question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Easy Python Solution
|
easy-python-solution-by-ravkishore27-kdtz
|
Explanation\n1. Loop twice \n2. For each subarry, check if the number of elements divisble is less than or equal to \'k\'.\n3. If greated than given \'k\' then
|
ravkishore27
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-17T17:06:44.416893+00:00
|
2022-05-17T17:06:44.416935+00:00
| 123 | false |
Explanation\n1. Loop twice \n2. For each subarry, check if the number of elements divisble is less than or equal to \'k\'.\n3. If greated than given \'k\' then break the inner loop. Else add the current substring to set().add(nums[i:j+1] )\n4. Convert each subarray to string and add it to Set() to easily maintain/discard duplicates.\n\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n n = len(nums)\n res = set()\n\n for i in range(n):\n k1 = 0\n for j in range(i, n):\n if nums[j] % p == 0:\n k1 += 1\n if k1 <= k:\n res.add(str(nums[i:j+1]))\n else:\n break\n\n return len(res)\n```\n\ntime: O(n\\*\\*2)\nspace: O(n)\n
| 1 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
98% Faster || 96% Less Space || Hash || Hash table
|
98-faster-96-less-space-hash-hash-table-t7w2v
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n #define FastRead ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0)\n #define ULL unsigned long long\n #define LL
|
i_see_you
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-08T04:26:24.076023+00:00
|
2022-05-08T04:26:24.076051+00:00
| 183 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n #define FastRead ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0)\n #define ULL unsigned long long\n #define LL long long\n #define eps 1e-9\n #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f\n #define INF 2e18\n #define all(a) a.begin(),a.end()\n #define Unique(a) sort(all(a)),a.erase(unique(all(a)),a.end())\n\n #define Cube(a) ((a)*(a)*(a))\n #define Sqr(a) ((a)*(a))\n ULL hs = 3797;\n vector <ULL> table[1 << 16];\n \n bool Insert(ULL y) {\n unsigned short x = y;\n for (int i = 0; i < table[x].size(); i++) if (y == table[x][i]) return false;\n table[x].push_back(y);\n return true;\n }\n \n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int n = nums.size();\n int res = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n int have = 0;\n ULL hs_val = 0;\n for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {\n hs_val = hs_val * hs + nums[j];\n if (nums[j] % p == 0) {\n if (++have > k) break;\n } \n if (Insert(hs_val)) {\n res++;\n }\n }\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C++, STL, rolling hash and collision check: true O(n^2) in space and time
|
c-stl-rolling-hash-and-collision-check-t-dhs4
|
I\'ve seen hellishlot many broken rolling-hash-without-collision-check solutions (O(n^2), but really and hopelessly broken, collisions are trivial to find), and
|
yumkam
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-06T19:44:18.148240+00:00
|
2022-05-06T19:44:18.148280+00:00
| 271 | false |
I\'ve seen *hellishlot* many broken rolling-hash-without-collision-check solutions (O(n^2), but *really and hopelessly broken*, collisions are trivial to find), and a lot of (non-broken but slow) solutions claming to be O(n^2), but actually O(n^3) or worse, so I decided to share my solution:\n```c++\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n typedef typename vector<int>::const_iterator iterator;\n typedef tuple<size_t,iterator,iterator> item_t;\n // { hash, begin, end }\n\t\t// we save pre-calculated hash value (it MUST match subarray content),\n\t\t// begin and end subarray pointers (iterators);\n // beware: you must avoid operations invalidating iterators,\n // or hell break loose\n struct item_ops {\n // hash\n size_t operator() (const item_t& v) const {\n return get<0>(v); // pre-computed hash value\n }\n // equals\n bool operator() (const item_t&a, const item_t &b) const {\n return\n // same length\n distance(get<1>(a), get<2>(a)) == distance(get<1>(b), get<2>(b))\n // same content\n && equal(get<1>(a), get<2>(a), get<1>(b));\n // avoid temptation of preliminary optimizations:\n // comparing hashes first useless (never happens)\n // comparing get<1>(a) and get<1>(b) before equal() is useless\n // (we never insert items with both same length and same start)\n }\n };\n // time: O(n^2) (average), space = O(n^2)\n // Comparison:\n // 1) unordered<ull> (set of hashes) is prone to collisions, no matter of trick\n\t\t// and "happy"/"popular"/"large" constants you use;\n // 2) unordered_set<string> is O(n^3) time and O(n^3) space;\n\t\t// 3) set<vector<int>> is O(n^3 log n) time and O(n^3) space;\n unordered_set<item_t, item_ops, item_ops> s ((nums.size()+1)*nums.size()/2);\n\t\t// << hints about expected number of items, saves time\n\t\t// and avoids memory fragmentation on resizing hash table\n for (auto i = nums.cbegin(); i != nums.cend(); ++i) {\n size_t hash = 0;\n int t = 0;\n for (auto j = i; j != nums.cend(); ) {\n if (*j % p == 0)\n if (++t > k)\n break;\n // polynomial hash parameters:\n // base = 211 (can be any prime larger than 200)\n // modulo = 2**(8*sizeof(size_t)), that is commonly 2**64 (implicit)\n // you can use any other parameters as you like (e.g. larger base, prime modulo),\n // or hash combination, etc;\n // hash collisions here harms performance, but not algorithm correctness\n hash = 211*hash + *j;\n ++j;\n\t\t\t\t// end iterator should be one after last subarray element, so just increment it here\n s.emplace(hash, i, j);\n }\n }\n return s.size();\n }\n};\n```\nThat said, while it is improvement over commonly-seen O(n^3) (and equally-commonly-seen broken implementations), but there are LCP-based solutions out there, and they are O(n) in both time and space (and unlike any hash-based solution, it is *worst* case performance), so look them up too.
| 1 | 0 |
['C', 'Rolling Hash']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Scala
|
scala-by-fairgrieve-msv6
|
\nobject Solution {\n def countDistinct(nums: Array[Int], k: Int, p: Int): Int = {\n val cumulativeDivisible = nums.scanLeft(0) {\n case (numDivisible,
|
fairgrieve
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T22:38:52.021254+00:00
|
2022-05-01T22:38:52.021295+00:00
| 32 | false |
```\nobject Solution {\n def countDistinct(nums: Array[Int], k: Int, p: Int): Int = {\n val cumulativeDivisible = nums.scanLeft(0) {\n case (numDivisible, num) if num % p == 0 => numDivisible + 1\n case (numDivisible, _) => numDivisible\n }\n val view = nums.view\n (1 to nums.length)\n .iterator\n .map { length =>\n (0 to nums.length - length)\n .iterator\n .collect { case i if cumulativeDivisible(i + length) - cumulativeDivisible(i) <= k => (i, i + length) }\n .distinctBy { case (from, until) => view.slice(from, until).toSeq }\n .size\n }\n .sum\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Prefix Sum', 'Scala']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Naive brute force | Find all subarrays | Clear Comments
|
naive-brute-force-find-all-subarrays-cle-6c1y
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n HashSet<String> hs = new HashSet<>();\n // Traverse arrays\n
|
alfran
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T22:04:22.481357+00:00
|
2022-05-01T22:04:22.481388+00:00
| 79 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n HashSet<String> hs = new HashSet<>();\n // Traverse arrays\n for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){\n String s ="";\n int c =0;\n //Calculate subarrays\n for(int j=i;j<nums.length;j++){\n // Generate unique string for integer value, apply any hash mechanism to optmise\n s+=\'0\'+nums[j];\n // Check divisible numbers\n if(nums[j]%p==0) c++;\n if(c>k) break;\n // If at most k divisible add in set\n hs.add(s);\n }\n }\n return hs.size();\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
✔✔Java || HashSet || 2 For Loops || Easy-Understanding
|
java-hashset-2-for-loops-easy-understand-i0np
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] arr, int k, int p) {\n Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){\
|
vaibh_20
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T20:48:45.846552+00:00
|
2022-05-01T20:48:45.846594+00:00
| 92 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] arr, int k, int p) {\n Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){\n int count = 0;\n \n StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();\n \n for(int j=i;j<arr.length;j++){\n if(arr[j]%p==0)\n count++;\n \n if(count>k)\n break;\n\n /*There is a reason why I have added space in between sb, try to dry run for \n below commented testcase you will get to know*/\n \n sb.append(arr[j]+" ");\n set.add(sb.toString());\n }\n }\n return set.size();\n }\n}\n\n\n/*[19, 198, 1987, 1, 198719, 7, 987, 8, 9, 98719, 8719, 98, 87, 719] */\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['String', 'Java']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
JAVA | SET| EASY
|
java-set-easy-by-yuvrajaggarwal10-r747
|
```\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n HashSetmap=new HashSet<>();\n int c=0;\n for(int i=0;i<nu
|
yuvrajaggarwal10
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T14:21:05.621961+00:00
|
2022-05-01T14:21:05.622008+00:00
| 74 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n HashSet<String>map=new HashSet<>();\n int c=0;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++)\n {\n StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();\n c=0;\n \n for(int j=i;j<nums.length ;j++)\n {\n sb.append(nums[j]+" ");\n if(nums[j]%p==0) c++;\n if(c>k)break;\n \n map.add(sb.toString());\n }\n }\n return map.size();\n }\n\n}
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C++ Unordered set of string || Easy and Crisp
|
c-unordered-set-of-string-easy-and-crisp-j3lf
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n //as we cannot make an unordered set of vector I thought of makin
|
dee_stroyer
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T10:24:55.751192+00:00
|
2022-05-01T10:24:55.751225+00:00
| 189 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n //as we cannot make an unordered set of vector I thought of making unordered set of string\n //as the constraints are very low so this gave the intuition that brute force is gonna work\n \n //we will generate substring containing numbers having at most k elements divisible by p\n //we put those substrings into the set to eliminate the duplicates\n unordered_set<string>us;\n\n for(int i = 0; i<nums.size(); i++){\n string curr = "";\n int count = 0;\n for(int j = i; j<nums.size(); j++){\n curr+=(to_string(nums[j]));\n curr+="_";\n if(nums[j]%p == 0){\n count++;\n }\n \n if(count<=k){\n us.insert(curr);\n }\n \n else{\n break;\n }\n }\n }\n \n return us.size();\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['String', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Simple JAVA , Set soln
|
simple-java-set-soln-by-anshulpro27-t4ln
|
\n public int countDistinct(int[] a, int k, int p) {\n int n =a.length;\n HashSet<String> hs = new HashSet<>();\n \n for(int i=0;
|
anshulpro27
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T07:46:35.508439+00:00
|
2022-05-01T07:46:35.508482+00:00
| 41 | false |
```\n public int countDistinct(int[] a, int k, int p) {\n int n =a.length;\n HashSet<String> hs = new HashSet<>();\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n { \n String s ="";\n int count=0;\n for(int j=i;j<n;j++)\n {\n if(a[j]%p==0) count++;\n \n if(count>k) break; \n \n s=s+a[j]+";"; \n hs.add(s); \n }\n }\n return hs.size();\n }\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Java | Brute Force
|
java-brute-force-by-gauravvv2204-nnqw
|
\npublic int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n HashSet<List<Integer>> set = new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++){\n
|
gauravvv2204
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T06:54:44.238265+00:00
|
2022-05-01T06:55:29.204565+00:00
| 75 | false |
```\npublic int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n HashSet<List<Integer>> set = new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++){\n int count = 0;\n List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();\n for(int j=i; j<nums.length; j++){\n if(count>=k && nums[j]%p==0)\n break;\n if(nums[j]%p==0){\n count++;\n }\n temp.add(nums[j]);\n List<Integer> temp2 = new ArrayList<>(temp);\n set.add(temp2);\n }\n }\n return set.size();\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
java
|
java-by-nadi1173-vbfh
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n int q=0;\n HashSet<String> set=new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=
|
Nadi1173
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T06:01:47.844167+00:00
|
2022-05-01T06:01:47.844211+00:00
| 61 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n int q=0;\n HashSet<String> set=new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){\n String s="";\n for(int j=i;j<nums.length;j++){\n if(nums[j]%p==0)\n q++;\n if(q>k)\n break;\n s=s+\',\'+nums[j];\n set.add(s); \n }\n q=0; \n } \n return set.size();\n }\n}\n```\n
| 1 | 0 |
['String', 'Java']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C++ String Hashing Set Solution | O(N^2logN) Time O(N^2) Space
|
c-string-hashing-set-solution-on2logn-ti-ixty
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n //==================APPROACH 1 - BRUTE FORCE - Generating all substrings========================//\n int countDistinct(vec
|
emblaze
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T05:48:34.898054+00:00
|
2022-05-06T15:15:00.099389+00:00
| 123 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n //==================APPROACH 1 - BRUTE FORCE - Generating all substrings========================//\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n\n int n=nums.size();\n set<string>s;\n\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n string res = "";\n int cnt=0;\n for(int j=i;j<n;j++)\n {\n res += ((to_string(nums[j])+"-")); //adding "-" to handle the edge case of: 1,12 OR 11,2 in substring that would concatenate to the same string otherwise\n if(nums[j]%p==0)\n ++cnt;\n if(cnt>k)\n break;\n s.insert(res);\n \n }\n }\n return s.size();\n \n \n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Python Solution
|
python-solution-by-sambitpuitandi26-8dlw
|
```\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n ans = 0\n n = len(nums)\n for i in range(n):\n
|
sambitpuitandi26
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:48:23.506226+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:48:23.506266+00:00
| 89 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n ans = 0\n n = len(nums)\n for i in range(n):\n temp2 = []\n l = 0\n check = set()\n for j in range(i,n):\n if i == 0:\n if nums[j]%p == 0:\n temp2.append(1)\n else:\n temp2.append(0)\n if temp2[l] <= k and nums[j] not in check:\n ans+=1\n check.add(nums[j])\n else:\n if nums[j]%p == 0:\n temp2.append(temp1[l]+1)\n else:\n temp2.append(temp1[l])\n if temp2[l] <= k and tuple(nums[l:j+1]) not in check:\n ans+=1\n check.add(tuple(nums[l:j+1]))\n l+=1\n temp1 = list(temp2)\n \n return ans
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
generating all substring O(n^2log(n))
|
generating-all-substring-on2logn-by-para-dd6v
|
\n``int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int n=nums.size();\n set<vector<int>>s;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n
|
paras352
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:31:02.077373+00:00
|
2022-05-02T14:58:04.933674+00:00
| 40 | false |
```\n``int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int n=nums.size();\n set<vector<int>>s;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n int c=0;\n vector<int>l;\n for(int j=i;j<n;j++)\n {\n if(nums[j]%p==0)\n c++;\n if(c>k)\n break;\n l.push_back(nums[j]);\n s.insert(l);\n }\n }\n return s.size();\n }\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Why its showing TLE ?|| even all 129 test cases have been passed
|
why-its-showing-tle-even-all-129-test-ca-096e
|
\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int ans = 0;\n set<vector<int>> set;\n for(int i=0; i <nums.size(); i++){\n
|
yayush2002
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:29:13.310825+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:29:13.310853+00:00
| 72 | false |
```\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n int ans = 0;\n set<vector<int>> set;\n for(int i=0; i <nums.size(); i++){\n int r = k;\n if(nums[i] % p == 0)\n --r;\n vector<int> s;\n s.push_back(nums[i]);\n int j = i + 1;\n while(r >= 0 && j<=nums.size()){\n if(!set.count(s)){\n ++ans;\n set.insert(s);\n }\n if(j<nums.size())\n s.push_back(nums[j]);\n else break;\n if(nums[j] % p == 0){\n --r;\n }\n ++j;\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Ordered Set']
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Java Solution | Brute Force | Set
|
java-solution-brute-force-set-by-rajput6-t8jo
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n int count = 0;\n Set<String> set = new HashSet();\n int len
|
Rajput616
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:25:01.830541+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:25:01.830576+00:00
| 133 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n int count = 0;\n Set<String> set = new HashSet();\n int len = nums.length;\n for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i){\n int countForK = 0;\n StringBuilder sub = new StringBuilder();\n for(int j = i; j < len; ++j){\n sub.append(nums[j]+ " ");\n if(nums[j] % p == 0) countForK++;\n if(countForK > k) break;\n if(!set.contains(sub.toString())){\n count++;\n set.add(sub.toString());\n }\n }\n\n }\n return count;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Ordered Set', 'Java']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Java Prefix Sum + All Substrings
|
java-prefix-sum-all-substrings-by-kamun-2esb
|
Time: O(n^2)\n\nimport java.sql.Array;\nimport java.util.*;\n\npublic class Solution {\n\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n int
|
kamun
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:22:18.099040+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:23:31.156831+00:00
| 192 | false |
