question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
simple and easy C++ solution || Hash Table
|
simple-and-easy-c-solution-hash-table-by-jtzw
|
if it\'s help, please up \u2B06 vote! \u2764\uFE0F\n###### Let\'s Connect on Linkedin: www.linkedin.com/in/shishirrsiam\n\n\n\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\
|
shishirRsiam
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T06:01:07.460172+00:00
|
2024-10-28T06:01:07.460199+00:00
| 185 | false |
# if it\'s help, please up \u2B06 vote! \u2764\uFE0F\n###### Let\'s Connect on Linkedin: www.linkedin.com/in/shishirrsiam\n\n\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) \n {\n set<int>st;\n int maxValue = 1e5 + 5;\n unordered_set<int>values(begin(nums), end(nums));\n for(int i = 1; i * i <= maxValue; i++)\n {\n if(values.count(i)) st.insert(i);\n if(values.count(i * i)) st.insert(i * i);\n }\n\n vector<int>store(begin(st), end(st));\n int ans = 1, count = 1, n = store.size();\n\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n count = 1;\n int val = store[i];\n for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)\n {\n if((long(val) * val) > 2e5) break;\n if(val * val == store[j])\n {\n count += 1;\n val = store[j];\n }\n }\n ans = max(ans, count);\n }\n\n return ans == 1 ? -1 : ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Sorting', 'C++']
| 5 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Unordered set ! O(n) easy to understand approach for substring size questions C++
|
unordered-set-on-easy-to-understand-appr-42fd
|
Intuition\nsubstring problems just call the inner hash user in me. \nPS:idk bitset yet \n\n# Approach\n- Create a unordered set from the input vector/array.\n-
|
GitClown
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T05:58:17.375884+00:00
|
2024-10-28T12:54:34.963665+00:00
| 82 | false |
# Intuition\nsubstring problems just call the inner hash user in me. \nPS:idk bitset yet \n\n# Approach\n- Create a unordered set from the input vector/array.\n- iteratively find strings in the vector by checking if the square of it exists in hash/unordered set.\n- We can use the check before the while loop to check if its the start of substring like *sqrt of i dosnt exist in unordered set* which can be useful when the substring can go to a very high no. unlike the max 5 length here.\n- even Long long cant keep squares of 10^5 even when its limit is 10^18 so we just stopped when k goes outside the limit 10^5 of a single element. PS: can lmk in comments if you know how would 10^5^2 goes more than long long int size ??\n\n# Complexity\n\n- ##### Time complexity:\n O(n)\n *still gotta calc the TC of that inner while loop*\n\n- ##### Space complexity:\n O(n)\n\n### Pls consider upvoting if it helped !! kinda new to this\nThanks for all the views !! if theres any suggestion do lmk, will give proper time for writing solutions with detailed intuition and approaches next time i do :0\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {\n unordered_set<int> numSet(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n\n int maxStreakLength = 0;\n\n for (int num : nums) {\n int streakLength = 0;\n\n long long currentNum = num;\n\n while (numSet.count(currentNum)) \n {\n streakLength++;\n currentNum = currentNum * currentNum; \n if (currentNum > 100000) break; //bcz the element value cannot be more than 10^5 so :0\n }\n\n maxStreakLength = max(streakLength, maxStreakLength);\n\n }\n\n return (maxStreakLength > 1) ? maxStreakLength : -1;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'C++']
| 2 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
C solution
|
c-solution-by-csld-hp31
|
Solution\nGood day, let\u2019s tease our brain.\n\nSo the problem asks us to find the maxinum subsequence that does not necessarily need to be adjacent. Moreove
|
csld
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T05:56:38.206279+00:00
|
2024-10-28T06:04:34.072157+00:00
| 88 | false |
# Solution\nGood day, let\u2019s tease our brain.\n\nSo the problem asks us to find the maxinum subsequence that does not necessarily need to be adjacent. Moreover, the task is to find the given value exist or not. Given these information, fearing that there may be some testcases full of 2, or 1, we shirnk the given nums into a set.\n\nNext, we sort the set, and iterate through every element within. Starting from a given position, we find the maximu strak length we cam obtain from it. The halting condition should be:\n\n1. the square of the current value does not exist in the given set\n2. the current value is greater than the root of the maxmum value $10^5$\n\nAnd for each halting situation, we record the maximum length, compare it to the final answer.\n# Code\n```c []\n#define maxN 100005\n\nint max(int a, int b) { return a > b ? a : b; }\n\nint cmp(const void *a, const void *b) { return *(int *)a - *(int *)b; }\n\nint biSearch(int *arr, int n, int target) {\n int left = 0;\n int right = n - 1;\n while (left <= right) {\n int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;\n if (arr[mid] == target) {\n return mid;\n } else if (arr[mid] < target) {\n left = mid + 1;\n } else {\n right = mid - 1;\n }\n }\n return -1;\n}\n\nint longestSquareStreak(int *nums, int numsSize) {\n int seen[maxN] = {0};\n int *set = (int *)malloc(maxN * sizeof(int));\n int setidx = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) {\n if (!seen[nums[i]]) {\n seen[nums[i]] = 1;\n set[setidx++] = nums[i];\n } else {\n continue;\n }\n }\n qsort(set, setidx, sizeof(int), cmp);\n int ans = -1;\n for (int i = 0; i < setidx; i++) {\n int curr = set[i];\n if (curr >= 400) {\n continue;\n }\n int big = curr * curr;\n int currRes = -1;\n while (biSearch(set, setidx, big) != -1) {\n if (currRes == -1) {\n currRes = 2;\n } else {\n currRes++;\n }\n curr = big;\n if (curr >= 400) {\n break;\n }\n big = curr * curr;\n // printf("curr = %d, big = %d\\n", curr, big);\n }\n ans = max(ans, currRes);\n }\n return ans;\n}\n\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C']
| 2 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
2 Methods || JAVA C++ PYTHON.
|
2-methods-java-c-python-by-abhishekkant1-k29w
|
BOISS JUST UPVOTE , I WORK SO HARD WRITNG THIS OUT AND YOU SHAMELESS PEOPLE DONT EVEN LIKE THE POST . PLS UPVOTE IT.\n\n\n# M1:) ---> O(NLOGN) SORT+BINARY+DP (m
|
Abhishekkant135
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T05:30:06.782199+00:00
|
2024-10-28T05:30:06.782236+00:00
| 299 | false |
# BOISS JUST UPVOTE , I WORK SO HARD WRITNG THIS OUT AND YOU SHAMELESS PEOPLE DONT EVEN LIKE THE POST . PLS UPVOTE IT.\n\n\n# M1:) ---> O(NLOGN) SORT+BINARY+DP (memoization).\n\n\n**1. Sorting the Array:**\n - The `nums` array is sorted in ascending order. This helps in using binary search to efficiently find the square of a number in the array.\n\n**2. Dynamic Programming:**\n - A `dp` array is used to memoize the length of the longest square streak starting from each index.\n - The `solve` function recursively calculates the length of the square streak for a given index.\n - If the result for the current index is already stored in the `dp` array, it is returned directly.\n - The square of the current number is calculated using `long` multiplication to avoid potential integer overflow.\n - Binary search is used to find the index of the square in the sorted array. If found, the `maxStreak` is incremented by the result of the recursive call on the next index.\n - The calculated `maxStreak` is stored in the `dp` array for future reference.\n\n**3. Finding the Maximum Streak:**\n - The `maxStreak` variable is initialized to 0.\n - The `solve` function is called for each index in the sorted array.\n - The maximum `maxStreak` value is updated after each call.\n\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int longestSquareStreak(int[] nums) {\n Arrays.sort(nums); // Step 1: Sort the array\n int n = nums.length;\n int[] dp = new int[n]; // Step 2: Memoization array\n int maxStreak = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n maxStreak = Math.max(maxStreak, solve(i, nums, dp));\n }\n\n return maxStreak > 1 ? maxStreak : -1; // If no valid streak, return -1\n }\n\n private int solve(int index, int[] nums, int[] dp) {\n if (dp[index] != 0) {\n return dp[index]; // Use memoized result\n }\n\n long square = (long) nums[index] * nums[index]; // Calculate square\n int maxStreak = 1; // Initialize streak length to 1\n\n // Use binary search to find the square in the sorted array\n int nextIndex = binarySearch(nums, square);\n if (nextIndex != -1) {\n maxStreak += solve(nextIndex, nums, dp); // Extend the streak\n }\n\n dp[index] = maxStreak; // Memoize the result\n return maxStreak;\n }\n\n // Helper method to perform binary search for a target value\n private int binarySearch(int[] nums, long target) {\n int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;\n while (left <= right) {\n int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;\n if (nums[mid] == target) {\n return mid;\n } else if (nums[mid] < target) {\n left = mid + 1;\n } else {\n right = mid - 1;\n }\n }\n return -1; // Target not found\n }\n}\n```\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def longestSquareStreak(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n nums.sort() # Step 1: Sort the array\n n = len(nums)\n dp = [0] * n # Step 2: Memoization array\n max_streak = 0\n\n def solve(index):\n if dp[index] != 0:\n return dp[index] # Use memoized result\n\n square = nums[index] * nums[index] # Calculate square\n max_streak = 1 # Initialize streak length to 1\n\n next_index = binary_search(nums, square) # Find the square in the array\n if next_index != -1:\n max_streak += solve(next_index) # Extend the streak\n\n dp[index] = max_streak # Memoize the result\n return max_streak\n\n def binary_search(nums, target):\n left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1\n while left <= right:\n mid = left + (right - left) // 2\n if nums[mid] == target:\n return mid\n elif nums[mid] < target:\n left = mid + 1\n else:\n right = mid - 1\n return -1 # Target not found\n\n for i in range(n):\n max_streak = max(max_streak, solve(i))\n\n return max_streak if max_streak > 1 else -1 # If no valid streak, return -1\n```\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(std::vector<int>& nums) {\n std::sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); // Step 1: Sort the array\n int n = nums.size();\n std::vector<int> dp(n, 0); // Step 2: Memoization array\n int maxStreak = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {\n maxStreak = std::max(maxStreak, solve(i, nums, dp));\n }\n\n return maxStreak > 1 ? maxStreak : -1; // If no valid streak, return -1\n }\n\nprivate:\n int solve(int index, const std::vector<int>& nums, std::vector<int>& dp) {\n if (dp[index] != 0) return dp[index]; // Use memoized result\n\n long long square = (long long)nums[index] * nums[index]; // Calculate square\n int maxStreak = 1; // Initialize streak length to 1\n\n int nextIndex = binarySearch(nums, square); // Find the square in the array\n if (nextIndex != -1) {\n maxStreak += solve(nextIndex, nums, dp); // Extend the streak\n }\n\n dp[index] = maxStreak; // Memoize the result\n return maxStreak;\n }\n\n // Helper method to perform binary search\n int binarySearch(const std::vector<int>& nums, long long target) {\n int left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1;\n while (left <= right) {\n int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;\n if (nums[mid] == target) return mid;\n else if (nums[mid] < target) left = mid + 1;\n else right = mid - 1;\n }\n return -1; // Target not found\n }\n};\n```\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n# M2:) ---> O(N) -> HASHSET.\n\n**1. HashSet Initialization:**\n\n- A HashSet `hs` is created to efficiently check if a number exists in the array.\n\n**2. Main Loop:**\n\n- The code iterates through each number `num` in the array.\n- For each `num`, the `dp` function is called to calculate the length of the square streak starting from that number.\n- The `maxStreak` variable is updated with the maximum streak length found so far.\n\n**3. `dp` Function:**\n\n- The `dp` function recursively calculates the length of the square streak starting from a given number `num`.\n- A `streak` variable is initialized to 0.\n- While the current `num` is in the HashSet:\n - The `streak` is incremented.\n - The square of `num` is calculated. To avoid potential integer overflow, the calculation is done using `long` multiplication.\n - If the squared value exceeds the maximum integer value, the function returns the current `streak`.\n - The `num` is updated to the squared value (safely cast back to `int`).\n- The final `streak` is returned.\n\n\n\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n HashSet<Integer> hs = new HashSet<>();\n\n public int longestSquareStreak(int[] nums) {\n for (int num : nums) {\n hs.add(num);\n }\n int maxStreak = 0;\n\n for (int num : nums) {\n maxStreak = Math.max(maxStreak, dp(num));\n }\n return maxStreak > 1 ? maxStreak : -1;\n }\n\n private int dp(int num) {\n int streak = 0;\n\n while (hs.contains(num)) {\n streak++;\n long value = (long) num * num; // Use long multiplication\n\n if (value > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {\n return streak; // Break if the value overflows\n }\n\n num = (int) value; // Safely cast the result back to int\n }\n return streak;\n }\n}\n\n```\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(std::vector<int>& nums) {\n std::unordered_set<int> hs(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n int maxStreak = 0;\n\n for (int num : nums) {\n maxStreak = std::max(maxStreak, dp(num, hs));\n }\n return maxStreak > 1 ? maxStreak : -1;\n }\n\npublic:\n int dp(int num, std::unordered_set<int>& hs) {\n int streak = 0;\n\n while (hs.count(num)) {\n streak++;\n long long value = (long long)num * num;\n\n if (value > INT_MAX) {\n return streak;\n }\n num = static_cast<int>(value);\n }\n return streak;\n }\n};\n\n```\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def longestSquareStreak(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n hs = set(nums)\n max_streak = 0\n\n def dp(num):\n streak = 0\n while num in hs:\n streak += 1\n value = num * num\n if value > 2**31 - 1: # Prevent overflow beyond int limit\n return streak\n num = value\n return streak\n\n for num in nums:\n max_streak = max(max_streak, dp(num))\n \n return max_streak if max_streak > 1 else -1\n```\nYOu can optimise this as well using memoization. Do give it a try.\n\n
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Binary Search', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Sorting', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java']
| 2 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
brute to better | 2 approach + optimization | sorting + constrain (dp) | nlog(n) + n
|
brute-to-better-2-approach-optimization-37u5y
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nproblem -> find subsequence in which after sorting values are square of previous.\n\nsu
|
anain829
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T05:28:22.639889+00:00
|
2024-10-28T05:28:22.639929+00:00
| 45 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nproblem -> find subsequence in which after sorting values are square of previous.\n\nsubsequence => so order does not matter - a hint to sort\nsorting values => 2nd hint to sort the problem\ncondition => square so some maths is involved either sqrt or a*a used.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1st Approach - out of bound => thought of making state like dp[index][previous] after observing that 1e5 sqrt is 316.something so at max previous value can be 316 but still 1e5*(316) was out of bound.\n\n2nd Approach - sort given data, than traverse it and for every value if it\'s sqrt is present than we add length.\n\nsorting will be nlogn\nfinding sqrt is maths o(1)\nfinding sqrt in data is o(1) using len array to keep track and also maintain answer till that sqrt value.\n\noptimization - values can be from 2 to 1e5 it is hint in itself.\nAs we can have a array to store values occurance as 1 if present.\n\nThan we can build our answer on top of this occurance array as making a loop for 2 to 1e5 and for every value -\n1) if it is present in occurance array.\nif(occ[i]!=0)\n2) if it\'s sqrt is present in occurance array.\nocc[i] = 1 + occ[sqrt(i)]\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n1st approach - n*(sqrt(maxvalue = 1e5))\n2nd approach - O(nlog(n) + n)\noptimization - O(1e5) - O(max value)\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n1st approach - O(1e5*(317)) // out of bound\n2nd approach - O(1e5) - O(max value)\noptimization - O(1e5) - O(max value)\n\n**open for discussion feel free to teach me :-)**\n# Code\n```cpp []\n\n#include <bits/stdc++.h>\nusing namespace std;\ntypedef long long ll;\ntypedef unsigned long long ull;\ntypedef long double lld;\n \n# define vi vector<int>\n# define vl vector<ll>\n# define vc vector<char>\n# define vvc vector<vector<char>>\n# define vvi vector<vector<int>>\n# define vvl vector<vector<ll>>\n# define pii pair<int,int>\n# define vpii vector<pii>\n# define vvpii vector<vector<pii>>\n \n#define ff first\n#define ss second\n#define yup cout<<"YES"<<endl;\n#define nope cout<<"NO"<<endl;\n#define pb push_back\n#define pp pop_back\n#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()\n#define endl \'\\n\'\n#define fast_io ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(NULL);\n#define pout(x,e) cout<<fixed<<setprecision(e)<<x<<endl;\n#define FOR(i,s,e,j) for(int i=s; i<e; i+=j)\n#define sz(x) (x).size()\n \nclass Solution {\npublic:\n // int dp[100000][317];\n int n;\n\n // int solve(vi& a, int ind, int prev){\n // if(prev>=317){\n // return 0;\n // }\n // if(ind>=n){return 0;}\n\n // // if(dp[ind][prev]!=-1){\n // // return dp[ind][prev];\n // // }\n\n // int ans = solve(a, ind+1, prev);\n\n // if(prev==1 && a[ind]<400){\n // ans = max(ans, 1 + solve(a, ind+1, a[ind]));\n // }\n // else if(prev*prev == a[ind]){\n // ans = max(ans, 1 + solve(a, ind+1, a[ind]));\n // }\n\n\n // // return dp[ind][prev] = ans;\n // return ans;\n // }\n\n int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {\n sort(all(nums));\n\n n = sz(nums);\n\n // // memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));\n\n // int len = solve(nums, 0, 1);\n\n // if(len<=1){return -1;}\n // return len;\n\n int len[100001] = {0};\n \n int ans = 0;\n for(auto i:nums){\n len[i]=1;\n int sq = sqrt(i);\n if((sq*sq == i) && len[sq]!=0){\n len[i] = 1 + len[sq];\n ans = max(ans, len[i]);\n }\n }\n\n if(ans<=1){\n return -1;\n }\n return ans;\n\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 1 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Sorting', 'C++']
| 1 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Java Clean Solution
|
java-clean-solution-by-shree_govind_jee-ugdq
|
Code\njava []\nclass Solution {\n public int longestSquareStreak(int[] nums) {\n Set<Long> set = new HashSet<>();\n for (int num : nums)\n
|
Shree_Govind_Jee
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T05:11:39.857589+00:00
|
2024-10-28T05:11:39.857619+00:00
| 484 | false |
# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int longestSquareStreak(int[] nums) {\n Set<Long> set = new HashSet<>();\n for (int num : nums)\n set.add((long) num);\n\n Arrays.sort(nums);\n int res = -1;\n\n for (int num : nums) {\n long temp = (long) num;\n int cnt = 1;\n while (set.contains(temp * temp)) {\n cnt++;\n temp = temp * temp;\n res = Math.max(res, cnt);\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Binary Search', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Sorting', 'Java']
| 5 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Longest chain in a graph. O(n) time & O(n) space regardless of arbitrarily large input values.
|
longest-chain-in-a-graph-on-time-on-spac-v3po
|
Intuition\nWe can create a graph where each node points to its square if that square exists in the input. The solution is then the number of nodes in the longes
|
mo-kiani
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T04:34:21.767526+00:00
|
2024-10-28T04:34:21.767556+00:00
| 139 | false |
# Intuition\nWe can create **a graph where each node points to its square** if that square exists in the input. The solution is then the number of nodes in the **longest chain in the graph**.\n\nThis graph in practice ends up being **a set of linked lists**. That is because, for all positive integers `n` and `m`, if `n != m` then `pow(n, 2) != pow(m, 2)` and vice versa.\n\nNotice that we don\'t need to sort the input since regardless of the order that we create the edges in our graph the end result will be the same and we do all our processing after the graph is fully constructed.\n\n# Approach\nWe can use a set to quickly check if the square exists for each number in the input and construct the edges of the graph accordingly. Once the graph is fully constructed, we can recursively calculate the length of the chain starting at each node. By caching the result of the recursion (Dynamic Programming) we will only need to visit each node once. We return the length of the longest chain we found unless it is less than `2` in which case we return `-1` because the problem statement does not consider that to be a "square streak".\n\n# Complexity\n\n### Time complexity:\nWe check for the square of each node while constructing the graph, which takes *O(n)*.\nWe then find the length of the longest chain the graph which takes *O(n)* as well since we are only visiting each node once thanks to recursive dynamic programming.\nOur total time complexity is then *O(n)* + *O(n)* = ***O(n)***.\n\n### Space complexity:\nThere are three sources of memory usage:\n- The set used to check for squares\n- The graph\n- The cache used for dynamic programming\n\nAll three use *O(n)* space, so the total space complexity is ***O(n)***.\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def longestSquareStreak(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n num_set = set(nums)\n\n graph = dict() # Each element points to its square if it exists\n for n in nums:\n square = n**2\n if square in num_set:\n graph[n] = square\n\n @cache\n def get_length(n):\n if n in graph:\n return 1 + get_length(graph[n])\n elif n in num_set:\n return 1\n else:\n return 0\n\n longest_streak = max(map(get_length, nums))\n return longest_streak if longest_streak >= 2 else -1\n\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Simple Java solution using HashSet.
