.begin(),neg1.end());\n reverse(neg2.begin(),neg2.end());\n }else{\n reverse(pos1.begin(),pos1.end());\n reverse(pos2.begin(),pos2.end());\n }\n long long low = -1e10,high = 1e10;\n while(low<high){\n long long mid = (long long)(low + (high-low)/2); \n if(getnum(pos1,iskneg?neg2:pos2,neg1,iskneg?pos2:neg2,mid)>=k){\n high = mid;\n }else{\n low = mid+1;\n }\n \n }\n return high;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Binary Search Only C++
|
binary-search-only-c-by-tus_tus-pydz
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n1) We could do it using min Heap like this https://leetcode.com/problems/find-k-pairs
|
Tus_Tus
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-20T08:23:48.398970+00:00
|
2024-01-20T08:23:48.398996+00:00
| 89 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n1) We could do it using min Heap like this [https://leetcode.com/problems/find-k-pairs-with-smallest-sums/description/]() but the constraint for k is of the order 10^9 something. So we can not use min heap here.\n\n2) If I consider midVal to be the Kth smallest then the number of products less than midVal must be K - 1;\n3) If the number of products less than midVal is **x** then number of products less than midVal + 1 will be greater than or equal to **x**.\nThe same thing goes for midVal + 2 and so on.\n\n4) It means we can apply binary search on this midVal. And try to find smallest midVal which is having k - 1 number of products less than midVal.\n\n\n5) In order to count the product which is less than midVal.We can fix one value one and try to find the other value using binary search.\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n bool helper(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k, long long midVal) {\n\n int n = nums1.size();\n int m = nums2.size();\n\n long long cnt = 0;\n\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n\n long long val = nums1[i];\n\n if(val == 0 && midVal >= 0) {\n cnt += m;\n } else if(val > 0) {\n int maxIdx = -1;\n int l = 0;\n int r = m - 1;\n while(l <= r) {\n int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;\n long long product = nums2[mid] * val * 1LL;\n if(product <= midVal) {\n maxIdx = mid;\n l = mid + 1;\n } else {\n r = mid - 1;\n }\n }\n if(maxIdx != -1) {\n cnt += (maxIdx + 1);\n }\n } else if(val < 0){\n int minIdx = -1;\n int l = 0;\n int r = m - 1;\n while(l <= r) {\n int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;\n long long product = nums2[mid] * val * 1LL;\n if(product <= midVal) {\n minIdx = mid;\n r = mid - 1;\n } else {\n l = mid + 1;\n }\n }\n if(minIdx != -1) {\n cnt += (m - minIdx);\n }\n }\n }\n\n\n if(cnt >= k) {\n return true;\n } else {\n return false;\n }\n\n }\n \n\n\n\n \n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) {\n \n\n long long left = -1e13;\n long long right = 1e13;\n\n long long ans;\n\n while(left <= right) {\n long long midVal = left + (right - left) / 2;\n\n bool poss = helper(nums1, nums2, k, midVal);\n\n if(poss) {\n ans = midVal;\n right = midVal - 1;\n } else {\n left = midVal + 1;\n }\n\n }\n\n\n return ans;\n\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Binary Search', 'C++']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
C++ solution using Binary Search | with detailed explanation on Time complexity
|
c-solution-using-binary-search-with-deta-ryue
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(log(P) * m log n)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\nfindmaxIndex and findminIndex: Both use binary search, which h
|
haseena_hassan
|
NORMAL
|
2023-12-30T21:48:02.469510+00:00
|
2023-12-30T21:48:02.469553+00:00
| 37 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(log(P) * m log n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\nfindmaxIndex and findminIndex: Both use binary search, which has a time complexity of O(log n), where n is the size of nums2. These functions are called for each element in nums1, so the overall complexity for both combined is O(m log n), where m is the size of nums1 and n is the size of nums2.\n\ncountProdLessEqualMid: It iterates through each element in nums1 and performs a binary search for each element in nums2. Therefore, its time complexity is O(m log n), where m is the size of nums1 and n is the size of nums2.\n\nkthSmallestProduct: It performs binary search on the range of possible products. In each iteration of the binary search, it calls countProdLessEqualMid, which has a time complexity of O(m log n). The binary search is performed until the range is exhausted. Therefore, the overall time complexity of kthSmallestProduct is O(log(P) * m log n), where P is the difference between the maximum and minimum possible products.\n\nThe dominant factor in the time complexity is the binary search operation, and the overall complexity can be expressed as O(log(P) * m log n).\n\n- Space complexity: O(1)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nThe overall space complexity is dominated by the constant amount of extra space used in the functions, and it does not depend on the input size. Hence, the space complexity of the entire code is O(1).\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int findmaxIndex(vector<int>& nums2, long long val, long long productNeeded){\n long long low = 0, high = nums2.size()-1;\n long long resIndex = -1;\n\n while(low <= high){\n long long mid = (low + high) / 2;\n long long productObtained = nums2[mid] * val;\n\n if(productObtained <= productNeeded) resIndex = mid, low = mid + 1;\n else high = mid - 1; \n }\n return resIndex + 1;\n }\n int findminIndex(vector<int>& nums2, long long val, long long productNeeded){\n long long low = 0, high = nums2.size()-1;\n long long resIndex = nums2.size();\n\n while(low <= high){\n long long mid = (low + high) / 2;\n long long productObtained = nums2[mid] * val;\n\n if(productObtained <= productNeeded) resIndex = mid, high = mid - 1; \n else low = mid + 1;\n }\n return nums2.size() - resIndex;\n }\n \n // countProdLessEqualMid(x) - how many products are less or equal than x.\n long long countProdLessEqualMid(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long product){\n long long count = 0;\n for(int num : nums1){\n if(num == 0 && product >= 0) count += nums2.size(); \n else if(num > 0) count += findmaxIndex(nums2, num, product);\n else if(num < 0) count += findminIndex(nums2, num, product);\n }\n return count;\n }\n\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) {\n \n long long low = -1e10, high = 1e10; // Search space = min product to max product (-1e10 to +1e10)\n while(low <= high){ // Binary search - find the first moment where we have exactly k products\n long long mid = (low + high) / 2;\n if(countProdLessEqualMid(nums1, nums2, mid) >= k) high = mid - 1;\n else low = mid + 1;\n }\n return low;\n }\n};\n\n\n// If num=0: (num * each element in nums2) = 0. all products <= midProduct. So we can count all products in the answer\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
C++ O(NLogN) Binary Search + Sliding Window solution
|
c-onlogn-binary-search-sliding-window-so-fbzs
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Pawan525
|
NORMAL
|
2023-12-10T10:17:49.856097+00:00
|
2023-12-10T10:17:49.856129+00:00
| 24 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long getPairsCount(vector<long long>& b, vector<long long>& d, long long prod){\n long long count = 0;\n int index1, index2;\n\n if(b.empty() || d.empty()){\n return 0;\n }\n\n index1 = 0;\n index2 = d.size() - 1;\n while(index1 < b.size()){\n while(index2 >= 0 && (b[index1] * d[index2] > prod)){\n index2--;\n }\n count += index2 + 1;\n index1++;\n }\n return count;\n }\n\n bool isValid(vector<long long>& a, vector<long long>& b, vector<long long>& c, vector<long long>& d, long long k, long long prod){\n long long count = 0;\n \n count += getPairsCount(b, d, prod);\n\n reverse(a.begin(), a.end());\n reverse(c.begin(), c.end());\n count += getPairsCount(a, c, prod);\n reverse(a.begin(), a.end());\n reverse(c.begin(), c.end());\n\n reverse(b.begin(), b.end());\n count += getPairsCount(b, c, prod);\n reverse(b.begin(), b.end());\n\n reverse(d.begin(), d.end());\n count += getPairsCount(a, d, prod);\n reverse(d.begin(), d.end());\n return count >= k;\n }\n\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) {\n int m = nums1.size();\n int n = nums2.size();\n\n long long p = (nums1[0] < 0) ? ((long long)nums1[0] * nums2[n - 1]) : ((long long)nums1[0] * nums2[0]);\n long long q = (nums1[m - 1] < 0) ? ((long long)nums1[m - 1] * nums2[n - 1]) : ((long long)nums1[m - 1] * nums2[0]);\n long long r = (nums1[m - 1] >= 0) ? ((long long)nums1[m - 1] * nums2[n - 1]) : ((long long)nums1[m - 1] * (nums2[0]));\n long long s = (nums1[0] < 0) ? ((long long)nums1[0] * nums2[0]) : ((long long)nums1[0] * nums2[n - 1]);\n\n long long start = min(p, q);\n long long end = max(r, s);\n long long mid;\n\n vector<long long> a;\n vector<long long> b;\n vector<long long> c;\n vector<long long> d;\n int i;\n\n for(i = 0; i < m; i++){\n if(nums1[i] < 0){\n a.push_back(nums1[i]);\n }\n else{\n b.push_back(nums1[i]);\n }\n }\n\n for(i = 0; i < n; i++){\n if(nums2[i] < 0){\n c.push_back(nums2[i]);\n }\n else{\n d.push_back(nums2[i]);\n }\n }\n\n while(start <= end){\n mid = start + (end - start) / 2;\n if(mid == start){\n return isValid(a, b, c, d, k, start) ? start : end;\n }\n else{\n if(isValid(a, b, c, d, k, mid)){\n end = mid;\n }\n else{\n start = mid;\n }\n }\n }\n return start;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Binary Search | Time: O(Nlog(R)log(M)) | Space: O(1)
|
binary-search-time-onlogrlogm-space-o1-b-j9r8
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: $O(N\log({R})\log({M}))$\n - $N$: nums1.length\n - $M$: nums2.length\n - $R$: The range size of $nums1[i] * nums2[j]$\n
|
rojas
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-06T15:37:34.033956+00:00
|
2023-11-06T15:49:45.912441+00:00
| 65 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $O(N\\log({R})\\log({M}))$\n - $N$: nums1.length\n - $M$: nums2.length\n - $R$: The range size of $nums1[i] * nums2[j]$\n - $-10^5 <= nums1[i], nums2[j] <= 10^5$\n - $-10^{10} <= nums1[i] * nums2[j] <= 10^{10}$\n - $R = 10^{10} - (-10^{10}) = 2(10)^{10} = 2e10$\n - $\\log_2{R} = \\log_2(2e10) = 34.219 \\approx 35$\n- Space complexity: $O(1)$\n\n# Code\n```Typescript\nfunction kthSmallestProduct(nums1: number[], nums2: number[], k: number): number {\n let min = -1e10;\n let max = 1e10;\n\n const negs = binarySearch(nums1, 0);\n const zeroes = binarySearch(nums1, 1, negs) - negs;\n while (min < max) {\n const mid = min + Math.floor((max - min)/2);\n if (k > check(nums1, nums2, negs, zeroes, mid)) {\n min = mid + 1;\n } else {\n max = mid;\n }\n }\n\n return min;\n};\n\nfunction binarySearch(arr: number[], target: number, min = 0, max = arr.length): number {\n while (min < max) {\n const mid = min + Math.floor((max - min)/2);\n if (target > arr[mid]) {\n min = mid + 1;\n } else {\n max = mid;\n }\n }\n return min;\n}\n\nfunction check(nums1: number[], nums2: number[], negs: number, zeroes: number, x: number): number {\n const N = nums1.length;\n const M = nums2.length;\n \n // Process negatives\n let i = 0;\n let count = M * negs;\n while (i < negs) {\n count -= binarySearch(nums2, Math.ceil(x / nums1[i++]));\n }\n\n // Process zeroes\n count += (x >= 0) ? M * zeroes : 0;\n i += zeroes;\n\n // Process positives\n while (i < N) {\n count += binarySearch(nums2, Math.floor(x / nums1[i++]) + 1);\n }\n\n return count;\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Binary Search', 'TypeScript', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
2040. Kth Smallest Product of Two Sorted Arrays || Binary search || 2-pointers
|
2040-kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-8quv8
|
This question involved using binary search on Ans-\n\nkey idea - we keep find out the number of product\u2264 our mid value and comparing it with our k\nwe keep
|
daring_jackson
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-22T17:13:18.558121+00:00
|
2023-08-22T17:13:18.558147+00:00
| 21 | false |
This question involved using binary search on Ans-\n\n**key idea** - we keep find out the **number of product\u2264 our mid value** and comparing it with our k\nwe keep shortening our upper bound when we have found our ans.\n\nchallenges faced-\n\n1. **effectively calculating the number of products of array in O(N) time**\nfor this we maintained a 2-pointer approach , since the array was sorted , we kept our **j pointer** to **last value of second array** and **i pointer** on **first value of second array** , if that value gave the answer less than our num, all the values before that would give the same ans, so we update the cnt as j+1 and move i pointer ahead. Once j value reaches 0, increasing i pointer would not mean much and thus we exit out the loop.\n\n2.**handling negative numbers**\n\nour negative number would disturb the above approach and hence we have to handle them separately.\n\nWe first check **whether k lies in the negative side and positive side**, and according to that we proceed.\n\neg: if k lies in negative than we need only negative numbers to check and we multiply neg1 * pos2 and neg2 * pos1;\n\nalso **value of k decide which array we have to reverse**\n\n\u2192if k is in negative side to effectively get negative products count we would have to r**everse positive numbers** so as to fit our above logic\n\neg: arr1 = [-2,-1], arr2 = [3,4]\n\n-2 * 4 = -8 < -7 but -2 * 3 =-6 > -7\n\n\u2192by same logic when k is in positive side **we reverse negative numbers** to fit our logic\n\nI have taken low and high as most minimum and maximum values but you can take them as min and max value of products array\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long getnum(vector<int>& arr1,vector<int>& arr2,vector<int>& arr3,vector<int>& arr4,long long num){\n int i = 0;\n int j = arr2.size()-1;\n long long cnt = 0;\n while(i<arr1.size() and j>=0 and arr2.size()>0){\n if(1l*arr1[i]*arr2[j]<=num){\n i++;\n cnt+=(j+1);\n }\n else j--;\n }\n i=0;j=arr4.size()-1;\n while(i<arr3.size() and j>=0 and arr4.size()>0){\n if(1l*arr3[i]*arr4[j]<=num){\n i++;\n cnt+=(j+1);\n }\n else j--;\n }\n \n return cnt;\n }\n \n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) {\n \n vector<int> pos1;\n vector<int> neg1;\n vector<int> pos2;\n vector<int> neg2;\n for(auto x:nums1){\n if(x<0){\n neg1.push_back(x);\n }\n else{\n pos1.push_back(x);\n }\n }\n for(auto x:nums2){\n if(x<0){\n neg2.push_back(x);\n }\n else{\n pos2.push_back(x);\n }\n }\n long long nofneg = neg1.size() * pos2.size() + neg2.size()*pos1.size();\n bool iskneg = k>nofneg?false:true;\n k = !iskneg?k-nofneg:k;\n if(!iskneg){\n reverse(neg1.begin(),neg1.end());\n reverse(neg2.begin(),neg2.end());\n }else{\n reverse(pos1.begin(),pos1.end());\n reverse(pos2.begin(),pos2.end());\n }\n long long low = -1e10,high = 1e10;\n while(low<high){\n long long mid = (long long)(low + (high-low)/2); \n if(getnum(pos1,iskneg?neg2:pos2,neg1,iskneg?pos2:neg2,mid)>=k){\n high = mid;\n }else{\n low = mid+1;\n }\n \n }\n return high;\n }\n};\n```\n\n