Time: O(n^2)\n```\nimport java.sql.Array;\nimport java.util.*;\n\npublic class Solution {\n\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n int []pSum = new int[nums.length + 1];\n\t\t// how many at interview (0, i) are divisible by p\n for(int i = 0; i<nums.length; i++) {\n if(i == 0) {\n if(nums[i] % p == 0) {\n pSum[i + 1] = 1;\n }\n } else {\n if(nums[i] % p == 0) {\n pSum[i + 1] = pSum[i] + 1;\n } else {\n pSum[i + 1] = pSum[i];\n }\n }\n }\n\t\t// count all unique valid subsets. Subset (i, j) is valid if pSum(i, j) <= k\n int n = nums.length;\n Set<List<Integer>> distinctAnswers = new HashSet<>();\n for(int i = 0; i< n; i++) {\n List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList<>();\n for(int j = i; j<n; j++) {\n cur.add(nums[j]);\n if(pSum[j + 1] - pSum[i] > k) {\n break;\n }\n\n distinctAnswers.add(new ArrayList<>(cur));\n }\n }\n\n return distinctAnswers.size();\n }\n\n}\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['String', 'Prefix Sum', 'Java']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Clean Java
|
clean-java-by-rexue70-r574
|
It varies between framework version; in older versions StringBuilder works on a string directly, so there is no additional cost in .ToString(): it just hands yo
|
rexue70
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:20:43.034845+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:21:56.085607+00:00
| 111 | false |
It varies between framework version; in older versions StringBuilder works on a string directly, so there is no additional cost in .ToString(): it just hands you the data directly (which can mean oversized, but it makes it work); so O(1).\n\nIn newer framework version, it uses a char[] backing buffer, so now when you .ToString() it will probably need to copy 2 x Length bytes, making it O(N).\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();\n getAll(nums, set, k, p);\n return set.size();\n }\n \n private void getAll(int[] nums, Set<String> res, int k, int p) {\n int N = nums.length;\n for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {\n StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();\n int countK = 0;\n for (int j = i; j < N && countK <= k; j++) {\n if (nums[j] % p == 0) countK++;\n sb.append(",").append(nums[j]);\n if (countK <= k) res.add(sb.toString());\n }\n }\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
✔✔ C++ , easy ,map/set
|
c-easy-mapset-by-harshkrgautam-21t9
|
\tclass Solution {\n\tpublic:\n\t\tint countDistinct(vector& nums, int k, int p) {\n\t\t\tmap,int>m;\n\t\t\tint n = nums.size();\n\t\t\tfor(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n\t
|
harshkrgautam
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:13:58.319961+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:13:58.319990+00:00
| 115 | false |
\tclass Solution {\n\tpublic:\n\t\tint countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n\t\t\tmap<vector<int>,int>m;\n\t\t\tint n = nums.size();\n\t\t\tfor(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tint count=0;\n\t\t\t\tvector<int>v;\n\t\t\t\tfor(int j=i;j<n;j++)\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\tif(nums[j]%p == 0)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tcount++;\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t\tif(count <= k)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tv.push_back(nums[j]);\n\t\t\t\t\t\tm[v]++;\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t\telse break;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\treturn m.size();\n\t\t}\n\t};
| 1 | 0 |
['C', 'Ordered Set', 'C++']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
[Python] Count distinct subarrays
|
python-count-distinct-subarrays-by-ghibl-dz6q
|
\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n N = len(nums)\n substrings = set()\n \n de
|
Ghibli
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:10:54.960726+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:25:38.891100+00:00
| 439 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n N = len(nums)\n substrings = set()\n \n def subarray(idx, curr, s):\n if idx == N:\n return 0\n \n curr += nums[idx]%p == 0\n s += str(nums[idx])+","\n if curr <= k:\n not_exists = s not in substrings\n substrings.add(s)\n return not_exists + subarray(idx+1, curr, s)\n else:\n return 0 \n \n res = 0\n for idx in range(N):\n res += subarray(idx, 0, "")\n return res\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python']
| 2 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Python Efficient Solution | Generate Substrings | Easy to Understand
|
python-efficient-solution-generate-subst-fbvn
|
\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n l = set()\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n a =
|
AkashHooda
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:08:49.967202+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:08:49.967242+00:00
| 120 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n l = set()\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n a = 0 \n x = ""\n for j in range(i,len(nums)):\n x+=str(nums[j])+\'-\'\n if nums[j]%p==0:\n a+=1\n if a>k:\n break \n l.add(x)\n return len(l)\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Combinatorics', 'Ordered Set', 'Python']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Javascript recursion solution
|
javascript-recursion-solution-by-rishabh-crbj
|
\nvar countDistinct = function(nums, k, p) {\n let ans = [];\n \n let rec = (index,k,p,nums,ans,curr) => {\n let val = nums[index];\n let
|
rishabhthakkar7
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:08:20.533044+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:08:20.533089+00:00
| 124 | false |
```\nvar countDistinct = function(nums, k, p) {\n let ans = [];\n \n let rec = (index,k,p,nums,ans,curr) => {\n let val = nums[index];\n let check = val%p;\n let isdiv = false;\n if(check == 0) isdiv=true;\n \n if(index == nums.length) {\n if(curr.length>0){\n ans.push(curr.join(","));\n }\n return;\n }\n \n //take conditions\n if(isdiv && k==0){\n ans.push(curr.join(","));\n } else if(isdiv){\n curr.push(val)\n rec(index+1,k-1,p,nums,ans,curr);\n curr.pop()\n } else {\n curr.push(val)\n rec(index+1,k,p,nums,ans,curr);\n curr.pop()\n }\n \n \n //non take conditions\n if(curr.length == 0){\n rec(index+1,k,p,nums,ans,curr);\n } else {\n ans.push(curr.join(","));\n }\n \n }\n rec(0,k,p,nums,ans,[]);\n let set = new Set(ans);\n \n return set.size\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Recursion', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Python |set| straight forward O(n^2)
|
python-set-straight-forward-on2-by-ezcat-radd
|
Since the size is just 200, just iterate all the subarrays.\n\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n n
|
ezcat
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:07:38.884594+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:07:38.884629+00:00
| 83 | false |
Since the size is just 200, just iterate all the subarrays.\n```\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n n = len(nums)\n res = set()\n for i in range(n):\n for j in range(i+1,n+1):\n cnt = 0\n for c in nums[i:j]:\n if c%p == 0:\n cnt += 1\n if cnt <= k:\n res.add(tuple(nums[i:j]))\n return len(res) \n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C++ Easy solution
|
c-easy-solution-by-developer25-nyhy
|
I used set of vectors to count distinct arrays.\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int & k, int & p) {\n int n=
|
developer25
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:06:48.157420+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:06:48.157452+00:00
| 81 | false |
I used set of vectors to count distinct arrays.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int & k, int & p) {\n int n=nums.size();\n set<vector<int>> s;\n for (int i=0; i <n; i++){\n vector<int> v;\n int c=0;\n for (int j=i; j<n; j++){\n if(nums[j]%p==0) c++;\n v.push_back(nums[j]);\n if(c>k){break;}\n if(c<=k){s.insert(v);}\n }\n }\n \n \n return s.size();\n }\n};\n```\n\n**upvote if you learnt from this post**
| 1 | 0 |
['C', 'Ordered Set']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Easy to understand || Recursion || Generate all Subarrays
|
easy-to-understand-recursion-generate-al-rcj4
|
\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @param {number} k\n * @param {number} p\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar countDistinct = function(nums, k, p) {\n \n le
|
vj98
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:05:13.310097+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:12:43.366719+00:00
| 115 | false |
```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @param {number} k\n * @param {number} p\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar countDistinct = function(nums, k, p) {\n \n let ans = new Set();\n let temp = [];\n let hash = {};\n function solve(nums, k, p, ind, cnt, str) { \n if (cnt > k || (temp.length >= 2 && temp[temp.length-2]+1 != temp[temp.length-1])) {\n return;\n }\n \n if (str.length > 0 && cnt <= k) {\n ans.add(str);\n }\n \n for (let i = ind; i < nums.length; i++) {\n temp.push(i);\n solve(nums, k, p, i+1, (nums[i] % p == 0) ? cnt + 1 : cnt, str+"~"+nums[i]);\n temp.pop();\n }\n }\n \n solve(nums, k, p, 0, 0, "");\n return [...ans].length;\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['String', 'Recursion', 'Ordered Set', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Java bruteforce
|
java-bruteforce-by-henzhengchang-faii
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n // save sub arrays in a string format to count the uniqueness\n //
|
henzhengchang
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:04:34.136236+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:04:34.136287+00:00
| 172 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n // save sub arrays in a string format to count the uniqueness\n // i.e. [3,3,2] is saved as "3-3-2" in the hash set\n // return the size of the hash set\n HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();\n for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++) {\n for(int j=i; j<nums.length; j++) {\n int count=0;\n StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();\n for(int r=i; r<=j; r++) {\n sb.append(nums[r]).append("-");\n if(nums[r]%p == 0) count++;\n if (count>k) break;\n }\n if (count<=k) set.add(sb.toString());\n }\n }\n return set.size();\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C++ || Short solution
|
c-short-solution-by-arihantjain01-dy5u
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n set<vector<int>>s;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n
|
arihantjain01
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:02:23.321631+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:12:14.283883+00:00
| 143 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {\n set<vector<int>>s;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n int cnt=0;\n for(int j=i;j<nums.size();j++){\n if(nums[j]%p==0) cnt++;\n if(cnt==k+1){break;}\n s.insert(vector<int>(nums.begin()+i,nums.begin()+j+1));\n }\n }\n return s.size();\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Python | Easy to Understand
|
python-easy-to-understand-by-mikey98-2txz
|
```\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n used = set()\n n = len(nums)\n count = 0\n
|
Mikey98
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:02:07.305105+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:02:07.305136+00:00
| 234 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:\n used = set()\n n = len(nums)\n count = 0\n \n for i in range(n):\n divisible_num = 0\n s = []\n for j in range(i, n):\n if nums[j] % p == 0:\n divisible_num += 1\n \n if divisible_num <= k:\n s.append(nums[j])\n if tuple(s) not in used:\n used.add(tuple(s))\n count += 1\n else:\n continue\n \n elif divisible_num > k:\n break\n \n return count\n
| 1 | 0 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
[Java] Slide window with serial array
|
java-slide-window-with-serial-array-by-0-xb8v
|
Use slide window with at most k.\n\nSerial array to count distinct subarrays: [1, 2, 3] ==> "1 2 3 "\n\nTime: O(N^2)\nSpace: O(N^2)\n\n\nclass Solution {\n pub
|
0x4c0de
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-01T04:00:31.759564+00:00
|
2022-05-01T04:08:42.203337+00:00
| 432 | false |
Use slide window with at most k.\n\nSerial array to count distinct subarrays: [1, 2, 3] ==> "1 2 3 "\n\nTime: O(N^2)\nSpace: O(N^2)\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int countDistinct(int[] nums, int k, int p) {\n final int n = nums.length;\n Set<String> candidate = new HashSet<>();\n int count = 0;\n for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; i++) {\n if (nums[i] % p == 0) {\n count++;\n }\n if (count > k) {\n // window is full, so move left side\n while (nums[j] % p != 0) {\n j++;\n }\n\n j++;\n count--;\n }\n\n // all subarray among [i, j] is valid\n for (int m = j; m <= i; m++) {\n StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();\n for (int l = m; l <= i; l++) {\n sb.append(nums[l]).append(\' \');\n }\n // use set to distinct\n candidate.add(sb.toString());\n }\n }\n\n return candidate.size();\n }\n}\n```\n
| 1 | 0 |
['Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Solution
|
solution-by-3nomis-86pk
|
Complexity
Time complexity: O(n3)
Space complexity: O(n2)
Code
|
3nomis
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-08T13:37:46.516008+00:00
|
2025-03-08T13:37:46.516008+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity: $$O(n^3)$$
- Space complexity: $$O(n^2)$$
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:
res = set()
for i in range(len(nums)):
cur_sub = []
cur_k = 0
for j in range(i, len(nums)):
if nums[j] % p == 0:
cur_k += 1
if cur_k <= k:
cur_sub.append(nums[j])
res.add(tuple(cur_sub))
return len(res)
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Hash Function', 'Python3']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
K Divisible Elements Subarrays | Python
|
k-divisible-elements-subarrays-python-by-okfj
|
IntuitionWe need to count distinct subarrays where at most k numbers are divisible by p. Instead of checking all possible subarrays in a slow way, we can effici
|
thejayvasani
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-06T06:48:21.574240+00:00
|
2025-03-06T06:48:21.574240+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition
We need to count distinct subarrays where at most k numbers are divisible by p. Instead of checking all possible subarrays in a slow way, we can efficiently track unique subarrays using a set.
# Approach
Use a set to store unique subarrays.
Loop through the array, picking a starting point for each subarray.
Extend the subarray step by step, keeping track of numbers divisible by p.
If more than k numbers are divisible by p, stop extending.
Convert each subarray into a tuple and store it in the set to avoid duplicates.
The total count of unique subarrays is the size of the set.
# Complexity
- Time Complexity: O(n²)
- Space complexity: O(n²)
# Code
```python []
class Solution(object):
def countDistinct(self, nums, k, p):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type k: int
:type p: int
:rtype: int
"""
seen = set() # To store unique subarrays
n = len(nums)
for i in range(n):
divisible_count = 0
subarray = []
for j in range(i, n):
subarray.append(nums[j])
if nums[j] % p == 0:
divisible_count += 1
if divisible_count > k:
break # Stop if more than k elements are divisible by p
# Convert list to tuple (hashable) and add to set
seen.add(tuple(subarray))
return len(seen)
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Easy solution
|
easy-solution-by-koushik_55_koushik-esnr
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
Koushik_55_Koushik
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-05T06:24:38.276231+00:00
|
2025-03-05T06:24:38.276231+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:
f1 = set()
for i in range(len(nums)):
c = 0
f = []
for j in range(i, len(nums)):
f.append(nums[j])
if nums[j] % p == 0:
c += 1
if c > k:
break
f1.add(tuple(f))
return len(f1)
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Simple using prefix count 🟢✔️
|
simple-using-prefix-count-by-lokesh6468-tior
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
Lokesh6468
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-21T08:08:09.670234+00:00
|
2025-02-21T08:08:09.670234+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:
n=len(nums)
prefixCount=[0]*n
tracedup=set()
c=0
for i in range(n):
if nums[i]%p==0:
c+=1
prefixCount[i]=c
for i in range(n):
a=i
b=n-1
while(a<=b):
if i>0:
res=prefixCount[b]-prefixCount[a-1]
else:
res=prefixCount[b]-0
if res<=k:
if tuple(nums[a:b+1]) not in tracedup:
#print(nums[a:b+1])
tracedup.add(tuple(nums[a:b+1]))
b-=1
return(len(tracedup))
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
O(n^2) Tuple counting
|
on2-tuple-counting-by-trieutrng-hwl2
|
Complexity
Time complexity: O(n2)
Space complexity: O(n2)
Code
|
trieutrng
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-16T12:35:22.253943+00:00
|
2025-02-16T12:35:22.253943+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity: $$O(n^2)$$
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: $$O(n^2)$$
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def countDistinct(self, nums: List[int], k: int, p: int) -> int:
subs = set()
for i in range(len(nums)):
total, divCount = 0, 0
sub = ()
for j in range(i, len(nums)):
if nums[j] % p == 0:
divCount += 1
if divCount > k:
break
sub += (nums[j],)
subs.add(tuple(sub))
return len(subs)
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'Rolling Hash', 'Hash Function', 'Enumeration', 'Python3']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
100% || C++
|
100-c-by-giri_69-dfgq
|
IntuitionTry putting element one by one in the vector and if any of the condition is not violated, just put it in the setCode
|
giri_69
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-14T06:15:29.141497+00:00
|
2025-02-14T06:15:29.141497+00:00
| 10 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
Try putting element one by one in the vector and if any of the condition is not violated, just put it in the set
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {
unordered_set <string> hash;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
string temp="";
int count=0;
for(int j=i;j<nums.size();j++){
int ele=nums[j];
temp+=to_string(ele)+",";
if(ele%p==0) count++;
if(count>k) break;
hash.insert(temp);
}
}
return hash.size();
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C++ Solution using Binary Array - Two Pointers and Sliding Window
|
c-solution-using-binary-array-two-pointe-4nwe
|
Approach
Create a set of vectors to store the unique/distinct subarrays.