|
simple-java-solution-using-hashset-by-th-f1ni
|
Intuition\nMy initial thought is to leverage a set to efficiently check for the existence of squares of numbers. By iterating through the given array, I can com
|
theLearningNinja
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T03:44:56.439594+00:00
|
2024-10-28T03:44:56.439616+00:00
| 63 | false |
# Intuition\nMy initial thought is to leverage a set to efficiently check for the existence of squares of numbers. By iterating through the given array, I can compute the square of each number and see if that square is also present in the array. The goal is to find the longest sequence of numbers such that each number\'s square is also part of the sequence.\n# Approach\n1. Set Creation: First, I\'ll create a Set<Integer> to store all the numbers from the input array for O(1) look-up times.\n\n2. Iteration: For each number in the array, I\'ll attempt to form a streak by checking if the square of the current number exists in the set.\n\n3. Streak Counting: I\'ll maintain a count of how many valid squares I can find in sequence. If I reach a number whose square isn\'t in the set, I\'ll break the loop.\n\n4. Update Maximum Streak: After checking each number, I\'ll update the maximum streak found so far.\n\n5. Return Result: Finally, if the longest streak is less than 2, I\'ll return -1, indicating no valid streak was found; otherwise, I\'ll return the longest streak.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n), where n is the number of elements in the input array. Each number is processed once, and set operations (insert and contains) are average O(1).\n- Space complexity: O(n), for storing the elements of the input array in the set.\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int longestSquareStreak(int[] nums) {\n Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();\n int longestStreak = 1;\n for(int num : nums){\n set.add(num);\n }\n for(int num : nums){\n int current = 1;\n boolean flag = true;\n while(num<1000){\n if(set.contains(num*num)){\n current++;\n num = num*num;\n } else {\n break;\n }\n }\n longestStreak = Math.max(longestStreak, current);\n }\n return longestStreak < 2 ? -1 : longestStreak;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Simple solution using Map
|
simple-solution-using-map-by-harshitalee-saua
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nIn the first glance it looked like Longest Increasing Subsequence(LIS), but then realiz
|
harshitaleet
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T02:05:38.208024+00:00
|
2024-10-28T02:05:38.208055+00:00
| 317 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nIn the first glance it looked like Longest Increasing Subsequence(LIS), but then realized we just need to look for one element, it\'s square.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nSort the array. Loop on the array and check if it\'s square root is present or not. Store the length of subsequence using an unordered map. If it\'s present we can add our current element to the subsequence, else start a new subsequence.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {\n sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n unordered_map<int, int> ump;\n int res = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)\n {\n int temp = sqrt(nums[i]);\n if(temp * temp == nums[i] && ump[temp])\n {\n ump[nums[i]] = ump[temp] + 1;\n res = max(res, ump[nums[i]]);\n }\n else\n ump[nums[i]] = 1;\n }\n if(res == 0)\n return -1;\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Sorting', 'C++']
| 3 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Swift💯Set
|
swiftset-by-upvotethispls-hyyj
|
Good Interview Answer (accepted answer)\nApproach: Brute Force, No Sort\n\nclass Solution {\n func longestSquareStreak(_ nums: [Int]) -> Int {\n let s
|
UpvoteThisPls
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T00:46:39.357064+00:00
|
2024-10-28T04:54:56.940044+00:00
| 29 | false |
**Good Interview Answer (accepted answer)**\nApproach: Brute Force, No Sort\n```\nclass Solution {\n func longestSquareStreak(_ nums: [Int]) -> Int {\n let s = Set(nums)\n var maxStreak = -1\n \n for var n in s where s.contains(n*n) {\n var streak = 0\n while s.contains(n) {\n n = n*n\n streak += 1\n }\n maxStreak = max(maxStreak, streak)\n }\n return maxStreak\n }\n}\n```\n\n---\n\n**BONUS: One-Liner, terse (accepted answer)** \n\u26A0\uFE0F-For fun only, this is twice as slow as brute force. \n```\nclass Solution {\n func longestSquareStreak(_ nums: [Int]) -> Int {\n [Set(nums)].map{s in s.map{n in sequence(first: n){$0*$0}.prefix{s.contains($0)}.count}.filter{$0>1}.max() ?? -1}[0]\n }\n}\n```\n**One-Liner, expanded and annotated (accepted answer)**\n```\nclass Solution {\n func longestSquareStreak(_ nums: [Int]) -> Int {\n [\n Set(nums)\n ] // <-- put the set of `num` into monad\n .map{ s in\n\t\t\ts.map{ n in // we need `nums` as set, otherwise time limit exceeded\xA0(TLE)\n\t\t\t\tsequence(first: n, next:{$0*$0})\n .prefix{n in s.contains(n)} // create seq while square streak exists\n .count // return the count of the square streak\n }\n .filter{$0>1} // square streak count must be at least 2\n .max() ?? -1 // if max subseq count < 2, return -1 else return max count\n }.first! // <-- pull result out of monad\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Swift']
| 1 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Beats 100%
|
beats-100-by-tejya2107-v399
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Tejas2107
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-22T06:36:42.828195+00:00
|
2024-10-22T06:36:42.828232+00:00
| 27 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n.logn)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(1)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& n) {\n sort(n.begin(),n.end());\n int a=0;\n for(int i=0; i<n.size();++i){\n long long c=1,sqr=n[i];\n while(binary_search(n.begin(),n.end(),sqr*sqr*1LL)){\n ++c;\n sqr=sqr*sqr;\n }\n if(c>1)a=max(c,a*1LL);\n \n }\n if(a==0)a=-1;\n return a;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Binary Search', 'Sorting', 'C++']
| 2 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
C++ O(n) easy solution faster than 99.8% explained
|
c-on-easy-solution-faster-than-998-expla-2dey
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nUse an array to store the presence of numbers. And loop through it.\n\n# Approach\n Des
|
yyyyy7105
|
NORMAL
|
2023-05-10T05:13:28.063972+00:00
|
2023-05-11T06:14:57.016402+00:00
| 99 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nUse an array to store the presence of numbers. And loop through it.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. Ceates a boolean array called `A`, where `A[i]` is true if and only if `i` is present in nums. \n2. Store a global max `maxCnt` and a local max `cnt` for the while loop. \n3. Note that We only need to iterate from 2 to 316 in the outer loop since $317^2 > 100000$, which means elements after 317 cannot form a sequence starting from it. \n4. Same for the while loop, we only need to continue the loop when `j` is less than 317.\n\n5. Note that `A[j]` can be set to `false` to speed up the performance since we have seen it and there is no need to start at `j` again. i.e. If we find `3,9,81`, it is redundant to start from `9` again.\n6. If `maxCnt < 2`, we don\'t find a valid sequence thus return -1; otherwise return `maxCnt`.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n)\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {\n vector<bool> A(100001, false); \n for (int i : nums) {\n A[i] = true;\n }\n\n int maxCnt = 0, cnt, j;\n for (int i = 2; i < 317; ++i) { \n cnt = 0;\n j = i;\n while (A[j]) {\n ++cnt;\n A[j] = false;\n if (j < 317) {\n j *= j;\n } else {\n break;\n }\n }\n maxCnt = max(maxCnt, cnt);\n }\n \n return maxCnt < 2 ? -1 : maxCnt;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'C++']
| 0 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
✔ Python3 Solution | DP | Clean & Concise
|
python3-solution-dp-clean-concise-by-sat-d8cb
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(nlogn)\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution:\n def longestSquareStreak(self, A):\n A.sort()\n
|
satyam2001
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-21T16:50:29.356324+00:00
|
2022-12-21T16:50:29.356367+00:00
| 207 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(nlogn)$$\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def longestSquareStreak(self, A):\n A.sort()\n n = len(A)\n dp = [1] * n\n r = n - 1\n for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):\n while A[i] * A[i] < A[r]: r -= 1\n if A[i] * A[i] == A[r]: dp[i] = dp[r] + 1\n ans = max(dp)\n return ans if ans > 1 else -1\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Sorting', 'Python3']
| 0 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Dart: O(1) space by abusing the numerical bounds of the problem
|
dart-o1-space-by-abusing-the-numerical-b-cuue
|
Intuition\nBecause the problem guarantees that input values are $<=10^5$, there are actually only a small number of input values that could start a sequence of
|
alexhutcheson
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-20T00:55:47.549459+00:00
|
2022-12-20T00:55:47.549496+00:00
| 26 | false |
# Intuition\nBecause the problem guarantees that input values are $<=10^5$, there are actually only a small number of input values that could start a sequence of length 2, of length 3, etc. For example, $317^2 > 10^5$, so we know that any value $>316$ cannot be the first value in a sequence of lenght 2 or more. We extend this to sequences of lengths 3, 4, and 5.\n\nThis allows us to put constant bounds on how many iterations we perform in our main loop.\n\n# Approach\n1. Sort\n2. Iterate through the sorted values, but exit early as soon as we see a value that would be too large to be the start of a sequence longer than the current max.\n3. For each value, binary search to check if the next square exists, then the next, etc.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $O(n\\log{n})$ for the sort operation. Main loop is technically $O(\\log{n})$, since the outer loop is bounded at 316 iterations and the inner one is bounded at 5.\n\n- Space complexity: $O(1)$\n\n# Code\n```dart\nclass Solution {\n int longestSquareStreak(List<int> nums) {\n var longestStreak = 1;\n nums.sort();\n for (var i = 0; i < nums.length && nums[i] <= _maxStartValueByLength[longestStreak+1]!; i++) {\n if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) {\n // Repeat, skip it.\n }\n var index = i;\n var streak = 1;\n var square = nums[index];\n while (true) {\n square *= square;\n index = binarySearch(nums, square, index + 1);\n if (index == -1) {\n break;\n }\n streak++;\n longestStreak = max(longestStreak, streak);\n }\n }\n if (longestStreak == 1) {\n return -1;\n }\n return longestStreak;\n }\n\n /// Returns the index of an arbitrary occurrence of [target] in sorted list [list] on or after the [start index].\n int binarySearch(List<int> list, int target, int start) {\n var l = start, r = list.length - 1;\n while (l <= r) {\n var mid = l + ((r - l) ~/ 2);\n if (list[mid] == target) {\n return mid;\n }\n if (target < list[mid]) {\n r = mid - 1;\n } else {\n l = mid + 1;\n }\n }\n return -1;\n }\n\n static const _maxStartValueByLength = {\n // sqrt(10^5).floor() = 316 \n // Any value higher cannot be the first in a sequence of length 2, \n // because the second value would be out of range\n 2: 316,\n // (10^5)^(1/4).floor() = 17\n 3: 17,\n // (10^5)^(1/16).floor = 2\n 4: 2,\n 5: 2,\n 6: 1\n };\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dart']
| 0 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Count Streaks
|
count-streaks-by-ayushy_78-s0f2
|
# Intuition \n\n\n\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n * log n)\n\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n\n\n# Code\n\n#define has(m, x) m.find(x) != m.end()\ncla
|
SelfHelp
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-18T10:54:33.686856+00:00
|
2022-12-18T10:54:33.686890+00:00
| 168 | false |
<!-- # Intuition -->\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n<!-- # Approach -->\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: *`O(n * log n)`*\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: *`O(n)`*\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n#define has(m, x) m.find(x) != m.end()\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {\n sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n unordered_map<int, int> sqr;\n double st;\n for(int num: nums) {\n st = sqrt(num);\n if(ceil(st) == floor(st))\n sqr[num] = max(sqr[num], sqr[st] + 1);\n else\n sqr[num] = (sqr[num] == 0) ? 1 : sqr[num];\n }\n int streak = -1;\n for(auto el: sqr) {\n if(el.second > 1)\n streak = max(streak, el.second);\n }\n return streak;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Sorting', 'C++']
| 0 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
JAVA Solution time beats 100% || space beats 100%
|
java-solution-time-beats-100-space-beats-8v5h
|
\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n \n- Space complexity: O(n)\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public int
|
srikanth-macha
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-11T15:51:51.608322+00:00
|
2022-12-11T15:52:08.072190+00:00
| 571 | false |
\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n \n- Space complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int longestSquareStreak(int[] nums) {\n Set<Long> set = new HashSet<>();\n\n for(int i: nums) set.add(Long.valueOf(i));\n\n int max = 0;\n for(int i: nums) {\n int cnt = 1;\n long num = i;\n\n while(set.contains(num*num)) {\n num = num*num;\n cnt++;\n }\n\n max = Math.max(max, cnt);\n }\n\n return max == 1 ? -1: max;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Java']
| 3 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
[python] O(n) solution without sort
|
python-on-solution-without-sort-by-natha-b9ap
|
Intuition\nSince each subsequence has a smallest number, just count from the smallest to the biggest.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n\n- Space comple
|
nathan-tw
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-11T10:23:20.442021+00:00
|
2022-12-11T10:24:38.343351+00:00
| 55 | false |
# Intuition\nSince each subsequence has a smallest number, just count from the smallest to the biggest.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n\n- Space complexity:$$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def longestSquareStreak(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n s = set(nums)\n res = -1\n for item in s:\n if sqrt(item) in s: continue\n else: \n curr = 1\n while item*item in s:\n item*=item\n curr+=1\n res = max(curr, res)\n return -1 if res <= 1 else res\n \n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
JS sort and set
|
js-sort-and-set-by-vaslisaidmuradov-guws
|
Code\n### #1\n\nconst longestSquareStreak = function(nums) {\n nums.sort((a, b) => a-b)\n const set = new Set(nums)\n let max = -1\n let visited = n
|
vaslisaidmuradov
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-11T10:14:22.441769+00:00
|
2022-12-11T10:33:08.610835+00:00
| 230 | false |
# Code\n### #1\n```\nconst longestSquareStreak = function(nums) {\n nums.sort((a, b) => a-b)\n const set = new Set(nums)\n let max = -1\n let visited = new Set()\n for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {\n let num = nums[i]\n if (visited.has(num)) continue;\n let count = 0\n visited.add(num)\n while (set.has(num*num)) {\n visited.add(num*num)\n num = num*num\n count++\n }\n if (count > 0) {\n max = Math.max(max, count+1)\n }\n }\n return max\n};\n```\n### #2\n```\nconst longestSquareStreak = function(nums) {\n const set = new Set(nums)\n let max = -1\n for (let num of nums) {\n let count = 0\n while (set.has(num)) {\n num = num*num\n count++\n }\n if (count > 1) {\n max = Math.max(max, count)\n }\n }\n \n return max\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Java | Simple DP 1 pass
|
java-simple-dp-1-pass-by-nadaralp-ml97
|
Intuition\nStore the numbers we\'ve seen in a hash map as the key, and the length of the increasing subsequence as value.\n\nAt any value x we check if sqrt(x)
|
nadaralp
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-11T09:57:53.752667+00:00
|
2022-12-11T09:57:53.752706+00:00
| 892 | false |
# Intuition\nStore the numbers we\'ve seen in a hash map as the key, and the length of the increasing subsequence as value.\n\nAt any value `x` we check if `sqrt(x)` is in the map, if it is, we add map[sqrt(x)] to our current subsequence length, otherwise there is no streak and we set `map[x]` to 1.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int longestSquareStreak(int[] nums) {\n Arrays.sort(nums);\n Map<Integer, Integer> squareStreak = new HashMap<>();\n int best = -1;\n\n for (int x : nums) {\n double sqrt = Math.pow(x, 0.5);\n if (sqrt % 1 == 0 && squareStreak.containsKey((int) sqrt)) {\n squareStreak.put(x, squareStreak.get((int) sqrt) + 1);\n best = Math.max(best, squareStreak.get(x));\n } else {\n squareStreak.put(x, 1);\n }\n }\n\n return best;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 2 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Very easy O(N) solution (no need to sort)
|
very-easy-on-solution-no-need-to-sort-by-5zgm
|
Intuition\nFound this question similar to question where we have to find longest-consecutive-sequence\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/longest-consecutive-sequenc
|
amritanshusharma25
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-11T07:44:06.178143+00:00
|
2022-12-11T08:05:05.456890+00:00
| 193 | false |
# Intuition\nFound this question similar to question where we have to find longest-consecutive-sequence\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/longest-consecutive-sequence/description/\n\n# Approach\nStore all numbers intially in a map(no need to sort)\n\nItterate over the array and try to find all consecutive numbers in array\n\nLike for eg. we are standing at 2\nwe try to find 4, then 16\n\nImp-> remember to erase numbers we have founded so that there is no overlap\nSee solution for more clarity \n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(N)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(N)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {\n unordered_map<long long int,long long int>mp;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)\n {\n if(mp.find(nums[i])==mp.end())\n mp[nums[i]]++;\n }\n long long int ans=1;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)\n {\n if(mp.find(nums[i])==mp.end())\n {\n continue;\n }\n long long int count=mp[nums[i]];\n if(nums[i]<(INT_MAX/nums[i]))\n {\n long long int x=nums[i]*nums[i];\n while(mp.find(x)!=mp.end())\n {\n count=count+mp[x];\n mp.erase(x);\n if(x>(INT_MAX/x))\n {\n break;\n }\n x=x*x;\n\n }\n }\n mp[nums[i]]=count;\n ans=max(ans,count);\n }\n if(ans<2)\n {\n return -1;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Easy C++ solution using hashmap
|
easy-c-solution-using-hashmap-by-dheerut-ma7i
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
DheeruThakur
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-11T06:02:35.632059+00:00
|
2022-12-11T06:02:35.632098+00:00
| 189 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {\n sort(nums.begin() , nums.end() , greater<int>());\n unordered_map<int , int> mp;\n\n for(auto it: nums){\n mp[it] = 1;\n }\n int count;\n int maxi = -1;\n\n for(int i=0 ; i<nums.size()-1 ; i++){\n count = 1;\n int x = nums[i];\n\n while(mp[sqrt(x)]>0){\n int t = sqrt(x);\n if(t*t == x)\n count++;\n else break;\n mp[sqrt(x)]--;\n x = sqrt(x); \n }\n maxi = max(maxi , count);\n }\n return maxi==1?-1:maxi;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
C++ || Very easy approach using unordered_set
|
c-very-easy-approach-using-unordered_set-o83t
|
```\nint longestSquareStreak(vector& nums) {\n long long n=nums.size();\n unordered_setst;\n sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n for(a
|
sb5
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-11T05:24:15.550428+00:00
|
2022-12-11T05:24:15.550467+00:00
| 29 | false |
```\nint longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {\n long long n=nums.size();\n unordered_set<long long>st;\n sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n for(auto x:nums){\n st.insert(x);\n }\n vector<int>vec;\n long long ans=0;\n if(nums[0]>316){\n return -1;\n }\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n if(nums[i]>316){\n break;\n }\n long long temp=1;\n if(st.find(nums[i]*nums[i])!=st.end()){\n long long curr=nums[i]*nums[i];\n temp++;\n while(true){\n if(st.find(curr*curr)!=st.end()){\n temp++;\n curr=curr*curr;\n } \n else{\n break;\n }\n }\n }\n ans=max(ans, temp);\n }\n if(ans==1){\n return -1;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\t*Sort the input vector and insert all items of the vector into an unordered_set.\n\t*Then traverse over all the items in the input vector and for each element check if it\'s square is present. \n\t*keep in mind that if element exceeds 316 then square of it will not be present as 317*317 \n\texceeds the constraints of the elements of the input \n\t*even though you will be using two loops in this approach the time complexity will be o(nlogn) \n\tthat\'s because of the sorting as search in an unordered_set is an O(1) operation and at max \n\tthe traversal will go to 316th element of the vector only.\n\t\n\tPS: hope this makes sense thank you :)
| 2 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'C']
| 1 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
[C++|Java|Python3] dp
|
cjavapython3-dp-by-ye15-a0qm
|
Please pull this commit for solutions of weekly 323. \n\nIntuition\nIt is quite strange that sorting is allowed in this problem. However, since sorting is allow
|
ye15
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-11T04:09:27.807760+00:00
|
2022-12-11T05:46:13.590373+00:00
| 274 | false |
Please pull this [commit](https://github.com/gaosanyong/leetcode/commit/8f409c5e220a4a1a1d7fdfbfcc1dcd24eeead232) for solutions of weekly 323. \n\n**Intuition**\nIt is quite strange that sorting is allowed in this problem. However, since sorting is allowed, all that matters is whether a squared number exists. One solution via DP is to check if a number x is a squared number if so its streak is 1+dp[r] where r is the square root of x. \n\n**Implementation**\n**C++**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {\n vector<int> dp(100\'001); \n sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); \n for (auto& x : nums) {\n dp[x] = max(1, dp[x]); \n int v = sqrt(x); \n if (v * v == x) dp[x] = 1 + dp[v]; \n }\n int ans = *max_element(dp.begin(), dp.end()); \n return ans > 1 ? ans : -1; \n }\n};\n```\n**Java**\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int longestSquareStreak(int[] nums) {\n int[] dp = new int[100_001]; \n Arrays.sort(nums); \n int ans = 0; \n for (int x : nums) {\n dp[x] = Math.max(1, dp[x]); \n int v = (int) Math.sqrt(x); \n if (v*v == x) dp[x] = 1 + dp[v]; \n ans = Math.max(ans, dp[x]); \n }\n return ans > 1 ? ans : -1; \n }\n}\n```\n**Python3**\n```\nclass Solution:\n def longestSquareStreak(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n dp = defaultdict(int)\n for x in sorted(nums): \n dp[x] = max(dp[x], 1)\n v = isqrt(x)\n if v**2 == x: dp[x] = 1 + dp[v]\n ans = max(dp.values())\n return ans if ans > 1 else -1\n```\n**Complexity**\nTime `O(NlogN)`\nSpace `O(N)`
| 2 | 0 |
['C', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 0 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Using sqrt() function and Hashmap.
