question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
scala union find
|
scala-union-find-by-vititov-f1na
|
scala []\nobject Solution {\n import scala.util.chaining._\n def friendRequests(n: Int, restrictions: Array[Array[Int]], requests: Array[Array[Int]]): Array[B
|
vititov
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-26T22:39:36.954112+00:00
|
2024-11-26T22:39:36.954146+00:00
| 1 | false |
```scala []\nobject Solution {\n import scala.util.chaining._\n def friendRequests(n: Int, restrictions: Array[Array[Int]], requests: Array[Array[Int]]): Array[Boolean] = {\n val djs = Array.range(0,n)\n val restrs = Vector.fill(n)(collection.mutable.Set.empty[Int])\n .tap(rs => restrictions.foreach{a => rs(a.head)+=a.last; rs(a.last)+=a.head})\n def root(i: Int): Int = if(djs(i)==i) i else root(djs(i)).tap{rc => djs(i) = rc}\n def join(i:Int,j:Int):Unit =\n ().tap(_ => restrs(root(i)) ++= restrs(root(j)).map(root))\n .tap(_ => djs(root(j))=root(i)).tap(_ => root(j))\n requests.map(_.sorted).map{a =>\n lazy val (r0,r1) = (root(a.head), root(a.last))\n (!restrs(r0).contains(r1) && !restrs(r1).contains(r0))\n .tap(if(_) join(a.head,a.last))\n }\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Union Find', 'Graph', 'Scala']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
Union-Find
|
union-find-by-s_t_s-rk3i
|
Code\nrust []\nuse std::cell::Cell;\n\n#[derive(Debug)]\nstruct Node {\n\tparent : Cell<u32>, // using Cell so find only takes a &self and not a &mut self (not
|
S_T_S
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-14T18:42:12.218723+00:00
|
2024-11-14T18:42:12.218757+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Code\n```rust []\nuse std::cell::Cell;\n\n#[derive(Debug)]\nstruct Node {\n\tparent : Cell<u32>, // using Cell so find only takes a &self and not a &mut self (not that it matters much, its just nicer)\n size : i32,\n}\n\n#[derive(Debug)]\nstruct UF {\n data : Vec<Node>,\n}\n\nimpl UF {\n fn new(n : usize) -> Self {\n assert!(n <= u32::MAX as usize);\n let mut data = Vec::with_capacity(n);\n for i in 0..n {\n data.push(Node { parent: Cell::new(i as u32), size: 1, });\n }\n return Self { data, };\n }\n fn find<U : TryInto<usize>>(&self, i : U) -> usize {\n let i : usize = i.try_into().unwrap_or(usize::MAX); // :-)\n fn find_mono(this : &UF, i : usize) -> usize {\n if this.data[i].parent.get() as usize == i {\n return i;\n }\n let sub = this.find(this.data[i].parent.get() as usize);\n this.data[i].parent.set(sub as u32);\n return sub;\n }\n find_mono(self, i)\n }\n fn union<U1 : TryInto<usize>, U2 : TryInto<usize>>(&mut self, i : U1, j : U2) {\n let i : usize = i.try_into().unwrap_or(usize::MAX); // :-)\n let j : usize = j.try_into().unwrap_or(usize::MAX); // :-)\n fn union_mono(this : &mut UF, i : usize, j : usize) {\n let sub1 = this.find(i);\n let sub2 = this.find(j);\n if sub1 == sub2 {\n return;\n }\n let sz1 = this.data[sub1].size;\n let sz2 = this.data[sub2].size;\n if sz1 < sz2 {\n this.data[sub1].parent.set(sub2 as u32);\n this.data[sub2].size += sz1;\n } else {\n this.data[sub2].parent.set(sub1 as u32);\n this.data[sub1].size += sz2;\n }\n }\n union_mono(self, i, j)\n }\n}\n\nuse std::cmp::*;\nimpl Solution {\n // O(n + |restrictions| * |requests| * alpha(n))\n pub fn friend_requests(n: i32, restrictions: Vec<Vec<i32>>, requests: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<bool> {\n let mut uf = UF::new(n as usize);\n let mut ans = Vec::with_capacity(requests.len());\n for request in requests {\n let i1 = uf.find(request[0]);\n let i2 = uf.find(request[1]);\n let (i1, i2) = (min(i1, i2), max(i1, i2));\n let mut conflict = false;\n for restriction in restrictions.iter() {\n let r1 = uf.find(restriction[0]);\n let r2 = uf.find(restriction[1]);\n let (r1, r2) = (min(r1, r2), max(r1, r2));\n if i1 == r1 && i2 == r2 {\n conflict = true;\n break;\n }\n }\n if conflict {\n ans.push(false);\n } else {\n uf.union(i1, i2);\n ans.push(true);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Union Find', 'Rust']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
[C++] Union find/ DisjointSet || Self Explanatory Code
|
c-union-find-disjointset-self-explanator-wqv5
|
\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass DisjointSet {\n vector<int> parent, rank;\npublic:\n DisjointSet(int n) {\n rank.resize(n, 0);\n parent.resize(n);\n
|
daks_05
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-07T12:35:16.703739+00:00
|
2024-11-07T12:35:16.703805+00:00
| 29 | false |
\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass DisjointSet {\n vector<int> parent, rank;\npublic:\n DisjointSet(int n) {\n rank.resize(n, 0);\n parent.resize(n);\n iota(parent.begin(), parent.end(), 0);\n }\n\n int find(int node) {\n if(node == parent[node]) return node;\n return parent[node] = find(parent[node]);\n }\n\n void unionByRank(int u, int v) {\n int rootU = find(u);\n int rootV = find(v);\n\n if(rootU == rootV) return;\n\n if(rank[rootU] < rank[rootV]) {\n parent[rootU] = rootV;\n } else if(rank[rootU] > rank[rootV]) {\n parent[rootV] = rootU;\n } else {\n parent[rootV] = rootU;\n rank[rootU]++;\n }\n }\n\n bool isInSameComponent(int u, int v) {\n return find(u) == find(v);\n }\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& restrictions, vector<vector<int>>& requests) {\n DisjointSet ds(n);\n vector<bool> result(requests.size());\n\n for(int i = 0; i < requests.size(); ++i) {\n int u = requests[i][0], v = requests[i][1];\n int rootU = ds.find(u);\n int rootV = ds.find(v);\n\n bool canBecomeFriends = true;\n if(rootU != rootV) {\n for(auto& restriction : restrictions) {\n int x = restriction[0], y = restriction[1];\n int rootX = ds.find(x), rootY = ds.find(y);\n\n if((rootU == rootX && rootV == rootY) ||(rootU == rootY && rootV == rootX)) {\n canBecomeFriends = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n }\n\n if(canBecomeFriends) {\n ds.unionByRank(u, v);\n result[i] = true;\n } else {\n result[i] = false;\n }\n }\n\n return result;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
Python (Simple Union Find)
|
python-simple-union-find-by-rnotappl-9mak
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
rnotappl
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-31T15:25:04.520994+00:00
|
2024-10-31T15:25:04.521034+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def friendRequests(self, n, restrictions, requests):\n m, dict1, result = len(requests), {}, []\n\n def find(x):\n if x not in dict1:\n return x \n else:\n if x != dict1[x]:\n dict1[x] = find(dict1[x])\n return dict1[x]\n\n def union(x,y):\n a, b = find(x), find(y)\n\n if a != b:\n dict1[b] = a \n\n for i in range(m):\n found_set, val = {find(requests[i][0]),find(requests[i][1])}, True\n\n for a,b in restrictions:\n if find(a) in found_set and find(b) in found_set:\n val = False \n break \n\n result.append(val)\n\n if val:\n union(requests[i][0],requests[i][1])\n\n return result \n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
[python3] faster than 100%, extensively explained. (assign group for each people)
|
python3-faster-than-100-extensively-expl-ucut
|
\n\n# Code\npython3 []\nclass Solution:\n def friendRequests(self, n: int, restrictions: List[List[int]], requests: List[List[int]]) -> List[bool]:\n
|
SNURO
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-30T13:49:15.780240+00:00
|
2024-10-30T13:49:15.780264+00:00
| 5 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def friendRequests(self, n: int, restrictions: List[List[int]], requests: List[List[int]]) -> List[bool]:\n # start by assigning people to group (group_idx[person]=group)\n # group index is defined as minimum index of person in group\n # initially, group_idx[i] = i for all i in range(n), since everyone is in their own group\n\n # we also keep ban_set[i] = set()\n # set of group indices that cannot be merged with group i \n \n # upon each request, we think about "merging" two groups A and B, which two people a,b are in\n # they will all become indirect friends if two groups merge\n \n # case 1 : A == B\n # two people are already in same group. append True to answer\n # case 2 : A and B are in each other\'s ban_set\n # cannot merge. append False to answer\n # case 3 : B is not in ban_set[A] and vice versa:\n # merge ok. merge and update by\n # (1) update all group_idx. determine new group idx by min(A,B) and update all group_idx\n # (2) update ban_set. ban_set[min(A,B)] should newly include all of ban_set[max(A,B)]\n \n def update_group(x,y):\n """\n set group_idx of everyone that was in group y to group x\n """\n # TODO: can we do it efficiently?\n for a in group_idx:\n if group_idx[a] == y:\n group_idx[a] = x\n\n \n def update_ban(x,y):\n """\n group x and group y is being merged to group x\n add all that was in ban_set[y] to ban_set[x]\n also, other groups which were banning group y should now also ban group x (because x and y is merged to x)\n """\n ban_set[x] |= ban_set[y]\n for a in ban_set:\n if y in ban_set[a]:\n ban_set[a].add(x)\n\n group_idx = {i:i for i in range(n)}\n ban_set = defaultdict(set)\n # TODO: merging operation is commutative. Do we really have to keep track of both ban_set[A] and ban_set[B]?\n for x,y in restrictions:\n ban_set[x].add(y)\n ban_set[y].add(x)\n \n ans = []\n for a,b in requests:\n A = group_idx[a]\n B = group_idx[b]\n if A == B:\n ans.append(True)\n elif (A in ban_set[B]) or (B in ban_set[A]):\n ans.append(False)\n else:\n ans.append(True)\n update_group(min(A,B), max(A,B))\n update_ban(min(A,B), max(A,B))\n \n return ans\n\n\n\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
2076. Process Restricted Friend Requests.cpp
|
2076-process-restricted-friend-requestsc-h9fp
|
Code\n\nclass UnionFind {\npublic: \n vector<int> parent, rank; \n UnionFind(int n) {\n parent.resize(n); \n iota(begin(parent), end(parent)
|
202021ganesh
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-30T10:19:55.698664+00:00
|
2024-10-30T10:19:55.698691+00:00
| 1 | false |
**Code**\n```\nclass UnionFind {\npublic: \n vector<int> parent, rank; \n UnionFind(int n) {\n parent.resize(n); \n iota(begin(parent), end(parent), 0); \n rank.resize(n); \n fill(rank.begin(), rank.end(), 1); \n } \n \n int find(int p) {\n if (parent[p] != p) \n parent[p] = find(parent[p]); \n return parent[p]; \n }\n \n bool connect(int p, int q) {\n /* union with rank */\n int prt = find(p), qrt = find(q); \n if (prt == qrt) return false; \n if (rank[prt] > rank[qrt]) swap(prt, qrt);\n parent[prt] = qrt; \n rank[qrt] += rank[prt]; \n return true; \n }\n};\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& restrictions, vector<vector<int>>& requests) {\n vector<bool> ans; \n UnionFind *uf = new UnionFind(n); \n for (auto& request : requests) {\n int u = uf->find(request[0]), v = uf->find(request[1]); \n bool found = false; \n for (auto& restriction : restrictions) {\n int x = uf->find(restriction[0]), y = uf->find(restriction[1]); \n if ((u == x && v == y) || (u == y && v == x)) {\n found = true; \n break; \n }\n }\n ans.push_back(!found); \n if (!found) uf->connect(u, v); \n }\n delete uf; \n return ans; \n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
Beats 94.58% Python3
|
beats-9458-python3-by-ioakim-8j19
|
Code\npython3 []\nfrom collections import defaultdict\n\nclass Solution:\n def friendRequests(self, n: int, restrictions: List[List[int]], requests: List[Lis
|
ioakim
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-07T20:19:20.201988+00:00
|
2024-10-07T20:19:20.202010+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Code\n```python3 []\nfrom collections import defaultdict\n\nclass Solution:\n def friendRequests(self, n: int, restrictions: List[List[int]], requests: List[List[int]]) -> List[bool]:\n result = []\n network = [set([i]) for i in range(n)]\n restrict_network = defaultdict(set)\n\n for user1, user2 in restrictions:\n restrict_network[user1].add(user2)\n restrict_network[user2].add(user1)\n\n for user1, user2 in requests:\n if user1 == user2:\n result.append(True)\n continue\n\n can_be_friends = True\n for friend1 in network[user1]:\n if friend1 in restrict_network:\n if restrict_network[friend1] & network[user2]:\n can_be_friends = False\n break\n if not can_be_friends:\n result.append(False)\n continue\n\n new_group = network[user1] | network[user2]\n for member in new_group:\n network[member] = new_group\n result.append(True)\n\n return result\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
✅DSU || cPP
|
dsu-cpp-by-darkenigma-8tqh
|
\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass DSU{\n public:\n vector<int>size,par;\n DSU(int n){\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n size.push_back(1);\n
|
darkenigma
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-12T03:58:23.190811+00:00
|
2024-09-12T03:58:23.190834+00:00
| 5 | false |
\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass DSU{\n public:\n vector<int>size,par;\n DSU(int n){\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n size.push_back(1);\n par.push_back(i);\n }\n\n }\n int getP(int i){\n if(par[i]==i)return i;\n return par[i]=getP(par[i]);\n }\n\n void UnionBySize(int i,int j){\n if(size[i]>=size[j]){\n par[j]=i;\n size[j]+=size[i];\n return ;\n }\n par[i]=j;\n size[i]+=size[j];\n return ;\n }\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& restrictions, vector<vector<int>>& requests) {\n vector<vector<int>>dp(n,vector<int>(n,0));\n DSU arr(n);\n for(vector<int>v:restrictions){\n dp[v[0]][v[1]]=1;\n dp[v[1]][v[0]]=1;\n }\n vector<bool>ans;\n for(vector<int>q:requests){\n int a=arr.getP(q[0]);\n int b=arr.getP(q[1]);\n if(dp[a][b]){\n ans.push_back(0);\n continue;\n }\n arr.UnionBySize(a,b);\n for(vector<int>r:restrictions){\n int a=arr.getP(r[0]);\n int b=arr.getP(r[1]);\n dp[a][b]=1;\n dp[b][a]=1;\n }\n ans.push_back(1);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Union Find', 'Graph', 'C++']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
👥Process Restricted Friend Request👥 - 🔗Union Find🔗
|
process-restricted-friend-request-union-ylc3s
|
Intuition\nThe problem can be solved using a Union-Find data structure, which allows us to efficiently manage the friend relationships between people. We iterat
|
sultanalif533
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T22:15:15.188069+00:00
|
2024-09-06T22:15:15.188088+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n*The problem can be solved using a Union-Find data structure, which allows us to efficiently manage the friend relationships between people. We iterate through each friend request and check if the two people can become friends by verifying that they don\'t have any restrictions. If they can become friends, we union their groups. We use the find function to determine the root of each person\'s group, and the parent array to store the parent of each person.*\n# Approach\n# 1. Initialize the parent array\n* We create a parent array of size n, where parent[i] represents the parent of person i. Initially, each person is their own parent, so we set parent[i] = i for all i.\n\n# 2. Process each friend request\n* We iterate through each friend request in the requests array. For each request, we find the roots of the two people involved using the find function.\n\n# 3. Check for restrictions\n* We iterate through each restriction in the restrictions array. If the roots of the two people involved in the request match with the roots of the restricted people, we set the result for this request to false and break out of the loop.\n\n# 4. Union the groups\n* If there are no restrictions, we union the groups of the two people involved in the request by setting the parent of one person to the other.\n\n# 5. Return the results\n* Finally, we return the ans array, which contains the result of each friend request.\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(M*N)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(N)$$\n\n# Code\n```csharp []\npublic class Solution {\n static int find(int x, int[] parent)\n {\n if(parent[x]!=x) parent[x] = find(parent[x],parent);\n return parent[x];\n }\n public bool[] FriendRequests(int n, int[][] restrictions, int[][] requests) {\n bool[] ans = new bool[requests.Length];\n int[] parent = new int[n];\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++) parent[i] = i;\n for(int i=0;i<requests.Length;i++)\n {\n int rx = find(requests[i][0],parent);\n int ry = find(requests[i][1],parent);\n ans[i] = true;\n foreach(var j in restrictions)\n {\n if((find(j[0],parent)==rx&&find(j[1],parent)==ry)||(find(j[0],parent)==ry&&find(j[1],parent)==rx))\n {\n ans[i] = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n if(ans[i]) parent[ry] = rx;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Union Find', 'Graph', 'C#']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
simple dsu , just imagine and draw the example testcase step by step
|
simple-dsu-just-imagine-and-draw-the-exa-gw57
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nRequests between two friends will be success only if both friends will lie on component
|
thamanbharti
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-04T20:00:17.049075+00:00
|
2024-09-04T20:00:17.049102+00:00
| 10 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n*Requests between two friends will be success only if both friends will lie on component other than the restricted friend requests;\nif after analysing we find request is success than we can make connection between them.*\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n**we can use dsu for the above purpose mention**\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:**O(N)**\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:**O(N)**\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Disjoint{\npublic:\n vector<int> parent, rank;\n \n Disjoint(int n) {\n parent.resize(n+1);\n rank.resize(n+1, 0); \n for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {\n parent[i] = i; \n }\n }\n\n int findP(int u) {\n if(parent[u] == u) return u;\n return parent[u] = findP(parent[u]); \n }\n\n void do_union(int u, int v) {\n int ulp_u = findP(u);\n int ulp_v = findP(v);\n if(ulp_u != ulp_v) {\n \n if(rank[ulp_u] > rank[ulp_v]) {\n parent[ulp_v] = ulp_u;\n } else if(rank[ulp_u] < rank[ulp_v]) {\n parent[ulp_u] = ulp_v;\n } else {\n parent[ulp_v] = ulp_u;\n rank[ulp_u]++;\n }\n }\n }\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool valid(int u, int v, Disjoint& ds, const vector<vector<int>>& restrictions) {\n int ulp_u = ds.findP(u);\n int ulp_v = ds.findP(v);\n \n for(const auto& restriction : restrictions) {\n int r1 = ds.findP(restriction[0]);\n int r2 = ds.findP(restriction[1]);\n if((ulp_u == r1 && ulp_v == r2) || (ulp_u == r2 && ulp_v == r1)) {\n return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n \n vector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& restrictions, vector<vector<int>>& requests) {\n Disjoint ds(n);\n vector<bool> ans(requests.size(), false);\n \n for(int i = 0; i < requests.size(); i++) {\n int u = requests[i][0];\n int v = requests[i][1];\n \n if(valid(u, v, ds, restrictions)) {\n ds.do_union(u, v); \n ans[i] = true;\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
simple dsu , just imagine and draw the example testcase step by step
|
simple-dsu-just-imagine-and-draw-the-exa-fih6
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nRequests between two friends will be success only if both friends will lie on component
|
thamanbharti
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-04T20:00:14.078926+00:00
|
2024-09-04T20:00:14.078944+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n*Requests between two friends will be success only if both friends will lie on component other than the restricted friend requests;\nif after analysing we find request is success than we can make connection between them.*\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n**we can use dsu for the above purpose mention**\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:**O(N)**\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:**O(N)**\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Disjoint{\npublic:\n vector<int> parent, rank;\n \n Disjoint(int n) {\n parent.resize(n+1);\n rank.resize(n+1, 0); \n for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {\n parent[i] = i; \n }\n }\n\n int findP(int u) {\n if(parent[u] == u) return u;\n return parent[u] = findP(parent[u]); \n }\n\n void do_union(int u, int v) {\n int ulp_u = findP(u);\n int ulp_v = findP(v);\n if(ulp_u != ulp_v) {\n \n if(rank[ulp_u] > rank[ulp_v]) {\n parent[ulp_v] = ulp_u;\n } else if(rank[ulp_u] < rank[ulp_v]) {\n parent[ulp_u] = ulp_v;\n } else {\n parent[ulp_v] = ulp_u;\n rank[ulp_u]++;\n }\n }\n }\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool valid(int u, int v, Disjoint& ds, const vector<vector<int>>& restrictions) {\n int ulp_u = ds.findP(u);\n int ulp_v = ds.findP(v);\n \n for(const auto& restriction : restrictions) {\n int r1 = ds.findP(restriction[0]);\n int r2 = ds.findP(restriction[1]);\n if((ulp_u == r1 && ulp_v == r2) || (ulp_u == r2 && ulp_v == r1)) {\n return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n \n vector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& restrictions, vector<vector<int>>& requests) {\n Disjoint ds(n);\n vector<bool> ans(requests.size(), false);\n \n for(int i = 0; i < requests.size(); i++) {\n int u = requests[i][0];\n int v = requests[i][1];\n \n if(valid(u, v, ds, restrictions)) {\n ds.do_union(u, v); \n ans[i] = true;\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
Easy DSU Solution, Simple Brute Force
|
easy-dsu-solution-simple-brute-force-by-omcb0
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
kndudhushyanthan
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-29T07:17:26.167262+00:00
|
2024-08-29T07:17:26.167310+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Disjoint{\n public:\n vector<int>par,size;\n Disjoint(int n){\n par.resize(n);\n size.resize(n,1);\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n par[i]=i;\n }\n }\n int findPar(int node){\n if(node == par[node]){\n return node;\n }\n return par[node]=findPar(par[node]);\n }\n void unionBySize(int u,int v){\n int ulp_u = findPar(u);int ulp_v = findPar(v);\n if(ulp_u == ulp_v) return;\n if(size[ulp_u]<size[ulp_v]){\n size[ulp_v]+=size[ulp_u];\n par[ulp_u]=ulp_v;\n }\n else{\n size[ulp_u]+=size[ulp_v];\n par[ulp_v]=ulp_u;\n }\n }\n};\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& res, vector<vector<int>>& req) {\n vector<bool>ans(req.size());\n Disjoint ds(n);\n map<pair<int,int>,int>mp;\n for(auto x:res){\n mp[{x[0],x[1]}]=1;\n mp[{x[1],x[0]}]=1;\n }\n for(int i=0;i<req.size();i++){\n if(mp.find({req[i][0],req[i][1]})!=mp.end()){\n ans[i]=0;\n }\n else{\n Disjoint use(n);\n use=ds;\n int u = req[i][0];\n int v = req[i][1];\n ds.unionBySize(u,v);\n bool flag=true;\n for(int j =0;j<res.size();j++){\n int x = res[j][0];\n int y = res[j][1];\n if(ds.findPar(x)==ds.findPar(y)){\n flag=false;\n }\n }\n ans[i]=flag;\n if(!flag){\n ds=use;\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
shortest code in java using union find
|
shortest-code-in-java-using-union-find-b-84ev
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
AfshanAhmed
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-05T09:30:32.353100+00:00
|
2024-08-05T09:30:32.353130+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n int[] parent;\n public boolean[] friendRequests(int n, int[][] restrictions, int[][] requests) {\n parent = new int[n];\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n parent[i] = i;\n }\n return processRequests(requests, restrictions);\n }\n private boolean[] processRequests(int[][] requests, int[][] restrictions) {\n boolean[] res = new boolean[requests.length];\n for (int i = 0; i < requests.length; i++) {\n int a = find(requests[i][0]);\n int b = find(requests[i][1]);\n res[i] = checkRestrictions(a, b, restrictions);\n }\n return res;\n }\n private boolean checkRestrictions(int a, int b, int[][] restrictions) {\n for (int i = 0; i < restrictions.length; i++) {\n boolean isClear = isRestrictionClear(a, b, restrictions[i]);\n if (!isClear) return false;\n }\n union(a, b);\n return true;\n }\n private boolean isRestrictionClear(int a, int b, int[] restriction) {\n int x = find(restriction[0]);\n int y = find(restriction[1]);\n if (a == x && b == y) return false;\n if (a == y && b == x) return false;\n return true;\n }\n private void union(int a, int b) {\n int rootA = find(a);\n int rootB = find(b);\n parent[rootA] = rootB;\n }\n private int find(int a) {\n if (parent[a] != a) {\n parent[a] = find(parent[a]);\n }\n return parent[a];\n } \n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