| 0 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Binary Tree']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
C++ Binary Search with O((m+n)lg10**10)
|
c-binary-search-with-omnlg1010-by-j2gg0s-f0ke
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
j2gg0s_foo
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-20T16:05:29.590796+00:00
|
2023-07-20T16:05:29.590828+00:00
| 59 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n#include <iostream>\n#include <vector>\n#include <chrono>\n#include <limits>\n#include <algorithm>\n\nusing std::vector;\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& left, vector<int>& right, long long k) {\n long long min = 0l, max = 0l, mid = 0l;\n if (left[0] > 0) {\n if (right[0] > 0) {\n // \u7EAF\u6B63 \u7EAF\u6B63\n min = static_cast<long long>(left[0]) * static_cast<long long>(right[0]);\n max = static_cast<long long>(left[left.size()-1]) * static_cast<long long>(right[right.size()-1]);\n } else if (right[right.size()-1] <= 0) {\n // \u7EAF\u6B63 \u7EAF\u8D1F\n min = static_cast<long long>(left[left.size()-1]) * static_cast<long long>(right[0]);\n max = static_cast<long long>(left[0]) * static_cast<long long>(right[right.size()-1]);\n } else {\n // \u7EAF\u6B63 \u6DF7\u5408\n min = static_cast<long long>(left[left.size()-1]) * static_cast<long long>(right[0]);\n max = static_cast<long long>(left[left.size()-1]) * static_cast<long long>(right[right.size()-1]);\n }\n } else if (left[left.size()-1] <= 0) {\n if (right[0] > 0) {\n // \u7EAF\u8D1F \u7EAF\u6B63\n min = static_cast<long long>(left[0]) * static_cast<long long>(right[right.size()-1]);\n max = static_cast<long long>(left[left.size()-1]) * static_cast<long long>(right[0]);\n } else if (right[right.size()-1] <= 0) {\n // \u7EAF\u8D1F \u7EAF\u8D1F\n min = static_cast<long long>(left[left.size()-1]) * static_cast<long long>(right[right.size()-1]);\n max = static_cast<long long>(left[0]) * static_cast<long long>(right[0]);\n } else {\n // \u7EAF\u8D1F \u6DF7\u5408\n min = static_cast<long long>(left[0]) * static_cast<long long>(right[right.size()-1]);\n max = static_cast<long long>(left[0]) * static_cast<long long>(right[0]);\n }\n } else {\n if (right[0] > 0) {\n // \u6DF7\u5408 \u7EAF\u6B63\n min = static_cast<long long>(left[0]) * static_cast<long long>(right[right.size()-1]);\n max = static_cast<long long>(left[left.size()-1]) * static_cast<long long>(right[right.size()-1]);\n } else if (right[right.size()-1] <= 0) {\n // \u6DF7\u5408 \u7EAF\u8D1F\n min = static_cast<long long>(left[left.size()-1]) * static_cast<long long>(right[0]);\n max = static_cast<long long>(left[0]) * static_cast<long long>(right[0]);\n } else {\n // \u6DF7\u5408 \u6DF7\u5408\n min = std::min(left[0] * static_cast<long long>(right[right.size()-1]), static_cast<long long>(left[left.size()-1]) * static_cast<long long>(right[0]));\n max = std::max(left[0] * static_cast<long long>(right[0]), static_cast<long long>(left[left.size()-1]) * static_cast<long long>(right[right.size()-1]));\n }\n }\n\n auto findLastNegative = [](vector<int>& nums) -> const int {\n int i = 0;\n for (; i < nums.size(); i++) {\n if (nums[i] >= 0) {\n return i-1;\n }\n }\n return nums.size()-1;\n };\n auto findFirstPositive = [](vector<int>& nums) -> const int {\n int i = 0;\n for (; i < nums.size(); i++) {\n if (nums[i] > 0) {\n return i;\n }\n }\n return nums.size();\n };\n\n int lx = findLastNegative(left);\n int ly = findFirstPositive(left);\n int rx = findLastNegative(right);\n int ry = findFirstPositive(right);\n\n while (true) {\n if (max - min <= 1) {\n if (find(left, right, min, lx, ly, rx, ry) >= k) {\n return min;\n } else {\n return max;\n }\n }\n\n mid = (min+max)/2;\n if (find(left, right, mid, lx, ly, rx, ry) < k) {\n min = mid;\n } else {\n max = mid;\n }\n }\n return mid;\n }\n\n long long find(vector<int>& left, vector<int>& right, long long target, int lx, int ly, int rx, int ry) {\n long long k = 0;\n if (target >= 0l) {\n // -8, -4, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 4, 8 -> 3, 5\n // -8, -4, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 4, 8 -> 3, 5\n k += static_cast<long long>(lx+1)*static_cast<long long>((right.size()-ry)); // left \u7684\u8D1F\u6570 * right \u7684\u6B63\u6570\n k += static_cast<long long>(left.size()-ly)*static_cast<long long>((rx+1)); // left \u7684\u6B63\u6570 * right \u7684\u8D1F\u6570\n k += static_cast<long long>(ly-lx-1)*static_cast<long long>(right.size()); // left \u7684\u96F6 * right\n k += static_cast<long long>(ry-rx-1)*static_cast<long long>(left.size()); // right \u7684\u96F6 * left\n k -= static_cast<long long>(ly-lx-1)*static_cast<long long>((ry-rx-1)); // left \u7684\u96F6 * right \u7684\u96F6\n\n int i = 0, j = rx;\n // -8, -4, -2, -1\n // -8, -4, -2, -1\n for (; i <= lx; i++) {\n // j \u662F\u4ECE\u53F3\u5F80\u5DE6\u7B2C\u4E00\u4E2A\u4E0D\u6EE1\u8DB3\u7684\u8D1F\u6570\n while (j >= 0) {\n long long d = static_cast<long long>(left[i]) * static_cast<long long>(right[j]);\n if (d <= target) {\n j--;\n } else {\n break;\n }\n }\n k += static_cast<long long>(rx-j);\n }\n\n // 1, 2, 4, 8 -> 3,5\n // 1, 2, 4, 8 -> 3,5\n j = right.size()-1;\n for (i = ly; i < left.size(); i++) {\n // j \u662F\u4ECE\u53F3\u5F80\u5DE6, \u6700\u540E\u4E00\u4E2A\u6EE1\u8DB3\u7684\n while (j >= ry) {\n long long d = static_cast<long long>(left[i]) * static_cast<long long>(right[j]);\n if (d > target) {\n j--;\n } else {\n break;\n }\n }\n k += static_cast<long long>(j-ry+1);\n }\n } else {\n int i = 0, j = ry;\n // -8, -4, -2, -1 -> 3,5\n // 1, 2, 4, 8 -> 3,5\n for (; i <= lx; i++) {\n // j \u662F\u4ECE\u5DE6\u5F80\u53F3, \u7B2C\u4E00\u4E2A\u6EE1\u8DB3\u7684\n while (j < right.size()) {\n long long d = static_cast<long long>(left[i]) * static_cast<long long>(right[j]);\n if (d > target) {\n j++;\n } else {\n break;\n }\n }\n k += static_cast<long long>(right.size()-j);\n }\n\n // 1, 2, 3, 4\n // -8,-4,-2,-1\n j = 0;\n for(i = ly; i < left.size(); i++) {\n // j \u4ECE\u5DE6\u5F80\u53F3, \u7B2C\u4E00\u4E2A\u4E0D\u6EE1\u8DB3\u7684\n while (j <= rx) {\n long long d = static_cast<long long>(left[i]) * static_cast<long long>(right[j]);\n if (d <= target) {\n j++;\n } else {\n break;\n }\n }\n k += static_cast<long long>(j);\n }\n }\n\n return k;\n }\n\n int countLess(vector<int>& right, int curr, int target) {\n for (; curr >= 0; curr--) {\n if (right[curr] <= target) {\n return curr;\n }\n }\n return -1;\n }\n\n int countGreater(vector<int>& right, int curr, int target) {\n for (; curr >= 0; curr--) {\n if (right[curr] < target) {\n return curr+1;\n }\n }\n return right.size();\n }\n};\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
C# Solution
|
c-solution-by-tibnewusa-pqky
|
C# solutin based on this explanation https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays/solutions/1524856/binary-search-with-detailed-expla
|
tibnewusa
|
NORMAL
|
2023-06-04T14:05:17.059321+00:00
|
2023-06-04T14:05:17.059345+00:00
| 28 | false |
C# solutin based on this explanation https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays/solutions/1524856/binary-search-with-detailed-explanation/\n\n# Code\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public long KthSmallestProduct(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, long k) {\n var a1 = nums1.Where(x => x < 0).ToArray();\n a1 = rev(inv(a1));\n var a2 = nums1.Where(x => x >= 0).ToArray();\n var b1 = nums2.Where(x => x < 0).ToArray();\n b1 = rev(inv(b1));\n var b2 = nums2.Where(x => x >= 0).ToArray();\n\n var negCount = a1.Length * b2.Length + b1.Length * a2.Length;\n\n var sign = 1;\n\n if (k > negCount)\n {\n k -= negCount;\n }\n else\n {\n k = negCount - k + 1;\n var temp = b1;\n b1 = b2;\n b2 = temp;\n sign = -1;\n }\n\n\n var lo = 0L;\n var hi = 10000000000L;\n\n while (lo < hi)\n {\n var mid = (lo + hi) / 2;\n var count = CountProductsSmallerOrEqualToNumber(mid, a1, b1)\n + CountProductsSmallerOrEqualToNumber(mid, a2, b2);\n Console.WriteLine($"guess: {mid}. count: {count}");\n if (count >= k)\n {\n hi = mid;\n }\n else\n {\n lo = mid + 1;\n }\n }\n return sign * lo;\n }\n\n public long CountProductsSmallerOrEqualToNumber(long number, int[] nums1, int[] nums2)\n {\n var count = 0L;\n var j = nums2.Length - 1;\n for (int i = 0; i < nums1.Length && j >= 0; i++)\n {\n while (j >= 0 && (long)nums1[i] * (long)nums2[j] > number)\n {\n j--;\n }\n count += j + 1;\n\n }\n return count;\n }\n\n public int[] inv(int[] nums)\n {\n for(int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++)\n {\n nums[i] = -nums[i];\n\n }\n return nums;\n\n }\n\n public int[] rev(int[] nums)\n {\n for (int l = 0, r = nums.Length - 1; l < r; l++, r--)\n {\n nums[l] ^= nums[r];\n nums[r] ^= nums[l];\n nums[l] ^= nums[r];\n }\n return nums;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
C++ Binary Search Solution
|
c-binary-search-solution-by-whoinsane-xfmv
|
\n\n# Code\n\n#define ll long long\n\nclass Solution {\n\n bool isPossible(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b, ll midVal, ll k) {\n ll cnt = 0;\n
|
whoinsane
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-30T11:24:36.195872+00:00
|
2023-03-30T11:24:36.195909+00:00
| 213 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\n#define ll long long\n\nclass Solution {\n\n bool isPossible(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b, ll midVal, ll k) {\n ll cnt = 0;\n for(auto num: a) {\n if(num >= 0) { // smallest products will be on left side\n \n ll l = 0, h = b.size() - 1, res = -1;\n while(l <= h) {\n ll mid = (l + h) / 2;\n\n if((long long) b[mid] * num <= midVal) {\n l = mid + 1;\n res = mid; // go higher because ve * -ve = -ve;\n } else\n h = mid - 1;\n }\n \n cnt += res + 1; // left side to maximum side\n \n } else { // smallest products will be on right side\n \n ll l = 0, h = b.size() - 1, res = b.size();\n while(l <= h) {\n ll mid = (l + h) / 2;\n\n if((long long) b[mid] * num <= midVal) {\n h = mid - 1;\n res = mid; // go lower because -ve * +ve = -ve\n } else\n l = mid + 1;\n }\n \n cnt += b.size() - res; // left side to maximum side\n \n }\n }\n\n return cnt >= k;\n }\n\npublic:\n ll kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b, ll k) {\n ll low = -1e10;\n ll high = 1e10; \n ll res = 0;\n\n while(low <= high) {\n ll mid = (low + high) / 2;\n if(isPossible(a, b, mid, k)) {\n res = mid;\n high = mid - 1;\n } else\n low = mid + 1;\n }\n\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Binary Search with Visualization for Different Regions | Java, 79ms, 100%
|
binary-search-with-visualization-for-dif-hqb7
|
Intuition\nIt\'s basically the same idea as "". Just that we should separate the matrix into four regions, as the order in each region is different and we shoul
|
yzwang271828
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-12T07:47:40.438891+00:00
|
2023-03-12T07:48:39.424900+00:00
| 140 | false |
# Intuition\nIt\'s basically the same idea as "". Just that we should separate the matrix into four regions, as the order in each region is different and we should traverse the matrix from different starting position and in different direction. A general rule to remember is that "**starting from the max value of a column and walk along ascending direction to the next column**".\n\nA visualization of the four regions are: \n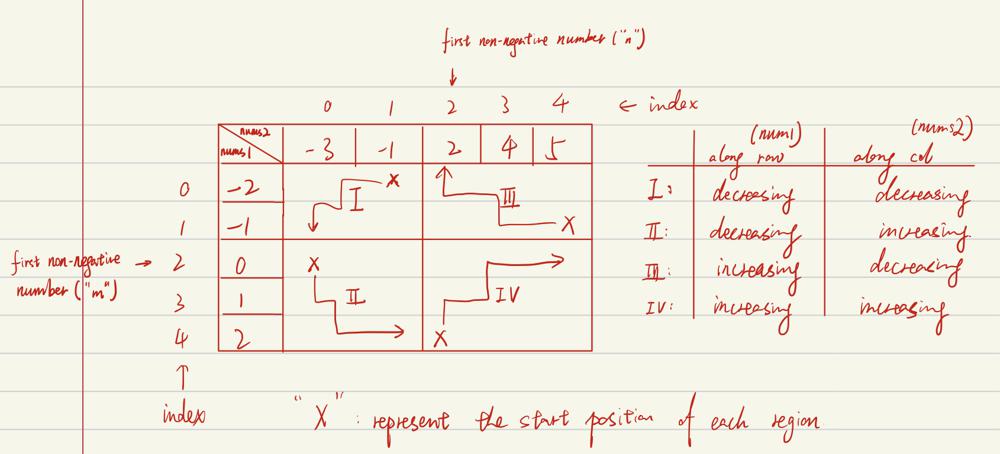\n\n#### Triky Points to Notice\n1. `k` could exceed the integer limit. So the return type of the count function should be `long`.\n2. The product could also exceed the integer limit. Cast to `long` before computing the product.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public long kthSmallestProduct(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, long k) {\n if (nums1.length == 1 && nums2.length == 1)\n return nums1[0] * nums2[0];\n\n long[] extremes = {(long) nums1[0] * nums2[0],\n (long) nums1[0] * nums2[nums2.length - 1],\n (long) nums1[nums1.length - 1] * nums2[0],\n (long) nums1[nums1.length - 1] * nums2[nums2.length - 1]};\n Arrays.sort(extremes);\n int firstNonNegative1 = binarySearch(nums1, 0);\n int firstNonNegative2 = binarySearch(nums2, 0);\n long low = extremes[0];\n long high = extremes[3];\n //System.out.println("Indices: " \n // + String.join(",", String.valueOf(firstNonNegative1), String.valueOf(firstNonNegative2)));\n //System.out.println("Boundary: "\n // + String.join(",", String.valueOf(low), String.valueOf(high)));\n while(low < high) {\n long mid = low + (high - low) / 2;\n if (countLessThan(nums1, nums2, firstNonNegative1, firstNonNegative2, mid) < k) {\n low = mid + 1;\n } else {\n high = mid;\n }\n }\n return high;\n }\n\n /**\n m: index of first element >= 0 in nums1.\n n: index of first element >= 0 in nums2.\n */\n private long countLessThan(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int m, int n, long target) {\n long count = 0;\n // First Region:\n int row = 0;\n int col = n - 1;\n while(row < m && col >= 0) {\n while(row < m && ((long) nums1[row]) * nums2[col] > target) {\n row++;\n }\n count += m - row;\n col--;\n }\n\n // Second Region:\n row = m;\n col = 0;\n while(row < nums1.length && col < n) {\n while(row < nums1.length && ((long) nums1[row]) * nums2[col] > target) {\n row++;\n }\n count += nums1.length - row;\n col++;\n }\n\n // Third Region:\n row = m - 1;\n col = nums2.length - 1;\n while(row >= 0 && col >= n) {\n while(row >= 0 && ((long) nums1[row]) * nums2[col] > target) {\n row--;\n }\n count += row - 0 + 1;\n col--;\n }\n\n // Fourth Region:\n row = nums1.length - 1;\n col = n;\n while(row >= m && col < nums2.length) {\n while(row >= m && ((long) nums1[row]) * nums2[col] > target) {\n row--;\n }\n count += row - m + 1;\n col++;\n }\n return count;\n }\n\n // Find the leftmost element that >= than target.\n private int binarySearch(int[] nums, int target) {\n int left = 0;\n int right = nums.length;\n while(left < right) {\n int mid = (left + right) / 2;\n if (nums[mid] >= target) {\n right = mid;\n } else {\n left = mid + 1;\n }\n }\n return right;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
[C++] Binary Search Solution !!!