Convert the vector into a binary vector with 1’s representing elements divisible by p a
|
vvidhig
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-09T15:49:58.862548+00:00
|
2025-02-09T15:49:58.862548+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
- Create a set of vectors to store the unique/distinct subarrays.
- Convert the vector into a binary vector with 1’s representing elements divisible by p and 0’s representing elements not divisible by p.
- Using Two Pointers ‘left’ and ‘right’ iterate over the binary vector and keep count of the 1’s in the array.
- if count exceeds k, stop further execution.
- Insert the subarray into the set.
- Return the size of the set.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(N)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(N)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Dry Run :-
nums = [2,3,3,2,2], k = 2, and let's assume p = 2 for this example.
Let's go step by step:
1. First, we create A[] array marking numbers divisible by p(2):
```
Copy
nums = [2,3,3,2,2]
A = [1,0,0,1,1] // 1 for numbers divisible by 2
```
2. Now let's iterate through each left position and generate subarrays:
For left = 0:
```
Copy
[2] - countDivisible=1, add to set
[2,3] - countDivisible=1, add to set
[2,3,3] - countDivisible=1, add to set
[2,3,3,2] - countDivisible=2, add to set
[2,3,3,2,2] - countDivisible=3, break (>k)
```
For left = 1:
```
Copy
[3] - countDivisible=0, add to set
[3,3] - countDivisible=0, add to set
[3,3,2] - countDivisible=1, add to set
[3,3,2,2] - countDivisible=2, add to set
```
For left = 2:
```
Copy
[3] - countDivisible=0, add to set
[3,2] - countDivisible=1, add to set
[3,2,2] - countDivisible=2, add to set
```
For left = 3:
```
Copy
[2] - countDivisible=1, add to set
[2,2] - countDivisible=2, add to set
```
For left = 4:
```
Copy
[2] - countDivisible=1, add to set
```
Let's count unique subarrays:
- [2]
- [2,3]
- [2,3,3]
- [2,3,3,2]
- [3]
- [3,3]
- [3,3,2]
- [3,3,2,2]
- [3,2]
- [3,2,2]
- [2,2]
The answer would be 11 as there are 11 unique subarrays where the count of numbers divisible by 2 is ≤ 2.
Note that even though we generated some subarrays multiple times (like [2]), the set data structure ensures we only count unique subarrays once.
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {
set<vector<int>> uniqueSubarrays;
vector<int> A(nums.size(), 0);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (nums[i] % p == 0) {
A[i] = 1;
}
}
int n = nums.size();
for (int left = 0; left < n; left++) {
vector<int> subarray;
int countDivisible = 0;
for (int right = left; right < n; right++) {
subarray.push_back(nums[right]);
countDivisible += A[right];
if (countDivisible > k) {
break;
}
uniqueSubarrays.insert(subarray);
}
}
return uniqueSubarrays.size();
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
C++ Solution using Binary Array - Two Pointers and Sliding Window
|
c-solution-using-binary-array-two-pointe-yp78
|
Approach
Create a set of vectors to store the unique/distinct subarrays.
Convert the vector into a binary vector with 1’s representing elements divisible by p a
|
vvidhig
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-09T15:49:54.672876+00:00
|
2025-02-09T15:49:54.672876+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
- Create a set of vectors to store the unique/distinct subarrays.
- Convert the vector into a binary vector with 1’s representing elements divisible by p and 0’s representing elements not divisible by p.
- Using Two Pointers ‘left’ and ‘right’ iterate over the binary vector and keep count of the 1’s in the array.
- if count exceeds k, stop further execution.
- Insert the subarray into the set.
- Return the size of the set.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(N)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(N)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Dry Run :-
nums = [2,3,3,2,2], k = 2, and let's assume p = 2 for this example.
Let's go step by step:
1. First, we create A[] array marking numbers divisible by p(2):
```
Copy
nums = [2,3,3,2,2]
A = [1,0,0,1,1] // 1 for numbers divisible by 2
```
2. Now let's iterate through each left position and generate subarrays:
For left = 0:
```
Copy
[2] - countDivisible=1, add to set
[2,3] - countDivisible=1, add to set
[2,3,3] - countDivisible=1, add to set
[2,3,3,2] - countDivisible=2, add to set
[2,3,3,2,2] - countDivisible=3, break (>k)
```
For left = 1:
```
Copy
[3] - countDivisible=0, add to set
[3,3] - countDivisible=0, add to set
[3,3,2] - countDivisible=1, add to set
[3,3,2,2] - countDivisible=2, add to set
```
For left = 2:
```
Copy
[3] - countDivisible=0, add to set
[3,2] - countDivisible=1, add to set
[3,2,2] - countDivisible=2, add to set
```
For left = 3:
```
Copy
[2] - countDivisible=1, add to set
[2,2] - countDivisible=2, add to set
```
For left = 4:
```
Copy
[2] - countDivisible=1, add to set
```
Let's count unique subarrays:
- [2]
- [2,3]
- [2,3,3]
- [2,3,3,2]
- [3]
- [3,3]
- [3,3,2]
- [3,3,2,2]
- [3,2]
- [3,2,2]
- [2,2]
The answer would be 11 as there are 11 unique subarrays where the count of numbers divisible by 2 is ≤ 2.
Note that even though we generated some subarrays multiple times (like [2]), the set data structure ensures we only count unique subarrays once.
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int countDistinct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int p) {
set<vector<int>> uniqueSubarrays;
vector<int> A(nums.size(), 0);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (nums[i] % p == 0) {
A[i] = 1;
}
}
int n = nums.size();
for (int left = 0; left < n; left++) {
vector<int> subarray;
int countDivisible = 0;
for (int right = left; right < n; right++) {
subarray.push_back(nums[right]);
countDivisible += A[right];
if (countDivisible > k) {
break;
}
uniqueSubarrays.insert(subarray);
}
}
return uniqueSubarrays.size();
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
k-divisible-elements-subarrays
|
Python (Simple Maths)
|
python-simple-maths-by-rnotappl-d9ea
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
rnotappl
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-05T07:35:05.690447+00:00
|
2025-02-05T07:35:05.690447+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def countDistinct(self, nums, k, p):
n, left, count, res = len(nums), 0, 0, set()
for right in range(n):
if nums[right]%p == 0:
count += 1
while count > k:
if nums[left]%p == 0:
count -= 1
left += 1
ans = nums[left:right+1]
for i in range(len(ans)):
res.add(tuple(ans[i:]))
return len(res)
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
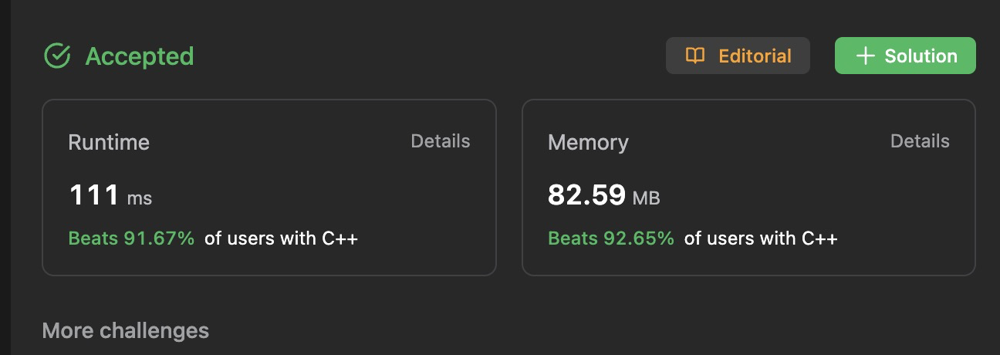
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Simple Solution with reasoning || c++ || java
|
simple-solution-with-reasoning-c-java-by-szmd
|
For the beauty value of the ith element to be 2, it should be greater than all the elements on its left and smaller than all the elements on its right.\nSo, it
|
book11she
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-19T04:01:04.825158+00:00
|
2021-09-21T03:38:33.832923+00:00
| 6,240 | false |
For the beauty value of the ith element to be 2, it should be greater than all the elements on its left and smaller than all the elements on its right.\nSo, it should be greater than the maximum of all elements on the left and smaller than minimum of all elements on the right.\n \nFor the beauty value of the ith element to be 1, it should firstly not satisfy the above statement and secondly the ith element should be greater than the (i - 1)th element and lesser than (i + 1)th element\n\nC++:\n```\nint sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<int> minOnRight(n, 0);\n minOnRight[n - 1] = nums[n - 1];\n \n // loop for maintaing values of minimum on the right\n for(int i = n - 2; i >= 2; i--){\n //minimum is either the number itself or the minimum that is on right of this element we are traversing\n minOnRight[i] = min(minOnRight[i + 1], nums[i]); \n }\n \n int maxOnLeft = nums[0];\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++){\n if(nums[i] > maxOnLeft && nums[i] < minOnRight[i + 1]) ans += 2;\n else if(nums[i] > nums[i - 1] && nums[i] < nums[i + 1]) ans += 1;\n maxOnLeft = max(nums[i], maxOnLeft);\n }\n \n return ans;\n}\n```\n\nJava: \n```\npublic int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n int n = nums.length;\n int minOnRight[] = new int[n];\n minOnRight[n - 1] = nums[n - 1];\n\t\n\t// loop for maintaing values of minimum on the right\n for(int i = n - 2; i >= 2; i--){\n\t //minimum is either the number itself or the minimum that is on right of this element we are traversing\n minOnRight[i] = Math.min(minOnRight[i + 1], nums[i]); \n }\n \n int maxOnLeft = nums[0];\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++){\n if(nums[i] > maxOnLeft && nums[i] < minOnRight[i + 1]) ans += 2;\n else if(nums[i] > nums[i - 1] && nums[i] < nums[i + 1]) ans += 1;\n maxOnLeft = Math.max(nums[i], maxOnLeft);\n }\n \n return ans; \n}\n```
| 69 | 4 |
['C', 'Java']
| 9 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
python3 precomputation
|
python3-precomputation-by-saurabht462-1j21
|
\n\n\n\n Case1: for each index in nums if every element before this is smaller and every element after this is bigger \nthan we have to increase count by 2\nfor
|
saurabht462
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-19T04:05:30.965774+00:00
|
2023-08-09T14:55:56.980314+00:00
| 2,544 | false |
\n\n\n\n* **Case1**: for each index in nums if every element before this is smaller and every element after this is bigger \nthan we have to increase count by 2\nfor this can we can make two array which will store minimum and maximum till now for each index\n* **Case2**: simply compare with left and right neighbour ,if condition satisfies we will increase count by 1\n\n```\n\ndef sumOfBeauties(self, nums) :\n N=len(nums)\n \n # for each index we have to check if all element before it is smaller than this\n min_=[None for _ in range(N)]\n mi_=float(\'-inf\')\n for i in range(N):\n min_[i]=mi_\n mi_=max(nums[i],mi_)\n \n # for each index we have to check if all element after it is bigger than this \n max_=[None for _ in range(N)]\n mx_=float(\'inf\')\n for i in range(N-1,-1,-1):\n max_[i]=mx_\n mx_=min(mx_,nums[i])\n \n ans=0\n for i in range(1,N-1):\n if min_[i]<nums[i]<max_[i]:\n ans+=2\n elif nums[i-1]<nums[i]<nums[i+1]:\n ans+=1\n return ans\n```\n\t\t\n* **TC - O(N)**
| 22 | 3 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 1 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
C++ O(n) very simple (Using left and right Array)
|
c-on-very-simple-using-left-and-right-ar-7cit
|
```\nint sumOfBeauties(vector& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n \n vector left(n);\n vector right(n);\n \n left[0]=nums[
|
pawan_mehta
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-19T04:03:15.379889+00:00
|
2021-09-19T04:42:07.150905+00:00
| 2,768 | false |
```\nint sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n \n vector<int> left(n);\n vector<int> right(n);\n \n left[0]=nums[0];\n right[n-1]=nums[n-1];\n \n for(int i=1; i<n; i++)\n {\n left[i]=max(left[i-1],nums[i]);\n }\n for(int i=n-2; i>=0; i--)\n {\n right[i]=min(nums[i],right[i+1]);\n }\n \n int count=0;\n \n for(int i=1; i<n-1; i++)\n { \n if(left[i-1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < right[i+1])\n {\n count+=2;\n }\n else if(nums[i-1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i+1])\n {\n count++;\n }\n }\n \n return count;\n }
| 20 | 1 |
[]
| 5 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Very simple java solution using boolean array
|
very-simple-java-solution-using-boolean-5kad9
|
Approach:\n All the numbers left to current should be less and all the numbers right to current should be high.\n So First we loop from left to right by maintai
|
leet4242
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-19T04:28:40.625080+00:00
|
2021-09-19T04:29:51.244945+00:00
| 1,288 | false |
**Approach**:\n* All the numbers left to current should be less and all the numbers right to current should be high.\n* So First we loop from left to right by maintaining the maxLeft and if current is greater than maxLeft then all nums to the left are less.\n* Similarly we loop from right to left by maintaining the minRight and if current is less than minRight then all nums to the right are high. \n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n boolean[] left = new boolean[nums.length];\n boolean[] right = new boolean[nums.length];\n \n left[0] = true;\n int leftMax = nums[0];\n for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {\n if(nums[i] > leftMax) {\n left[i] = true;\n leftMax = nums[i];\n }\n }\n \n right[nums.length-1] = true;\n int rightMin = nums[nums.length-1];\n for(int i = nums.length-2; i >= 0; i--) {\n if(nums[i] < rightMin) {\n right[i] = true;\n rightMin = nums[i];\n }\n }\n \n int beautyCount = 0;\n for(int i = 1; i < nums.length-1; i++) {\n if(left[i] && right[i]) {\n beautyCount += 2;\n }\n \n else if(nums[i-1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i+1]) {\n beautyCount += 1;\n }\n \n }\n return beautyCount;\n }\n}\n```
| 14 | 0 |
['Java']
| 4 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
[Java/Python 3] O(n) code: running max/min from left and right, w/ brief explanation and analysis.