classic disjoint det
|
classic-disjoint-det-by-sovlynn-4wng
|
Intuition\nThis question can be solved by a classic Disjoint Set data structure.\n\n# Approach\nFor each request just check if all restrictions are not violated
|
sovlynn
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-03T02:07:15.204742+00:00
|
2024-08-03T02:07:15.204764+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Intuition\nThis question can be solved by a classic [Disjoint Set](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Disjoint-set_data_structure) data structure.\n\n# Approach\nFor each request just check if all restrictions are not violated.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n\\times k\\times\\alpha(n))$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```\n#[derive(Debug)]\nstruct DSet{\n size: Vec<usize>,\n parent: Vec<usize>,\n}\n\nimpl DSet{\n fn new(n: usize)->Self{\n Self{size: vec![1; n], parent: vec![n; n]}\n }\n\n fn set(&self, mut a: usize)->usize{\n while self.parent[a]<self.parent.len(){\n a=self.parent[a];\n }\n a\n }\n\n fn uni(&mut self, mut a: usize, mut b: usize){\n (a, b)=(self.set(a), self.set(b));\n if a!=b{\n if self.size[a]<self.size[b]{(a, b)=(b, a);}\n self.parent[b]=a;\n self.size[a]+=self.size[b];\n }\n }\n\n fn force_uni(&mut self, mut a: usize, mut b: usize){\n if self.size[a]<self.size[b]{(a, b)=(b, a);}\n self.parent[b]=a;\n self.size[a]+=self.size[b];\n }\n}\n\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn friend_requests(n: i32, restrictions: Vec<Vec<i32>>, requests: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<bool> {\n let mut ds=DSet::new(n as usize);\n let restrictions:Vec<_>=restrictions.into_iter().map(|r|(r[0] as usize, r[1] as usize)).collect();\n\n let mut result=Vec::new();\n \'out: for req in &requests{\n let (mut a, mut b)=(ds.set(req[0] as usize), ds.set(req[1] as usize));\n if a==b{\n result.push(true);\n }else{\n if a>b{(a, b)=(b, a);}\n for res in &restrictions{\n let (mut c, mut d)=(ds.set(res.0), ds.set(res.1));\n if c>d{(c, d)=(d, c);}\n if a==c&&b==d{\n result.push(false);\n continue \'out;\n }\n }\n result.push(true);\n ds.force_uni(a, b);\n }\n }\n result\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Union Find', 'Rust']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
ap
|
ap-by-ap5123-ygr7
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
ap5123
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-21T06:56:01.933953+00:00
|
2024-06-21T06:56:01.933981+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\nint find(int n,vector<int>&par)\n{\n if(n==par[n])return n;\n return par[n]=find(par[n],par);\n}\nvoid join(int u,int v,vector<int>&size,vector<int>&par)\n{\n int pu=find(u,par);\n int pv=find(v,par);\n if(pu==pv)return;\n if(size[pu]>size[pv])\n {\n size[pu]+=size[pv];\n par[pv]=pu;\n }else\n {\n size[pv]+=size[pu];\n par[pu]=pv;\n }\n}\n vector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& re, \n vector<vector<int>>& req) {\n vector<int> size(n,1),par(n,0);\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)par[i]=i;\n vector<bool> ans;\n for(auto i:req)\n {\n int f=1;\n for(auto j:re)\n {\n if((find(j[0],par)==find(i[0],par)&&find(j[1],par)==find(i[1],par))||(find(j[0],par)==find(i[1],par)&&find(j[1],par)==find(i[0],par)))\n {\n f=0;\n }\n }\n if(f)\n {\n ans.push_back(true);\n join(i[0],i[1],size,par);\n }else\n {\n ans.push_back(false);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
Union find with rollback
|
union-find-with-rollback-by-ashutoshdaya-xl3g
|
Algorithm Union Find\n\n# Approach\nFor each request, process it, and check restrictions. If restricted rollback to previous state. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time com
|
ashutoshdayal
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-09T08:16:58.182414+00:00
|
2024-06-09T08:16:58.182446+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Algorithm `Union Find`\n\n# Approach\nFor each request, process it, and check restrictions. If restricted rollback to previous state. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(restrictions.length*requests.length*log(n))$$\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```\nclass UnionFind {\nprivate:\n int n,set_size, *parent, *rank;\n stack<pair<int,pair<int,int>>> st;\npublic:\n UnionFind(){}\n UnionFind(int a) { //a: set size, {1,2...n}\n n=set_size=a;\n parent=new int[n+1];\n rank=new int[n+1];\n for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) parent[i]=i, rank[i]=1;\n }\n\n int find(int x) { //O(logn)\n if (x!=parent[x]) return find(parent[x]);\n return x;\n }\n\n bool merge(int x, int y) { //O(logn)\n int xroot=find(x), yroot=find(y);\n if (xroot!=yroot) { //rank-compression\n if (rank[xroot]>=rank[yroot]) {\n st.push({yroot,{parent[yroot],rank[xroot]}});\n parent[yroot]=xroot;\n rank[xroot]+=rank[yroot];\n } else {\n st.push({xroot,{parent[xroot],rank[yroot]}});\n parent[xroot]=yroot;\n rank[yroot]+=rank[xroot];\n }\n set_size--; \n return 1;\n }\n return 0;\n }\n\n bool rollback() { //O(1)\n if (st.empty()) return 0;\n auto &his=st.top();\n rank[parent[his.first]]=his.second.second;\n parent[his.first]=his.second.first;\n st.pop();\n set_size++;\n return 1;\n }\n\n void reset() {\n set_size=n;\n for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) parent[i]=i, rank[i]=1; \n } \n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\nvector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& restrictions, vector<vector<int>>& requests) {\n UnionFind frds(n);\n vector<bool> ans;\n for (const auto &req:requests) {\n bool _=1;\n frds.merge(req[0]+1,req[1]+1);\n for (const auto &res:restrictions)\n if (frds.find(res[0]+1)==frds.find(res[1]+1)) {_=0;break;}\n if (!_) frds.rollback();\n ans.push_back(_);\n }\n return ans;\n}\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
java union find
|
java-union-find-by-pseudo_intelligent-zrpi
|
```\n\nclass UF{\n public int[] parent;\n public int[] rank;\n public UF(int n){\n parent = new int[n];\n rank = new int[n];\n fo
|
Pseudo_intelligent
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-04T02:35:26.152641+00:00
|
2024-06-04T02:35:26.152659+00:00
| 1 | false |
```\n\nclass UF{\n public int[] parent;\n public int[] rank;\n public UF(int n){\n parent = new int[n];\n rank = new int[n];\n for(int i = 0; i <parent.length;i++){\n parent[i] = i;\n rank[i] = 0;\n }\n }\n public int find(int x){\n if(x != parent[x]){\n parent[x] = find(parent[x]);\n }\n return parent[x];\n }\n public boolean union(int x, int y){\n int xp = find(x); int yp = find(y);\n if(xp==yp){\n return true;\n }\n if(rank[xp] > rank[yp]){\n parent[yp] = xp;\n }\n else if(rank[yp]>rank[xp]){\n parent[xp] = yp;\n }\n else{\n parent[xp] = yp;\n rank[yp] += 1;\n }\n return false;\n \n }\n}\n\nclass Solution {\n public boolean[] friendRequests(int n, int[][] restrictions, int[][] requests) {\n UF dsu = new UF(n);\n boolean[] res = new boolean[requests.length];\n int r = restrictions.length;\n int cnt = 0;\n for(int[] pair : requests){\n int f1 = pair[0]; int f2 = pair[1];\n int f1p = dsu.find(f1); int f2p = dsu.find(f2);\n if(f1p == f2p){\n res[cnt] = true;\n }\n else{\n boolean flag = true;\n for(int i = 0; i < r; i++){\n int x = restrictions[i][0]; int y = restrictions[i][1];\n int xp = dsu.find(x); int yp = dsu.find(y);\n if((xp == f1p && yp == f2p)| (xp==f2p && yp==f1p))\n {\n flag = false;\n break;\n }\n \n }\n res[cnt] = flag;\n }\n if(res[cnt] == true){\n dsu.union(f1,f2);\n }\n \n cnt ++;\n }\n return res;\n }\n}
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
Easiest Solution || Disjoint Set || Beats 100% || C++
|
easiest-solution-disjoint-set-beats-100-fvjxs
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n^2)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity:O(n)\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n# Co
|
dubeyad2003
|
NORMAL
|
2024-05-04T12:27:21.893591+00:00
|
2024-05-04T12:27:21.893612+00:00
| 17 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity:$$O(n^2)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:$$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass DisjointSet{\n vector<int> rank, size, parent;\npublic:\n DisjointSet(int n){\n rank.resize(n+1,0);\n size.resize(n+1,0);\n parent.resize(n+1);\n for(int i=0; i<=n; i++){\n parent[i] = i;\n size[i] = 1;\n }\n }\n int findPar(int node){\n if(node == parent[node])\n return node;\n return parent[node] = findPar(parent[node]);\n }\n\n void unionByRank(int u, int v){\n int ulp_u = findPar(u);\n int ulp_v = findPar(v);\n\n if(ulp_u == ulp_v) return;\n if(rank[ulp_u] < rank[ulp_v]){\n parent[ulp_u] = ulp_v;\n }else if(rank[ulp_u] > rank[ulp_v]){\n parent[ulp_v] = ulp_u;\n }else{\n parent[ulp_v] = ulp_u;\n rank[ulp_u]++;\n }\n }\n\n void unionBySize(int u, int v){\n int ulp_u = findPar(u);\n int ulp_v = findPar(v);\n\n if(ulp_u == ulp_v) return;\n if(size[ulp_u] < size[ulp_v]){\n parent[ulp_u] = ulp_v;\n size[ulp_v] += size[ulp_u];\n }else{\n parent[ulp_v] = ulp_u;\n size[ulp_u] += size[ulp_v];\n }\n }\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& res, vector<vector<int>>& req) {\n DisjointSet dsu(n);\n int a = res.size(), b = req.size();\n vector<bool> ans(b, false);\n for(int i=0; i<b; i++){\n int upa = dsu.findPar(req[i][0]), upb = dsu.findPar(req[i][1]);\n bool fg = true;\n for(int j=0; j<a; j++){\n int vpa = dsu.findPar(res[j][0]), vpb = dsu.findPar(res[j][1]);\n if(vpa == upa && vpb == upb || vpa == upb && vpb == upa){\n fg = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n if(fg){\n ans[i] = fg;\n dsu.unionByRank(req[i][0], req[i][1]);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
Java, Union-Find
|
java-union-find-by-taranovski-gkcf
|
\nclass Solution {\n public boolean[] friendRequests(int n, int[][] restrictions, int[][] requests) {\n \n Map<Integer, UF> ufs = new HashMap<>
|
taranovski
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-19T06:11:51.854460+00:00
|
2024-04-19T06:11:51.854497+00:00
| 5 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public boolean[] friendRequests(int n, int[][] restrictions, int[][] requests) {\n \n Map<Integer, UF> ufs = new HashMap<>();\n Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> groupMembers = new HashMap<>();\n Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> groupToExcludedMembers = new HashMap<>();\n \n int groupId = 1;\n \n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n UF uf = new UF();\n uf.group = groupId;\n \n ufs.put(i, uf);\n groupMembers.put(groupId, new HashSet<>());\n groupMembers.get(groupId).add(i);\n \n groupToExcludedMembers.put(groupId, new HashSet<>());\n \n groupId++;\n }\n \n for (int[] restriction : restrictions) {\n int one = restriction[0];\n int other = restriction[1];\n \n groupToExcludedMembers.get(one + 1).add(other);\n groupToExcludedMembers.get(other + 1).add(one);\n }\n \n int length = requests.length;\n \n boolean[] result = new boolean[length];\n \n int index = 0;\n \n for (int[] request : requests) {\n \n int alice = request[0];\n int bob = request[1];\n \n UF uf1 = ufs.get(alice).get();\n UF uf2 = ufs.get(bob).get();\n \n int group1 = uf1.group;\n int group2 = uf2.group;\n \n if (group1 == group2) {\n result[index] = true;\n } else {\n Set<Integer> members1 = groupMembers.get(group1);\n Set<Integer> members2 = groupMembers.get(group2);\n \n Set<Integer> excludedMembers1 = groupToExcludedMembers.get(group1);\n Set<Integer> excludedMembers2 = groupToExcludedMembers.get(group2);\n \n if (Collections.disjoint(members1, excludedMembers2) && Collections.disjoint(members2, excludedMembers1)) {\n if (group1 < group2) {\n members1.addAll(members2);\n excludedMembers1.addAll(excludedMembers2);\n \n groupMembers.remove(group2);\n groupToExcludedMembers.remove(group2);\n uf2.parent = uf1;\n } else {\n members2.addAll(members1);\n excludedMembers2.addAll(excludedMembers1);\n \n groupMembers.remove(group1);\n groupToExcludedMembers.remove(group1);\n uf1.parent = uf2;\n }\n \n result[index] = true;\n } else {\n result[index] = false;\n }\n }\n \n index++;\n }\n \n return result;\n }\n \n static class UF {\n Integer group;\n UF parent;\n \n UF get() {\n if (parent == null) {\n return this;\n } else {\n if (parent.parent != null) {\n parent = parent.parent;\n }\n return parent.get();\n }\n }\n \n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Union Find', 'Java']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
Group Hashmap || runtime 50.00% memory 75.00% || Python
|
group-hashmap-runtime-5000-memory-7500-p-vyfg
|
Idk why runtime and memory is exactly at half and 3/4. Apparently my runtime(1304ms) falls right between two ends of the spectrum. Don\'t know why, but oh well.
|
dgeyfman
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-29T02:02:47.806365+00:00
|
2024-03-29T02:02:47.806395+00:00
| 1 | false |
Idk why runtime and memory is exactly at half and 3/4. Apparently my runtime(1304ms) falls right between two ends of the spectrum. Don\'t know why, but oh well. I guess nobody else tried this solution.\n\n\n\n\nThe main idea here is to build up "groups" of friends where two friends belong to the same group if they have some common friend. We store which group an element belongs in with a hashmap mapping the element to its group. So, if we have\nA and B are friends\nB and C are friends\nA and E are friends\nF and G are friends\nD has no friends\nThen A,B,C,E is a group(say group 1), F,G is a group(say group 2), and we don\'t actually need to put D in a group. The purpose of the group is to see if there are other people connected to a person you\'re trying to friend who may have restrictions to you, and if D has no friends, there\'s nobody else to worry about, and hence no need for a group. So, our group map will look like:\n```\n{\nA: 1,\nB: 1,\nC: 1,\nE: 1,\nF: 2,\nG: 2\n}\n```\nNow, let\'s say B and F wanted to become friends. We would now have to merge the two groups. So, we\'d check if there are any restrictions between A/B/C/E and F, or restrictions between A/B/C/E and G. If there aren\'t any, we merge, and convert F and G to group 1. Inspired by this, we can now write an outline for our code:\n\nLoop over all friend requests. Say the current request is [A,B]\n1. If there\'s an immediate restriction(A is trying to connect with B when [A,B] is a restriction) block the FR\n2. If A and B are both not in a group, assign A and B to a new group. We can do this by keeping a group counter and increase it whenever a new group is created(so new groups are always unique). There\'s nothing requiring the groups to be continuous or anything, so when two groups merge we don\'t need to worry about updating the other group numbers or the counter.\n3. If A isn\'t in a group and B is(or vice versa), check for any restrictions between A and members of B\'s group. If there aren\'t any, add A to B\'s group\n4. If A and B are both in the same group, the request is obviously fine, nothing needs to change\n5. If A and B are both in different groups, check for any restrictions between members of A\'s group and members of B\'s group. If there aren\'t any, update everyone in the smaller group to the bigger group(smaller->bigger so less overhead)\n6. If the FR was handled fine, push "true" to the results list\n\nThis is all we need! The code implementation is below.\n\n\n\n```\n"""\nRuntime: 1304 ms, faster than 50.00% of Python online submissions for Process Restricted Friend Requests.\nMemory Usage: 12.4 MB, less than 75.00% of Python online submissions for Process Restricted Friend Requests.\n"""\n\nclass Solution(object):\n def friendRequests(self, n, restrictions, requests):\n """\n :type n: int\n :type restrictions: List[List[int]]\n :type requests: List[List[int]]\n :rtype: List[bool]\n """\n \n groupMap = {}\n groupCounter = 0\n result = []\n for req in requests:\n ans = False\n if [req[0],req[1]] not in restrictions and [req[1],req[0]] not in restrictions:\n # 1\n if req[0] not in groupMap.keys() and req[1] not in groupMap.keys():\n groupMap.update({req[0]:groupCounter})\n groupMap.update({req[1]:groupCounter})\n groupCounter += 1\n ans = True\n # 2\n elif (req[0] not in groupMap.keys() and req[1] in groupMap.keys()) or (req[1] not in groupMap.keys() and req[0] in groupMap.keys()):\n if req[1] not in groupMap.keys() and req[0] in groupMap.keys():\n req[0], req[1] = req[1], req[0]\n \n failed = False\n for rest in restrictions:\n if (rest[0] == req[0] and rest[1] in groupMap and groupMap[rest[1]] == groupMap[req[1]]) or (rest[1] == req[0] and rest[0] in groupMap and groupMap[rest[0]] == groupMap[req[1]]):\n failed = True\n break\n if failed == False:\n groupMap.update({req[0]:groupMap[req[1]]})\n ans = True\n elif req[0] in groupMap.keys() and req[1] in groupMap.keys():\n if groupMap[req[0]] == groupMap[req[1]]:\n ans = True\n else:\n g1List = [k for k,v in groupMap.items() if v == groupMap[req[0]]]\n g2List = [k for k,v in groupMap.items() if v == groupMap[req[1]]]\n failed = False\n for rest in restrictions:\n if (rest[0] in g1List and rest[1] in g2List) or (rest[1] in g1List and rest[0] in g2List):\n failed = True\n break\n if failed == False:\n ans = True\n if len(g1List) <= len(g2List):\n for k in g1List:\n groupMap.update({k:groupMap[req[1]]})\n else:\n for k in g2List:\n groupMap.update({k:groupMap[req[0]]})\n \n \n \n \n result.append(ans)\n \n return result\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
Javascript - Union Find
|
javascript-union-find-by-faustaleonardo-yc1u
|
Code\n\n/**\n * @param {number} n\n * @param {number[][]} restrictions\n * @param {number[][]} requests\n * @return {boolean[]}\n */\nvar friendRequests = funct
|
faustaleonardo
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-12T01:01:38.632350+00:00
|
2024-03-12T01:04:05.464704+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Code\n```\n/**\n * @param {number} n\n * @param {number[][]} restrictions\n * @param {number[][]} requests\n * @return {boolean[]}\n */\nvar friendRequests = function (n, restrictions, requests) {\n const ans = new Array(requests.length).fill(false);\n const dsu = new DSU(n);\n\n for (let i = 0; i < requests.length; i++) {\n const [req1, req2] = requests[i];\n const reqParent1 = dsu.find(req1);\n const reqParent2 = dsu.find(req2);\n\n let isOk = true;\n if (reqParent1 !== reqParent2) {\n for (const [res1, res2] of restrictions) {\n const resParent1 = dsu.find(res1);\n const resParent2 = dsu.find(res2);\n\n const case1 = reqParent1 === resParent1 && reqParent2 === resParent2;\n const case2 = reqParent1 === resParent2 && reqParent2 === resParent1;\n if (case1 || case2) {\n isOk = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n }\n\n if (isOk) {\n ans[i] = true;\n dsu.union(req1, req2);\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n};\n\nclass DSU {\n constructor(n) {\n this.parent = new Array(n).fill();\n for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n this.parent[i] = i;\n }\n }\n\n find(x) {\n if (this.parent[x] !== x) {\n this.parent[x] = this.find(this.parent[x]);\n }\n\n return this.parent[x];\n }\n\n union(x, y) {\n this.parent[this.find(x)] = this.parent[this.find(y)];\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Union Find', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
DSU || C++
|
dsu-c-by-lotus18-oero
|
Code\n\nclass DisjointSet \n{\npublic:\n vector<int> parent, size;\n DisjointSet(int n) \n {\n parent.resize(n);\n size.resize(n);\n
|
lotus18
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-24T11:10:32.538565+00:00
|
2024-02-24T11:10:32.538589+00:00
| 17 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass DisjointSet \n{\npublic:\n vector<int> parent, size;\n DisjointSet(int n) \n {\n parent.resize(n);\n size.resize(n);\n for(int x=0; x<n; x++) \n {\n parent[x]=x;\n size[x]=1;\n }\n }\n\n int findPar(int node) \n {\n if(node==parent[node]) return node;\n return parent[node]=findPar(parent[node]);\n }\n\n void unionn(int u, int v) \n {\n int upar=findPar(u);\n int vpar=findPar(v);\n if(upar==vpar) return;\n if(size[upar]<size[vpar]) \n {\n parent[upar]=vpar;\n size[vpar]+=size[upar];\n }\n else \n {\n parent[vpar]=upar;\n size[upar]+=size[vpar];\n }\n }\n};\nclass Solution \n{\npublic:\n vector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& restrictions, vector<vector<int>>& requests) \n {\n vector<bool> ans;\n DisjointSet ds(n);\n for(auto request: requests)\n {\n DisjointSet prev=ds;\n ds.unionn(request[0],request[1]);\n bool success=true;\n for(auto restriction: restrictions)\n {\n if(ds.findPar(restriction[0])==ds.findPar(restriction[1]))\n {\n success=false;\n break;\n }\n }\n if(success) ans.push_back(true);\n else\n {\n ds=prev;\n ans.push_back(false);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
C++ | Union Find | Simple reset approach
|
c-union-find-simple-reset-approach-by-nr-y3s3
|
Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nIf any request is causing a restriction to happen, reset disjointSet to previous state\n\n\n# Code\n
|
nroutray
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-11T07:35:32.522259+00:00
|
2024-02-11T07:35:32.522291+00:00
| 18 | false |
# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nIf any request is causing a restriction to happen, reset disjointSet to previous state\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass DisjointSet {\npublic:\n vector<int> parent, size;\n\n DisjointSet(int n) {\n parent.resize(n );\n size.resize(n );\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n parent[i] = i;\n size[i] = 1;\n }\n }\n\n int findUPar(int node) {\n if (node == parent[node])\n return node;\n return parent[node] = findUPar(parent[node]);\n }\n\n \n void unionBySize(int u, int v) {\n int ulp_u = findUPar(u);\n int ulp_v = findUPar(v);\n if (ulp_u == ulp_v) return;\n if (size[ulp_u] < size[ulp_v]) {\n parent[ulp_u] = ulp_v;\n size[ulp_v] += size[ulp_u];\n }\n else {\n parent[ulp_v] = ulp_u;\n size[ulp_u] += size[ulp_v];\n }\n }\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& rest, vector<vector<int>>& req) {\n vector<bool> ans;\n DisjointSet ds(n);\n for(int i=0;i<req.size();i++){\n int u = req[i][0];\n int v = req[i][1];\n\n DisjointSet prev=ds;\n ds.unionBySize(u,v);\n bool restricted=false;\n\n for(int j =0 ; j<rest.size();j++){\n int x=rest[j][0];\n int y=rest[j][1];\n if(ds.findUPar(x)==ds.findUPar(y)){\n restricted=true;\n break;\n }\n\n }\n\n if(restricted){\n //reset disjoint set\n ds=prev;\n ans.push_back(false);\n }else ans.push_back(true);\n\n }\n\n\n\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
[C++] Easy dfs solution
|
c-easy-dfs-solution-by-ashigup-oz4b
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
princegup678
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-30T17:41:18.909125+00:00
|
2024-01-30T17:41:18.909166+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\nvector<int> par;\n\nint find(int x){\n if(x == par[x]) return x;\n return par[x] = find(par[x]);\n}\n\nvoid merge(int x,int y){\n x = find(x);\n y = find(y);\n\n if(y>x) swap(x,y);\n\n par[x] = y;\n}\n\n vector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& restrictions, vector<vector<int>>& requests) {\n\n vector<bool> finalStatus;\n\n par.resize(n);\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n par[i] = i;\n\n\n for(auto &request:requests){\n int x = find(request[0]);\n int y = find(request[1]);\n\n bool flag = 1;\n\n for(auto &restriction:restrictions){\n int a = find(restriction[0]);\n int b = find(restriction[1]);\n\n if((a==x && y==b) || (a==y && x==b)){\n flag = 0;\n break;\n }\n }\n if(flag)\n merge(x,y);\n finalStatus.push_back(flag);\n\n }\n\n return finalStatus;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
Optimized UF. Let's learn + dry run.