|
c-binary-search-solution-by-kylewzk-jc2p
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
kylewzk
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-21T11:45:32.187241+00:00
|
2022-11-21T11:45:32.187273+00:00
| 273 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n using ll = long long;\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B, long long k) {\n ll l = -1e10, r = 1e10;\n auto count_le = [&](ll x){\n ll total = 0;\n for(auto a : A) {\n if(a > 0) {\n int l = 0, r = B.size()-1;\n while(l < r) {\n int m = l + (r-l+1)/2;\n if((ll)a*B[m] > x) r = m-1;\n else l = m;\n }\n total += (ll)a*B[l] <= x ? l+1 : 0;\n } else {\n int l = 0, r = B.size()-1;\n while(l < r) {\n int m = l + (r-l)/2;\n if((ll)a*B[m] > x) l = m+1;\n else r = m;\n }\n total += (ll)a*B[l] <= x ? B.size() -l : 0;\n }\n }\n return total;\n };\n\n while(l < r) {\n ll x = l + (r-l)/2;\n if(count_le(x) < k) l = x+1;\n else r = x;\n }\n return l;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
BinarySearch Counting Fully Explained Python
|
binarysearch-counting-fully-explained-py-hbn8
|
there can be |nums1| * |nums2| products, so finding every product and then couting k smallest is too slow.\n\nIf you knew what k was, can you count number of pr
|
sarthakBhandari
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-30T15:58:08.086803+00:00
|
2022-10-30T15:58:08.086851+00:00
| 291 | false |
there can be |nums1| * |nums2| products, so finding every product and then couting k smallest is too slow.\n\nIf you knew what k was, can you count number of products less than k?\nIf intgers were all positive heres how u would do it in O(n) time\nMaintatin two pointers (i, j), one points to beggining of arr1 and other to the end of arr2.\n```\nIf nums[i]*nums[j] <= k, count += (j + 1),\n```\nbecause all elements to the left of j also satisfy the inequality.\n```\nif nums[i]*nums[j] > k, j -= 1,\n```\nbecause all elements to the right of i will also not work with nums[j]\n\nBut elements can also be negative and in this case you just need to handle them separately.\n\nNow that you have an efficient way of counting, u still dont know k.\n**But you can guess k using binary search.**\n```\nif countOfProducts(guess) < k, guess is too small\nif countOfProducts(guess) > k, guess is too large\n```\n\n**Time: O(n * log(maxProduct - minProduct))**\nSpace: O(n) if you separate negaitve and positive nummbers into different arrays. But you can do it O(1). \n\n```\ndef kthSmallestProduct(self, nums1, nums2, k):\n #elements can be negative, so max and min prod need to calculated properly\n L = min(nums1[0]*nums2[0], nums1[0]*nums2[-1], nums2[0]*nums1[-1])\n R = max(nums1[0]*nums2[0], nums1[-1]*nums2[-1], nums1[-1]*nums2[0], nums1[0]*nums2[-1])\n\n neg1 = [i for i in nums1 if i < 0]; nums1 = nums1[len(neg1): ]\n neg2 = [i for i in nums2 if i < 0]; nums2 = nums2[len(neg2): ]\n def getCount(k):\n #4 combinations to count\n #(neg, neg), (neg, pos), (pos, neg), (pos, pos)\n count = 0\n #(neg, neg)\n i = len(neg1) - 1; j = 0\n while i >= 0 and j < len(neg2):\n if neg1[i]*neg2[j] <= k:\n count += (len(neg2) - j)\n i -= 1\n else:\n j += 1\n \n #(neg, pos)\n i = 0; j = 0\n while i < len(neg1) and j < len(nums2):\n if neg1[i]*nums2[j] <= k:\n count += (len(nums2) - j)\n i += 1\n else:\n j += 1\n \n #(pos, neg)\n i = len(nums1) - 1; j = len(neg2) - 1\n while i >= 0 and j >= 0:\n if nums1[i]*neg2[j] <= k:\n count += (j + 1)\n i -= 1\n else:\n j -= 1\n \n #(pos, pos)\n i = 0; j = len(nums2) - 1\n while i < len(nums1) and j >= 0:\n if nums1[i]*nums2[j] <= k:\n count += (j + 1)\n i += 1\n else:\n j -= 1\n \n return count\n \n while L < R:\n M = (L+R)//2\n if getCount(M) < k:\n L = M+1\n else:\n R = M\n \n return L\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Binary Search', 'Python']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
[C++] O((M+N)log(10^10)) time, O(1) extra space
|
c-omnlog1010-time-o1-extra-space-by-neop-iq1h
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n using ll = long long;\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) {\n int n =
|
neophyte_123
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-26T17:36:58.990248+00:00
|
2022-09-26T17:36:58.990292+00:00
| 161 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n using ll = long long;\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) {\n int n = nums1.size(), m = nums2.size();\n ll lo = -(ll)1e10 - 1, hi = (ll)1e10 + 1;\n \n int ln = -1;\n for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {\n if (nums2[i] < 0) ln = i;\n }\n \n while (hi - lo > 1) {\n ll mid = (hi + lo) / 2;\n // cnt number of pairs whose product <= mid\n // This is not as simple as addition\n // Because product of two negative integers becomes positive\n \n ll cnt = 0;\n ll l = 0;\n \n ll pos = ln + 1, neg = ln;\n \n // negative in nums1\n while (l < n && nums1[l] < 0) {\n while (pos < m && (ll)nums1[l] * nums2[pos] > mid) pos++; \n cnt += m - pos;\n while (neg >= 0 && (ll)nums1[l] * nums2[neg] <= mid) neg--;\n cnt += ln - neg;\n ++l;\n }\n \n neg = 0, pos = m - 1;;\n \n // positive in nums1\n while (l < n) {\n while (neg <= ln && (ll)nums1[l] * nums2[neg] <= mid) neg++;\n cnt += neg;\n while (pos > ln && (ll)nums1[l] * nums2[pos] > mid) pos--;\n cnt += pos - ln;\n ++l;\n }\n \n if (cnt < k) lo = mid;\n else hi = mid;\n }\n \n return hi;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Binary Search']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Simple Binary-Search O(NlogA) Solution [C++]
|
simple-binary-search-onloga-solution-c-b-sfy0
|
Since It\'s really confusing that you tackle this problem without division into cases, you\'d be better determine the sign of number at first.\n\nAt first, I tr
|
omuraisu
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-25T06:52:38.250306+00:00
|
2022-09-25T06:52:38.250339+00:00
| 47 | false |
Since It\'s really confusing that you tackle this problem without division into cases, you\'d be better determine the sign of number at first.\n\nAt first, I tried O(NlogNlogA) Soluiton, but it was too slow to finish in TL.\n\nHere\'s my implemention in C++.\n\nTime Complexity : O(NlogA)\nSpace Complexity : O(N)\n\n```\ntypedef long long ll;\n\ntemplate<class T = int>int bisect_right(const std::vector<T> & V, T val){if (V.size() == 0){return 0;}auto it = upper_bound(V.begin(), V.end(), val);int index = it - V.begin();return index;}\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& arr1, vector<int>& arr2, long long k){\n vector<vector<ll>> nums1(3);\n vector<vector<ll>> nums2(3);\n\n const int n1 = arr1.size();\n const int n2 = arr2.size();\n\n for (auto & e : arr1){\n if (e > 0){\n nums1[0].emplace_back(e);\n }else if (e == 0){\n nums1[1].emplace_back(e); \n }else{\n nums1[2].emplace_back(-e);\n }\n }\n reverse(nums1[2].begin(), nums1[2].end());\n\n for (auto & e : arr2){\n if (e > 0){\n nums2[0].emplace_back(e);\n }else if (e == 0){\n nums2[1].emplace_back(e); \n }else{\n nums2[2].emplace_back(-e);\n }\n }\n reverse(nums2[2].begin(), nums2[2].end());\n\n auto count_not_less_than = [&](ll x){\n ll res = 0;\n if (x < 0){\n res += 1ll * nums1[2].size() * nums2[0].size();\n res += 1ll * nums1[0].size() * nums2[2].size();\n res -= countNoLessThan(nums1[2], nums2[0], -x - 1);\n res -= countNoLessThan(nums1[0], nums2[2], -x - 1);\n // for (auto & e : nums1[2]){\n // res -= bisect_right<ll>(nums2[0], (-x - 1) / e);\n // }\n // for (auto & e : nums1[0]){\n // res -= bisect_right<ll>(nums2[2], (-x - 1) / e);\n // }\n }else if (x == 0){\n res += 1ll * n1 * n2;\n res -= 1ll * nums1[0].size() * nums2[0].size();\n res -= 1ll * nums1[2].size() * nums2[2].size();\n }else if (x > 0){\n res += 1ll * n1 * n2;\n res -= 1ll * nums1[0].size() * nums2[0].size();\n res -= 1ll * nums1[2].size() * nums2[2].size();\n res += countNoLessThan(nums1[2], nums2[2], x);\n res += countNoLessThan(nums1[0], nums2[0], x);\n // for (auto & e : nums1[2]){\n // res += bisect_right<ll>(nums2[2], x / e);\n // }\n // for (auto & e : nums1[0]){\n // res += bisect_right<ll>(nums2[0], x / e);\n // }\n }\n return res;\n };\n \n ll ng = -1e10 - 1, ok = 1e10 + 1;\n while(ok - ng > 1){\n ll mid = (ng + ok) / 2;\n if (count_not_less_than(mid) < k){\n ng = mid;\n }else{\n ok = mid;\n }\n }\n return ok;\n }\n long long countNoLessThan(vector<ll>& arr1, vector<ll>& arr2, long long k){\n //assume both array are sorted.\n const int n1 = arr1.size();\n const int n2 = arr2.size();\n ll res = 0;\n for (int i = n1 - 1, ptr = 0; i >= 0; i--){\n while(ptr < n2 && arr2[ptr] <= k / arr1[i]){\n ptr++;\n }\n res += ptr;\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Binary Tree']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
C++
|
c-by-isgnad-d782
|
\ntypedef long long int ll;\n\nclass Solution \n{\npublic:\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) \n {\n
|
trymtrym
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-05T19:58:52.678124+00:00
|
2022-09-05T19:59:06.404750+00:00
| 111 | false |
```\ntypedef long long int ll;\n\nclass Solution \n{\npublic:\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) \n {\n ll left = -(ll)(1e10) - 1;\n ll right = (ll)(1e10) + 1;\n \n while(right - left > 1)\n {\n ll mid = (left + right) / 2;\n ll num = 0;\n \n for(int number : nums1)\n {\n if(number == 0)\n {\n if(mid >= 0)\n {\n num += nums2.size();\n }\n }\n else if(number > 0)\n {\n ll roundedNumber = floor(mid / (double)number); // round down\n auto iter = upper_bound(nums2.begin(), nums2.end(), roundedNumber);\n num += iter - nums2.begin();\n }\n else\n {\n ll roundedNumber = ceil(mid / (double)number); // round up\n auto iter = lower_bound(nums2.begin(), nums2.end(), roundedNumber);\n num += nums2.size() - (iter - nums2.begin()); \n }\n }\n \n if(num >= k)\n {\n right = mid;\n }\n else\n {\n left = mid;\n }\n }\n \n return right;\n }\n};\n\n// The complexity is O(NlogNlogA), where N denotes max(nums1.size(), nums2.size()) and A denotes the size of the range\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Binary Tree']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Python, binary search + two pointers, explained
|
python-binary-search-two-pointers-explai-8j1n
|
Discuss 2 cases: k-th smallest is negetive/positive splitArr\n2. In helper function, arr1[i+1] * arr2[j] > arr1[i] * arr2[j] and arr1[i] * arr2[j+1] > arr1[i] *
|
Wolfoo
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-03T22:46:59.718393+00:00
|
2022-09-03T22:49:04.714296+00:00
| 206 | false |
1. Discuss 2 cases: k-th smallest is negetive/positive `splitArr`\n2. In `helper` function, arr1[i+1] * arr2[j] > arr1[i] * arr2[j] and arr1[i] * arr2[j+1] > arr1[i] * arr2[j]. Same for arr3 and arr4. Do binary search in range [smallest_product, largest_product].\n3. Then for arr1 and arr2 (or arr3 and arr4), we can use two pointers to find how many products is smaller than mid. `countSmaller`\n```\nclass Solution:\n def kthSmallestProduct(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n def splitArr(arr):\n for i in range(len(arr)):\n if arr[i] >= 0:\n return arr[:i], arr[i:]\n return arr[:], []\n \n def countSmaller(target, arr1, arr2) -> int:\n i, j = 0, len(arr2)-1\n cnt = 0\n for i in range(len(arr1)):\n while j>=0 and arr1[i]*arr2[j] > target:\n j -= 1\n cnt += j + 1\n return cnt\n \n def helper(k, arr1, arr2, arr3, arr4) -> int:\n b1 = len(arr1) and len(arr2)\n b2 = len(arr3) and len(arr4)\n l = min(arr1[0]*arr2[0] if b1 else math.inf, arr3[0]*arr4[0] if b2 else math.inf) \n r = max(arr1[-1]*arr2[-1] if b1 else -math.inf, arr3[-1]*arr4[-1] if b2 else -math.inf)\n while l <= r:\n mid = l+(r-l)//2\n rank = countSmaller(mid, arr1, arr2) + countSmaller(mid, arr3, arr4)\n if rank < k:\n l = mid + 1\n else:\n r = mid - 1\n return l\n \n \n neg1, pos1 = splitArr(nums1)\n neg2, pos2 = splitArr(nums2)\n N_neg = len(pos1)*len(neg2) + len(pos2)*len(neg1)\n if k > N_neg:\n return helper(k-N_neg, pos1, pos2, neg1[::-1], neg2[::-1])\n else:\n return helper(k, neg1, pos2[::-1], neg2, pos1[::-1])\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Binary Tree', 'Python']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
binary search
|
binary-search-by-user0443f-20wv
|
class Solution {\npublic:\n long long solve(vector& nums1,vector& nums2,long long product)\n {\n long long count=0;\n for(int a:nums1)\n
|
user0443F
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-13T13:15:09.614684+00:00
|
2022-08-13T13:15:09.614717+00:00
| 97 | false |
class Solution {\npublic:\n long long solve(vector<int >& nums1,vector<int >& nums2,long long product)\n {\n long long count=0;\n for(int a:nums1)\n {\n if(a>0)\n {\n int l=0;\n int h=nums2.size()-1;\n \n int temp=-1;\n while(l<=h)\n {\n int mid = l+(h-l)/2;\n \n if((long long)a*nums2[mid]<=product)\n {\n temp = mid;\n l=mid+1;\n }\n else\n {\n h=mid-1;\n }\n }\n count += temp+1;\n }\n else\n {\n int l=0;\n int h=nums2.size()-1;\n int temp=nums2.size();\n while(l<=h)\n {\n int mid = l+(h-l)/2;\n if((long long)a*nums2[mid]<=product)\n {\n temp = mid;\n h=mid-1;\n }\n else\n {\n l=mid+1;\n }\n }\n count += nums2.size()-temp;\n }\n }\n return count;\n }\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) \n {\n long long int low = -1e10;\n long long int high = 1e10;\n \n long long ans;\n long long mid;\n \n while(low<=high)\n {\n mid = low+(high-low)/2;\n if(solve(nums1,nums2,mid)>=k)\n {\n ans = mid;\n high = mid-1;\n }\n else\n {\n low = mid+1;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Accepted C# Solution. Binary search based approach.
|
accepted-c-solution-binary-search-based-1nibb
|
\n\t\tpublic class Solution\n\t\t{\n\n\t\t\tprivate long FindNegative(List<long> p1, List<long> p2, List<long> n1, List<long> n2, long k)\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tp1.S
|
maxpushkarev
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-23T15:07:12.122183+00:00
|
2022-07-23T15:07:12.122209+00:00
| 85 | false |
```\n\t\tpublic class Solution\n\t\t{\n\n\t\t\tprivate long FindNegative(List<long> p1, List<long> p2, List<long> n1, List<long> n2, long k)\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tp1.Sort();\n\t\t\t\tp2.Sort();\n\t\t\t\tn1.Sort();\n\t\t\t\tn2.Sort();\n\n\t\t\t\tp1.Reverse();\n\t\t\t\tp2.Reverse();\n\t\t\t\tn1.Reverse();\n\t\t\t\tn2.Reverse();\n\n\t\t\t\tlong l = long.MinValue;\n\t\t\t\tlong r = -1;\n\n\t\t\t\twhile (r - l > 1)\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\tvar mid = l + (r - l) / 2;\n\t\t\t\t\tif (CalculateNegProdsCount(p1, p2, n1, n2, -mid) >= k)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tr = mid;\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t\telse\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tl = mid;\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\tif (CalculateNegProdsCount(p1, p2, n1, n2, -l) < k)\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\treturn r;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\treturn l;\n\t\t\t}\n\n\n\t\t\tprivate long CalculatePosProdsCount(List<long> l1, List<long> l2, long cand)\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tif (l1.Count == 0 || l2.Count == 0)\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\treturn 0;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\tlong c = 0;\n\t\t\t\tfor (int i = 0; i < l1.Count; i++)\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\tint l = 0;\n\t\t\t\t\tint r = l2.Count - 1;\n\n\t\t\t\t\twhile (r - l > 1)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tint mid = l + (r - l) / 2;\n\t\t\t\t\t\tif (l1[i] * l2[mid] > cand)\n\t\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\tr = mid;\n\t\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t\t\telse\n\t\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\tl = mid;\n\t\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\t\tif (l1[i] * l2[r] <= cand)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tc += (r + 1);\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t\telse if(l1[i] * l2[l] <= cand)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tc += (l + 1);\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\treturn c;\n\t\t\t}\n\n\n\t\t\tprivate long CalculateNegProdsCount(List<long> l1, List<long> l2, long cand)\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tif (l1.Count == 0 || l2.Count == 0)\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\treturn 0;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\tlong c = 0;\n\t\t\t\tfor (int i = 0; i < l1.Count; i++)\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\tint l = 0;\n\t\t\t\t\tint r = l2.Count - 1;\n\n\t\t\t\t\twhile (r - l > 1)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tint mid = l + (r - l) / 2;\n\t\t\t\t\t\tif (l1[i] * l2[mid] < cand)\n\t\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\tr = mid;\n\t\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t\t\telse\n\t\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\tl = mid;\n\t\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\t\tif (l1[i] * l2[r] >= cand)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tc += (r + 1);\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t\telse if (l1[i] * l2[l] >= cand)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tc += (l + 1);\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\treturn c;\n\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\tprivate long CalculateNegProdsCount(List<long> p1, List<long> p2, List<long> n1, List<long> n2, long cand)\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tlong c1 = CalculateNegProdsCount(p1, n2, cand);\n\t\t\t\tlong c2 = CalculateNegProdsCount(n1, p2, cand);\n\t\t\t\treturn c1 + c2;\n\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\tprivate long CalculatePosProdsCount(List<long> p1, List<long> p2, List<long> n1, List<long> n2, long cand)\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tlong c1 = CalculatePosProdsCount(p1, p2, cand);\n\t\t\t\tlong c2 = CalculatePosProdsCount(n1, n2, cand);\n\t\t\t\treturn c1 + c2;\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\tprivate long FindPositive(List<long> p1, List<long> p2, List<long> n1, List<long> n2, long k)\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tp1.Sort();\n\t\t\t\tp2.Sort();\n\t\t\t\tn1.Sort();\n\t\t\t\tn2.Sort();\n\n\t\t\t\tlong l = 1;\n\t\t\t\tlong r = long.MaxValue;\n\n\t\t\t\twhile (r-l > 1)\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\tvar mid = l + (r - l) / 2;\n\t\t\t\t\tif (CalculatePosProdsCount(p1, p2, n1, n2, mid) >= k)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tr = mid;\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t\telse\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tl = mid;\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\tif (CalculatePosProdsCount(p1, p2, n1, n2, l) < k)\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\treturn r;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\treturn l;\n\n\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\tpublic long KthSmallestProduct(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, long k)\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tList<long> p1 = new List<long>(nums1.Length);\n\t\t\t\tList<long> n1 = new List<long>(nums1.Length);\n\t\t\t\tList<long> p2 = new List<long>(nums2.Length);\n\t\t\t\tList<long> n2 = new List<long>(nums2.Length);\n\n\t\t\t\tlong z1 = 0, z2 = 0;\n\n\t\t\t\tforeach (var num in nums1)\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\tif (num == 0)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tz1++;\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\t\tif (num > 0)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tp1.Add(num);\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\t\tif (num < 0)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tn1.Add(-num);\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t}\n\n\n\t\t\t\tforeach (var num in nums2)\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\tif (num == 0)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tz2++;\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\t\tif (num > 0)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tp2.Add(num);\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\t\tif (num < 0)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tn2.Add(-num);\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\tlong negativePairs = p1.Count * n2.Count + p2.Count * n1.Count;\n\t\t\t\tlong zeroPairs = z1 * (p2.Count + n2.Count) + z2 * (p1.Count + n1.Count) + z1 * z2;\n\n\t\t\t\tif (k <= negativePairs)\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\treturn FindNegative(p1, p2, n1, n2, k);\n\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\tk -= negativePairs;\n\n\t\t\t\tif (k <= zeroPairs)\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\treturn 0;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\tk -= zeroPairs;\n\t\t\t\treturn FindPositive(p1, p2, n1, n2, k);\n\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Binary Tree']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Numpy Solution - Least Runtime Solution
|
numpy-solution-least-runtime-solution-by-zclr
|
\nimport numpy as np\nclass Solution:\n def kthSmallestProduct(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n A = np.sort(nums1)\n
|
Day_Tripper
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-14T08:11:45.792552+00:00
|
2022-07-14T08:11:45.792592+00:00
| 138 | false |
```\nimport numpy as np\nclass Solution:\n def kthSmallestProduct(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int], k: int) -> int:\n A = np.sort(nums1)\n B = np.sort(nums2)\n Aneg, Azero, Apos = A[A < 0], A[A == 0], A[A > 0]\n\n def f(x):\n # Count number of a * b <= x, casing on the sign of a\n countZero = len(Azero) * len(B) if x >= 0 else 0\n countPos = np.searchsorted(B, x // Apos, side="right").sum()\n countNeg = len(Aneg) * len(B) - np.searchsorted(B, (-x - 1) // (-Aneg), side="right").sum()\n return countNeg + countZero + countPos\n\n lo = -(10 ** 10)\n hi = 10 ** 10\n while lo < hi:\n mid = (lo + hi) // 2\n if f(mid) >= k:\n hi = mid\n else:\n lo = mid + 1\n return hi\n \n# A, B = nums1, nums2\n# n, m = len(A), len(B)\n# A1,A2 = [-a for a in A if a < 0][::-1], [a for a in A if a >= 0]\n# B1,B2 = [-a for a in B if a < 0][::-1], [a for a in B if a >= 0]\n\n# neg = len(A1) * len(B2) + len(A2) * len(B1)\n# if k > neg:\n# k -= neg\n# s = 1\n# else:\n# k = neg - k + 1\n# B1, B2 = B2,B1\n# s = -1\n\n# def count(A, B, x):\n# res = 0\n# j = len(B) - 1\n# for i in range(len(A)):\n# while j >= 0 and A[i] * B[j] > x:\n# j -= 1\n# res += j + 1\n# return res\n\n# left, right = 0, 10**10\n# while left < right:\n# mid = (left + right) // 2\n# if count(A1, B1, mid) + count(A2, B2, mid) >= k:\n# right = mid\n# else:\n# left = mid + 1\n# return left * s\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
test case 25/112?
|
test-case-25112-by-15651966935-gftd
|
For test case 25/112, the input is \n\n[-9,6,10]\n[-7,-1,1,2,3,4,4,6,9,10]\n15\n\n\nMy expection is that the result should be 9 as,\n\n// kth number, nums1 inde
|
15651966935
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-23T00:22:49.413597+00:00
|
2022-05-23T00:22:49.413636+00:00
| 92 | false |
For test case 25/112, the input is \n```\n[-9,6,10]\n[-7,-1,1,2,3,4,4,6,9,10]\n15\n```\n\nMy expection is that the result should be 9 as,\n```\n// kth number, nums1 index, nums2 index, product\n0 0 9 -90\n1 0 8 -81\n2 2 0 -70\n3 0 7 -54\n4 1 0 -42\n5 0 6 -36\n6 0 5 -36\n7 0 4 -27\n8 0 3 -18\n9 2 1 -10\n10 0 2 -9\n11 1 1 -6\n13 1 2 6\n14 0 1 9\n```\n\nI don\'t really understand why the answer is 10. Anyone can help?