|
javapython-3-on-code-running-maxmin-from-hawh
|
Compute running max from left and running min from left in order to check if nums[i] < nums[j] < nums[k] , for all 0 <= j < i and for all i < k <= nums.length -
|
rock
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-19T04:05:27.509557+00:00
|
2021-09-28T12:32:57.294415+00:00
| 1,082 | false |
1. Compute running max from left and running min from left in order to check if `nums[i] < nums[j] < nums[k]` , for all `0 <= j < i` and for all `i < k <= nums.length - 1`;\n2. Traverse the input array `nums` to get the beauty value.\n\n```java\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n int sum = 0, n = nums.length;\n int[] mi = new int[n + 1], mx = new int[n + 1];\n mi[n] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n for (int i = 0, j = n - 1; i < n; ++i, --j) {\n mx[i + 1] = Math.max(nums[i], mx[i]);\n mi[j] = Math.min(nums[j], mi[j + 1]);\n }\n for (int i = 1; i < nums.length - 1; ++i) {\n if (mx[i] < nums[i] && nums[i] < mi[i + 1]) {\n sum += 2;\n }else if (nums[i - 1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i + 1]) {\n ++sum;\n }\n }\n return sum;\n }\n```\n\n```python\n def sumOfBeauties(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n n, sm = len(nums), 0\n mi, mx = [0] * n + [math.inf], [0] * (n + 1)\n for i, num in enumerate(nums):\n mx[i + 1] = max(num, mx[i])\n mi[~i - 1] = min(nums[~i], mi[~i])\n for i in range(1, len(nums) - 1):\n if mx[i] < nums[i] < mi[i + 1]:\n sm += 2\n elif nums[i - 1] < nums[i] < nums[i + 1]:\n sm += 1\n return sm \n```\n\n----\n\n`mx` array is not necessary, and a running max value suffices. - credit to **@lattu**.\n\n```java\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n int sum = 0, n = nums.length;\n int[] mi = new int[n + 1];\n mi[n] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {\n mi[i] = Math.min(nums[i], mi[i + 1]);\n }\n for (int i = 1, mx = nums[0]; i < nums.length - 1; ++i) {\n if (mx < nums[i] && nums[i] < mi[i + 1]) {\n sum += 2;\n }else if (nums[i - 1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i + 1]) {\n ++sum;\n }\n mx = Math.max(mx, nums[i]);\n }\n return sum;\n }\n```\n```python\n def sumOfBeauties(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n mi, mx, sm = [math.inf], nums[0], 0\n for num in reversed(nums):\n mi.append(min(mi[-1], num))\n mi.reverse()\n for i in range(1, len(nums) - 1):\n if mx < nums[i] < mi[i + 1]:\n sm += 2\n elif nums[i - 1] < nums[i] < nums[i + 1]:\n sm += 1\n mx = max(mx, nums[i]) \n return sm \n```\n**Analysis:**\n\nTime & space: `O(n)`, where `n = nums.length`.
| 14 | 4 |
[]
| 2 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
easy cpp code || using heaps
|
easy-cpp-code-using-heaps-by-thor69-luk0
|
everytime we just need to find max element on our leftside and min element on our right side, and we can easily find the answer :) \n\nclass Solution {\npublic:
|
Thor69
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-19T06:13:33.367479+00:00
|
2021-09-19T06:13:33.367512+00:00
| 382 | false |
everytime we just need to find max element on our leftside and min element on our right side, and we can easily find the answer :) \n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n priority_queue<pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int>>,greater<pair<int,int>>> minh;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n minh.push({nums[i],i});\n }\n int a=INT_MIN,ans=0;\n for(int i=1;i<nums.size()-1;i++){\n a=max(a,nums[i-1]);\n while(minh.top().second<=i) minh.pop();\n if(a<nums[i]&&nums[i]<minh.top().first) ans+=2;\n else if(nums[i]>nums[i-1]&&nums[i]<nums[i+1]) ans++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 7 | 1 |
[]
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
C++ Simple Clean & Concise TC: O(n) Explanation with code ☑ ☑
|
c-simple-clean-concise-tc-on-explanation-lg4u
|
The approcah is to know the max element in left part and min element in right part\nfor O(n^2) Solution use two loop inside one loop one traversing in left part
|
Hashcode-Ankit
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-19T04:11:04.044998+00:00
|
2021-09-19T04:33:38.846951+00:00
| 727 | false |
The approcah is to know the max element in left part and min element in right part\nfor O(n^2) Solution use two loop inside one loop one traversing in left part and one in right part searching for max and min element respectively *But it will result in TLE as the solution is O(n^2)\n\nThe O(n) Solution :\nin this solution we are going to create two array so that we can store min and max element to a specific index i. And now we good to go and our work simply complete in single loop.\nCheck the max array for index less then the i and min array for i+1 (i have stored min elements in other way you can store it in increasing order of index) ;\nUpvote if you like the solution\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int sum=0;\n vector<int> minV,maxV;\n int maximum=0;\n int minimum=INT_MAX;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)\n {\n maximum=max(maximum,nums[i]);\n maxV.push_back(maximum);\n }\n for(int i=nums.size()-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n minimum=min(minimum,nums[i]);\n minV.push_back(minimum);\n }\n for(int i=1;i<nums.size()-1;i++)\n {\n if((maxV[i-1]<nums[i] && minV[minV.size()-i-2]>nums[i]))\n sum+=2;\n else if(nums[i-1]<nums[i] && nums[i+1]>nums[i])\n sum+=1;\n }\n return sum; \n }\n};\n```
| 7 | 2 |
['C']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Two Sweeps vs. Max Heap
|
two-sweeps-vs-max-heap-by-votrubac-w4af
|
Two Sweeps\nWe could use a heap and one sweep, but for O(n) solution we can just do two sweeps.\n\nC++\ncpp\nint sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int res
|
votrubac
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-19T05:32:04.858818+00:00
|
2021-09-19T20:08:22.684926+00:00
| 1,167 | false |
#### Two Sweeps\nWe could use a heap and one sweep, but for O(n) solution we can just do two sweeps.\n\n**C++**\n```cpp\nint sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int res = 0, maxj = nums[0], mink = nums.back();\n vector<bool> b2(nums.size());\n for (int i = 1; i < nums.size() - 1; maxj = max(maxj, nums[i++])) {\n b2[i] = maxj < nums[i];\n res += nums[i - 1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i + 1];\n }\n for (int i = nums.size() - 2; i > 0; mink = min(mink, nums[i--]))\n res += b2[i] && nums[i] < mink;\n return res;\n}\n```\n#### Max Heap\nIt may not be obvious why max heap works, but an example can help. Say we have `[7,1,2,3,4,5]`, and the initial heap state is `[7,3,2,1]`. After we check 7|3 < 4 < 5|5 (one point), we remove 7 (top of the head). Now we check 3|2 < 3 < 4|4 (also one point). Note that this works for a strict "less" comparison; it won\'t work for "less or equal".\n\n**C++**\n```cpp\nint sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int res = 0, mink = nums.back();\n priority_queue<int> pq(begin(nums), prev(prev(end(nums))));\n for (int i = nums.size() - 2; i > 0; --i) {\n res += nums[i - 1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i + 1];\n res += pq.top() < nums[i] && nums[i] < mink;\n mink = min(mink, nums[i]);\n pq.pop();\n }\n return res;\n}\n```
| 6 | 0 |
[]
| 4 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
[C++] easy solution - beats 92% runtime, 93% memory
|
c-easy-solution-beats-92-runtime-93-memo-fzzx
|
\n\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n int premax[n]; premax[0] = nums[0];
|
vanshdhawan60
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-09T13:47:21.755147+00:00
|
2023-10-09T13:47:54.176500+00:00
| 374 | false |
\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n int premax[n]; premax[0] = nums[0]; //stores prefix max\n int sufmin[n]; sufmin[n-1] = nums[n-1]; //store suffix min\n for (int i=1; i<n; i++) premax[i] = max(nums[i], premax[i-1]);\n for (int i=n-2; i>=0; i--) sufmin[i] = min(nums[i], sufmin[i+1]);\n\n int ans = 0;\n for (int i=1; i<=n-2; i++) {\n if (nums[i] > premax[i-1] && nums[i] < sufmin[i+1]) ans+=2;\n else if (nums[i] > nums[i-1] && nums[i] < nums[i+1]) ans++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Array', 'C++']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
C++ O(N) || Stack
|
c-on-stack-by-abhay5349singh-x8cy
|
Connect with me on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/abhay5349singh/\n\nApproach: Nearest Smaller on Right\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n vector<
|
abhay5349singh
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-30T18:11:30.357964+00:00
|
2023-07-14T04:52:58.354635+00:00
| 127 | false |
**Connect with me on LinkedIn**: https://www.linkedin.com/in/abhay5349singh/\n\n**Approach:** Nearest Smaller on Right\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n vector<int> smaller(vector<int>& a){\n int n=a.size();\n vector<int> nsr(n,n);\n stack<pair<int,int>> st;\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){\n while(st.size()>0 && st.top().first>a[i]) st.pop();\n if(st.size()!=0){\n nsr[i]=st.top().second;\n }\n st.push({a[i],i});\n }\n return nsr;\n }\n \n vector<int> greater(vector<int>& a){\n int n=a.size();\n vector<int> ngl(n,-1);\n stack<pair<int,int>> st;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n while(st.size()>0 && st.top().first<a[i]) st.pop();\n if(st.size()!=0){\n ngl[i]=st.top().second;\n }\n st.push({a[i],i});\n }\n return ngl;\n }\n \n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& a) {\n int n=a.size();\n \n vector<int> nsr=smaller(a); // storing index of Nearest Smaller in Right to current element\n vector<int> ngl=greater(a); // storing index of Nearest Greater in Left to current element\n \n vector<bool> type1(n,false);\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++){\n if(ngl[i]==-1 && nsr[i]==n){\n ans+=2;\n type1[i]=true;\n }\n }\n for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++){\n if(type1[i]==false && a[i-1]<a[i] && a[i]<a[i+1]) ans++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Stack', 'C++']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
C++ Simple and Easy Solution, Explained
|
c-simple-and-easy-solution-explained-by-7p59r
|
Idea:\nWe need to know if the current number is smaller than all the elements ahead. \nSo first, we keep a minimum suffix array.\nThen, while iterating the arra
|
yehudisk
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-19T14:09:32.967016+00:00
|
2021-09-19T21:53:39.376713+00:00
| 400 | false |
**Idea:**\nWe need to know if the current number is smaller than all the elements ahead. \nSo first, we keep a minimum suffix array.\nThen, while iterating the array, we keep a prefix maximum to know if the current element is greater than all the previous elements, and just check the options in the statement.\n\n**Time Complexity:** O(n)\n**Space Complexity:** O(n)\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size(), res = 0, prefix_max = nums[0];\n vector<int> suffix(n, nums[n-1]);\n \n for (int i = n-2; i >= 0; i--) suffix[i] = min(suffix[i+1], nums[i]);\n \n for (int i = 1; i < n-1; i++) {\n if (prefix_max < nums[i] && nums[i] < suffix[i+1]) res += 2;\n else if (nums[i-1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i+1]) res++;\n \n prefix_max = max(prefix_max, nums[i]);\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```\n**Like it? please upvote!**
| 4 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
C++ Left and Right
|
c-left-and-right-by-lzl124631x-m44t
|
See my latest update in repo LeetCode\n\n## Solution 1.\n\nIntuition: Let left[i] be the greatest value in A[0..i], and right[i] be the smallest value in A[i..(
|
lzl124631x
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-19T06:08:51.870984+00:00
|
2021-09-19T06:08:51.871014+00:00
| 603 | false |
See my latest update in repo [LeetCode](https://github.com/lzl124631x/LeetCode)\n\n## Solution 1.\n\n**Intuition**: Let `left[i]` be the greatest value in `A[0..i]`, and `right[i]` be the smallest value in `A[i..(N-1)]`. For the first condition, we just need to check if `A[i] > left[i - 1] && A[i] < right[i + 1]`.\n\n**Algorithm**:\n\nWe can precompute the `right` array and then compute `left` on the fly. \n\n```cpp\n// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/sum-of-beauty-in-the-array/\n// Author: github.com/lzl124631x\n// Time: O(N)\n// Space: O(N)\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& A) {\n int N = A.size(), left = A[0], ans = 0;\n vector<int> right(N, A[N - 1]);\n for (int i = N - 2; i > 0; --i) right[i] = min(right[i + 1], A[i]);\n for (int i = 1; i < N - 1; ++i) {\n if (A[i] > left && A[i] < right[i + 1]) ans += 2;\n else if (A[i] > A[i - 1] && A[i] < A[i + 1]) ans++;\n left = max(left, A[i]);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
[C++] Simplest Intuitive Solution | O(n)
|
c-simplest-intuitive-solution-on-by-myth-qax3
|
For nums[i] to be greater than nums[j] for all 0 <= j < i & less than nums[k] for all i < k <= n-1, it is enough if nums[i] is greater than the largest element
|
Mythri_Kaulwar
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-01T01:47:12.743642+00:00
|
2022-02-01T01:47:12.743675+00:00
| 623 | false |
* For ```nums[i]``` to be greater than ```nums[j]``` for all ```0 <= j < i``` & less than nums[k] for all ```i < k <= n-1```, it is enough if nums[i] is greater than the largest element on it\'s left & smaller than the smallest element on it\'s right. Than we add +2 to ```beauty``` at every such ```i```.\n* For this, we need to keep track of ```max``` element seen so far on the left & minimum most element on the right. \n* We can compute maximum element as we go but we need to precompute the minimum most element on the right of an index ```i```.\n* If the above condition doesn\'t hold, we check whether ```nums[i] > nums[i-1]``` && ```nums[i] < nums[i+1]```, if so we add +1 to ```beauty```.\n* If neither of these conditions hold, we move on to the next element.\n\n**Time Complexity :** O(n) - Two-pass solution \n\n**Space Complexity :** O(n) - for ```mini``` array\n\n**Code :**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size(), maxi = nums[0], beauty = 0;\n vector<int> mini(n, INT_MAX); //mini[i] stores the least element until i from n-1\n mini[n-1] = nums[n-1];\n \n for(int i=n-2; i>=0; i--) mini[i] = min(nums[i], mini[i+1]);\n \n for(int i=1; i<n-1; i++){\n if(nums[i] > maxi && nums[i] < mini[i+1]) beauty += 2;\n else if(nums[i] > nums[i-1] && nums[i] < nums[i+1]) beauty++;\n maxi = max(maxi, nums[i]); //updating max so far on-the-fly\n }\n return beauty;\n }\n};\n```\n
| 3 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Java | Easy | Prefix + Suffix Arrays
|
java-easy-prefix-suffix-arrays-by-user85-lee6
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] arr) {\n int n = arr.length;\n int left[] = new int[n]; //pre-calculate minimum\n
|
user8540kj
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-04T09:24:47.699080+00:00
|
2022-01-04T09:26:23.720373+00:00
| 382 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] arr) {\n int n = arr.length;\n int left[] = new int[n]; //pre-calculate minimum\n int right[] = new int[n];//pre-calculate maximum\n \n left[0] = arr[0];\n for(int i = 1 ; i < n ; i++){\n left[i] = Math.max(left[i - 1],arr[i]);\n }\n \n right[n - 1] = arr[n - 1];\n for(int i = n - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i--){\n right[i] = Math.min(right[i + 1],arr[i]);\n }\n \n int beauty = 0;\n for(int i = 1 ; i < n - 1; i++){\n //According to the question, calculate beauty for every element.\n if(arr[i] > left[i - 1] && arr[i] < right[i + 1]){\n beauty += 2;\n }\n else if(arr[i] > arr[i - 1] && arr[i] < arr[i + 1]){\n beauty += 1;\n }\n }\n return beauty;\n } \n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Suffix Array']
| 2 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Easy C++ O(N) solution || commented
|
easy-c-on-solution-commented-by-saiteja_-3lu9
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n \n //for case 1\n //get the max for every element to the left and
|
saiteja_balla0413
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-19T06:31:46.500035+00:00
|
2021-09-19T06:32:08.692200+00:00
| 174 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n \n //for case 1\n //get the max for every element to the left and the min of every element to the right\n //if max<arr[i]<min\n //beauty for arr[i] becomes 2\n //else check for either case 2 or case 3\n \n int n=nums.size();\n vector<int> right(n);\n int mini=nums[n-1];\n for(int i=n-2;i>0;i--)\n {\n right[i]=mini;\n mini=min(mini,nums[i]);\n }\n int maxi=nums[0];\n int sum=0;\n for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++)\n {\n if(maxi<nums[i] && nums[i]<right[i])\n {\n sum+=2;\n }\n else if(nums[i-1]<nums[i] && nums[i]<nums[i+1])\n {\n sum+=1;\n }\n maxi=max(maxi,nums[i]);\n }\n return sum;\n }\n};\n```\n**Upvote if this helps you**
| 3 | 1 |
['C']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Java easy solution with min-heap and max-heap.