|
optimized-uf-lets-learn-dry-run-by-s7w0_-dfxr
|
Intuition\nif you can see application of UF here, you are on the right track.\n> cannot become friends, either directly or indirectly through other people.\n\nT
|
s7w0_0p
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-17T13:54:58.966989+00:00
|
2024-01-17T13:54:58.967021+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\nif you can see application of UF here, you are on the right track.\n> cannot become friends, either directly or **indirectly** through other people.\n\nThe word **indirectly** basically hints to **Union Find** solution.\n\n- Groups\n- Friends\n- Restrictions\n- Queries\n\nit all should ignite the spark of Union Find in your head if you are familiar with this data structure.\n\nIf not, check some resources:\n- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/introduction-to-disjoint-set-data-structure-or-union-find-algorithm/\n- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wU6udHRIkcc&t=1210s\n\n\n# Approach\n- initially all people are by themselves\n> become direct friends for all future friend requests\n- so, traverse through requests and check if **U** can be friends with **V**. In other words check if we can **union(u, v)**\n\n# check\nWe need to check:\n- **u and v can be direct friends** (same as 2)\n- **if friend any pair from requests has formed a group that if we union(u,v) any pair from restrictions will become connected**\n\n---\n- initially U and V can be friends\n```\nlet areWeFriends = true\n```\n- find groups of **U** and **V**\n```\nconst [uRep, vRep] = [find(u), find(v)]\n```\n- traverse through all restrictions. We have to do it for each request, since ...\n\n- find groups of people from restrictions\n```\nconst [aRep, bRep] = [find(a), find(b)]\n```\n\n# walk through example\n```\nn = 5, restrictions = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3]], requests = [[0,4],[1,2],[3,1],[3,4]]\n\nDSU: {0}, {1}, {2}, {3}, {4}\n\n\n```\n```\n-------------------\n\nreq = [0, 4]\nuRep, vRep = [0, 4] -> they belong to these groups\nwhat if we connect 0 and 4?\nfind groups of all restriction pair\n-> [0, 1]: [0, 1]\n-> [1, 2]: [1, 2]\n-> [2, 3]: [2, 3]\n\nso they can become friends -> union(0, 4)\nDSU: {0, 4}, {1}, {2}, {3}\n\n-------------------\n\nreq = [1, 2]\nuRep, vRep = [1, 2] -> they belong to these groups\nwhat if we connect 1 and 2?\nwe will form: \nDSU: {0, 4}, {1, 2}, {3}\nfind groups of all restriction pair\n-> [0, 1]: [0, 1] fine\n-> [1, 2]: [1, 2] -> 1 and 2 cannot be in one group\nif we union (1, 2) -> we will create {1, 2} set -> we can\'t union\nDSU: {0, 4}, {1}, {2}, {3}\n\n-------------------\n\nreq = [3, 1]\nuRep, vRep = [3, 1] -> they belong to these groups\n\nwhat if we connect 3 and 1?\nwe will form: \nDSU: {0, 4}, {1, 3}, {2}\n\nfind groups of all restriction pair:\n\n-> [0, 1]: [0, 1] fine\n-> [1, 2]: [1, 2] fine\n-> [2, 3]: [2, 3] fine\n\nunion(3, 1)\n\nDSU: {0, 4}, {1, 3}, {2}\n\n-------------------\n\nreq = [3, 4]\nuRep, vRep = [1, 0] -> they belong to these groups, meaning\nif (1, 0) will be in the same group \n\nwhat if we connect 3 and 4?\nwe will form: \nDSU: {0, 4, 1, 3}, {2}\n\ncan we allow it?\n\nIF ANY OF THESE GROUPS CANNOT EXIST, meaning\nCONTAINS PAIR OF PEOPLE THAT CANNOT BE TOGETHER\n\nTHEN DO NOT UNION(U, V)\nELSE UNION(U, V)\n\nfind groups of all restriction pair:\n\n-> [0, 1]: [0, 1] -> we see that 0 and 1 cannot be in one group\n so do not union(3, 4)\n\nDSU: {0, 4}, {1, 3}, {2}\n\nans = [true, false, true, false]\n```\n\n```\n THANK YOU\n```\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * @param {number} n\n * @param {number[][]} restrictions\n * @param {number[][]} requests\n * @return {boolean[]}\n */\nvar friendRequests = function(n, restrictions, requests) {\n const parent = Array(n)\n const size = Array(n)\n for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n parent[i] = i\n size[i] = 1\n }\n\n const find = i => parent[i] === i ? i : find(parent[i])\n\n const union = (x, y) => {\n const [xRep, yRep] = [find(x), find(y)]\n if (xRep === yRep) return\n\n if (size[xRep] > size[yRep]) {\n parent[yRep] = xRep\n size[xRep] += size[yRep]\n }\n else if (size[yRep] > size[xRep]) {\n parent[xRep] = yRep\n size[yRep] += size[xRep]\n }\n else {\n parent[yRep] = xRep\n size[xRep]++\n }\n }\n\n const ans = []\n\n for (const [u, v] of requests) {\n let areWeFriends = true\n const [uRep, vRep] = [find(u), find(v)]\n for (const [a, b] of restrictions) {\n const [aRep, bRep] = [find(a), find(b)]\n if (\n (uRep === aRep && vRep === bRep) ||\n (uRep === bRep && vRep === aRep)\n ) \n {\n ans.push(false)\n areWeFriends = false\n break\n }\n }\n if (areWeFriends) {\n union(u, v)\n ans.push(true)\n }\n \n }\n return ans\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Union Find', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
Hash Table + Union Find | 661 ms - faster than 71.86% solutions
|
hash-table-union-find-661-ms-faster-than-jt0n
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(m \cdot\log(m) + k \cdot m \cdot \alpha(n))\n- Space complexity: O(n + m + k)\n\nwhere m = restrictions.length, k = requests.le
|
tigprog
|
NORMAL
|
2023-12-13T18:39:43.325756+00:00
|
2023-12-13T18:40:41.501547+00:00
| 28 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(m \\cdot\\log(m) + k \\cdot m \\cdot \\alpha(n))$$\n- Space complexity: $$O(n + m + k)$$\n\nwhere `m = restrictions.length, k = requests.length`,\n$\\alpha(n)$ is inverse Ackermann function ([wiki](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ackermann_function#Inverse)).\n\nBecause `n < 1000, m < 1000, k < 1000`, let `p = max(n, m, k)`.\n\n- Time complexity: $$O(p^2 \\cdot \\alpha(p))$$\n- Space complexity: $$O(p)$$\n\n# Code\n``` python3 []\nclass DJS:\n def __init__(self, n):\n self._d = list(range(n))\n \n def find(self, a):\n aa = self._d[a]\n if a == aa:\n return aa\n self._d[a] = self.find(aa)\n return self._d[a]\n\n def union(self, a, b):\n aa = self.find(a)\n bb = self.find(b)\n if aa != bb:\n self._d[aa] = bb\n\nclass Solution:\n def friendRequests(self, n: int, restrictions: List[List[int]], requests: List[List[int]]) -> List[bool]:\n pairs = defaultdict(set)\n for x, y in sorted(restrictions):\n x, y = min(x, y), max(x, y)\n pairs[x].add(y)\n \n djs = DJS(n)\n\n def check(uu, vv):\n for x, ys in pairs.items():\n xx = djs.find(x)\n if xx != uu and xx != vv:\n continue\n for y in ys: \n yy = djs.find(y)\n if yy == uu or yy == vv:\n return False\n return True\n\n result = []\n for u, v in requests: \n uu = djs.find(u)\n vv = djs.find(v)\n if uu == vv:\n result.append(True)\n continue\n \n current = check(uu, vv)\n result.append(current)\n if current:\n djs.union(uu, vv)\n \n return result\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Union Find', 'Graph', 'Python3']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
Complexity?
|
complexity-by-calex75-00sw
|
Complexity\nSomeone can help calculate the complexity of my solution?\nI think it\'s O(#reqs.#restr.log(#reqs)) but really unsure.\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {
|
calex75
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-21T21:52:13.987165+00:00
|
2023-10-21T21:52:13.987192+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Complexity\nSomeone can help calculate the complexity of my solution?\nI think it\'s O(#reqs.#restr.log(#reqs)) but really unsure.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n // 13:51 -> 14:24\n\n private int[] parents;\n\n // [[0,1]] -- [[0,2],[2,1]]\n public boolean[] friendRequests(int n, int[][] restrictions, int[][] requests) {\n parents = new int[n]; // 2 -1 -1\n Arrays.fill(parents, -1);\n int index = 0;\n boolean[] res = new boolean[requests.length];\n for (int[] request : requests) {\n int root1 = parent(request[0]); // 2\n int root2 = parent(request[1]); // 1\n\n if (root1 == root2) {\n res[index++] = true;\n } else {\n boolean canBeFriend = true;\n for (int[] restr : restrictions) {\n if ((parent(restr[0]) == root1 && parent(restr[1]) == root2)\n || (parent(restr[0]) == root2 && parent(restr[1]) == root1)) { // 1 2\n canBeFriend = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n\n if (canBeFriend) {\n parents[root1] = root2;\n }\n res[index++] = canBeFriend;\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n\n private int parent(int person) {\n int parent = parents[person];\n if (parent == -1) {\n return person;\n } else {\n return parents[person] = parent(parent);\n }\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
Time Complexity -> O(N*N) using DSU
|
time-complexity-onn-using-dsu-by-tus_tus-l2x3
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n1) Consider each person as a node of a graph and there is an unidrected edge between
|
Tus_Tus
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-05T10:28:16.404587+00:00
|
2023-10-05T10:28:16.404605+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n1) Consider each person as a node of a graph and there is an unidrected edge between two node if both are friends.\n\n2) For each request we can simply add an edge between two nodes. After connecting an edge check is there any restriction that is connected.\n\n3) If there is restriction that is connected it means that particular request is unsuccessful and if there is no restriction that is connected it means that particular request is successful.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\nclass DSU {\n\n private:\n \n int parent[1001];\n int rank[1001];\n \n public:\n \n DSU(int n) {\n \n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n parent[i] = i;\n rank[i] = 0;\n }\n\n }\n\n int ultparent(int node) {\n if(parent[node] == node) return node;\n return parent[node] = ultparent(parent[node]);\n }\n\n bool connected(int node1, int node2) {\n \n int parent1 = ultparent(node1);\n int parent2 = ultparent(node2);\n\n if(parent1 == parent2) return true;\n else return false;\n\n }\n\n void unionbyrank(int node1, int node2) {\n \n int parent1 = ultparent(node1);\n int parent2 = ultparent(node2);\n\n if(parent1 == parent2) return;\n else {\n if(rank[parent1] < rank[parent2]) {\n parent[parent1] = parent2;\n } else if(rank[parent1] > rank[parent2]) {\n parent[parent2] = parent1;\n } else {\n parent[parent1] = parent2;\n rank[parent2]++;\n }\n }\n\n }\n\n };\n \n \n\n\n\n\n vector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& res, vector<vector<int>>& req) {\n \n DSU graph(n);\n vector<bool>ans(req.size());\n\n for(int i = 0; i < req.size(); i++) {\n \n int u = req[i][0];\n int v = req[i][1];\n\n DSU dummyGraph(n);\n dummyGraph = graph;\n\n dummyGraph.unionbyrank(u, v);\n\n bool successful = true;\n\n\n for(int j = 0; j < res.size(); j++) {\n \n int a = res[j][0];\n int b = res[j][1];\n\n if(dummyGraph.connected(a, b)) {\n successful = false;\n }\n\n }\n\n if(successful) {\n ans[i] = true;\n graph.unionbyrank(u, v);\n } else {\n ans[i] = false;\n }\n\n }\n\n return ans;\n\n } \n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
96% | Best reusable DisjointSet Template | Bonus tip inside!!
|
96-best-reusable-disjointset-template-bo-ddif
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThis problem is pretty straightforwad. Basically they are saying that two people can be
|
shaw1331
|
NORMAL
|
2023-09-09T23:13:02.876226+00:00
|
2023-09-09T23:15:17.155737+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThis problem is pretty straightforwad. Basically they are saying that two people can be friends if they have no restrictions or any of their mutual friends have no restriction.\n\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nThe simplest way to solve this would be to use the union-find technique to link all the persons with mutual friends to one common ancestor. Now for every request we simply check that whether those ancestors have any restrictions or not. If they do they can\'t be friends or else they can be.\n\nPLEASE UPVOTE IF YOU FIND THIS BLOG ANY DIFF THAN OTHERS!!\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n*m)$$ -> n = restrictions.length, m = requests.length\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n \n- Space complexity:$$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int find(int node, vector<int> &par){\n if(par[node] == node){\n return node;\n }\n return par[node] = find(par[node], par);\n }\n int join(int u, int v, vector<int> &par, vector<int> &si){\n int pu = find(u, par);\n int pv = find(v, par);\n\n if(pu!=pv){\n if(si[pu]>=si[pv]){\n par[pv] = pu;\n si[pu] += si[pv];\n }\n else{\n par[pu] = pv;\n si[pv] += si[pu];\n }\n return 0;\n }\n return 1;\n }\n vector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& restrictions, vector<vector<int>>& requests) {\n vector<bool> ans;\n vector<int> par(n,-1), si(n,1);\n for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){\n par[i] = i;\n }\n\n for(auto &edge:requests){ // putting & changes 1800ms code \n int u = edge[0], v = edge[1]; // to 200 ms!!!\n int pu = find(u, par), pv = find(v, par);\n\n bool flag = true;\n\n for(auto &ed:restrictions){ // same by putting & here\n int uu = ed[0], vv = ed[1];\n int puu = find(uu, par), pvv = find(vv, par);\n if((puu==pu && pvv==pv) || (puu==pv && pvv==pu)){\n flag = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n\n if(flag) join(u,v,par,si);\n ans.push_back(flag);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
Simple DFS code
|
simple-dfs-code-by-ankitsuthar8607-3iqv
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nwe need to take care that the restriction edge\'s node should not belong from the same
|
ankitsuthar8607
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-28T04:08:05.480765+00:00
|
2023-08-28T04:08:05.480784+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nwe need to take care that the restriction edge\'s node should not belong from the same node \n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nfirst we will assign different components to each node \nas we get a request we will check that do they belong to same component or not, if they belong to different component then we will check that no nodes between these components shoudl lie in restriction edges\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n^2)$$ \n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n^2)$$ \n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n bool dfs(int val, int node,int par, vector<vector<int>>&g,set<pair<int,int>>&st){\n if(st.find({val,node})!=st.end() || st.find({node,val})!=st.end()) return 0;\n int ans=1;\n for(auto i: g[node]) if(i!=par) ans&=dfs(val,i,node,g,st);\n return ans;\n }\n\n bool check(int u,int v,int a,int b,vector<vector<int>>&g,set<pair<int,int>>&st){\n int ans=dfs(u,v,v,g,st);\n for(auto i: g[u]){\n if(i==a) continue;\n ans&=check(i,v,u,v,g,st);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\n void assign(int node,int par,int col,vector<vector<int>>&g,vector<int>&comp){\n comp[node]=col;\n for(auto child: g[node]){\n if(child!=par) assign(child,node,col,g,comp);\n }\n }\n\n vector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& restrictions, vector<vector<int>>& requests) {\n set<pair<int,int>>st;\n for(auto i : restrictions) st.insert({i[0],i[1]});\n vector<int>comp(n);\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++) comp[i]=i;\n vector<vector<int>>g(n);\n vector<bool>ans;\n for(auto i: requests){\n int u=i[0],v=i[1];\n if(st.find({u,v})!=st.end() || st.find({v,u})!=st.end()){\n ans.push_back(false);\n continue;\n }\n if(comp[u]==comp[v]){\n ans.push_back(true);\n continue;\n }\n\n if(check(u,v,u,v,g,st)){\n g[u].push_back(v);\n g[v].push_back(u);\n assign(u,v,comp[v],g,comp);\n ans.push_back(true);\n }\n else ans.push_back(false);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
✅✅ Easy C++ Solution using Disjoint Set
|
easy-c-solution-using-disjoint-set-by-ab-03h9
|
Use Disjoint Set and apply brute force .\n\n# Code\n\n\nclass DisjointSet {\n vector<int> rank, parent, size;\npublic:\n DisjointSet(int n) {\n ran
|
Abhay_sisodia
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-07T08:48:52.704427+00:00
|
2023-08-07T08:48:52.704464+00:00
| 13 | false |
Use Disjoint Set and apply brute force .\n\n# Code\n```\n\nclass DisjointSet {\n vector<int> rank, parent, size;\npublic:\n DisjointSet(int n) {\n rank.resize(n + 1, 0);\n parent.resize(n + 1);\n size.resize(n + 1);\n for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {\n parent[i] = i;\n size[i] = 1;\n }\n }\n\n int findUPar(int node) {\n if (node == parent[node])\n return node;\n return parent[node] = findUPar(parent[node]);\n }\n\n void unionByRank(int u, int v) {\n int ulp_u = findUPar(u);\n int ulp_v = findUPar(v);\n if (ulp_u == ulp_v) return;\n if (rank[ulp_u] < rank[ulp_v]) {\n parent[ulp_u] = ulp_v;\n }\n else if (rank[ulp_v] < rank[ulp_u]) {\n parent[ulp_v] = ulp_u;\n }\n else {\n parent[ulp_v] = ulp_u;\n rank[ulp_u]++;\n }\n }\n\n void unionBySize(int u, int v) {\n int ulp_u = findUPar(u);\n int ulp_v = findUPar(v);\n if (ulp_u == ulp_v) return;\n if (size[ulp_u] < size[ulp_v]) {\n parent[ulp_u] = ulp_v;\n size[ulp_v] += size[ulp_u];\n }\n else {\n parent[ulp_v] = ulp_u;\n size[ulp_u] += size[ulp_v];\n }\n }\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n bool is_valid(DisjointSet ds,int n,int u,int v,map<pair<int,int>,bool> ¬_join){\n ds.unionByRank(u,v);\n\n for(auto it:not_join){\n int u1=it.first.first;\n int v1=it.first.second;\n if(ds.findUPar(u1)==ds.findUPar(v1)){\n return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n\n vector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& restrictions, vector<vector<int>>& requests) {\n \n DisjointSet ds(n);\n vector<bool> ans;\n map<pair<int,int>,bool> not_join;\n\n for(auto it:restrictions){\n not_join[{it[0],it[1]}]=true;\n not_join[{it[1],it[0]}]=true;\n }\n\n for(auto it:requests){\n\n int u=it[0];\n int v=it[1];\n\n if(ds.findUPar(u)==ds.findUPar(v)){\n ans.push_back(true);\n continue;\n }\n else{\n\n if(is_valid(ds,n,u,v,not_join)){\n ds.unionByRank(u,v);\n ans.push_back(true);\n }\n else{\n ans.push_back(false);\n }\n\n }\n\n }\n\n return ans;\n\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
Union FInd
|
union-find-by-rajiv6-957d
|
\nclass UnionFind{\n int n;\n vector<int> parent;\n vector<int> rank;\n vector<unordered_set<int>> rest;\n \n vector<se
|
rajiv6
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-03T03:21:23.525225+00:00
|
2023-08-03T03:21:23.525257+00:00
| 1 | false |
```\nclass UnionFind{\n int n;\n vector<int> parent;\n vector<int> rank;\n vector<unordered_set<int>> rest;\n \n vector<set<int>>& adj;\n public:\n UnionFind(int _n, vector<set<int>>& _adj) : n(_n), adj(_adj), parent(vector<int>(n, 0)), rank(vector<int>(n, 1)), rest(vector<unordered_set<int>>(_n))\n {\n for(int i=0; i<_n; i++)\n {\n parent[i]=i;\n if(!adj[i].empty())\n {\n rest[i].emplace(i);\n }\n }\n }\n \n int find(int v)\n {\n if(v != parent[v])\n {\n parent[v] = find(parent[v]);\n }\n return parent[v];\n }\n \n bool add(int v, int u)\n {\n \n int pv = find(v);\n int pu = find(u);\n \n \n if(pv == pu)\n return true;\n \n for(auto itr : rest[pv])\n {\n for(auto itr1 : rest[pu])\n if(adj[itr1].count(itr))\n return false;\n }\n \n auto& rpv = rank[pv];\n auto& rpu = rank[pu];\n \n if(rpv >= rpu)\n {\n if(rpv == rpu)\n rpv++;\n parent[pu] = pv;\n rest[pv].insert(rest[pu].begin(), rest[pu].end());\n }\n else{\n parent[pv] = pu;\n rest[pu].insert(rest[pv].begin(), rest[pv].end());\n }\n find(v);find(u);\n return true;\n }\n };\n\nclass Solution {\n public:\n vector<set<int>> adj;\n \npublic:\n vector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& restrictions, vector<vector<int>>& requests) {\n adj = vector<set<int>>(n);\n for(auto r : restrictions)\n {\n adj[r[0]].emplace(r[1]);\n adj[r[1]].emplace(r[0]);\n }\n UnionFind uf(n, adj);\n vector<bool> ans(requests.size(), false);\n for(int i=0; i<requests.size(); i++)\n {\n auto ret = uf.add(requests[i][0], requests[i][1]);\n ans[i] = ret;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
DSU with Rollback
|
dsu-with-rollback-by-techbugaman-ww16
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nDSU with rollback\nbrute force according to me\n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach t
|
techbugaman
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-01T10:24:00.176835+00:00
|
2023-08-01T10:24:00.176853+00:00
| 14 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nDSU with rollback\nbrute force according to me\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\ndo union\ncheck if it violates conditions or not\nif it is then rollback\notherwise move on\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n*n*logn)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```\nclass DisjointSet {\npublic :\n vector<int> size, parent;\n stack<pair<int, int>> parentHistory, sizeHistory; // {element, currentValue of element}\n DisjointSet(int n) {\n parent.resize(n + 1);\n size.resize(n + 1, 1);\n \n for(int i = 0 ; i <= n ; i++) {\n parent[i] = i;\n }\n }\n // T.C = O(logN) as no path compression is there\n int findUltimateParent(int node) {\n if(node == parent[node]) {\n return node;\n }\n return findUltimateParent(parent[node]);\n }\n // T.C = O(logN)\n void unionBySize(int node1, int node2) {\n int ultimateParent1 = findUltimateParent(node1);\n int ultimateParent2 = findUltimateParent(node2);\n \n if(ultimateParent1 == ultimateParent2) return;\n \n if(size[ultimateParent1] > size[ultimateParent2]) {\n parentHistory.push({ultimateParent2, ultimateParent2});\n sizeHistory.push({ultimateParent1, size[ultimateParent1]});\n \n parent[ultimateParent2] = ultimateParent1;\n size[ultimateParent1] += size[ultimateParent2];\n }\n else{\n parentHistory.push({ultimateParent1, ultimateParent1});\n sizeHistory.push({ultimateParent2, size[ultimateParent2]});\n \n parent[ultimateParent1] = ultimateParent2;\n size[ultimateParent2] += size[ultimateParent1];\n }\n }\n // T.C = O(1)\n void rollback() {\n // restore the previous state of size and parent\n // if(sizeHistory.size() == 0 || parentHistory.size() == 0) return ;\n\n int node = sizeHistory.top().first;\n int previousSize = sizeHistory.top().second;\n sizeHistory.pop();\n \n size[node] = previousSize;\n \n int targetNode = parentHistory.top().first;\n int previousParent = parentHistory.top().second;\n parentHistory.pop();\n \n parent[targetNode] = previousParent;\n }\n};\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<bool> friendRequests(int n, vector<vector<int>>& restrictions, vector<vector<int>>& requests) {\n DisjointSet ds(n);\n vector<bool> ans(requests.size(), false);\n\n // Traversing requests vector\n for(int i = 0 ; i < requests.size() ; i++) {\n int node1 = requests[i][0];\n int node2 = requests[i][1];\n\n ds.unionBySize(node1, node2);\n ans[i] = true;\n\n // Traversing restrictions vector\n for(auto it : restrictions) {\n if(ds.findUltimateParent(it[0]) == ds.findUltimateParent(it[1])) {\n ds.rollback();\n ans[i] = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Stack', 'Union Find', 'Graph', 'C++']
| 0 |
process-restricted-friend-requests
|
Java 🔥 | Comments✔ | Clean Code✔ | Simple Explanation🔥✅
|
java-comments-clean-code-simple-explanat-bjkl
|
Intuition\nMake them friend first, and then check if parent of restriction node belongs to same component or not \nIf they belong to same component then revert
|
harshjaiswal9450
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-30T18:27:10.705728+00:00
|
2023-07-30T18:29:03.473974+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition\nMake them friend first, and then check if parent of restriction node belongs to same component or not \nIf they belong to same component then revert back your ans\nIf not then mark your answer as true and continue for others.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n class Disjoint{ //basic disjoint class tempelate\n int V;\n int[] parent,size;\n\n Disjoint(int V){\n this.V=V;\n parent=new int[V];\n size=new int[V];\n for(int i=0; i<V; i++){\n parent[i]=i;\n size[i]=1;\n }\n }\n\n int findParent(int x){\n if(parent[x]==x)\n return x;\n return findParent(parent[x]);\n }\n\n void unionBySize(int x,int y){\n int px=findParent(x);\n int py=findParent(y);\n\n if(px==py)return ;\n if(size[px]<size[py]){\n size[py]+=size[px];\n parent[px]=py;\n }else{\n size[px]+=size[py];\n parent[py]=px;\n }\n }\n\n\n }\n public boolean[] friendRequests(int n, int[][] rest , int[][] requests) {\n Disjoint ds=new Disjoint(n);\n boolean[] ans=new boolean[requests.length];\n Arrays.fill(ans,true);\n\n for(int i=0; i<requests.length; i++){\n int x=requests[i][0];\n int y=requests[i][1];\n\n int opx=ds.findParent(x);// old parent of x\n int opy=ds.findParent(y);// old parent of y\n\n ds.unionBySize(x,y); // make them friend irrespective of restrictions\n\n if( isRuleVoilated(rest,ds)){// now check if any restriction rule is voilated.\n ds.parent[opx]=opx; // if rule is violated then restore.\n ds.parent[opy]=opy; // parent of x and y should point them self showing they were not friend.\n ans[i]=false; // mark ans as false\n }\n\n // remember ans is filled with true. So no need to add ans[i]=true;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\n\n boolean isRuleVoilated(int[][] res,Disjoint ds){\n for(int i=0; i<res.length; i++){\n int p1=ds.findParent(res[i][0]);\n int p2=ds.findParent(res[i][1]); // if parent of both restriction node belongs to same component then notify rule is voilated \n\n if(p1==p2){\n return true;\n }\n }\n return false;\n }\n}\n```\n# Upvote button is below, don\'t mind hitting it \uD83E\uDD24\n
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
design-browser-history
|
Two Stacks, Pretty code.