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Self explanatory intuitive C++ code
|
self-explanatory-intuitive-c-code-by-sub-g71s
|
\nusing ll=long long;\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n // This returns TRUE, iff the number of elements in the set(A)*set(B) <= \'val\' is >= \'K\' \n bool pr
|
subhram
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-22T08:10:35.343001+00:00
|
2022-05-22T08:10:35.343029+00:00
| 314 | false |
```\nusing ll=long long;\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n // This returns TRUE, iff the number of elements in the set(A)*set(B) <= \'val\' is >= \'K\' \n bool predicate(ll val, const ll K, vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B){\n ll cnt=0;\n for(auto a:A){\n if(a<0){\n cnt += findNumberOfNumbersLessThanEqualToValInNonIncreasingArray(val,\n B,a);\n } else if (a==0) {\n if (val>=0) cnt+=B.size();\n } else if (a>0) {\n cnt += findNumberOfNumbersLessThanEqualToValInNonDecreasingArray(val,\n B,a);\n }\n }\n return cnt>=K;\n }\n \n int findNumberOfNumbersLessThanEqualToValInNonIncreasingArray(const ll val,\n vector<int>& B,\n const int a){\n // find the smallest index for which B[i]<=val\n int n = B.size();\n int lo=0,hi=n-1;\n // if the smallest numebr is > val, then there is no such element\n if((ll)B[hi]*a > val)return 0;\n while(lo!=hi){\n int mid=lo+(hi-lo)/2;\n if((ll)B[mid]*a <= val)hi=mid;\n else lo=mid+1;\n }\n return n-lo;\n }\n \n int findNumberOfNumbersLessThanEqualToValInNonDecreasingArray(const ll val,\n vector<int>& B,\n const int a){\n // find the largest index for which B[i]<=val\n int n = B.size();\n int lo=0,hi=n-1;\n // if the smallest value if > val, then there is no such elements present\n if((ll)B[lo]*a > val) return 0;\n while(lo!=hi){\n int mid=lo+(hi-lo+1)/2;\n if((ll)B[mid]*a <= val)lo=mid;\n else hi=mid-1;\n }\n return lo+1;\n }\n \n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B, long long K) {\n // if x=A[i]*B[j], then we need to find the set of \'x\'(s) for which number of numbers <= \'x\' will be >= \'K\' ans choose smallest in that set(smallest \'x\')\n \n ll lo=-1e10-100;\n ll hi=1e10+100;\n \n while(lo!=hi){\n ll mid=lo+(hi-lo)/2;\n if(predicate(mid,K,A,B))hi=mid;\n else lo= mid+1;\n }\n \n // since k <= A.length * B.length as given in the question, Here no need to check whetehr the answer exists or not\n \n return lo;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Binary Tree']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Binary Search (n+m)log(10^10) - Faster than 98%
|
binary-search-nmlog1010-faster-than-98-b-opbs
|
\ntypedef long long ll;\n#define all(nums) nums.begin(), nums.end()\n#define reverse(nums1, nums2) reverse(all(nums1)), reverse(all(nums2))\nclass Solution {\np
|
salamnamaste
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-22T03:27:56.553859+00:00
|
2022-05-22T04:35:00.404329+00:00
| 316 | false |
```\ntypedef long long ll;\n#define all(nums) nums.begin(), nums.end()\n#define reverse(nums1, nums2) reverse(all(nums1)), reverse(all(nums2))\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n inline ll count(vector<int> &nums1, vector<int> &nums2, ll limit) {\n ll result = 0;\n for(int i = 0, j = nums2.size()-1; i < nums1.size(); i++, result += (j+1))\n while(j >= 0 && (ll)nums1[i]*nums2[j] > limit) j--;\n return result;\n }\n tuple<ll, ll, ll, vector<int>, vector<int>> getStats(vector<int> nums) {\n vector<int> pos(upper_bound(all(nums), 0), nums.end()), neg(nums.begin(), lower_bound(all(nums), 0));\n return {neg.size(), std::count(all(nums), 0), pos.size(), neg, pos};\n }\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) {\n ll n = nums1.size(), m = nums2.size();\n auto [neg1, zero1, pos1, nums1Neg, nums1Pos] = getStats(nums1);\n auto [neg2, zero2, pos2, nums2Neg, nums2Pos] = getStats(nums2);\n ll negCount = pos1*neg2+pos2*neg1, zeroCount = n*zero2+m*zero1-zero1*zero2, left=-1e10-5, right=1e10+5, mid;\n if(k > negCount) {\n if(k <= negCount+zeroCount) return 0;\n reverse(nums1Neg, nums2Neg);\n left = 1;\n k -= (negCount + zeroCount);\n } else {\n reverse(nums1Pos, nums2Pos);\n right = 0;\n swap(nums2Pos, nums2Neg);\n }\n while(left < right) {\n mid = left + (right-left)/2;\n if(count(nums1Pos, nums2Pos, mid) + count(nums2Neg, nums1Neg, mid) < k) left = mid+1;\n else right = mid;\n }\n return left;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Binary Search O(nmlog(nm))
|
binary-search-onmlognm-by-gaurav2023-rm1h
|
class Solution {\npublic:\n \n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector& nums1, vector& nums2, long long k) {\n long long hi=10000000000;\n long
|
Gaurav2023
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-20T11:42:33.517623+00:00
|
2022-05-20T11:43:21.086780+00:00
| 251 | false |
class Solution {\npublic:\n \n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) {\n long long hi=10000000000;\n long long lo=-10000000000;\n long long ans1=0;\n while(lo<=hi){\n long long mid=(hi+lo)/2;\n if(countElement(nums1,nums2,mid)>=k){\n ans1=mid;\n hi=mid-1;\n }\n else{\n lo=mid+1;\n }\n }\n return ans1;\n }\n \n long long countElement(vector<int> &arr1,vector<int> &arr2,long long dot_prod){\n long long ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<arr1.size();i++){\n long long count=0;\n long long e1=arr1[i];\n long long lo=0;\n long long hi=arr2.size()-1;\n if(e1>=0){\n while(lo<=hi){\n int mid=(lo+hi)/2;\n if((long long)e1*arr2[mid]<=dot_prod){\n count=mid+1;\n lo=mid+1;\n }\n else{\n hi=mid-1;\n }\n }\n ans=ans+count;\n }\n else{\n while(lo<=hi){\n int mid=(lo+hi)/2;\n if((long long)e1*arr2[mid]<=dot_prod){\n count=arr2.size()-mid;\n hi=mid-1;\n }\n else{\n lo=mid+1;\n }\n }\n ans=ans+count;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};
| 0 | 0 |
['C', 'Binary Tree']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Java Binary Search
|
java-binary-search-by-tomythliu-7idl
|
Notable issues:\n1. type cast to long BEFORE min max\n2. be aware of whether the binary search end is inclusive or not\n3. be aware the count/index update is ha
|
tomythliu
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-20T02:19:37.537403+00:00
|
2022-03-20T02:19:37.537428+00:00
| 508 | false |
Notable issues:\n1. type cast to long BEFORE min max\n2. be aware of whether the binary search end is inclusive or not\n3. be aware the count/index update is happening in which if clause to confirm it is the largest value have k count less than it or smallest\n\n```\n\n\nclass Solution {\n int m;\n int n;\n int[] nums1;\n int[] nums2;\n \n public long kthSmallestProduct(int[] n1, int[] n2, long k) {\n this.nums1 = n1.length < n2.length? n1: n2;\n this.nums2 = n1.length < n2.length? n2: n1;\n \n m = nums1.length;\n n = nums2.length;\n // Do binary search on product value range\n long l = Math.min(Math.min((long)nums1[m-1]*nums2[n-1], (long)nums1[0]*nums2[0]), Math.min((long)nums1[0]*nums2[n-1], (long)nums2[0]*nums1[m-1]));\n long r = Math.max(Math.max((long)nums1[m-1]*nums2[n-1], (long)nums1[0]*nums2[0]), Math.max((long)nums1[0]*nums2[n-1], (long)nums2[0]*nums1[m-1]));\n long res = -1;\n \n while(l <= r) {\n long mid = l + (r-l)/2;\n long count = countTillMidVal(mid);\n\n if(count < k) {\n l = mid+1;\n } else {\n res = mid;\n r = mid-1;\n }\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n \n private long countTillMidVal(long val) {\n long count = 0;\n \n for(int num: nums1) {\n // if num > 0, product order is the same as nums2\n // if nums < 0, product order is reverse as nums2\n long c = 0;\n if(num < 0) {\n c = getCountNums2Reverse(val, num);\n } else {\n c = getCountNums2(val, num);\n }\n count += c;\n }\n \n return count;\n }\n \n private long getCountNums2(long val, long num1){\n int l = 0;\n int r = n - 1;\n long count = 0;\n \n while(l <= r) {\n int mid = l + (r-l)/2;\n \n if(nums2[mid]*num1 <= val) {\n count = mid+1;\n l = mid+1;\n } else {\n r = mid-1;\n }\n }\n \n return count;\n }\n \n private long getCountNums2Reverse(long val, long num1) {\n int l = 0;\n int r = n - 1;\n long count = 0;\n \n while(l <= r) {\n int mid = l + (r-l)/2;\n \n if(nums2[mid]*num1 > val) {\n l = mid+1;\n } else {\n count = n-mid;\n r = mid-1;\n }\n }\n \n return count; \n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Swift Binary Search
|
swift-binary-search-by-jav_solo-a0os
|
Thank you to Ankush093 for their solution in C++ here\n\n\nclass Solution {\n func kthSmallestProduct(_ nums1: [Int], _ nums2: [Int], _ k: Int) -> Int {\n
|
jav_solo
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-20T23:29:07.109752+00:00
|
2022-02-20T23:30:42.366720+00:00
| 327 | false |
Thank you to Ankush093 for their solution in C++ [here](https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays/discuss/1753363/Binary-search)\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n func kthSmallestProduct(_ nums1: [Int], _ nums2: [Int], _ k: Int) -> Int {\n var nums1 = nums1\n var nums2 = nums2\n \n var n = nums1.count\n var m = nums2.count\n var result = 0\n var minIndex = min(nums1[0], nums2[0])\n var maxIndex = max(nums1[n - 1], nums2[m - 1])\n \n var left = min(minIndex, maxIndex*minIndex)\n var right = max(maxIndex*maxIndex, minIndex*minIndex)\n \n while left <= right {\n var mid = left + (right - left) / 2\n if valid(&nums1,&nums2,n,m,mid,k) {\n result = mid\n right = mid - 1\n } else {\n left = mid + 1\n }\n }\n \n return result\n }\n \n func getValue1(_ x: Int, _ nums2: inout [Int], _ m: Int, _ val: Int) -> Int {\n var left = 0\n var right = m - 1\n var result = m\n \n while left <= right {\n var mid = left + (right - left) / 2\n if x * nums2[mid] <= val {\n result = mid\n right = mid - 1\n } else {\n left = mid + 1\n }\n }\n return m - result\n }\n \n func getValue2(_ x: Int, _ nums2: inout [Int], _ m: Int, _ val: Int) -> Int {\n var left = 0\n var right = m - 1\n var result = 0\n \n while left <= right {\n var mid = left + (right - left) / 2\n if x * nums2[mid] <= val {\n result = mid + 1\n left = mid + 1\n } else {\n right = mid - 1\n }\n }\n return result\n }\n \n func valid(_ nums1: inout [Int], _ nums2: inout [Int], _ n : Int, _ m: Int, _ mid: Int, _ k : Int) -> Bool {\n var result = 0\n for index in 0 ..< n {\n if nums1[index] < 0 {\n result += getValue1(nums1[index], &nums2, m, mid)\n } else {\n result += getValue2(nums1[index], &nums2, m, mid)\n }\n }\n return result >= k\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Binary Search', 'Swift']
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
What's wrong? why a vector is not taking long long data type inside it?
|
whats-wrong-why-a-vector-is-not-taking-l-a3av
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) {\n vector<long long>nums3;\n f
|
ishi_kumari
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-10T13:38:05.088618+00:00
|
2022-01-10T13:38:05.088683+00:00
| 184 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) {\n vector<long long>nums3;\n for(int i=0;i<nums1.size();i++){\n for(int j=0;j<nums2.size();j++){\n nums3.push_back(nums1[i]*nums2[j]);\n }\n }\n sort(nums3.begin(),nums3.end());\n return nums3[k-1];\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C']
| 1 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Kth Smallest Product of Two Sorted Arrays
|
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-array-g5qj
|
guys please evaluate this code and let me know is there any bug in this approach \n\n#include <iostream>\nusing namespace std ;\n\nint main() {\n int nums1[] =
|
Aditya_7378
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-06T16:03:11.395063+00:00
|
2022-01-06T16:03:11.395094+00:00
| 669 | false |
guys please evaluate this code and let me know is there any bug in this approach \n```\n#include <iostream>\nusing namespace std ;\n\nint main() {\n int nums1[] = {2,5};\n int nums2[] = {3 , 4 };\n int n = sizeof(nums1)/sizeof(nums1[0]);\n int m = sizeof(nums2)/sizeof(nums2[0]);\n\n int count=0;\n int k=2;\n int ans=0;\n\n for(int i=0; i<n ; i++){\n for(int j=0; j<m ; j++){\n\n \n count++;\n\n if(count == k){\n ans = nums1[i] * nums2[j];\n cout<< ans;\n \n }\n \n\n }\n }\n} \n```
| 0 | 15 |
['C']
| 2 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
中文 binary search
|
zhong-wen-binary-search-by-wuzhenhai-8mq0
|
\nclass Solution\n{\npublic:\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int> &nums1, vector<int> &nums2, long long k)\n {\n // \u4E58\u79EF\u503C\u4E00\
|
wuzhenhai
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-04T12:13:11.056539+00:00
|
2022-01-04T12:13:11.056569+00:00
| 736 | false |
```\nclass Solution\n{\npublic:\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int> &nums1, vector<int> &nums2, long long k)\n {\n // \u4E58\u79EF\u503C\u4E00\u5B9A\u5728 [-10000000000, 10000000000]\u4E4B\u95F4.\n // \u503C\u7684\u6700\u5927\u8303\u56F4\u8DE8\u5EA6(MAX-VLAUE-RANGE) = 20000000000\n\n // \u7B97\u6CD5\u590D\u6742\u5EA6\u8003\u8651: Log(MAX-VLAUE-RANGE) * |nums1| * log(|nums2|)\n // \u56E0\u6B64, \u5C06nums1\u8BBE\u5B9A\u4E3A\u957F\u5EA6\u8F83\u5C0F\u7684\u6570\u7EC4\n if (nums1.size() > nums2.size())\n {\n nums1.swap(nums2);\n }\n\n long long begin = -10000000000ll;\n long long end = 10000000000ll;\n long long result = -1;\n while (begin <= end)\n {\n auto middle = (begin + end) / 2;\n\n //\u4E0D\u5927\u4E8Emiddle\u7684\u4E58\u79EF\u5BF9\u7684\u4E2A\u6570\n long long count = 0;\n for (auto &n1 : nums1)\n {\n count += getTotalNotGreaterThan(nums2, n1, middle);\n }\n if (count >= k)\n {\n result = middle;\n end = middle - 1;\n }\n else\n {\n begin = middle + 1;\n }\n }\n return result;\n }\n\n //\u5728nums2\u4E2D, \u4E0En1\u76F8\u4E58\uFF0C\u4F46\u662F\u4E58\u79EF\u503C\u4E0D\u5927\u4E8Evalue\u7684\u5143\u7D20\u4E2A\u6570.\n long long getTotalNotGreaterThan(vector<int> &nums2, long long n1, long long value)\n {\n //\u53EF\u4EE5\u81EA\u5DF1\u5199\u4E00\u4E2Abinary search, \u6211\u8FD9\u91CC\u5957\u7528stl upper_bound/lower_bound\u65B9\u6CD5.\n if (n1 >= 0)\n {\n return distance(nums2.begin(), upper_bound(nums2.begin(), nums2.end(), -1, [=](int v1, int v2)\n { return value < (long)v2 * n1; }));\n }\n else\n {\n n1 *= -1;\n return distance(lower_bound(nums2.begin(), nums2.end(), -1, [=](int v1, int v2)\n { return (long)v1 * n1 < -value; }),\n nums2.end());\n }\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
Kth Smallest Product of Two Sorted Arrays .....problem in ide
|
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-array-l8zt
|
\nimport java.io.;\nimport java.util.;\n\npublic class striver {\n\n\n\n\tpublic static void main(String[] args) {\n\t\ttry {\n\t\t\tSystem.setIn(new FileInputS
|
Jarvis_123
|
NORMAL
|
2021-12-17T12:16:01.901691+00:00
|
2021-12-17T12:18:10.898311+00:00
| 452 | false |
\nimport java.io.*;\nimport java.util.*;\n\npublic class striver {\n\n\n\n\tpublic static void main(String[] args) {\n\t\ttry {\n\t\t\tSystem.setIn(new FileInputStream("input.txt"));\n\t\t\tSystem.setOut(new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("output.txt")));\n\t\t} catch (Exception e) {\n\t\t\tSystem.err.println("Error");\n\t\t}\n\n\t\t//code here\n\t\t//int []arr1 = new int[2];\n\t\t//int []arr2 = new int[1];\n\n\t\tint [] nums1 = { 4, -2, 0, 3};\n\t\tint [] nums2 = { 2, 4};\n\t\tlong k = 6;\n\n\n\n\t\tList <Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();\n\n\t\tList <Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();\n\n\t\tfor (int i : nums1) {\n\t\t\tlist.add(i);\n\n\t\t}\n\n\t\tfor (int i : nums2) {\n\t\t\tlist.add(i);\n\t\t}\n\n\n\t\tfor (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {\n\n\t\t\tfor (int j = i + 1; j < list.size(); j++) {\n\n\t\t\t\tint pr = list.get(i) * list.get(j);\n\n\t\t\t\tans.add(pr);\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t}\n\n\t\tCollections.sort(ans);\n\t\tLong dere = new Long(k);\n\t\tint kk = dere.intValue();\n\t\tint a = ans.get(kk - 1);\n\t\tlong Ans = a;\n\t\tSystem.out.println(Ans);\n\t\tSystem.out.println(ans);\n\n\t}\n}\n\n\n\n
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
[JavaScript] 2040. Kth Smallest Product of Two Sorted Arrays
|
javascript-2040-kth-smallest-product-of-7bvix
|
---\n\n- This is compressed answer, not easy to understand at first, core logic is minimal\n\n---\n\nHope it is simple to understand.\n\n---\n\n\nconst lessthan
|
pgmreddy
|
NORMAL
|