|
using-sqrt-function-and-hashmap-by-ayush-rx0a
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {\n int ans=0;\n sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());\n uno
|
ayush_srivastava02
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-11T04:03:57.171941+00:00
|
2022-12-11T04:04:42.364008+00:00
| 78 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {\n int ans=0;\n sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());\n unordered_map<float,int> mp;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n float temp = sqrt(nums[i]);\n if(mp.find(temp)!=mp.end()){\n mp[nums[i]] = mp[temp]+1;\n }\n else{\n mp[nums[i]]=1;\n }\n }\n for(auto i:mp){\n ans=max(ans,i.second);\n }\n if(ans==1) return -1;\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Python | Optimal O(n) | easy to understand
|
python-optimal-on-easy-to-understand-by-9fisc
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution:\n def longestSquareStreak(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n nums.sort()\n d = {}\n ans = 0\n for i,
|
jubinsoni
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-11T04:03:22.092228+00:00
|
2022-12-11T04:04:39.503547+00:00
| 440 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def longestSquareStreak(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n nums.sort()\n d = {}\n ans = 0\n for i, n in enumerate(nums):\n sqrt = n ** 0.5\n if sqrt in d and sqrt.is_integer():\n d[n] = d[sqrt] + 1\n ans = max(ans, d[n])\n else:\n d[n] = 1\n \n return ans if ans > 0 else -1\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Python3']
| 2 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
C++ || SET
|
c-set-by-up1512001-ntpv
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {\n set<long long> st(nums.begin(),nums.end());\n long long ans=-1;\n
|
up1512001
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-11T04:01:38.589917+00:00
|
2022-12-11T04:01:38.589953+00:00
| 530 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {\n set<long long> st(nums.begin(),nums.end());\n long long ans=-1;\n for(auto it : nums){\n if(st.find((long long)it*it)!=st.end()){\n long long cnt=2,val=(long long)it*it;\n while(st.find(val*val)!=st.end()){\n cnt += 1;\n val = val*val;\n }\n if(ans<cnt) ans = cnt;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C', 'Ordered Set', 'C++']
| 1 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
beter solution using unordered set
|
beter-solution-using-unordered-set-by-s_-usnn
|
dd your space complexity here, e.g. O(n) -->Code
|
s_malay
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-17T16:41:12.163146+00:00
|
2025-03-17T16:41:12.163146+00:00
| 24 | false |
dd your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
int n=nums.size();
unordered_set<int>uset(nums.begin(),nums.end());
int ans=-1;
for(auto it:uset)
{
int cnt=0;
long long elem=it;
while(elem<INT_MAX && uset.count(elem))
{
cnt++;
elem*=elem;
}
ans=max(ans,cnt);
}
if(ans>=2)return ans;
return -1;
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Sorting', 'C++']
| 0 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
C#
|
c-by-adchoudhary-o257
|
Code
|
adchoudhary
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-04T04:56:18.525420+00:00
|
2025-03-04T04:56:18.525420+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Code
```csharp []
public class Solution {
public int LongestSquareStreak(int[] nums)
{
// Convert nums to a sorted set to remove duplicates and have ordered numbers
var numSet = new HashSet<int>(nums);
var sortedNums = numSet.OrderBy(x => x).ToList();
// Track the maximum streak length found
int maxLength = 0;
// Iterate through each number in sorted order
foreach (int num in sortedNums)
{
// Initialize streak length for current number
int length = 0;
// Start with current number
long current = num;
// Keep squaring the number while it exists in our set
while (current <= int.MaxValue && numSet.Contains((int)current))
{
length++;
current = current * current;
}
// Only update maxLength if we found a streak of length > 1
if (length > 1)
{
maxLength = Math.Max(maxLength, length);
}
}
// Return maxLength if we found a valid streak, otherwise return -1
return maxLength > 1 ? maxLength : -1;
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
93% run time
|
93-run-time-by-lathika17-iu6w
|
IntuitionThe problem requires finding the longest sequence of numbers in the input such that each number is the square of the previous one. My initial thought i
|
lathika17
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-24T14:31:47.065758+00:00
|
2025-01-24T14:31:47.065758+00:00
| 10 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
The problem requires finding the longest sequence of numbers in the input such that each number is the square of the previous one. My initial thought is to use a brute force approach where for every number in the input, I keep checking if its square exists in the list, and continue forming a sequence. However, to make it efficient, I can use a set for O(1) lookups and avoid redundant calculations.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
Preprocessing: Convert the list nums into a set to allow for fast lookups.
Iterate Through the List:
For each number, check if its square exists in the set.
If it does, initialize a streak counter to 2 (current number and its square) and repeatedly square the number until no further square exists in the set.
Avoid Redundant Work: Numbers already part of a streak do not need to be processed again.
Track Maximum Streak: Update the maximum streak length encountered during the iterations.
Edge Cases:
If no valid streak is found, return -1 (default value).
Handle single-element or empty input lists appropriately.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:O(nlogm)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:O(n)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def longestSquareStreak(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
res = -1
nums_set = set(nums) # Convert to a set for O(1) lookups
for num in nums:
if num * num in nums_set:
st = 2
prev = num * num
while prev:
if prev * prev in nums_set:
prev = prev * prev
st += 1
else:
break # Exit the loop if no further square exists
res = max(st, res)
return res
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Simple HashMap + Sorting Question || O(nlogn) + O(n⋅log(max_value)) || C++
|
simple-hashmap-sorting-question-onlogn-o-dyxj
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity: O(nlogn) + O(n⋅log(max_value))
Space complexity: O(n)
Code
|
puneet_3225
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-30T07:08:50.283477+00:00
|
2024-12-30T07:08:50.283477+00:00
| 14 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(nlogn) + O(n⋅log(max_value))
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(n)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int n = nums.size();
map<int,int> mp;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
mp[nums[i]] = i;
}
int ans = -1;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){
int curr = nums[i];
long long nxt = pow(nums[i], 2);
if(nxt > 1e5)continue;
int len = 1;
if(curr != -1){
while(mp.find(nxt) != mp.end()){
len++;
nums[mp[nxt]] = -1;
if(nxt > 1e6)break;
nxt *= nxt;
}
}
ans = max(len , ans);
}
return ans == 1 ? -1 : ans;
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Java | HashSet
|
java-hashset-by-siyadhri-ymt9
|
\n\n# Code\njava []\nclass Solution {\n public int longestSquareStreak(int[] nums) {\n Set<Long> set = new HashSet<>();\n for (int num : nums)\
|
siyadhri
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-29T16:41:29.777267+00:00
|
2024-10-29T16:41:29.777303+00:00
| 7 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int longestSquareStreak(int[] nums) {\n Set<Long> set = new HashSet<>();\n for (int num : nums)\n set.add((long) num);\n\n Arrays.sort(nums);\n int res = -1;\n\n for (int num : nums) {\n long temp = (long) num;\n int cnt = 1;\n while (set.contains(temp * temp)) {\n cnt++;\n temp = temp * temp;\n res = Math.max(res, cnt);\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
C++ Solution for Longest Square Streak in an Array – Easy to Understand with Explanation 🟢
|
c-solution-for-longest-square-streak-in-87a37
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\nProblem:\nGiven an array of integers, the task is to find the length of t
|
Abhinav_Shakya
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T23:58:36.026925+00:00
|
2024-10-28T23:58:36.026956+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n**Problem:**\nGiven an array of integers, the task is to find the length of the longest "square streak," where a square streak is a sequence starting from an integer in the array where each subsequent number is the square of the previous one and also appears in the array.\n\n**Solution Explanation:**\n\n1. **Sort the Array**: We first sort the array to process elements in increasing order.\n2. **Store Elements in a Set**: By using an `unordered_set`, we can efficiently check if a squared number exists in the array.\n3. **Iterate Through Each Element**: For each element in the array, we initialize a `count` and start squaring the number to find a potential streak.\n4. **Update Maximum Streak Length**: For each number, we square it repeatedly and check if the result is in the set. If it is, we continue the streak; if not, we break out of the loop. We then update the maximum streak length.\n5. **Return the Result**: If a streak longer than 1 is found, return the maximum length; otherwise, return `-1`.\n\nThis approach has a time complexity of \\(O(n \\log n)\\) due to sorting, and then \\(O(n)\\) for iterating through the array and checking streaks, making it efficient for large arrays.\n\nHere\u2019s the code:\n\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {\n // Step 1: Sort the array\n sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n \n // Step 2: Create a set to store elements for quick look-up\n unordered_set<int> st(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n \n int maxi = 0; // To store the longest square streak\n \n // Step 3: Iterate over each element in the sorted array\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {\n int count = 1;\n long long number = nums[i];\n \n // Step 4: Attempt to create a square streak starting from the current element\n while (true) {\n long long val = number * number;\n \n // Stop if `val` exceeds INT_MAX or isn\'t found in the set\n if (val > INT_MAX || st.find(val) == st.end()) {\n break;\n }\n \n count++;\n number = val; // Move to the next squared value\n }\n \n // Update the maximum streak length if the current one is the longest so far\n maxi = max(maxi, count);\n }\n\n // Step 5: Return the result, -1 if no valid streak is found\n return (maxi > 1) ? maxi : -1;\n }\n};\n```\n\n---\n\n\n\n**Why This Solution Works**:\nSorting ensures that smaller numbers come first, so if we start a streak from any number, we\u2019ve already processed smaller numbers that could start their own streaks. By checking squares within the range of `INT_MAX`, we prevent overflow issues.\n\n---\n\n**Edge Cases Considered**:\n1. **Single-element arrays**: Returns `-1` because there\u2019s no valid streak.\n2. **Arrays with no streak**: Returns `-1` if no square relationships are found.\n3. **Large arrays with high values**: Checks for overflow with `INT_MAX` to avoid errors.\n\nHope this helps! Feel free to ask questions if you have any doubts \uD83D\uDE0A\n\n# Complexity Analysis\n- **Time Complexity**: O(nlog n) due to sorting, and O(n) for iterating through each number.\n- **Space Complexity**: O(n) for the set storing elements of the array.\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {\n sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n unordered_set<int> st(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n \n int maxi = 0; \n unordered_map<int, int> mp; \n\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {\n int count = 1;\n long long number = nums[i];\n\n while (true) {\n long long val = number * number;\n \n if (val > INT_MAX || st.find(val) == st.end()) {\n break;\n }\n \n count++;\n number = val;\n }\n \n mp[nums[i]] = count; \n maxi = max(maxi, count); \n }\n\n return (maxi > 1) ? maxi : -1;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Easy NlogN solution using sorting and using a set
|
easy-nlogn-solution-using-sorting-and-us-lzk4
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nPut all the numbers is a set and sort the original array. Loop through the numbers in t
|
user0095ll
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T19:59:50.771154+00:00
|
2024-10-28T19:59:50.771175+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nPut all the numbers is a set and sort the original array. Loop through the numbers in the array. \nIf the number is in the set, check if its square is in the set. Keep doing this and increasing count and removing the squares and the original number from the set. \n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(nlogn)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def longestSquareStreak(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n \n numSet = set()\n for n in nums:\n numSet.add(n)\n \n nums.sort()\n res = 1\n \n for n in nums:\n if n in numSet:\n count = 1\n while n*n in numSet:\n count += 1\n numSet.remove(n)\n n = n*n\n res = max(count, res)\n \n return res if res != 1 else -1\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
C# Solution for Longest Square Streak In An Array Problem
|
c-solution-for-longest-square-streak-in-d723m
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe goal is to find the longest subsequence in nums where each successive element is th
|
Aman_Raj_Sinha
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T19:17:53.065047+00:00
|
2024-10-28T19:17:53.065082+00:00
| 30 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe goal is to find the longest subsequence in nums where each successive element is the square of the previous one. Since a valid subsequence must follow this \u201Csquared\u201D relationship, we need to be able to quickly check if each squared number exists in the array\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1.\tUnique Element Storage: Use a HashSet to store all unique elements from nums, allowing for efficient O(1) lookups to check if the next number in a potential square streak exists.\n2.\tIterate Through Each Element: Treat each element in nums as a potential starting point of a square streak.\n\t\u2022\tInitialize currentStreak to count the streak length and current to track the current number.\n\t\u2022\tFor each starting element, try to build a square streak by repeatedly squaring current and checking if it exists in uniqueNumbers.\n\t\u2022\tConstraint Check: If current * current exceeds 10^5, stop extending the streak to avoid overflow and respect problem constraints.\n3.\tUpdate Longest Streak: After attempting a streak from each starting point, update longestStreak if the current streak is the longest seen so far.\n4.\tReturn Result: If longestStreak is less than 2, return -1 (indicating no valid streak); otherwise, return longestStreak.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n1.\tBuilding the HashSet: This requires O(n) time, where n is the length of nums.\n2.\tIterating Through Each Element:\n\t\u2022\tFor each element x in nums, we attempt to build a streak by squaring current until it exceeds 10^5 or can no longer be found in the set.\n\t\u2022\tThe number of times we can square a number before it exceeds 10^5 is logarithmic in growth, specifically O(log(log x)).\n\t\u2022\tOverall, due to this limit on streaks, the amortized complexity remains close to O(n), even though we repeatedly square numbers within a limited range.\n3.\tTotal Complexity: O(n).\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n1.\tHashSet Storage: The HashSet uses O(n) space to store all unique elements in nums.\n2.\tAuxiliary Variables: Minimal additional space is used for variables like currentStreak and current.\n\nOverall Space Complexity: O(n).\n\n# Code\n```csharp []\npublic class Solution {\n public int LongestSquareStreak(int[] nums) {\n int longestStreak = 0;\n\n // Create a HashSet to store all unique numbers from the input array\n HashSet<int> uniqueNumbers = new HashSet<int>(nums);\n\n // Iterate through each number in the input array\n foreach (int startNumber in nums) {\n int currentStreak = 0;\n long current = startNumber;\n\n // Continue the streak as long as we can find the next square in the set\n while (uniqueNumbers.Contains((int)current)) {\n currentStreak++;\n \n // Break if the next square would be larger than 10^5 (problem constraint)\n current *= current;\n if (current > 100000) break;\n }\n\n // Update the longest streak if necessary\n longestStreak = Math.Max(longestStreak, currentStreak);\n }\n\n // Return -1 if no valid streak found, otherwise return the longest streak\n return longestStreak < 2 ? -1 : longestStreak;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Java Solution for Longest Square Streak In An Array Problem
|
java-solution-for-longest-square-streak-1230c
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe problem requires finding the longest \u201Csquare streak\u201D in the array, which
|
Aman_Raj_Sinha
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T19:14:04.116876+00:00
|
2024-10-28T19:14:04.116912+00:00
| 10 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe problem requires finding the longest \u201Csquare streak\u201D in the array, which is defined as a sequence where each successive element is the square of the previous element. This approach:\n\n1.\tUses a HashSet to store all unique elements in the array, allowing for constant-time lookups to check if the next number in the streak exists.\n2.\tIterates through each number, treating it as a potential starting point of a square streak and attempts to build a streak by repeatedly squaring the current element.\n3.\tTracks the longest streak found, provided that the streak length is at least 2, which qualifies it as a valid square streak.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1.\tStore Unique Elements: Insert all numbers in a HashSet for efficient lookups.\n2.\tIterate Through Each Number:\n\t\u2022\tFor each number, initialize currentStreak to track the length of the streak starting from that number.\n\t\u2022\tUse a while loop to continue the streak as long as the square of the current element is found in the HashSet.\n\t\u2022\tUpdate current by squaring it and checking if it\u2019s within bounds (<= 10^5); if it exceeds this limit, break the loop to avoid overflow.\n3.\tUpdate Longest Streak: After evaluating each potential starting point, update longestStreak if the current streak is longer than the previous maximum.\n4.\tReturn Result: If longestStreak is less than 2, return -1 as no valid square streak was found; otherwise, return longestStreak.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n1.\tBuilding the HashSet: Takes O(n) time, where n is the number of elements in nums.\n2.\tIterating Through Each Element: For each element x in nums, we try to form a streak by repeatedly squaring it until it exceeds 10^5 or the square is no longer in the set.\n\t\u2022\tThe number of times we can square a number before it exceeds 10^5 is logarithmic, specifically O(log(log x)).\n\t\u2022\tThis results in an amortized complexity close to O(n), since only a limited number of streaks can be built within the constraints.\n3.\tTotal Complexity: The overall time complexity is O(n).\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n1.\tHashSet Storage: We use a HashSet to store all unique elements in nums, requiring O(n) space.\n2.\tAuxiliary Variables: Minimal extra space is used for variables like currentStreak and current.\n\nOverall Space Complexity: O(n).\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int longestSquareStreak(int[] nums) {\n int longestStreak = 0;\n\n // Create a Set to store all unique numbers from the input array\n Set<Integer> uniqueNumbers = new HashSet<>();\n for (int num : nums) {\n uniqueNumbers.add(num);\n }\n\n // Iterate through each number in the input array\n for (int startNumber : nums) {\n int currentStreak = 0;\n long current = startNumber;\n\n // Continue the streak as long as we can find the next square in the set\n while (uniqueNumbers.contains((int) current)) {\n currentStreak++;\n \n // Calculate the square and check if it is within bounds\n current = current * current;\n if (current > 100000) break; // Stop if the square exceeds the constraint\n }\n\n // Update the longest streak if necessary\n longestStreak = Math.max(longestStreak, currentStreak);\n }\n\n // Return -1 if no valid streak found, otherwise return the longest streak\n return longestStreak < 2 ? -1 : longestStreak;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
"Unlocking the Longest Square Streak: A Java Solution Using HashSet"
|
unlocking-the-longest-square-streak-a-ja-djbc
|
Intuition\nThe goal is to find the longest sequence in an array where each subsequent element is the square of the previous one. Given that the elements can be
|
deleted_user
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T18:38:11.181529+00:00
|