|
two-stacks-pretty-code-by-interviewrecip-kbz8
|
It\u2019s not difficult to realize that we need a stack so that back can be implemented. However, what to do for forward. Because you want the ability to visit
|
interviewrecipes
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T04:07:39.140739+00:00
|
2020-08-08T05:21:08.556442+00:00
| 34,723 | false |
It\u2019s not difficult to realize that we need a stack so that `back` can be implemented. However, what to do for `forward`. Because you want the ability to visit all pages in the backward as well as the forward direction, we need to store the URLs whenever we go back. If you see the order in which we want to visit, you will quickly realize that we need two stacks. One to store history and another to store the next URLs in case we go back.\n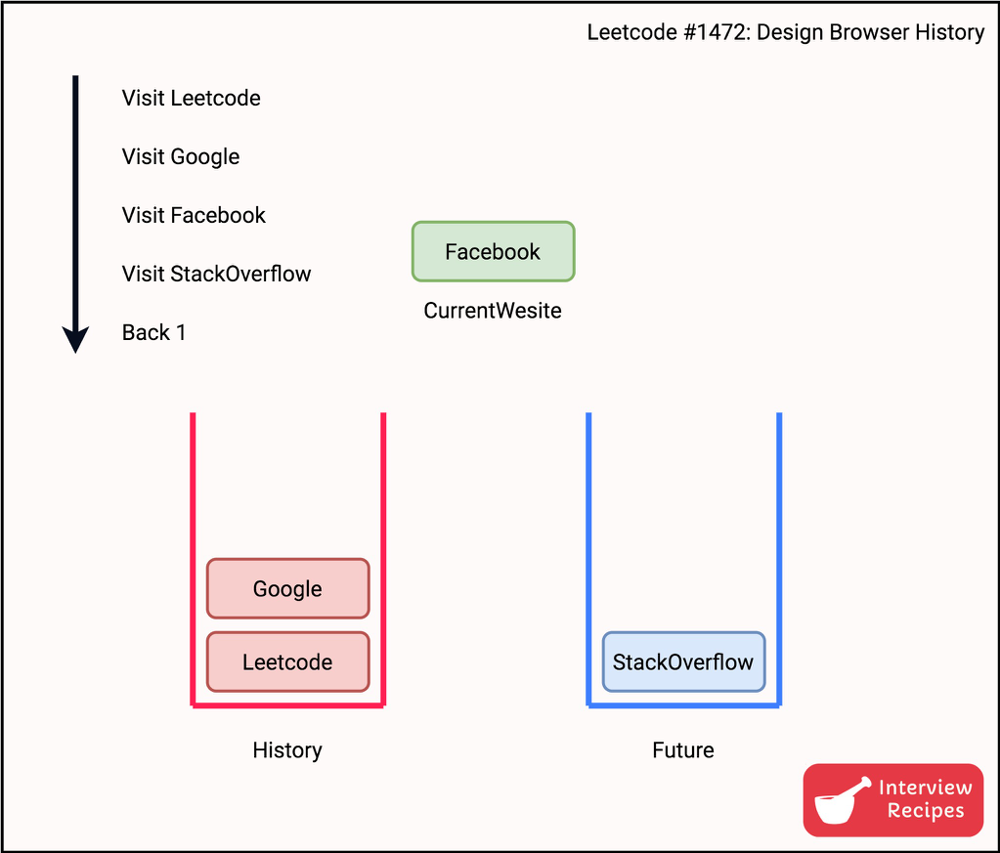\n\nTwo special cases:\nYou must always have at least one element in the history stack which is the page that you are currently at.\nBut for the forward stack, this condition is not necessary.\n\nI am sure the following code will make it even clearer.\n\n**Thanks**\nPlease upvote if you find this helpful, it encourages me to write.\n\n**More?**\nKindly visit my blog.\n\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n stack<string> history;\n stack<string> future;\n\t\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n history.push(homepage);\n future = stack<string>(); // Reset the forward stack.\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n history.push(url);\n future = stack<string>(); // Reset the forward stack.\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n while(steps > 0 && history.size() > 1) { // Always keep at least one element in the stack. \n future.push(history.top());\n history.pop();\n steps--;\n }\n return history.top();\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n while(steps > 0 && future.size() > 0) {\n history.push(future.top());\n future.pop();\n steps--;\n }\n return history.top();\n }\n};\n\n/**\n * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n * BrowserHistory* obj = new BrowserHistory(homepage);\n * obj->visit(url);\n * string param_2 = obj->back(steps);\n * string param_3 = obj->forward(steps);\n */\n```\n\n
| 412 | 9 |
['Stack']
| 25 |
design-browser-history
|
Java use dual LinkedList
|
java-use-dual-linkedlist-by-hobiter-y941
|
I cannot think of a better data structure than dual-linked list to solve this problem.\nLooks like DDL is born to solve it.\n\n\nclass BrowserHistory {\n \n
|
hobiter
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T04:02:59.203454+00:00
|
2024-01-08T08:58:38.038854+00:00
| 15,333 | false |
I cannot think of a better data structure than dual-linked list to solve this problem.\nLooks like DDL is born to solve it.\n\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\n \n public class Node{\n String url;\n Node next, prev;\n public Node(String url) {\n this.url = url;\n next = null;\n prev = null;\n }\n }\n \n Node curr;\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n curr = new Node(homepage);\n }\n \n public void visit(String url) {\n Node node = new Node(url);\n curr.next = node;\n node.prev = curr;\n curr = node;\n }\n \n public String back(int steps) {\n while (curr.prev != null && steps-- > 0) {\n curr = curr.prev;\n }\n return curr.url;\n }\n \n public String forward(int steps) {\n while (curr.next != null && steps-- > 0) {\n curr = curr.next;\n }\n return curr.url;\n }\n}\n```\nUpdate 20240108, removing unused "head", thanks to @gotit.
| 190 | 2 |
['Java']
| 24 |
design-browser-history
|
Clean Python 3, O(1) in each method with dynamic array
|
clean-python-3-o1-in-each-method-with-dy-e7d6
|
Time: O(1) for each method\nSpace: O(N), where N is the most URLs we save\n\nclass BrowserHistory:\n\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.histo
|
lenchen1112
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T04:01:41.429302+00:00
|
2020-06-07T04:31:42.712221+00:00
| 11,175 | false |
Time: `O(1)` for each method\nSpace: `O(N)`, where N is the most URLs we save\n```\nclass BrowserHistory:\n\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.history = [homepage]\n self.curr = 0\n self.bound = 0\n\n def visit(self, url: str) -> None:\n self.curr += 1\n if self.curr == len(self.history):\n self.history.append(url)\n else:\n self.history[self.curr] = url\n self.bound = self.curr\n\n def back(self, steps: int) -> str:\n self.curr = max(self.curr - steps, 0)\n return self.history[self.curr]\n\n def forward(self, steps: int) -> str:\n self.curr = min(self.curr + steps, self.bound)\n return self.history[self.curr]\n```
| 172 | 1 |
[]
| 17 |
design-browser-history
|
Two Stacks vs. List
|
two-stacks-vs-list-by-votrubac-xmye
|
Two stacks (first solution) are natural fit for this problem. It\'s easier to implement during the contest. Using a single list (second solution) is faster, but
|
votrubac
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T04:01:03.833991+00:00
|
2020-06-07T05:21:59.910601+00:00
| 20,065 | false |
Two stacks (first solution) are natural fit for this problem. It\'s easier to implement during the contest. Using a single list (second solution) is faster, but it\'s a bit trickier to maintain the current position.\n\n> One thing that is unclear is what should we do if we visit exactly the same url. In the real browser, that would not create a history item. But for this problem we are supposed to do. They should better clarify that int the description!\n\n**Two Stacks**\nThe top of the first stack is the first element in the back history. And the top of the other stack - first element of the forward history. Move urls from one stack to another as you go back and forward.\n\n```cpp\nstack<string> h_back, h_forward;\nstring cur;\nBrowserHistory(string homepage) { cur = homepage; }\nvoid visit(string url) {\n h_forward = stack<string>();\n h_back.push(cur);\n cur = url;\n}\nstring back(int steps) {\n while (--steps >= 0 && !h_back.empty()) {\n h_forward.push(cur);\n cur = h_back.top();\n h_back.pop();\n }\n return cur;\n}\nstring forward(int steps) {\n while (--steps >= 0 && !h_forward.empty()) {\n h_back.push(cur);\n cur = h_forward.top();\n h_forward.pop();\n }\n return cur;\n}\n```\n**List**\n```cpp\nvector<string> history;\nint pos = 0;\nBrowserHistory(string homepage) { history.push_back(homepage); }\nvoid visit(string url) {\n ++pos;\n history.resize(pos);\n history.push_back(url);\n}\nstring back(int steps) {\n pos = max(0, pos - steps);\n return history[pos];\n}\nstring forward(int steps) {\n pos = min((int)history.size() - 1, pos + steps);\n return history[pos];\n}\n```
| 137 | 0 |
[]
| 29 |
design-browser-history
|
[Python] Very simple solution using Double Linked List
|
python-very-simple-solution-using-double-f41v
|
\n## APPROACH : LINKED LISTS ##\n## LOGIC : GREEDY ##\n\nclass ListNode:\n def __init__(self, x):\n self.val = x\n self.next = None\n se
|
101leetcode
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T04:04:44.478687+00:00
|
2020-06-07T04:07:35.353770+00:00
| 8,088 | false |
```\n## APPROACH : LINKED LISTS ##\n## LOGIC : GREEDY ##\n\nclass ListNode:\n def __init__(self, x):\n self.val = x\n self.next = None\n self.prev = None\n \nclass BrowserHistory:\n\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.root = ListNode(homepage)\n\n def visit(self, url: str) -> None:\n node = ListNode(url)\n node.prev = self.root\n self.root.next = node\n self.root = self.root.next\n\n def back(self, steps: int) -> str:\n while(steps and self.root.prev):\n self.root = self.root.prev\n steps -= 1\n return self.root.val\n\n def forward(self, steps: int) -> str:\n while(steps and self.root.next):\n self.root = self.root.next\n steps -= 1\n return self.root.val\n\n\n# Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n# obj = BrowserHistory(homepage)\n# obj.visit(url)\n# param_2 = obj.back(steps)\n# param_3 = obj.forward(steps)\n```
| 80 | 1 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 12 |
design-browser-history
|
✅✅Python Simple Solution 🔥🔥 Easiest🔥Video
|
python-simple-solution-easiestvideo-by-c-92o9
|
Please UPVOTE \uD83D\uDC4D\n\n!! BIG ANNOUNCEMENT !!\nI am Giving away my premium content videos related to computer science and data science and also will be s
|
cohesk
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T00:13:46.408861+00:00
|
2023-03-18T04:44:17.948840+00:00
| 5,489 | false |
# Please UPVOTE \uD83D\uDC4D\n\n**!! BIG ANNOUNCEMENT !!**\nI am Giving away my premium content videos related to computer science and data science and also will be sharing well-structured assignments and study materials to clear interviews at top companies to my first 1000 Subscribers. So, **DON\'T FORGET** to Subscribe\n\nhttps://www.youtube.com/@techwired8/?sub_confirmation=1\n\n**Video in Comment section Below** \uD83D\uDC47\n\nFor Video Search \uD83D\uDC49 **"Design Browser History Tech Wired Leetcode"** on YouTube\n\n\n\n\n```\nclass BrowserHistory:\n\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.history = [homepage]\n self.current = 0\n\n def visit(self, url: str) -> None:\n self.history = self.history[:self.current+1] + [url]\n self.current += 1\n\n def back(self, steps: int) -> str:\n self.current = max(0, self.current - steps)\n return self.history[self.current]\n\n def forward(self, steps: int) -> str:\n self.current = min(len(self.history)-1, self.current + steps)\n return self.history[self.current]\n\n```\n\n\n# Please UPVOTE \uD83D\uDC4D
| 65 | 0 |
['Design', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 4 |
design-browser-history
|
Java Easy with List faster than 100%
|
java-easy-with-list-faster-than-100-by-v-i4y8
|
\nclass BrowserHistory {\n int currentIndex = 0;\n List<String> history = new ArrayList<>();\n\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n hist
|
vikrant_pc
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T04:02:40.522025+00:00
|
2020-06-08T03:08:17.284657+00:00
| 6,374 | false |
```\nclass BrowserHistory {\n int currentIndex = 0;\n List<String> history = new ArrayList<>();\n\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n history.add(homepage);\n }\n \n public void visit(String url) {\n // Clear the unwanted browser history\n history.subList(currentIndex + 1, history.size()).clear();\n history.add(url);\n currentIndex++;\n }\n \n public String back(int steps) {\n currentIndex=Math.max(currentIndex - steps, 0);\n return history.get(currentIndex);\n }\n \n public String forward(int steps) {\n currentIndex=Math.min(currentIndex + steps, history.size() - 1);\n return history.get(currentIndex);\n }\n}\n```
| 65 | 3 |
[]
| 6 |
design-browser-history
|
Clean Codes🔥🔥|| Full Explanation✅|| Doubly Linked List✅|| C++|| Java|| Python3
|
clean-codes-full-explanation-doubly-link-je0z
|
What Problem says ?\n- Create a class called BrowserHistory that keeps track of the web pages a user has visited in a web browser. \n- Also make a visit method
|
N7_BLACKHAT
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T03:06:22.389684+00:00
|
2023-03-18T03:06:22.389718+00:00
| 7,649 | false |
# What Problem says ?\n- Create a class called `BrowserHistory` that keeps track of the web pages a user has visited in a web browser. \n- Also make a `visit` method to add new pages to the `history` and `back` and `forward` methods to move the user back and forward in their browsing history. \n\n# Approach : Using Doubly Linked List\n- Define a `Node` class which represents a node in a linked list. Each node contains a URL and has references to the previous and next nodes in the list.\n- In `BrowserHistory` class ,use the Node class to implement a browser history that allows the user to navigate back and forward through visited URLs. \n- It has a constructor that takes a homepage URL, and a visit method that adds a new URL to the history by creating a new node and updating the current node\'s next reference to point to it.\n- In `back` method ,navigate backwards through the history by updating the current node\'s reference to the previous node, until the desired number of steps have been taken or there are no more previous nodes. and return the URL of the current node.\n- In `forward` method ,navigate forward through the history by updating the current node\'s reference to the next node, until the desired number of steps have been taken or there are no more next nodes and return the URL of the current node.\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Let\'s See an Example :\n```\nBrowserHistory history = new BrowserHistory("https://www.google.com");\n\n// Visit some websites\nhistory.visit("https://en.wikipedia.org");\nhistory.visit("https://www.nytimes.com");\nhistory.visit("https://www.youtube.com");\n\n// Go back to the previous website twice\nSystem.out.println(history.back(2)); // Outputs: https://en.wikipedia.org\n\n// Go forward to the next website\nSystem.out.println(history.forward(1)); // Outputs: https://www.nytimes.com\n\n// Visit a new website\nhistory.visit("https://www.reddit.com");\n\n// Go back to the previous website\nSystem.out.println(history.back(1)); // Outputs: https://www.nytimes.com\n\n\n```\n- In this example, we create a new `BrowserHistory` object with the homepage set to `https://www.google.com.` We then visit some websites and move back and forward through the history using the `back` and `forward` methods. Finally, we visit a new website and go back to the previous site again.\n# Complexity :\n- Time complexity : O(steps)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity : O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Please Upvote\uD83D\uDC4D\uD83D\uDC4D\n```\nThanks for visiting my solution.\uD83D\uDE0A\n```\n# Codes [C++ |Java |Python3] : With Comments\n```Java []\n// A class to represent a node in a linked list\nclass Node {\n // The previous and next nodes in the list\n public Node prev;\n public Node next;\n // The URL represented by this node\n public final String url;\n \n // Constructor that sets the URL for this node\n public Node(final String url) {\n this.url = url;\n }\n}\n\n// A class to represent a browser history\nclass BrowserHistory {\n // The current node in the history\n private Node curr;\n \n // Constructor that creates a new history with the given homepage\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n // Create a new node to represent the homepage\n curr = new Node(homepage);\n }\n\n // Method to add a new URL to the history\n public void visit(String url) {\n // Create a new node to represent the new URL\n curr.next = new Node(url);\n // Set the previous node for the new node to be the current node\n curr.next.prev = curr;\n // Make the new node the current node\n curr = curr.next;\n }\n\n // Method to navigate back in the history by the given number of steps\n public String back(int steps) {\n // While there are previous nodes and we haven\'t gone back enough steps yet\n while (curr.prev != null && steps-- > 0) {\n // Move back one node by setting the current node to the previous node\n curr = curr.prev;\n }\n // Return the URL represented by the current node\n return curr.url;\n }\n\n // Method to navigate forward in the history by the given number of steps\n public String forward(int steps) {\n // While there are next nodes and we haven\'t gone forward enough steps yet\n while (curr.next != null && steps-- > 0) {\n // Move forward one node by setting the current node to the next node\n curr = curr.next;\n }\n // Return the URL represented by the current node\n return curr.url;\n }\n}\n\n```\n```C++ []\n// A struct to represent a node in a doubly linked list\nstruct Node {\n // The previous and next nodes in the list\n Node* prev = nullptr;\n Node* next = nullptr;\n // The URL represented by this node\n const string url;\n\n // Constructor that sets the URL for this node\n Node(const string& url) : url(url) {}\n};\n\n// A class to represent a browser history\nclass BrowserHistory {\n public:\n // Constructor that creates a new history with the given homepage\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n // Create a new node to represent the homepage\n curr = new Node(homepage);\n }\n\n // Method to add a new URL to the history\n void visit(string url) {\n // Create a new node to represent the new URL\n curr->next = new Node(url);\n // Set the previous node for the new node to be the current node\n curr->next->prev = curr;\n // Make the new node the current node\n curr = curr->next;\n }\n\n // Method to navigate back in the history by the given number of steps\n string back(int steps) {\n // While there are previous nodes and we haven\'t gone back enough steps yet\n while (curr->prev && steps-- > 0) {\n // Move back one node by setting the current node to the previous node\n curr = curr->prev;\n }\n // Return the URL represented by the current node\n return curr->url;\n }\n\n // Method to navigate forward in the history by the given number of steps\n string forward(int steps) {\n // While there are next nodes and we haven\'t gone forward enough steps yet\n while (curr->next && steps-- > 0) {\n // Move forward one node by setting the current node to the next node\n curr = curr->next;\n }\n // Return the URL represented by the current node\n return curr->url;\n }\n\n private:\n // The current node in the history\n Node* curr = nullptr;\n};\n\n```\n```Python []\n# A class to represent a node in a doubly linked list\nclass Node:\n def __init__(self, url: str):\n # The previous and next nodes in the list\n self.prev = None\n self.next = None\n # The URL represented by this node\n self.url = url\n\n# A class to represent a browser history\nclass BrowserHistory:\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n # Create a new node to represent the homepage\n self.curr = Node(homepage)\n\n # Method to add a new URL to the history\n def visit(self, url: str) -> None:\n # Create a new node to represent the new URL\n self.curr.next = Node(url)\n # Set the previous node for the new node to be the current node\n self.curr.next.prev = self.curr\n # Make the new node the current node\n self.curr = self.curr.next\n\n # Method to navigate back in the history by the given number of steps\n def back(self, steps: int) -> str:\n # While there are previous nodes and we haven\'t gone back enough steps yet\n while self.curr.prev and steps > 0:\n # Move back one node by setting the current node to the previous node\n self.curr = self.curr.prev\n steps -= 1\n # Return the URL represented by the current node\n return self.curr.url\n\n # Method to navigate forward in the history by the given number of steps\n def forward(self, steps: int) -> str:\n # While there are next nodes and we haven\'t gone forward enough steps yet\n while self.curr.next and steps > 0:\n # Move forward one node by setting the current node to the next node\n self.curr = self.curr.next\n steps -= 1\n # Return the URL represented by the current node\n return self.curr.url\n\n```\n\n# Please Upvote\uD83D\uDC4D\uD83D\uDC4D\n\n
| 57 | 0 |
['Doubly-Linked List', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 3 |
design-browser-history
|
[C++/Python] Stack and Two Pointers (C++ can be more concise than Python!)