2021-12-09T04:34:32.985823+00:00
|
2021-12-09T14:15:57.394682+00:00
| 409 | false |
---\n\n- This is compressed answer, not easy to understand at first, core logic is minimal\n\n---\n\nHope it is simple to understand.\n\n---\n\n```\nconst lessthan_4ge = (a, b) => a < b;\nconst lessthanequal_4g = (a, b) => a <= b;\nfunction blu_midVal4mFunc(compFunc, getMidVal, target, left, right) {\n while (left < right) {\n let mid = left + Math.trunc((right - left) / 2);\n if (compFunc(getMidVal(mid), target)) left = mid + 1;\n else right = mid;\n }\n return compFunc(getMidVal(left), target) ? left + 1 : left;\n}\nvar kthSmallestProduct = function (nums1, nums2, k) {\n let prod_left = -((10 ** 5) ** 2), // from question constraints\n prod_right = (10 ** 5) ** 2,\n getMidVal = (mid) => nums2[mid]; // just arr[mid]\n\n var getVal = function (prod_mid) {\n let count = 0;\n for (let n1 of nums1) {\n if (n1 > 0)\n count += blu_midVal4mFunc(lessthan_4ge, getMidVal, prod_mid / n1, 0, nums2.length - 1);\n else if (n1 < 0)\n count += nums2.length - blu_midVal4mFunc(lessthanequal_4g, getMidVal, prod_mid / n1, 0, nums2.length - 1);\n else if (n1 === 0)\n if (prod_mid > 0)\n count += nums2.length;\n }\n return count;\n };\n\n return blu_midVal4mFunc(lessthan_4ge, getVal, k, prod_left, prod_right) - 1;\n};\n```\n\n---\n
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
regular binary search (need to be improved later on)
|
regular-binary-search-need-to-be-improve-ykcc
|
\tlong long lessEqual(const vector& A, const vector& B, double mid, long long cnt = 0){\n for(long long x : A)\n if(!x) cnt += (0 <= mid)*B.si
|
liqiangc
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-30T07:32:50.291714+00:00
|
2021-11-30T07:34:54.673750+00:00
| 224 | false |
\tlong long lessEqual(const vector<int>& A, const vector<int>& B, double mid, long long cnt = 0){\n for(long long x : A)\n if(!x) cnt += (0 <= mid)*B.size();\n else cnt += x>0 ? (upper_bound(B.begin(), B.end(), mid/x)-B.begin()) : (B.end()-lower_bound(B.begin(), B.end(), mid/x));\n return cnt;\n }\n long long kthSmallestProduct(const vector<int>& A, const vector<int>& B, long long k, long long l = -1e10, long long r = 1e10) {\n while(l<r){\n long long mid = l+(r-l)/2;\n lessEqual(A, B, mid) < k ? l = mid+1 : r = mid;\n }\n return l;\n }
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays
|
[C++] Binary search using std::partition_point and std::reverse_iterator without copying
|
c-binary-search-using-stdpartition_point-hxkm
|
The problem has "BinarySearch" tag, so it can be solved with std::partition_point, just like any other binary search problem. A small than minimal implementatio
|
smitsyn
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-04T08:49:01.835587+00:00
|
2021-11-04T08:49:18.235740+00:00
| 270 | false |
The problem has "BinarySearch" tag, so it can be solved with `std::partition_point`, just like any other binary search problem. A small than minimal implementation of `counting_iterator` is presented such that it compiles with gcc 9, but I guess something from ranges could be used with later standard. To eliminate `nums` copying, `std::reverse_iterator` and templated function for product counting are employed. \n\nFor each `m`, there\'s a fixed number of pairs from (cartesian) product of nums1 and nums2 whose product is less than `m`, so we binary search for `m=k`. For more detailed explanation, see this explanation by @votrubac that I used: https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-product-of-two-sorted-arrays/discuss/1527753/Binary-Search-and-Two-Pointers .\n\n```\n#include <algorithm>\n\nstruct counting_iterator\n{\n using value_type = long long;\n using reference = long long;\n using difference_type = long long;\n using iterator_category = std::random_access_iterator_tag;\n using pointer = void;\n\n long long n_;\n\n counting_iterator& operator++() { ++n_; return *this; }\n counting_iterator& operator--() { --n_; return *this; }\n void operator+=(long long d) { n_ += d; }\n friend long long operator-(const counting_iterator& lhs, const counting_iterator &rhs) { return lhs.n_ - rhs.n_; }\n long long operator*() const { return n_; }\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long kthSmallestProduct(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, long long k) {\n\n auto mid1 = std::lower_bound(nums1.begin(), nums1.end(), 0);\n auto mid2 = std::lower_bound(nums2.begin(), nums2.end(), 0);\n\n auto neg1 = std::make_pair(nums1.begin(), mid1), pos1 = std::make_pair(mid1, nums1.end());\n auto neg2 = std::make_pair(nums2.begin(), mid2), pos2 = std::make_pair(mid2, nums2.end());\n\n auto neg1_r = std::make_pair(std::make_reverse_iterator(mid1), std::make_reverse_iterator(nums1.begin()))\n , pos1_r = std::make_pair(std::make_reverse_iterator(nums1.end()), std::make_reverse_iterator(mid1));\n auto neg2_r = std::make_pair(std::make_reverse_iterator(mid2), std::make_reverse_iterator(nums2.begin()))\n , pos2_r = std::make_pair(std::make_reverse_iterator(nums2.end()), std::make_reverse_iterator(mid2));\n\n auto local_count_of_prods_less_than = [](auto range_pair1, auto range_pair2, long long m)->long long {\n if (range_pair2.first == range_pair2.second)\n return 0;\n\n long long cnt = 0;\n\n auto it2 = std::prev(range_pair2.second);\n\n for (auto it1 = range_pair1.first; it1 != range_pair1.second; ++it1)\n {\n while ((long long)*it1 * *it2 > m)\n {\n if (it2 == range_pair2.first)\n return cnt;\n else\n --it2;\n }\n cnt += std::distance(range_pair2.first, it2) + 1;\n }\n return cnt;\n };\n\n auto pos1_size = std::distance(pos1.first, pos1.second);\n auto pos2_size = std::distance(pos2.first, pos2.second);\n auto neg1_size = std::distance(neg1.first, neg1.second);\n auto neg2_size = std::distance(neg2.first, neg2.second);\n\n\n auto count_of_prods_less_than = [&](auto m)->long long\n {\n if (m >= 0)\n return local_count_of_prods_less_than(pos1, pos2, m)\n + local_count_of_prods_less_than(neg1_r, neg2_r, m)\n + pos1_size * neg2_size + pos2_size * neg1_size;\n else\n return local_count_of_prods_less_than(neg1, pos2_r, m)\n + local_count_of_prods_less_than(neg2, pos1_r, m);\n };\n\n constexpr auto min_m = -100000LL*100000;\n constexpr auto max_m = 100000LL*100000;\n\n auto it = std::partition_point(\n counting_iterator{ min_m }, counting_iterator{ max_m+1 }\n , [&,k](auto m_cand) {\n return count_of_prods_less_than(m_cand) < k; \n });\n\n return *it;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Python 1-line sorting based solution
|
python-1-line-sorting-based-solution-by-euv35
|
\ndef allCellsDistOrder(self, R: int, C: int, r0: int, c0: int) -> List[List[int]]:\n return sorted([(i, j) for i in range(R) for j in range(C)], key=lambda
|
twohu
|
NORMAL
|
2019-04-21T04:18:01.607558+00:00
|
2019-05-07T02:09:45.587314+00:00
| 6,241 | false |
```\ndef allCellsDistOrder(self, R: int, C: int, r0: int, c0: int) -> List[List[int]]:\n return sorted([(i, j) for i in range(R) for j in range(C)], key=lambda p: abs(p[0] - r0) + abs(p[1] - c0))\n```\n\nThe same code, more readable:\n```\ndef allCellsDistOrder(self, R: int, C: int, r0: int, c0: int) -> List[List[int]]:\n def dist(point):\n pi, pj = point\n return abs(pi - r0) + abs(pj - c0)\n\n points = [(i, j) for i in range(R) for j in range(C)]\n return sorted(points, key=dist)\n```
| 96 | 3 |
['Sorting', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 10 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
O(N) Java BFS
|
on-java-bfs-by-_topspeed-i5g4
|
\npublic int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n boolean[][] visited = new boolean[R][C];\n int[][] result = new int[R * C][2];\n i
|
_topspeed_
|
NORMAL
|
2019-04-21T04:50:26.287530+00:00
|
2019-04-21T04:50:26.287589+00:00
| 8,758 | false |
```\npublic int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n boolean[][] visited = new boolean[R][C];\n int[][] result = new int[R * C][2];\n int i = 0;\n Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<int[]>();\n queue.offer(new int[]{r0, c0});\n while (!queue.isEmpty()) {\n int[] cell = queue.poll();\n int r = cell[0];\n int c = cell[1];\n\n if (r < 0 || r >= R || c < 0 || c >= C) {\n continue;\n }\n if (visited[r][c]) {\n continue;\n }\n\n result[i] = cell;\n i++;\n visited[r][c] = true;\n\n queue.offer(new int[]{r, c - 1});\n queue.offer(new int[]{r, c + 1});\n queue.offer(new int[]{r - 1, c});\n queue.offer(new int[]{r + 1, c});\n }\n return result;\n }\n ```
| 88 | 4 |
[]
| 13 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Simple C++ Solution
|
simple-c-solution-by-bdwan-cp3l
|
1\u3001calculate the distance\n2\u3001sort by distance\n3\u3001remove the distance\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int
|
bdwan
|
NORMAL
|
2019-07-29T09:40:12.626855+00:00
|
2019-07-29T09:40:12.626906+00:00
| 3,250 | false |
1\u3001calculate the distance\n2\u3001sort by distance\n3\u3001remove the distance\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n vector<vector<int>> ans;\n for (int i = 0; i < R; i++)\n for (int j = 0; j < C; j++)\n ans.push_back({i, j, abs(i - r0) + abs(j - c0)});\n\n sort(ans.begin(), ans.end(), [](vector<int>& c1, vector<int>& c2) {\n return c1[2] < c2[2];\n });\n\n for (vector<int>& d: ans) \n d.pop_back();\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 54 | 1 |
['C']
| 10 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
4ms O(n) Java Counting Sort (計數排序) Solution
|
4ms-on-java-counting-sort-ji-shu-pai-xu-fjps1
|
The max distance is R + C, and the result array\'s length is R * C. Since the distance is limited (generally, compared with the cell count), we can use Counting
|
nullpointer01
|
NORMAL
|
2019-04-21T07:54:31.548447+00:00
|
2019-04-21T07:54:31.548478+00:00
| 4,199 | false |
The max distance is `R + C`, and the result array\'s length is `R * C`. Since the distance is limited (generally, compared with the cell count), we can use Counting Sort (\u8A08\u6578\u6392\u5E8F) to solve it efficiently.\n\nTime complexity is `O(R * C)`, i.e. `O(n)`.\n\n> **66 / 66** test cases passed.\n> **Status**: Accepted\n> **Runtime**: 4 ms\n> **Memory Usage**: 38.5 MB\n\n```java\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n int[] counter = new int[R + C + 1];\n for (int r = 0; r < R; r++) {\n for (int c = 0; c < C; c++) {\n int dist = Math.abs(r - r0) + Math.abs(c - c0);\n counter[dist + 1] += 1;\n }\n }\n \n for (int i = 1; i < counter.length; i++) {\n counter[i] += counter[i - 1];\n }\n \n int[][] ans = new int[R * C][];\n for (int r = 0; r < R; r++) {\n for (int c = 0; c < C; c++) {\n int dist = Math.abs(r - r0) + Math.abs(c - c0);\n ans[counter[dist]] = new int[] { r, c };\n counter[dist]++;\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 52 | 1 |
[]
| 11 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
O(n) with picture
|
on-with-picture-by-votrubac-qjji
|
Solution\n1. Increment the distance from 0 till R + C.\n2. From our point, generate all points with the distance.\n3. Add valid poits (within our grid) to the r
|
votrubac
|
NORMAL
|
2019-04-21T04:01:20.289582+00:00
|
2020-04-28T07:39:49.241058+00:00
| 6,432 | false |
# Solution\n1. Increment the distance from 0 till ```R + C```.\n2. From our point, generate all points with the distance.\n3. Add valid poits (within our grid) to the result.\n\nThe image below demonstrates the generation of points with distance 5:\n\n```\nvector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n vector<vector<int>> res = { { r0, c0 } };\n auto max_d = max({ r0 + c0, c0 + R - r0, r0 + C - c0, R - r0 + C - c0 });\n for (auto d = 1; d <= max_d; ++d)\n for (int x = d; x >= -d; --x) {\n auto r1 = r0 + x, c1_a = c0 + d - abs(x), c1_b = c0 + abs(x) - d;\n if (r1 >= 0 && r1 < R) {\n if (c1_a >= 0 && c1_a < C) \n res.push_back({ r1, c1_a });\n if (c1_a != c1_b && c1_b >= 0 && c1_b < C) \n res.push_back({ r1, c1_b });\n }\n }\n return res;\n}\n```\n# Complexity Analysis\nRuntime: *O((R + C) ^ 2)*, which is linear to the total number of cells. We analyze maximum 4(R + C - 2)(R + C - 2) cells once.\nMemory: *O(1)*. We do not use any additional memory (except for returning the result, which does not count).
| 43 | 2 |
[]
| 10 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
c++ sorting / min heap solutions
|
c-sorting-min-heap-solutions-by-itsmedav-y5vp
|
sorting:\nRuntime: 112 ms, faster than 87.50% of C++ online submissions\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, in
|
itsmedavid
|
NORMAL
|
2019-04-21T04:25:33.763568+00:00
|
2019-04-21T04:25:33.763609+00:00
| 2,777 | false |
**sorting:**\nRuntime: 112 ms, faster than 87.50% of C++ online submissions\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n auto comp = [r0, c0](vector<int> &a, vector<int> &b)\n {\n return abs(a[0]-r0) + abs(a[1]-c0) < abs(b[0]-r0) + abs(b[1]-c0);\n };\n \n vector<vector<int>> resp;\n for(int i=0 ; i<R ; i++)\n {\n for(int j=0; j<C ; j++)\n {\n resp.push_back({i, j});\n }\n }\n\n sort(resp.begin(), resp.end(), comp);\n\n return resp;\n }\n};\n```\n\n**min heap:**\nRuntime: 168 ms, faster than 25.00% of C++ online submissions\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n auto comp = [r0, c0](vector<int> &a, vector<int> &b)\n {\n return abs(a[0]-r0) + abs(a[1]-c0) > abs(b[0]-r0) + abs(b[1]-c0);\n };\n priority_queue<vector<int>, vector<vector<int>>, decltype(comp)> minHeap(comp);\n\n for(int i=0 ; i<R ; i++)\n {\n for(int j=0; j<C ; j++)\n {\n minHeap.push({i, j});\n }\n }\n \n vector<vector<int>> resp;\n while(!minHeap.empty())\n {\n resp.push_back(minHeap.top());\n minHeap.pop();\n } \n \n return resp;\n }\n}; \n```
| 29 | 2 |
['C', 'Sorting', 'Heap (Priority Queue)']
| 3 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Python straightforward DFS & BFS
|
python-straightforward-dfs-bfs-by-cenkay-8gfx
|
\nclass Solution:\n def allCellsDistOrder(self, R: int, C: int, r0: int, c0: int) -> List[List[int]]:\n def dfs(i, j):\n seen.add((i, j))\n
|
cenkay
|
NORMAL
|
2019-04-21T04:06:36.693540+00:00
|
2019-04-21T04:06:36.693571+00:00
| 2,783 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def allCellsDistOrder(self, R: int, C: int, r0: int, c0: int) -> List[List[int]]:\n def dfs(i, j):\n seen.add((i, j))\n res.append([i, j])\n for x, y in (i - 1, j), (i + 1, j), (i, j - 1), (i, j + 1):\n if 0 <= x < R and 0 <= y < C and (x, y) not in seen:\n dfs(x, y)\n res, seen = [], set()\n dfs(r0, c0)\n return sorted(res, key = lambda x: abs(x[0] - r0) + abs(x[1] - c0))\n```\n```\nclass Solution:\n def allCellsDistOrder(self, R: int, C: int, r0: int, c0: int) -> List[List[int]]:\n bfs, res, seen = [[r0, c0]], [], {(r0, c0)}\n while bfs:\n res += bfs\n new = []\n for i, j in bfs:\n for x, y in (i - 1, j), (i + 1, j), (i, j + 1), (i, j - 1):\n if 0 <= x < R and 0 <= y < C and (x, y) not in seen:\n seen.add((x, y))\n new.append([x, y])\n bfs = new\n return res\n```
| 25 | 2 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Breadth-First Search', 'Python']
| 7 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Java Sorting Solution
|
java-sorting-solution-by-self_learner-g2rj
|
```\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n int[][] origin = new int[R * C][2];\n for (int i = 0
|
self_learner
|
NORMAL
|
2019-04-21T04:24:36.889441+00:00
|
2019-04-21T04:24:36.889477+00:00
| 2,321 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n int[][] origin = new int[R * C][2];\n for (int i = 0; i < R; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < C; j++) {\n origin[i * C + j] = new int[] {i, j};\n }\n }\n\n Arrays.sort(origin, new Comparator<int[]>(){\n public int compare(int[] a, int[] b) {\n return Math.abs(a[0] - r0) + Math.abs(a[1] - c0)\n - Math.abs(b[0] - r0) - Math.abs(b[1] - c0);\n }\n });\n return origin;\n }\n}
| 23 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Java | 2ms 100% O(max_dist^2) | Equal distance diamond patterns | No sorting | Explanation
|
java-2ms-100-omax_dist2-equal-distance-d-jpyf
|
This code will usually run in 3ms, but about ⅓ of my submits will run in 2ms.Update 2025: If you want to see my updated solution with this approach, plus 3 oth
|
dudeandcat
|
NORMAL
|
2021-03-05T12:05:08.784498+00:00
|
2025-03-15T10:19:17.020164+00:00
| 1,978 | false |
This code will usually run in 3ms, but about ⅓ of my submits will run in 2ms.