|
java-easy-solution-with-min-heap-and-max-daay
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n int count = 0;\n int n = nums.length;\n \n PriorityQueue<Integer> m
|
phung_manh_cuong
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-19T04:04:50.156256+00:00
|
2021-09-19T04:05:15.731716+00:00
| 254 | false |
``` \nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n int count = 0;\n int n = nums.length;\n \n PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>();\n PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<>(){\n public int compare(Integer cur, Integer next) {\n return next - cur;\n }\n });\n \n maxHeap.offer(nums[0]);\n for(int i = 2; i < n; i++) {\n minHeap.offer(nums[i]);\n }\n \n for(int i = 1; i < n-1; i++) {\n if(nums[i-1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i+1]) {\n if(nums[i] > maxHeap.peek() && nums[i] < minHeap.peek()) {\n count += 2;\n } else {\n count += 1;\n }\n }\n \n maxHeap.offer(nums[i]);\n minHeap.poll();\n }\n \n return count;\n }\n} \n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Sum of Beauty in the Array
|
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array-by-mansha_19-uglg
|
Complexity
Time complexity:O(1)
Space complexity: O(n)
Code
|
Mansha_19
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-31T14:58:15.893853+00:00
|
2025-03-31T14:58:15.893853+00:00
| 92 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity:O(1)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(n)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int totalBeauty = 0;
int minRight = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int[] minRightArr = new int[n];
for(int i=n-1; i>=0; i--){
minRight = Math.min(minRight, nums[i]);
minRightArr[i] = minRight;
}
int maxLeft = nums[0];
for(int i = 1; i<n-1; i++){
if(nums[i] > maxLeft && nums[i] < minRightArr[i+1]){
totalBeauty += 2;
}else if(nums[i-1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i+1]){
totalBeauty += 1;
}
maxLeft = Math.max(maxLeft, nums[i]);
}
return totalBeauty;
}
}
```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Easy C++ solution || Beginner-friendly approach with explanation || O(N) time complexity
|
easy-c-solution-beginner-friendly-approa-pw1q
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<int> minRight(n, 0); // Vector to ma
|
prathams29
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-03T09:09:53.148977+00:00
|
2023-07-03T09:09:53.149004+00:00
| 557 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<int> minRight(n, 0); // Vector to maintain the minimum value on the right side of an element\n minRight[n - 1] = nums[n - 1];\n for(int i = n - 2; i >= 2; i--){\n minRight[i] = min(minRight[i + 1], nums[i]); \n } \n int maxLeft = nums[0], ans = 0;\n for(int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++)\n {\n if(nums[i] > maxLeft && nums[i] < minRight[i + 1]) ?? Check for 1st condition\n ans += 2;\n else if(nums[i] > nums[i - 1] && nums[i] < nums[i + 1]) // If condition 1 is not followed, check for condition 2\n ans += 1;\n maxLeft = max(nums[i], maxLeft); // Update the maximum value in the left side of the element\n } \n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
C++ || 2 Approach || Segment Tree OR Pre Compute
|
c-2-approach-segment-tree-or-pre-compute-um2j
|
2 Approaches.\n Approach 1: Just simply pre-compute the prefix maximum and suffix minimum.\n Approach 2: Using Segment Tree. Specifically merge sort segment tre
|
__phoenixer__
|
NORMAL
|
2023-06-02T17:01:58.681175+00:00
|
2023-06-03T07:13:30.300612+00:00
| 94 | false |
**2 Approaches.**\n* Approach 1: Just simply pre-compute the prefix maximum and suffix minimum.\n* Approach 2: Using Segment Tree. Specifically merge sort segment tree\n\n**CODE: APPROACH 1:**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n= nums.size();\n vector<int> prefix(n); // prefix[i] represent max from [0, i]\n vector<int> suffix(n); // suffix[i] represent min from [i, n-1]\n \n int maxi= INT_MIN;\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++){\n maxi= max(maxi, nums[i]);\n prefix[i]= maxi;\n }\n int mini= INT_MAX;\n for(int i=n-1; i>=0; i--){\n mini= min(mini, nums[i]);\n suffix[i]= mini;\n }\n \n int ans=0;\n for(int i=1; i<n-1; i++){\n if(prefix[i-1]<nums[i] && nums[i]<suffix[i+1]){ ans+=2; }\n else if(nums[i-1]<nums[i] && nums[i]<nums[i+1]){ ans+=1; }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\nTime Complexity: O(N) || Space Complexity: O(2*N)\n\n**CODE: APPROACH 2:**\n```\nvector<vector<int>> seg;\n\nvoid build(int si, int ss, int se, vector<int>& nums){\n if(ss==se){\n seg[si].push_back(nums[ss]);\n return;\n }\n int mid= ss+ (se-ss)/2;\n build(2*si+1, ss, mid, nums); // build left half recursively\n build(2*si+2, mid+1, se, nums); // build right half recursively\n \n // Now 2 sorted half are seg[2*si+1] and seg[2*si+2]. So, we need to merge them to make seg[si]\n int i=0; int j=0; int left=2*si+1; int right= 2*si+2;\n while(i<seg[left].size() && j<seg[right].size()){\n if(seg[left][i]<seg[right][j]){\n seg[si].push_back(seg[left][i]);\n i++;\n }\n else{\n seg[si].push_back(seg[right][j]);\n j++;\n }\n }\n while(i<seg[left].size()){\n seg[si].push_back(seg[left][i]);\n i++;\n }\n while(j<seg[right].size()){\n seg[si].push_back(seg[right][j]);\n j++;\n }\n // seg[si] is ready\n return;\n}\n\nint binSearch1(vector<int>& vec, int val){ // max index that is smaller than val\n int low= 0; int high= vec.size()-1; int potCand=-1;\n while(low<=high){\n int mid= low+ (high-low)/2;\n \n if(vec[mid]<val){\n potCand=mid;\n low= mid+1;\n }\n else if(vec[mid]>=val){\n high= mid-1;\n }\n }\n return (potCand==-1) ? 0 : potCand-0+1;\n}\nint binSearch2(vector<int>& vec, int val){ // min index that is larger than val\n int low= 0; int high= vec.size()-1; int potCand=-1;\n while(low<=high){\n int mid= low+ (high-low)/2;\n \n if(vec[mid]>val){\n potCand=mid; //cout<<potCand<<endl;\n high=mid-1;\n }\n else if(vec[mid]<=val){\n low= mid+1;\n }\n }\n return (potCand==-1) ? 0 : (vec.size()-1-potCand+1);\n}\n\nint query(int si, int ss, int se, int qs, int qe, int val, int type){ \n // Type 1: --> find number of ele in [qs-qe] that are <val\n // Type 2: --> find number of ele in [qs-qe] that are >val\n if(ss>qe || se<qs){ // completely outside our query\n return 0;\n }\n if(qs<=ss && qe>=se){ // completely inside my query range\n int idx;\n if(type==1){\n idx= binSearch1(seg[si], val); // max index that is smaller than val\n }\n else if(type==2){\n idx= binSearch2(seg[si], val); // min index that is larger than val\n }\n return idx;\n }\n \n int mid= ss + (se-ss)/2;\n int leftAns= query(2*si+1, ss, mid, qs, qe, val, type);\n int rightAns= query(2*si+2, mid+1, se, qs, qe, val, type);\n return leftAns+rightAns;\n}\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n // Solve using segment tree (precisely merge sort segment tree)\n int n= nums.size();\n seg.clear(); seg.resize(4*n, {});\n \n build(0, 0, n-1, nums);\n \n int sum=0;\n for(int i=1; i<n-1; i++){\n int val=nums[i];\n int q1= query(0, 0, n-1, 0, i-1, val, 1); // type 1\n int q2= query(0, 0, n-1, i+1, n-1, val, 2); // type 2\n \n if( q1==i && q2==((n-1)-(i+1)+1) ){ sum+=2; }\n else if(nums[i-1]<nums[i] && nums[i]<nums[i+1]){ sum+=1; }\n }\n return sum;\n }\n};\n```\nTime Complexity: O(logN + N*2*(logN)^2) || Space Complexity: O(NlogN)
| 2 | 0 |
['Tree', 'C', 'Merge Sort']
| 1 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
using prefix and suffix array approach
|
using-prefix-and-suffix-array-approach-b-nq90
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<int> prefix(n+1),suffix(n+1);\n
|
Pulkit123123
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-25T05:57:40.104608+00:00
|
2023-02-25T05:57:40.104646+00:00
| 576 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<int> prefix(n+1),suffix(n+1);\n prefix[0]=nums[0];\n suffix[n-1]=nums[n-1];\n int sum=0;\n for(int i=1;i<nums.size()-1;i++)\n {\n prefix[i]=max(prefix[i-1],nums[i]);\n }\n for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--)\n {\n suffix[i]=min(suffix[i+1],nums[i]);\n }\n for(int i=1;i<nums.size()-1;i++)\n {\n if(nums[i]>prefix[i-1]&&nums[i]<suffix[i+1])\n sum+=2;\n else if (nums[i-1]<nums[i]&&nums[i]<nums[i+1])\n sum+=1;\n }\n return sum;\n \n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Python | Two Passes | O(n)
|
python-two-passes-on-by-aryonbe-ephn
|
Code\n\nclass Solution:\n def sumOfBeauties(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n n = len(nums)\n d = [0]*n\n d[-1] = nums[-1]\n for i
|
aryonbe
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-13T07:27:46.217283+00:00
|
2023-01-13T07:27:46.217311+00:00
| 297 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def sumOfBeauties(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n n = len(nums)\n d = [0]*n\n d[-1] = nums[-1]\n for i in range(n-2,-1,-1):\n d[i] = min(d[i+1], nums[i])\n curmax = nums[0]\n res = 0\n for i in range(1,n-1):\n if curmax < nums[i] < d[i+1]:\n res += 2\n elif nums[i-1] < nums[i] < nums[i+1]:\n res += 1\n curmax = max(curmax, nums[i])\n return res\n \n\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
python | Prefix + Suffix | Easy to understand
|
python-prefix-suffix-easy-to-understand-hj65r
|
\nclass Solution:\n """\n approach: \n create two arrays prefix and suffix array\n prefix[i] records the maximum value in range (0, i - 1) inclusive
|
rktayal
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-18T09:04:45.818817+00:00
|
2022-07-18T09:04:45.818862+00:00
| 323 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n """\n approach: \n create two arrays prefix and suffix array\n prefix[i] records the maximum value in range (0, i - 1) inclusive.\n suffix[i] records the minimum value in range (i + 1, n - 1) inclusive.\n """\n def sumOfBeauties(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n prefix = [float(\'-inf\') for _ in range(len(nums))]\n suffix = [float(\'inf\') for _ in range(len(nums))]\n for i in range(1, len(nums)):\n prefix[i] = max(nums[i-1], prefix[i-1])\n for i in range(len(nums)-2, -1, -1):\n suffix[i] = min(nums[i+1], suffix[i+1])\n pts = 0\n for i in range(1, len(nums)-1):\n if prefix[i] < nums[i] < suffix[i]:\n pts += 2\n elif nums[i-1] < nums[i] < nums[i+1]:\n pts += 1\n return pts\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python']
| 1 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Fastest Solution (time = O(n)), completed in 84ms
|
fastest-solution-time-on-completed-in-84-ubp4
|
This is the fastest solution, far ahead of the second.\n\n\n\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar sumOfBeauties = function(nums) {\n
|
vaibhavgattyani32
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-18T17:55:57.382263+00:00
|
2022-04-18T17:55:57.382300+00:00
| 169 | false |
This is the fastest solution, far ahead of the second.\n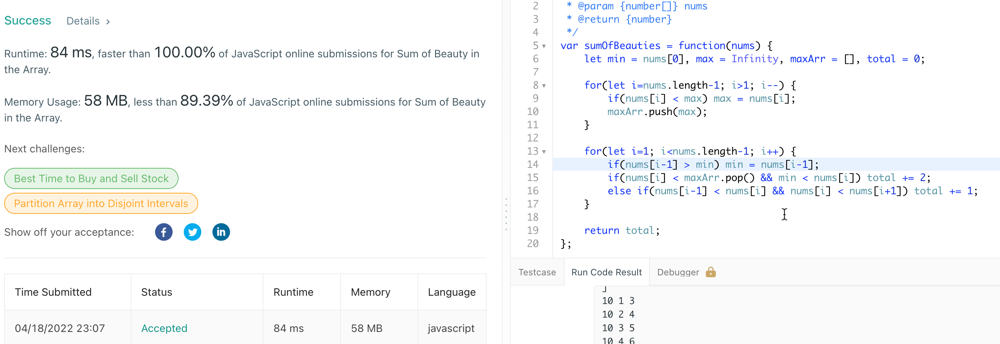\n\n```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar sumOfBeauties = function(nums) {\n let min = nums[0], max = Infinity, maxArr = [], total = 0;\n \n\t// Creating an array, which will keep the record of minimum values from last index\n for(let i=nums.length-1; i>1; i--) {\n if(nums[i] < max) max = nums[i];\n maxArr.push(max);\n }\n\n\t// iterating through array to check the given conditions\n for(let i=1; i<nums.length-1; i++) {\n\t\n\t\t// Keeping a record of max value from all index < i\n if(nums[i-1] > min) min = nums[i-1];\n\t\t\n\t\t// Checking conditions\n if(nums[i] < maxArr.pop() && min < nums[i]) total += 2;\n else if(nums[i-1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i+1]) total += 1;\n }\n \n return total;\n};\n```\n\nIf you have any doubt, I will be very happy to clear it. **Please upvote if you like this.**
| 2 | 1 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Simple C++ O(n) Solution
|
simple-c-on-solution-by-roshan_aswal-3ai4
|
Just find the max in left side of index and min of right side then compare with current index element\n```\n int sumOfBeauties(vector& nums) {\n int m
|
Roshan_Aswal
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-06T11:19:19.095635+00:00
|
2022-01-06T11:19:19.095677+00:00
| 204 | false |
Just find the max in left side of index and min of right side then compare with current index element\n```\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int m=nums[0];\n vector<int> mp(nums.size(),0);\n for(int i=1;i<nums.size()-1;i++){\n if(nums[i]>m){\n mp[i]=1;\n m=nums[i];\n }\n }\n m=nums[nums.size()-1];\n for(int i=nums.size()-2;i>0;i--){\n if(nums[i]<m){\n mp[i]+=1;\n m=nums[i];\n }\n }\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=1;i<nums.size()-1;i++){\n if(mp[i]==2)ans+=2;\n else if(nums[i-1]<nums[i] && nums[i]<nums[i+1])ans+=1;\n }\n return ans;\n }
| 2 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Python - Dynamic programming - Explained
|
python-dynamic-programming-explained-by-ab74c
|
\nQuestion: The beauty of nums[i] equals 2, if nums[j] < nums[i] < nums[k], for all 0 <= j < i and for all i < k <= nums.length - 1.\n\nExplanation:\n\nIn simpl
|
ajith6198
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-19T17:58:47.420791+00:00
|
2021-09-19T18:21:30.440876+00:00
| 384 | false |
\n***Question***: The beauty of nums[i] equals 2, if nums[j] < nums[i] < nums[k], for all 0 <= j < i and for all i < k <= nums.length - 1.\n\n**Explanation:**\n\nIn simpler terms, for each index from ```1``` till ```n-2```, \n* All the values left of ```i```th index should be less than ```i```th index\'s value.\n* All the values right of ```i```th index should be greater than ```i```th index\'s value.\n\nWe create two dp arrays\n* ```max_dp``` - computation starts from start of array (index 0) - to keep track of maximum value of array from index ```0``` till ```i```th index\n* ```min_dp``` - computation starts from end of array (index n-1) - to keep track of minimum value of array from ```n-1``` index till ```i```th index\n\nWith ```max_dp```, we can find if all values in left side are smaller - ```if max_dp[i] > max_dp[i-1]```\nWith ```min_dp```, we can find if all values in right side are greater - ```if nums[i] < min_dp[i+1]```\n\nThe second condition ```nums[i-1] < nums[i] < nums[i+1]``` is self explanatory\n\n**Code:**\n```\nclass Solution:\n def sumOfBeauties(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n n = len(nums)\n max_dp = [0] * n\n min_dp = [float(inf)] * n\n max_dp[0] = nums[0]\n min_dp[-1] = nums[-1]\n \n for i in range(1, n):\n max_dp[i] = max(nums[i], max_dp[i-1])\n \n for i in range(n-2, -1, -1):\n min_dp[i] = min(nums[i], min_dp[i+1])\n \n ans = 0\n for i in range(1, n-1):\n if max_dp[i-1] < max_dp[i] and nums[i] < min_dp[i+1]:\n ans += 2\n elif nums[i-1] < nums[i] < nums[i+1]:\n ans += 1\n return ans\n```\n\n**Time and space complexity: O(n)**