|
cpython-stack-and-two-pointers-c-can-be-md8rn
|
c++. The = operator in c++ returning a reference works perfectly here!.\n\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n string stack[5005];\n int p, t;\t// current p
|
wangqiuc
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T04:02:13.533659+00:00
|
2020-06-07T18:43:31.845023+00:00
| 5,575 | false |
c++. The `=` operator in c++ returning a reference works perfectly here!.\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n string stack[5005];\n int p, t;\t// current pointer, stack\'s top\n \n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n stack[p = t = 0] = homepage;\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n stack[t = ++p] = url;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n return stack[p = max(0, p-steps)];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n return stack[p = min(t, p+steps)];\n }\n};\n```\nPython\n```\nclass BrowserHistory:\n\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.stack = [""] * 5005\n self.p = self.t = 0\n self.stack[0] = homepage\n \n def visit(self, url: str) -> None:\n self.p += 1\n self.stack[self.p] = url\n self.t = self.p\n\n def back(self, steps: int) -> str:\n self.p = max(0, self.p-steps)\n return self.stack[self.p]\n \n def forward(self, steps: int) -> str:\n self.p = min(self.t, self.p + steps)\n return self.stack[self.p]\n```
| 40 | 4 |
['C']
| 5 |
design-browser-history
|
[C++] Easy to understand with explanation and a bit of advice
|
c-easy-to-understand-with-explanation-an-kw5l
|
Pls upvote if you find this helpful :)\nFirst of all if you are attempting this problem so let me tell you these kind of problems teach you a lot and have vast
|
shubhambhatt__
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T07:22:27.989475+00:00
|
2020-06-07T07:27:05.951387+00:00
| 3,673 | false |
***Pls upvote if you find this helpful :)***\nFirst of all if you are attempting this problem so let me tell you these kind of problems teach you a lot and have vast application in the industry.Try to have the essence of this question.Give your time to it if you haven\'t and then come back again.\nIf you are still reading this i assume you have given your shot to this question.\nComing to the solution,it asks you to create browser history.First of all create an array **browser**\nand an integer **pos**to keep track of position.\n**BrowserHistory**-Just push the homepage to the browser array.\n**Visit**-There are two parts of this function.If you are at any position between (0 - browser.size()-2) then increase the position and resize the array holding only elements upto the current position else if you were at the end then just add that element to the array.\n**Back**-You need to move back the given number of steps from your current position and return the corresponding element.The catch was you cannot move behind 0.Hence if your pos changes to less than 0.You make it 0 and return browser[0].\n**Forward**-Just like back ,here you cannot exceed the last element and return the last element if your pos exceeds it.\n\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n vector<string>browser;\n int pos=0;\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n browser.push_back(homepage);\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n pos++;\n if(pos<=browser.size()-1){\n browser[pos]=url;\n browser.resize(pos+1);\n }\n else browser.push_back(url); \n }\n string back(int steps) {\n pos-=steps;\n if(pos<0)pos=0;\n return browser[pos];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n pos+=steps;\n if(pos>browser.size()-1)pos=browser.size()-1;\n return browser[pos];\n }\n};\n```\nAdvice-Keep giving the contests and the changes do come .I started from doing 1 question that too in about 1:15 hours and today(7th June 2020) i completed 3 questions including this one.Just can\'t wait to complete all 4 in the upcoming contests.Pls keep up the motivation and happy coding :)
| 36 | 1 |
['C', 'C++']
| 4 |
design-browser-history
|
[Javascript] Simple Solution (LinkedList)
|
javascript-simple-solution-linkedlist-by-mzml
|
If you have basic knowledge of object. Congrat! It should be a very easy problem for you in JS!\n\nvar BrowserHistory = function(homepage) {\n this.page = {\
|
alanchanghsnu
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T04:01:36.307443+00:00
|
2020-06-07T04:05:35.585174+00:00
| 1,928 | false |
If you have basic knowledge of object. Congrat! It should be a very easy problem for you in JS!\n```\nvar BrowserHistory = function(homepage) {\n this.page = {\n url: homepage,\n back: null,\n next: null,\n };\n};\n\nBrowserHistory.prototype.visit = function(url) {\n this.page.next = {\n url,\n back: this.page,\n next: null\n };\n this.page = this.page.next;\n};\n\nBrowserHistory.prototype.back = function(steps) {\n while (this.page.back && steps) {\n this.page = this.page.back;\n steps--;\n }\n \n return this.page.url;\n};\n\nBrowserHistory.prototype.forward = function(steps) {\n while (this.page.next && steps) {\n this.page = this.page.next;\n steps--;\n }\n \n return this.page.url;\n};\n```
| 32 | 1 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
design-browser-history
|
Java HashMap.
|
java-hashmap-by-poorvank-hscy
|
\nclass BrowserHistory {\n\n Map<Integer,String> map;\n int current,max;\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n current=max=1;\n ma
|
poorvank
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-10T06:13:22.091437+00:00
|
2020-08-10T06:13:22.091469+00:00
| 1,824 | false |
```\nclass BrowserHistory {\n\n Map<Integer,String> map;\n int current,max;\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n current=max=1;\n map = new HashMap<>();\n map.put(current,homepage);\n }\n\n public void visit(String url) {\n current++;\n map.put(current,url);\n max= current;\n }\n\n public String back(int steps) {\n current = Math.max(current -steps,1);\n return map.get(current);\n }\n\n public String forward(int steps) {\n current =Math.min(current +steps,max);\n return map.get(current);\n }\n}\n```
| 26 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
design-browser-history
|
Dual Stack and DLL || Easy With Comment || Java
|
dual-stack-and-dll-easy-with-comment-jav-xv47
|
\n//APPROACH 1\n\nclass BrowserHistory \n{\n Stack<String> Hist_B;//backward history of web pages\n Stack<String> Hist_F;//forward history of web pages\n
|
swapnilGhosh
|
NORMAL
|
2021-06-24T16:39:19.034160+00:00
|
2021-06-24T18:58:58.573953+00:00
| 1,437 | false |
```\n//APPROACH 1\n\nclass BrowserHistory \n{\n Stack<String> Hist_B;//backward history of web pages\n Stack<String> Hist_F;//forward history of web pages\n \n public BrowserHistory(String homepage)\n {\n Hist_B=new Stack<String>();\n Hist_F=new Stack<String>();\n \n Hist_B.push(homepage);//homepage is pushed, it has no forward history \n }\n \n public void visit(String url) \n {\n Hist_F.clear();//forward histrory of the previous web page is cleared \n Hist_B.push(url);//forward history will be based on this current web page \n }\n \n public String back(int steps) \n {\n while(steps-->0 && Hist_B.size()>1)//at least 1 web page mus be present for whomem we are finding the forward history \n {\n Hist_F.push(Hist_B.pop());//storing the history for forward operation after\n }\n return Hist_B.peek();//this web page forward history is made \n }\n \n public String forward(int steps) \n {\n while(steps-->0 && !Hist_F.isEmpty())\n {\n Hist_B.push(Hist_F.pop());//popping from history till a particular limit \n }\n return Hist_B.peek();//and the new current web page \n }\n}//Please do vote me, It helps a lot\n```\n```\n//APPROACH 2\n\nclass Node//for the node in the DoublyLinkedList\n{\n String url;\n Node prev,next;\n Node(String url)\n {//iinitializing the data member \n prev=null;\n next=null;\n this.url=url;\n }\n }\nclass BrowserHistory \n{\n Node curr;//pointer to the current node \n public BrowserHistory(String homepage)\n {\n Node head=new Node(homepage);//innsertion of the homepage in the DLL \n curr=head;\n }\n \n public void visit(String url) \n {\n Node temp=new Node(url);//creation of node \n temp.prev=curr;//current node previous pointing to the previous node \n curr.next=temp;//pevious node pointing to the current node \n curr=curr.next;//current poining\n }\n \n public String back(int steps) \n {\n while(curr.prev != null & steps-->0)\n {\n curr=curr.prev;//moving the current pointer in the reverse direction till the limit step \n }\n return curr.url;//returning the url of the current desired page \n }\n \n public String forward(int steps) \n {\n while(curr.next !=null && steps-->0)\n {\n curr=curr.next;//moving the current pointer in the forward direction till the limit step \n }\n return curr.url;//returning the url of the current desired page\n }\n}//Please do vote me, It helps a lot\n```
| 25 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'Stack', 'Java']
| 2 |
design-browser-history
|
Two Approaches and Code | C++ | 2 Stacks | Doubly Linked List
|
two-approaches-and-code-c-2-stacks-doubl-2qhj
|
There are Two Approaches\n1) Using Two Stacks\n\tCreate two stacks history and future\n\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n stack<string> history;\n stack<
|
roughking_07
|
NORMAL
|
2021-12-23T14:36:55.988082+00:00
|
2021-12-23T14:36:55.988109+00:00
| 2,399 | false |
# There are Two Approaches\n1) **Using Two Stacks**\n\tCreate two stacks history and future\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n stack<string> history;\n stack<string> future;\n \n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n history.push(homepage);\n future = stack<string>(); //resets stack\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n history.push(url);\n future = stack<string>();\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n while(steps>0 && history.size() > 1){\n future.push(history.top());\n history.pop();\n steps--;\n }\n return history.top();\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n while(steps>0 && future.size()>0){\n history.push(future.top());\n future.pop();\n steps--;\n }\n return history.top();\n }\n};\n```\n**2) Using Doubly Linked List as a data structure**\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n class Node{\n public:\n string url;\n Node* next;\n Node* prev;\n \n Node(string url){\n this->url =url;\n next = NULL;\n prev = NULL;\n }\n };\n Node* curr;\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n curr = new Node(homepage);\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n Node* temp = new Node(url);\n curr->next = temp;\n temp->prev = curr;\n curr = curr->next;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n while(curr->prev!=nullptr && steps-- >0){\n curr = curr->prev;\n }\n return curr->url;\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n while(curr->next!=nullptr && steps-- >0){\n curr = curr->next;\n }\n return curr->url;\n }\n};\n```\n*Pls upvote if you like the post!!! *
| 23 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'Stack', 'C', 'C++']
| 2 |
design-browser-history
|
✔ C++ || 95% faster, 99% less memory || very easy solution with a small array || explained
|
c-95-faster-99-less-memory-very-easy-sol-4xgg
|
we only need to keep track, curr page and curr size\n1. count-> current page\n2. curr -> current size of the array\n\n int count=0,curr=0;\n string v[110];\n
|
aynburnt
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-28T08:13:07.916178+00:00
|
2021-05-28T08:13:07.916210+00:00
| 1,060 | false |
we only need to keep track, curr page and curr size\n1. count-> current page\n2. curr -> current size of the array\n```\n int count=0,curr=0;\n string v[110];\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n v[count]=homepage;\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n v[++count]=url;\n curr=count;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n count = max(count-steps, 0);\n return v[count];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n count = min(curr, count+steps);\n return v[count];\n }\n```\n# if you find it helpful, plz upvote
| 17 | 1 |
['C']
| 3 |
design-browser-history
|
Java solution using hashmap - O(1) operation
|
java-solution-using-hashmap-o1-operation-pkov
|
\nclass BrowserHistory {\n\n int max = 0;\n int current = 0;\n HashMap<Integer, String> urlMap = new HashMap<>();\n public BrowserHistory(String hom
|
nir16r
|
NORMAL
|
2021-01-16T13:55:03.349132+00:00
|
2021-01-16T13:55:03.349173+00:00
| 1,640 | false |
```\nclass BrowserHistory {\n\n int max = 0;\n int current = 0;\n HashMap<Integer, String> urlMap = new HashMap<>();\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n urlMap.put(current, homepage);\n }\n \n public void visit(String url) {\n current++;\n urlMap.put(current, url);\n max = current;\n }\n \n public String back(int steps) {\n current = Math.max(0, current-steps);\n return urlMap.get(current);\n }\n \n public String forward(int steps) {\n current = Math.min(max, current+steps);\n return urlMap.get(current);\n }\n}\n```
| 16 | 0 |
['Java']
| 3 |
design-browser-history
|
[Java/Python 3] Use List and two pointers
|
javapython-3-use-list-and-two-pointers-b-5t23
|
Use List to store history; Use cur and end to record the current and the end of history indices. -- credit to @fighting_for_flag.\n\njava\n private List<Str
|
rock
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T04:02:33.170918+00:00
|
2020-06-13T06:13:52.131235+00:00
| 1,543 | false |
Use `List` to store history; Use `cur` and `end` to record the current and the end of history indices. -- credit to **@fighting_for_flag**.\n\n```java\n private List<String> history = new ArrayList<>();\n private int cur, end;\n \n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n history.add(homepage);\n }\n \n public void visit(String url) {\n if (++cur < history.size()) {\n history.set(cur, url);\n }else {\n history.add(url);\n }\n end = cur;\n }\n \n public String back(int steps) {\n cur = Math.max(0, cur - steps);\n return history.get(cur);\n }\n \n public String forward(int steps) {\n cur = Math.min(end, cur + steps);\n return history.get(cur);\n }\n```\n```python\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.history = [homepage]\n self.cur = self.end = 0\n def visit(self, url: str) -> None:\n self.cur += 1\n if self.cur < len(self.history):\n self.history[self.cur] = url\n else:\n self.history.append(url)\n self.end = self.cur\n \n def back(self, steps: int) -> str:\n self.cur = max(0, self.cur - steps)\n return self.history[self.cur] \n\n def forward(self, steps: int) -> str:\n self.cur = min(self.end, self.cur + steps)\n return self.history[self.cur]\n```
| 16 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
design-browser-history
|
c++|| beat 100% || intuition + approch || easy || vector
|
c-beat-100-intuition-approch-easy-vector-svjy
|
Intuition\nWe have perform simple task of return some index value (string) of some data structure in call of back and forword.\n\n=>> simplest way to return val
|
amankatiyar783597
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T03:59:24.052333+00:00
|
2023-03-18T04:19:45.993171+00:00
| 4,926 | false |
# Intuition\nWe have perform simple task of return some index value (string) of some data structure in call of back and forword.\n\n=>> simplest way to return value of any index in most efficiet manner\n can be done in vector if we have known of index.\n\n=>> In visit we need to remove some element from last , that also can be done in vector easly.\n\n=>> from above observation we came to use vector as our data structure.\n\n# Approach\n=>> While moving forword or back we just need to , are we not going out of index ,\n **if we going out of index.....**\n\n=>> In case of **back** we have to stop on index no 0 , set index =0\n\n=>> In case of **forword** , we have stop on size of vector , set index = vector.size()-1.\n\n=>> In case of **visit** , we hace to pop out all the element having index greater than or equal to our current index, At which pointing.\n\n**IF YOU READ IT LET ME KNOW BY UP VOTE IT !!**\n\n***GOT THE INTUITION AND APPROCH ? UPVOTE : IGNORE.***\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n=>> For back = O(1)\n=>> for forword O(1)\n=>> visit O(n) in worse case.\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n) Need to store data atlest. ( mota moti space complexcity)\n\n# Code\n```\n#define pb push_back\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n int ele;\n vector<string> vc;\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n vc.pb(homepage);\n ele =0;\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n int l = vc.size()-1;\n while(l>ele){\n vc.pop_back();\n l--;\n }\n ele++;\n vc.pb(url);\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n ele-=steps;\n if(ele<0) ele=0;\n return vc[ele];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n ele +=steps;\n if(ele>=vc.size()) ele = vc.size()-1;\n return vc[ele];\n }\n};\n\n/**\n * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n * BrowserHistory* obj = new BrowserHistory(homepage);\n * obj->visit(url);\n * string param_2 = obj->back(steps);\n * string param_3 = obj->forward(steps);\n */\n```
| 15 | 1 |
['C++']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
Clean Codes🔥🔥|| Full Explanation✅|| Stack Method✅|| C++|| Java|| Python3
|
clean-codes-full-explanation-stack-metho-lv5m
|
What Problem says ?\n- Create a class called BrowserHistory that keeps track of the web pages a user has visited in a web browser. \n- Also make a visit method
|
N7_BLACKHAT
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T02:46:06.719653+00:00
|
2023-03-18T02:46:06.719681+00:00
| 2,596 | false |
# What Problem says ?\n- Create a class called `BrowserHistory` that keeps track of the web pages a user has visited in a web browser. \n- Also make a `visit` method to add new pages to the `history` and `back` and `forward` methods to move the user back and forward in their browsing history. \n\n# Approach : Using Stacks\n- Here we are using two stacks: \n 1. `history` to keep track of the pages visited in the past, and \n 2. `future` to keep track of the pages that the user has "visited" in the future (i.e., after clicking the back button). \n- When the user clicks the `back` button, the `back` method pops URLs from the `history` stack and pushes them onto the `future` stack until it reaches the desired page. \n- When the user clicks the `forward` button, the `forward` method pops URLs from the `future` stack and pushes them onto the `history` stack until it reaches the desired page.\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Let\'s See an Example :\n```\nBrowserHistory history = new BrowserHistory("https://www.google.com");\n\n// User visits a few pages\nhistory.visit("https://www.google.com/search?q=java");\nhistory.visit("https://www.wikipedia.org/");\nhistory.visit("https://www.amazon.com/");\n\n// User clicks back button once\nString previousPage = history.back(1);\nSystem.out.println("User is now on page: " + previousPage);\n\n// User clicks forward button twice\nString nextPage = history.forward(2);\nSystem.out.println("User is now on page: " + nextPage);\n\n```\n- In this example, we create a new `BrowserHistory` object with the starting page of `https://www.google.com.` The user then visits three more pages by calling the visit method with the URLs of the pages.\n- Afterwards, the user clicks the `back` button once by calling `back(1)`, which pops one page from the `history` stack and pushes it onto the `future` stack. \n- The `back` method returns the current page URL after the navigation is complete, which we store in the `previousPage` variable and print out to the console.\n- Finally, the user clicks the `forward` button twice by calling `forward(2)`, which pops two pages from the `future` stack and pushes them onto the `history` stack. \n- The `forward` method also returns the current page URL after the navigation is complete, which we store in the `nextPage` variable and print out to the console.\n# Complexity :\n- Time complexity : O(steps)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity : O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Please Upvote\uD83D\uDC4D\uD83D\uDC4D\n```\nThanks for visiting my solution.\uD83D\uDE0A\n```\n# Codes [C++ |Java |Python3] : With Comments\n```Java []\nclass BrowserHistory {\n private Deque<String> history = new ArrayDeque<>(); // Stack to store past pages\n private Deque<String> future; // Stack to store future pages\n\n // Constructor that takes the starting page URL and adds it to the history\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n visit(homepage);\n }\n\n // Adds a new page to the history and clears the future stack\n public void visit(String url) {\n history.push(url);\n future = new ArrayDeque<>();\n }\n\n // Moves the user back a certain number of pages in the history\n public String back(int steps) {\n while (history.size() > 1 && steps-- > 0)\n future.push(history.pop()); // Move pages from history to future stack\n return history.peek(); // Return the current page after navigation\n }\n\n // Moves the user forward a certain number of pages in the future\n public String forward(int steps) {\n while (!future.isEmpty() && steps-- > 0)\n history.push(future.pop()); // Move pages from future to history stack\n return history.peek(); // Return the current page after navigation\n }\n}\n\n```\n```C++ []\nclass BrowserHistory {\n private:\n stack<string> history; // Stack to store past pages\n stack<string> future; // Stack to store future pages\n public:\n // Constructor that takes the starting page URL and adds it to the history\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n visit(homepage);\n }\n\n // Adds a new page to the history and clears the future stack\n void visit(string url) {\n history.push(url);\n future = stack<string>(); // Clear the future stack\n }\n\n // Moves the user back a certain number of pages in the history\n string back(int steps) {\n while (history.size() > 1 && steps-- > 0)\n future.push(history.top()), history.pop(); // Move pages from history to future stack\n return history.top(); // Return the current page after navigation\n }\n\n // Moves the user forward a certain number of pages in the future\n string forward(int steps) {\n while (!future.empty() && steps-- > 0)\n history.push(future.top()), future.pop(); // Move pages from future to history stack\n return history.top(); // Return the current page after navigation\n }\n};\n```\n```Python []\nclass BrowserHistory:\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.history = [] # Create an empty list to store the browsing history\n self.visit(homepage) # Add the starting URL to the history list\n\n def visit(self, url: str) -> None:\n self.history.append(url) # Add the new URL to the history list\n self.future = [] # Create an empty list to store future pages\n\n def back(self, steps: int) -> str:\n while len(self.history) > 1 and steps > 0:\n # Move pages from the history list to the future list\n self.future.append(self.history.pop())\n steps -= 1\n # Return the current page after navigation\n return self.history[-1]\n\n def forward(self, steps: int) -> str:\n while self.future and steps > 0:\n # Move pages from the future list to the history list\n self.history.append(self.future.pop())\n steps -= 1\n # Return the current page after navigation\n return self.history[-1]\n\n```\n# Please Upvote\uD83D\uDC4D\uD83D\uDC4D\n\n
| 14 | 0 |
['Stack', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
Python | Two Stacks Solution | Easy to Understand
|
python-two-stacks-solution-easy-to-under-5fs0
|
\nclass BrowserHistory:\n \n \'\'\'\n We use two stacks here because anytime we\'ll need to go forward or backward to the \n most recent page we wer
|
frenzyboi
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-08T00:34:43.622532+00:00
|
2021-11-08T00:35:11.916764+00:00
| 1,059 | false |
```\nclass BrowserHistory:\n \n \'\'\'\n We use two stacks here because anytime we\'ll need to go forward or backward to the \n most recent page we were at. A Stack helps us accomplish exactly that\n \n Eg: We are at "YouTube" -> We then visit "Facebook" -> We then visit "Google"\n At this point our prevStack = ["YouTube", "Facebook"]\n If we called back(1), we need to go to Facebook (which was the most recent before Google)\n - We need to go back to Facebook (top of our prevStack rn)\n - But we need to add our curPage to the forward stack because I called forward(1) after this operation, I would need to go back to Google\n \n You should be able to do the same analysis for forward(steps) \n \n This should help you see the intuition behind using 2 stacks and the general logic\n \'\'\'\n\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.curPage = homepage # We keep track of the page we are currently on\n self.prevStack = [] # We keep track of the pages if we were to go back \n self.forwardStack = [] # We keep track of the pages if we were to go forward\n\n def visit(self, url: str) -> None:\n \'\'\'\n Step 1: Since we\'re visiting a new page from curPage (our current page/url), if we go back, we need to go back to curPage first, hence add curPage to the top of prevStack\n \n Step 2: Reset forwardStack as mentioned in question\n \n Step 3: Now we need to make sure we update our current page correctly\n \'\'\'\n \n \n self.prevStack.append(self.curPage) # Step 1\n self.forwardStack = [] # Step 2\n self.curPage = url # Step 3\n \n\n def back(self, steps: int) -> str:\n \n \'\'\'\n \n Algorithm: \n Step 0. Keep repeating until we still have to go back\n Step 1. If we\'re going to go back from our curPage to page X, if we go forward from page X, we need to land at curPage, so add it to the forwardStack\n Step 2. We need to go back now so update the curPage as needed and remove it from the prevStack\n Step 3. We went back one more step at this point, so decrement possible by 1\n \n \'\'\'\n \n possible = min(steps, len(self.prevStack)) # In order to hamdle cases where steps > len(self.prevStack) ,we take the minimum of the two at all times\n \n while possible: # Step 0\n self.forwardStack.append(self.curPage) # Step 1\n self.curPage = self.prevStack.pop() # Step 2\n possible -= 1 # Step 3 \n \n \n return self.curPage # We need to return the page we\'re at currently\n \n\n def forward(self, steps: int) -> str:\n \n \'\'\'\n \n Algorithm: \n Step 0. Keep repeating until we still have to go forward\n Step 1. If we\'re going to go forward from our curPage to page X, if we go backward from page X, we need to land at curPage, so add it to our prevStack\n Step 2. We need to go forward now so update the curPage as needed and remove it from the forwardStack\n Step 3. We went forward one more step at this point, so decrement possible by 1\n \n \'\'\'\n \n possible = min(steps, len(self.forwardStack)) # In order to hamdle cases where steps > len(self.forwardStack) ,we take the minimum of the two at all times\n \n while possible: # Step 0\n self.prevStack.append(self.curPage) # Step 1\n self.curPage = self.forwardStack.pop() # Step 2\n possible -= 1 # Step 3\n \n return self.curPage # We need to return the page we\'re at currently\n```\n \n\nI\'ve put in comments in my code so I hope that helps with understanding the code :))\n\n
| 14 | 0 |
['Python']
| 3 |
design-browser-history
|
Py3 Easy Sol: 1 Stack only, faster than 90%
|
py3-easy-sol-1-stack-only-faster-than-90-xgxh
|
\nclass BrowserHistory:\n\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.history = [homepage]\n self.index = 0\n\n\n def visit(self, url: str)
|
ycverma005
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-13T10:09:45.710126+00:00
|
2020-06-13T10:09:45.710174+00:00
| 1,001 | false |
```\nclass BrowserHistory:\n\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.history = [homepage]\n self.index = 0\n\n\n def visit(self, url: str) -> None:\n while len(self.history) > self.index + 1:\n self.history.pop()\n self.history.append(url)\n self.index += 1\n\n\n def back(self, steps: int) -> str:\n self.index = max(0, self.index - steps)\n return self.history[self.index]\n\n\n def forward(self, steps: int) -> str:\n self.index = min(len(self.history)-1, self.index + steps)\n return self.index\n```
| 11 | 0 |
['Stack', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 2 |
design-browser-history
|
Javascript One Array Solution
|
javascript-one-array-solution-by-serious-hfh6
|
\nvar BrowserHistory = function(homepage) {\n this.cur = 1;\n this.history = [homepage];\n};\n\n/** \n * @param {string} url\n * @return {void}\n */\nBrow
|
seriously_ridhi
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T04:57:54.751563+00:00
|
2020-06-07T04:57:54.751612+00:00
| 1,421 | false |
```\nvar BrowserHistory = function(homepage) {\n this.cur = 1;\n this.history = [homepage];\n};\n\n/** \n * @param {string} url\n * @return {void}\n */\nBrowserHistory.prototype.visit = function(url) {\n if(this.cur !== this.history.length){\n this.history = this.history.slice(0,this.cur);\n }\n this.cur++;\n this.history.push(url);\n};\n\n/** \n * @param {number} steps\n * @return {string}\n */\nBrowserHistory.prototype.back = function(steps) {\n if(this.cur-steps-1 < 0){\n this.cur = 1;\n }else{\n this.cur = this.cur - steps;\n }\n return this.history[this.cur-1];\n};\n\n/** \n * @param {number} steps\n * @return {string}\n */\nBrowserHistory.prototype.forward = function(steps) {\n if(this.cur+steps>this.history.length){\n this.cur = this.history.length\n }else{\n this.cur = this.cur+steps\n }\n return this.history[this.cur-1];\n};\n```
| 11 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
design-browser-history
|
[Python] Solution with explanation,100% faster runtime, 100% less memory usage
|
python-solution-with-explanation100-fast-e0y0
|
\n\nclass BrowserHistory:\n\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.arr = [homepage]\n self.frwd = 0 # number of urls which will be displa
|
it_bilim
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T09:10:53.799929+00:00
|
2021-06-21T09:33:11.718971+00:00
| 2,225 | false |
\n```\nclass BrowserHistory:\n\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.arr = [homepage]\n self.frwd = 0 # number of urls which will be displayed after passing forward\n self.cur = 0 # current displayed url\'s index\n\n def visit(self, url: str) -> None:\n self.arr = self.arr[:self.cur+1] # previous history(urls which will be displayed after forward) will be deleted\n self.arr.append(url)\n self.frwd = 0 # there is no forward history and set to 0\n self.cur += 1 # current index is increased\n \n\n def back(self, n: int) -> str:\n if n <= self.cur: # switch to the page which is n steps back \n self.cur -= n \n self.frwd += n\n\t else: # switch to home page when n is greater than possible back steps\n self.cur = 0 # current index is set to homepage\n self.frwd = len(self.s)-1 # the number of remaining pages for which there is access to the switch\n return self.arr[self.cur] # returns the current page\n\n def forward(self, n: int) -> str:\n if n <=self.frwd: # switch to the page which is n steps forward \n self.frwd -= n \n self.cur += n \n else: # switch to the last page when n is greater than possible forward steps\n self.cur = len(self.s)-1 # current index is set to last page\'s index\n self.frwd = 0 # there is no else forward page\n return self.arr[self.cur] # returns the current page\n\n\n\n```
| 10 | 4 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 3 |
design-browser-history
|
Day 77 || O(1) time for Visit, Back and Forward || Easiest Beginner Friendly Sol
|
day-77-o1-time-for-visit-back-and-forwar-my03
|
NOTE - PLEASE READ INTUITION AND APPROACH FIRST THEN SEE THE CODE. YOU WILL DEFINITELY UNDERSTAND THE CODE LINE BY LINE AFTER SEEING THE APPROACH.\n\n# Intuitio