2024-10-28T18:38:11.181563+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\nThe goal is to find the longest sequence in an array where each subsequent element is the square of the previous one. Given that the elements can be in any order, sorting the array would help in building these sequences. However, since we need to check for squares repeatedly, using a HashSet will allow quick lookups for potential square values.\n\n\n\n# Approach\nStore Elements in a HashSet: Create a HashSet to store all elements of the array. This allows for O(1) average time complexity for lookups.\nIterate Through Each Element: For each number in the array, treat it as the starting point of a possible square streak.\nCalculate Squares: Use a while loop to keep squaring the current number and check if the squared value exists in the HashSet. If it does, increment the streak length.\nTrack Maximum Streak Length: Throughout the iteration, maintain a record of the longest streak found.\nReturn Result: Finally, return the maximum streak length found. If no valid streak is found, return -1.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nThe outer loop runs in O(n), where n is the length of the nums array. The inner while loop potentially runs multiple times based on how many squares exist in the set. Since we are squaring the number, it reduces quickly, making it logarithmic relative to the maximum streak length.\n\n- Space complexity:\nWe use a HashSet to store all elements from the array, leading to a space complexity that is linear with respect to the size of nums.\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int longestSquareStreak(int[] nums) {\n // Step 1: Use HashSet to store all elements in nums for quick lookup\n\n HashSet<Integer>set = new HashSet<>();\n for(int num :nums) set.add(num);\n\n int max_=Integer.MIN_VALUE; // Initialize max streak length\n\n // Step 2: Check each number in nums as the start of a possible square streak\n\n for(int num: nums){\n int len =1; // Initial length of streak\n long square = num; // Initialize square as num (using long to avoid overflow)\n\n // Step 3: Continue squaring until out of bounds or square not found in set\n\n while(square*square<=Integer.MAX_VALUE && set.contains((int)(square*square))){\n len++;// Increment streak length\n square = square*square;// Update square to its square\n }\n\n // Update max streak length\n max_ = Math.max(len, max_);\n }\n // Step 4: Return result based on max streak found\n return max_==1 ? -1: max_;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Very easy code|| Easy to understand
|
very-easy-code-easy-to-understand-by-him-yrah
|
Intuition\nFirstly store all the elements in an unordered set .\nSort the elements.\nIncreasing the value if we find the square of a number in the set.\n Descri
|
Himanshu-kansal
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T18:37:34.518380+00:00
|
2024-10-28T18:37:34.518422+00:00
| 11 | false |
# Intuition\nFirstly store all the elements in an unordered set .\nSort the elements.\nIncreasing the value if we find the square of a number in the set.\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n<!-- # Approach -->\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n<!-- # Complexity -->\n<!-- - Time complexity: -->\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n<!-- - Space complexity: -->\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int longestSquareStreak(vector<int>& nums) {\n int res=0;\n unordered_set<long long> st;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n st.insert(nums[i]);\n }\n sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n int temp=1;\n long long a=nums[i];\n int cnt=1;\n while(cnt<nums.size() && st.find(a*a)!=st.end()){\n cnt++;\n a=a*a;\n temp++;\n // if(cnt==nums.size())\n // return max(temp,res);\n }\n // if()\n res=max(res,temp);\n }\n if(res<2)\n return -1;\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
longest-square-streak-in-an-array
|
Easy Java Solution using Hashmap with explanation
|
easy-java-solution-using-hashmap-with-ex-pho9
|
\n\n# Approach\nThe basic idea is that if we need a subsequence in sorted order, why not sort the whole array and then fine subsequence.\nFor every sorted eleme
|
akshay1610
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T18:00:34.041495+00:00
|
2024-10-28T18:02:04.020743+00:00
| 17 | false |
\n\n# Approach\nThe basic idea is that if we need a subsequence in sorted order, why not sort the whole array and then fine subsequence.\nFor every sorted element (descending), check if the element\'s square has always been visited (using hashmap), if yes, then add 1 to the value of the square\'s value in dp array and set the current dp value. If n, set the current dp value as 0.\neg. nums = [4,3,6,16,8,2]\n sort the array in desc - [16,8,6,4,3,2]\n dp = [0,0,0,0,0,0]\n The first value will be always 0. Start with index=1;\n Add 16 to hashmap along with its index. map.put(16,0)\n i=1; 8*8 is not present in a map, so dp[1] = 0; map.put(8,1)\n i=2; 6*6 is not present. dp[2]=0; map.put(6,2)\n i=3;4*4 is present, so dp[3] = 1+ dp[16] = 1\nAnd so on..\n\nAt last return the maximum value from dp array + 1;\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n(nlog(n))\n\n- Space complexity:\n<O(n)\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int longestSquareStreak(int[] nums) {\n Arrays.sort(nums);\n int n = nums.length;\n Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();\n int[] dp = new int[n];\n dp[0]=0;\n map.put(nums[n-1],0);\n int max = 0;\n int j = 1;\n for (int i = n-2;i>=0;i--) {\n if (map.containsKey(nums[i]*nums[i])) {\n dp[j] = 1+dp[map.get(nums[i]*nums[i])]; \n }else{dp[j] = 0;}\n if (!map.containsKey(nums[i])) {\n map.put(nums[i],j);\n }\n max = Math.max(dp[j],max);\n j++;\n }if (max==0) {return -1;}\n return max+1;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Binary Search', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Sorting', 'Java']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
✔ C++ | Set | Clean and Concise
|
c-set-clean-and-concise-by-jk20-ovai
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n \n int n=nums.size();\n set<vector<int>>ans;\n
|
jk20
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:04:42.671845+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:05:02.873332+00:00
| 10,219 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n \n int n=nums.size();\n set<vector<int>>ans;\n \n int i,j;\n for(i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n vector<int>tt;\n int ct=0;\n for(j=i;j<n;j++)\n {\n tt.push_back(nums[j]);\n if(nums[j]%p==0)\n ++ct;\n if(ct>k)\n break;\n ans.insert(tt);\n \n }\n }\n return ans.size();\n }\n \n};\n```\n\n\n**Pls upvote the solution if you found helpful, it means a lot.\nAlso comment down your doubts.\nHappy Coding : )**
| 114 | 8 |
['C', 'C++']
| 14 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
O(n ^ 2): Rabin-Karp vs. Trie
|
on-2-rabin-karp-vs-trie-by-votrubac-phn5
|
It\'s tempting to apply a sliding window technique here, however, it won\'t help us identify distinct subarrays.\n\nBecause constraints are low (n <= 200), we c
|
votrubac
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:03:21.703605+00:00
|
2022-05-01T21:12:11.344664+00:00
| 11,875 | false |
It\'s tempting to apply a sliding window technique here, however, it won\'t help us identify **distinct** subarrays.\n\nBecause constraints are low (n <= 200), we can just identify all valid subarrays *O(n ^ 2)*, and use a set to dedup them *O(n)*. So, the overall complexity would be *O(n ^ 3)*.\n\nFor O(n ^ 2) solution, we can use a rolling hash (Rabin-Karp). Note that we only need to check hashes for arrays of the same size, which reduces the collision probability.\n\nWe can also use a Trie to achieve a quadratic complexity - check the second solution below.\n\n#### Rolling Hash (Simple)\nWe need to do the collision check, but here I omitted it for simplicity (see third solution below if you want to handle collisions).\n**C++**\n```cpp\nint countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int cnt[201] = {}, hash[201] = {}, res = 0;\n for (int sz = 0; sz < nums.size(); ++sz) {\n unordered_set<int> s;\n for (int i = 0; i + sz < nums.size(); ++i) {\n cnt[i] += nums[i + sz] % p == 0;\n if (cnt[i] <= k) {\n hash[i] = ((long long)hash[i] * 200 + nums[i + sz]) % 1000000007;\n res += s.insert(hash[i]).second;\n }\n }\n }\n return res;\n}\n```\n#### Trie\nWe increment counters for each Trie node to detect if a substring is a duplicate.\n\n**C++**\n```cpp\nstruct Trie {\n unordered_map<int, Trie*> ch;\n int cnt = 0;\n int insert(vector<int>& nums, int i, int k, int p) {\n if (i == nums.size() || k - (nums[i] % p == 0) < 0)\n return 0;\n if (ch[nums[i]] == nullptr)\n ch[nums[i]] = new Trie();\n return (++ch[nums[i]]->cnt == 1) + \n ch[nums[i]]->insert(nums, i + 1, k - (nums[i] % p == 0), p);\n }\n};\nint countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int res = 0;\n Trie t;\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)\n res += t.insert(nums, i, k, p);\n return res;\n}\n```\n#### Rolling Hash (Collision Check)\n**C++**\n```cpp\nint countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int cnt[201] = {}, hash[201] = {}, res = 0;\n for (int sz = 0; sz < nums.size(); ++sz) {\n unordered_map<int, vector<int>> s;\n auto collision = [&](const auto &ids, int i) {\n for (int j : ids)\n if (equal(begin(nums) + i, begin(nums) + i + sz + 1, begin(nums) + j))\n return true;\n return false;\n };\n for (int i = 0; i + sz < nums.size(); ++i) {\n cnt[i] += nums[i + sz] % p == 0;\n if (cnt[i] <= k) {\n hash[i] = ((long long)hash[i] * 200 + nums[i + sz]) % 1000000007;\n if (!collision(s[hash[i]], i)) {\n s[hash[i]].push_back(i);\n ++res;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n return res;\n}\n```
| 104 | 4 |
['C']
| 26 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C++ | Trie Solution | O(N^2)
|
c-trie-solution-on2-by-callmepandey-lqw7
|
We will be using TRIE, considering each subarray as a string and only inserting subarrays with total number of elements divisible by \'P\' is less than \'K\'.\n
|
callmepandey
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T06:36:26.604399+00:00
|
2022-05-02T18:37:16.853473+00:00
| 3,948 | false |
We will be using TRIE, considering each subarray as a string and only inserting subarrays with total number of elements divisible by \'P\' is less than \'K\'.\n\n**How we managed to cope with Duplicacy?**\n\nLets say there are two diffrent equal subarray with total divisible elements less than \'K\', once we insert the first subarray there will be all nodes already allocated for the next subarray once we start inserting it. (Look into code for better undestanding)\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n class trie {\n public:\n unordered_map < int , trie* > next;\n int c;\n trie() {\n }\n };\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n trie *root = new trie();\n int n = nums.size();\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){\n \n // Temp Pointer, which copies the root.\n trie *temp = root;\n \n // Count stores total number divisible by \'P\' so far.\n int count = 0;\n for(int j = i;j<n;j++){\n if(nums[j] % p == 0)\n count++;\n \n // If count is greater than \'K\' we do not have valid subarray. \n if(count > k)\n break;\n \n // Else if we do not have already existing node for new insertion we will create one.\n // Also increase \'ANS\' by \'1\' as we encountered this position first time.\n if(!temp->next[nums[j]]){\n temp->next[nums[j]] = new trie();\n ans++;\n }\n temp = temp->next[nums[j]];\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 70 | 2 |
['Trie', 'C++']
| 7 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Generate all Subarray
|
generate-all-subarray-by-kamisamaaaa-bcem
|
Generate all subarray and check the given condition.\n\nPS : Appending characters corresponding to ascii into currSubArray\ntreating Integer values as ASCII val
|
kamisamaaaa
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:00:54.183929+00:00
|
2024-07-24T06:43:03.087051+00:00
| 10,925 | false |
**Generate all subarray and check the given condition.**\n\n**PS : Appending characters corresponding to ascii into currSubArray**\n**treating Integer values as ASCII values so that they become unique**\n```\nstring str;\nstr.push_back(65);\ncout << str;\n\nIt will print "A".\n```\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n \n int n(size(nums)), res(0);\n unordered_set<string> all; // stores unique substrings which satisfy the given condition.\n \n for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {\n int cnt(0);\n string currSubArray; // stores subarray starting from index i.\n for (int j=i; j<n; j++) {\n currSubArray.push_back(nums[j]); // Appending charcter with nums[j] ascii value.\n if (nums[j] % p == 0) cnt++;\n // if the current array have at most k elements divisible by then add it to the set.\n if (cnt <= k) all.insert(currSubArray);\n }\n }\n return size(all);\n }\n};\n```
| 40 | 3 |
['C']
| 20 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Three solutions: Trie, Rabin-Karp + Set, LCP-array O(N) time, O(N) space
|
three-solutions-trie-rabin-karp-set-lcp-q0ram
|
First solution (Trie)\nWe use a trie to compactly store all possible subarrays.\n When we find out that the prefix doesn\'t exist, we increment answer and creat
|
rs9
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-02T04:53:19.448308+00:00
|
2022-05-02T04:56:32.847315+00:00
| 3,065 | false |
# First solution (Trie)\nWe use a trie to compactly store all possible subarrays.\n When we find out that the prefix doesn\'t exist, we increment answer and create another node in the tree\n```\nimport java.util.ArrayList;\nimport java.util.List;\n\npublic class Solution {\n private static final int MAX_P = 200;\n\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n int n = nums.length;\n List<int[]> child = new ArrayList<>();\n child.add(new int[MAX_P + 1]);\n int nxt = 1, ans = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n int count = 0, node = 0;\n int j = i;\n while (j < n && count <= k) {\n int c = nums[j++];\n if (c % p == 0) if (count++ == k) break;\n if (child.get(node)[c] == 0) {\n ans++;\n child.get(node)[c] = nxt++;\n child.add(new int[MAX_P + 1]);\n }\n node = child.get(node)[c];\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```\n\nThis solution has O(N^2) space complexity and O(N^2) time complexity. \n\n# Rabin-Karp Rolling Hash\nWe use some incremental hashing function as we don\'t want to recalculate it for every possible subarray.\nI took as mod the largest prime number below `(Long.MAX_VALUE-200)/201`, so the hash calculation never overflows.\nThis solution has drawbacks and it depends on some luck, cause it doesn\'t check any hash collisions.\n```\npublic class Solution {\n private static final int MAX_P = 200;\n private static final long base = MAX_P + 1;\n private static final long mod = 45887423068929227L;\n\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n int n = nums.length;\n Set<Long> set = new HashSet<>();\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n long hash = 0;\n for (int j = i, count = 0; j < n; j++) {\n if (nums[j] % p == 0) if (count++ == k) break;\n hash = (hash * base + nums[j]) % mod;\n set.add(hash);\n }\n }\n return set.size();\n }\n}\n```\nThis solution also has O(N^2) time complexity and O(N^2) space complexity.\n\n\n# Suffix Array and Longest Common Prefix Array\nConstruction of Suffix Arrays is pretty hard theme, so I won\'t explain it here, but the listing of algos can be seen in appendix. You can read more about Suffix Arrays Construction at other resources.\n\nWe build suffix array, lcp-array and also for each position we calculate what is the longest valid string can start from this index.\nFor each element we calculate additional strings it can form. But we remember that some of this strings can be added also by the next element in the suffix array.\n\n```\npublic class Solution {\n private static final int MAX_P = 200;\n\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n int n = nums.length;\n if (n == 0) return 0;\n if (n == 1) {\n if (k >= 1 || nums[0] % p != 0) return 1;\n else return 0;\n }\n int[] maxLength = new int[n];\n for (int l = n - 1, r = n, count = 0; l >= 0; l--) {\n if (nums[l] % p == 0) {\n count++;\n while (count > k) if (nums[--r] % p == 0) count--;\n }\n maxLength[l] = r - l;\n }\n\n int[] suffixArray = buildSuffixArray(nums, MAX_P);\n int[] invSuffixArray = inverseSuffixArray(suffixArray);\n int[] lcp = buildLongestCommonPrefixArray(nums, suffixArray, invSuffixArray);\n\n int ans = maxLength[suffixArray[n - 1]];\n for (int sortedPos = n - 2; sortedPos >= 0; sortedPos--) {\n int maxLen = maxLength[suffixArray[sortedPos]];\n int commonLength = lcp[sortedPos];\n if (commonLength < maxLen) ans += maxLen - commonLength;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```\n\nThis solution has O(N) time complexity and O(N) space compelxity.\n\n# Appendix\nUsed algo:\nK\xE4rkk\xE4inen, Sanders algorithm to build suffix array in O(n)\nKasai, Arimura, Arikawa, Lee, Park algorithm to build LCP array in O(n)\n\n```\n\t// arr.length>=2, s[i]>=1, s[i]<=K\n private static int[] buildSuffixArray(int[] arr, int K) {\n int n = arr.length;\n int[] s = Arrays.copyOf(arr, n + 3);\n int[] SA = new int[n];\n suffixArray(s, SA, n, K);\n return SA;\n }\n\n private static int[] inverseSuffixArray(int[] suffixArray) {\n int n = suffixArray.length;\n int[] ans = new int[n];\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) ans[suffixArray[i]] = i;\n return ans;\n }\n\n private static int[] buildLongestCommonPrefixArray(int[] arr, int[] suffixArray, int[] invSuffixArray) {\n int n = arr.length;\n int[] lcp = new int[n - 1];\n int k = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n if (k > 0) k--;\n if (invSuffixArray[i] == n - 1) {\n k = 0;\n } else {\n int j = suffixArray[invSuffixArray[i] + 1];\n while (i + k < n && j + k < n && arr[i + k] == arr[j + k]) k++;\n lcp[invSuffixArray[i]] = k;\n }\n }\n return lcp;\n }\n\n //Lexicographic order for pairs.\n private static boolean leq(int a1, int a2, int b1, int b2) {\n return (a1 < b1 || (a1 == b1 && a2 <= b2));\n }\n\n //Lexicographic order for triples.\n private static boolean leq(int a1, int a2, int a3, int b1, int b2, int b3) {\n return (a1 < b1 || (a1 == b1 && leq(a2, a3, b2, b3)));\n }\n\n private static void suffixArray(int[] s, int[] SA, int n, int K) {\n int n0 = (n + 2) / 3, n1 = (n + 1) / 3, n2 = n / 3, n02 = n0 + n2;\n int[] s12 = new int[n02 + 3], SA12 = new int[n02 + 3], s0 = new int[n0], SA0 = new int[n0];\n\n for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n + (n0 - n1); i++) if (i % 3 != 0) s12[j++] = i;\n\n radixPass(s12, SA12, s, 2, n02, K);\n radixPass(SA12, s12, s, 1, n02, K);\n radixPass(s12, SA12, s, 0, n02, K);\n\n // find lexicographic names of triples\n int name = 0, c0 = -1, c1 = -1, c2 = -1;\n for (int i = 0; i < n02; i++) {\n if (s[SA12[i]] != c0 || s[SA12[i] + 1] != c1 || s[SA12[i] + 2] != c2) {\n name++;\n c0 = s[SA12[i]];\n c1 = s[SA12[i] + 1];\n c2 = s[SA12[i] + 2];\n }\n if (SA12[i] % 3 == 1) {\n s12[SA12[i] / 3] = name;\n } // left half\n else {\n s12[SA12[i] / 3 + n0] = name;\n } // right half\n }\n\n // recurse if names are not yet unique\n if (name < n02) {\n suffixArray(s12, SA12, n02, name);\n // store unique names in s12 using the suffix array\n for (int i = 0; i < n02; i++) s12[SA12[i]] = i + 1;\n } else // generate the suffix array of s12 directly\n for (int i = 0; i < n02; i++) SA12[s12[i] - 1] = i;\n\n // stably sort the mod 0 suffixes from SA12 by their first character\n for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n02; i++) if (SA12[i] < n0) s0[j++] = 3 * SA12[i];\n radixPass(s0, SA0, s, 0, n0, K);\n\n // merge sorted SA0 suffixes and sorted SA12 suffixes\n for (int p = 0, t = n0 - n1, k = 0; k < n; k++) {\n int i = getI(SA12, n0, t); // pos of current offset 12 suffix\n int j = SA0[p]; // pos of current offset 0 suffix\n if (SA12[t] < n0 ? // different compares for mod 1 and mod 2 suffixes\n leq(s[i], s12[SA12[t] + n0], s[j], s12[j / 3]) :\n leq(s[i], s[i + 1], s12[SA12[t] - n0 + 1], s[j], s[j + 1], s12[j / 3 + n0])\n ) {// suffix from SA12 is smaller\n SA[k] = i;\n t++;\n if (t == n02) // done --- only SA0 suffixes left\n for (k++; p < n0; p++, k++) SA[k] = SA0[p];\n } else {// suffix from SA0 is smaller\n SA[k] = j;\n p++;\n if (p == n0) // done --- only SA12 suffixes left\n for (k++; t < n02; t++, k++) SA[k] = getI(SA12, n0, t);\n }\n }\n }\n\n private static int getI(int[] SA12, int n0, int t) {\n return SA12[t] < n0 ? SA12[t] * 3 + 1 : (SA12[t] - n0) * 3 + 2;\n }\n\n private static void radixPass(int[] a, int[] b, int[] r, int shift, int n, int K) {\n int[] c = new int[K + 1]; // counter array\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) c[r[a[i] + shift]]++; // count occurrences\n for (int i = 0, sum = 0; i <= K; i++) { // exclusive prefix sums\n int t = c[i];\n c[i] = sum;\n sum += t;\n }\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) b[c[r[a[i] + shift]]++] = a[i];\n }\n```\n\n
| 26 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Suffix Array', 'Java']
| 6 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
✅ Python - Simple Count all combinations
|
python-simple-count-all-combinations-by-nqcco
|
\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n n = len(nums) \n sub_arrays = set
|
constantine786
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:42:53.149122+00:00
|
2022-06-16T23:59:47.197083+00:00
| 3,571 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n n = len(nums) \n sub_arrays = set()\n \n\t\t# generate all combinations of subarray\n for start in range(n):\n cnt = 0\n temp = \'\'\n for i in range(start, n):\n if nums[i]%p == 0:\n cnt+=1 \n temp+=str(nums[i]) + \',\' # build the sequence subarray in CSV format \n if cnt>k: # check for termination \n break\n sub_arrays.add(temp) \n \n return len(sub_arrays)\n```\n\n**T = O(N^3)**\n**S = O(N^2)**\n\n---\n\n***Please upvote if you find it useful***
| 26 | 0 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 3 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
O(N) C++ solution using Suffix array template.