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Easy to understand || c++ || easy and concise solution || using sets
|
easy-to-understand-c-easy-and-concise-so-r0e7
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n multiset<int> a,b;\n for(auto x:nums)a.insert(x);\n a.erase(a.fin
|
balashekhar
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-19T04:15:29.587405+00:00
|
2021-09-19T04:15:29.587446+00:00
| 70 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n multiset<int> a,b;\n for(auto x:nums)a.insert(x);\n a.erase(a.find(nums[0]));\n int c=0;\n for(int i=1;i<nums.size()-1;i++)\n {\n b.insert(nums[i-1]);\n a.erase(a.find(nums[i]));\n if(*prev(b.end())<nums[i] and *(a.begin())>nums[i])c+=2;\n else if(nums[i-1]<nums[i] and nums[i]<nums[i+1])c+=1;\n }\n return c; \n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
[Javascript] Easy Solution | Prefix | Postfix
|
javascript-easy-solution-prefix-postfix-998vf
|
\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar sumOfBeauties = function(nums) {\n \n let preMin = [];\n let postMax = [];\n \n p
|
vj98
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-19T04:05:29.544087+00:00
|
2021-09-19T04:05:29.544117+00:00
| 319 | false |
```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar sumOfBeauties = function(nums) {\n \n let preMin = [];\n let postMax = [];\n \n preMin[0] = nums[0];\n for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {\n preMin[i] = Math.max(nums[i], preMin[i-1]); \n }\n \n postMax[nums.length-1] = nums[nums.length-1];\n for (let i = nums.length-2; i >= 0; i--) {\n postMax[i] = Math.min(nums[i], postMax[i+1]);\n }\n \n let ans = 0;\n for (let i = 1; i < nums.length-1; i++) {\n if (preMin[i-1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < postMax[i+1]) {\n ans += 2;\n }\n else if (nums[i-1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i+1]) {\n ans += 1;\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'JavaScript']
| 1 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Java
|
java-by-wushangzhen-mh9t
|
Find the min[i]: Minimum Value from Right to i + 1\n2. For loop and keep track of Max value so far \n\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums
|
wushangzhen
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-19T04:03:19.931578+00:00
|
2021-09-19T04:23:45.200160+00:00
| 224 | false |
1. Find the min[i]: Minimum Value from Right to i + 1\n2. For loop and keep track of Max value so far \n```\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n int n = nums.length;\n int max = nums[0];\n int[] min = new int[n];\n min[n - 1] = nums[n - 1];\n for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {\n min[i] = Math.min(min[i + 1], nums[i + 1]);\n }\n int res = 0;\n for (int i = 1; i <= n - 2; i++) {\n if (max < nums[i] && min[i] > nums[i]) {\n res += 2;\n } else if (nums[i - 1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i + 1]) {\n res += 1;\n } \n max = Math.max(nums[i], max);\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
[Kotlin] Clean & Short O(n) Solution
|
kotlin-clean-short-on-solution-by-catcat-su19
|
\nclass Solution {\n fun sumOfBeauties(nums: IntArray): Int {\n var leftMax = nums[0]\n val rightMins = IntArray(nums.size).also { \n
|
catcatcute
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-19T04:02:15.879125+00:00
|
2021-09-19T04:09:28.690874+00:00
| 110 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n fun sumOfBeauties(nums: IntArray): Int {\n var leftMax = nums[0]\n val rightMins = IntArray(nums.size).also { \n it[it.lastIndex] = nums[nums.lastIndex]\n for (i in it.lastIndex - 1 downTo 2) {\n it[i] = minOf(it[i + 1], nums[i])\n }\n }\n return (1 until nums.lastIndex).fold(0) { acc, index ->\n when {\n nums[index] > leftMax && nums[index] < rightMins[index + 1] -> acc + 2\n nums[index] > nums[index - 1] && nums[index] < nums[index + 1] -> acc + 1\n else -> acc\n }.also {\n leftMax = maxOf(leftMax, nums[index])\n }\n }\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Kotlin']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Java || Suffix Array Problem || Time complexity : O(n)
|
java-suffix-array-problem-time-complexit-dkv0
|
Complexity
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
Code
|
shikhargupta0645
|
NORMAL
|
2025-04-05T16:30:01.937958+00:00
|
2025-04-05T16:30:01.937958+00:00
| 15 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(n)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(n)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {
int sum = 0;
int n = nums.length;
int[] minSuffix = new int[n];
minSuffix[n-1] = nums[n-1];
for(int i=n-2; i>=0; i--){
minSuffix[i] = Math.min(minSuffix[i+1], nums[i]);
}
int prefix = nums[0];
for(int i=1; i<n-1; i++){
if(prefix < nums[i] && nums[i] < minSuffix[i+1]){
sum += 2;
prefix = Math.max(prefix, nums[i]);
}
else if(nums[i-1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i+1]){
sum += 1;
prefix = Math.max(prefix, nums[i]);
}
else{
prefix = Math.max(prefix, nums[i]);
}
}
return sum;
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Suffix Array', 'Java']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
🔥Use prefix AND/OR suffix array (full intuition included)
|
use-prefix-andor-suffix-array-by-akshar-4l5p
|
IntuitionThe first beauty condition is difficult to calculate, the second condition is pretty easy to check in O(1) time. Let's consider the first condition:If
|
akshar_
|
NORMAL
|
2025-04-03T07:24:07.070625+00:00
|
2025-04-03T07:28:43.173992+00:00
| 91 | false |
# Intuition
The first beauty condition is difficult to calculate, the second condition is pretty easy to check in $O(1)$ time. Let's consider the first condition:
If we naively iterate over all $j$ and all $k$ for each $i$, time complexity will be $O(n^2)$ ($n$ steps for each index $i$)
> Let number at index $i$ be $num$
What if we knew maximum number to the left of $num$ (say $\text{maxLeft}$) and minimum number to the right of $num$, say $\text{minRight}$?
> Then we can calculate first condition simply by checking if maxLeft < num < minRight
We can calculate maxLeft and minRight using prefix and suffix arrays. But we only need to compute one of them, as ***one of them*** can be computed in $O(1)$ space by storing a variable and updating it while traversing the array from any one direction
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
$$O(n)$$ for two passes of the array of size $n$
- Space complexity:
$$O(n)$$ for either the prefix or suffix array
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {
int maxLeft = 0;
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> minRight(n);
// minRight[j] = smallest number to the right of index j
minRight[n - 1] = INT_MAX;
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
minRight[i] = min(minRight[i + 1], nums[i + 1]);
}
int beauty = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++) {
int num = nums[i];
maxLeft = max(maxLeft, nums[i - 1]);
if (maxLeft < num && num < minRight[i]) {
beauty += 2;
} else if (nums[i - 1] < num && num < nums[i + 1]) {
beauty++;
}
}
return beauty;
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Suffix Array', 'Prefix Sum', 'C++']
| 1 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Easiest c++ solution 0ms beats 100% solve by prefix and suffix
|
easiest-c-solution-0ms-beats-100-solve-b-aher
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
Code
|
albert0909
|
NORMAL
|
2025-04-03T04:29:00.265459+00:00
|
2025-04-03T04:29:00.265459+00:00
| 39 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {
int ans = 0, mx = nums[0], mn = nums.back();
vector<int> prefix(nums.size(), 0), suffix(nums.size(), 0);
for(int i = 1;i < nums.size();i++){
if(nums[i] > mx){
prefix[i] = 1;
mx = nums[i];
}
}
for(int i = nums.size() - 2;i >= 0;i--){
if(nums[i] < mn){
suffix[i] = 1;
mn = nums[i];
}
}
for(int i = 1;i < nums.size() - 1;i++){
if(prefix[i] + suffix[i] == 2) ans += 2;
else ans += (nums[i] > nums[i - 1] && nums[i + 1] > nums[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};
// auto init = []()
// {
// ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
// cin.tie(0);
// cout.tie(0);
// return 'c';
// }();
```
| 1 | 1 |
['Array', 'Suffix Array', 'Prefix Sum', 'C++']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
🔥BEATS 100% || ☠️TWO PASS SOLUTION || OPTIMAL || C++
|
beats-100-two-pass-solution-optimal-c-by-bc3k
|
JUST USE A SUFFIX ARRAYCode
|
thevineetdixit
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-28T10:58:52.277337+00:00
|
2025-03-28T10:58:52.277337+00:00
| 141 | false |
# JUST USE A SUFFIX ARRAY
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size(),ans=0;
vector<int>minright(n,nums[n-1]);
for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--)
minright[i]=min(nums[i],minright[i+1]);
int currmax = nums[0];
for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++)
{
if(currmax < nums[i] && minright[i+1]>nums[i])ans+=2;
else if(nums[i - 1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i + 1])ans++;
currmax=max(currmax,nums[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'C++']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Trapping Rain water Similar Approach using prefix and postfix max and min.
|
trapping-rain-water-similar-approach-usi-goc9
|
IntuitionWe need to compute the sum of beauties for each element in the array (except the first and last). The beauty of an element is determined by specific co
|
Prateek_Sarna_24
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-16T14:58:18.222766+00:00
|
2025-02-16T14:58:18.222766+00:00
| 71 | false |
## Intuition
We need to compute the **sum of beauties** for each element in the array (except the first and last). The beauty of an element is determined by specific conditions:
- It gets **2 points** if it is strictly greater than all elements to its left and strictly smaller than all elements to its right.
- Otherwise, it gets **1 point** if it is **greater than its previous element and smaller than its next element**.
- If none of the conditions are met, it gets **0 points**.
A brute force approach would check **all previous and next elements** for each position, but this is inefficient. Instead, we optimize using **prefix maximums and postfix minimums**.
---
## Approach
1. **Compute postfix minimums**:
- Create an array `postfixMins[]` where `postfixMins[i]` stores the **minimum element from index `i` to the end**.
- This helps us quickly check if `nums[i]` is smaller than all elements to its right.
2. **Iterate through the array**:
- Maintain a **prefix maximum** (`maxi`) to track the maximum value encountered so far.
- At each `i`, check:
- If `nums[i] > prefixMax` **and** `nums[i] < postfixMin`, add `2` to `beautySum`.
- Otherwise, if `nums[i] > nums[i-1]` **and** `nums[i] < nums[i+1]`, add `1` to `beautySum`.
3. **Update the prefix maximum** as we iterate.
This approach ensures that we efficiently check conditions in **O(1) per element** after preprocessing.
---
## Complexity
- **Time Complexity:**
- **Computing `postfixMins`**: $$O(n)$$
- **Iterating through `nums`**: $$O(n)$$
- **Total Complexity**: **$$O(2n)$$**
- **Space Complexity:**
- **Postfix minimums array**: $$O(n)$$
- **Other variables**: $$O(1)$$
- **Total Complexity**: **$$O(n)$$**
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> postfixMins(n, INT_MAX);
int mini = INT_MAX;
for (int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {
mini = min(mini, nums[i]);
postfixMins[i] = mini;
}
int maxi = nums[0];
int beautySum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n-1; i++) {
int prefixMax = maxi;
int postfixMin = postfixMins[i+1];
if (nums[i] > prefixMax && nums[i] < postfixMin) {
beautySum += 2;
}
else if (nums[i] > nums[i-1] && nums[i] < nums[i+1]) {
beautySum++;
}
maxi = max(maxi, nums[i]);
}
return beautySum;
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Math', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Greedy', 'Memoization', 'Prefix Sum', 'C++']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Simple Java Solution beats 98% | O(n) Time and Space
|
simple-java-solution-beats-98-on-time-an-vtc3
|
Intuition\nMaintain 2 arrays, first to store if an element is greater than all elements to the left of it, and other to store if an element is smaller than all
|
ayushprakash1912
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-21T19:48:59.863160+00:00
|
2024-03-21T19:48:59.863187+00:00
| 34 | false |
# Intuition\nMaintain 2 arrays, first to store if an element is greater than all elements to the left of it, and other to store if an element is smaller than all elements to the right of it.\n\n# Approach\n1. Declare two boolean arrays of size=nums.length.\n2. Iterate through array from the left to the right side and check if an element is an element is greater than the maximum element on its left side. If so, set the value of that index in the first declared array to true.\n3. Iterate through array from the right to the left side and check if an element is an element is lesser than the minimum element on its right side. If so, set the value of that index in the second declared array to true.\n4. Iterate through nums, if for an index the corresponding index in both the declared arrays is set to true, add 2 to some. Otherwise if the element is greater than its neighbours, add 1 to the sum.\nReturn the sum.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n\n boolean[] prefixMaxLeft = new boolean[nums.length], prefixMinRight = new boolean[nums.length];\n int minFromRight = nums[nums.length - 1], maxFromLeft = nums[0];\n int sum = 0;\n\n for (int i = 1; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {\n\n if (maxFromLeft < nums[i]) {\n prefixMaxLeft[i] = true;\n maxFromLeft = nums[i];\n }\n\n if (nums[nums.length - 1 - i] < minFromRight) {\n prefixMinRight[nums.length - 1 - i] = true;\n minFromRight = nums[nums.length - 1 - i];\n }\n }\n\n for (int i = 1; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {\n if (prefixMaxLeft[i] && prefixMinRight[i]) {\n sum = sum + 2;\n } else if (nums[i - 1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i + 1]) {\n sum = sum + 1;\n }\n }\n\n return sum;\n }\n}\n```\n\nFeel free to comment any optimizations.\nPlase upvote if found helpful!