*Update 2025:* If you want to see my updated solution with this approach, plus 3 other approaches, with more formalized explations and analyses, with all approaches having sample code in Java, C++, and Python, then see my [updated post here](https://leetcode.com/problems/matrix-cells-in-distance-order/solutions/6432773/c-java-python3-4-approaches-sort-counting-sort-bfs-contour/). But the code in this post is faster.
Cells at equal distance from the start point r0,c0 will form concentric nested diamond-shaped paths of cells in the matrix, as seen in the diagram below. This code follows the four sides of these diamond-shaped paths, adding valid cells' row and column to the result. Then move to the next outward diamond-shape path which will have a distance value of one more than the previous inner diamond-shape path.
In the diagram below, the digits within the grid represent the distance of each cell from the r0,c0 start cell. The colored diamond-shapes are paths through cells of equal distance. Some of the larger diamond-shaped paths are not shown in the diagram because the full pattern became too hard on my eyes.
The order for processing the sides of the diamond-shapes, and the direction of processing the side, is listed below as a series of paths between vertices of a diamond-shape:
1. top to left
2. left to bottom
3. bottom to right
4. right to top
Each side of the diamond-shaped path has its own section within the code below.
Please upvote if useful.
```java []
class Solution {
public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {
int[][] result = new int[R * C][];
result[0] = new int[] {r0, c0}; // Add start point r0,c0 which has distance 0.
int resultIdx = 1;
int lim = Math.max( r0, R-r0-1 ) + Math.max( c0, C-c0-1 );
// lim is highest distance value.
for (int dist = 1; dist <= lim; dist++) { // Process 'lim' diamond-shapes having distance 'dist'.
int r = r0 - dist;
int c = c0;
// Diamond side: Top Left
for (int count = dist; count > 0; count--) {
if (r >= 0 && c >= 0) result[resultIdx++] = new int[] {r, c};
r++;
c--;
}
// Diamond side: Left Bottom
for (int count = dist; count > 0; count--) {
if (r < R && c >= 0) result[resultIdx++] = new int[] {r, c};
r++;
c++;
}
// Diamond side: Bottom Right
for (int count = dist; count > 0; count--) {
if (r < R && c < C) result[resultIdx++] = new int[] {r, c};
r--;
c++;
}
// Diamond side: Right Top
for (int count = dist; count > 0; count--) {
if (r >= 0 && c < C) result[resultIdx++] = new int[] {r, c};
r--;
c--;
}
}
return result;
}
}
```
| 17 | 1 |
['Java']
| 1 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
C++ || power of STL || MULTIMAP
|
c-power-of-stl-multimap-by-mr_optimizer-i7qi
|
```\nvector> allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n multimap>mm;\n vector>ans;\n for(int i=0;i>(dist,pair\(i,j
|
mr_optimizer
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-12T16:20:19.109233+00:00
|
2021-07-12T16:20:19.109280+00:00
| 827 | false |
```\nvector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n multimap<int,pair<int,int>>mm;\n vector<vector<int>>ans;\n for(int i=0;i<rows;i++)\n for(int j=0;j<cols;j++){\n int dist=abs(rCenter-i)+abs(cCenter-j);\n mm.insert(pair<int,pair<int,int>>(dist,pair<int,int>(i,j)));\n }\n auto itr=mm.begin();\n while(itr!=mm.end()){\n vector<int>temp(2);\n temp[0]=(itr->second.first);\n temp[1]=(itr->second.second);\n ans.push_back(temp);\n itr++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\t\n\tFEEL FREE TO ASK DOUBTS.......\n\tPLEASE UPVOTE IF YOU LEARN SOMETHING NEW!!!!!
| 13 | 1 |
['C']
| 4 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
[JavaScript] Easy to understand - 2 solutions - 132ms
|
javascript-easy-to-understand-2-solution-13fl
|
The first solution is do it by counting sort. Here\'s the algorithm:\n\n1. Traversal the whole matrix, calculate the distance for each cell and save them into a
|
poppinlp
|
NORMAL
|
2019-09-23T11:38:15.572617+00:00
|
2019-09-23T11:38:15.572652+00:00
| 828 | false |
The first solution is do it by counting sort. Here\'s the algorithm:\n\n1. Traversal the whole matrix, calculate the distance for each cell and save them into a list whose index could be used as the distance value.\n2. Merge all items in the list and you will get the answer.\n\n```js\nconst allCellsDistOrder = (r, c, r0, c0) => {\n const buckets = [];\n const ret = [];\n for (let i = 0; i < r; ++i) {\n for (let j = 0; j < c; ++j) {\n const dis = Math.abs(i - r0) + Math.abs(j - c0);\n if (buckets[dis] === undefined) buckets[dis] = [];\n buckets[dis].push([i, j]);\n }\n }\n for (const bucket of buckets) {\n ret.push(...bucket);\n }\n return ret;\n};\n```\n\nThe second solution is based on BFS. Here\'s the algorithm:\n\n1. Traversal the whole matrix from the `(r0, c0)` cell with a queue by BFS.\n2. Do some validation for each cell and you will get the answer.\n\n```js\nconst allCellsDistOrder = (r, c, r0, c0) => {\n const visited = new Set();\n const ret = [];\n const queue = [[r0, c0]];\n while (queue.length) {\n const [x, y] = queue.shift();\n if (x > r - 1 || x < 0 || y > c -1 || y < 0 || visited.has(x * 100 + y)) continue;\n ret.push([x, y]);\n visited.add(x * 100 + y);\n [[0, -1], [0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]].forEach(move => {\n queue.push([x + move[0], y + move[1]]);\n });\n }\n return ret;\n};\n```
| 11 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 2 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Java Sorting (Easy Understang)
|
java-sorting-easy-understang-by-orangehu-pvk0
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n int[][] res = new int[R*C][2];\n int idx = 0;\n
|
orangehuang
|
NORMAL
|
2019-07-09T06:54:50.154557+00:00
|
2019-07-09T06:54:50.154608+00:00
| 1,745 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n int[][] res = new int[R*C][2];\n int idx = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < R; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < C; j++){\n res[idx][0] = i;\n res[idx][1] = j;\n idx++;\n } \n } \n \n Arrays.sort(res,(o1,o2)->\n Math.abs(o1[0]-r0)+Math.abs(o1[1]-c0) - (Math.abs(o2[0]-r0) + Math.abs(o2[1]-c0))\n );\n \n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 10 | 0 |
['Java']
| 3 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Python solution: easy to understand
|
python-solution-easy-to-understand-by-dr-g8fe
|
This code creates one list containing all possible cells and one list containing the cells\' distance from (r0,c0). Then, it sorts the two lists.\n\n\nclass Sol
|
dr_sean
|
NORMAL
|
2019-04-23T06:04:49.356453+00:00
|
2019-04-23T06:04:49.356515+00:00
| 937 | false |
This code creates one list containing all possible cells and one list containing the cells\' distance from (r0,c0). Then, it sorts the two lists.\n\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def allCellsDistOrder(self, R, C, r0, c0):\n ans, dist = [], []\n for r in range(R):\n for c in range(C):\n dist += [abs(r - r0) + abs(c - c0)]\n ans += [[r, c]]\n dist, ans = zip(*sorted(zip(dist, ans)))\n return ans\n```
| 9 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Custom sort for the Points [C++]
|
custom-sort-for-the-points-c-by-alucard3-6h3b
|
\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nWe simply create an array and sort it according to the given condition of minimizing the distanc
|
aluCard31
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-31T04:26:00.698020+00:00
|
2022-12-31T04:26:00.698061+00:00
| 1,053 | false |
\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nWe simply create an array and sort it according to the given condition of minimizing the distance between a point in the array and {rCenter, cCenter}. \n\nThe lambda takes 2 points `a` and `b`, and determines the order by distance of these points from the center.\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int r, int c) {\n vector<vector<int>> ans;\n for (int i=0; i<rows; i++) {\n for (int j=0; j<cols; j++)\n ans.push_back({i, j});\n }\n\n sort (ans.begin(), ans.end(), [&] (auto& a, auto& b) {\n return (abs(r-a[0]) + abs(c-a[1]) < abs(r-b[0]) + abs(c-b[1]));\n });\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 8 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Java With TreeMap, easy to understand
|
java-with-treemap-easy-to-understand-by-pliss
|
\npublic int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n TreeMap<Integer, List<int[]>> map = new TreeMap<>();\n for (int i = 0; i < R;
|
ansonluo
|
NORMAL
|
2019-04-21T06:34:26.672673+00:00
|
2019-04-21T06:34:26.672701+00:00
| 578 | false |
```\npublic int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n TreeMap<Integer, List<int[]>> map = new TreeMap<>();\n for (int i = 0; i < R; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < C; j++) {\n int distince = Math.abs(r0 - i) + Math.abs(c0 - j); //get the distance\n List<int[]> list = map.getOrDefault(distince, new ArrayList<>());\n list.add(new int[] {i, j});\n map.put(distince, list);\n }\n }\n int[][] result = new int[R * C][2]; \n int i = 0;\n for (Integer key : map.keySet()) { //straight forward\n for (int[] temp : map.get(key)) {\n result[i++] = temp;\n }\n }\n return result;\n }\n```
| 8 | 1 |
[]
| 2 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Java Breadth First Search
|
java-breadth-first-search-by-supercoder3-ms6r
|
This problem is asking to list the cells in the order you would reach them in an outwards fill from (rCenter, cCenter). This matches the way a bfs iterates over
|
superCoder384
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-04T06:06:17.229238+00:00
|
2023-01-04T06:06:17.229282+00:00
| 1,260 | false |
This problem is asking to list the cells in the order you would reach them in an outwards fill from (rCenter, cCenter). This matches the way a bfs iterates over nodes, so if we treat each coordinate point like a node, bfs is a valid solution.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n //bfs\n final int[][] directions = new int[][]{{0, -1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}};\n\n Queue<Integer[]> q = new LinkedList<>();\n boolean[][] seen = new boolean[rows][cols];\n\n q.add(new Integer[]{rCenter, cCenter});\n seen[rCenter][cCenter] = true;\n\n int[][] result = new int[rows * cols][];\n int i = 0;\n while(!q.isEmpty()){\n Integer[] curr = q.remove();\n result[i++] = new int[]{curr[0], curr[1]};\n\n for(int[] d : directions){\n int r = curr[0] + d[0];\n int c = curr[1] + d[1];\n\n if(r >= 0 && c >= 0 && r < rows && c < cols && !seen[r][c]){\n seen[r][c] = true;\n q.add(new Integer[]{r, c});\n }\n }\n }\n return result;\n }\n}\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Breadth-First Search', 'Java']
| 2 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Simple & Easy Solution by Python 3
|
simple-easy-solution-by-python-3-by-jame-6x9s
|
\nclass Solution:\n def allCellsDistOrder(self, R: int, C: int, r0: int, c0: int) -> List[List[int]]:\n cells = [[i, j] for i in range(R) for j in ran
|
jamesujeon
|
NORMAL
|
2020-12-08T01:42:17.065607+00:00
|
2020-12-08T01:42:17.065649+00:00
| 957 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def allCellsDistOrder(self, R: int, C: int, r0: int, c0: int) -> List[List[int]]:\n cells = [[i, j] for i in range(R) for j in range(C)]\n return sorted(cells, key=lambda p: abs(p[0] - r0) + abs(p[1] - c0))\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Easy to Understand | Simple | Faster | 2 solutions | Counting sort | Python
|
easy-to-understand-simple-faster-2-solut-ln8a
|
\ndef using_counting_sort(self, R, C, r0, c0):\n out = [[] for _ in range(R + C)]\n for i in range(R):\n for j in range(C):\n
|
mrmagician
|
NORMAL
|
2020-07-18T11:47:06.511660+00:00
|
2020-07-18T11:47:06.511693+00:00
| 665 | false |
```\ndef using_counting_sort(self, R, C, r0, c0):\n out = [[] for _ in range(R + C)]\n for i in range(R):\n for j in range(C):\n diff = abs(i - r0) + abs(j - c0)\n out[diff].append([i, j])\n ret = []\n for arr in out:\n ret.extend(arr)\n return ret\n \n def brute_force(self, R, C, r0, c0):\n out = []\n for i in range(R):\n for j in range(C):\n out.append({\n "dist": abs(i - r0) + abs(j - c0),\n "val": [i, j]\n })\n return [i[\'val\'] for i in sorted(out, key=lambda x: x[\'dist\'])]\n```\n\n**I hope that you\'ve found the solution useful.**\n*In that case, please do upvote and encourage me to on my quest to document all leetcode problems\uD83D\uDE03*\nPS: Search for **mrmagician** tag in the discussion, if I have solved it, You will find it there\uD83D\uDE38
| 6 | 3 |
['Sorting', 'Counting Sort', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 1 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
✅C++✅C#✅JavaScript.🔥Fast and Explained solutions.💯
|
ccjavascriptfast-and-explained-solutions-ifu8
|
1.Create a list of all cells in the matrix, sorted by their distance from the given center cell. To do this, we can calculate the distance of each cell from the
|
aloneguy
|
NORMAL
|
2023-05-03T01:46:03.906766+00:00
|
2023-05-03T01:46:03.906801+00:00
| 837 | false |
# 1.Create a list of all cells in the matrix, sorted by their distance from the given center cell. To do this, we can calculate the distance of each cell from the center cell using the Manhattan distance formula: |r1 - r2| + |c1 - c2|.\n# 2.\n# Sort the list of cells based on their distance from the center cell.\n\n# 3.Return the sorted list of cells.\n\nTo implement this approach, we can use a two-dimensional array or a vector of pairs to store the coordinates of each cell in the matrix. We can then calculate the distance of each cell from the center cell using the Manhattan distance formula and store the distance along with the cell coordinates in a vector of pairs. Finally, we can sort the vector of pairs based on the distance and return the sorted list of cell coordinates. Alternatively, we can use a priority queue to store the cell coordinates sorted by distance and return the sorted list of cell coordinates .\n\n```javascript []\nvar allCellsDistOrder = function(rows, cols, rCenter, cCenter) {\n const buckets = [];\n const result = [];\n const maxDist = Math.max(rCenter, rows - 1 - rCenter) + Math.max(cCenter, cols - 1 - cCenter);\n\n for (let i = 0; i <= maxDist; i++) {\n buckets.push([]);\n }\n \n for (let r = 0; r < rows; r++) {\n for (let c = 0; c < cols; c++) {\n const dist = Math.abs(r - rCenter) + Math.abs(c - cCenter);\n buckets[dist].push([r, c]);\n }\n }\n\n for (let i = 0; i <= maxDist; i++) {\n result.push(...buckets[i]);\n }\n \n return result;\n};\n```\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rc, int cc) {\n vector<vector<char>> vis(rows, vector<char>(cols, false));\n vector<vector<int>> dists;\n queue<pair<int, int>> q;\n q.push({rc, cc});\n vis[rc][cc] = true;\n dists.push_back({rc, cc});\n\n while (!q.empty()) {\n auto [x, y] = q.front();\n q.pop();\n for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {\n int nx = x + dX[i];\n int ny = y + dY[i];\n if (nx < 0 || nx >= rows || ny < 0 || ny >= cols || vis[nx][ny]) continue;\n q.push({nx, ny});\n vis[nx][ny] = true;\n dists.push_back({nx, ny});\n }\n }\n\n return dists;\n }\nprivate:\n const int dX[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0};\n const int dY[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};\n};\n```\n```C# []\npublic class Solution {\n private readonly int[] dX = {-1, 0, 1, 0};\n private readonly int[] dY = {0, 1, 0, -1};\n \n public int[][] AllCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n var vis = new bool[rows][];\n for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {\n vis[i] = new bool[cols];\n }\n \n var dists = new List<int[]>();\n var q = new Queue<int[]>();\n q.Enqueue(new int[] {rCenter, cCenter});\n vis[rCenter][cCenter] = true;\n dists.Add(new int[] {rCenter, cCenter});\n\n while (q.Count > 0) {\n var curr = q.Dequeue();\n int x = curr[0], y = curr[1];\n for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {\n int nx = x + dX[i];\n int ny = y + dY[i];\n if (nx < 0 || nx >= rows) continue;\n if (ny < 0 || ny >= cols) continue;\n if (vis[nx][ny]) continue;\n q.Enqueue(new int[] {nx, ny});\n vis[nx][ny] = true;\n dists.Add(new int[] {nx, ny});\n }\n }\n\n return dists.ToArray();\n }\n}\n```\n\n\n
| 4 | 0 |
['C++', 'JavaScript', 'C#']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
c++ | bfs | faster than 94.25% with Explanation
|
c-bfs-faster-than-9425-with-explanation-0sf7w
|
let\'s suppose x (in black) as my starting position, the nearest points with distance = 1 are in red, then if we move to red cells, the nearest cells to them ar
|
raoufghrissi96
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-04T21:10:47.206037+00:00
|
2022-09-04T21:12:25.298974+00:00
| 598 | false |
let\'s suppose x (in black) as my starting position, the nearest points with distance = 1 are in red, then if we move to red cells, the nearest cells to them are green cells distance = 1 to reds ans distance = 1 + 1 to black x ... and that\'s the idea to traverse the graph with bfs, don\'t use dfs as it goes in depth and we will losse the order of distance.\n\n\n```\nconst int N = 102;\nbool vis[N][N];\nint dx[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};\nint dy[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};\nint n, m;\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool safe(int i, int j)\n {\n return i>-1 && j>-1 && i<n && j<m; \n }\n \n void bfs(int i, int j, vector<vector<int>> &ans)\n {\n queue<pair<int,int>> q;\n q.push({i, j});\n vis[i][j] = 1;\n vector<int> pt(2);\n pt[0]=i;\n pt[1]=j;\n ans.push_back(pt);\n \n while(!q.empty())\n {\n auto p = q.front();\n q.pop();\n int pi = p.first;\n int pj = p.second;\n \n for (int d=0 ; d<4 ; d++)\n {\n int ci = pi + dx[d];\n int cj = pj + dy[d];\n if (safe(ci, cj) && !vis[ci][cj])\n {\n vis[ci][cj] = 1;\n q.push({ci, cj});\n pt[0]=ci;\n pt[1]=cj;\n ans.push_back(pt);\n }\n }\n }\n }\n \n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int r, int c, int x, int y) \n {\n memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));\n vector<vector<int>> ans;\n n=r;\n m=c;\n bfs(x, y, ans);\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Breadth-First Search', 'Sorting']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
✅C++ || Logic Explained || Simple Logic
|
c-logic-explained-simple-logic-by-abhina-lqjz
|