|
singhabhinash
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T03:18:58.369063+00:00
|
2023-03-18T03:18:58.369112+00:00
| 2,023 | false |
**NOTE - PLEASE READ INTUITION AND APPROACH FIRST THEN SEE THE CODE. YOU WILL DEFINITELY UNDERSTAND THE CODE LINE BY LINE AFTER SEEING THE APPROACH.**\n\n# Intuition of this Problem :\nThis code implements the BrowserHistory class which allows the user to visit URLs and navigate between them using back and forward methods. The class stores the history of visited URLs in a vector called URLsHistory.\n\nWhen a new URL is visited, it is added to the URLsHistory vector, and the current URL index currURL is updated to point to the latest URL. If the user navigates backward or forward, the currURL is updated accordingly to the desired index.\n\nThe back and forward methods simply update the currURL index by a certain number of steps, making sure not to exceed the boundaries of the URLsHistory vector. Then they return the URL at the new currURL index.\n\n**By avoiding the use of the erase function, the code achieves a time complexity of O(1) for the visit, forward methods and back method. This is an improvement over the O(n) time complexity achieved when using the erase function.**\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach for this Problem :\n1. Create a class called BrowserHistory.\n2. Define a vector of strings named URLsHistory, and two integers currURL and lastURL.\n3. Define the constructor of the class, which takes a string named homepage as an argument.\n4. Inside the constructor, push homepage string to the URLsHistory vector, set currURL and lastURL to 0.\n5. Define the visit function which takes a string named url as an argument.\n6. Inside the visit function, increment currURL by 1.\n7. If the size of URLsHistory is greater than currURL, set URLsHistory[currURL] to url.\n8. If the size of URLsHistory is not greater than currURL, push url to the end of URLsHistory.\n9. Set lastURL to currURL.\n10. Define the back function which takes an integer named steps as an argument.\n11. Inside the back function, set currURL to the maximum value of 0 and currURL - steps.\n12. Return URLsHistory[currURL].\n13. Define the forward function which takes an integer named steps as an argument.\n14. Inside the forward function, set currURL to the minimum value of lastURL and currURL + steps.\n15. Return URLsHistory[currURL].\n16. The main program instantiates the BrowserHistory class, calls its visit, back, and forward functions as required.\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Code :\n```C++ []\n//By avoiding the use of the erase function, the code achieves a time\n//complexity of O(1) for the visit, forward methods and back method.\n//This is an improvement over the O(n) time complexity achieved when\n//using the erase function.\n\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n vector<string> URLsHistory;\n int currURL, lastURL;\n \n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n URLsHistory.push_back(homepage);\n currURL = 0;\n lastURL = 0;\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n currURL++;\n if (URLsHistory.size() > currURL) {\n // We have enough space in our array to overwrite an old \'url\' entry with new one. \n URLsHistory[currURL] = url;\n }\n else {\n // We have to insert a new \'url\' entry at the end.\n URLsHistory.push_back(url);\n }\n // Now this will be out last url \n lastURL = currURL;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n // move currURL to the leftmost place\n currURL = max(0, currURL - steps);\n return URLsHistory[currURL];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n // move currURL to the rightmost place\n currURL = min(lastURL, currURL + steps);\n return URLsHistory[currURL];\n }\n};\n\n/**\n * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n * BrowserHistory* obj = new BrowserHistory(homepage);\n * obj->visit(url);\n * string param_2 = obj->back(steps);\n * string param_3 = obj->forward(steps);\n */\n```\n```C++ []\n// using erase function which takes O(n) time for visit which is costly.\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n vector<string> history;\n int currIndex;\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n history.push_back(homepage);\n currIndex = 0;\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n // clear forward history\n history.erase(history.begin() + currIndex + 1, history.end());\n // add new url to history\n history.push_back(url);\n currIndex++;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n currIndex = max(0, currIndex - steps);\n return history[currIndex];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n currIndex = min((int)history.size() - 1, currIndex + steps);\n return history[currIndex];\n }\n};\n\n```\n```Java []\nclass BrowserHistory {\n private List<String> URLsHistory;\n private int currURL;\n private int lastURL;\n \n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n URLsHistory = new ArrayList<>();\n URLsHistory.add(homepage);\n currURL = 0;\n lastURL = 0;\n }\n \n public void visit(String url) {\n currURL++;\n if (URLsHistory.size() > currURL) {\n URLsHistory.set(currURL, url);\n }\n else {\n URLsHistory.add(url);\n }\n lastURL = currURL;\n }\n \n public String back(int steps) {\n currURL = Math.max(0, currURL - steps);\n return URLsHistory.get(currURL);\n }\n \n public String forward(int steps) {\n currURL = Math.min(lastURL, currURL + steps);\n return URLsHistory.get(currURL);\n }\n}\n```\n```Python []\nclass BrowserHistory:\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.URLsHistory = [homepage]\n self.currURL = 0\n self.lastURL = 0\n \n def visit(self, url: str) -> None:\n self.currURL += 1\n if len(self.URLsHistory) > self.currURL:\n self.URLsHistory[self.currURL] = url\n else:\n self.URLsHistory.append(url)\n self.lastURL = self.currURL\n \n def back(self, steps: int) -> str:\n self.currURL = max(0, self.currURL - steps)\n return self.URLsHistory[self.currURL]\n \n def forward(self, steps: int) -> str:\n self.currURL = min(self.lastURL, self.currURL + steps)\n return self.URLsHistory[self.currURL]\n```\n\n# Time Complexity and Space Complexity:\n- Time complexity : \n**Time complexity of O(1) for the visit, forward methods and back method.**\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity : \n**Overall space complexity is O(n).**\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
| 9 | 0 |
['Array', 'Design', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 1 |
design-browser-history
|
[JavaScript] O(1) Time For All 3 Operations
|
javascript-o1-time-for-all-3-operations-7jglm
|
Time: O(1)\nSpace: O(N)\njavascript\nclass BrowserHistory {\n \n constructor(homepage) {\n this.history = [homepage];\n this.curr = 0;\n
|
control_the_narrative
|
NORMAL
|
2021-04-28T00:53:55.988517+00:00
|
2021-04-28T00:53:55.988546+00:00
| 827 | false |
Time: `O(1)`\nSpace: `O(N)`\n```javascript\nclass BrowserHistory {\n \n constructor(homepage) {\n this.history = [homepage];\n this.curr = 0;\n this.limit = 0;\n }\n \n visit(url) {\n this.curr++;\n if(this.curr == this.history.length) this.history.push(url);\n else this.history[this.curr] = url;\n this.limit = this.curr;\n }\n \n back(steps) {\n this.curr = Math.max(0, this.curr-steps);\n return this.history[this.curr];\n }\n \n forward(steps) {\n this.curr = Math.min(this.limit, this.curr+steps);\n return this.history[this.curr];\n }\n}\n```
| 9 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
design-browser-history
|
Java Node with two pointers (aka doubly LinkedList) faster than 97%
|
java-node-with-two-pointers-aka-doubly-l-oysc
|
\nclass BrowserHistory {\n \n class Node {\n Node forward;\n Node backward; \n String page; \n \n public Node(String pa
|
likeabbas
|
NORMAL
|
2021-02-20T21:27:58.428590+00:00
|
2021-03-14T19:42:39.811814+00:00
| 912 | false |
```\nclass BrowserHistory {\n \n class Node {\n Node forward;\n Node backward; \n String page; \n \n public Node(String page, Node backward) {\n this.page = page;\n this.backward = backward;\n forward = null;\n }\n }\n \n Node cur;\n\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n cur = new Node(homepage, null); \n }\n \n public void visit(String url) {\n\t\tif (cur.forward != null)\n\t\t\tcur.forward.backward = null; \n cur = (cur.forward = new Node(url, cur));\n }\n \n public String back(int steps) {\n while (steps-- > 0 && cur.backward != null)\n cur = cur.backward;\n return cur.page;\n }\n \n public String forward(int steps) {\n while (steps-- > 0 && cur.forward != null)\n cur = cur.forward;\n return cur.page;\n }\n}\n```
| 9 | 0 |
['Java']
| 2 |
design-browser-history
|
C++✅✅ | Using Vectors🆗 | Beginner Friendly Approach🔥 | Clean Code |
|
c-using-vectorsok-beginner-friendly-appr-mpre
|
PLEASE DO UPVOTE!!!!!!\n\n# Code\n\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n\nvector<string>v;\nint curr, cnt = 0;\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n \n
|
mr_kamran
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T03:54:34.168244+00:00
|
2023-03-18T03:54:34.168288+00:00
| 664 | false |
# PLEASE DO UPVOTE!!!!!!\n\n# Code\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n\nvector<string>v;\nint curr, cnt = 0;\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n \n v.push_back(homepage);\n curr = 0;\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n \n curr++;\n v.resize(curr);\n v.push_back(url); \n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n \n curr = max(0, curr - steps);\n return v[curr];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n int n = v.size();\n curr = min(n-1, curr+steps);\n\n return v[curr];\n }\n};\n\n```
| 8 | 3 |
['C++']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
C++ | Doubly Linked List | Easy-to-understand | 100ms
|
c-doubly-linked-list-easy-to-understand-3aqp1
|
\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n list<string> historyPages; // the pages that are present in my browser history\n list<string> :: iterator it;\n Br
|
damian_arado
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-12T08:53:20.675887+00:00
|
2022-04-12T17:20:29.482736+00:00
| 536 | false |
```\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n list<string> historyPages; // the pages that are present in my browser history\n list<string> :: iterator it;\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n historyPages.emplace_back(homepage);\n it = historyPages.begin();\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n auto del = it; \n del++; // delete the history: (here, last]\n historyPages.erase(del, historyPages.end()); \n historyPages.emplace_back(url); // add a new page after here\n it++; \n }\n \n string back(int steps) { // at most we can reach start of list\n while(it != historyPages.begin() && steps--) it--;\n return *it; // return value by dereferencing the pointer/iterator\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) { // at most we can reach the end of list\n while(it != (--historyPages.end()) && steps--) it++;\n return *it;\n }\n};\n```\n\nAn upvote would be appreciated. ^_^
| 8 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
JavaScript two stacks easy to understand
|
javascript-two-stacks-easy-to-understand-vhca
|
\nclass BrowserHistory {\n constructor(homepage) {\n this.backArr = [homepage];\n this.forwardArr = [];\n }\n visit(url) {\n this.
|
ChaoWan_2021
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-09T20:57:31.243791+00:00
|
2020-06-09T20:57:31.243839+00:00
| 596 | false |
```\nclass BrowserHistory {\n constructor(homepage) {\n this.backArr = [homepage];\n this.forwardArr = [];\n }\n visit(url) {\n this.forwardArr = [];\n this.backArr.push(url);\n }\n back(steps) {\n while(steps && this.backArr.length > 1) {\n this.forwardArr.push(this.backArr.pop());\n steps--;\n }\n return this.backArr[this.backArr.length - 1];\n }\n forward(steps) {\n while(steps && this.forwardArr.length) {\n this.backArr.push(this.forwardArr.pop());\n steps--;\n }\n return this.backArr[this.backArr.length - 1]\n }\n}\n\n```
| 8 | 0 |
['Stack', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
Java, one List and a pointer, O(1) time
|
java-one-list-and-a-pointer-o1-time-by-f-srft
|
\nclass BrowserHistory {\n \n List<String> history;\n int last=-1;\n int cur=-1;\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n history=new
|
fighting_for_flag
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T04:26:55.219577+00:00
|
2020-06-07T04:26:55.219607+00:00
| 988 | false |
```\nclass BrowserHistory {\n \n List<String> history;\n int last=-1;\n int cur=-1;\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n history=new ArrayList<>();\n history.add(homepage);\n last=0;\n cur=0;\n }\n \n public void visit(String url) {\n last=cur+1;\n if(history.size()==last) history.add(url);\n else history.set(last,url);\n cur=last;\n }\n \n public String back(int steps) {\n int first=Math.max(0,cur-steps);\n cur=first;\n return history.get(first);\n }\n \n public String forward(int steps) {\n int l=Math.min(last,cur+steps);\n cur=l;\n return history.get(l);\n }\n}\n```
| 8 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
[Java] Clean & Concise Code
|
java-clean-concise-code-by-manrajsingh00-idvd
|
```\nclass BrowserHistory {\n static List list;\n int i;\n int j;\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n list = new ArrayList<>();\n
|
manrajsingh007
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T04:02:01.841264+00:00
|
2020-06-07T04:02:01.841318+00:00
| 626 | false |
```\nclass BrowserHistory {\n static List<String> list;\n int i;\n int j;\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n list = new ArrayList<>();\n list.add(homepage);\n i = 0;\n j = 0;\n }\n \n public void visit(String url) {\n if(i < list.size() - 1) list.set(i + 1, url);\n else list.add(url);\n i++;\n j = i;\n }\n \n public String back(int steps) {\n i = Math.max(0, i - steps);\n return list.get(i);\n }\n \n public String forward(int steps) {\n i = Math.min(j, i + steps);\n return list.get(i);\n }\n}\n
| 8 | 2 |
[]
| 1 |
design-browser-history
|
2 Approach| Stack And Linked List | Explained
|
2-approach-stack-and-linked-list-explain-klzb
|
!- Approach 1 Using Two Stacks -!\n\n## Intuition\nUse two stacks: one for back history, and one for forward history. You can simulate the functions by popping
|
lokhande__aditya
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-05T11:56:12.091839+00:00
|
2024-02-23T01:45:45.408095+00:00
| 630 | false |
<h1> !- Approach 1 Using Two Stacks -!\n\n## Intuition\nUse two stacks: one for back history, and one for forward history. You can simulate the functions by popping an element from one stack and pushing it into the other.\n\n# Approach\nDetailed approach for the provided solution, which simulates a web browser history using two lists: `self.cur` for the current page history and `self.forward_` for the forward history.\n\n1. **Initialization (`__init__` method)**:\n - The `BrowserHistory` class is initialized with the `homepage`, which is the page where the browsing session starts.\n - The `self.cur` list is created, initially containing only the `homepage`. This list will be used to represent the current page and the back history.\n - The `self.forward_` list is created as an empty list to represent the forward history.\n\n2. **Visiting a New URL (`visit` method)**:\n - When a user visits a new URL, the `visit` method is called with the `url` as a parameter.\n - The `url` is appended to the `self.cur` list to represent the current page history. This indicates that the user has visited a new page.\n - To maintain the forward history, the `self.forward_` list is cleared because visiting a new URL invalidates the forward history.\n\n3. **Navigating Backward (`back` method)**:\n - The `back` method allows the user to go back a certain number of steps in the browsing history.\n - A loop is used to iterate while there are more than one page in the `self.cur` list (to ensure at least one page remains) and while there are still `steps` left to go back.\n - In each iteration of the loop, the most recent page (the last URL in `self.cur`) is popped from the `self.cur` list.\n - The popped URL is then added to the `self.forward_` list to maintain a record of pages that were navigated away from.\n - The `steps` variable is decremented in each iteration, and this process continues until the desired number of steps have been taken.\n - After going back, the URL of the current page (which is now the last URL in `self.cur`) is returned.\n\n4. **Navigating Forward (`forward` method)**:\n - The `forward` method allows the user to go forward a certain number of steps in the browsing history.\n - It first checks if the `self.forward_` list is empty, which means there is no forward history to navigate.\n - If the `self.forward_` list is empty, it simply returns the URL of the current page (the last URL in `self.cur`).\n - If there is a forward history, a loop is used to iterate while there are URLs in the `self.forward_` list and while there are still `steps` left to go forward.\n - In each iteration, the most recent URL from the forward history (`self.forward_`) is popped and added back to the `self.cur` list to simulate going forward.\n - The `steps` variable is decremented in each iteration, and this process continues until the desired number of steps have been taken.\n - After going forward, the URL of the current page (which is now the last URL in `self.cur`) is returned.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n - `visit` method: O(1)\n - `back` method: O(steps), where `steps` is the number of steps to go back.\n - `forward` method: O(steps), where `steps` is the number of steps to go forward.\n\n- Space complexity:\n - The space complexity is primarily determined by the storage of URLs in the `self.cur` and `self.forward_` lists.\n - `self.cur` stores the current page history and potentially past pages, so its space complexity is O(n), where n is the number of pages visited.\n - `self.forward_` stores URLs representing the forward history, and its space complexity is also O(n) in the worst case.\n - Overall, the space complexity is O(n), where n is the total number of unique pages visited during the browsing session.\n\n\n```c++ []\n class BrowserHistory {\nprivate:\n vector<string> cur; // Current page list\n vector<string> forward_; // Forward history list\n\npublic:\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n cur.push_back(homepage);\n forward_.clear();\n }\n\n void visit(string url) {\n // Visit a new URL, append it to the current page list, and clear the forward history.\n cur.push_back(url);\n forward_.clear();\n }\n\n string back(int steps) {\n while (cur.size() > 1 && steps > 0) {\n // Go back a certain number of steps by popping URLs from the current page list\n // and adding them to the forward history.\n string url = cur.back();\n cur.pop_back();\n forward_.push_back(url);\n steps--;\n }\n\n // Retrieve the current page URL after going back.\n return cur.back();\n }\n\n string forward(int steps) {\n if (forward_.empty()) {\n return cur.back();\n }\n\n while (!forward_.empty() && steps > 0) {\n // Go forward a certain number of steps by popping URLs from the forward history\n // and adding them back to the current page list.\n string url = forward_.back();\n forward_.pop_back();\n cur.push_back(url);\n steps--;\n }\n\n // Retrieve the current page URL after going forward.\n return cur.back();\n }\n};\n\n```\n\n```python []\n class BrowserHistory:\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.cur = [homepage] # Initialize the current page list with the homepage.\n self.forward_ = [] # Initialize an empty forward history list.\n\n def visit(self, url: str) -> None:\n # Visit a new URL, append it to the current page list, and clear the forward history.\n self.cur.append(url)\n self.forward_ = []\n\n def back(self, steps: int) -> str:\n while len(self.cur) > 1 and steps:\n # Go back a certain number of steps by popping URLs from the current page list\n # and adding them to the forward history.\n url = self.cur.pop()\n self.forward_.append(url)\n steps -= 1\n\n # Retrieve the current page URL after going back.\n url = self.cur[-1]\n return url\n\n def forward(self, steps: int) -> str:\n if not self.forward_:\n return self.cur[-1]\n\n while self.forward_ and steps:\n # Go forward a certain number of steps by popping URLs from the forward history\n # and adding them back to the current page list.\n url = self.forward_.pop()\n self.cur.append(url)\n steps -= 1\n\n # Retrieve the current page URL after going forward.\n url = self.cur[-1]\n return url\n\n```\n \n<h1> !- Approach 2 Using Doubly Linked List -! </h1>\n\n\n```C++ []\nclass Node {\npublic:\n string url;\n Node* prev;\n Node* next;\n\n Node(string _url) : url(_url), prev(nullptr), next(nullptr) {}\n};\n\nclass BrowserHistory {\nprivate:\n Node* current;\npublic:\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n current = new Node(homepage);\n }\n\n void visit(string url) {\n Node* newNode = new Node(url);\n newNode->prev = current;\n current->next = newNode;\n current = newNode;\n }\n\n string back(int steps) {\n while (current->prev && steps > 0) {\n current = current->prev;\n steps--;\n }\n return current->url;\n }\n\n string forward(int steps) {\n while (current->next && steps > 0) {\n current = current->next;\n steps--;\n }\n return current->url;\n }\n};\n```\n# Please Upvote\n
| 7 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'Stack', 'Doubly-Linked List', 'C++', 'Python3']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
Easiest C++ Code Design (Vector)
|
easiest-c-code-design-vector-by-baibhavs-uwk7
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
baibhavsingh07
|
NORMAL
|
2023-05-24T06:04:56.563441+00:00
|
2023-05-24T06:04:56.563470+00:00
| 102 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n)\n- Each method takes O(1)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\nvector<string>a;\nint ind=-1;\nint end=0;\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n a.push_back(homepage);\n ind=0;\n \n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n if(ind<a.size()-1){\n a[++ind]=url;\n end=ind;\n }\n else{\n a.push_back(url);\n ind=a.size()-1;\n end=ind;}\n \n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n ind-=steps;\n \n if(ind<0)\n ind=0;\n\n return a[ind];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n ind+=steps;\n \n if(ind>end)\n ind=end;\n return a[ind];\n\n }\n};\n\n/**\n * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n * BrowserHistory* obj = new BrowserHistory(homepage);\n * obj->visit(url);\n * string param_2 = obj->back(steps);\n * string param_3 = obj->forward(steps);\n */\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Array', 'Design', 'C++']
| 2 |
design-browser-history
|
☕Java Solution | 🤠 Simple Logic | 🚀beats 65% | Beginner Friendly
|
java-solution-simple-logic-beats-65-begi-1ydl
|
Problem Link : https://leetcode.com/problems/design-browser-history/\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nI have used LinkedList data
|
5p7Ro0t
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T16:23:53.773227+00:00
|
2023-03-18T16:34:41.644413+00:00
| 660 | false |
**Problem Link :** https://leetcode.com/problems/design-browser-history/\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nI have used LinkedList data structure to store the `urls` and perform operation on them.\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass BrowserHistory{\n ArrayList<String> ll = new ArrayList<>(); \n int position = 0;\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n ll.add(homepage);\n }\n \n public void visit(String url) {\n int len = ll.size();\n if(position+1 < len){\n while(position+1 != len){\n ll.remove(len-1);\n len--;\n }\n }\n position+=1;\n ll.add(url);\n }\n \n public String back(int steps) {\n if(position - steps <= 0){\n position = 0;\n return ll.get(0);\n }\n position = position - steps;\n return ll.get(position);\n }\n \n public String forward(int steps) {\n if(steps+position >= ll.size()){\n position = ll.size()-1;\n return ll.get(position);\n }\n position+=steps;\n return ll.get(position);\n }\n}\n\n/**\n * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n * BrowserHistory obj = new BrowserHistory(homepage);\n * obj.visit(url);\n * String param_2 = obj.back(steps);\n * String param_3 = obj.forward(steps);\n */\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Array', 'Java']
| 2 |
design-browser-history
|
Complete Explanation with Example || Simple Code || Easy to understand
|
complete-explanation-with-example-simple-3atp
|
\n\n\n\n\n\n\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n vector<string>v;\n int end, curr;\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) \n {\n v.push_back(homepa
|
mohakharjani
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T01:09:23.260421+00:00
|
2023-03-18T02:04:28.764001+00:00
| 852 | false |
\n\n\n\n\n\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n vector<string>v;\n int end, curr;\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) \n {\n v.push_back(homepage);\n end = 0; curr = 0;\n }\n \n void visit(string url) \n {\n if (curr == end)\n {\n if (end == v.size() - 1) { v.push_back(url); end++; } //push the new url, mark the end at end of array\n else v[++end] = url; //increment end and then add the url there \n curr++; //increment curr\n }\n else \n {\n v[++curr] = url; //increment curr then add url there\n end = curr; //rest all url\'s next to curr need to be erased, so simply mark end = curr;\n }\n }\n \n string back(int steps) \n {\n curr = max(0, curr - steps);\n return v[curr];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps)\n {\n curr = min(end, curr + steps);\n return v[curr];\n }\n};\n```
| 6 | 1 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
C++ | Array | Easy approach
|
c-array-easy-approach-by-iamnav1-sjii
|
\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n string history[105] = {};\n int idx = 0;\n int end = 0;\n \n BrowserHistory(string homepage) { \n hi
|
iamnav1
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-22T18:32:57.414291+00:00
|
2022-02-22T18:32:57.414330+00:00
| 429 | false |
```\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n string history[105] = {};\n int idx = 0;\n int end = 0;\n \n BrowserHistory(string homepage) { \n history[idx] = homepage;\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n history[++idx] = url;\n end = idx;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n idx = max(idx - steps, 0);\n return history[idx];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n idx = min(idx + steps, end);\n return history[idx];\n }\n};\n\n/**\n * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n * BrowserHistory* obj = new BrowserHistory(homepage);\n * obj->visit(url);\n * string param_2 = obj->back(steps);\n * string param_3 = obj->forward(steps);\n */\n```\n\nExplanation:\n1. For moving back and front we just have to validate if we have enough steps to move in the required direction and adjust accordingly\n2. The bit complicated case is of when we are visiting a new URL, I just save the current end of the array in order to clear the forward history
| 6 | 0 |
['Array', 'C']
| 1 |
design-browser-history
|
Python3 solution using Doubly LinkedList
|
python3-solution-using-doubly-linkedlist-ug7u
|
\nclass BrowserHistory:\n\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.head = Node(homepage)\n self.current = self.head\n\n def visit(self, u
|
EklavyaJoshi
|
NORMAL
|
2021-06-20T04:32:28.372501+00:00
|
2021-06-20T04:32:28.372534+00:00
| 448 | false |
```\nclass BrowserHistory:\n\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.head = Node(homepage)\n self.current = self.head\n\n def visit(self, url: str) -> None:\n self.current.right = Node(url)\n self.current.right.left = self.current\n self.current = self.current.right\n\n def back(self, steps: int) -> str:\n while steps > 0 and self.current.left:\n steps -= 1\n self.current = self.current.left\n return self.current.val\n\n def forward(self, steps: int) -> str:\n while steps > 0 and self.current.right:\n steps -= 1\n self.current = self.current.right\n return self.current.val\n \nclass Node:\n def __init__(self, val, left = None, right = None):\n self.val = val\n self.left = left\n self.right = right\n```\n**If you like this solution, please upvote for this**
| 6 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'Python3']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
Python sol by deque [w/ Comment]
|
python-sol-by-deque-w-comment-by-brianch-2hf2
|
Python sol by deque\n\n---\n\nImplementation by deque:\n\n\nfrom collections import deque\n\nclass BrowserHistory:\n\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n\t
|
brianchiang_tw
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-30T04:23:57.213838+00:00
|
2020-06-30T04:23:57.213887+00:00
| 888 | false |
Python sol by deque\n\n---\n\n**Implementation** by deque:\n\n```\nfrom collections import deque\n\nclass BrowserHistory:\n\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n\t\n self.history = deque([homepage])\n self.cur_index = 0\n\n \n \n def visit(self, url: str) -> None:\n \n # clear all forward history\n tail_len = len(self.history)-1-self.cur_index\n while tail_len:\n self.history.pop()\n tail_len -= 1\n \n self.history.append(url)\n self.cur_index += 1\n\n \n \n def back(self, steps: int) -> str:\n \n\t\t# boundary check\n if steps > self.cur_index:\n self.cur_index = 0\n else:\n self.cur_index -= steps\n \n return self.history[self.cur_index]\n\n \n \n def forward(self, steps: int) -> str:\n \n\t\t# boundary check\n if steps >= len(self.history) - self.cur_index:\n self.cur_index = len(self.history) - 1\n else:\n self.cur_index += steps\n \n return self.history[self.cur_index]\n```\n\n---\n\nReference:\n\n[1] [Python official docs about deque( ... )](https://docs.python.org/3.8/library/collections.html#collections.deque)
| 6 | 0 |
['Queue', 'Iterator', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 1 |
design-browser-history
|
C++ Browser History using std::list (100% faster and 100% memory efficient)
|
c-browser-history-using-stdlist-100-fast-hviu
|
\nstatic const auto ____ = [](){\n ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);\n return 0;\n}();\n\nclass BrowserHistory {
|
vasugoel
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T11:18:45.764563+00:00
|
2020-06-07T11:18:45.764603+00:00
| 518 | false |
```\nstatic const auto ____ = [](){\n ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);\n return 0;\n}();\n\nclass BrowserHistory {\n list<string> history;\n list<string>::iterator tab;\n \npublic:\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n history.clear();\n tab = history.insert(history.end(), homepage);\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n if(!history.empty() && history.back() == url) return; \n else if(!history.empty() && tab != history.end()) history.erase(++tab, history.end());\n\n tab = history.insert(history.end(), url);\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n if(*tab == history.front()) return history.front();\n while(steps--) {\n tab--;\n if(*tab == history.front()) return history.front();\n }\n return *tab;\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n if(*tab == history.back()) return history.back();\n while(steps--) {\n tab++;\n if(*tab == history.back()) return history.back();\n }\n return *tab;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 6 | 1 |
[]
| 1 |
design-browser-history
|
C++ Simple and Precise solution using Vector only!!!