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Java']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Python Accumulate Max and Min
|
python-accumulate-max-and-min-by-hong_zh-pjbh
|
\nclass Solution:\n def sumOfBeauties(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n nums1 = list(accumulate(nums, lambda x, y: max(x, y)))\n nums2 = list(ac
|
hong_zhao
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-25T00:26:13.979534+00:00
|
2023-02-25T00:26:13.979578+00:00
| 496 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def sumOfBeauties(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n nums1 = list(accumulate(nums, lambda x, y: max(x, y)))\n nums2 = list(accumulate(nums[::-1], lambda x, y: min(x, y)))[::-1]\n cnt = 0\n for i in range(1, len(nums) - 1):\n if nums1[i - 1] < nums[i] < nums2[i + 1]:\n cnt += 2\n elif nums[i - 1] < nums[i] < nums[i + 1]:\n cnt += 1\n return cnt\n```\n
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
C# O(n)
|
c-on-by-zloytvoy-0tk6
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
zloytvoy
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-16T10:02:03.905431+00:00
|
2023-02-16T10:02:03.905469+00:00
| 147 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public int SumOfBeauties(int[] nums) \n {\n // keep max from left \n // min from right \n var maxFromLeft = nums[0];\n\n var n = nums.Length;\n var minFromRight = new int[n];\n minFromRight[n-1] = nums[n-1];\n for(int i = n-2; i >= 0; --i)\n {\n minFromRight[i] = Math.Min(minFromRight[i+1], nums[i]);\n }\n\n var result = 0;\n\n for(int i = 1; i <= nums.Length - 2; ++i)\n {\n if(nums[i-1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i+1])\n {\n ++result;\n\n if(maxFromLeft < nums[i] && nums[i] < minFromRight[i+1])\n {\n ++result;\n }\n }\n \n maxFromLeft = Math.Max(maxFromLeft, nums[i]);\n }\n\n return result;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Java easy solution using Stack.
|
java-easy-solution-using-stack-by-hd145-1yk7
|
Simplest and basic approach of Nearest greater to the left and nearest smaller to right and get this done. \n\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n ArrayList<Integ
|
HD145
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-15T13:57:54.746910+00:00
|
2023-01-15T13:57:54.746939+00:00
| 347 | false |
Simplest and basic approach of Nearest greater to the left and nearest smaller to right and get this done. \n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n ArrayList<Integer>vec1=new ArrayList<>();\n ArrayList<Integer>vec2=new ArrayList<>();\n \n public void lg(int [] nums){\n Stack<Integer>st=new Stack<>();\n int i=0;\n while(i<nums.length){\n \n if(st.size()==0)vec1.add(-1);\n else if(st.peek()>=nums[i]){\n vec1.add(st.peek());\n }else{\n while(!st.empty() && st.peek()<nums[i]){\n st.pop();\n } \n \n if(st.empty())vec1.add(-1);\n else vec1.add(st.peek());\n }\n \n st.push(nums[i]);\n i++;\n }\n }\n \n public void rs(int nums[]){\n \n Stack<Integer>st=new Stack<Integer>();\n \n int i=nums.length-1;\n \n while(i>=0){\n \n if(st.empty())vec2.add(-1);\n else if(st.peek()<=nums[i]){\n vec2.add(st.peek());\n }else{\n while(!st.empty() && st.peek()>nums[i]){\n st.pop();\n } \n if(st.empty())vec2.add(-1);\n else vec2.add(st.peek());\n }\n \n st.push(nums[i]);\n i--;\n }\n Collections.reverse(vec2);\n \n }\n \n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n lg(nums);\n rs(nums);\n int sum=0;\n for(int i=1;i<nums.length-1;i++){\n if(vec1.get(i)==-1 && vec2.get(i)==-1)sum+=2;\n else if(nums[i]>nums[i-1] && nums[i]<nums[i+1])sum++;\n }\n return sum;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Stack', 'Java']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Easy Java Solution Using Stack (Nearest Greater to left & Nearest Smaller to right)
|
easy-java-solution-using-stack-nearest-g-u79z
|
\n\nclass Solution {\n ArrayList<Integer>vec1=new ArrayList<>();\n public void lg(int [] nums){\n Stack<Integer>st=new Stack<>();\n int i=0
|
Shivam7380
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-15T13:57:04.028953+00:00
|
2023-01-15T13:57:04.029000+00:00
| 830 | false |
\n```\nclass Solution {\n ArrayList<Integer>vec1=new ArrayList<>();\n public void lg(int [] nums){\n Stack<Integer>st=new Stack<>();\n int i=0;\n while(i<nums.length){\n \n if(st.size()==0)vec1.add(-1);\n else if(st.peek()>=nums[i]){\n vec1.add(st.peek());\n }else{\n while(!st.empty() && st.peek()<nums[i]){\n st.pop();\n } \n \n if(st.empty())vec1.add(-1);\n else vec1.add(st.peek());\n }\n \n st.push(nums[i]);\n i++;\n }\n }\n ArrayList<Integer>vec2=new ArrayList<>();\n public void rl(int [] nums){\n Stack<Integer>st=new Stack<>();\n int i=nums.length-1;\n while(i>=0){\n \n if(st.size()==0)vec2.add(-1);\n else if(st.peek()<=nums[i]){\n vec2.add(st.peek());\n }else{\n while(!st.empty() && st.peek()>nums[i]){\n st.pop();\n } \n \n if(st.empty())vec2.add(-1);\n else vec2.add(st.peek());\n }\n \n st.push(nums[i]);\n i--;\n }\n Collections.reverse(vec2);\n }\n\n\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n int sum=0;\n rl(nums);\n lg(nums);\n for(int i=1;i<vec1.size()-1;i++){\n if(vec1.get(i)==-1 && vec2.get(i)==-1)sum+=2;\n else if(nums[i]>nums[i-1] && nums[i]<nums[i+1])sum+=1;\n else sum+=0;\n }\n \n return sum;\n \n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Stack', 'Java']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
✅[Python] Simple and Clean, beats 92.65%✅
|
python-simple-and-clean-beats-9265-by-_t-00sv
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nTo keep the min and max value for the list.\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to sol
|
_Tanmay
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-27T11:00:25.780498+00:00
|
2022-12-27T11:00:25.780534+00:00
| 163 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nTo keep the min and max value for the list.\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n**Case 1 (Increment +2)**\nPrecomputing the minimum and maximum value till ```i```th index.\nWe can maintain a MinArray and MaxArray and check if the current number is smaller or greater.\n\n**Case 2 (Increment +1)**\nThis can be checked directly while tranversing the list.\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n)$$\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n)$$\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def sumOfBeauties(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n n=len(nums)\n ans=0\n minArr=[0 for _ in range(n)]\n maxArr=[999999 for _ in range(n)]\n minArr[0]=nums[0]\n maxArr[-1]=nums[-1]\n for i in range(1,n):\n minArr[i]=max(nums[i-1],minArr[i-1])\n for i in range(n-2,-1,-1):\n maxArr[i]=min(nums[i+1],maxArr[i+1])\n for i in range(1,n-1):\n if minArr[i]<nums[i]<maxArr[i]:\n ans+=2\n elif nums[i-1]<nums[i]<nums[i+1]:\n ans+=1\n return ans\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Suffix Array', 'Iterator', 'Python3']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
C++ || Prefix and Suffix || Array
|
c-prefix-and-suffix-array-by-itsmak02-kfeb
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<int>left(n,-1); //store next greater element
|
itsmak02
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-25T16:19:08.993641+00:00
|
2022-09-25T16:19:08.993688+00:00
| 352 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<int>left(n,-1); //store next greater element in left side\n vector<int>right(n,-1); //store next smaller element in right side\n stack<int>st;\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){\n while(!st.empty() and nums[st.top()]<=nums[i]){\n left[st.top()]=nums[i];\n st.pop();\n }\n st.push(i);\n }\n while(!st.empty()){\n st.pop();\n }\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n while(!st.empty() and nums[st.top()]>=nums[i]){\n right[st.top()]=nums[i];\n st.pop();\n }\n st.push(i);\n }\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++){\n if(left[i]==-1 and right[i]==-1){\n ans+=2;\n }else if(nums[i-1]<nums[i] and nums[i]<nums[i+1]){\n ans+=1;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Java | Array | easy to understand
|
java-array-easy-to-understand-by-conchwu-yc72
|
\n //Runtime: 10 ms, faster than 61.96% of Java online submissions for Sum of Beauty in the Array.\n //Memory Usage: 95.5 MB, less than 65.03% of Java onl
|
conchwu
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-14T14:19:44.020564+00:00
|
2022-09-14T14:20:43.770802+00:00
| 818 | false |
```\n //Runtime: 10 ms, faster than 61.96% of Java online submissions for Sum of Beauty in the Array.\n //Memory Usage: 95.5 MB, less than 65.03% of Java online submissions for Sum of Beauty in the Array.\n //Time: O(2N); Space: O(N)\n //Time: O(N); Space: O(N)\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n int[] minInRight = new int[nums.length];\n minInRight[nums.length - 1] = nums[nums.length - 1];\n for (int i = nums.length - 2; i >= 2; i--)\n minInRight[i] = Math.min(minInRight[i + 1], nums[i]);\n\n int maxInLeft = nums[0], sum = 0;\n for (int i = 1; i < nums.length - 1; i++){\n if (nums[i] > maxInLeft && nums[i] < minInRight[i + 1]) sum += 2;\n else if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1] && nums[i] < nums[i + 1]) sum += 1;\n\n maxInLeft = Math.max(maxInLeft, nums[i]);\n }\n return sum;\n }\n\t\n\t\n\t //Runtime: 13 ms, faster than 36.81% of Java online submissions for Sum of Beauty in the Array.\n //Memory Usage: 92.9 MB, less than 67.48% of Java online submissions for Sum of Beauty in the Array.\n //Time: O(2N); Space: O(2N)\n public int sumOfBeauties1(int[] nums) {\n int[] max = new int[nums.length];\n int[] min = new int[nums.length];\n max[0] = nums[0];\n min[nums.length - 1] = nums[nums.length - 1];\n\n for (int i = 1; i < nums.length - 1; i++){\n max[i] = Math.max(max[i - 1], nums[i]);\n int j = nums.length - 1 - i;\n min[j] = Math.min(min[j + 1], nums[j]);\n }\n\n int sum = 0;\n for (int i = 1; i < nums.length - 1; i++){\n if (nums[i] > max[i - 1] && nums[i] < min[i + 1]) sum += 2;\n else if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1] && nums[i] < nums[i + 1]) sum += 1;\n }\n return sum;\n }\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
javascript Solution easy to understand O(n) using stack (prefix and sufix)
|
javascript-solution-easy-to-understand-o-kr4p
|
\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar sumOfBeauties = function(nums) {\n \n const n = nums.length\n \n //we gonna use stack
|
brahim360
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-06T07:51:33.711833+00:00
|
2022-08-06T07:51:33.711873+00:00
| 92 | false |
```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar sumOfBeauties = function(nums) {\n \n const n = nums.length\n \n //we gonna use stack to maintain the smalest right value to statisfy our first condions\n let sufix=[nums[n-1]]\n for(let i = n-2;i>=2;i--){\n const min=Math.min(sufix[sufix.length-1],nums[i])\n sufix.push(min) \n }\n \n //pref will maintain the bigest left value to statisfy our first condions\n let pref=nums[0]\n let sum=0\n // we gonna itirate our nums array starting from index 1 to index n-2\n for(let i=1;i<n-1;i++){\n const current=nums[i]\n let sufi=sufix.pop()//take the tope value in the stack\n \n if(pref<current && sufi>current ) sum+=2 //first condition\n \n else if(current >nums[i-1] && current<nums[i+1]) sum+=1; //second condition if first is not satisfied \n \n \n pref=Math.max(pref,current)\n }\n \n return sum \n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Stack', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
c++ 0(n) solution
|
c-0n-solution-by-gauravkumart-fd51
|
```\nint n=nums.size();\n vectorvt1(n);\n vectorvt2(n);\n \n vt1[0]=nums[0];\n vt2[n-1]=nums[n-1];\n for(int i=1;i=0;i
|
gauravkumart
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-09T05:57:09.324006+00:00
|
2022-07-09T05:57:09.324043+00:00
| 132 | false |
```\nint n=nums.size();\n vector<int>vt1(n);\n vector<int>vt2(n);\n \n vt1[0]=nums[0];\n vt2[n-1]=nums[n-1];\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++){\n vt1[i]=max(vt1[i-1],nums[i]);\n // vt2[i]=min(vt2[i-1],nums[i]);\n }\n for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--){\n vt2[i]=min(vt2[i+1],nums[i]);\n }\n \n int ans=0;\n for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++){\n if(vt1[i-1]<nums[i] && vt2[i+1]>nums[i]){\n ans+=2;\n }\n else if(nums[i-1]<nums[i]&&nums[i]<nums[i+1]){\n ans++;\n }\n \n }\n \n return ans;
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Java Solution
|
java-solution-by-deborupsinha-g05d
|
```java\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n int n=nums.length, beauty=0;\n int[] leftMax=new int[n];\n leftMax[
|
DeborupSinha
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-26T14:45:35.712878+00:00
|
2022-06-26T14:45:35.712933+00:00
| 269 | false |
```java\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n int n=nums.length, beauty=0;\n int[] leftMax=new int[n];\n leftMax[0]=nums[0];\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++) {\n leftMax[i]=Math.max(leftMax[i-1], nums[i]);\n }\n int[] rightMin=new int[n];\n rightMin[n-1]=nums[n-1];\n for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--) {\n rightMin[i]=Math.min(rightMin[i+1], nums[i]);\n }\n for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++) {\n if(leftMax[i-1]<nums[i] && nums[i]<rightMin[i+1]) {\n beauty+=2;\n }\n else if(nums[i-1]<nums[i] && nums[i]<nums[i+1]) {\n beauty+=1;\n }\n }\n return beauty;\n }\n}
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Java']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
JAVA || PREFIX & SUFFIX ARRAY || TIME : O(N) || SPACE : O(2N)
|
java-prefix-suffix-array-time-on-space-o-go2x
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) \n {\n int n=nums.length;\n int max_left[]=new int[n];\n int min_right[]=ne
|
29nidhishah
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-25T04:51:25.543489+00:00
|
2022-06-25T04:51:25.543529+00:00
| 177 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) \n {\n int n=nums.length;\n int max_left[]=new int[n];\n int min_right[]=new int[n];\n int ans=0;\n \n for(int i=1;i<n;i++)\n {\n max_left[i]=Math.max(max_left[i-1],nums[i-1]);\n }\n \n min_right[n-1]=nums[n-1];\n for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--)\n {\n min_right[i]=Math.min(min_right[i+1],nums[i+1]);\n }\n \n for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++)\n {\n if(nums[i]>max_left[i] && nums[i]<min_right[i])\n ans+=2;\n \n else if(nums[i]>nums[i-1] && nums[i]<nums[i+1])\n ans++;\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Suffix Array', 'Java']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
✅✅Faster || Easy To Understand || C++ Code
|
faster-easy-to-understand-c-code-by-__kr-xo78
|
Time Complexity : O(N)\n\n Space Complexity : O(N)*\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n \n int n = nums.s
|
__KR_SHANU_IITG
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-07T05:29:26.877284+00:00
|
2022-06-07T05:29:26.878064+00:00
| 193 | false |
* ***Time Complexity : O(N)***\n\n* ***Space Complexity : O(N)***\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n \n int n = nums.size();\n \n // store the max. element till ith index from left side\n \n vector<int> left_max(n, 0);\n \n left_max[0] = nums[0];\n \n for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)\n {\n left_max[i] = max(left_max[i - 1], nums[i]);\n }\n \n // store the min. element till ith index from right side\n \n vector<int> right_min(n, 0);\n \n right_min[n - 1] = nums[n - 1];\n \n for(int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)\n {\n right_min[i] = min(right_min[i + 1], nums[i]);\n }\n \n // calculate the beauty on the basis of condition given\n \n int beauty_sum = 0;\n \n for(int i = 1; i <= n - 2; i++)\n {\n if(nums[i] > left_max[i - 1] && nums[i] < right_min[i + 1])\n {\n beauty_sum += 2;\n }\n else if(nums[i] > nums[i - 1] && nums[i] < nums[i + 1])\n {\n beauty_sum += 1;\n }\n }\n \n return beauty_sum;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'C']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
O(n) simple solution c++ || just maintain min and max ||
|
on-simple-solution-c-just-maintain-min-a-zgez
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n vector<int> left_max(nums.size());\n vector<int> right_min(nums.size());
|
mayankwatts
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-21T08:05:22.262021+00:00
|
2022-05-21T08:05:42.922881+00:00
| 79 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n vector<int> left_max(nums.size());\n vector<int> right_min(nums.size());\n\t\t\n int x = nums[0];\n left_max[0]=x;\n for(int i=1;i<nums.size();i++){\n x = max(x,nums[i-1]);\n left_max[i]=x;\n }\n\t\t\n x = nums[nums.size()-1];\n right_min[nums.size()-1]=x;\n for(int i=nums.size()-2;i>=0;i--){\n x = min(x,nums[i+1]);\n right_min[i]=x;\n }\n\t\t\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i=1;i<nums.size()-1;i++){\n if(left_max[i]<nums[i] && right_min[i]>nums[i]){\n ans+=2;\n }\n else if(nums[i]>nums[i-1] && nums[i]<nums[i+1]){\n ans+=1;\n }\n }\n\t\t\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Python Fast and Readable