\n\nLogic -> Distance of (i,j) from (rCen,cCen) == Distance of (rCen,cCen) from (i,j)\n\nn==size of map\nT->O(r * c) && S->O(n)\n\n\tclass Solution {\n\tpublic:
|
abhinav_0107
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-13T09:01:42.808982+00:00
|
2022-07-13T09:03:30.920325+00:00
| 611 | false |
\n\n***Logic -> Distance of (i,j) from (rCen,cCen) == Distance of (rCen,cCen) from (i,j)***\n\n**n==size of map\nT->O(r * c) && S->O(n)**\n\n\tclass Solution {\n\tpublic:\n\t\tvector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int r, int c, int rCen, int cCen) {\n\t\t\tvector<vector<int>>ans;\n\t\t\tmap<int,vector<vector<int>>>mp;\n\t\t\tfor(int i=0;i<r;i++){\n\t\t\t\tfor(int j=0;j<c;j++){\n\t\t\t\t\tint dis=abs(i-rCen)+abs(j-cCen);\n\t\t\t\t\tmp[dis].push_back({i,j});\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\tfor(auto i:mp){\n\t\t\t\tfor(auto j:i.second) ans.push_back(j);\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\treturn ans;\n\t\t}\n\t};
| 4 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Python3 simple solution using dictionary
|
python3-simple-solution-using-dictionary-06tk
|
\nclass Solution:\n def allCellsDistOrder(self, R: int, C: int, r0: int, c0: int) -> List[List[int]]:\n d = {}\n for i in range(R):\n
|
EklavyaJoshi
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-11T04:33:33.643198+00:00
|
2021-05-11T04:33:33.643242+00:00
| 223 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def allCellsDistOrder(self, R: int, C: int, r0: int, c0: int) -> List[List[int]]:\n d = {}\n for i in range(R):\n for j in range(C):\n d[(i,j)] = d.get((i,j),0) + abs(r0-i) + abs(c0-j)\n return [list(i) for i,j in sorted(d.items(), key = lambda x : x[1])]\n```\n**If you like this solution, please upvote for this**
| 4 | 1 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Solution in Python 3 (one line) (beats ~90%)
|
solution-in-python-3-one-line-beats-90-b-9s23
|
```\nclass Solution:\n def allCellsDistOrder(self, R: int, C: int, r: int, c: int) -> List[List[int]]:\n \treturn sorted([[i,j] for i in range(R) for j in
|
junaidmansuri
|
NORMAL
|
2019-09-15T08:13:10.976729+00:00
|
2019-09-15T08:15:23.594637+00:00
| 433 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def allCellsDistOrder(self, R: int, C: int, r: int, c: int) -> List[List[int]]:\n \treturn sorted([[i,j] for i in range(R) for j in range(C)], key = lambda y: abs(y[0]-r)+abs(y[1]-c))\n\t\t\n\t\t\n- Junaid Mansuri\n(LeetCode ID)@hotmail.com
| 4 | 2 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Simple Solution || Using Multimap || Without comparator
|
simple-solution-using-multimap-without-c-5bau
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n int i, j, dis = 0;\n
|
Divyanshu_Kaintura
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-23T17:42:55.224124+00:00
|
2024-01-23T17:42:55.224154+00:00
| 455 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n int i, j, dis = 0;\n multimap<int, vector<int>> mp;\n for (i = 0; i < rows; i++) \n {\n for (j = 0; j < cols; j++) \n {\n vector<int> temp;\n dis = abs(i - rCenter) + abs(j - cCenter);\n temp.push_back(i);\n temp.push_back(j);\n mp.insert(pair<int, vector<int>>(dis, temp));\n }\n }\n\n // converting multimap into a 2d vector\n vector<vector<int>> ans;\n for (auto x: mp)\n {\n ans.push_back(x.second);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
JAVA easy solution using comparator
|
java-easy-solution-using-comparator-by-2-jrag
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n int a[][]=new int[rows*cols][2];//for storing
|
21Arka2002
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-25T07:26:32.117806+00:00
|
2022-09-25T07:26:32.117839+00:00
| 937 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n int a[][]=new int[rows*cols][2];//for storing coordinates\n int k=0;\n for(int i=0;i<rows;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<cols;j++)\n {\n a[k][0]=i;\n a[k][1]=j;\n k+=1;\n }\n }\n Arrays.sort(a,new Comparator<int[]>()\n {\n @Override\n public int compare(int a[],int b[])\n {\n int d1=(int)Math.abs(a[0]-rCenter)+(int)Math.abs(a[1]-cCenter);//distance of first point\n int d2=(int)Math.abs(b[0]-rCenter)+(int)Math.abs(b[1]-cCenter);//distance of second point\n if(d1>d2)return 1;\n else if(d1<d2)return -1;\n else return 0;\n }\n });\n return a;\n \n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
JavaScript: simple solution
|
javascript-simple-solution-by-sdi-8ph4
|
\nvar allCellsDistOrder = function(rows, cols, r, c) {\n let res = [];\n\t// add all cells\n for (let i = 0; i<rows; i++) {\n for (let j = 0; j<col
|
SDI
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-18T13:55:46.208723+00:00
|
2022-04-18T13:55:46.208765+00:00
| 235 | false |
```\nvar allCellsDistOrder = function(rows, cols, r, c) {\n let res = [];\n\t// add all cells\n for (let i = 0; i<rows; i++) {\n for (let j = 0; j<cols; j++)\n res.push([i, j]);\n }\n\t// sort cells by distance\n res.sort((a, b)=>Math.abs(r-a[0]) + Math.abs(c-a[1]) - Math.abs(r-b[0]) - Math.abs(c-b[1]));\n return res;\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Simple approach | C++
|
simple-approach-c-by-tusharbhart-0ouh
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n static bool cmp(vector<int> a, vector<int> b){\n return a[0] < b[0];\n }\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(i
|
TusharBhart
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-24T15:59:56.701918+00:00
|
2022-02-24T15:59:56.701961+00:00
| 356 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n static bool cmp(vector<int> a, vector<int> b){\n return a[0] < b[0];\n }\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n vector<vector<int>> v;\n for(int i=0; i<rows; i++){\n for(int j=0; j<cols; j++){\n int d = abs(i - rCenter) + abs(j - cCenter);\n v.push_back({d, i, j});\n }\n }\n \n sort(v.begin(), v.end(), cmp);\n for(vector<int> &i : v) i.erase(i.begin());\n\n return v;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
JAVA || Comparator || Easy to understand
|
java-comparator-easy-to-understand-by-ig-lwo4
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r, int c) {\n int index = 0;\n int[][] result = new int[R*C][2];\n
|
Igloo11
|
NORMAL
|
2021-01-06T12:26:05.336766+00:00
|
2021-01-06T12:26:05.336793+00:00
| 368 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r, int c) {\n int index = 0;\n int[][] result = new int[R*C][2];\n \n for(int i = 0; i < R; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < C; j++){\n result[index][0] = i;\n result[index][1] = j;\n index++;\n }\n }\n \n Arrays.sort(result, (a, b)-> \n (Math.abs(r-a[0])+Math.abs(c-a[1])) - (Math.abs(r-b[0])+Math.abs(c-b[1]))\n );\n \n return result;\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Straightforward Java BST
|
straightforward-java-bst-by-bamboowind-h02t
|
\nclass Solution {\n int[][] dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};\n \n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n
|
bamboowind
|
NORMAL
|
2019-05-15T14:28:20.761311+00:00
|
2019-05-15T14:28:20.761353+00:00
| 242 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n int[][] dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};\n \n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n int[][] res = new int[R * C][2];\n boolean[][] visited = new boolean[R][C]; \n visited[r0][c0] = true;\n Queue<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();\n queue.offer(new int[]{r0, c0});\n int i = 0;\n while (!queue.isEmpty()) {\n int[] cur = queue.poll();\n res[i][0] = cur[0];\n res[i++][1] = cur[1];\n for (int[] dir : dirs) {\n int row = cur[0] + dir[0];\n int col = cur[1] + dir[1];\n if (row >= 0 && row < R && col >= 0 && col < C && !visited[row][col]) {\n visited[row][col] = true;\n queue.offer(new int[]{row, col});\n }\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Python 3 solution with dict, beats 100%
|
python-3-solution-with-dict-beats-100-by-oenw
|
The idea is to use distances as a dict key. Then get the cells by looping through the dict keys.\n\n\nfrom collections import defaultdict\n\nclass Solution:\n
|
amosipov
|
NORMAL
|
2019-05-04T19:48:19.330231+00:00
|
2019-05-12T21:32:38.989234+00:00
| 465 | false |
The idea is to use distances as a dict key. Then get the cells by looping through the dict keys.\n\n```\nfrom collections import defaultdict\n\nclass Solution:\n def allCellsDistOrder(self, R: int, C: int, r0: int, c0: int) -> List[List[int]]:\n i = 0\n dist = defaultdict(list)\n \n while i < R:\n j = 0\n while j < C:\n d = abs(r0 - i) + abs(c0 - j)\n dist[d].append((i,j))\n j += 1\n i += 1\n \n i = 0\n res = []\n while i <= (R + C):\n if i in dist:\n res += dist[i]\n i += 1\n \n return res\n```
| 3 | 1 |
['Python']
| 1 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Python2 and Python3, both One-Liner and Difference!
|
python2-and-python3-both-one-liner-and-d-xegr
|
I found the PEEP3113 saying that Python3 remove the tuple parameter unpacking. \nhttps://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-3113/#no-loss-of-abilities-if-removed\n\nSo
|
firman7777
|
NORMAL
|
2019-04-27T07:12:22.880373+00:00
|
2019-04-27T07:12:22.880434+00:00
| 321 | false |
I found the `PEEP3113` saying that Python3 remove the tuple parameter unpacking. \nhttps://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-3113/#no-loss-of-abilities-if-removed\n\nSo there are slight difference between Py2 and Py3 answer:\n* Python2:\n```return sorted([[x, y] for x in range(R) for y in range(C)], key=lambda (r, c): abs(r - r0) + abs(c - c0))```\n\n* Python 3:\n```return sorted([(i, j) for i in range(R) for j in range(C)], key=lambda x: abs(x[0] - r0) + abs(x[1] - c0))```\n\n\n\t\tPy2 tuple: lambda (x, y): x + y \n\t\twill be translate into Py3: lambda x_y: x_y[0] + x_y[1]\n\nThank you for reading this.
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
C# BFS
|
c-bfs-by-xiaonangeo-m2n9
|
BFS, output by each level during traverse, O(R*C).\n\n\npublic int[][] AllCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n List<int[]> res=new List<int[]
|
xiaonangeo
|
NORMAL
|
2019-04-21T04:23:17.122966+00:00
|
2019-04-21T04:23:17.123007+00:00
| 195 | false |
BFS, output by each level during traverse, O(R*C).\n\n``` \npublic int[][] AllCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n List<int[]> res=new List<int[]>();\n Queue<int[]> q=new Queue<int[]>();\n int[,] visited=new int[R,C];\n \n q.Enqueue(new int[]{r0,c0});\n visited[r0,c0]=1;\n while(q.Count>0){\n int[] current=q.Dequeue();\n res.Add(current);\n enqueue(R,C,current[0]-1,current[1], visited,q);\n enqueue(R,C,current[0]+1,current[1],visited,q);\n enqueue(R,C,current[0],current[1]-1,visited,q);\n enqueue(R,C,current[0],current[1]+1,visited,q); \n }\n return res.ToArray();\n }\n \n public void enqueue(int R, int C, int i,int j, int[,] visited, Queue<int[]> q){\n if(i>=0&&i<R&&j>=0&&j<C&&visited[i,j]==0){\n q.Enqueue(new int[]{i,j});\n visited[i,j]=1;\n }\n }\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Breadth-First Search']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
🚀 Optimized Approach to Sort Grid Cells by Distance || C++ || Sorting
|
optimized-approach-to-sort-grid-cells-by-i3i4
|
💡IntuitionThe intuition was to find the distance of all the cells from the given rCenter and cCenter and then sort the cells according to their distances.🧪 Appr
|
deep_soumya617
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-07T15:37:46.976764+00:00
|
2025-03-07T15:37:46.976764+00:00
| 114 | false |
# 💡Intuition
The intuition was to find the **distance of all the cells from the given rCenter and cCenter and then sort the cells** according to their distances.
---
# 🧪 Approach
- I took a 2D vector ans to store the final answer and a vector v of `pair<int, pair<int, int>>` to store the `distance` and the corresponding `row` and `column` number.
- So basically, while we traverse the matrix of `rows * col` size, `v.first` stores the distance of the current cell from `rCenter` & `cCenter`.`v.second.first` store the row number and `v.second.second` stores the column number.
- Then we sort the elements of the vector `v` according to their first element i.e `distances`.
- At the end, we traverse the vector `v` and push the `row` number and `col` number in a sorted order.
---
# ⌛📦 Complexity
- Time complexity: `O(nlogn)` or `O((rows×cols)log(rows×cols))`
- Space complexity: `O(rows*cols)`
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rc, int cc) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<pair<int, pair<int, int>>> v;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {
int distance = abs(i - rc) + abs(j - cc);
v.push_back({distance, {i, j}});
}
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i) {
ans.push_back({v[i].second.first, v[i].second.second});
}
return ans;
}
};
```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Sorting', 'Matrix', 'C++']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
C# Sorting with Linq
|
c-sorting-with-linq-by-ilya-a-f-m559
|
csharp\npublic class Solution\n{\n public int[][] AllCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) =>\n [..\n from row in Enumerable
|
ilya-a-f
|
NORMAL
|
2024-05-01T10:28:09.130753+00:00
|
2024-05-01T10:28:09.130775+00:00
| 30 | false |
```csharp\npublic class Solution\n{\n public int[][] AllCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) =>\n [..\n from row in Enumerable.Range(0, rows)\n from col in Enumerable.Range(0, cols)\n orderby int.Abs(row - rCenter) + int.Abs(col - cCenter)\n select new[] { row, col }\n ];\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Sorting', 'C#']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Very Easy JAVA Soln | Brute Force
|
very-easy-java-soln-brute-force-by-sumo2-wuwa
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n int[][] ans=new int[rows*cols][2];
|
sumo25
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-13T07:44:51.797791+00:00
|
2024-02-13T07:44:51.797824+00:00
| 686 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n int[][] ans=new int[rows*cols][2];\n int idx=0;\n for(int i=0;i<rows;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<cols;j++){\n ans[idx][0]=i;\n ans[idx++][1]=j;\n }\n }\n\n Arrays.sort(ans,new Comparator<int[]>(){\n public int compare(int[] a,int[] b){\n int x=Math.abs(a[0]-rCenter)+Math.abs(a[1]-cCenter);\n int y=Math.abs(b[0]-rCenter)+Math.abs(b[1]-cCenter);\n return x-y;\n }\n });\n\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Sorting', 'Java']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
One Line Python3 Solution
|
one-line-python3-solution-by-aimilios-g4m0
|
Intuition\nIterate through all the point in matrix, get the distance from the Center Point, and then sort by the distance\n\n# Approach\nA simpler code is this
|
Aimilios
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-06T14:42:32.151415+00:00
|
2024-02-06T14:42:32.151446+00:00
| 248 | false |
# Intuition\nIterate through all the point in matrix, get the distance from the Center Point, and then sort by the distance\n\n# Approach\nA simpler code is this:\n\n- Define a lambda function to calculate the Manhattan distance between a point and the center point\n\n```\ndist = lambda point: abs(point[0] - rCenter) + abs(point[1] - cCenter)\n```\n\n- Generate a list containing all possible combinations of row and column indices within the matrix\n```\nindices = [[r,c] for r in range(rows) for c in range(cols)]\n```\n\n- Sort the list of indices based on their distances from the center using the dist function as the key\n```\nsorted_indices = sorted(indices, key=dist)\n```\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def allCellsDistOrder(self, rows: int, cols: int, rCenter: int, cCenter: int) -> List[List[int]]:\n return sorted([[r,c] for r in range(rows) for c in range(cols)], key=lambda point: abs(point[0] - rCenter) + abs(point[1] - cCenter))\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Brute force O(n log(n)) approach
|
brute-force-on-logn-approach-by-kedarnat-vym7
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
kedarnathpc
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-18T11:08:12.556428+00:00
|
2024-01-18T11:08:12.556469+00:00
| 283 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(nlog(n) + rows*cols)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(row * cols)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n vector<vector<int>> ans;\n vector<pair<int, pair<int,int>>> v;\n\n for(int i = 0; i < rows; ++i){\n for(int j = 0; j < cols; ++j){\n v.push_back({abs(i - rCenter) + abs(j - cCenter), {i, j}});\n }\n }\n\n sort(v.begin(), v.end());\n\n for(auto &i : v){\n ans.push_back({i.second.first, i.second.second});\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Sorting', 'C++']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Quite easily done
|
quite-easily-done-by-sy1392790-qt3e
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \ncreate an array with the values from 0 to max value, where max value is the addition va
|
sy1392790
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-01T09:21:28.844321+00:00
|
2024-01-01T09:21:28.844368+00:00
| 211 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\ncreate an array with the values from 0 to max value, where max value is the addition value obtained after performing subtraction between row and column indices.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(N^4)\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(2*N^2)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n int [][] arr = new int[rows][cols];\n int num=0;\n \n //filling values inside the array\n for(int i=0 ; i<rows ; i++){\n for(int j=0 ; j<cols ; j++){\n arr[i][j]=Math.abs(i-rCenter)+Math.abs(j-cCenter);\n }\n }\n int max=arr[0][0];\n //finding the maximum value in the array\n for(int i=0 ; i<arr.length ; i++){\n for(int j=0 ; j<arr[0].length ; j++){\n if(arr[i][j]>max){\n max=arr[i][j];\n }\n }\n }\n int [][] rvalue = new int[rows*cols][2];\n int index=0;\n while(num<=max){\n for(int l=0 ; l<arr.length ; l++){\n for(int m=0 ; m<arr[0].length ; m++){\n if(arr[l][m]==num){\n rvalue[index][0]=l;\n rvalue[index][1]=m;\n index++;\n }\n \n }\n }\n num++;\n }\n return rvalue;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 2 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Beginner Brute force solution using sorting.