|
c-simple-and-precise-solution-using-vect-bu0m
|
# Pls upvote you like the solution:)\n# Intuition\nThis question simple states that you have to push and just return the url which is present at a certain posit
|
Rajanner
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T05:37:12.439187+00:00
|
2023-03-18T05:37:12.439223+00:00
| 363 | false |
# ***# Pls upvote you like the solution:)***\n# Intuition\nThis question simple states that you have to push and just return the url which is present at a certain position (i).\n\n# Approach\n- **BrowserHistory(string homepage)** :- Push back the homepage in a vector.\n- **void visit(string url)** :- I decalred a vector v in which we will push the url (*you just need to erase all the elements from the vector which are present after the position where you are going to insert a new url*).\n- **string back(int steps)** :- You just need to go back a certain number of steps from where you are current position is(i) in the vector and return that element.\n**Edge Case:-** Just remember you should not go beyond your **1st element**. Therefore I have handled that test case using the if condition.\n- **string forward(int steps)** :- You just need to go forward a certain number of steps from where you are current position is(i) in the vector and return that element.\n**Edge Case:-** Just remember you should not go beyond your **Last element**. Therefore I have handled that test case using the if condition.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n vector<string> v;\n int i=0;\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n v.push_back(homepage);\n i=v.size()-1;\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n v.erase(v.begin()+i+1,v.end());\n v.push_back(url);\n i=v.size()-1;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n if(steps>i){\n i=0;\n return v[0];\n } \n i = i - steps;\n return v[i];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n if(steps>((v.size()-1)-i)){\n i=v.size()-1;\n return v[i];\n } \n i = i + steps;\n return v[i];\n }\n};\n```
| 5 | 1 |
['Array', 'C++']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
JAVA || Easy Solution || ArrayList || Easy to Understand
|
java-easy-solution-arraylist-easy-to-und-j2xm
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
shivrastogi
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T01:38:56.092124+00:00
|
2023-03-18T01:38:56.092154+00:00
| 2,923 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\n\nList<String> list;\nint total = 0;\nint curr = 0;\n\npublic BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n\tlist = new ArrayList<String>();\n\tlist.add(homepage);\n\ttotal++;\n curr++;\n}\n\npublic void visit(String url) {\n\tif (list.size() > curr) {\n\t\tlist.set(curr, url);\n\t} else {\n\t\tlist.add(url);\n\t}\n\tcurr++;\n\ttotal = curr;\n}\n\npublic String back(int steps) {\n\tcurr = Math.max(1, curr - steps);\n\treturn list.get(curr - 1);\n}\n\npublic String forward(int steps) {\n\tcurr = Math.min(total, curr + steps);\n\treturn list.get(curr - 1);\n}\n}\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
design-browser-history
|
🔥Easy Solutions in Java 📝, Python 🐍, and C++ 🖥️🧐Look at once 💻
|
easy-solutions-in-java-python-and-c-look-4m3e
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nWe need to maintain the history of visited URLs so that we can move back and forward. W
|
Vikas-Pathak-123
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T01:07:01.962098+00:00
|
2023-03-18T01:07:01.962133+00:00
| 2,224 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nWe need to maintain the history of visited URLs so that we can move back and forward. We can use a stack to maintain the history of visited URLs.\n\n\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n- We can maintain two stacks, stackBack and stackForward, to represent the back and forward history respectively.\n- When we visit a new URL, we push it onto the stackBack and clear the stackForward since we can no longer move forward after visiting a new URL.\n- When we move back, we pop the top element from stackBack and push it onto stackForward.\n- When we move forward, we pop the top element from stackForward and push it onto stackBack.\n\n\n\n\n\n# Complexity\n1. Time complexity:\n- visit method takes O(1) time complexity since we only push the URL onto the stackBack.\n- back method takes O(min(steps, size(stackBack))) time complexity since we need to pop the top elements from stackBack and push them onto stackForward at most steps times.\n- forward method takes O(min(steps, size(stackForward))) time complexity since we need to pop the top elements from stackForward and push them onto stackBack at most steps times.\n\n\n2. Space complexity:\n - O(n) where n is the total number of visited URLs. We need to store the visited URLs in stackBack and stackForward.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n# Please Upvote\uD83D\uDC4D\uD83D\uDC4D\n```\nThanks for visiting my solution.\uD83D\uDE0A Keep Learning\nPlease give my solution an upvote! \uD83D\uDC4D\nIt\'s a simple way to show your appreciation and\nkeep me motivated. Thank you! \uD83D\uDE0A\n```\n# Code\n``` Java []\nimport java.util.*;\n\nclass BrowserHistory {\n\n private Deque<String> history;\n private Deque<String> forward;\n\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n history = new LinkedList<>();\n history.push(homepage);\n forward = new LinkedList<>();\n }\n \n public void visit(String url) {\n history.push(url);\n forward.clear();\n }\n \n public String back(int steps) {\n while (steps > 0 && history.size() > 1) {\n forward.push(history.pop());\n steps--;\n }\n return history.peek();\n }\n \n public String forward(int steps) {\n while (steps > 0 && !forward.isEmpty()) {\n history.push(forward.pop());\n steps--;\n }\n return history.peek();\n }\n}\n\n/**\n * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n * BrowserHistory obj = new BrowserHistory(homepage);\n * obj.visit(url);\n * String param_2 = obj.back(steps);\n * String param_3 = obj.forward(steps);\n */\n\n\n```\n```Python []\nclass BrowserHistory(object):\n\n def __init__(self, homepage):\n """\n :type homepage: str\n """\n self.history = [homepage]\n self.current_index = 0\n\n def visit(self, url):\n """\n :type url: str\n :rtype: None\n """\n # Clear forward history\n self.history = self.history[:self.current_index+1]\n # Add new url to history\n self.history.append(url)\n # Update current index\n self.current_index = len(self.history) - 1\n\n def back(self, steps):\n """\n :type steps: int\n :rtype: str\n """\n # Calculate new index after moving back steps\n self.current_index = max(0, self.current_index - steps)\n return self.history[self.current_index]\n\n def forward(self, steps):\n """\n :type steps: int\n :rtype: str\n """\n # Calculate new index after moving forward steps\n self.current_index = min(len(self.history) - 1, self.current_index + steps)\n return self.history[self.current_index]\n\n\n# Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n# obj = BrowserHistory(homepage)\n# obj.visit(url)\n# param_2 = obj.back(steps)\n# param_3 = obj.forward(steps)\n\n\n```\n```C++ []\n\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n history.push_back(homepage);\n cur_idx = 0;\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n // Clear forward history\n history.resize(cur_idx + 1);\n history.push_back(url);\n cur_idx++;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n int prev_idx = max(0, cur_idx - steps);\n cur_idx = prev_idx;\n return history[cur_idx];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n int next_idx = min((int)history.size() - 1, cur_idx + steps);\n cur_idx = next_idx;\n return history[cur_idx];\n }\n\nprivate:\n vector<string> history;\n int cur_idx;\n};\n\n\n\n```\n# Please Comment\uD83D\uDC4D\uD83D\uDC4D\n```\nThanks for visiting my solution comment below if you like it.\uD83D\uDE0A\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'Queue', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
Kotlin
|
kotlin-by-kotlinc-29ia
|
Thank you for upvoting.\n\n\nclass BrowserHistory(homepage: String) {\n\n private val chain = mutableListOf<String>(homepage)\n private var idx = 0\n\n fun v
|
kotlinc
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T00:38:06.778609+00:00
|
2023-03-18T00:38:06.778650+00:00
| 90 | false |
Thank you for upvoting.\n\n```\nclass BrowserHistory(homepage: String) {\n\n private val chain = mutableListOf<String>(homepage)\n private var idx = 0\n\n fun visit(url: String) {\n while (idx != chain.size - 1)\n chain.removeAt(chain.size - 1)\n chain.add(url)\n idx++\n }\n\n fun back(steps: Int): String {\n idx = maxOf(idx - steps, 0)\n return chain[idx]\n }\n\n fun forward(steps: Int): String {\n idx = minOf(chain.size - 1, idx + steps)\n return chain[idx]\n }\n\n}\n\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Kotlin']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
python super easy to understand with list and pointer (no stack and no double link list)
|
python-super-easy-to-understand-with-lis-upiw
|
\nclass BrowserHistory:\n\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.history = [homepage]\n self.pointer = 0\n\n def visit(self, url: str)
|
harrychen1995
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-11T20:03:43.576305+00:00
|
2022-10-11T20:03:43.576346+00:00
| 412 | false |
```\nclass BrowserHistory:\n\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.history = [homepage]\n self.pointer = 0\n\n def visit(self, url: str) -> None:\n self.history = self.history [:self.pointer+1]\n self.history.append(url)\n self.pointer = len(self.history ) - 1\n def back(self, steps: int) -> str:\n self.pointer = max(self.pointer - steps, 0)\n return self.history [self.pointer]\n\n def forward(self, steps: int) -> str:\n self.pointer = min(self.pointer +steps, len(self.history )-1)\n return self.history [self.pointer]\n```
| 5 | 0 |
[]
| 3 |
design-browser-history
|
Java O(1) for all methods
|
java-o1-for-all-methods-by-achillesgreat-22mu
|
we use nodes to store the data, use a map to save the index to node, and save rightIndex and currentIndex\n\nback(): \n\tget the new currentIndex and use the ma
|
achillesgreat
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-28T06:54:12.184190+00:00
|
2022-04-28T06:54:12.184223+00:00
| 409 | false |
we use nodes to store the data, use a map to save the index to node, and save rightIndex and currentIndex\n\nback(): \n\tget the new currentIndex and use the map to get the node, notice the rightIndex value isnt changed here\nvisit(): \n\tmove currentIndex forward 1 step and make the rightIndex the value of the currentIndex since we\'re overriding\n\tnotice here that we aren\'t updating the latter values in the map so the map will have extra data, but this isn\'t a big deal \n\tas we never access it, and we just end up overwriting it when we add more visits, we don\'t want to delete the data\n\tbecause then the solution will no longer be O(1)\nforward():\n\there we just move forward with max at the rightindex\n\n\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\n \n Node head;\n Node current;\n int currentIndex;\n Map<Integer, Node> map;\n int rightIndex;\n\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n head = new Node(homepage);\n current = head;\n currentIndex = 0;\n map =new HashMap<>();\n map.put(0, head);\n rightIndex = 0;\n }\n \n public void visit(String url) {\n currentIndex++;\n current.right = new Node(url);\n current = current.right;\n map.put(currentIndex, current);\n rightIndex = currentIndex;\n }\n \n public String back(int steps) {\n currentIndex = currentIndex - steps >= 0 ? currentIndex - steps : 0;\n current = map.get(currentIndex);\n return current.value;\n }\n \n public String forward(int steps) {\n currentIndex = currentIndex + steps <= rightIndex ? currentIndex + steps : rightIndex;\n current = map.get(currentIndex);\n return current.value;\n }\n}\n\nclass Node {\n String value;\n Node left;\n Node right;\n \n public Node(String value){\n this.value = value;\n }\n}\n\n/**\n * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n * BrowserHistory obj = new BrowserHistory(homepage);\n * obj.visit(url);\n * String param_2 = obj.back(steps);\n * String param_3 = obj.forward(steps);\n */\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
JavaScript - Singly Linked List
|
javascript-singly-linked-list-by-sktlez-o4pd
|
\n/**\n * @param {string} homepage\n */\nvar BrowserHistory = function(homepage) {\n this.homepage = homepage;\n this.currentUrl = new Node(homepage);\n};
|
sktlez
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-18T23:22:48.156546+00:00
|
2022-01-18T23:22:48.156575+00:00
| 363 | false |
```\n/**\n * @param {string} homepage\n */\nvar BrowserHistory = function(homepage) {\n this.homepage = homepage;\n this.currentUrl = new Node(homepage);\n};\n\n/** \n * @param {string} url\n * @return {void}\n */\nBrowserHistory.prototype.visit = function(url) {\n this.currentUrl = this.currentUrl.insert(url);\n \n};\n\n/** \n * @param {number} steps\n * @return {string}\n */\nBrowserHistory.prototype.back = function(steps) {\n while(steps > 0 && this.currentUrl.prev !== null) {\n this.currentUrl = this.currentUrl.prev;\n steps--;\n }\n return this.currentUrl.val;\n \n};\n\n/** \n * @param {number} steps\n * @return {string}\n */\nBrowserHistory.prototype.forward = function(steps) {\n while(steps > 0 && this.currentUrl.next !== null) {\n this.currentUrl = this.currentUrl.next;\n steps--;\n }\n return this.currentUrl.val;\n};\n\n/** \n * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n * var obj = new BrowserHistory(homepage)\n * obj.visit(url)\n * var param_2 = obj.back(steps)\n * var param_3 = obj.forward(steps)\n */\n\nfunction Node(val, next = null, prev = null) {\n this.val = val;\n this.next = next;\n this.prev = prev;\n}\n\nNode.prototype.insert = function(val) {\n const node = new Node(val);\n\n if (this.next === null) {\n this.next = node;\n node.prev = this;\n } else {\n let nextNode = this.next;\n this.next = node;\n node.prev = this;\n \n if (nextNode !== null) {\n nextNode.prev = node;\n }\n }\n \n return node;\n}\n```
| 5 | 1 |
['Linked List', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
One Vector | Clean and Intuitive Code with Explanation
|
one-vector-clean-and-intuitive-code-with-nd0i
|
\n\nSteps:\n\n Initialise a vector to store all the URLs that you visit and a current variable to denote index of current url in vector\n Push homepage in vecto
|
bitmasker
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-18T05:59:43.041585+00:00
|
2021-11-18T05:59:43.041640+00:00
| 357 | false |
<br/>\n\n**Steps:**\n\n* Initialise a vector to store all the URLs that you visit and a current variable to denote index of current url in vector\n* Push homepage in vector and make it current\n* The tricky part is implementing Visit function **you have to clear the forward history in visit function** , so erase all the urls after current url and push the new url and make it current\n* You can go at max `current - steps` steps back, so make it current and return that url\n* You can go at max `urls.size() - current - 1` steps forward, so make it current and return that url\n<br/>\n\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n \n vector<string> urls;\n int current;\n \n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n urls.push_back(homepage); \n current = 0;\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n urls.erase(urls.begin() + current + 1, urls.end());\n urls.push_back(url);\n current++;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n current = max(0, current - steps);\n return urls[current];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n current = min((int)urls.size() - 1, current + steps);\n return urls[current];\n }\n};\n```\n<br/>\nDo upvote if you liked the code and explanation :)\n<br/>
| 5 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 1 |
design-browser-history
|
Easy C++ solution using Linked List with Comments
|
easy-c-solution-using-linked-list-with-c-n2f9
|
This is pretty stright forward question , we just need to use a doubly linked list and do as stated in the question.\n\n## Code\n\nclass BrowserHistory {\n// we
|
rishabh_devbanshi
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-23T07:18:07.362553+00:00
|
2021-10-23T07:19:51.579473+00:00
| 191 | false |
This is pretty stright forward question , we just need to use a doubly linked list and do as stated in the question.\n\n## Code\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\n// we declare a doubly linked list and an iterator for the same\n list<string> bro;\n list<string> :: iterator it;\npublic:\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n\t//push the homepage in the list and \n\t// and set the iterator at the beginning of the lsit\n bro.push_back(homepage);\n it = bro.begin();\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n\t\t// delete the part of list after the current iterator\n auto del = it;\n del++;\n bro.erase(del,bro.end());\n\t\t\n\t\t//push the new url in the list\n\t\t//and point the iterator to this url\n bro.push_back(url);\n it++;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n\t// move the it backwards till either the steps = 0 \n\t// or we reach head of the lsit\n while(it != bro.begin() and steps-- > 0)\n {\n it--;\n }\n \n\t\t// return value at ths it\n return *it;\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n\t// move the it backwards till either the steps = 0 \n\t// or we reach last element of the lsit\n while(it != --bro.end() and steps-- > 0)\n {\n it++;\n }\n \n\t\t// return value at ths it\n return *it;\n }\n};\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'C']
| 2 |
design-browser-history
|
C++ | Vector Implementation | Easy | ~99% Space ~74% Time
|
c-vector-implementation-easy-99-space-74-5u4d
|
\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n int curr, r;\n vector<string> ds;\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n ds.resize(1);\n ds[0] = homepage;
|
amanswarnakar
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T04:59:58.939295+00:00
|
2023-03-18T04:59:58.939326+00:00
| 360 | false |
```\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n int curr, r;\n vector<string> ds;\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n ds.resize(1);\n ds[0] = homepage;\n curr = 0; r = ds.size();\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n curr++;\n if(curr == ds.size()){\n ds.emplace_back(url);\n r = ds.size();\n } \n else {\n r = curr + 1;\n // ds.resize(curr);\n // ds.emplace_back(url);\n ds[curr] = url;\n }\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n curr = max(0, curr - steps);\n return ds[curr];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n curr = min(r - 1, curr + steps);\n return ds[curr];\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Array', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
✅✅C++ || Easy Solution || 💯💯Vector Approach || Heavily Commented
|
c-easy-solution-vector-approach-heavily-gdfkh
|
\u2705\u2705C++ || Easy Solution || \uD83D\uDCAF\uD83D\uDCAFVector Approach || Heavily Commented\n# Please Upvote as it really motivates me\n\n\n\nclass Browser
|
Conquistador17
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T04:33:59.899905+00:00
|
2023-03-18T04:35:18.347331+00:00
| 202 | false |
## **\u2705\u2705C++ || Easy Solution || \uD83D\uDCAF\uD83D\uDCAFVector Approach || Heavily Commented**\n# **Please Upvote as it really motivates me**\n\n```\n\nclass BrowserHistory {\n\t//we are creating a vector of strings to store the url string \n vector<string>list;\n\t//idx will show on which index of vector are we on\n int idx=-1;\n\t//the maxSize is used to store the maximum size of the vector \n\t\t//it contain size of the possible vector \n int maxSize=0;\npublic:\n//In BrowserHistory we will simply initialize our vector and idx to 0 and maxSize to one\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n list.push_back(homepage);\n idx=0;\n maxSize=1;\n }\n //when we are visiting a url we can have two options\n\t\t//1. if we are not on the end of list.size() i.e. idx<list.size()-1\n\t\t\t//then we will simply put the url at next index and increase idx and also update maxSize to idx+1\n\t\t//2. else we are on the end of vector we will have to push back to the vector and the both idx and maxSize increase by one\n void visit(string url) {\n\t//First condition\n if(list.size()-1>idx){\n list[idx+1]=url;\n idx++;\n maxSize=idx+1;\n }\n\t\t//2nd condition\n else{\n list.push_back(url);\n idx++;\n maxSize++;\n }\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n\t\t//we will find the val to which we can go back\n int val=min(steps,idx);\n\t\t//substract from the idx\n idx-=val;\n\t\t//return the list[idx]\n return list[idx];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n\t\t//we will find the val to which we can go back\n int val=min(steps,maxSize-idx-1);\n\t\t//add from the idx\n idx+=val;\n\t\t//return the list[idx]\n return list[idx];\n }\n};\n\n```\n\n\n
| 4 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
Java - Faster than 100%. O(1) for ALL operations.