|
on-c-solution-using-suffix-array-templat-bhvn
|
I used O(N log N) template of suffix array but you can use O(N) template.\nRest I used LCP array for removing duplicate subarray , and suffix array to get total
|
itachi_god
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:02:51.837134+00:00
|
2022-05-04T15:11:27.460214+00:00
| 3,466 | false |
I used O(N log N) template of suffix array but you can use O(N) template.\nRest I used LCP array for removing duplicate subarray , and suffix array to get total subarrays.\nyou can get suffix array and lcp array template here https://cp-algorithms.com/string/suffix-array.html.\nmy template of suffix array function and lcp array, you can get here https://p.ip.fi/b1qd\n```\nvector<int> boundary(vector<int> &v,int k,int p){\n\t/// Function for getting right boundary for each index for at most k divisible elements by p\n int n = v.size();\n\tvector<int> ret(n);\n\tfor(int i = n-1, j = n - 1; i >= 0; i--){\n\t\tk -= v[i] % p == 0;\n\t\twhile(k < 0) {k += v[j--] % p == 0;}\n\t\tret[i] = j + 1;\n\t}\n\treturn ret;\n}\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n vector<int> vv = boundary(nums,k,p) , lcp = lcp_array(nums) , sfx = suffix_array(nums);\n int ans = 0 , n = nums.size();\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) \n ans += vv[sfx[i]] - sfx[i];\n for(int i = 0; i + 1 < n; i++) \n ans -= min(vv[sfx[i]] - sfx[i], lcp[i]);\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 25 | 1 |
['Sliding Window']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
[Java] Simple HashSet Solution (Easy to understand)
|
java-simple-hashset-solution-easy-to-und-x2x7
|
\tclass Solution {\n\t\tpublic int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n\t\t\tHashSet hs = new HashSet<>();\n\n\t\t\tfor(int i=0; i<nums.length; ++i) {\n\
|
Samuel3Shin
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:02:23.922140+00:00
|
2022-05-02T18:46:07.073870+00:00
| 2,778 | false |
\tclass Solution {\n\t\tpublic int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n\t\t\tHashSet<String> hs = new HashSet<>();\n\n\t\t\tfor(int i=0; i<nums.length; ++i) {\n\t\t\t\tint cnt = 0;\n\t\t\t\tStringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();\n\n\t\t\t\tfor(int j=i; j<nums.length; ++j) {\n\n\t\t\t\t\tif(nums[j]%p == 0) {\n\t\t\t\t\t\tcnt++;\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\t\tif(cnt > k) {\n\t\t\t\t\t\tbreak;\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\t\tsb.append(nums[j] + ",");\n\n\t\t\t\t\ths.add(sb.toString());\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\treturn hs.size();\n\t\t}\n\n\t}
| 24 | 0 |
['Java']
| 4 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
✅[C++] Intuitive Trie Approach w/Explanation
|
c-intuitive-trie-approach-wexplanation-b-a4x7
|
This question is a little tricky. At first, i thought it could be done with two pointers, just like its base questions, but \nthen i realised that we have to sk
|
biT_Legion
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-15T10:34:06.846598+00:00
|
2022-06-15T10:34:06.846643+00:00
| 929 | false |
This question is a little tricky. At first, i thought it could be done with two pointers, just like its base questions, but \nthen i realised that we have to skip the repeated occurrances of subarrays. Thats where that method fails. That method counts the repeated subarrays as well, but this question has asked us to skip them.\n\nNow, since we are asked to skip the repeated subarrays, we can also use set to store all the subarrays generated(since constraints are small) but that would be space consuming. \n**Therefore, best way to solve such problems is Trie**\n\n#### How do we solve with Trie?\nI assume that you alread know about Trie Data structure and its functioning. In case you dont, you can learn it from [TechDose](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6PX6wqDQE20&list=PLEJXowNB4kPyi859E6qGUs7jlpQehJndl) who has explained it in the best way possible. \n\n\n\nNow, we will maintain a Trie of subsets of the array. We will iterate the array in O(n<sup>2</sup>) and in each iteration, we will count the valid subarrays starting from nums[i]. If at any point, the count(that stores the count of numbers divisible by p in that subarray) is greater than k, we break the loop for that i. \nWe check if this subset is already present in our Trie or not. If it is present, we just skip it, else, we add the current element to trie, update the subset and update our ans variable. \nFor ex.\n```\n[8,8,8]\n3\n17\nPossible subsets are [8], [8,8], [8,8,8]. Lets do a dry run. \ni=0, j=0, 8 will be inserted and ans = 1\ni=0, j=1, another 8 will be inserted and ans = 2\ni=0, j=2, another 8 will be inserted and ans = 3\n\ni=1,j=1, this time, 8 will not be inserted because temp->next[8] already exists\ni=1,j=2, this time also, 8 wont be inserted because temp->next[8] exists already\n\ni=2,j=2, this time too, nothing happens.\nThus \'ans = 3\'\n```\n\n```\nclass Trie {\npublic:\n int val;\n unordered_map <int,Trie*> next;\n};\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int ans = 0;\n Trie* root = new Trie();\n for(int i = 0; i<nums.size(); i++){\n Trie* temp = root;\n int count = 0;\n for(int j = i; j<nums.size(); j++){\n if(nums[j]%p==0) count++;\n if(count>k) break;\n \n if(!temp->next[nums[j]]){\n temp->next[nums[j]] = new Trie();\n ans++;\n }\n temp = temp->next[nums[j]];\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 15 | 0 |
['Trie', 'C', 'C++']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
O(n^2) python Trie
|
on2-python-trie-by-netflix77799-2bj2
|
\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n trie = {}\n n = len(nums)\n ans = 0\n for
|
netflix77799
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T12:10:36.928733+00:00
|
2022-05-01T12:10:36.928766+00:00
| 667 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n trie = {}\n n = len(nums)\n ans = 0\n for start in range(n):\n count = 0\n cur = trie\n for j in range(start, n):\n num = nums[j]\n if num % p == 0:\n count += 1\n \n if count > k:\n break\n \n if num not in cur:\n cur[num] = {}\n ans += 1\n cur = cur[num]\n \n return ans \n```
| 13 | 1 |
['Trie', 'Python']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C++ || Easy to Understand
|
c-easy-to-understand-by-satyam_1911-84xd
|
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector& nums, int k, int p) {\n \n sets;\n int n = nums.size();\n for(int i = 0
|
Satyam_1911
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:03:49.881578+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:03:49.881613+00:00
| 1,504 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n \n set<string>s;\n int n = nums.size();\n for(int i = 0;i<n;i++)\n {\n int c = 0;\n string str = "";\n for(int j = i;j<n;j++)\n {\n str += nums[j]+\'0\';\n if(nums[j]%p == 0)\n c++;\n if(c<=k)\n s.insert(str);\n else\n break;\n \n }\n }\n return s.size(); \n }\n};
| 13 | 0 |
['C', 'Ordered Set']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
JAVA | Set | Hashing | 2 For loops | Clean and Concise
|
java-set-hashing-2-for-loops-clean-and-c-vqnj
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n int n = nums.length;\n\t\t// we are storing hashcode for all the substring
|
priyank-doshi
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:29:31.157706+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:31:43.765968+00:00
| 2,461 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n int n = nums.length;\n\t\t// we are storing hashcode for all the substrings so that we can compare them faster.\n\t\t// main goal is to avoid entire sub array comparision using hashcode.\n Set<Long> ways = new HashSet<>(); \n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n int cnt = 0;\n long hc = 1; // this is the running hashcode for sub array [i...j]\n for(int j = i; j < n; j++) {\n hc = 199L * hc + nums[j]; // updating running hashcode, since we nums are <=200, we shall consider a prime near 200 to avoid collision\n if(nums[j] % p == 0)\n cnt++;\n if(cnt <= k) { // if current subarray [i...j] is valid, add its hashcode in our storage.\n ways.add(hc);\n }\n }\n }\n return ways.size();\n }\n}\n```
| 12 | 1 |
['Java']
| 9 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C++ clean and clear concise solution || Set
|
c-clean-and-clear-concise-solution-set-b-0txv
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) \n {\n unordered_set<string> s; // use string instead of vector<in
|
ChaturvediParth
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-05T15:55:26.300702+00:00
|
2022-05-05T15:55:26.300727+00:00
| 857 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) \n {\n unordered_set<string> s; // use string instead of vector<int> because it\'s less time consuming\n int n=nums.size();\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n int count=0;\n string str="";\n \n for(int j=i;j<n;j++)\n {\n if(nums[j]%p==0)\n count++;\n \n if(count>k)\n break;\n \n str+=to_string(nums[j])+"->";\n s.insert(str);\n }\n }\n return s.size();\n }\n};\n```\n\n# Please upvote if you liked this solution.\n# If you have any doubt in this solution, comment down below. I would be more than happy to help you
| 10 | 0 |
['C', 'Ordered Set', 'C++']
| 3 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Java Solution | Sliding Window + Trie | Runtime: 41 ms, faster than 98.46%
|
java-solution-sliding-window-trie-runtim-5pm5
|
\nclass Solution {\n private static class Node {\n\t\tprivate int val;\n\t\tprivate boolean isEnd;\n\t\tprivate Node[] children;\n\n\t\tpublic Node(int val)
|
nitwmanish
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-30T22:35:17.377790+00:00
|
2022-11-05T02:33:15.250030+00:00
| 844 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n private static class Node {\n\t\tprivate int val;\n\t\tprivate boolean isEnd;\n\t\tprivate Node[] children;\n\n\t\tpublic Node(int val) {\n\t\t\tthis.val = val;\n\t\t\tthis.isEnd = false;\n\t\t\tthis.children = new Node[201];\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\n\tprivate int totalCount = 0;\n\tprivate Node root = new Node(0);\n\t\n\tprivate void insert(int[] nums, int left, int right) {\n\t\tNode curr = this.root;\n\t\tfor (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {\n\t\t\tint childIdx = nums[i];\n\t\t\tif (curr.children[childIdx] == null) {\n\t\t\t\tcurr.children[childIdx] = new Node(childIdx);\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\tcurr = curr.children[childIdx];\n\t\t\tif (!curr.isEnd) {\n\t\t\t\ttotalCount++;\n\t\t\t\tcurr.isEnd = true;\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\n\tpublic int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n\t\tint count = 0;\n\t\tint n = nums.length;\n\t\tint left = 0;\n\t\tint right = 0;\n\t\twhile (left < n) {\n\t\t\twhile (right < n) {\n\t\t\t\tif (nums[right] % p == 0) {\n\t\t\t\t\tcount++;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\tif (count == k + 1) {\n\t\t\t\t\tcount--;\n\t\t\t\t\tbreak;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\tright++;\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\tinsert(nums, left, right - 1);\n\t\t\tif (nums[left] % p == 0) {\n\t\t\t\tcount--;\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\tleft++;\n\t\t}\n\t\treturn totalCount;\n\t}\n}\n```\nSome Other Problems Using Trie Data Structure \n[1268 : Search Suggestions System](https://leetcode.com/problems/search-suggestions-system/discuss/2638534/java-solution-using-trie-runtime-37-ms-beats-7219)\n[1233 : Remove Sub-Folders from the Filesystem](https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-sub-folders-from-the-filesystem/discuss/2638522/java-solution-using-trie-runtime-43-ms-beats-9605)\n[648\t: Replace Words](https://leetcode.com/problems/replace-words/discuss/2638625/java-solution-using-trie-runtime-14-ms-beats-962219)\n[820\t: Short Encoding of Words](https://leetcode.com/problems/short-encoding-of-words/discuss/2639021/java-solution-using-trie)\n[208\t: Implement Trie (Prefix Tree)](https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-trie-prefix-tree/discuss/2638657/simple-java-solution)\n[386\t: Lexicographical Numbers](https://leetcode.com/problems/lexicographical-numbers/discuss/2639107/java-solution-using-trie)\n[1023 : Camelcase Matching](https://leetcode.com/problems/camelcase-matching/discuss/2639736/java-solution-using-trie)\n[677\t: Map Sum Pairs](https://leetcode.com/problems/map-sum-pairs/discuss/2639994/java-solution-using-trie-and-hashmap)\n[676\t: Implement Magic Dictionary](https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-magic-dictionary/discuss/2640276/java-solution-using-trie)\n[421\t: Maximum XOR of Two Numbers in an Array](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-xor-of-two-numbers-in-an-array/discuss/2643276/java-trie-approach-add-number-and-check-its-max-xor-on-fly-tc-on-and-sc-on)\n[792\t: Number of Matching Subsequences](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-matching-subsequences/discuss/2643489/java-solutions-two-approach-1-using-trie-2-hashmap)\n[720\t: Longest Word in Dictionary](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-word-in-dictionary/discuss/2643586/java-solution-using-trie-dfs)\n[2261 : K Divisible Elements Subarrays](https://leetcode.com/problems/k-divisible-elements-subarrays/discuss/2643761/java-solution-sliding-window-trie-runtime-41-ms-faster-than-9846)\n[139\t: Word Break](https://leetcode.com/problems/word-break/discuss/2643915/java-solutions-two-approach-1-using-trie-bfs-2-dp)\n[211\t: Design Add and Search Words Data Structure](https://leetcode.com/problems/design-add-and-search-words-data-structure/discuss/2643839/java-solution-using-trie-dfs)\n[1948 : Delete Duplicate Folders in System](https://leetcode.com/problems/delete-duplicate-folders-in-system/discuss/2646138/java-solution-using-trie-with-postorder-and-inorder-dfs-traversal)\n[1032 : Stream of Characters](https://leetcode.com/problems/stream-of-characters/discuss/2646970/java-solution-using-trie)\n[212. Word Search II](https://leetcode.com/problems/word-search-ii/discuss/2779677/Java-Solution-or-Using-Trie)
| 8 | 0 |
['Tree', 'Trie', 'Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Python 5-Liner || Binary Search || Prefix Sum
|
python-5-liner-binary-search-prefix-sum-fvuzp
|
\n5-Liner:\npy\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n pref_sum,l,s,sol=list(accumulate(nums2:=[int(x%p=
|
subin_nair
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:11:36.875512+00:00
|
2022-05-01T08:17:45.789865+00:00
| 1,857 | false |
\n5-Liner:\n```py\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n pref_sum,l,s,sol=list(accumulate(nums2:=[int(x%p==0) for x in nums])),len(nums),set(),0\n for left,x in enumerate(pref_sum):\n for end in range(left+1,bisect_left(pref_sum,x+k if nums2[left] else x+1+k ,lo=left)+1):\n if (t:=tuple(nums[left:end])) not in s:s.add(t)\n return len(s)\n\n```\n\nExpanded Code :\n```py\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n nums2 = [int(x % p == 0) for x in nums]\n pref_sum = list(accumulate(nums2))\n l = len(pref_sum)\n s = set()\n sol = 0\n for left, x in enumerate(pref_sum):\n if nums2[left] == 1:\n tar = x + k\n else:\n tar = x + 1 + k\n right = bisect_left(pref_sum, tar, lo=left)\n for end in range(left + 1, right + 1):\n t = tuple(nums[left:end])\n if t not in s:\n s.add(t)\n return len(s)\n```\n\n**Happy Coding !!**
| 8 | 0 |
['Binary Tree', 'Prefix Sum', 'Python']
| 2 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Use Set
|
use-set-by-yadavharsha50-aw0r
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n Set<String> set=new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){\
|
yadavharsha50
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:01:50.799164+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:31:17.445872+00:00
| 456 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n Set<String> set=new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){\n StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();\n int count=0;\n for(int j=i;j<nums.length;j++){\n if(nums[j]%p==0) count++;\n if(count>k) break;\n sb.append(nums[j]+"*");\n set.add(sb.toString());\n \n \n }\n }\n return set.size();\n }\n}\n```
| 6 | 1 |
[]
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
simple and shortest using string | map
|
simple-and-shortest-using-string-map-by-0gawr
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& arr, int k, int p) {\n int n=arr.size();\n int ans = 0 ,ct=0;\n \n u
|
suman_061
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T08:11:31.860472+00:00
|
2022-05-01T08:18:03.353935+00:00
| 283 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& arr, int k, int p) {\n int n=arr.size();\n int ans = 0 ,ct=0;\n \n unordered_map<string,int> mp;\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int ct=0;\n string s=""; // subarry represent into string format\n \n for(int j=i;j<n;j++){\n \n s = s + "$" + to_string(arr[j]); // \'$\' is used to make unique representaion of subarray\n \n if(arr[j]%p == 0) ct++;\n \n if(ct <= k) mp[s]++; // stored in map to avoid duplicate\n } \n }\n \n return mp.size();\n }\n};\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['String', 'C']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C++ simple solution using set
|
c-simple-solution-using-set-by-samarpan2-l7wl
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nSimply traversing through all subarrays and checking condition and updating answer\n# A
|
Samarpan27
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-06T10:04:21.927432+00:00
|
2023-07-06T10:04:21.927453+00:00
| 222 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nSimply traversing through all subarrays and checking condition and updating answer\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nWe are traversing all subarrays using 2 loops of i and j. Whilr traversing in subarray using j, we keep a variable count which keeps record of no of elements in that subarray divisible by p. If count<k, then whether next element is divisible by p or not, we can use that subarray and push in set. If count is equal to k, then we can\'t insert another element in that subarray if it is divisible by p, so we check that if number is divisible by p, then we break or else we puch in subarray and insert in set>\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(N^2)\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(N^2) (worst case)\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n set<vector<int>> s;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)\n {\n int count=0;\n vector<int> temp;\n for(int j=i;j<nums.size();j++)\n {\n if(count<k)\n {\n temp.push_back(nums[j]);\n s.insert(temp);\n\n if(nums[j]%p==0)\n count++;\n }\n else if(count==k)\n {\n if(nums[j]%p!=0)\n {\n temp.push_back(nums[j]);\n s.insert(temp);\n }\n else\n break;\n }\n }\n temp.clear();\n }\n return s.size();\n }\n};\n```\nPlease upvote if you liked solution
| 4 | 0 |
['Ordered Set', 'C++']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Simple prefix sum: O(n^2). 84% fast and 87% memory efficient. Enjoy!!