|
beginner-brute-force-solution-using-sort-fu16
|
Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n1. In STEP-1 we fill the array sequentially i.e., giving the elements indexes like that of a 2D arra
|
AayushThakur21
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-17T14:12:57.335367+00:00
|
2023-11-17T14:12:57.335388+00:00
| 349 | false |
# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. In <b>STEP-1</b> we fill the array sequentially i.e., giving the elements indexes like that of a 2D array :-> \n ```\n (0,0) (0,1) (0,2)\n (1,0) (1,1) (1,2)\n (2,0) (2,1) (2,2)\n\n2. After this we sort the array in STEP-2 on the basis of the distance between the cells from :->\n ```\n (rCenter, cCenter)\n ```\n3. If the <b>j<sup>th</sup></b> cell distance from (rCenter,cCenter) which is measured using \n ```\n |r1 - rCenter| + |c1 - cCenter|\n ```\n is lesser than <b>(j-1)<sup>th</sup></b> cell distance from (rCenter,cCenter), we swap the two arrays i.e., bring the array which is closer to (rCenter, cCenter) forward.\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$ O(m*n) $$\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$ O(m*n) $$\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n int[][] arr = new int[rows*cols][2];\n // variable to traverse through the array\n int cntr = 0;\n // STEP-1\n for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++){\n arr[cntr][0] = i;\n arr[cntr++][1] = j;\n } \n }\n // STEP-2\n insertionSort(arr, rCenter, cCenter);\n return arr;\n }\n\n public void insertionSort(int[][] arr, int rC, int cC){\n for(int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++){\n for(int j = i + 1; j > 0; j--){\n // STEP-3\n if((Math.abs(arr[j][0] - rC) + Math.abs(arr[j][1] - cC)) < (Math.abs(arr[j - 1][0] - rC) + Math.abs(arr[j - 1][1] - cC))){\n swap(arr, j, j - 1);\n }\n }\n }\n }\n\n public void swap(int[][] arr, int n1, int n2){\n int[] temp = arr[n1];\n arr[n1] = arr[n2];\n arr[n2] = temp;\n }\n}\n```\n\n#### <i>Any improvement or suggestion is welcomed</i> \uD83D\uDE4F\uD83C\uDFFB
| 2 | 0 |
['Sorting', 'Java']
| 1 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Best Java Solution || Beats 100%
|
best-java-solution-beats-100-by-ravikuma-ho4o
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
ravikumar50
|
NORMAL
|
2023-09-24T20:49:39.638930+00:00
|
2023-09-24T20:49:39.638967+00:00
| 635 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n int[][] result = new int[R * C][];\n result[0] = new int[] {r0, c0}; // Add start point r0,c0 which has distance 0.\n int resultIdx = 1;\n int lim = Math.max( r0, R-r0-1 ) + Math.max( c0, C-c0-1 );\n\t\t // lim is highest distance value.\n for (int dist = 1; dist <= lim; dist++) { // Process \'lim\' diamond-shapes having distance \'dist\'.\n int r = r0 - dist;\n int c = c0;\n // Diamond side: Top Left\n for (int count = dist; count > 0; count--) { \n if (r >= 0 && c >= 0) result[resultIdx++] = new int[] {r, c};\n r++;\n c--;\n }\n \n // Diamond side: Left Bottom\n for (int count = dist; count > 0; count--) {\n if (r < R && c >= 0) result[resultIdx++] = new int[] {r, c};\n r++;\n c++;\n }\n \n // Diamond side: Bottom Right\n for (int count = dist; count > 0; count--) {\n if (r < R && c < C) result[resultIdx++] = new int[] {r, c};\n r--;\n c++;\n }\n \n // Diamond side: Right Top\n for (int count = dist; count > 0; count--) {\n if (r >= 0 && c < C) result[resultIdx++] = new int[] {r, c};\n r--;\n c--;\n }\n }\n return result;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Simple BFS Traversal (C++)
|
simple-bfs-traversal-c-by-tanyas1108-xtbg
|
Intuition\n BFS Traversal will help to traverse every cells, and also store the distance along with it.\n\n# Approach\n - Push the center coordinates in queue
|
tanyas1108
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-10T16:30:11.189122+00:00
|
2023-04-10T16:30:28.318879+00:00
| 429 | false |
# Intuition\n BFS Traversal will help to traverse every cells, and also store the distance along with it.\n\n# Approach\n - Push the center coordinates in queue with curr dis = 0;\n - Created a visited array , so that you dont come back to same element again.\n - While queue is not empty\n i) Pop the front and w.r.t to that element check in all 4 directions if cell is not visited , push them in the queue and increase the distance\n ii) Mark cells visited along with that\n\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int r, int c, int a, int b) {\n int visited[r][c];\n for(int i=0;i<r;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<c;j++)\n visited[i][j]=0;\n }\n queue<pair<pair<int,int>, int> >q;\n q.push({{a, b},0 });\n visited[a][b]=1;\n int xdir[4]={1,-1, 0, 0};\n int ydir[4]={0,0, 1,-1};\n vector<pair<int, pair<int,int> > >res;\n vector<vector<int>>coord;\n while(!q.empty())\n {\n auto p = q.front();\n q.pop();\n int x = p.first.first;\n int y = p.first.second;\n int dis = p.second;\n res.push_back({dis,{x, y}});\n for(int k =0;k<=3;k++)\n {\n int xnew = x+xdir[k];\n int ynew = y+ydir[k];\n if(xnew>=0 && xnew<r && ynew>=0 &&ynew<c && visited[xnew][ynew]==0)\n {\n q.push({{xnew, ynew}, dis+1});\n visited[xnew][ynew]=1;\n\n }\n }\n }\n sort(res.begin(), res.end());\n for(int i=0;i<res.size();i++)\n {\n vector<int>temp(2,0);\n temp[0] = res[i].second.first;\n temp[1] = res[i].second.second;\n coord.push_back(temp);\n }\n return coord;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Breadth-First Search', 'C++']
| 1 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
c++ | easy | short
|
c-easy-short-by-venomhighs7-z2vu
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n vector<vector<int>>
|
venomhighs7
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-02T03:57:51.914757+00:00
|
2022-11-02T03:57:51.914806+00:00
| 1,342 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n vector<vector<int>> ans;\n for (int r = 0; r < rows; r++) {\n for (int c = 0; c < cols; c++) {\n ans.push_back({r, c});\n }\n }\n\n sort(ans.begin(), ans.end(), DistFromCenterSorter(rCenter, cCenter));\n return ans;\n }\n\nprivate:\n struct DistFromCenterSorter {\n int rCenter;\n int cCenter;\n DistFromCenterSorter(int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n this->rCenter = rCenter;\n this->cCenter = cCenter;\n }\n\n bool operator()(const vector<int>& cell1, const vector<int>& cell2) {\n return distFromCenter(cell1) < distFromCenter(cell2);\n }\n\n int distFromCenter(const vector<int>& cell) {\n return abs(cell[0] - this->rCenter) + abs(cell[1] - this->cCenter);\n }\n };\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Java solution using record & stream
|
java-solution-using-record-stream-by-fll-0nq5
|
\npublic int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n List<Cell> cells = new ArrayList<>();\n\n for (int row = 0; r
|
FLlGHT
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-17T11:52:37.619262+00:00
|
2022-10-17T11:52:37.619305+00:00
| 885 | false |
```\npublic int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n List<Cell> cells = new ArrayList<>();\n\n for (int row = 0; row < rows; ++row)\n for (int column = 0; column < cols; ++column)\n cells.add(new Cell(row, column, Math.abs(row - rCenter) + Math.abs(column - cCenter)));\n\n return cells.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Cell::distance)).map(cell -> new int[]{cell.row(), cell.column()}).toArray(int[][]::new);\n }\n\n private record Cell(int row, int column, int distance) {}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Matrix Cells in Distance Order
|
matrix-cells-in-distance-order-by-ayushi-r5ps
|
class Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n int[][] arr=new int[rows*cols][2];\n for(
|
Ayushi98
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-14T05:29:58.002619+00:00
|
2022-08-14T05:29:58.002673+00:00
| 408 | false |
class Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n int[][] arr=new int[rows*cols][2];\n for(int i=0;i<rows;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<cols;j++){\n int idx=i*cols+j;\n arr[idx][0]=i;\n arr[idx][1]=j;\n }\n }\n Arrays.sort(arr,(a,b)->{\n int d1=Math.abs(a[0]-rCenter)+Math.abs(a[1]-cCenter);\n int d2=Math.abs(b[0]-rCenter)+Math.abs(b[1]-cCenter);\n return d1-d2;\n });\n return arr;\n }\n}
| 2 | 0 |
['Sorting', 'Java']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Python | BFS | O(mn)
|
python-bfs-omn-by-aryonbe-jemw
|
```\nfrom collections import deque\nclass Solution:\n def allCellsDistOrder(self, rows: int, cols: int, rCenter: int, cCenter: int) -> List[List[int]]:\n
|
aryonbe
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-13T13:58:37.658079+00:00
|
2022-07-13T13:58:37.658129+00:00
| 226 | false |
```\nfrom collections import deque\nclass Solution:\n def allCellsDistOrder(self, rows: int, cols: int, rCenter: int, cCenter: int) -> List[List[int]]:\n que = deque([(rCenter,cCenter)])\n visited = set()\n res = []\n while que:\n r,c = que.popleft()\n if (r,c) in visited: continue\n visited.add((r,c))\n res.append([r,c])\n for dr, dc in [[-1,0],[1,0],[0,-1],[0,1]]:\n if 0<=r+dr<rows and 0<=c+dc<cols:\n que.append((r+dr,c+dc))\n return res
| 2 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Using Min Heap Java
|
using-min-heap-java-by-haemogoblin-d3oy
|
Storing pairs of distance and an array containing row and col index in priority queue. Now min heap will automatically sort the pairs according to distance\n\ni
|
Haemogoblin
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-16T16:01:01.543754+00:00
|
2022-02-16T16:01:01.543781+00:00
| 280 | false |
Storing pairs of distance and an array containing row and col index in priority queue. Now min heap will automatically sort the pairs according to distance\n```\nimport java.util.PriorityQueue;\n\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCentre, int cCentre) {\n\n PriorityQueue<Pair<Integer, int[]>> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(rows*cols,(a,b) -> a.getKey() - b.getKey());\n int[][] ans = new int[rows*cols][];\n\n Integer dist;\n\n for(int i=0;i<rows;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<cols;j++){\n dist = Math.abs(rCentre-i) + Math.abs(cCentre-j);\n pq.add(new Pair<Integer, int[]>(dist, new int[]{i,j}));\n }\n }\n\n int i=0;\n while(!pq.isEmpty()){\n ans[i] = pq.poll().getValue();\n i++;\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Heap (Priority Queue)', 'Java']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
C++ solution 90% solution
|
c-solution-90-solution-by-itsayush-96ye
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n vector<pair<int,pair<int,int>>>
|
itsayush__
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-27T13:16:34.087872+00:00
|
2022-01-27T13:16:34.087917+00:00
| 125 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n vector<pair<int,pair<int,int>>> v;\n for(int i=0;i<rows;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<cols;j++){\n int dist=abs(i-rCenter) + abs(j-cCenter);\n v.push_back(make_pair(dist,make_pair(i,j)));\n }\n }\n sort(v.begin(),v.end());\n vector<vector<int>> vect(rows*cols, vector<int> (2,0));\n for(int i=0;i<v.size();i++){\n vect[i][0]=(v[i].second.first);\n vect[i][1]=(v[i].second.second);\n }\n return vect;\n }\n};\n```\nPlease upvote!
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Java, Sort based on distance array
|
java-sort-based-on-distance-array-by-stu-oqhm
|
This question description can use some improvement imo, but we just have to compute a distance array and sort all the index pairs based on that. This is likely
|
Student2091
|
NORMAL
|
2021-12-19T22:01:17.162657+00:00
|
2021-12-19T22:01:17.162696+00:00
| 349 | false |
This question description can use some improvement imo, but we just have to compute a distance array and sort all the index pairs based on that. This is likely the most straight forward solution. Another solution would be based on BFS, which I won\'t explore here as other posters have posted them.\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n int[][] dist = new int[rows][cols];\n int[][] ans = new int[rows * cols][2];\n for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++){\n for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++){\n dist[i][j] = Math.abs(i - rCenter) + Math.abs(j - cCenter); //dist\n ans[i * cols + j] = new int[]{i, j}; //add all the index pairs\n }\n }\n\n Arrays.sort(ans, Comparator.comparingInt(o -> dist[o[0]][o[1]])); //sort based on dist\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Sorting', 'Java']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
C++ | Using vector of pair | Simple approach
|
c-using-vector-of-pair-simple-approach-b-rltb
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n vector<pair<int,vector<int>>>
|
mrankur801
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-19T17:33:37.638411+00:00
|
2021-11-19T17:33:37.638453+00:00
| 329 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int rows, int cols, int rCenter, int cCenter) {\n vector<pair<int,vector<int>>> pr; \n for(int i=0; i<rows; i++){\n for(int j=0; j< cols; j++){\n int d = abs(rCenter-i) + abs(cCenter - j);\n vector<int>temp;\n temp.push_back(i);\n temp.push_back(j);\n pr.push_back(make_pair(d,temp));\n }\n }\n \n sort(pr.begin(), pr.end());\n vector<vector<int>> ans;\n \n for(int i=0; i<pr.size(); i++){\n ans.push_back(pr[i].second);\n }\n return ans;\n \n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 1 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
C++ BFS - Time: O(R*C) - Faster than 96.74%
|
c-bfs-time-orc-faster-than-9674-by-jhonr-buds
|
We just have to run BFS algorithm starting at (r0, c0).\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0)
|
jhonrayo
|
NORMAL
|
2021-04-12T21:04:13.041086+00:00
|
2021-04-12T21:19:21.197003+00:00
| 148 | false |
We just have to run BFS algorithm starting at (r0, c0).\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n vector<vector<int>> m;\n m.reserve(R * C);\n \n queue<pair<int, int>> q;\n \n q.push({r0, c0});\n bool v [100][100];\n memset(v, 0, sizeof(v));\n v[r0][c0] = true;\n \n pair<int, int> n[4] = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};\n\n while (!q.empty()) {\n pair<int, int> u = q.front();\n q.pop();\n\n m.push_back({u.first, u.second});\n \n for (const auto& p: n) {\n auto w = make_pair(u.first + p.first, u.second + p.second);\n if (w.first >= 0 && w.first < R && w.second >= 0 && w.second < C && !v[w.first][w.second]) {\n v[w.first][w.second] = true;\n q.push({w.first, w.second});\n }\n }\n }\n \n return m;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 1 |
['Breadth-First Search', 'C']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
C# easy to understand
|
c-easy-to-understand-by-luantt87-i75p
|
\n\n\t\tpublic class Solution {\n\t\t\n\t\tpublic int[][] AllCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) { \n List cells=new List();\n for
|
luantt87
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-27T21:41:39.421186+00:00
|
2020-08-27T21:42:35.886252+00:00
| 85 | false |
\n\n\t\tpublic class Solution {\n\t\t\n\t\tpublic int[][] AllCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) { \n List<cell> cells=new List<cell>();\n for(int i=0; i<R; i++){ \n for(int j=0;j<C; j++){\n var c=new cell(){x=i,y=j, dis=Math.Abs(i-r0)+ Math.Abs(j-c0)};\n cells.Add(c);\n }\n }\n return cells.OrderBy(t=>t.dis).Select(t=> new int[]{t.x,t.y}).ToArray();\n }\n\t}\n\tpublic class cell{\n public int x;\n public int y;\n public int dis;\n\t }
| 2 | 1 |
[]
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Java Arrays.sort() solution with Comparator
|
java-arrayssort-solution-with-comparator-y4mc
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n int[][] res = new int[R * C][2];\n int count = 0;\n
|
squidimenz
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-19T01:13:56.379253+00:00
|
2020-08-19T01:13:56.379309+00:00
| 245 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int[][] allCellsDistOrder(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {\n int[][] res = new int[R * C][2];\n int count = 0;\n \n for(int i = 0; i < R; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < C; j++) res[count++] = new int[]{i, j};\n }\n \n Arrays.sort(res, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> \n Math.abs(a[0] - r0) + Math.abs(a[1] - c0)));\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Ruby solution: 2 loops, sort and map.
|
ruby-solution-2-loops-sort-and-map-by-us-y1eb
|
Leetcode: 1030. Matrix Cells in Distance Order.\n\nAlgorithm of this solution: \n- Iterate all cells of a matrix in two loops, first loop is external second is
|
user9697n
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-01T18:55:48.282893+00:00
|
2020-08-01T18:55:48.282936+00:00
| 59 | false |
##### Leetcode: 1030. Matrix Cells in Distance Order.\n\nAlgorithm of this solution: \n- Iterate all cells of a matrix in two loops, first loop is external second is nested.\n- During iteration fill array with parks, cell coordinates and distance from input cell.\n- Sort array by second element of a pair.\n- Map array to leave only cell coordinate as an element of the array.\n- Return this array as result.\n\nRuby code:\n```Ruby\n# Leetcode: 1030. Matrix Cells in Distance Order.\n# https://leetcode.com/problems/matrix-cells-in-distance-order/\n# Runtime: 208 ms, faster than 50.00% of Ruby online submissions for Matrix Cells in Distance Order.\n# Memory Usage: 14.3 MB, less than 50.00% of Ruby online submissions for Matrix Cells in Distance Order.\n# @param {Integer} r\n# @param {Integer} c\n# @param {Integer} r0\n# @param {Integer} c0\n# @return {Integer[][]}\ndef all_cells_dist_order(r, c, r0, c0)\n array = []\n (0...r).each do |row|\n (0...c).each do |cell|\n array.push([[row,cell], (row-r0).abs + (cell-c0).abs])\n end\n end\n array.sort_by(&:last).map(&:first)\nend\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Ruby']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Custom sorting indices in Python3
|
custom-sorting-indices-in-python3-by-bri-zprv
|
We can create a custom sort to order pairs of indices in the array by \'Manhattan distance\' from (r0, c0).\n\n\nclass Solution:\n def allCellsDistOrder(self
|
brightglow
|
NORMAL
|
2020-07-27T01:27:34.439788+00:00
|
2020-07-27T01:29:12.237389+00:00
| 150 | false |
We can create a custom sort to order pairs of indices in the array by \'Manhattan distance\' from (r0, c0).\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def allCellsDistOrder(self, R: int, C: int, r0: int, c0: int):\n def f(pair):\n return abs(r0 - pair[0]) + abs(c0 - pair[1]) #returns distance from (r0, c0)\n return sorted([[i,j] for i in range(R) for j in range(C)], key = f) #sorts result by distance\n```\n\nThis ensures our resulting array is sorted via distance from (r0, c0).
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Sorting', 'Python3']
| 0 |
matrix-cells-in-distance-order
|
Swift - Short and easy with sorted(), but slow. 100% memory
|
swift-short-and-easy-with-sorted-but-slo-eq6y
|
\n func allCellsDistOrder(_ R: Int, _ C: Int, _ r0: Int, _ c0: Int) -> [[Int]] {\n var grid = [[Int]]()\n for i in 0..<R {\n for j i
|
cydonian
|
NORMAL
|
2020-07-11T23:01:35.602083+00:00
|
2020-07-11T23:05:42.608902+00:00
| 62 | false |
```\n func allCellsDistOrder(_ R: Int, _ C: Int, _ r0: Int, _ c0: Int) -> [[Int]] {\n var grid = [[Int]]()\n for i in 0..<R {\n for j in 0..<C {\n grid.append([i, j])\n }\n }\n \n return grid.sorted { abs(r0 - $0[0]) + abs(c0 - $0[1]) < abs(r0 - $1[0]) + abs(c0 - $1[1]) }\n }\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.