|
python-fast-and-readable-by-true-detecti-wxjv
|
\nclass Solution:\n def sumOfBeauties(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n pre, suf = [0], [math.inf]\n for n in nums:\n pre.append(max(
|
true-detective
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-07T09:11:37.150013+00:00
|
2022-05-07T09:11:37.150057+00:00
| 115 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def sumOfBeauties(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n pre, suf = [0], [math.inf]\n for n in nums:\n pre.append(max(pre[-1], n))\n for n in nums[::-1]:\n suf.append(min(suf[-1], n))\n \n suf.reverse()\n ans = 0\n for i in range(1, len(nums)-1):\n if suf[i+1] > nums[i] > pre[i]:\n ans += 2\n elif nums[i-1] < nums[i] < nums[i+1]:\n ans += 1\n return ans\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Simple Solution in Java || Elegant and Concise || O(n) Space and O(n) Time
|
simple-solution-in-java-elegant-and-conc-hez3
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n int[] minEle = new int[nums.length];\n \n int min = nums[nums.length-1];\n
|
PRANAV_KUMAR99
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-21T04:40:35.024170+00:00
|
2022-03-21T04:41:09.586872+00:00
| 74 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n int[] minEle = new int[nums.length];\n \n int min = nums[nums.length-1];\n for(int i=nums.length-2; i>=1; i--){\n minEle[i] = min;\n min = Math.min(min, nums[i]);\n }\n \n int max = nums[0];\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i=1; i<nums.length-1; i++){\n if(max < nums[i] && nums[i] < minEle[i]){\n ans += 2; \n }else if(nums[i-1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i+1]){\n ans += 1;\n }\n \n max = Math.max(max, nums[i]);\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
O(N) solution beats 98%
|
on-solution-beats-98-by-hannah_zhang-4bz4
|
\'\'\'\n\n\n\nclass Solution:\n def sumOfBeauties(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n n = len(nums)\n left, right = [False] * n, [False] * n\n
|
Hannah_Zhang
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-09T02:34:24.438076+00:00
|
2022-03-09T02:34:24.438119+00:00
| 196 | false |
\'\'\'\n\n\n\nclass Solution:\n def sumOfBeauties(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n n = len(nums)\n left, right = [False] * n, [False] * n\n left_max, right_min = 0, float(\'inf\')\n \n \n for i in range(n):\n if left_max < nums[i]:\n left[i] = True\n left_max = nums[i]\n \n \n for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):\n if right_min > nums[i]:\n right[i] = True\n right_min = nums[i]\n \n ans = 0\n for i in range(1, n - 1):\n if left[i] and right[i]:\n ans += 2\n elif nums[i] > nums[i - 1] and nums[i] < nums[i + 1]:\n ans += 1\n return ans\n\'\'\'
| 1 | 0 |
['Python']
| 1 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Python solution with O(n) time complexity and constant memory
|
python-solution-with-on-time-complexity-523wj
|
Runtime: 1273 ms, faster than 70.00% of Python online submissions for Sum of Beauty in the Array.\nMemory Usage: 25.1 MB, less than 100.00% of Python online sub
|
pedro_esser
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-28T13:46:30.578251+00:00
|
2022-02-28T13:46:30.578283+00:00
| 70 | false |
* Runtime: 1273 ms, faster than 70.00% of Python online submissions for Sum of Beauty in the Array.\nMemory Usage: 25.1 MB, less than 100.00% of Python online submissions for Sum of Beauty in the Array.\n\nThis solution sweeps throught the array twice, first from left to right setting the elements to their negative if they fullfil the first part of the first condition.\nOn the second sweep, i check the second part of the first condition, if this is also true I sum 1. I sum 1 instead of 2 because i\'ll be checking the second condition next, which will be true if the first condition is true.\n\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def sumOfBeauties(self, nums):\n big_left, small_right = nums[0], nums[-1]\n \n for i in range(1, len(nums)-1):\n if big_left < nums[i]:\n big_left = nums[i]\n nums[i] = -nums[i]\n \n sum = 0\n for i in range(len(nums)-2, 0, -1):\n if nums[i] < 0:\n nums[i] = -nums[i]\n if small_right > nums[i]:\n sum += 1\n if abs(nums[i - 1]) < nums[i] and nums[i] < nums[i + 1]:\n sum += 1\n small_right = min(small_right, nums[i])\n return sum\n\t\t
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
C++ || O(N)
|
c-on-by-in_sidious-gugz
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);\n int n
|
iN_siDious
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-11T04:22:34.661897+00:00
|
2022-02-11T04:22:34.661939+00:00
| 97 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);\n int n=nums.size();\n int ans=0;\n vector <int> greater(n);\n vector <int> smaller(n);\n smaller[n-1]=nums[n-1];\n greater[0]=nums[0];\n for (int i=1;i<n;i++){\n greater[i]=max(greater[i-1],nums[i]);\n int j=n-i-1;\n smaller[j]=min(smaller[j+1],nums[j]);\n \n }\n for (int i=1;i<n-1;i++){\n if (greater[i-1]<nums[i] && nums[i]<smaller[i+1]) ans+=2;\n else if (nums[i-1]<nums[i] && nums[i]<nums[i+1]) ans+=1;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Simple solution using prefix and suffix sum || C++ || TC: 2*O(N) || SC: 2*O(N)
|
simple-solution-using-prefix-and-suffix-i66qr
|
\nIntuition is: if the element at ith index > max of all the elements of left that means ith element is \ngreater than all the elements on left hand side,\n\nsi
|
will_shock_u_soon
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-01T19:43:44.351434+00:00
|
2022-02-01T19:47:46.267438+00:00
| 58 | false |
```\nIntuition is: if the element at ith index > max of all the elements of left that means ith element is \ngreater than all the elements on left hand side,\n\nsimilarly if the ith index element is less than min of all the elements of right that implies\nith index element is smaller than all the elements on right hand side.\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n void print(vector<int> &arr) {\n int l = arr.size();\n for(int i = 0; i < l; i++) {\n cout<<arr[i]<<" ";\n }\n cout<<endl;\n }\n \n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int l = nums.size();\n vector<int> maxL(l, 0);\n vector<int> minR(l, 1e9);\n \n maxL[0] = nums[0];\n \n minR[l-1] = nums[l-1];\n \n for(int i = 1; i < l; i++) {\n maxL[i] = max(maxL[i-1], nums[i]);\n \n minR[l-1-i] = min(minR[l-1-i+1], nums[l-1-i]);\n \n }\n \n \n // cout<<"maxL "<<endl;\n // print(maxL);\n \n \n \n // cout<<"minR "<<endl;\n // print(minR);\n \n int ans = 0;\n \n for(int i = 1; i < l-1; i++) {\n if(maxL[i-1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < minR[i+1]) {\n ans += 2;\n }\n else if(nums[i-1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i+1]) {\n ans += 1;\n }\n }\n \n // cout<<"ans "<<ans<<endl;\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C', 'Suffix Array']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
3 passes, O(n) space, python
|
3-passes-on-space-python-by-pathak_kapil-dpcj
|
```\nclass Solution:\n def sumOfBeauties(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n R = nums.copy()\n L = nums.copy()\n for i in range(len(nums)-2
|
pathak_kapil_jayesh
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-01T05:00:48.100772+00:00
|
2022-02-01T05:00:48.100813+00:00
| 99 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def sumOfBeauties(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n R = nums.copy()\n L = nums.copy()\n for i in range(len(nums)-2, -1, -1):\n R[i] = min(R[i], R[i+1])\n for i in range(1, len(nums)):\n L[i] = max(L[i], L[i-1])\n ans = [0]\n for i in range(1, len(nums)-1):\n if L[i-1]<nums[i]<R[i+1]:\n ans.append(2)\n elif nums[i]>nums[i-1] and nums[i]<nums[i+1]:\n ans.append(1)\n else:\n ans.append(0)\n return sum(ans)
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming']
| 1 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Simple C++ Solution | O(N) Time Complexity | O(N) Space Complexity
|
simple-c-solution-on-time-complexity-on-p7dc2
|
Problem\nGiven an array nums[] and for each index i (1 <= i <= nums.length - 2) the beauty of nums[i] equals:\n\n2, if nums[j] < nums[i] < nums[k], for all 0 <=
|
sandeep2601
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-27T09:53:33.194961+00:00
|
2022-01-27T09:53:33.194988+00:00
| 80 | false |
**Problem**\nGiven an array nums[] and for each index i (1 <= i <= nums.length - 2) the beauty of nums[i] equals:\n\n2, if nums[j] < nums[i] < nums[k], for all 0 <= j < i and for all i < k <= nums.length - 1.\n1, if nums[i - 1] < nums[i] < nums[i + 1], and the previous condition is not satisfied.\n0, if none of the previous conditions holds.\n\n**Approach**\nconsider the initial value of **sum=0**\n**Step 1 :**\n*For each index i (i>=1 and i<=n-2) check if i is the greatest element in range [0,i] and i is the smallest element in range [i,n] where n is the size of the array.\nif **true** increment the value of **sum** by 2 i.e **sum=sum+2***\n\n**Step 2**\nIf **Step 1** fails then check whether **nums[i]>nums[i-1] and nums[i]<nums[i+1]** \nif **true** increment the value of **sum** by 1 i.e. **sum++**\n\nreturn the value **sum** after iterating the array\n\n**Code**\n```\nint sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n\n int size = nums.size();\n \n int maxval = nums[0];\n \n // intial sum value is 0 \n int sum = 0;\n // array to store min value upto particular index from end\n int minvalues[size]; \n \n int minval = nums[size-1];\n minvalues[size-1] = nums[size-1];\n \n //storing the minimum value upto a particular index \'i\' from the end\n for(int i=size-2;i>=1;i--) {\n minval = min(minval,nums[i]);\n minvalues[i] = minval;\n }\n \n for(int i=1;i<size-1;i++) {\n \n //checking the first condition\n if(nums[i]>maxval && nums[i]<minvalues[i+1])\n {\n sum+=2;\n }\n \n //checking the second condition if first condition fails\n else if((nums[i]>nums[i-1]) && (nums[i]<nums[i+1]))\n {\n sum++;\n }\n \n //updating max value as we are not using any additional space for storing maxvalues\n maxval = max(maxval,nums[i]);\n }\n \n return sum; \n }\n```\nIn this solution we are prefetching min values because it is gives us the minimum value in the range **[i,n]** in O(1) time if we don\'t do it we need to calculate the minimum value in the range **[i,n]** each and every time.Where as max value before an index **i** can easily be obtained during the traversal.\n\nDo **upvote** the post if you find it useful.Feel free to **comment** if you have any queries.\n\n**Happy Coding** \uD83D\uDE42
| 1 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
O(N) time O(N) space
|
on-time-on-space-by-akash_fm99-t0oe
|
```class Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vectorsmin(n,nums[n-1]);\n for(int i=n-2;i>=0;
|
akash_fm99
|
NORMAL
|
2021-12-27T05:55:20.126901+00:00
|
2021-12-27T05:55:20.126946+00:00
| 67 | false |
```class Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<int>smin(n,nums[n-1]);\n for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--)\n smin[i] = min(smin[i+1],nums[i+1]);\n int pmax = nums[0];\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++){\n if(nums[i]>pmax && nums[i] < smin[i])\n ans += 2;\n else if(nums[i]> nums[i-1] && nums[i] < nums[i+1])\n ans += 1;\n \n pmax = max(pmax,nums[i]);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Max (L->R) and Min(R->L)- Sliding Window
|
max-l-r-and-minr-l-sliding-window-by-aks-fl6z
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n int n = nums.length;\n int[] max = new int[nums.length];\n int[] min = new
|
akshitg8340
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-21T04:57:11.349934+00:00
|
2021-10-21T04:57:11.349979+00:00
| 81 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n int n = nums.length;\n int[] max = new int[nums.length];\n int[] min = new int[nums.length];\n \n int maxi = Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n int mini = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {\n max[i] = Math.max(maxi,nums[i]);\n maxi = max[i];\n min[n-i-1] = Math.min(mini, nums[n-i-1]);\n mini = min[n-i-1];\n }\n \n int count = 0;\n for(int i=1; i<n-1; i++) {\n if(nums[i-1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i+1]) {\n count++;\n if(nums[i] < min[i+1] && nums[i] > max[i-1]) {\n count++;\n }\n }\n }\n \n return count;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
c++ o(n) o(n)
|
c-on-on-by-dolaamon2-lgx4
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<bool> dp(n,true);\n int maxleft = n
|
dolaamon2
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-20T04:25:25.287668+00:00
|
2021-10-20T04:25:25.287719+00:00
| 106 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<bool> dp(n,true);\n int maxleft = nums[0];\n int minright = nums[n-1];\n for(int i=1; i<n-1; i++)\n {\n if (nums[i]<=maxleft) \n dp[i] = false;\n if (nums[n-i-1]>=minright)\n dp[n-i-1] = false;\n maxleft = max(maxleft,nums[i]) ;\n minright = min(minright,nums[n-i-1]) ;\n }\n int res = 0; \n for(int i=1; i<n-1; i++)\n {\n if (dp[i])\n res+=2;\n else if (nums[i-1]<nums[i] && nums[i+1]>nums[i])\n res+=1;\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
java neat solution with boolean array
|
java-neat-solution-with-boolean-array-by-8qsh
|
```\n/\nMany solution comes with int array. I use boolean array to save memory and operation whlile comparing.\n/\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeautie
|
ananthakrg
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-02T07:13:42.935554+00:00
|
2021-10-02T07:13:42.935584+00:00
| 76 | false |
```\n/*\nMany solution comes with int array. I use boolean array to save memory and operation whlile comparing.\n*/\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n int sum = 0;\n int n = nums.length;\n boolean[] r = new boolean [n];\n \n int maxl = nums[0], minr = nums[n - 1];\n \n for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)\n {\n if (nums[i] < minr) r[i] = true;\n minr = Math.min(minr , nums[i]);\n }\n \n \n for (int i = 1; i < nums.length - 1; i++)\n {\n if (maxl < nums[i] && r[i])\n sum += 2;\n else if (nums[i - 1] < nums[i] && nums[i] < nums[i + 1])\n sum += 1;\n \n maxl = Math.max(maxl, nums[i]); \n }\n \n return sum;\n }\n}
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
Simple Java 2 Sweep with Boolean array
|
simple-java-2-sweep-with-boolean-array-b-z068
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n int len = nums.length;\n boolean satisfied[] = new boolean[len];\n int lef
|
Shubham2077
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-25T07:41:33.854663+00:00
|
2021-09-25T07:41:33.854723+00:00
| 124 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int sumOfBeauties(int[] nums) {\n int len = nums.length;\n boolean satisfied[] = new boolean[len];\n int leftmax = Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n int rightmin = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n int ans = 0;\n \n for(int i=1;i<len-1;i++){\n // 1. Check if current element is the max element while going right \n leftmax = Math.max(leftmax, nums[i-1]);\n if(nums[i]>leftmax)\n satisfied[i]=true;\n }\n for(int i=len-2;i>0;i--){\n // 2. Check if the current element is smallest while going left\n rightmin = Math.min(rightmin, nums[i+1]);\n // 3. Mark condition 1 (for 2 points) as satisfied iff satisfied[i] is true already\n if(nums[i]<rightmin)\n satisfied[i] = satisfied[i] && true;\n else\n satisfied[i] = false;\n // 4. if condition 1 is satisfied add 2 points else if condition 2 is satisfied add 1 point\n if(satisfied[i])\n ans+=2;\n else if(nums[i-1]<nums[i] && nums[i]<nums[i+1])\n ans+=1;\n \n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
sum-of-beauty-in-the-array
|
C++, Simple O(n), Easy to understand
|
c-simple-on-easy-to-understand-by-narend-llhl
|
class Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector& ar) {\n \n int n =ar.size(), ans = 0, l[n], r[n];\n \n l[0]=ar[0];\n
|
narendraregar
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-25T04:32:38.234057+00:00
|
2021-09-25T04:32:38.234089+00:00
| 177 | false |
class Solution {\npublic:\n int sumOfBeauties(vector<int>& ar) {\n \n int n =ar.size(), ans = 0, l[n], r[n];\n \n l[0]=ar[0];\n r[n-1]=ar[n-1];\n \n for(int i=1;i<n;i++){\n l[i]=max(l[i-1],ar[i]);\n r[n-1-i]=min(r[n-i],ar[n-1-i]);\n }\n \n for(int i=1;i<=n-2;i++)\n if(l[i-1]<ar[i] && ar[i]<r[i+1])\n ans+=2;\n else if(ar[i-1]<ar[i] && ar[i]<ar[i+1])\n ans+=1;\n \n return ans;\n }\n};
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.