|
simple-prefix-sum-on2-84-fast-and-87-mem-8svw
|
This problem can be easily done with calculating prefix sum of numbers which are divisible by p.\n- In this approach, the subarrays are kept as strings, as we d
|
The-Mavericks
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-20T04:46:38.267646+00:00
|
2022-06-20T04:46:38.267686+00:00
| 442 | false |
This problem can be easily done with calculating prefix sum of numbers which are divisible by p.\n- In this approach, the subarrays are kept as strings, as we do not want the actual subarrays, rather only the count.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int n = nums.size();\n unordered_set<string> set;\n \n vector<int> prefSum(n + 1);\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n prefSum[i + 1] = prefSum[i] + (nums[i] % p == 0);\n \n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n string subAr = "";\n for(int j = i; j < n; j++){\n if(prefSum[j + 1] - prefSum[i] <= k){\n subAr.push_back(nums[j]);\n set.insert(subAr);\n }\n else break;\n }\n }\n \n return set.size();\n }\n};\n```\n**Upvote ^** if you like.
| 4 | 0 |
['C', 'Prefix Sum', 'C++']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
✅ C++ Solution [Accepted]
|
c-solution-accepted-by-siddharth153-fbfz
|
\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int & k, int & p) {\n int n=nums.size();\n set<vector<int>> s;\n
|
siddharth153
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:03:36.703487+00:00
|
2022-05-01T05:51:02.090400+00:00
| 173 | false |
```\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int & k, int & p) {\n int n=nums.size();\n set<vector<int>> s;\n vector<vector<int>> mat;\n for (int i=0; i <n; i++)\n {\n vector<int> v;\n int c=0;\n for (int j=i; j<n; j++)\n {\n if(nums[j]%p==0) c++;\n v.push_back(nums[j]);\n if(c>k)\n break;\n if(c<=k){\n s.insert(v);\n\n }\n \n }\n }\n \n \n return s.size();\n }\n};\n```\n\n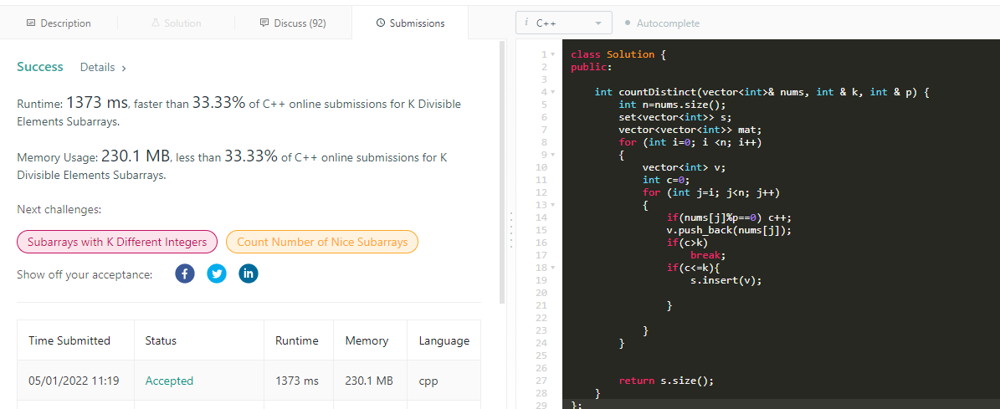\n
| 4 | 0 |
['Ordered Set']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
c++ || solution
|
c-solution-by-soujash_mandal-rpud
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int n=nums.size();\n \n\n set<string> s;\n \
|
soujash_mandal
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:01:50.667398+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:01:50.667439+00:00
| 387 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int n=nums.size();\n \n\n set<string> s;\n \n\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n int count=0;\n int sum=0;\n string str="";\n for(int j=i;j<n;j++)\n {\n str+=to_string(nums[j]);\n str+=\'.\';\n \n \n if(nums[j]%p==0)count++;\n if(count>k) break;\n s.insert(str);\n }\n }\n return s.size();\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
✅Easy C++ Solution | Intuition & Approach
|
easy-c-solution-intuition-approach-by-ri-7ddg
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nLooking at the constraints, we can conclude that if we generate all subarrays in O(n^3)
|
rishabhagg
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-04T13:22:22.656518+00:00
|
2024-01-04T13:22:22.656550+00:00
| 606 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nLooking at the constraints, we can conclude that if we generate all subarrays in O(n^3), it will be accepeted.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nGenerate all subarrays, while pushing elements in the subarray which we are generating we will check if it is divisible by p or not and maintain a count variable. If count <= k then we will store it in a set, since we need different subarrays.\n \n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n^3)\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n^2)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n set<vector<int>>s;\n for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){\n for(int j = i; j < nums.size(); j++){\n vector<int> arr;\n int count = 0;\n for(int l = i; l <= j; l++){\n arr.push_back(nums[l]);\n if(nums[l]%p == 0){\n count++;\n }\n }\n if(count <= k){\n s.insert(arr);\n }\n }\n }\n return s.size();\n }\n};\n```\n\nWe can do small optimisation, it is not required to build subarray from the start we can also keep track of it in two loops only. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n^2 log n)\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n^2)\n\n# Code\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n set<vector<int>>s;\n for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){\n vector<int> arr;\n int count = 0;\n for(int j = i; j >= 0; j--){\n arr.push_back(nums[j]);\n if(nums[j]%p == 0){\n count++;\n }\n if(count <= k){\n s.insert(arr);\n }else{\n break;\n }\n }\n }\n return s.size();\n }\n};\n```\n
| 3 | 0 |
['Ordered Set', 'C++']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Sliding Window Technique: O(N^2)
|
sliding-window-technique-on2-by-deleted_-imhr
|
Intuition\nSince the problem is about subarrays, I felt like the sliding window method is great at dealing with subarrays.\n\n# Approach\nWe\'re gonna run throu
|
deleted_user
|
NORMAL
|
2023-06-14T20:09:58.994203+00:00
|
2023-06-14T20:09:58.994220+00:00
| 710 | false |
# Intuition\nSince the problem is about subarrays, I felt like the sliding window method is great at dealing with subarrays.\n\n# Approach\nWe\'re gonna run through the list with two pointers, i and j. They both start at the beginning, but we keep moving j ahead until we hit more than k numbers in the nums[i:j+1] section that can be divided by p. Every time we find a section that fits the requirements, we add it into a set. Once we can\'t push j any more without breaking the rules, we increase i up a spot and repeat the process.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N^2)\nThe sliding window approach goes through the list twice, once for each "start" point and once for each "end" point of a subarray. Since we\'re looping twice for each item in the list, we say it takes O(N^2).\n\n- Space complexity: O(N)\nThe main thing taking up extra space is the set where we keep track of the subarrays. Given we might end up storing a bunch of subarrays in the set, and each subarray can be as big as the original list, our space usage can be roughly proportional to the size of the list, making it O(N).\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n res = set()\n N = len(nums)\n\n for i in range(N):\n count = 0\n\n for j in range(i, N):\n if nums[j] % p == 0:\n count += 1\n if count > k:\n break\n \n res.add(tuple(nums[i:j + 1]))\n\n return len(res)\n```
| 3 | 1 |
['Sliding Window', 'Python3']
| 3 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
O(n^2) : Rabin Karp (rolling hash)
|
on2-rabin-karp-rolling-hash-by-samahakal-v8id
|
\n\n# Code\n\ntypedef long long ll;\nll mod = 1e11+7;\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n set<ll>st;
|
samahakal04
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-23T17:11:23.448412+00:00
|
2023-01-23T17:11:23.448458+00:00
| 147 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\ntypedef long long ll;\nll mod = 1e11+7;\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n set<ll>st;\n int n = nums.size();\n\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n ll hash = 0;\n int cnt = 0;\n for(int j=i;j<n;j++){\n if(nums[j]%p == 0){\n cnt++;\n }\n if(cnt>k) break;\n hash = (hash*201+nums[j])%mod;\n st.insert(hash);\n }\n }\n return st.size();\n }\n};\n```\n\n# upvote if it\'s help you HAPPY CODING :)\n
| 3 | 0 |
['Rolling Hash', 'C++']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
[Python3] Rolling Hash Simple Solution
|
python3-rolling-hash-simple-solution-by-pkk1j
|
python\nclass Solution:\n POW = 397\n MODULO = 100000000069\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n arr = list(map(
|
huangweijing
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-22T12:49:22.689710+00:00
|
2022-10-22T12:49:22.689769+00:00
| 731 | false |
```python\nclass Solution:\n POW = 397\n MODULO = 100000000069\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n arr = list(map(lambda x: 1 if x % p == 0 else 0, nums))\n ans_set = set[int]()\n for i in range(len(arr)):\n cnt_one = 0\n hash1 = 0\n for j in range(i, len(arr)):\n hash1 = (hash1 * Solution.POW + nums[j] + (j + 1 - i)) % Solution.MODULO\n if arr[j] == 1:\n cnt_one += 1\n if cnt_one <= k:\n ans_set.add(hash1)\n else:\n break\n\n return len(ans_set)\n```\n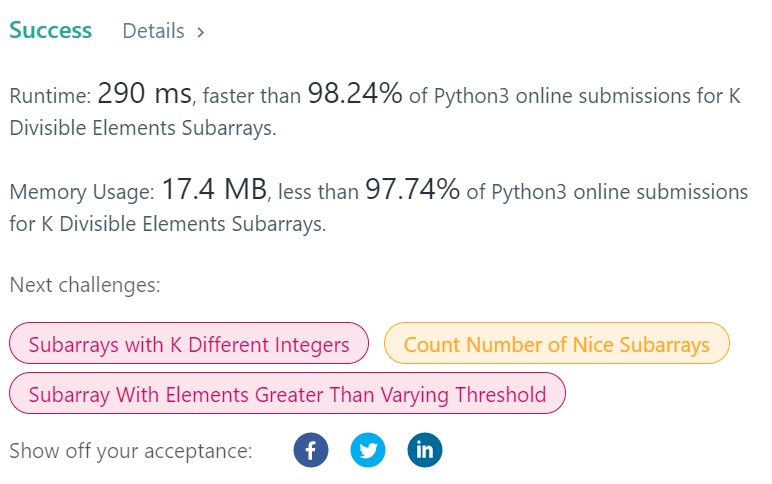\n
| 3 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 3 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
✅✅C++ || Easy To understand solution using set
|
c-easy-to-understand-solution-using-set-u946b
|
\nclass Solution\n{\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p)\n {\n set<vector<int>> visited;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < nu
|
King07
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-30T18:28:25.285030+00:00
|
2022-08-30T18:28:25.285077+00:00
| 326 | false |
```\nclass Solution\n{\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p)\n {\n set<vector<int>> visited;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)\n {\n int count = 0;\n vector<int> currSubArray;\n\n for (int j = i; j < nums.size(); j++)\n {\n currSubArray.push_back(nums[j]);\n if (nums[j] % p == 0)\n count++;\n\n if (count > k)\n break;\n\n visited.insert(currSubArray);\n }\n }\n\n return visited.size();\n }\n};\n```\nTime Complexity = O(n^2)\ns.c=o(n)
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Convert each subarray to string and keep that as hash. It will be unique always
|
convert-each-subarray-to-string-and-keep-o9nh
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int n = nums.size();\n unordered_set<string> mp;\n
|
asquare14
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-02T18:12:42.148094+00:00
|
2022-06-02T18:12:42.148133+00:00
| 177 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int n = nums.size();\n unordered_set<string> mp;\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {\n string hash;\n hash+=to_string(nums[i])+",";\n int count = 0;\n for(int j=i;j<n;j++){\n hash+=to_string(nums[j])+",";\n if(nums[j] % p == 0)\n count++;\n if(count>k) break;\n if(mp.count(hash)==false)\n {\n mp.insert(hash);\n ans++;\n }\n }\n \n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Clean and easy to understand C++ code using Set
|
clean-and-easy-to-understand-c-code-usin-5p92
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n struct hashFunction \n {\n size_t operator()(const vector<int> \n &myVector) const \n {\n
|
bokolom_coder
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-26T06:57:31.051268+00:00
|
2022-06-12T19:10:31.579128+00:00
| 308 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n struct hashFunction \n {\n size_t operator()(const vector<int> \n &myVector) const \n {\n std::hash<int> hasher;\n size_t answer = 0;\n\n for (int i : myVector) \n {\n answer ^= hasher(i) + 0x9e3779b9 + \n (answer << 6) + (answer >> 2);\n }\n return answer;\n }\n };\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n unordered_set<vector<int>, hashFunction> dist;\n \n for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {\n vector<int> t; // create a temporary vector each time to insert in the set\n int count = 0; // count should be 0 after each inner loop iteration finishes\n for (int j = i; j < nums.size(); j++) {\n t.push_back(nums[j]);\n if (nums[j] % p == 0) count++; // count number elements divisible by p\n if (count <= k) {\n dist.insert(t);\n }\n else if (count > k) break; // if number of elements divisible by p is more than k then no point to traverse further, break\n }\n }\n \n return (int)dist.size();\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Ordered Set']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Easily implemented using Trie
|
easily-implemented-using-trie-by-rohit_v-df9t
|
\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n trie = {}\n cnt = 0\n for i in range(len(nums)):\
|
rohit_vishwas_
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-02T17:20:38.199679+00:00
|
2022-05-02T17:20:38.199729+00:00
| 792 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n trie = {}\n cnt = 0\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n count = 0\n divis = 0 #contain count of element in array divisible by p\n d = trie\n for j in range(i,len(nums)):\n if nums[j] % p == 0:\n divis += 1\n if divis > k:\n break\n if nums[j] not in d:\n d[nums[j]] = {}\n count += 1\n d = d[nums[j]]\n cnt += count #count contain all subarrays that can be made from nums[i:j]\n return cnt```
| 3 | 0 |
['Trie', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
[Java] Trie vs Sliding Window | With Explanation
|
java-trie-vs-sliding-window-with-explana-rgnf
|
Trie Approach\n##### Steps\n1. For every index i in nums, insert nums[i,n-1] to the trie\n2. During the insertion, check if it\'s valid (at most k elements divi
|
visonli
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T13:53:10.001084+00:00
|
2022-05-01T13:58:01.853719+00:00
| 356 | false |
### Trie Approach\n##### Steps\n1. For every index `i` in `nums`, insert `nums[i,n-1]` to the trie\n2. During the insertion, check if it\'s valid (at most k elements divisible by p)\n3. If the `trie.next` doesn\'t exist, increase the count because this subarray never visited\n4. Finally, sum up the count\n\n##### Solution\n- time: `O(n^2)`\n- space: `O(n^2)`\n```java\nclass Trie {\n Trie[] next = new Trie[201];\n}\n\npublic int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n int n = nums.length, count = 0;\n Trie t = new Trie();\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n count += insert(t, nums, i, k, p);\n }\n return count;\n}\n\nint insert(Trie t, int[] nums, int start, int k, int p) {\n int n = nums.length, count = 0;\n for (int i = start; i < n; i++) {\n int num = nums[i];\n\n if (num % p == 0) k--;\n if (k < 0) return count;\n if (t.next[num] == null) {\n t.next[num] = new Trie();\n count++;\n }\n t = t.next[num];\n }\n return count;\n}\n```\n\n### Sliding Window Approach\n##### Steps\n1. Move the right pointer `i` to check the subarray with tail at `i`\n2. By moving left pointer `j`, we can get the longest valid `subarray(j,i)`\n3. Add all valid subarrays with tail at `i` to a set\n4. Finally, the size of set is the result\n\n##### Solution\n- time: `O(n^2)`\n- space: `O(n^2)`\n```java\npublic int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n int n = nums.length, j = 0, count = 0;\n Set<String> res = new HashSet<>();\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n if (nums[i] % p == 0) count++;\n\n while (count > k) {\n if (nums[j++] % p == 0) count--;\n }\n Set<String> set = tailSubstrings(nums, j, i);\n res.addAll(set);\n }\n return res.size();\n}\n\nSet<String> tailSubstrings(int[] nums, int start, int end) {\n Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();\n StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();\n for (int i = end; i >= start; i--) {\n sb.append(nums[i]).append(",");\n set.add(sb.toString());\n }\n return set;\n}\n```\n\nPlease let me know if you have questions or better solutions. Thanks :)
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Java Solution | Set
|
java-solution-set-by-_sithcoder-6ws6
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n int res=0;\n Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=
|
_SithCoder_
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T11:08:33.897977+00:00
|
2022-05-01T11:08:33.898018+00:00
| 120 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n int res=0;\n Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){\n int cnt = 0;\n StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();\n for(int j = i;j<nums.length;j++){\n sb.append(nums[j]).append(",");\n if(nums[j] % p == 0) cnt++;\n if(cnt > k) break;\n set.add(sb.toString());\n }\n }\n return set.size();\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
EASY TO UNDERSTAND || Simple c++ || Explanation added
|
easy-to-understand-simple-c-explanation-5tpwh
|
Basically, I am counting the number of divisibles by using a prefix vector. Firstly, I store 1 to vector when its divisible by p otherwise storing zero there-in
|
aarindey
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:00:55.088186+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:19:23.925914+00:00
| 578 | false |
**Basically, I am counting the number of divisibles by using a prefix vector. Firstly, I store 1 to vector when its divisible by p otherwise storing zero there-in. Then we find the prefix vector. We use brute force approach next and use a set of strings to check unique subarrays(to avoid getting duplicated results). Also one important thing is to separate the strings from eachother using \'.\' as [1,9] and [19] should bear a different meaning.**\n\n**C++**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<int> v(n,0);\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n if(nums[i]%p==0)\n v[i]=1;\n }\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++)\n {\n v[i]=v[i]+v[i-1];\n }\n set<string> s;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n string str=""; \n for(int j=i;j<n;j++)\n {\n str+=to_string(nums[j]);\n str+=\'.\';\n if(i==0)\n {\n if(v[j]<=k&&s.find(str)==s.end())\n ans++;\n s.insert(str);\n }\n else\n {\n if(v[j]-v[i-1]<=k&&s.find(str)==s.end())\n ans++;\n s.insert(str);\n }\n \n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Easy set implementation..