|
java-faster-than-100-o1-for-all-operatio-sk3i
|
\n// Time complexity = O(1) for all operations\n// Space complexity = O(n), where n is the amount of times visit is called (this fairly inaccurate, but should s
|
PreetMangatt
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-10T23:25:17.934581+00:00
|
2022-06-10T23:28:20.138593+00:00
| 418 | false |
```\n// Time complexity = O(1) for all operations\n// Space complexity = O(n), where n is the amount of times visit is called (this fairly inaccurate, but should suffice as a loose upperbound. the actual space complexity depends on the amount of visit() and back() called, as data is overwritten.\n\nclass BrowserHistory {\n int currIndex, endIndex;\n List<String> history;\n \n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n currIndex = 0; \n endIndex = 0;\n history = new ArrayList<>();\n visit(homepage);\n }\n \n public void visit(String url) {\n history.add(currIndex++, url);\n endIndex = currIndex;\n }\n \n public String back(int steps) {\n currIndex = Math.max(1, currIndex - steps);\n\t return history.get(currIndex - 1);\n }\n \n public String forward(int steps) {\n currIndex = Math.min(endIndex, currIndex + steps);\n\t return history.get(currIndex - 1);\n }\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
design-browser-history
|
C++ | Doubly Linked List | Clean and Concise
|
c-doubly-linked-list-clean-and-concise-b-aicw
|
\nclass Node\n{\n public:\n string data;\n Node *prev,*next;\n \n Node()\n {\n data="";\n prev=next=NULL;\n }\n Node(strin
|
jk20
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-22T02:59:34.811068+00:00
|
2022-02-22T03:00:19.990296+00:00
| 298 | false |
```\nclass Node\n{\n public:\n string data;\n Node *prev,*next;\n \n Node()\n {\n data="";\n prev=next=NULL;\n }\n Node(string _data)\n {\n data=_data;\n prev=next=NULL;\n }\n};\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n \n Node *curr=new Node();\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n Node *begin=new Node(homepage);\n begin->prev=curr;\n curr->next=begin;\n curr->prev=NULL;\n curr=curr->next;\n \n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n Node *newNode=new Node(url);\n curr->next=newNode;\n newNode->prev=curr;\n newNode->next=NULL;\n curr=curr->next;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n \n while(steps-- and curr->prev->data!="")\n {\n curr=curr->prev;\n\t\t}\n return curr->data;\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n \n while(steps-- and curr->next)\n {\n curr=curr->next;\n }\n return curr->data;\n }\n};\n\n/**\n * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n * BrowserHistory* obj = new BrowserHistory(homepage);\n * obj->visit(url);\n * string param_2 = obj->back(steps);\n * string param_3 = obj->forward(steps);\n */\n```\n\n**Pls upvote if you found helpful.**
| 4 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'C', 'C++']
| 1 |
design-browser-history
|
c++(108ms 97%) simple, small, easy
|
c108ms-97-simple-small-easy-by-zx007pi-fyxy
|
Runtime: 108 ms, faster than 96.95% of C++ online submissions for Design Browser History.\nMemory Usage: 57.4 MB, less than 78.89% of C++ online submissions for
|
zx007pi
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-25T06:07:33.684982+00:00
|
2021-09-25T06:07:33.685029+00:00
| 216 | false |
Runtime: 108 ms, faster than 96.95% of C++ online submissions for Design Browser History.\nMemory Usage: 57.4 MB, less than 78.89% of C++ online submissions for Design Browser History.\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n vector<string> v;\n int id; \n \n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n id = 0;\n v.push_back(homepage);\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n v.resize(++id);\n v.push_back(url);\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n return v[id = max(0, id - steps)];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n return v[id = min( int(v.size() - 1), id + steps)];\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
C++ unordered_map 100% faster
|
c-unordered_map-100-faster-by-wtfisdietc-jmb4
|
\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n int i, sz;\n unordered_map<int, string> m;\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n m[0] = homepage;\n i
|
wtfisdietcoke
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T04:26:35.416963+00:00
|
2020-06-07T04:57:10.953432+00:00
| 238 | false |
```\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n int i, sz;\n unordered_map<int, string> m;\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n m[0] = homepage;\n i = 0;\n sz = 1;\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n i++;\n m[i] = url;\n sz = i + 1;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n if (i - steps < 0) i = 0;\n else i -= steps;\n return m[i];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n if (i + steps < sz) i += steps; \n else i = sz - 1;\n return m[i];\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
[Java] Elegant O(n) Solution with 2 Stacks - Comments Included
|
java-elegant-on-solution-with-2-stacks-c-7gda
|
n accounts to the number of steps for back and forward method inputs.\n\nclass BrowserHistory {\n\n private Stack<String> back;\n private Stack<String> fo
|
nadie
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T04:05:40.150629+00:00
|
2020-06-07T04:15:20.136936+00:00
| 364 | false |
n accounts to the number of steps for back and forward method inputs.\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\n\n private Stack<String> back;\n private Stack<String> forward;\n \n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n back = new Stack<>();\n forward = new Stack<>();\n back.push(homepage);\n }\n \n public void visit(String url) {\n back.push(url);\n\t\t// if I visit a new url, there is no more going forward. Clear the forward stack.\n forward.clear();\n }\n \n public String back(int steps) {\n int count = 0;\n\t\t\n\t\t// go back in history for given number of steps. To make sure that you can forward to each url, keep them piled up in the forward stack\n while(count < steps && back.size() > 1){\n count++;\n forward.push(back.pop());\n }\n return back.peek();\n }\n \n public String forward(int steps) {\n int count = 0;\n\t\t\n\t\t//go forward in history for given number of steps. To make sure you can go back to each url, keep them piled in the back stack\n while(count < steps && forward.size() > 0){\n count++;\n back.push(forward.pop());\n }\n return back.peek();\n }\n \n \n}\n\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
[C++] Using vector for simulation
|
c-using-vector-for-simulation-by-zhanghu-zruf
|
Design a data structure that mocks the behaviour of a web browser.\n\n# Explanation\n\nThe key is to understand the behaviour of a web browser. It acts like a s
|
zhanghuimeng
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-07T04:03:39.965432+00:00
|
2020-06-07T04:03:39.965514+00:00
| 119 | false |
Design a data structure that mocks the behaviour of a web browser.\n\n# Explanation\n\nThe key is to understand the behaviour of a web browser. It acts like a stack with a pointer. When you go "forward" / "backward", you move the pointer closer / further from the top of the stack; and when you visit a new webpage, you pop all the pages on top of the pointer, insert in the new page and point to it.\n\nThe time complexity of each operation:\n\n* `visit`: `O(n)` (`n` is the size of stack)\n* `back`: `O(1)`\n* `forward`: `O(1)`\n\n# C++ Solution\n\n```cpp\nclass BrowserHistory {\n vector<string> history;\n int pos;\n \npublic:\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n history.push_back(homepage);\n pos = 0;\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n while (pos < history.size() - 1) {\n history.pop_back();\n }\n history.push_back(url);\n pos++;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n pos -= steps;\n if (pos < 0) pos = 0;\n return history[pos];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n pos += steps;\n if (pos >= history.size()) pos = history.size() - 1;\n return history[pos];\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
✅$$O(1)$$🔥||✅99.73%🔥||✅Array Approach||🔥Easy to understand||✅4 Simple Steps
|
o19973array-approacheasy-to-understand4-qe022
|
Approach:\nInit: Define an array, initally with value homepage.\nVisit: Check if it\'s a new site, if so append. If not set it as a new site and delete the rest
|
gezxgen
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-08T08:59:28.188357+00:00
|
2024-10-08T08:59:28.188389+00:00
| 94 | false |
**Approach:**\nInit: Define an array, initally with value *homepage*.\nVisit: Check if it\'s a new site, if so append. If not set it as a new site and delete the rest.\nBack: Move the index back and check out of bounds errors. Return the string.\nForward: Move the index forward and also check out of bounds. Return the string.\n\n---\n**Complexity:**\n* Time complexity: O(1)\n\n* Space complexity: O(n)\n\n*Because we used an array indexing is a constant time operation.\n*Also appending is constant because on average it is still O(1) and not the worst case O(n)!\n\n---\n**Code:**\n```\nclass BrowserHistory:\n\n def __init__(self, homepage: str):\n self.nums: list(str) = [homepage]\n self.index: int = 0\n\n def visit(self, url: str) -> None:\n if self.index == len(self.nums)-1:\n self.nums.append(url)\n self.index += 1\n else:\n self.index += 1\n self.nums[self.index] = url\n self.nums = self.nums[:self.index+1]\n\n def back(self, steps: int) -> str:\n self.index -= steps\n if self.index < 0:\n self.index = 0\n return self.nums[self.index]\n\n def forward(self, steps: int) -> str:\n n: int = len(self.nums)-1\n self.index += steps\n if self.index > n:\n self.index = n\n return self.nums[self.index]\n```\n\n---\n\n\n---\nIf you have any suggestions, let me know!\n**Litterally you after upvoting:**\n\n\n\n---
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
✅ Double-Linked List || Super Easy Solution || Beginner Friendly || Easy to understand
|
double-linked-list-super-easy-solution-b-uifm
|
Code\n\n// create a class "Node" for implementing double-linked list\nclass Node { \npublic: \n string data;\n Node* next;\n Node* prev;\n\n Node()
|
Divyanshu_01
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-26T20:06:34.660749+00:00
|
2024-01-26T20:06:34.660767+00:00
| 42 | false |
# Code\n```\n// create a class "Node" for implementing double-linked list\nclass Node { \npublic: \n string data;\n Node* next;\n Node* prev;\n\n Node() : data(0), next(nullptr), prev(nullptr) {}; // constructors\n Node(string x) : data(x), next(nullptr), prev(nullptr) {}; // constructors\n}; \n\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n Node* currentPage;\n\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) { // constructor\n currentPage = new Node(homepage);\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n Node* newNode = new Node(url);\n currentPage->next = newNode;\n newNode->prev = currentPage;\n currentPage = newNode; \n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n while(steps != 0){\n if(currentPage->prev)\n currentPage = currentPage->prev;\n else\n break;\n \n steps--;\n }\n return currentPage->data;\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n while(steps != 0){\n if(currentPage->next)\n currentPage = currentPage->next;\n else\n break;\n \n steps--;\n }\n return currentPage->data;\n }\n};\n\n/**\n * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n * BrowserHistory* obj = new BrowserHistory(homepage);\n * obj->visit(url);\n * string param_2 = obj->back(steps);\n * string param_3 = obj->forward(steps);\n */\n```\n\n\n\n
| 3 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'Doubly-Linked List', 'C++']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
Easy Linked List Solution - 0(n) solution
|
easy-linked-list-solution-0n-solution-by-dlxd
|
Intiuition - Consider each website as a node which contains data to the next website and the pointer to it and pointer to the previous website.\nRest is like in
|
adityagarg217
|
NORMAL
|
2023-12-18T22:17:38.282758+00:00
|
2023-12-18T22:17:38.282777+00:00
| 267 | false |
* **Intiuition** - Consider each website as a node which contains data to the next website and the pointer to it and pointer to the previous website.\nRest is like inserting in Linked list,deleting in Linked List ques.\nFor making the node use a class.\n\n**1. Time complexity - 0(steps) \n2. Space complexity - 0(N)**\n\n\n\nIf you like the solution pls upvote ;)\n\n\n\n \n \n class Node{\n public:\n string data ; \n Node* prev ; \n Node* next ;\n public:\n Node(string data1,Node* prev1,Node* next1){\n data = data1;\n prev = prev1 ; \n next = next1 ; \n }\n Node(string data1){\n data = data1 ; \n prev = NULL ; \n next = NULL ; \n }\n };\n\n\n class BrowserHistory {\n public:\n Node* atcurrent = NULL ; \n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n Node* newnode = new Node(homepage);\n atcurrent = newnode ;\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n Node* temp = new Node(url);\n temp->prev = atcurrent ; \n atcurrent->next = temp ; \n temp->next = NULL ; \n atcurrent = temp;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n Node* back = atcurrent ; \n while(steps){\n if(back->prev==NULL){\n atcurrent = back ;\n return back->data ; \n break ;\n }\n back = back->prev ;\n steps--;\n }\n atcurrent = back ; \n return back->data ; \n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n Node* forward = atcurrent ;\n while(steps){\n if(forward->next==NULL){\n atcurrent = forward ; \n return forward->data ; \n break ; \n }\n forward = forward->next ; \n steps--;\n }\n atcurrent = forward ; \n return forward->data ; \n }\n };\n
| 3 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'C']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
Design Browser History - Java Solution using Doubly Linked List
|
design-browser-history-java-solution-usi-n24q
|
\n\n# Code\n\npublic class ListNode{\n ListNode next;\n String data;\n ListNode prev;\n public ListNode(String data) {\n this.data = data;\n }\n}\
|
Khushi1002
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-27T15:18:38.629186+00:00
|
2023-10-27T15:18:38.629207+00:00
| 63 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\npublic class ListNode{\n ListNode next;\n String data;\n ListNode prev;\n public ListNode(String data) {\n this.data = data;\n }\n}\nclass BrowserHistory {\n ListNode dummy,hehe;\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n dummy=new ListNode(homepage); \n }\n \n public void visit(String url) {\n ListNode temp=new ListNode(url);\n dummy.next=temp;\n temp.prev=dummy;\n dummy=temp; \n }\n \n public String back(int steps) {\n while(steps--!=0 && dummy.prev!=null)\n {\n dummy=dummy.prev;\n }\n return dummy.data;\n }\n \n public String forward(int steps) {\n while(steps--!=0 && dummy.next!=null)\n {\n dummy=dummy.next;\n }\n return dummy.data;\n }\n}\n\n/**\n * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n * BrowserHistory obj = new BrowserHistory(homepage);\n * obj.visit(url);\n * String param_2 = obj.back(steps);\n * String param_3 = obj.forward(steps);\n */\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
easy c++ solution || using double linked list
|
easy-c-solution-using-double-linked-list-xr1p
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Rhythm_1383
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-20T13:49:33.003537+00:00
|
2023-08-20T13:49:33.003569+00:00
| 1,106 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nstruct Node {\n string val;\n Node* prev=NULL;\n Node* next=NULL;\n};\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\nNode* curr=NULL;\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n curr=new Node();\n curr->val=homepage;\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n Node* temp=new Node();\n temp->val=url;\n curr->next=temp;\n temp->prev=curr;\n curr=temp;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n while(curr->prev && steps>0)\n {\n curr=curr->prev;\n steps--;\n }\n return curr->val;\n \n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n while(curr->next&& steps>0)\n {\n curr=curr->next;\n steps--;\n } \n return curr->val;\n }\n};\n\n/**\n * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n * BrowserHistory* obj = new BrowserHistory(homepage);\n * obj->visit(url);\n * string param_2 = obj->back(steps);\n * string param_3 = obj->forward(steps);\n */\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Doubly-Linked List', 'C++']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
The easiest Java solution.
|
the-easiest-java-solution-by-olcha_a-8618
|
Intuition\nThe easiest solution. You need only ArraList (for fast retriving browser history and creating sublist) and value for the current pointer.\n\n# Approa
|
olcha_a
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T17:40:59.790439+00:00
|
2023-03-18T17:41:51.898797+00:00
| 164 | false |
# Intuition\nThe easiest solution. You need only ArraList (for fast retriving browser history and creating sublist) and value for the current pointer.\n\n# Approach\nUse **current** to store current index. \n- If you visit a new site, just increment it. \n- If you go back just check that current + steps less that browser history. If is true, set current = current + steps. If not, set current = 0 (this is your homepage). \n- If you go forward do the opposite.\n\nUse **history list** to store browser history.\n- If you visit a new site and your pointer in the middle of the browser history, *you must remove all values on the ride side of history*, because the new site should be the last in the history of the browser. I chose sublist(), but you can find something more efficient. \n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\n private int current;\n private List<String> history = new ArrayList<>();\n\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n history.add(homepage);\n current = 0;\n }\n\n public void visit(String url) {\n history.add(++current, url);\n if (current < history.size() - 1)\n history = history.subList(0, Integer.min(current + 1, history.size() - 1));\n }\n\n public String back(int steps) {\n current = Math.max(current - steps, 0);\n return history.get(current);\n }\n\n public String forward(int steps) {\n current = Math.min(current + steps, history.size() - 1);\n return history.get(current);\n }\n}\n```\n**If you like my solution, please, upvote it.**
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
design-browser-history
|
C++ - 2 solutions - Using Stacks & Doubly Linked List
|
c-2-solutions-using-stacks-doubly-linked-aj0d
|
# Intuition \n\n\n\n\n# Using 2 Stacks \n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n)\n\n\n- Space complexity:O(n)\n\n\n# Code\nC++ []\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic
|
nipunrathore
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T16:03:18.345167+00:00
|
2023-03-18T16:03:18.345214+00:00
| 212 | false |
<!-- # Intuition -->\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n<!-- # Approach -->\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n# *Using 2 Stacks* \n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:$$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:$$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```C++ []\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n stack<string> history ;\n stack<string> future ;\n \n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n history.push(homepage) ;\n future = stack<string>() ;\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n history.push(url) ;\n future = stack<string>() ;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n while(steps > 0 && history.size() > 1)\n {\n future.push(history.top()) ;\n history.pop() ;\n steps -- ;\n }\n return history.top() ;\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n while(steps>0 && future.size()>0)\n {\n history.push(future.top()) ;\n future.pop() ;\n steps -- ;\n }\n return history.top() ; \n }\n};\n\n/**\n * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n * BrowserHistory* obj = new BrowserHistory(homepage);\n * obj->visit(url);\n * string param_2 = obj->back(steps);\n * string param_3 = obj->forward(steps);\n */\n```\n---\n# *Using Doubly Linked List* [Fastest Solution]\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:$$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:$$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```C++ []\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n// Using Doubly Linked List\nclass node{\n private:\n public:\n node *next ;\n node *prev ; \n string url ; \n\n node (string url)\n {\n this -> url = url ; \n this -> next = NULL ; \n this -> prev = NULL ; \n }\n};\nnode *curr ; \n\n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n curr = new node(homepage) ; \n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n node *temp = new node (url) ; \n curr -> next = temp ; \n temp -> prev = curr ; \n curr = curr -> next ;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n while (curr -> prev != NULL && steps -- > 0)\n {\n curr = curr -> prev ; \n }\n return curr -> url ; \n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n while (curr -> next != NULL && steps -- > 0)\n {\n curr = curr -> next ; \n }\n return curr -> url ; \n }\n};\n\n/**\n * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n * BrowserHistory* obj = new BrowserHistory(homepage);\n * obj->visit(url);\n * string param_2 = obj->back(steps);\n * string param_3 = obj->forward(steps);\n */\n```\n\n
| 3 | 0 |
['Linked List', 'Stack', 'Data Stream', 'C++']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
Java || Runtime 136 ms Beats 6.57% Memory 50.9 MB Beats 13.15%
|
java-runtime-136-ms-beats-657-memory-509-xlkg
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Akash2023
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T05:54:12.588032+00:00
|
2023-03-18T05:54:12.588077+00:00
| 959 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\n Stack<String> bStack = new Stack<>();\n Stack<String> fStack = new Stack<>();\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n bStack.push(homepage);\n }\n \n public void visit(String url) {\n while(!fStack.isEmpty()) fStack.pop();\n bStack.push(url);\n\n }\n \n public String back(int steps) {\n while(bStack.size()>1 && steps-- > 0){\n fStack.push(bStack.peek());\n bStack.pop();\n }\n return bStack.peek();\n }\n \n \n public String forward(int steps) {\n while(!fStack.isEmpty() && steps-- > 0){\n bStack.push(fStack.peek());\n fStack.pop();\n }\n return bStack.peek();\n }\n}\n\n/**\n * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n * BrowserHistory obj = new BrowserHistory(homepage);\n * obj.visit(url);\n * String param_2 = obj.back(steps);\n * String param_3 = obj.forward(steps);\n */\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
JAVA || DOUBLY LL. || EASY || FULL EXPLANATION || STRAIGHT FORWARD
|
java-doubly-ll-easy-full-explanation-str-0b2y
|
Intuition\nEASY SOLUTION USING DOUBLEY LL.\n\n\n# Approach\n this problem is nothing but triversal of DLL\n such as -:\n\n FOR creating homepage - we initialize
|
harshverma2702
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T05:24:13.925069+00:00
|
2023-03-18T05:24:13.925114+00:00
| 624 | false |
# Intuition\nEASY SOLUTION USING DOUBLEY LL.\n\n\n# Approach\n this problem is nothing but triversal of DLL\n such as -:\n\n* FOR creating homepage - we initialize and create a head node , named head (it is fix)\n\n* VISIT - keep track of current tail node and add node(URL)accordingly\n\n* BACK - if step>size return node and update tail =head else triverse tail to steps and return that node(URL page)\n\n* FORWARD - if step>size return tail else triverse upto step and return tail\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(N+N)\n- Space complexity:\nO(N)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass BrowserHistory {\n node head;\n node tail;\n int size;\n public BrowserHistory(String homepage) {\n node n =new node(homepage);\n head = n;\n tail = n;\n size=1;\n }\n \n public void visit(String url) {\n tail.next =null;\n size=size(head);\n node nd = new node(url);\n tail.next = nd;\n nd.prev = tail;\n tail = tail.next;\n size++;\n }\n \n public String back(int steps) {\n if(steps>=size){\n tail = head;\n return head.data;\n }\n\n while(steps-->0 && tail.prev!=null){\n tail = tail.prev;\n }\n\n return tail.data;\n }\n \n public String forward(int steps) { \n while(steps-->0 && tail.next!=null){\n tail = tail.next;\n }\n return tail.data;\n }\n \n public int size(node head){\n if(head==null)\n return 0;\n node temp = head;\n int s =0;\n while(temp!=null){\n temp = temp.next;\n s++;\n }\n return s;\n }\n\n}\n\nclass node{\n node next;\n node prev;\n String data;\n node(String data){\n this.data= data;\n }\n}\n\n/**\n * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:\n * BrowserHistory obj = new BrowserHistory(homepage);\n * obj.visit(url);\n * String param_2 = obj.back(steps);\n * String param_3 = obj.forward(steps);\n */\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
design-browser-history
|
SPACE 100% BEATS || SHORT & SWEET C++ CODE
|
space-100-beats-short-sweet-c-code-by-ya-bmof
|
\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n int curr=0;\n int max_fwd=0;\n unordered_map<int, string> umap;\n \n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n
|
yash___sharma_
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-18T05:21:02.655574+00:00
|
2023-03-18T05:21:02.655601+00:00
| 101 | false |
```\nclass BrowserHistory {\npublic:\n int curr=0;\n int max_fwd=0;\n unordered_map<int, string> umap;\n \n BrowserHistory(string homepage) {\n curr=0;\n max_fwd=0;\n umap[curr] = homepage;\n }\n \n void visit(string url) {\n curr++;\n umap[curr]=url; \n max_fwd=curr;\n }\n \n string back(int steps) {\n int goback = min(curr, steps);\n curr-=goback;\n return umap[curr];\n }\n \n string forward(int steps) {\n curr=min(max_fwd, curr+steps);\n return umap[curr];\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 1 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.