|
easy-set-implementation-by-manyaagargg-c5a8
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
manyaagargg
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-27T09:18:39.311494+00:00
|
2024-07-27T09:18:39.311524+00:00
| 288 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int ans=0;\n set<vector<int>> st;\n for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); i++){\n int cnt=0;\n vector<int> vec;\n for(int j=i; j<nums.size(); j++){\n vec.push_back(nums[j]);\n \n if(nums[j]%p==0){\n ++cnt;\n }\n if(cnt>k) break;\n st.insert(vec);\n }\n }\n return st.size();\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Trie', 'Rolling Hash', 'Hash Function', 'Enumeration', 'Ordered Set', 'C++']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
BEATS 100% of users✅ || Goldman Sachs⭐ || Easy✔️ || Challenge🏆
|
beats-100-of-users-goldman-sachs-easy-ch-wxc4
|
"Your thoughts are welcome! \uD83D\uDCAD"\n\n\n#ReviseWithArsh #6Companies30Days challenge 2k24*\nCompany 1 :- Goldman Sachs\n\n### CODE\nCPP []\nclass Solution
|
nandini-gangrade
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-05T14:18:59.523517+00:00
|
2024-01-05T14:18:59.523552+00:00
| 654 | false |
> ***"Your thoughts are welcome! \uD83D\uDCAD"***\n\n\n***```#ReviseWithArsh #6Companies30Days challenge 2k24```**\n**`` Company 1 :- Goldman Sachs ``***\n\n### CODE\n```CPP []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n static const int BASE = 397; // Base for rolling hash\n static const long long MOD = 100000000069; // Modulo to prevent overflow\n\n int countDistinct(std::vector<int>& nums, int maxOnes, int moduloFactor) {\n std::vector<int> isDivisible(nums.size()); // 1 if divisible by moduloFactor, else 0\n std::transform(nums.begin(), nums.end(), isDivisible.begin(),\n [moduloFactor](int x) { return x % moduloFactor == 0 ? 1 : 0; });\n\n std::unordered_set<long long> distinctHashes;\n\n for (int start = 0; start < nums.size(); ++start) {\n int onesCount = 0; // Count of elements divisible by moduloFactor in the current subarray\n long long hashValue = 0; // Rolling hash value for the current subarray\n\n for (int end = start; end < nums.size() && onesCount <= maxOnes; ++end) {\n // Update the rolling hash value\n hashValue = (hashValue * BASE + nums[end] + (end + 1 - start)) % MOD;\n\n // Update the count of elements divisible by moduloFactor\n onesCount += (isDivisible[end] == 1);\n\n // Add the hash value to the set if the count of divisible elements is within the limit\n if (onesCount <= maxOnes) {\n distinctHashes.insert(hashValue);\n } else {\n // Break the loop if the count exceeds the limit\n break;\n }\n }\n }\n\n // Return the count of distinct hash values\n return distinctHashes.size();\n }\n};\n\n```\n\n*Let\'s collaborate! Join me on GitHub to work on this challenge together* :- \n*[https://github.com/nandini-gangrade/6Companies30Days](GITHUB)*\n\n> ***Happy Coding \uD83D\uDCBB***
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C++ || O(N^2) |
|
c-on2-by-raushanp414-tw3m
|
Intuition\nsince the time complexity of the given problem can go to N^2, we can easily track all the subarrayys with the given conditions.\n# Approach\nJust kee
|
raushanp414
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-02T09:05:53.904464+00:00
|
2023-08-02T09:05:53.904491+00:00
| 35 | false |
# Intuition\nsince the time complexity of the given problem can go to N^2, we can easily track all the subarrayys with the given conditions.\n# Approach\nJust keep pusing the elements in set of strings if the conditions are satisfied, finally we return the distinct non-empty subarrays by size fo the set\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(N^2)\n- Space complexity:\nO(Set elements)\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& a, int k, int p) {\n \n // we can use hashmap: with a[i] = 1 if divisible by p else 0.\n int n = a.size(), ans = 0;\n unordered_set<string>s;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int cnt = 0;\n string temp = "";\n for(int j = i; j < n; j++){\n // cnt += (a[j]%p == 0) ? 1 : 0;\n if(a[j]%p == 0) cnt++;\n if(cnt <= k) { temp += a[j]; s.insert(temp);}\n if(cnt>k)break;\n }\n // s.insert(temp);\n }\n return s.size(); // count of distinct sets.\n\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
[Python] Check duplicate using Trie - O(N^2)
|
python-check-duplicate-using-trie-on2-by-qy35
|
python\nclass TrieNode:\n def __init__(self):\n self.children = {}\n\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) ->
|
hiepit
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-04T21:13:51.814531+00:00
|
2023-07-05T21:45:35.881979+00:00
| 75 | false |
```python\nclass TrieNode:\n def __init__(self):\n self.children = {}\n\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n trieRoot = TrieNode()\n n = len(nums)\n ans = 0\n\n for i in range(n):\n cntDivisible = 0\n cur = trieRoot\n for j in range(i, n):\n if nums[j] % p == 0:\n cntDivisible += 1\n if cntDivisible > k: break\n if nums[j] not in cur.children:\n ans += 1\n cur.children[nums[j]] = TrieNode()\n cur = cur.children[nums[j]]\n\n return ans\n```\nComplexity\n- Time: `O(N^2)`, where `N` is length of `nums` array\n- Space: `O(N^2)`
| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
c+ | set | easy to understand
|
c-set-easy-to-understand-by-venomhighs7-5w2j
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n \n int n=nums.size();\n set<vector<int>
|
venomhighs7
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-02T16:15:09.603530+00:00
|
2022-10-02T16:15:09.603571+00:00
| 791 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n \n int n=nums.size();\n set<vector<int>>ans;\n \n int i,j;\n for(i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n vector<int>tt;\n int ct=0;\n for(j=i;j<n;j++)\n {\n tt.push_back(nums[j]);\n if(nums[j]%p==0)\n ++ct;\n if(ct>k)\n break;\n ans.insert(tt);\n \n }\n }\n return ans.size();\n }\n \n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
PYTHON | SIMPLEST HASHMAP SOLUTION
|
python-simplest-hashmap-solution-by-saty-m7hh
|
```class Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n s = set()\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n cou
|
satyampd5340
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-06T15:45:00.999373+00:00
|
2022-08-06T15:45:00.999412+00:00
| 337 | false |
```class Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n s = set()\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n count = 0\n curr = ""\n for j in range(i,len(nums)):\n if nums[j]%p == 0:\n count += 1\n if count > k:\n break\n curr += str(nums[j])+"-"\n s.add(curr)\n return len(s)\n \n
| 2 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Trie
|
trie-by-prachiti1998-gr32
|
\nI have tried to depict map contents, cz I took way too much time to understand myself.\n\n\nint cnt = 0;\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n struct Trie {\n un
|
prachiti1998
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-03T11:42:51.455292+00:00
|
2022-05-03T11:45:03.891697+00:00
| 194 | false |
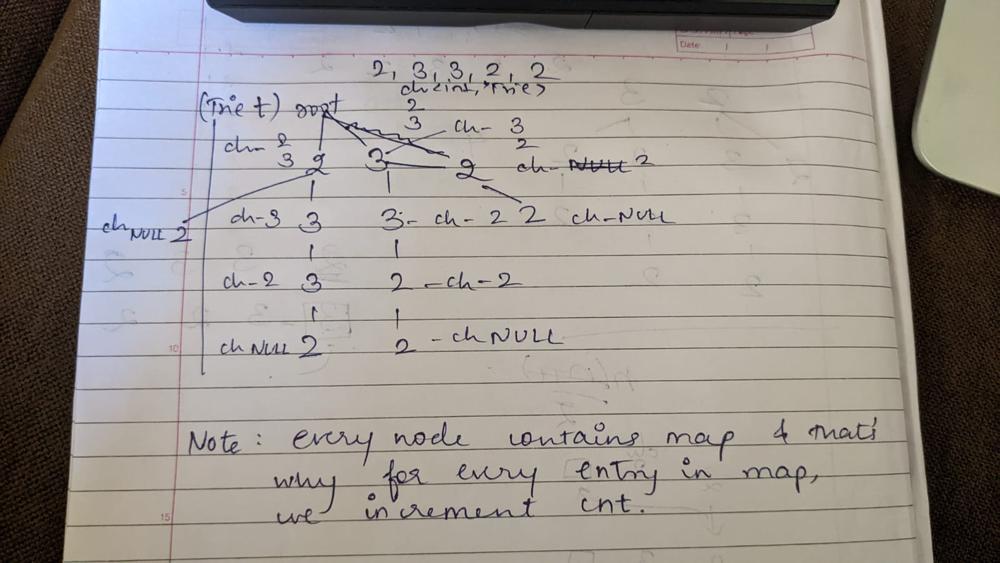\nI have tried to depict map contents, cz I took way too much time to understand myself.\n\n```\nint cnt = 0;\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n struct Trie {\n unordered_map<int, Trie*> ch;\n \n void insert(vector<int>& nums, int i, int k, int p) {\n if (i == nums.size() || k - (nums[i] % p == 0) < 0)\n return ;\n if (ch[nums[i]] == nullptr) {\n ch[nums[i]] = new Trie();\n cnt++;\n }\n ch[nums[i]]->insert(nums, i + 1, k - (nums[i] % p == 0), p);\n }\n};\nint countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n cnt = 0;\n Trie t;\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)\n t.insert(nums, i, k, p);\n return cnt;\n}\n};\n```\n
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C++| Trie | Handwrittten | Easy to understand. :)
|
c-trie-handwrittten-easy-to-understand-b-gcbh
|
\n\n\nint cnt = 0;\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n struct Trie {\n unordered_map<int, Trie*> ch;\n \n void insert(vector<int>& nums, int i, int k, int
|
Fly_ing__Rhi_no
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-02T09:06:19.052007+00:00
|
2022-05-02T09:10:04.242321+00:00
| 131 | false |
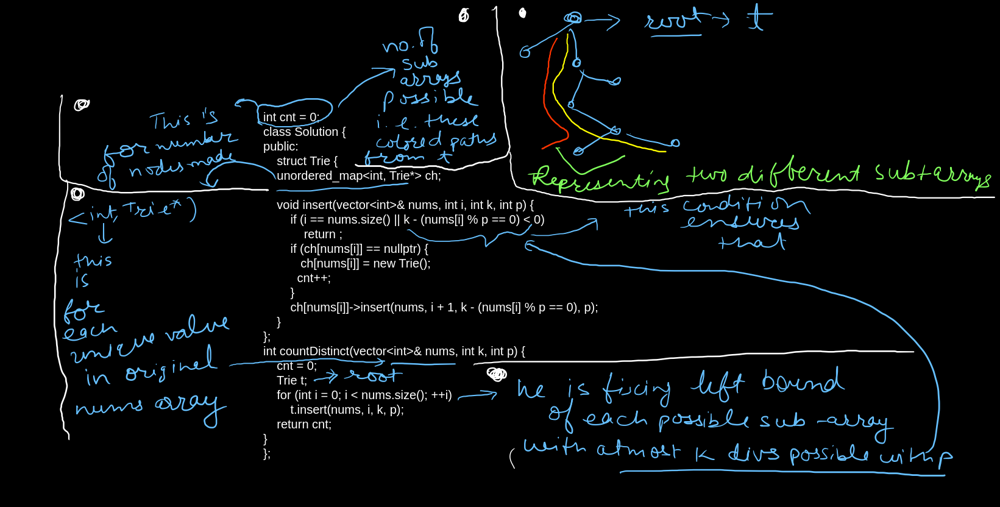\n\n```\nint cnt = 0;\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n struct Trie {\n unordered_map<int, Trie*> ch;\n \n void insert(vector<int>& nums, int i, int k, int p) {\n if (i == nums.size() || k - (nums[i] % p == 0) < 0)\n return ;\n if (ch[nums[i]] == nullptr) {\n ch[nums[i]] = new Trie();\n cnt++;\n }\n ch[nums[i]]->insert(nums, i + 1, k - (nums[i] % p == 0), p);\n }\n};\nint countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n cnt = 0;\n Trie t;\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)\n t.insert(nums, i, k, p);\n return cnt;\n}\n};\n```\nThis post is an attempt to explain @doppler comment on the post: \nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/k-divisible-elements-subarrays/discuss/1996294/O(n-2)%3A-Rabin-Karp-vs.-Trie\n\nHope it helps someone. Any corrections or suggestions are welcomed. :)
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Java Sliding Window + Trie as Hash 86ms beat 100%
|
java-sliding-window-trie-as-hash-86ms-be-9cw9
|
Algorithm:\n(1) Using Sliding Window to get the longest valid sub array, O(N)\n(2) Insert into Trie and mark all the way isEnd == true, O(N)\n(3) Total time is
|
sakamono
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:17:58.348841+00:00
|
2022-05-01T06:19:35.012122+00:00
| 495 | false |
Algorithm:\n(1) Using Sliding Window to get the longest valid sub array, O(N)\n(2) Insert into Trie and mark all the way isEnd == true, O(N)\n(3) Total time is O(N^2)\n\n```\nclass TrieNode {\n public int val;\n public boolean isEnd;\n public Map<Integer, TrieNode> children;\n public TrieNode(int val) {\n this.val = val;\n this.isEnd = false;\n this.children = new HashMap<>();\n }\n}\nclass Trie {\n public TrieNode root;\n public int totalCount;\n public Trie() {\n this.root = new TrieNode(-1);\n }\n public void insert(int[] nums, int left, int right) {\n TrieNode cur = this.root;\n for(int i = left; i <= right; i++){\n \n int cn = nums[i];\n if (!cur.children.containsKey(cn)){\n cur.children.put(cn, new TrieNode(cn));\n }\n cur = cur.children.get(cn);\n if (!cur.isEnd) {\n totalCount++;\n cur.isEnd = true;\n }\n }\n }\n public int getCount() {\n return totalCount;\n }\n}\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n int count = 0;\n int n = nums.length;\n Trie curTrie = new Trie();\n int left = 0;\n int right = 0;\n while (left < n) {\n while (right < n) {\n if (nums[right] % p == 0) {\n count++;\n }\n if (count == k + 1) {\n count--;\n break;\n }\n right++;\n }\n curTrie.insert(nums, left, right - 1);\n if (nums[left] % p == 0) {\n count--;\n }\n left++;\n }\n \n return curTrie.getCount();\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Trie', 'Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
javascript brute force 2550ms
|
javascript-brute-force-2550ms-by-henrych-ff59
|
\nconst countDistinct = (a, k, p) => {\n let n = a.length, se = new Set();\n for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for (let j = i; j < n; j++) {\n
|
henrychen222
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:09:39.428367+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:10:08.199664+00:00
| 263 | false |
```\nconst countDistinct = (a, k, p) => {\n let n = a.length, se = new Set();\n for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for (let j = i; j < n; j++) {\n let sub = a.slice(i, j + 1);\n if (ok(sub, k, p)) se.add(JSON.stringify(sub)); // transfer array to string to remove duplicates\n }\n }\n return se.size;\n};\n\nconst ok = (a, k, p) => {\n let cnt = 0;\n for (const x of a) {\n if (x % p == 0) cnt++;\n }\n return cnt <= k;\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
[Python3] Backtracking
|
python3-backtracking-by-alanlihy1805-ccrl
|
\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n def dfs(idx, k, path):\n nonlocal res, visited\n
|
alanlihy1805
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:08:48.418502+00:00
|
2022-05-02T17:28:52.037309+00:00
| 433 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n def dfs(idx, k, path):\n nonlocal res, visited\n if idx == len(nums):\n visited.add(tuple(path[:]))\n return\n \n if nums[idx] % p == 0 and k > 0:\n path.append(nums[idx])\n if tuple(path) not in visited:\n visited.add(tuple(path))\n res += 1\n dfs(idx + 1, k - 1, path)\n elif nums[idx] % p != 0:\n path.append(nums[idx])\n if tuple(path) not in visited:\n visited.add(tuple(path))\n res += 1\n dfs(idx + 1, k, path)\n \n res = 0\n visited = set()\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n dfs(i, k, [])\n return res\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Backtracking', 'Python3']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
simple sol using set
|
simple-sol-using-set-by-rruc-vguo
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
rruc
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-25T10:40:27.853925+00:00
|
2025-03-25T10:40:27.853925+00:00
| 41 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {
int n=nums.size();
set<vector<int>>ans;
vector<int>temp;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
temp.clear();
int count=0;
for(int j=i;j<n;j++){
count+=(nums[j]%p==0);
if(count>k)break;
temp.push_back(nums[j]);
ans.insert(temp);
}
}
return ans.size();
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
[Rust] Trie solution O(N^2), beats 100%
|
rust-trie-solution-on2-beats-100-by-tala-2cps
|
Complexity
Time complexity: O(N2)
Code
|
talalshafei
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-23T19:33:53.562409+00:00
|
2024-12-23T19:33:53.562409+00:00
| 57 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity: $$O(N^2)$$
# Code
```rust []
use std::collections::HashMap;
struct Trie {
pub children: HashMap<i32, Trie>,
}
impl Trie {
pub fn new() -> Self {
Self { children: HashMap::new() }
}
}
impl Solution {
pub fn count_distinct(nums: Vec<i32>, k: i32, p: i32) -> i32 {
let (mut ans, mut root, n) = (0, Trie::new(), nums.len());
for i in 0..n {
let (mut cur, mut divs) = (&mut root, 0);
for j in i..n {
if nums[j]%p==0 { divs+=1; }
if divs > k { break; }
if !cur.children.contains_key(&nums[j]) {
cur.children.insert(nums[j], Trie::new());
ans+=1;
}
cur = cur.children.get_mut(&nums[j]).unwrap();
}
}
ans
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Trie', 'Rust']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Java Trie O(n) clean solution beats 86% at the moment
|
java-trie-on-clean-solution-beats-86-at-jn6uc
|
Approach\n\nWe keep a count of numbers that are divisible by p. If count is less than k we iterate the trie. If the the trie node is not visited we increase res
|
piyush1024
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-16T00:00:40.879840+00:00
|
2024-07-16T00:00:40.879869+00:00
| 36 | false |
# Approach\n\nWe keep a count of numbers that are divisible by p. If count is less than k we iterate the trie. If the the trie node is not visited we increase result. One thing to make sure is to iterate from the back side of subarray. This will give us only the new additions. Example if we have a trie branch 1,2,3,4 and the next valid integer is 5. The new subarray formed are [5], [5,4], [5,4,3], [5,4,3,2], [5,4,3,2,1].\nSo count increase by 5.\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N^2)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n\n class Node{\n\n boolean found;\n Node[] ch;\n public Node(){\n this.found = false;\n this.ch = new Node[201];\n }\n }\n\n Node curr = new Node();\n int res=0;\n\n void build(int[] nums, int a, int b){\n\n //Building the Trie and increasing the count (res) if\n //the node is visited for the first time \n Node root = curr;\n for(int i=b;i>=a;i--){\n\n if(root.ch[nums[i]]==null){\n root.ch[nums[i]] = new Node();\n res++;\n }\n root = root.ch[nums[i]];\n }\n \n }\n \n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n \n //Queue<Integer> que = new LinkedList<>();\n int n = nums.length;\n int start =0;\n int count=0;\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n\n if(nums[i]%p==0)count++;\n\n while(count>k){\n if(nums[start++]%p==0)count--;\n }\n // Can also use a queue to find the index\n // of last occurence of an element divisible by p\n //if(que.size()>k)start = que.poll()+1;\n build(nums, start, i); \n }\n return res;\n\n }\n}
| 1 | 0 |
['Trie', 'Queue', 'Java']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Easy C++ Solution | Set | O(n^2)
|
easy-c-solution-set-on2-by-sourabhsikarw-98jw
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n^2)\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int n = nums.siz
|
sourabhsikarwar
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-21T06:56:00.225988+00:00
|
2024-01-21T06:57:23.806554+00:00
| 344 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n^2)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int n = nums.size();\n\n // creating a set for storing distinct subarrays \n // which have atmost k elements divisible by p\n set<vector<int>> st;\n\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n // counting the number of element \n // which are divible by p \n int count = 0;\n\n // subarray\n vector<int> vec;\n\n for(int j = i; j < n; j++){\n vec.push_back(nums[j]);\n if(nums[j] % p == 0){\n count++;\n }\n // storing the subarray if the count of elements\n // divisible by p are atmost k\n if(count <= k){\n st.insert(vec);\n } else {\n break;\n }\n }\n }\n return st.size();\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C# Brute-Force with array keys - Straightforward
|
c-brute-force-with-array-keys-straightfo-cshh
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nFrom studying the given examples, and reading the problem carefully, here is what the p
|
Cocamo1337
|
NORMAL
|
2023-12-04T06:13:22.277638+00:00
|
2023-12-04T06:13:22.277670+00:00
| 17 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nFrom studying the given examples, and reading the problem carefully, here is what the problem wants us to do:\n\nCount all unique subarrays of nums where the count of numbers evenly divisible by p in the subarray is no greater than k.\n\nThe keyword here is unique. For example:\n\nif nums = [2, 2, 2], p = 5, and k = 3, the answer would be 3.\n\nEven though, for example, there are 2 subarrays of [2, 2], we only count the first [2, 2] that appears, and none after. The same goes for the 3 subarrays of [2], we only count the first [2].\n\nWhat is a data structure that only stores 1 instance of each element, and can quickly determine whether we\'ve seen that element before or not? A HashSet!\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. Instantiate a HashSet of strings - seenArr.\n\n2. Initialize two integers - len = nums.Length and total (to count new sub arrays) = 0.\n\n3. Instantiate a StringBuilder - sb - it will be used to build the array-keys that we will run against seenArr to determine if we\'ve seen an array before.\n\n4. Run a for-loop, starting at 0 and ending when i = len. Inside of this loop, initialize two integers - currP = 0 and ind = i. Also use sb.Clear() at the start to clear the StringBuilder without having to use memory by creating a new one. \n\ncurrP will be our count of elements in the sub array that are divisble by p, ind will be how we extend the range of our sub array.\n\n5. Inside the for-loop, run a while-loop while ind is less than len, and in that while-loop:\n\nFirst check to see if nums[ind] is divisible by p. If it is, check to see if your currP is equal to k. If currP == k, break from the loop. Otherwise if currP != k, increment currP by 1.\n\nIf the previous section didn\'t cause a break in the loop, then we can continue and append nums[ind] and a de-limiting character, \'-\', to sb.\nConvert sb to a string with the .ToString() method and check if that string is contained in seenArr.\n\nIf it is not in seenArr, add it to seenArr and increment total by 1.\n\nFinally at the end increment ind by 1.\n\n6. Return total.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n * n)$$\n\nThe worst-case time complexity would be if every single ind can travel from the starting point all the way to len. This is tantamount to n squared run-time.\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n * n)$$\n\nFor every valid index we create 1 key from StringBuilder. Because the above could run n * n times, that means we may have to create n * n strings/keys.\n\n# Code\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public int CountDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n HashSet<string> seenArr = new();\n // Each subarray will have a key - Only count new subarrays\n // if they aren\'t in seenArr.\n\n int len = nums.Length;\n int total = 0;\n\n StringBuilder sb = new(); // For building arr-keys\n\n for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){\n sb.Clear();\n int currP = 0;\n int ind = i;\n while (ind < len){\n if (nums[ind] % p == 0){\n if (currP == k) break;\n currP++;\n }\n sb.Append(nums[ind]).Append(\'-\');\n var key = sb.ToString();\n if (!seenArr.Contains(key)){\n seenArr.Add(key);\n total++;\n }\n ind++;\n }\n }\n\n return total;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C#']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
[Java | Strict O(n^2) | Using Hashing with Polynomial Function]
|
java-strict-on2-using-hashing-with-polyn-z3ag
|
\n/*\n NOTE: Concept Wise it can be tagged in Hard Category.\n \n Tool/Technique you need to add, into your toolbox\n ------------------------------
|
_LearnToCode_
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-19T17:57:10.657324+00:00
|
2023-01-19T18:00:38.468495+00:00
| 911 | false |
```\n/*\n NOTE: Concept Wise it can be tagged in Hard Category.\n \n Tool/Technique you need to add, into your toolbox\n --------------------------------------------------\n + Two subarays are equal or NOT can be checked in O(1) time.\n - Provided pre-computation time complexity O(n * n), where n = len(given_array)\n - Like: hashes[l1][r1] == hashes[l2][r2], where first subarray is : nums[l1:r1]\n and second subarray is : nums[l2:r2], indices are inclusive.\n + Look at the beauty of Hashing. [alongwith Prime + Polynomial + Modulo Operator(loved it)]\n \n NOTE: The larger "M"(for mod) you\'ve, the more hashes will have.\n*/\n\nclass Solution {\n\t \n\t// <= 40th [173] prime number didn\'t work well for all test-cases. Ir-respective of what \n\t// M = 10^9 + 7 / 10^15 + 7 is.\n private static final int P = 229; // 229 = 50th Prime Number, 541 = 100th prime number\n private static final long M = (long)(1e15 + 7);\n private static final long[] PP;\n private static final int MAX_LENGTH = 2 * 1_00;\n\n static {\n PP = new long[MAX_LENGTH + 1];\n PP[0] = P;\n for(int i = 1; i <= MAX_LENGTH; i += 1) {\n PP[i] = (PP[i - 1] % M * P % M) % M;\n }\n }\n\n private void computeHashesForAllSubarrays(int[] nums, long[][] hashes, int n) {\n\t\t// hashes[i][j] = is the unique hash value for subarray nums[i:j]\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i += 1) {\n long subHash = 0;\n for(int j = i; j < n; j += 1) {\n int ele = nums[j];\n subHash += (PP[j - i] * ele) % M;\n hashes[i][j] = subHash;\n }\n }\n }\n \n private void buildDivisibleCountForAllSubarrays(int[] nums, int[][] count, int n, int p) {\n // count[i][j] = returns how many elements are there in the subarray\n // nums[i:j], divisible by p. -> Helps to check (count_of_divisibles <= k) in O(1) time\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i += 1) {\n for(int j = i; j < n; j += 1) {\n int rem = nums[j] % p;\n count[i][j] = rem == 0 ? 1 : 0;\n // Computing prefix count array\n if(j > 0) {\n count[i][j] = rem == 0 ? count[i][j - 1] + 1 : count[i][j - 1];\n }\n // Actual computation where storing(at count[i][j]) how many elements\n // are divisible by p in the sub-array (i, j)\n count[i][j] = (count[i][j] - count[i][i]) + (nums[i] % p == 0 ? 1 : 0);\n }\n }\n }\n \n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n int n = nums.length, countSubarrays = 0;\n int[][] count = new int[n][n];\n long[][] hashes = new long[n][n];\n \n buildDivisibleCountForAllSubarrays(nums, count, n, p);\n computeHashesForAllSubarrays(nums, hashes, n);\n \n Set<Long> subarrayHash = new HashSet<>();\n \n for(int i = 0; i < n; i += 1) {\n for(int j = i; j < n; j += 1) {\n if(count[i][j] <= k) {\n if(!subarrayHash.contains(hashes[i][j])) {\n countSubarrays += 1;\n subarrayHash.add(hashes[i][j]);\n }\n }\n }\n }\n \n return countSubarrays;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Prefix Sum', 'Java']
| 2 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C++ rolling hash
|
c-rolling-hash-by-sanzenin_aria-d4bl
|
didn\'t check collision\n```\n int countDistinct(vector& nums, int k, int p) {\n unordered_map> hashMap; //len, {hash}\n int res = 0;\n
|
sanzenin_aria
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-08T15:38:34.305875+00:00
|
2022-10-08T15:38:34.305909+00:00
| 1,006 | false |
didn\'t check collision\n```\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n unordered_map<int, unordered_set<int>> hashMap; //len, {hash}\n int res = 0;\n for (int i=0; i<nums.size(); i++){\n long long hash = 0, cntP = 0, mod = 1e9+7, pow = 200;\n for(int j=i; j < nums.size(); j++){\n if (nums[j] % p == 0) cntP++;\n if (cntP > k) break;\n hash = (hash * pow + nums[j]) % mod;\n if (hashMap[j-i+1].insert(hash).second) res++;\n }\n }\n return res;\n }
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Beats 99.7% | No hashing or Trie |sliding window | Longest common substring | DP
|
beats-997-no-hashing-or-trie-sliding-win-gfsi
|
Maintain an array lcs[n][n]. lcs[i][j] gives longest common substring starting at i and j in the same array.\n\nVector dp is created where dp[[i] = max(dp[k][j]
|
coder4321
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-08T11:51:55.196397+00:00
|
2022-10-08T11:51:55.196448+00:00
| 373 | false |
Maintain an array lcs[n][n]. lcs[i][j] gives longest common substring starting at i and j in the same array.\n\nVector dp is created where dp[[i] = max(dp[k][j]) (0<=k and k<=i-1) it is created to see if there exists an index i such that i and j have a common substring length greater than a particular value.\n\nApply sliding window from length = 1 to length = n. and use the dp array to check for distinct arrays\n\n\n \n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector < vector <int> > lcs(n+1, vector <int> (n+1));\n lcs[n][n] = 0;\n \n for(int j=n; j>=0; j--)\n {\n for(int i = j; i>=0; i--)\n {\n if(j==n) lcs[i][j] = 0;\n else\n {\n if(nums[i] == nums[j])\n lcs[i][j] = 1 + lcs[i+1][j+1];\n else\n lcs[i][j] = 0;\n }\n }\n }\n \n vector <int> dp(n+1);\n \n for(int j=0; j<n; j++)\n {\n int temp = 0;\n for(int i=0; i<j; i++)\n dp[j] = max(dp[j], lcs[i][j]);\n }\n \n int ans = 0;\n for(int len = 1; len <= n; len++)\n {\n int cnt = 0;\n int lo = 0, hi = len-1;\n for(int i = lo; i<=hi; i++)\n {\n if(nums[i]%p==0) cnt++;\n }\n if(cnt <= k) ans++;\n while(hi+1 < n)\n {\n hi = hi+1;\n if(nums[lo] % p == 0) cnt--;\n if(nums[hi] % p == 0) cnt++;\n lo++;\n \n if(cnt <= k && dp[lo] < len)\n ans++;\n }\n \n }\n return ans;\n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n }\n};\n
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
JAVA solution | O(n^2) | Hashset | Stringbuilder
|
java-solution-on2-hashset-stringbuilder-vhlua
|
Please Upvote !!! (\u25E0\u203F\u25E0)\n\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
|
sourin_bruh
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-29T17:53:45.120094+00:00
|
2022-09-29T17:53:45.120164+00:00
| 287 | false |
### ***Please Upvote !!!*** **(\u25E0\u203F\u25E0)**\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();\n\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {\n int count = 0;\n StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();\n\n for (int j = i; j < nums.length; j++) {\n if (nums[j] % p == 0) count++;\n if (count > k) break;\n\n sb.append(nums[j] + " ");\n set.add(sb.toString());\n }\n }\n\n return set.size();\n }\n}\n\n// TC: O(n ^ 2), SC: O(n ^ 2)\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['String', 'Java']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C++ Trie Solution With Comments
|
c-trie-solution-with-comments-by-harshse-38uf
|
\n// approach: \n// for all subarray starting from i (from 0 to n-1)\n// insert only the maximum valid subarray in the trie\n// if you make a new node in the tr
|
harshseta003
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-04T17:44:04.247197+00:00
|
2022-08-04T17:44:04.247242+00:00
| 112 | false |
```\n// approach: \n// for all subarray starting from i (from 0 to n-1)\n// insert only the maximum valid subarray in the trie\n// if you make a new node in the trie, implies that this is a distinct subarray\n// keep a count (cnt) in the Trie, to count the number of distinct subarrays (the number of times you had to create a new node).\nclass TrieNode{\n int cnt=0;\n public:\n unordered_map<int,TrieNode*> next;\n void insert(vector<int>arr){\n TrieNode* node= this;\n int n=arr.size();\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n if(!node->next.count(arr[i])){\n node->next[arr[i]]= new TrieNode();\n this->cnt++;\n }\n node=node->next[arr[i]];\n }\n }\n int getCount(){\n return this->cnt;\n }\n};\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int n=nums.size(),ans=0;\n vector<bool> isDiv(n,false);\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n isDiv[i]=(nums[i]%p==0); // if divisible, it sets isDiv[i] to true\n }\n TrieNode* node= new TrieNode();\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int cnt=0; // to count the number of elements divisible by p, in the current subarray\n vector<int>temp;\n for(int j=i;j<n;j++){\n cnt+= isDiv[j];\n if(cnt>k)\n break;\n temp.push_back(nums[j]);\n }\n node->insert(temp); \n }\n return node->getCount();\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Trie', 'C']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
simple C++ solution ,Comlexity:O(n^2)
|
simple-c-solution-comlexityon2-by-gopija-w00s
|
class Solution {\n# public:\n int countDistinct(vector& nums, int k, int p) {\n set>s;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n int count=0
|
gopijada55
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-03T10:24:12.455262+00:00
|
2022-08-03T10:26:45.801771+00:00
| 110 | false |
class Solution {\n# public:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n set<vector<int>>s;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n int count=0;\n for(int j=i;j<nums.size();j++){\n if(nums[j]%p==0){\n count++;\n } if(count>k){\n break;\n }else{\n vector<int>v(nums.begin()+i,nums.begin()+j+1);\n s.insert(v);\n }\n }\n } \n return s.size();\n }\n};
| 1 | 1 |
['C', 'Ordered Set']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C++ using SET clean code
|
c-using-set-clean-code-by-drv_rawt19-slf9
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n // generate all subsets and then count\n set<string>s;// t
|
drv_rawt19
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-04T14:04:21.702573+00:00
|
2022-07-04T14:04:21.702638+00:00
| 219 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n // generate all subsets and then count\n set<string>s;// to store unique subarr(contiguous)\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)\n {\n int cnt(0);\n string currstr=""; // stores subarray starting from index i. \n for(int j=i;j<nums.size();j++)\n {\n currstr+=nums[j]+\'0\'; // Appending charcter with nums[j] ascii value.\n // \'0\' + 1 = 49 == \'1\'\n if(nums[j]%p==0)cnt++;\n // if the current array have at most k elements divisible by then add it to the set.\n if(cnt<=k)\n s.insert(currstr);\n }\n \n }\n return s.size();\n }\n \n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C', 'Ordered Set']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Python. Faster than 91%.... Hashing..
|
python-faster-than-91-hashing-by-nag007-xacc
|
\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, x: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n prime=10**9+7\n l=len(x)\n se=set()\n for i i
|
nag007
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-30T07:07:23.710806+00:00
|
2022-06-30T07:07:23.710840+00:00
| 80 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, x: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n prime=10**9+7\n l=len(x)\n se=set()\n for i in range(l):\n c=0\n q=0\n for j in range(i,l):\n if x[j]%p==0:\n c+=1\n q=q*prime+x[j]\n if c<=k:\n se.add(q)\n else:\n break\n return len(se)\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Sliding Window Approach || Brute Force || Simple Solution with Comments
|
sliding-window-approach-brute-force-simp-omlz
|
\tclass Solution {\n\tpublic:\n //Brute Force O(n^2) time complexity \n int countDistinct(vector& nums, int maxi, int p) {\n int n=nums.size();\n
|
Sufyan_Khan_
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-28T21:08:00.497605+00:00
|
2022-06-28T21:08:35.528813+00:00
| 390 | false |
\tclass Solution {\n\tpublic:\n //Brute Force O(n^2) time complexity \n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int maxi, int p) {\n int n=nums.size();\n int ans=0;\n //k represents the window size\n \n for(int k=1;k<=n;k++){\n int cnt=0;\n //cnt represent the count of values divisible by p \n \n set<vector<int>>s; //set of vector used to get distinct subarray\n \n vector<int>tt;//store the subarray\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n //Sliding window Approach\n \n if(i<k){\n tt.push_back(nums[i]);\n if(nums[i]%p==0){\n cnt++;\n }\n continue; \n }\n if(cnt<=maxi){ //Base condition for valid Sliding Window\n s.insert(tt);\n }\n if(tt[0]%p==0) cnt--; //Removed from Sliding window \n tt.erase(tt.begin());\n \n if(nums[i]%p==0) cnt++; //Included in Sliding window\n tt.push_back(nums[i]);\n }\n if(cnt<=maxi){ //for including last sliding window\n s.insert(tt);\n }\n \n ans+=s.size(); //Adding up the answer\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\t};
| 1 | 0 |
['C', 'Sliding Window']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Short C++ code | using set stl
|
short-c-code-using-set-stl-by-achak47-zuyy
|
```\nint countDistinct(vector& nums, int k, int p) {\n int ans = 0 , n = nums.size() ;\n set st ;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int temp
|
achak47
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-16T08:45:04.544801+00:00
|
2022-06-16T08:45:41.456733+00:00
| 126 | false |
```\nint countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int ans = 0 , n = nums.size() ;\n set<string> st ;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int temp = 0 ;\n string t = "" ;\n for(int j=i;j<n;j++){\n if(nums[j]%p==0) temp++ ;\n if(temp>k) break ;\n t += to_string(nums[j]) ;\n t+= " " ;\n if(st.count(t)==0)ans++ ;\n st.insert(t) ;\n }\n }\n return ans ;\n }
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
JAVA | Trie Solution | HashSet Solution
|
java-trie-solution-hashset-solution-by-s-i29s
|
\n//--------------Trie Solution---------------------\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n TrieNode root = new Tr
|
sxs8814
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-12T09:30:03.131763+00:00
|
2022-06-12T09:31:06.422470+00:00
| 186 | false |
```\n//--------------Trie Solution---------------------\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n TrieNode root = new TrieNode();\n int res = 0;\n for(int i=0; i< nums.length; i++) {\n TrieNode curr = root;\n int count = 0;\n for(int j=i; j<nums.length; j++) {\n if(nums[j]%p==0) count++;\n if(count>k) break;\n if(!curr.links.containsKey(nums[j])) {\n res++;\n TrieNode next = new TrieNode();\n curr.links.put(nums[j], next);\n }\n curr = curr.links.get(nums[j]);\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n \n class TrieNode {\n Map<Integer, TrieNode> links;\n \n public TrieNode() {\n links = new HashMap<>();\n }\n }\n}\n\n```\n\n```\n//--------------HashSet Solution---------------------\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n\t\tSet<String> res = new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++) {\n StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();\n int count = 0;\n for(int j=i; j<nums.length; j++) {\n if(nums[j]%p==0) count++;\n if(count>k) break; \n sb.append(nums[j] + ":");\n res.add(sb.toString());\n }\n }\n return res.size();\n\t}\n}\n```\n
| 1 | 0 |
['Trie', 'Java']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C++ | Trie
|
c-trie-by-kena7-hqg6
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n struct Trie\n {\n unordered_map<int,Trie*>child;\n bool isend;\n Trie()\n {\n isend=f
|
kenA7
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-08T17:45:24.239789+00:00
|
2022-06-08T17:45:24.239828+00:00
| 135 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n struct Trie\n {\n unordered_map<int,Trie*>child;\n bool isend;\n Trie()\n {\n isend=false;\n }\n };\n Trie *root;\n int insert(vector<int>&nums,int i,int j)\n {\n Trie *p=root;\n int count=0;\n for(int k=i;k<=j;k++)\n {\n if(p->child[nums[k]]==NULL)\n p->child[nums[k]]=new Trie();\n p=p->child[nums[k]];\n if(!p->isend)\n count++;\n p->isend=true;\n }\n return count;\n }\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) \n {\n root=new Trie();\n int n=nums.size(),res=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n int c=0,j=i;\n for(j=i;j<n;j++)\n {\n if(nums[j]%p==0)\n c++;\n if(c>k)\n break;\n }\n res+=insert(nums,i,j-1);\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
python
|
python-by-alex72112-riae
|
\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n count = 0\n d = {}\n \n for i in range(len
|
alex72112
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-21T23:35:41.314646+00:00
|
2022-05-21T23:35:41.314676+00:00
| 108 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n count = 0\n d = {}\n \n for i in range(len(nums)):\n temp = k\n lst = []\n \n for j in range(i, len(nums)):\n lst.append(nums[j])\n \n if nums[j] % p == 0:\n temp -= 1\n \n if temp >= 0 and not str(lst) in d:\n count += 1\n d[str(lst)] = 1\n \n \n return count\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Faster than 99.6%, simple C++ Solutiion
|
faster-than-996-simple-c-solutiion-by-mr-2ncp
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n vector<int> v(nums.size(), 0);\n for(int i=0; i<nums.size(
|
MrGamer2801
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-19T13:11:41.249784+00:00
|
2022-05-19T13:12:12.343605+00:00
| 157 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n vector<int> v(nums.size(), 0);\n for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); i++)\n {\n for(int j=i+1; j<nums.size(); j++)\n {\n int x=i, y=j, cnt=0;\n while(y<nums.size() && nums[x]==nums[y])\n {\n x++; y++;\n cnt++;\n }\n v[j]=max(v[j], cnt);\n }\n }\n int res=0;\n for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); i++)\n {\n int cnt=0, can=0;\n for(int j=i; j<nums.size(); j++)\n {\n if(nums[j]%p==0)\n cnt++;\n if(cnt>k)\n break;\n if(v[i]--<=0)\n res++;\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.